
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Copyright © 2016 Pepwave Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Pepwave and the
Pepwave logo are trademarks of Pepwave Ltd. Other brands or products mentioned may be trademarks or registered trademarks
of their respective owners.
User Manual
Pepwave AP One Series:
AP One Enterprise / AP One AC mini / AP One In-Wall / AP One Rugged / AP One Rugged M12 /
AP One Flex 300M
Pepwave AP Pro Series:
AP Pro / AP Pro 300M / AP Pro Duo
May 2016
COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Table of Contents
1 Introduction and Scope ............................................................................................. 4
2 Product Features and Benefits .................................................................................. 5
3 Package Contents ....................................................................................................... 6
3.1 AP One Enterprise .................................................................................................. 6
3.2 AP One AC mini ....................................................................................................... 6
3.3 AP One In-Wall ........................................................................................................ 6
3.4 AP One Rugged / AP One Rugged M12 ................................................................. 6
3.5 AP One Flex 300M ................................................................................................... 6
3.6 AP Pro / AP Pro 300M / AP Pro Duo ....................................................................... 6
4 Hardware Overview ..................................................................................................... 7
4.1 AP One Enterprise .................................................................................................. 7
4.2 AP One AC mini ....................................................................................................... 8
4.3 AP One In-Wall ........................................................................................................ 9
4.4 AP One Rugged / AP One Rugged M12 ............................................................... 10
4.5 AP One Flex 300M ................................................................................................. 11
4.6 AP Pro / AP Pro 300M / AP Pro Duo ..................................................................... 12
5 Installation ................................................................................................................. 13
5.1 Installation Procedures ......................................................................................... 14
6 Using the Dashboard ................................................................................................ 15
6.1 General ................................................................................................................... 15
6.2 AP ............................................................................................................................ 17
7 Configuration ............................................................................................................ 19
7.1 System ................................................................................................................... 19
7.1.1 Admin Security ................................................................................................... 19
7.1.2 Firmware ............................................................................................................. 21
7.1.3 Time ..................................................................................................................... 21
7.1.4 Event Log ............................................................................................................ 22
7.1.5 SNMP ................................................................................................................... 23
7.1.6 Controller ............................................................................................................ 25
7.1.7 Configuration ...................................................................................................... 26
7.1.8 Reboot ................................................................................................................. 27
http://www.pepwave.com 2 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
7.2 AP ........................................................................................................................... 27
7.2.1 Wireless SSID ................................................................................................... 277
7.2.2 Settings ............................................................................................................... 37
7.2.3 WDS ..................................................................................................................... 40
7.3 Network .................................................................................................................. 41
7.3.1 WAN .................................................................................................................... 41
7.3.2 LAN ...................................................................................................................... 43
7.3.3 PepVPN ................................................................................................................ 46
8 Tools .......................................................................................................................... 49
8.1 Ping ........................................................................................................................ 49
8.2 Traceroute ............................................................................................................. 49
8.3 Nslookup ................................................................................................................. 50
9 Monitoring Device Status ......................................................................................... 51
9.1 Device .................................................................................................................... 51
9.2 Client List ............................................................................................................. 511
9.3 WDS Info ................................................................................................................ 52
9.4 Portal .................................................................................................................... 522
9.5 Rogue AP ............................................................................................................... 53
9.6 Event Log ............................................................................................................... 53
10 Restoring Factory Defaults ................................................................................... 54
11 Appendix ................................................................................................................. 55
12 Datasheets ............................................................................................................... 57
http://www.pepwave.com 3 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
1 Introduction and Scope
Our AP Series of enterprise-grade 802.11b/g/n Wi-Fi access points is engineered to provide fast,
dependable, and flexible operation in a variety of environments, all controlled by an easy-to-use
centralized management system. From the small but powerful AP One AC mini to the top-ofthe-line AP One 300M our AP Series offers wireless networking solutions to suit any business
need, and every access point is loaded with essential features such as multiple SSIDs, VLAN,
WDS, and Guest Protect.
A single access point provides as many as 32 virtual access points (16 on single-radio models),
each with its own security policy (WPA, WPA2, etc.) and authentication mechanism (802.1x,
open, captive portal, etc.), allowing faster, easier, and more cost effective network builds. Each
member of the AP Series family also features a high powered Wi-Fi transmitter that greatly
enhances coverage and performance while reducing equipment costs and maintenance.
http://www.pepwave.com 4 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
2 Product Features and Benefits
Key features and benefits of AP Series access points:
• High-powered Wi-Fi transmitter enhances coverage and lowers cost of ownership.
• Independent security policies and encryption mechanisms for each virtual access point
allow fast, flexible, cost-effective network builds.
• Centralized management via InControl reduces maintenance expense and time.
• WDS support allows secure and fast network expansion.
• Guest Protect support guards sensitive business data and subnetworks.
• WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia) and QoS (Quality of Service) support keeps video and other
bandwidth-intensive data flowing fast and lag-free.
http://www.pepwave.com 5 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
3 Package Contents
3.1 AP One Enterprise
1x AP One Enterprise
1 x Instruction sheet
3.2 AP One AC mini
1 x AP One mini
1 x Omni-directional antenna
1 x Power supply
1 x Instruction sheet
3.3 AP One In-Wall
1 x AP One In-Wall
1 x Mounting kit
1 x Instruction sheet
3.4 AP One Rugged
1 x AP One Rugged
3 x Omni-directional antennas
1 x Power supply
1 x Instruction sheet
3.5 AP One Flex 300M
1 x AP One Flex 300M
1 x Instruction sheet
3.6 AP Pro / AP Pro 300M / AP Pro Duo
1 x AP Pro / AP Pro 300M / AP Pro Duo
1 x Instruction sheet
1 x Installation guide
http://www.pepwave.com 6 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
LED Indicators
RED – Access point initializing
Status
GREEN – Access point ready
OFF – No device connected to Ethernet port BLINKING –
Ethernet port sending/receiving data
LAN 1
ON – Powered-on device connected to Ethernet port
Note that LAN 5 displays the status of the uplink connection
4 Hardware Overview
4.1 AP One Enterprise
Bottom View Top View Front View
http://www.pepwave.com 7 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
LED Indicators
Status
RED – Access point initializing
GREEN – Access point ready
Wi-Fi
OFF – 2.4/5GHz Wi-Fi radio off
BLINKING – AP sending/receiving data
GREEN – 2.4/5GHz Wi-Fi radio on
Note that this model includes a 2.4GHz Wi-Fi radio and a 5GHz Wi-Fi radio that can operate
simultaneously to increase speed and reduce interference.
4.2 AP One AC mini
Front View Rear Panel View
http://www.pepwave.com 8 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
LED Indicators
Status
RED – Access point initializing
GREEN – Access point ready
WLAN 1/2
OFF – 2.4/5GHz Wi-Fi radio off
BLINKING – AP sending/receiving data
GREEN – 2.4/5GHz Wi-Fi radio on
Note that this model includes a 2.4GHz Wi-Fi radio and a 5GHz Wi-Fi radio that can operate
simultaneously to increase speed and reduce interference. WLAN1 displays the status of the
2.4GHz Wi-Fi radio, while WLAN2 displays the status of the 5GHz WiFi radio.
LAN 1-5
OFF – No device connected to Ethernet port
BLINKING – Ethernet port sending/receiving data
ON – Powered-on device connected to Ethernet port
Note that LAN 5 displays the status of the uplink connection
4.3 AP One In-Wall
Front View (US) Front View (International)
Rear Panel View Top View
http://www.pepwave.com 9 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
LED Indicators
Power
On – Power On
OFF – Power Off
Status
RED – Access point initializing
GREEN – Access point ready
Wireless
OFF – 2.4/5GHz Wi-Fi radio off
BLINKING – AP sending/receiving data
GREEN – 2.4/5GHz Wi-Fi radio on
Note that this model can operate in either 2.4GHz or 5GHz mode, depending on Wi-Fi radio
settings.
4.4 AP One Rugged / AP One Rugged M12
AP One Rugged
Front View (AP One Rugged) Rear Panel View (AP One Rugged)
AP One Rugged M12
Front View (AP One Rugged M12) Rear Panel View (AP One Rugged M12)
http://www.pepwave.com 10 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
LED Indicators
Status
RED – Access point initializing
GREEN – Access point ready
LAN
OFF – No device connected to Ethernet port
BLINKING – Ethernet port sending/receiving data
ON – Powered-on device connected to Ethernet port
Number of connected clients (1-10, 11-20, 21-30, 31-40)
4.5 AP One Flex 300M
Front View Rear Panel View
Connector Panel (Inside the Lid)
http://www.pepwave.com 11 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
4.6 AP Pro / AP Pro 300M / AP Pro Duo
Front/Top View Rear Panel View
http://www.pepwave.com 12 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
5 Installation
Your access point acts as a bridge between wireless and wired Ethernet interfaces. A typical
setup follows:
http://www.pepwave.com 13 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
5.1 Installation Procedures
1. Connect the Ethernet port on the unit to the backbone network using an Ethernet
cable. The port should auto sense whether the cable is straight through or crossover.
2. Connect the power adapter to the power connector of the unit. Plug the power
adapter into a power source.
3. Wait for the status LED to turn green.
4. Connect a PC to the backbone network. Configure the IP address of the PC to be any
IP address between 192.168.0.4 and 192.168.0.254, with a subnet mask of
255.255.255.0.
5. Using Microsoft Internet Explorer 6 or above, Mozilla Firefox 2.0 or above, or Google
Chrome 2.0 or above, connect to https://192.168.0.3.
6. Enter the default admin login ID and password, admin and public respectively.
7. After logging in, the Dashboard appears. Click the System tab to begin setting up
your access point.
http://www.pepwave.com 14 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
WAN
IP Address
When your access point is connected to a WAN, this field displays the WAN IP address. For
more information, click the Details… link, which displays the following:
Status
This field displays the current WAN connection status.
6 Using the Dashboard
The Dashboard section contains a number of displays to keep you up-to-date on your access
point’s status and operation. Remote assistance can also be enabled here.
6.1 General
This section contains WAN status and general device information.
http://www.pepwave.com 15 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Device Information
Model
This field displays your access point’s model number.
Firmware
The firmware version currently running on your access point appears here.
Uptime
This field displays your access point’s uptime since the last reboot or shutdown.
http://www.pepwave.com 16 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
AP Status
Wireless Network
This field displays your access point’s SSID.
SSID
6.2 AP
This section displays a variety of information about your wireless network.
http://www.pepwave.com 17 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
The radio frequency currently used by your access point appears here. If you’re using
Radio the AP One AC mini or the AP One In-Wall and have configured both radios, this displays both
radios in use.
This field displays the security policy your access point is currently using. If you’re using
Security Policy the AP One AC mini and have configured both radios, this displays channels in use for the
2.4GHz and 5GHz bands.
Channel The channel currently used by your access point is displayed in this field.
VLAN
If your access point is using a VLAN ID for management traffic, it will appear here. A value of 0 indicates
that a VLAN ID is not being used.
MAC Address Your access point’s MAC address appears here. If you’re using the AP One AC mini and have
configured both radios, this displays a MAC address for both the 2.4GHz and
(BSSID)
5
GHz radio.
Click this link to display the following information panel:
Info
Click this link to display the following statistics panel:
Stat
Usage Data Type Select
below.
Per SSID or AP Send / Recv to determine the data displayed in the graphs
Hourly Check this box to graph wireless network usage on an hourly basis.
Wireless Network
Usage/Number of These graphs detail recent wireless network usage.
Wireless Clients
http://www.pepwave.com 18 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
7 Configuration
7.1 System
The options on the System tab control login and security settings, firmware upgrades, SNMP
settings, and other settings.
7.1.1 Admin Security
The Admin Security section allows you to set up your access point’s name, password, security
settings, and other options.
http://www.pepwave.com 19 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Admin Security
AP Name Enter a name to identify your access point. This name can be retrieved via SNMP.
Location Enter a name to identify
via SNMP.
the location of your access point. This name can be retrieved
Admin User This field specifies the administrator username of the web admin. It is set as admin by Name
default.
Admin Password T
public
his field allows you to specify a new administrator password. The default password is
.
Confirm Admin
Password
Re-enter the admin password.
Web Admin
Interface
Check this box to turn on the web administration interface, which allows remote AP
management.
Security
Choose HTTP or HTTPS as the protocol to use when accessing the web admin interface. To
automatically redirect HTTP access to HTTPS, check HTTP to HTTPS Redirection.
Web Admin Port
Specify the port number on which the web admin interface can be accessed.
Allowed Source IP
Subnets
This field allows you to restrict access to the web admin to only defined IP subnets.
• Any - Allow web admin accesses from anywhere, without IP address restrictions.
• Allow access from the following IP subnets only – Restricts the ability to access web
admin to only defined IP subnets. When this option is chosen, a text input area will
appear:
Enter your allowed IP subnet addresses into this text area. Each IP subnet must be in the form
of w.x.y.z/m. w.x.y.z represents an IP address (e.g., 192.168.0.0), and m represents the subnet
mask in CIDR format, which is between 0 and 32 inclusively. For example: 192.168.0.0/24. To
define multiple subnets, separate each IP subnet, one per line. For example:
192.168.0.0/24
10.8.0.0/16
http://www.pepwave.com 20 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Language
Choose a language for the administration interface.
Time
7.1.2 Firmware
The Firmware section lets you check the firmware version currently used by your access point, as
well as check for and install new firmware via online download. You can also upgrade your
firmware using a firmware file stored locally.
To check for new firmware, click the Check for Firmware button. If new firmware is available,
your access point will automatically download and install it.
To upgrade your access point using a firmware file on your network, click Choose File to select
the firmware file. Then click Manual Upgrade to initiate the firmware upgrade process using the
selected file.
Note that your access point can store two different firmware versions in two different
partitions. A firmware upgrade will always replace the inactive partition. If you want to keep the
inactive firmware, simply reboot your device with the inactive firmware and then perform the
firmware upgrade.
7.1.3 Time
The settings in this section govern the access point’s system time zone and allow you to specify
a custom timeserver.
http://www.pepwave.com 21 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Time Zone
Time region used by the system. All choices are based on UTC.
Time Server
To choose a time server other than the default, enter the URL here. To restore the default time
server, click the Default button.
Event Log
Remote Syslog
Check this box to turn on remote system logging.
Remote Syslog
Host
Enter the IP address or hostname of the remote syslog server, as well as the port number.
7.1.4 Event Log
The section allows you to turn on event logging at a specified remote syslog server.
http://www.pepwave.com 22 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
SNMP Settings
SNMP Device
Name
This field shows the AP name defined at System>Admin Security.
SNMP Port
This option specifies the port which SNMP will use. The default port is 161.
SNMPv1
This option allows you to enable SNMP version 1.
SNMPv2c
This option allows you to enable SNMP version 2c.
SNMPv3
This option allows you to enable SNMP version 3.
7.1.5 SNMP
SNMP, or simple network management protocol, is an open standard that can be used to collect
information about your access point. The SNMP section offers a range of settings to control simple
network management protocol access.
http://www.pepwave.com 23 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
SNMP Community Settings
Community Name Enter a name for the SNMP community.
IP Address/IP These settings specify a subnet from which access to the SNMP server is allowed.
Enter the subnet address here (e.g., 192.168.1.0) and select the appropriate subnet
Mask mask.
Access Mode Select Read Only or Read and Write as the SNMP community access mode.
Status Use these controls to enable or disable SNMP community access.
SNMPv3 User Settings
To add a community for either SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c, click the Add SNMP Community button in
the Community Name table, which displays the following screen:
To define a user name for SNMPv3, click Add SNMP User in the SNMPv3 User Name table,
which displays the following screen:
http://www.pepwave.com 24 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
SNMPv3 User
Name
Enter a user name to be used in SNMPv3.
Authentication
Protocol
Select one of the following valid authentication protocols:
• NONE
• HMAC-MD5
• HMAC-SHA
When HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA is selected, an entry field will appear for the password.
Authentication
Password
Enter a password to use with the selected authentication protocol.
Confirm
Authentication
Password
Re-enter the authentication password.
Privacy Protocol
Select None or CBC-DES as the SNMPv3 privacy protocol. When CBC-DES is selected, an entry
field will appear for the password.
Access Mode
Select Read Only or Read and Write as the SNMPv3 access mode.
Status
Use these controls to enable or disable SNMPv3 access.
Controller Management Settings
Controller
Management
Check this box to enable remote management.
7.1.6 Controller
In the Controller section, you can set up Peplink InControl or AP Controller remote
management.
http://www.pepwave.com 25 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Controller Type
Select Auto, InControl, or AP Controller as your remote AP management method. When Auto
is selected, your access point will automatically choose the appropriate mode.
Configuration
Restore The Restore Factory Settings button resets the configuration to factory default
settings. After clicking the button, click the Apply Changes button on the top right
Configuration to corner to make the settings effective. To save existing network settings when restoring Factory
Settings factory settings, check the Network Settings box before clicking Restore Factory Settings.
Download Active
Configurations
Click Download to backup the current active settings.
To restore or change settings based on a configuration file, click Choose File to locate
Upload the configuration file on the local computer, and then click Upload. The new settings
Configurations can then be applied by clicking the Apply Changes button on the page header, or you can
cancel the procedure by pressing discard on the main page of the web admin interface.
7.1.7 Configuration
In section, you can manage and backup access point configurations, as well as reset your access
point to its factory configuration. Backing up your access point’s settings immediately after
successful initial setup is strongly recommended.
http://www.pepwave.com 26 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
7.1.8 Reboot
This section provides a reboot button for restarting the system. For maximum reliability, your
access point can equip with two copies of firmware, and each copy can be a different version.
You can select the firmware version you would like to reboot the device with. The firmware
marked with (Running) is the current system boot up firmware.
Please note that a firmware upgrade will always replace the inactive firmware partition.
7.2 AP
Use the controls on the AP tab to set the wireless SSID and AP settings, as well as wireless
distribution system (WDS) settings.
7.2.1 Wireless SSID
Wireless network settings, including the name of the network (SSID) and security policy, can be
defined and managed in this section.
http://www.pepwave.com 27 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
SSID Settings
Enable
Check this box to enable wireless SSID.
Radio Selection
Available only on the AP One AC mini, this setting, shown below, allows you to enable or
disable either of the two on-board radios.
SSID
This setting specifies the AP SSID that Wi-Fi clients will see when scanning.
Broadcast SSID
This setting specifies whether or not Wi-Fi clients can scan the SSID of this wireless network.
Broadcast SSID is enabled by default.
Click New SSID to create a new network profile, or click the existing network profile to modify
its settings.
http://www.pepwave.com 28 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Data Rate
Select Auto to allow your access point to set the data rate automatically, or select Fixed and
choose a rate from the drop-down menu. Click the MCS Index link to display a reference
table containing MCS and matching HT20 and HT40 values.
Multicast Filter
This setting enables the filtering of multicast network traffic to the wireless SSID.
Multicast Rate
This setting specifies the transmit rate to be used for sending multicast network traffic.
IGMP Snooping
To allow your access point to convert multicast traffic to unicast traffic for associated clients,
select this option.
DHCP Setting
To set your access point as a DHCP server or relay, select Server or Relay. Otherwise, select
None.
DHCP Option 82
If you use a distributed DHCP server/relay environment, you can enable this option to
provide additional information on the manner in which clients are physically connected to
the network.
Default VLAN ID
This setting specifies the VLAN ID to be tagged on all outgoing packets generated from this
wireless network (i.e., packets that travel from the Wi-Fi segment through your access point
to the Ethernet segment via the LAN port). If 802.1x is enabled and a per-user VLAN ID is
specified in authentication reply from the Radius server, then the value specified by Default
VLAN ID will be overridden. The default value of this setting is 0, which means VLAN tagging
is disabled (instead of tagged with zero).
VLAN Pooling
Check this box to enable VLAN pooling using the values specified in VLAN Pool.
VLAN Pool
If VLAN pooling is enabled, enter VLAN pool values separated by commas.
Network Priority
(QoS)
Select from Gold, Silver, and Bronze to control the QoS priority of this wireless network’s
traffic.
Layer 2 Isolation
Layer 2 refers to the second layer in the ISO Open System Interconnect model.
When this option is enabled, clients on the same VLAN, SSID, or subnet are isolated to that
VLAN, SSID, or subnet, which can enhance security. Traffic is passed to upper communication
layer(s). By default, the setting is disabled.
Maximum Number
of Clients
Enter the maximum number of clients that can simultaneously connect to your access point,
or enter 0 to allow unlimited Wi-Fi clients.
Security Settings
http://www.pepwave.com 29 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Security Policy
This setting configures the wireless authentication and encryption methods. Available
options are Open (No Encryption), WEP, 802.1X, WPA2 – Personal, WPA2 – Enterprise,
WPA/WPA2 - Personal, and WPA/WPA2 – Enterprise. To allow any Wi-Fi client to access
your AP without authentication, select Open (No Encryption).
Details on each of the available authentication methods follow.
WEP
Key Size
Select 40 bits (64-bit WEP) or 104 bits (128-bit WEP).
Key Format
Choose ASCII or Hex format for the WEP key. ASCII can be applied only to encryption keys that
are manually entered. Hex can be applied to encryption keys that are manually entered or
automatically generated.
Passphrase
Enter a series of alphanumeric characters, and then click Generate Key to create a WEP key
using the passphrase.
Encryption Key
The generated WEP key appears here. Click Hide / Show Passphrase to toggle visibility.
Shared Key
Authentication
Check to enable shared key authentication. The default is disabled, meaning open
authentication is used.
802.1X
http://www.pepwave.com 30 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Choose v1 or v2 of the 802.1x EAPOL. When v1 is selected, both v1 and v2 clients can
802.1X Version associate with the access point. When v2 is selected, only v2 clients can associate with the
access point. Most modern wireless clients support v2. For stations that do not support v2,
select v1. The default is v2.
WEP Key Size Select 40 bits (64-bit WEP) or 104 bits (128-bit WEP).
This option specifies the length of time throughout which the broadcast key remains
Re-keying Period valid. When the re-keying period expires, the broadcast key is no longer valid and broadcast key
renewal is required. The default is 14400 seconds (four hours). 0 disables re-keying.
WPA/WPA2 – Personal
Passphrase
Enter a passphrase of between 8 and 63 alphanumeric characters to create a passphrase used
for data encryption and authentication. Click Hide / Show Passphrase to toggle visibility.
WPA/WPA2 – Enterprise
802.1X Version
Choose v1 or v2 of the 802.1x EAPOL. When v1 is selected, both v1 and v2 clients can associate
with the access point. When v2 is selected, only v2 clients can associate with the access point.
Most modern wireless clients support v2. For stations that do not support v2, select v1. The
default is v2.
http://www.pepwave.com 31 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Web Portal Login
Web Portal Select Enable to turn on your access point’s built-in web portal functionality.
Authentication Choose Open Access to allow users to connect without authentication or RADIUS to Method
require authentication. If RADIUS is selected, you’ll be given the opportunity to select a RADIUS security method in
the next field.
RADIUS Security Select PAP, EAP-TTLS PAP, EAP-TTLS MSCHAPv2, or PEAPv0 EAP-MSCHAPv2.
Splash Page If your web portal will use a splash page, choose HTTP or HTTPS and enter the splash page’s URL.
Landing Page If your web portal will use a landing page, check this box.
Landing Page
URL If you have checked Landing Page, enter your landing page’s URL here.
Concurrent Login Check this box to allow users to have more than one logged in session active at a time.
http://www.pepwave.com 32 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Enter a value in minutes to limit access time on a given login or enter 0 to allow
Access Quota unlimited use time on a single login. Likewise, enter a value in MB for the total bandwidth
allowed or enter 0 to allow unlimited bandwidth on a single login.
Inactive Timeout Enter a value in minutes to logout following the specified period of inactivity or enter 0 to disable
inactivity logouts.
This menu determines how your usage quota resets. Setting it to Daily will reset it at a
Quota Reset Time specified time every day. Setting a number of minutes after quota reached establishes a timer for
each user that begins after the quota has been reached.
Allowed Domains To whitelist a domain or IP address, enter the domain name / IP address here and click / IPs
. To delete an existing entry, click the button next to it.
address, enter the IP address here and click . To Allowed Client IPs To whitelist a client IP
delete an existing entry, click the button next to it.
Access Control
The settings allow administrator to control access using Mac address filtering. Available
Restricted Mode options are None, Deny all except listed, Accept all except listed, and RADIUS MAC Authentication.
MAC Address List Connections coming from the MAC addresses in this list will be either denied or accepted based on
the option selected in the previous field.
http://www.pepwave.com 33 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
RADIUS Server Settings
Host
Enter the IP address of the primary RADIUS server and, if applicable, the secondary RADIUS
server.
Secret
Enter the RADIUS shared secret for the primary server and, if applicable, the secondary RADIUS
server.
Authentication
Port
Enter the UDP authentication port(s) used by your RADIUS server(s) or click the Default button
to enter 1812.
Accounting Port
Enter the UDP accounting port(s) used by your RADIUS server(s) or click the Default button to
enter 1813.
Maximum
Retransmission
Enter the maximum number of allowed retransmissions.
RADIUS Request
Interval
Enter a value in seconds to limit RADIUS request frequency. Note the initial value will double on
each retransmission.
http://www.pepwave.com 34 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Guest Protect
Block LAN
Access
Check this box to block access from the LAN.
Custom Subnet
To specify a subnet to block, enter the IP address and choose a subnet mask from
the drop-down menu. To add the blocked subnet, click . To delete a blocked
subnet, click .
Block Exception
To create an exception to a blocked subnet (above), enter the IP address
and choose a subnet mask from the drop-down menu. To add the exception,
click . To delete an exception, click .
Block PepVPN
To block PepVPN access, check this box.
Bandwidth Management
Bandwidth
Management Check this box to enable bandwidth management.
Upstream Limit Enter a value in kpbs to limit the wireless network’s upstream bandwidth. Enter 0 to allow unlimited
upstream bandwidth.
Downstream Limit Enter a value in kpbs to limit the wireless network’s downstream bandwidth. Enter 0 to allow
unlimited downstream bandwidth.
http://www.pepwave.com 35 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Client Upstream
Enter a value in kpbs to limit connected clients’ upstream bandwidth. Enter 0 to allow Limit
unlimited upstream bandwidth.
Client Enter a value in kpbs to limit connected clients’ downstream bandwidth. Enter 0 to allow
Firewall Settings
Firewall Mode
Choose Flexible – Allow all except… or Lockdown – Block all except… to turn on the firewall,
then create rules for the firewall exceptions by clicking . See the discussion below
for details on creating a firewall rule. To delete a rule, click the associated button.
To turn off the firewall, select Disable.
Firewall Rule
Name
Enter a descriptive name for the firewall rule in this field.
Type
Choose Port, Domain, IP Address, or MAC Address to allow or deny traffic from any of those
identifiers. Depending on the option chosen, the following fields will vary.
Protocol / Port
Choose TCP or UDP from the Protocol drop-down menu to allow or deny traffic using either of
those protocols. From the Port drop-down menu, choose Any Port to allow or deny TCP or UDP
traffic on any port. Choose Single Port and then enter a port number in the provided field to
allow or block TCP or UDP traffic from that port only. You can also choose Port Range and enter
a range of ports in the provided fields to allow or deny TCP or UDP traffic from the specified
port range.
IP Address /
Subnet Mask
If you have chosen IP Address as your firewall rule type, enter the IP address and subnet mask
identifying the subnet to allow or deny.
Downstream Limit unlimited downstream bandwidth.
http://www.pepwave.com 36 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
MAC Address
If you have chosen MAC Address as your firewall rule type, enter the MAC address identifying
the machine to allow or deny.
AP Settings
Choose 802.11ng or 802.11na as your access point’s Wi-Fi protocol.
The AP One AC mini provides the 802.11ng protocol for the 2.4 GHz band and the Protocol
802.11ac protocol for the 5GHz band, as shown below.
This drop-down menu specifies the national / regional regulations the AP should follow.
If a North American region is selected, RF channels 1 to 11 will be available and the maximum
transmission power will be 26 dBm (400 mW).
Operating
If European region is selected, RF channels 1 to 13 will be available. The maximum Country
transmission power will be 20 dBm (100 mW).
NOTE: Users are required to choose an option suitable to local laws and regulations.
Per FCC regulation, the country selection is not available on all models marketed in the US. All US
models are fixed to US channels only.
7.2.2 Settings
Basic access point operation settings, such as the protocol and channels used, as well as
scanning interval and other advanced settings, can be defined and managed in this section.
http://www.pepwave.com 37 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
There are three options: 20 MHz, 40 MHz, and 20/40 MHz. With this feature enabled, the Wi-Fi
system can use two channels at once. Using two channels improves the performance of the WiFi connection.
Channel Bonding The AP One AC mini offers channel bonding options for the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, as shown below.
In addition to 20 MHz, 40 MHz, and 20/40 MHz, the 5Ghz band offers 80Mhz, which is the
default setting.
Channel
This drop-down menu selects the 5GHz 802.11 channel to be used. If Auto is set, the system will
perform channel scanning based on the scheduled time set and choose the most suitable
channel automatically.
The AP One AC mini allows setting channels on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, as shown below.
Output Power
This drop-down menu determines the power at which your access point will broadcast. When
fixed settings are selected, the AP will broadcast at the specified power level, regardless of
context. When Auto is selected, the AP will adjust its power level based on surrounding APs to
maximize performance.
While single-radio models allow setting power output levels for one frequency band only, the AP
One AC mini provide output power settings for both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, as shown
below.
Beacon Rate
This drop-down menu provides the option to send beacons in different transmit bit rates. The bit
rates are 1Mbps, 2Mbps, 5.5Mbps, 6Mbps, and 11Mbps.
Beacon Interval
Set the time between each beacon send. Available options are 100ms, 250ms, and 500ms.
DTIM
Set the frequency for the beacon to include delivery traffic indication messages (DTIM). The
interval unit is measured in milliseconds.
RTS Threshold
Set the minimum packet size for your access point to send an RTS using the RTS/CTS handshake.
Setting 0 disables this feature.
Fragmentation
Threshold
Enter a value to limit the maximum frame size, which can improve performance.
Distance / Time
Convertor
This slider and text entry field can be used to interactively set slot time.
Slot Time
This field provides the option to modify the unit wait time before your access point transmits.
The default value is 9μs.
http://www.pepwave.com 38 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
ACK Timeout
Set the wait time to receive an acknowledgement packet before retransmitting. The default
value is 48μs.
Frame
Aggregation
With this feature enabled, throughput will be increased by sending two or more data frames in a
single transmission.
Aggregation
Length
This field is only available when Frame Aggregation is enabled. It specifies the frame length for
frame aggregation. By default, it is set to 50000.
Max number of
Clients
Enter the maximum clients that can simultaneously connect to your access point or set the value
to 0 to allow unlimited clients.
Client Signal
This field determines the minimum acceptable client signal strength, specified in
Strength
Threshold
megawatts. If client signal strength does not meet this minimum, the client will not be allowed
to connect.
Advanced Features
Discover Nearby
Check this box to enable network discovery. Note that setting Channel to Auto will Networks
activate this feature automatically.
Scanning Interval This setting controls the interval, in seconds, that your access point scans for nearby networks.
Scanning Time This setting specifies the time, in milliseconds, that your access point scans any particular
channel while searching for nearby networks.
Scheduled Radio
Click Custom Schedule to specify radio availability schedule options or select Always Availability
On to make the radio continuously available.
WMM This checkbox enables Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM), also known as Wireless Multimedia Extensions (WME),
on your access point. The default is enabled.
http://www.pepwave.com 39 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
WDS
Enable
Check this box to enable WDS.
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address of the access point with which to form a WDS link.
Encryption
Select AES to enable encryption for WDS peer connections. Selecting None disables encryption.
7.2.3 WDS
A wireless distribution system (WDS) provides a way to link access points when wires are not
feasible or desirable. A WDS can also extend wireless network coverage for wireless clients. Note
that your access point’s channel setting should not be set to Auto when using WDS.
To create a new WDS, click Add.
http://www.pepwave.com 40 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Basic
Keep Default IP When enabled, this option maintains 192.168.0.3 as your access point’s IP address.
IP Address Mode options are Automatic and Manual. In Automatic mode, the IP IP Address
Mode address of your access point is acquired from a DHCP server on the Ethernet segment. In Manual mode, a user-
specified IP address is used for your access point, as described below.
Static IP Address You can use these fields to specify a unique IP address that your access point will use to communicate
on the Ethernet segment. This IP address is distinct from the admin IP
/ Subnet Mask
address (192.168.0.3) on the Ethernet segment.
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the default gateway to the internet.
DNS Server Enter the DNS server address that your access point will use to resolve host names.
7.3 Network
The settings on the AP tab control WAN and LAN settings, as well as allow you to set up PepVPN
profiles.
7.3.1 WAN
This section provides basic and advanced WAN settings.
http://www.pepwave.com 41 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Advanced
Management
VLAN ID
This field specifies the VLAN ID to tag to management traffic, such as AP-to-AP controller
communication traffic. The value is 0 by default, meaning that no VLAN tagging will be applied.
NOTE: change this value with caution as alterations may result in loss of connection to the AP
controller.
Spanning Tree
Protocol
Checking this box enables spanning tree protocol, used to prevent loops in bridged Ethernet LANs
Scheduled
Reboot
When this box is checked, your access point can be scheduled to reboot automatically on a
recurring basis, as indicated by the values under the Schedule, Day, and Time headings.
Ethernet
Speed/Duplex
Select a speed and duplex setting for sending and receiving. When selecting a speed manually,
you can also control whether the access point’s speed will be advertised on the network by
checking or unchecking the Advertise Speed box. When Auto is selected, your access point will
automatically negotiate speeds.
AP Mode
Your access point can act as a bridge or as a router, depending on your selection here. When
Router is selected, you can additionally select whether the access point will function in NAT or IP
Forwarding mode.
http://www.pepwave.com 42 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
IP Settings
IP Address
Enter the LAN IP address and subnet mask to assign to your access point on the LAN.
7.3.2 LAN
This section offers a variety of settings that affect your access point’s operation on the LAN,
such as settings for DHCP, DMZ, and port forwarding. Note that the following settings will be
available only when your access point is operating in router mode.
http://www.pepwave.com 43 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
DHCP Server Settings
DHCP Server
Check to enable the DHCP server feature of your access point. Enabling DHCP is the best option
for most users. The following options will be enabled once you have checked and enabled the
DHCP server.
IP Range
Enter the first and last IP addresses of the range of addresses that your access point will make
available to DHCP clients. The default range is from 192.168.1.100 to
192.168.1.200, with 24-bit subnet mask.
Broadcast
Address
Enter the broadcast address that DHCP clients will use when communicating with the entire LAN
segment. The default value is 192.168.1.255.
Gateway
Enter the default gateway address that DHCP clients will use to access the internet. By default,
this address will be the same as your access point’s IP address on the LAN.
DNS 1/2/3
In DNS 1, enter the IP address of the primary DNS server offered to DNS clients or accept the
default of 192.168.1.1, which is your access point’s address on the LAN. You can also specify up
to two additional DNS servers to use when the primary server is busy or down.
Lease Time
Specify the length of time that an IP address of a DHCP client remains valid. When an address
lease time has expired, the assigned IP address is no longer valid, and renewal of the IP address
assignment is required. By default, this value is set to one day.
DHCP
Reservation
To reserve certain addresses for specific clients, such as network printers, enter
the device’s MAC Address and a static IP to be assigned to the device. Click to add
the DHCP reservation. To delete a DHCP reservation, click .
http://www.pepwave.com 44 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave
User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
DMZ
DMZ
Check this box to forward traffic sent to the WAN IP address to the DMZ IP address.
DMZ IP
Enter an IP address clients will use to connect to the DMZ.
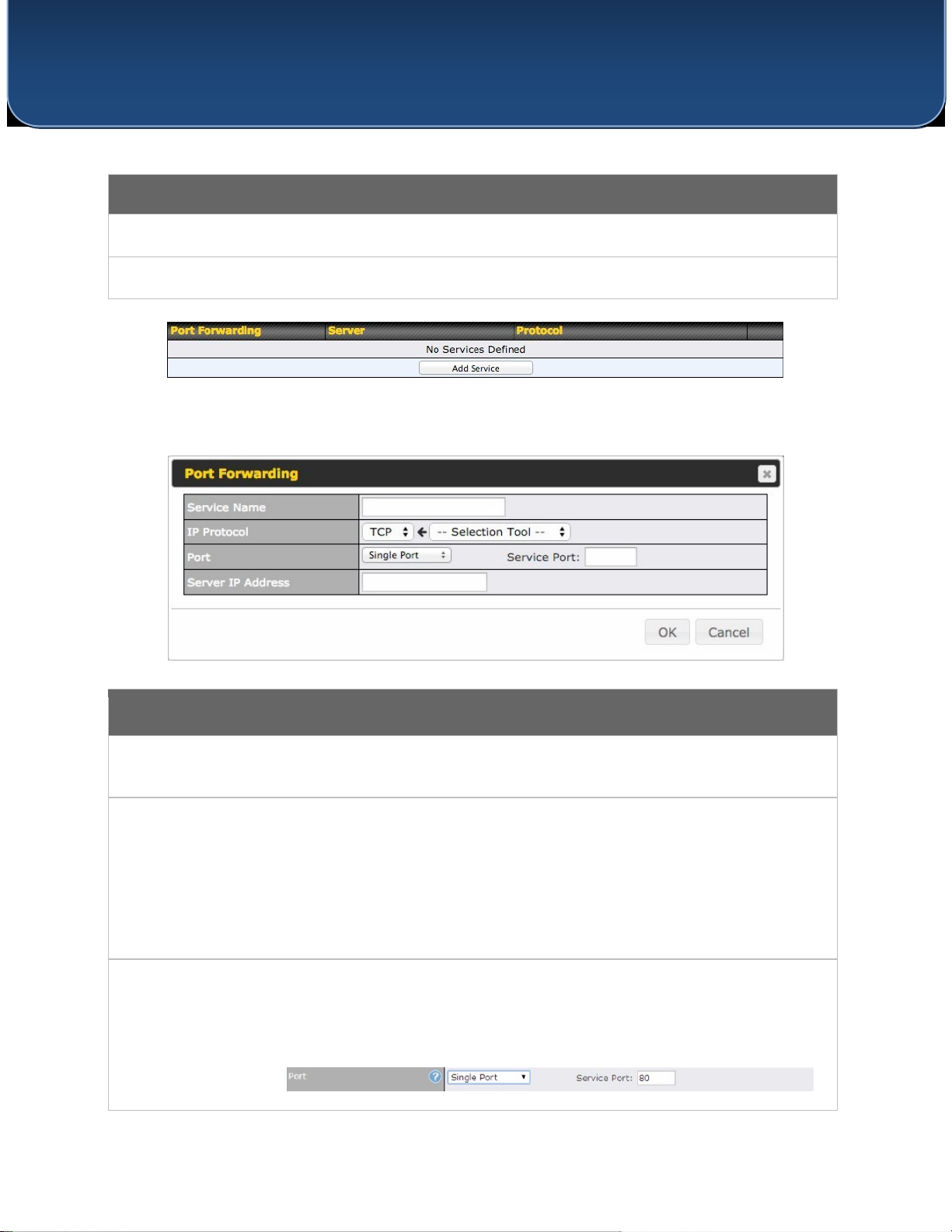
Port Forwarding
Service Name
Enter a name for the new port forwarding rule. Valid values for this setting consist of
alphanumeric and underscore “_” characters only.
IP Protocol
The IP Protocol setting, along with the Port setting, specifies the protocol of the service as TCP,
UDP, ICMP, or IP. Traffic that is received by your access point via the specified protocol at the
specified port(s) is forwarded to the LAN hosts specified by the Servers setting. Please see below
for details on the Port and Servers settings.
Alternatively, the Protocol Selection Tool drop-down menu can be used to automatically fill in
the protocol and a single port number of common Internet services (e.g., HTTP, HTTPS, etc.).
After selecting an item from the Protocol Selection Tool drop-down menu, the protocol and port
number remain manually modifiable.
Port
The Port setting specifies the port(s) that correspond to the service, and can be configured to
behave in one of the following manners:
Single Port, Port Range, Port Mapping
To create a port forwarding rule, first click the Add Service button, located in the Port
Forwarding section.
http://www.pepwave.com 45 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Single Port: Traffic that is received by your access point via the specified protocol at the
specified port is forwarded via the same port to the servers specified by the Server IP Address
setting. For example, with IP Protocol set to TCP, and Port set to Single Port and Service Port 80,
TCP traffic received on port 80 is forwarded to the configured servers via port 80.
Port Range: Traffic that is received by your access point via the specified protocol at the
specified port range is forwarded via the same respective ports to the LAN hosts specified by the
Server IP Address setting. For example, with IP Protocol set to TCP, and Port set to Port Range
and Service Ports 80-88, TCP traffic received on ports 80 through 88 is forwarded to the
configured servers via the respective ports.
Port Mapping: Traffic that is received by your access point via the specified protocol at the
specified port is forwarded via a different port to the servers specified by the Server IP Address
setting.
For example, with IP Protocol set to TCP, and Port set to Port Mapping, Service Port 80, and
Map to Port 88, TCP traffic on Port 80 is forwarded to the configured server via Port 88.
Server IP
Address
Enter the LAN IP address of the server that handles requests for the forwarded service.
7.3.3 PepVPN
PepVPN securely connects one or more remote sites to the site running your access point.
http://www.pepwave.com 46 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
PepVPN Profile Settings
Enable Check this box to enable PepVPN.
Enter a name to represent this profile. The name can be any combination of
Name alphanumeric characters (0-9, A-Z, a-z), underscores (_), dashes (-), and/or nonleading/trailing
spaces ( ).
Encryption By default, VPN traffic is encrypted with 256-bit AES. If Off is selected on both sides of a VPN
connection, no encryption will be applied.
Remote ID To allow your access point to establish a VPN connection with a specific remote peer using a
unique identifying number, enter the peer’s ID or serial number here.
Select By Remote ID Only or Preshared Key to specify the method your access point
Authentication will use to authenticate peers. When selecting By Remote ID Only, be sure to enter a unique
peer ID number in the Remote ID field.
To set up PepVPN, first give your site a local PepVPN ID. To modify an existing local ID, click .
Once you’ve specified a local ID, click the New Profile button to configure PepVPN.
http://www.pepwave.com 47 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
This optional field becomes available when Pre-shared Key is selected as the VPN
Authentication method, as explained above. Pre-shared Key defines the pre-shared
Pre-shared Key key used for this particular VPN connection. The VPN connection's session key will be
further protected by the pre-shared key. The connection will be up only if the pre-shared keys
on each side match. Click Hide / Show Passphrase to toggle passphrase visibility.
Optionally, you can enter a remote peer’s WAN IP address or hostname(s) here. If the remote
client uses more than one address, enter only one of them here. Multiple Remote IP hostnames are allowed
and can be separated by a space character or carriage return. Address / Host Dynamic-DNS host names are also
accepted. Names (Optional) With this field filled, your access point will initiate connection to each of the remote IP
addresses until it succeeds in making a connection. If the field is empty, your access point will wait for connection from the
remote peer. Therefore, at least one of the two
VPN peers must specify this value. Otherwise, VPN connections cannot be established.
When this check box is unchecked, traffic between local and remote networks will be IP
forwarded. To bridge the Ethernet network of an Ethernet port on a local and remote
Layer 2 Bridging network, select Layer 2 Bridging. When this check box is selected, the two networks will become a
single LAN, and any broadcast (e.g., ARP requests) or multicast traffic (e.g., Bonjour) will be sent
over the VPN.
Management This field specifies the VLAN ID that will be tagged to management traffic, such as AP-
VLAN ID to-AP controller communication traffic. A value of 0 indicates that no VLAN tagging will be
applied.
Choose Automatic or Manual. In automatic mode, your access point acquires an IP
IP Address Mode from a DHCP server on the Ethernet segment. In manual mode, your access point uses a user-
specified IP address.
IP
Address/Subnet When using manual IP addressing (above), enter an IP address and subnet mask in these fields.
Mask
This field specifies the outgoing UDP port number for transporting VPN data. If Default
Data Port is selected, port 4500 will be used by default. Port 32015 will be used if port 4500 is unavailable.
If Custom is selected, you can input a custom outgoing port number between 1 and 65535.
http://www.pepwave.com 48 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
8 Tools
8.1 Ping
The ping test tool tests connectivity pinging the specified destination IP address. The ping utility
is located at System>Tools>Ping.
8.2 Traceroute
The traceroute test tool traces the routing path to the specified IP address. The traceroute test
utility is located at System>Tools>Traceroute.
http://www.pepwave.com 49 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
8.3 Nslookup
The nslookup tool is used to test DNS name servers. The nslookup utility can be found at
System>Tools>Nslookup.
http://www.pepwave.com 50 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
9 Monitoring Device Status
The displays available on the Status tab help you monitor device data, client activity, rogue
device access, and more.
9.1 Device
Here you can access a variety of data about your access point, download a diagnostic report,
and check MAC addresses. To download a diagnostic report, click the Download link.
9.2 Client List
The Client List displays all currently connected clients. Use the Expand and Collapse buttons to
control the amount of data displayed.
http://www.pepwave.com 51 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
9.3 WDS Info
Here you can monitor the status of your wireless distribution system (WDS) and track activity by
MAC address. If you’re using the AP One AC mini, this section will display information for both
the 2.4GHz and 5GHz radios.
9.4 Portal
If you’ve turned on your access point’s captive portal, client connection data will appear here.
Use the Expand and Collapse buttons to control the amount of data displayed.
http://www.pepwave.com 52 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
9.5 Rogue AP
This section displays a list of nearby suspected rogue access points.
9.6 Event Log
The Event Log displays a list of all events associated with your access point. Check Auto Refresh
to refresh log entries automatically. Click the Clear Log button to clear the log.
http://www.pepwave.com 53 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
10 Restoring Factory Defaults
The following procedure restores the settings of your access point to factory defaults:
• Power on the unit and wait for one minute.
• Press and hold the reset button for at least five seconds, then release.
• The unit will automatically reboot.
• Wait for one minute or until the status LED turns green, upon which the settings of the
device will have been restored to the factory defaults.
By default, the unit will acquire an IP address from a DHCP server.
http://www.pepwave.com 54 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
11 Appendix
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely
to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference
at his own expense.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
IEEE 802.11b or 802.11g operation of this product in the U.S.A. is firmware-limited to channels 1
through 11.
5.15 ~ 5.25GHz is for indoor user only.
IMPORTANT NOTE
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
The availability of some specific channels and/or operational frequency bands are country
dependent and are firmware programmed at the factory to match the intended destination.
http://www.pepwave.com 55 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement (AP One Rugged
M12)
Caution: The user is cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
—Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
—Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
—Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
—Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
IMPORTANT NOTE
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC’s RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. The antenna(s) used for this transmitter must be installed and operated to
provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all persons and must not be collocated or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter. Installers must ensure that
20cm separation distance will be maintained between the device (excluding its handset) and
users.
http://www.pepwave.com 56 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

User Manual
PEPWAVE AP Series
Industry Canada Statement
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject
to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this device
must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of the
device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil ne
doit pas produire de brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage
radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le
fonctionnement.
For devices with detachable antenna(s), the maximum antenna gain permitted for devices in the
band 5725-5850 MHz shall be such that the equipment still complies with the e.i.r.p. limits as
appropriate;
This equipment complies with ISED radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body.
12 Datasheets
http://www.pepwave.com 57 Copyright © 5/23/16 Pepwave

www.pepwave.com
Contact Us: Sales
http://www.pepwave.com/contact/sales/
Support
http://www.pepwave.com/contact/
Business Development and Partnerships
http://www.pepwave.com/partners/channelpartner-program/
 Loading...
Loading...