Page 1

Avid® Interplay® Media Services
Setup and User’s Guide
Version 2.3
Page 2

Legal Notices
Product specifications are subject to change without notice and do not represent a commitment on the part of Avid Technology,
Inc.
This product is subject to the terms and conditions of a software license agreement provided with the software. The product
may only be used in accordance with the license agreement.
Avid products or portions thereof are protected by one or more of the following United States Patents: 5,267,351; 5,309,528;
5,355,450; 5,396,594; 5,440,348; 5,467,288; 5,513,375; 5,528,310; 5,557,423; 5,577,190; 5,584,006; 5,640,601; 5,644,364;
5,654,737; 5,724,605; 5,726,717; 5,745,637; 5,752,029; 5,754,851; 5,799,150; 5,812,216; 5,828,678; 5,842,014; 5,852,435;
5,986,584; 5,999,406; 6,038,573; 6,141,007; 6,211,869; 6,532,043; 6,546,190; 6,596,031; 6,747,705; 6,763,523; 6,766,357;
6,847,373; 7,081,900; 7,403,561; 7,433,519; 7,555,557; 7,562,099; D352,278; D372,478; D373,778; D392,267; D392,268;
D392,269; D395,291; D396,853; D398,912. Other patents are pending.
Avid products or portions thereof are protected by one or more of the following European Patents: 0506870; 0635188;
0674414; 0752174; 1111910; 1629675. Other patents are pending.
Avid products or portions thereof are protected by one or more of the following United States Patents: 5,267,351; 5,309,528;
5,355,450; 5,396,594; 5,440,348; 5,467,288; 5,513,375; 5,528,310; 5,557,423; 5,577,190; 5,584,006; 5,640,601; 5,644,364;
5,654,737; 5,715,018; 5,724,605; 5,726,717; 5,745,637; 5,752,029; 5,754,851; 5,799,150; 5,812,216; 5,828,678; 5,842,014;
5,852,435; 5,987,501; 6,223,211; 6,532,043; 6,546,190; 6,747,705; 6,763,523. Other patents are pending.
Avid products or portions thereof are protected by one or more of the following European Patents: 0506870; 0635188;
0674414; 0752184; 1111910. Other patents are pending.
This document is protected under copyright law. An authorized licensee of Avid Interplay Media Services may reproduce this
publication for the licensee’s own use in learning how to use the software. This document may not be reproduced or
distributed, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes, such as selling copies of this document or providing support or
educational services to others. This document is supplied as a guide for Avid Interplay Media Services. Reasonable care has
been taken in preparing the information it contains. However, this document may contain omissions, technical inaccuracies, or
typographical errors. Avid Technology, Inc. does not accept responsibility of any kind for customers’ losses due to the use of
this document. Product specifications are subject to change without notice.
Copyright © 2010 Avid Technology, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The following disclaimer is required by Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics, Inc. for the use of their TIFF library:
Copyright © 1988–1997 Sam Leffler
Copyright © 1991–1997 Silicon Graphics, Inc.
Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and sell this software [i.e., the TIFF library] and its documentation for any purpose
is hereby granted without fee, provided that (i) the above copyright notices and this permission notice appear in all copies of
the software and related documentation, and (ii) the names of Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics may not be used in any
advertising or publicity relating to the software without the specific, prior written permission of Sam Leffler and Silicon
Graphics.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS-IS” AND WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR
OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL SAM LEFFLER OR SILICON GRAPHICS BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE,
DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER OR NOT ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF DAMAGE, AND ON ANY THEORY OF
LIABILITY, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
The following disclaimer is required by the Independent JPEG Group:
This software is based in part on the work of the Independent JPEG Group.
This Software may contain components licensed under the following conditions:
Copyright (c) 1989 The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms are permitted provided that the above copyright notice and this paragraph
are duplicated in all such forms and that any documentation, advertising materials, and other materials related to such
distribution and use acknowledge that the software was developed by the University of California, Berkeley. The name of the
University may not be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written
permission. THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED ``AS IS'' AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES,
INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
2
Page 3

Copyright (C) 1989, 1991 by Jef Poskanzer.
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby
granted, provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission
notice appear in supporting documentation. This software is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
Copyright 1995, Trinity College Computing Center. Written by David Chappell.
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby
granted, provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission
notice appear in supporting documentation. This software is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
Copyright 1996 Daniel Dardailler.
Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and sell this software for any purpose is hereby granted without fee, provided that
the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear in
supporting documentation, and that the name of Daniel Dardailler not be used in advertising or publicity pertaining to
distribution of the software without specific, written prior permission. Daniel Dardailler makes no representations about the
suitability of this software for any purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
Modifications Copyright 1999 Matt Koss, under the same license as above.
Copyright (c) 1991 by AT&T.
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software for any purpose without fee is hereby granted, provided that this
entire notice is included in all copies of any software which is or includes a copy or modification of this software and in all
copies of the supporting documentation for such software.
THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY. IN PARTICULAR,
NEITHER THE AUTHOR NOR AT&T MAKES ANY REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY OF ANY KIND CONCERNING THE
MERCHANTABILITY OF THIS SOFTWARE OR ITS FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
This product includes software developed by the University of California, Berkeley and its contributors.
The following disclaimer is required by Nexidia Inc.:
© 2010 Nexidia Inc. All rights reserved, worldwide. Nexidia and the Nexidia logo are trademarks of Nexidia Inc. All other
trademarks are the property of their respective owners. All Nexidia materials regardless of form, including without limitation,
software applications, documentation and any other information relating to Nexidia Inc., and its products and services are the
exclusive property of Nexidia Inc. or its licensors. The Nexidia products and services described in these materials may be
covered by Nexidia's United States patents: 7,231,351; 7,263,484; 7,313,521; 7,324,939; 7,406,415, 7,475,065; 7,487,086
and/or other patents pending and may be manufactured under license from the Georgia Tech Research Corporation USA.
The following disclaimer is required by Paradigm Matrix:
Portions of this software licensed from Paradigm Matrix.
The following disclaimer is required by Ray Sauers Associates, Inc.:
“Install-It” is licensed from Ray Sauers Associates, Inc. End-User is prohibited from taking any action to derive a source code
equivalent of “Install-It,” including by reverse assembly or reverse compilation, Ray Sauers Associates, Inc. shall in no event be
liable for any damages resulting from reseller’s failure to perform reseller’s obligation; or any damages arising from use or
operation of reseller’s products or the software; or any other damages, including but not limited to, incidental, direct, indirect,
special or consequential Damages including lost profits, or damages resulting from loss of use or inability to use reseller’s
products or the software for any reason including copyright or patent infringement, or lost data, even if Ray Sauers Associates
has been advised, knew or should have known of the possibility of such damages.
The following disclaimer is required by Videomedia, Inc.:
“Videomedia, Inc. makes no warranties whatsoever, either express or implied, regarding this product, including warranties with
respect to its merchantability or its fitness for any particular purpose.”
“This software contains V-LAN ver. 3.0 Command Protocols which communicate with V-LAN ver. 3.0 products developed by
Videomedia, Inc. and V-LAN ver. 3.0 compatible products developed by third parties under license from Videomedia, Inc. Use
of this software will allow “frame accurate” editing control of applicable videotape recorder decks, videodisc recorders/players
and the like.”
The following disclaimer is required by Altura Software, Inc. for the use of its Mac2Win software and Sample
Source Code:
©1993–1998 Altura Software, Inc.
3
Page 4

The following disclaimer is required by Ultimatte Corporation:
Certain real-time compositing capabilities are provided under a license of such technology from Ultimatte Corporation and are
subject to copyright protection.
The following disclaimer is required by 3Prong.com Inc.:
Certain waveform and vector monitoring capabilities are provided under a license from 3Prong.com Inc.
The following disclaimer is required by Interplay Entertainment Corp.:
The “Interplay” name is used with the permission of Interplay Entertainment Corp., which bears no responsibility for Avid
products.
This product includes portions of the Alloy Look & Feel software from Incors GmbH.
This product includes software developed by the Apache Software Foundation (http://www.apache.org/).
© DevelopMentor
This product may include the JCifs library, for which the following notice applies:
JCifs © Copyright 2004, The JCIFS Project, is licensed under LGPL (http://jcifs.samba.org/). See the LGPL.txt file in the Third
Party Software directory on the installation CD.
Avid Interplay contains components licensed from LavanTech. These components may only be used as part of and in
connection with Avid Interplay.
Portions © Copyright 2003-2007 of MOG Solutions.
Attn. Government User(s). Restricted Rights Legend
U.S. GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. This Software and its documentation are “commercial computer software” or
“commercial computer software documentation.” In the event that such Software or documentation is acquired by or on behalf
of a unit or agency of the U.S. Government, all rights with respect to this Software and documentation are subject to the terms
of the License Agreement, pursuant to FAR §12.212(a) and/or DFARS §227.7202-1(a), as applicable.
Trademarks
003, 192 Digital I/O, 192 I/O, 96 I/O, 96i I/O, Adrenaline, AirSpeed, ALEX, Alienbrain, AME, AniMatte, Archive, Archive II,
Assistant Station, AudioPages, AudioStation, AutoLoop, AutoSync, Avid, Avid Active, Avid Advanced Response, Avid DNA,
Avid DNxcel, Avid DNxHD, Avid DS Assist Station, Avid Liquid, Avid Media Engine, Avid Media Processor, Avid MEDIArray,
Avid Mojo, Avid Remote Response, Avid Unity, Avid Unity ISIS, Avid VideoRAID, AvidRAID, AvidShare, AVIDstripe, AVX,
Axiom, Beat Detective, Beauty Without The Bandwidth, Beyond Reality, BF Essentials, Bomb Factory, Boom, Bruno, C|24,
CaptureManager, ChromaCurve, ChromaWheel, Cineractive Engine, Cineractive Player, Cineractive Viewer, Color Conductor,
Command|24, Command|8, Conectiv, Control|24, Cosmonaut Voice, CountDown, d2, d3, DAE, Dazzle,
Dazzle Digital Video Creator, D-Command, D-Control, Deko, DekoCast, D-Fi, D-fx, Digi 003, DigiBase, DigiDelivery,
Digidesign, Digidesign Audio Engine, Digidesign Development Partners, Digidesign Intelligent Noise Reduction,
Digidesign TDM Bus, DigiLink, DigiMeter, DigiPanner, DigiProNet, DigiRack, DigiSerial, DigiSnake, DigiSystem,
Digital Choreography, Digital Nonlinear Accelerator, DigiTest, DigiTranslator, DigiWear, DINR, DNxchange, DPP-1, D-Show,
DSP Manager, DS-StorageCalc, DV Toolkit, DVD Complete, D-Verb, Eleven, EM, Euphonix, EUCON, EveryPhase, Expander,
ExpertRender, Fader Pack, Fairchild, FastBreak, Fast Track, Film Cutter, FilmScribe, Flexevent, FluidMotion, Frame Chase,
FXDeko, HD Core, HD Process, HDPack, Home-to-Hollywood, HYBRID, HyperControl, HyperSPACE, HyperSPACE HDCAM,
iKnowledge, Image Independence, Impact, Improv, iNEWS, iNEWS Assign, iNEWS ControlAir, Instantwrite, Instinct,
Intelligent Content Management, Intelligent Digital Actor Technology, IntelliRender, Intelli-Sat,
Intelli-sat Broadcasting Recording Manager, InterFX, Interplay, inTONE, Intraframe, iS Expander, ISIS, IsoSync, iS9, iS18,
iS23, iS36, ISIS, IsoSync, KeyRig, KeyStudio, LaunchPad, LeaderPlus, LFX, Lightning, Link & Sync, ListSync, LKT-200, Lo-Fi,
Luna, MachineControl, Magic Mask, Make Anything Hollywood, make manage move | media, Marquee, MassivePack,
Massive Pack Pro, M-Audio, M-Audio Micro, Maxim, Mbox, Media Composer, MediaFlow, MediaLog, MediaMatch, MediaMix,
Media Reader, Media Recorder, MEDIArray, MediaServer, MediaShare, MetaFuze, MetaSync, MicroTrack, MIDI I/O, Midiman,
Mix Rack, MixLab, Moviebox, Moviestar, MultiShell, NaturalMatch, NewsCutter, NewsView, Nitris, NL3D, NLP, Nova,
NRV-10 interFX, NSDOS, NSWIN, Octane, OMF, OMF Interchange, OMM, OnDVD, Open Media Framework,
Open Media Management, Ozone, Ozonic, Painterly Effects, Palladium, Personal Q, PET, Pinnacle, Pinnacle DistanTV,
Pinnacle GenieBox, Pinnacle HomeMusic, Pinnacle MediaSuite, Pinnacle Mobile Media, Pinnacle Scorefitter, Pinnacle Studio,
Pinnacle Studio MovieBoard, Pinnacle Systems, Pinnacle VideoSpin, Podcast Factory, PowerSwap, PRE, ProControl,
ProEncode, Profiler, Pro Tools LE, Pro Tools M-Powered, Pro Transfer, Pro Tools, QuickPunch, QuietDrive,
Realtime Motion Synthesis, Recti-Fi, Reel Tape Delay, Reel Tape Flanger, Reel Tape Saturation, Reprise, Res Rocket Surfer,
Reso, RetroLoop, Reverb One, ReVibe, Revolution, rS9, rS18, RTAS, Salesview, Sci-Fi, Scorch, Scorefitter, ScriptSync,
SecureProductionEnvironment, Serv|LT, Serv|GT, Session, Shape-to-Shape, ShuttleCase, Sibelius, SIDON, SimulPlay,
SimulRecord, Slightly Rude Compressor, Smack!, Soft SampleCell, Soft-Clip Limiter, Solaris, SoundReplacer, SPACE,
SPACEShift, SpectraGraph, SpectraMatte, SteadyGlide, Streamfactory, Streamgenie, StreamRAID, Strike, Structure,
4
Page 5

Studiophile, SubCap, Sundance Digital, Sundance, SurroundScope, Symphony, SYNC HD, Synchronic, SynchroScope,
SYNC I/O, Syntax, TDM FlexCable, TechFlix, Tel-Ray, Thunder, Titansync, Titan, TL Aggro, TL AutoPan, TL Drum Rehab,
TL Everyphase, TL Fauxlder, TL In Tune, TL MasterMeter, TL Metro, TL Space, TL Utilities, tools for storytellers, Torq,
Torq Xponent, Transfuser, Transit, TransJammer, Trigger Finger, Trillium Lane Labs, TruTouch, UnityRAID, Vari-Fi, Velvet,
Video the Web Way, VideoRAID, VideoSPACE, VideoSpin, VTEM, Work-N-Play, Xdeck, X-Form, Xmon, XPAND!, Xponent,
X-Session, and X-Session Pro are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Avid Technology, Inc. in the United States
and/or other countries.
Adobe and Photoshop are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States
and/or other countries. Apple and Macintosh are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other
countries. Windows is either a registered trademark or trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other
countries. All other trademarks contained herein are the property of their respective owners.
Avid Interplay Media Services Setup and User’s Guide • 0130-07633-05 Rev C • December 2010 • This document is
distributed by Avid in online (electronic) form only, and is not available for purchase in printed form.
5
Page 6

6
Page 7

Contents
Using This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Symbols and Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
If You Need Help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Viewing User Guides on the Interplay Portal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Avid Training Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Chapter 1 Working with the Avid Interplay Media Services System. . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Understanding the Interplay Media Services System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Media Services Engine Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Understanding the Media Services Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Understanding the Avid Interplay Media Services and Transfer Status Tool . . . 23
Understanding the Various Media Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Check Lists for Setting Up and Using Service Providers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Configuration Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Chapter 2 Interplay Media Services Engine Installation and Configuration . . . . . 29
Check List for Setting Up the Media Services Engine. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Registering the Media Services Engine in an Avid Interplay Workgroup . . . . . . . . . 30
Configuring the Media Services Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Starting the Interplay Media Services Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Chapter 3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Opening the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Using the Jobs Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Jobs Page Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Customizing the Reporting of Service Job Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Customizing the Jobs Page Columns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Filtering the Jobs List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Viewing Details About a Job. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Job Details Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Purging the Jobs List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
7
Page 8

Prioritizing a Job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Canceling a Job. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Deleting a Job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Retrying a Job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Exporting the Jobs List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Using the Providers Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Opening the Providers Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Customizing the Providers Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Viewing Details About a Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Deleting Providers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Using the Services Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Opening the Services Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Displaying Details About a Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Deleting a Media Services Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Using the Users Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Opening the Users Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Setting Up User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Reassigning Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Deleting User Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Chapter 4 Installing Services and Registering Providers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Understanding Service Descriptions and Service Packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Installing a Service Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Registering the Provider. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Connecting a Provider to the Media Services Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Starting the Service Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Verifying That a Service Provider Is Connected. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Rules for Upgrading a Service and Preserving Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Chapter 5 Working with Media Services Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Understanding Media Services Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Creating a Service Provider Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Modifying Multiple Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Modifying Changed or New Options in a Profile. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
8
Page 9

Chapter 6 Working with the Transcode Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Understanding the Transcode Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Check List for Transcoding Assets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Installing and Registering the Transcode Service Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Installing the Transcode Service Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Registering the Transcode Provider. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Connecting the Transcode Provider to the Media Services Engine . . . . . . . . . . 88
Starting the Transcode Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Creating a Interplay Transcode Service Profile. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Transcode Profile Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
WHOLE Mode - Transcode Profile Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
CONSOLIDATE Mode - Transcode Profile Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
MIXDOWN Mode - Transcode Profile Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
DUALMIXDOWN Mode - Transcode Profile Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Mapping of Audio Tracks in MIXDOWN and DUALMIXDOWN Modes . . . . . . 100
Mapping Multichannel Audio Tracks in Transcode Mixdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Understanding the Transcode Services Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Understanding MIXDOWN Mode During the Transcode Process . . . . . . . . . . 105
Understanding the DUALMIXDOWN Mode During the Transcode Process . . 107
Transcoding an Asset from Avid Interplay Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Transcoding an Asset from an Avid Editing Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Transcoding OMF Clips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Working with an Auto Transcode Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Preparing the Workgroup for Auto Transcode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Configuring the Auto Transcode Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Verifying that the Auto Transcode Service is Running . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Identifying an Auto Transcode Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Transcoding Avid Assets Using an Auto Transcode Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Location of Automatically Transcoded Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Chapter 7 Working with the Archive and Restore Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Understanding Archive and Restore Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Check List for Archiving and Restoring Assets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Archive Configuration and Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
9
Page 10

Installing and Registering the Archive Service Provider and Restore Service Provider.
127
Installing the Archive and Restore Service Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Registering the Archive Provider or the Restore Provider. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Connecting the Archive Provider or Restore Provider to the Media Services Engine
132
Starting the Archive Provider or the Restore Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Configuring the Archive Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Specifying the Archive Server, Segment Size, and Restore Process . . . . . . . 136
Archiving Duplicate Versions of Media . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Adding AAF Metadata to an Archive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Defining the Maximum Number of Simultaneous Jobs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Overriding Metadata When You Archive an Asset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Connecting to the Archive Database and Creating Folders in Interplay Access . . 141
Working with Interplay Archive and Interplay Restore Profiles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Creating an Interplay Archive or Interplay Restore Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Interplay Archive Profile and Interplay Restore Profile Options. . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Locating the Partition Value for an Archive Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Archiving Assets from an Avid Editing Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Consolidating Clips and Sequences Before an Archive Operation . . . . . . . . . 152
Deleting Online Media After an Archive Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Archiving Assets Using Avid Interplay Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Working with an Auto Archive Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Preparing the Workgroup for Auto Archive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Configuring Auto Archive Using the Avid Service Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Verifying That the Auto Archive Service is Running . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Setting Up an Auto Archive Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Archiving Assets Using an Auto Archive Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Location of Automatically Archived Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Searching the Archive Database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Restoring a Clip from the Archive Database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
10
Page 11

Working with Partial Restore. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Performing a Partial Restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Viewing Partially Restored Reference Tracks in Interplay Access. . . . . . . . . . 172
How the System Defines the Size of a Partially Restored File. . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Chapter 8 Working with the Stream Publish Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Understanding the Stream Publish Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Workflows for Creating Streaming Media . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Workflow for Creating Streaming Media from MPEG-4 Proxy Media. . . . . . . . 177
Workflow for Creating Streaming Media from H.264 Proxy Media. . . . . . . . . . 180
Check List for Stream Publish Workflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Installing and Registering the Stream Publish Service Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Installing the Stream Publish Service Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Registering the Stream Publish Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Connecting the Stream Publish Provider to the Media Services Engine . . . . . 190
Starting the Stream Publish Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Creating a Stream Publish Service Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Manually Creating QuickTime Reference Movies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
Deleting QuickTime Reference Movies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
Stream Publishing Media During Ingest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Automatically Publishing Streaming Media During Ingest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Manually Publishing Streaming Media During Ingest. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Setting the Maximum Number of Concurrent Stream Publish Jobs . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Chapter 9 Automating the Stream Publish Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Understanding the Auto Publish Workflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Check List for Auto Publish Workflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Verifying the Workflow Engine Database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Allowing Internet Explorer to Access the Avid Interplay Workflow Engine
Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Importing Auto-Publish Flow Charts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Modifying the Flow Chart Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
Chapter 10 Working with the Copy Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Understanding the Copy Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Workflow for Copying Metadata and Media Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
11
Page 12

Check List for Copying Assets to Another Workgroup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
Installing and Registering the Copy Service Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Installing the Copy Service Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Registering the Copy Provider. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Connecting the Copy Provider to the Media Services Engine. . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Starting the Copy Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Using an Interplay Copy Service Profile. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
Creating an Interplay Copy Service Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
Interplay Copy Service Profile Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Copying Assets and Media to Another Workgroup Using Interplay Access. . . . . . 234
Copying Assets and Media to Another Workgroup Using an Avid Editing Application. .
237
Copying Assets During Ingest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Setting Registry Keys for Copying During Ingest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
Chapter 11 Automatically Copying Assets to Another Workgroup . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Understanding the Auto-Copy Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Check List for the Auto-Copy Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
Installing the Avid Interplay Auto-Copy Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
Configuring the Auto-Copy Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
Verifying the Auto-Copy Service is Running . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
Understanding the Auto-Copy Folder Process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
Rules of Auto-Copy Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
Identifying an Auto-Copy Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
Automatically Copying Assets To Another Workgroup Using an Auto-Copy Folder 254
Automatically Backing Up the Complete Database and Media . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
Changing the Number of Auto-Copy Replication Jobs Submitted. . . . . . . . . . 257
Resetting the Auto-Copy Replication Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
Chapter 12 Working with the Move Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
Understanding the Move Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
Workflow for Moving Media to Another Workspace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
Check List for Moving Assets to Another Workspace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
12
Page 13

Installing and Registering the Move Service Provider. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
Installing the Avid Interplay Move Service Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
Registering the Move Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
Connecting the Move Provider to the Media Services Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
Starting the Move Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
Creating a Avid Interplay Move Service Profile. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
Moving Media to Another Workspace Using Interplay Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
Chapter 13 Working with the Delivery Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
Understanding the Delivery Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
Check List for the Delivery Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
Registering the Delivery Receiver in an Avid Interplay Workgroup. . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
Installing and Registering the Delivery Service Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
Installing the Delivery Service Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
Registering the Delivery Provider. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
Connecting the Delivery Provider to the Media Services Engine . . . . . . . . . . . 290
Starting the Delivery Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
Creating an Avid Interplay Delivery Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 294
Transferring Assets through Interplay Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
Transferring Assets through an Avid Editing System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
Viewing the Transfer Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298
Verifying the Delivery Receiver Service is Running Using Avid Service Framework . .
300
Monitoring the Health of the Interplay Delivery Receiver Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 301
Overriding Delivery of Already Existing Media Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
Chapter 14 Exporting and Transferring Long GOP OP1a Media in the Background .
305
Understanding Long GOP OP1a and STP Encode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 305
Workflow for Background Processing of Long GOP Splicing and Transferring of Long
GOP OP1a Media . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306
Check List for Transferring Long GOP OP1a Media in the Background. . . . . . . . . 309
Installing and Registering the STP Encode Service Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 310
Installing the Interplay STP Encode Service Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
Registering the Interplay STP Encode Provider. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313
Connecting the STP Encode Provider to the Media Services Engine . . . . . . . 315
13
Page 14

Starting the STP Encode Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
Connecting to the Media Services Engine From Interplay Assist or an Avid Editing Ap-
plication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
Connecting to the Media Services Engine from Interplay Assist. . . . . . . . . . . 319
Connecting to the Media Services Engine from an Avid Editing Application. . 319
Performing a Send to Playback as a Background Process from Interplay Assist . 320
Performing a Send-to-Playback as a Background Process from an Avid Editing Appli-
cation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 322
Chapter 15 Working with the ProEncode Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
Understanding ProEncode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
Check List for Using ProEncode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
Setting Up ProEncode Client and Providers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 328
Configuring the ProEncode Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 328
ProEncode Provider Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
Creating an Interplay ProEncode Provider Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
Setting Up a ProEncode Client. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
Installing the ProEncode Client Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
Configuring a ProEncode Client on an Avid Editing Application . . . . . . . . . . . 332
Setting up a Standalone ProEncode Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
Encoding a Clip or a Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
Sharing Folders in an Avid Shared-Storage Environment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
Sending a Clip or Sequence to ProEncode from an Avid Editing
Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
Adding a File to ProEncode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
Monitoring the Encoding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
ProEncode Provider Post-to-Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
Check List for ProEncode Provider Post-to-Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
Configuring Telestream FlipFactory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
Creating a FlipFactory Administrator Account for ProEncode. . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
Creating a Factory for the ProEncode Account. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
Preparing Java for Avid NewsPoller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 352
14
Page 15

Appendix A Installing Encoding Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 353
Anystream Agility Workgroup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 353
Check List for Installing Anystream Agility Workgroup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
Installing the Anystream Agility Workgroup Software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 355
Uninstalling the GLOBEtrotter FlexID and Sentinel Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 355
Telestream FlipFactory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
Installing Telestream FlipFactory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
Configuring Telestream FlipFactory for Avid Shared-Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Appendix B Troubleshooting Interplay Media Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
General Troubleshooting for Media Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
Checking Media Services Log Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
Troubleshooting Using Avid Diagnostics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 362
Archive and Restore Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
Finding Solutions to Specific Archive and Restore Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
Compatibility of Archive and Restore Services and Third-Party Software . . . . 365
Getting Information About an Archive Job from the Jobs Page . . . . . . . . . . . . 366
Getting Information About an Archive Job from the Log File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 366
How the Media Services Status Tool Reports Archive and Restore Operations . .
366
Archive and Restore Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
Manually Updating the Status of Media Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
ProEncode Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
Using a HOSTS File for Media Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
Understanding the HOSTS File (Windows) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
Updating the HOSTS File (Windows). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 378
Appendix C Media Supported by Partial Restore and Interplay Delivery . . . . . . . . 379
Appendix D AVC-Intra Resolutions Supported by the Interplay Media Services . . 381
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
15
Page 16

16
Page 17

Using This Guide
Congratulations on your purchase of the Avid® Interplay® Media Services system consisting
of the Interplay Media Services Engine, the Interplay Media Services and Transfer Status
Tool, and the media services.
The Media Services Engine lets you take advantage of a network environment and pass
compute-intensive tasks to other workstations on your network. This allows video editors to
stay focused on their editing tasks.
For example, today’s production houses face a rising demand for translating media into
formats suitable for distribution via the Web, DVD, or CD-ROM — often at the same time.
The encoding operation is a critical part of this work. By moving or distributing this
operation to lower cost, dedicated workstations, editing workstations are free to perform
other tasks allowing you to generate two streams of revenue-producing work in parallel.
The Interplay Media Services Engine and its Media Services and Transfer Status Tool are
the keys to managing these resource-intensive process. This software infrastructure manages
all of the Interplay Media Services. As Avid develops new Media Services services, the
Media Services Engine will manage those services as well.
This guide is intended for all Interplay Media Services users, from beginning to advanced.
Unless noted otherwise, the material in this document applies to the Windows
Mac OS
on a Windows system, but the information applies to both Windows and Mac OS X systems.
Where differences exist, both Windows and Mac OS X screen shots are shown.
The documentation describes the features and hardware of all models. Therefore, your
n
system might not contain certain features and hardware that are covered in the
documentation.
®
X operating systems. The majority of screen shots in this document were captured
®
and
Page 18
Symbols and Conventions
Avid documentation uses the following symbols and conventions:
Symbol or Convention Meaning or Action
n
c
w
> This symbol indicates menu commands (and subcommands) in the
(Windows), (Windows
only), (Macintosh), or
(Macintosh only)
Bold font Bold font is primarily used in task instructions to identify user interface
Italic font Italic font is used to emphasize certain words and to indicate variables.
Courier Bold font
A note provides important related information, reminders,
recommendations, and strong suggestions.
A caution means that a specific action you take could cause harm to
your computer or cause you to lose data.
A warning describes an action that could cause you physical harm.
Follow the guidelines in this document or on the unit itself when
handling electrical equipment.
order you select them. For example, File > Import means to open the
File menu and then select the Import command.
This symbol indicates a single-step procedure. Multiple arrows in a list
indicate that you perform one of the actions listed.
This text indicates that the information applies only to the specified
operating system, either Windows or Macintosh OS X.
items and keyboard sequences.
Courier Bold font identifies text that you type.
18
Ctrl+key or mouse action Press and hold the first key while you press the last key or perform the
mouse action. For example, Command+Option+C or Ctrl+drag.
Page 19

If You Need Help
If you are having trouble using your Avid product:
1. Retry the action, carefully following the instructions given for that task in this guide. It
is especially important to check each step of your workflow.
2. Check the latest information that might have become available after the documentation
was published:
- If the latest information for your Avid product is provided as printed release notes,
they are shipped with your application and are also available online.
- If the latest information for your Avid product is provided as a ReadMe file, it is
supplied on your Avid installation CD or DVD as a PDF document
(README_product.pdf) and is also available online.
You should always check online for the most up-to-date release notes or ReadMe
because the online version is updated whenever new information becomes
available. To view these online versions, select ReadMe from the Help menu, or visit
the Knowledge Base at www.avid.com/readme.
3. Check the documentation that came with your Avid application or your hardware for
maintenance or hardware-related issues.
If You Need Help
4. Visit the online Knowledge Base at www.avid.com/onlinesupport. Online services are
available 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. Search this online Knowledge Base to find
answers, to view error messages, to access troubleshooting tips, to download updates,
and to read or join online message-board discussions.
Viewing User Guides on the Interplay Portal
You can quickly access the Interplay user guides from any system in the Interplay
environment.
To open the Interplay Portal web page:
1. Type the following line in your web browser:
http://Interplay_Engine_name
For Interplay_Engine_name substitute the name of the computer running the Interplay
Engine software. For example, the following line opens the portal web page on a system
named docwg:
http://docwg
2. Click the “Avid Interplay Documentation” link to access the User Information
Center page.
19
Page 20

Avid Training Services
Avid makes lifelong learning, career advancement, and personal development easy and
convenient. Avid understands that the knowledge you need to differentiate yourself is always
changing, and Avid continually updates course content and offers new training delivery
methods that accommodate your pressured and competitive work environment.
For information on courses/schedules, training centers, certifications, courseware, and
books, please visit www.avid.com/support and follow the Training links, or call Avid Sales
at 800-949-AVID (800-949-2843).
20
Page 21

1 Working with the Avid Interplay Media
Services System
The following topics provide an overview of the Interplay Media Services system:
• Understanding the Interplay Media Services System
• Media Services Engine Components
• Understanding the Various Media Services
• Check Lists for Setting Up and Using Service Providers
• Configuration Requirements
Understanding the Interplay Media Services System
The Interplay Media Services system is a software infrastructure on which media services
are layered. Interplay Media Services uses the concept of service providers. A service
provider (or provider) is a software program that can perform a particular service, such as
transcoding media or archiving assets. The Interplay Media Services Engine serves as a
broker for services in an Interplay workgroup.
Avid editing applications allow you to work with clips of any frame rate or field motion type
n
(interlaced or progressive) in a project. Clips that do not match the frame rate or field
motion type of the project are known as mixed-rate clips. Avid Interplay supports working
with mixed-rate clips and sequences with mixed-rate clips.
Media Services Engine Components
The software used to manage service providers is composed of two major components: the
Media Services Engine and the Media Services and Transfer Status tool.
The following topics describe these components:
• Understanding the Media Services Engine
• Understanding the Avid Interplay Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
Page 22
1 Working with the Avid Interplay Media Services System
Understanding the Media Services Engine
The Media Services Engine matches jobs and their corresponding settings with suitable
providers. The Media Services Engine is a repository of job and provider information.
Individual providers select jobs that they are able to process according to the service they
provide.
For example, a Media Composer system (a client) needs a clip transcoded. It sends a request
to the Media Services Engine (the server) with information about the job. The Media
Services Engine places the information in a queue. When a Transcode provider is available
to do the transcoding, it selects the job, gets the information from the Media Services
Engine, and transcodes the media. The Media Services Engine provides status on the job
through the Media Services and Transfer Status tool.
The Media Services Engine should not reside on the same computer as an Avid editing
application. A provider can be installed on the same computer as the Media Services Engine,
depending on the individual provider and the workload and memory usage of the particular
computer.For specific information on configuration requirements, see the Avid Interplay
Software Installation and Configuration Guide.
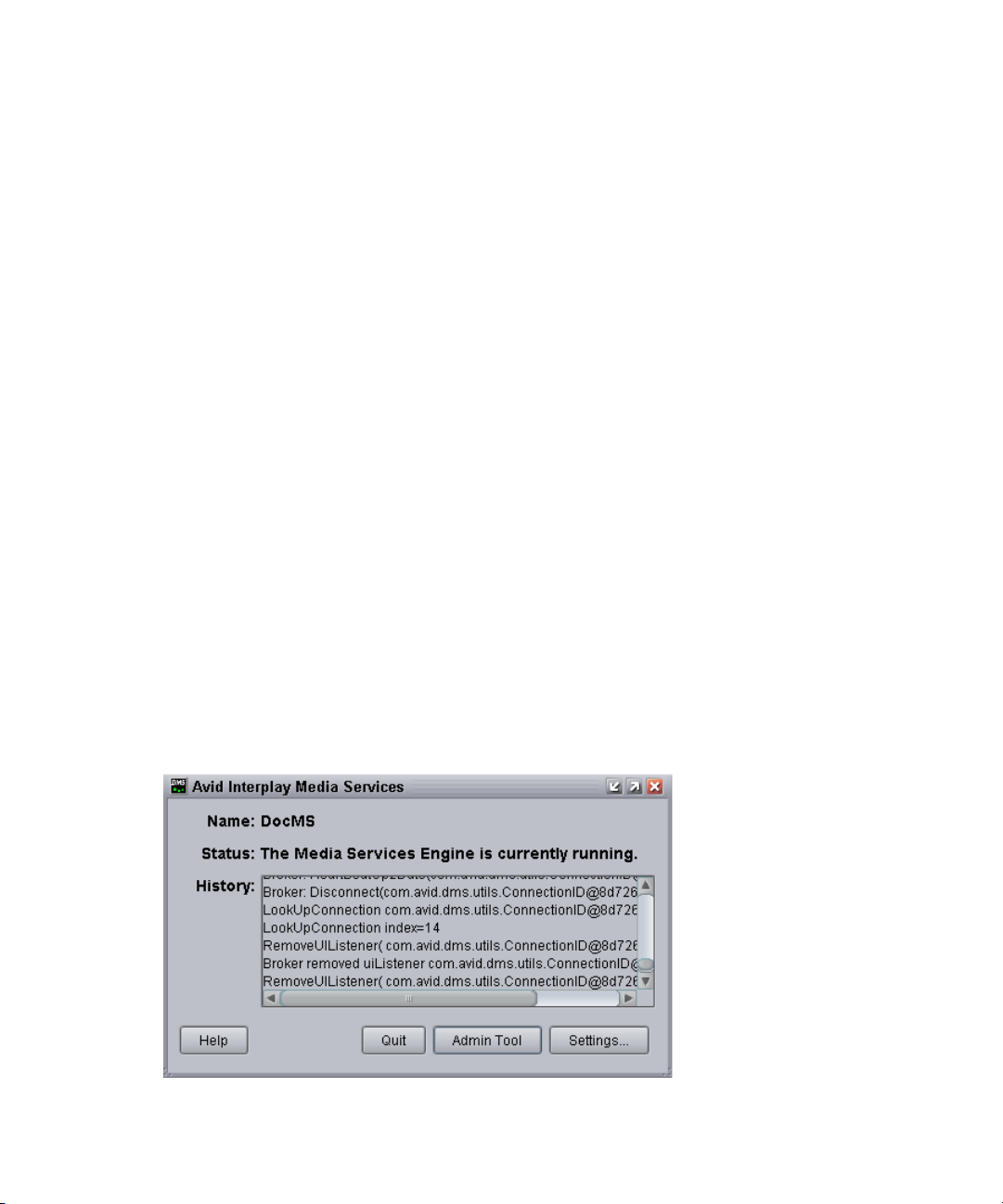
The Avid Interplay Media Services window opens when you start the Media Services
Engine. The window displays current information about the status of the Media Services
Engine, including the host name for the system on which the Media Services Engine resides.
The Media Services Engine uses the host name to identify itself on the network.
22
The following illustration of the Avid Media Services window shows the host name DocMS,
which is the host name of the computer on which the Interplay Media Services Engine is
installed.
Page 23
Media Services Engine Components
The Avid Interplay Media Services window provides access to the Media Services and
Transfer Status tool through the Admin Tool button. See “Understanding the Avid Interplay
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 23.
The Avid Interplay Media Services window also provides access to Interplay Media Services
settings through the Settings button. See “Configuring the Media Services Engine” on
page 33.
For information on starting the Interplay Media Services Engine, see “Starting the Interplay
Media Services Engine” on page 36.
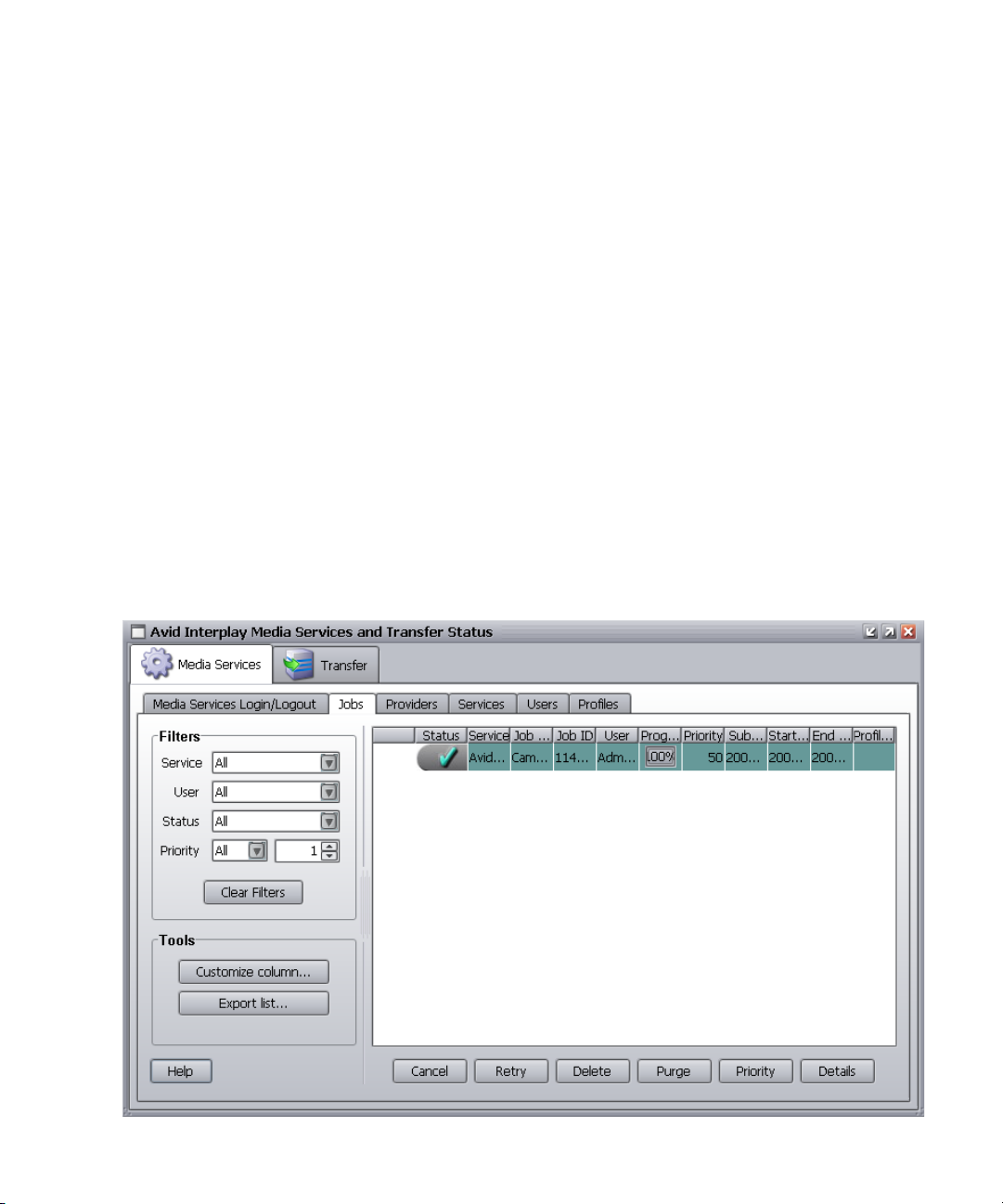
Understanding the Avid Interplay Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
The Avid Interplay Media Services and Transfer Status tool communicates with the Avid
Interplay Media Services Engine to let you manage media services. The Media Services and
Transfer Status tool is installed with the Interplay Media Services Engine software.
The Media Services and Transfer Status tool also includes a tab for monitoring transfers that
use Interplay Transfer. For more information, see the Avid Interplay Transfer Setup and
User’s Guide.
23
Page 24

1 Working with the Avid Interplay Media Services System
The Media Services and Transfer Status tool is installed with the Media Services Engine.
You can install it on another computer from the Individual Optional Installers page of the
Interplay Installation DVD, so that you can manage Interplay Media Services from that
computer. The tool is also installed with Interplay Access, but you need to open the Media
Services Status tab and the Transfer Status tab as separate windows.
The Media Services and Transfer Status tool performs three types of functions:
• Provides detailed information about Media Services, based on lists of jobs, encoders,
profiles, and users.
• Provides controls for managing services and registering providers.
• Provides controls for managing Media Services such as canceling jobs, deleting
provider software, creating or deleting profiles, and creating or deleting users.
The functions you can perform depends on your user rights (see “Using the Users Page” on
page 57). Administrators can perform the following tasks:
• Register and delete providers
• View details on any job
• Delete jobs submitted by any user
• Purge the jobs list
Regular users can perform administrative tasks only on their own jobs.
For more information, see “Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
Understanding the Various Media Services
Interplay Media Services can be distributed to dedicated workstations in a networked
environment, thereby freeing computer resources to perform other tasks.
When you install a Media Services service on a computer, the installation program installs
provider software for that service. You can install the same service on more than one
computer in an Interplay workgroup, and as a result have multiple providers for the same
service.
After you install a service, you use the Media Services and Transfer Status tool to register
the provider of the service. In a workgroup with multiple providers, you need to register
each provider.
The following table lists the services managed by the Media Services Engine.
24
Page 25

Understanding the Various Media Services
The services managed by the Media Services Engine are not limited to the services listed in
n
this table.
Interplay Media Services Service Providers
Service Description
Avid Interplay Transcode service Lets you transcode Avid assets from one Avid-supported resolution
to another. For example, you can use the Avid Interplay Transcode
service to create a low-resolution version of a sequence or master
clip. For more information, see “Working with the Transcode
Service” on page 81.
Avid Interplay Archive service
Avid Interplay Restore service
Avid Interplay Stream Publish service Lets you create QuickTime reference movies that refer to proxy
Avid Interplay Copy service Lets you copy assets (metadata) and their media files from one
Avid Interplay Move service Lets you move media files from one Avid ISIS workspace to another.
Avid Interplay Delivery service Lets you transfer a clip and its media files or only the portion that is
Provides access to archive and restore features. The Avid Interplay
Archive and Restore services manage the process of moving data,
instead of using the Avid Interplay Transfer Engine. For more
information, see “Working with the Archive and Restore Services”
on page 121.
video files (MPEG-4 or H.264) and MPEG1 Level 2 audio files. The
files are checked into the Interplay database so you can play the
assets in the Interplay Access. For more information, see “Working
with the Stream Publish Service” on page 175 and “Automating the
Stream Publish Service” on page 201.
workgroup to another. For more information, see “Working with the
Copy Service” on page 215.
For more information, see “Working with the Move Service” on
page 259.
used in a subclip or a sequence. For more information, see “Working
with the Delivery Service” on page 281.
25
Page 26

1 Working with the Avid Interplay Media Services System
Interplay Media Services Service Providers (Continued)
Service Description
Avid Interplay Auto Media Service
• Auto Archive
• Auto Transcode
• Auto Transfer
• Auto Copy
Avid Interplay STP Encode service Lets you offload time-consuming processing involved in exporting
™
Avid Interplay ProEncode
service Provides integration to AnyStream™ and Telestream for non-Avid
Lets you configure folders and subfolders to perform tasks
automatically. You can use the Avid Service Configuration settings to
configure the various auto media services.
An auto archive and auto transcode operation includes
n
subfolders. An auto transfer operation does not include
subfolders. An auto copy operation maintains the same folder
structure as the source workgroup.
For installation instructions, see the Avid Interplay Software
Installation and Configuration Guide.
and transferring of Long GOP OP1a media, during a
send-to-playback request from the Avid editing application or Avid
Interplay Assist. For more information, see “Exporting and
Transferring Long GOP OP1a Media in the Background” on
page 305.
format transcode services (for example, transcoding from an Avid
resolution to Windows Media File format). For more information, see
“Working with the ProEncode Service” on page 325.
26
Page 27
Check Lists for Setting Up and Using Service Providers
Check Lists for Setting Up and Using Service
Providers
The following table provides a list of the various Media Services service providers with a
reference to the specific check list for each service. These check lists provide a list of the
steps to set up and use the various services.
For a check list for setting up the Interplay Media Services Engine, see “Check List for
Setting Up the Media Services Engine” on page 29.
Media Services Service
Provider Documentation
Interplay Transcode service “Check List for Transcoding Assets” on page 82
Interplay Archive service
Interplay Restore service
Interplay Stream Publish service “Check List for Stream Publish Workflow” on page 183 and
Interplay Copy service “Check List for Copying Assets to Another Workgroup” on
Interplay Move service “Check List for Moving Assets to Another Workspace” on
Interplay Delivery service “Check List for the Delivery Service” on page 282
Interplay STP Encode service “Check List for Transferring Long GOP OP1a Media in the
Interplay ProEncode Provider “Check List for Using ProEncode” on page 326
“Check List for Archiving and Restoring Assets” on page 123
“Check List for Auto Publish Workflow” on page 202.
page 220
page 262
Background” on page 309
Configuration Requirements
An Interplay workgroup enables collaborative workflows by allowing multiple editors to
share media. For diagrams showing typical shared-storage workgroup configurations, see
Avid Interplay Best Practices.
For specific information on configuration requirements, see the Avid Interplay Software
Installation and Configuration Guide.
For any configuration issues that are not included in the published documents, see the Avid
n
Interplay Media Services ReadMe or the Avid Interplay ReadMe.
27
Page 28

1 Working with the Avid Interplay Media Services System
28
Page 29
2 Interplay Media Services Engine
Installation and Configuration
The following topics describe installation and configuration of the Media Service Engine:
• Check List for Setting Up the Media Services Engine
• Registering the Media Services Engine in an Avid Interplay Workgroup‘
• Configuring the Media Services Engine
• Starting the Interplay Media Services Engine
For details on setting up the Media Services system in an Interplay workgroup environment,
see the Avid Interplay Software Installation and Configuration Guide.
Check List for Setting Up the Media Services Engine
The following table provides a list of steps to perform when setting up the Media Services
Engine in an Interplay workgroup.
Setting up the Media Services Engine Check List
Task Section Reference
Add the Interplay Media Services server to
the Interplay workgroup.
Make sure an Interplay Media Services
administrator account is set up on Avid
shared-storage.
Make sure the Interplay Media Services
application key is connected to the server.
See the Avid Interplay Software Installation
and Configuration Guide.
See the Avid Interplay Software Installation
and Configuration Guide.
Page 30

2 Interplay Media Services Engine Installation and Configuration
Setting up the Media Services Engine Check List (Continued)
Task Section Reference
Install the Interplay Media Services Engine
software and the supporting software.
• Avid Service Framework for Client
• Avid Interplay Access
• Avid Interplay Media Services
Configure the SQL Server. See the Avid Interplay Software Installation
Register the Media Services Engine in the
Interplay workgroup.
Configure the Media Service Engine.
• Setup e-mail notifications
• Identify the workgroup’s Interplay
Engine system
• Setup auto-purging of jobs
Start the Avid Interplay Media Services
Engine software.
Install and configure any Media Services
service providers.
See the Avid Interplay Software Installation
and Configuration Guide.
and Configuration Guide.
See “Registering the Media Services Engine in
an Avid Interplay Workgroup” on page 30.
See “Configuring the Media Services Engine”
on page 33.
See “Starting the Interplay Media Services
Engine” on page 36.
See “Check Lists for Setting Up and Using
Service Providers” on page 27.
After you set up the Media Services Engine, install and configure the Media Services service
providers. See “Check Lists for Setting Up and Using Service Providers” on page 27.
Registering the Media Services Engine in an Avid Interplay Workgroup
Before you can use any Media Services Engine services, you must register the Media
Services Engine in an Interplay workgroup by opening the Avid Interplay Administrator and
identifying the system that runs the Media Services Engine. After you register the Media
Services Engine, the Media Services and Transfer Status tool automatically connects to the
Media Services Engine.
If you are performing an upgrade, you do not have to register existing Media Services
n
Engines.
30
Page 31

Registering the Media Services Engine in an Avid Interplay Workgroup
To register the Media Services Engine in an Interplay workgroup:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Avid > Avid Interplay Access Utilities > Avid
Interplay Administrator.
The Avid Interplay Administrator opens.
2. Log in to the server for the workgroup in which you want to register the Media Services
Engine.
3. Click Server Hostname Settings in the Site Settings area.
The following illustration shows the Site Settings area of the Avid Interplay
Administrator.
The Server Hostname Settings window opens.
4. In the Interplay Media Services Settings area, type the name of the system that runs the
Media Services Engine and click Apply Changes.
If your Interplay environment includes the Interplay Delivery workflow, to receive transfers
n
you must add the hostname and the port number of the system where the Delivery Receiving
service is installed. For more information, see “Registering the Delivery Receiver in an Avid
Interplay Workgroup” on page 283.
31
Page 32

2 Interplay Media Services Engine Installation and Configuration
5. (Option) While you have the Server Hostname Settings window open, it is a good time
to check whether you have entered the name of the workgroup in the Workgroup and
MediaIndexer Settings area of the window. The Avid Instinct and Avid Interplay Assist
applications use this setting to locate the Media Indexer that is used to monitor shared
storage.
a. Near the center of the Server Hostname Settings window, make sure your
Workgroup name is in the Workgroup Name field. Type the workgroup name if
necessary. This field is case sensitive.
b. Click Check MediaIndexer to check whether the Media Indexer that monitors
shared storage is running.
32
If the Media Indexer is running, the system displays the message “Connected to
Media Indexer successfully.”
6. Click Log out and close the Avid Interplay Administrator.
Page 33

Configuring the Media Services Engine
Configuring the Media Services Engine
After installing the Media Services Engine software, you can configure the Media Services
Engine for the following optional settings:
• Send e-mail notifications about the status of jobs.
• Identify the workgroup’s Avid Interplay Engine system.
By identifying the Avid Interplay Engine system, when you log in to the Media Services
Engine, the Media Services user information is updated with the user information in the
Avid Interplay Administrator. As a result, you do not need to manage a separate user
database for Media Services. See “Using the Users Page” on page 57.
• Automatically purge Media Services jobs to improve the performance of the Avid
Interplay Media Services and Transfer Status tool. There are two different types of
auto-purge processes you can set:
- An auto-purge process that runs once a day based on the start time and types of jobs
that you select. You can set a start time for the auto-purge to begin within 15 minute
intervals.
- An auto-purge process that starts at an interval that you select, checks the number of
jobs, and purges the jobs based on the job count and types of jobs that you select.
c
n
You can select either process or both processes. The auto-purge settings take effect
immediately; you do not have to restart the Interplay Media Services Engine. If you
want to cancel a scheduled auto-purge process, you must cancel the process before it
starts. After an auto-purge process begins you cannot cancel the process.
When scheduling the auto-purge process, you should choose a low activity time. The
auto-purge process might impact the server’s performance and the ability to connect.
The History area on the Avid Interplay Media Services Engine window provides information
about the auto-purge settings, such as any changes made to the settings.
To configure the Interplay Media Services Engine settings:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Avid > Avid Interplay Media Services.
The Avid Interplay Media Services window opens.
2. Click the Settings button.
The Avid Interplay Media Services Engine Settings dialog box opens.
33
Page 34

2 Interplay Media Services Engine Installation and Configuration
34
3. Type the computer name of the local host in the Database Computer Name text box.
4. In the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) Server text box, type the name of your
local mail server (for example, mail.mycompany.com). If you don’t know the name of
your local mail server, ask your network administrator.
5. In the From Address text box, type an e-mail address for the Media Services Engine. For
example, broker@mycompany.com.
6. (Option) You can configure an SMTP Username and SMTP Password if your network
supports secure e-mail. These settings give the Media Services Engine a name and
password so that is can successfully send e-mail notification. If a network does not use
secure e-mail, the settings do not apply and are disregarded.
The Clean Start option is reserved for future use. Make sure it is set to No.
n
Page 35

Configuring the Media Services Engine
7. In the Interplay Engine Hostname text box, type the host name of the Avid Interplay
Engine system.
If this text box is left blank, the Media Services user information in the Avid Interplay
Administrator is not used for authentication during login.
8. (Option) If you want to use the once-a-day auto-purge, select On from the auto-purge
Enabled list, then select the following settings:
- Purge Start Time—Select a time to start the auto-purge (15 minute intervals).
- Purge PENDING Jobs?—Yes, purges all pending jobs for all service providers.
- Purge CANCELLED Jobs?—Yes, purges all cancelled jobs for all service
providers.
- Purge COMPLETED Jobs?—Yes, purges all completed jobs including jobs with the
Warning status (question mark icon) for all service providers.
- Purge ERROR Jobs?—Yes, purges all error jobs for all service providers.
For the chosen job type, all jobs for all service providers, and for all users are purged.
n
Therefore, you cannot purge jobs for a specific service provider, such as Interplay
Transcode.
9. (Option) If you want to schedule an interval auto-purge, select On from the Interval
Auto Purge list, then select the following settings.
- Purge PENDING Jobs?—Does not apply to interval auto-purge.
- Purge CANCELLED Jobs?—Yes, purges all cancelled jobs for all service
providers.
- Purge COMPLETED Jobs?—Yes, purges all completed jobs including jobs with the
Warning status (question mark icon) for all service providers.
- Purge ERROR Jobs?—Yes, purges all error jobs for all service providers.
- Purge Interval Time: Enter the number of minutes between runs of the auto-purge
interval timer. The auto-purge interval timer checks if there are a sufficient number
of jobs to purge (see the next option). For example, if you enter 50, the auto-purge
interval timer starts every fifty minutes. The default value is 60. The minimum
value is 15 and the maximum value is 1,440 minutes (24 hours).
- Purge Job Count: Enter the number of jobs that cause an auto-purge process to run.
If the number of jobs in the Media Services queue is greater than or equal to this
number when the interval timer runs, Media Services will purge the jobs you have
selected for purging (cancelled jobs, completed jobs, or error jobs - pending jobs are
not included). The default value is 5000. The minimum value is 100 and the
maximum value is 15,000.
35
Page 36

2 Interplay Media Services Engine Installation and Configuration
For both these options, if you enter a number below the minimum value, the Media
Services Engine will use the minimum value. If you enter a number above the
maximum value, the engine will use the maximum value. If you enter nothing or
enter an invalid value in the field, the engine will use the default value.
For the chosen job type, all jobs for all service providers, and for all users are purged.
n
Therefore, you cannot purge jobs for a specific service provider, such as Interplay
Transcode.
10. Click OK.
The Avid Interplay Media Services Engine Settings dialog box closes.
Starting the Interplay Media Services Engine
To start the Interplay Media Services Engine:
t Click Start and select Programs > Avid > Avid Interplay Media Services.
The Avid Interplay Media Services window opens.
36
Page 37

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer
Status Tool
The following topics explain how to use the Media Services and Transfer Status tool:
• Opening the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
• Media Services and Transfer Status Tool User Interface
• Using the Jobs Page
• Using the Providers Page
• Using the Services Page
• Using the Users Page
For an overview of the Media Services and Transfer Status tool, see “Understanding the
Avid Interplay Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 23.
Opening the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
The Media Services and Transfer Status tool can be used on any computer that has an
internet connection to a computer running the Media Services Engine.
The Media Services and Transfer Status tool is installed with the Media Services Engine.
You can install it on another computer from the Individual Optional Installers page of the
Interplay Installation DVD. The tool is also installed with Interplay Access, but you need to
open the Media Services Status tab and the Transfer Status tab as separate windows.
To open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool:
1. Do one of the following:
t From the Avid Interplay Media Services window, click Admin Tool.
t For a standalone application, click Start and select Programs > Avid > Avid Media
Services and Transfer Status.
t From Avid Interplay Access, select View > Interplay Media Services Status.
Page 38

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
t From the Avid Interplay Administrator, in the Site Settings area, click the Interplay
Media Services icon.
2. Type your username and password. See “Using the Users Page” on page 57.
If you opened Media Services Status from Interplay Access or the Interplay
Administrator, access is controlled by the information you used when you logged into
Interplay Access or the Interplay Administrator.
3. Type the host name of the system on which the Media Services Engine resides in the
Media Services Host text box.
The Media Services host name is the name of the computer that the Media Services
Engine runs on. You can find the host name in the Name field of the Avid Interplay
Media Services window. Previously typed host names are available from the Media
Services Host menu.
38
4. Click the Login button.
If the username and password are accepted, the Jobs page opens.
Page 39

Media Services and Transfer Status Tool User Interface
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool User
Interface
The Media Services and Transfer Status tool user interface is made up of five pages. The tab
selected determines which page of the Media Services and Transfer Status tool is displayed.
The page displayed determines the Media Services and Transfer Status tool’s functional
mode and which of the mode-related controls — also referred to as pages — are displayed.
The pages are described in the following table:
Media Services Status Administration Tool Pages
Page Description Section Reference
Jobs Displays the status and other information about jobs
submitted to the Media Services Engine. Lets you
cancel or retry jobs, depending on your level of
privilege.
See “Using the Jobs Page” on
page 40.
39
Page 40

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
Media Services Status Administration Tool Pages
Page Description Section Reference
Providers Displays information about systems that are running
Media Services provider software. Lets you register
and delete providers, depending on your level of
privilege.
Services Displays a list of services and service information.
Lets you install and delete services.
Users Displays a list of user accounts. Lets you create and
delete accounts, depending on your level of
privilege.
Profiles Lets you create templates to use when performing
an operation.
Using the Jobs Page
The Jobs page displays information about Media Services jobs and lets you cancel, delete,
and retry jobs. The Jobs page opens by default after you log in to the Media Services and
Transfer Status tool.
The following topics describe the options available from the Jobs page:
• Jobs Page Information
• Customizing the Reporting of Service Job Status
See “Using the Providers Page”
on page 51.
See “Using the Services Page”
on page 54.
See “Using the Users Page” on
page 57.
See “Working with Media
Services Profiles” on page 75.
40
• Customizing the Jobs Page Columns
• Filtering the Jobs List
• Viewing Details About a Job
• Purging the Jobs List
• Prioritizing a Job
• Canceling a Job
• Deleting a Job
• Retrying a Job
• Exporting the Jobs List
For information about the Auto-Purge feature, see “Configuring the Media Services Engine”
on page 33.
Page 41

Jobs Page Information
The Jobs page displays information about jobs submitted to the Media Services Engine. You
can specify how the status of the various service jobs are reported, see “Customizing the
Reporting of Service Job Status” on page 42.
The following table describes the information displayed on the Jobs page.
Jobs Page
Column Description
Status The colors and icons in the display indicate the status of the job:
• Yellow bar with no icon = Job is processing.
• Green bar with Check Mark icon = Job is completed.
• Gray bar with Stop icon = Job has been canceled.
• Caution icon = Job has failed with an error.
• Gray bar with no icon = Job is pending or is in a queue.
For information on changing the status reporting of jobs, see “Customizing the
Reporting of Service Job Status” on page 42.
Using the Jobs Page
Service The name of the service to which the job was sent.
Job Name The file name submitted by the client to the Media Services Engine. This might
have a suffix — determined by the particular service — appended to it.
Administrators can view information about all jobs. Users without
n
administrator privileges can view all jobs, but can see only the user name
and job name of their own jobs.
Job ID A number automatically generated by the Media Services Engine.
User The name of the user who submitted the job.
Administrators can view information about all jobs. Users without
n
administrator privileges can view all jobs, but can see only the user name
and job name of their own jobs.
Progress (%) The percentage of the job completed.
Priority The priority of the job, as submitted by the client.
Submit Time The date and time the job was submitted by the client to the Media Services
Engine.
Start Time The date and time that the provider started the job.
End Time The date and time that the provider reports the job is complete.
41
Page 42

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
Jobs Page
Column Description
Profile Name Indicates if a profile was used and displays the profile’s name.
Customizing the Reporting of Service Job Status
You can customize the status reporting for the following Media Services services:
• Archive service
• Restore service
• Copy service
• Move service
•Delivery service
For example, during an archive operation, if one of the media files cannot be found, you can
set the reporting to the Jobs tab of the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool to display
one of the following status indicators:
Job Status Display Description
Green with check mark icon Job completed
Green with question mark icon Job completed with a warning
Caution icon Job failed with an error
This section describes how to use the Avid Service Configuration tool to set which reporting
status displays with the various conditions of service jobs.
Avid Service Configuration is an application that is included with the Avid Service
Framework services. It lets you set and change parameters for each of the different Avid
services and applications in your workgroup environment. For more information about Avid
Service Framework, see the Avid Service Fram ework User’s Guide.
42
Page 43

Using the Jobs Page
To customize the job status displays for various Media Services services:
1. On any system running the Avid Service Framework services, click Start and select
Programs > Avid > Avid Service Framework > Avid Service Configuration.
The Select Workgroup dialog box opens.
The Select Workgroup dialog box does not open if the check box specifying to always select
n
and use this workgroup option was previously selected. When you select this option, the
Select Workgroup dialog box no longer opens when you start the application. The default
workgroup is selected, and the Avid Service Configuration window opens. To change this
option and display the Select Workgroup dialog box, click the Login tab of the Avid
Framework Workgroup Properties application and clear the check box for the option.
2. (Option) If the Select Workgroup dialog box opens, select the workgroup you want to
connect to and click Select.
The Avid Service Configuration window opens.
3. In the Directory pane, click the Processes tab and verify that the service is running.
If the service does not appear in the Avid Service Configuration window, the service is not
n
running or the system it runs on is not properly connected to the workgroup. Click the Hosts
tab and make sure that the Avid Service Framework services displays the name of the system
that the service is running on.
4. On the Processes tab, expand the service entry, such as Archive Service.
The system displays the name of the computer running the service.
5. Click the computer name.
The Administrator Password Needed dialog box opens.
6. Type the Avid Service Framework Administrator password and click OK.
By default, Avid Service Framework does not require a password. When a password is used,
n
it is set through the System Configuration Service. Check with your system administrator for
the correct password.
The system displays the setting tab for the service.
Depending on the service you selected, different conditions are available for you to
n
customize.
The following example shows the Archive Service settings.
43
Page 44

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
7. Select the type of status you want to display for each job condition.
Option Job Status Display / Description
OK Green with check mark icon / Job completed
Warning Green with question mark icon / Job completed with a warning
Error Caution icon / Job failed with an error
8. Click Apply.
Customizing the Jobs Page Columns
The Media Services and Transfer Status tool provides options to customize the columns
displayed on the Jobs page.
To customize which columns display on the Jobs page:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool. For more information, see “Opening
the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
The Jobs page opens by default after you log in to the Media Services and Transfer
Status tool.
2. In the Tools area, click Customize columns.
The Choose Columns dialog box opens.
3. Select the name of the columns you want to display.
4. Click OK.
The columns change to show the selections.
5. (Option) Click a column heading and drag it to a new location.
44
Page 45

Filtering the Jobs List
By default, the Jobs list displays all jobs that the Media Services Engine is currently
monitoring. You can customize your view to show only your jobs, to show jobs for a specific
service, or to show only jobs in a selected state.
Users with Administrator privileges are allowed to cancel or delete any job. Users without
n
administrator privileges can only cancel or delete jobs submitted by that user.
To customize the Jobs list:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool. For more information, see “Opening
the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
The Jobs page opens by default after you log in to the Media Services and Transfer
Status tool.
2. In the Filters area, click the Service menu, and select a service.
3. In the Filters area, click the User menu, and select All Users or a specific user name.
4. In the Filters area, click the Status menu, and select one of the following:
- All — Displays all jobs with their current status.
- Processing — Displays only jobs that are currently being processed.
Using the Jobs Page
- Completed — Displays only jobs that have been successfully processed.
- Canceled — Displays only jobs that have been canceled by a user with
administrator privileges.
- Error — Displays only jobs that have stopped with an error.
- Pending — Displays only jobs that are waiting to be processed.
5. In the Filters area, click the Priority and select one of the following:
- ALL — Displays all priority jobs.
- > — Displays all priority jobs greater than the number indicated.
- < — Displays all priority jobs fewer than the number indicated.
- = — Displays all priority jobs equal to the number indicated.
The Jobs page displays jobs that meet the criteria you selected.
Viewing Details About a Job
You must be logged in as the job owner or as an administrator to view a job’s details.
45
Page 46

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
To view details about a job:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool. For more information, see “Opening
the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. On the Jobs page, select the job that you want details about.
3. Click the Details button.
The Job Details window opens.
46
Page 47

Using the Jobs Page
Job Details Window
The following table provides descriptions of the type of job information displayed in the Job
Details window.
Entry Description
Job Information
Name The name of the file submitted by a client to Media Services Engine. It might
include information appended to the file name, depending on the service
requirements.
Service The Media Services service for which the job was submitted; for example, Avid
Interplay Archive Service.
State The current state of the job.
Submitted By: The user name associated with the job, as submitted by the client.
Priority The priority of the job, as submitted by the client.
Provider The name of the provider, as registered with the Media Services Engine.
Requested Provider The name of the provider requested (not currently supported)
Job ID A number automatically generated by the Media Services Engine.
Batch ID The number of the batch containing the job.
Profile Name The name of the profile used for the job, if a profile is used.
Submit Time The date and time the job was submitted by the client to the Media Services
Engine.
Start Time The date and time the provider picked up the job.
End Time The date and time the job was reported as complete by the provider.
Progress The percentage of the job that has been processed.
Notification Displays whether notification of job completed or job error is enabled or
disabled.
Input Parameters The list of Input parameters varies for each service.
47
Page 48

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
Purging the Jobs List
The purge function is available only to users with administrator privileges.
You can set the Media Services settings to allow for auto-purging of jobs. See “Configuring
n
the Media Services Engine” on page 33.
To purge the Jobs list:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool and log in as a user with administrator
privileges. For more information, see “Opening the Media Services and Transfer
Status Tool” on page 37.
2. On the Jobs page, click the Purge button.
The Purge Jobs dialog box opens.
48
3. Click the Service menu, and select the applicable service.
4. Click the Submitted By menu, and select a particular user or All, depending on the jobs
you want to purge.
5. Select which states of jobs you want to purge.
6. Click the Purge button.
The Jobs list no longer contains the jobs you selected. If a purge fails, a dialog box
opens with a list of the jobs that failed to delete and a reason for the failure.
Page 49

Prioritizing a Job
You can prioritize the order of the pending jobs. The priority number assigned to a job
indicates the job’s position in the queue for a specific provider. This setting lets you order
jobs in a desired sequence and also move a job to the top of the queue. Priority numbers
range from 1 (highest priority) through 100 (lowest priority). The default priority number
assigned to each job is 50.
When you assign a priority number to a job, the actual order in the queue depends on the
following:
• Priority numbers are relative only to jobs within a given service. For example, a
transcode job set with priority 1 might not execute before an archive job with
priority 100.
• If the same priority number is assigned to several jobs of a specific provider, then all
these jobs have an equal chance of executing.
To prioritize a job:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. On the Jobs page, select the job you want to prioritize.
Using the Jobs Page
3. Click the Priority button.
The Set Job Priority dialog box opens.
4. Click the arrow button to select a priority number.
The default is 50. The priority range is 1 (highest priority) through 100 (lowest priority).
5. Click OK.
The Priority column displays the new priority for the job.
Canceling a Job
Jobs can be canceled during the Pending or the Processing state. A user can cancel only jobs
that have been submitted under his or her Media Services user name. An administrator can
cancel any job.
Providers periodically check the Media Services Engine for jobs that might need to be
canceled. When a job is canceled, it might take a short time for the job to actually stop and
the status change to be reflected. It is also possible that a job might finish before it can be
canceled. In this case, a dialog box might open stating that the Media Services Engine was
unable to cancel the job.
49
Page 50

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
To cancel a job:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. On the Jobs page, select the job that you want to cancel.
3. Click the Cancel button. A dialog box opens and asks if you are sure you want to cancel
the job.
4. Click OK to cancel the job.
The job remains in the Jobs list, but the state changes to canceled.
Deleting a Job
To delete a specific job or all jobs on the Jobs page:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. On the Jobs page, select the specific job you want to delete.
3. Click the Delete button. A dialog box opens and asks if you are sure you want to delete
the job.
4. Click OK to delete the job.
Retrying a Job
You can retry a job that is in the canceled state or error state.
To retry a job:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. On the Jobs page, select the job you want to retry.
3. Click the Retry button.
The Media Services Engine changes the state to Pending and places the job in the queue
for the next available provider.
50
Page 51

Exporting the Jobs List
You can export the current Jobs list from the Media Services and Transfer Status tool.
To export the Jobs list:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool. For more information, see “Opening
the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
The Jobs page opens by default after you log in to the Media Services and Transfer
Status tool.
2. In the Tools area, click Export list.
A Save dialog box opens.
3. Select a location for the Jobs list file.
4. Type a name for the Jobs list file.
5. Click Save.
Using the Providers Page
The Providers page displays information about computers that are running provider software
and are registered with the Media Services Engine. You can also view specific provider
details and capabilities.
Using the Providers Page
The following topics provide information about using the Providers page:
• Opening the Providers Page
• Customizing the Providers Display
• Viewing Details About a Provider
• Deleting Providers
For information about using the Providers page to register a provider, see “Registering the
Provider” on page 65.
Opening the Providers Page
To open the Providers page:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Providers tab.
The Providers page opens.
51
Page 52

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
The following table describes the information displayed on the Providers page.
Providers Page Description
Status Indicates whether or not the provider is connected to the Media Services
Engine.
Provider The name of the service provider, as registered with the Media Services
Engine.
Service The Media Services service for which the provider has been registered.
Host The computer name of the provider.
Application The name of the service provider application.
IP The IP address of the computer of the provider.
Customizing the Providers Display
By default, the Providers page displays all providers that are registered with the Media
Services Engine. You can customize your view to show only the connected providers or
providers of a particular service.
To customize the Providers display:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Providers tab. The Providers page opens.
52
Page 53

3. In the Filters area, click the Service menu, and select the applicable service.
4. In the Filters area, click the Status menu, and select the applicable condition.
The Providers page displays providers that match your selections.
Viewing Details About a Provider
To view details about a provider:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. On the Providers page, select the provider that you want details about.
3. Click the Details button.
The Provider Details window opens.
The following table provides descriptions of the type of provider information displayed
in the Provider Details window.
Providers Page Description
Name The name of the service provider, as registered with the Media Services
Engine.
Using the Providers Page
Service The Media Services service for which the provider has been registered.
Host Name The computer name of the provider.
Application The name of the service provider application.
IP Address The IP address of the computer of the provider.
Connected Indicates whether or not the provider is connected to the Media Services
Deleting Providers
If a provider is connected to the Media Services Engine, the provider cannot be deleted until
it has been disconnected and all processing jobs are stopped. You must be logged in as an
administrator to delete any providers.
To delete a service, see “Deleting a Media Services Service” on page 56.To delete the
provider software, use the Add/Remove Programs in the Windows Control Panel on the
provider system.
Engine.
53
Page 54

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
To delete a provider:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Providers tab. The Providers page opens.
3. Select the provider, and click Delete.
A dialog box opens and asks if you are sure you want to delete the provider.
4. Click OK.
The provider is no longer registered with the Media Services Engine. To register it
again, see “Registering the Provider” on page 65.
Using the Services Page
The Services page displays information about the services that are installed and lets the user
install new services, upgrade existing services, or delete services that were previously
installed.
For information about installing a service, see “Installing a Service Description” on page 62.
The following topics provide information about the Servers page:
• Opening the Services Page
• Displaying Details About a Service
• Deleting a Media Services Service
Opening the Services Page
To open the Services page:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Services tab.
The Services page opens.
54
Page 55

Displaying Details About a Service
To display information about a specific service:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
Using the Services Page
2. Click the Services tab. The Services page opens.
3. Select the service about which you want information.
4. Click Details.
The Service Details page opens.
55
Page 56

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
The specific information displayed on the Service Details page differs for each
installed service.
Deleting a Media Services Service
Deleting a Media Services service from the Services page deletes the information required
for the service to operate. If one or more providers have been registered for the service on
the Providers page, you must first delete the providers for the service. For more information,
see “Deleting Providers” on page 53.
To delete the provider software, use the Add/Remove Programs in the Windows Control
Panel on the provider system.
56
Page 57

To delete a service:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool and log in as a user with administrator
privileges. For more information, see “Opening the Media Services and Transfer
Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Make sure all providers for the services that you are deleting have been deleted prior to
deleting the services themselves. See “Deleting Providers” on page 53.
3. Click the Services tab. The Services page opens.
4. Select the service you want to delete.
5. Click Delete.
The service is removed. To add the service again, see “Installing a Service Description”
on page 62.
Using the Users Page
The Users page lets you create and manage user accounts. The default login for the
Media Services and Transfer Status tool is the user name Administrator, without a password.
Avid recommends assigning a password to this account after installing the Media Services
Engine. For more information, see “Reassigning Passwords” on page 59.
Using the Users Page
The Users page displays information based on the user’s login profile. A user logged in as an
Administrator can view information about all jobs, whereas users without administrator
privileges can view all jobs, but can only see the username and clip names of their own jobs.
There are two methods for managing Media Services users:
• Using Avid Interplay authentication
If you set a host name in the Avid Interplay Media Services Engine Settings dialog box,
the Media Services Engine authenticates user names and passwords with the Avid
Interplay Engine (see “Configuring the Media Services Engine” on page 33). As a
result, you do not need to manage a separate user database for Media Services. If a host
name is set, when you attempt to log in to the Interplay Media Services Engine, and the
login is successful, the user name and password are added to or updated in the Media
Services database user’s table. The user name and password appear on the Users page.
Adding or changing users on the Users page has no effect if a host name is set in the
Interplay Engine Hostname setting in the Avid Interplay Media Services Engine
Settings dialog box.
57
Page 58

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
• Managing a separate user database
Managing Media Services users through a separate database can be useful if you want to
give administrator privileges to users who do not have administrator privileges in the
Interplay database. However, if you do not use Avid Interplay authentication, make sure
any user name and password exactly matches a user name and password in the Interplay
database, because Media Services operations usually require login by a valid Interplay
user.
The following topics describe the Users page:
• Opening the Users Page
• Setting Up User Accounts
• Reassigning Passwords
• Deleting User Accounts
Opening the Users Page
To open the Media Services Users page:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
58
2. Click the Users tab.
The Users page opens with user accounts listed in the User name column.
Page 59

Setting Up User Accounts
To set up a user account:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening the
Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Users tab. The Users page opens.
3. Click the Add button. A dialog box opens.
4. Type a user name in the Username text box.
User names and passwords are case sensitive and can contain only letters, numbers, and
underscores. They can be up to 255 characters.
5. (Option) You can assign a password by typing a password in the Password text box, then
typing it again in the Retype Password text box. Passwords are not required.
6. Type the applicable information about the user in the other text boxes.
7. (Option) If this user is an administrator, select the “is Administrator” option.
8. Click Save.
Reassigning Passwords
Using the Users Page
If a user forgets his or her password, a new one must be assigned. If you forget the
Administration password, it must be reset. Contact Avid Customer Support.
To reassign a user password:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool and log in as a user with administrator
privileges. For more information, see “Opening the Media Services and Transfer
Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Users tab. The Users page opens.
3. Select the user that you want to change the password.
4. Click the Edit button. A dialog box opens.
5. Type a new password in the Password text box, then type it again in the Retype
Password text box.
6. Click Save.
59
Page 60

3 Using the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool
Deleting User Accounts
You must be logged in as an administrator to delete user accounts.
The user “Administrator” cannot be deleted. If you try to delete Administrator, you receive
n
an error message.
To delete a user account:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool and log in as a user with administrator
privileges. For more information, see “Opening the Media Services and Transfer
Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Users tab. The Users page opens.
3. Select the User Name for each account you want to delete.
4. Click the Delete button.
A dialog box opens and asks if you are sure you want to delete the user account.
5. Click OK.
The user account is deleted.
To re-create user accounts, see “Setting Up User Accounts” on page 59.
60
Page 61

4 Installing Services and Registering
Providers
This chapter provides general procedures for installing a service, registering a provider, and
connecting it to the Media Services Engine. For specific information about each service, see
“Understanding the Various Media Services” on page 24 and the chapter that provides
information about the service.
The following topics provide information about the required tasks:
• Understanding Service Descriptions and Service Packages
• Installing a Service Description
• Registering the Provider
• Connecting a Provider to the Media Services Engine
• Starting the Service Provider
• Verifying That a Service Provider Is Connected
• Rules for Upgrading a Service and Preserving Profiles
Understanding Service Descriptions and Service Packages
Before you can use a service or register a provider, you must install the service description.
When you install the provider software on a provider system, a .zip file is also installed. This
.zip file (or service package) contains a service description file, which tells the Media
Services Engine the parameters for a given service and allows providers to be configured. In
some cases it may also contain other supporting files for the service.
You only need to install the service description once for each service, even if you are
configuring multiple providers.
The following table provides a list of Media Services services and the name of each service
package.
Page 62

4 Installing Services and Registering Providers
Service File Name of Service Package
Avid Interplay Transcode TranscodeService.zip
Avid Interplay Archive Archive.zip
Avid Interplay Restore Restore.zip
Avid Interplay Stream Publish Publishing.zip
Avid Interplay Copy CopyMedia.zip
Avid Interplay Move MoveMedia.zip
Avid Interplay Delivery PTFService.zip
Avid Interplay ProEncode ProEncode.zip
Avid Interplay STP Encode LongGOPExport.zip
You do not use the Media Services Engine to configure the Auto Archive, Auto Transcode,
n
and Auto Copy services. Instead, use the Avid Interplay Administrator and the Avid Service
Framework services. For more information, see “Configuring Auto Archive Using the Avid
Service Configuration” on page 158.
Installing a Service Description
You use the Media Services and Transfer Status tool to install the service description (see
“Understanding Service Descriptions and Service Packages” on page 61).
You only need to install a service description once, even if you configure multiple providers.
Before you upgrade a service, see “Rules for Upgrading a Service and Preserving Profiles”
n
on page 72
For the Avid Interplay ProEncode service installation, you must install the service
n
description using the Media Services and Transfer Status tool on the Interplay Media
Services server. You cannot use a remote system. This allows the appropriate files that are
needed for communication through port 8080 and http to be placed on the Interplay Media
Services server. You can install the Interplay ProEncode provider software on a server other
than the Media Services server. You must, however, have access to the location of the
ProEncode.zip file, which is installed with the provider software. You can also copy the
ProEncode.zip file from the provider system to the Interplay Media Services server before
you install the ProEncode service.
62
Page 63

Installing a Service Description
To install a Media Services service description:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool and log in as administrator, as
described in “Opening the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Services tab.
The Services page displays the currently configured services.
3. Click Install/Upgrade.
The Install/Upgrade Service dialog box opens.
4. Click the Browse button and navigate to the folder containing the service package (.zip
file). Make sure you have access to the folder.
The following is an example of the location of a service package. In this case, the
service package is for the Transcode service.
- C:\Program Files\Avid\Avid Interplay Transcode\TranscodeService
63
Page 64

4 Installing Services and Registering Providers
You can use the Microsoft Windows Search tool to help you locate the folder that
contains the service package. For a list of package file names, see “Understanding
Service Descriptions and Service Packages” on page 61.
5. In the folder, select the service.zip file.
The following illustration shows the TranscodeService.zip file selected.
64
6. Click Save.
The path to the file appears in the Install/Upgrade Service dialog box.
7. Click Install/Upgrade.
The service and its description appear on the Services page. The following illustration
shows the Transcode Service added to the Services page.
Page 65

Registering the Provider
Registering the Provider
After you install a service description, you need to register the provider.
The Provider page on the Media Services and Transfer Status tool is used to register a
provider for a particular service. The provider receives information about jobs and supplies
the Media Services Engine with information about the provider, job status, and other
information depending on the service. In some cases it passes the information to other
applications.
To register the provider with the Media Services Engine:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool and log in as administrator, as
described in “Opening the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Providers tab.
The Providers page displays all of the currently registered providers.
65
Page 66

4 Installing Services and Registering Providers
3. Click Register.
The Register Provider dialog box opens.
4. Do the following:
66
a. Service menu — Select a service. For a list of services, see “Understanding Service
Descriptions and Service Packages” on page 61.
b. Provider Name — Type the name that you want to use to identify this particular
provider. You can have several providers on your workgroup for the same service,
so you should use a meaningful name.
c. Application Name — For future use. Leave this text box blank.
As an example, the following illustration shows the Register Provider dialog box with
the values filled in for a Transcode Service.
5. Click Register.
Page 67

Connecting a Provider to the Media Services Engine
The provider appears on the Providers page. If the service is not connected to the Media
Services Engine, a Stop icon is displayed in the Status column. In this case, you must
connect the provider to the Media Services Engine. See “Connecting a Provider to the
Media Services Engine” on page 67.
Connecting a Provider to the Media Services
Engine
After you install a service description and register the provider, you need to connect the
provider to the Media Services Engine. You can use the following procedure as an example.
For specific procedures for the various services, see “Understanding the Various Media
Services” on page 24.
The following procedure uses the Transcode service as an example.
To connect a provider to the Media Services Engine:
1. Depending on the service, click Start and select Programs > Avid > Avid Interplay
Service, for example, Avid Interplay Transcode.
The service dialog box opens.
The following example shows the Transcode Service dialog box.
67
Page 68

4 Installing Services and Registering Providers
2. Click Settings.
The Provider Settings dialog box opens.
3. Do the following:
a. Provider Name — Type the name of the provider you specified in “Registering the
Provider” on page 65. In this example, the name is Transcode_01.
b. Media Services Engine Host Name — Type the name of the system running the
Media Services Engine application.
c. Automatically Connect — Select either Yes or No (default) to automatically
connect to the Media Services Engine when the application starts.
The following illustration shows the Provider Settings dialog box with the values filled
in for a Transcode Service.
4. Click OK.
68
Page 69

Connecting a Provider to the Media Services Engine
5. Click Connect in the service dialog box.
The following example shows the Transcode Service.
The Transcode Service dialog box now shows that the service is connected and shows
the provider you selected to connect to. This example shows Transcode_01 as the
provider.
69
Page 70

4 Installing Services and Registering Providers
The Provider page in the Media Services and Transfer Status tool now shows that the
service is connected, indicated by a check mark in the Status column.
Starting the Service Provider
To start the service, you need to start the service provider.
Auto services, such as Auto Archive, start automatically.
n
To start the service provider:
t Click Start and select Programs > Avid > Avid Interplay service.
Depending on the service settings, one of the following happens:
- Automatically Connect—Yes, the service dialog box opens for the service you
selected and is connected to the service.
- Automatically Connect—No, the service dialog box opens for the service you
selected and displays Idle. Click the Connect button to connect to the service.
The service provider dialog box displays the start date and start time of the providers based
n
on the Microsoft® Windows® time.
After the connection is made, the Status line in the service dialog box reads “Checking
for Jobs,” and the History window displays the message “Connection Established.” The
Connect button changes to a Disconnect button.
70
Page 71

Verifying That a Service Provider Is Connected
The following example shows the Transcode Service dialog box as connected.
If the provider cannot connect to the Media Services Engine, the Status line reads
n
“Connection Error.” Ensure the Media Services Engine is running, the service is installed,
the provider is properly registered, and then click Connect again.
Verifying That a Service Provider Is Connected
To verify that a service provider is running and connected:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool. See “Opening the Media Services
and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Providers tab.
The system displays the status of the Media Services providers. In the following
illustration, the Transcode service is connected, indicated by a check mark in the Status
column. If the provider is not connected (indicated by a stop sign), see “Starting the
Service Provider” on page 70.
71
Page 72

4 Installing Services and Registering Providers
Auto services, such as Auto Archive, do not appear in this list. Use the Avid Service
n
Framework Configuration window to verify that an Auto service is running. See “Verifying
That the Auto Archive Service is Running” on page 161.
Rules for Upgrading a Service and Preserving Profiles
When you are upgrading a Media Services service you need to perform the same procedures
as a new installation, such as installing the service description, registering the service
provider and connecting the provider to the Media Services Engine. However, before and
after you upgrade a service you need to follow a few rules:
• You need to log in with a user account that has administrator privileges.
• You should perform the upgrade of the service during a low usage time or when the
Media Services engine is offline.
• You can only install a newer version of an existing service.
• The Media Service Engine only supports one version of a service at a time.
• When upgrading a the ProEncode service, you must install the service using the Media
Services and Transfer Status tool on the Interplay Media Services server. For other
services, you can use the tool remotely. See “Installing a Service Description” on
page 62.
72
Page 73

Rules for Upgrading a Service and Preserving Profiles
• Make sure the service providers are disconnected, by verifying the Interplay Media
Services and Transfer Status tool’s Providers page shows Stop in the Status column.
You do not need to delete the service profiles or unregister the service before performing the
n
upgrade, as was required in versions prior to v2.0. However, if you want to delete a service
completely, you need to first delete all the profiles and providers, and then delete the service.
• During the service upgrade, you cannot cancel the upgrade, however you can continue
to work.
• When upgrading any of the Media Services services, all existing profiles are saved.
However, because the new version of the service might contain new or modified profile
settings, you must review your profiles after the upgrade. New and modified settings are
marked with a caution icon in the Parameters area of the profile. These marked settings
require you to either set a valid value or leave the text box blank, depending on the
requirements for the new or modified profile setting.
For information about the various profile settings, see “Working with Media Services
Profiles” on page 75.
You can modify multiple profile setting values using the Profiles page. For information, see
n
“Modifying Multiple Profiles” on page 78.
• On the Profiles page, after the service is upgraded, a caution icon displays next to any
profile settings that were removed in the new version of the service. You need to check
each existing profile to make sure it meets your needs. The existing profile retains the
older profile settings to provide backward compatibility, however these older settings
are not used with the new version of the service.
• On the Profiles page, after the service is upgraded, a caution icon displays next to any
profile settings that the values were modified by the new version of the service. You
need to check each existing profile to make sure it meets your needs. The existing
profile retains the older profile setting values to provide backward compatibility,
however these older setting values are not used with the new version of the service.
73
Page 74

4 Installing Services and Registering Providers
74
Page 75

5 Working with Media Services Profiles
The following topics provide information about working with Media Services profiles:
• Understanding Media Services Profiles
• Creating a Service Provider Profile
• Modifying Multiple Profiles
• Modifying Changed or New Options in a Profile
Understanding Media Services Profiles
Profiles let you set up templates to use when performing an operation. For example, you can
create a profile to use with the Interplay Transcode service. When you select the profile, the
Transcode service automatically performs the transcode operation using the specified target
resolution, stores the new media on the specified workspace, and stores the new asset in the
designated target folder, as defined in the profile.
Profiles are required if you request a service from an Avid editing application. If you request
a service from Interplay Access, some services require a profile, and others provide the
option of using a profile or setting the parameters for the current operation.
You can update the values set in multiple profiles at the same time by using the Multiple
Profile Select mode. To use this mode, the profiles must be of the same type. For example,
you can select multiple Transcode service profiles and then change the Workspace value to
update the values in all the selected Transcode service profiles. For more information, see
“Modifying Multiple Profiles” on page 78.
Before you upgrade a service you can preserve existing profiles by following the rules listed
in “Rules for Upgrading a Service and Preserving Profiles” on page 72.
Page 76

5 Working with Media Services Profiles
This chapter provides an example of how to create a profile. For specific procedures to
create profiles for the various services, see the references in the following table.
Service name Documentation
Interplay Transcode Service “Creating a Interplay Transcode Service Profile” on page 92
Interplay Archive Service
Interplay Restore Service
Interplay Copy Service “Using an Interplay Copy Service Profile” on page 231
Interplay Move Service “Creating a Avid Interplay Move Service Profile” on page 273
Interplay Stream Publish Provider “Creating a Stream Publish Service Profile” on page 193
Interplay Delivery Provider “Creating an Avid Interplay Delivery Profile” on page 294
Interplay ProEncode Provider “Creating an Interplay ProEncode Provider Profile” on
You do not need to create a Media Services profile for the STP Encode service. The service
n
requests profile information directly from the Transfer Engine during the STP Encode
workflow.
“Creating an Interplay Archive or Interplay Restore Profile” on
page 145
page 330
Creating a Service Provider Profile
This section gives an example of how to create a service provider profile. It uses the
Transcode service as an example.
To create a profile:
76
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool. For more information, see “Opening
the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Profiles tab.
3. In the Service menu, select a service, for example, Avid Interplay Transcode Service.
Page 77

4. Click Add in the Profiles area.
The Add Profile dialog box opens.
Creating a Service Provider Profile
5. Type a descriptive name for the new profile in the Add Profile dialog box. This is the
name that users see when they right-click an asset and select a service, for example
Transcode.
6. Click OK.
The name appears in the Profiles list and an empty template appears in the
Parameters area.
7. In the Parameters area, set a value for each option as needed.
8. Click Save in the Parameters area.
The Save Profile dialog box opens.
77
Page 78

5 Working with Media Services Profiles
9. Click Yes to save your changes.
You can define several operations under one main profile name. For example, you can
add subjobs to transcode several resolutions using one profile. The system processes
each subjob in turn.
To add subjobs:
t Click Add in the Sub Jobs area.
Modifying Multiple Profiles
From the Profiles page of the Avid Interplay Media Services and Transfer Status tool, you
can select multiple profiles to batch modify option values at the same time. When you select
more than one profile in the Profiles list, the Parameters area changes to multi-select mode
with the title “Parameters for All Selected Profiles.”
For example, you can select several Transcode profiles, and then change the Workspace
value once in the parameters area for all the selected profiles.
This feature is useful after you upgrade a service provider and you need to modify your
existing profiles to correct any values that are not supported with the new version of the
service provider. In the Parameters area of the profile, a caution icon indicates which profile
settings require attention. This feature is also useful for setting the parameters of multiple
profiles after installing a new Media Services service.
78
To modify multiple profiles at the same time:
1. Open and log in to the Media Services and Transfer Status tool:
t From the Avid Interplay Media Services window, click Admin Tool.
t From the Avid Interplay Administrator, in the Site Settings area, click the Interplay
Media Services icon.
When you open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool from the Avid Interplay
n
Administrator, the name is “Interplay Media Services.”
2. Click the Profiles tab.
3. In the Service menu, select a service. For example, Avid Interplay Transcode Service.
4. In the Profiles list, select all the profiles you want to batch modify the setting values.
Page 79

Modifying Multiple Profiles
The Parameters for All Selected Profiles displays in the parameters area.
5. In the Parameters for All Selected Profiles area, click the option with the value you want
to change.
The option’s value field displays.
6. Type or select a new value for the option.
7. Click Save All.
Only the options displaying their value field are updated for all of the selected profiles.
79
Page 80

5 Working with Media Services Profiles
Modifying Changed or New Options in a Profile
If you upgrade a service provider, you might need to modify your existing profiles to correct
any values that are not supported with the new version of the service provider, or to add a
value for a new option. In the Parameters area of the profile, a caution icon indicates which
profile settings require attention.
To remove the Caution icon for a new profile value:
t Make any change to the option value.
In some cases, you might need to enable and then disable an option to remove the icon.
80
Page 81

6 Working with the Transcode Service
The following topics provide information about working with the Transcode service:
• Understanding the Transcode Service
• Check List for Transcoding Assets
• Installing and Registering the Transcode Service Provider
• Starting the Transcode Provider
• Creating a Interplay Transcode Service Profile
• Understanding the Transcode Services Modes
• Transcoding an Asset from Avid Interplay Access
• Transcoding an Asset from an Avid Editing Application
• Transcoding OMF Clips
• Working with an Auto Transcode Folder
Understanding the Transcode Service
Transcoding Avid assets from one resolution to another resolution is available with the Avid
Interplay Transcode service and Avid Interplay Auto Transcode service. For example, you
can use the Avid Interplay Transcode service to create a low-resolution version of a
sequence or master clip. You can also use the Interplay Transcode process to mix down the
video and audio tracks during the transcode.
Before you can use the Transcode service, you need to check that the Transcode service is
installed and connected. For a list of the steps to prepare for transcoding, see “Check List for
Transcoding Assets” on page 82.
To transcode non-Avid assets, use the Avid Interplay ProEncode provider. For more
n
information, see “Working with the ProEncode Service” on page 325.
When accessing an Interplay Transcode system remotely, you should use the Microsoft
n
Windows Remote Desktop Connect command instead of VNC. The Remote Desktop Connect
feature requires setup on the Interplay Transcode system. For information, see the Microsoft
Windows documentation.
Page 82

6 Working with the Transcode Service
Check List for Transcoding Assets
For the transcode process, the following table provides a check list of steps for installing and
configuring the Interplay Media Services system in an Avid shared-storage environment, and
configuring an Avid editing system. The check list also provides references where to find
more information about each step.
Transcoding Assets Check List
Task Section Reference
Check your configuration. See “Configuration Requirements” on page 27.
Make sure the Interplay Media Services application
key is connected to a USB port. If a Transcode
provider is not running on the Interplay Media
Services server, you must also connect an application
key to a USB port on the server running the Transcode
provider.
Make sure the Interplay Media Services Engine
software and the supporting software are installed and
configured in the workgroup.
• Avid Service Framework for Client
• Avid Interplay Access
• Avid Interplay Media Services
• Avid Interplay Transcode service (install this on
each server used as a provider)
(Option) Install the Interplay Auto Media Services
service, which includes the Interplay Auto Transcode
software.
Install and register the Interplay Transcode service
provider.
Connect the Interplay Transcode service provider to
the Media Service Engine.
Start the Interplay Transcode service provider. See “Starting the Transcode Provider” on
Verify the Interplay Transcode service is connected. See “Verifying That a Service Provider Is
See Avid Interplay Software Installation and
Configuration Guide and “Interplay Media
Services Engine Installation and Configuration”
on page 29.
See “Preparing the Workgroup for Auto
Transcode” on page 114.
See “Installing and Registering the Transcode
Service Provider” on page 83.
See “Connecting the Transcode Provider to the
Media Services Engine” on page 88.
page 91.
Connected” on page 71.
82
Page 83

Installing and Registering the Transcode Service Provider
Transcoding Assets Check List (Continued)
Task Section Reference
(Option) Create a Interplay Transcode profile. See “Creating a Interplay Transcode Service
Profile” on page 92.
Perform a transcode using Interplay Access. See “Transcoding an Asset from Avid Interplay
Access” on page 108.
Perform a transcode using an Avid editing system. See “Transcoding an Asset from an Avid
Editing Application” on page 110.
Installing and Registering the Transcode Service
Provider
Before you can use the Transcode service provider, you must install the provider software
needed by the service from the Avid Interplay installation DVD. Then install the service
description in the Media Services Engine, register the provider, and start and connect the
service.
These tasks are explained in the following topics:
• Installing the Transcode Service Description
• Registering the Transcode Provider
• Connecting the Transcode Provider to the Media Services Engine
You do not use the Media Services Engine to configure the Auto Archive, Auto Transcode,
n
and Auto Copy services. Instead, use the Avid Interplay Administrator and the Avid Service
Framework services. For more information, see “Configuring the Auto Transcode Service”
on page 114.
Installing the Transcode Service Description
You use the Media Services and Transfer Status tool to install the Transcode service
description. For more information, see “Understanding Service Descriptions and Service
Packages” on page 61.
You only need to install a service description once, even if you configure multiple providers.
83
Page 84

6 Working with the Transcode Service
To install the Transcode service description:
1. Make sure the Interplay Transcode provider software is installed.
2. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool and log in as an administrator, as
described in “Opening the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
3. Click the Services tab.
The Services page displays the currently configured services.
84
4. Click Install/Upgrade.
The Install/Upgrade Service dialog box opens.
5. Click the Browse button and navigate to the folder containing the Transcode service
package (TranscodeService.zip file). Make sure you have access to the folder. By
default the service package is installed in the following folder:
C:\Program Files\Avid\Avid Interplay Transcode\TranscodeService
Page 85

Installing and Registering the Transcode Service Provider
You can use the Microsoft Windows Search tool to help you locate the folder that
contains the TranscodeService.zip file. Make sure you have access to the folders.
6. In the folder, select the TranscodeService.zip file.
The following illustration shows the TranscodeService.zip file selected.
7. Click Save.
The path to the file appears in the Install/Upgrade Service dialog box.
8. Click Install/Upgrade.
The Avid Interplay Transcode Service appears on the Services page.
85
Page 86

6 Working with the Transcode Service
Registering the Transcode Provider
After you install the Transcode service description, you need to register the Transcode
provider with the Media Services Engine. If you are configuring multiple providers, you
need to register each provider.
86
The Provider page on the Media Services and Transfer Status tool is used to register the
Transcode provider for the Transcode service. The provider receives information about jobs
and supplies the Media Services Engine with information about the provider, job status, and
other information depending on the service. In some cases it passes the information to other
applications.
To register the Transcode provider with the Media Services Engine:
1. Open the Media Services and Transfer Status tool and log on as an administrator, as
described in “Opening the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Providers tab.
The Providers page displays all of the currently registered providers.
Page 87

3. Click the Register button.
The Register Provider dialog box opens.
4. Do the following:
Installing and Registering the Transcode Service Provider
a. Service menu — Select Avid Interplay Transcode Service
b. Provider Name — Type the name that you want to use to identify this particular
provider. You can have multiple providers on your workgroup for the same service,
so you should use a meaningful name.
c. Application Name — For future use. Leave this text box blank.
The following illustration shows the Register Provider dialog box with the values filled
in for a Transcode service.
5. Click Register.
87
Page 88

6 Working with the Transcode Service
The Transcode provider appears in the Providers page. If the service is not connected to
the Media Services Engine, a Stop icon is displayed in the Status column. In this case,
you must connect the Transcode provider to the Media Services Engine software. See
“Connecting the Transcode Provider to the Media Services Engine” on page 88.
Connecting the Transcode Provider to the Media Services Engine
After you install the Transcode service description and register the Transcode provider, you
need to connect the Transcode provider to the Media Services Engine software.
To connect the Transcode provider to the Media Services Engine:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Avid > Avid Interplay Transcode.
The Transcode Service dialog box opens.
88
Page 89

2. Click Settings.
The Provider Settings dialog box opens.
Installing and Registering the Transcode Service Provider
3. Do the following:
a. Provider Name — Type the name of the provider you specified in “Registering the
Transcode Provider” on page 86. In this example, the name is Transcode_01.
b. Media Services Engine Host Name — Type the name of the system running the
Media Services Engine application.
c. Automatically Connect — Select either Yes or No (default) to automatically
connect to the Media Services Engine when the application starts.
The following illustration shows the Provider Settings dialog box with the values filled
in for the Transcode provider.
89
Page 90

6 Working with the Transcode Service
4. Click OK.
5. Click Connect in the Service window.
The Transcode Service dialog box now shows that the service is connected and shows
the name of the provider you connected.
90
The Provider page in the Media Services and Transfer Status tool now shows that the
service is connected, indicated by a check mark in the Status column.
Page 91

Starting the Transcode Provider
To start the Transcode provider:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Avid > Avid Interplay Transcode.
Depending on the service settings, one of the following happens:
- Automatically Connect—Yes, the service dialog box opens for the service you
selected and is connected to the service.
- Automatically Connect—No, the service dialog box opens for the service you
selected and displays Idle. Click the Connect button to connect to the service.
The service provider dialog box displays the start date and start time of the providers based
n
on the Microsoft Windows time.
After the connection is made, the Status line in the service dialog box reads “Checking
for Jobs,” and the History window displays the message “Connection Established.” The
Connect button changes to a Disconnect button.
The following example shows the Transcode Service dialog box as connected.
Starting the Transcode Provider
If the provider cannot connect to the Media Services Engine, the Status line reads
n
“Connection Error.” Ensure the Media Services Engine is running, the service description is
installed, the provider is properly registered, and then click Connect again.
91
Page 92

6 Working with the Transcode Service
Creating a Interplay Transcode Service Profile
You must create a profile to use when performing a Transcode or an Auto Transcode
operation. You select a Transcode profile after selecting an asset in Interplay Access or in an
Avid editing application.
Transcode profiles let you define the following:
• The portion of the Avid asset that is transcoded
• Job priority
• Resolution and format
• Workspace for the media files
For information on transcoding MultiRez clips, see the “Using MultiRez and Dynamic
n
Relink” chapter in the Interplay Help or the Help for your Avid editing application.
To create a transcode profile:
1. Open and log in to the Media Services and Transfer Status tool as described in “Opening
the Media Services and Transfer Status Tool” on page 37.
2. Click the Profiles tab.
92
3. In the Service menu, select Avid Interplay Transcode Service.
Page 93

Creating a Interplay Transcode Service Profile
4. Click Add in the Profiles area.
The Add Profile dialog box opens.
5. Type a descriptive name for the new profile in the Add Profile dialog box. This is the
name that users see when they right-click an asset and select Transcode.
6. Click OK.
The name appears in the Profiles list and an empty template appears in the
Parameters area.
7. In the Parameters area, select a Mode as follows:
- WHOLE — Transcodes the entire clip. For sequences, the full source clips that
make up the sequence are transcoded. For subclips, the full source clip that makes
up the subclip is transcoded.
93
Page 94

6 Working with the Transcode Service
- CONSOLIDATE — For subclips, transcodes only the portion of the clip that makes
up the subclip. For sequences, transcodes only the portion of the clips that are
contained in the sequence. This creates partially online media for the related clips.
- MIXDOWN — During the transcode, the video and audio are mixed down, as
specified in the profile, to create one master clip. See “Understanding MIXDOWN
Mode During the Transcode Process” on page 105.
- DUALMIXDOWN — Performs two transcodes of the selected asset, to create a
single master clip with two resolutions associated with it. See “Understanding the
DUALMIXDOWN Mode During the Transcode Process” on page 107.
8. In the Parameters area, define the other values you want in the profile for the selected
mode.
See “Transcode Profile Parameters” on page 94.
9. Click Save in the Parameters area.
The Save Profile dialog box opens.
10. Click Yes to save your changes.
You can define several transcode operations under one main profile name. For example,
you can add subjobs to transcode several resolutions using one profile. The system
processes each subjob in turn.
To add subjobs:
t Click Add in the Sub Jobs area.
Transcode Profile Parameters
The parameters available in a transcode profile depends on the Mode setting.
• WHOLE—see “WHOLE Mode - Transcode Profile Settings” on page 95
• CONSOLIDATE—see “CONSOLIDATE Mode - Transcode Profile Settings” on
page 96
• MIXDOWN—see “MIXDOWN Mode - Transcode Profile Settings” on page 97
•DUALMIXDOWN—see “DUALMIXDOWN Mode - Transcode Profile Settings” on
page 98
94
Page 95

Avid Interplay Access v1.6 or higher is required to use some XDCAM HD resolutions in the
n
TargetVideoQuality menu.
WHOLE Mode - Transcode Profile Settings
WHOLE Mode Transcode Profile Settings
Parameter Description
Mode Select WHOLE
The WHOLE mode transcodes the entire clip. For
sequences, the full source clips that make up the sequence
are transcoded. For subclips, the full source clip that makes
up the subclip is transcoded.
Priority Select a priority. This value allows you to assign job
priorities to different profiles. Priority numbers range from
1 (highest priority) through 100 (lowest priority). The
default priority number assigned to each job is 50.
Creating a Interplay Transcode Service Profile
TargetAudioQuality Select an audio resolution for the transcode or select None.
TargetAudioQualityDual Not used in WHOLE mode, only available with
DUALMIXDOWN mode.
TargetAudioTrackMapping Not used in WHOLE mode, only available with
MIXDOWN and DUALMIXDOWN mode.
TargetVideoQuality Select a video resolution for the transcode or select None.
TargetVideoQualityDual Not used in WHOLE mode, only available with
DUALMIXDOWN mode.
VideoTimeCodeFormat Not used - for future use.
Workspace Type the name of the Avid shared-storage workspace that
will hold the new media files.
95
Page 96

6 Working with the Transcode Service
CONSOLIDATE Mode - Transcode Profile Settings
CONSOLIDATE Mode Transcode Profile Settings
Parameter Description
Mode Select CONSOLIDATE
For subclips, transcodes only the portion of the clip that
makes up the subclip. For sequences, transcodes just the
portion of the clips that are contained in the sequence. This
creates partially online media for the related clips.
Priority Select a priority. This value allows you to assign job
priorities to different profiles. Priority numbers range from
1 (highest priority) through 100 (lowest priority). The
default priority number assigned to each job is 50.
TargetAudioQuality Select an audio resolution for the transcode.
TargetAudioQualityDual Not used in CONSOLIDATE mode, only available with
DUALMIXDOWN mode.
96
TargetAudioTrackMapping Not used in CONSOLIDATE mode, only available with
MIXDOWN mode and DUALMIXDOWN mode.
TargetVideoQuality Select a video resolution for the transcode.
TargetVideoQualityDual Not used in CONSOLIDATE mode, only available with
DUALMIXDOWN mode.
VideoTimeCodeFormat Not used - for future use.
Workspace Type the name of the Avid shared-storage workspace that
will hold the new media files.
Page 97

MIXDOWN Mode - Transcode Profile Settings
See also “Understanding MIXDOWN Mode During the Transcode Process” on page 105
MIXDOWN Mode Transcode Profile Settings
Parameter Description
Mode Select MIXDOWN
The MIXDOWN mode sets the transcode process to mix
down the audio and video. You can control whether the
audio or video is included in the mixdown by using the
TargetAudioQuality and TargetVideoQuality settings.
Priority Select a priority. This value allows you to assign job
priorities to different profiles. Priority numbers range from
1 (highest priority) through 100 (lowest priority). The
default priority number assigned to each job is 50.
TargetAudioQuality Select an audio resolution for the transcode.
• None - the mixed-down clip does not include the audio
• MPEG1 Layer 2 - digital audio compressed to the
• Uncompressed PCM - uncompressed digital audio
Creating a Interplay Transcode Service Profile
tracks.
For example, if you select None from the
TargetAudioQuality menu, then the audio tracks are not
mixed down during the Interplay Transcode operation.
MPEG1 Layer 2 specification at 96 Kb/s.
(standard Avid audio).
TargetAudioQualityDual Not used in MIXDOWN mode, only available with
DUALMIXDOWN mode.
TargetAudioTrackMapping This text box lets you identify the mapping of source audio
tracks to the output (target) audio tracks. See “Mapping of
Audio Tracks in MIXDOWN and DUALMIXDOWN
Modes” on page 100.
97
Page 98

6 Working with the Transcode Service
MIXDOWN Mode Transcode Profile Settings (Continued)
Parameter Description
TargetVideoQuality Select a video resolution for the transcode.
• None - the mixed-down clip does not include the video
tracks.
For example, if you select None from the
TargetVideoQuality menu, then the video tracks are not
mixed down during the Interplay Transcode operation.
• Select the video resolution for the mix down.
TargetVideoQualityDual Not used in MIXDOWN mode, only available with
DUALMIXDOWN mode.
VideoTimeCodeFormat Not used - for future use.
Workspace Type the name of the Avid shared-storage workspace that
will hold the new media files.
DUALMIXDOWN Mode - Transcode Profile Settings
98
See also “Understanding the DUALMIXDOWN Mode During the Transcode Process” on
page 107.
DUALMIXDOWN Mode Transcode Profile Settings
Parameter Description
Mode Select DUALMIXDOWN
The DUALMIXDOWN mode sets the transcode process to
mix down the two sets of video and audio tracks to
different resolutions. A single master clip is created with
both resolutions. You can control whether the audio or
video are included in each mixdown by using the
TargetAudioQuality. TargetAudioQualityDual,
TargetVideoQuality and TargetVideoQualityDual settings.
Priority Select a priority. This value allows you to assign job
priorities to different profiles. Priority numbers range from
1 (highest priority) through 100 (lowest priority). The
default priority number assigned to each job is 50.
Page 99

Creating a Interplay Transcode Service Profile
DUALMIXDOWN Mode Transcode Profile Settings (Continued)
Parameter Description
TargetAudioQuality Select an audio resolution for the first (primary) transcode.
• None - the mixed-down clip does not include the audio
tracks.
For example, if you select None from the
TargetAudioQuality menu, then the audio tracks are not
mixed down during the Interplay Transcode operation.
• MPEG1 Layer 2 - digital audio compressed to the
MPEG1 Layer 2 specification at 96 Kb/s.
• Uncompressed PCM - uncompressed digital audio
(standard Avid audio).
TargetAudioQualityDual Select an audio resolution for the second transcode.
• None - the mixed-down clip does not include the audio
tracks.
For example, if you select None from the
TargetAudioQualityDual menu, then the audio tracks
are not mixed down during the Interplay Transcode
operation.
• MPEG1 Layer 2 - digital audio compressed to the
MPEG1 Layer 2 specification at 96 Kb/s.
• Uncompressed PCM - uncompressed digital audio
(standard Avid audio).
If you select a dual target, you should also select a
n
primary target.
TargetAudioTrackMapping This text box lets you identify the mapping of source audio
tracks to the output (target) audio tracks. See “Mapping of
Audio Tracks in MIXDOWN and DUALMIXDOWN
Modes” on page 100.
TargetVideoQuality Select a video resolution for the first (primary) transcode.
• None - the mixed-down clip does not include the video
tracks.
For example, if you select None from the
TargetVideoQuality menu, then the video tracks are not
mixed down during the Interplay Transcode operation.
• Select the video resolution for the mix down.
99
Page 100

6 Working with the Transcode Service
DUALMIXDOWN Mode Transcode Profile Settings (Continued)
Parameter Description
TargetVideoQualityDual Select a video resolution for the second transcode.
• None - the mixed-down clip does not include the video
tracks.
For example, if you select None from the
TargetVideoQualityDual menu, then the video tracks
are not mixed down during the Interplay Transcode
operation.
• Select the video resolution for the mixdown.
If you select a dual target, you should also select a
n
primary target.
VideoTimeCodeFormat Not used - for future use.
Workspace Type the name of the Avid shared-storage workspace that
will hold the new media files.
Mapping of Audio Tracks in MIXDOWN and DUALMIXDOWN Modes
100
When you create a Avid Interplay Transcode profile for mixing down the source audio, you
can also specify how the source audio tracks map to the target audio tracks. The
TargetAudioTrackMapping text box lets you identify the source audio tracks and how you
want them mapped to the target audio tracks.
Use the following rules in the TargetAudioTrackMapping text box:
AudioMode[S or A]TargetAudioTrack=SourceAudioTrack+SourceAudioTrack;
For example, S1=1+2; performs a stereo mapping of the source audio track 1 to the target
audio track 1 and the source audio track 2 to the target audio track 2.
If you leave the TargetAudioTrackMapping text box blank, then the default audio track
mapping is used: S1=0; which is stereo mode with all source audio tracks mapping to target
audio tracks 1 and 2.
You can enter a series of output (target) track mapping specifications. The following table
explains the specifications:
 Loading...
Loading...