Philips TZA3005H-C1 Datasheet
DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Aug 05
File under Integrated Circuits, IC19
2000 Feb 17
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TZA3005H
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 and
STM4/OC12 transceiver

2000 Feb 17 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 and STM4/OC12
transceiver
TZA3005H
FEATURES
• Supports STM1/OC3(155.52 Mbits/s) and STM4/OC12
(622.08 Mbits/s)
• Supports reference clock frequencies of 19.44, 38.88,
51.84 and 77.76 MHz
• Meets Bellcore, ANSI and ITU-T specifications
• Meets ITU jitter specification typically to a factor of 2.5
• Integral high-frequency PLL for clock generation
• Interface to TTL logic
• Low jitter PECL (Positive Emitter Coupled Logic)
interface
• 4 or 8-bit STM1/OC3 TTL data path
• 4 or 8-bit STM4/OC12 TTL data path
• No external filter components required
• QFP64 package
• Diagnostic and line loopback modes
• Lock detect
• LOS (Loss of Signal) input
• Low power (0.9 W typical)
• Selectable frame detection and byte realignment
• Loop timing
• Forward and reverse clocking
• Squelched clock operation
• Self-biased PECL inputs to support AC coupling.
APPLICATIONS
• SDH/SONET modules
• SDH/SONET-based transmission systems
• SDH/SONET test equipment
• ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) over SDH/SONET
• Add drop multiplexers
• Broadband cross-connects
• Section repeaters
• Fibre optic test equipment
• Fibre optic terminators.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TZA3005H SDH/SONET transceiver chip is a fully
integrated serialization/deserialization STM1/OC3
(155.52 Mbits/s) and STM4/OC12 (622.08 Mbits/s)
interfacedevice. It performsallnecessaryserial-to-parallel
and parallel-to-serial functions in accordance with
SDH/SONET transmission standards. It is suitable for
SONET-based applications and can be used in
conjunction with the data and clock recovery unit
(TZA3004), optical front-end (TZA3023 with TZA3034/44)
anda laser driver(TZA3001). A typicalnetworkapplication
is shown in Fig.10.
A high-frequency phase-locked loop is used for on-chip
clock synthesis, which allows a slower external transmit
reference clock to be used. A reference clock of 19.44,
38.88,51.84 or 77.76 MHzcan be usedtosupportexisting
system clocking schemes. The TZA3005H also performs
SDH/SONET frame detection.
The low jitter PECL interface ensures that Bellcore, ANSI,
and ITU-T bit-error rate requirements are satisfied.
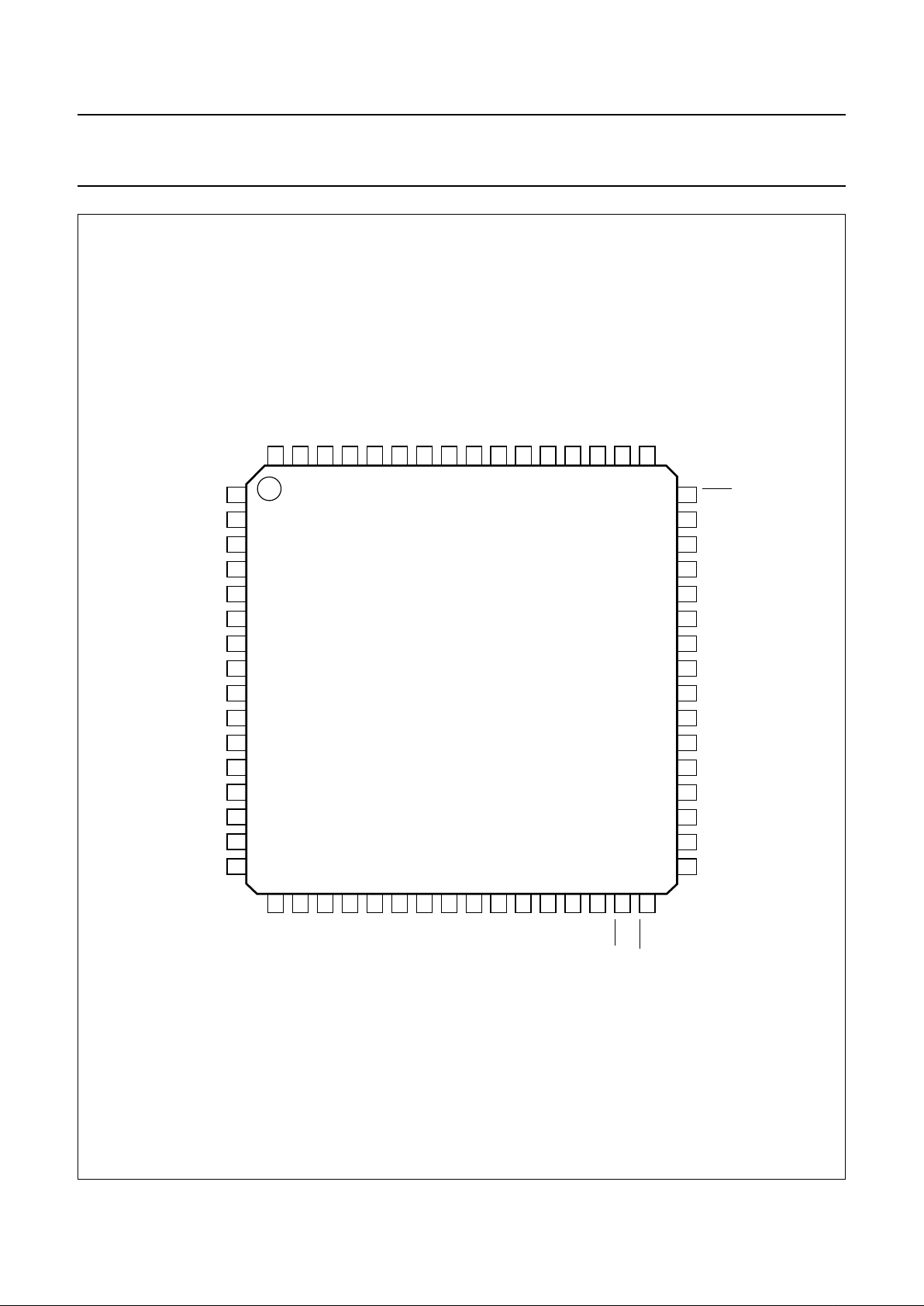
The TZA3005H is supplied in a compact QFP64 package.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TZA3005H QFP64 plastic quad flat package; 64 leads (lead length 1.6 mm);
body 14 × 14 × 2.7 mm
SOT393-1
2000 Feb 17 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 and STM4/OC12
transceiver
TZA3005H
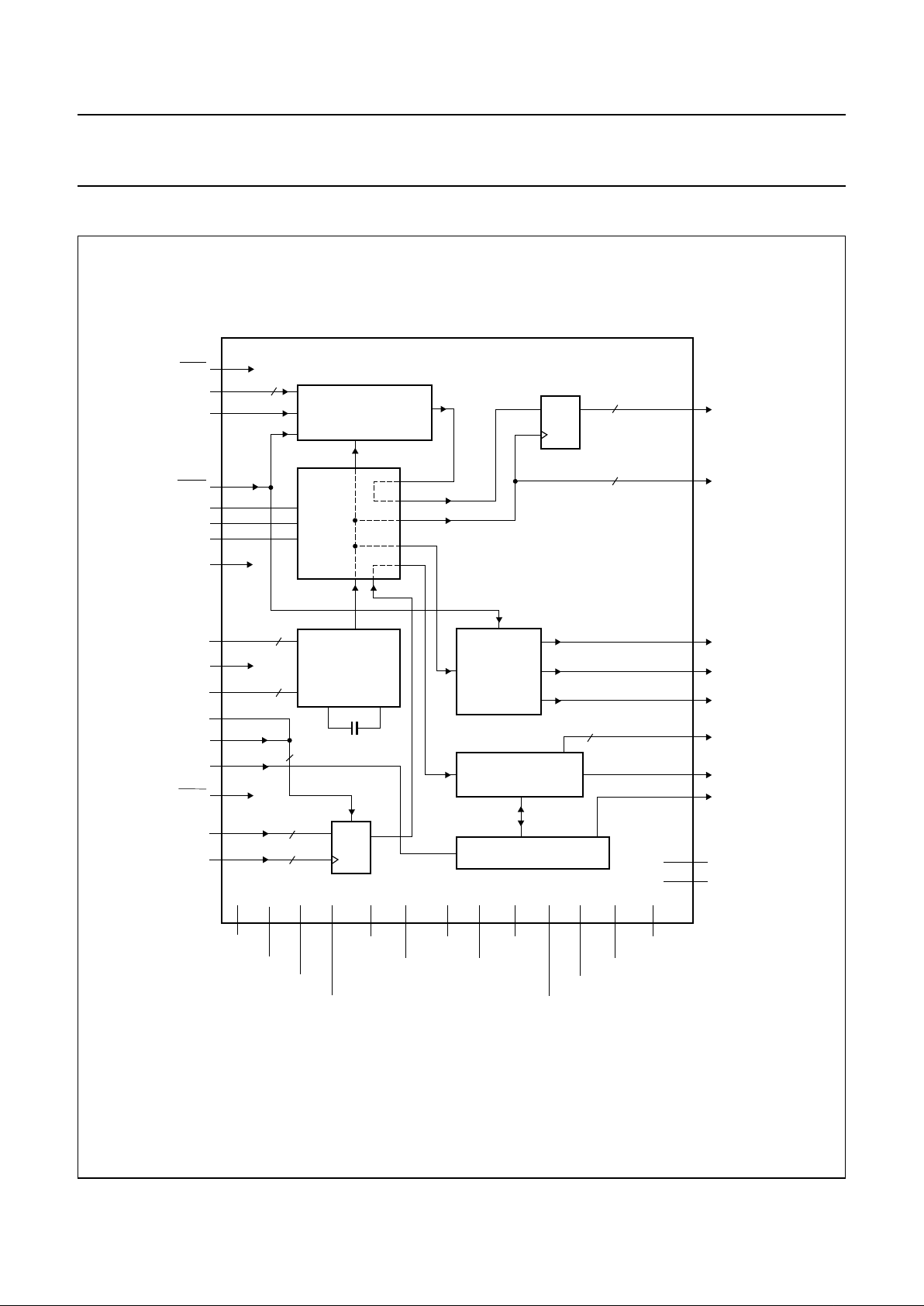
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
CLOCK
DIVIDER
BY 4 OR BY 8
CLOCK
SYNTHESIZER
RF
SWITCH
BOX
(1)
1:8 OR 1:4
SERIAL TO P ARALLEL
8:1 OR 4:1
P ARALLEL T O SERIAL
on-chip capacitor
RECEIVER
TZA3005H
TRANSMITTER
FRAME HEADER DETECT
D
D
LLEN
31
53 to 60
61
TXPCLK
TXPD0 to
TXPD7
8
2
2
2
8
2
2
REFSEL0 and
REFSEL1
REFCLK and
REFCLKQ
MRST
TEST1
MODE
BUSWIDTH
3, 4
2
RXSD and
RXSDQ
24, 25
2
RXSCLK and
RXSCLKQ
27, 28
48
10
TEST2
11
TEST3
13
49
SDTTL
22
SDPECL
23
OOF
33
15, 14
30
DLEN
32
17, 18
21, 20
62
63
64
36, 37, 39, 40,
41, 43 to 45
47
35
TXSD and
TXSDQ
TXSCLK and
TXSCLKQ
SYNCLKDIV
LOCKDET
RXPD0 to
RXPD7
19MHZO
RXPCLK
FP
V
CC(TXCORE)
52
GND
TXCORE
51
MGS975
1
V
CC(SYNOUT)
V
CCD(SYN)
V
CCA(SYN)
V
CC(TXOUT)
V
CC(RXCORE)
V
CC(RXOUT)
GND
RXOUT
DGND
SYN
AGND
SYN
GND
SYNOUT
GND
TXOUT
GND
RXCORE
2 5 8, 9 6 7 16 19
26
29
38, 46
GND
12
34, 42
Fig.1 Block diagram.
(1) Dashed lines represent normal operation mode.
2000 Feb 17 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 and STM4/OC12
transceiver
TZA3005H
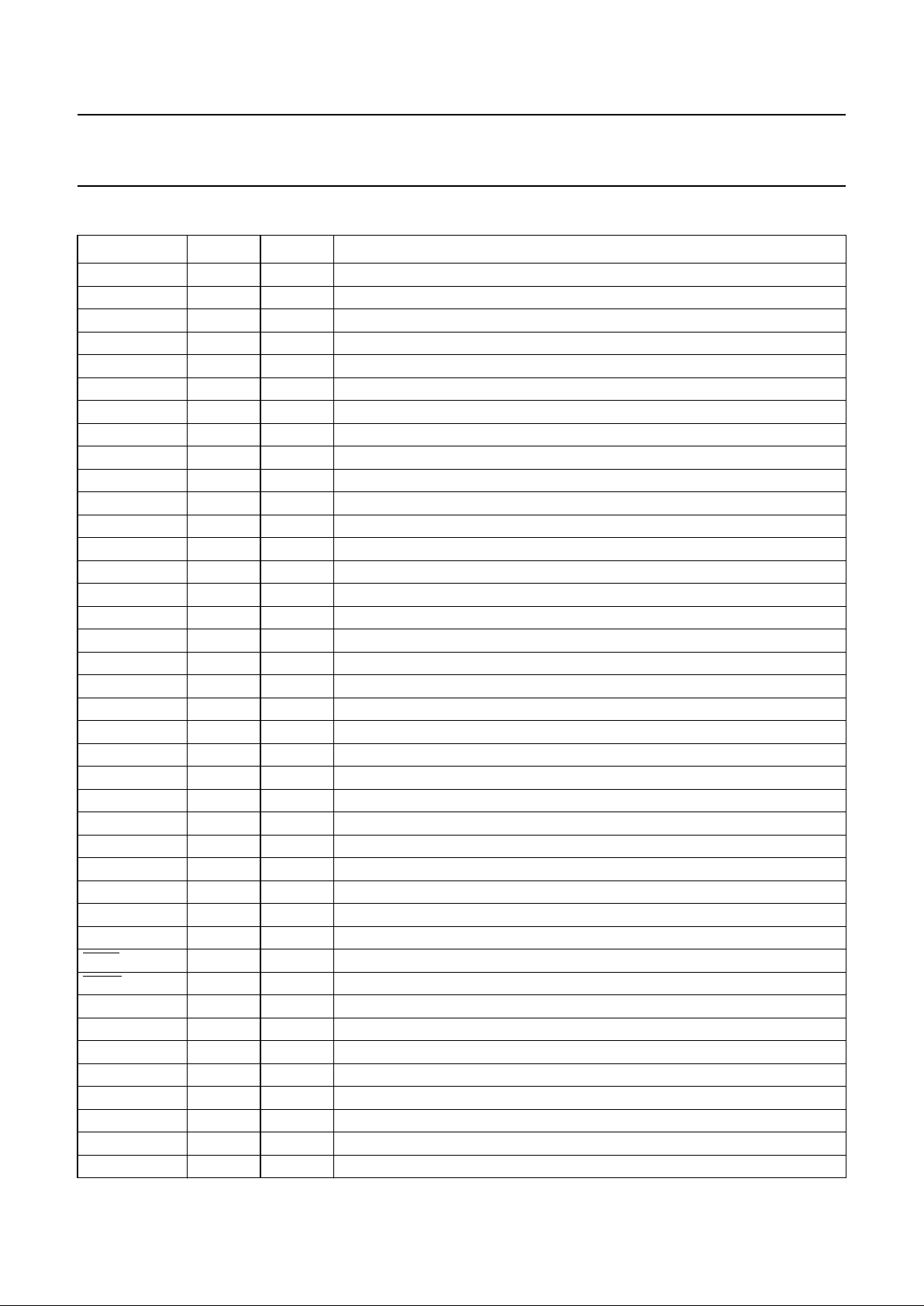
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
V
CC(SYNOUT)
1 S supply voltage (synthesizer output)
GND
SYNOUT
2 G ground (synthesizer output)
REFSEL0 3 I reference clock select input 0
REFSEL1 4 I reference clock select input 1
DGND
SYN
5 G digital ground (synthesizer)
V
CCD(SYN)
6 S digital supply voltage (synthesizer)
V
CCA(SYN)
7 S analog supply voltage (synthesizer)
AGND
SYN
8 G analog ground (synthesizer)
AGND
SYN
9 G analog ground (synthesizer)
TEST1 10 I test and control input
TEST2 11 I test and control input
GND 12 G ground
TEST3 13 I test and control input
REFCLKQ 14 I inverted reference clock input
REFCLK 15 I reference clock input
V
CC(TXOUT)
16 S supply voltage (transmitter output)
TXSD 17 O serial data output
TXSDQ 18 O inverted serial data output
GND
TXOUT
19 G ground (transmitter output)
TXSCLKQ 20 O inverted serial clock output
TXSCLK 21 O serial clock output
SDTTL 22 I TTL signal detect input
SDPECL 23 I PECL signal detect input
RXSD 24 I serial data input
RXSDQ 25 I inverted serial data input
V
CC(RXCORE)
26 S supply voltage (receiver core)
RXSCLK 27 I serial clock input
RXSCLKQ 28 I inverted serial clock input
GND
RXCORE
29 G ground (receiver core)
BUSWIDTH 30 I 4/8 bus width select input
LLEN 31 I line loopback enable input (active LOW)
DLEN 32 I diagnostic loopback enable input (active LOW)
OOF 33 I out-of-frame enable input
GND
RXOUT
34 G ground (receiver output)
FP 35 O frame pulse output
RXPD0 36 O parallel data output 0
RXPD1 37 O parallel data output 1
V
CC(RXOUT)
38 S supply voltage (receiver output)
RXPD2 39 O parallel data output 2
RXPD3 40 O parallel data output 3
2000 Feb 17 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 and STM4/OC12
transceiver
TZA3005H
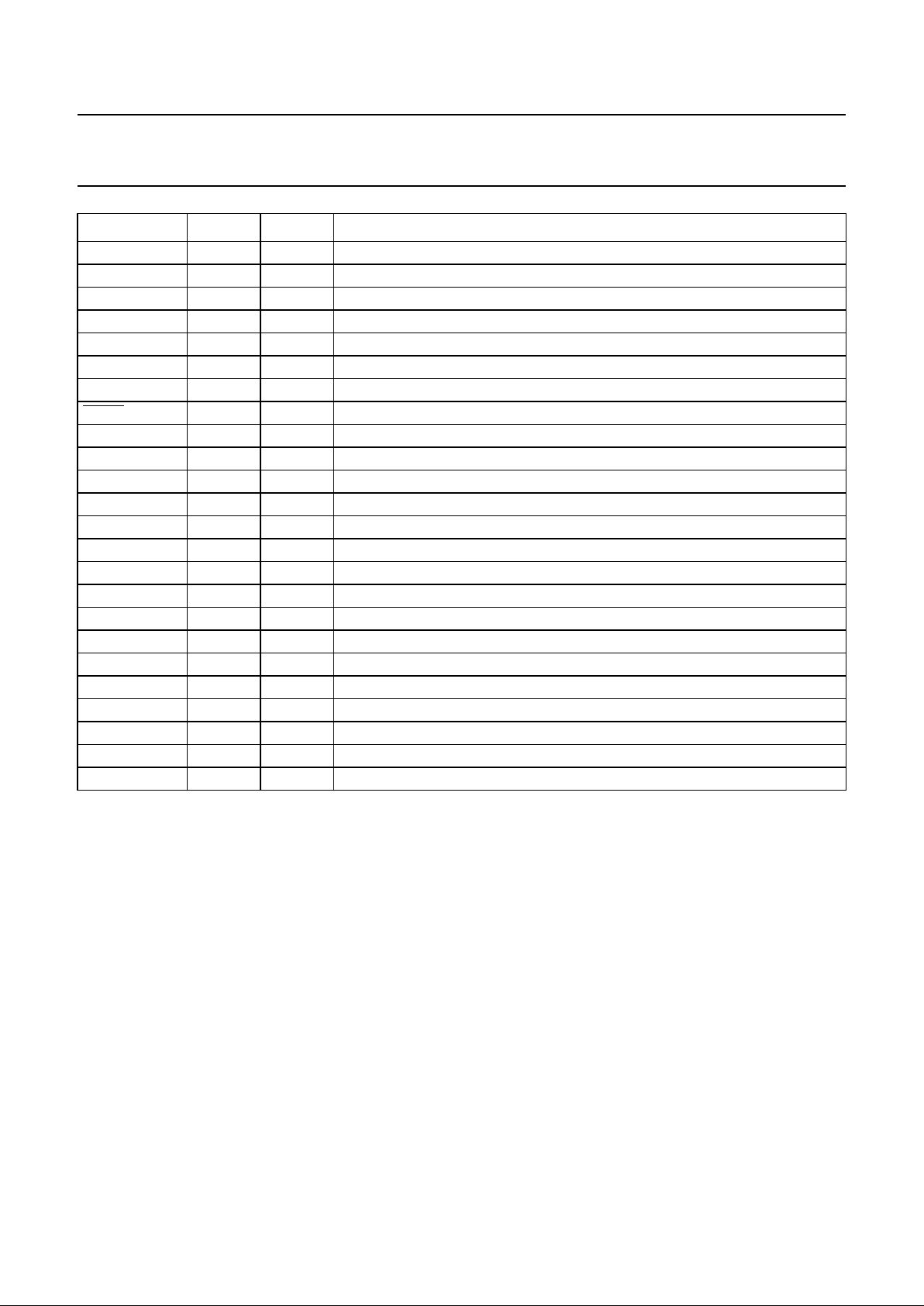
Note
1. Pin type abbreviations: O = Output, I = Input, S = Supply, G = Ground.
RXPD4 41 O parallel data output 4
GND
RXOUT
42 G ground (receiver output)
RXPD5 43 O parallel data output 5
RXPD6 44 O parallel data output 6
RXPD7 45 O parallel data output 7
V
CC(RXOUT)
46 S supply voltage (receiver output)
RXPCLK 47 O receive parallel clock output
MRST 48 I master reset (active LOW)
MODE 49 I serial data rate select STM1/STM4
ALTPIN 50 I test and control input
GND
TXCORE
51 G ground (transmitter core)
V
CC(TXCORE)
52 S supply voltage (transmitter core)
TXPD0 53 I parallel data input 0
TXPD1 54 I parallel data input 1
TXPD2 55 I parallel data input 2
TXPD3 56 I parallel data input 3
TXPD4 57 I parallel data input 4
TXPD5 58 I parallel data input 5
TXPD6 59 I parallel data input 6
TXPD7 60 I parallel data input 7
TXPCLK 61 I transmit parallel clock input
SYNCLKDIV 62 O transmit byte/nibble clock output (synchronous)
LOCKDET 63 O lock detect output
19MHZO 64 O 19 MHz reference clock output
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
2000 Feb 17 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 and STM4/OC12
transceiver
TZA3005H
handbook, full pagewidth
TZA3005H
MGK483
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
MRST
RXPCLK
V
CC(RXOUT)
RXPD7
RXPD6
RXPD5
GND
RXOUT
RXPD4
RXPD3
RXPD2
V
CC(RXOUT)
RXPD1
RXPD0
FP
GND
RXOUT
OOF
V
CC(SYNOUT)
REFSEL0
GND
SYNOUT
REFSEL1
DGND
SYN
V
CCD(SYN)
V
CCA(SYN)
AGND
SYN
AGND
SYN
TEST1
TEST2
GND
TEST3
REFCLKQ
REFCLK
V
CC(TXOUT)
33
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
19MHZO
LOCKDET
SYNCLKDIV
TXPCLK
TXPD7
TXPD6
TXPD5
TXPD4
TXPD3
TXPD2
TXPD1
TXPD0
V
CC(TXCORE)
GND
TXCORE
ALTPIN
MODE
TXSD
TXSDQ
GND
TXOUT
TXSCLKQ
TXSCLK
SDTTL
SDPECL
RXSD
RXSDQ
V
CC(RXCORE)
RXSCLK
RXSCLKQ
GND
RXCORE
BUSWIDTH
LLEN
DLEN 49
Fig.2 Pin configuration.

2000 Feb 17 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 and STM4/OC12
transceiver
TZA3005H
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Introduction
The TZA3005H transceiver implements SDH/SONET
serialization/deserialization, transmission and frame
detection/recovery functions. The TZA3005Hcan beused
as the front-end for SONET equipment. It handles the
serial receive and transmit interface functions including
parallel-to-serial and serial-to-parallel conversion and
clock generation. A block diagram showing the basic
operation of the chip is shown in Fig.1.
The TZA3005H has a transmitter section, a receiver
section, and an RF switch box. The sequence of
operations is as follows:
• Transmitter operations:
– 4 or 8-bit parallel input
– parallel-to-serial conversion
– serial output.
• Receiver operations:
– serial input
– frame detection
– serial-to-parallel conversion
– 4 or 8-bit parallel output.
The RF switch box receives serial clock and data signals
from the transmitter section, the receiver inputbuffers and
from the clock synthesizer. These signals are routed by
multiplexers to the transmitter section, the transmitter
output, the receiver andto the clock divider, dependingon
the status of the control inputs. The switch box also
supports a number of test and loop modes.
Transmitter operation
The transmitter section of the TZA3005H converts
STM1/OC3 or STM4/OC12 byte-serial input data to a
bit-serial output data format. Input data rates of 19.44,
38.88, 77.76 or 155.52 Mbytes/s are converted to an
output data rate of either 155.52 or 622.08 Mbits/s. It also
provides diagnostic loopback (transmitterto receiver), line
loopback (receiver to transmitter) and also loop timing
(transmitter clocked by the receiver clock).
An integral frequency synthesizer, comprising a
phase-locked loop and a divider, can be used to generate
a high-frequency bit clock from an input reference clock
frequency of 19.44, 38.88, 51.84 or 77.76 MHz.
CLOCK SYNTHESIZER
The clock synthesizer generates a serial output clock
(TXSCLK) which is phase synchronised with the input
reference clock (REFCLK). The serial output clock is
synthesized from one of four SDH/SONET input reference
clock frequencies and can have a frequency of either
155.52 MHz for STM1/OC3 or 622.08 MHz for
STM4/OC12 selected by the MODE input (see Table 1).
Table 1 Transmitter output clock (TXSCLK)
frequency options
The frequency of the input reference clock is divided to
obtain a frequency of about 19 MHz which is fed to the
phase detector in the PLL. The appropriate divisor is
selected by control inputs REFSEL0 and REFSEL1 as
shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Reference frequency (REFCLK) options
To ensure the TXSCLK frequency is accurate enough to
operate ina SONET system,REFCLK must begenerated
from a differential PECL crystal oscillator having a
frequency accuracy better than 4.6 ppm for compliance
with
“ITU G.813 (option 1)”
, or 20 ppm for
“ITU G.813
(option 2)”
.
To comply with SONET jitter requirements, the maximum
value specified for reference clock signal jitter must be
guaranteed over the 12 kHz to 1 MHz bandwidth (see
Table 3).
MODE
INPUT
TXSCLK
FREQUENCY
OPERATING
MODE
0 155.52 MHz STM1/OC3
1 622.08 MHz STM4/OC12
REFSEL1 REFSEL0
REFCLK
FREQUENCY
0 0 19.44 MHz
0 1 38.88 MHz
1 0 51.84 MHz
1 1 77.76 MHz
2000 Feb 17 8
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 and STM4/OC12
transceiver
TZA3005H
Table 3 ITU reference clock signal (REFCLK) jitter limits
The on-chip PLL contains a phase detector, a loop filter
and a VCO. The phase detector compares the phases of
the VCO and the divided REFCLK signals. The loop filter
convertsthephase detector outputtoa smooth DCvoltage
which controls the VCO frequency and ensures that it is
always 622.08 MHz. In STM1/OC3 mode, the correct
output frequency at TXSCLK is obtained by dividing the
VCO frequency by 4. The loop filter parameters are
optimized for minimal output jitter.
CLOCK DIVIDER
The clock divider generates either a byte rate or a nibble
rate version of the serial output clock (TXSCLK) which is
output on pin SYNCLKDIV (see Table 4).
Table 4 SYNCLKDIV frequency
SYNCLKDIV is intended for use as a byte speed clock for
upstream multiplexing and overhead processing circuits.
Using SYNCLKDIV for upstream circuits ensures a stable
frequency and phase relationship is maintained between
the data in to and out of the TZA3005H.
For parallel-to-serial data conversion, the parallel input
data is transferred from the TXPCLK byte clock timing
domain to theinternally generatedbit clocktiming domain.
The internally generated bit clock does not have to be
phase aligned to the TXPCLK signal but must be
synchronized by the master reset (MRST) signal.
Receiver operation
The receiver section of the TZA3005H converts
STM1/OC3 or STM4/OC12 bit-serial input data to a
parallel data output format. In byte mode, input data rates
of 155.52 or 622.08 Mbits/s are converted to an output
data rate of either 19.44 or 77.76 Mbytes/s. In nibble
mode, a 4-bit parallel data stream is generated having a
clock frequency of either 38.88 or 155.52 MHz. It also
provides diagnostic loopback (transmitterto receiver), line
loopback (receiver to transmitter) and squelched clock
operation (transmitter clock to receiver).
FRAME AND BYTE BOUNDARY DETECTION
The frame and byte boundary detection circuit searches
the incoming data for the correct 48-bit frame pattern
whichis asequenceof threeconsecutive A1 bytes ofF0 H
followed immediately by three consecutive A2 bytes of
28 H. Frame pattern detection is enabled and disabled by
the out-of-frame enable input (OOF). Detection isenabled
by a rising edge on pin OOF, and remains enabled while
the level on pin OOF is HIGH. It is disabled when at least
one frame pattern is detected and the level on pin OOF is
no longer HIGH.When framepattern detectionis enabled,
the frame pattern is used to locate byte and frame
boundaries in the incoming data stream (Received Serial
Data (RXSD) or looped transmitter data). The serial to
parallel converterblock uses thelocated byte boundaryto
divide the incoming data stream into bytes for output on
theparallel output databus(RXPD0 to RXPD7). When the
correct 48-bit frame pattern is detected, the occurrence of
the frame boundary is indicated by the Frame Pulse (FP)
signal. When frame pattern detection is disabled, the byte
boundaryis fixed,and only frame patterns whichalign with
the fixed byte boundary produce an output on pin FP.
It is extremely unlikely that random data in an STM1/OC3
or STM4/OC12 data stream will replicate the 48-bit frame
pattern. Therefore, the time taken to detect the beginning
of the frame should be less than 250 µs (as specified in
“ITU G.783”
) even at extremely high bit error rates.
Once down-stream overhead circuits verify that frame and
byte synchronization are correct, OOF can be set LOW to
prevent the frame search process synchronizing to a
mimic frame pattern.
SERIAL-TO-PARALLEL CONVERTER
The serial-to-parallel converter causes a delay between
thefirst bitof an incomingserial data byteto thestartof the
parallel output of thatbyte. Thedelay dependson the time
taken for the internal parallel load timing circuit to
synchronizethe databyte boundaries tothe fallingedge of
RXPCLK. The timing of RXPCLK is independent of the
byte boundaries. RXPCLK is neither truncated nor
extended during reframe sequences.
MAXIMUM JITTER OF REFCLK
12 kHz TO 1 MHz
OPERATING
MODE
56 ps (RMS) STM1/OC3
14 ps (RMS) STM4/OC12
MODE
INPUT
BUSWIDTH
SYNCLKDIV
FREQUENCY
OPERATING
MODE
0 0 (nibble) 38.88 MHz STM1/OC3
0 1 (byte) 19.44 MHz STM1/OC3
1 0 (nibble) 155.52 MHz STM4/OC12
1 1 (byte) 77.76 MHz STM4/OC12

2000 Feb 17 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 and STM4/OC12
transceiver
TZA3005H
Transceiver pin descriptions
TRANSMITTER INPUT SIGNALS
Parallel data inputs (TXPD0 to TXPD7)
These areTTL data word inputs. The input data is aligned
with the TXPCLK parallel input clock. TXPD7 is the most
significant bit (corresponding to bit 1 of each PCM word,
the first bit transmitted). TXPD0 is the least significant bit
(corresponding to bit 8 of each PCM word, the last bit
transmitted). Bits TXPD0 to TXPD7 are sampled on the
rising edge of TXPCLK. If a 4-bit bus width is selected,
TXPD7 is the most significant bit and TXPD4 is the least
significant bit. Inputs TXPD0 to TXPD3 are unused.
Parallel clock input (TXPCLK)
This is a TTL input clock signal having a frequency of
either19.44,38.88, 77.76 or 155.52 MHz andadutyfactor
of nominally 50%, to which input data bits TXPD0 to
TXPD7 are aligned. TXPCLK transfers the input data to a
holding register in the parallel-to-serial converter.
The rising edge of TXPCLK samples bits TXPD0 to
TXPD7. After a master reset, one rising edge of TXPCLK
is required to fully initialize the internal data path.
RECEIVER INPUT SIGNALS
Receive serial data (RXSD and RXSDQ)
These are differential PECL serial data inputs, normally
connectedto an opticalreceiver module orto the TZA3004
dataand clockrecovery unit, and clocked byRXSCLK and
RXSCLKQ. These inputs can be AC coupled without
external biasing.
Receive serial clock (RXSCLK and RXSCLKQ)
These are differential PECL recovered clock signals
synchronized to the input data RXSD and RXSDQ. It is
used by the receiver as the master clock for framing and
deserialization functions. These inputs can be AC coupled
without external biasing.
Out-of-frame (OOF)
This is aTTL signalwhich enablesframe patterndetection
logic in the TZA3005H. The frame pattern detection logic
is enabled by a rising edge on pin OOF, and remains
enabled until a frameboundary isdetected andOOF goes
LOW. OOF is an asynchronous signal with a minimum
pulse width of one RXPCLK period (see Fig.3).
Signal detect PECL (SDPECL)
This is a single-ended PECL input with an internal
pull-down resistor. This input is driven by an external
optical receiver module to indicate a loss of received
optical power (LOS). SDPECL is active HIGH when
SDTTL is at logic 0 and active LOW when SDTTL is at
logic 1or unconnected. When there is a loss of signal,
SDPECL is inactive and the bit-serial data on pins RXSD
and RXSDQ is internally forced to a constant zero. When
SDPECL is active, the bit-serial data on pins RXSD and
RXSDQ is processed normally (see Table 5).
Signal detect TTL (SDTTL)
This is a single-ended TTL input with an internal pull-up
resistor. This input isdriven byan external optical receiver
module toindicate a loss of received optical power (LOS).
SDTTL is active HIGH when pin SDPECL is logic 0 or
unconnected, and active LOW when pin SDPECL is at
logic 1. When there is a loss of signal, SDTTL is inactive
and the bit-serial data on pins RXSD and RXSDQ is
internallyforced to aconstantzero. When SDTTLisactive,
thebit-serialdata on pins RXSD and RXSDQ isprocessed
normally (see Table 5).
If pin SDTTLinstead of pin SDPECL is to be connected to
the optical receiver module, connect pin SDPECL to a
logic HIGH-level to implement an active-LOW signal
detect, or leave pin SDPECL unconnected to implement
an active-HIGH signal detect.
Table 5 SDPECL/SDTTL truth table
COMMON INPUT SIGNALS
Bus width selection (BUSWIDTH)
This is a TTL signal which selects 4-bit or 8-bit operation
for the transmit and receive parallel interfaces.
BUSWIDTH LOW selects a 4-bit bus width. BUSWIDTH
HIGH selects an 8-bit bus width.
SDPECL SDTTL RXPD OUTPUT DATA
0 or floating 0 0
0 or floating 1 or floating RXSD input data
1 0 RXSD input data
1 1 or floating 0
 Loading...
Loading...