Page 1

Effects Reference
for
Avid Xpress
®
Avid Xpress DV
Pro
make manage move | media
™
Avid
®
Page 2

Copyright and Disclaimer
Product specifications are subject to change without notice and do not represent a commitment on the part
of Avid Technology, Inc.
The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement. You can obtain a copy of
that license by visiting Avid's Web site at www.avid.com. The terms of that license are also available in the
product in the same directory as the software. The software may not be reverse assembled and may be
used or copied only in accordance with the terms of the license agreement. It is against the law to copy the
software on any medium except as specifically allowed in the license agreement.
Avid products or portions thereof are protected by one or more of the following United States Patents:
4,746,994; 4,970,663; 5,045,940; 5,267,351; 5,309,528; 5,355,450; 5,396,594; 5,440,348; 5,452,378;
5,467,288; 5,513,375; 5,528,310; 5,557,423; 5,568,275; 5,577,190; 5,584,006; 5,640,601; 5,644,364;
5,654,737; 5,715,018; 5,724,605; 5,726,717; 5,729,673; 5,745,637; 5,752,029; 5,754,851; 5,799,150;
5,812,216; 5,852,435; 5,905,841; 5,929,836; 5,930,445; 5,946,445; 5,987,501; 6,016,152; 6,018,337;
6,023,531; 6,058,236; 6,061,758; 6,091,778; 6,105,083; 6,118,444; 6,128,001; 6,134,607; 6,137,919;
6,141,691; 6,198,477; 6,201,531; 6,223,211; 6,249,280; 6,269,195; 6,317,158; 6,317,515; 6,330,369;
6,351,557; 6,353,862; 6,357,047; 6,392,710; 6,404,435; 6,407,775; 6,417,891; 6,426,778; 6,477,271;
6,489,969; 6,512,522; 6,532,043; 6,546,190; 6,552,731; 6,553,142; 6,570,624; 6,571,255; 6,583,824;
D392,269; D396,853; D398,912. Other patents are pending.
Copyright © 2003 Avid Technology, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
The following disclaimer is required by Apple Computer, Inc.
APPLE COMPUTER, INC. MAKES NO WARRANTIES WHATSOEVER, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
REGARDING THIS PRODUCT, INCLUDING WARRANTIES WITH RESPECT TO ITS
MERCHANTABILITY OR ITS FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE EXCLUSION OF
IMPLIED WARRANTIES IS NOT PERMITTED BY SOME STATES. THE ABOVE EXCLUSION MAY NOT
APPLY TO YOU. THIS WARRANTY PROVIDES YOU WITH SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS. THERE MAY BE
OTHER RIGHTS THAT YOU MAY HAVE WHICH VARY FROM STATE TO STATE.
The following disclaimer is required by Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics, Inc. for the use of
their TIFF library:
Copyright © 1988–1997 Sam Leffler
Copyright © 1991–1997 Silicon Graphics, Inc.
Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and sell this software [i.e., the TIFF library] and its
documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee, provided that (i) the above copyright notices
and this permission notice appear in all copies of the software and related documentation, and (ii) the
names of Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics may not be used in any advertising or publicity relating to the
software without the specific, prior written permission of Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS-IS” AND WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS,
IMPLIED OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL SAM LEFFLER OR SILICON GRAPHICS BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR ANY DAMAGES
WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER OR NOT ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF DAMAGE, AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, ARISING OUT OF OR IN
CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
The following disclaimer is required by the Independent JPEG Group:
Portions of this software are based on work of the Independent JPEG Group.
The following disclaimer is required by Paradigm Matrix:
Portions of this software licensed from Paradigm Matrix.
The following disclaimer is required by Ray Sauers Associates, Inc.:
“Install-It” is licensed from Ray Sauers Associates, Inc. End-User is prohibited from taking any action to
derive a source code equivalent of “Install-It,” including by reverse assembly or reverse compilation, Ray
Sauers Associates, Inc. shall in no event be liable for any damages resulting from reseller’s failure to
perform reseller’s obligation; or any damages arising from use or operation of reseller’s products or the
software; or any other damages, including but not limited to, incidental, direct, indirect, special or
Page 3

consequential Damages including lost profits, or damages resulting from loss of use or inability to use
reseller’s products or the software for any reason including copyright or patent infringement, or lost data,
even if Ray Sauers Associates has been advised, knew or should have known of the possibility of such
damages.
The following disclaimer is required by Videomedia, Inc.:
“Videomedia, Inc. makes no warranties whatsoever, either express or implied, regarding this product,
including warranties with respect to its merchantability or its fitness for any particular purpose.”
“This software contains V-LAN ver. 3.0 Command Protocols which communicate with V-LAN ver. 3.0
products developed by Videomedia, Inc. and V-LAN ver. 3.0 compatible products developed by third parties
under license from Videomedia, Inc. Use of this software will allow “frame accurate” editing control of
applicable videotape recorder decks, videodisc recorders/players and the like.”
The following disclaimer is required by Altura Software, Inc. for the use of its Mac2Win
software and Sample Source Code:
©1993–1998 Altura Software, Inc.
The following disclaimer is required by Ultimatte Corporation:
Certain real-time compositing capabilities are provided under a license of such technology from Ultimatte
Corporation and are subject to copyright protection.
The following disclaimer is required by 3Prong.com Inc.:
Certain waveform and vector monitoring capabilities are provided under a license from 3Prong.com Inc.
Attn. Government User(s). Restricted Rights Legend
U.S. GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. This Software and its documentation are “commercial
computer software” or “commercial computer software documentation.” In the event that such Software or
documentation is acquired by or on behalf of a unit or agency of the U.S. Government, all rights with
respect to this Software and documentation are subject to the terms of the License Agreement, pursuant to
FAR §12.212(a) and/or DFARS §227.7202-1(a), as applicable.
Trademarks
888 I/O, Adrenaline, AirPlay, AirSPACE, AirSPACE HD, AniMatte, AudioSuite, AudioVision, AutoSync, Avid,
Avid DNA, AVIDdrive, AVIDdrive Towers, Avid Mojo, AvidNet, AvidNetwork, AVIDstripe, Avid Unity,
Avid Xpress, AVoption, AVX, CamCutter, ChromaCurve, ChromaWheel, DAE, D-Fi, D-fx, Digidesign,
Digidesign Audio Engine, Digidesign Intelligent Noise Reduction, DigiDrive, Digital Nonlinear Accelerator,
DigiTranslator, DINR, D-Verb, Equinox, ExpertRender, FieldPak, Film Composer, FilmScribe, FluidMotion,
HIIP, HyperSPACE, HyperSPACE HDCAM, IllusionFX, Image Independence, Intraframe, iS9, iS18, iS23,
iS36, Lo-Fi, Magic Mask, make manage move | media, Marquee, Matador, Maxim, MCXpress,
Media Composer, MediaDock, MediaDock Shuttle, Media Fusion, Media Illusion, MediaLog,
Media Reader, Media Recorder, MEDIArray, MediaShare, Meridien, MetaSync, NaturalMatch, Nearchive,
NetReview, NewsCutter, Nitris, OMF, OMF Interchange, OMM, Open Media Framework,
Open Media Management, ProEncode, Pro Tools, QuietDrive, Recti-Fi, RetroLoop, rS9, rS18, Sci-Fi,
Softimage, Sound Designer II, SPACE, SPACEShift, Symphony, the Avid|DS logo, Trilligent, UnityRAID,
Vari-Fi, Video Slave Driver, VideoSPACE, and Xdeck are either registered trademarks or trademarks of
Avid Technology, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
iNEWS, iNEWS ControlAir, and Media Browse are trademarks of iNews, LLC.
Apple, Macintosh, and Mac are registered trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and
other countries. Kodak is a trademark of Eastman Kodak Company. Windows is either a registered
trademark or trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. All other
trademarks contained herein are the property of their respective owners.
Page 4

Footage
Arri — Courtesy of Arri™/Fauer — John Fauer, Inc.
Bell South “Anticipation” — Courtesy of Two Headed Monster — Tucker/Wayne Atlanta/GMS.
Canyonlands — Courtesy of the National Park Service/Department of the Interior.
Eco Challenge British Columbia — Courtesy of Eco Challenge Lifestyles, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Eco Challenge Morocco — Courtesy of Discovery Communications, Inc.
It’s Shuttletime — Courtesy of BCP & Canadian Airlines.
Nestlé Coffee Crisp — Courtesy of MacLaren McCann Canada.
Saturn “Calvin Egg” — Courtesy of Cossette Communications.
“Tigers: Tracking a Legend” — Courtesy of www.wildlifeworlds.com.
Windhorse — Courtesy of Paul Wagner Productions.
Arizona Images — KNX-TV Production — Courtesy of Granite Broadcasting, Inc.,
Editor/Producer Bryan Foote.
Canyonlands — Courtesy of the National Park Service/Department of the Interior.
WCAU Fire Story — Courtesy of NBC-10, Philadelphia, PA.
Paragliding — Courtesy of Legendary Entertainment, Inc.
GOT FOOTAGE?
Editors — Filmmakers — Special Effects Artists — Game Developers — Animators — Educators —
Broadcasters — Content creators of every genre — Just finished an incredible project and want to
share it with the world?
Send us your reels and we may use your footage in our show reel or demo!*
For a copy of our release and Avid’s mailing address, go to www.avid.com/footage.
*Note: Avid cannot guarantee the use of materials submitted.
Effects Reference for Avid Xpress Pro, Avid Xpress DV • Part 0130-05716-01 •
September 2003
Page 5

Contents
Using This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Who Should Use This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
About This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Symbols and Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
If You Need Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
If You Have Documentation Comments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
How to Order Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Avid Educational Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2D Effects Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Global and Keyframeable Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Acceleration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Avid Pan & Zoom Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Other Options button for the Avid Pan & Zoom Effect. . . . . . . . 23
Display. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Display Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Position for the Avid Pan & Zoom Effect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Velocity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Path . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Background for the Avid Pan & Zoom Effect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Advanced. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Background . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Border . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Color Effect Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Luma Adjust. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Luma Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
5
Page 6

Luma Clip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Chroma Adjust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Color Style . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Color Gain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Crop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Foreground . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Illusion FX Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Background . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Border . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Circle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Glow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Illumination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Motion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Movement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Start Timecode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Key Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Secondary Key. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Spill Suppression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Key Color . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Chroma Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Matte Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Color Correction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Matrix Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Traditional Motion Effect Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Freeze Frame Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Variable Speed and Strobe Motion Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Plug-in Effect Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
6
Page 7

Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Scroll Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Region Stabilize Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Region of Interest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Auto Zoom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Progressive Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Scaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Transition Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
2D Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Blend Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Dip to Color . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Dissolve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Fade from Color. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Fade to Color. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Picture-in-Picture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Superimpose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Box Wipe Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Bottom Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Bottom Left to Top Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Bottom Right to Top Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Left Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Right Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Top Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Top Left to Bottom Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Top Right to Bottom Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Conceal Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Bottom Left to Top Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Bottom Right to Top Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Bottom to Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Left to Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Right to Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Top Left to Bottom Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Top Right to Bottom Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Top to Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
7
Page 8

Edge Wipe Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Horizontal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Horizontal Open . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Lower Left Diagonal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Lower Right Diagonal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Upper Left Diagonal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Upper Right Diagonal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Vertical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Vertical Open . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Film Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
1.66 Mask. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
1.85 Mask. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
16:9 Mask. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Anamorphic Mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Blowup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Film Dissolve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Film Fade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Mask. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Illusion FX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Color Mix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Crystal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Film Grain. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Flare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
FluidBlur . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
FluidColorMap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
FluidMorph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Iris . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Kaleidoscope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Lightning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Melt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Motion Blur . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Page Curl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Particle Blast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Particle Orbit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Particle Wind . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
8
Page 9

Pattern Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Pinch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Radial Blur . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Random Blend. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Ripple . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Rollup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Shear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Sparkler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Sphere . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Swirl. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Timecode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Twist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Wave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Image Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Avid Pan & Zoom (AVX Plug-In Effect) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Color Correction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Color Effect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Flip. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Flip-Flop. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Flop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Region Stabilize. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Resize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Submaster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Key Effects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Chroma Key. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Luma Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Matte Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
RGB Keyer (AVX Plug-in Effect) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
L-Conceal Effects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
Bottom Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
Bottom Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Top Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
Top Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
9
Page 10

Matrix Wipe Effects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
Grid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
One-Way Row . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Speckle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Spiral . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Zig-Zag. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Motion Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Freeze Frame. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Variable Speed and Strobe Motion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Peel Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Bottom Left Corner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Bottom Right Corner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Bottom to Top. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
Left to Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
Right to Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
Top Left Corner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
Top Right Corner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Top to Bottom. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Push Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Bottom Left to Top Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
Bottom Right to Top Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Bottom to Top. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Left to Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
Right to Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
Top Left to Bottom Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Top Right to Bottom Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Top to Bottom. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
Sawtooth Wipe Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Horizontal Sawtooth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Horizontal Open Sawtooth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Vertical Open Sawtooth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Vertical Sawtooth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Shape Wipe Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
4 Corners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Center Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
10
Page 11

Circle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Diamond . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Ellipse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Horizontal Bands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
Horizontal Blinds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
Vertical Blinds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Spin Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
X Spin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Y Spin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
Squeeze Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
Bottom Centered . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
Bottom Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Bottom Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 244
Bottom to Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Centered Zoom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
Horizontal Centered. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
Left Centered. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
Left to Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
Right Centered . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Right to Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
Top Centered. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
Top Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
Top Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 254
Top to Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
Vertical Centered. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
Timewarp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
Timewarp: 0% To 100% . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 258
Timewarp: 100% To 0% . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
Timewarp: 50% Speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
Timewarp: Trim to Fill . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
Timewarp: Reverse Motion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
Timewarp: Speed Boost . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
Timewarp: Speed Bump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
11
Page 12

Title Effects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
Comparison of Similar Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
Chapter 2 3D Effects Reference. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
3D Effects Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
Global Versus Keyframeable Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
The Hierarchy of Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
Direct Manipulation of 3D Effect Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
Acceleration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
Axis. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
Background . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
Border. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
Crop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 277
Foreground . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 278
Position. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279
Rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
Scaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
Shadow. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
Shape . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
Spline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
Target . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
Trail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
Xpress 3D Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
3D Shape Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
3D PIP Effect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
Page Fold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
Tips for Page Fold Creation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
3D Ball . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
Limitations to 3D Ball Shapes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
3D Slats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
12
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
Page 13

Using This Guide
Congratulations on your purchase of an Avid editing application. You can
use it to create broadcast-quality output incorporating every possible
production element from full-speed, high-resolution footage, to
multimedia artwork and animation, to computer-generated effects and
titling.
n
The documentation describes the features and hardware of all models.
Therefore, your system might not contain certain features and hardware
that are covered in the documentation.
Who Should Use This Guide
This guide is intended for all Avid users, from beginning to advanced.
About This Guide
This guide contains reference material for your Avid application’s effects
capabilities. It is a companion volume to the Effects Guide for Avid Xpress
Pro, Avid Xpress DV, which contains a complete explanation of all the tools
and techniques required to create, apply, and adjust various effects and
graphics, including useful tips, shortcuts, and custom options.
Page 14

Using This Guide
Symbols and Conventions
Unless noted otherwise, the material in this document applies to the
Windows
®
XP and Mac® OS X operating systems. When the text applies
to a specific operating system, it is marked as follows:
• (Windows) or (Windows only) means the information applies to the
Windows XP operating system.
• (Macintosh) or (Macintosh only) means the information applies to the
Mac OS X operating system.
The majority of screen shots in this document were captured on a
Windows XP system, but the information applies to both Windows XP and
Mac OS X systems. Where differences exist, both Windows XP and
Mac OS X screen shots are shown.
The following terms are used in this document:
• “effects guide” refers to the Effects Guide for Avid Xpress Pro,
Avid Xpres s DV
• “user’s guide” refers to the User’s Guide for Avid Xpress Pro,
Avid Xpres s DV
• “supplement” refers to the User’s Guide Supplement for
Avid Xpress Pro, Avid Xpress DV
14
• “online library CD-ROM” refers to the Avid Xpress Products Online
Library CD-ROM
The effects guide, user’s guide, and supplement are all available on the
online library CD-ROM.
Page 15

Symbols and Conventions
Avid documentation uses the following symbols and conventions:
Symbol or Convention Meaning or Action
n
c
w
> This symbol indicates menu commands (and
t
k This symbol represents the Apple or Command key.
A note provides important related information,
reminders, recommendations, and strong
suggestions.
A caution means that a specific action you take could
cause harm to your computer or cause you to lose
data.
A warning describes an action that could cause you
physical harm. Follow the guidelines in this
document or on the unit itself when handling
electrical equipment.
subcommands) in the order you select them. For
example, File > Import means to open the File menu
and then select the Import command.
This symbol indicates a single-step procedure.
Multiple arrows in a list indicate that you perform
one of the actions listed.
Press and hold the Command key and another key to
perform a keyboard shortcut.
Margin tips In the margin, you will find tips that help you
perform tasks more easily and efficiently.
Italic font Italic font is used to emphasize certain words and to
indicate variables.
Courier Bold font
Click Quickly press and release the left mouse button
Double-click Click the left mouse button (Windows) or the mouse
Courier Bold font identifies text that you type.
(Windows) or the mouse button (Macintosh).
button (Macintosh) twice rapidly.
15
Page 16

Using This Guide
Symbol or Convention Meaning or Action
Right-click Quickly press and release the right mouse button
(Windows only).
Drag Press and hold the left mouse button (Windows) or
the mouse button (Macintosh) while you move the
mouse.
Ctrl+key
k+key
If You Need Help
If you are having trouble using your Avid editing product:
1. Retry the action, carefully following the instructions given for that task
in this guide. It is especially important to check each step of your
workflow.
2. Check the release notes supplied with your Avid application for the
latest information that might have become available after the hardcopy
documentation was printed.
3. Check the documentation that came with your Avid application or your
hardware for maintenance or hardware-related issues.
4. Visit the online Knowledge Center at www.avid.com/support. Online
services are available 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. Search this
online Knowledge Center to find answers, to view error messages, to
access troubleshooting tips, to download updates, and to read/join
online message-board discussions.
Press and hold the first key while you press the
second key.
16
5. For Technical Support, please call 800-800-AVID (800-800-2843).
For Broadcast On-Air Sites and Call Letter Stations, call
800-NEWSDNG (800-639-7364).
Page 17

If You Have Documentation Comments
If You Have Documentation Comments
Avid Technology continuously seeks to improve its documentation. We
value your comments about this guide, the Help, the online library DVD,
and other Avid-supplied documentation.
Simply e-mail your documentation comments to Avid Technology at
TechPubs@avid.com
Please include the title of the document, its part number, and the specific
section you are commenting on in all correspondence.
How to Order Documentation
To order additional copies of this documentation from within the
United States, call Avid Sales at 800-949-AVID (800-949-2843). If you are
placing an order from outside the United States, contact your local
Avid representative.
Avid Educational Services
For information on courses/schedules, training centers, certifications,
courseware, and books, please visit www.avid.com/training or call
Avid Sales at 800-949-AVID (800-949-2843).
17
Page 18

Using This Guide
18
Page 19

Chapter 1
2D Effects Reference
This chapter describes all 2D effects parameters and then summarizes all
2D effects in alphabetical order within each effect category. For
information on effects editing, see the chapter “Basics of Effects Editing”
in the effects guide or the Help.
• 2D Effects Parameters
• 2D Effects
• Comparison of Similar Effects
Page 20

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
2D Effects Parameters
This section provides a general description of all 2D parameters, in
alphabetical order. Some parameters apply to a wide range of effects;
others are specific to a small group of effects, such as keys or motion
effects.
Effect parameters are grouped in the following categories:
• Acceleration
• Avid Pan & Zoom Parameters
• Background
• Border
• Color Effect Parameters
• Crop
• Foreground
• Illusion FX Parameters
20
• Key Parameters
• Matrix Parameters
• Traditional Motion Effect Parameters
• Plug-in Effect Parameters
• Position
• Region Stabilize Parameters
• Scaling
• Transition Parameters
For an explanation of how to change a parameter, see “Understanding
Effect Parameters” in the effects guide or the Help.
Page 21

Global and Keyframeable Parameters
The effects parameters are divided into two types:
• Global
Changes apply to all keyframes. When you change a global parameter,
the system automatically sets the value for all keyframes in the effect.
• Keyframeable
Changes can be applied to individual keyframes. You can use keyframe
parameters to alter an effect over time.
This distinction is noted throughout this section for each parameter.
Acceleration
2D Effects Parameters
Parameter Type Global
Description Adjusts the effect’s speed over time by having the effect ease in and ease out of every
keyframe. This gives the effect a more natural appearance. The overall speed of an
effect is determined by the duration of the effect, which is determined by the length of
the clip in the sequence. If you want to slow down or speed up the movement of an
effect, you will need to change the length of your effect or use add edits to limit the
portion of the clip affected by the effect.
Use of Control Drag the slider to control ease in and ease out motion. When the slider is to the left
(value of 0), there is no ease in and ease out motion. The effect maintains a constant
speed throughout its path. As the slider moves to the right (toward a maximum value
of 100), ease in and ease out motion increases.
21
Page 22
Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
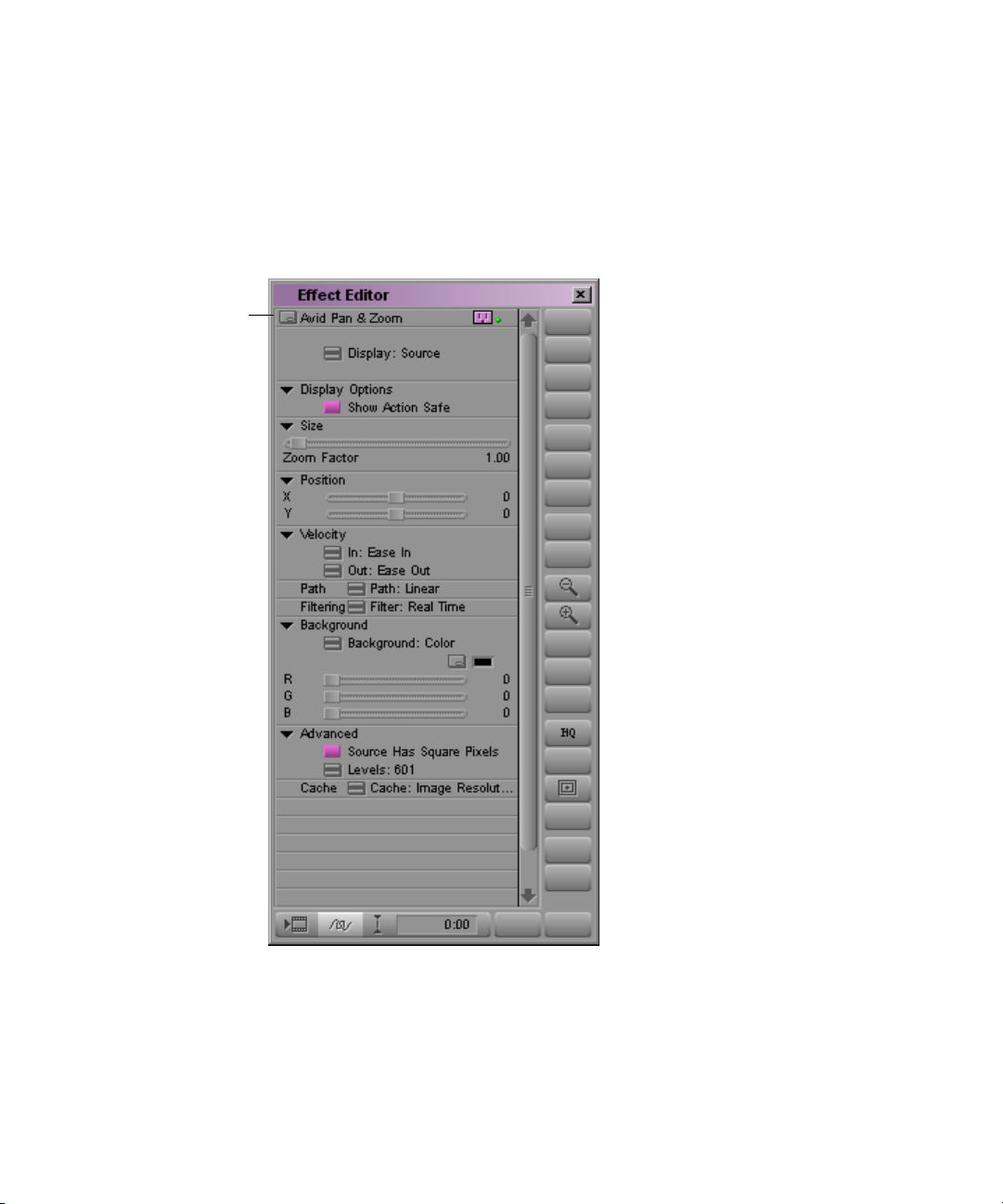
Avid Pan & Zoom Parameters
This section describes the parameter categories available for the
Avid Pan & Zoom AVX plug-in effect.
Other Options button
22
Page 23

Other Options button for the Avid Pan & Zoom Effect
Parameter type: Global
The Other Options button opens a file selection dialog box. Use it to
specify the image file for the Avid Pan & Zoom effect.
2D Effects Parameters
Display
n
If you move the image file after importing it into the Avid Pan & Zoom
effect, the effect will not be able to locate the file and you must reimport the
image.
Parameter type: Global
The Display Fast menu lets you choose how you view the image as you
work on it.
• Source shows you the entire image scaled to fit inside the Effect
Preview monitor. Use Source as you draft the effect.
• Tar ge t shows you the results of your pan and zoom settings. Use
Target for previewing your moves.
For more information, see “Viewing the Image While You Work” in the
effects guide or the Help.
Display Options
Parameter type: Global
Show Action Safe in the Display Options parameter category selects or
deselects the display of the safe action area. When Show Action Safe is
selected, the safe action area appears as a rectangle superimposed on the
field of view.
23
Page 24

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Size
Parameter type: Keyframeable
The Size parameter category contains the Zoom Factor slider. This slider
controls how far you zoom into or out from the source image.
The Zoom Factor ranges from .1 to 20. At .1, the application scales down
the image to one-tenth the original. At 1, the application applies no
magnification to the source image. At 20, the application scales up the
image 20 times - that is, by 2,000%.
The larger the Zoom Factor, the smaller the field of view rectangle appears
when you use Source mode.
Position for the Avid Pan & Zoom Effect
24
Parameter type: Keyframeable
You control pan by either using the X and Y Position parameters or
dragging the field of view across the source image.
The Position parameters refer to the center of the field of view. A Position
of 0, 0 centers the field of view over the center of the image.
For more information, see “Panning Over the Source Image” in the effects
guide or the Help.
Page 25

Velocity
Parameter type: Keyframeable
The Avid Pan & Zoom effect uses Velocity In and Velocity Out at each
keyframe to modify apparent camera speed as it pans across the image
between keyframes. It modifies changes in the Zoom Factor setting in the
same way.
The Velocity parameters divide the time between keyframes in half.
Velocity In controls the rate of movement in the first half; Velocity Out
controls the rate of movement in the second half.
Table 1 Velocity Parameter Options
Parameter Option Description
2D Effects Parameters
Velocity In Linear For the first half of the time between the selected keyframe and the next
keyframe (starting at the selected keyframe and ending at the midpoint
between keyframes), the effect makes no modification to the pan and zoom
movement. This results in apparent camera movement that begins immediately
with no ease in.
Constant The effect does not use the keyframe’s Position parameters to calculate the
speed of the effect. However, the effect still uses the keyframe’s Position
parameters to determine the path of the effect (the pan) and the keyframe’s
Zoom Factor to calculate the zoom between the selected keyframe and the
next keyframe. For more information on using the Constant option, see
“Creating a Path with Constant Velocity” in the effects guide or the Help.
When you select Constant for Velocity In, the effect automatically selects
Constant for Velocity Out, and vice versa.
25
Page 26

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Table 1 Velocity Parameter Options (Continued)
Parameter Option Description
Ease In For the first half of the time between the selected keyframe and the next
keyframe (starting at the selected keyframe and ending at the midpoint
between keyframes), the effect modifies the pan and zoom movement by
providing a slight acceleration. To ease in and ease out of the entire effect, see
“Using Ease In and Ease Out” in the effects guide or the Help.
Velocity Out Linear For the second half of the time between the selected keyframe and the next
keyframe (starting at the midpoint and ending at the next keyframe), the effect
makes no modification to the pan and zoom movement. This results in
parameters that change at a constant rate up to the next keyframe.
Ease Out For the second half of the time between the selected keyframe and the next
keyframe (starting at the midpoint and ending at the next keyframe), the effect
modifies the pan and zoom movement by providing a slight deceleration. To
ease in and ease out of the entire effect, see “Using Ease In and Ease Out” in
the effects guide or the Help.
Constant The effect does not use the keyframe’s Position parameters to calculate the
speed of the effect. However, the effect still uses the keyframe’s Position
parameters in determining the path of the effect (the pan) and the keyframe’s
Zoom Factor to calculate the zoom between the selected keyframe and the
next keyframe. For more information on using the Constant option, see
“Creating a Path with Constant Velocity” in the effects guide or the Help.
When you select Constant for Velocity Out, the effect automatically selects
Constant for Velocity In, and vice versa.
Hold At the midpoint between the selected keyframe and the next keyframe, the
image freezes (pan and zoom movement stops). Movement resumes at the next
keyframe. The effect disregards the Velocity In value of the next keyframe.
If you have Background set to Video, the background continues to update.
26
Page 27

Path
2D Effects Parameters
Parameter type: Global
The Path parameter controls how the Avid Pan & Zoom effect interpolates
Position parameter changes between keyframes.
• Linear interpolation creates straight-line changes from one keyframe
to the next.
• Spline interpolation smooths out changes between keyframes to create
a more natural movement.
The Avid Pan & Zoom effect calculates a Spline path so that it is
smooth through all points. If you move a point the effect recalculates
the entire path.
n
If you combine a Spline path with Constant velocity, when you move a
keyframe the path recalculation might result in a change to the velocity of
the effect.
27
Page 28

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Filtering
Parameter type: Global
Filtering controls the method by which the Avid Pan & Zoom effect
renders and determines the quality of the rendered result. The various
filtering methods allow you to trade off the clarity or sharpness of the
resized image and the speed at which the effect renders.
The following illustration ranks the Filtering options from fastest render
time and lowest quality image to longest render time and highest quality
image. For more information, see “Filtering” in the effects guide or the
Help.
Longest Render
Time
Shortest Render
Time
Quadratic
Triangle
Real Time
Lowest Image Quality
Avid Ultra Qual
Avid Hi Qual
Gaussian
B-Spline Catmull
Cubic
Highest Image Quality
28
Page 29

Background for the Avid Pan & Zoom Effect
Parameter type: Global
With the Avid Pan & Zoom effect you can select a field of view from the
original image that does not fill the entire screen. The Background
parameter determines what appears outside the field of view.
• Color lets you select a background color using one of the following
methods:
t Manipulate the RGB sliders directly, or use the numeric keypad to
enter values.
t Click the Other Options button to use the Windows Color dialog
box or the Macintosh Color Picker.
2D Effects Parameters
t Click the Color Preview window, and use the eyedropper.
For more information, see “Adjusting a Color Parameter” in the effects
guide or the Help.
• Video uses the video from the segment upon which you placed the
Avid Pan & Zoom effect.
29
Page 30

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Advanced
Parameter type: Global
The Advanced parameter category provides controls to compensate for
differences in pixel shape between source and output, and to select input
color levels.
• Source Has Square Pixels is enabled by default. The Avid Pan &
Zoom effect makes the calculations necessary to produce results
compatible with rectangular pixels.
When you deselect Source Has Square Pixels, the Avid Pan & Zoom
effect makes no changes to the pixel shape.
•The Level setting tells the effect how to treat the color levels in the
image.
- RGB is for images with a black level of 0 and a white level of 255.
Most images you import into the Avid Pan & Zoom effect (except
those from a video source) use RGB values. The effect maps
colors to video black and white levels, which are 16 and 235
respectively. RGB is the default Level setting.
30
- 601 refers to the ITU-R-601 standard for video black and white
levels. Select 601 in the rare case when you use images from a
video source. When you select 601 for the Level setting, the effect
makes no adjustment to color levels.
Page 31

Cache
2D Effects Parameters
Parameter type: Global
The Cache parameter gives you control over the amount of memory used to
store your images for playback. A full resolution image is always used for
rendering.
• Video Resolution — The effect stores the resized source image at
720 x 480 pixels, using about 1 MB per image. Use Video Resolution
if you have many images in your sequence and you need to limit how
much memory they occupy.
• Image Resolution — The effect stores the resized source image at its
original resolution. The amount of memory used varies with the size of
the image.
• Multi-Resolution — The effect stores several versions of the image:
original image resolution, half resolution, quarter resolution, and so
on, for 8 versions of the image. The result is higher quality real-time
preview and faster rendering. Multi-Resolution uses about twice the
memory of Image Resolution.
• Free Current Cache — The effect frees all memory used for image
storage and then reverts to Image Resolution. Use this setting to free
up memory after you have rendered the clip.
• Cache All — The Cache All settings are shortcuts for setting the same
parameter for all instances of the effect in a sequence. The descriptions
are the same as above.
• Free All Caches — Frees the caches for all instances of the plug-in in
that sequence.
31
Page 32

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Background
Parameter Type Global
Description Sets the color for the background in effects that display a background. For example,
the background parameters determine the color to be used in a Fade to Color, Fade
from Color, or Dip to Color effect.
Use of Controls
Other Options
button
Hue Identifies the background color. The Hue parameter is
Sat (saturation)
Lum
(luminance)
Opens the Windows Color dialog box or Macintosh Color
Picker for precise color selection. For more information, see
“Using the Windows Color Dialog Box” and “Using the
Macintosh Color Picker” in the effects guide or the Help.
measured as values on a color wheel ranging from 0 to 255.
The start (0) and ending (255) values are both red.
Specifies the amount or intensity of the color. Values range
from 0 to 255, where 0 is no chrominance and 255 is a fully
saturated color.
Specifies the brightness of the color. Values range from 0 to
255, where 0 is black and 255 is full brightness or white.
32
Page 33

2D Effects Parameters
Border
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description Allows you to place a border on the inner or incoming picture in many effects. The
Border parameters allow you to specify the color, softness, and width of the border.
Some effects also include Blend Color parameters for blending border color.
Use of Controls Other Options
button
Hue Identifies the border or blend color. The Hue parameter is
Sat (saturation) Specifies the intensity of the color. Values range from 0 to
Lum
(luminance)
Width Specifies the width of the border. Values range from 0 (no
Soft (softness) Blends the border with the background image. Values range
Opens the Windows Color dialog box or Macintosh Color
Picker for precise color selection. For more information, see
“Using the Windows Color Dialog Box” and “Using the
Macintosh Color Picker” in the effects guide or the Help.
measured as values on a color wheel ranging from 0 to 255.
The start (0) and ending (255) values are both red.
255, where 0 is no chrominance and 255 is a fully saturated
color.
Specifies the brightness of the color. Values range from 0 to
255, where 0 is black and 255 is full brightness or white.
border) to 63 (widest border).
from 0 (no softness) to 63 (maximum softness).
33
Page 34

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Color Effect Parameters
The Color Effect parameters, which apply to the Color Effect only, allow
you to perform color correction or to create certain colorization effects
such as posterization or solarization.
Luma Adjust
Parameter Type Global
Description Allows you to adjust the luminance characteristics of the image.
Use of Controls Bright
(brightness)
Cont (contrast) Controls the contrast of light and dark areas in the image. Values
Invert Reverses the image’s brightness, such that the brightest parts
Changes the brightness of the image. The parameter ranges from
–100 to +100, where a value of 0 indicates no change. A value of
–100 darkens the image; a value of +100 brightens the image.
range from –100 to +100, where a value of 0 indicates the image is
unchanged. A negative value is less contrast; a positive value is
more contrast.
become the darkest and the darkest parts become the lightest.
34
Page 35

2D Effects Parameters
Brightness Example
Original – Brightness 0 Brightness –50 Brightness +50
Contrast Example
Original – Contrast 0 Contrast –50 Contrast +50
Luma Range
Parameter Type Global
Description Allows you to adjust the range of brightness of the image.
Use of Controls Fast menu:
16 to 235
The default for video images.
35
Page 36

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Fast menu:
0to255
W Point
(white point)
B Point
(black point)
Allows you to map normal video to alpha ranges. This is useful if
you have a high-contrast image that you want to expand to the full
dynamic range. For example, use this value when you want to
convert video to alpha for Matte Key effects.
When you change the Luma Range to 0 to 255, the system
n
attempts to go from 0 to 255 but will be clipped by the Low
Clip and High Clip values in the Luma Clip parameter
category. If it is your intent to “open up” the image to the full
dynamic range, you need to change the Low Clip and High
Clip values to 0 and 255, respectively.
Allows you to set the white point in the image. All pixels with that
value become white, and all pixels with higher values are also
clipped to white. The default is 235 (the broadcast value for white).
Raising the black point and lowering the white point values
increase the contrast by reducing the number of shades of gray in an
image. The number of shades is reduced because you map some to
extreme black and others to extreme white.
Allows you to set the black point in the image. All pixels with that
value become black, and all pixels with lower values are also
clipped to black.
For example, you could use the eyedropper to select a shadow on
the floor and change it from gray to black, clipping everything
below that shade to black. The default is 16 (the broadcast value for
black).
36
Raising the black point and lowering the white point values
increase the contrast by reducing the number of shades of gray in an
image. The number of shades is reduced because you map some to
extreme black and others to extreme white.
Black point control does not change the Black setup level. To
n
adjust the Black setup level, use the Video Output tool. For
more information, see “Output Options” in the Help.
Page 37

Luma Clip
2D Effects Parameters
Gamma Allows you to adjust the midtones in an image without affecting the
extreme white or black values. Lowering the value darkens
midtones and brings the image closer to black. Raising the value
lightens the midtones and brings the image closer to white.
For example, a person shot in front of a window in daylight may be
very dark, almost in silhouette. You can use gamma correction to
increase the midtones without changing the blacks or whites.
Values range from –100 to +100 with 0 being no change.
The W Point, B Point, and Luma Clip sliders determine the number
of shades of gray. The Gamma point allows you to move the
distribution of the shades closer to black or closer to white.
Negative values move the distribution closer to black. Positive
values move the distribution closer to white.
Parameter Type Global
Description Allows you to determine the levels at which the effect limits the brightness or
darkness in the picture.
Use of Controls High Provides a simple clip function for brightness values. When you
specify a value for High, no pixel in the image can be brighter than
that value. The default is 235 (the broadcast value for white).
Low Provides a simple clip function for darkness values. When you
specify a value for Low, no pixel in the image can be darker than
that value. The default is 16 (the broadcast value for black).
When preparing video for broadcast, normally you do not adjust
these values. They allow you to adjust the brightness and contrast
(using other controls in the Color Effect) while still maintaining
legal broadcast values for black and white.
37
Page 38

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Chroma Adjust
Parameter Type Global
Description Allows you to adjust the chrominance characteristics of the entire image.
Use of Controls Invert Invert reverses the colors in both Hue and Saturation such that all
colors display as their complement.
Hue Hue varies the tint of all colors in the image. The Hue parameter is
measured as degrees on a color wheel from –180 to +180, where 0
does not change the hue. Changing the value of the Hue causes all
colors in the image to rotate around the color spectrum. For
example, a Hue setting of –20 causes skin tones to look more red,
while a Hue setting of +20 causes skin tones to look more green.
Sat (saturation) Saturation varies the amount of all colors in the image. The
Saturation parameter has a value of –100 to +100. Zero is the
default. A value of –100 displays as gray tones. Positive values
display all colors with more saturation.
Color Style
Parameter Type Global
Description Allows you to create effects by limiting or inverting the color values of the image.
38
Page 39

2D Effects Parameters
Use of Controls Post
(posterization)
Solar
(solarization)
Posterization allows you to limit the number of colors in the image
by controlling the number of luminance steps that are displayed.
This gives the image a graphic appearance. The range of values is 0
to 25, where 0 displays all colors and 25 displays the least number
of colors.
Solarization allows you to make the lightest points in the image
dark to achieve a partial inversion of the luminance. Values above
the threshold set for the parameter will be inverted. Solarization can
have a value of 0 to 255, where 0 is normal luminance and 255
inverts all luminance values in the picture. Values of 0 to 127
display the lightest points in the image as dark. Values of 128 to
255 display both the lightest points as dark and the darkest points as
light, which gives the appearance of a film negative.
Posterization Example
Original image Posterization 10 Posterization 20
Solarization Example
Original image Solarization 100 Solarization 200
39
Page 40

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Color Gain
Parameter Type Global
Description Allows individual control of the Color Gain for each of the three color components:
red, green, and blue.
Use of Controls Red Changes the amount of red in the whole image. The parameter
value is a percentage of the range from 0 to 200, where a value of
100 indicates that the color is unchanged.
Green Changes the amount of green in the whole image. The parameter
value is a percentage of the range from 0 to 200, where a value of
100 indicates that the color is unchanged.
Blue Changes the amount of blue in the whole image. The parameter
value is a percentage of the range from 0 to 200, where a value of
100 indicates that the color is unchanged.
40
Page 41

2D Effects Parameters
Crop
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description Removes material from the top, bottom, left, and right edges of the video.
Use of Controls T (top) Removes video from the top of the inner or incoming video. Values
range from 0 to 999; 0 is the top of the screen, 500 is the middle of
the screen, and 999 is the bottom of the screen.
B (bottom) Removes video from the bottom of the inner or incoming video.
Values range from –999 to 0; 0 is the bottom of the screen, –500 is
the middle of the screen, and –999 is the top of the screen.
L (left) Removes video from the left side of the inner or incoming video.
Values range from 0 to 999; 0 is the left side of the screen, 500 is
the middle of the screen, and 999 is the right side of the screen.
R (right) Removes video from the right side of the inner or incoming video.
Values range from –999 to 0; 0 is the right side of the screen, –500
is the middle of the screen, and –999 is the left side of the screen.
41
Page 42

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Foreground
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description Used, together with keyframes, to set the relative amount of the effect to be displayed
over time. The additional options included with the Level slider vary, depending on
the effect.
Use of Controls Level Controls the opacity of the foreground image. A Level of 0 is
0 percent opacity (the foreground is transparent), a Level of 50 is 50
percent opacity, and a Level of 100 is 100 percent opacity (no
transparency).
42
Swap Sources This option applies to key effects (such as Chroma Key or Luma
Key) and the PIP (Picture-in-Picture) effect only.
Click Swap Sources to swap the image source for the foreground
and background layers of the effect.
Reverse
Animation
This option is available for all effects.
Click the Reverse Animation button to cause the entire effect to be
reversed, including the direction of movement as well as the
incoming and outgoing sources.
This maintains the shot continuity while reversing the movement.
For example, instead of the outgoing shot peeling off from the top
left corner, the incoming shot peels on from the bottom right corner.
This option effectively creates a mirror image of the sequence of
keyframes for the effect as they appear in the Effect Preview
monitor’s position bar.
Page 43

2D Effects Parameters
Invert Key This option applies to key effects only (such as Chroma Key or
Luma Key). Select Invert Key to reverse the key.
In the case of a Chroma Key effect, inverting the key displays the
key color regions while showing the background image source
through the foreground image area.
In the case of a Luma Key effect, inverting the key displays the
background image source through the darker areas rather than the
lighter areas of the foreground image source.
In the case of a Matte Key effect, inverting the key effectively
reverses the black and white areas of the alpha channel so that
foreground and background are reversed.
Show Alpha This option applies to key effects only (such as Chroma Key or
Luma Key).
Displays the grayscale alpha channel used to apply the key effect to
the foreground and background source. This allows you to examine
the problem areas of the key while making adjustments.
43
Page 44

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Illusion FX Parameters
This section describes the parameter categories available for the
Illusion FX AVX plug-in effects.
Background
Pattern Type Fast menu
Axis Fast menu
Base Color
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Background parameter category is available only for the Pattern Generator effect.
For more information, see “Pattern Generator” on page 168.
44
Page 45

2D Effects Parameters
Use of Controls
Axis Fast menu
•X axis
•Y axis
Pattern Type
Fast menu
• Solid color
• EBU bars
(75%)
• Color bars
(75%)
• Color bars
(100%)
•EIA bars
•SMPTE bars
• Color ramps
• Cross ramp
•Grid
R, G, B
(Base Color)
Selects whether color bars are drawn horizontally (X axis) or
vertically (Y axis).
Sets the pattern to be used.
If you select the Grid option, the background color is black if Base
Color has 50% or greater luminance, or white if Base Color has less
than 50% luminance.
Sets the color of the clip when the Pattern Type is set to Solid Color
Sets the color of the grid lines when the Pattern Type is set to Grid.
Select the color by doing one of the following:
t Directly manipulate the RGB sliders.
t Use the Windows Color dialog box or the Macintosh Color
Picker.
t Use the eyedropper.
The background color of the grid is black if Base Color has 50% or
greater luminance, or white if Base Color has less than 50%
luminance.
45
Page 46

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Border
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description Use the Left, Right, Top, and Bottom sliders to prevent black edges of the source clip
from warping into the effect.
Use of Controls Left, Right,
Top, Bottom
Remove between 0 and 20 pixels from the edge of the image.
Center
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description Sets the center of the Kaleidoscope effect. The Center parameter category is available
only for the Kaleidoscope effect. For more information, see “Kaleidoscope” on
page 159.
Use of Controls X, Y The X and Y values range from –999 to +999, where 0, 0 is the
center of the screen. Use the sliders, or click the corresponding
marker and drag within the image, to set the center of the mirrors.
46
Page 47

2D Effects Parameters
Circle
Color
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Circle parameter category is available only for the Pattern Generator effect. For
more information, see “Pattern Generator” on page 168.
Use of Controls
Size Sets the radius of the circle.
Width Sets the width of the circle outline.
Opacity Sets the opacity of the circle.
R, G, B (Color) Sets the color of the circle. Select the color by doing one of the
following:
t Directly manipulate the RGB sliders.
t Use the Windows Color dialog box or the Macintosh Color
Picker.
t Use the eyedropper.
47
Page 48

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Core
Lightning Sparkler
Color
Color
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Core parameter category is available for the Lightning effect and the Sparkler
effect. For more information, see “Lightning” on page 160 and “Sparkler” on
page 175.
Use of Controls
Core Radius,
Sets the radius of the core in pixels.
Width
R, G, B (Color) Sets the color of the core. Select the color by doing one of the
following:
t Directly manipulate the RGB sliders.
t Use the Windows Color dialog box or the Macintosh Color
Picker.
t Use the eyedropper.
48
Page 49

2D Effects Parameters
Generation
Lightning effect Sparkler effectRipple effect
Render Mode Fast menu
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Generation parameter category is available for the Lightning, Ripple, and
Sparkler effects. For more information, see “Lightning” on page 160, “Ripple” on
page 172, and “Sparkler” on page 175.
Use of Controls Parameter Effect Description
Amount Lightning
Anti-alias Ripple Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
Birth Rate Sparkler Sets the number of sparks generated every frame.
Branch
Probability
Length Ripple Sets the distance between the wave peaks.
Lightning
Sets the proportion of the lightning to be displayed. A
value of 0 is no lightning. 100 is the complete lightning
bolt. Typical keyframing is 0 at the first keyframe to
100 at the last keyframe.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Sets the likelihood that the lightning will have few or
many branches. A value of 0 displays no branches. The
higher the value, the more branches are likely.
49
Page 50

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Length Sparkler Sets the cumulative exposure of the sparks. For
Lifetime Sparkler Sets (in frames) how long each spark lives.
Link Speed Sparkler If you keyframe the center of the effect, Link Speed
example, a value of 3 produces an image that looks as
though you left a virtual camera shutter open for the
last three frames.
causes the movement of the center to be added to the
movement of the sparks.
Number of
Ripples
Random Seed Lightning,
Render Mode
Fast menu
•Quick
• Standard
• Anti-aliased
Speed Bias X,
Speed Bias Y
Strength Ripple Sets the height of the waves.
X, Y Sparkler Sets the center of the effect. The X and Y values range
Ripple Sets the number of ripples.
Sets the base number upon which all random values
Ripple
Lightning
Sparkler Sets the bias to the direction of the sparks. The system
are calculated. Each value will result in a different
random effect.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Sets the quality of the rendered lightning:
• Quick to view just the motion of the lightning.
• Standard to view the full lightning without antialiasing while editing the animation.
• Anti-aliased to ensure that fine branches do not
break up.
adds these values to the initial random directions.
from –999 to +999, where 0, 0 is the center of the
screen.
50
Page 51

Glow
2D Effects Parameters
Lightning effect Sparkler effect
Color
Color
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Glow parameter category is available for the Lightning effect and the Sparkler
effect. Use it to control the effect’s glow. For more information, see “Lightning” on
page 160 and “Sparkler” on page 175.
Use of Controls Parameter Effect Description
Glow Radius Sparkler Sets the radius of the glow in pixels.
R, G, B (Color) Lightning,
Sparkler
Sets the color of the glow. Select the color by doing
one of the following:
t Directly manipulate the RGB sliders.
t Use the Windows Color dialog box or the
Macintosh Color Picker.
t Use the eyedropper.
Width Lightning Sets the radius of the glow in pixels.
51
Page 52

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Illumination
Color
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Illumination parameter category is available only for the Ripple effect. Use it to
highlight the ripples in the effect. For more information, see “Ripple” on page 172.
Use of Controls
Angle Sets the source direction of the light. A value of 0 degrees is three
o’clock; positive values move counterclockwise.
R, G, B (Color) Sets the color of the light. Select the color by doing one of the
following:
t Directly manipulate the RGB sliders.
t Use the Windows Color dialog box or the Macintosh Color
Picker.
t Use the eyedropper.
52
Page 53

Input
2D Effects Parameters
The set of Input parameters varies between Illusion FX effects. Each set of
parameters is listed in its own section:
• Color Mix Input Parameters
• Crystal Input Parameters
• Film Grain Input Parameters
• Flare Input Parameters
• FluidBlur Input Parameters
• FluidColorMap Input Parameters
• FluidMorph Input Parameters
• Iris Input Parameters
• Kaleidoscope Input Parameters
• Melt Input Parameters
• Motion Blur Input Parameters
• Page Curl Input Parameters
• Particle Blast Input Parameters
• Particle Orbit Input Parameters
• Particle Wind Input Parameters
• Pinch Input Parameters
• Radial Blur Input Parameters
• Random Blend Input Parameters
• Rollup Input Parameters
• Shear Input Parameters
• Sphere Input Parameters
• Swirl Input Parameters
• Timecode Input Parameters
• Twist Input Parameters
• Wave Input Parameters
53
Page 54

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Color Mix Input Parameters
Color
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Color Mix effect control the color and the color level.
For more information, see “Color Mix” on page 153.
Use of Controls
Color Level Sets the amount of color to add, from 0 (no color) to 100
(maximum color).
R, G, B (Color) Sets the color. Select the color by doing one of the following:
t Directly manipulate the RGB sliders.
t Use the Windows Color dialog box or the Macintosh Color
Picker.
t Use the eyedropper.
54
Page 55

2D Effects Parameters
Crystal Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Crystal effect control the size and randomness of the
polygons. For more information, see “Crystal” on page 154.
Use of Controls
Size Sets the radius of the polygons in pixels.
Jitter Sets the randomness of the shape of the polygons. A value of 0
creates regular hexagons — the higher the value, the more random
the shapes.
Random Seed Sets the base number upon which all random values are calculated.
Each value will result in a different random effect. This parameter
is not keyframeable.
Anti-alias Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
55
Page 56

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Film Grain Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Film Grain effect add a grainy texture to a video clip to
simulate the imperfections present in some film footage. For more information, see
“Film Grain” on page 155.
Use of Controls
Level Sets the amount of graininess.
Size Sets the size of the individual grain elements.
Color Film footage often contains slight color and luminance
imperfections caused by the chemical processes used to transfer the
negative to the film. You can think of these as very small color
smears on the film. The default setting applies a balanced
combination of color and luminance imperfections. Increase the
color value to add more color imperfections and fewer luminance
imperfections. Decrease the value to increase the luminance
imperfections and decrease the color imperfections.
Field Mode When selected, the grain pattern updates every field.
Hilite Grain Adds grain to the brighter areas of the image.
Shadow Grain Adds grain to the darker areas of the image.
56
Page 57

2D Effects Parameters
Flare Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Flare effect create a random flare ring. For more
information, see “Flare” on page 156.
Use of Controls
Brightness Sets the brightness of the flare, from 0 (no flare) to 100 (maximum
brightness).
Size Sets the diameter of the flare ring.
Width Sets the distance between the inner and outer edges of the flare
ring.
Amount Sets the amount of distortion to the flare ring; 0 is no distortion.
Random Seed Sets the base number upon which all random values are calculated.
Each value will result in a different random effect.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
X, Y Sets the center of the flare ring.
57
Page 58

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
FluidBlur Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the FluidBlur effect create a motion blur. For more
information, see “FluidBlur” on page 156.
Use of Controls
Blur Amount The level of blur for objects that are moving.
The amount of blur ramps linearly from 0 to Blur Amount as the
pixel motion increases from the Lower Motion Threshold value to
the Upper Motion Threshold value. This means that the faster an
object moves, the more it is blurred.
Lower Motion
Threshold,
Upper Motion
Threshold
Objects moving less than the Lower Motion Threshold number of
pixels between frames or fields are not blurred. Objects moving
more than the Upper Motion Threshold number of pixels between
frames or fields are not blurred. Objects whose movement falls
between the two values are blurred by the Blur Amount.
Trail Instructs the system to add an amount from the previous frame’s (or
field’s) blur to the current frame. This produces smooth movement,
especially as objects move along curved paths.
Sharpen Leading
Edge
Progressive
Source
Allows you to keep the front edge of an object crisp and clear while
other portions are blurred.
Use this option if your footage was captured or converted to
progressive footage (i.e., not interlaced). If your sources are
progressive, enabling Progressive Source produces smoother
results. This option has no effect in 24p projects because the system
assumes that you are using progressive footage.
58
Page 59

2D Effects Parameters
FluidColorMap Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the FluidColorMap effect create a color representation of
motion in a scene. For more information, see “FluidColorMap” on page 157.
Use of Controls
Min Motion
Threshold, Max
Motion
Threshold
Constant
Saturation
Progressive
Source
Objects moving less than the Min Motion Threshold number of
pixels between frames (or fields) will have the minimum saturation
and luminance. Objects moving more than the Max Motion
Threshold number of pixels between frames (or fields) receive the
maximum saturation and luminance. The amount of saturation
depends on the Constant Saturation value.
Brightness and color saturation increase as the motion of an object
increases from the minimum threshold value to the maximum
threshold value. The faster an object moves, the brighter and more
color saturated it becomes.
This setting controls how much the Min Motion Threshold and
Max Motion Threshold values affect the color saturation. The
minimum and maximum values always control the luminance
(brightness) of the image. However, for a low Constant Saturation
value, the minimum and maximum values strongly affect saturation
as well as luminance. For a high Constant Saturation value, the
minimum and maximum values affect saturation to a lesser degree.
If Constant Saturation is set to the maximum value, motion will
have no effect on color saturation.
Use this option if your footage was captured or converted to
progressive footage (i.e., not interlaced). If your sources are
progressive, enabling Progressive Source produces smoother
results. This option has no effect in 24p projects because the system
assumes that you are using progressive footage.
59
Page 60

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
FluidMorph Input Parameters
Parameter Type Global
Description The Input parameters for the FluidMorph effect control morphing between two clips.
For more information, see “FluidMorph” on page 157.
Use of Controls
Feature Match When selected, the system attempts to match features between the
two clips when it creates the morph for each frame.
When deselected, the system creates the morph based on the
brightness of the two images.
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
video.
Progressive
Source
Use this option if your footage was captured or converted to
progressive footage (i.e., not interlaced). If your sources are
progressive, enabling Progressive Source produces smoother
results. This option has no effect in 24p projects because the system
assumes that you are using progressive footage.
60
Page 61

2D Effects Parameters
Iris Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Iris effect create a wipe transition. For more information,
see “Iris” on page 158.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the proportion of each clip to be displayed. A value of 0
displays all of the foreground clip; a value of 100 displays all of the
background clip. Typical keyframing would be from 0 at the first
keyframe to 100 at the last keyframe.
Softness Sets the size of the area over which the pixels are faded from the
foreground clip to the background clip.
X, Y Sets the center of the iris wipe.
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
video.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
61
Page 62

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Kaleidoscope Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Kaleidoscope effect create an image resembling a
kaleidoscope using the input video. For more information, see “Kaleidoscope” on
page 159.
Use of Controls
Symmetry Sets the number of mirrors.
Angle Sets the angle of the mirrors.
Scale Sets the scale of the image.
62
Page 63

2D Effects Parameters
Melt Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Melt effect control a transition effect that “melts” the
foreground image away to reveal the background image. For more information, see
“Melt” on page 161.
Use of Controls
Bleed Changes the melt image to a more dramatic effect.
Melt Up Reverses the direction of the melt.
Amount Sets the progression of the effect. A value of 0 is no effect; all of the
foreground clip shows. The higher the value, the more of the
foreground clip melts away, and more of the background clip
shows. Typical keyframing would be from 0 at the first keyframe to
100 at the last keyframe.
Strength Sets the strength of the distortion; the higher the value, the greater
the distortion.
Random Seed Sets the base number upon which all random values are calculated.
Each value results in a different random effect.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
63
Page 64

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Anti-alias Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
Motion Blur Input Parameters
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
video.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Motion Blur effect allow you to blur the edges of
moving objects. For more information, see “Motion Blur” on page 162.
Use of Controls
64
Amount Sets the length of the blur.
Direction Sets the direction of the blur. A value of 0 degrees is three o’clock;
positive values move counterclockwise.
Page 65

2D Effects Parameters
Page Curl Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Page Curl effect create a transition effect that peels the
foreground video off the background video. For more information, see “Page Curl”
on page 163. For examples of the Page Curl parameter combinations, see Table 2 on
page 66.
Use of Controls
Turn Left Controls the direction of the page curl.
Reverse When selected, incoming video peels on. When deselected,
outgoing video peels off.
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
video.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
65
Page 66

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Tabl e 2 describes the possible combinations of the three parameters and
shows an example of the results.
Table 2 Page Curl Parameter Combinations
Turn L e ft Reverse Swap Sources Result
Off Off Off
Off Off On
On Off Off
On Off On
Outgoing video
peels off
Incoming video
peels off
Outgoing video
peels off
Incoming video
peels off
66
Page 67

2D Effects Parameters
Table 2 Page Curl Parameter Combinations (Continued)
Turn L e ft Reverse Swap Sources Result
Off On Off
Off On On
On On Off
On On On
Incoming video
peels on
Outgoing video
peels on
Incoming video
peels on
Outgoing video
peels on
67
Page 68

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Particle Blast Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Particle Blast effect create a transition effect that turns
the foreground video into particles that blow off to reveal the background video. For
more information, see “Particle Blast” on page 164.
68
Page 69

2D Effects Parameters
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the progression of the effect. The larger the difference in the
Amount value between keyframes, the faster the effect happens.
Size Sets the radius of the particles.
Spacing Sets the space between the center of the original position of the
particles.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Front Speed Controls whether the particles in the center of the blast start to
move before the particles at the outside edges.
Front
Randomness
Speed Sets the speed at which particles move apart.
Speed
Randomness
Acceleration Controls how quickly a particle reaches the full speed of the blast.
Bumpiness Adds a shadow to the edge of the particles.
Allows particles nearest the center to move at different speeds.
Allows particles to move at different speeds to give a more natural
effect.
The higher the value, the more quickly the particle reaches full
speed.
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
video.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
69
Page 70

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Particle Orbit Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Particle Orbit effect create a transition effect that turns
the foreground video into circular particles that orbit around their original position.
For more information, see “Particle Orbit” on page 165.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the progression of the effect. The larger the difference in the
Amount value between keyframes, the faster the effect happens.
Size Sets the radius of the particles.
Spacing Sets the space between the center of the original position of the
particles.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Bumpiness Adds a shadow to the edge of the particles.
Speed Sets the speed at which particles orbit.
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
video.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
70
Page 71

Particle Wind Input Parameters
2D Effects Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Particle Wind effect create a transition effect that turns
the foreground video into circular particles that blow off to reveal the background
video. For more information, see “Particle Wind” on page 167.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the progression of the effect. The larger the difference in the
Amount value between keyframes, the faster the effect happens.
Size Sets the radius of the particles.
Spacing Sets the space between the center of the original position of the
particles.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Front Speed Controls whether the particles near the front edge (where the wind
first hits) start to move before the particles at the outside edge.
Front
Randomness
Allows particles nearest the front to move at different speeds.
71
Page 72

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Speed Sets the wind speed.
Speed
Randomness
Acceleration Controls how quickly a particle reaches the full speed of the wind.
Angle Sets the source direction of the wind. A value of 0 degrees is three
Bumpiness Adds a shadow to the edge of the particles.
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
Allows particles anywhere within the effect to move at different
speeds, giving a more natural effect.
The higher the value, the more quickly the particle reaches full
speed.
o’clock; positive values move counterclockwise.
video.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
72
Page 73

2D Effects Parameters
Pinch Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Pinch effect create an effect that pinches the image in
toward or pushes it out from a user-defined point. For more information, see “Pinch”
on page 169.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the progression of the effect. The larger the difference in the
Amount value between keyframes, the faster the effect happens.
Size Sets the diameter of the affected area.
X, Y Sets the center of the effect.
Anti-alias Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
73
Page 74

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Radial Blur Input Parameters
Render Mode
Fast m enu
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Radial Blur effect create an effect that blurs the image
inward or outward from a user-defined point. For more information, see “Radial Blur”
on page 170.
Use of Controls
Zoom Sets the scaling of the blur. Smaller values zoom in and larger
values zoom out.
Angle Sets the rotation of the blur.
This effect can take a long time to render. The greater the
n
angle, the more time the rendering takes.
X, Y Sets the center of the effect.
Render Mode
Fast menu
• Locate
• Render Low
Quality
• Render
Medium
Quality
• Render High
Quality
Sets whether only the center marker shows, or how the effect is
rendered.
Select Locate to show the center marker. Use it while setting up the
center.
74
Page 75

2D Effects Parameters
Random Blend Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Random Blend effect control a random pattern to blend
incoming and outgoing video. For more information, see “Random Blend” on
page 171.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the amount of blend.
Random Scale Sets the amount of randomness. This allows the system to blend
different portions of the image at different rates.
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
video.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
75
Page 76

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Rollup Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Rollup effect control a transition effect that rolls up the
foreground video to reveal the background video. For more information, see “Rollup”
on page 173.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the proportion of each clip to be displayed. A value of 0
displays all of the foreground clip; 100 displays all of the
background clip. Typical keyframing is from 0 at the first keyframe
to 100 at the last keyframe.
Curl Size Sets the size of the roll.
Direction Sets the direction of the roll. A value of 0 degrees is three o’clock;
positive values move counterclockwise.
Anti-alias Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
video.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
76
Page 77

Shear Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
2D Effects Parameters
Description The Input parameters for the Shear effect control a transition effect that divides the
foreground video into strips and slides them away in opposite directions to reveal the
background video. For more information, see “Shear” on page 174.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the proportion of each clip to be displayed. A value of 0
displays all of the foreground clip; 100 displays all of the
background clip. Typical keyframing is from 0 at the first keyframe
to 100 at the last keyframe.
Min Width, Max
Sets the minimum and maximum possible width of the slats.
Width
Width
Randomness
Controls the variety of sizes of slats. The system creates slats of
various widths in between the minimum and maximum width
value.
Spread Sets the randomness of when individual strips start moving. A
value of 0 causes all strips to start at the same time.
Angle Sets the direction of the effect. A value of 0 degrees is three
o’clock; positive values move counterclockwise.
77
Page 78

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Random Seed Sets the base number upon which all random values are calculated.
Anti-alias Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
Swap Sources Specifies whether to apply the effect to incoming or outgoing
Sphere Input Parameters
Each value results in a different random effect.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
video.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Sphere effect control a spherical distortion in the image.
For more information, see “Sphere” on page 176.
Use of Controls
78
Amount Sets the scale of the distortion. Negative values distort the image
inward; positive values distort it outward.
Size Sets the diameter of the circle as a normalized proportion of the
vertical size of the image.
X, Y Sets the center of the effect.
Anti-alias Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Page 79

2D Effects Parameters
Swirl Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Swirl effect control a distortion in the image where
pixels swirl within a circular area. For more information, see “Swirl” on page 177.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the scale of swirl. Negative values swirl the image
counterclockwise; positive values swirl it clockwise.
Size Sets the diameter of the circle as a normalized proportion of the
vertical size of the image.
X, Y Sets the center of the effect.
Anti-alias Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
79
Page 80

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Timecode Input Parameters
Timecode Color Fast menu
Timecode Font and Size Fast menu
Timecode Type Fast menu
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Timecode effect control burn-in timecode. For more
information, see “Timecode” on page 178.
Use of Controls
Timecode Color
Fast menu
• White no background
• Black no background
• White on Black
• Black on White
Timecode Font
and Size Fast
menu
X, Y Sets the position of the lower left corner of the effect.
Select a color and background for the timecode text.
Select a font and size for the timecode text.
You can also drag the marker in the Effect Preview monitor.
n
80
Page 81

2D Effects Parameters
Timecode Type
Fast menu
Selects the timecode type:
• Non-drop — Uses a colon (:) as a separator
• Drop frame — Uses a semicolon (;) as a separator (applies only
to NTSC projects)
• Feet and Frames — Uses either a plus sign (+) or an ampersand
(&) symbol as a separator.
The separator changes from + to & between the values 24 and 25.
The + sign is used for 16mm projects and the & symbol is used for
35mm projects.
Frames per Foot Use the slider to specify the number of frames per foot. This option
applies when you select Feet and Frames from the Timecode Type
Fast menu.
81
Page 82

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Twist Input Parameters
Axis Fast menu
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Input parameters for the Twist effect create an effect that distorts the image by
twisting the two ends in opposite directions. For more information, see “Twist” on
page 179.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the amount of twist.
X, Y Sets the center of the effect.
Axis Fast menu
•X axis
•Y axis
Anti-alias Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
Sets whether the twist applies horizontally (X axis) or vertically
(Y axis).
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
82
Page 83

Wave Input Parameters
Parameter Type Keyframeable
2D Effects Parameters
Description The Input parameters for the Wave effect create an effect that distorts the image by
applying waves to it. For more information, see “Wave” on page 180.
Use of Controls
Amount Sets the scale of swirl. Negative values swirl the image
counterclockwise; positive values swirl it clockwise.
Minimum Size,
Sets the minimum wavelength and the maximum wavelength.
Maximum Size
Horizontal
Factor, Vertical
The amount of horizontal distortion and vertical distortion, where 0
is no distortion and 100 is maximum distortion.
Factor
Number of
Wav es
Sets the number of waves. Wave effects are superimposed upon
each other.
Speed Sets the progress of the effect.
83
Page 84

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Random Seed Sets the base number upon which all random values are calculated.
Anti-alias Sets whether or not transformed areas are smoothed.
Motion
Each value results in a different random effect.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Motion parameter category is available only for the Ripple effect. Use it to
control the ripples in the effect. For more information, see “Ripple” on page 172.
Use of Controls
84
Amount Sets the progression of the effect. The larger the difference in the
time value between keyframes, the faster the effect will happen.
Wave Speed Sets how fast the waves move.
Ripple Spread Sets the width of the ripple from the inner ring to the outer ring.
Reflections When selected, waves reflect off the edges of the image, as though
hitting a wall.
Page 85

2D Effects Parameters
Movement
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Movement parameter category is available only for the Sparkler effect. Use it to
control the movement of the sparkler in the effect. For more information, see
“Sparkler” on page 175.
Use of Controls
Speed Sets the value around which the speed of the sparks is randomized.
Gravity Sets the attraction of the sparks downward or upward. The greater
the value, the more the sparks are attracted downward.
Air Resistance Sets the air resistance. The higher the value, the less the sparks
radiate outward.
Wind X, Wind Y Sets a virtual directional wind, which affects the trajectory of the
sparks.
Air Resistance must be greater than 0 for Wind to have an
n
effect.
Turbulence Adds randomness to the movement of the sparks.
85
Page 86

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Number
Text color
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Number parameter category is available only for the Pattern Generator effect. For
more information, see “Pattern Generator” on page 168.
Use of Controls
86
Number Offset Sets the offset of the number from the current frame number.
Opacity Sets the opacity of the number.
Text Size Sets the size of the number.
Stroke Width Sets the width of the number stroke.
R, G, B
(Text color)
Sets the color of the number. Select the color by doing one of the
following:
t Directly manipulate the RGB sliders.
t Use the Windows Color dialog box or the Macintosh Color
Picker.
t Use the eyedropper.
Page 87

2D Effects Parameters
Offset
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Offset parameter category is available only for the Kaleidoscope effect. For more
information, see “Kaleidoscope” on page 159.
Use of Controls
X, Y Use the X and Y sliders to set the offset from the original source
area.
You can also click the corresponding marker, and drag within
n
the image.
Anti-alias
Sets whether or not transformed areas will be smoothed.
This parameter is not keyframeable.
n
87
Page 88

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Source
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Source parameter category is available only for the FluidMorph effect. Select the
morphing method from the Source Fast menu. For more information, see
“FluidMorph” on page 157.
Use of Controls Source Fast menu Select the morphing method from the Source Fast menu:
• Still Image — The system takes snapshots of the first frame of outgoing video and
the last frame of incoming video and creates an output that is a morph of the two
images.
• Video Stream — The system creates the output by morphing the two clips, frame
by frame.
88
Page 89

2D Effects Parameters
Start Timecode
Parameter Type Keyframeable
Description The Start Timecode parameter category is available only for the Timecode effect. For
more information, see “Timecode” on page 178.
Use of Controls
Starting timecode
day
Starting timecode
hour
Starting timecode
minute
Starting timecode
second
Starting timecode
frame
Starting timecode
feet
Sets the day for the starting timecode.
When Starting timecode day is 0, the value does not appear. You
can use a non-zero Starting timecode day to identify items such as
spool, reel, and so forth.
Sets the hour for the starting timecode.
Sets the minute for the starting timecode.
Sets the second for the starting timecode.
Sets the frame for the starting timecode.
When you select Feet and Frames as the Timecode Type, you can
specify the starting feet. See “Timecode Input Parameters” on
page 80.
89
Page 90

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Key Parameters
Key parameters appear only in the Chroma Key, Luma Key, and RGB
Keyer effects. These parameters control the key color and allow you to
fine-tune the edges of key effects and the appearance of the foreground
elements.
For information on the workflow for applying key effects, see “Creating
Key Effects” in the effects guide or the Help.
Key
Chroma Key and Luma Key Effects
Parameter Type Global
Description Selects the primary key color to be replaced by video. Available in both Chroma Key
and Luma Key.
Use of Controls Other Options
button
Hue Identifies the key color. The Hue parameter is measured as
Sat (saturation) Specifies the amount or intensity of the color. Values range from
Lum (luminance) Specifies the brightness of the color. Values range from 0 to
90
Opens the Windows Color dialog box or Macintosh Color
Picker for precise color selection. For more information, see
“Using the Windows Color Dialog Box” and “Using the
Macintosh Color Picker” in the effects guide or the Help.
values on a color wheel ranging from 0 to 255. The start (0) and
ending (255) values are both red.
0 to 255, where 0 is no chrominance and 255 is a fully saturated
color.
255, where 0 is black and 255 is full brightness or white.
Page 91

Secondary Key
2D Effects Parameters
Gain Specifies how much of the foreground and the background
video is displayed. Values range from 0 to 63. A Gain of 0
shows only the foreground. A Gain of 63 replaces all the
foreground video with the background video.
Soft (softness) Determines how the bordering colors along the edge of the key
are processed in the effect. Colors that border the luminance or
chroma specified for the key are displayed as a blend of the
foreground and the background video. Values range from 0 to
63. The higher the Softness value, the more of the background
video is blended in the border colors. Use the Soft slider to
improve the appearance of the edges of the keyed areas.
Chroma Key Effect Only
Parameter Type Global
Description Selects a secondary background color to key out. For example, the floor in a blue
screen or green screen shot might be a slightly different shade from the background.
You can select the floor color as your secondary color and key it out. Available for the
Chroma Key effect only.
Use of Controls See “Key” on page 90.
91
Page 92

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Spill Suppression
Chroma Key Effect Only
Parameter Type Global
Description Neutralizes the selected color for the Chroma Key effect without affecting the
luminance. The effect changes the spill color to a grayscale, allowing it to blend more
easily with the foreground image.
Use the Spill Suppression key color to fix the following problems:
• Remove background color spill from the foreground image. Color spill occurs
when the background color is present in the foreground image due to backdrop
reflection.
• If the foreground object retains an outline of the chroma key color, you can use
Spill Suppression to reduce the color effect in the outline.
Use of Controls See “Key” on page 90.
92
Page 93

2D Effects Parameters
Key Color
RGB Keyer Only
Parameter Type Global
Description Use the Key Color parameters in the RGB Keyer effect to select a color for the
chroma key.
Use of Controls H (hue)
S (saturation)
V (value)
See “RGB Keyer (AVX Plug-in Effect)” on page 195.
Specifies the hue or tint measured as values on a color wheel
ranging from 0 to 255. The start (0) and ending (255) values are
both red.
Specifies the amount or intensity of the color. Values range from
0 to 255, where 0 is no chrominance and 255 is a fully saturated
color.
Specifies the value of the color.
93
Page 94

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Chroma Key
RGB Keyer Only
Parameter Type Global
Description Use the Chroma Key parameters in the RGB Keyer effect to fine-tune the key effect.
Use of Controls Gain
Soft (softness)
Show Alpha
Spill
Level
Reverse
See “RGB Keyer (AVX Plug-in Effect)” on page 195.
Softens the edge of the key, with a range from 0 to 100.
Specifies the amount or intensity of the color. Values range from
0 to 255, where 0 is no chrominance and 255 is a fully saturated
color.
Displays the grayscale alpha channel used to apply the key
effect to the foreground and background sources. Viewing the
alpha channel directly allows you to examine problem areas of
the key while making adjustments.
Suppresses the spill from the key color onto foreground objects
that often occurs due to color reflection in the scene. The range
is from 0 to 100.
Controls transparency of the foreground elements against the
key background.
Inverts the key.
94
Page 95

2D Effects Parameters
Matte Control
RGB Keyer Only
Parameter Type Global
Description Use Matte Control in the RGB Keyer effect to fine-tune the edges of the matte used in
the chroma key.
Use of Controls Blur
Erode
See “RGB Keyer (AVX Plug-in Effect)” on page 195.
Uses a box filter to blur the matte for the key. The range is 0 to
100; 0 indicates a blurring of 0 pixels, and 100 indicates a
blurring of 10 pixels.
Used with blur, decreases or “erodes” the outer edges of the
blurred matte key.
95
Page 96

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Color Correction
RGB Keyer Only
Parameter Type Global
Description Use the Color Correction parameters in the RGB Keyer effect for post-key color
correction of the foreground elements in the Chroma Key effect. Because the
foreground and background elements are often shot at different times and locations,
post-key color correction is especially useful for maintaining the key while matching
the visual characteristics of the foreground to the background.
Use of Controls Sat (saturation)
Bright (brightness) Specifies the brightness level. Values range from 0 to 255,
Cont (contrast) Controls the contrast of light and dark areas in the picture.
See “RGB Keyer (AVX Plug-in Effect)” on page 195.
Specifies the amount or intensity of the color. Values range from
0 to 255, where 0 is no chrominance and 255 is a fully saturated
color.
where 0 is black and 255 is full brightness or white.
Values range from –100 to +100, where a value of 0 indicates
the image is unchanged. A negative value is less contrast; a
positive value is more contrast.
96
Page 97

2D Effects Parameters
Matrix Parameters
Parameter Type Global
Description Allows you to customize the grid used to define the position or progress of the
Matrix effect over time. For example, the grid defines the number of squares used
for the Grid and Speckle effects, or the number of horizontal bars used for the
One-Way Row effect. Available for Matrix Wipe effects, Sawtooth Wipe effects,
and some Shape Wipe effects.
Use of Controls Other Options
button
Click to open the Matrix Effect dialog box.
Columns Rows
Graphical representation
of the grid
Select a standard grid size or enter a custom number of rows
and columns, and then click OK. The minimum number of
rows and columns is 2 x 2. A graphical representation of the
grid you select appears on the right side of the dialog box.
97
Page 98

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Traditional Motion Effect Parameters
Traditional motion effect parameters apply to Freeze Frame, Variable
Speed, and Strobe Motion effects. For information about applying and
editing various motion effects, see “Creating Traditional Motion Effects”
in the effects guide or the Help. See also “Timewarp” on page 257.
Freeze Frame Parameters
Duration
98
Custom duration
Page 99

2D Effects Parameters
Parameter Type Global
Description Allows you to create and customize a freeze frame clip based on the image
currently displayed in the Source pop-up monitor.
Use of Menu
Commands
Freeze frame parameters are menu commands in the Clip menu. To create a freeze
frame and access freeze frame parameters, select Clip > Freeze Frame, and then
select the appropriate submenu commands.
• Duration commands
(in seconds or
minutes)
Specifies the length of the freeze frame clip that the Avid editing application
creates in the Source pop-up monitor. You can either select a duration from the
Freeze Frame submenu or select Other to enter a custom duration.
• Other Opens a dialog box that allows you to specify a custom duration for the freeze
frame clip.
• Two Field Freeze
Frames
• Using Duplicated
Field
Opens a submenu with commands that allow you to determine how the system
creates and displays the effect media when working with two fields.
The system uses a single field to create the effect. This option reduces the vertical
resolution of the image by one-half, resulting in a lower quality image.
• Using Both Fields The system uses both fields to create the effect. This option is especially useful
when there is motion in the footage.
• Using Interpolated
Field
The system creates a second field for the effect by combining scan line pairs from
the first field in the original media. This might result in a slightly softer look to the
freeze frame.
99
Page 100

Chapter 1 2D Effects Reference
Variable Speed and Strobe Motion Parameters
Variable Speed
effect
Strobe Motion
effect
Parameter type Global
Description Allows you to create and customize variable speed or strobe motion clips based on
all or part of the clip currently displayed in the Source pop-up monitor.
Use of controls Variable Speed and Strobe Motion parameters are available in the Motion Effect
dialog box. To open the Motion Effect dialog box, click the Motion Effect button
in the Source pop-up monitor.
Variable Speed
• Duration The duration of the effect in frames. Doubling the number of frames causes the
frame rate to be half the current rate.
• Rate The rate of speed in frames per second (fps) at which the video will be played.
Normal speed is 30 fps for NTSC, 25 fps for PAL.
100
 Loading...
Loading...