Page 1

Avid® Interplay™ Engine
Failover Guide
make manage move | media
™
Avid
®
Page 2

Copyright and Disclaimer
Product specifications are subject to change without notice and do not represent a commitment on the part of
Avid Technology, Inc.
The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement. You can obtain a copy of that license by
visiting Avid's Web site at www.avid.com. The terms of that license are also available in the product in the same directory as
the software. The software may not be reverse assembled and may be used or copied only in accordance with the terms of the
license agreement. It is against the law to copy the software on any medium except as specifically allowed in the license
agreement.
Avid products or portions thereof are protected by one or more of the following United States Patents: 4,746,994; 4,970,663;
5,045,940; 5,267,351; 5,309,528; 5,355,450; 5,396,594; 5,440,348; 5,452,378; 5,467,288; 5,513,375; 5,528,310; 5,557,423;
5,577,190; 5,584,006; 5,640,601; 5,644,364; 5,654,737; 5,715,018; 5,724,605; 5,726,717; 5,729,673; 5,745,637; 5,752,029;
5,754,851; 5,799,150; 5,812,216; 5,828,678; 5,842,014; 5,852,435; 5,987,501; 6,061,758; 6,223,211; 6,301,105; 6,532,043;
6,546,190; 6,636,869; 6,747,705, 6,763,523; 6,813,622. Other patents are pending.
This document is protected under copyright law. An authorized licensee of Avid Interplay may reproduce this publication for the
licensee’s own use in learning how to use the software. This document may not be reproduced or distributed, in whole or in
part, for commercial purposes, such as selling copies of this document or providing support or educational services to others.
This document is supplied as a guide for Avid Interplay. Reasonable care has been taken in preparing the information it
contains. However, this document may contain omissions, technical inaccuracies, or typographical errors. Avid Technology,
Inc. does not accept responsibility of any kind for customers’ losses due to the use of this document. Product specifications
are subject to change without notice.
Copyright © 2007 Avid Technology, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved.
The following disclaimer is required by Apple Computer, Inc.
APPLE COMPUTER, INC. MAKES NO WARRANTIES WHATSOEVER, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING
THIS PRODUCT, INCLUDING WARRANTIES WITH RESPECT TO ITS MERCHANTABILITY OR ITS FITNESS FOR ANY
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE EXCLUSION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES IS NOT PERMITTED BY SOME STATES. THE
ABOVE EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. THIS WARRANTY PROVIDES YOU WITH SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS.
THERE MAY BE OTHER RIGHTS THAT YOU MAY HAVE WHICH VARY FROM STATE TO STATE.
The following disclaimer is required by Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics, Inc. for the use of their TIFF library:
Copyright © 1988–1997 Sam Leffler
Copyright © 1991–1997 Silicon Graphics, Inc.
Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and sell this software [i.e., the TIFF library] and its documentation for any purpose
is hereby granted without fee, provided that (i) the above copyright notices and this permission notice appear in all copies of
the software and related documentation, and (ii) the names of Sam Leffler and Silicon Graphics may not be used in any
advertising or publicity relating to the software without the specific, prior written permission of Sam Leffler and Silicon
Graphics.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS-IS” AND WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR
OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL SAM LEFFLER OR SILICON GRAPHICS BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE,
DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER OR NOT ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF DAMAGE, AND ON ANY THEORY OF
LIABILITY, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
The following disclaimer is required by the Independent JPEG Group:
Portions of this software are based on the work of the Independent JPEG Group.
This Software may contain components licensed under the following conditions:
Copyright © 1989 The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms are permitted provided that the above copyright notice and this paragraph
are duplicated in all such forms and that any documentation, advertising materials, and other materials related to such
distribution and use acknowledge that the software was developed by the University of California, Berkeley. The name of the
University may not be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written
permission. THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED ``AS IS'' AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES,
INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
2
Page 3

Copyright © 1989, 1991 by Jef Poskanzer.
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby
granted, provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission
notice appear in supporting documentation. This software is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
Copyright 1995, Trinity College Computing Center. Written by David Chappell.
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby
granted, provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission
notice appear in supporting documentation. This software is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
Copyright 1996 Daniel Dardailler.
Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and sell this software for any purpose is hereby granted without fee, provided that
the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear in
supporting documentation, and that the name of Daniel Dardailler not be used in advertising or publicity pertaining to
distribution of the software without specific, written prior permission. Daniel Dardailler makes no representations about the
suitability of this software for any purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
Modifications Copyright 1999 Matt Koss, under the same license as above.
Copyright © 1991 by AT&T.
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software for any purpose without fee is hereby granted, provided that this
entire notice is included in all copies of any software which is or includes a copy or modification of this software and in all
copies of the supporting documentation for such software.
THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY. IN PARTICULAR,
NEITHER THE AUTHOR NOR AT&T MAKES ANY REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY OF ANY KIND CONCERNING THE
MERCHANTABILITY OF THIS SOFTWARE OR ITS FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
This product includes software developed by the University of California, Berkeley and its contributors.
The following disclaimer is required by Paradigm Matrix:
Portions of this software licensed from Paradigm Matrix.
The following disclaimer is required by Ray Sauers Associates, Inc.:
“Install-It” is licensed from Ray Sauers Associates, Inc. End-User is prohibited from taking any action to derive a source code
equivalent of “Install-It,” including by reverse assembly or reverse compilation, Ray Sauers Associates, Inc. shall in no event be
liable for any damages resulting from reseller’s failure to perform reseller’s obligation; or any damages arising from use or
operation of reseller’s products or the software; or any other damages, including but not limited to, incidental, direct, indirect,
special or consequential Damages including lost profits, or damages resulting from loss of use or inability to use reseller’s
products or the software for any reason including copyright or patent infringement, or lost data, even if Ray Sauers Associates
has been advised, knew or should have known of the possibility of such damages.
The following disclaimer is required by Videomedia, Inc.:
“Videomedia, Inc. makes no warranties whatsoever, either express or implied, regarding this product, including warranties with
respect to its merchantability or its fitness for any particular purpose.”
“This software contains V-LAN ver. 3.0 Command Protocols which communicate with V-LAN ver. 3.0 products developed by
Videomedia, Inc. and V-LAN ver. 3.0 compatible products developed by third parties under license from Videomedia, Inc. Use
of this software will allow “frame accurate” editing control of applicable videotape recorder decks, videodisc recorders/players
and the like.”
The following disclaimer is required by Altura Software, Inc. for the use of its Mac2Win software and Sample
Source Code:
©1993–1998 Altura Software, Inc.
The following disclaimer is required by 3Prong.com Inc.:
Certain waveform and vector monitoring capabilities are provided under a license from 3Prong.com Inc.
3
Page 4

The following disclaimer is required by Interplay Entertainment Corp.:
The “Interplay” name is used with the permission of Interplay Entertainment Corp., which bears no responsibility for Avid
products.
This product includes portions of the Alloy Look & Feel software from Incors GmbH.
This product includes software developed by the Apache Software Foundation (http://www.apache.org/
© DevelopMentor
This product may include the JCifs library, for which the following notice applies:
JCifs © Copyright 2004, The JCIFS Project, is licensed under LGPL (http://jcifs.samba.org/). See the LGPL.txt file in the Third
Party Software directory on the installation CD.
Avid Interplay contains components licensed from LavanTech. These components may only be used as part of and in
connection with Avid Interplay.
Attn. Government User(s). Restricted Rights Legend
U.S. GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. This Software and its documentation are “commercial computer software” or
“commercial computer software documentation.” In the event that such Software or documentation is acquired by or on behalf
of a unit or agency of the U.S. Government, all rights with respect to this Software and documentation are subject to the terms
of the License Agreement, pursuant to FAR §12.212(a) and/or DFARS §227.7202-1(a), as applicable.
Trademarks
888 I/O, Adrenaline, AirPlay, AirSPACE, AirSPACE HD, AirSpeed, AniMatte, AudioSuite, AudioVision, AutoSync, Avid,
Avid DNA, Avid DNxcel, Avid DNxHD, AVIDdrive, AVIDdrive Towers, Avid DS Assist Station, Avid ISIS,
Avid Learning Excellerator, Avid Liquid, Avid Mojo, AvidNet, AvidNetwork, Avid Remote Response, AVIDstripe, Avid Unity,
Avid Unity ISIS, Avid Xpress, AVoption, AVX, CamCutter, ChromaCurve, ChromaWheel, DAE, Dazzle, Deko, DekoCast, D-Fi,
D-fx, DigiDelivery, Digidesign, Digidesign Audio Engine, Digidesign Intelligent Noise Reduction, DigiDrive,
Digital Nonlinear Accelerator, DigiTranslator, DINR, DNxchange, do more, D-Verb, Equinox, ExpertRender, Face Robot,
FieldPak, Film Composer, FilmScribe, FluidMotion, HIIP, HyperSPACE, HyperSPACE HDCAM, IllusionFX,
Image Independence, iNEWS, iNEWS ControlAir, Instinct, Interplay, Intraframe, iS9, iS18, iS23, iS36, LaunchPad, Lightning,
Lo-Fi, Magic Mask, make manage move | media, Marquee, Matador, Maxim, MCXpress, Media Browse, Media Composer,
MediaDock, MediaDock Shuttle, Media Fusion, Media Illusion, MediaLog, Media Reader, Media Recorder, MEDIArray,
MediaShare, MediaStream, Meridien, MetaSync, MissionControl, NaturalMatch, Nearchive, NetReview, NewsCutter, Nitris,
OMF, OMF Interchange, OMM, Open Media Framework, Open Media Management, PCTV, Pinnacle MediaSuite,
Pinnacle Studio, Pinnacle Systems, ProEncode, Pro Tools, QuietDrive, Recti-Fi, RetroLoop, rS9, rS18, Sci-Fi, ScriptSync,
SecureProductionEnvironment, Show Center, Softimage, Sound Designer II, SPACE, SPACEShift, SpectraGraph,
SpectraMatte, SteadyGlide, Symphony, TARGA, Thunder, Trilligent, UnityRAID, Vari-Fi, Video RAID, Video Slave Driver,
VideoSPACE, and Xdeck are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Avid Technology, Inc. in the United States and/or
other countries.
).
Adobe and Photoshop are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States
and/or other countries. Apple and Macintosh are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other
countries. Windows is either a registered trademark or trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other
countries. All other trademarks contained herein are the property of their respective owners.
Footage
Arizona Images — KNTV Production — Courtesy of Granite Broadcasting, Inc.,
Editor/Producer Bryan Foote.
Eco Challenge Morocco — Courtesy of Discovery Communications, Inc.
News material provided by WFTV Television Inc.
Tornados + Belle Isle footage — Courtesy of KWTV News 9.
WCAU Fire Story — Courtesy of NBC-10, Philadelphia, PA.
Women in Sports – Paragliding — Courtesy of Legendary Entertainment, Inc.
GOT FOOTAGE?
Editors — Filmmakers — Special Effects Artists — Game Developers — Animators — Educators — Broadcasters — Content
creators of every genre — Just finished an incredible project and want to share it with the world?
Send us your reels and we may use your footage in our show reel or demo!*
For a copy of our release and Avid’s mailing address, go to www.avid.com/footage.
*Note: Avid cannot guarantee the use of materials submitted.
Avid Interplay Engine Failover Guide • 0130-07643-02 Rev B • November 2007 • 11/09/07 16:04
4
Page 5

Contents
Using This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Symbols and Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
If You Need Help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Accessing the Online Library . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
How to Order Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Avid Training Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Chapter 1 Automatic Server Failover Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Summary of the Way it Works. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Installing the Failover Hardware Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
SR2400 Slot Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
SR2500 Slot Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Installing a Failover Cluster in Avid Unity ISIS Environment (SR2400) . . . . . . . 18
Installing a Failover Cluster in Avid Unity ISIS Environment (SR2500) . . . . . . . 19
Failover Cluster Connections in an Unity ISIS Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Installing a Failover Cluster in an Avid Unity MediaNetwork
Environment (SR2400) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Installing a Failover Cluster in an Avid Unity MediaNetwork
Environment (SR2500) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Failover Cluster Connections in an Unity MediaNetwork Environment . . . . 23
Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Server Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Space Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Antivirus Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Need To Know . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Before You Start: Preparation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
List of IP Addresses and Network Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5
Page 6

Renaming Local Area Network Interface on Each Node. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Configuring the Binding Order Networks on Each Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Configuring Private Network Adapter on Each Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Configuring Public Network Adapter on Each Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Join Both Servers to the Active Directory Domain. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Setting Up a Cluster User Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configuring the Cluster Shared RAID Disks on Each Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configuring the Cluster Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Configuring the Cluster Service on the First Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Validating the Cluster Service on the First Node. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Configuring the Cluster Service on the Second Node. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Configuring Rules For The Cluster Networks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Prioritizing the Heartbeat Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
After Setting Up the Cluster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Verifying the Quorum Disk. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Setting the Startup Times on Each Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Testing the Cluster Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Installing the Distributed Transaction Coordinator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Creating a Resource Group for the Distributed Transaction Coordinator . . . . . 55
Assigning an IP Address to the MSDTC Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Assigning a Network Name to the MSDTC Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Creating a Physical Resource for the MSDTC Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Assigning Distributed Transaction Coordinator Resource to the MSDTC Group 58
Bring the MSDTC Online. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Disabling Any Web Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Preparation and Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Starting the Installation and Accepting the License Agreement . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Preparing the Server for the Interplay Engine Installation Using Custom Mode 62
Specify Cluster Mode During a Custom Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Specifying the Interplay Engine Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Specifying the Interplay Engine Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Specifying the Destination Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
6
Page 7

Specifying the Default Database Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Specifying the Share Name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Specifying the Configuration Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Specifying the Server User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Specifying the Server Cache. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Enabling Email Notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Preparing the Server for the Interplay Engine Installation Using Typical Mode . 74
Specify Cluster Mode During a Typical Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Specifying the Cluster Information During a Typical Installation . . . . . . . . . 75
Specifying the Server User During a Typical Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Beginning the Installation of Interplay Engine on the First Node . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Bringing the Disk Resource Online . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Installing Interplay Engine on the Second Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Bring the Interplay Engine Online . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Testing the Complete Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Updating a Clustered Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Updating the Workgroup.xml File for a Split Database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Uninstalling the Interplay Engine. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Chapter 3 Automatic Server Failover Tips and Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Don't Access the Machines Directly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Make Sure to Connect to the Interplay Engine Resource Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Do Not Rename Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Do Not Install the Server on a Shared Disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Do Not Change the Interplay Engine Execution User. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Do Not Edit the Registry While the Server is Offline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Do Not Remove the Dependencies of the Affiliated Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Consider Disabling Failover When Experimenting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
7
Page 8

8
Page 9

Using This Guide
Congratulations on your purchase of Avid Interplay, a powerful system for managing media
in a shared storage environment.
This guide is intended for all Avid Interplay administrators who are responsible for
installing, configuring and maintaining an Avid Interplay Engine with the Automatic Server
Failover module integrated.
n
The documentation describes the features and hardware of all models. Therefore, your
system might not contain certain features and hardware that are covered in the
documentation.
Page 10
Using This Guide
Symbols and Conventions
Avid documentation uses the following symbols and conventions:
Symbol or Convention Meaning or Action
n
c
w
> This symbol indicates menu commands (and subcommands) in the
t
k
Margin tips
Italic font Italic font is used to emphasize certain words and to indicate
Courier Bold font
A note provides important related information, reminders,
recommendations, and strong suggestions.
A caution means that a specific action you take could cause harm to
your computer or cause you to lose data.
A warning describes an action that could cause you physical harm.
Follow the guidelines in this document or on the unit itself when
handling electrical equipment.
order you select them. For example, File > Import means to open the
File menu and then select the Import command.
This symbol indicates a single-step procedure. Multiple arrows in a
list indicate that you perform one of the actions listed.
This symbol represents the Apple or Command key. Press and hold
the Command key and another key to perform a keyboard shortcut.
In the margin, you will find tips that help you perform tasks more
easily and efficiently.
variables.
Courier Bold font identifies text that you type.
10
Ctrl+key or mouse action
k+key or mouse action
Press and hold the first key while you press the last key or perform
the mouse action. For example, k+Option+C or Ctrl+drag.
Page 11

If You Need Help
If you are having trouble using Avid Interplay:
1. Retry the action, carefully following the instructions given for that task in this guide. It
is especially important to check each step of your workflow.
2. Check for the latest information that might have become available after the
documentation was published:
- If the latest information for your Avid product is provided as printed release notes,
they ship with your application and are also available online.
- If the latest information for your Avid product is provided as a ReadMe file, it is
supplied on your Avid installation CD or DVD as a PDF document and is also
available online.
You should always check online for the most up-to-date release notes or ReadMe
because the online version is updated whenever new information becomes
available. To view the online ReadMe, visit the Knowledge Base at
www.avid.com/readme.
3. Check the documentation that came with your Avid application or your hardware for
maintenance or hardware-related issues.
If You Need Help
4. Visit the online Knowledge Base at www.avid.com/onlinesupport. Online services are
available 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. Search this online Knowledge Base to find
answers, to view error messages, to access troubleshooting tips, to download updates,
and to read or join online message-board discussions.
Accessing the Online Library
The Avid Interplay Online Library DVD contains all the Avid Interplay product
documentation in PDF format.
n
You need Adobe® Reader® to view the documentation online. You can download the latest
version from the Adobe web site.
To access the online library from the Online Library DVD:
1. Insert the Online Library DVD into the drive.
2. Double-click the Mainmenu file.
The Online Library includes a Master Glossary of all specialized terminology used in the
documentation for Avid products.
11
Page 12

Using This Guide
Most Avid online libraries also include multimedia content such as feature presentations.
This multimedia content is an excellent first resource for learning how to use your
application or for helping you understand a particular feature or workflow.
How to Order Documentation
To order additional copies of this documentation from within the United States, call Avid
Sales at 800-949-AVID (800-949-2843). If you are placing an order from outside the United
States, contact your local Avid representative.
Avid Training Services
Avid makes lifelong learning, career advancement, and personal development easy and
convenient. Avid understands that the knowledge you need to differentiate yourself is always
changing, and Avid continually updates course content and offers new training delivery
methods that accommodate your pressured and competitive work environment.
To learn about Avid's new online learning environment, Avid Learning Excellerator
(ALEX), visit http://learn.avid.com.
12
For information on courses/schedules, training centers, certifications, courseware, and
books, please visit www.avid.com/training or call Avid Sales at 800-949-AVID
(800-949-2843).
Page 13

Chapter 1
Automatic Server Failover Introduction
This chapter covers the following topics:
• Introduction
• Summary of the Way it Works
• Installing the Failover Hardware Components
• Terminology
Introduction
The automatic server failover mechanism in Avid Interplay allows client access to the
Interplay Engine in the event of failures or during maintenance, with minimal impact on the
availability. A failover server is activated in the event of application, operating system, or
hardware failures. The server can be configured to notify the administrator about such
failures using email.
c
Additional monitoring of the hardware and software components of a high availability
solution is always required. Avid delivers Interplay preconfigured, but additional
attention on the customer side is required to prevent outage (for example, when a
private network fails, RAID disk fails, or a power supply loses power). In a mission
critical environment, monitoring tools and tasks are needed to be sure there are no
silent outages. If another (unmonitored) component fails, only an event is generated,
and while this does not interrupt availability, it might go unnoticed and lead to
problems. Additional software reporting such issues to the IT administration lowers
downtime risk.
The failover cluster is a system made up of two server nodes and a shared storage device
connected over Fibre Channel. These are to be deployed in the same location given the
shared access to the storage device. The cluster uses the concept of virtual servers to specify
groups of resources that failover together.
Page 14
Chapter 1 Automatic Server Failover Introduction
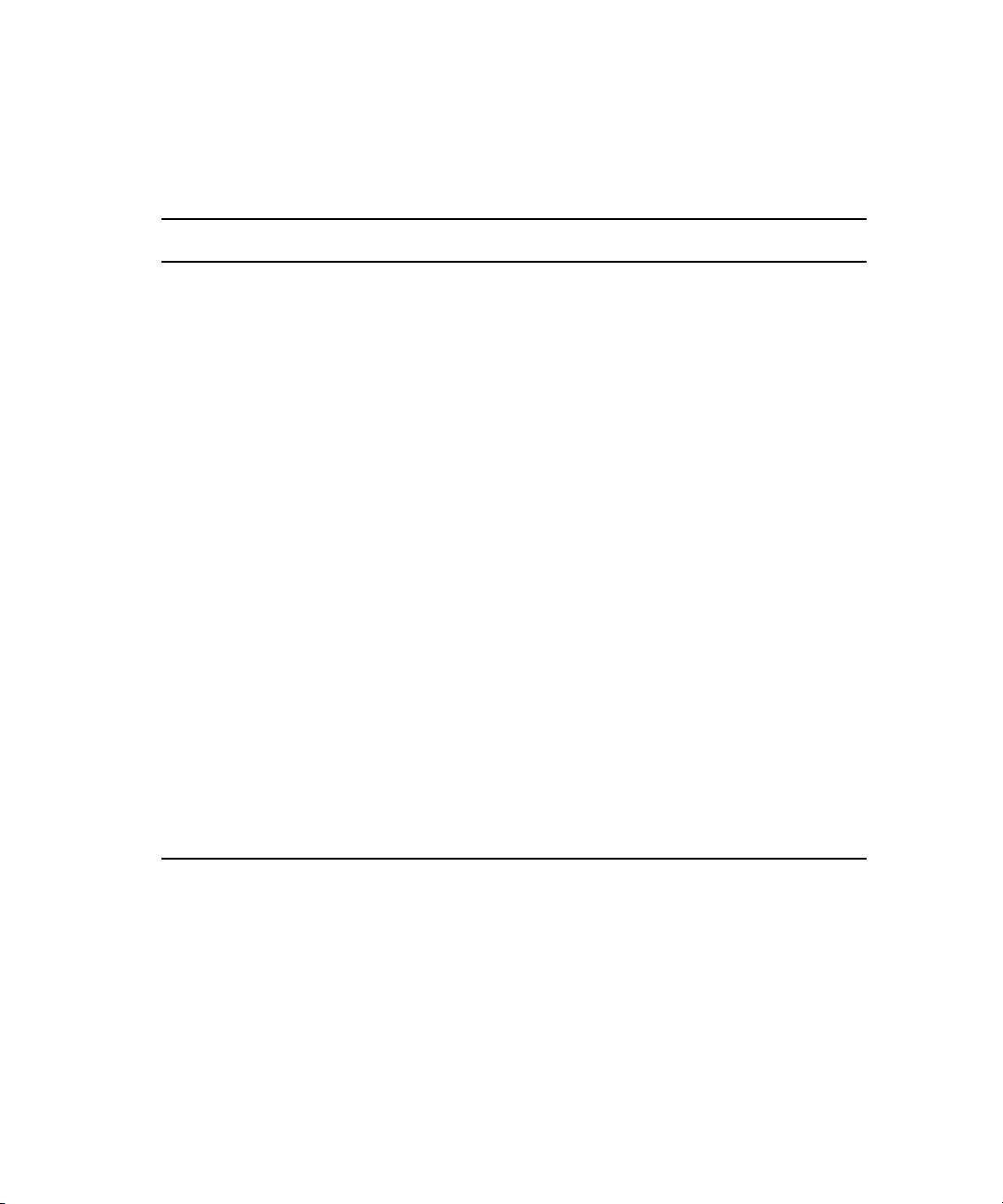
The following diagram illustrates the failover cluster architecture.
Two-Node Cluster in
Unity MediaNetwork environment
Interplay clients
Intranet
Cluster shared
RAID array
Network Switch
Private network
for heartbeat
Interplay Engine - Cluster Node
Interplay Engine - Cluster Node
n
14
Fibre Switch
If you are already using clusters, the Avid Interplay Engine won't interfere with your
current setup.
Page 15
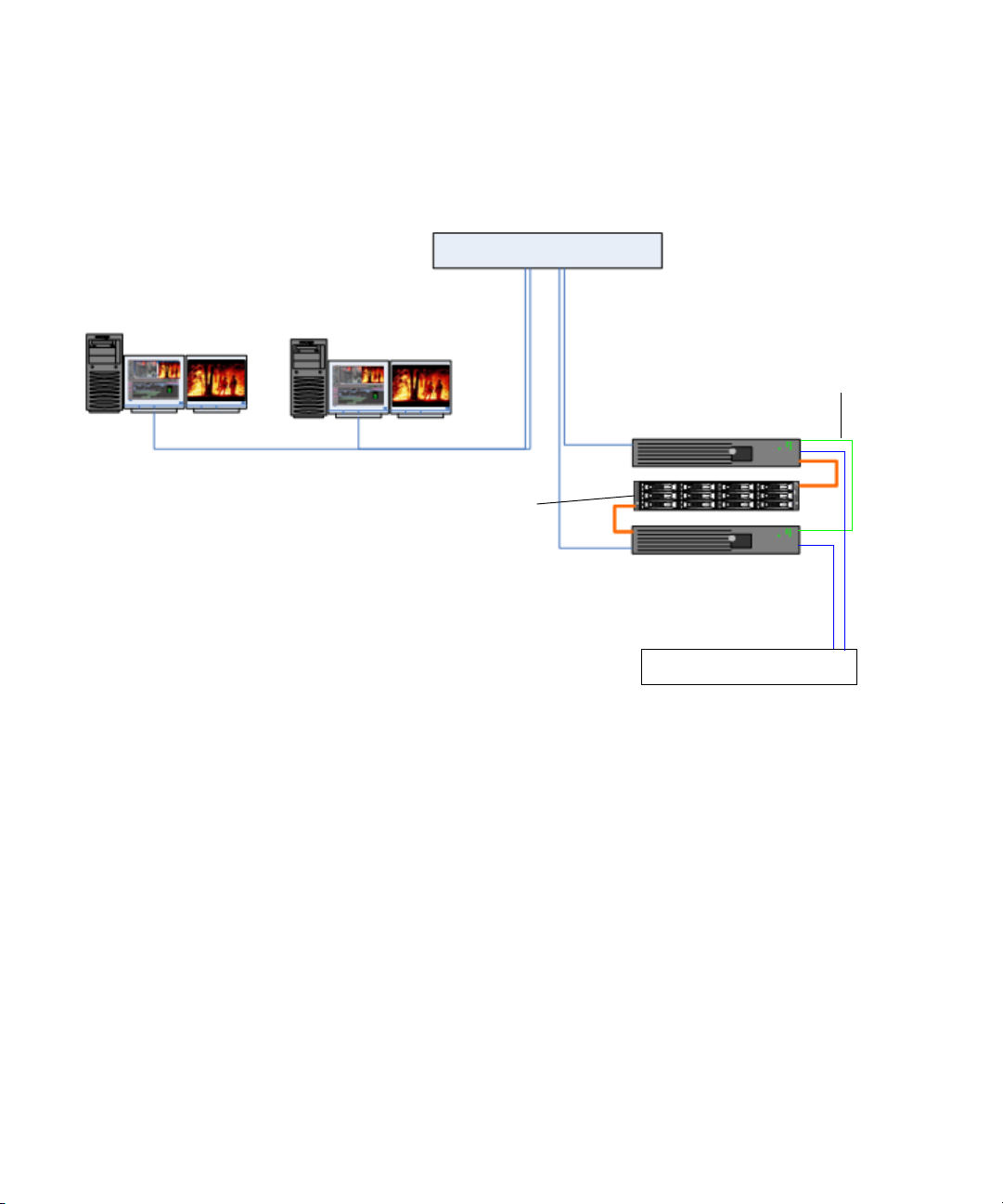
Summary of the Way it Works
When the Microsoft® Windows® cluster service is running on the machines and the server is
deployed in cluster mode, the Interplay Engine and its accompanying services are exposed to
users as a virtual server. To clients, however, connecting to the clustered virtual Interplay
Engine appears to be the same process as connecting to a single, physical machine. The user
or client application does not know which node is actually hosting the virtual server.
When the server is online, the resource monitor regularly checks its availability and
automatically restarts the server or initiates a failover to the other node if a failure is
detected. The exact behavior can be configured using the Windows Cluster Administrator
console. Given that clients connect to the virtual network name and IP address, which are
also taken over by the failover node, this minimizes the impact on the availability of the
server. The following diagram illustrates the cluster group.
Summary of the Way it Works
Avid Unity MediaNetwork
environment
Failover Cluster
11.22.33.200
Node #1
Intranet: 11.22.33.44
Private: 10.10.10.10
Disk #1
Quorum
4GB
Cluster Group
Intranet
Interplay Server
(virtual)
11.22.33.201
Private Network
FibreChannel
Disk #2
MSDTC
5GB
MSDTC
11.22.33.202
Intranet
Node #2
Intranet: 11.22.33.45
Private: 10.10.10.11
Disk #3
Database
925GB +
15
Page 16
Chapter 1 Automatic Server Failover Introduction
Installing the Failover Hardware Components
A failover cluster system includes the following components:
• Two Interplay Engine nodes or two Interplay Archive nodes (SR2400 or SR2500)
• Cluster shared storage - RAID array
SR2400 Slot Locations
The SR2400 is supported as a server for the Interplay applications. This section describes
the slot locations that are specific to the Interplay components in a cluster configuration.
Use the following figure and table as guides to how your SR2400 is configured in an
Interplay cluster environment.
SR2400 Back Panel
Small form factor slots not used
Mouse
PCI slots
Slot 3
Slot 2
Slot 1
n
16
Keyboard
RJ 45 to
serial B
1 Gig
Enet
Video
USB
Serial A to F/C switch if needed
SCSI B
Power supply
2
1
On the SR2400, all boards must be installed starting in the top slot, and the second board
must be in the middle slots, it cannot be in the bottom slot with the middle slot left open.
SR2400 Back Panel Configuration for Avid Unity Environment
Slot
Unity ISIS
Interplay Engine Node and
Archive Engine Node
Unity MediaNetwork
Interplay Engine Node and
Archive Engine Node
3 Intel Pro 1000MT ATTO
2 QLogic Card QLogic Card
1 Empty Intel Pro 1000MT
a. Unity MediaNetwork environment; the Pro 1000MT card is shipped in slot 3 (top). You must move the
card to slot 1 (bottom) and install the ATTO card in slot 3 (top). The Pro 1000MT is not used in an Unity
MediaNetwork environment.
a
Page 17
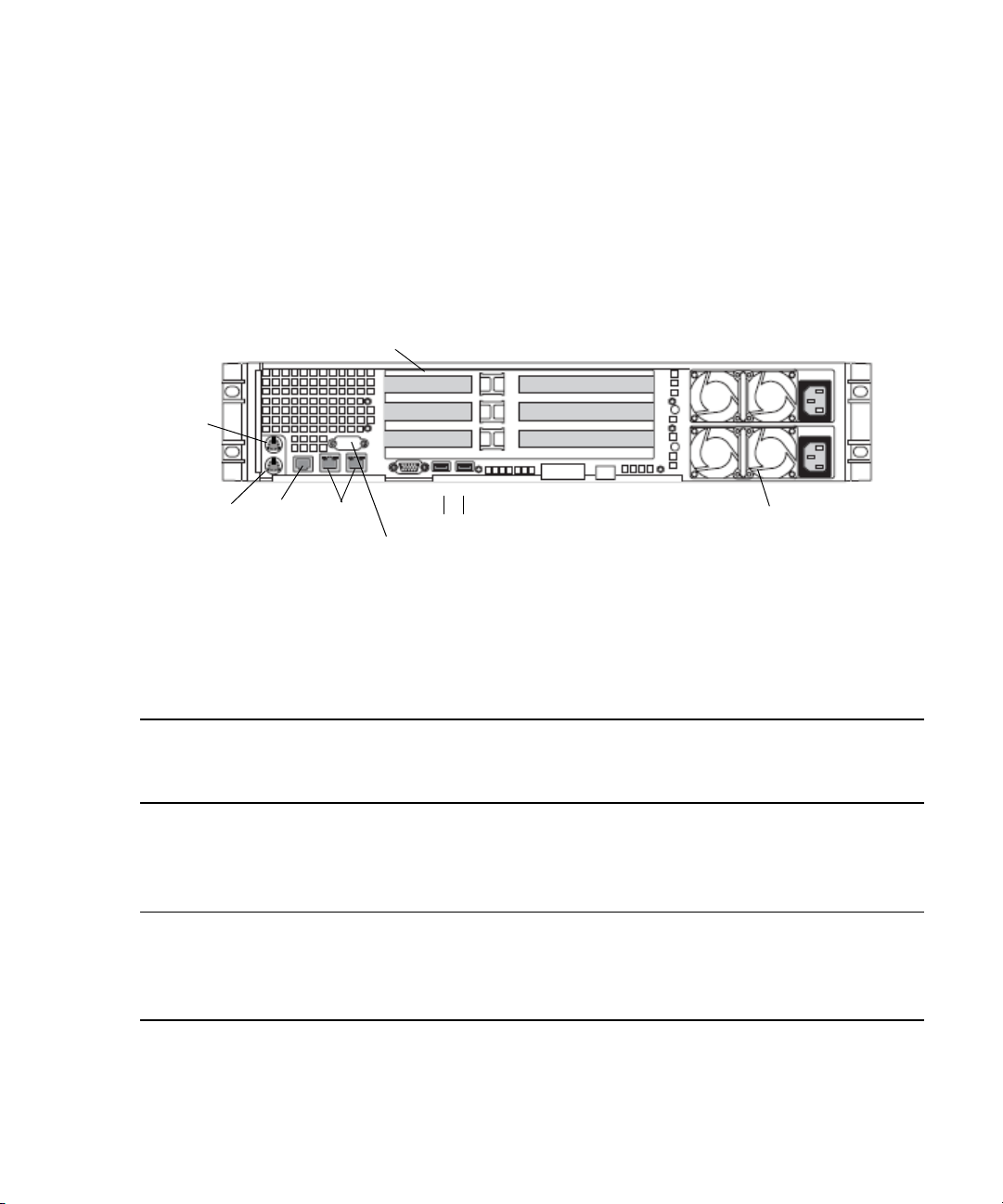
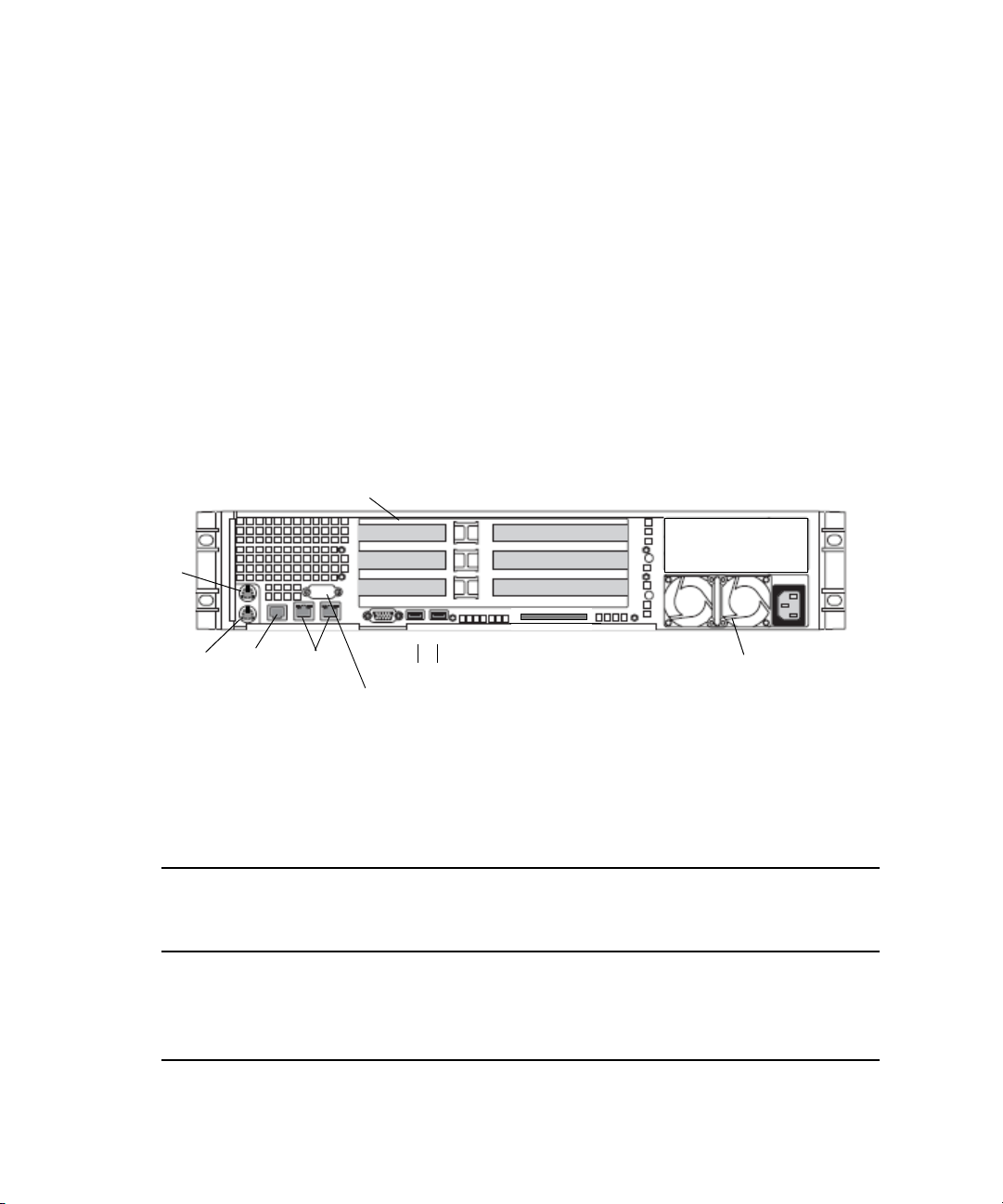
SR2500 Slot Locations
The SR2500 is supported as a server for the Interplay applications. This section describes
the slot locations that are specific to the Interplay components in a cluster configuration.
Use the following figure and table as guides to how your SR2500 is configured in an
Interplay cluster environment.
SR2500 Back Panel
Installing the Failover Hardware Components
Mouse
n
Small form factor slots
Slot 2
Slot 1
12
Keyboard
RJ 45 to
serial B
1 Gig
Enet
Video
USB
Serial A to F/C switch if needed
Its important to match the slot locations in the following tables because they match the order
that the drivers are loaded on the SR2500 Recovery DVDs.
PCI slots
Slot 3
Slot 2
Slot 1
SR2500 Back Panel Configuration for Avid Unity Environment
Slot Type Slot
Unity ISIS
Interplay Engine Node and
Archive Engine Node
Unity MediaNetwork
Interplay Engine Node and
Archive Engine Node
PCI-X 3 Empty ATTO
2 Empty Empty
1 QLogic Card
a
QLogic Card
Power supplies
Primary power
supply on bottom
a
PCIe NA NA NA
2 Intel Pro 1000PT Intel Pro 1000PT
1 Empty Empty
a. The SR2500 server might ship with the QLogic card in PCI-X slot 2 (middle). You must move the QLogic card to
PCI-X slot 1 (bottom), because this configuration matches the order that the drivers are loaded on the SR2500
Recovery DVDs.
17
Page 18
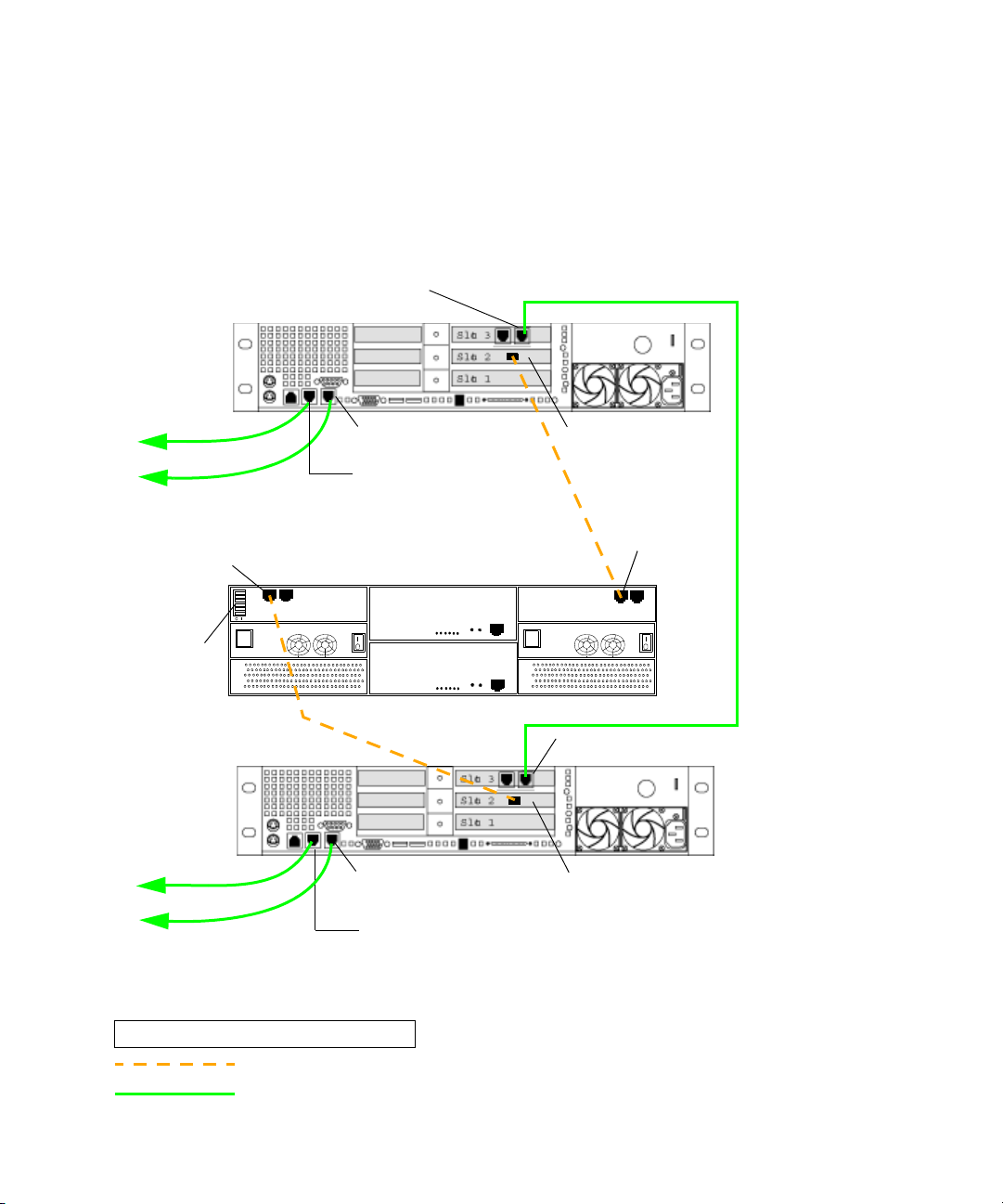
Chapter 1 Automatic Server Failover Introduction
Installing a Failover Cluster in Avid Unity ISIS Environment (SR2400)
The following illustration shows the required cable connections when adding a failover
cluster in an Unity ISIS environment (SR2400 servers). For a description of the connections,
see “Failover Cluster Connections in an Unity ISIS Environment” on page 20.
PCI adapter network interface
right connector
Interplay Engine
Cluster Node
SR2400
To Unity ISIS
left subnet
To Unity ISIS right subnet
Fibre Channel 0
left connector
Right - on board
network interface
Left - on board
network interface
Cluster Shared Storage RAID array
QLogic card
Fibre Channel 1
left connector
Back Panel
Private network
for heartbeat
all switches
set to default
“enabled” left
Interplay Engine
Cluster Node
To Unity ISIS
left subnet
To Unity ISIS
right subnet
FC CH0
LEGEND
Fibre connection
1GB Ethernet connection
Right - on board
network interface
Left - on board
network interface
FC CH1
PCI adapter network interface
right connector
SR2400
Back Panel
QLogic card
18
Page 19
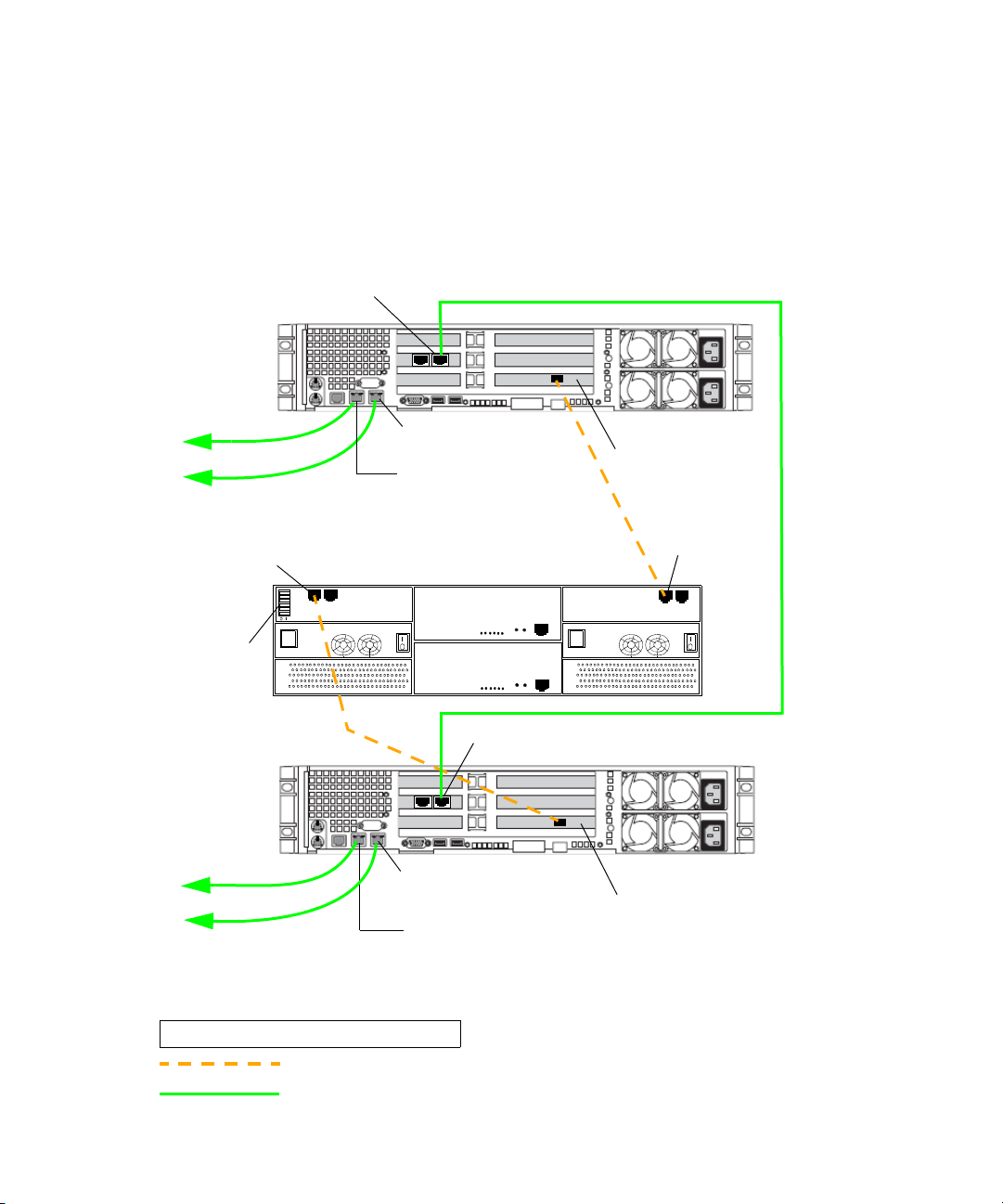
Installing the Failover Hardware Components
Installing a Failover Cluster in Avid Unity ISIS Environment (SR2500)
The following illustration shows the required cable connections when adding a failover
cluster in an Unity ISIS environment (SR2500 servers). For a description of the connections,
see “Failover Cluster Connections in an Unity ISIS Environment” on page 20.
PCI adapter network interface
right connector
Interplay Engine
Cluster Node
To Unity ISIS
left subnet
To Unity ISIS right subnet
Fibre Channel 0
left connector
Right - on board
network interface
Left - on board
network interface
Cluster Shared Storage RAID array
Slot 3
Slot 2
Slot 1
QLogic card
Fibre Channel 1
left connector
SR2500
Back Panel
Private network
for heartbeat
all switches
set to default
“enabled” left
Interplay Engine
Cluster Node
To Unity ISIS
left subnet
To Unity ISIS
right subnet
FC CH0
LEGEND
Fibre connection
1GB Ethernet connection
PCI adapter network interface right connector
Right - on board
network interface
Left - on board
network interface
FC CH1
SR2500
Back Panel
QLogic card
19
Page 20

Chapter 1 Automatic Server Failover Introduction
Failover Cluster Connections in an Unity ISIS Environment
Make the following cable connections to add a failover cluster to an Unity ISIS environment:
• First cluster node:
- Left - on board network interface connector to Unity ISIS Left subnet
- Right - on board network interface connector to Unity ISIS Right subnet
- QLogic card connector to cluster shared storage RAID array - left Fibre Channel 1
connector
• Second cluster node:
- Left - on board network interface connector to Unity ISIS Left subnet
- Right - on board network interface connector to Unity ISIS Right subnet
- QLogic card connector to cluster shared storage RAID array - left Fibre Channel 0
connector
• Right connector on PCI adapter network interface in the first cluster node to right
connector on PCI adapter network interface in second cluster node (private network for
heartbeat)
• All switches on the Infortrend cluster shared storage RAID array are in the default
“enable” position (left)
20
For more details, see the illustrations in:
• “Installing a Failover Cluster in Avid Unity ISIS Environment (SR2400)” on page 18.
• “Installing a Failover Cluster in Avid Unity ISIS Environment (SR2500)” on page 19.
Page 21
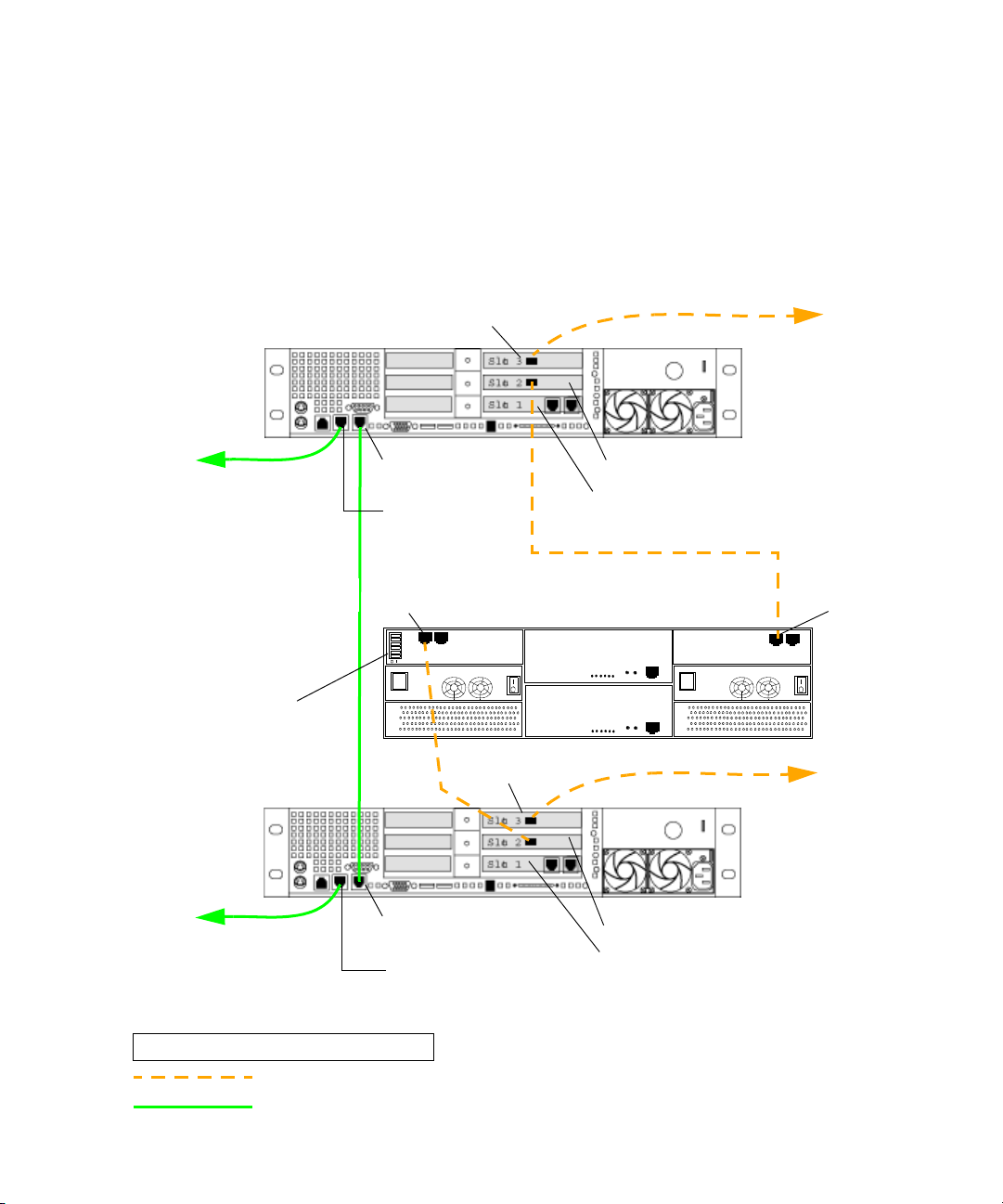
Installing the Failover Hardware Components
Installing a Failover Cluster in an Avid Unity MediaNetwork Environment (SR2400)
The following illustration shows the required cable connections when adding a failover
cluster in an Unity MediaNetwork environment (SR2400 servers). For a description of the
connections, see “Failover Cluster Connections in an Unity MediaNetwork Environment” on
page 23.
ATTO ca r d
Interplay Engine
Cluster Node
SR2400
Back Panel
To Unity
MediaNetwork
FC switch
To Ethernet
Public Network
all switches set to
default “enabled” left
Interplay Engine
Cluster Node
To Ethernet
Public Network
Private network
for heartbeat
Right - on board
network interface
Left - on board
network interface
Fibre Channel 0
left connector
FC CH0
ATTO ca r d
Right - on board
network interface
Left - on board
network interface
QLogic card
PCI adapter network interface - not used
Fibre Channel 1
left connector
Cluster Shared Storage RAID array
FC CH1
To Unity
MediaNetwork
FC switch
SR2400
Back Panel
QLogic card
PCI adapter network interface - not used
LEGEND
Fibre connection
1GB Ethernet connection
21
Page 22
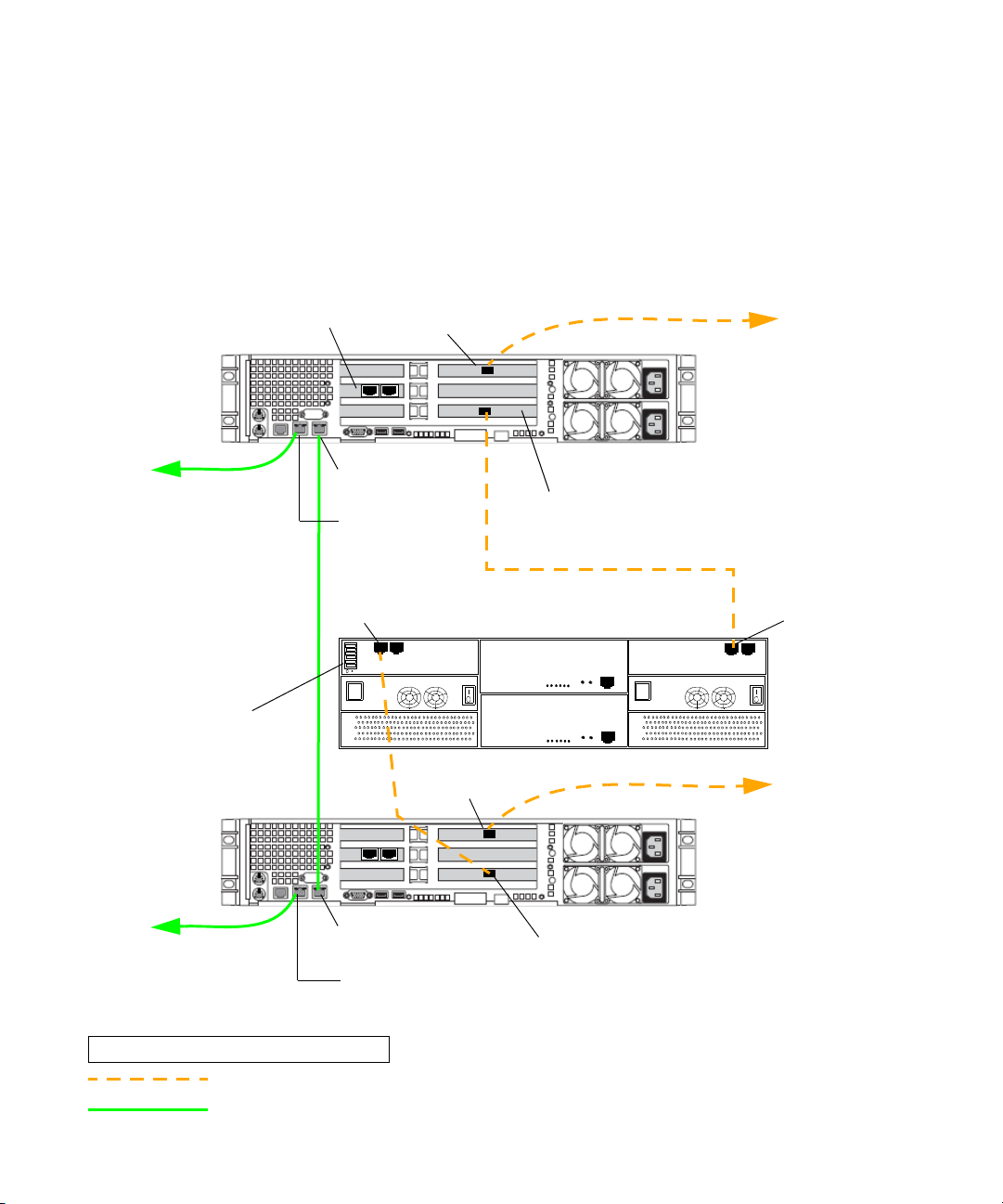
Chapter 1 Automatic Server Failover Introduction
Installing a Failover Cluster in an Avid Unity MediaNetwork Environment (SR2500)
The following illustration shows the required cable connections when adding a failover
cluster in an Unity MediaNetwork environment (SR2500 servers). For a description of the
connections, see “Failover Cluster Connections in an Unity MediaNetwork Environment” on
page 23.
PCI adapter network
interface - not used
Interplay Engine
Cluster Node
To Ethernet
Public Network
all switches set to
default “enabled” left
Interplay Engine
Cluster Node
Private network
for heartbeat
ATTO ca r d
Slot 3
Slot 2
Slot 1
Right - on board
network interface
Left - on board
network interface
Fibre Channel 0
left connector
FC CH0 FC CH1
Cluster Shared Storage RAID array
ATTO ca r d
QLogic card
To Unity
MediaNetwork
FC switch
SR2500
Back Panel
Fibre Channel 1
left connector
To Unity
MediaNetwork
FC switch
To Ethernet
Public Network
22
LEGEND
Fibre connection
1GB Ethernet connection
Right - on board
network interface
Left - on board
network interface
SR2500
Back Panel
QLogic card
Page 23

Installing the Failover Hardware Components
Failover Cluster Connections in an Unity MediaNetwork Environment
The Interplay Engine Cluster nodes (SR2400 servers) ship with an Intel Pro 1000 MT card
in slot 3 (top). You need to move this card to slot 1 (bottom). Then add an ATTO host bus
adapter in slot 3 (top).
Make the following cable connections to add a failover cluster to an Unity MediaNetwork
environment:
• First cluster node:
®
- Left - on board network interface connector to Ethernet
public network
- QLogic card connector to cluster shared storage RAID array - left Fibre Channel 1
connector
- ATTO card connector to Unity MediaNetwork FC switch
• Second cluster node:
- Left - on board network interface connector to Ethernet
public network
- QLogic card connector to cluster shared storage RAID array - left Fibre Channel 0
connector
- ATTO card connector to Unity MediaNetwork FC switch
• Right on board network interface connector on the first cluster node to right on board
network interface connector on the second cluster node (private network for heartbeat)
• All switches on the Infortrend cluster shared storage RAID array are in the default
“enable” position (left)
For more details, see the illustration in:
• “Installing a Failover Cluster in an Avid Unity MediaNetwork Environment (SR2400)”
on page 21.
• “Installing a Failover Cluster in an Avid Unity MediaNetwork Environment (SR2500)”
on page 22.
23
Page 24

Chapter 1 Automatic Server Failover Introduction
Terminology
Clustering is not always straightforward, so it is important that you get familiar with the
terminology of server clusters before you start. A good source of information is the
Microsoft Technology Center for Clustering Services under:
http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2003/technologies/clustering/default.mspx
Detailed architecture documentation can be found here:
http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2003/techinfo/overview/servercluster.mspx
Here is a brief summary of the major concepts and terms:
• Nodes - refers to individual computers.
• Cluster service - refers to the group of components on each node that perform a
cluster-specific activity.
• Resource - refers to cluster components (hardware and software) that are managed by
the cluster service. Physical hardware devices such as disk drives, and logical items such
as IP addresses and applications are referred to as resources.
• Online - refers to a resource that is available and is providing its service.
• Quorum resource - is a special common cluster resource. This resource plays a critical
role in cluster operations.
24
• Resource group - refers to a collection of resources that are managed by the cluster
service as a single, logical unit.
Page 25

Chapter 2
Automatic Server Failover Installation
This chapter describes the processes for configuring the automatic server failover. It is
crucial that you follow the instructions given in this chapter completely, otherwise the
automatic server failover will not work.
You can install the cluster service during any step of the overall Avid Interplay
installation process. For the Cluster Group, create a partition on the cluster shared RAID
array. This partition is used as the quorum disk (4GB). You also need to create two more
partitions: a partition for the MSDTC (see “Installing the Distributed Transaction
Coordinator” on page 54) and a large partition for the server databases. The latter is to store
both the database and the non Avid files. Activate the volumes on both nodes and assign
identical drive letters as described in “Configuring the Cluster Shared RAID Disks on Each
Node” on page 37.
n
Do not install any other software on the cluster machines except the Interplay engine.
For more details about server clusters, see the Microsoft document "Guide to Creating and
Configuring a Server Cluster under Windows Server 2003":
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/windowsserver2003/technologies/cluste
ring/confclus.mspx
Page 26

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
This chapter covers the following topics:
• Requirements
• Before You Start: Preparation
• Configuring the Cluster Service
• Configuring Rules For The Cluster Networks
• After Setting Up the Cluster
• Installing the Distributed Transaction Coordinator
• Disabling Any Web Servers
• Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
• Installing Interplay Engine on the Second Node
• Bring the Interplay Engine Online
• Testing the Complete Installation
• Updating a Clustered Installation
• Uninstalling the Interplay Engine
Requirements
Hardware
A dual server failover cluster capable system with a cluster shared RAID disk set is needed.
The automatic server failover system was developed on and tested with the following:
• Intel Server Chassis SR2500 Packaged Cluster, which is the recommended hardware:
http://www.intel.com/design/servers/chassis/sr2500/
• Intel Server Chassis SR2400 Packaged Cluster:
http://www.intel.com/design/servers/chassis/sr2400/
The servers in a cluster are connected using one or more cluster shared storage buses and
one or more physically independent networks acting as a heartbeat.
Server Software
Two licenses of Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition or Windows Server 2003
Datacenter Edition are needed.
26
Page 27

Space Requirements
The default disk configuration for the cluster shared RAID array is as follows:
• Quorum disk - 4GB
•MSDTC disk - 5GB
• Database disk - 925GB or larger
Antivirus Software
You can run antivirus software on a cluster, if the antivirus software is cluster-aware. For
information about cluster-aware versions of your antivirus software, contact the antivirus
vendor. If you are running antivirus software on a cluster, make sure you exclude these
locations from the virus scanning: Q:\ (Quorum disk), C:\Windows\Cluster, and
S:\Workgroup_Databases (database).
Need To Know
Before you setup a cluster in an Avid Interplay environment, you should be familiar with the
following functions:
• Microsoft Windows Active Directory Domains & Domain Users
Requirements
• Microsoft Windows Clustering (current version, as there are changes from prior version)
• Disk configuration (format, partition, naming)
• Network configuration
27
Page 28

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Before You Start: Preparation
Before you begin the installation process you need to obtain some IP addresses, IP host
names, domain user accounts, and establish server addresses on your network.
• Establish the subnet mask, the gateway, DNS and WINS server addresses on your
network.
• Install and setup an Avid Unity client on the Interplay Engine servers. See the Avid
Unity MediaNetwork File Manager Setup Guide or the Avid Unity ISIS System Setup
Guide.
• An Avid Unity user account with read and write privileges. This account is not needed
for the installation of Interplay Engine, but is required for the operation of
Interplay Engine.
• You need two domain user accounts when configuring a cluster:
n
You can use one account for the Cluster Service Account and the Cluster Installation
Account. However, this allows the Cluster Service Account more privileges than are needed.
- Cluster Service Account (Server Execution)—Decide on the cluster user name. The
procedures in this document use sqauser as an example for the Cluster Service
Account. This user account must have a unique name and be a domain user. This
user is assigned administrative rights on both servers. The Interplay Engine service
also runs under this account; you should be aware of this during the set up. The
server needs to access the media files and this might be a consideration when these
are to be located on a non-default location, that is, when the Avid Unity mounting
feature is going to be used.
For information on creating a cluster user account, see the Microsoft document
"Guide to Creating and Configuring a Server Cluster under Windows Server 2003":
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/windowsserver2003/technologies/cl
ustering/confclus.mspx
- Cluster Installation Account—Identify the user account to use during the
installation process. This user account is a domain user account with privileges to
add servers to the domain. This user account is only required during the installation
of the cluster.
• An existing Active Directory Domain is required before installing or configuring the
cluster.
• You need several static IP addresses for all network interfaces and host names. See “List
of IP Addresses and Network Names” on page 29.
28
Page 29

List of IP Addresses and Network Names
You need to reserve IP host names and static IP addresses before you begin the installation
process. A Unity ISIS environment needs 8 IP addresses and a Unity MediaNetwork needs
5 IP addresses. The following table provides a list of example names that you can use when
configuring the cluster. The procedures in this chapter use these example names.
Before You Start: Preparation
n
n
Make sure that these IP addresses are outside of the range that is available to DHCP so they
cannot automatically be assigned to other machines.
If your Active Directory Domain and/or DNS domain include more than one cluster, to avoid
conflicts, you need to make sure the cluster names, MSDTC names, and IP addresses are
different for each cluster.
Required IP Addresses and Node Names
Node or Service Item Required Example Name Where Used
First Cluster Node • 1 Host Name
• 2 ISIS IP addresses - public
(one for left and one for right)
• 1 IP address - private
(Heartbeat)
Second Cluster Node • 1 Host Name
• 2 ISIS IP addresses - public
(one for left and one for right)
• 1 IP address - private
(Heartbeat)
Cluster service • 1 Network Name
(virtual host name)
• 1 ISIS IP address
MSDTC service —
Distributed Transaction
Coordinator
Interplay Engine
service
• 1 Network Name
(virtual host name)
• 1 IP address
• 1 Network Name
(virtual host name)
• 2 ISIS IP addresses - public
(one for left and one for right)
a
a
a
a
a
SECLUSTER1 See “Configuring the Cluster
Service on the First Node”
b
SECLUSTER2 See “Configuring the Cluster
b
SECLUSTER See “Configuring the Cluster
CLUSTERMSDTC See “Assigning a Network
SEENGINE See “Specifying the Interplay
b
on page 39 and “Creating a
Resource Group for the
Distributed Transaction
Coordinator” on page 55.
Service on the Second Node”
on page 44 and “Creating a
Resource Group for the
Distributed Transaction
Coordinator” on page 55.
Service on the First Node”
on page 39.
Name to the MSDTC Group”
on page 57.
Engine Details” on page 64
and “Specifying the Interplay
Engine Name” on page 65.
a. All names must be a valid and unique network host name.
b. In an Avid Unity MediaNetwork environment you only need one public IP address.
29
Page 30

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Renaming Local Area Network Interface on Each Node
When you rename the LAN interface on each node, make sure you use the same names. The
names and network connections must match on both nodes.
To rename the local area network connections:
1. Open the Network Connections window.
a. Click Start and select Control Panel.
b. Right-click Network Connections, and select Open.
The Network Connections window opens.
30
2. Right-click one of the listed network connections and select Rename.
Page 31

Before You Start: Preparation
3. Depending on your Avid Unity environment, type a new name for the network
connection using the following table and press Enter.
This illustration shows
Unity ISIS environment.
c
Both nodes must use identical network interface names. Although you can use any
name for the network connections, Avid suggests that you use the naming conventions
provided in the following table.
Naming Network Connections
Network Interface
Left - on board network
interface
Right - on board network
interface
SR2400 back view
Unity ISIS
New Names
Left-subnet number
Right-subnet number
Left - PCI adapter network interface
Right - PCI adapter network interface
Right - on board network interface
Left - on board network interface
Unity MediaNetwork
New Names Comment
a
Public Public network
a
Private Unity ISIS - Public network
MediaNetwork - Private
network used for Heartbeat
between the two servers in
the cluster
Left - PCI adapter network
Not used Not used Disabled
interface
Right - PCI adapter network
interface
b
Private Not used Unity ISIS - Used for
Heartbeat between the two
servers in the cluster
MediaNetwork - Disabled
a. Use the subnet number of the Interface. The examples in this document use Left-74 and Right-75.
b. From the back of the server use the right connector on the PCI adapter.
31
Page 32

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
The following Network Connections window shows the new names used in an Avid Unity
ISIS environment.
4. Close the Network Connections window.
32
Page 33

Before You Start: Preparation
Configuring the Binding Order Networks on Each Node
Repeat this procedure on each node and make sure the configuration matches on both nodes.
To configure the binding order networks:
1. Open the Network Connections window.
2. Select Advanced > Advanced Settings.
3. In the Connections area, position the network connections in the following order:
- For Unity ISIS environment use connection order listed in this illustration.
- For Unity MediaNetwork environment the connection order is as follows:
•Public
•Private
4. Click OK.
5. Repeat this procedure on each node and make sure the configuration matches on
both nodes.
33
Page 34

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Configuring Private Network Adapter on Each Node
To configure the private network adapter for the heartbeat connection:
1. Open the Network Connections window.
2. Right-click the Private network connection and select Properties.
The Private Properties dialog box opens.
Select this check box.
All others are unchecked.
34
3. On the General tab, click the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) check box. Make sure all other
components are unchecked.
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box opens.
Page 35

Before You Start: Preparation
Type the private IP
address for the node
you are configuring.
n
n
5. On the General tab of the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box:
a. Select “Use the following IP address.”
b. IP address: type the IP address for the Private network connection for the node you
are configuring. See “List of IP Addresses and Network Names” on page 29.
When performing this procedure on the second node in the cluster make sure you use the
static private IP addresses for that node. In this example, use 192 . 168 . 100 . 2.
c. Subnet mask: type the subnet mask address
Make sure you use a completely different IP address scheme from the one used for the public
network.
d. Make sure the “Default gateway” and “Use the Following DNS server addresses”
text boxes are empty.
6. Click Advanced.
35
Page 36

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
The Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box opens.
7. On the DNS tab, make sure no values are defined and that the “Register this
connection’s addresses in DNS” and “Use this connection’s DNS suffix in DNS
registration” are not selected.
8. On the WINS tab, do the following:
t Make sure no values are defined in the WINS addresses area.
t Uncheck “Enable LMHOSTS Lookup”.
t Select “Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP.”
9. Click OK.
n
A message might display stating “This connection has an empty primary WINS address. Do
you want to continue?” Click Yes.
10. Repeat this procedure on the second node in the cluster using the static private IP
addresses for that node.
Configuring Public Network Adapter on Each Node
Make sure you configure the IP address network interfaces for the Public Network Adapter
as you normally would. For examples of public network settings, see “List of IP Addresses
and Network Names” on page 29.
36
Page 37

Before You Start: Preparation
Join Both Servers to the Active Directory Domain
Make sure you join the two servers to the Active Directory Domain.
Setting Up a Cluster User Account
Before you configure the Cluster service you need to create or have available, a domain user
account that will become a member of the Local Administrators group on each node. This
user account starts the Cluster service and the Interplay Engine services. For more
information, see “Before You Start: Preparation” on page 28.
Configuring the Cluster Shared RAID Disks on Each Node
Both nodes must have the same cluster shared RAID disk configuration. When you
configure the disks on the second node, make sure the disks match the disk configuration
you setup on the first node.
n
Before you create the partitions on the cluster members, make sure the cluster shared RAID
disks were pre-configured (mirror, stripe, etc.) by the vendor. Make sure the disks are Basic
and not Dynamic.
To configure the disks on each node:
1. Turn off the server for the node you are not configuring at this time.
2. Open Disk Management tool.
3. Initialize the disks, if not already initialized:
t Right-click the disk and select Initialize Disk.
4. Configure the Quorum (Q:) 4GB, MSDTC (R:) 5GB, and Database (S:) 925GB, as
shown in the following illustration:
37
Page 38

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Configure disks
as shown
38
5. (First node only) Format the disks.
6. Verify you can access the disk and that it is working, by creating a file and deleting it.
7. Turn off the first node and turn on the second node.
8. Repeat this procedure on the second node, with the exception of formatting the disks
because you only need to format the disks once.
Page 39

Configuring the Cluster Service
List of steps to configure the cluster service:
• Turn off the second node.
• Configure the first node using the New Server Cluster Wizard. See “Configuring the
Cluster Service on the First Node” on page 39.
• Validate the cluster service installation on the first node. See “Validating the Cluster
Service on the First Node” on page 44.
• Turn on the second node. Leave first node turned on.
• Configure the second node using Add Cluster Computers Wizard. See “Configuring the
Cluster Service on the Second Node” on page 44.
Configuring the Cluster Service on the First Node
To configure the cluster service on the first node:
1. Turn off the server for the node you are not configuring at this time.
2. Make sure all storage devices are turned on.
3. Click Start and select All Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster Administrator.
Configuring the Cluster Service
The Open Connection to Cluster dialog box opens.
4. Select Create new cluster from the Action menu.
5. Make sure you have the prerequisites to configure the cluster, as shown in the New
Server Cluster Wizard Welcome window.
6. Click Next.
39
Page 40

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
7. In the Cluster Name and Domain dialog box, do the following:
- Domain: select the name of your Active Directory domain
- Cluster name: type the Cluster service name, for example SECLUSTER — see
“List of IP Addresses and Network Names” on page 29.
Type the Cluster
service name.
n
40
8. Click Next.
You might be prompted for an account. This user account is not the account the cluster
service uses to start. It must be a domain user account, such as the Cluster Installation
Account mentioned in “Before You Start: Preparation” on page 28.
Page 41

Configuring the Cluster Service
9. In the Select Computer dialog box, in the Computer name text box, type the Cluster
node host name of the first node. For example, SECLUSTER1, see “List of IP
Addresses and Network Names” on page 29.
10. Click Advanced.
The Advanced Configuration Options dialog box opens.
11. Select Advanced (minimum) configuration, and click OK.
41
Page 42
Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
12. Click Next.
The setup process analyzes the node for hardware or software problems that might cause
problems during installation. A warning icon displays next to “Checking Cluster
feasibility.” This is ok.
13. Click Next after the analyze is complete and the Task Complete bar is green.
14. In the IP Address dialog box, type a unique Cluster Service ISIS IP address in the IP
Address text box. See “List of IP Addresses and Network Names” on page 29.
15. Click Next.
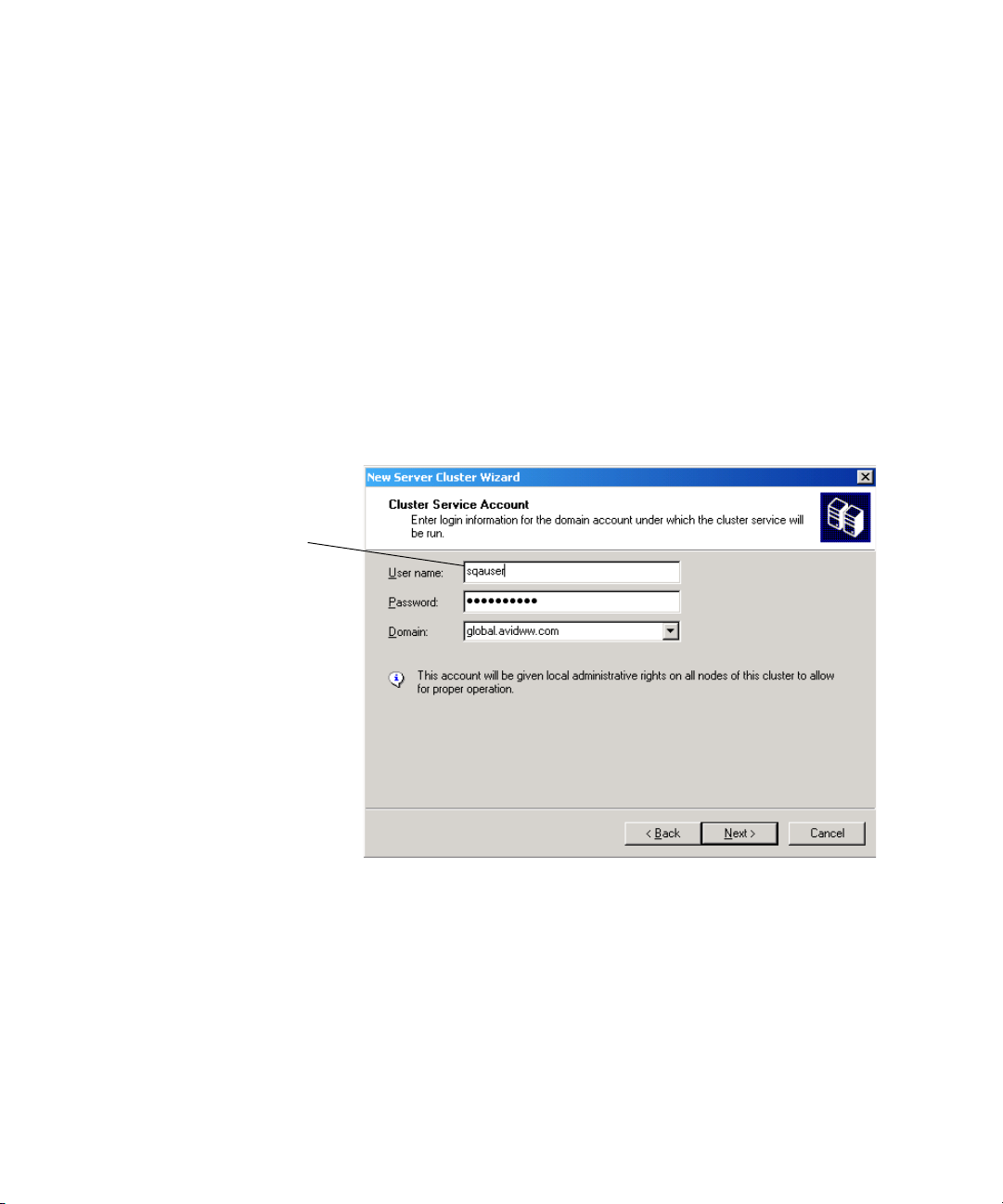
16. In the Cluster Service Account dialog box, type the cluster user name and password, and
select the domain. This is the Cluster Service Account (Server Execution) used to start
the cluster service. It is also used by the Interplay Engine. It must be a unique name that
will not be used for any other purpose. See “Before You Start: Preparation” on page 28.
Type the Cluster Service
Account user name. See
“Before You Start:
Preparation” on page 28.
42
17. Click Next.
The Proposed Cluster Configuration dialog box opens.
Page 43

Configuring the Cluster Service
n
18. Click Quorum.
The Cluster Configuration Quorum dialog box opens.
19. Select Disk Q: from the menu, and click OK.
20. Review the summary on the Proposed Cluster Configuration dialog box to verify all the
information for creating the cluster is correct.
21. Click Next. The Creating the Cluster dialog box opens.
22. Review any errors during the cluster creation.
If red errors display, check the Cluster Service ISIS IP address you entered in step 14.
23. Click Next.
24. Click Finish.
43
Page 44

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Validating the Cluster Service on the First Node
To validate the first node cluster installation:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster Administrator.
2. In the left pane, click Resources to make sure all resources are online.
Ver ify
Resources
Configuring the Cluster Service on the Second Node
n
44
To configure the cluster service on the second node:
1. Make sure the first node is on and all storage devices are turned on.
2. Turn on the server for the second node.
3. In the first node, click Start and select Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster
Administrator.
4. Select File > New > Node.
The Add Node Wizard opens.
5. Click Next.
You might be prompted for an account. This user account is not the account the cluster
service uses to start. It must be a domain user account, such as the Cluster Installation
Account mentioned in “Before You Start: Preparation” on page 28.
6. In the Select Computers dialog box, in the Computer name text box, type the Cluster
node host name of the second node and click Add. For example, SECLUSTER2, see
“List of IP Addresses and Network Names” on page 29.
Page 45

Configuring the Cluster Service
7. Click Advanced.
The Advanced Configuration Options dialog box opens.
8. Select Advanced (minimum) configuration, and click OK.
45
Page 46

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
9. Click Next.
The setup process analyzes the node for hardware or software problems that might cause
problems during installation. A warning icon displays next to “Checking Cluster
feasibility.” This is ok.
10. Click Next after the analyze is complete and the Task Complete bar is green.
11. Type the password for the cluster service account. This account is used to start the
cluster service.
12. Click Next.
13. In the Proposed Cluster Configuration dialog box, review the summary to verify all the
information for creating the cluster is correct.
14. Click Next.
The Adding Nodes To The Cluster dialog box opens.
15. Review any errors during the cluster creation.
16. Click Next.
17. Click Finish.
46
Page 47

Configuring Rules For The Cluster Networks
Configuring Rules For The Cluster Networks
After the networks are configured on each node and the cluster service is configured, you
need to configure the network roles to determine the function within the cluster.
n
The Private network
(virtual cluster) is used
for the Heartbeat.
The procedures in this section use Left-74 and Right-75, as examples of the public networks.
You should replace the numbers with your subnet numbers.
To configure the rules for the cluster networks:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster Administrator.
2. In the left pane, click Cluster Configuration > Networks, and right-click Private and
select Properties.
3. Select “Internal cluster communications only (private network).”
4. Click OK.
5. In the left pane, click Cluster Configuration > Networks, and right-click Left-74 and
select Properties.
47
Page 48

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
6. In the Left-74 Properties dialog box, verify these options:
- Name: Left-74
- Enable this network for cluster use
- All communications (mixed network)
7. Click OK.
8. In the left pane, click Cluster Configuration > Networks, and right-click Right-75 and
select Properties.
9. In the Right-75 Properties dialog box, verify these options:
- Name: Right-75
- Enable this network for cluster use
- All communications (mixed network)
10. Click OK.
Prioritizing the Heartbeat Adapter
After you configure network roles for how the cluster service uses the network adapter, you
need to prioritize the order in which they are used for intra-cluster communications. The
cluster service will use the next network adapter in the list when it cannot communicate by
using the first network adapter.
48
To prioritize the heartbeat adapter:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster Administrator.
2. In the left pane, right-click the cluster name at the top of the list and select Properties.
3. Click the Network Priority tab.
Page 49

After Setting Up the Cluster
4. Verify the Private network is at the top of the list. You can use the Move Up and Move
Down buttons to change the priority order.
5. Click OK.
After Setting Up the Cluster
After you finish setting up the cluster you need to verify the quorum disk is using disk Q, set
the startup times for each node, and test the cluster installation.
The following sections provide procedures for these tasks:
• “Verifying the Quorum Disk” on page 50
• “Setting the Startup Times on Each Node” on page 51
• “Testing the Cluster Installation” on page 52
49
Page 50

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Verifying the Quorum Disk
The Cluster Configuration Wizard automatically selects the disk used as the quorum device.
Check to make sure the quorum device is using disk Q.
To verify the quorum disk:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster Administrator.
2. In the left pane, right-click the cluster name at the top of the list and select Properties.
3. Click the Quorum tab and make sure Quorum resource displays Disk Q.
50
4. Click OK.
Page 51

Setting the Startup Times on Each Node
Avid recommends that you offset the startup time of each node’s operating system used
during the power up of the cluster.
To set the time for displaying the list of operating systems:
1. Click Start and right-click My Computer and select Properties.
2. Click the Advanced tab.
3. In the Startup And Recovery area, click Settings.
The Setup and Recovery dialog box opens.
After Setting Up the Cluster
51
Page 52

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
4. Select “Time to display list of operating systems.”
5. Depending on the node you are settings, do one of the following:
t First Node: Set the time to 15 seconds for the Select Time to display list of
operating systems option.
t Second Node: Set the time to 75 seconds for the Select Time to display list of
operating systems option.
6. Click OK.
Testing the Cluster Installation
You must test the cluster installation to make sure the failover process is working.
To verify that resources will failover:
1. Click Start, and select Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster Administrator.
Click
Groups
52
2. In the left pane, click Groups, and right-click Cluster Group and select Move Group.
The group and all its resources are moved to another node. Disk Q is brought online on
the second node. Make sure the window displays that the other node is now the owner of
the Resources and that all resources are online.
Page 53

After Setting Up the Cluster
Second node is now
All resources are online
owner of the resources
3. Move the group back to node 1 after you finish testing the cluster installation.
4. Close the Cluster Administrator.
Configuration of the cluster service on all nodes is complete and the cluster is fully
operational. You can now install cluster resources, such as file shares, cluster aware services
such as Distributed Transaction Coordinator.
53
Page 54

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Installing the Distributed Transaction Coordinator
Interplay Engine requires DCOM services in the cluster. To allow DCOM services in the
cluster, create a resource group for the Distributed Transaction Coordinator. This resource
group needs its own physical 5GB disk, an IP address and a network name (MSDTC). Finish
the group by adding a resource of the Distributed Transaction Coordinator type.
The following sections provide procedures for creating a resource group for the Distributed
Transaction Coordinator by using the Cluster Administrator tool.
• “Creating a Resource Group for the Distributed Transaction Coordinator” on page 55
• “Assigning an IP Address to the MSDTC Group” on page 56
• “Assigning a Network Name to the MSDTC Group” on page 57
• “Creating a Physical Resource for the MSDTC Group” on page 58
• “Assigning Distributed Transaction Coordinator Resource to the MSDTC Group” on
page 58
When performing these procedures Avid suggests you use the same entries shown in the
procedure. These entries are from the list in section, “List of IP Addresses and Network
Names” on page 29.
54
For more information about Distributed Transaction Coordinator, see the Microsoft
Knowledge Base article addressing this topic (301600):
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;301600
Page 55

Installing the Distributed Transaction Coordinator
Creating a Resource Group for the Distributed Transaction Coordinator
To create a resource group named MSDTC for the Distributed Transaction
Coordinator:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster Administrator.
2. Select File > New > Group.
The New Group Wizard opens.
3. In the Name text box, type MSDTC.
You can use any name for the group name, however Avid suggests you use MSDTC.
4. Click Next.
The Preferred Owners dialog box opens.
55
Page 56

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
5. Select both owners in the Available nodes list and add them to the Preferred owners list.
6. Click Finish.
Assigning an IP Address to the MSDTC Group
To assign an IP address to MSDTC group:
1. In the Cluster Administrator, right-click MSDTC group and select New > Resource.
2. Complete the New Resource dialog box as follows:
- Name: MSDTC IP
- Resource Type: IP Address
- Group: MSDTC
3. Complete the Possible Owners dialog box as follows:
t Add the cluster node host names to the Possible owners lists. For example,
SECLUSTER1 and SECLUSTER2. See “List of IP Addresses and Network
Names” on page 29.
4. Complete the Dependencies dialog box as follows:
t Leave the Resource dependencies list empty.
56
Page 57

Installing the Distributed Transaction Coordinator
5. Complete TCP/IP Address Parameters dialog box as follows:
- Address: type the IP address of the MSDTC service. See “List of IP Addresses and
Network Names” on page 29.
- Subnet mask: displays subnet for the network
- Network: select a network connection: Right-subnet, Left-subnet, or Public
- Select Enable NetBIOS for this address
6. Click Next.
Assigning a Network Name to the MSDTC Group
To assign a network name to MSDTC group:
1. In the Cluster Administrator, right-click MSDTC group and select New > Resource.
2. Complete the New Resource dialog box as follows:
-Name: MSDTC NAME
- Resource Type: Network Name
-Group: MSDTC
3. Click Next.
4. Complete the Possible Owners dialog box as follows:
t Add the cluster node host names to the Possible owners lists. For example,
SECLUSTER1 and SECLUSTER2. See “List of IP Addresses and Network
Names” on page 29.
5. Click Next.
6. Complete the Dependencies dialog box as follows:
t Add MSDTC IP to the Resource dependencies list.
7. Click Next.
8. Complete Network Name Parameters dialog box as follows:
- Name: CLUSTERMSDTC
- Uncheck “DNS Registration must succeed” and uncheck “Enable kerberos
authentication.”
9. Click Finish.
57
Page 58

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Creating a Physical Resource for the MSDTC Group
To create a physical disk resource for MSDTC group:
1. In the Cluster Administrator, right-click MSDTC group and select New > Resource.
2. Complete the New Resource dialog box as follows:
- Name: MSDTC DISK R
- Resource Type: Physical disk
- Group: MSDTC
3. Click Next.
4. Complete the Possible Owners dialog box as follows:
t Add the cluster node host names to the Possible owners lists. For example,
SECLUSTER1 and SECLUSTER2. See “List of IP Addresses and Network
Names” on page 29.
5. Click Next.
6. Complete the Dependencies dialog box as follows:
t Leave the Resource dependencies list empty.
7. Click Next.
8. Complete Disk Parameters dialog box as follows:
- Select: R: (MSDTC)
9. Click Finish.
Assigning Distributed Transaction Coordinator Resource to the MSDTC Group
To assign Distributed Transaction Coordinator Resource to MSDTC group:
1. In the Cluster Administrator, right-click MSDTC group and select New > Resource.
2. Complete the New Resource dialog box as follows:
- Name: MSDTC Resource
- Resource Type: Distributed Transaction Coordinator
- Group: MSDTC
3. Click Next.
58
Page 59

4. Complete the Possible Owners dialog box as follows:
t Add the cluster node host names to the Possible owners lists. For example,
SECLUSTER1 and SECLUSTER2. See “List of IP Addresses and Network
Names” on page 29.
5. Click Next.
6. Complete the Dependencies dialog box as follows:
t Add MSDTC DISK R and MSDTC NAME to Resource dependencies list.
7. Click Finish.
Bring the MSDTC Online
The following illustration shows the Cluster Administrator after you complete the setup of
the MSDTC group.
Installing the Distributed Transaction Coordinator
n
1. Initialize the MSDTC Log file, do the following:
a. Bring MSDTC DISK R online; right-click MSDTC DISK R and select Bring
Online.
b. In the Command Window, run the following command on the node that is the owner
to reset the log: msdtc -resetlog
2. Bring MSDTC Group online.
t Right-click MSDTC, and select Bring Online.
If you are running Active Directory on the cluster nodes, the MSDTC Resource might fail to
run on the backup domain controller. If this occurs, see the Microsoft article:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/900216/en-us
59
Page 60

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Disabling Any Web Servers
n
If you followed the procedures in the document no action is required, since the only web
server install at this point is the IIS and is disabled.
The Interplay Engine uses an Apache web server that can only be registered as a service if
no other web server (for example, IIS) is serving the port 80 (or 443). Stop and disable or
uninstall the other http services before you start the installation of the server. You must
perform this procedure on both nodes.
Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
The following sections provide procedures for installing the Interplay Engine on the first
node. For a list of example entries, see “List of IP Addresses and Network Names” on
page 29.
• “Preparation and Notes” on page 60
• “Starting the Installation and Accepting the License Agreement” on page 61
• “Preparing the Server for the Interplay Engine Installation Using Custom Mode” on
page 62
• “Preparing the Server for the Interplay Engine Installation Using Typical Mode” on
page 74
• “Beginning the Installation of Interplay Engine on the First Node” on page 78
• “Bringing the Disk Resource Online” on page 79
c
Shut down the second node while installing Interplay Engine for the first time.
Preparation and Notes
n
60
When installing Interplay Engine for the first time on a machine with cluster services, you
are asked to choose between clustered and regular installation. The installation on the
second node or later updates reuse the configuration from the first installation without
allowing you to change the cluster-specific settings. In other words, it is not possible to
change the configuration settings without uninstalling the Interplay Engine.
Page 61

Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
You are ready to start the server installer. During setup you must enter the following cluster
related information:
n
c
For a list of example names, see “List of IP Addresses and Network Names” on page 29.
• Virtual IP Address: the Interplay Engine service IP address of the resource group
• Subnet Mask: the subnet mask
• Public Network: the name of the public network connection. For example, Left-subnet,
Right-subnet, Public.
• Shared Drive: S: database
• Cluster Service Account User and Password: the domain account that is used to run the
cluster. See “Before You Start: Preparation” on page 28.
Shut down the second node while installing Interplay Engine for the first time.
Starting the Installation and Accepting the License Agreement
1. Insert the Avid Interplay installation DVD, a start screen opens.
2. Double-click Install Avid Interplay Engine to begin the Avid Interplay Engine
Installation Wizard, which guides you through the installation.
The Welcome dialog box opens.
3. Close all Windows programs before proceeding with the installation.
4. Information about the installation of Apache is provided in the Welcome dialog box.
Read the text and then click Next.
The License Agreement dialog box opens.
5. Read the license agreement information and then accept the license agreement by
selecting “I accept the agreement”. Click Next.
The Specify Installation Type dialog box opens.
6. Do one of the following:
- For custom installation (recommended), see “Preparing the Server for the Interplay
Engine Installation Using Custom Mode” on page 62.
- For typical installation, see “Preparing the Server for the Interplay Engine
Installation Using Typical Mode” on page 74.
61
Page 62

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Preparing the Server for the Interplay Engine Installation Using Custom Mode
The first time you install the Interplay Engine on a system, you should use the Custom
installation mode. This lets you specify all the available options for the installation. This is
the recommended option to use.
The Typical installation mode, installs the default components of the software. If you have
installed the Avid Interplay Engine previously, the settings from the previous installation are
used. The Typical installation mode is usually used for upgrading the software. For
procedures using the Typical installation mode, see “Preparing the Server for the Interplay
Engine Installation Using Typical Mode” on page 74.
The following procedures are used to perform a Custom installation of the Interplay Engine:
• “Specify Cluster Mode During a Custom Installation” on page 63
• “Specifying the Interplay Engine Details” on page 64
• “Specifying the Interplay Engine Name” on page 65
• “Specifying the Destination Location” on page 66
• “Specifying the Default Database Folder” on page 67
62
• “Specifying the Share Name” on page 68
• “Specifying the Configuration Server” on page 69
• “Specifying the Server User” on page 70
• “Specifying the Server Cache” on page 71
• “Enabling Email Notifications” on page 72
Page 63

Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
Specify Cluster Mode During a Custom Installation
1. In the Specify Installation Type dialog box, select Custom.
2. Click Next.
The Specify Cluster Mode dialog box opens.
63
Page 64

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
3. Select Cluster and click Next to continue the installation in cluster mode.
The Specify Interplay Engine Details dialog box opens.
Specifying the Interplay Engine Details
c
64
1. Type the following values:
- Virtual IP address: This is the Interplay Engine services IP Address, not the Cluster
IP address.
- Subnet Mask: The subnet mask on the local network. Ask your system
administrator for more information on this.
- Public Network: The name of the public network connection. For example,
Left-subnet, Right-subnet, Public. (the other adapter is used for the cluster
heartbeat).
To check the public network connection: Open the Network Connections panel in
the Windows Control Panel and look up the name there.
- Shared Drive: S: for the database.
Make sure you type the correct information here, as this data cannot be changed
afterwards. Should you require any changes to the above values later, you will need to
uninstall the Interplay Engine on both nodes.
2. Click Next.
The Specify Interplay Engine Name dialog box opens.
Page 65

Specifying the Interplay Engine Name
Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
1. Choose the public names for the Avid Interplay Engine by typing the following values:
- The Network Name will be associated with the virtual IP Address that you've
entered in the previous Interplay Engine Details dialog box. It is registered in the
DNS so that clients can find the server without having to specify its address. The
name must not exist yet. This is the Interplay Engine service name, see “List of IP
Addresses and Network Names” on page 29.
- The Server Name is used by clients to identify the server. It defaults to the Network
Name. If you only use Avid Interplay Clients on Windows computers, you can use
the Network Name of the resource group as the server name. If you use several
®
platforms as client systems, such as Macintosh
and Linux, you need to specify the
static IP address that was entered for the resource group. Macintosh systems are not
always able to map server names to IP addresses. If you type a static IP address,
make sure this IP address is not provided by a DHCP server.
2. Click Next.
The Specify Destination Location dialog box opens.
65
Page 66

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Specifying the Destination Location
The Destination Location is the location of the Interplay Engine program files.
c
66
1. Do one of the following:
t Keep the default.
t Type another location or use the Browse button to select another location.The
installation needs to be on a local disk of the host and not on a shared cluster disk. It
is also essential that the same location is used on the other machine.
Under no circumstances attempt to install to a shared disk; independent installations
are required on both nodes. This is because local changes are also necessary on both
machines. Also, with independent installations you can use a rolling upgrade approach
later, upgrading each node individually without affecting the operation of the cluster.
2. Click Next.
The Specify Default Database Folder dialog box opens.
Page 67

Specifying the Default Database Folder
Specify a default database folder. The database folder is the place where the database data is
stored.
Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
1. Type or browse to the database folder name.
This folder should reside on the shared drive that is owned by the resource group of the
server. While, theoretically, this folder could also be on another drive or even on another
computer, in cluster deployments, Avid strongly recommends using the shared drive
resource so that it too can be monitored and managed by the cluster service. The drive
must be assigned to the physical drive resource that is mounted under the same drive
letter on the other machine.
2. Click Next.
The Specify Share Name dialog box opens.
67
Page 68

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Specifying the Share Name
Specify a share name used by the File Share resource.
68
1. Type the share name.
Avid recommends you use the default sharing name of "WG_Database$". This name is
visible on all client platforms, such as Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows NT
Windows 2000 and Windows XP. Other sharing names such as "Interplay Database" are
only reachable from Windows NT, Windows 2000 and Windows XP. The "$" at the end
makes the share invisible if you browse through the network with the Windows
Explorer. For security reasons, Avid suggests using a "$" at the end of the share name. If
you use the default settings, the directory <Shared Drive>:\WG_Database is accessible
as \\InterplayEngine\WG_Database$.
2. Click Next.
This step takes a few minutes. When finished the Specify Configuration Server dialog
box opens.
Page 69

Specifying the Configuration Server
The configuration server setting indicates whether this server is to act as a Central
Configuration Server.
Set for both
Interplay Engines
Use this option for
Interplay Archive
Engine
Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
c
A Central Configuration Server (CCS) is an Avid Interplay Engine with a special module
which is used to store server and database-spanning information. Cross-server and
cross-database management of administrative tasks, such as User Management and mime
type determined behaviors, is possible because all of the servers under the CCS inherit its
settings by default.
During the installation of each Avid Interplay Engine, the responsible CCS for the server
installed must be specified.
To specify the server to act as the CCS server:
1. Select either the server you are installing or a previously installed server to act as the
central configuration server.
Typically you are working with only one server, so the appropriate choice is “This Avid
Interplay Engine”, which is the default.
Only use a CCS that is at least as high availability as this cluster installation, typically
another clustered installation.
69
Page 70

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
If you do select “Another Avid Interplay Engine,” you need to type the name of the other
server to be used as the CCS in the next dialog box. For example, use this option when
using an Interplay Archive Engine as the CCS.
If you specify the wrong CCS, you can change the setting later on the server machine in
the Windows Registry under:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/Software/Avid Technology/Workgroup/DatabaseServer
The string value CMS specifies the server. Make sure to set the CMS to a valid entry
while the Interplay Engine is online, otherwise your changes to the registry won't be
effective. After the registry is updated, stop and restart the server using the Cluster
Administrator (in the Administration Tools folder in Windows).
2. Click Next.
The Specify Server User dialog box opens.
Specifying the Server User
The Specify Server User dialog box lets you specify the server execution user account used
to run the Avid Interplay Engine.
70
Page 71
Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
1. Type the Cluster Service Account user login information. The "Server Execution User"
is the Windows domain user that runs the Interplay Engine and the cluster service. This
user needs to have administrative access to the file server. This user must be the one that
was used to set up the cluster service. See “Before You Start: Preparation” on page 28.
c
c
Specifying the Server Cache
The installer cannot check the username or password you type in this dialog. Make
sure that the password is set correctly, or else you will need to uninstall the server and
repeat the entire installation procedure. Avid does not recommend changing the Server
Execution User in cluster mode afterwards, so choose carefully.
When typing the domain name do not use the full DNS name such as
mydomain.company.com, because the DCOM part of the server will be unable to start.
You should use the NetBIOS name, for example, mydomain.
2. Click Next.
The Specify Preview Server Cache dialog box opens.
The Specify Preview Server Cache dialog box lets you specify the path for the cache folder.
n
1. Type or browse to the path of the server cache folder. Typically, the default path is used.
For more information on the Preview Server cache and Preview Server configuration, see
“Configuring the Preview Service” in the Avid Interplay Installation Guide: Avid Interplay
Engine, Avid Interplay Archive Engine, and Avid Interplay Access.
71
Page 72

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
2. Click Next.
The Enable Email Notification dialog box opens if you are installing the Avid Interplay
Engine for the first time.
Enabling Email Notifications
The first time you install the Avid Interplay Engine, the Enable Email Notification dialog
box opens. The email notification feature sends emails to your administrator when special
events, such as "Cluster Failure", "Disk Full", and "Out Of Memory" occur. Activate email
notification if you want to receive emails on special events, server or cluster failures.
72
1. (Option) Select Enable email notification on server events.
The Email Notification Details dialog box opens.
Page 73

Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
- Type the administrator's email address and the email address of the server, which is
the sender. If an event, such as "Resource Failure" "Disk Full" occurs on the server
machine, the administrator receives an email from the sender's email account
explaining the problem, so that the administrator can react to the problem. You also
need to type the static IP address of your SMTP server. The notification feature
needs the SMTP server in order to send emails. If you do not know this IP, ask your
administrator.
- If you also want to inform Avid Support automatically using email if problems
arise, select “Send critical notifications also to Avid Support.”
2. Click Next.
The Ready to Install dialog box opens.
The installer modifies the file Config.xml in the Workgroup_Data\Server\Config\Config
directory with your settings.
3. Continue to “Beginning the Installation of Interplay Engine on the First Node” on
page 78.
73
Page 74

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Preparing the Server for the Interplay Engine Installation Using Typical Mode
The Typical installation mode, installs the default components of the software. If you have
installed the Avid Interplay Engine previously, the settings from the previous installation are
used. The Typical installation mode is usually used for upgrading the software.
The following procedures are used to perform a Typical installation of the Interplay Engine:
• “Specify Cluster Mode During a Typical Installation” on page 74
• “Specifying the Cluster Information During a Typical Installation” on page 75
• “Specifying the Server User During a Typical Installation” on page 77
Specify Cluster Mode During a Typical Installation
1. In the Specify Installation Type dialog box, select Typical.
74
2. Click Next.
The Specify Cluster Mode dialog box opens only if the installer detected that the node is
a member of a cluster so that failover support can be provided.
Page 75

Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
3. Do one of the following:
t Select Cluster to continue the installation in cluster mode.
t Select Standalone to install a standalone server (on the physical node) without
cluster integration. If you select standalone mode, follow the standard installation
procedure (see the Avid Interplay Installation Guide: Avid Interplay Engine, Avid
Interplay Archive Engine, and Avid Interplay Access).
4. Click Next.
Specifying the Cluster Information During a Typical Installation
If you selected Cluster mode, the Specify Interplay Engine Details dialog box opens. You
are requested to provide the minimum set of information that is required to set up the server
in cluster mode. The data that you've gathered previously should be entered here.
75
Page 76

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
1. Type the following values:
c
76
- Virtual IP address: This is the Interplay Engine services IP Address.
- Subnet Mask: The subnet mask on the local network. Ask your system
administrator for more information on this.
- Public Network: The name of the public network connection. For example,
Left-subnet, Right-subnet, Public. (the other adapter is used for the cluster
heartbeat).
To check the public network connection: Open the Network Connections panel in
the Windows Control Panel and look up the name there.
- Shared Drive: S: for the database.
Make sure you type the correct information here, as this data cannot be changed
afterwards. Should you require any changes to the above values later, you will need to
uninstall the server on both nodes.
2. Click Next.
The Specify Server User dialog box opens.
Page 77

Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
Specifying the Server User During a Typical Installation
The Specify Server User dialog box opens.
c
c
1. Type the Cluster Service Account user login information. The "Server Execution User"
is the Windows domain user that runs the Interplay Engine and the cluster service. This
user needs to have administrative access to the file server. This user must be the one that
was used to set up the cluster service. See “Before You Start: Preparation” on page 28.
The installer cannot check the username or password you type in this dialog. Make
sure that the password is set correctly, or else you will need to uninstall the server and
repeat the entire installation procedure. Avid does not recommend changing the Server
Execution User in cluster mode afterwards, so choose carefully.
When typing the domain name do not use the full DNS name such as
mydomain.company.com, because the DCOM part of the server will be unable to start.
You should use the NetBIOS name, for example, mydomain.
2. Click Next.
3. Continue to “Beginning the Installation of Interplay Engine on the First Node” on
page 78.
77
Page 78

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Beginning the Installation of Interplay Engine on the First Node
When all of the settings have been entered, whether you used the Custom mode or Typical
mode to prepare the installation, the Ready to Install dialog box opens.
78
1. Click Next to start the actual installation process of the Interplay Engine, or use Back to
revisit the data you have entered. You can also terminate the installer using the Cancel
button, since no changes were done to the system yet.
The Installation Completed dialog box opens once the installation is completed.
Page 79

2. Do one of the following:
t Click Finish.
Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
t Analyze and resolve any issues or failures reported.
3. Click OK if prompted for a restart the system. The installation procedure requires the
machine to restart (up to twice). For this reason it is very important that the other node is
shut down, otherwise the current node loses ownership of the Avid Workgroup resource
group. This applies to the installation on the first node only.
n
Subsequent installations should be run as described in “Updating a Clustered Installation”
on page 85.
Bringing the Disk Resource Online
To bring the Disk Resource online:
1. After the installation is complete, start the Cluster Administrator tool:
t Click Start and select Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster Administrator.
2. Open the Avid Workgroup Server resource group. It should look similar to the following
illustration.
79
Page 80

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Avid Workgroup Disk is online
n
80
The Avid Workgroup Disk resource should be online, all other resources offline.
3. Bring the disk resource online manually before continuing if necessary.
Avid does not recommend starting the server at this stage yet, since it is not installed on the
other node and a failover would be impossible.
4. (Unity ISIS only) Add IP address on the second subnet for the Interplay Engine.
a. In the Cluster Administrator, right-click Avid Workgroup Server and select New >
Resource.
Page 81

Installing the Interplay Engine on the First Node
b. Complete the New Resource dialog box as follows:
- Name: Avid Workgroup Address 2
- Resource Type: IP Address
- Group: Avid Workgroup Server
c. Complete the Possible Owners dialog box as follows:
t Add the cluster server host names to the Possible owners lists. For example,
SECLUSTER1 and SECLUSTER2. See “List of IP Addresses and Network
Names” on page 29.
d. Complete the Dependencies dialog box as follows:
t Leave the Resource dependencies list empty.
e. Complete TCP/IP Address Parameters dialog box as follows:
- Address: type the second Interplay Engine service Unity ISIS IP address. See
“List of IP Addresses and Network Names” on page 29.
- Subnet mask: displays subnet for the second subnet network
- Network: select a network connection: Right-subnet
- Select Enable NetBIOS for this address
f. Click Finish.
The following illustration shows the new entry.
Avid Workgroup Address 2
81
Page 82

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
g. Right-click Avid Workgroup Address 2 and select Properties.
h. Click the Advanced tab.
i. Deselect Affect the Group as shown in the following illustration.
Affect the group
option
j. Click OK.
5. When the installation is complete, leave this node running so that it maintains ownership
of the resource group and proceed to “Installing Interplay Engine on the Second Node”
on page 82.
Installing Interplay Engine on the Second Node
To install Interplay Engine on the second node:
1. Leave the first machine running so that it maintains ownership of the resource group and
start the second node.
c
82
Do not attempt to move the resource group over to the second node, or similarly, do not
shut down the first node while the second is up, before the installation is completed on
the second node.
Page 83

Bring the Interplay Engine Online
2. Perform the installation procedure for the second node as described in “Installing the
Interplay Engine on the First Node” on page 60. In contrast to the installation on the first
node, the installer automatically detects all settings previously entered on the first node.
The Attention dialog box opens.
3. Click OK.
4. The same installation dialog boxes will open that you saw before, except for the cluster
related settings that only has to be entered once. Enter the requested information and
allow the installation to proceed.
c
Make sure you use the installation mode that you used for the first node and enter the
same information throughout the installer. Using different values results in a corrupted
installation.
5. The installation procedure requires the machine to restart (up to twice). Allow the restart
as requested.
Bring the Interplay Engine Online
To bring the Interplay Engine online:
1. Click Start and select Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster Administrator.
2. Click Groups and right-click Avid Workgroup Server and select Bring on line.
All resources are now online.
83
Page 84

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
Testing the Complete Installation
After you complete all the previously described steps, you are now ready to test the
installation. Make yourself familiar with the Cluster Administrator and review the different
failover-related settings.
To test the complete installation:
1. To start the server, bring the resource group online; this starts the Interplay Engine and
its affiliated services. After starting the Avid Interplay Engine on the first node, the
Cluster Administrator should look similar to the following figure.
n
84
2. Start an Interplay Administrator, install the licenses if needed, create a test database and
add some files to it. If the other node is also running, you are ready to test the failover
functionality.
3. Initiate a failover by moving the resource group; do this through the context menu of the
resource group. Failures can also be simulated, again through the context menu of the
appropriate resource.
Failures do not necessarily initiate failover.
4. You might also want to experiment by terminating the Interplay Engine manually using
the Windows Task Manager (NxNServer.exe). This is also a good way to get familiar
with the failover settings which can be found in the Properties Panel of the Avid
Workgroup resource, under the Advanced tab.
Page 85

5. Look at the related settings of the resource group. If you need to change any
configuration files, make sure that the Avid Workgroup Disk resource is online; the
configuration files can be found on the resource drive in the Workgroup_Data folder.
Updating a Clustered Installation
A major benefit of a clustered installation is that you can perform rolling upgrades. You can
keep a node in production while updating the installation on the other, then move the
resource over and update the second node as well. You are also able to experiment by
temporarily keeping two different versions (must be compatible in database format though)
on the two nodes if, for example, you want to test a patch.
When updating a clustered installation, the settings that were entered to set up the cluster
resources cannot be changed. Additionally, all other values must be reused, so Avid strongly
recommends choosing the Typical installation mode. As noted before, changes to the
fundamental attributes can only be achieved by uninstalling both nodes first and installing
again with the new settings.
Make sure you follow the procedure in this order, otherwise you might end up with a
corrupted installation.
Updating a Clustered Installation
n
The four executable resources referred to are:
• Avid Workgroup Server
• Avid Workgroup Server Browser
• Avid Workgroup TCP COM Bridge
• Avid Workgroup Preview Server
For information about updating specific versions of the Interplay Engine and a cluster, see
the Avid Interplay ReadMe.
To update a cluster:
1. Make sure the first node is online.
2. Move all resource groups to the first node (don't forget the cluster or the MSDTC
groups):
t In the Cluster Administrator, right-click the resource group entries and select Move
Group.
3. Update the installation on the second node using the WorkgroupServer.exe installer.
Select the Typical mode to reuse values set during installation of the first node. Restart
as requested and continue with Part 2 of the installation. The installer will ask to restart
again after Part 2.
85
Page 86

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
c
n
Do not move the Avid Workgroup resource group over yet.
4. Make sure that first node is online. Update the installation on the first node using the
WorkgroupServer.exe installer. Select the Typical mode so that all values are reused.
This restarts the first node.
5. During installation, the installer asks you to move the resource groups to the second
node. Move the resource groups. Then click OK in the installation dialog box to
continue. Restart as requested and continue with Part 2 of the installation. The installer
will ask you to restart again after Part 2.
6. You might want to test the final result of the update by moving the server back to the
first node. The Interplay Administrator can be used to display the version of the server.
After completing the above steps, your entire clustered installation is updated to the new
version. Should you encounter any complications or face a specialized situation, contact
Avid Support as instructed in “If You Need Help” on page 11.
If you intend to use different versions on the two nodes, make sure that their database
formats are compatible. Consult Avid Support as instructed in “If You Need Help” on
page 11.
Updating the Workgroup.xml File for a Split Database
If you have a split database, you must edit or replace the workgroup.xml file after the
upgrade.
86
A split database allows you to store non-Avid assets such as graphics files and Microsoft
Office files on shared storage. The Interplay Engine and Interplay Archive Engine
Administration Guide describes how to set up a split database.
During installation, a new workgroup.xml file is created and the existing workgroup.xml file
is renamed in the format workgroup.ddmmyy-hhmmss. If your Interplay Engine stores file
assets on a split database, make sure the workgroup.xml file contains the correct path. If not,
edit the file or replace it with the renamed backup file after the upgrade has been finished.
For example:
In a non-cluster system, copy
C:\Program Files\Avid\Avid Interplay
Engine\Data\Apache\conf\workgroup.080807-101852.xml
over the file
C:\Program Files\Avid\Avid Interplay
Engine\Data\Apache\conf\workgroup.xml
Page 87

Uninstalling the Interplay Engine
On a cluster system, (after both nodes have been upgraded), do the following on the
active node: Copy
S:\WorkgroupData\Apache\conf\workgroup.080807-101852.xml
over the file
S:\WorkgroupData\Apache\conf\workgroup.xml
n
On a cluster system, the following file is installed on both nodes: C:\Program
Files\Avid\Avid Interplay Engine\Data\Apache\conf\workgroup.xml. These files are not
currently used and do not need to be edited or overwritten. Edit or overwrite the version on
the S drive: S:\WorkgroupData\Apache\conf\workgroup.xml.
Uninstalling the Interplay Engine
The Avid Interplay Engine can be uninstalled using the standard uninstaller.
n
If you decide to reinstall the Interplay Engine after you uninstall it, make sure you rename or
remove the workgroup_data and workgroup_database directory on the shared storage to
prevent any problems due to corrupt or missing data.
To uninstall the Interplay Engine:
1. Make sure that both nodes are running before starting the uninstaller and begin with the
inactive node.
2. Before performing the uninstall procedure on the second node, take the entire Avid
Workgroup resource group offline.
3. When uninstalling a clustered installation, you are asked whether the cluster resources
are to be removed.
Typically you should select Yes to delete the resources only when uninstalling the
second node, otherwise the other installation becomes useless.
87
Page 88

Chapter 2 Automatic Server Failover Installation
4. (Option) If you plan to reinstall the Interplay Engine after you uninstall it, make sure
you rename or remove the workgroup_data and workgroup_database directory on the
shared storage to prevent any problems due to corrupt or missing data.
c
The uninstall mechanism of the cluster resources only functions properly if the names
of the resources or the resource group were not changed. Never change these names.
88
Page 89

Chapter 3
Automatic Server Failover Tips and Rules
This chapter provides some important tips and rules to use when configuring the automatic
server failover.
Don't Access the Machines Directly
Don’t access the machines directly. Refer to the projects using the "virtual" network name or
IP address that has been assigned to the resource group; never use the actual physical names
or IP addresses of the machines that are part of the cluster.
Make Sure to Connect to the Interplay Engine Resource Group
The network names and the virtual IP addresses resolve to the physical machine they are
being hosted on. For example, it is possible to mistakenly connect to the Interplay Engine
using the network name or IP address of the cluster group. The server is found using the
alternative address also, but only while it is online on the same node. Therefore, under no
circumstances connect the clients to a network name other than what was used to set up the
Interplay Engine resource group. The default name is WorkgroupServer.
Do Not Rename Resources
Do not rename resources. The resource plugin, the installer, and the uninstaller all depend on
the names of the cluster resources. These are assigned by the installer and even though it is
possible to modify them using the cluster administrator, doing so corrupts the installation
and is most likely to result in the server not functioning properly.
Page 90

Chapter 3 Automatic Server Failover Tips and Rules
Do Not Install the Server on a Shared Disk
The Interplay Engine must be installed on the local disk of the cluster nodes and not on a
shared resource. This is because local changes are also necessary on both machines. Also,
with independent installations you can later use a rolling upgrade approach, upgrading each
node individually without affecting the operation of the cluster. The Microsoft
documentation is also strongly against installing on shared disks.
Do Not Change the Interplay Engine Execution User
The domain account that was entered when setting up the cluster also has to be the execution
user of the Interplay Engine. Given that you cannot easily change the cluster user, the
Interplay Engine execution user has to stay fixed as well.
Do Not Edit the Registry While the Server is Offline
If you edit the registry while the server is offline, you will lose your changes. This is
something that most likely will happen to you since it is very easy to forget the implications
of the registry replication. Remember that the registry is restored by the resource monitor
before the process is put online, thereby wiping out any changes that you made while the
resource (the server) was offline. Only changes that take place while the resource is online
are accepted.
Do Not Remove the Dependencies of the Affiliated Services
The TCP-COM Bridge, the Preview Server, and the Server Browser services must be in the
same resource group and assigned to depend on the server. Removing these dependencies
might speed up some operations but prohibit automatic failure recovery in some scenarios.
Consider Disabling Failover When Experimenting
If you are performing changes that could make the Avid Interplay Engine fail, consider
disabling failover. The default behavior is to restart the server twice (threshold = 3) and then
initiate the failover, with the entire procedure repeating several times before final failure.
This can take quite a while.
90
Page 91

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Index
A
Antivirus software
running on a cluster 27
Apache web server 60
Architecture 14
Avid Unity environment
SR2400 server slot locations 16
SR2500 server slot locations 17
Unity ISIS illustration SR2400 18
Unity ISIS illustration SR2500 19
Unity MediaNetwork illustration SR2400 21
Unity MediaNetwork illustration SR2500 22
B
Binding order networks
configuring 33
C
Central Configuration Server
specifying 69
Cluster group
illustration 15
partition 25, 37
Cluster installation
connections in Unity ISIS 20
connections in Unity MediaNetwork 23
testing 52
Cluster Installation account
defined 28
Cluster network
configuring rules 47
Cluster service
configuring 39
configuring on second node 44
defined 24
specify name 40
validating on first node 44
Cluster Service account
defined 28
Interplay Engine installation 70
setting up 37
specify name 42
Cluster shared RAID array 61
Cluster system components 13
Cluster User/Password 61
Custom installation 63
D
Database folder
default location 67
Disk
default configuration 27
Distributed Transaction Coordinator
assigning resource to MSDTC group 58
creating MSDTC resource group 55
installing 54
resource group for 54
E
Email notification
setting 72
F
Fibre Channel 13
Page 92

Index A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
H
Hardware
requirements 26
Heartbeat adapter
prioritizing 48
Heatbeat connection
configuring 34
I
Installation
custom 63
Distributed Transaction Coordinator 54
testing 52
types 61
typical 74
Interplay Engine
Central Configuration Server, specifying 69
cluster details 65
default database location 67
installation cluster information 64
installing on first node 60
server user, specifying 70
share name 68
SR2400 slot locations 16
Interplay Engine process 15
IP addresses
assigning to MSDTC group 56
private network adapter 34
public network adapter 36
required 29
N
Network connections
naming 30
Network interface
renaming LAN 30
Network name
assigning MSDTC group 57
Network names
examples 29
Node
defined 24
name examples 29
setting startup time 51
SR2400 slot locations 16
O
Online
defined 24
P
Partition
for the cluster group 25
Port for Apache web server 60
Private network adapter
configuring 34
Public Network 61, 64, 76
Public network adapter
configuring 36
L
License
agreement 61
License Information dialog box 61
Windows Server 26
M
Monitoring 13
MSDTC
resource group, creating 55
MSDTC group
creating physical resource 58
92
Q
Quorum disk 25
configuring 43
verifying 50
Quorum resource
defined 24
R
RAID array
configuring 37
default configuration 27
Registry
editing while offline 90
Page 93

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Index
Requirements
hardware 26
IP addresses 29
software 26
space 27
Resource group 24
connecting 89
services 90
Resources
defined 24
renaming 89
S
Server
setting startup time 51
SR2400 slot locations 16
Server cache
Interplay Engine installation 71
Server Execution User
changing 90
Service name
examples 29
Services
dependencies 90
Shared Drive 61, 64, 76
configuring 37
default configuration 27
Slot locations
SR2400 server 16
SR2500 server 17
Space requirements 27
Specify Installation Type dialog box 61
SR2400 server
slot location 16
SR2500 server
slot location 17
Subnet Mask 61, 64, 76
System
monitoring 13
U
Uninstalling 87
Unity ISIS
cluster installation SR2400 18
cluster installation SR2500 19
Unity MediaNetwork
cluster installation SR2400 21
cluster installation SR2500 22
V
Virtual IP address 64, 76
Virtual Server Address 61
W
Web servers
disabling 60
T
Troubleshooting 89
Typical
installation 74
93
Page 94

Index A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
94
 Loading...
Loading...