Page 1

Avid® Network and
Switch Guide
Page 2

Legal Notices
Product specifications are subject to change without notice and do not represent a commitment on the part of Avid Technology, Inc.
This product is subject to the terms and conditions of a software license agreement provided with the software. The product may
only be used in accordance with the license agreement.
This product may be protected by one or more U.S. and non-U.S patents. Details are available at www.avid.com/patents
Part of the software embedded in this product is gSOAP software.
Portions created by gSOAP are Copyright (C) 2001-2004 Robert A. van Engelen, Genivia inc. All Rights Reserved.
THE SOFTWARE IN THIS PRODUCT WAS IN PART PROVIDED BY GENIVIA INC AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN
IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
The following disclaimer is required by Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics, Inc. for the use of their TIFF library:
Copyright © 1988–1997 Sam Leffler
Copyright © 1991–1997 Silicon Graphics, Inc.
Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and sell this software [i.e., the TIFF library] and its documentation for any purpose is
hereby granted without fee, provided that (i) the above copyright notices and this permission notice appear in all copies of the
software and related documentation, and (ii) the names of Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics may not be used in any advertising or
publicity relating to the software without the specific, prior written permission of Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS-IS” AND WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR OTHERWISE,
INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL SAM LEFFLER OR SILICON GRAPHICS BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE, DATA OR
PROFITS, WHETHER OR NOT ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF DAMAGE, AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, ARISING
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
The following disclaimer is required by the Independent JPEG Group:
This software is based in part on the work of the Independent JPEG Group.
This Software may contain components licensed under the following conditions:
Copyright (c) 1989 The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms are permitted provided that the above copyright notice and this paragraph are
duplicated in all such forms and that any documentation, advertising materials, and other materials related to such distribution and
use acknowledge that the software was developed by the University of California, Berkeley. The name of the University may not be
used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission. THIS SOFTWARE IS
PROVIDED ``AS IS'' AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Copyright (C) 1989, 1991 by Jef Poskanzer.
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby
granted, provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission notice
appear in supporting documentation. This software is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
Copyright 1995, Trinity College Computing Center. Written by David Chappell.
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby
granted, provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission notice
appear in supporting documentation. This software is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
Copyright 1996 Daniel Dardailler.
.
2
Page 3

Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and sell this software for any purpose is hereby granted without fee, provided that the
above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear in supporting
documentation, and that the name of Daniel Dardailler not be used in advertising or publicity pertaining to distribution of the software
without specific, written prior permission. Daniel Dardailler makes no representations about the suitability of this software for any
purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
Modifications Copyright 1999 Matt Koss, under the same license as above.
Copyright (c) 1991 by AT&T.
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software for any purpose without fee is hereby granted, provided that this entire
notice is included in all copies of any software which is or includes a copy or modification of this software and in all copies of the
supporting documentation for such software.
THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY. IN PARTICULAR,
NEITHER THE AUTHOR NOR AT&T MAKES ANY REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY OF ANY KIND CONCERNING THE
MERCHANTABILITY OF THIS SOFTWARE OR ITS FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
This product includes software developed by the University of California, Berkeley and its contributors.
The following disclaimer is required by Paradigm Matrix:
Portions of this software licensed from Paradigm Matrix.
The following disclaimer is required by Ray Sauers Associates, Inc.:
“Install-It” is licensed from Ray Sauers Associates, Inc. End-User is prohibited from taking any action to derive a source code
equivalent of “Install-It,” including by reverse assembly or reverse compilation, Ray Sauers Associates, Inc. shall in no event be liable
for any damages resulting from reseller’s failure to perform reseller’s obligation; or any damages arising from use or operation of
reseller’s products or the software; or any other damages, including but not limited to, incidental, direct, indirect, special or
consequential Damages including lost profits, or damages resulting from loss of use or inability to use reseller’s products or the
software for any reason including copyright or patent infringement, or lost data, even if Ray Sauers Associates has been advised,
knew or should have known of the possibility of such damages.
The following disclaimer is required by Videomedia, Inc.:
“Videomedia, Inc. makes no warranties whatsoever, either express or implied, regarding this product, including warranties with
respect to its merchantability or its fitness for any particular purpose.”
“This software contains V-LAN ver. 3.0 Command Protocols which communicate with V-LAN ver. 3.0 products developed by
Videomedia, Inc. and V-LAN ver. 3.0 compatible products developed by third parties under license from Videomedia, Inc. Use of this
software will allow “frame accurate” editing control of applicable videotape recorder decks, videodisc recorders/players and the like.”
The following disclaimer is required by Altura Software, Inc. for the use of its Mac2Win software and Sample Source
Code:
©1993–1998 Altura Software, Inc.
The following disclaimer is required by Interplay Entertainment Corp.:
The “Interplay” name is used with the permission of Interplay Entertainment Corp., which bears no responsibility for Avid products.
This product includes portions of the Alloy Look & Feel software from Incors GmbH.
This product includes software developed by the Apache Software Foundation (http://www.apache.org/
© DevelopMentor
).
This product may include the JCifs library, for which the following notice applies:
JCifs © Copyright 2004, The JCIFS Project, is licensed under LGPL (http://jcifs.samba.org/). See the LGPL.txt file in the Third Party
Software directory on the installation CD.
Avid Interplay contains components licensed from LavanTech. These components may only be used as part of and in connection
with Avid Interplay.
Attn. Government User(s). Restricted Rights Legend
U.S. GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. This Software and its documentation are “commercial computer software” or
“commercial computer software documentation.” In the event that such Software or documentation is acquired by or on behalf of a
unit or agency of the U.S. Government, all rights with respect to this Software and documentation are subject to the terms of the
License Agreement, pursuant to FAR §12.212(a) and/or DFARS §227.7202-1(a), as applicable.
3
Page 4

Trademarks
003, 192 Digital I/O, 192 I/O, 96 I/O, 96i I/O, Adrenaline, AirSpeed, ALEX, Alienbrain, AME, AniMatte, Archive, Archive II, Assistant
Station, AudioPages, AudioStation, AutoLoop, AutoSync, Avid, Avid Active, Avid Advanced Response, Avid DNA, Avid DNxcel, Avid
DNxHD, Avid DS Assist Station, Avid Ignite, Avid Liquid, Avid Media Engine, Avid Media Processor, Avid MEDIArray, Avid Mojo, Avid
Remote Response, Avid Unity, Avid Unity ISIS, Avid VideoRAID, AvidRAID, AvidShare, AVIDstripe, AVX, Beat Detective, Beauty
Without The Bandwidth, Beyond Reality, BF Essentials, Bomb Factory, Bruno, C|24, CaptureManager, ChromaCurve,
ChromaWheel, Cineractive Engine, Cineractive Player, Cineractive Viewer, Color Conductor, Command|24, Command|8,
Control|24, Cosmonaut Voice, CountDown, d2, d3, DAE, D-Command, D-Control, Deko, DekoCast, D-Fi, D-fx, Digi 002, Digi 003,
DigiBase, Digidesign, Digidesign Audio Engine, Digidesign Development Partners, Digidesign Intelligent Noise Reduction,
Digidesign TDM Bus, DigiLink, DigiMeter, DigiPanner, DigiProNet, DigiRack, DigiSerial, DigiSnake, DigiSystem, Digital
Choreography, Digital Nonlinear Accelerator, DigiTest, DigiTranslator, DigiWear, DINR, DNxchange, Do More, DPP-1, D-Show, DSP
Manager, DS-StorageCalc, DV Toolkit, DVD Complete, D-Verb, Eleven, EM, Euphonix, EUCON, EveryPhase, Expander,
ExpertRender, Fader Pack, Fairchild, FastBreak, Fast Track, Film Cutter, FilmScribe, Flexevent, FluidMotion, Frame Chase, FXDeko,
HD Core, HD Process, HDpack, Home-to-Hollywood, HYBRID, HyperSPACE, HyperSPACE HDCAM, iKnowledge, Image
Independence, Impact, Improv, iNEWS, iNEWS Assign, iNEWS ControlAir, InGame, Instantwrite, Instinct, Intelligent Content
Management, Intelligent Digital Actor Technology, IntelliRender, Intelli-Sat, Intelli-sat Broadcasting Recording Manager, InterFX,
Interplay, inTONE, Intraframe, iS Expander, iS9, iS18, iS23, iS36, ISIS, IsoSync, LaunchPad, LeaderPlus, LFX, Lightning, Link &
Sync, ListSync, LKT-200, Lo-Fi, MachineControl, Magic Mask, Make Anything Hollywood, make manage move | media, Marquee,
MassivePack, Massive Pack Pro, Maxim, Mbox, Media Composer, MediaFlow, MediaLog, MediaMix, Media Reader, Media
Recorder, MEDIArray, MediaServer, MediaShare, MetaFuze, MetaSync, MIDI I/O, Mix Rack, Moviestar, MultiShell, NaturalMatch,
NewsCutter, NewsView, NewsVision, Nitris, NL3D, NLP, NSDOS, NSWIN, OMF, OMF Interchange, OMM, OnDVD, Open Media
Framework, Open Media Management, Painterly Effects, Palladium, Personal Q, PET, Podcast Factory, PowerSwap, PRE,
ProControl, ProEncode, Profiler, Pro Tools, Pro Tools|HD, Pro Tools LE, Pro Tools M-Powered, Pro Transfer, QuickPunch,
QuietDrive, Realtime Motion Synthesis, Recti-Fi, Reel Tape Delay, Reel Tape Flanger, Reel Tape Saturation, Reprise, Res Rocket
Surfer, Reso, RetroLoop, Reverb One, ReVibe, Revolution, rS9, rS18, RTAS, Salesview, Sci-Fi, Scorch, ScriptSync,
SecureProductionEnvironment, Serv|GT, Serv|LT, Shape-to-Shape, ShuttleCase, Sibelius, SimulPlay, SimulRecord, Slightly Rude
Compressor, Smack!, Soft SampleCell, Soft-Clip Limiter, SoundReplacer, SPACE, SPACEShift, SpectraGraph, SpectraMatte,
SteadyGlide, Streamfactory, Streamgenie, StreamRAID, SubCap, Sundance, Sundance Digital, SurroundScope, Symphony, SYNC
HD, SYNC I/O, Synchronic, SynchroScope, Syntax, TDM FlexCable, TechFlix, Tel-Ray, Thunder, TimeLiner, Titansync, Titan, TL
Aggro, TL AutoPan, TL Drum Rehab, TL Everyphase, TL Fauxlder, TL In Tune, TL MasterMeter, TL Metro, TL Space, TL Utilities,
tools for storytellers, Transit, TransJammer, Trillium Lane Labs, TruTouch, UnityRAID, Vari-Fi, Video the Web Way, VideoRAID,
VideoSPACE, VTEM, Work-N-Play, Xdeck, X-Form, Xmon and XPAND! are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Avid
Technology, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
Apple, Macintosh, and Safari are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and
other countries. HP is a registered trademark of Hewlett-Packard Company. Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
Kingston is a registered trademarks of Kingston Technology Corporation. Small Tree is a registered trademark of Small Tree
Communications, LLC used in the site are trademarks or registered trademarks of Small Tree Communications, LLC. All other marks
may be the property of their respective titleholders. Windows is either a registered trademark or trademark of Microsoft Corporation
in the United States and/or other countries. All other trademarks contained herein are the property of their respective owners.
Avid Network and Switch Guide • 0175-31139-00 Rev. C • May 2014• Created 5/8/14
4
Page 5

Contents
Using This Guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Symbols and Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
If You Need Help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Accessing the Online Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Avid Training Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Chapter 1 Avid Network Planning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Default Switch Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Redundant Switch Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Switch Vendor Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Sample Switch Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
ISIS | 7500 External Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Switch Redundancy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
ISIS | 7500 Network Zone Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
ISIS | 7500 Zone 1 Client Configuration (Direct Connect) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
ISIS | 7500 Zone 2 Client Configuration (Indirect Connect) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
ISIS | 7500 Zone 1 and Zone 2 Client Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
ISIS | 7500 Zone 3 and Zone 4 Client Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Client Connection Speed to ISIS | 7500. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
ISIS | 7500 Link Aggregation Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
ISIS | 5500 Network Zone Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
ISIS | 5500 Switch Consideration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
ISIS | 5500 Zone 1 Client Configuration (Direct Connect) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
ISIS | 5500 Zone 2 Configuration (System Director and Switch 1 Gb Connections) 29
ISIS | 5500 Zone 2 Configuration (System Director and Switch 10 Gb Connections) 29
ISIS | 5500 Zone 3 and Zone 4 Client Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
ISIS | 2500 Network Zone Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
1
Page 6

ISIS | 2500 Zone 1 Client Configuration (Direct Connect) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
ISIS | 2500 Zone 2 Client Configuration (Indirect Connect) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
ISIS | 2500 Zone 3 and Zone 4 Client Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Network Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Time Synchronization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
TFTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Network and Switch Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Ping and Tracert Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Tracert . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Sluggish Switch Performance On the Dell Networking S25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Replacing the Network Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Chapter 2 Avid Network Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Avid ISIS IP Port Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Avid Interplay Port Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Avid Interplay Central Port Usage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Media Composer | Cloud Port Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Chapter 3 Dell Networking Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Dell Networking Switch Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Dell Networking S25 Switch Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10 Gb Ethernet S25 Switch Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Stacking the Dell Networking S25 Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Dell Networking S60 Switch Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
10 Gb Ethernet S60 Switch Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Stacking the Dell Networking S60 Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Dell Networking S4810 Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Accessing the Dell Networking Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Configuring the Dell Networking Switch Through a Network Connection . . . . . . . . 64
Configuring the Dell Networking Switch Through the Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Restoring From Flash Memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Sample Switch Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Restoring From the Avid Software Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
2
Page 7

Turning on Flow Control in the Dell Networking S25 Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Customize the Uplink on the Dell Networking Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Network Setup Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configure Dell Networking Switch for Uplink On the Dell Networking S25 . . . . . . . 74
Changing the IP Address Associated with the VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Changing the IP Address Associated with the Corporate Uplink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Changing Buffer Pool to a Single Queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Removing/Adding Ports Associated with a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Creating a Link Aggregation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Setting Up IP-Helper Addresses for DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Upgrading FTOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Upgrading U-Boot. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Cascading Dell Networking Switches in an ISIS Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Chapter 4 Cisco Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Accessing the Cisco Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Configuring the Cisco Switch Through the Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Cisco Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Loading the Avid Cisco Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Restoring From the Avid Software Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Changing the IP Address Associated with the VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Network Setup Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Uplinking Your Cisco Switch to the Corporate Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Sample Cisco Switch Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Configuring the Cisco Switch Through a Network Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Adding Ports Associated to a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Setting Up IP-Helper Addresses for DHCP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Enabling or Disabling IP Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Creating an EtherChannel (Link Aggregation) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Upgrading the IOS on Cisco Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Chapter 5 Brocade Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Foundry/Brocade FESX624 and FESX424 2XG. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Configuring the Foundry/Brocade Switch Through the Serial Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Loading a Switch Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
3
Page 8

Changing the IP Address Associated with the VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Changing the IP Address Associated with the Corporate Uplink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Changing Buffer Pool on Uplink Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Configuring Buffer Pool to Support Editing Clients. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Removing/Adding Ports Associated to a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Enabling or Disabling IP Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Creating Trunked Ports (Link Aggregation) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Setting Up IP-Helper Addresses for DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Upgrading Firmware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Chapter 6 Sample Switch Topologies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Configuration A (ISIS | 7500) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Configuration B (ISIS | 7500) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Configuration C (ISIS | 7500) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Configuration D (ISIS | 7500) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Configuration E (ISIS | 7500) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Chapter 7 Switch Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Supported Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Dimensions and Weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Electrical Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Environmental Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
4
Page 9
Using This Guide
This document describes switch setup information for the Avid® ISIS® shared storage networks.
Your network might not contain certain topologies that are covered in the documentation. The
Avid network and switches are tuned for high-speed and high-capacity shared storage primarily
for Avid editing workstations and servers that manage media.
Symbols and Conventions
Avid documentation uses the following symbols and conventions:
Symbol or Convention Meaning or Action
n
c
w
> This symbol indicates menu commands (and subcommands) in the order you
(Windows) or (Macintosh) This text indicates that the information applies only to the specified
Bold font Bold font is primarily used in task instructions to identify user interface
Italic font Italic font is used to emphasize certain words and to indicate variables.
Courier Bold font
A note provides important related information, reminders,
recommendations, and strong suggestions.
A caution means that a specific action you take could cause harm to your
computer or cause you to lose data.
A warning describes an action that could cause you physical harm. Follow
the guidelines in this document or on the unit itself when handling electrical
equipment.
select them. For example, File > Import means to open the File menu and
then select the Import command.
This symbol indicates a single-step procedure. Multiple arrows in a list
indicate that you perform one of the actions listed.
operating system, either Windows or Macintosh OS X.
items and keyboard sequences.
Courier Bold font identifies text that you type.
Page 10

Symbol or Convention Meaning or Action
Ctrl+key or mouse action Press and hold the first key while you press the last key or perform the
If You Need Help
If you are having trouble using your Avid product:
1. Retry the action, carefully following the instructions given for that task in this guide. It is
especially important to check each step of your workflow.
2. Check the latest information that might have become available after the documentation was
published.
New information would be found in the ReadMe file supplied on your Avid software
installation kit as a PDF document and is also available online.
You should always check online for the most up-to-date release notes or ReadMe
because the online version is updated whenever new information becomes available. To
view the online versions, visit the Knowledge Base at
3. Check the documentation that came with your Avid application or your hardware for
maintenance or hardware-related issues.
If You Need Help
mouse action. For example, Command+Option+C or Ctrl+drag.
www.avid.com/US/support.
4. Visit the online Knowledge Base at
available 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. Search this online Knowledge Base to find
answers, to view error messages, to access troubleshooting tips, to download updates, and to
read or join online message-board discussions.
www.avid.com/US/support. Online services are
Accessing the Online Documentation
The Avid ISIS online documentation contains all the product documentation in PDF format. You
can access the documentation in the AvidISISDocumentation folder on the Avid ISIS installer
kit. Download and install Acrobat Reader on your Avid ISIS before you can access the PDF
documentation.
To access the online documentation from the installer kit:
1. Insert your Avid ISIS USB flash drive with the Avid ISIS software kit into the USB port.
2. Navigate to the [USB flash drive]:\.AvidISISDocumentation folder, and double-click the
PDF file for the document you want to view.
6
Page 11

Avid Training Services
Avid makes lifelong learning, career advancement, and personal development easy and
convenient. Avid understands that the knowledge you need to differentiate yourself is always
changing, and Avid continually updates course content and offers new training delivery methods
that accommodate your pressured and competitive work environment.
For information on courses/schedules, training centers, certifications, courseware, and books,
please visit
800-949-AVID (800-949-2843).
www.avid.com/support and follow the Training links, or call Avid Sales at
Avid Training Services
7
Page 12

1 Avid Network Planning
The purpose of this document is to provide ISIS Administrators with a single reference regarding
the implementation, configuration and troubleshooting of all Avid
switches for use as the Avid Production Network (APN) switch. The switches covered in this
documented have been qualified or approved by Avid in the configurations presented. However,
in order to reduce the complexity of this document, configurations are limited to the qualified
APN switches offered by Avid. Most of this information can also be applied to the approved
switches not offered by Avid. Avid recommends you refer to the vendor’s documentation for
specifics. Switches listed in this document have been qualified or approved in the ISIS | 7500,
ISIS | 5500, and ISIS | 2500 environments.
This document also applies to ISIS 7000, ISIS 5000, and ISIS 2000 systems, but for simplicity, it
n
refers only to the current model names.
®
ISIS qualified Ethernet
Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
The following switches have been qualified or approved for the specified Avid ISIS
environments.
• Qualified — tested with each major software release.
• Approved — tested once with no subsequent re-testing.
APN Switches Qualified for the ISIS Environment
ISIS | 7500
External
Expansion
Switch ISIS | 7500
Dell S4820T 10Gb Base-T ✓
Cisco Catalyst 4948E ✓✓✓
Cisco Catalyst 4948-10GE ✓✓✓
Cisco Catalyst 4900M ✓✓✓✓
Switches (EXS) ISIS | 5500 ISIS | 2500
Page 13

Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
APN Switches Qualified for the ISIS Environment (Continued)
ISIS | 7500
External
Expansion
Switch ISIS | 7500
Switches (EXS) ISIS | 5500 ISIS | 2500
Dell Networking S25N and
✓✓
S25P
Dell Networking S60 ✓✓✓
Dell Networking S4810 ✓✓✓
Foundry/Brocade FESX424 and
FESX624
✓✓
✓
APN Switches Approved for the ISIS Environment
ISIS | 7500
External
Expansion
Switch ISIS | 7500
Switches (EXS) ISIS | 5500 ISIS | 2500
Arista Networks 7048T-A ✓✓
Cisco Nexus 7000 series ✓✓
a
✓✓
Cisco Catalyst 4500-X ✓✓ ✓✓
Foundry/Brocade SuperX ✓✓✓
Foundry/Brocade FESX448
✓✓
and FESX648
Foundry/Brocade MLXe
b
✓✓✓
a. The Cisco Nexus 7000 Series N7K-F248XP-25E and N7K-M224XP-23L can be used as External Expansion Switches.
b. Specific I/O cards only.
Most Windows editing clients must use the 1 Gb Intel Pro 1000 PT or PF Ethernet board to
connect to all Avid ISIS system. Many on-board Ethernet ports are also suitable; see the Avid
ISIS ReadMe for client platforms with supported on-board Ethernet ports or specific exceptions.
®
Macintosh clients can use the built-in Ethernet port or Small Tree
PEG1F or PEG2F optical
adapters.
9
Page 14

Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
Configuration information on the Ethernet switches that are qualified with Avid ISIS shared
storage network is provided later in this document. For sample configurations provided in the
ISIS software kit, see “Sample Switch Topologies” on page 104
Configuration
Avid has qualified or approved the following layer 2 and layer 3 switches used in a Zone 2 and
Zone 3 configurations.
All Dell Networking switches ship from Avid preconfigured for an Avid ISIS | 5500 environment.
n
You should upgrade your switch to the latest configuration file found in the ISIS software kit. For
information on configuring the switches, see “Dell Networking Switches” on page 55.
When connecting 10 Gb clients in the ISIS | 5500 environment, you must enable flow control RX
n
on the 10 Gb switch port. Flow control for both TX and RX is enabled on the ISIS Clients; see
“Turning on Flow Control in the Dell Networking S25 Switch” on page 71.
• Dell S4820T 10Gb Base-T switch (qualified in the ISIS | 5500) is supported along with the
Intel and Small Tree Network adapters that are required for client connectivity
- Windows/Linux: Intel® Ethernet Converged Network Adapter X540-T1
- Mac: Small Tree petg1-cat6a
folder, and select the folder for your model ISIS and switch.
. Navigate to the
\Switch
• Dell S4820T 10Gb Base-T switch (qualified in the ISIS | 5500) is supported along with the
40Gb to 4 x 10Gb optical cable for connecting the ISIS | 5500 Engines to this switch
- Dell Networking,Transceiver,40GE QSFP+ Short Reach Optics,850nm
Wavelength,100-150m Reach on OM3/OM4 (430-4543)
- Dell Networking,Cable,40GbE MTP (QSFP+) to 4xLC Optical
Connctrs,5M(QSFP+,SFP+ Optics REQ,not incl) (331-5323)
®
•Cisco
• Cisco Catalyst 4948E switch (qualified in the ISIS | 7500 and ISIS | 5500 environments)
• Cisco Catalyst 4948-10GE (qualified in the ISIS | 7500 and ISIS | 5500 environment)
• Cisco Catalyst 4500-X switch (approved in the ISIS | 7500, 5500, and 2500 environments) is
Catalyst 4900M switch (qualified in the ISIS | 7500, 5500, and 2500 environments)
can accommodate one or two modules offering a variety of 1 Gb Ethernet and 10 Gb
Ethernet ports. (Avid supports both long range (LR) and short range (SR) X2s)
contains 48 1 Gb ports and four alternative wired ports that can accommodate optional 1 Gb
Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) or 10 Gb Small Form-Factor Pluggable Plus (SFP+)
optics.
contains 48 1 Gb ports and two X2 based 10 Gb ports (Avid supports both LR and SR X2s)
available in 32- and 16-port versions configured with optional network and uplink modules.
The Small Form-Factor Pluggable Plus (SFP+) interface supports both 10 Gigabit Ethernet
and 1 Gigabit Ethernet ports.
10
Page 15

Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
• Cisco Catalyst 6500-E series switch (approved in the ISIS | 7500, 5500, and 2500
environments) can be configured to meet a wide variety of 1 Gb and 10 Gb high-density
Ethernet ports while providing high levels of network resilience. Depending on the base unit,
there are from 3 to 13 slots with configurations offering SFP, SFP+, and XL support. (Avid
supports both LR and SR X2s) This series is ideally suited for enterprise core and
aggregation environments.
• Cisco Nexus 7000 series (approved in the ISIS | 7500, 5500, and 2500 environments) can be
configured to meet a wide variety of combinations of 1 Gb Ethernet and 10 Gb Ethernet
connections. Depending on the base unit, there are from 4 to 18 slots that allow for
supervisor modules and up to 16 I/O modules offering a variety of ports (including SFP+
with XL option).
®
• Dell Networking
containing 24 1 Gb ports on the front, and two slots on the back for 10 Gb XFP modules or
12 Gb stacking modules. The 12 Gb stacking modules allow for interconnecting two S25N
switches when more than 24 1 Gb or two 10 Gb client connections are in use.
If using either version of the Dell Networking S25 switch for 10 Gb client connections, you must
n
enable flow control on the 10 Gb ports of the switch. For instructions, see “Turning on Flow
Control in the Dell Networking S25 Switch” on page 71. Flow control is disabled in the Avid
default Dell Networking S25 switch configuration.
Networks S25N switch (qualified in the ISIS | 5500 environment)
• Dell Networking Networks S25P switch (qualified in the ISIS | 5500 environment)
containing 24 optical 1 Gb ports on the front, and two slots on the back for 10 Gb XFP
modules or 12 Gb stacking modules. The 12 Gb stacking modules allow for interconnecting
two S25P switches when more than 24 1 Gb or two 10 Gb client connections are in use.
• Dell Networking Networks S60 switch (qualified in the ISIS | 7500 and ISIS | 5500
environments) contains 48 1 Gb ports and two slots for 10 Gb Small Form-Factor Pluggable
Plus (SFP+) modules or 24 Gb stacking modules. (One slot is on the front of the switch and
the other is on the back.) The 24 Gb stacking modules allow for interconnecting two S60
switches when more than 48 1 Gb or two 10 Gb client connections are in use.
The Dell Networking S60 switch is only supported in the ISIS | 7500 environment when clients
n
are using ISIS Client v3.5 or later software.
There are Dell Networking S25 switch configuration files in the ISIS v4.0 software kit but that
n
switch is not supported in the ISIS | 7500 environment.
• Dell Networking Networks S4810 switch (qualified in the ISIS | 7500, 5500, and 2500
environments) containing 48 dual-speed 1/10 Gb (SFP+) ports (as well as four 40 Gb
QSFP+ uplinks not supported in an Avid environment).
11
Page 16

Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
The Avid ISIS | 5500 Setup Guide includes information on the Dell Networking Networks S4810
n
switch. Like all other Dell Networking switches, the S4810 ships from Avid preconfigured for an
Avid ISIS | 5500 environment. If you need to reload the Avid S4810 switch configuration file it is
available in the Avid ISIS software kit.
• Arista Networks 7048T switch (approved in the ISIS | 7500 and ISIS | 5500 environments)
contains 48 1 Gb ports and four SFP+ 10 Gb ports
®
• Brocade
/Foundry Networks® FastIron® Edge X (FESX) 624 and 424 switches (qualified in
the ISIS | 7500 and ISIS | 5500 environments) contain 24 1 Gb ports and two XFP 10 Gb
ports (Avid supports both LR and SR XFPs)
• Brocade/Foundry Networks FastIron SuperX switch (approved in the ISIS | 7500, 5500, and
2500 environments) with the 8 slot configuration is supported with the dual port 10 Gb card
and the 24 port SFP or 10/100/1000 interface cards. The 16 slot version is not supported.
The SX800 has redundant management cards without additional 1Gb Ethernet ports,
whereas the SuperX has a single management card with 12 Gb Ethernet ports.
Avid has qualified the following external switches (EXS) for linking two individual ISIS | 7500
Management Domains using 10 Gb Ethernet connections.
• Cisco Catalyst 4900M switch can be configured to meet a wide variety of combinations of
1 Gb Ethernet and 10 Gb Ethernet connections. The base unit can accommodate one or two
modules offering a variety of ports. (Avid supports both LR and SR X2s)
• Cisco Catalyst 4500-X switch is available in 32- and 16-port versions configured with
optional network and uplink modules. The Small Form-Factor Pluggable Plus (SFP+)
interface supports both 10 Gigabit Ethernet and 1 Gigabit Ethernet ports.
• Dell Networking Networks S4810 switch (qualified in the ISIS | 7500, 5500, and 2500
environments) containing 48 dual-speed 1/10 Gb (SFP+) ports (as well as four 40 Gb
QSFP+ uplinks not supported in an Avid environment).
Minimum Supported Switch Firmware and IOS Versions
Manufacturer Model Firmware/IOS
Cisco Catalyst 4900M Rommon: 12.2(44r)SG (and latera)
IOS: 12.2 (46)SG (and later
Cisco Catalyst 4500-X ROM: 15.0(1R)SG6 (and later
IOS: 03.04.02.SG (and later
a
a
)
a
)
a
)
12
Description and
Approved Blades
40 1 Gb (RJ-45), WS-X4920-GB-RJ45
or
8 10 Gb (X2/SC)WS-X4904-10GE
8 10 Gb (X2/SC)
32 dual-speed 1/10Gb ports (SFP+)
Page 17

Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
Minimum Supported Switch Firmware and IOS Versions (Continued)
Manufacturer Model Firmware/IOS
Cisco Catalyst C4948E Rommon: 12.2(44r)SG8 (and
later
a
)
IOS: 12.2 (54)SG (and later
Cisco Catalyst 4948-10GE Rommon: 12.2(31r)SGA (and
later
a
)
a
a
IOS: 12.2 (25) EWA8 (and later
Description and
Approved Blades
48 1 Gb (RJ-45),
four 10 Gb (SFP+/LC)
)
48 1 Gb (RJ-45),
two 10 Gb (X2/SC)
a
)
Cisco Nexus 6500-E Series Supervisor:
WS-SUP720/WS-F6K-PFC3B
WS-X6704-10GE/ WS-F6700-CFC
WS-X6708-10GE/WS-F6700-DFC3CXL
Due to limited buffering, the following
blades only supports direct connected
clients and do not support uplinks to
additional switches.
Supervisor:
WS-X6748-GE-TX/WS-F6700-CFC/DFC
WS-X6748-SFP/WS-F6700-CFC/DFC
Cisco Nexus 7000 Series BIOS 3.19.0 (and later
Kickstart 4.2(4) (and later
System 4.2(4) (and later
CMP BIOS 02.01.05 (and later
CMP Image 4.2(1) (and later
)
a
)
a
)
48 1 Gb module (copper) N7K-M148GT-11
32 10 Gb module (optical)
N7K-M132XP-12 (only 8 supported
running simultaneously due to 4 to 1
a
)
oversubscription)
a
)
N7K-M108x2
a
48 port 10 Gb/1 Gb module (optical)
N7K-F248XP-25E
24 port 10 Gb module (optical)
N7K-M224XP-23L
48 port 1 Gb copper N25-C2248TP-E-1GE
a
Dell Networking
(ISIS | 5500 and
S25N FTOS 8.3.1.1 (and later
) 24 1 Gb (RJ-45),
two slots for 10 Gb XFP modules (XFP/LC)
ISIS | 2500 only)
Dell Networking S60 FTOS 8.3.3.4 (and later
a
) 48 1 Gb (RJ-45),
two slots for modules, two 10 Gb SFP+
ports per module (SFP+/LC)
13
Page 18
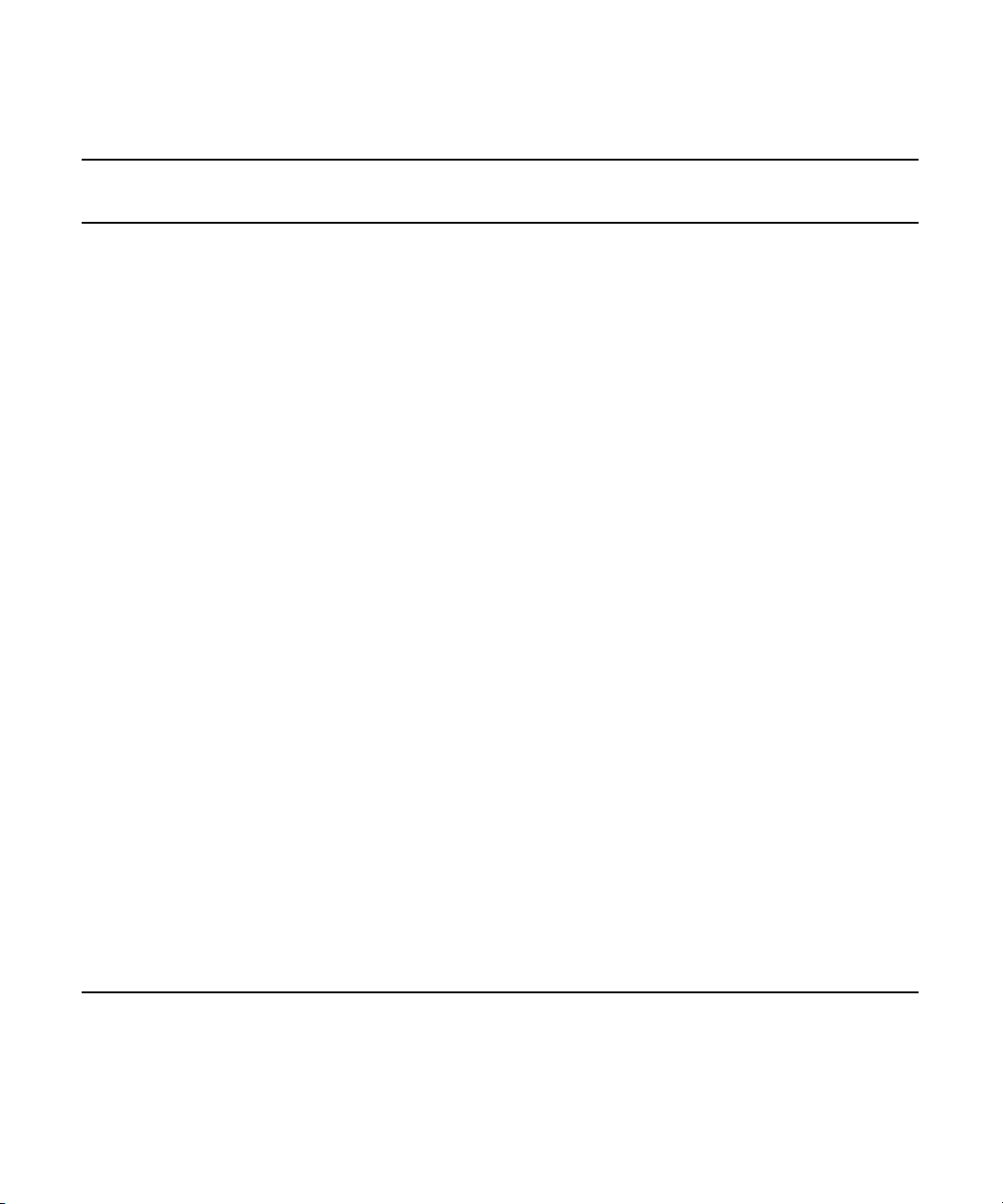
Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
Minimum Supported Switch Firmware and IOS Versions (Continued)
Description and
Approved Blades
Manufacturer Model Firmware/IOS
a
Dell Networking S4810 FTOS 8.3.7.0 (and latera) 48 dual-speed 1/10 Gb (SFP+)
(four 40 Gb QSFP+ uplinks, not supported
in the Avid Environment)
a
Arista Networks 7048T Software image 4.8.6 (and later
) 48 1 Gb (RJ-45),
four 10 Gb (SFP+)
Brocade/Foundry FESX624 Firmware v07.2.02aT3e3 (and
later
a
)
24 1 Gb (RJ-45),
4 1 Gb (SFP),
2 10 Gb (XFP/LC)
Brocade/Foundry SuperX
2
This switch require Queue Depth changes.
fi-sx4-12-combo-port-management-module
fi-sx4-24-port-gig-copper-module
fi-sx4-24-port-gig-fiber-module
fi-sx4-2-port-10g-module
Brocade/Foundry RX RX-BI-MR Management Module
RX-BI-SFM3 Fabric Module
RX-BI-24C
RX-BI24F
RX-BI-4XG
Brocade/Foundry
(Obsolete)
FESX424 Firmware v02.3.01T3e3
Boot ROM v02.3.01Te6 (and
a
)
later
24 1 Gb (RJ-45),
4 1 Gb (SFP),
2 10 Gb (XFP/LC)
Brocade/Foundry MLXe Boot: Version 5.1.0T175
Monitor: Version 5.1.0T175
IronWare: Version 5.1.0bT177
a. Later firmware/IOS version should be acceptable but are not tested by Avid.
14
Chassis: MLXe
NI-MLX-MR Management Module
NI-MLX-10Gx8-D 8-port 10GbE (D)
Module
NI-MLX-1Gx20-GC 20-port 10/100/1000
Copper Module
BR-MLX-1GFx24-X 24-port 1GbE SPF
Module
Page 19

Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
Default Switch Passwords
It should also be noted that the following default passwords exist in order for one to access
enable mode on the switches. The following table lists the passwords for each vendor.
Manufacturer Model Password Comment
Cisco 4900M
4948E;
4948-10GE
Dell Networking S25
S60
S4810
Foundry/Brocade FESX624
FESX424
Not Set by Default To get into enable mode in a Telnet session,
create an enable password on the serial
connection in Global Configure Mode by
using the “Enable Secret” command.
User: avid
Password: avid
Not Set by Default Press Enter to access enable mode.
The S25 switch is only supported with ISIS |
5500 environment.
The S4810 switch is supported only with
ISIS | 7500 in dual Management Domains in
an External Switch configuration.
Redundant Switch Configurations
The following table provides redundant switch configuration examples by ISIS VLAN.
Command VLAN 10 VLAN 20
Cisco HSRP
Switch 1
ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0
standby ip 192.168.10.4
standby priority 95
standby preempt
ip address 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.0
standby ip 192.168.20.4
standby priority 90
Cisco HSRP
Switch 2
Cisco GLBP
Switch 1
ip address 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
standby ip 192.168.10.4
standby priority 90
ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0
glbp 110 ip 192.168.10.4
glbp 110 preempt
15
ip address 192.168.20.3 255.255.255.0
standby ip 192.168.20.4
standby priority 95
standby preempt
ip address 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.0
glbp 120 ip 192.168.20.4
glbp 120 priority 90
Page 20
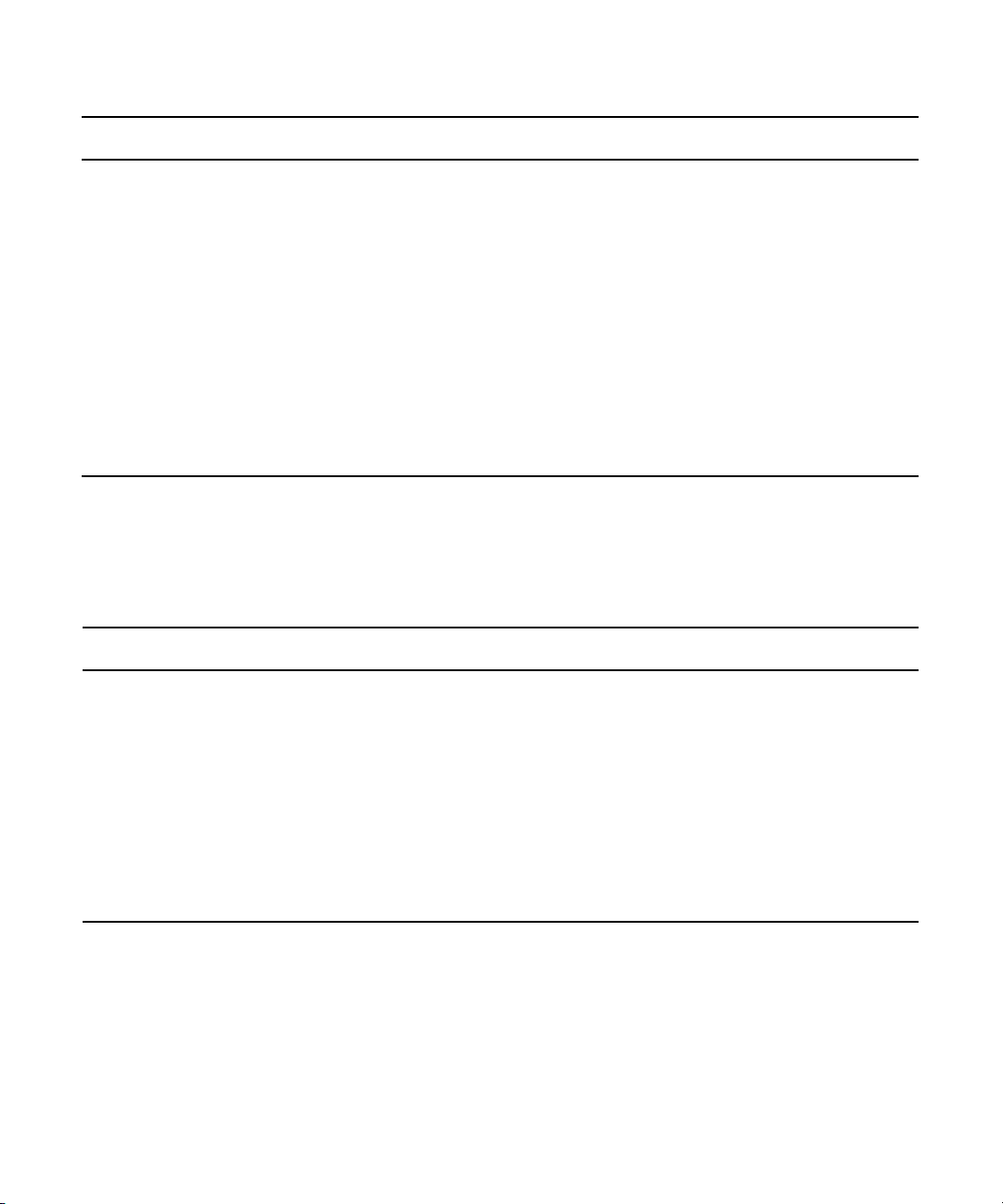
Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
Command VLAN 10 VLAN 20
Cisco GLBP
Switch 2
Foundry/Brocade VRRPE
Switch 1
Foundry/Brocade VRRPE
Switch 2
a. Foundry/Brocade VRRPE must also specify the following Global Configuration: router vrrp-extended.
ip address 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
glbp 110 ip 192.168.10.4
glbp 110 priority 90
a
ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0
ip vrrp-extended vrid 10
backup priority 120
advertise backup ip-address 192.168.10.4
ip address 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
ip vrrp-extended vrid 10
backup priority 110
advertise backup ip-address 192.168.10.4
ip address 192.168.20.3 255.255.255.0
glbp 120 ip 192.168.20.4
glbp 120 preempt
ip address 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.0
ip vrrp-extended vrid 20
backup priority 110
advertise backup ip-address 192.168.20.4
ip address 192.168.20.3 255.255.255.0
ip vrrp-extended vrid 20
backup priority 120
advertise backup ip-address 192.168.20.4
Switch Vendor Commands
The following table provides a few command similarities and differences between vendors.
Command Dell Networking Cisco Foundry/Brocade
Entering Enable
Mode
en en en
Entering Global
Config Mode
Enabling IP Routing ip routing ip routing Automatic if more than one router
Changing IP
addresses
conf t conf t conf t
interface is defined
New IP address
automatically replaces old
New IP address
automatically replaces old
You must remove the old IP
address first using the “no ip
address” command
Sample Switch Configurations
Avid includes switch configuration files outlined in “Sample Switch Topologies” on page 104.
You can load and modify one of the configurations provided in the software kit to create a switch
configuration file compatible with your environment. These configurations can be applied using
16
Page 21

Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
the procedures outlined in this document or by vendor. Some configuration files provided in the
ISIS software kit have a provision for one port to connect to the house network for Zone 4
support.
The following table provides information on the available ports and connections.
Model Rack Units 1 Gb Ports 10 Gb Ports Mgmt. Ports Comments
Cisco Catalyst
4900M
Cisco Catalyst
4948E
Cisco Catalyst
4948-10GE
Dell Networking
S4810
2 Up to 40 RJ-45 8 x X2 (SC)
Base
Up to 8 x X2
uncontended 1:1
Up to 16 x X2
contended 2:1
(cannot connect
2:1 ports to ISIS
1 48 RJ-45 2 SFP+ (LC) 2 RJ-45
1 48 RJ-45 2 X2 (SC) 2 RJ-45
1 48 RJ-45 48 SFP+ (LC) Custom RJ-45 Avid Supports both SR (850
2 RJ-45
(one serial,
one Ethernet)
(one serial,
one Ethernet)
(one serial,
one Ethernet)
Avid Supports both SR (850
nm) and LR (1310 nm) X2s
in 10 Gb ports.
Ethernet Mgmt. Port used in
Rommon mode only.
Avid Supports both SR (850
nm) and LR (1310 nm) X2s
in 10 Gb ports.
The 4 optical ports can be
used independently as 10 Gb
or 1 Gb with SFP+ or SFP
respectively, The connector
physical presentation is LC
Avid Supports both SR (850
nm) and LR (1310 nm) X2s
in 10 Gb ports.
nm) and LR (1310 nm) SFP+
in 10 Gb ports. The four
QSFP+ uplinks are not used.
ISIS | 7500 only
n
supports this switch as
an External Expansion
Switch.
Dell Networking
S25
Dell Networking
S60
1 ??? ??? ??? ???
1 ??? ??? ??? ???
17
Page 22

Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
Model Rack Units 1 Gb Ports 10 Gb Ports Mgmt. Ports Comments
Foundry/Brocade
FESX624
Foundry/Brocade
FESX424 2XG
2 24 RJ-45
4 SFP (LC)
2 24 RJ-45
4 SFP (LC)
ISIS | 7500 External Switches
ISIS v2.4 introduced support for expanding the number of Engines in an ISIS | 7500
configuration from a maximum of 12 Engines up to 24 Engines. This is accomplished by
combining two ISIS stacks (referred to as Management Domains) under one ISIS file system.
When building an ISIS that is greater than 12 Engines, two External Expansion Switches (EXS)
are needed, one EXS per VLAN that interconnects each Management Domain.
The two stacks are interconnected via 10 Gb links (link aggregation) to the EXS switch. Each
10 Gb link can provide 600 MB/s of bandwidth full duplex. This is the maximum bandwidth an
ISS can support.
2 XFP (LC) 1 DB-9 serial Avid Supports SR (850 nm)
and LR (1310 nm) XFPs in
10 Gb ports.
Optical 1 Gb SFP Ports 1F –
4F can be used in place of
RJ-45 Ports 1 – 4.
2 XFP (LC) 1 DB-9 serial Avid Supports SR (850 nm)
and LR (1310 nm) XFPs in
10 Gb ports.
Optical 1 Gb SFP Ports 1F –
4F can be used in place of
RJ-45 Ports 1 – 4.
n
c
Up to eight EXS 10 Gb aggregated links (configured as two, four member aggregated links) are
supported between the switch and ISIS | 7500 Management Domain.
If you plan to utilize 600 MB/sec of bandwidth on the links to the EXS then you should not
use any 1 Gb connections as uplinks as you would exceed per switch bandwidth. You
should plan your client bandwidth allocation carefully so as to not oversubscribe a segment
of the network.
Each EXS is configured with 2 X 4 port groups of aggregated 10 Gb links. Each group connects
to a VLAN on one of the Management Domains. For the sample configurations the first 8 ports
of the switch are used to build the 2 X 4 port groups. The following two switches are qualified as
EXS.
• Dell Networking S4810: the interface ports are TenGigabitEthernet 0/0 through 0/7
• Cisco 4900M: the interface ports are TenGigabitEthernet 1/1 through 1/8
18
Page 23

Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
Each stack, regardless of the number of Engines, is configured into two subnets. The following
illustration shows the division, and the 10 Gb Link Aggregation used to link the two
Management Domains. You can connect the right and left VLANs to the Zone 2 switch using
either the 10 Gb ports on the Engine or EXS switch as shown as Option 1 and Option 2
(respectively) in the illustration.
19
Page 24
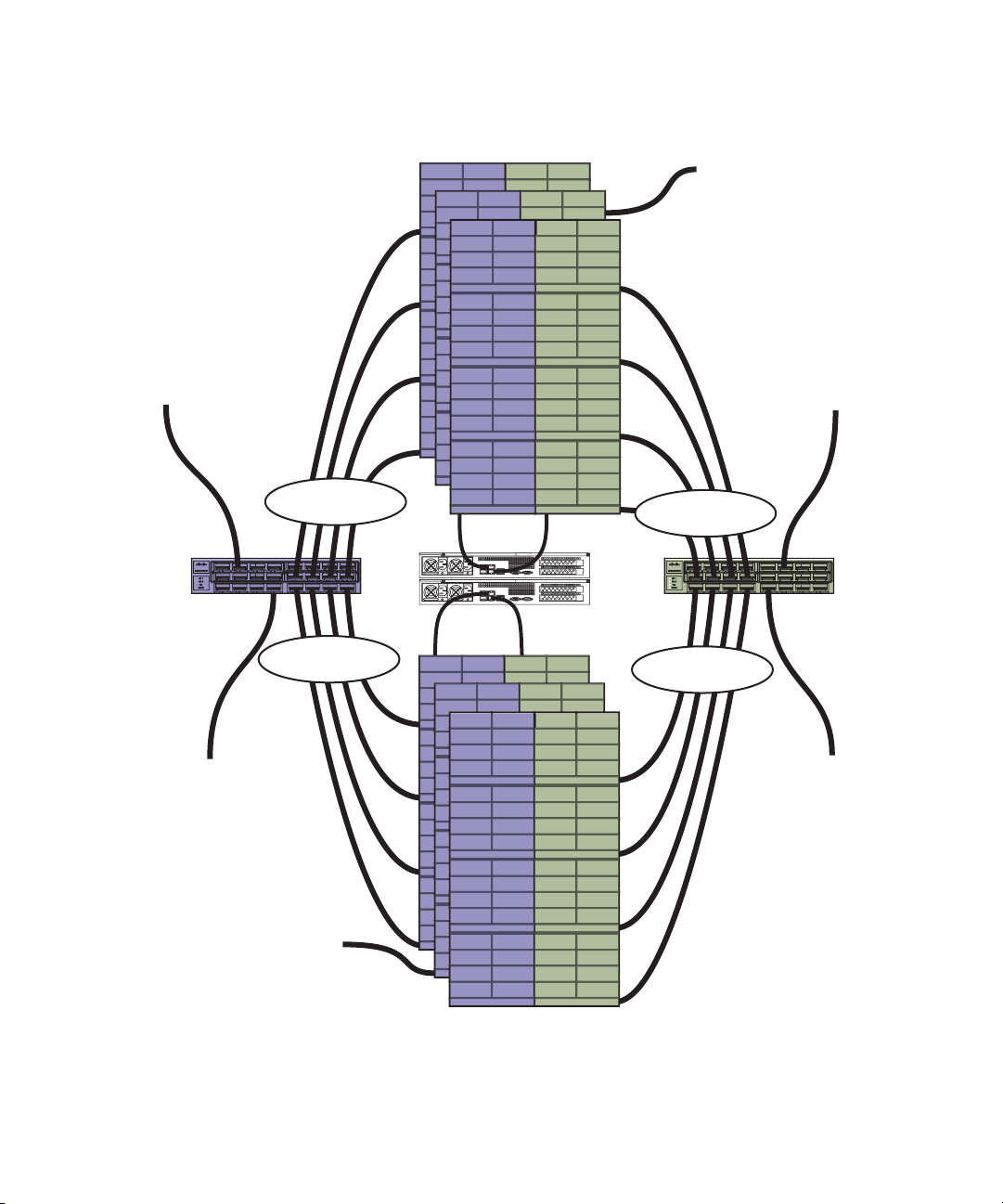
Two Stack Configuration — Example
4 x 10 Gb
4 x 10 Gb
4 x 10 Gb
4 x 10 Gb
Right side
(default subnet 200)
Left side
(default subnet 100)
(Option 1) 10 Gb connection
to Zone 2 switch
(Option 1) 10 Gb connection
to Zone 2 switch
10 Gb connection
to house network
(Option 2) 10 Gb connection
to Zone 2 switch
System Directors
External 10 Gb
Ethernet switch
External 10 Gb
Ethernet switch
(Option 2) 10 Gb connection
to Zone 2 switch
10 Gb connection
to house network
Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches
20
Page 25

Switch Redundancy
The ISIS | 7500 switch Configuration E file (found in the ISIS software kit), outlines the
redundant APN switch configuration, see
highly recommended and common configuration in an ISIS environment. In this configuration
VRRP, VRRP-E, HSRP or GLBP (depending on the switch vendor and firmware version) is used
between the redundant ISIS VLANs, while a routing protocol like RIP or OSPF is used on the
uplink to the “House” network. For specific configuration examples by protocol see
Switch Configurations” on page 15
For the Foundry/Brocade based configurations, Avid has only tested VRRP-E. For the Cisco
based configurations HSRP and GLBP have been tested. For Cisco, Avid has found GLBP to be
the best performer. However, GLBP is not offered in all switch models and is not retested in
every release; therefore, HSRP may be the only option.
Avid has only tested OSPF between the APN and House Uplink. It was found to provide the
fastest repair time when failures were introduced into the network. Recovery times vary
depending on the type and size of your network.
“Configuration E (ISIS | 7500)” on page 110. This is a
.
ISIS | 7500 Network Zone Configurations
Switch Redundancy
“Redundant
All clients in the shared storage network are classified by zones, depending on how they connect
to the network. The following list defines the ISIS clients in each network layer by their zone
classification. Zone terminology does not apply other clients such as Interplay Central.
A System Director must be attached to both subnets, but can only be attached once to each
n
subnet.
• Zone 1 Client — Connected to ISIS VLANs via an ISS 1 Gb or 10 Gb port (direct connect)
• Zone 2 Client — Connected to ISIS VLANs via a 1 Gb or 10 Gb port on an Avid qualified
layer-2 switch (non-routed)
• Zone 3 Client — Connected to an Avid qualified layer-3 switch (routed) with known Quality
of Service (QoS); traffic routed to ISIS (one hop) and load-balanced across ISIS VLANs
(approximately a 60/40 ratio)
• Zone 4 Client — Connected to the house network using a switch with unknown QoS; traffic
routed to Avid ISIS (measured by the number of hops) and load-balanced across ISIS
VLANs (approximately a 60/40 ratio)
Clients which can connect to one zone can run in any lower-numbered zone — for example, a
n
Zone 3 client can also run as a Zone 2 or Zone 1 client.
The following four examples show different types of Avid ISIS | 7500 configurations.
21
Page 26
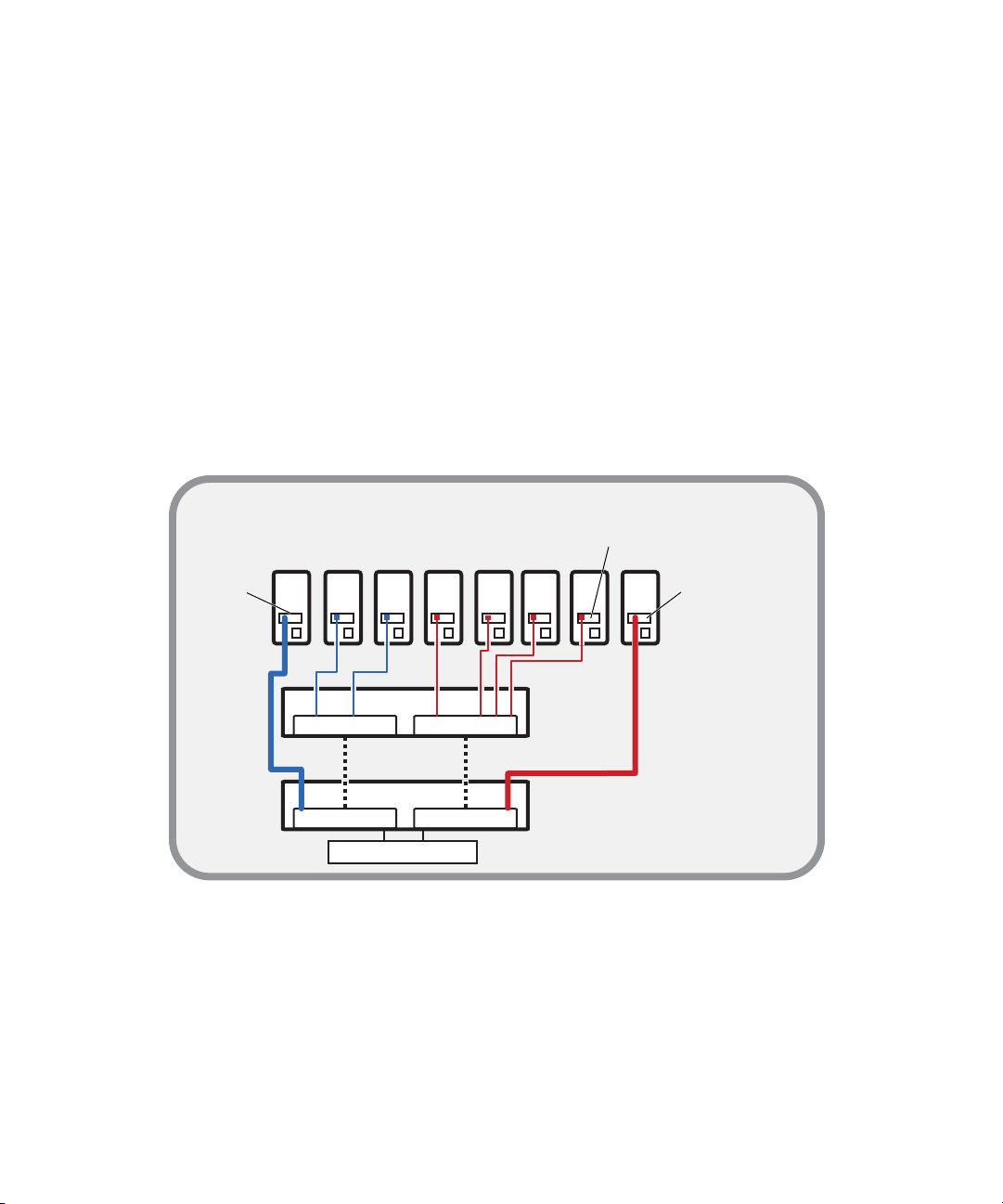
ISIS | 7500 Network Zone Configurations
Zone 1
Chassis
interconnect
10 Gb ethernet
Engine
Engine
Intel Pro 1000
PT board
Client systems
in Zone 1
1 Gb ethernet
10 Gb ethernet
10 Gb board
10 Gb board
System Director
ISS VLAN 10
ISS VLAN 20
ISS VLAN 20ISS VLAN 10
ISIS | 7500 Zone 1 Client Configuration (Direct Connect)
Any client that is connected directly to an ISIS is considered a Zone 1 or direct connected client.
Each Integrated Switch Blade (labeled ISS2000) has a total of eight, 1 Gb Ethernet ports and one
10 Gb Ethernet port. A single Engine has the capacity to support 18 clients or servers, including
any ports that are to be used by the System Director(s). The total number of 1 Gb ports in Zone 1
is based on the number of Engines and System Directors in the configuration.
Connect TransferManagers and AirSpeed servers to Zone 1 or Zone 2.
n
A Zone 1 (direct connect) configuration consists of a group of clients connected directly to the
1-Gb and 10 Gb connections of the ISS in the Engine. The System Director also connects to both
subnets via both ISS modules using a 1 Gb port.
Avid ISIS | 7500 Zone 1 Network Configuration
ISIS | 7500 Zone 2 Client Configuration (Indirect Connect)
There is support for external switches connected through the 10 Gb port on each ISS. Clients that
are connected to an external switch are referred to as Zone 2 clients and have a layer 2
relationship connection to ISIS. For a list of supported switches, see the
Approved ISIS Switches” on page 8
“Qualified and
.
22
Page 27
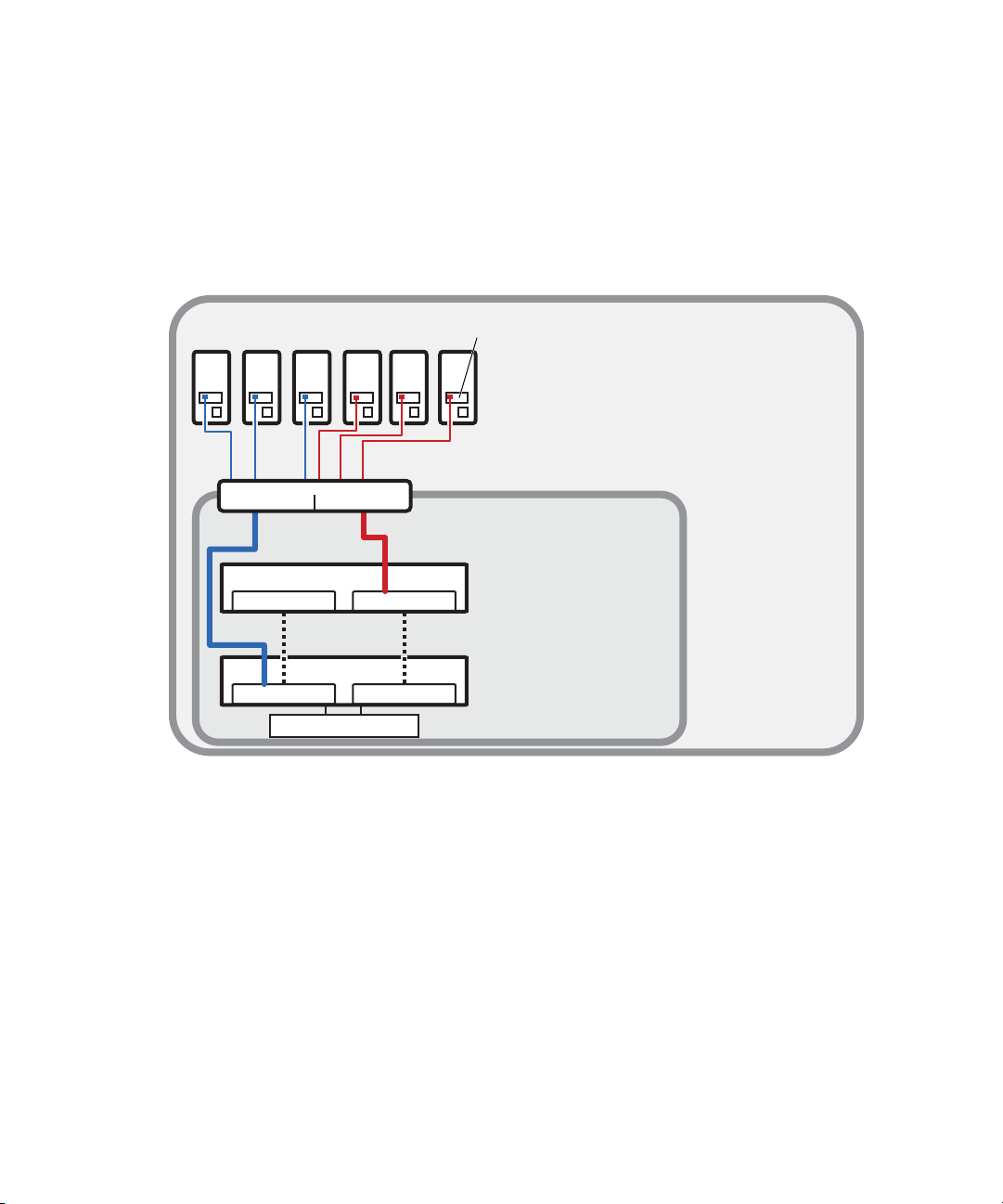
ISIS | 7500 Network Zone Configurations
Chassis
interconnect
Engine
Engine
Zone 1
Zone 2
System Director
Intel Pro 1000
PT board
Client systems
in Zone 2
1 Gb ethernet
ISS VLAN 10
ISS VLAN 20
ISS VLAN 20ISS VLAN 10
VLAN 10 VLAN 20
10 Gb ethernet
Zone 2 switch with two 10-Gb Ports
A Zone 2 (indirect connect) configuration consists of group of clients connected to an Ethernet
switch with a 10 Gb port connected to an ISS located in the Engine. The System Director also
connects to both subnets via both ISS modules using a 1 Gb port. Depending upon the switch
configuration, each client shown connected to the external switch is connected to one of the two
subnets through one of the two 10 Gb connections.
Avid ISIS | 7500 Zone 2 Network Configuration
The 10 Gb ports connected to the ISIS are also serving as uplinks to the ISIS for clients on either
VLAN. Each VLAN on the switch is connected to the appropriate VLAN in the shared storage
network using the 10 Gb port.
Client count can be scaled according to the number of switches and available switch ports.
ISIS | 7500 Zone 1 and Zone 2 Client Configuration
The number of ports available on the ISS (Zone 1) makes it necessary to add another layer of
clients through a qualified network switch to create a (Zone 2) in the ISIS shared storage
network.
23
Page 28

ISIS | 7500 Network Zone Configurations
Zone 1
Zone 2
Intel Pro 1000
PT board
Client systems
in Zone 2
VLAN 10 VLAN 20
10 Gb Ethernet
Intel Pro 1000
PT board
Client systems
in Zone 1
1 Gb Ethernet
Chassis interconnect
ISS VLAN 10
ISS VLAN 20
Engine
Engine
System Director
ISS VLAN 20ISS VLAN 10
System Director
System Director
connections
1 Gb Ethernet
1 Gb Ethernet
Zone 2 switch with two 10-Gb Ports
A mixed configuration (Zone 1 and Zone 2) consists of clients connected directly and indirectly
through ports on the Engine’s ISS. The following illustration shows two System Directors that
connect to the Engine via two separate Zone 1 ISS 1 Gb ports for use as a redundant System
Director in case of a failure. Both System Directors also connect to each other through the
onboard Ethernet connections to monitor if one of the System Director fails.
Avid ISIS | 7500 Zone 1 and Zone 2 Mixed Network Configuration
Although it is not shown in the previous diagram, to ensure high availability, whenever possible,
n
the System Directors should be connected to two different subnets through two different Engines.
ISIS | 7500 Zone 3 and Zone 4 Client Configuration
A Zone 3 (indirect connect) configuration consist of a group of clients connected to an Avid
qualified layer-3 switch (routed) with known Quality of Service (QoS); traffic routed to ISIS
(one hop) and load-balanced across ISIS VLANs (approximately a 60/40 ratio).
A Zone 4 (indirect connect) configuration consists of group of clients using an Ethernet switch
with unknown QoS; traffic routed to Avid ISIS (measured by the number of hops) and
load-balanced across ISIS VLANs (approximately a 60/40 ratio).
24
Page 29
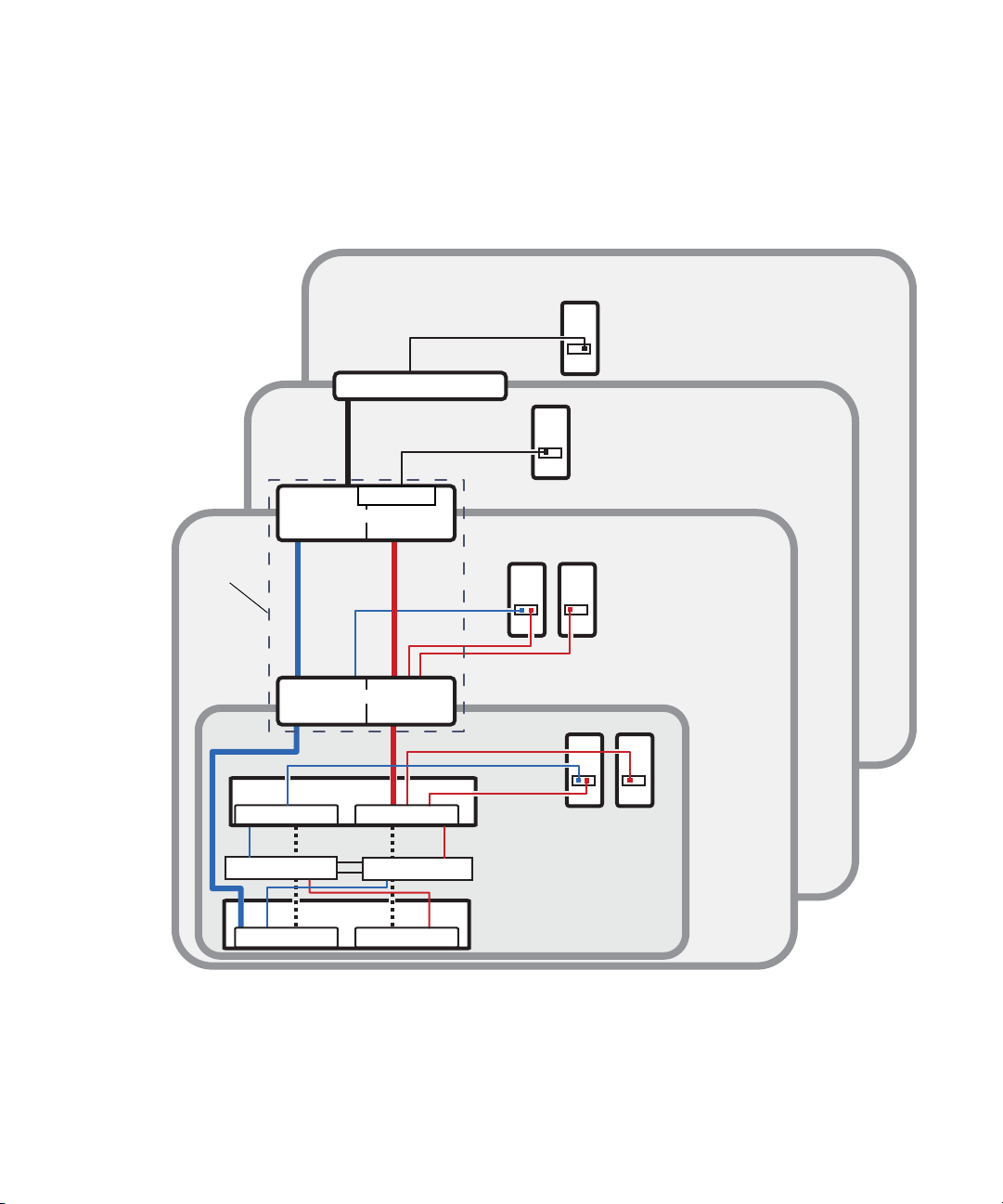
ISIS | 7500 Network Zone Configurations
Zone 4
Zone 3
Zone 3 client
routed VLAN 30
Zone 4 clients
corporate network
Zone 1
Client systems
in Zone 1
Chassis
interconnect
ISS VLAN 10
Engine
Engine
System Director
System Director
System Director
connections
1 Gb Ethernet
Zone 2
Avid Production Network (Zone 1, 2, and 3)
1 Gb Ethernet
VLAN 10 VLAN 20
Zone 2 Layer 2 switch
(Layer 3 routed/switched)
(Layer 2 switched)
Can be one
multilayer switch
(Layer 2 switched)
(Layer 3 routed/switched)
VLAN 10 VLAN 20
VLAN 30
Zone 3 layer 3 switch
House switch
ISS VLAN 20
ISS VLAN 10 ISS VLAN 20
The house switch should have uplinks to the Avid Production Network through an Ethernet
switch that contains a 10 Gb port connected to an ISS located in the Engine. The System Director
connects to the both subnets via both ISS modules using a 1 Gb Zone 1 port.
Avid ISIS | 7500 Zone 3 and Zone 4 Network Configuration
25
Page 30

ISIS | 5500 Network Zone Configurations
Client Connection Speed to ISIS | 7500
The ISS in the ISIS | 7500 Engine supports any combination of 1 Gb UTP and 10 Gb optical
clients (Zone 1). The ISS does not negotiate at any rate below 1 Gb. Zone 2 and Zone 3 also
support 1 Gb and 10 Gb client connections.
ISIS | 7500 Link Aggregation Support
A link aggregation configuration from the ISS ports to the qualified or approved Avid Production
Network switch supports Zone 2, Zone 3, and Zone 4 clients.
ISIS | 5500 Network Zone Configurations
The Avid workgroup uses an Avid ISIS to provide clients access to Avid ISIS workspaces
(shared folders) over a 1 Gb Ethernet network (see
with One or Two Switches” on page 29
Storage” on page 30
multiple Ethernet clients. The following sections define the ISIS clients in each network layer by
their zone classification. Zone terminology does not apply other clients such as Interplay Central.
). You can have several workgroups at your site, each accommodating
and “Avid ISIS | 5500 Infrastructure — with Optional
“Avid ISIS | 5500 Infrastructure — Clients
When connecting 10 Gb clients in the ISIS | 5500 environment, you must enable flowcontrol RX
n
on the 10 Gb ports in the ISIS | 5500 switches, see “Turning on Flow Control in the Dell
Networking S25 Switch” on page 71.
ISIS | 5500 Switch Consideration
Several Avid ISIS Ethernet client connection options are listed as follows. See the Avid ISIS
ReadMe for the latest list of qualified Ethernet switches.
• Up to four clients can connect directly into the Intel Pro network ports (1, 3, 4, and 6) on the
rear of the System Director (see
on page 27
• Up to eight clients can connect directly to a single Engine configuration when using the
built-in Intel Pro network ports and when the optional Quad Port 1 Gb Ethernet adapter is
installed (ports 8, 9, 10, and 11).
• 10 Gb clients connect into a 10 Gb port on a qualified switch or can connect directly into the
ISIS | 5500 System Director 10 Gb port on a switch-less configuration. You can have one 10
Gb client per ISIS | 5500 Engine. For example, in a six Engine configuration you can have
six 10 Gb clients.).
).
“ISIS | 5500 Zone 1 Client Configuration (Direct Connect)”
26
Page 31

ISIS | 5500 Network Zone Configurations
• Up to 20, 1 Gb Ethernet clients are supported on the Dell Networking S25 Ethernet switch
using four 1 Gb connections to the System Director. This is nonblocking gigabit Ethernet
switch (see “ISIS | 5500 Zone 2 Configuration (System Director and Switch 1 Gb
Connections)” on page 29
• Up to 24, 1 Gb Ethernet clients are supported on the Dell Networking S25 Ethernet switch
using a 10 Gb connection to the System Director (see
(System Director and Switch 10 Gb Connections)” on page 29
• Up to 44, 1 Gb Ethernet clients are supported on the Dell Networking S60 Ethernet switch
using four 1 Gb connections to the System Director.
• Up to 47, 1 Gb Ethernet clients are supported on the Dell Networking S4810 Ethernet switch
using a 10 Gb connection to the System Director.
• Up to 48, 1 Gb Ethernet clients are supported on the Dell Networking S60 Ethernet switch
using a 10 Gb connection to the System Director.
• Up to 44, 1 Gb Ethernet clients are supported across two stacked Dell Networking S25
Ethernet switches using four 1 Gb connections to the System Director. (20 clients in the first
Dell Networking S25 switch, 24 on the second). These switches are stacked using a 12 Gb
stacking connection.
• Up to 48, 1 Gb Ethernet clients are supported across two stacked Dell Networking S25
Ethernet switches using a 10 Gb connection to the System Director. (24 clients in the first
Dell Networking S25 switch, 24 on the second, two ports unused). These two switches are
stacked using a 12 Gb stacking connection.
).
“ISIS | 5500 Zone 2 Configuration
).
• Up to 90, 1 Gb Ethernet clients are supported with the Dell Networking S4810, Cisco 4900,
and Cisco 4948-10GE Ethernet switches.
ISIS | 5500 Zone 1 Client Configuration (Direct Connect)
The Avid ISIS | 5500 direct connect configuration provides access to shared workspaces by
connecting up to nine clients directly into a single ISIS | 5500 Engine. The following illustration
shows the ISIS | 5500 Engine rear panel with optional Quad Port 1 Gb Ethernet adapter board
installed and the Myricom 10 Gb Ethernet board (shipped installed in the ISIS | 5500-32 and
ISIS 5000-32 Engines). Depending if you have installed the optional Quad Port 1 Gb Ethernet
adapter board, four or eight direct connect 1 Gb clients are available. The Myricom 10 Gb
Ethernet board offers one 10 Gb direct connect client.
You cannot mix directly connected clients (Zone 1) with an switch configuration as described in
n
a Zone 2 and greater configurations.
27
Page 32

ISIS | 5500 Network Zone Configurations
Up to 4 clients
1 Gb Ethernet
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
ISIS 5500
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
Ether
net client
Up to 4 clients
1 Gb Ethernet
10 Gb Ethernet client
10 Gb Ethernet
1
3
4
6
Ethernet client
Ether
net client
Direct connect options include:
• The ISIS | 5500-32 and ISIS | 5500-16 Engines both support up to eight 1 Gb clients directly
connected to the built-in Intel Pro 1000 Ethernet ports and when using the optional Quad
Port 1 Gb Ethernet adapter board. The built-in Intel Pro 1000 ports are the four outside ports
(labeled 1, 3, 4, and 6). The Quad Port Ethernet boards are not labeled but are ports 8 to 11
from top to bottom.
• The Quad Port 1 Gb Ethernet adapter board does not ship installed in either the
ISIS | 5500-32 or the ISIS | 5500-16 Engines. This optional board is only supported in single
Engine direct connect configurations when you want 5 to 8, 1 Gb clients connected to the
ISIS Engine.
The Quad Port 1 Gb and 10 Gb Ethernet adapter boards are options in the ISIS | 5500-16
n
Engine. For instructions on installing the Ethernet adapter boards, see the Avid ISIS | 5500
Setup Guide.
• The Myricom 10 Gb Ethernet board is shipped installed in the ISIS | 5500-32 Engine. This
board is the 10 Gb connection for configurations with multiple ISIS | 5500 Engines or for a
single 10 Gb client in a direct connect configuration. This is an optional adapter board in the
ISIS | 5500-16 Engine.
Avid ISIS | 5500 direct connect configurations do not support dual-link client connections or
n
Avid Interplay environments.
Avid ISIS | 5500 Infrastructure — Direct Connect Clients
28
Page 33

ISIS | 5500 Network Zone Configurations
1 Gb Ethernet
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
ISIS 5000
Up to 90 clients
Ethernet switch
1
3
4
6
ISIS | 5500 Zone 2 Configuration (System Director and Switch 1 Gb Connections)
A single ISIS Engine can connect to a switch using the four Intel Pro 1000 1 Gb Ethernet ports
(1, 3, 4, and 6) on the rear of the Engine. When using a single Engine, that Engine must be
configured as the System Director. Clients access workspaces on the System Director through
the Ethernet switch. If any of the four Ethernet port connections to the switch fails, the Avid ISIS
continues to operate. Clients can continue to access workspaces through the switch even when
only one Ethernet port is connected to the System Director. This is not an approved
configuration, but a safeguard if the other Ethernet connections are lost. If you stack or cascade
switches, you can connect up to 90, 1 Gb Ethernet clients.
Avid ISIS | 5500 Infrastructure — Clients with One or Two Switches
ISIS | 5500 Zone 2 Configuration (System Director and Switch 10 Gb Connections)
A 10 Gb connection between your Engine and switch allows you setup the switch and clients a
greater distance away from the Avid ISIS system. When using a single Engine, that Engine must
be configured as the System Director and can use either the 1 Gb ports or 10 Gb port to connect
to the switch. You can use the 10 Gb port in the Engine for a single or multiple Engine
configuration. When using multiple Engines, you are required to connect the System Director
and other Engines to the switch using the Engines’ 10 Gb ports. A stacked or cascaded switch
configuration allows you to connect up to 90 1 Gb Ethernet clients.
29
Page 34

ISIS | 2500 Network Zone Configurations
Avid ISIS
Avid ISIS
ISIS 5000
Up to 90 clients
Ethernet switch
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
Ethernet client
Optional storage enclosures
10 Gb Ethernet
Avid ISIS
Avid ISIS
Avid ISIS
The 10 Gb board is an option in the ISIS | 5500-16 Engine. For instructions on installing the
n
10 Gb Ethernet adapter board, see the Avid ISIS | 5500 Setup Guide.
Avid ISIS | 5500 Infrastructure — with Optional Storage
ISIS | 5500 Zone 3 and Zone 4 Client Configuration
A Zone 3 (indirect connect) configuration consist of a group of clients, connected to an Avid
qualified layer-3 switch (routed), with known Quality of Service (QoS); traffic routed to ISIS
(one hop).
A Zone 4 (indirect connect) configuration consists of a group of clients, using an Ethernet switch
with unknown QoS; traffic routed to Avid ISIS (measured by the number of hops).
ISIS | 2500 Network Zone Configurations
ISIS | 2500 systems typically are integrated with ISIS | 7500 or ISIS | 5500 environments. The
ISIS | 2500 System Director and ISIS | 2500 Engine are connected to ISIS | 7500 or ISIS | 5500
switches that have been configured with a separate VLAN on the Zone 2 switch. See your site
network administrator for assistance with configuring the separate VLAN on your switch. The
following sections defines the ISIS clients in each network layer by their zone classification.
Zone terminology does not apply other clients such as Interplay Central.
30
Page 35

ISIS | 2500 Network Zone Configurations
VLAN
Zone 2
Intel Pro 1000
PT board
Client systems
in Zone 2
1 Gb or 10 Gb Ethernet
10 Gb Ethernet
Zone 2 switch with
1-Gb and 10-Gb Ports
Engine
System Director
ISIS | 2500 Zone 1 Client Configuration (Direct Connect)
The ISIS | 2500 does not provide any client connections directly to the Engine or System
Director. Client connections are only available through a switch.
ISIS | 2500 Zone 2 Client Configuration (Indirect Connect)
Clients that are connected to a switch are referred to as Zone 2 clients. Zone 2 clients are not
routed. For a list of supported switches, see the
.
page 8
A Zone 2 configuration consists of a group of clients, connected to an Ethernet switch with a 10
Gb port connected to the ISIS | 2500 Engine. The System Director also connects to the switch
using a 1 Gb port or 10 Gb port. Each client connects to the Zone 2 switch using either a 1 Gb or
10 Gb connection.
Avid ISIS | 2500 Zone 2 Network Configuration
“Qualified and Approved ISIS Switches” on
31
Page 36

ISIS | 2500 Network Zone Configurations
ISIS | 2500 Zone 3 and Zone 4 Client Configuration
A Zone 3 (indirect connect) configuration consist of a group of clients, connected to an Avid
qualified layer-3 switch (routed), with known Quality of Service (QoS); traffic routed to ISIS
(one hop).
A Zone 4 (indirect connect) configuration consists of a group of clients, using an Ethernet switch
with unknown QoS; traffic routed to Avid ISIS (measured by the number of hops).
The house switch should have uplinks to the Avid Production Network through an Ethernet
switch that contains a 10 Gb port connected to the Engines. The ISIS | 2500 System Director also
connects to the switch using a 1 Gb port or 10 Gb port. The ISIS | 2500 can connect to the same
APN switches as the primary ISIS | 7500 or ISIS | 5500, but must used a different subnet to other
ISIS storage systems.
32
Page 37

Avid ISIS | 2500 Zone 3 and Zone 4 Network Configuration
Zone 4
Zone 3
House switch
Zone 3 client
routed VLAN 40
Zone 4 clients
corporate network
ISIS 7000
Client systems
in Zone 1
Chassis
interconnect
ISS VLAN 10
ISS VLAN 20
Engine
Engine
System Director
ISS VLAN 20ISS VLAN 10
System Director
Zone 2
Avid Production Network (Zone 1, 2, and 3)
1 Gb Ethernet
VLAN 10 VLAN 20
VLAN 40
Zone 3 layer 3 switch
VLAN 10 VLAN 20
Zone 2 Layer 2 switch
(Layer 3 routed/switched)
(Layer 2 switched)
Can be one
multilayer switch
(Layer 3 routed/switched)
Zone 1
Engine
System Director
10 Gb Ethernet
ISIS 2000
VLAN
Zone 2 clients
VLAN 30
Network Considerations
Network Considerations
Carefully plan for space, environmental, and power requirements for your Avid hardware. This
section contains topics related to setting up your an Avid network environment.
33
Page 38

Network Considerations
Computer Names
A hostname must comply with RFC 952 standards. For example, you cannot use an underscore
in a hostname. For more information, see “Naming Conventions in Active Directory for
Computers, Domains, Sites, and OUs” on the Microsoft Support Knowledge Base.
Verify Entries on the DNS Server
Make sure that you correct any errors in DNS entries for name to IP resolution. The Avid
network can become sluggish and unstable if there are incorrect entries in the DNS server for any
of the computers in the Interplay environment. Symptoms include excessive CPU usage by the
Interplay Framework Lookup service and Interplay Diagnostics. The tree view in the Interplay
Service Configuration or Health Monitor may also fail to populate if there are incorrect DNS
entries.
Configure the DNS Server to Support Reverse Lookup
Ensure that the DNS server is configured to support Reverse Lookups. If DNS is not configured
for Reverse Lookup, Interplay Framework cannot resolve IP addresses to host names. Symptoms
include; tree views fail to populate in the Interplay Service Configuration, Interplay Diagnostics,
and Health Monitor.
Non-DNS Environments
In a non-DNS environment you must configure a host file on all systems, including Avid Low
Res Encode systems. This is necessary so that the Interplay Framework can list the systems in its
client applications such as the Interplay Service Configuration or Health Monitor.
Computers with Multiple Network Interfaces
Computers that have multiple network interfaces in use must be entered in DNS so that all
IP addresses have the exact same hostname.
If you have multiple network interfaces on a computer and one is not used, use the Device
Manager to disable the interface. If not, the computer might have problems communicating with
the Interplay Framework Multicast Repeater. If multiple network interfaces are used, you should
adjust the binding order and local specific routes to insure the intended operation. Use the
Advance setting the Network adapter properties to change the priority order on the network
interfaces.
Configuring an Avid Shared Storage System
On an Avid Production Network, if your network extends outside of ISIS Zone 1 and Zone 2,
you must configure a Layer 3 switch to route between subnetworks.
34
Page 39

Know Where Your Subnets Are on the Network
Create a system diagram that identifies the subnets on your Avid network environment. Avid
recommends you use Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) IP ranges of contiguous addresses
instead of non-contiguous ranges VLAN 16, 17, 18, 19.
Time Synchronization
If you already have a system in place to maintain Time Sync on your network, you can continue
to use that system. Avid Interplay provides the Interplay Framework Time Synchronization
service to perform the same task. Avid has created a detailed guide on synchronizing many Avid
products. Search for “A Guide to Time Synchronisation for Avid Interplay Systems” posted on
the Avid Knowledge Base at
The Avid Time Synchronization Service enables time synchronization between different
machines in a workgroup. The Time Synchronization Service can operate in either Master mode
or Slave mode. In Master mode, the service retrieves a reference time from a configured time
source and redistributes it to the Slave services within the workgroup. The time source can be the
local PC clock, an NTP server, or a timecode card installed in a server, such as the
CaptureManager server. In Slave mode, the Time Synchronization Service listens for time
notifications from the workgroup and (optionally) sets the local PC clock to match.
TFTP
www.avid.com/US/support.
TFTP
n
It is important to use only one time synchronism mechanism to set the local PC clocks in the
Interplay environment. If a Time Synchronization Slave service is configured to set the local PC
clock and it detects that some other mechanism (such as Windows 32 Time Services) changes the
local clock, then the Time Sync Slave service will disable itself to avoid the local clock from
jumping back and forth. The Time Sync slave will also post a Warning in the Health Monitor.
Copy firmware and configuration files from the Host to the switch using a TFTP application.
You can find several on the Internet. The most common application used at Avid is called
TFTPD32.exe. You can download a copy of this program at the following Web link:
http://tftpd32.jounin.net/.
When configuring the TFTP application makes sure that the IP address of the Server Interface is
on the same subnet as the switch with which you are attempting to communicate. Also, make
sure that the files you are trying to transfer are in the directory designated as the root for the
TFTP application. This is sometimes referred to as the Base Directory.
Make sure the firewall settings of the device permit incoming unsolicited use of the UDP port 69
used by the TFTP.
35
Page 40

Network and Switch Troubleshooting
Network and Switch Troubleshooting
The following sections include some suggestions that might help you troubleshoot the switch or
clients’ connections to the switch.
Ping and Tracert Commands
Ethernet networking is the backbone for the Avid ISIS workgroup. If your Ethernet network is
not performing properly, it will affect your workgroup. The following sections describe how to
use two commands, ping and tracert, to troubleshoot your network.
Ping
You can use the ping command to confirm that the physical and logical aspects of your network
are configured correctly. Physical aspects include network interface card, cables, and Ethernet
switches. Logical aspects include IP addresses, subnet masks, and routing.
Ping works by sending a packet over the network from an originating host to a destination host.
The destination host receives the packet and sends a response packet over the network to the
originating host. If the originating host receives the response packet, it is a good indication that
the network is configured correctly.
In the ISIS environment you can use the PathDiag tool to do multiple pings using Network
Connectivity Test located in the Custom Test Setting area of the window.
You can use many options with ping. This section discusses two types of ping syntax:
ping
[System Name]
where [System Name] is the network name of the remote system to which you are testing
connectivity
or
ping
[IP Address]
where [IP Address] is the IP address of the remote system to which you are testing connectivity.
To run the ping command:
1. Open an MS-DOS® command prompt window (click Start > Run and type
2. At the command line, type the ping command (for example,
The ping result should resemble the following:
Reply from 192.168.10.5: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
36
ping 192.168.10.5
cmd
).
).
Page 41

Tracert
Network and Switch Troubleshooting
Reply from 192.168.10.5: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.10.5: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.10.5: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=255
Four responses of “Reply from…” indicate the network is configured correctly and the
originating and destination hosts can see each other on the network.
If any one of the responses in the ping result says:
Request timed out.
or
Destination host unreachable.
it indicates the network is not configured correctly or there are other network problems.
Some items that can cause network problems are:
- Bad, loose, or incorrectly connected cables
- An incorrectly configured IP address or subnet mask on a local or remote system
- Excessive network traffic
While ping can test for connectivity between two network hosts, tracert (short for “trace route”)
can verify the network path that the data uses to travel between the two hosts.
Because Avid editing applications are data intensive, it is important that large amounts of data be
transferred between the Avid ISIS and its clients in a timely fashion. An incorrectly configured
network might get the data to its destination, but be too slow for your application to work
effectively.
You can use the tracert command to confirm that the data is traveling along an optimal path. In an
Avid ISIS workgroup, the Avid ISIS and its clients should send traffic directly to each other.
Routers should not be used to direct traffic between them.
It is possible for network traffic to take one path going to a system and a different path coming
back. Therefore, it is important to run tracert from both the Avid ISIS and its clients to test the
data path in both directions.
As with ping, you can use many options with tracert. This section discusses two types of tracert
syntax:
tracert [System Name]
where [System Name] is the network name of the remote system to which you are testing
connectivity
37
Page 42

Network and Switch Troubleshooting
Tracing route to [remote system name or IP address] ove
maximum of 30 hops:
1 10 ms <10 ms <10 ms [remote system name or IP address
Trace complete.
One entry indicates
an optimal route.
or
tracert [IP Address]
where [IP Address] is the IP address of the remote system to which you are testing connectivity
To run the tracert command:
1. Open an MS-DOS command prompt window (click Start > Run and type
2. At the command line, type the tracert command (for example,
tracert 192.168.10.5
The tracert result should resemble the following:
If your network is configured correctly, the tracert result will show only one entry and then
indicate that the trace is complete. More than one entry indicates that the traffic is going
through a router and is appropriate for a test of a Zone 3 client, which significantly affects
performance. More than one entry is appropriate for a test of a Zone 3 client.
If your tracert result shows more than one entry, most likely there is an incorrect IP address
or subnet mask configuration on the local host.
Sluggish Switch Performance On the Dell Networking S25
Avid recommends the following configuration setting on the Dell Networking S25 switch to
optimize the switch memory buffers for use in dedicated storage networks. This does not apply
to the Dell Networking S60 or S4810. If you feel that your Dell Networking switch has become
sluggish, use the following information to verify the buffer size. If your buffer does not match the
following information, reload the Avid configuration file; see
on page 66
.
“Restoring From Flash Memory”
cmd
).
).
Type the following command to show the buffer profile details for 1 Gb ports.
To verify your 1 Gb port buffer size:
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
en
2. Type
3. Type
Global Pre-defined buffer policy: 1Q
.
sh buffer-profile detail int gig 0/1
38
.
Page 43

Network and Switch Troubleshooting
Interface : Gi 0/1
Buffer-profile : Dynamic Buffer 1603.75 KB (Current), 1603.75 KB (Configured)
-----------------------------------------------------------------Queue# Dedicated Buffer (KB) | Buffer Packet-Pointers
Current Configured | Current Configured
-----------------------------------------------------------------0 3.00 3.00 | 1920 1920
1 3.00 3.00 | 64 64
2 0.00 0.00 | 0 0
3 0.00 0.00 | 0 0
4 0.00 0.00 | 0 0
5 0.00 0.00 | 0 0
6 0.00 0.00 | 0 0
7 3.00 3.00 | 63 63
4. Type
To verify your 10 Gb port buffer size:
exit
.
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
en
2. Type
3. Type
Global Pre-defined buffer policy: 1Q
Interface : Te 0/25
Buffer-profile : Dynamic Buffer 1603.75 KB (Current), 1603.75 KB (Configured)
-----------------------------------------------------------------Queue# Dedicated Buffer (KB) | Buffer Packet-Pointers
Current Configured | Current Configured
-----------------------------------------------------------------0 3.00 3.00 | 1600 1600
1 3.00 3.00 | 64 64
2 3.00 3.00 | 64 64
3 3.00 3.00 | 64 64
.
sh buffer-profile detail int ten 0/25
.
39
Page 44

Replacing the Network Switch
4 3.00 3.00 | 64 64
5 3.00 3.00 | 64 64
6 3.00 3.00 | 64 64
7 3.00 3.00 | 63 63
4. Type
exit
.
Replacing the Network Switch
Before replacing a switch in the ISIS environment:
• Have a backup copy of the switch configuration file.
• Disable any Link Aggregation that might be set in your ISIS | 7500 environment. This
prevents odd network behavior and the inevitable trunking errors.
• Disable any trunking to other switches before removing the switch. Any trunking involved
with the switch would be part of the configuration file and would help when reconfiguring
the trunk on the new switch.
• You do not have to shut down the System Director or Engines when replacing a switch,
particularly if you have a redundant switch configuration.
To replace a switch you need a console connection to the switch and a tftp server. The following
are high level steps that assumes the failed switch is still capable of making a tftp backup. If the
switch is completely dead, you must either restore the configuration from a previous backup or
configure it manually.
To capture the switch configuration file:
1. Copy the startup configuration of the failed switch to the tftp server.
2. Install the replacement switch.
3. Configure a temporary interface on the new switch to connect to the tftp server (best to use a
no switchport interface with IP address on same subnet as TFTP server).
4. Copy the backup copy of the old switch startup configuration to the new switch (copy tftp
startup-config).
5. Reload the switch configuration and old switch configuration should be restored on the new
switch.
The specific commands will be different between Cisco and Dell Networking but they all
should be in the switch configuration guide.
40
Page 45

Replacing the Network Switch
If a TFTP server is not available:
t Use a console/telnet client such as PUTTY to list the configuration and copy it to a text file,
which can then be pasted back into the new switch and save to NVRAM.
The PUTTY scroll back buffer needs to be increased from the default 200 to at least 2000. If you
n
increase it to 50000 and make the screen longer and wider you can capture “show tech-support”
output,
To replace a switch:
1. Disconnect all network cables.
2. Pull out the power cables from the back of the switch.
3. Replace the failed switch with a new switch in the rack.
4. Replace the power cables in the back of the switch to power the switch on.
5. (Option) If you have transceivers in the failed switch, move the working transceivers into the
new switch.
6. (Option) If you have modified Avid’s default Dell Networking switch configuration, use
your terminal emulation program or telnet into the switch.
41
Page 46

Replacing the Network Switch
Avid ships Dell Networking switches configured for ISIS | 5500 configurations. Any
changes you have made to the default configuration would have to be reapplied.
Avid provides sample Cisco switch configurations in the ISIS software kit. Any changes you
have made need to be reapplied.
7. Reconnect all network cables in the front of the switch.
42
Page 47

2 Avid Network Ports
Most facilities that have an Avid network environment use firewalls to protect their corporate
network. You often need to open holes in your firewall to allow Avid components to
communicate with each other in that network. This section list the ports used in the ISIS and
Interplay environments.
There is a wide range of ports used by the Windows operating system that provide network
n
services for Avid products. For information on ports used by the Windows operating system, see
the Microsoft documentation.
Avid ISIS IP Port Usage
The following table lists the ports used in the ISIS | 7500, ISIS | 5500, and ISIS | 2500
environments. Some ports are common in all environments and others are unique to the ISIS |
5500 or ISIS 7500 | 7000.
ISIS
Component Port
Common for all ISIS Environments
ISIS System
Director
ISIS System
Director
ISIS Storage
Manager
ISIS Storage
Managers
21 TCP Anonymous FTP login allowed — open ftp Microsoft ftpd
443
3443
3000 UDP ISIS uServers communication
3001 — 3400 UDP or
Network
Protocol Purpose
UDP System Director ports that are used during the license
TCP
ftp-anon:
The FTP Service is included in the ISIS | 2500 and used in
the Avid ISIS File Gateway server.
activation. The Avid License Control tool utilizes both port
3443 and port 443 for license request and response
communication. Port 3443 is the primary port, but if this
port is blocked, the Activation Service tries port 443
(which is more likely to be open for web communication).
To or from ISIS Client or other uServer
Page 48

Avid ISIS IP Port Usage
ISIS
Component Port
ISIS Storage
3434, 3435 TCP Data connect ports (clients and other Storage Managers)
Manager
ISIS Storage
5001 UDP System Director to uServer for failover control
Manager
ISIS Storage
5004 UDP Administrative agent and related to uServer (localhost
Manager
ISIS System
5005 UDP ISS/IXS status reporting to System Director
Director
ISIS System
5015 TCP Management Console Administrative Login via https
Director
ISIS Storage
5015 TCP Agent administrative login via https
Manager, ISS,
and IXS
ISIS System
5000 UDP System Director to System Director failover/resiliency
Director
ISIS System
5003 UDP Client, uServer and System Director to System Director
Director
Network
Protocol Purpose
normally)
The ISIS | 2500 uses two ports for this function and the
ISIS | 7500 just uses 5004.
control
control (well known port).
ISIS System
5004 UDP Administrative server and related to System Director
Director
ISIS System
5016 UDP ISIS transfer agent traffic.
Director
ISIS System
6002 TCP Sentinel License Monitor — open http SafeNet Sentinel
Director/Engine
ISIS | 5500 Environment only
ISIS System
3071 TCP Array Manager RAID management — open raid-mgt
Director/Engine
ISIS Storage
5015 TCP Agent administrative login via https
Element
ISIS System
49156 TCP MegaRaid Monitoring Agent — open
Director/Engine
(localhost normally)
License Monitor httpd 7.3
ssl/megaraid-monitor
44
Page 49

Avid ISIS IP Port Usage
ISIS
Component Port
ISIS | 2500 Environment only
ISIS Storage
Manager
ISIS Clients
ISIS Windows
Client
ISIS Windows
Client
ISIS Clients 5008 TCP ISIS Client transfer agent.
5004, 5009 UDP Administrative agent and related to uServer (localhost
4000 — 4399 UDP or
4200 — 4599 UDP or
Network
Protocol Purpose
normally)
The ISIS | 2500 uses two ports for this function and the
ISIS | 7500 just uses 5004.
ISIS Client Firewall access to/from System Director for
TCP
TCP
Storage Manager Data Transfer, Storage Manager msg and
System Director msg traffic (range migration) up to ISIS
v1.3 (dynamic basis for Firewall access)
ISIS Client Firewall access to/from System Director for
Storage Manager Data Transfer, Storage Manager msg and
System Director msg traffic (range migration) ISIS v1.4
and later (dynamic basis for Firewall access)
Also search the Avid Knowledge Base for “Network
Requirements for ISIS and Interplay Production” at
www.avid.com/US/support
.
ISIS Macintosh
Clients
ISIS Linux
Clients
ISIS Clients 5017
5016 — 5415 UDP or
TCP
5000 — 5399 UDP ISIS Client for Firewall access to System Director.
Server
5013
5014
TCP
UDP
ISIS Client Firewall access to/from System Director.
The Avid Benchmark Utility agent is installed with all ISIS
client software installations. The network ports are
configurable through the Avid Benchmark Utility
Preferences.
• Server port: default setting is 5017
• TCP port: default setting is 5013
• UPD port: default setting is 5014
Avid ISIS | 5500, and ISIS | 7500 v2.0 and later supports Active Directory. Active Directory uses
the following ports for both Active Directory client to the Domain Controller, and Domain
Controller to Domain Controller communications. The following table lists all the Active
45
Page 50

Avid Interplay Port Usage
Directory ports that may be used by the System Director and clients. The specific ports used
depend on whether or not systems are members of the Active Directory domain and the types of
services requested from the Active Directory resource.
Network
Active Directory Component Port
Protocol
Active Directory
(Avid ISIS LDAP implementation)
RPC endpoint mapper 135 TCP/UDP
Network basic input/output system (NetBIOS) name
service
NetBIOS datagram service 138 UDP
NetBIOS session service 139 TCP
RPC dynamic assignment 1024 — 65535 TCP
Server message block (SMB) over IP (Microsoft-DS) 445 TCP/UDP
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) 389 TCP
LDAP ping 389 TCP
LDAP connectionless 389 UDP
LDAP over SSL 636 TCP
Global catalog LDAP 3268 TCP
Kerberos 88 TCP/UDP
Domain Name Service (DNS) 53 TCP/UDP
135 TCP
137 TCP/UDP
Avid Interplay Port Usage
The following table lists networks ports used by Avid Interplay. This information is useful to
network administrators when configuring the network and firewalls, setting up ISIS Zone 3
clients, and resolving network conflicts.
Workgroup
Component Port
Access 8321 UDP Server browser.
Network
Protocol Purpose
46
Page 51

Avid Interplay Port Usage
Workgroup
Component Port
Network
Protocol Purpose
80 TCP Server communication.
Access can also be a Media Indexer client (update media
status, Resync), Media Services client (status tool plugin and
submit jobs to archive and Transcode), and Transfer Engine
client (status tool plugin, initiate WG2WG transfers); see
appropriate sections.
Active
Directory
Archive
135 TCP RPC for Active Directory / Windows Domain
Authentication.
1433 TCP #Microsoft-SQL-Server (ms-sql-s).
Provider
1433 UDP #Microsoft-SQL-Server (ms-sql-s).
1434 TCP #Microsoft-SQL-Monitor (ms-sql-m).
1434 UDP #Microsoft-SQL-Monitor (ms-sql-m).
8192 TCP #FlashNetBackupClient (sdss).
Assist Assist uses Access ports for Interplay Engine
communication. It is also a Media Indexer client. See
appropriate sections for port usage.
Cluster Service 135 TCP RP; also used by Distributed Link Tracking Server - Service
Name TrkSvr and Distributed Transaction Coordinator Service Name MSDTC).
Random TCP Randomly allocated high TCP ports; also used by
Distributed Link Tracking Server - Service Name TrkSvr and
Distributed Transaction Coordinator - Service Name
MSDTC).
3343 UDP Cluster Services (service name: ClusSvc).
Delivery
Service
33321 TCP Command port. Also identified in the Interplay
Administration tool under Server Hostname Settings.
2002021020
TCP Data ports. To change the default port numbers, see the
Media Services Setup and User’s Guide.
DNS 53 UDP/TCP DNS Client.
iNews 1 TCP iNEWS Inter-system Messaging.
47
Page 52

Avid Interplay Port Usage
Workgroup
Component Port
21 TCP (FTP) FTP into iNEWS database: Teleprompters, NewsCutter
22 TCP/UDP ssh.
25 TCP/UDP sendmail.
67 UDP Used by PCU's to obtain an IP address via bootp.
80 TCP http Web Access, for read-only database access.
513 TCP/UDP rlogin.
600 TCP FTP into Linux partition (obsolete in iNEWS 2.5 and later -
698 TCP/ UDP Might be required for Web access through cgi-bin.
699 TCP Used by dbvisit (maintenance program) for on-line dbvisits.
1019 TCP Server listens for client connections: iNEWS Workstation,
1020 TCP Network dbdump / dbrestore between iNEWS Servers.
1020 UDP Server updates/notifications sent to client, specified by
Network
Protocol Purpose
newsroom system tool, Data Receiver.
see port 49152).
Web Client, iNEWS COM, Data Receiver, iNEWS Instinct.
client. Each client running on a machine must bind to a
unique socket. If a user intends to run N sessions of iNEWS
on the same machine, then ports 1020 through 1020 + (N–1)
must be opened in the firewall. (TCP and UDP)
1020 TCP Search results sent to client from server, specified by client.
Each client running on a machine must bind to a unique
socket. If a user intends to run N sessions of iNEWS on the
same machine, then ports 1020 through 1020 + (N–1) must
be opened.
1022 TCP iNEWS bioserver communication. Each bioserver is
connected to every other bioserver. On an ABC system the A
bioserver has a connection to both the B and C bioservers,
The B bioserver is connected to the A and C bioservers. The
C bioserver is connected to the A and B bioservers.
1023 TCP Used by connect and reconnect commands during startup.
5901 TCP/SCTP First remote access port for VNC to Linux UI, might have
more than one VNC session configured (5902, 5903, and so
on). These are not required to run iNEWS.
48
Page 53

Avid Interplay Port Usage
Workgroup
Component Port
Network
Protocol Purpose
6100 TCP FTS indexing (configurable).
6101 TCP FTS searching (configurable).
6825 TCP Monitor for ControlAir.
6826 TCP Monitor for MOS.
6827 TCP Monitor for iNEWS Command
49152 TCP
TCP (FTP)
Telnet (obsolete in iNEWS 2.5 and later - see port 49153).
FTP into Linux Partition.
49153 TCP Telnet.
Instinct Instinct uses Access ports for Interplay Engine
communication. It is also a Media Indexer client. Instinct
E3is also an iNEWS client. See appropriate sections for port
usage.
Interplay
8321 UDP Server browser.
Engine
80 TCP Client communication.
Avid Service
Framework
Ports are dynamic and services register themselves with
firewall to use any port.
(used with
Interplay)
161 UDP SNMP.
162 UDP SNMP Traps.
dynamic -
TCP TCP/UDP communications/notifications/http servers/snmp.
above 1024
4160 TCP Jini
4160 UDP Jini Discovery.
LDAP 389 TCP
636 If SSL is enabled.
Media Services
8080 TCP Listen for editor clients (SOAP).
Engine
1099 TCP Listen; RMI protocol for providers and Status/Admin tool.
49
™
Discovery.
Page 54

Avid Interplay Port Usage
Workgroup
Component Port
Network
Protocol Purpose
42000-42060TCP If 1099 not available.
Media Services
Providers /
1099 TCP Outbound; RMI protocol for providers and Status/Admin
tool.
Status Tool
42000-42060TCP If 1099 not available.
NewsCutter 21 Required for NRCS tool.
8080 TCP Outbound; Media Services connection to Media Services
Engine (SOAP).
NewsCutter uses Access ports for Engine communication. It
also runs the Interplay Framework and a local Media
E3Indexer; see appropriate sections for port usage.
ProEncode
Client
8080 TCP/IP SOAP Connection to Media Services (TCP, outbound) - run
on editing systems (NewsCutter).
Transfer Cache 1099 TCP Listen; RMI protocol for providers and Status/Admin tool.
42000-42060TCP If 1099 not available.
6539 TCP Outbound for Transfer Engine status.
Transfer Engine 6532 TCP/IP Media Connectivity tool (defined in
system32\drivers\etc\services com.avid.mct). The TM server
listens on this port for requests from other TM servers (for
example, initiating a workgroup transfer.).
6535 TCP/IP Playback protocol (defined in system32\drivers\etc\services
com.avid.pbp). This is the default port used by TM Server
for connecting to Playback Servers (Airspace etc.). This is
configurable for some playback servers.
6539 TCP/IP Transfer Engine (defined in system32\drivers\etc\services
com.avid.pbp com.avid.xmgr). The TM Server listens on this
port for incoming requests from the TM Client.
50
Page 55

Avid Interplay Central Port Usage
Interplay Central clients that connect through the public Internet require VPN access into the
server network. All connections pass through the VPN router/firewall through identified ports.
Once the data has passed into the “house network” it is secured using the customer’s existing
network security infrastructure.
Users connected within the corporate LAN/WAN would not typically use VPN access but would
likely need to pass through firewalls and other network security devices with ACLs before
accessing the Avid Interplay network.
Outbound ACLs should be used to allow packets from the ICS server to the IPC client over
n
“established” TCP sessions only.
The Interplay Central web service and Interplay Central application services operate on the same
server so there are no proxies or firewalls between these components. Access to the Interplay
Central database is also direct, with no database firewall protection required.
The following table lists the ports used by Interplay Central that should be allowed through the
VPN firewall.
Avid Interplay Central Port Usage
Workgroup
Component Port
Interplay Central
Web application
Interplay Central
mobile
applications
80 TCP Interplay Common Playback Service (ICPS) HTTP calls
443 IPC HTTPS calls
843 Loading the Flash Player for playback
26000 Inbound ICPS data
5000 Serving outbound JPEG images to the Flash player
5000 –
5399
8000 Optional administration user interface
80 TCP IPCS HTTP calls.
443 IPC HTTPS calls
Network
Protocol Purpose
UDP and
TCP
for ISIS
51
Page 56

Media Composer | Cloud Port Usage
Remote editors using Media Composer | Cloud typically access the Interplay environment using
a secure virtual private network (VPN) connection. Any VPN, Firewall, IPS or other network
security devices between the Sphere clients and Interplay core network need to be configured to
allow access to the Media Composer | Cloud servers. These security devices might require access
configuration based on IP addresses as well as the TCP and UDP ports used by the Sphere
services.
Depending on the security at your site, a VPN connection might not guarantee full access to the
Interplay servers. For example, intranet VPN might give access while extranet VPN might have
restrictions. The VPN is one layer of security and in many cases internal security devices might
also need to be modified. It is the responsibility of the site network administrators to ensure that
the Sphere users have access to the Interplay servers.
If your site implements additional firewalls or other network security devices between the VPN
connection and the Interplay environment, you must open ports on the firewall or security device
for successful communication with the remote client. For information on modifying the port
usage in the Avid Interplay products, see the Avid Interplay documentation. The following table
shows the ports that should be open. In some cases both inbound and outbound ports must be
open.
Media Composer | Cloud Port Usage
Port Usage for Media Composer | Cloud
Servers
Component and
Location Port Protocol
Interplay Delivery
Receiver
80 TCP Inbound
33321 TCP Inbound
User defined
range starting
at 20020
TCP Inbound
Inbound/
Outbound Purpose
Communication with the Interplay Engine
only
Communication port. The default is 33321
only
only
52
but you can change the value in the Interplay
Administrator tool.
Data ports. The default range is 20020
through 21020 but you can lock down the
range to the number of Sphere users you
have in the field.You need one port for each
active delivery job. Each concurrent Sphere
user requires one port. For more information,
see the Media Composer | Cloud
documentation.
Page 57

Port Usage for Media Composer | Cloud
Servers (Continued)
Media Composer | Cloud Port Usage
Component and
Location Port Protocol
Inbound/
Outbound Purpose
58889 TCP Inbound
only
7 TCP Inbound/
Outbound
ICPS server 80 TCP Inbound
only
5000 TCP Inbound
only
26000 TCP Inbound
only
843 TCP Inbound
only
443 TCP Inbound
only
System running the DNS
server
53 UDP Inbound
only
Web Services. The Web Services
implementation used by Sphere is
automatically installed on the Delivery
Receiver system when you check the
Delivery Receiver with Sphere option.
Jini server verification
Communication with the ICPS playback
service
Serving outbound JPEG images to Flash
player and Sphere clients
Inbound ICPS data
Loading the Flash player for playback
HTTPS communication
DNS communication
Interplay Engine 80 TCP Inbound/
Outbound
7 TCP Inbound/
Outbound
System running the Avid
Service Framework
4160 TCP Inbound
only
Lookup Service
56025 through
56399
TCP Inbound/
Outbound
53
Client communication
Jini server verification for Remote Upload.
Communication with remote client
Jini connection
In order for these limited port number ranges
to apply to the Lookup Service, you must
add a custom vmoptions file. For more
information, see the Media Composer |
Cloud documentation.
Page 58

Port Usage for Media Composer | Cloud
Servers (Continued)
Media Composer | Cloud Port Usage
Component and
Location Port Protocol
Systems running the Media
Indexer servers
56025 through
56399
24444 through
TCP Inbound/
TCP Inbound
24450
Inbound/
Outbound Purpose
Jini connection
Outbound
In order for these limited port number ranges
to apply to the Media Indexer, you must
change the vmoptions file. For more
information, see the Media Composer |
Cloud documentation.
Media Indexer jmx process
only
54
Page 59

3 Dell Networking Switches
This section describes the procedures for configuring and recovering Dell Networking switches
in the Avid ISIS environment. Avid preconfigures Dell Networking switches (Dell Networking
S25N, S25P (fiber), S60, and S4810) for the ISIS | 5500 environments but any of the switches
can be custom configured for your environment by your network administrator.
The Dell Networking S25N and S25P (fiber) switches have the same design configuration. All the
n
setup and configuration information in this guide applies to both models, the only difference is
the S25P uses 1 Gb optical Ethernet ports in place of 1 Gb copper Ethernet ports. The S25N
offers four shared 1 Gb SPF optical ports, when these four ports are used (21 – 24), the copper
Ethernet ports with the same port numbers are disabled. For more information, see the
manufacturer’s documentation.
Dell Networking Switch Configuration
Dell Networking switches are preconfigured with Avid specific ISIS | 5500 configurations. A
backup copy of the Avid configuration is stored on the Dell Networking switch. The Avid
configuration files support the configurations described under
Configurations” on page 26
Switch Consideration” on page 26
. For list of ISIS | 5500 client connection options see “ISIS | 5500
.
“ISIS | 5500 Network Zone
The Avid configuration file is provided in flash memory on the switch and in the Avid ISIS
n
software kit in the following location:
x000\Force10\
configuration file shipped on the switch.
A VLAN has been setup that includes all of the 1 Gb and 10 Gb ports and is configured with an
IP address for management purposes. The management IP address is 192.168.255.254/24. For
information on accessing the switch through the management IP address, see
Dell Networking Switch Through a Network Connection” on page 64
. Configuration files in the software kit typically are a newer version than the
[drive]:\Switch Configuration\ISIS
“Configuring the
.
Page 60

Dell Networking S25 Switch Modules
Dell Networking S25 Switch Modules
The Dell Networking S25 switch has two expansion slots in the back of the switch, into which
you can insert either a dual port 10 Gb Ethernet module or 12 Gb stacking modules. The 10 Gb
module provides a 10 Gb Ethernet connection between the Avid ISIS | 5500 Engine and the
switch. The 12 Gb module is for stacking two Dell Networking switches, one module is needed
in each switch. Modules are ordered separately and can install in either slot on the back of the
Dell Networking switch. The Dell Networking S25 switches support up to four Engines with two
10 Gb Ethernet modules in a single switch or two 10 Gb Ethernet modules in stacked switches.
c
n
All Dell Networking switches are shipped from Avid with a switch configuration file that
supports the switch configurations documented in this guide. Avid recommends you install
optional switch modules before you power on the switch for the first time. The appropriate
switch configuration is read during power-up. If you install or remove switch modules after
power on, and have not changed the Avid switch configuration, the Avid configuration
automatically adjust to the changes. If you have modified the switch configuration in any
way, see “Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration” on page 66.
The Dell Networking S25 Ethernet switch has been configured for all supported Avid 5500 |
5000 configurations. After setting up the switch, the proper configuration is detected at power
on. For more information on the Dell Networking switch see
Switch” on page 63
The Dell Networking S25N and S25P (fiber) switches have the same design configuration. All the
setup and configuration information in this guide applies to both models, the only difference is
the S25P uses 1 Gb optical Ethernet ports in place of 1 Gb copper Ethernet ports. The S25N
offers four shared 1 Gb SPF optical ports, when these four ports are used (21 – 24), the copper
Ethernet ports with the same port numbers are disabled. For more information, see the
manufacturer’s documentation.
.
“Accessing the Dell Networking
56
Page 61

Dell Networking S25 Switch Modules
OK
AC
XFP25
XFP26
Ethernet 1 Gb Ports
LEDs
Alarm
DC
XFP27
XFP28
SFP
Ports (21-24)
Status Panel
Shared
Ports (21-24)
Stack ID
Indicator
LED
P2827XFP26
AC
XFP25
DC
Alarm
STACK ID
RJ-45 Console Port
S25-01-GE-24V
Link/Active
Indicator LEDs
(SFP Ports 21-24)
Dell Networking S25N Switch — Front
Avid has also qualified the following optical adapters to be used with the Dell Networking S24P
optical (fibre) switch:
• Macintosh clients have been qualified with the Small Tree PEG1F single port or PEG2F dual
port optical adapters in slot 2 of a Macintosh Pro Nehalem system (2.66 GHz or 2.93 GHz)
®
• Windows clients have been qualified with the 1 Gb Intel
Pro 1000 PF Ethernet adapter.
10 Gb Ethernet S25 Switch Connections
The optional 10 Gb Ethernet board in the Avid ISIS | 5500 connects to a switch using the 10 Gb
Ethernet connection. If you need to connect more than 20 clients using the S25 switch, see
“Stacking the Dell Networking S25 Switches” on page 58.
To connect the Avid ISIS | 5500 to a 10 Gb Ethernet port on the switch:
1. (If connected) Remove both power cords from the back of the switch.
2. Remove the left blank faceplate cover on the back of the switch by removing the two screws
that secure the cover to the switch.
3. Insert the 10 Gb Ethernet module into the open slot where the blank cover was removed.
Dell Networking S25 Switch — Module Installation
57
Page 62

Dell Networking S25 Switch Modules
4. Secure the module in the switch with the two captive thumb screws.
5. Repeat steps 2, 3, and 4 if installing a second 10 Gb module in the right side slot on the
switch.
6. Insert an XFP transceiver into an open connector on the 10 Gb Ethernet module in the
switch.
Inserting the XFP Transceiver into to the 10 Gigabit Ethernet Port
7. Insert an SFP+ transceiver into the 10 Gb Ethernet connector in the Avid ISIS system.
8. Connect one end of the LC to LC cable into the transceiver on the rear of the switch.
Use standard duplex 10 foot (3 meter) LC to LC cables for the 10 Gb connections. For LC to LC
n
cable specifications, see “Supported Cabling” on page 113.
9. Connect the other end of the cable to the 10 Gb port on the ISIS system.
10. Plug in the two switch power cords to power on the switch. The Avid switch configuration
file automatically detects the 10 Gb modules. If you need to change your switch
configuration, see
All Dell Networking switches shipped from Avid include a switch configuration file that supports
n
the 1 Gb, 10 Gb, and stacking configurations. For valid switch configurations, see “ISIS | 7500
Network Zone Configurations” on page 21, “ISIS | 5500 Network Zone Configurations” on
page 26, and “ISIS | 2500 Network Zone Configurations” on page 30.
“Accessing the Dell Networking Switch” on page 63.
Stacking the Dell Networking S25 Switches
Avid supports stacking two Dell Networking S25 switches. The expansion slots in the Dell
Networking switches allow you to stack similar switches together into a single virtual switch.
When two Dell Networking S25 switches are stacked, you have the capability of connecting up
to 48, 1 Gb clients. The stacking modules are ordered separately and install in the back of the
Dell Networking switch.
58
Page 63

Dell Networking S25 Switch Modules
The Dell Networking stacking modules use a 12 Gb connection between the two S25 switches.
Once the modules are installed, connect the stacking cables as described in the following
procedure. For more information on stacking the Dell Networking switches, see the
documentation provided by the switch manufacturer. The stacked switch configuration uses LC
connectors to connect the cables to the switch.
If using a stacked switch configuration, the 10 Gb connection from the Avid ISIS can be to either
n
switch.
To stack Dell Networking S25 switches:
1. Install a 12 Gb stacking module into the right slot of the Dell Networking switch, similar to
the process described in
2. Remove the right blank cover on the back of the that switch as you did when installing the
10 Gb module.
3. Insert the stacking module into the open slot where the blank cover was removed.
4. Secure the stacking module in the switch with the two captive thumb screws.
5. Repeat steps 2, 3, and 4 on the right slot of the second switch.
6. Connect the stacking cable from one stacking port on the top switch to one stacking port on
the bottom switch.
“Dell Networking S25 Switch Modules” on page 56.
Either one of the ports on the stacking module can be used to connect the stacking module to the
n
other.
Dell Networking S25 Switch — Stacking Module Configuration
The Avid default Dell Networking switch configuration automatically detects whether modules
n
are installed or not. You do not need to modify your switch configuration for the addition of the
stacking modules.
7. Plug in the two power cords to power on your switch.
The Avid switch configuration file automatically detects the 12 Gb modules. If you need to
change your switch configuration, see
“Accessing the Dell Networking Switch” on page 63.
59
Page 64

Dell Networking S60 Switch Modules
Ethernet Ports
SFP Ports
Optional Module
Management ports
Stack ID
Alarm LEDs
When connecting the 10 Gb Ethernet clients, evenly divide the number of client between the two
n
switches so the network load is spread across both switches.
Dell Networking S60 Switch Modules
The Dell Networking S60 switch has two expansion slots: one in the front and one in the back of
the switch. The 10 Gb module provides a 10 Gb Ethernet connection between the Avid ISIS and
the switch. The 24 Gb module is for stacking two S60 switches, one module is needed in each
switch. Modules are ordered separately and can install in either the front or rear slot of the Dell
Networking S60 switch. The Dell Networking S60 switches support two 10 Gb Ethernet
modules in a single switch or two 10 Gb Ethernet modules in a stacked switches.
c
All Dell Networking switches shipped from Avid with a switch configuration file that
supports the switch ISIS | 5500 configurations. Avid recommends you install optional
switch modules before you power on the switch for the first time. The appropriate switch
configuration is read during power-up. If you install or remove switch modules after power
on, and have not changed the Avid switch configuration, the Avid configuration
automatically adjust to the changes. If you have modified the switch configuration in any
way, see “Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration” on page 66.
The Dell Networking S60 Ethernet switches have been configured for all supported Avid ISIS |
5500 configurations. After setting up the switch, the proper configuration is detected at power
on. For more information on the Dell Networking switch see
Switch” on page 63
Dell Networking S60 Switch — Rear
.
“Accessing the Dell Networking
10 Gb Ethernet S60 Switch Connections
The optional 10 Gb Ethernet board in the Avid ISIS connects to a switch using the 10 Gb
Ethernet connection. If you need to connect more than 44 clients using the S60 switch, see
“Stacking the Dell Networking S60 Switches” on page 62.
60
Page 65

Dell Networking S60 Switch Modules
Front
Rear
To connect the Avid ISIS to a 10 Gb Ethernet port on the switch:
1. (If connected) Remove both power cords from the front of the switch.
2. Remove the blank faceplate cover on the back of the switch by removing the screw that
secures the cover to the switch.
3. Insert the 10 Gb Ethernet module into the open slot where the blank cover was removed.
Dell Networking S60 Switch — Module Installation
4. Secure the module in the switch with the captive thumb screw.
5. Repeat steps 2, 3, and 4 if installing a second 10 Gb module in the front slot on the switch.
6. Insert an SFP+ transceiver into an open connector on the 10 Gb Ethernet module in the
switch.
Inserting the SFP+ Transceiver into to the 10 Gigabit Ethernet Port
7. Insert an SFP+ transceiver into the 10 Gb Ethernet connector in the Avid ISIS.
8. Connect one end of the LC to LC cable into the transceiver on the rear of the switch.
Use a standard duplex 10 foot (3 meter) LC to LC cable for the 10 Gb connections. For LC to LC
n
cable specifications, see “Supported Cabling” on page 113.
9. Connect the other end of the cable to the 10 Gb port on the ISIS system.
61
Page 66

Stacking the Dell Networking S60 Switches
Avid supports stacking two Dell Networking S60 switches. The expansion slots in the Dell
Networking switches allow you to stack similar switches together into a single virtual switch.
When two Dell Networking S60 switches are stacked you have the capability of connecting up to
88 1 Gb clients. The stacking modules are ordered separately and install in either the front or
back slot of the Dell Networking S60 switch.
The Dell Networking S60 stacking modules use a 24 Gb connection between the two switches.
Once the modules are installed, connect the stacking cables as described in the following
procedure. For more information on stacking the Dell Networking switches, see the
documentation provided by the switch manufacturer. The stacked switch configuration uses a
stacking cable to interconnect switches.
If using a stacked switch configuration, the 10 Gb connection from the Avid ISIS can be to either
n
switch.
Install a 24 Gb stacking module into the front left slot of the Dell Networking S60 switch, similar
to the process described in
To stack Dell Networking S60 switches:
“10 Gb Ethernet S60 Switch Connections” on page 60.
Dell Networking S60 Switch Modules
1. Remove the blank cover on the front of the Dell Networking S60 switch.
2. Insert the stacking module into the open slot where the blank cover was removed.
3. Secure the stacking module in the switch with the captive thumb screw.
4. Repeat steps 1, 2, and 3 on the front slot of the second switch.
5. Connect the stacking cable from the stacking port on the top switch to the stacking port on
the bottom switch.
Dell Networking S60 Switch — Stacking Module Configuration
The Avid default Dell Networking S60 switch configuration automatically detects whether
n
modules are installed or not. You do not need to modify your switch configuration for the
addition of the stacking modules.
6. Plug in the two power cords to power on your switch.
62
Page 67

Dell Networking S4810 Port Configuration
1753 9 11 13 191715 21 23 25 312927 33 35 37 434139 45 47
0642 8 10 12 181614 20 22 24 302826 32 34 36 424038 44 46
The Avid switch configuration file automatically detects the 24 Gb modules. If you need to
change your switch configuration, see “Accessing the Dell Networking Switch” on page 63
When connecting the 10 Gb Ethernet clients, evenly divide the number of client between the two
n
switches so the network load is spread across both switches.
Dell Networking S4810 Port Configuration
Avid ships the Dell Networking S4810 switch preconfigured for an Avid ISIS | 5500
environment. This configuration has specific requirements on where the Engines and clients
need to be connected. The S4810 switch contains 48 dual-speed 1/10 Gb (SFP+) ports (as well as
four 40 Gb QSFP+ uplinks not supported by Avid). The S4810 switch ports are numbered as
shown in the following illustration. Engines and clients connect as follows:
• Avid ISIS | 5500 Engines connect via 10 Gb to ports 0 – 5 (these six ports are configured for
10 Gb connections and require 10 Gb transceivers)
• Client connect to ports 6 – 47 (these 42 ports are configured for 1 Gb connections and
require 1 Gb transceivers, either optical or 1000BASE-T copper))
.
The Dell Networking S4810 Ethernet switches have been configured for all supported ISIS |
5500 configurations. After setting up the switch, the proper configuration is detected at power
on. For more information on the Dell Networking switch see
Switch” on page 63
The Dell Networking S4810 switch is also qualified as an External Expansion Switch (EXS) to
n
interconnect Management Domains in the ISIS | 7500 environment. Configuration files for the
S4810 EXS are available in the ISIS software kit.
.
“Accessing the Dell Networking
Accessing the Dell Networking Switch
Two methods for accessing the switch are described in the following sections.
“Configuring the Dell Networking Switch Through a Network Connection” on page 64
•
• “Configuring the Dell Networking Switch Through the Serial Port” on page 64
63
Page 68

Accessing the Dell Networking Switch
If you are viewing the Dell Networking console while the switch is powered on, errors might be
n
seen during start-up for devices that are not in the running configuration. These can be safely
ignored. If you change the running configuration in memory and save it, these errors will not be
seen on the next restart. Errors are shown in the “Sample Switch Output” on page 68.
Configuring the Dell Networking Switch Through a Network Connection
A Management IP address has been configured so that a network connection can made to any of
the standard 1 Gb ports (or 10 Gb port if the module is installed) on the Dell Networking switch.
The Avid switch configuration file groups the 1 Gb Ethernet ports as members of a VLAN that
responds to the IP address of 192.168.255.254 (S25 or S60) or 192.168.255.253 (S4810). Use
the Management IP address to modify the switch configuration file through a network
connection.
The Avid configuration on the Dell Networking switch has the Telnet function enabled. If you
n
reload default Dell Networking configuration, the Telnet function is not enabled. The Telnet
function requires a user name (avid) and a password (avid).
To configure the Dell Networking switch through a Telnet connection:
1. Using a laptop (or computer), assign a static IP address of
255.255.255.0
of
2. Connect an Ethernet cable between the Ethernet port on the laptop (or computer) and any 1
Gb Ethernet port on the switch.
3. Make sure your switch is powered on.
4. From the laptop (or computer), click Start > Run.
5. Type
6. You are prompted for a user name, type
7. You are prompted for a password, type
Telnet 192.168.255.254
management IP address if it has been changed, and press
to the network adapter (NIC) in the laptop (or computer).
(S25 or S60) or 192.168.255.253 (S4810) or the current
avid
.
avid
.
192.168.255.1
Enter
.
and a Netmask
Configuring the Dell Networking Switch Through the Serial Port
A serial connection can be used to access the Dell Networking switch configuration file. This is
done with an Ethernet cable and the following.
• A laptop (or computer) connected to the Console port of the Dell Networking switch
• A terminal emulation application such as xterm, Terminator, or PuTTY
• A standard Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors at either end and long enough to reach
between the computer and the Dell Networking switch
• RJ-45 to DB-9 adapter (included with the Dell Networking switch)
64
Page 69

Accessing the Dell Networking Switch
arm
D
23
24
21
22
STA
CK ID
USB console port
To configure the Dell Networking switch through a serial connection:
1. Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the Console port of the Dell Networking switch.
- The Dell Networking S25 switch uses a standard RJ-45 console port located on the left
side of front panel.
Dell Networking S25 Switch — Console Port
- The Dell Networking S4810 switch uses a custom RJ-45 port on the right side of the
switch.
- The Dell Networking S60 switch ships with a USB adapter that plugs into a console port
on the right rear of the switch.
Dell Networking S60 Switch — Console Port
2. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the RJ-45 to DB-9 adapter (included with the
switch) and plug the DB-9 adapter into the serial port on your laptop (or computer).
3. Start your terminal emulation program.
4. Follow your the on screen instructions selecting a COM port with the following settings for
your serial connection.
In most systems, the serial port uses COM1.
n
65
Page 70

Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration
Option Setting
Bits per second 9600
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration
Access the Dell Networking switch console as previously described either through a serial or
Telnet (management IP address) connection, and do the following.
The Dell Networking switch configuration file can be seen by accessing the switch console,
en
entering enable mode (typing
The default Dell Networking configuration is not the same as the Avid default configuration. If
n
you reload the default configuration according to the Dell Networking documentation, you will
not get the Avid default configuration.
), and typing in the command
show run
.
The Dell Networking documentation also has a reference to a router ISIS mode. This ISIS mode
is not associated with Avid ISIS.
Restoring From Flash Memory
A copy of the Avid configuration file is saved in the flash memory of the Dell Networking
switch.
To copy the Avid configuration file from flash memory in the switch:
1. From the System Director, use your terminal emulation or telnet into the switch.
en
2. Type
3. You are prompted for a password, type
4. Type
A message displays stating “File with the same name already exist. Proceed to copy the file
[confirm yes/no]:” type
If the copy is successful, you see the following: (number of “!” and bytes copied could vary
slightly):
.
Copy flash://avid-default startup-config
yes
avid
and press Enter.
66
.
.
Page 71

!!
6982 bytes successfully copied
5. Type Y.
Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration
6. Type
7. You are sometimes prompted to save, type
8. When asked to reload, type
When the Dell Networking S25 switch restarts, a Disconnected message appears; log back in
n
before continuing.
9. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type en.
10. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type
11. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type
12. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type
13. Manually reapply any switch changes you might have applied during your initial switch
A sample output when restoring from flash is provided; see “Sample Switch Output” on page 68.
n
Reload
setup.
.
No
.
Yes
.
Wr mem
Reload
Yes
.
.
.
67
Page 72

Sample Switch Output
The following is a sample of the switch output displayed when viewed thorough your terminal
emulation program or telnet.
ISIS_Force10>en Password:
ISIS_Force10#copy flash://avid-default startup-config
File with same name already exist.
Proceed to copy the file [confirm yes/no]: yes
!
1346 bytes successfully copied
ISIS_Force10# reload
System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: no
Proceed with reload [confirm yes/no]: yes
00:04:28: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %CHMGR-5-RELOAD: User request to reload the
chassis
Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration
U-Boot
[The switch is restarted and displays System Boot information.]
.
.
.
[At the end of the restart several error messages are displayed. This is
normal and varies, depending if the 10 Gb modules are installed on your
switch.]
ISIS_Force10# untagged TenGigabitEthernet 0/25-26
% Error: Value out of range at "^" marker.
ISIS_Force10# untagged TenGigabitEthernet 0/27-28
% Error: Value out of range at "^" marker.
ISIS_Force10# untagged TenGigabitEthernet 1/25-26
% Error: Value out of range at "^" marker.
68
Page 73

Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration
ISIS_Force10# untagged TenGigabitEthernet 1/27-28
% Error: Value out of range at "^" marker.
Avid ISIS Force10 Base Configuration Version V1.4 4/8/2010
ISIS_Force10>
ISIS_Force10>en
Password:
ISIS_Force10#wr mem
00:03:42: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %FILEMGR-5-FILESAVED: Copied running-config to
startup-config in flash by default
ISIS_Force10#
ISIS_Force10#reload
Proceed with reload [confirm yes/no]: yes
00:03:59: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %CHMGR-5-RELOAD: User request to reload
U-Boot
[The switch is restarted and displays System Boot information.]
.
.
.
Avid ISIS Force10 Base Configuration Version V1.4 4/8/2010
% Info: For the global pre-defined buffer profile to take effect, please
save the config and reload the system.
ISIS_Force10>00:00:28: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %SEC-5-LOGIN_SUCCESS: Login
successful for user on line console
00:00:32: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %IFMGR-5-OSTATE_UP: Changed interface state to up:
Gi 0/24
00:00:32: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %IFMGR-5-ACTIVE: Changed Vlan interface state to
active: Vl 10
00:00:32: %STKUNIT0-M:CP %IFMGR-5-OSTATE_UP: Changed interface state to up:
Vl 10
69
Page 74

ISIS_Force10>
Restoring From the Avid Software Kit
This section describes how to restore the Avid default Dell Networking switch configuration to
your switch from the ftp folder on your ISIS | 5500 System Director. The procedure in this
section assumes the following:
• The System Director has been setup and the Avid ISIS software has been installed.
• The switch is connected to the ISIS environment.
• The IP Address on the ISIS | 5500 Engines are configured with the default values
(192.168.255.11, 13, 14, 16 for 1 Gb or 192.168.255.21 for 10 Gb)
The Avid default configuration files (avid-default) are also located on the Avid ISIS software
n
installer kit [drive]:\Switch Configuration\ISIS 5000\Dell Networking\. The configuration files
are text files that can be viewed using an application such as WordPad. You should upgrade your
switch to the latest configuration file found in the ISIS software kit.
To copy the Avid configuration file from the Avid software kit to the switch:
1. On System Director copy the Avid supplied Dell Networking configuration file:
Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration
From — [Avid software kit]:
Networking\
C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Avid ISIS Shared\ftp\
To —
switch folder
\Switch Configuration\ISIS 5000\Dell
2. From the System Director, use your terminal emulation or telnet into switch.
en
3. Type
4. You are prompted for a password, type
.
avid
.
5. Copy the new configuration (replace “S25” with “S60” or “S4810” in the following path if
using the S60 or S4810 switch).
t For 1 Gb type “
avid-default startup-config
t For 10 Gb type “
avid-default startup-config
When asked to confirm the file copy type
copy ftp://administrator:is-admin@192.168.254.11/
”
copy ftp://administrator:is-admin@192.168.254.21/
”
yes
and press Enter.
If the copy is successful, you see the following:
(number of “!” and bytes copied could vary slightly)
!!
2831 bytes successfully copied
6. Type
Reload
.
70
Page 75

Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration
7. You are sometimes prompted to save, type No.
Yes
8. When asked to reload, type
When you perform a reload the Dell Networking S25 switch restarts, you see a Disconnected
n
message, and have to log back in before continuing.
9. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type en.
.
10. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type
11. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type
12. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type
13. Manually reapply any switch changes you might have applied during your initial switch
setup
Wr mem
Reload
Yes
.
.
.
Turning on Flow Control in the Dell Networking S25 Switch
The Avid default Dell Networking S25N and S25P (fiber) switch configurations do not have
Flow Control turned on. Flow Control is needed to support ISIS | 5500 10 Gb clients. Use the
following procedure to turn on Flow Control in the Dell Networking switch.
Avid is turning rx and tx on in the Forece10 S25 switch, but the Forec10 S60 and S4810 switches
n
have rx
To turn on Flow Control:
on
with tx
1. Use your terminal emulation or telnet into switch.
2. Type
3. You are prompted for a password, type
4. Type
5. Type
en
conf
Int range tengigabitethernet 0/25 - 28
off
in the Avid default configuration.
.
avid
.
.
.
Depending on your Dell Networking S25 switch module options, one of the following
command would be used in place of this step.
t Left 10 Gb module installed (numbered right to left, facing rear)
tengigabitethernet 0/27 - 28
t Right 10 Gb module installed (numbered right to left, facing rear)
tengigabitethernet 0/25 - 26
t Right stacking module installed (numbered right to left, facing rear)
tengigabitethernet 1/25 - 26
6. Type
flowcontrol rx on tx on threshold 1024 1024 1054
.
.
.
71
Int range
Int range
Int range
.
Page 76

Restoring the Avid Dell Networking Configuration
The following steps turn the port off and back on to enable the change. Make sure this isn't an
n
interface from which you are gaining remote access because you will be disconnected.
7. Type
8. Type
9. Type
10. Type
11. Type
12. Type
To confirm the setting change, look for the “Flowcontrol rx on tx on” entry:
shut
.
no shut
exit
.
exit
.
wr mem
exit
.
.
.
1. Type en.
avid
2. You are prompted for a password, type
3. Type
sho int tengigabitethernet 0/25
.
(port number depends on optional modules).
Information similar to the following should display, verify “Flowcontrol rx on tx on” is
included in the configuration:
TenGigabitEthernet 0/25 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is Dell NetworkingEth, address is 00:01:e8:d6:84:7b
Current address is 00:01:e8:d6:84:7b
Pluggable media present, XFP type is 10GBASE-SR
Medium is MultiRate, Wavelength is 850.00nm
XFP receive power reading is -4.0994dBm
Interface index is 40436228
Internet address is not set
MTU 1554 bytes, IP MTU 1500 bytes
LineSpeed 10000 Mbit
Flowcontrol rx on tx on
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 4w5d1h
Queueing strategy: fifo
Input Statistics:
4372398864 packets, 5575634120385 bytes
645279553 64-byte pkts, 15320069 over 64-byte pkts, 30588757 over
127-byte pkts
72
Page 77

Customize the Uplink on the Dell Networking Switch
7206136 over 255-byte pkts, 59117205 over 511-byte pkts, 3614887144
over 10
23-byte pkts
693485 Multicasts, 34501 Broadcasts
0 runts, 0 giants, 682022 throttles
0 CRC, 0 overrun, 0 discarded
Output Statistics:
8393098546 packets, 12349453356270 bytes, 0 underruns
155227351 64-byte pkts, 26414194 over 64-byte pkts, 54970467 over
127-byte pkts
47132113 over 255-byte pkts, 8010284 over 511-byte pkts, 8101344137
over 10
23-byte pkts
151510 Multicasts, 283941 Broadcasts, 8392663095 Unicasts
0 throttles, 0 discarded, 0 collisions
Rate info (interval 299 seconds):
Input 00.00 Mbits/sec, 0 packets/sec, 0.00% of line-rate
Output 00.00 Mbits/sec, 1 packets/sec, 0.00% of line-rate
Customize the Uplink on the Dell Networking Switch
This section describes how to customize the Dell Networking switch configuration to uplink to
your house network. The procedure in this section assumes the following:
• The System Director has been setup and the Avid ISIS software has been installed.
• The Dell Networking switch is currently running with the “avid-default” configuration
loaded and has not been modified.
• The Avid ISIS is connected to the Dell Networking switch using either the 1 Gb or 10 Gb
connection.
• The IP Address on the ISIS | 5500 Engine are configured with the default values
(192.168.255.11, 13, 14, 16 for 1 Gb or 192.168.255.21 for 10 Gb)
You might need to change the IP address on the ISIS | 5500 Engines and clients when
n
customizing your uplink in these procedures.
73
Page 78

Customize the Uplink on the Dell Networking Switch
Network Setup Requirements
You need to obtain following information from your corporate Information Technology (IT)
department before you customize your Dell Networking uplink:
• Uplink IP address for Vlan or Port IP address/subnet mask
______.______.______.______ /_____ (slash notation for subnet mask)
• Vlan IP address for local subnet ______.______.______.______ /_____ (slash notation for
subnet mask)
• Switch's default gateway Address ______.______.______.______
• (Optional) DHCP server (ip helper addresses)
- First: ______.______.______.______
- Second: ______.______.______.______
• Static IP addresses for each Avid ISIS Engine; four IP addresses for the 1 Gb connections,
one IP addresses per Engine for the 10 Gb connections)
• Port on a corporate network switch to connect the Dell Networking switch
Configure Dell Networking Switch for Uplink On the Dell Networking S25
After you have obtained the information previously listed for from your corporate administrator,
configure the Dell Networking switch as using the following procedure.
To copy the Avid configuration file from flash memory in the switch:
1. On System Director copy the Avid supplied Dell Networking configuration file:
From — [Avid software kit]:
Networking\
C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Avid ISIS Shared\ftp\
To —
switch folder
\Switch Configuration\ISIS 5000\Dell
2. Make a copy of the “avid-port-uplink” or “avid-vlan-uplink” file in the same folder and
name it “custom-config.”
a. Choose “avid-port-uplink” if you want to use a single port with one IP address to uplink.
b. Choose “avid-vlan-uplink” if you want to use a VLAN with routing enabled.
3. Edit the copied file, using the information above from IT (preferably using wordpad.exe
instead of notepad.exe)
a. Set Uplink IP address in “int gig 0/24” or “int vlan 110” depending on the type chosen
in Step 2.
b. In “int Vlan 10” set the following:
- ISIS Vlan IP address
74
Page 79

Customize the Uplink on the Dell Networking Switch
- (Optional) Set the ip helper addresses
c. Set the IP route from 10.10.10.1 to your default gateway.
d. Increment Local Version number.
4. Save the file.
5. Telnet to the switch via 192.168.255.254 (S25 or S60) or 192.168.255.253 (S4810) or use
serial Use your terminal emulation connection.
avid
6. You are prompted for a user, type
7. You are prompted for a password, type
en
8. Enter enable mode, type
.
9. You are prompted for a password, type
.
avid
avid
.
.
10. Copy the new configuration (replace “S25” with “S60” or S4810 in the following path if
using the S60 or S4810 switch).
t For 1 Gb type “
ftp://administrator:is-admin@192.168.254.11/custom-config
startup-config
t For 10 Gb type “
ftp://administrator:is-admin@192.168.254.21/custom-config
startup-config
When asked to confirm the file copy type
copy
”
copy
”
yes
and press Enter.
If the copy is successful, you see the following:
(number of “!” and bytes copied could vary slightly)
!!
2831 bytes successfully copied
11. Type
12. You are sometimes prompted to save, type
13. When asked to reload, type
When you perform a reload the Dell Networking S25 switch restarts, you see a Disconnected
n
message, and have to log back in before continuing.
Reload
.
No
.
Yes
.
14. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type en.
15. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type
Wr mem
.
16. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type
17. (Dell Networking S25 only) Type
Reload
Yes
.
75
.
Page 80

Customize the Uplink on the Dell Networking Switch
18. Manually reapply any switch changes you might have applied during your initial switch
setup
19. Connect an Ethernet cable (Cat6) from port 24 of the Dell Networking switch, to the switch
port provided by your IT department.
Be sure to set the Gateway, DNS, and any other settings as specified by your IT department. This
n
cannot be done through the Avid “Network Configuration Tool” and must be done manually
through the Windows controls.
Changing the IP Address Associated with the VLAN
The Avid default Dell Networking switch configuration includes a VLAN with an IP address of
192.168.255.254/24
following procedure to reassign the IP address on the Dell Networking switch.
You might need to change the IP address on the ISIS | 5500 Engine and the clients when doing
n
this procedure.
To change the IP Address of the VLAN:
1. Use your terminal emulation or telnet into switch.
. If this IP address conflicts with your corporate network, use the
en
2. Type
3. You are prompted for a password, type
4. Type
5. Type
6. Type
The IP address replaces the default
n
192.168.10.2/24
The
with your network.
7. Type
8. Type
9. Type
10. Type
11. Type
12. Type
13. Type
.
conf
.
int vlan 10
ip address 192.168.10.2/24
untagged gi 0/1-24
untagged te 0/25-28
no shut
exit
exit
wr mem
exit
.
.
.
.
.
avid
.
.
.
192.168.255.254/24
is an example and you need to assign an address that does not conflict
.
.
IP address to
192.168.10.2/24
.
76
Page 81

Customize the Uplink on the Dell Networking Switch
You cannot assign an IP address or untagged ports to VLAN 1 because it is the default VLAN on
n
the switch. To assign an IP address and untagged ports to a VLAN, you need to create a new
VLAN.
Changing the IP Address Associated with the Corporate Uplink
To set the IP Address for the corporate uplink:
1. Use your terminal emulation or telnet into switch.
en
2. Type
3. You are prompted for a password, type
4. Type
.
conf
avid
.
.
5. Type
6. Type
7. Type
8. Type
9. Type
10. Type
You cannot assign an IP address to a port if that switch port is enabled. Adding an IP address to
n
an enabled switch port makes it a layer 2 port.
int gig 0/1
ip address 192.168.10.1/24
no shut
exit
.
wr mem
exit
.
.
.
.
.
Changing Buffer Pool to a Single Queue
To create single queue:
1. Use your terminal emulation or telnet into switch.
en
2. Type
3. You are prompted for a password, type
4. Type
5. Type
6. Type
.
conf
.
buffer-profile global 1q
exit
.
avid
.
.
7. Type
8. Type
9. Type
wr mem
Reload
Yes
.
.
.
77
Page 82

Customize the Uplink on the Dell Networking Switch
Removing/Adding Ports Associated with a VLAN
To add ports associated with a VLAN:
1. Use your terminal emulation or telnet into switch.
en
2. Type
3. You are prompted for a password, type
4. Type
.
conf
avid
.
.
5. Type
6. Type
7. Type
8. Type
9. Type
10. Type
To remove ports associated with a VLAN:
int vlan x
untagged gig 0/a-0/b (where a and b are the port numbers)
exit
.
exit
.
wr mem
Yes
.
(where x is the VLAN number).
.
1. Use your terminal emulation or telnet into switch.
en
2. Type
3. You are prompted for a password, type
4. Type
5. Type
6. Type
7. Type
8. Type
9. Type
10. Type
.
avid
.
conf
.
int vlan x
no untagged gig 0/a-0/b (where a and b are the port numbers)
exit
.
exit
.
wr mem
Yes
.
(where x is the VLAN number).
.
.
.
Creating a Link Aggregation
To creating a link aggregation:
1. Use your terminal emulation or telnet into switch.
en
2. Type
3. You are prompted for a password, type
4. Type
5. Type
.
conf
.
interface port-channel 10
78
.
avid
.
Page 83

Customize the Uplink on the Dell Networking Switch
6. Type
7. Type
8. Type
9. Type
10. Type
11. Type
12. Type
13. Type
14. Type
15. Type
no shutdown
switchport
channel-member gig 0/22-23
exit
.
int vlan 10
untagged port-channel 10
exit
.
exit
.
wr mem
Yes
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Setting Up IP-Helper Addresses for DHCP
To use DHCP on the clients that are connected to the Avid Production switch you must add an IP
Helper Address to each VLAN. The IP Helper Address points the hosts to the DHCP Server that
is on the house network.
To add an IP Helper Address:
1. Use your terminal emulation or telnet into switch.
2. Type
en
3. You are prompted for a password, type
4. Type
5. Type
6. Type
conf
int vlan n
ip helper-address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
DHCP server)
7. Type
8. Type
9. Type
10. Type
exit
exit
wr mem
Yes
Upgrading FTOS
To upgrade the ftos (Dell Networking operating system):
1. Type en.
2. Type
upgrade system tftp://tftp_server_ip_address/ftos_file_name
.
avid
.
.
(where n is the VLAN)
(where x's equals the IP address of the
.
.
.
79
Page 84

Cascading Dell Networking Switches in an ISIS Environment
3. Type
4. Type
Reload
Yes
.
.
Upgrading U-Boot
To upgrade the u-boot (universal bootloader):
1. Type en.
2. Type
3. Type
4. Type
upgrade boot tftp://tftp_server_ip_address/u-boot_file_name
Reload
Yes
.
.
Cascading Dell Networking Switches in an ISIS
Environment
Depending on the quantity of available 10 Gb ports on the core (upstream) switch and the
bandwidth/resilience required, multiple switches can be cascaded from the core switch.
For example, an S4810 switch using eight 10 Gb ports can be connected to four S25N switches
with 20 Gb aggregate interconnects. The same switch with four 10 Gb ports can cascade two
S25N switches, each using a single 10 Gb uplink, while connecting two ISIS | 5500 Engines.
The following provides guidance on cascaded switch configurations supported in the Avid
ISIS | 5500 environment using Dell Networking switches:
• Dell Networking S25N cascaded from a core Dell Networking S4810, S60, or S25N switch
• Dell Networking S60 cascaded from a core Dell Networking S4810, S60, or S25N switch
• Dell Networking S4810 cascaded from a core Dell Networking S60, S25N, S4810 switch
When cascading switches:
1. Attach the ISIS to the first switch.
2. Before connecting the second 10 Gb cables, Telnet or serial to the second switch.
3. You are prompted for a user name/password, default is avid/avid.
en
4. Type
5. You are prompted for a password, type
6. Type
7. Type
8. Type
.
avid
conf
.
int vlan 10
ip address 192.168.255.253/24
.
80
.
.
Page 85

Cascading Dell Networking Switches in an ISIS Environment
9. Type
10. Type
exit
exit
.
.
11. Attach the 10 Gb cable to the second switch.
To test:
1. Attach a client and assign it an IP address in the proper subnet.
2. Ping client from the ISIS system.
The following is a typical example of cascaded switches using ISIS | 5500.
81
Page 86

4 Cisco Switches
This section describes the procedures for configuring and recovering the Cisco switch in the
Avid ISIS environment. Avid has qualified the Cisco Catalyst
Cisco switches do not come preconfigured with Avid configurations. All Cisco switches need to
be configured for your environment by your network administrator.
Sample Avid configuration files for Cisco 4900M and 4948E switches are included in the
Installer link of the Management Console.
The Avid configuration file is provided in the Avid ISIS software kit in the following location:
n
[drive]:\Switch Configuration\ISIS x000\Cisco\49xx\
Accessing the Cisco Switch
The Avid configuration in the Cisco switch supports the following configurations:
• A single Cisco switch supports up to 48 1 Gb clients.
- A Catalyst 4900M comes with 8 x 10 Gb ports and supports a maximum of 40 x 1 Gb
ports.
- A Catalyst 4948E and Catalyst 4948-10GE comes with 48 x 1 Gb copper ports and 4 x
10 Gb/1 Gb optical ports (a cascaded configuration is shown in
Configuration” on page 87
• A cascaded Cisco switch configuration supports up to 88 clients (see
Configuration” on page 87
).
).
®
4900M and 4948E switches. The
.
“Sample Cisco Switch
“Sample Cisco Switch
• When using an additional Engine (second Avid ISIS Engine), a 10 Gb connection is required
between the Cisco switch and Engines.
The 10 Gb connection requires the optional 10 Gb modules to be installed in the switch. For
n
information on installing the 10 Gb modules in the Cisco switch, see the Cisco documentation.
Two methods for accessing the switch are described in the following sections.
“Configuring the Cisco Switch Through the Serial Port” on page 83
•
• “Configuring the Cisco Switch Through a Network Connection” on page 88
Page 87

Configuring the Cisco Switch Through the Serial Port
Configuring the Cisco Switch Through the Serial
Port
A serial connection can be used to access the Cisco switch configuration file. This is done with
an Ethernet cable and the following.
• A laptop (or computer) connected to the Console port of the Cisco switch
• A terminal emulation application such as xterm, Terminator, or PuTTY
• A standard (straight through) Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors at either end and long
enough to reach between the computer and the Cisco switch
• RJ-45 to DB-9 adapter (included with the Cisco switch)
To configure the Cisco switch through a serial connection:
1. Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the Console port of the Cisco switch. The Console
port is a standard RJ-45 port located on the right side of the Cisco switch front panel.
2. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the serial port on your laptop (or computer).
The RJ-45 to DB-9 adapter might be needed.
3. Start your terminal emulation program.
4. Follow your the on screen instructions selecting a COM port with the following settings for
your serial connection.
In most systems, the serial port uses COM1.
n
Option Setting
Bits per second 9600
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
Cisco Password
An Avid password is not set by default on the Cisco switches. You must use a console connection
as Telnet is disabled by default. You must enter “enable” mode before setting the password using
the “Enable Secret” command in configuration mode.
83
Page 88

To set a password on the Cisco switches:
1. Connect using the Console port of the switch.
Loading the Avid Cisco Configuration
2. SwitchHostName >
3. SwitchHostName#
4. SwitchHostName(config)#
The enable secrete “password” is now set to
Without an enable secret password, the Cisco switch will not accept a Telnet connection.
n
Cisco Password Examples
Method Command
Console password to Cisco Router(config)#
When logging synchronous is enabled on a
console, all status messages are displayed on a new
line.
Set a Telnet password Router(config)#
en
conf t
enable secret mypassword
mypassword
Router(config-line)#
Router(config-line)#
Router(config-line)#
Router(config-line)#
Router(config-line)#
.
line con 0
line vty 0 4
login
password cisco
logging synchronous
login
password cisco
Set the enable password to Cisco Router(config)#
Set the enable secret password to peter.
This password overrides the enable password and
is encrypted within the config file.
Router(config)#
enable password cisco
enable secr peter
Loading the Avid Cisco Configuration
Access the Cisco switch console as previously described either through a serial or Telnet
(management IP address) connection, and do the following.
The Cisco switch configuration file can be seen by accessing the switch console, entering enable
en
mode (typing
), and typing in the command
84
show run
.
Page 89

The default Cisco configuration is not the same as the Avid default configuration. If you reload
n
the default configuration according to the Cisco documentation, you will not get the Avid default
configuration.
Restoring From the Avid Software Kit
This section describes how to restore the Avid default Cisco switch configuration to your switch
from the ftp folder on your System Director. The procedure in this section assumes the
following:
• The System Director has been setup and the Avid ISIS software has been installed.
• The switch is connected to the ISIS environment.
• The IP Address on the ISIS | 5500 Engines are configured with the default values
(192.168.255.11, 13, 14, 16 for 1 Gb or 192.168.255.21 for 10 Gb)
The Avid default configuration files are also located on the Avid ISIS software installer kit
n
[drive]:\Switch Configuration\ISIS x000\Cisco\. These are text files that can be viewed using an
application such as WordPad. Copy the switch configuration files to an ftp directory if you want
to access the file using the switch.
To copy the Avid configuration file from the Avid software kit to the switch:
Loading the Avid Cisco Configuration
1. From the System Director, use your terminal emulation program or telnet into the switch.
en
2. Type
3. Copy the new configuration.
t For 4900 type “
t For 4948 type “
When asked to confirm the file copy type
If the copy is successful, you see the following on the C4900M switch:
Accessing ftp://administrator:is-admin@10.105.52.2/ThirdParty/Cisco/
4900/Cisco4900_dual2...
Loading ThirdParty/Cisco/4900/Cisco4900_dual2 !
OK - 6396/4096 bytes]
6396 bytes copied in 5.100 secs (1254 bytes/sec)
4. Type
5. You are sometimes prompted to save, type
6. When asked to reload, type
.
copy ftp://administrator:is-admin@192.168.254.11/
ThirdParty/Cisco/4900/Cisco4900_dual2 startup-config
copy ftp://administrator:is-admin@192.168.254.21/
ThirdParty/Cisco/4948/Cisco4948e_dual1 startup-config
yes
and press Enter.
Reload
.
No
.
Yes
.
”
”
85
Page 90

Loading the Avid Cisco Configuration
When you perform a reload the switch restarts, you see a Disconnected message, and have to log
n
back in before continuing.
7. Type en.
8. Manually reapply any switch changes you might have applied during your initial switch
setup
Changing the IP Address Associated with the VLAN
Use the following procedure to assign the IP address on the Cisco switch.
To change the IP Address of the VLAN:
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
2. SwitchHostName >
3. SwitchHostName#
4. SwitchHostName(config)#
5. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
(where x's equals IP address and y's equals subnet mask)
6. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
7. SwitchHostName(config-if)# exit
8. SwitchHostName(config)# exit
9. SwitchHostName#
10. SwitchHostName#
en
conf t
copy run start
exit
Network Setup Requirements
Obtain the following information from your corporate Information Technology (IT) department
before you customize your Cisco uplink:
• Uplink IP address for Vlan or Port IP address/subnet mask
______.______.______.______ ______.______.______.______
• Vlan IP address for local subnet
______.______.______.______ ______.______.______.______
int vlan ww
ip address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
no shut
(where ww is for the VLAN)
• Switch's default gateway Address ______.______.______.______
• (Optional) DHCP server (ip helper addresses)
- First: ______.______.______.______
- Second: ______.______.______.______
86
Page 91

Loading the Avid Cisco Configuration
• Static IP addresses for each Avid ISIS Engine; four IP addresses for the 1 Gb connections,
one IP addresses per Engine for the 10 Gb connections
• Port on a corporate network switch to connect the Cisco switch
Uplinking Your Cisco Switch to the Corporate Network
The following procedure sets the IP address for the corporate uplink on the Cisco switch using a
route link.
To set the IP address for the corporate uplink:
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
2. SwitchHostName >
3. SwitchHostName #
4. SwitchHostName(config)#
5. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
6. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
en
conf t
interface Gi x/y
no switchport
ip address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
(where x's equals IP address and y's equals subnet mask)
7. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
8. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
9. SwitchHostName#
10. SwitchHostName#
copy run start
exit
no shut
end
.
Sample Cisco Switch Configuration
Multiple switches can be cascaded from the core switch depending on the quantity of available
10 Gb ports on the core switch (upstream) and the bandwidth/resilience required.
For example, an C4900M switch has more 10 Gb aggregate interconnects, where a C4948E and
C4948-10GE do not provide as many 10 Gb ports.
The following illustration is a sample switch configuration using the C4900M and C4948E
switches. It includes four Engines using 10 Gb links and up to 88 1 Gb clients.
(where x/y is for the unit/port number)
87
Page 92

1 Gb
clients
1 Gb
clients
Engines 1 Gb Clients
Up to 4 Up to 88
10 Gb
connections
Aggregated
link
Configuring the Cisco Switch Through a Network Connection
Configuring the Cisco Switch Through a Network
Connection
After you have configured the Cisco switch with a network IP address, use the Management IP
address to modify the switch configuration file through a network connection.
88
Page 93

To configure the Cisco switch through a Telnet connection:
Adding Ports Associated to a VLAN
1. Using a laptop (or computer), assign a static IP address of
255.255.255.0
of
to the network adapter (NIC) in the laptop (or computer).
2. Connect an Ethernet cable between the Ethernet port on the laptop (or computer) and any 1
Gb Ethernet port on the switch.
3. Make sure your switch is powered on.
4. From the laptop (or computer), click Start > Run.
5. Type
Telnet 192.168.255.25x
(or the current management IP address) and press
The Avid ISIS | 5500 configuration files use the following IP addresses.
t 4900 — Telnet 192.168.255.253
t 4948 — Telnet 192.168.255.254
6. Enter the user name and password you might have set for the switch; see “Cisco Password”
on page 83
.
Adding Ports Associated to a VLAN
To add a single port to a VLAN:
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
2. SwitchHostName >
en
192.168.255.1
and a Netmask
Enter
.
3. SwitchHostName #
4. SwitchHostName(config)#
5. SwitchHostName(config-if-range)#
6. SwitchHostName(config-if-range)#
conf t
int gigabitEthernet 1/x
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan x
which you want to assign)
7. SwitchHostName(config-if-range)#
8. SwitchHostName(config)#
9. SwitchHostName#
To add multiple ports to a VLAN:
copy run start
exit
exit
.
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
2. SwitchHostName >
3. SwitchHostName #
4. SwitchHostName(config)#
en
conf t
int range gigabitEthernet 1/x-y
starting and ending ports)
89
(where x is the port number)
(where x is the VLAN to
(where x and y are
Page 94

Setting Up IP-Helper Addresses for DHCP
5. SwitchHostName(config-if-range)#
6. SwitchHostName(config-if-range)#
which you want to assign)
7. SwitchHostName(config-if-range)#
8. SwitchHostName(config)#
9. SwitchHostName#
copy run start
exit
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan x
exit
.
(where x is the VLAN to
Setting Up IP-Helper Addresses for DHCP
To use DHCP on the clients that are connected to the Avid Production switch you must add an IP
Helper Address to each VLAN. The IP Helper Address points the hosts to the DHCP Server that
is on the house network.
To add an IP Helper Address:
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
2. SwitchHostName >
3. SwitchHostName #
4. SwitchHostName(config)#
5. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
the IP address of the DHCP server)
en
conf t
int vlan n
ip helper-address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
(where n is the VLAN)
(where x's equals
6. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
7. SwitchHostName(config)#
8. SwitchHostName#
Repeat these step for each VLAN that requires an IP-Helper.
n
copy run start
exit
exit
.
Enabling or Disabling IP Routing
If the “No IP Routing” command does not show up in the show run output then IP Routing is
enabled. This would be located in the upper portion of the show run output. Here is an example
from a Cisco C4948E and C4948-10GE where IP Routing is Disabled:
!
version 12.2
no service pad
90
Page 95

service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
service compress-config
!
hostname Switch
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
vtp mode transparent
Enabling or Disabling IP Routing
ip subnet-zero
no ip routing
To enable IP routing:
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
2. SwitchHostName >
3. SwitchHostName #
4. SwitchHostName(config)#
5. SwitchHostName(config)#
6. SwitchHostName#
To disable IP routing:
en
conf t
ip routing
exit
.
copy run start
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
2. SwitchHostName >
3. SwitchHostName #
4. SwitchHostName(config)#
5. SwitchHostName(config)#
en
conf t
no ip routing
exit
.
91
Page 96

Creating an EtherChannel (Link Aggregation)
Creating an EtherChannel (Link Aggregation)
With the Cisco C4948E and C4948-10GE switches you can create multiple EtherChannels (link
aggregation) with up to eight ports. The C4948E and C4948-10GE switch configuration B and
configuration E files provided by Avid use ports 45 to 48 for this function.
Depending on what you are connecting to the EtherChannel, you might have to change the load
balancing algorithm of the switch on the other end. Also consider the type of link aggregation
protocol used on the link. For example, if you are connecting to a Cisco EtherChannel, change
the load balancing to support source-destination IP address. In this example a range of ports is
assigned to a VLAN and an Ether Channel (Layer 2) created.
Use the same procedure for creating 10 Gb EtherChannel groups that connect to ISIS.
n
To create a link aggregation:
1. Use your terminal emulation program or telnet into switch.
2. SwitchHostName >
3. SwitchHostName #
4. SwitchHostName(config)#
5. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
6. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
7. SwitchHostName(config-if)#
8. SwitchHostName(config)#
range of ports)
9. SwitchHostName(config-if-range)#
port-channel number)
10. SwitchHostName(config-if-range)#
11. SwitchHostName(config)#
12. SwitchHostName(config)#
13. SwitchHostName#
14. SwitchHostName#
The following is information on the Cisco 6509 Etherchannel Configuration for use with 10 Gb
ISIS link aggregation:
en
conf t
int port-channel x
switchport
switchport access vlan n
exit
int range GigabitEthernet 1/a-b
channel-group x mode on
exit
port-channel load-balance src-dst-ipxit
exit
copy run start
exit
(where x is the port-channel number)
(where n is the VLAN number)
(where a and b are a
(where x is the
Mode on is the simplest of aggregation methods and with the least features, this variant of link
n
aggregation is used by ISIS.
92
Page 97

interface Port-channel10
switchport
switchport access vlan 10
switchport mode access
no ip address
interface TenGigabitEthernet1/1
description v10 ISIS echannel
switchport
switchport access vlan 10
switchport mode access
no ip address
channel-group 10 mode on
interface TenGigabitEthernet1/2
Creating an EtherChannel (Link Aggregation)
description v10 ISIS echannel
switchport
switchport access vlan 10
switchport mode access
no ip address
channel-group 10 mode on
Additional information:
• In the previous example, Channel-group 10 was used. Make the proper channel group
assignment for your site.
• The Cisco 6509 defaults to using a “source/destination” IP load balancing algorithm, which
is required by Avid. This should not have to be changed.
To verify the current load-balancing algorithm use the following command on the 6509 console:
Cisco 6509 # show etherchannel load-balance
EtherChannel Load-Balancing Configuration:
93
Page 98

Upgrading the IOS on Cisco Switches
src-dst-ip
mpls label-ip
Upgrading the IOS on Cisco Switches
This procedure differs slightly from the one documented by Cisco. Cisco Catalyst 4948-10GE
switches supplied by Avid are configured with a Configuration Register value of 0x2101, which
means the switch boots from the first IOS that appears in bootflash. Cisco instructs you to set the
Configuration Register to 0x2102, which means the switch will look for a boot string that points
to the IOS from which to boot. The following procedure is based on Avid’s current shipping
product.
To update the IOS:
1. Use the
dir bootflash
: command to ensure that there is sufficient space in Flash memory
to store the PROM upgrade image. In most cases there will only be one file in bootflash,
which leaves plenty of space for the new file. If there is insufficient space, delete one or
more images, and then issue the
squeeze bootflash
: command to reclaim the space. For
example:
- SwitchHostName#
- SwitchHostName#
2. Download the <filename> program into Flash memory using the
delete bootflash:<filename.bin>
squeeze bootflash:
copy tftp
command. For
Example:
- SwitchHostName#
copy tftp bootflash:
- Address or name of remote host [172.20.58.78]?
- Source filename [<filename>]?
- Destination filename [<filename>]?
3. Use the
config-register
command to set the configuration register to 0x2101. For
Example:
- SwitchHostName#
- SwitchHostName(config)#
- SwitchHostName(config)#
- SwitchHostName#
configure terminal
config-register 0x2101
exit
write
- Building configuration...
- Compressed configuration from 3723 to 1312 bytes [OK]
4. Archive the previous IOS image in case you need to re-apply at a later time. For example:
94
Page 99

Upgrading the IOS on Cisco Switches
- SwitchHostName#
copy bootflash: tftp:
- Source filename []? <filename.bin>
- Address or name of remote host []? 172.20.98.3
- Destination filename [<filename.bin>]?
5. Delete the old IOS images, and then issue the
squeeze bootflash
the space. For example:
- SwitchHostName#
- SwitchHostName#
delete bootflash:<filename.bin>
squeeze bootflash:
6. Once the squeeze is complete (it will take a few minutes), enter the
reset the switch and load the software. For example:
- SwitchHostName#
Use the
show version
reload
command to verify that the new Cisco IOS release is operating on
the switch.
: command to reclaim
reload
command to
95
Page 100

5 Brocade Switches
This section describes provides information on Brocade switches (formerly known as Foundry
switches) that have been qualified in the ISIS | 7500 environment.
The Brocade configuration files provided in the Avid ISIS software kit in the following location:
n
[drive]:\Switch Configuration\ISIS 7000\Foundry_Brocade\X4242XG\
“foundryX4242XG” files in the folder are the same configuration files used in the newer
Brocade FESX624 switch.
Foundry/Brocade FESX624 and FESX424 2XG
The Foundry/Brocade FESX624 and FESX424 2XG switches have been qualified in ISIS | 7500
and ISIS | 5500 environments and may be used with ISIS | 2500 with customized configuration
files (not supplied by Avid).
Configuring the Foundry/Brocade Switch Through the Serial Port
Access the switch console through Telnet (management IP address), TFTP connection (see
“TFTP” on page 35, or a serial connection. The serial management interface enables you to
configure and manage the device using a third-party terminal emulation application (such as
xterm, Terminator, or PuTTY) on a directly connected PC. A straight-through EIA/TIA DB-9
serial cable (M/F) ships with the device.
. The
To configure the Foundry/Brocade switch through a serial connection:
1. Connect one end of the serial cable to the Console port of the Foundry/Brocade switch. The
serial management interface (the port labeled Console) is located in the left corner of the
front panel.
2. Connect the other end of the serial cable to your laptop (or computer).
3. Start your terminal emulation program.
4. Follow your the on screen instructions selecting a COM port with the following settings for
your serial connection.
In most systems, the serial port uses COM1.
n
 Loading...
Loading...