Philips XA-H4 Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
XA-H4
Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
Preliminary specification
IC28 Data Handbook
1999 Sep 24

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
DESCRIPTION
The powerful 16-bit XA CPU core and rich feature set make the
XA-H3 and XA-H4 devices ideal for high-performance real-time
applications such as industrial control and networking. By supporting
of up to 32 MB of external memory, these devices provide a low-cost
solution to embedded applications of any complexity. Features like
DMA, memory controller and four advanced USARTs help solve I/O
intensive tasks with a minimum of CPU load.
FEA TURES
•Large Memory Support
•De-multiplexed Address/Data Bus
•Six Programmable Chip Selects
– Support for Unified Memory – allows easy user modification of
all code
– External ISP Flash support for easy code download
•Dynamic Bus Sizing – each of 6 Chip Selects can be programmed
for 8-bit or 16-bit bus.
The XA-H3 feature set is a subset of the XA-H4 (see Table 1). The
XA-H3/H4 devices are members of the Philips XA (eXtended
Architecture) family of high performance 16-bit microcontrollers.
The XA-H3 and XA-H4 are designed to significantly minimize the
need for external components.
•Dynamic Bus Timing – each of 6 chip selects has individual
programmable bus timing.
•32 Programmable General Purpose I/O Pins
•Four USARTs with 230.4 kbps capability
•Eight DMA Channels
ADDITIONAL XA-H4 FEATURES (NOT AVAILABLE ON XA-H3)
•Complete DRAM controller supports up to four banks of 8 MB each
•Memory controller supports 16 MB in Unified Mode
•Memory controller supports 32 MB in Harvard Mode
– Four Match Characters are supported on each USART in
– Hardware Autobaud on all four USARTs in Async Mode
– USARTs are improved 85C30 style
•Serial ports are USARTs
– Synchronous capability up to 1 Mbps, and include
HDLC/SDLC support
Async Mode
1999 Sep 24
2

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
Table 1. XA-H3 and XA-H4 features comparison
Feature XA-H3 XA-H4
Maximum External Memory
(Harvard Memory Mode)
Maximum External Memory
(Unified Memory Mode)
Memory Controller supports both Harvard and Unified architectures Yes Yes
De-multiplexed Address/Data Bus Yes Yes
DRAM Controller No Yes
DMA Channels 8 8
Dynamic Bus Sizing Yes Yes
Dynamic Bus Timing Yes Yes
Programmable Chip Selects 6 6
General Purpose IO Pins 33 33
Potential Interrupt Pins 16 16
Interrupts (programmable priority) 7 Standard SW
Two Counter/Timers plus Watchdog Yes Yes
Baud Rate Generators
Serial Ports 4 UARTs 4 USARTs
Maximum Serial Data Rates asynch to 230.4 kbps (no sync) asynch to 230.4 kbps
Match Characters No 4 async chars per USART
Hardware Autobaud No up to 230.4 kbps
NOTE:
1. Can be used as additional counters if not needed as BRGs.
1
6 MB 32 MB
(16 MB Code, 16 MB Data)
6 MB 16 MB
4 High Priority SW
9 Hardware Event
4 4
7 Standard SW
4 High Priority SW
9 Hardware Event
sync to 1 Mbps
ORDERING INFORMATION
ROMless Only Temperature range °C and Package Freq (MHz) Package Drawing Number
H4 = PXAH40KFBE
NOTE
K=30 MHz, F = (–40 to +85), BE = LQFP
–40 to +85°C, 100-Pin Low Profile Quad Flat Package (LQFP)
30 SOT407-1
1999 Sep 24
3

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
PIN CONFIGURATION
DRAM CAS bits
NOTE: Address lines output during
various DRAM CAS cycles are shown
in parenthesis. See DRAM Controller
chapter in User Manual for details.
VDD
A7 (A21_22)
A8 (A19_A20)
A9 (A0_A18)
A10 (A1)
A11 (A2)
A12 (A3)
A13 (A4)
A14 (A5)
A15 (A6_A22)
VSS
VDD
A16 (A7_A20_A21)
A17 (A8_A18_A19)
A18
A19
VSS
VDD
XA-H4
D11
D10
P2.7_Sync3_BRG3
P2.6_RTS3
D13
D12
P0.0_Sync0_BRG0
P0.1_RTS0
P0.2_CTS0
P0.3_CD0
P0.4_TRClk0
P0.5_RTClk0
TxD0
RxD0
GPOut
P0.6
P0.7
9998979695949392919089888786858483828180797877
100
1VSS
2
3
A0
4
A1
5
A2
6
A3
7
A4
8
A5
9
A6
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
D0
26272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950
D2
D1
VSS
K = 30 MHz, F = –40 to +85°C, BE = LQFP pkg
MOLD MARK
D4
D3
VDD
Top View 100 Pin LQFP
Base Part Number PXAH4
Current Part = PXAH40KFBE
LQFP Package = SOT407-1
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
P2.3_ComClk_TRClk3
P2.4_CD3
P2.5_CTS3
D15
D14
VDD
P2.1_TxD3
P2.2_RTClk3
MOLD MARK
VSS
ClkOut
Int0
P2.0_RxD3
CS2_RAS2
CS3_RAS3
CD1_Int2
VDD
CS0
CS1_RAS1
VSS
76
75
P1.7_BRG2_Sync2
P1.6_RTS2
74
73
P1.5_CTS2
72
P1.4_CD2
71
P1.3_TRClk2
P1.2_RTClk2
70
P1.1_TxD2
69
P1.0_RxD2
68
P3.7_Int1_TRClk1
67
P3.6_TxD1
66
P3.5_RxD1
65
P3.4_CTS1
64
P3.3_Timer1_BRG1_Sync1
63
VDD
62
XTALOUT
61
XTALIN
60
VSS
59
P3.2_Timer0_ResetOut
58
57
P3.1_CS5_RAS5_RTS1
P3.0_CS4_RAS4_RTClk1
56
Reset_In
55
BLE_CASL
54
53
BHE_CASH
WAIT_Size16
52
OE
51
WE
SU01269
1999 Sep 24
4

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
LOGIC SYMBOL XA-H4
V
DDVSS
MISC. UART1 PORT3
Int2
CS4, RAS4
CS5, RAS5
ResetOut, Timer0
Timer1
Int1
Int0
CD1
RTClk1
RTS1
BRG1, Sync1
CTS1
RxD1
TxD1
TRClk1
UART3
RxD3
TxD3
RTClk3
ComClk, TRClk3
CD3
CTS3
RTS3
BRG3, Sync3
UART2
3.0
3.1
3.2
3.3
3.4
3.5
3.6
3.7
PORT2
2.0
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
PORT1
XTAL1
XTAL2
CS3, RAS3
CS2, RAS2
CS1, RAS1
CS0
A19 – A0 (DRAM A22 – A0)
D15 – D0
XA-H4
RxD2
TxD2
RTClk2
TRClk2
CD2
CTS2
RTS2
BRG2, Sync2
TxD0
RxD0
BRG0, Sync0
RTS0
CTS0
CD0
TRClk0
RTClk0
GPOut
1.0
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
ClkOut
CASH, BHE
CASL, BLE
OE
WE
PORT0UART0
Wait, Size16
ResetIn
SU01270
1999 Sep 24
5

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
XA-H4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
XA-H4 CPU Core
256 Bytes Data
SRAM
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Timer 0
Timer 1
Watchdog
Timer
Data
SFR Bus
MMR Bus
DMA R0
DMA T0
DMA R1
DMA T1
DMA R2
DMA T2
DMA R3
DMA T3
Match Chars
USART 0
Autobaud
Match Chars
USART 1
Autobaud
Match Chars
USART 2
Autobaud
Match Chars
USART 3
Autobaud
1999 Sep 24
DRAM
Controller
Memory Bus Controller
6 Chip Selects
Dynamic Bus Sizing
Dynamic Bus Timing
External
System Bus
SU01271
6

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
XA-H4 MEMORY MAPS
FFFFFFh
Code and Data
Intermixed
Throughout
16 MB Space
000000h
(also known as von Neuman architecture)
Unified Memory
FFFFFFh
FFFFFFh
Code in
Dedicated
16 MB Space
Data in
Dedicated
16 MB Space
1999 Sep 24
000000h
Harvard Architecture
000000h
SU01272
7

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Mnemonic
V
SS
V
DD
ResetIn 55 I
WAIT/
Size16
XTALIn 60 I
XTALOut 61 I Crystal 2: Output from the oscillator amplifier.
CS0 49 O
CS1_RAS1 48 O Chip Select 1 or RAS1: Chip Selects and RAS 1 through 5 come out of reset disabled. They can
CS2_RAS2 47 O Chip Select 2 or RAS2: Active low Chip Selects CS1 through CS5 come out of reset disabled.
CS3_RAS3 46 O CS3 or RAS3: See Chip Select 2 for description.
See Pins 56, 57 for 2 additional Chip Selects
WE 50 O Write Enable: Goes active low during all bus write cycles only.
OE 51 O Output Enable: Goes active low during all bus read cycles only.
BLE_CASL 54 O Byte Low Enable or CAS_Low_Byte: Goes active low during all bus cycles that access D7 – D0,
BHE_CASH 53 O Byte High Enable or CAS_High_Byte: Goes active low during all bus cycles that access data
ClkOut 45 O Clock Output: This pin outputs a buffered version of the internal CPU clock. The clock output
A19 – A0 24 – 21,
D15 – D0 42 – 30,
P0.0 90 I/O
P0.1 91 I/O P0.1_RTS0: Port 0 Bit 1, or USART0 RTS (Request T o Send) output. 1
P0.2 92 I/O P0.2_CTS0: Port 0 Bit 2, or USART0 CTS (Clear T o Send) input. 1
P0.3 93 I/O P0.3_CD0: Port 0 Bit 3, or USART0 Carrier Detect input. 1
P0.4 94 I/O P0.4_TRClk0: Port 0 Bit 4, or USART0 TR clock input. 1, 2
P0.5 95 I/O P0.5_RTClk0 : Port 0 Bit 5, or USART0 RT clock input. 1, 2
P0.6 99 I/O P0.6: Port 0 Bit 6 1
P0.7 100 I/O P0.7: Port 0 Bit 7 1
Lqfp
Pin No.
1, 19, 28,
44, 59,
76, 88
2, 20, 29,
43, 62,
77, 89
52 I
18 – 3
27 – 25
Type Name and Function
Ground: 0 V reference.
I
Power Supply: This is the power supply voltage for normal, idle, and power down operation.
I
Reset: A low on this pin resets the microcontroller, causing I/O ports and peripherals to take on
their default states, and the processor to begin execution at the address contained in the reset
vector.
Wait/Size16: During Reset, this input determines bus size for boot device (“1” = 16-bit boot
device; “0” = 8-bit.) During normal operation this is the Wait input (“1” = Wait; “0” = Proceed.)
Crystal 1: Input to the inverting amplifier used in the oscillator circuit and input to the internal
clock generator circuits.
Chip Select 0: This output provides the active low chip select to the boot device (usually ROM or
Flash.) It cannot be connected to DRAM. From reset, it is enabled and mapped to an address
range based at 000000h. It can be remapped by software to a higher base in the address map
(see the “Memory Interface” chapter in the
be programmed to function as normal chip selects, or as RAS strobes to DRAM. CS1 can be
“swapped” with CS0 (see the SWAP operation and control bit in the “Memory Controller” chapter
XA-H4 User Manual
of the
capable of being based anywhere in the 16 MB space.
They can be programmed to function as normal chip selects, or as RAS strobes to DRAM. CS2
through CS5 are not used with the “SWAP” operation (see the “Memory Controller” chapter in the
XA-H4 User Manual
read or write, Generic or DRAM. Functions as CAS during DRAM cycles.
bus lines D15 – D8, read or write, Generic or DRAM. Functions as CAS during DRAM cycles.
may be used in conjunction with the external bus to synchronize WAIT state generators, etc. The
clock output may be disabled by software.
WARNING: The capacitive loading on this output must not exceed 40 pf.
O Address[19:0]: These address lines output A19 – A0 during (SRAM, etc.) bus cycles.
DRAMS (H4 only) are connected only to pins 22, 21, 18 – 10 (pins A17 to A7; see user manual
“MIF Chapter” for connecting various DRAM sizes); the appropriate address values are
multiplexed onto these 11 pins for RAS
I/O Data[15:0]: Bi-directional data bus, D15 – D0.
P0.0_Sync0_BRG0: Port 0 Bit 0, or USART0 Sync input or output, or USART0 BRG output, or
USART0 TxClk output.
.) CS1 is usually mapped to be based at 000000h after the swap, but is
.) They are mappable to any region of the 16 MB address space.
XA-H4 User Manual
and CAS during DRAM bus cycles.
.)
See
Note
1
1999 Sep 24
8

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
Mnemonic
TxD0 96 O TxD0: Transmit data for USART0.
RxD0 97 I RxD0: Receive data for USART0.
GPOut 98 O GPOut – General Purpose Output Bar: Similar to GPIO, but Push/Pull and inverted output only.
P1.0 68 I/O P1.0_RxD2: Port 1 Bit 0, or USART2 RxD input
P1.1 69 I/O P1.1_TxD2: Port 1 Bit 1, or USART2 TxD output
P1.2 70 I/O P1.2_RTClk2 : Port 1 Bit 2, or USART2 RT Clock input 2
P1.3 71 I/O P1.3_TRClk2: Port 1 Bit 3, or USART2 TR Clock input 2
P1.4 72 I/O P1.4_CD2: Port 1 Bit 4, or USART2 Carrier Detect input
P1.5 73 I/O P1.5_CTS2: Port 1 Bit 5, or USART2 Clear T o Send input
P1.6 74 I/O P1.6_RTS2: Port 1 Bit 6, or USART2 Request T o Send output
P1.7 75 I/O P1.7_BRG2_Sync2: Port 1 Bit 7, or USART2 Sync input or output, or BRG output, or TxClk
P2.0 80 I/O P2.0_RxD3: Port 2 Bit 0, or USART3 Rx Data input
P2.1 81 I/O P2.1_TxD3: Port 2 Bit 1, or USART3 Tx Data output
P2.2 82 I/O P2.2_RTClk3 : Port 2 Bit 2, or USART3 RT Clock input 2
P2.3 83 I/O P2.3_ComClk_TRClk3: Port 2 Bit 3, or USART3 TR Clock input 2
P2.4 84 I/O P2.4_CD3: Port 2 Bit 4, or USART3 Carrier Detect input
P2.5 85 I/O P2.5_CTS3: Port 2 Bit 5, or USART3 Clear T o Send input
P2.6 86 I/O P2.6_RTS3: Port 2 Bit 6, or USART3 Request T o Send output
P2.7 87 I/O P2.7_Sync3_BRG3: Port 2 Bit 7, or USART3 Sync input or output, or BRG output, or TxClk
P3.0 56 I/O P3.0_CS4_RAS4_RTClk1: Port 3 Bit 0, or CS4 or RAS 4 output, or USART1 RT Clock input
P3.1 57 I/O
P3.2 58 I/O
P3.3 63 I/O
P3.4 64 I/O P3.4_CTS1: Port 3 Bit 4, or USART1 Clear T o Send input
P3.5 65 I/O P3.5_RxD1: Port 3 Bit 5, or USART1 Receive Data input
P3.6 66 I/O P3.6_TxD1: Port 3 Bit 6, or USART1 Transmit Data output
P3.7 67 I/O P3.7_Int1 _TRClk1: Port 3 Bit 7, or External Interrupt 1 input, or USART1 TR Clock input 2
CD1_Int2 78 I/O CD1_Int2: USART1 Carrier Detect, or External Interrupt 2
Int0 79 I/O External Interrupt 0
Lqfp
Pin No.
Name and FunctionType
WARNING: This output is inverted. The polarity of the pin is the opposite of the bit that drives it
(GPOut[7])
output (see USART clk diagrams in the user manual.)
output (see USART clock diagrams in the user manual.)
Active low chip selects CS1 through CS5 come out of reset disabled. They can be programmed to
function as normal chip selects, or as RAS strobes to DRAM. CS2 through CS5 are not used with
the “SWAP” operation (see the “Memory Controller” chapter in the
mappable to any region of the 16 MB address space.
P3.1_CS5_RTS1: Port 3 Bit 1, or CS5 output, or USART1 Request To Send output
Active low chip selects CS1 through CS5 come out of reset disabled. They can be programmed to
function as normal chip selects, or as RAS strobes to DRAM. CS2 through CS5 are not used with
the “SWAP” operation (see the “Memory Controller” chapter in the
mappable to any region of the 16 MB address space.
P3.2_Timer0_ResetOut: Port 3 Bit 2, or Timer0 input or output, or ResetOut output.
ResetOut: If the ResetOut function is selected, this pin outputs a low whenever the XA-H4
processor is reset by an internal source (Watchdog Reset or the RESET instruction.)
WARNING: Unlike the other 31 GPIO pins, during power up reset, this pin can output a strongly
driven low pulse. The duration of this low pulse ranges from 0 ns to 258 system clocks, starting at
the time that V
When used as GPIO, this pin can be driven low by software without resetting the XA-H4.
P3.3_Timer1_BRG1_Sync1: Port 3 Bit 3, or Timer1 input or output, or USART1 BRG output, or
USART1 Sync input or output.
is valid. The state of the ResetIn pin does not affect this pulse.
CC
XA-H4 User Manual
XA-H4 User Manual
.) They are
.) They are
See
Note
2
NOTES:
1. See
XA-H4 User Guide,
2. RTClk input is usually used for Rx Clock if an external clock is needed, but can be used for either Rx or Tx or both. TRClk is usually used for
Tx Clock, but can be used for Rx or Tx or both.
1999 Sep 24
“Pins Chapter,” for how to program selection of pin functions.
9

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
writing BTRL
40h in that order. Follow these two writes with five NOPS. This is
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
CONTROL REGISTER OVERVIEW
There are two types of control registers in the XA-H4, these are SFRs
(Special Function Registers), and MMRs (Memory Mapped Registers.)
The SFR registers, with the exception of MRBL, MRBH, MICFG, BCR,
BRTH, BRTL, and RSTSRC are the standard XA core registers. See
WARNINGs about BCR, BRTH, and BRTL in Table 2.
SFRs are accessed by “direct addressing” only (see
Manual
for direct addressing.) The MMRs are specific to the XA-H4
IC25 XA User
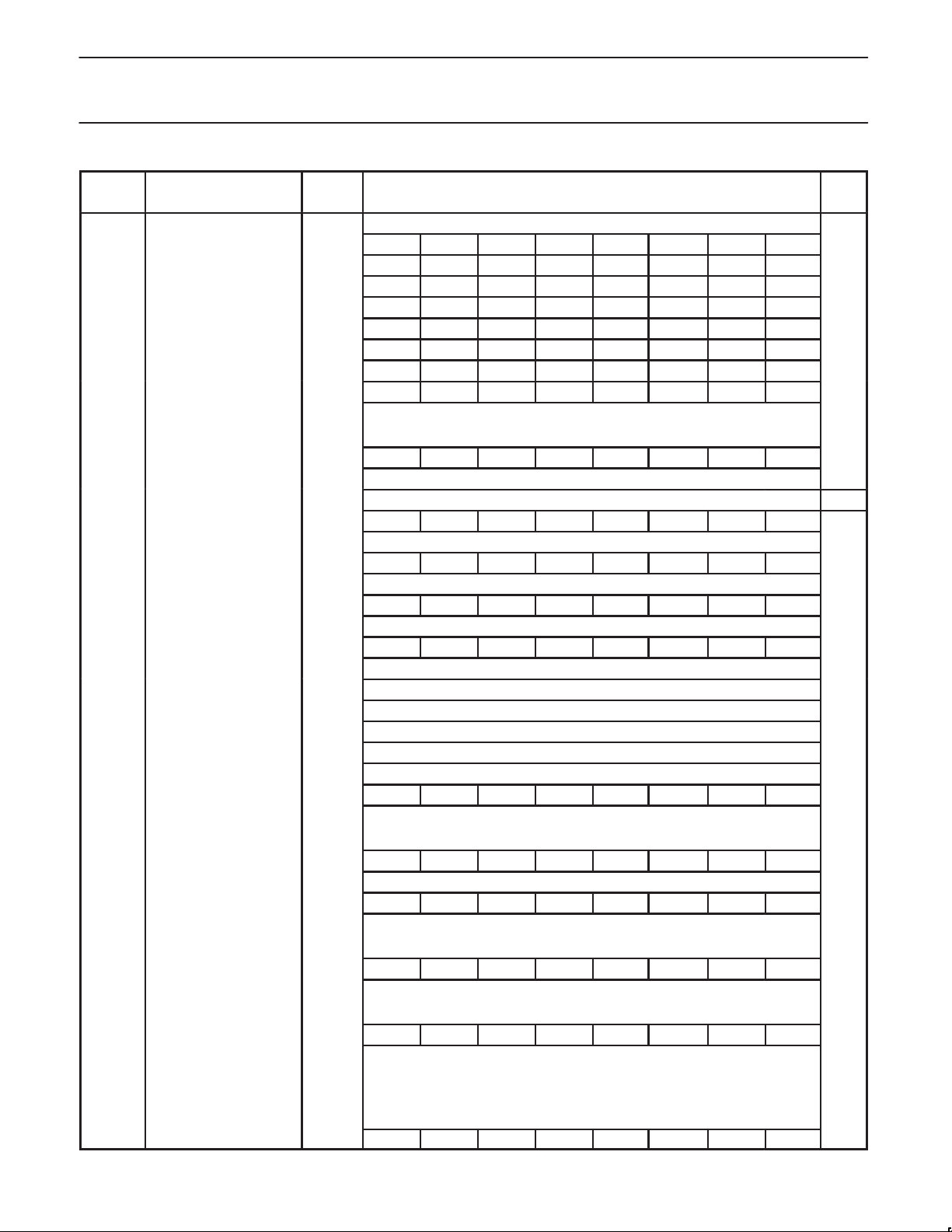
Table 2. Special Function Registers (SFR)
Name Description
BCR Bus Configuration Reg
RESERVED – see
Warning
BTRH Bus Timing Reg High 469h
BTRL Bus Timing Reg Low 468h
SFR
Address
46Ah WARNING – Never write to the BCR register in the XA-H4 – it is initialized to 07h,
MSB LSB
the only legal value. This is not the same as for some other XA derivatives.
WARNING – Immediately after reset, always write BTRH = 51h, followed by
=
not the same as for some other XA derivatives.
on-chip peripherals, and can be accessed by any addressing mode
that can be used for off-chip data accesses. The MMRs are
implemented in a relocatable block. See the “Memory Controller”
chapter in the
MMRs by writing a new base address into the MRBL and MRBH
(MMR Base Low and High) registers.
Bit Functions and Addresses
XA-H4 User Manual
for details on how to relocate the
Reset
Value
07h
FFh
EFh
MRBL# MMR Base Address Low 496h MA15 MA14 MA13 MA12 – – – MRBE x0h
MRBH# MMR Base Address High 497h MA23 MA22 MA21 MA20 MA19 MA18 MA17 MA16 xx
MICFG# ClkOut Tri-St Enable
1 = Enabled
CS Code Segment 443h 00h
DS Data Segment 441h 00h
ES Extra Segment 442h 00h
IEH* Interrupt Enable High 427h
IEL* Interrupt Enable Low 426h EA EDMAH EDMAL EX2 ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0 00h
IPA0 Interrupt Priority A0 4A0h – PT0 – PX0 00h
IPA1 Interrupt Priority A1 4A1h – PT1 – PX1 00h
IPA2 Interrupt Priority A2 4A2h – PDMAL – PX2 00h
IPA3 Interrupt Priority A3 4A3h Reserved – PDMAH 00h
IPA4 Interrupt Priority A4 4A4h – PSC23 – PSC01 00h
IPA5 Interrupt Priority A5 4A5h – – – PAutoB 00h
IPA6 Interrupt Priority A6 4A6h – PHSWR1 – PHSWR0 00h
IPA7 Interrupt Priority A7 4A7h – PHSWR3 – PHSWR2 00h
499h – – – – – – – CLKOE 01h
33F 33E 33D 33C 33B 33A 339 338
EHSWR3 EHSWR2 EHSWR1 EHSWR0 – EAuto ESC23 ESC01
337 336 335 334 333 332 331 330
00h
387 386 385 384 383 382 381 380
P0* Port 0 430h FFh
38F 38E 38D 38C 38B 38A 389 388
P1* Port 1 431h FFh
397 396 395 394 393 392 391 390
P2* Port 2 432h FFh
39F 39E 39D 39C 39B 39A 399 398
P3* Port 3 433h FFh
1999 Sep 24
10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
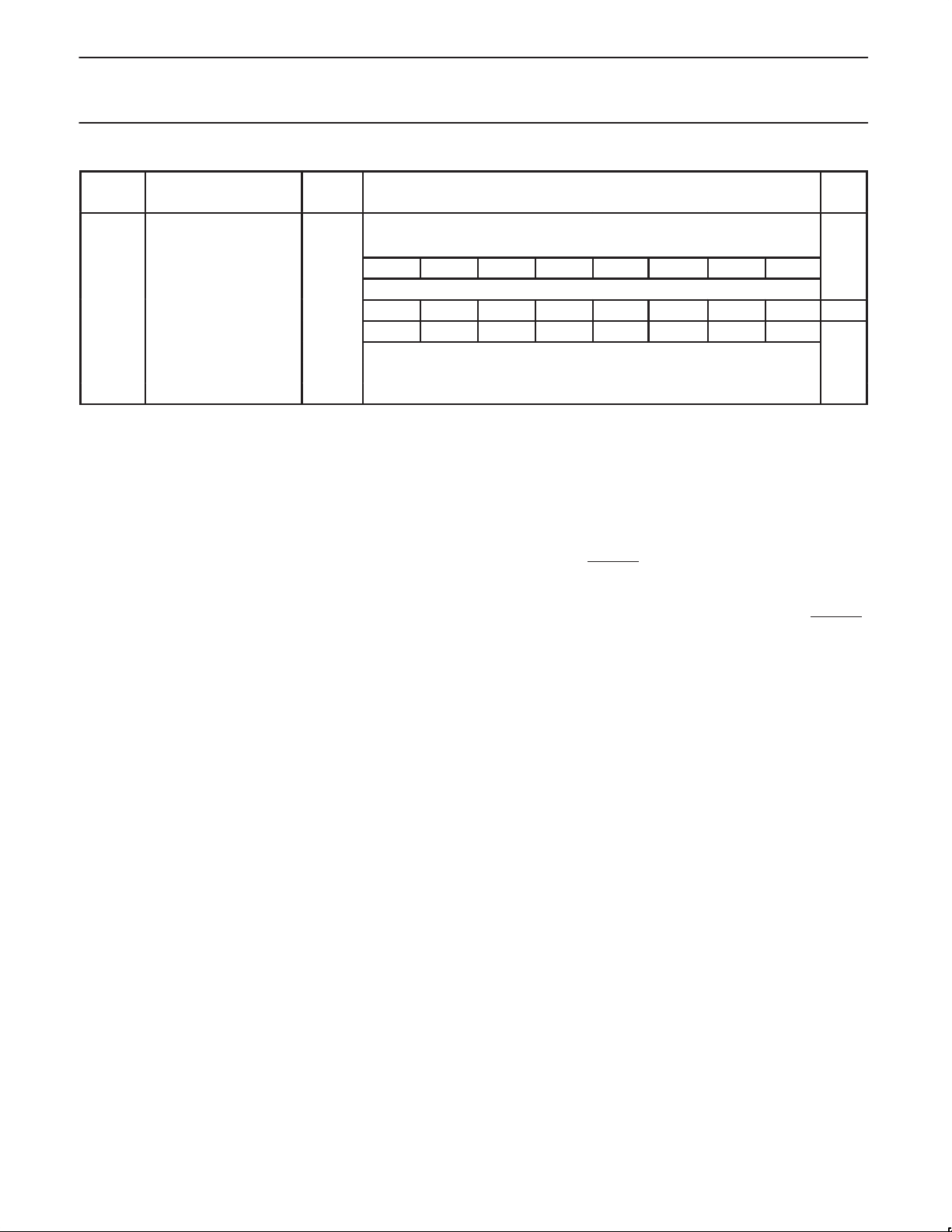
Name
P0CFGA Port 0 Configuration A 470h 5
P1CFGA Port 1 Configuration A 471h 5
P2CFGA Port 2 Configuration A 472h 5
P3CFGA Port 3 Configuration A 473h 5
P0CFGB Port 0 Configuration B 4F0h 5
P1CFGB Port 1 Configuration B 4F1h 5
P2CFGB Port 2 Configuration B 4F2h 5
P3CFGB Port 3 Configuration B 4F3h 5
PCON* Power Control Reg 404h – – – – – – PD IDL 00h
PSWH* Program Status Word High 401h SM TM RS1 RS0 IM3 IM2 IM1 IM0 2
PSWL* Program Status Word Low 400h C AC – – – V N Z 2
PSW51* 80C51 Compatible PSW 402h C AC F0 RS1 RS0 V F1 P 3
Description
SFR
Address
MSB LSB
227 226 225 224 223 222 221 220
20F 20E 20D 20C 20B 20A 209 208
207 206 205 204 203 202 201 200
217 216 215 214 213 212 211 210
Bit Functions and Addresses
Reset
Value
RSTSRC Reset Source Reg 463h ROEN – – – – R_WD R_CMD R_EXT 7
RTH0 T imer 0 Reload High 455h 00h
RTH1 T imer 1 Reload High 457h 00h
RTL0 T imer 0 Reload Low 454h 00h
RTL1 T imer 1 Reload Low 456h 00h
SCR System Configuration Reg 440h – – – – PT1 PT0 CM PZ 00h
21F 21E 21D 21C 21B 21A 219 218
SSEL* Segment Selection Reg 403h ESWEN R6SEG R5SEG R4SEG R3SEG R2SEG R1SEG R0SEG 00h
SWE Software Interrupt Enable 47Ah – SWE7 SWE6 SWE5 SWE4 SWE3 SWE2 SWE1 00h
357 356 355 354 353 352 351 350
SWR* 42Ah – SWR7 SWR6 SWR5 SWR4 SWR3 SWR2 SWR1 00h
287 286 285 284 283 282 281 280
TCON* Timer 0/1 Control 410h TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0 00h
TH0 Timer 0 High 451h 00h
TH1 Timer 1 High 453h 00h
TL0 Timer 0 Low 450h 00h
TL1 Timer 1 Low 452h 00h
TMOD Timer 0/1 Mode 45Ch GATE C/T M1 M0 GATE C/T M1 M0 00h
1999 Sep 24
11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
Name
TSTAT* Timer 0/1 Extended Status 411h – – – – – T1OE – T0OE 00h
WDCON* W atchdog Control 41Fh PRE2 PRE1 PRE0 – – WDRUN WDTOF – 6
WDL Watchdog Timer Reload 45Fh 00h
WFEED1 Watchdog Feed 1 45Dh x
WFEED2 Watchdog Feed 2 45Eh x
NOTES:
* SFRs marked with an asterisk (*) are bit addressable.
# SFRs marked with a pound sign (#) are additional SFR registers specific to the XA-H3 and XA-H4.
1. The XA-H4 implements an 8-bit SFR bus, as stated in Chapter 8 of the
8-bit operations. Attempts to write 16 bits to an SFR will actually write only the lower 8 bits. 16-bit SFR reads will return undefined data in
the upper byte.
2. SFR is loaded from the reset vector.
3. F1, F0, and P reset to “0”. All other bits are loaded from the reset vector.
4. Unimplemented bits in SFRs are “X” (unknown) at all times. “1”s should not be written to these bits since they may be used for other
purposes in future XA derivatives. The reset value shown for these bits is “0”.
5. Port configurations default to quasi-bidirectional when the XA begins execution after reset. Thus all PnCFGA registers will contain FFh and
PnCFGB register will contain 00h. See warning in
Basically, during this period, this pin may output a strongly-driven low pulse. If the pulse does occur, it will terminate in a transition to high at a
time no later than the 259th system clock after valid V
6. The WDCON reset value is E6 for a Watchdog reset; E4 for all other reset causes.
7. The RSTSRC register reflects the cause of the last XA reset. One bit will be set to “1”, the others will be “0”. RSTSRC[7] enables the ResetOut
function; “1” = Enabled, “0” = Disabled. See
8. The XA guards writes to certain bits (typically interrupt flags) that may be written by a peripheral function. This prevents loss of an interrupt or
other status if a bit was written directly by a peripheral action between the read and write of an instruction that performs a read-modify-write
operation. XA-H4 SFR bits that are guarded in this manner are: TF1, TF0, IE1, and IE0 (in TCON), and WDTOF (in WDCON).
Description
SFR
Address
MSB LSB
XA-H4 User Manual
XA-H4 User Manual
28F 28E 28D 28C 28B 28A 289 288
2FF 2FE 2FD 2FC 2FB 2FA 2F9 2F8
power up.
CC
for details; RSTSRC[7] differs in function from most other XA derivatives.
Bit Functions and Addresses
IC25 Data Handbook XA User Guide
about P3.2_Timer0_ResetOut pin during first 258 clocks after power up.
. All SFR accesses must be
Reset
Value
1999 Sep 24
12

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
XA-H4Single-chip 16-bit microcontroller
Table 3. Memory Mapped Registers (MMR)
MMR Name
USART0 Write Register 0 R/W 8 800h Command register 00h
USART0 Write Register 1 R/W 8 802h Tx/Rx Interrupt & data transfer mode xx
USART0 Write Register 2 R/W 8 804h Extended Features Control xx
USART0 Write Register 3 R/W 8 806h Receive Parameter and Control 00h
USART0 Write Register 4 R/W 8 808h Tx/Rx miscellaneous parameters & mode 00h
USART0 Write Register 5 R/W 8 80Ah Tx parameter and control 00h
USART0 Write Register 6 (XA-H4 only) R/W 8 80Ch
USART0 Write Register 7 R/W 8 80Eh HDLC/SDLC flag or Match Character 1 xx
USART0 Write Register 8 R/W 8 810h Transmit Data Buffer xx
USART0 Write Register 9 R/W 8 812h Master Interrupt control xx
USART0 Write Register 10 R/W 8 814h Miscellaneous Tx/Rx control register 00h
USART0 Write Register 11 R/W 8 816h Clock Mode Control xx
USART0 Write Register 12 R/W 8 818h Lower Byte of Baud rate time constant 00h
USART0 Write Register 13 R/W 8 81Ah Upper Byte of Baud rate time constant 00h
USART0 Write Register 14 R/W 8 81Ch Miscellaneous Control bits xx
USART0 Write Register 15 R/W 8 81Eh External/Status interrupt control f8h
USART0 Write Register 16 R/W 8 828h Match Character 2 (WR16) 00h
USART0 Write Register 17 R/W 8 82Ah Match Character 3 (WR17) 00h
USART0 Read Register 0 RO 8 820h Tx/Rx buffer and external status
USART0 Read Register 1 RO 8 822h Receive condition status/residue code
Reserved – do not write 824h –
USART0 Read Register 3 RO 8 826h Interrupt Pending Bits
see WR16 and 17 828–82Ah see WR16 and 17 above
USART0 Read Register 6 RO 8 82Ch SDLC byte count low register
USART0 Read Register 7 RO 8 82Eh SDLC byte count high and FIFO status
USART0 Read Register 8 RO 8 830h Receive Buffer
Reserved 832h
USART0 Read Register 10 RO 8 834h Loop/clock status
Reserved 836-83Eh –
USART1 Write Register 0 R/W 8 840h Command register 00h
USART1 Write Register 1 R/W 8 842h Tx/Rx Interrupt & data transfer mode xx
USART1 Write Register 2 R/W 8 844h Extended Features Control xx
USART1 Write Register 3 R/W 8 846h Receive Parameter and Control 00h
USART1 Write Register 4 R/W 8 848h Tx/Rx miscellaneous parameters & mode 00h
USART1 Write Register 5 R/W 8 84Ah Tx parameter and control 00h
USART1 Write Register 6 R/W 8 84Ch HDLC/SDLC address field or Match Character 0 00h
USART1 Write Register 7 R/W 8 84Eh HDLC/SDLC flag or async Match Character 1 xx
USART1 Write Register 8 R/W 8 850h Transmit Data Buffer xx
USART1 Write Register 9 R/W 8 852h Master Interrupt control xx
USART1 Write Register 10 R/W 8 854h Miscellaneous Tx/Rx control register 00h
USART1 Write Register 11 R/W 8 856h Clock Mode Control xx
USART1 Write Register 12 R/W 8 858h Lower Byte of Baud rate time constant 00h
USART1 Write Register 13 R/W 8 85Ah Upper Byte of Baud rate time constant 00h
Read/Write
or Read Only
Address
Size
Offset
USART0 Registers
USART1 Registers
Description
HDLC/SDLC address field or asynch Match Character 0
Reset
Value
00h
1999 Sep 24
13
 Loading...
Loading...