
Application Audio Aug. 12, 1999
S. Hepp 6251-423-1AN
Application Note
Virtual Dolby Surround Approval
ICs concerned:DPL35xx-A2 and MSP34x1G
Topic: This document serves in addition to Dolby documentation to evaluate
the implementation of Micronas Virtual Surround technology in the
DPL35xx or MSP34x1 chips and to ensure that the application meets all requirements.
1. Required equipment:
(1
• Document „Virtual Dolby Surround Test Procedure“ (Issue 2 S99/??
Preliminary draft, final version not available yet)
• Documen t „Virtual Performance Data Test Form“ (S98/11790/11996
(1
• Document „Virtual Technology Licensing Manual“ (S99/??
Dolby Laboratories – Prelimi-
Dolby Laboratories –
(1
Dolby Laboratories)
nary draft, final version not available yet)
• Signal Generator
• Signal Analyzer with spectrum analyzer, THD+N meter and CCIR 2k filter
(1
Documentation is onl y available via Dolby Laborator i es. Micronas is not authorized to supply this documentation.
(2
Micronas and Dolby use the Audio Precision „System One“ or „System Two“ ( AP1, AP2) m easuring system. Measu-
rement procedure software for AP1, AP2 is avialable from Dolby Laboratories.
(2
(2
2. Implementation of the Test:
The chapters in this Application Note are arranged in the order the tests have to take place.
When Fingerprinting and Listening Test are passed successfully, the approval will be given without any further test.
If the fingerprints don´t match exactly, the whole test procedure has to be completed.
Micronas APN Virtual Dolby Surround Approva l 1
3. Technical Terms
Virtualizer: The virtualizer processes the surround channel, creating two signals which are fed to
the left and right channels. Listening to this signal creates an impression of sound coming from
around the listener.
3D Panorama: A virtualizer algorithm developed by Micronas and implemented in the DPL35xx
and MSP34x1. It is approved by Dolby Laboratories.
Steered signals: In principle, a Virtual Surround system (as well as a ProLogic system) is able to
„steer“ in every direction within a 360 degree circle. A „steered“ condition means that the listener
recognizes the sound coming mainly from one direction.
For measurements during a decoder test, the decoder is steered only to L, C, R, S. These four
conditions are called „Cardinal Points“.
Input signals which force the decoder to one of the L, C, R, or S steered conditions (Cardinal
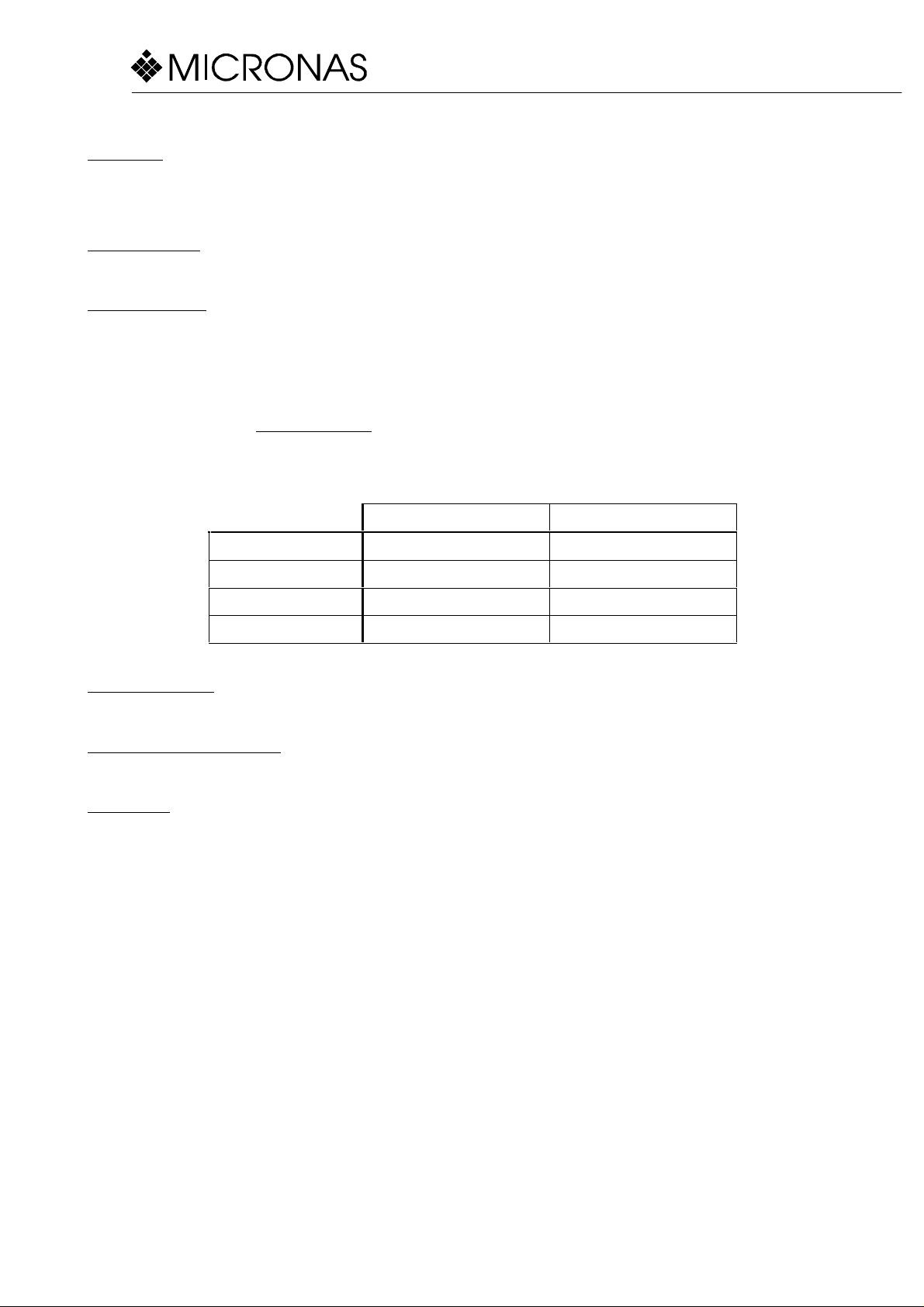
Points) can easily be created. Please see the following table:
Lt in Rt in
Left steered 0 dB No signal
Center steered -3 dB -3 dB (in phase)
Right steered No signal 0 dB
Surround steered -3 dB -3 dB (inverted phase)
Reference Level: is defined as the level, causing clipping at the Input of the Virtual Dolby device
and is marked as 0 dBFS.
Reference Operate Level: is defined as -20 dBFS relative to Reference Level. Normally, the Reference Operate Level is refered to as 0 dBr.
Fingerprint: Set of frequency response plots for the four steered signals L, C, R, S. During the
qualification of MSP34x1 and DPL35XX, Dolby has recorded a set of plots. This recorded set is
compared to the actual measured frequency response of the application under test.
4. Reference Level / Calibrating Inputs and Outputs
This test determines the maximum input voltage for the condition of 3% THD+N, steered surround, at a frequency with maximum amplitude (for MSP / DPL approx. 230 Hz). In other words:
The clipping point at the input is determined. For all following measurements, this value serves as
0 dBFS reference.
Limiting value: Reference Level > 2V
Troubleshooting:
If THD+N is 3% for input levels below 2V
, reduce the set´s volume until there is no change in
s
rrmms
THD+N. This is to ensure, that the input´s clipping is measured.
If 2 V
be set to maximum 19
Micronas APN Virtual Dolby Surround Approva l 2
are still not reached, decrease the MSP/DPL prescaler setting. SCART prescalers should
s
rrmms
, I2S prescalers to maximum 10
hex
hex
.
rrmms
s

5. Frequency Response / Fingerprinting
Both left and right channels have to be plotted for steered L, C, R, and S at –20 dBFS (or in other
words: at Reference Operate Level) and for Virtual Dolby Surround mode on and off.
The plots (Fig. 6.1 to Fig. 6.6) on the next two pages show typical values, the y-axis is scaled with
100 mV
Fig. 6.1 shows the L/R separation. The Surround Spatial Effect Register (44
corresponding to 0 dBr.
rms
) is set to 50%. This
hex
causes a basewidth enlargement for left- and right-steered signals and, along with that, an additional signal on the right channel. This results in a low L/R separation amplitude measurement.
The spatial enhancement improves the acoustical performance of the set. This is also confirmed
by Dolby Laboratories in listening tests.
Fig. 6.7 shows the influence of the Surround Spatial Effect register with the register setting [%] as
a parameter.
Micronas APN Virtual Dolby Surround Approva l 3
 Loading...
Loading...