Philips (Now NXP) BGA2711 Schematic [ru]
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
DATA SH EET
ook, halfpage
MBD128
BGA2711
MMIC wideband amplifier
Product specification
Supersedes data of 2001 Apr 04
2001 Oct 19
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MMIC wideband amplifier BGA2711
FEATURES
• Internally matched to 50 Ω
• Very wide frequency range
• Very flat gain
• Unconditionally stable.
APPLICATIONS
• Cable systems
• LNB IF amplifiers
• General purpose
• ISM.
DESCRIPTION
Silicon Monolithic Microwave Integrated Circuit (MMIC)
wideband amplifierwith internal matching circuit in a 6-pin
SOT363 SMD plastic package.
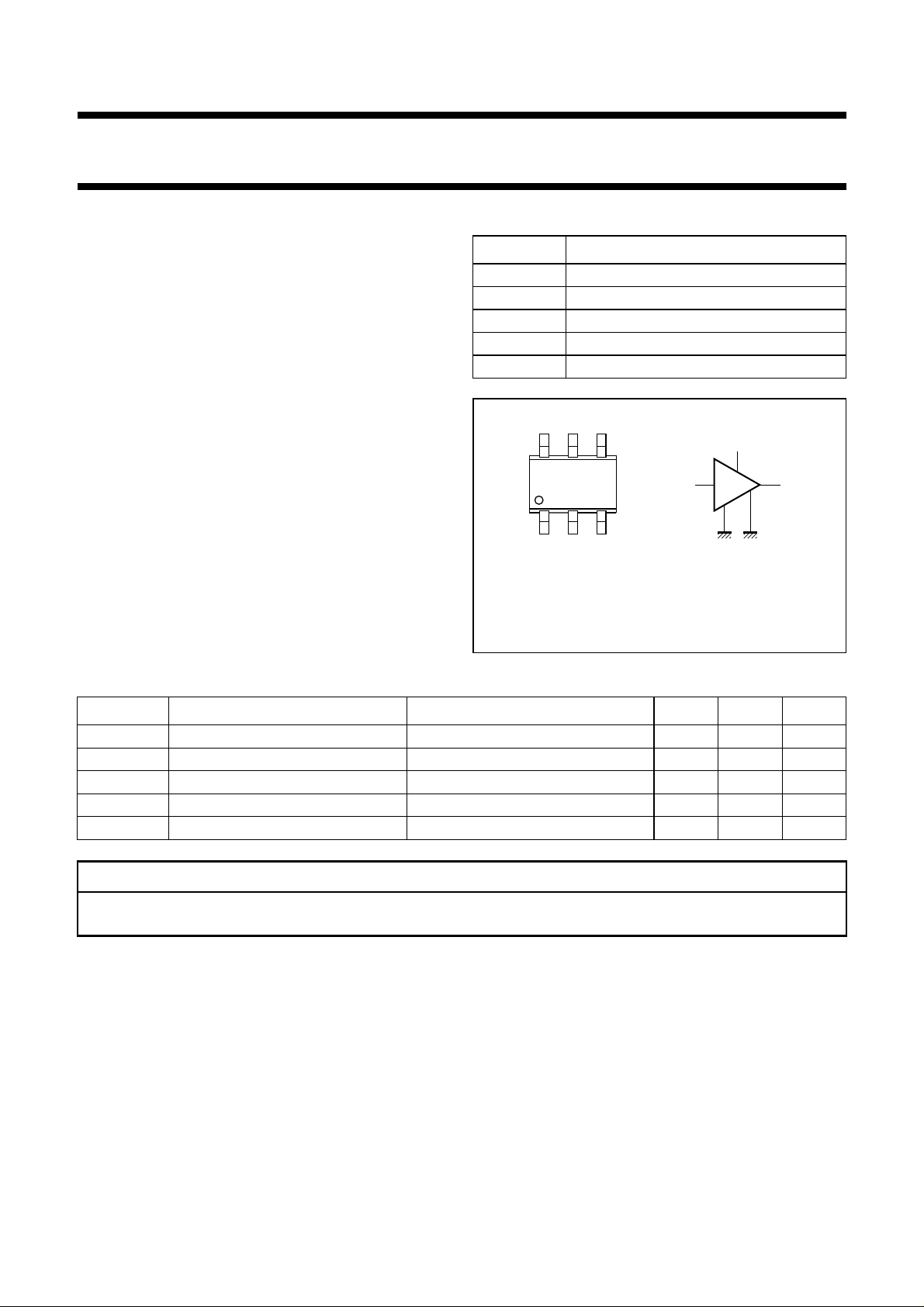
PINNING
PIN DESCRIPTION
1V
S
2, 5 GND2
3 RF out
4 GND1
6 RF in
4
56
63
132
Top view
Marking code: G2-.
MAM455
Fig.1 Simplified outline (SOT363) and symbol.
1
2, 54
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
S
I
S
2
|s
|
21
DC supply voltage 5 6 V
DC supply current 12.6 − mA
insertion power gain f = 1 GHz 13.1 − dB
NF noise figure f = 1 GHz 4.8 − dB
P
L(sat)
saturated load power f = 1 GHz 2.8 − dBm
CAUTION
This product is supplied in anti-static packing to prevent damage caused by electrostatic discharge during transport
and handling. For further information, refer to Philips specs.: SNW-EQ-608, SNW-FQ-302A and SNW-FQ-302B.
2001 Oct 19 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MMIC wideband amplifier BGA2711
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134)
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
S
I
S
P
tot
T
stg
T
j
P
D
THERMAL RESISTANCE
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th j-s
DC supply voltage RF input AC coupled − 6V
supply current − 20 mA
total power dissipation Ts≤ 80 °C − 200 mW
storage temperature −65 +150 °C
operating junction temperature − 150 °C
maximum drive power − 10 dBm
thermal resistance from junction to solder
P
= 200 mW; Ts≤ 80 °C 300 K/W
tot
point
CHARACTERISTICS
VS=5V; IS= 12.6 mA; f = 1 GHz; Tj=25°C unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
I
S
2
|s
|
21
supply current 10 12.6 16 mA
insertion power gain f = 1 GHz − 13.1 − dB
f = 2 GHz − 13.9 − dB
R
LIN
return losses input f = 1 GHz − 11 − dB
f = 2 GHz − 10 − dB
R
L OUT
return losses output f = 1 GHz − 18 − dB
f = 2 GHz − 13 − dB
NF noise figure f = 1 GHz − 4.8 − dB
f = 2 GHz − 4.8 − dB
BW bandwidth at |s
P
L(sat)
saturated load power f = 1 GHz − 2.8 − dBm
|2−3 dB below flat gain at 1 GHz − 3.6 − GHz
21
f = 2 GHz − 0.6 − dBm
P
L 1 dB
load power at 1 dB gain compression; f = 1 GHz −−0.7 − dBm
at 1 dB gain compression; f = 2 GHz −−1.8 − dBm
IP3
(in)
input intercept point f = 1 GHz −−4.8 − dBm
f = 2 GHz −−8.5 − dBm
IP3
(out)
output intercept point f = 1 GHz − 8.3 − dBm
f = 2 GHz − 5.4 − dBm
2001 Oct 19 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MMIC wideband amplifier BGA2711
APPLICATION INFORMATION
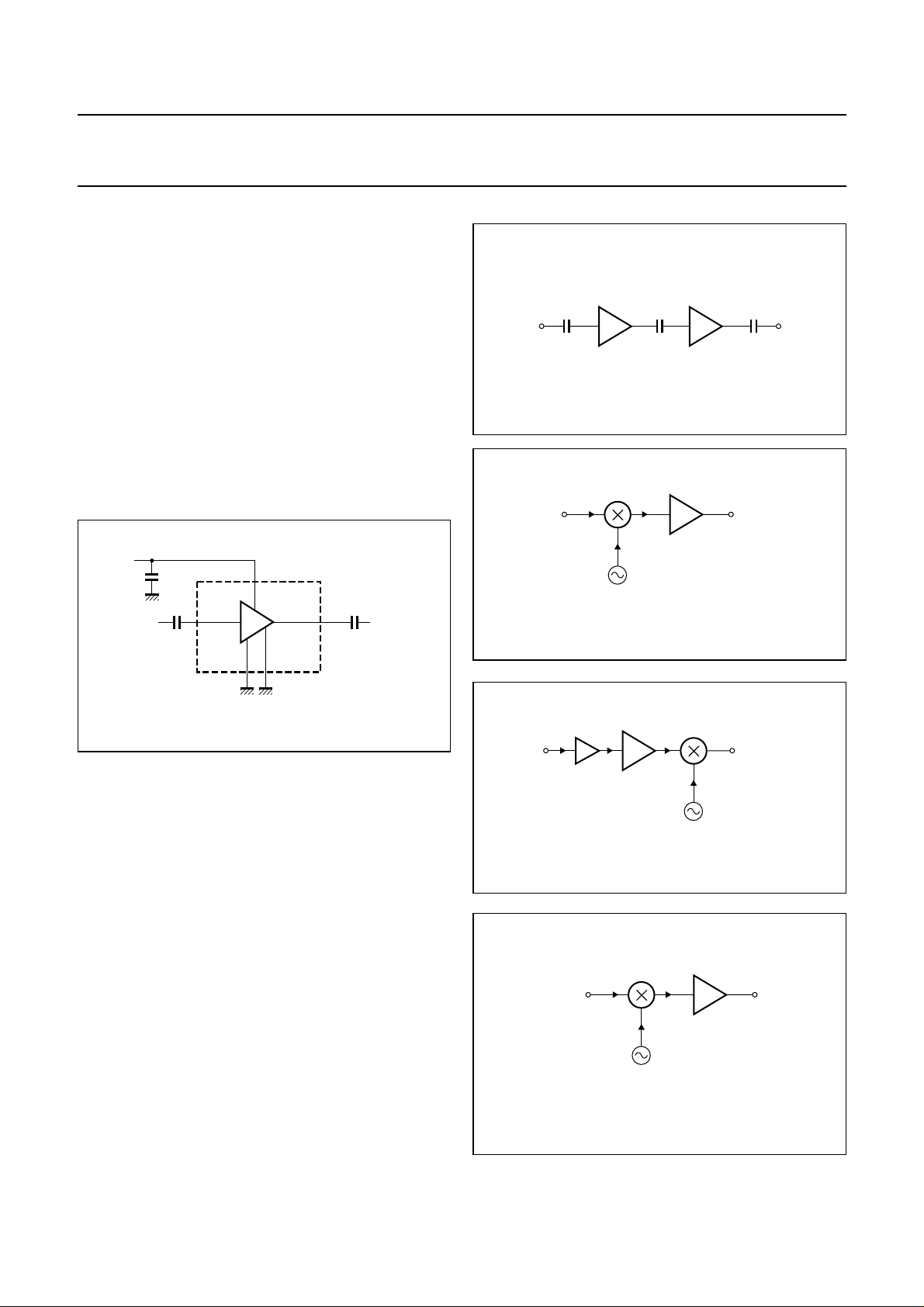
Figure 2 shows a typical application circuit for the
BGA2711MMIC.Thedeviceisinternallymatchedto50 Ω,
and therefore does not need any external matching. The
value of the input and output DC blocking capacitors C2,
C3 should be not more than 100 pF for applications above
100 MHz. However, when the device is operated below
100 MHz, the capacitor value should be increased.
The 22 nF supply decoupling capacitor, C1 should be
located as closely as possible to the MMIC.
Separate paths must be used for the ground planes of the
ground pins GND1, GND2, and these paths must be as
short as possible. When using vias, use multiple vias per
pin in order to limit ground path inductance.
V
handbook, halfpage
s
C1
V
s
RF input
C2 C3
RF outRF in
GND2GND1
RF output
MGU435
handbook, halfpage
DC-block
100 pF
input output
Fig.3 Easy cascading application circuit.
handbook, halfpage
from RF
circuit
oscillator
Fig.4 Application as IF amplifier.
mixer
DC-block
100 pF
wideband
amplifier
DC-block
100 pF
MGU437
to IF circuit
or demodulator
MGU438
Fig.2 Typical application circuit.
Figure 3 shows two cascaded MMICs. This configuration
doubles overall gain while preserving broadband
characteristics. Supply decoupling and grounding
conditions for each MMIC are the same as those for the
circuit of Fig.2.
The excellent wideband characteristics of the MMIC make
it and ideal building block in IF amplifier applications such
as LBNs (see Fig.4).
As a buffer amplifier between an LNA and a mixer in a
receiver circuit, the MMIC offers an easy matching, low
noise solution (see Fig.5).
InFig.6theMMICisused as a driver to the power amplifier
in part of a transmitter circuit. Good linear performance
and matched input and output offer quick design solutions
in such applications.
handbook, halfpage
antenna
handbook, halfpage
from modulation
or IF circuit
Fig.6 Application as driver amplifier.
LNA
mixer
wideband
amplifier
oscillator
to IF circuit
or demodulator
Fig.5 Application as RF amplifier.
mixer
wideband
amplifier
oscillator
MGU439
to power
amplifier
MGU440
2001 Oct 19 4
 Loading...
Loading...