Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA9605H
Audio processor with head amplifier
for VHS hi-fi
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1999 Apr 14
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
5 PINNING
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6.1 Record-mute mode or head identification
selection
6.2 Hi-fi audio output level
6.3 Reference current
6.4 Head amplifier
6.4.1 Playback mode
6.4.2 Record-mute mode
6.4.3 Record mode
6.4.4 Head amplifier power supply and ground
6.5 Automatic calibration
6.6 Power muting
6.7 Envelope output
6.8 RF converter output
6.9 Audio dubbing
6.9.1 Output mix
6.9.2 Input mix
7I
7.1 Addresses and data bytes
7.2 Valid transmissions to and from the TDA9605H
7.3 Overview of the TDA9605H I2C-bus control
7.4 Control byte at subaddress 00H
7.4.1 Audio FM mode
7.4.2 Playback mode
7.4.3 Record mode
7.4.4 System standard selection
7.4.5 Head amplifier playback amplification
7.4.6 Head amplifier record current
7.5 Select byte at subaddress 01H
7.5.1 Decoder output select
7.5.2 Head amplifier record current range select
7.5.3 Normal input level
7.6 Input byte at subaddress 02H
7.6.1 Input select
7.6.2 Normal select
7.7 Output byte at subaddress 03H
7.7.1 Line output amplification
7.7.2 Output select
7.7.3 Envelope output select
7.7.4 Line output select
7.7.5 Decoder output select
7.7.6 RF converter mute
2
C-BUS PROTOCOL
7.8 Volume bytes at subaddresses 04H, 05H
and 06H
7.8.1 Left and right volume control
7.9 Power byte at subaddress 07H
7.9.1 Calibration start
7.9.2 DC output voltage selection
7.9.3 Test mode
7.9.4 Power-on reset
7.9.5 Head amplifier disable
7.9.6 Power muting
7.9.7 Standby select
7.10 Read byte
7.10.1 Calibration ready
7.10.2 Auto-normal selection
7.10.3 Calibration error
7.10.4 Power-on reset
8 LIMITING VALUES
9 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
10 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
11 RECORD-MUTE MODE CHARACTERISTICS
12 RECORD MODE CHARACTERISTICS
13 PLAYBACK MODE CHARACTERISTICS
14 APPLICATION AND TEST INFORMATION
14.1 RM and HID control signals
14.2 Reference current resistor
14.3 Setting line output level
14.4 Test modes
15 INTERNAL CIRCUITRY
16 PACKAGE OUTLINE
17 SOLDERING
17.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
17.2 Reflow soldering
17.3 Wave soldering
17.4 Manual soldering
17.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for
wave and reflow soldering methods
18 DEFINITIONS
19 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
20 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
1999 Apr 14 2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
1 FEATURES
• All functions controlled via the serial 2-wire I2C-bus
• Integrated standby modes for low power consumption
• Audio FM head amplifier:
– Programmable recording current
– Programmable playback amplification
– Fast record-mute mode control input.
• Hi-fi signal processing:
– Adjustment free
– High performance
– Low distortion switching noise suppressor
– NTSC and PAL (SECAM) system.
• Linear audio input:
– Programmable (playback) level.
• 5 stereo inputs and additional mono Second Audio
Program (SAP) input
• 2 stereo outputs (line and decoder) with independent
output select function
• RF converter output with overload-protection AGC
• Integrated output power muting
• Audio level meter output
• Extensive input and output select function
• Full support of video recorder feature modes.
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA9605H is a single-chip device in a small package
that contains all the required functions, including the head
amplifier, to realize the audio FM hi-fi stereo system in a
VHS video recorder (see Fig.1). The device is adjustment
free by use of an integrated auto-calibration system.
Extensive signal select functions are offered to support
pay-TV decoding and video recorder feature modes.
The high performance and functionality of the TDA9605H
comprises world-wide system and application
requirements for NTSC, PAL, SECAM and multi-standard
video recorders from basic up to high-end models.
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
TDA9605H QFP44 plastic quad flat package; 44 leads (lead length 1.3 mm);
1999 Apr 14 3
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
body 10 × 10 × 1.75 mm
PACKAGE
SOT307-2
Page 4
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
n
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1999 Apr 14 4
V
CCH
GNDH
PBIN1
PBIN2
RECOUT
HMSW
SAP
TUNL
TUNR
CINL
CINR
EXT1L
EXT1R
EXT2L
EXT2R
AUXL
AUXR
40
39
37
35
36
38
playback. +
record-mute,
recording
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
SAP
TUL
TUR
E1L
E1R
E2L
E2R
HEAD AMPLIFIER
input select
I2C-bus
control
RMHID
41 44 42 43
DCL
HID
current
RM
M
HID
DCR
HF AGC
1.3 or 1.4 MHz
+
1.7 or 1.8 MHz
RM
playback head
amplification,
record head
carrier ratio select,
record-mute
FM (DE-)MODULATOR
volume left
M
M
volume right
M
normal select
TUL
TUR
E2L
E2R
N
dub
M
+
+
= mute
+
SAP
ENVOUT
envelope
output
select
+ playback
LEVEL
DETECTOR
HF LIMITER
HF LFP
LEVEL
DETECTOR
HF LIMITER
HF LFP
+ ++
I/O CONTROL
normal
input
level
21 22
LINOUT LININ
HI-FI
DETECTOR
DROPOUT
CANCELING
PLL
CCO
(1.3 or
1.4 MHz)
PLL
CCO
(1.7 or
1.8 MHz)
M
dbook, full pagewidth
SDA SCL
I2C-BUS
INTERFACE
AUTN
HID
NOISE
SUPPRESSION
AUDIO
CLIPPER
NOISE
SUPPRESSION
AUDIO
CLIPPER
output selectAUTN
L
R
+
N
envelope output
select + record
L
R
PEAK HOLD
PEAK HOLD
TDA9605H
V
CC
34 27 29 28
standby select
5th ORDER
AUDIO LPF
COMPRESSOR
5th ORDER
AUDIO LPF
COMPRESSOR
dub
M
DCL
DCR
GND
SUPPLY
NOISE REDUCTION
W + FM
EXPANDER
W + FM
EXPANDER
TUL
E1L
SAP
TUR
E1R
SAP
E2L
E2R
mute
V
CC
RFCAGC
V
ref
DETECTOR
RECTIFIER
CCA
DETECTOR
RECTIFIER
CCA
decoder
select
M
line select
AUTO-MUTE
M
RF converter
mute
12
I
ref
+1 dB 12 V
26
25
24
23
30
31
32
33
19
20
16
15
17
18
13
14
MGR834
DETL
DCL
EMPHL
DCFBL
DETR
DCR
EMPHR
DCFBR
DECL
DECR
LINEL
MUTEL
LINER
MUTER
RFCOUT
MUTEC
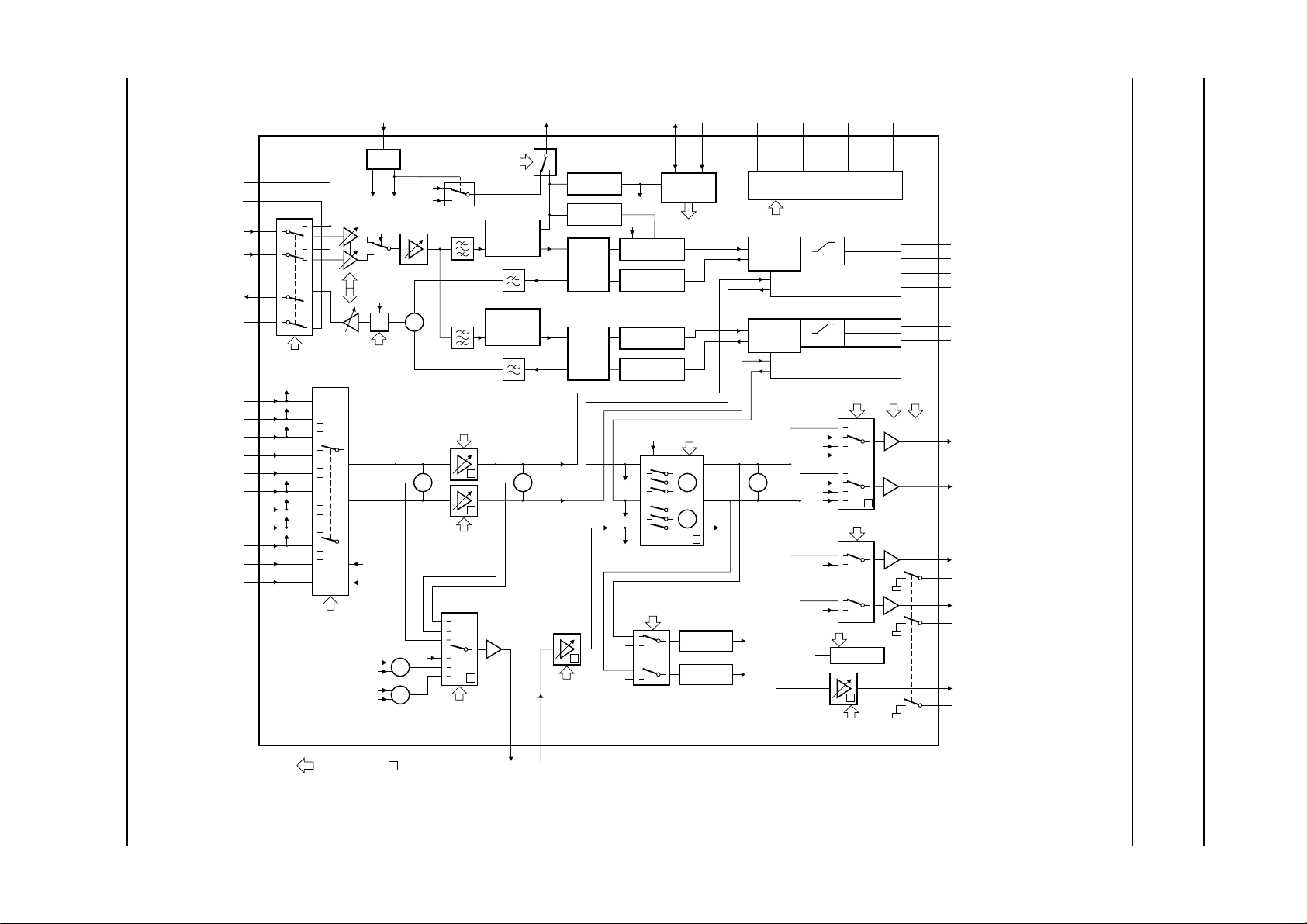
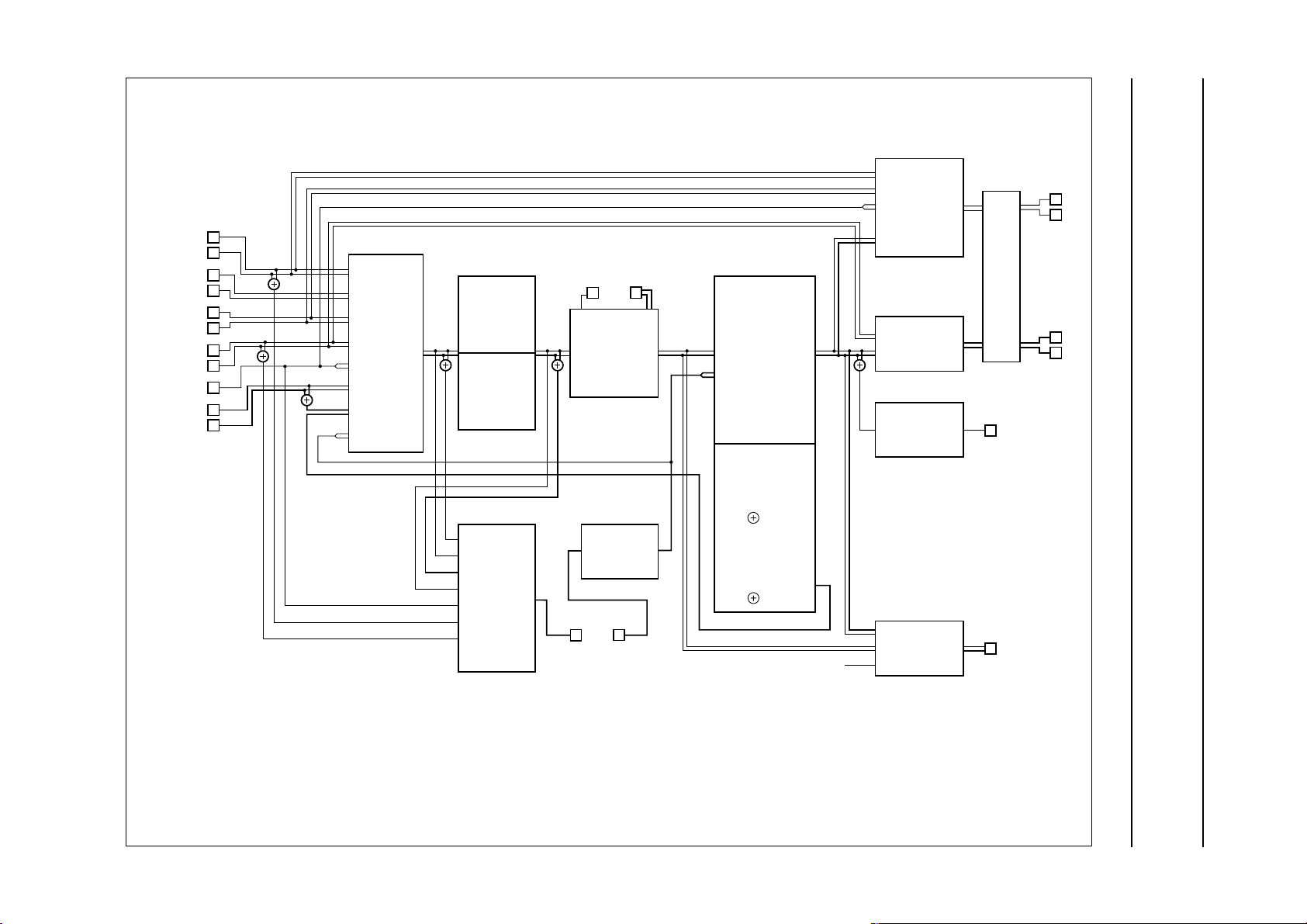
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fig.1 Block diagram.
Page 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
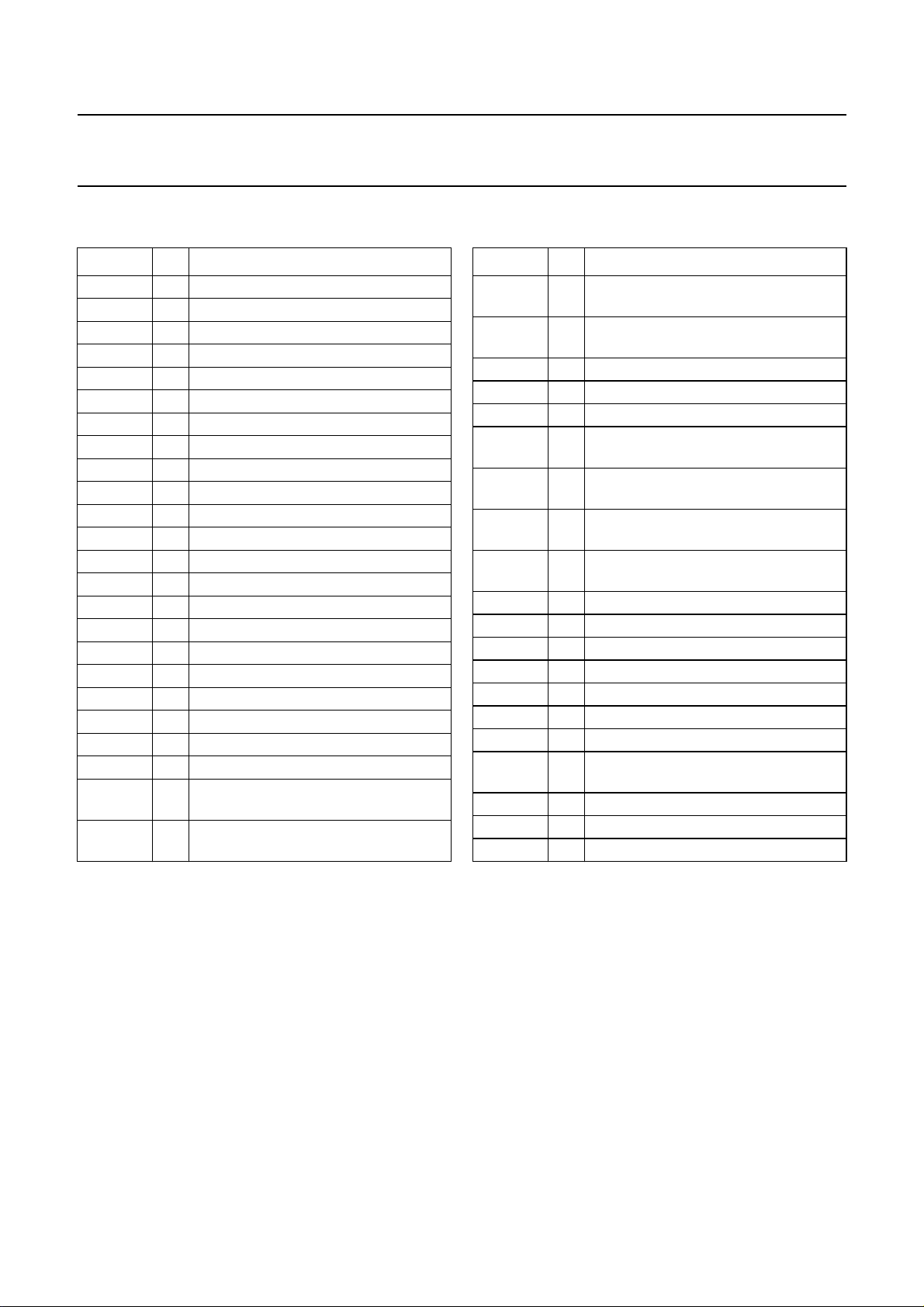
5 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
SAP 1 tuner input mono
TUNL 2 tuner input left
TUNR 3 tuner input right
CINL 4 CINCH input left
CINR 5 CINCH input right
EXT1L 6 external 1 input left
EXT1R 7 external 1 input right
EXT2L 8 external 2 input left
EXT2R 9 external 2 input right
AUXL 10 auxiliary input left
AUXR 11 auxiliary input right
RFCAGC 12 RF converter AGC timing connection
RFCOUT 13 RF converter output
MUTEC 14 mute for RF converter output
MUTEL 15 mute for line output left
LINEL 16 line output left
LINER 17 line output right
MUTER 18 mute for line output right
DECL 19 decoder output left
DECR 20 decoder output right
LINOUT 21 linear audio output
LININ 22 linear audio input
DCFBL 23 DC feedback noise reduction
connection left
EMPHL 24 emphasis noise reduction connection
left
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
DCL 25 DC decoupling noise reduction
connection left
DETL 26 detector noise reduction connection
left
GND 27 ground
I
ref
V
ref
28 reference standard current connection
29 reference voltage connection
DETR 30 detector noise reduction connection
right
DCR 31 DC decoupling noise reduction
connection right
EMPHR 32 emphasis noise reduction connection
right
DCFBR 33 DC feedback noise reduction
connection right
V
CC
34 power supply
PBIN2 35 head 2 playback input
RECOUT 36 recording current output
PBIN1 37 head 1 playback input
HMSW 38 head amplifier mode switch connection
GNDH 39 ground of head amplifier
V
CCH
40 power supply of head amplifier
RMHID 41 record-mute mode or head
identification input
SDA 42 I2C-bus data input/output
SCL 43 I
2
C-bus clock input
ENVOUT 44 HF or AF envelope output
1999 Apr 14 5
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
handbook, full pagewidth
SAP
TUNL
TUNR
CINL
CINR
EXT1L
EXT1R
EXT2L
EXT2R
AUXL
AUXR
SDA
ENVOUT
SCL
44
43
42
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
MUTEC
RFCAGC
RFCOUT
CCH
RMHID
V
41
40
TDA9605H
15
16
LINEL
MUTEL
GNDH
39
17
LINER
PBIN1
HMSW
38
37
18
19
DECL
MUTER
RECOUT
36
20
DECR
CC
V
PBIN2
35
34
21
22
LININ
LINOUT
33
DCFBR
EMPHR
32
31
DCR
30
DETR
V
29
28
I
GND
27
DETL
26
DCL
25
24
EMPHL
DCFBL
23
MGR835
ref
ref
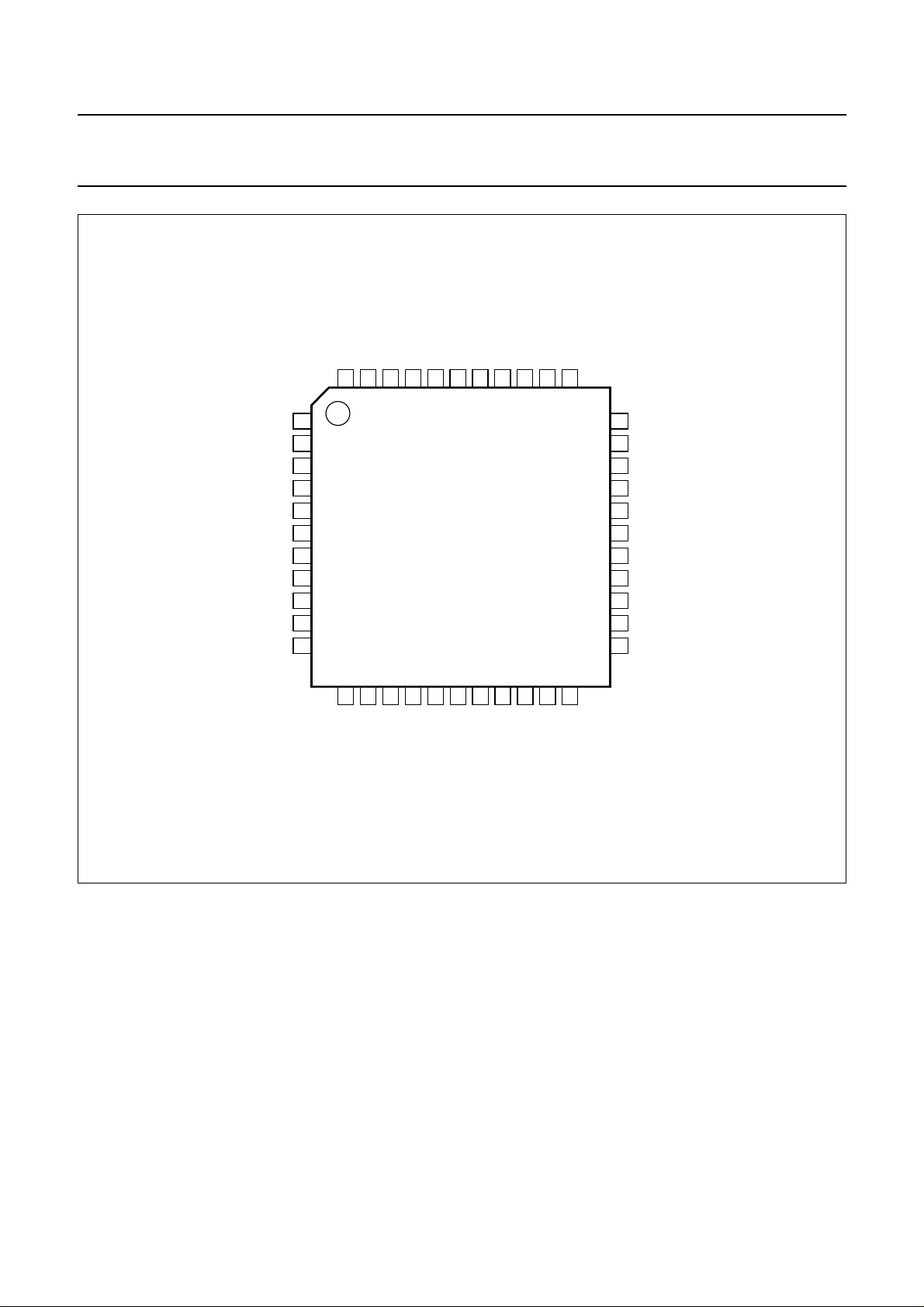
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
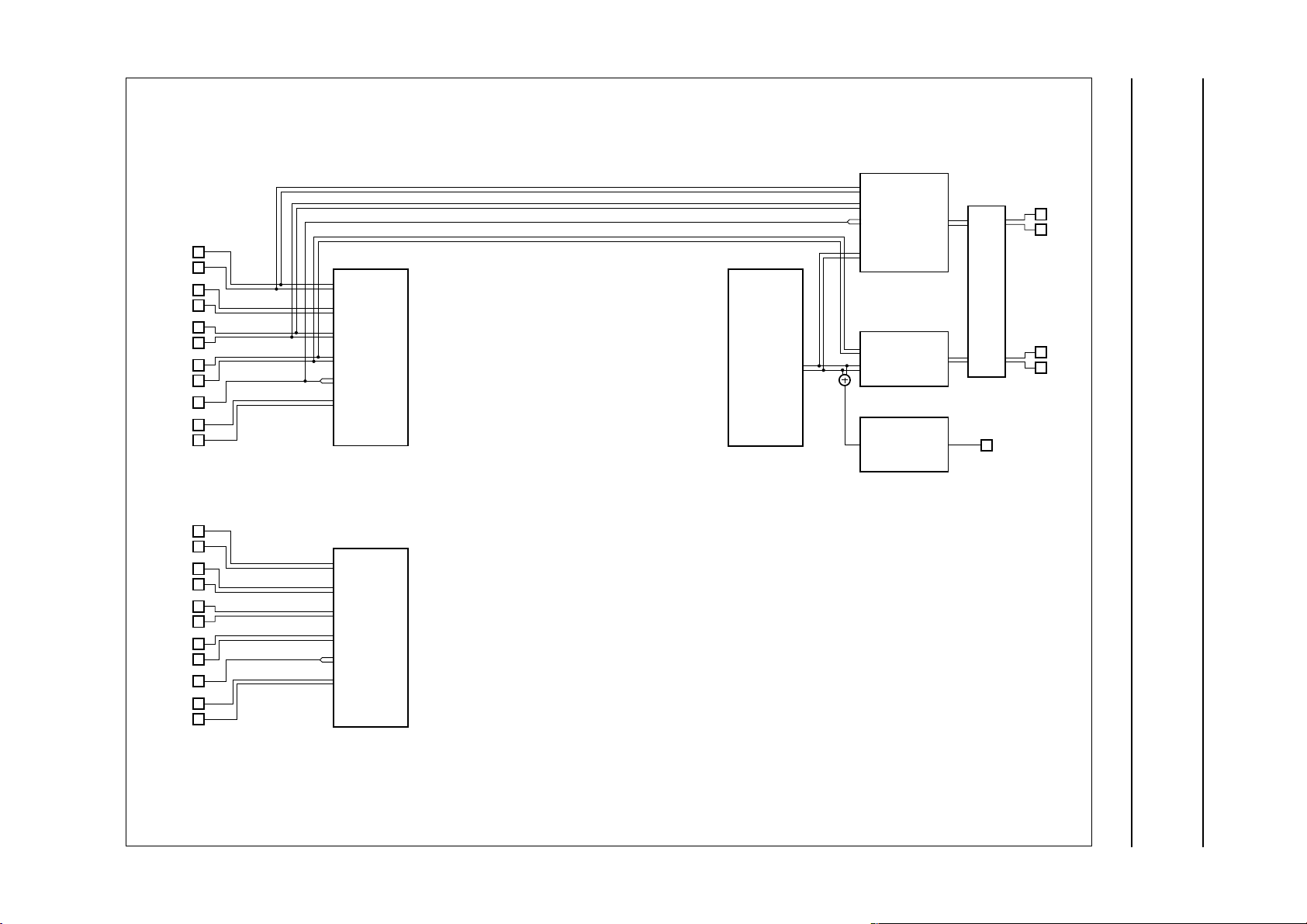
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Input and output selections for the various modes are given in the following diagrams:
• Standard operating mode (see Fig.3)
• Dub-mix mode (see Fig.4)
• Standby mode: active or passive (see Fig.5).
1999 Apr 14 6
Page 7

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
o
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1999 Apr 14 7
TUNL
TUNR
CINL
CINR
EXT1L
EXT1R
EXT2L
EXT2R
SAP
AUXL
AUXR
(1)
input select
TUNER
CINCH
EXT1
EXT2
SAP
AUX
DUB MIX
NORMAL
volume left
MUTE
(−47 to 0 dB;
0 to +15 dB)
MUTE
(−47 to 0 dB;
0 to +15 dB)
volume right
RECOUT
ok, full pagewidth
tape
PBIN1
PBIN2
HI-FI
AUDIO FM
PROCESSING
output select
MUTE
LEFT
RIGHT
STEREO
NORMAL
NORMAL LEFT
NORMAL RIGHT
NORMAL STEREO
decoder select
TUNER
EXT1
SAP
MUTE
OUTPUT SELECT
line select
EXT2
OUTPUT SELECT
RF converter AGC
0 dB AGC
MUTE
line output
amplification
0 dB
+1 dB
RFCOUT
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
DECL
DECR
LINEL
LINER
(1) For dub-mix mode signal selections see Fig.4.
normal input levelnormal select
INPUT SELECT
INPUT LEFT
VOLUME
VOLUME LEFT
SAP
TUNER
EXT2
MUTE
LINOUT
MUTE
(0 to +14 dB)
LININ
linear audio
processing
Fig.3 Input and output selections for standard operating mode.
envelope select
OUTPUT SELECT
STEREO
HF ENVELOPEHF envelope
MGR836
ENVOUT
Page 8
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
k
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1999 Apr 14 8
, full pagewidth
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
TUNL
TUNR
CINL
CINR
EXT1L
EXT1R
EXT2L
EXT2R
SAP
AUXL
AUXR
input select
DUB MIX
volume aux output select
MUTE
(−47 to 0 dB;
0 to +15 dB)
MUTE
(−47 to 0 dB;
0 to +15 dB)
volume hi-fi
INPUT SELECT
INPUT LEFT
VOLUME
VOLUME LEFT
SAP
TUNER
EXT2
MUTE
RECOUT
PROCESSING
normal input levelnormal select
LINOUT
linear audio
processing
(record)
tape
PBIN1
PBIN2
HI-FI
AUDIO FM
(playback)
MUTE
(0 to +14 dB)
LININ
MUTE
LEFT
RIGHT
STEREO
NORMAL
NORMAL
NORMAL
NORMAL
MUTE
LEFT
RIGHT
LEFT RIGHT
MUTE
LEFT
RIGHT
LEFT RIGHT
decoder select
TUNER
EXT1
SAP
MUTE
OUTPUT SELECT
line select
EXT2
OUTPUT SELECT
RF converter AGC
0 dB AGC
MUTE
envelope select
OUTPUT SELECT
STEREO
HF ENVELOPEHF envelope
MGR837
line output
amplification
0 dB
+1 dB
RFCOUT
ENVOUT
DECL
DECR
LINEL
LINER
Dub-mix mode: IS2 =1, IS1 = 0 and IS0 = 1.
Input mixing of the hi-fi (playback) signal with the auxiliary, used for linear audio dubbing recording.
Selections generally used in combination with dub-mix mode are shown in heavy line type.
Fig.4 Input and output selections for dub-mix mode.
Page 9
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1999 Apr 14 9
TUNL
TUNR
CINL
CINR
EXT1L
EXT1R
EXT2L
EXT2R
SAP
AUXL
AUXR
input select
MUTE
handbook, full pagewidth
output select
MUTE
decoder select
TUNER
EXT1
SAP
MUTE
OUTPUT SELECT
line select
EXT2
OUTPUT SELECT
RF converter AGC
MUTE
MGR838
line output
amplification
0 dB
+1 dB
a. Active standby mode (bit STBA = 1, bit STBP = 0); over 80% power reduction.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
DECL
DECR
LINEL
LINER
RFCOUT
TUNL
TUNR
CINL
CINR
EXT1L
EXT1R
EXT2L
EXT2R
SAP
AUXL
AUXR
input select
MUTE
b. Passive standby mode (bit STBP = 1); over 90% power reduction.
Fig.5 Input and output selections for standby modes.
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
6.1 Record-mute mode or head identification
selection
Pin RMHID allows input of two independent digital control
signals for selecting the record-mute or head identification
modes which are voltage coded. The RM control signal is
selected via a 10 kΩ resistor and the HID control signal is
selected via a 18 kΩ resistor. This set-up enables the two
signals within the TDA9605H to be separated. The RM
control signal is only in use during the record mode
(bit AFM = 1); during the playback mode (bit AFM = 0) the
RM signal is ignored. Pin RMHID should be connected to
ground when the RM control signal is not used.
The use of the RM control signal is optional since the same
function is available via the I
2
C-bus control in the
record-mute mode. However, accurate timing of recording
start and stop may sometimes be difficult to realize via the
I2C-bus control. In this event the RM control signal can be
used instead. There is also the possibility to use the
record-mute mode control line of the video head amplifier.
6.2 Hi-fi audio output level
When the application circuit is used in accordance with the
application diagram, the standard FM deviation of 50 kHz
equals a 1 kHz audio signal of −8 dBV line output level
(bit LOH = 0). A different standard audio level can be
selected by changing the external filter components of the
noise reduction on pins EMPHL and EMPHR
(see Section 14.3). The standard audio level changes
proportionally to the impedance of the external
de-emphasis filter.
6.3 Reference current
The external resistor connected to pin I
defines the
ref
internal reference currents and determines the
temperature stability of circuits adjusted by the
auto-calibration function.
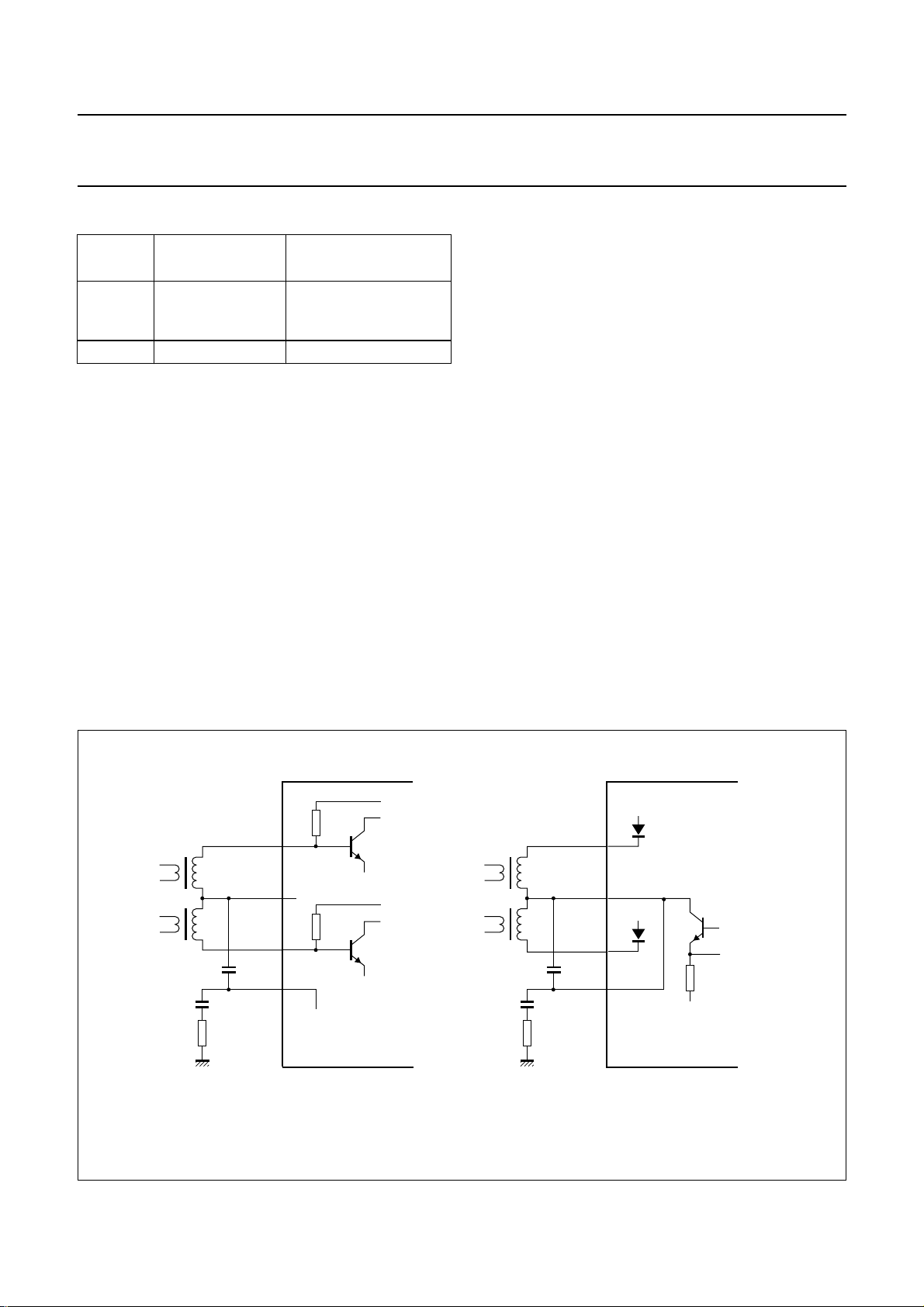
6.4 Head amplifier
6.4.1 PLAYBACK MODE
The playback mode is selected by setting bit AFM = 0.
During the playback mode the input circuit on pins PBIN2
and PBIN1 is enabled (see Fig.6). Pin RECOUT is
disabled and pin HMSW shows a low impedance to
ground, so realizing an AC ground for the head circuit via
the external capacitor connected between these pins.
The head identification (HID) signal on pin RMHID selects
between the head signals on pins PBIN2 or PBIN1. Head
selection is defined as shown in Table 1.
The state of the RM control signal on pin RMHID is don’t
care in the playback mode.
2
I
C-bus control bits HAC2, HAC1 and HAC0 offer a wide
selection of playback amplification to fit different head and
head transformer specifications. The advised setting of the
playback amplification realizes a level of 24 mV (RMS) for
each carrier signal after the head amplifier to obtain a
17 dB overhead compared to the auto-normal level (hi-fi
detection). However, performance is not critical and a
different setting can be used if desired.
The carrier level can be measured using the HF envelope
output voltage on pin ENVOUT (bit EOS = 1). During
standard operating mode the HF envelope signal is
derived from the left channel carrier amplitude
(1.3 or 1.4 MHz carrier) but the special test 10 of the test
mode also enables the HF envelope output of the right
channel carrier amplitude (1.7 or 1.8 MHz carrier).
The advised carrier playback level of 24 mV (RMS) equals
an HF envelope voltage of 3.3 V.
The head amplifier output signal can be monitored directly
by using test 8 of the test mode. Pin ENVOUT functions as
the test output showing 6 dB attenuation compared to the
actual head amplifier output level (see Section 14.4).
Table 1 Selection of the head signal
HID
SIGNAL
LEVEL ON PIN RMHID
LOW lower than 0.6 V or
between 2.65 and 3.8 V
HIGH between 1.0 and 2.35 V
or higher than 4.3 V
6.4.2 R
ECORD-MUTE MODE
SELECTION OF
HEAD SIGNAL
pin PBIN2
(head 2)
pin PBIN1
(head 1)
The record-mute mode is selected by setting bit AFM = 1
and either setting bits DOC, SHH and DETH to logic 0 or
switching the RM control signal to HIGH-level.
During the record-mute mode no recording current is
present on pin RECOUT (see Fig.6). The head amplifier
status actually equals the playback mode, however, the
second amplifier stage is disabled to minimize power
consumption.
The RM control signal on pin RMHID enables fast
switching between the record and record-mute modes
(see Table 2). If the I2C-bus control is set to the record
mode, the use of record-mute mode control via pin RM
allows for accurate timing of recording start and stop,
independent of the I2C-bus control (see Section 6.1).
1999 Apr 14 10
Page 11
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
Table 2 Selection of recording modes
RM
SIGNAL
LEVEL ON
PIN RMHID
RECORD MODE
LOW lower than 2.35 V record or record-mute
mode as defined by
2
I
C-bus control
HIGH higher than 2.65 V record-mute mode
6.4.3 R
ECORD MODE
The record mode is selected by setting bit AFM = 1 and
setting bits DOC, SHH and DETH from logic 001 to 111
and switching the RM control signal to LOW-level.
During the record mode actual recording is activated and
the recording current is output on pin RECOUT
(see Fig.6). Pins PBIN2 and PBIN1 form a connection to
the 5 V head amplifier supply voltage (V
). Pin HMSW
CCH
is internally connected to pin RECOUT and the external
capacitor has no function in this mode.
The desired carrier mix ratio is set via I2C-bus control
bits DOC, SHH and DETH. A wide selection of recording
currents is available to fit different head and head
transformer specifications and are set via bits HAC2,
HAC1, HAC0 and range bit HRL. The setting of the carrier
mix ratio does not change the selected recording current.
The DC bias current on pin RECOUT is changed
proportional to the selected recording current for
optimizing the performance and minimizing the power
consumption for each recording current selected.
A Boucherot damping circuit is connected between
pin HMSW and ground to prevent head current resonance
peaking. A capacitor of 10 nF and a resistor of 470 Ω are
specified in Fig.14, but the component values are not
critical.
6.4.4 H
EAD AMPLIFIER POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND
The head amplifier is supplied via a separate 5 V supply
(pin V
) and ground (pin GNDH).
CCH
A capacitor of 100 nF should be placed close to the device
between pins V
and GNDH for proper decoupling of
CCH
the power supply.
The head amplifier ground (pin GNDH) should be
connected to the main ground (pin GND).
handbook, full pagewidth
35
36
37
38
35 kΩ
GNDH
35 kΩ
GNDH
GNDH
TDA9605H
PBIN2
AH2
RECOUT
AH1
PBIN1
HMSW
a. Playback mode and record-mute mode. b. Record mode.
Fig.6 Simplified circuit diagrams of the head amplifier modes.
1999 Apr 14 11
AH2
AH1
PBIN2
RECOUT
PBIN1
HMSW
35
36
37
38
V
V
CCH
CCH
5 Ω
GNDH
TDA9605H
MGR841
Page 12
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
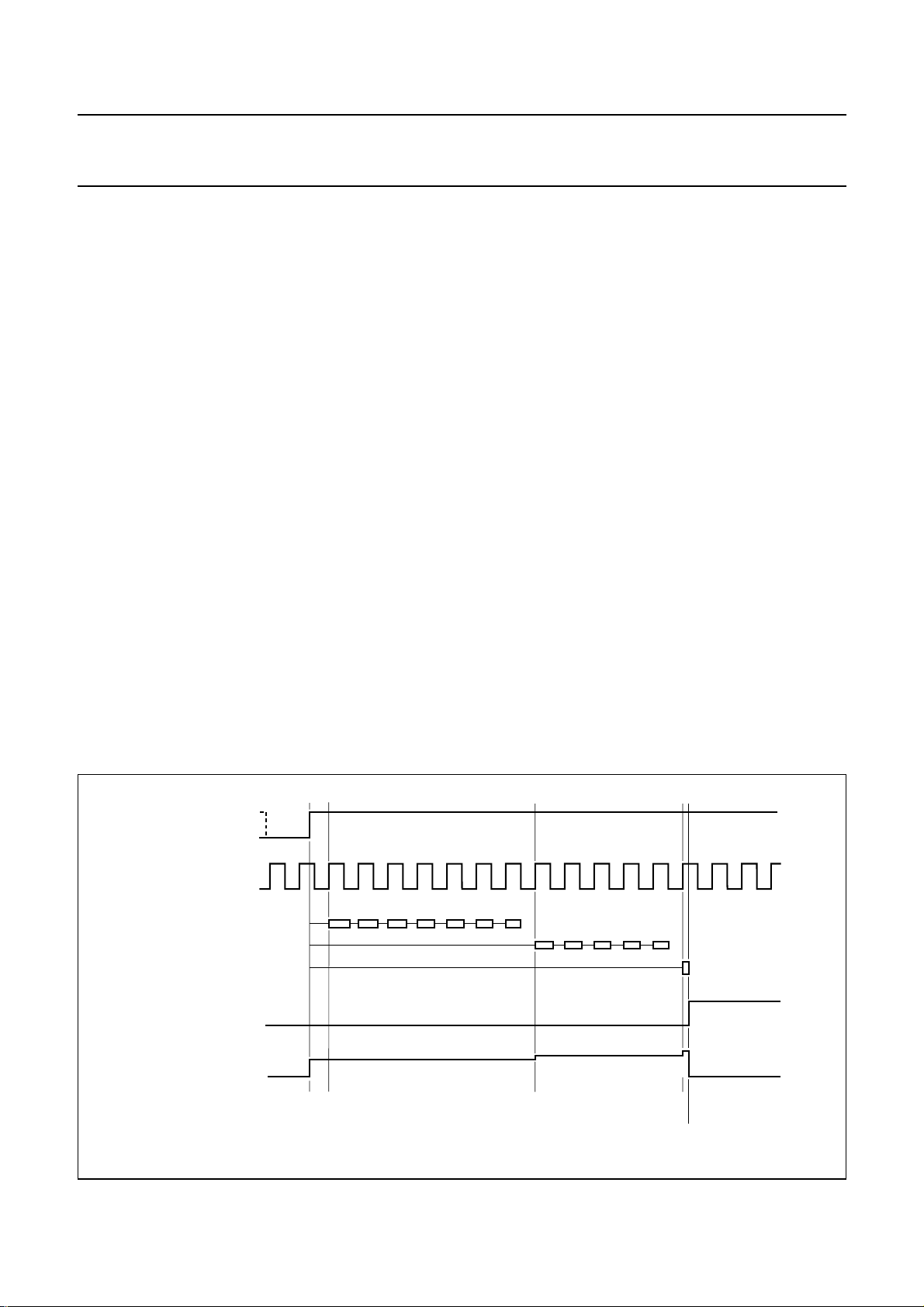
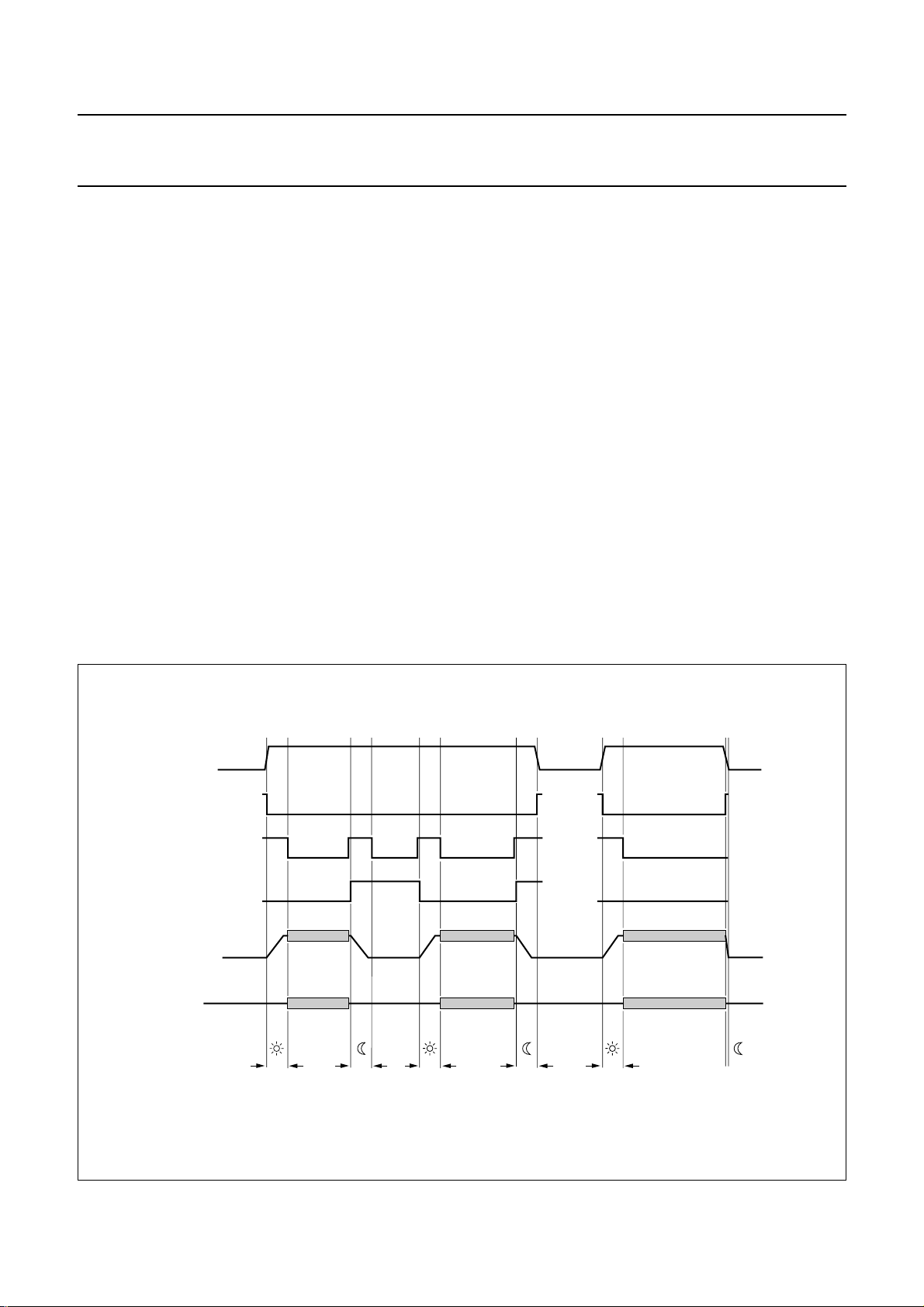
6.5 Automatic calibration
The integrated auto-calibration system is activated by
means of bit CALS of the power byte (see Fig.7).
The auto-calibration system ensures hi-fi processing is
well in accordance with the VHS hi-fi system standard by
an automated adjustment of carrier frequencies,
band-pass filters and noise reduction filters. Calibration is
only needed after start-up of the video recorder.
The calibration settings remain stable as long as the
supply voltage (VCC) is present.
Auto-calibration is only executed in the record-mute mode
or record mode and no standby mode or test mode should
be selected, i.e. auto-calibration requires the setting of
bit AFM = 1, bit STBP = 0, bit STBA = 0 and bit TEST = 0.
Auto-calibration is started after setting bit CALS = 1.
Calibration is performed fully automatically, using the HID
control signal as a time reference. Audio signals are not
disturbed during the calibration process.
Calibration of the oscillator frequencies is performed by
measuring the number of oscillator cycles within one
period when the HID control signal is at HIGH-level and
comparing this result with an internal value stored in the
Read Only Memory (ROM). Four different ROM values are
available for NTSC or PAL (SECAM) system calibration of
both the left and right channel carrier.
In case of NTSC a special routine is active for the
calibration of the right channel carrier which results in a
frequency difference between the left and right channel
carrier near to 401.2 kHz. This value effectively reduces
the crosstalk from hi-fi carriers to video colour signal as
present during Extended Play (EP) tape speed. NTSC
calibration uses a standard HID control signal of 29.97 Hz
(pulse width =16.683 ms) where PAL calibration uses a
standard HID control signal of 25 Hz (pulse
width = 20 ms). After auto-calibration the maximum
frequency error is ±5 kHz assuming a time error of
maximum of 5 µs when the HID control signal is at
HIGH-level. Jitter on the HID control signal should not
exceed 1 µs to realize EP optimization within ±2 kHz for
NTSC. In general, the crystal based HID control signal
available in the video recorder can be used without
modification.
When the calibration of the oscillators is completed the
band-pass filters are calibrated. The integrated weighting
and FM de-emphasis filters of the noise reduction are
calibrated at the same time.
The total auto-calibration time needed is maximum
17 cycles of the HID control signal. Completion of the
calibration is signalled by bit CALR =1 of the read byte.
The calibration can also be monitored by means of the
envelope output. For this purpose the voltage on
pin ENVOUT is forced to >2.5 V during the calibration.
The audio signal to the audio envelope function (level
meter) should be muted (i.e. output select = mute).
handbook, full pagewidth
2
I
C-bus write bit CALS
RMHD input
left channel oscillator
right channel oscillator
band-pass and
noise reduction filters
2
I
C-bus read bit CALR
ENVOUT output
logic 0
logic 1
Fig.7 Example of automatic calibration flow.
1999 Apr 14 12
logic 0
4 V3 V
5 V
logic 1
calibration
ready
MGR842
Page 13
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
Otherwise, the audio envelope output voltage may
become >2.5 V which makes it impossible to detect the
completion of the calibration on pin ENVOUT.
Calibration relies upon the frequency accuracy of the HID
control signal. The calibration result may be incorrect
when the HID control signal is disturbed during a critical
part of the calibration. An additional check is incorporated
to detect such a situation by reading bit CALE during
calibration. When bit CALE = 1, the calibration result is
detected to be unreliable due to external causes. A new
auto-calibration can be started by setting bit CALS = 0
followed by setting bit CALS = 1. Bit CALE always reads
logic 1 when bit CALS is logic 0.
The oscillators and band-pass filters can be switched
between NTSC and PAL system frequencies after a
calibration in NTSC or PAL mode without the need of
additional calibration. Switching between these system
modes is executed immediately and can be done in any
operating mode. The frequency accuracy of system
switching is 100 ±3 kHz for both carriers. To obtain the
best possible frequency accuracy in the record mode it is
good practice to recalibrate after system switching.
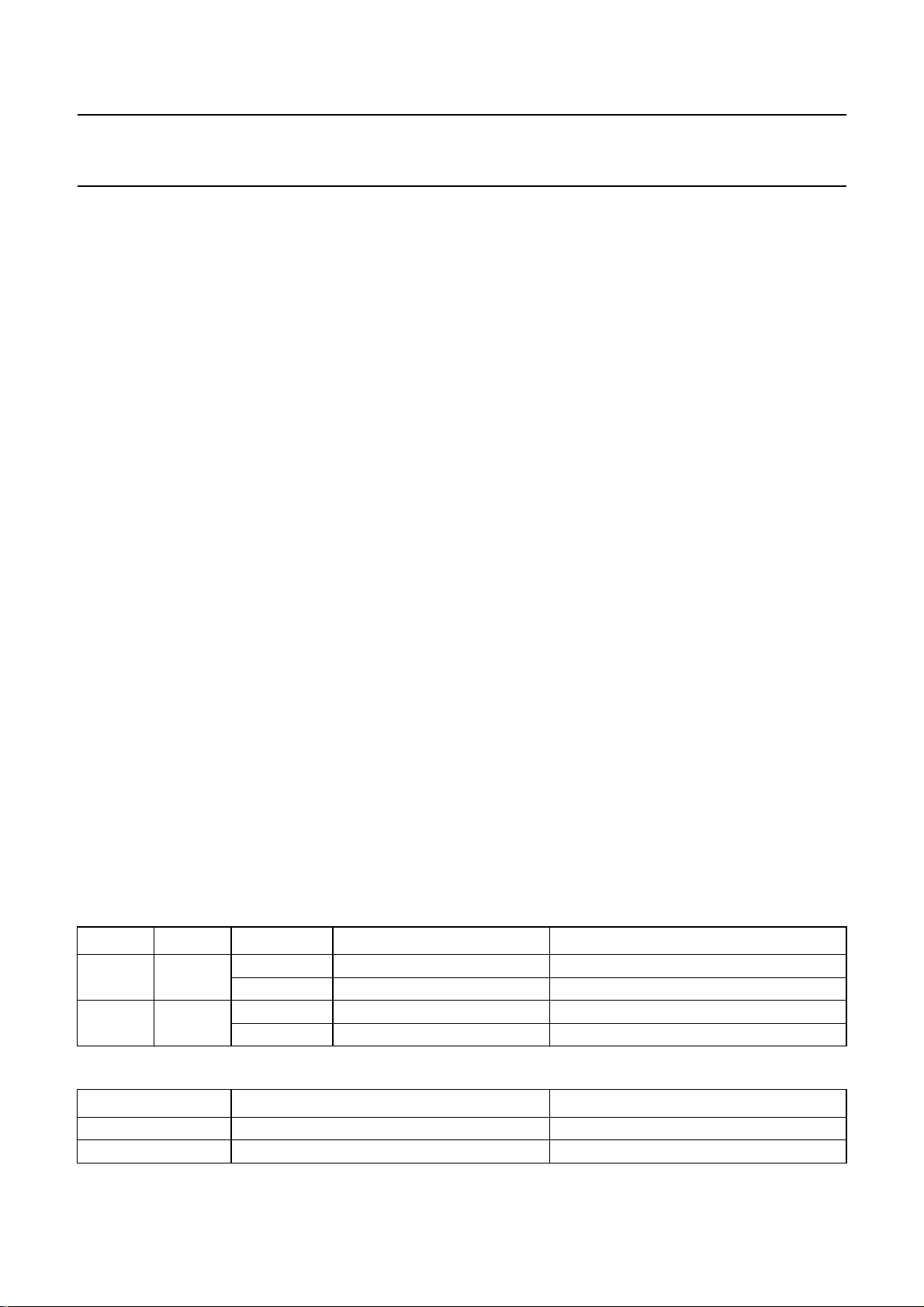
6.6 Power muting
Switching off and on of the power supply voltage or using
the built-in passive standby mode results in rising and
dropping of the output DC voltages and causes strong
disturbances on the output pins. The TDA9605H includes
three integrated mute switches to block such disturbances
so avoiding the need for an external mute circuit. Pop-free
line and RF converter output signals are realized by
connecting the integrated power mute switches behind the
line and RFC output capacitors.
Power muting is active when bit MUTE = 1 (see Fig.8).
Power muting is automatically activated when V
CC
is
switched on, because this situation is the Power-on reset
default state. The integrated mute switches on
pins MUTEC, MUTEL and MUTER are closed and form a
low-impedance path to ground. Furthermore, the
pins RFCOUT, LINEL and LINER are current limited to
−1 mA to avoid excessive supply currents and to achieve
good noise attenuation without the need for a series
resistor between the output and mute pins. Pins DECL and
DECR are also current limited for using the integrated
power mute switches or for assisting external muting.
handbook, full pagewidth
bit MUTE (I
bit STBP (I
RFCOUT
LINEL
LINER
output signal
with power mute
MUTEC
MUTEL
MUTER
(1) Power-on reset.
V
CC
auto-mute
(V
CC
2
2
C-bus)
< 7 V)
power off
(standby)
(
C-bus)
power
off
1)
(
t
mute
active
operation
t
mute
passive
standby
t
mute
active
operation
t
mute
Fig.8 Examples of power mute control and the auto-mute function.
1)
auto-mute
power
off
MGR843
t
mute
active
operation
1999 Apr 14 13
Page 14
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
During power muting the internal output signal is also
muted. After the output DC voltage has been established
power muting can be de-activated by setting bit MUTE = 0.
Now the mute switches are opened resulting in a
high-impedance path of 100 kΩ to ground. The output
current limiting is not active.
Power muting is also used in combination with the
integrated passive standby mode (bit STBP = 1). During
this mode the output circuits are switched off and the line,
decoder and RF converter output voltages decrease to 0 V
using a discharge current of 1 mA. Do not set power mute
mode and change the passive standby mode at the same
time. Power mute mode should be activated first, followed
by switching on or off of the passive standby mode to avoid
possible output glitches.
It should be noted that the time needed for stabilizing the
output DC voltage is proportional to the output capacitor
value. A safe mute time is 200 ms using a 10 µF capacitor
(t
=C×20000 s). Power muting consumes
mute
approximately 4 mA additional supply current, so to obtain
minimum power consumption the mute mode should be
de-activated after use. Very good performance is achieved
for power-up, power-down and passive standby mode
switching.
An auto-mute function is included which activates power
muting when the supply voltage drops below 7 V.
The performance of this auto-mute function depends upon
the power voltage drop rate. The voltage drop rate should
not exceed 1 V during 10 ms. The best performance
independent of voltage drop rate is realized by activating
the passive standby mode before switching off the power
supply voltage (by setting bit MUTE = 1 and bit STBP = 1).
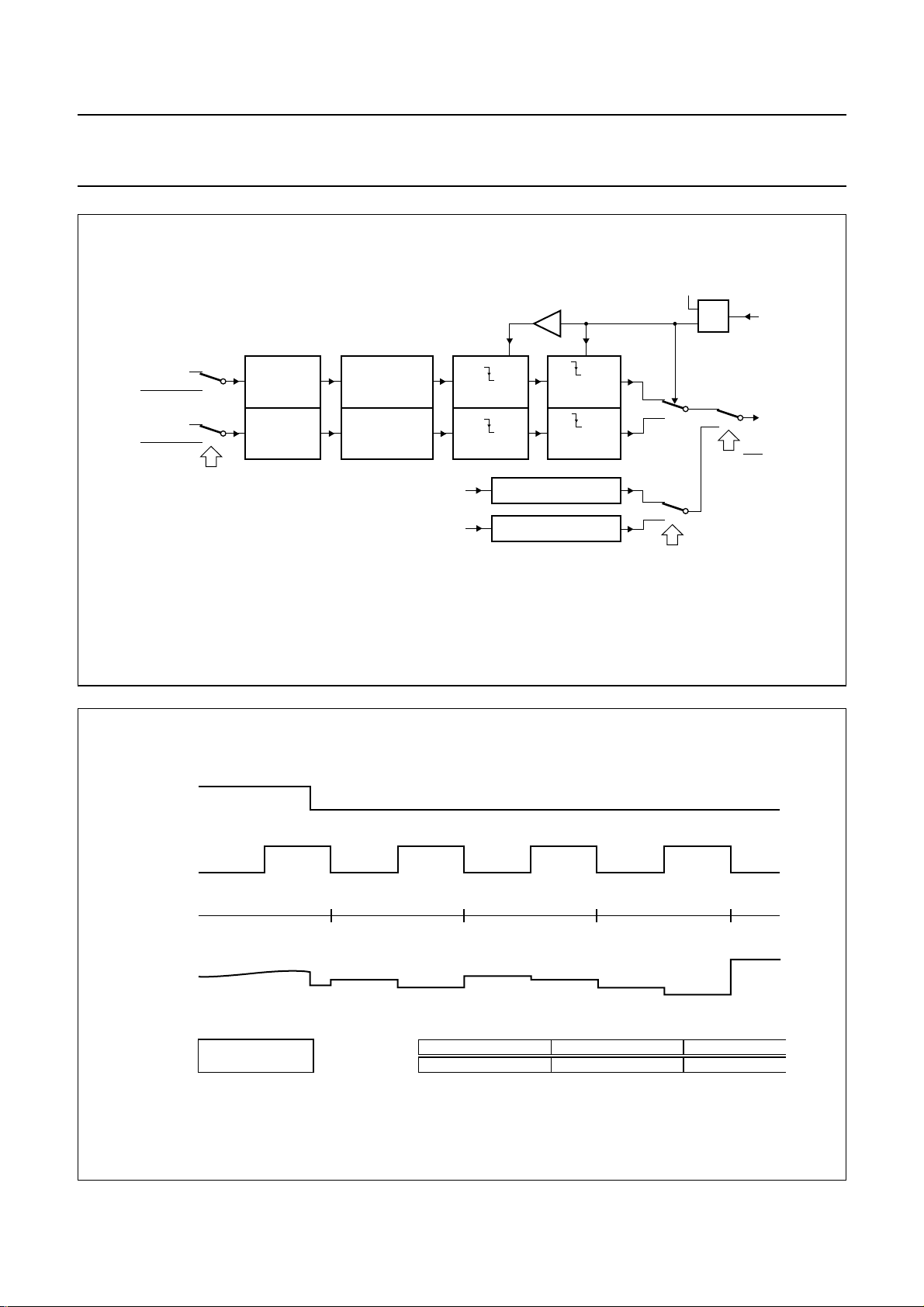
6.7 Envelope output
Pin ENVOUT is an analog output for stereo audio level
(e.g. level meter display) and for playback FM carrier level
(e.g. auto-tracking). The functional diagram is given in
Fig.9 and the timing diagram is shown in Fig.10. Only one
ADC input is needed on the microcontroller for reading all
the required information.
During the playback mode the selection between audio
level and carrier level information is realized by setting
2
I
C-bus control bit EOS (see Table 3). The AF envelope
output is defined by the signal selection made at the output
select.
During the record mode bit EOS offers the selection
between the audio level of the output select or the audio
level of the fixed hi-fi stereo signal. This is a helpful setting
when the microcontroller uses the audio level information
to adjust the hi-fi recording level (volume control).
The HF envelope output signal is continuous and is
derived from the left channel carrier. The HF envelope
output exhibits a logarithmic characteristic (see Fig.11).
In a standard application circuit only the left channel carrier
level is required to support auto-tracking or manual
tracking. However, test 10 of the special test mode allows
for the right channel carrier level output instead for
measurement purposes (see Section 14.4).
The AF envelope output as a function of the output level is
given in Fig.12.
The AF envelope circuit uses time multiplexing for the left
and right channel audio level. A peak-hold function and
dynamic range compression (square root function) are
included for easy read out. The peak-hold function and the
left and right channel multiplexing are controlled by the
HID control signal on pin RMHID (see Table 4).
Table 3 Selection of the envelope output
MODE BIT AFM BIT EOS ENVELOPE OUTPUT FUNCTION
Playback
Record
Table 4 AF envelope output with channel multiplexing
HID SIGNAL LEVEL ON PIN RMHID AF ENVELOPE OUTPUT
LOW lower than 0.6 V or between 2.65 and 3.8 V left channel audio peak level
HIGH between 1.0 and 2.35 V or higher than 4.3 V right channel audio peak level
1999 Apr 14 14
0
1
0 AF envelope: via output select level meter display
1 HF envelope auto-tracking or manual tracking display
0 AF envelope: via output select level meter display
1 AF envelope: hi-fi stereo record volume control (and level display)
Page 15
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
handbook, full pagewidth
left channel audio:
output select
hi-fi
right channel audio:
output select
hi-fi
EOS • AFM
t
d
FULL-WAVE
RECTIFIER
FULL-WAVE
RECTIFIER
SQUARE ROOT
COMPRESSION
SQUARE ROOT
COMPRESSION
1.3 or 1.4 MHz carrier
1.7 or 1.8 MHz carrier
RESET
PEAK HOLD
RESET
PEAK HOLD
HF LEVEL DETECTOR
HF LEVEL DETECTOR
SAMPLE-
AND-HOLD
SAMPLE-
AND-HOLD
Fig.9 Functional diagram of the envelope output circuit.
SAMPLE
SAMPLE
AF
envelope
HF
envelope
test
10
RM
HID
EOS • AFM
RMHID
ENVOUT
MGR845
handbook, full pagewidth
I2C-bus
registers
HID signal
HID period
ENVOUT
level meter
display
EOS = 1 and
AFM = 0
0123
HF envelope
tracking level
indication
EOS = 0 or AFM = 1
peak right
in period −1
in period 0
peak right
in period 0
peak left
left (period 0)
right (period 0)
Fig.10 Timing diagram of the envelope output signal.
1999 Apr 14 15
peak left
in period 1
peak right
in period +1
peak left
in period 2
left (period 1)
right (period 1)
peak right
in period +2
right (period 2)
peak left
in period +3
left (period 2)
MGR844
Page 16
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
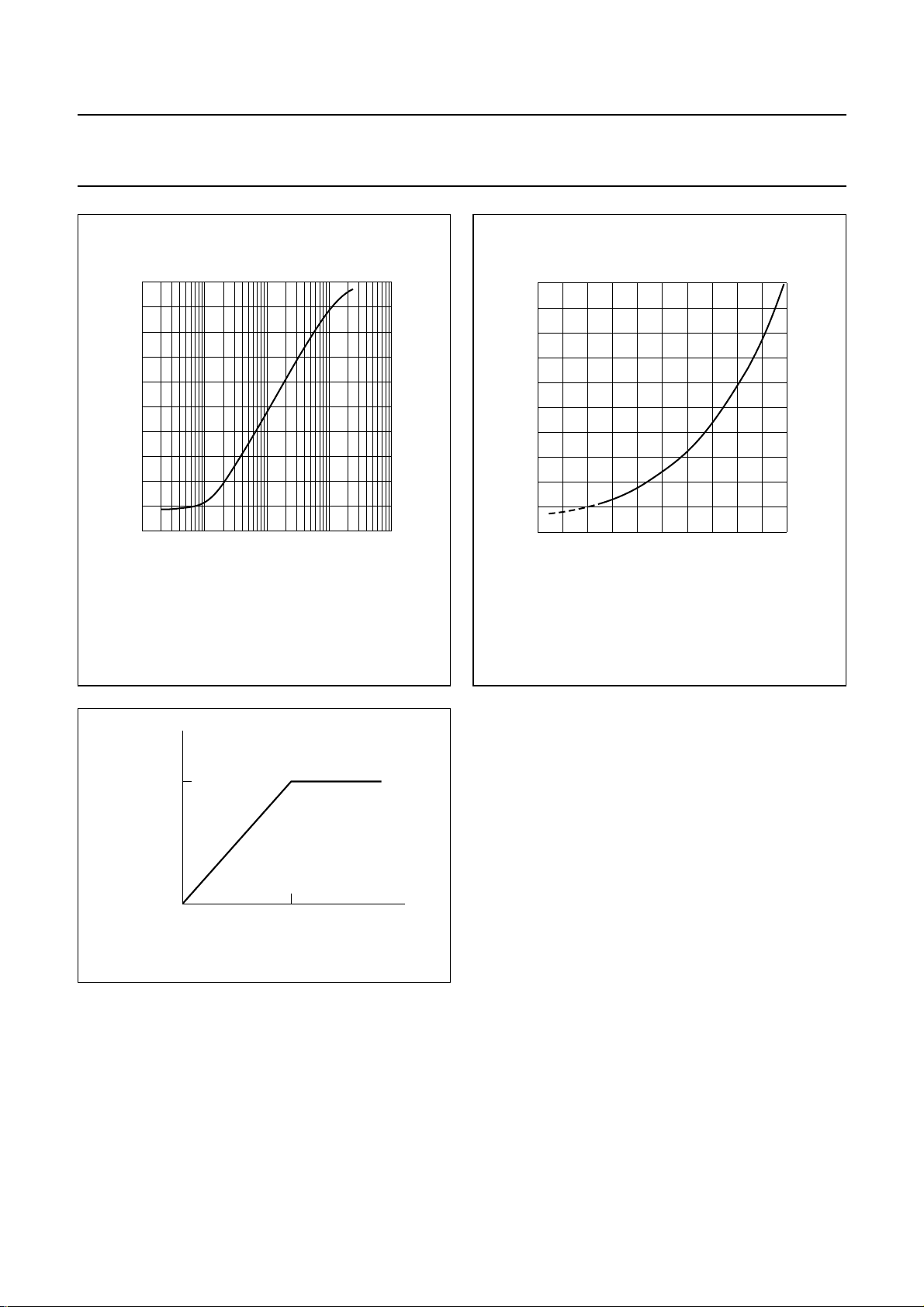
handbook, halfpage
5
ENVOUT
output
voltage
4
(V)
3
2
1
0
−1
10
1.3 MHz (NTSC) or 1.4 MHz (PAL) at internal node between head
amplifier and HF AGC.
11010
left channel carrier amplitude (RMS value) (mV)
MGR846
2103
Fig.11 HF envelope output (playback carrier level).
handbook, halfpage
RF
converter
output
(dBV)
−3
MGR848
MGR847
output
voltage
(V)
Bit LOH = 0.
5
4
3
2
1
0
−40 10−30 −20 −10 0
handbook, halfpage
ENVOUT
LINEL and LINER output level (dBV)
Fig.12 AF envelope output (audio peak level).
6.8 RF converter output
An AGC function is incorporated to avoid overmodulation
in the RF converter connected to pin RFCOUT. The AGC
limits the maximum signal level on the RF converter output
to −3 dBV (see Fig.13).
−3
line output (dBV)
Fig.13 AGC output of RF converter.
1999 Apr 14 16
The RF converter output can be muted by setting
bit RFCM = 1. When using this RF converter mute, the
AGC control is reset by discharging the capacitor
connected to pin RFACG.
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
6.9 Audio dubbing
The TDA9605H includes unparalleled functionality
supporting the audio dubbing function of hi-fi video
recorders. Audio dubbing is a feature which enables the
recording of new sound material on the linear audio track
(i.e. normal sound) of an existing recording. The dub-mix
mode is selected by setting bit IS2 = 1, bit IS1 = 0 and
bit IS0 = 1. Audio dubbing can be used in two different
ways:
• Output mix
• Input mix.
6.9.1 O
UTPUT MIX
A new additional recording is made on the linear audio
track. In the playback mode, the new linear audio sound
and the original hi-fi sound are combined. In this way the
hi-fi stereo quality remains and the linear audio sound is
partly used (e.g. for commentary only). However, there is
no control over the original hi-fi sound.
Mixing of the hi-fi and normal sound signals in the playback
mode is supported by the output select function mix-left,
mix-right and mix-stereo (bits OSN, OSR and OSL) and
creates a new fixed output signal of1⁄2× hi-fi plus
1
⁄2× normal.
6.9.2 I
NPUT MIX
A new complete recording is made on the linear audio
track (see Fig.4). In the playback mode, only the linear
audio sound is used. In this way the hi-fi stereo quality is
lost, but total freedom in defining the new sound material
is an extra advantage. Furthermore, such recording is no
longer restricted to playback on hi-fi video recorders (with
an output mix option).
The circuit changes into a mixing desk when using the
dub-mix mode of the input select function in combination
with the volume setting of normal select. A new linear
audio recording can be created by mixing together the new
and the original sound.
Continuous user control over amplitude and ratio mix of
the auxiliary input signal (e.g. a microphone input) and the
original hi-fi playback sound is possible using the left and
right channel volume controls. This function is realized
inside the IC by connecting the auxiliary input signal pair
(pins AUXL and AUXR) to the left channel volume control
and the hi-fi output signal pair to the right channel volume
control.
The settings of the output select function are used to
arrange the hi-fi selection and the output signals in the
dub-mix mode. However, some of these settings are
overruled in the dub-mix mode. The normal signal is
available on the line outputs for monitoring the dub-mix
recording signals in the output select function modes
mix-left, mix-right and mix-stereo.
Mix-stereo of the output select function is generally used
for audio dubbing. In combination with the volume setting
of normal select, user control over amplitude and ratio is
offered for the auxiliary and the hi-fi signal as follows:
1
⁄4× aux left +1⁄4× aux right) × volume left plus
(
(1⁄4× hi-fi left +1⁄4× hi-fi right) × volume right.
The dub-mix mode is to be used in the (hi-fi) playback
mode. In the record mode, a signal loop from output to
input can be closed which may cause audio oscillation.
The auto-normal switching is not active during the dub-mix
mode. The hi-fi sound is muted when no hi-fi input signal
is detected; bit AUTN is not affected.
Table 5 Dub-mix mode
OUTPUT SELECT
MODE
DUB-MIX OUTPUT
SELECTION
LEFT CHANNEL RIGHT CHANNEL
DUB-MIX INPUT
mute mute aux stereo mute
hi-fi left hi-fi left aux stereo hi-fi left
hi-fi right hi-fi right aux stereo hi-fi right
hi-fi stereo hi-fi stereo aux stereo hi-fi stereo
normal normal aux stereo mute
mix-left normal aux stereo hi-fi left
mix-right normal aux stereo hi-fi right
mix-stereo normal aux stereo hi-fi stereo
1999 Apr 14 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7I2C-BUS PROTOCOL
7.1 Addresses and data bytes
2
Full control of the TDA9605H is accomplished via the 2-wire I
accordance with the I2C-bus fast-mode specification.
Seven data byte registers are available for programming the device (write mode) and one data byte register is available
for reading data from the device (read mode). The registers are addressable via eight subaddresses. Automatic
subaddress incrementing enables writing of successive data bytes in one transmission.
During power-up, the data byte registers and auto-calibration registers are reset to a default state by the use of a
Power-On Reset (POR) circuit. The reset signal is derived from an internally generated voltage supplied by VCC.
Table 6 Addresses and POR state bits
NAME ADDRESS BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
Write mode
Slave byte B8H 10111000
Subaddress byte 00H to 07H;
000000or10or10or1
note 1
Control byte subaddress 00H AFM DOC SHH DETH NTSC HAC2 HAC1 HAC0
POR state 10001000
Select byte subaddress 01H DOS1 DOS0 s5 HRL NIL3 NIL2 NIL1 NIL0
POR state 0 0 0
Input byte subaddress 02H i7 IS2 IS1 IS0 NS2 NS1 NS0 i0
POR state 0
(2)
0001110
Output byte subaddress 03H LOH OSN OSR OSL EOS LOS DOS RFCM
POR state 00000001
Left volume byte subaddress 04H l7 VLS VL5 VL4 VL3 VL2 VL1 VL0
POR state 0
(2)
1000000
Right volume byte subaddress 05H r7 VRS VR5 VR4 VR3 VR2 VR1 VR0
POR state 0
(2)
1000000
Volume byte subaddress 06H simultaneous loading of the subaddress 04H and subaddress 05H registers
Power byte subaddress 07H CALS VCCS TEST PORR HPD MUTE STBP STBA
POR state 00000100
C-bus. Bus speeds up to 400 kbits/s can be used in
(2)
00000
(2)
Read mode
Slave address byte B9H 10111001
Read byte B9H CALR AUTN CALE POR 0
(3)
(3)
0
(3)
0
(3)
0
Notes
1. Continuous writing to a single data byte register is possible when subaddresses F0H to F7H (1111 0xxx) are used
instead of 00H to 07H (0000 0xxx). In that case automatic subaddress incrementing is disabled.
2. It is advised to keep the not-used write bits equal to the POR state to accommodate future compatibility.
3. You cannot rely upon the state of the not-used read bits because their state may change during development.
1999 Apr 14 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.2 Valid transmissions to and from the TDA9605H
Table 7 Examples of valid transmissions
FUNCTION DATA TRANSFER SEQUENCE
Write START, B8H, 00H, data for 00, STOP
Write with auto-increment START, B8H, 00H, data for 00, data for 01, data for 02, STOP
Write with auto-increment ‘wrap-around’ START, B8H, 07H, data for 07, data for 00, data for 01, STOP
Write without auto-increment START, BBH, F6H, data for 06, data for 06, data for 06, STOP
Read START, B9H, data from IC, STOP
Read (continued) START, B9H, data from IC, data from IC, data from IC, STOP
7.3 Overview of the TDA9605H I
Table 8 Condensed overview
FUNCTION MODES CONTROL BITS
Audio FM mode playback and record AFM
Playback dropout cancelling on and off DOC
Playback head switch noise cancel time 6 µs and 8 µs SHH
Playback hi-fi carrier detection time slow and fast DETH
Record-mute and carrier ratio select record-mute, 3, 4.5, 6, 8, 9.5, 11
System standard NTSC and PAL NTSC
Playback head amplifier amplification 48, 51, 54, 57, 60, 63, 66 and 69 dB HAC2, HAC1 and HAC0
Record head amplifier current 12.5, 15, 17.5, 21, 25, 30, 35, 42, 50, 60,
Normal input level 0 to 14 dB and mute NIL3, NIL2, NIL1 and NIL0
Input select tuner, CINCH, ext1, ext2, SAP, dub-mix,
Normal select input select, volume, input-left,
Line output amplification 0 dB and +1 dB LOH
Output select mute, left, right, stereo, normal, mix-left,
Envelope select output select, stereo and HF envelope EOS and AFM
Line select output select and ext2 LOS
Decoder select output select, tuner, ext1, SAP and mute DOS, DOS1 and DOS0
RF converter mute 0 dB AGC and mute RFCM
Volume left −47 to 0 dB, mute and 0 to 15 dB VLS and VL5 to VL0
Volume right −47 to 0 dB, mute and 0 to 15 dB VRS and VR5 to VR0
Auto-calibration off and start calibration CALS
Supply voltage select 9 V and 12 V VCCS
Test standard operating mode and test mode TEST, HRL, NIL3, NIL2, NIL1
2
C-bus control
and 12.5 dB mix ratio
71 and 84 mA (p-p)
normal and aux
volume-left, SAP, tuner, ext2 and mute
mix-right and mix-stereo
DOC, SHH and DETH
HAC2, HAC1, HAC0 and HRL
IS2, IS1 and IS0
NS2, NS1 and NS0
OSN, OSR and OSL
and NIL0
1999 Apr 14 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
FUNCTION MODES CONTROL BITS
Playback head amplifier disable standard operating mode and playback
disabled
Power output muting power mute MUTE
Operating mode standard operating mode, active standby
and passive standby
7.4 Control byte at subaddress 00H
The control byte is used to set the parameters of hi-fi processing and head amplifier control.
HPD
STBP and STBA
7.4.1 A
Bit AFM controls the main mode of the hi-fi processing and head amplifier. The function of other bits of the control byte
and bit EOS of the output byte depends on the state of bit AFM.
Table 9 Audio FM mode selection (bit AFM)
AFM MODE DESCRIPTION
0 playback hi-fi processing in playback mode and head amplifier in playback mode
1 record hi-fi processing in record mode and head amplifier is in record mode or record-mute mode
7.4.2 PLAYBACK MODE
When during the playback mode no FM carrier is detected from tape, the normal audio signal on pin LININ is
automatically selected by the output select function.
For this auto-normal mode:
• The timing of the hi-fi carrier detection can be selected via bit DETH which defines the auto-normal release time:
– Fast mode: hi-fi detection delay is 1 to 2 HID control signal periods (for NTSC: 33 to 66 ms; for PAL: 40 to 80 ms)
– Slow mode: hi-fi detection delay is 7 to 8 HID control signal periods (for NTSC: 233 to 267 ms;
• The state of hi-fi detection and auto-normal can be monitored by I2C-bus control bit AUTN of the read byte.
• In case automatic selection of the normal audio signal is not required the normal input level control can be set to mute
(bits NIL3 to NIL0 of the select byte).
UDIO FM MODE
for PAL: 280 to 320 ms).
Table 10 Dropout cancelling (bit DOC), sample-and-hold high-state (bit SHH) and detector time hi-fi (bit DETH) in the
playback mode; note 1
AFM DOC SHH DETH MODE DESCRIPTION
0 0 X X playback and DOC off dropout cancelling disabled
0 1 X X playback and DOC on dropout cancelling active
0 X 0 X playback and sample-and-hold time = 6 µs head switch noise cancel time set to 6 µs
0 X 1 X playback and sample-and-hold time = 8 µs head switch noise cancel time set to 8 µs
0 X X 0 playback and hi-fi detect = fast fast mode hi-fi detector timing
0 X X 1 playback and hi-fi detect = slow slow mode hi-fi detector timing
Note
1. X = don’t care.
1999 Apr 14 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.4.3 RECORD MODE
During the record-mute mode, the recording output current on pin RECOUT is muted and the head amplifier is partly
disabled. The record mode, set by I2C-bus control, can also be changed to the record-mute mode by an external control
signal on pin RMHID. Sometimes the record-mute mode is named loop-through mode or EE mode.
Table 11 Dropout cancelling (bit DOC), sample-and-hold high-state (bit SHH) and detector time hi-fi (bit DETH) in the
record mode
AFM DOC SHH DETH MODE DESCRIPTION
1000record-mute record-mute and no recording output current; note 1
1001record and 3 dB mix recording with 3 dB output carrier ratio (1 : 1.4)
1010record and 4.5 dB mix recording with 4.5 dB output carrier ratio (1 : 1.7)
1011record and 6 dB mix recording with 6 dB output carrier ratio (1 : 2)
1100record and 8 dB mix recording with 8 dB output carrier ratio (1 : 2.5)
1101record and 9.5 dB mix recording with 9.5 dB standard output carrier ratio (1 : 3)
1110record and 11 dB mix recording with 11 dB output carrier ratio (1 : 3.5)
1111record and 12.5 dB mix recording with 12.5 dB output carrier ratio (1 : 4.2)
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.4.4 S
Bit NTSC selects between the NTSC and PAL (SECAM) system carrier frequencies for the CCO modulators or PLL
demodulators and the band-pass filters. FM carrier frequencies of 1.3 and 1.7 MHz are used for the NTSC system where
1.4 and 1.8 MHz are used for the PAL system. Different code settings for the auto-calibration circuit assure proper
calibration using the standard HID control signal frequency of 29.97 Hz for NTSC mode and 25 Hz for PAL mode. After
auto-calibration is completed bit NTSC enables instant switching between the NTSC and PAL system.
Table 12 System standard selection (bit NTSC)
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
YSTEM STANDARD SELECTION
NTSC MODE DESCRIPTION
0 PAL hi-fi circuit in PAL mode
1 NTSC hi-fi circuit in NTSC mode; note 1
1999 Apr 14 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.4.5 HEAD AMPLIFIER PLAYBACK AMPLIFICATION
Eight settings of playback amplification can be selected for the head amplifier. The amplification values are valid for the
head signals from pins PBIN1 or PBIN2 to the internal node between the head amplifier and HF AGC circuit. The setting
of the playback amplification results in a selection of the hi-fi detection level (auto-normal function). The hi-fi detection
level indicated is the RMS value of the left channel carrier signal on pins PBIN1 and PBIN2.
The signal at the internal node can be monitored for testing purposes via pin ENVOUT using test 8 of the test mode.
It should be noted that the output level of test 8 shows 6 dB attenuation compared to the internal node level.
Table 13 Head amplifier control (bits HAC2, HAC1 and HAC0) in the playback mode
AFM HAC2 HAC1 HAC0 MODE DESCRIPTION
0 0 0 0 48 dB hi-fi detection level equals 13 µV (RMS) from head
0 0 0 1 51 dB hi-fi detection level equals 9.4 µV (RMS) from head
0 0 1 0 54 dB hi-fi detection level equals 6.7 µV (RMS) from head
0 0 1 1 57 dB hi-fi detection level equals 4.7 µV (RMS) from head
0 1 0 0 60 dB hi-fi detection level equals 3.3 µV (RMS) from head
0 1 0 1 63 dB hi-fi detection level equals 2.4 µV (RMS) from head
0 1 1 0 66 dB hi-fi detection level equals 1.7 µV (RMS) from head
0 1 1 1 69 dB hi-fi detection level equals 1.2 µV (RMS) from head
7.4.6 H
A total of twelve settings of the recording current can be selected for the head amplifier record output pin RECOUT.
Bit HRL of the select byte selects between high and low current settings. The recording current is defined as the
peak-to-peak value of the current of the record output signal which includes both the left and right carrier signal.
The selected recording current is independent of the selected record mix ratio setting, but recording is disabled during
the record-mute mode as defined by the bits DOC, SHH and DETH or the control signal on pin RMHID.
Table 14 Head amplifier control (bits HAC2, HAC1 and HAC0) and head record current low (bit HRL) in the record
AFM HAC2 HAC1 HAC0 HRL MODE DESCRIPTION
EAD AMPLIFIER RECORD CURRENT
mode
1000025mA(p-p) high recording current is 25 mA (p-p)
1001030mA(p-p) high recording current is 30 mA (p-p)
1010035mA(p-p) high recording current is 35 mA (p-p)
1011042mA(p-p) high recording current is 42 mA (p-p)
1100050mA(p-p) high recording current is 50 mA (p-p)
1101060mA(p-p) high recording current is 60 mA (p-p)
1110071mA(p-p) high recording current is 71 mA (p-p)
1111084mA(p-p) high recording current is 84 mA (p-p)
1000112.5 mA (p-p) low recording current is 12.5 mA (p-p)
1001115mA(p-p) low recording current is 15 mA (p-p)
1010117.5 mA (p-p) low recording current is 17.5 mA (p-p)
10111 21mA(p-p) low recording current is 21 mA (p-p)
1999 Apr 14 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.5 Select byte at subaddress 01H
The select byte is used for decoder output select, record current range select and linear audio volume control.
7.5.1 D
By setting bit DOS = 0 of the output byte, the decoder output signal on pins DECL and DECR is defined by the output
select function. However, by setting bit DOS = 1 the decoder select function enables several independent signal
selections controlled via bits DOS1 and DOS0. Via the decoder select function the input signals on pins TUNL
and TUNR, pins EXT1L and EXT1R and pin SAP can be selected. The mute mode can also be selected.
The indicated decoder select function modes are also available during the active standby mode by setting bit STBA = 1.
Table 15 Decoder output select (bits DOS1 and DOS0)
DOS1 DOS0 MODE DESCRIPTION
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.5.2 H
The default selection of eight recording currents set by bits HAC2, HAC1 and HAC0 of the control byte is extended with
four additional low level recording currents by setting bit HRL = 1.
Table 16 Head amplifier record low current (bit HRL)
ECODER OUTPUT SELECT
0 0 tuner selection of input signal on pins TUNL and TUNR; note 1
0 1 ext1 selection of input signal on pins EXT1L and EXT1R
1 0 SAP selection of input signal on pin SAP
1 1 mute muting the input signal
EAD AMPLIFIER RECORD CURRENT RANGE SELECT
HRL MODE DESCRIPTION
0 high current selection of 8 medium and high-level recording currents; note 1
1 low current selection of 4 low-level recording currents
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
1999 Apr 14 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.5.3 NORMAL INPUT LEVEL
Fifteen settings of amplification and mute can be selected for the linear audio input signal on pin LININ. The normal input
level control can replace the manual adjustment of the playback level at the linear audio circuit.
All selections using the normal linear audio signal include the normal input level control.
Table 17 Normal input level (bits NIL3 to NIL0)
NIL3 NIL2 NIL1 NIL0 MODE DESCRIPTION
0 0 0 0 0 dB amplification of linear audio of 0 dB; note 1
0 0 0 1 1 dB amplification of linear audio of 1 dB
::::: :
1 1 0 1 13 dB amplification of linear audio of 13 dB
1 1 1 0 14 dB amplification of linear audio of 14 dB
1 1 1 1 mute linear audio signal muted
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.6 Input byte at subaddress 02H
The input byte is used for input selection of the hi-fi and linear audio.
7.6.1 I
The input select function defines the input signal which is forwarded to the volume control function of hi-fi processing and
usually via the normal select function to the external linear audio circuit on pin LINOUT.
Table 18 Input select (bits IS2, IS1 and IS0)
Notes
1. Power-on reset state.
2. The dub-mix mode is a special selection which supports audio dubbing. This video recorder feature enables the
NPUT SELECT
IS2 IS1 IS0 MODE DESCRIPTION
0 0 0 tuner tuner input signal on pins TUNL and TUNR; note 1
0 0 1 CINCH CINCH input signal on pins CINL and CINR
0 1 0 ext1 TV input signal on pins EXT1L and EXT1R
0 1 1 ext2 decoder input signal on pins EXT2L and EXT2R
1 0 0 SAP mono input signal on pin SAP
1 0 1 dub-mix input signal on pins AUXL and AUXR (for left channel)
and from hi-fi output signal (for right channel); note 2
1 1 0 normal from linear audio circuit (from pin LININ)
1 1 1 aux input on pins AUXL and AUXR (e.g. camcorder input)
recording of the sound signal of the linear audio only (see Section 6.9).
1999 Apr 14 24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.6.2 NORMAL SELECT
The normal select function defines which of the input signals is forwarded to pin LINOUT for the connection to an external
linear audio circuit.
Table 19 Normal select (bits NS2, NS1 and NS0)
NS2 NS1 NS0 MODE DESCRIPTION
0 0 0 input select left plus right channel signal selected by input select
0 0 1 volume left plus right channel signal including hi-fi volume control
selected by input select
0 1 0 input-left left channel only (language 1) selected by input select
0 1 1 volume-left left channel only (language 1) including hi-fi volume control
selected by input select
1 0 0 SAP mono input signal from pin SAP
1 0 1 tuner tuner input signal from pins TUNL and TUNR
1 1 0 ext2 external input signals from pins EXT2L and EXT2R
1 1 1 mute mute of the input signals; note 1
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.7 Output byte at subaddress 03H
The output byte is used for selecting and controlling the output.
7.7.1 L
An additional 1 dB amplification for the line and decoder outputs on pins LINEL, LINER, DECL and DECR can be
selected by the line output high function.
Table 20 Line output high (bit LOH)
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.7.2 O
The auto-normal function is activated when no hi-fi signal is found on tape in the playback mode. Except for the mute
mode, all output select function modes will be overruled and changed to normal. Control of normal input level should be
set to mute for muting the hi-fi sound. The state of the auto-normal function can be monitored by reading bit AUTN of the
read byte.
INE OUTPUT AMPLIFICATION
LOH MODE DESCRIPTION
0 0 dB no line output amplification; note 1
1 1 dB 1 dB line output amplification
UTPUT SELECT
1999 Apr 14 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
Table 21 Output select normal, right and left (bits OSN, OSR and OSL)
OSN OSR OSL MODE DESCRIPTION
0 0 0 mute mute; no selection; note 1
0 0 1 left left hi-fi channel selected (language1)
0 1 0 right right hi-fi channel selected (language 2)
0 1 1 stereo hi-fi stereo selected
1 0 0 normal normal signal selected (linear audio from pin LININ)
1
1 0 1 mix-left mix of hi-fi left with normal (
1 1 0 mix-right mix of hi-fi right with normal (
1 1 1 mix-stereo mix of hi-fi stereo with normal (
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
In case the dub-mix mode is selected via the input select function, the performance of mix-left, mix-right and mix-stereo
modes is changed to support audio dubbing input mixing. The hi-fi channel is available for the input select function and
normal sound is available at the output for monitoring the linear audio recording. The auto-normal state is ignored during
the dub-mix mode and the hi-fi playback signal is muted instead.
⁄2× left +1⁄2× normal)
1
⁄2× right +1⁄2× normal)
1
⁄2× stereo +1⁄2× normal)
Table 22 Dub-mix mode (bits OSN, OSR and OSL)
OSN OSR OSL MODE OUTPUT IN DUB-MIX MODE INPUT IN DUB-MIX MODE
0 0 0 mute mute mute
0 0 1 left left channel left channel
0 1 0 right right channel right channel
1
0 1 1 stereo stereo signal
⁄2× left +1⁄2× right
1 0 0 normal normal signal mute
1 0 1 mix-left normal signal left channel
1 1 0 mix-right normal signal right channel
1 1 1 mix-stereo normal signal
7.7.3 E
NVELOPE OUTPUT SELECT
1
⁄2× left +1⁄2× right
The output signal on pin ENVOUT is selected via the envelope select function.
In the playback mode the HF envelope displays the amplitude of the left channel carrier. Display of the right channel
carrier amplitude for special measurement purposes can be selected via test 10 in the test mode.
Table 23 Envelope output select (bit EOS)
AFM EOS MODE DESCRIPTION
(1)
X
0 output select audio peak envelope of selected signal via output select function; note 2
0 1 HF envelope HF envelope of the left channel carrier in the playback mode
1 1 stereo envelope audio peak envelope of the hi-fi stereo signal in the record mode
Notes
1. X = don’t care.
2. Power-on reset state.
1999 Apr 14 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.7.4 LINE OUTPUT SELECT
An independent selection of the input signals from
pins EXT2L and EXT2R to the line outputs on pins LINEL
and LINER is offered by the line select function.
In the active standby mode (bit STBA = 1) the output
select signal is muted. However, the line select function of
the ext2 input signal is still operating.
In combination with the decoder select function a complete
pay-TV decoder switching feature is offered via the
SCART connector.
Table 24 Line output select (bit LOS)
LOS MODE DESCRIPTION
0 output
select
1 ext2 line output signal is from input
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.7.5 D
The output signals on pins DECL and DECR can be
selected by the decoder select function. By setting
bit DOS = 0, the output signals are selected by the output
select function. By setting bit DOS = 1, an independent
selection between the input signals on pins TUNL
and TUNR, pins EXT1L and EXT1R, pin SAP or mute is
possible. These signals are selected by the decoder select
function (bits DOS1 and DOS2).
ECODER OUTPUT SELECT
line output signal is set by output
select; note 1
signal on pins EXT2L and EXT2R
7.7.6 RF CONVERTER MUTE
The RF converter output signal on pin RFCOUT can be
muted by setting bit RFCM = 1. In this mute mode, the
AGC capacitor on pin RFCAGC is discharged and the
AGC control is reset.
Table 26 RF converter mute (bit RFCM)
RFCM MODE DESCRIPTION
0 AGC RF converter output signal is set by
the output select function:
AGC active
1 mute RF converter output signal is muted
and AGC control is reset; note 1
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.8 Volume bytes at subaddresses 04H, 05H and 06H
The volume bytes are used to set left and right channel
volume control.
7.8.1 Left and right volume control
Left channel volume control can be set by using
subaddress 04H. Right channel volume control can be set
by using subaddress 05H. Left and right channel volume
control can be set simultaneous by using subaddress 06H.
In the active standby mode (bit STBA = 1) the output
select signal is muted. However, the decoder select
function is still operating.
In combination with the line select function a complete
pay-TV decoder switching feature is offered via the
SCART connector.
Table 25 Decoder output select (bit DOS)
DOS MODE DESCRIPTION
0 output
select
1 decoder
select
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
1999 Apr 14 27
decoder output signal is set by the
output select function; note 1
decoder output signal is set by the
decoder select function
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
Table 27 Volume left sign (bit VLS), volume left (bits VL5 to VL0), volume right sign (bit VRS) and volume right
(bits VR5 to VR0); note 1
VLS VL5 VL4 VL3 VL2 VL1 VL0
MODE DESCRIPTION
VRS VR5 VR4 VR3 VR2 VR1 VR0
00000000dB volume 0 dB
0000001−1 dB volume −1dB
0000010−2 dB volume −2dB
:::::::: :
0101110−46 dB volume −46 dB
0101111−47 dB volume −47 dB
011XXXXmute mute
1XX00000dB volume 0 dB; note 2
1XX00011dB volume 1 dB
1XX00102dB volume 2 dB
:::::::: :
1XX111014dB volume 14 dB
1XX111115dB volume 15 dB
Notes
1. X = don’t care.
2. Power-on reset state.
7.9 Power byte at subaddress 07H
The power byte is used for power-up settings and the
standby control mode.
The combination of bit CALR = 1 and bit CALE = 0
indicates a successful calibration. Bit CALS should remain
at logic 1 after the calibration to keep a reliable state of
bit CALR and bit CALE.
7.9.1 C
ALIBRATION START
Automatic frequency calibration by setting the hi-fi modem,
the band-pass filter and the noise reduction is performed
after a change of bit CALS from logic 0 to logic 1. The use
of auto-calibration is only needed after power-up
(Power-on reset) of the supply voltage (see Section 6.5).
Table 28 Calibration start (bit CALS)
CALS MODE DESCRIPTION
0 no calibration note 1
1 start
calibration
start of the automatic calibration
cycle
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
The output signal on pin ENVOUT or bit CALR (calibration
ready) and bit CALE (calibration error) of the read byte can
be monitored to check for completion of the calibration.
1999 Apr 14 28
7.9.2 DC
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SELECTION
The DC output level on pins LINEL, LINER, DECL
and DECR can be changed by setting bit VCCS to
maximize the output power when using a supply voltage
of 12 V.
The use of power muting (bit MUTE = 1) ensures
disturbance free switching of the line output signal when
setting bit VCCS after power-up.
Table 29 V
supply voltage select (bit VCCS)
CC
VCCS MODE DESCRIPTION
0 9 V line and decoder output DC voltage
is 4.5 V; note 1
1 12 V line and decoder output DC voltage
is 6 V
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.9.3 TEST MODE
Several special tests can be selected for test, evaluation
and measurement purposes. The selection of these tests
is made by setting bit HRL and bits NIL3 to NIL0.
See Section 14.4 for an overview of the test modes.
Table 30 Test mode (bit TEST)
TEST MODE DESCRIPTION
0 operating
mode
1 test mode test mode for special
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.9.4 P
Setting bit PORR = 1 ensures a reset of bit POR of the
read byte to logic 0. In this way, a reading of logic 1 for
bit POR always indicates the occurrence of an actual
I2C-bus register Power-on reset and can not be caused
accidentally by other I2C-bus control bits. Bit PORR has no
control function but it is an unused bit, dedicated by name
to change the I2C-bus register content from the Power-on
reset state.
Bit POR of the read byte is a logic AND function for
checking all I2C-bus register bits. Bit POR will read logic 1
when the I2C-bus register content equals the Power-on
reset default state and also when this state is set via the
I2C-bus control. Since a setting of bit PORR = 1 differs
from the Power-on reset default state, it forces a reset of
bit POR to logic 0 independent of other bit settings.
OWER-ON RESET
standard operating; note 1
measurements
7.9.5 HEAD AMPLIFIER DISABLE
Bit HPD offers a special setting intended for use with some
of the built-in test modes and for support of particular
applications that do not require use of the integrated head
amplifier. By setting bit HPD = 1 the head amplifier
playback circuit is disabled. This mode enables direct input
signal to the HF AGC circuit via pin HMSW (AC coupled
via a 10 nF capacitor).
Table 32 Head amplifier playback disable (bit HPD)
HPD MODE DESCRIPTION
0 operating
mode
1 head
amplifier
disable
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.9.6 P
The power mute function controls the mute switches on the
line and RF converter outputs. The power mute mode is
automatically activated via the Power-on reset function
during power-up of the supply voltage. During
power-down, the mute switches are activated
automatically by means of the auto-mute circuit which is
independent of the setting of bit MUTE. When setting
bit MUTE = 1 the output current on pins RFCOUT, LINEL,
LINER, DECL and DECR is limited to −1 mA for controlled
power-up response and the selected output signal is
muted (see Section 6.6).
OWER MUTING
standard operating mode; note 1
head amplifier disabled in playback
mode (for test or special
application)
Table 31 Resetting of bit POR (bit PORR)
PORR MODE DESCRIPTION
0 no reset note 1
1 bit POR
reset
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
1999 Apr 14 29
reset of bit POR (read byte)
Table 33 Power mute (bit MUTE)
MUTE MODE DESCRIPTION
0 no mute power muting released: mute
switches are open
1 mute power muting activated: mute
switches are closed; note 1
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.9.7 STANDBY SELECT
The TDA9605H is switched in the low-power active
standby mode by setting bit STBA = 1. Most circuits are
switched inactive for reducing power consumption.
However, the RF converter, line and decoder outputs
remain active in this mode and the direct audio selections
offered via the line select function and the decoder select
function remain available. The selected output signal is
muted during the active standby mode.
The TDA9605H is switched in the minimum power passive
standby mode by setting bit STBP = 1. All circuits are
switched inactive to obtain minimum power consumption
except for the power mute circuit, the I
input reference buffer (i.e. the DC voltage on pins 1 to 11
remains active). When bit STBP = 1 a discharge current of
1 mA is active on pins RFCOUT, LINEL, LINER, DECL
and DECR.
Power muting ensures disturbance-free switching of the
line and RF converter outputs to and from the passive
standby mode. In the passive standby mode power muting
can be de-activated again to achieve minimum power
consumption. The calibration and I2C-bus registers are not
affected in the active standby or passive standby mode.
2
C-bus and the line
7.10.1 CALIBRATION READY
The completion of calibration is signalled by changing
bit CALR from logic 0 to logic 1. Bit CALR remains logic 0
if for some reason a calibration can not be completed (i.e.
no HID control signal available or the hi-fi processing is in
the playback mode). Bit CALR will also return to logic 0 if
calibration is lost due to a Power-on reset situation.
Additional information about the calibration result is
available via bit CALE. Calibration is found correct if
bit CALR = 1 and bit CALE = 0.
Pin ENVOUT can also be used to monitor calibration
(see Section 6.5).
Table 35 Calibration ready (bit CALR)
CALR DESCRIPTION
0 not calibrated; note 1
1 auto-calibration completed
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.10.2 A
UTO-NORMAL SELECTION
Table 34 Standby passive (bit STBP) and standby active
(bit STBA); note 1
STBP STBA MODE DESCRIPTION
0 0 operating standard operating mode:
full function; note 2
0 1 active
standby
1 X passive
standby
Notes
1. X = don’t care.
2. Power-on reset state.
7.10 Read byte
The read byte is used for reading the device state
information.
active standby mode:
reduced power
consumption
passive standby mode:
minimum power
consumption
The auto-normal function is activated when no hi-fi carrier
input signal is detected in the playback mode.
The auto-normal function overrules the settings of the
output select function and selects normal sound (i.e. linear
audio) instead of hi-fi. The state of the auto-normal
function can be checked by reading bit AUTN.
The auto-normal function and therefore bit AUTN is only
valid in the playback mode. Bit AUTN is always logic 0 in
the record mode.
Table 36 Auto-normal (bit AUTN)
AUTN DESCRIPTION
0 hi-fi carrier available; audio FM signal is
detected from tape in playback mode; note 1
1 normal sound selected instead of hi-fi carrier;
no audio FM signal is detected from tape
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
1999 Apr 14 30
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
7.10.3 CALIBRATION ERROR
An unreliable calibration result is indicated when reading
bit CALE = 1. The calibration result is not reliable when
during calibration the control signal on pin RMHID is
disturbed due to an external cause. Such a disturbance of
the HID control signal is detected when reading
bit CALE = 1. A new calibration should be started to
ensure proper calibration.
Calibration is found correct when bit CALR = 1 and
bit CALE = 0.
Table 37 Calibration error (bit CALE)
CALE DESCRIPTION
0 not calibrated or calibration result is found
correct; note 1
1 calibration error encountered during calibration
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
7.10.4 P
An internal Power-on reset signal is generated at
power-up or during a power voltage dip. The I2C-bus data
bits and auto-calibration registers are reset to a
pre-defined state. When reading bit POR = 1, it indicates
that the internal data bits are found to be in the POR state
due to an actual Power-on reset or the I2C-bus control
settings.
OWER-ON RESET
Detecting the occurrence of a Power-on reset by reading
bit POR requires a setting of bit PORR = 1 after power-up.
Bit POR is forced to logic 0 only by setting bit PORR = 1,
so this setting is independent of other I2C-bus bit settings.
After calibration a Power-on reset occurrence is also
indicated by bit CALR = 0, because calibration will be lost.
Table 38 Power-on reset (bit POR)
POR DESCRIPTION
0I2C-bus bit state differs from the Power-on reset
state
2
1I
Note
1. Power-on reset state.
C-bus bit state equals the Power-on reset
state; note 1
1999 Apr 14 31
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
8 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
V
CCH
T
stg
T
amb
V
es
I
lu(prot)
supply voltage 0 13.2 V
head amplifier supply voltage 0 5.5 V
storage temperature −65 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature 0 70 °C
electrostatic handling voltage machine model −300 +300 V
human body model −3000 +3000 V
latch-up protection current on Tj= 100 °C
pin HSMW −70 +100 mA
pin SDA −60 +100 mA
all other pins −100 +100 mA
9 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 60 K/W
10 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
CC
supply voltage VCCS = 0 8.1 9 13.2 V
VCCS = 1 8.1 12 13.2 V
V
I
CCH
CC
head amplifier supply voltage 4.75 5 5.5 V
supply current standard operating mode − 36 48 mA
active standby (STBA = 1) − 812mA
passive standby (STBP = 1) − 46mA
I
CCH
head amplifier supply current playback mode − 21 28 mA
record-mute mode − 18 24 mA
record mode (HAC = 000) − 23 31 mA
record mode (HAC = 011) − 35 47 mA
record mode, (HAC = 111) − 67 89 mA
active or passive standby
− 0 − mA
(STBA = 1 or STBP = 1)
1999 Apr 14 32
Page 33

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Internally generated voltage levels
V
n1
V
n2
V
n3
Control signal input: pin RMHID
V
I
DC voltage on pins SAP,
− 3.8 − V
TUNL, TUNR, CINL, CINR,
EXTL1, EXTLR, AUXL,
AUXR, LININ and RFCOUT
DC voltage on pin LINOUT − 4.5 − V
DC voltage on pins LINEL,
LINER, DECL and DECR
VCC= 9 V (VCCS = 0) − 4.5 − V
V
=12 V (VCCS = 1) − 6 − V
CC
input voltage record or record-mute with
I2C-bus control (RM = LOW)
for head 2 (HID = LOW) 0 − 0.6 V
for head 1 (HID = HIGH) 1.0 − 2.35 V
record-mute (RM = HIGH)
for head 2 (HID = LOW) 2.65 − 3.8 V
for head 1 (HID = HIGH) 4.3 − 5.5 V
11 RECORD-MUTE MODE CHARACTERISTICS
V
= 12 V; T
CC
=25°C; tuner audio input level −8 dBV at f = 1 kHz; Power-on reset state with output select = stereo;
amb
bit RFCM = 0; bit MUTE = 0; auto-calibrated; measured in typical application circuit of Fig.14; unless otherwise
specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Line inputs: pins SAP, TUNL, TUNR, CINL, CINR, EXT1L, EXT1R, EXT2L, EXT2R, AUXL and AUXR
V
i
R
i
input voltage −−9 dBV
input impedance 100 130 − kΩ
Linear audio input: pin LININ
V
i
R
i
input voltage −−8 dBV
input impedance 100 130 − kΩ
Linear audio output: pin LINOUT
V
o
R
o
output voltage −9 −8 −7 dBV
output impedance − 200 300 Ω
Line and decoder outputs: pins LINEL, LINER, DECL and DECR
V
o
output voltage normal output (LOH = 0) −9 −8 −7 dBV
output = 1 dB (LOH = 1) −8 −7 −6 dBV
V
o(max)
I
o(dch)
I
o(max)
R
o
maximum output voltage VCC= 9 V; note 1 7 8 − dBV
V
= 12 V; note 1 10 11 − dBV
CC
discharge output current passive standby (STBP = 1) − 1 − mA
output current limiting power mute (MUTE = 1) −−1−mA
output impedance − 100 150 Ω
THD total harmonic distortion − 0.01 0.1 %
1999 Apr 14 33
Page 34

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
α
cb
V
n
α
mute(v)
α
mute(o)
α
ct(ch)
α
ct(ch)(i)
RF converter output: pin RFCOUT
V
o
THD total harmonic distortion tuner input signal at
V
n
R
o
I
o(max)
I
o
Power mute outputs: pins MUTEC, MUTEL and MUTER
R
o
channel balance −1 0 +1 dB
noise level tuner input signal at zero level
−−94 −90 dBV
−∞ dBV; note 2
mute volume volume bytes left and right set
−−96 −70 dB
to mute mode
mute output output select bits set to mute
−−86 −70 dB
mode
crosstalk between channels one of tuner input signals at
−−90 −70 dB
zero level −∞ dBV
crosstalk between input
note 3 − <−93 − dB
channels
output voltage tuner input signal at
normal level -8 dB −9 −8 −7 dBV
high level 8 dBV −4.5 −3 −1.5 dBV
normal level −8 dBV − 0.03 − %
levels from −8to+8dBV − <0.2 − %
noise level tuner input signal on zero level
−−80 − dBV
−∞ dBV; note 2
output impedance − 200 300 Ω
output current limiting power mute (MUTE = 1) −−1−mA
discharge output current passive standby (STBP = 1) − 1 − mA
output impedance no mute (MUTE = 0) 50 100 − kΩ
muting (MUTE = 1);
− 15 −Ω
DC load from −1to+1mA
Audio peak envelope output: pin ENVOUT
V
o
output voltage tuner input signal at
normal level −8 dBV 1.65 1.8 1.96 V
at high level +8 dBV 4.0 4.5 5.0 V
at zero level −∞ dBV −−0.3 V
at zero level −∞ dBV and
−−0.35 V
maximum volume +15 dB
α
cb
R
o
channel balance −0.11 0 +0.11 V
output impedance − 1 1.5 kΩ
Notes
1. THD = 1%, output load with RL=5 kΩ and CL= 2.2 nF, volume = 3 dB for VCC= 12 V and tuner input level varied.
2. B = 20 Hz to 20 kHz, unweighted.
3. Crosstalk of any line input pair (tuner, CINCH, ext1, ext2, aux and SAP) to any other line input.
1999 Apr 14 34
Page 35

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
12 RECORD MODE CHARACTERISTICS
V
= 12 V; T
CC
circuit of Fig.14; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Noise reduction (test 25b)
THD total harmonic distortion tuner input signal at
α
cb
α
lin
α
n
t
att
t
rec
α
res(f1)
α
res(f2)
α
res(lpf1)
α
res(lpf2)
=25°C; tuner audio input level −8 dBV at f = 1 kHz; auto-calibrated; measured in typical application
amb
normal level −8 dBV − 0.1 0.3 %
high level +8 dBV − 0.2 1.0 %
channel balance −1 0 +1 dB
linearity tuner input signal at
low level −68 to −8 dBV −32 −30.5 −29 dB
high level −8 to +8 dBV 7.5 8 8.5 dB
noise level with respect to
signal level
tuner input signal level
from −∞ to −8 dBV; note 1
−−46 −41 dB
attack time in accordance with VHS specification − 5 − ms
recovery time in accordance with VHS specification − 70 − ms
frequency response 300 Hz tuner input frequency from
−0.7 −0.2 +0.3 dB
300 to 1000 Hz
frequency response 10 kHz tuner input frequency from
3.1 3.9 4.7 dB
10 to 1 kHz
audio low-pass filter
response 20 kHz
audio low-pass filter
response 60 kHz
tuner input frequency from
20 to 1 kHz; test 26b
tuner input frequency from
60 to 1 kHz; test 26b
−0.5 −0.1 +0.5 dB
−−24 −12 dB
FM modulator
THD total harmonic distortion ∆fFM= 50 kHz; test 25a and 26a − 0.1 0.2 %
∆f
FM(max)
maximum FM deviation of
test 25a and 26a 140 150 160 kHz
clipper
f
c(acc)
∆f
c
f
c(shift)
carrier frequency accuracy auto-calibration −5 0 +5 kHz
carrier frequency difference f
c(R)
− f
for NTSC auto-calibration 399.2 401.2 403.2 kHz
c(L)
carrier frequency shift NTSC/PAL system switching 97 100 103 kHz
TC temperature coefficient −±50 − ppm/K
Noise reduction and FM modulator
∆f
FM
FM deviation 44.5 50 56.1 kHz
Record output on pin RECOUT
I
o(acc)
α
f(acc)
α
IM2
output current accuracy left and right carrier 1st harmonic −1.5 0 +1.5 dB
carrier mix ratio accuracy left compared to right carrier −1 0 +1 dB
IM2 product note 2 −−66 − dB
Notes
1. B = 20 Hz to 20 kHz, unweighted.
2. Amplitude of 400 kHz intermodulation product f
c(R)
and f
compared to amplitude of recording current f
c(L)
c(R)+fc(L)
1999 Apr 14 35
.
Page 36

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
13 PLAYBACK MODE CHARACTERISTICS
V
= 12 V; T
CC
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Play back input on pins PBIN2 and PBIN1
R
i
C
i
V
n(i)
I
n(i)
Head mode switch: pin HSMW
R
i
Head amplifier
G
acc
G
bal
α
ct
HF AGC (test 5)
V
i(p-p)
B control bandwidth note 1 − 10 − kHz
=25°C; measured in typical application circuit of Fig.14; unless otherwise specified.
amb
input resistance − 700 −Ω
input capacitance − 35 − pF
input noise voltage − 0.5 − nV/√Hz
input noise current − 2.5 − pA/√Hz
input impedance with respect to ground − 12Ω
gain accuracy test 8 −3 0 +3 dB
gain balance between pins PBIN1 and PBIN2 −1 0 +1 dB
head-to-head crosstalk between pins PBIN1and PBIN2 −−45 − dB
AGC start level
(peak-to-peak value)
playback mode (HPD = 1);
left plus right channel
47 67 94 mV
Left channel band-pass filter (test 3)
α
t
d(g)
f
output voltage ratio (f0− 400 kHz)/f
ripple group delay (f0− 150 kHz) to (f0+ 150 kHz) − 0.5 −µs
Right channel band-pass filter (test 4)
α
t
d(g)
f
output voltage ratio (f0− 400 kHz)/f
ripple group delay (f0− 150 kHz) to (f0+ 150 kHz) − 0.5 −µs
0
(f
− 150 kHz)/f
0
(f
+ 150 kHz)/f
0
(f
+ 250 kHz)/f
0
(f
+ 250 kHz)/(f0+ 150 kHz) −−12 −9dB
0
(f
+ 400 kHz)/f
0
(f
− 250 kHz)/f
0
(f
− 250 kHz)/(f0− 150 kHz) −−12 −9dB
0
1 150 kHz)/f
(f
0
+ 150 kHz)/f
(f
0
(f
+ 400 kHz)/f
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
−−30 −20 dB
−9 −6 − dB
−9 −5 − dB
−−17 −12 dB
−−−30 dB
−−−30 dB
−−17 −10 dB
−9 −5 − dB
−9 −6 − dB
−−30 −20 dB
1999 Apr 14 36
Page 37

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Hi-fi detector (bit AUTN)
V
th(rms)
threshold level (RMS value) playback mode (HPD = 1);
left channel carrier
V
th(acc)
accuracy of threshold level left channel carrier on pins PBIN1
and PBIN2
t
d(sw)
switch-on delay carrier to no-carrier 150 300 500 µs
Hi-fi dropout cancelling (bit DOC)
V
th
threshold level with respect to threshold level of
bit AUTN
t
d(sw)
switch-off delay no-carrier to carrier 5 9 14 µs
Head switching noise suppression
t
h
hold time sample-and-hold time bit SHH = 0 5 6 7 µs
sample-and-hold time bit SHH = 1 7 8 9 µs
THD total harmonic distortion test 25c; note 2 −−−73 dB
t
d
delay between HID control signal and
hold status
2.4 3.3 4.6 mV
−5 0 +5 dB
−7 −4 −2dB
− 0.3 −µs
PLL FM demodulator (test 25c)
V
i
THD total harmonic distortion normal; ∆f
S/N signal-to-noise ratio ∆f
α
ct(ch)
sensitivity ∆fFM= 150 kHz; S/N = 35 dB − 0.3 1 mV
= 50 kHz − 0.05 0.3 %
FM
maximum; ∆f
= 50 to 0 kHz 54 60 − dB
FM
= 150 kHz − 0.2 1.5 %
FM
channel crosstalk left or right carrier; ∆fFM= 0 kHz −−80 − dB
Noise reduction (test 26c)
V
n
noise level tuner input signal level
at −∞ dBV; note 3
THD total harmonic distortion tuner input signal level
at −6.5 dBV
α
lin
linearity tuner input signal level
from −6.5 to −36.5 dBV
α
res(f1)
frequency response 300 Hz tuner input frequency from
300 to 1000 Hz
α
res(f2)
frequency response 10 kHz tuner input frequency from
10 to 1 kHz
−−95 −90 dBV
− 0.05 0.2 %
58 59.6 62 dB
−0.6 +0.4 +1.4 dB
−9.2 −7.7 −6.2 dB
1999 Apr 14 37
Page 38

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Envelope output: pin ENVOUT
V
o
FM demodulator and noise reduction: pins LINEL and LINER
V
o
α
cb
Notes
1. Amplitude modulated single carrier signal of 60 mV (RMS) on pin HMSW; for playback mode HPD = 1. Control
bandwidth is defined as the modulation frequency at which the amplitude modulation is attenuated with 3 dB by the
HF AGC.
2. Sample-and-hold audio distortion is measured using a HID control signal of 500 Hz on pin RMHID, f
∆fFM= 50 kHz. Audio distortion is measured using a 3 kHz 4th-order low-pass filter. The measured value is corrected
with 24 dB in order to calculate the equivalent distortion for the standard NTSC 29.97 Hz HID control signal.
3. B = 20 Hz to 20 kHz, unweighted.
output voltage left channel input signal at
1.6 mV (RMS) 0.6 0.9 1.2 V
16 mV (RMS) 2.5 2.9 3.3 V
160 mV (RMS) 4.2 4.7 5.0 V
output voltage −10 −8 −6 dBV
channel balance −1.5 0 +1.5 dB
= 10 kHz and
mod
1999 Apr 14 38
Page 39

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
n
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1999 Apr 14 39
head drum
AH1 AH2
10 nF
SAP
tuner
CINCH
ext1
ext2
aux
47 µF
100 nF
100 nF
470 Ω
5 V
220 nF
(11×)
40
39
37
35
36
38
playback. +
record-mute,
recording
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
SAP
TUL
TUR
E1L
E1R
E2L
E2R
HEAD AMPLIFIER
input select
I2C-bus
control
RM HID
10 kΩ 18 kΩ
41 44 42 43
HID
RM
HF AGC
HID
playback head
amplification,
record head
current
RM
M
+
carrier ratio select,
record-mute
N
dub
SAP
TUL
+
TUR
E2L
+
E2R
= mute
M
DCL
DCR
+
1.3 or 1.4 MHz
1.7 or 1.8 MHz
volume left
M
M
volume right
M
normal select
AF/HF envelope
envelope
output
select
+ playback
LEVEL
DETECTOR
HF LIMITER
HF LFP
LEVEL
DETECTOR
HF LIMITER
HF LFP
FM (DE-)MODULATOR
+ ++
I/O CONTROL
21 22
220 nF10 µF
linear audio
normal
input
level
HI-FI
DETECTOR
DROPOUT
CANCELING
PLL
CCO
(1.3 or
1.4 MHz)
PLL
CCO
(1.7 or
1.8 MHz)
M
dbook, full pagewidth
SDA SCL
I2C-BUS
INTERFACE
AUTN
HID
NOISE
SUPPRESSION
AUDIO
CLIPPER
NOISE
SUPPRESSION
AUDIO
CLIPPER
output selectAUTN
L
R
N
envelope output
select + record
L
R
+
PEAK HOLD
PEAK HOLD
TDA9605H
9 to 12 V
47 µF
10 nF
34 27 29 28
SUPPLY
standby select
5th ORDER
AUDIO LPF
5th ORDER
AUDIO LPF
dub
M
DCL
DCR
NOISE REDUCTION
W + FM
COMPRESSOR
EXPANDER
W + FM
COMPRESSOR
EXPANDER
TUL
E1L
SAP
TUR
E1R
SAP
E2L
E2R
mute
V
CC
3.3 MΩ
decoder
select
line select
AUTO-MUTE
M
RF converter
12
2.2 µF
DETECTOR
RECTIFIER
CCA
DETECTOR
RECTIFIER
CCA
M
mute
10 µF
39 kΩ
(2%)
+1 dB 12 V
MGR839
10 µF
26
47 µF
25
24
23
30
31
32
33
10 µF
19
10 µF
20
10 µF
16
15
10 µF
17
18
10 µF
13
14
2.7 kΩ
33 kΩ
10 µF
47 µF
2.7 kΩ
33 kΩ
6.8 nF
10 µF
6.8 nF
10 µF
decoder
line
RFC
14 APPLICATION AND TEST INFORMATION
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
Fig.14 Application diagram.
Page 40

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
14.1 RM and HID control signals
To assure proper input conditions on pin RMHID the RM and HID control signals (see Fig.15) should satisfy the
requirements given in Table 39.
handbook, full pagewidth
HID
10 kΩ (5 %)
18 kΩ (5 %)
RMHID
TDA9605H
41
RMRM
HID
10 kΩ (5 %)
18 kΩ (5 %)
RMHID
TDA9605H
41
MGR840
a. HID input only. b. HID and RM input.
Fig.15 RMHID input.
Table 39 Conditions of RM and HID input signal
HID INPUT SIGNAL ONLY HID AND RM INPUT SIGNALS
SIGNAL
CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. CONDITIONS MIN. MAX.
HID LOW 0 V 1.5 V LOW 0 V 0.4 V
HIGH 3 V 5.5 V HIGH 4.3 V 5.5 V
RM grounded −−LOW 0 V 0.4 V
HIGH 4.3 V 5.5 V
14.2 Reference current resistor
The requirements for the reference current resistor on pin 28 are:
• R = 39 kΩ±2%
• Temperature coefficient = ±50 ppm/°C.
1999 Apr 14 40
Page 41

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
14.3 Setting line output level
The audio level can be set by selecting the external filter components connected to the emphasis noise reduction
pins 24 and 32 (pins EMPHL and EMPHR).
Table 40 Component values for setting the line output level
LINE
OUTPUT
LEVEL
−4.9 dBV 47 kΩ 47 kΩ 3.9 kΩ 4.7 nF 3.9 kΩ 4.7 nF
−5.7 dBV 43 kΩ 43 kΩ 3.6 kΩ 5.1 nF 3.6 kΩ 5.1 nF
−6.4 dBV 39 kΩ 39 kΩ 3.3 kΩ 5.6 nF 3.3 kΩ 5.6 nF
−7.2 dBV 36 kΩ 36 kΩ 3.0 kΩ 6.2 nF 3.0 kΩ 6.2 nF
−8.0 dBV 33 kΩ 33 kΩ 2.7 kΩ 6.8 nF 2.7 kΩ 6.8 nF
−8.8 dBV 30 kΩ 30 kΩ 2.4 kΩ 7.5 nF 2.4 kΩ 7.5 nF
−9.6 dBV 27 kΩ 27 kΩ 2.2 kΩ 8.2 nF 2.2 kΩ 8.2 nF
−10.6 dBV 24 kΩ 24 kΩ 2.0 kΩ 9.1 nF 2.0 kΩ 9.1 nF
−11.4 dBV 22 kΩ 22 kΩ 1.8 kΩ 10 nF 1.8 kΩ 10 nF
Note
1. Standard 50 kHz FM deviation at f = 1 kHz.
14.4 Test modes
Special test modes are implemented for testing, evaluation and measurement purposes. These test modes are available
when bit TEST = 1 and the test select function is enabled via five bits of the select byte (see Table 41). When selecting
test modes the normal input level setting is changed as defined by bits NIL3 to NIL0. Calibration may be lost when a not
listed test mode is selected.
(1)
RESISTOR CONNECTED
BETWEEN
PINS 24 AND 23 PINS 32 AND 33 PIN 24 AND GROUND PIN 32 AND GROUND
RESISTOR IN SERIES WITH CAPACITOR CONNECTED
BETWEEN
1999 Apr 14 41
Page 42

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
Table 41 Test modes for evaluation and measurement purposes
TEST HRL NIL3 NIL2 NIL1 NIL0 MODE DESCRIPTION
100001test 1 record mode; left channel FM carrier only (1.3 or 1.4 MHz)
100010test 2 record mode; right channel FM carrier only (1.7 or 1.8 MHz)
100011test 3 playback mode; left channel band-pass filter with HF AGC off;
EOS = 1 (test output on pin ENVOUT); notes 1 and 2
100100test 4 playback mode; right channel band-pass filter with HF AGC off;
EOS = 1 (test output on pin ENVOUT); notes 1 and 2
100101test 5 playback mode; HF AGC (left channel band-pass filter);
EOS = 1 (test output on pin ENVOUT); notes 1 and 2
100110test 6 playback mode; HF AGC (right channel band-pass filter);
EOS = 1 (test output on pin ENVOUT); notes 1 and 2
101000test 8 playback mode; head amplifier output signal;
EOS = 1 (test output on pin ENVOUT; notes 2 and 3
101010test 10 playback mode; HF envelope of right channel carrier;
EOS = 1 (test output on pin ENVOUT)
111001test 25 noise reduction and modem; note 4
test 25a left channel FM modulator (left carrier only);
record mode; volume setting = −3 dB; test input = line input left
test 25b left and right noise reduction (compressor);
record mode; output select function = mute;
test output = line output
test 25c left and right channel FM demodulator; playback mode;
output select function = mute; test output = line output
111010test 26 noise reduction and modem; note 4
test 26a right channel FM modulator (right carrier only);
record mode; volume setting = −3 dB; test input = line input right
test 26b left and right channel audio lowpass filter; record mode;
volume setting = −3 dB; output select function = mute;
test input = line input; test output = line output
test 26c left and right channel noise reduction (expander); playback mode;
volume setting = −3 dB; test input = line input; note 5
Notes
1. This test can be used with a HIGH-level input signal by setting bit HPD = 1; test input signal applied to pin HMSW.
2. Auto-normal is activated (bit AUTN = 1) during the test, i.e. the playback audio signal is not available.
3. The output level on pin ENVOUT shows 6 dB attenuation compared to the internal signal of the head amplifier output.
4. This test connects internal signal lines between the noise reduction and (de-)modulator circuit. The signals found
here are not compensated for temperature or tolerance spread and therefore level measurements are only relative.
Absolute values are not an indication of the overall performance. Typical audio level of the test inputs and outputs is
approximately −6.5 dBV for the standard −8 dBV line level and 50 kHz FM deviation.
5. The expander test requires the auto-normal function to be set inactive; i.e. an FM carrier signal should be available.
1999 Apr 14 42
Page 43

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
15 INTERNAL CIRCUITRY
The indicated DC voltages are given for the record-mute mode in the typical application circuit without audio signal;
unless otherwise specified.
PIN SYMBOL VOLTAGE EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
1 SAP 3.8 V
2 TUNL
3 TUNR
4 CINL
5 CINR
6 EXT1L
7 EXT1R
8 EXT2L
9 EXT2R
10 AUXL
11 AUXR
12 RFCAGC 0 V
1 to 11
V
CC
57 kΩ
73 kΩ
3.8 V
MGR849
13 RFCOUT 3.8 V
14 MUTEC 0 V
15 MUTEL
18 MUTER
16 LINEL 4.5 V (VCCS = 0);
17 LINER
6 V (VCCS = 1)
19 DECL
20 DECR
bit VCCS V
bit RFCM
bit MUTE or VCC <7 V
CC
bit LOH
500 Ω
230
µA
100 kΩ
200 Ω
180 kΩ
20 kΩ2.8 kΩ22.8 kΩ
class AB
100 Ω
V
CC
14, 15, 18
MGR852
V
CC
MGR851
100 Ω
12
MGR850
13
V
CC
16, 17, 19, 20
MGR853
1999 Apr 14 43
Page 44

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
PIN SYMBOL VOLTAGE EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
21 LINOUT 4.5 V
V
CC
17.7 kΩ30 kΩ
200 Ω
600
µA
21
MGR854
22 LININ 3.8 V
3.8 V
96.4 kΩ
V
CC
23 DCFBL 3.8 V
33 DCFBR
24 EMPHL 3.8 V
32 EMPHR
25 DCL 3.8 V
31 DCR
22
total = 130 kΩ
V
CC
3.8 V
23, 33
bit
bit AFM
240 Ω
AFM
2.8 kΩ
V
MGR856
CC
V
3.8 V
CC
3.8 V
24, 32
MGR857
25, 31
bits NIL2 to NIL0
MGR855
3.8 V
1999 Apr 14 44
MGR858
Page 45

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
PIN SYMBOL VOLTAGE EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
26 DETL 0.7 V
30 DETR
7.5 kΩ
V
CC
26, 30
27 GND 0 V
28 I
29 V
34 V
ref
ref
CC
3.8 V
9to12V
3.8 V from
reference
generator
(3.8−a) V
bit STBA
bit STBP
3.8 V
0.5 V
27
substrate
MGR860
34
V
CC
MGR862
200 Ω
20
kΩ
MGR859
V
CC
V
CC
MGR861
28
29
1999 Apr 14 45
Page 46

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
PIN SYMBOL VOLTAGE EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
35 PBIN2 0.7 V;
36 RECOUT
4.3 V (recording)
37 PBIN1
38 HMSW 0 V;
4.3 V (recording)
V
CCH
35
kΩ
35
V
CC
36
GNDH
playback or
record-mute
mode
GNDH
signal RM
bit AFM
bit
DOC
bit
SHH
bit DETH
39 GNDH 0 V
37
38
MGR863
V
V
CCH
CC
GNDH
35
kΩ
GNDH
5 Ω
GNDH
39
&
&
bit HPD
to HF AGC
GNDH
MGR864
40 V
CCH
5V
1999 Apr 14 46
40
V
CCH
MGR865
Page 47

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
PIN SYMBOL VOLTAGE EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
41 RMHID 0 to 5 V
V
CC
2.5 V
signal RM
0.8 V
4.05 V
signal HID
MGR866
42 SDA 0 or 5 V
41
3 kΩ
43 SCL 0 or 5 V
44 ENVOUT 0 V
42
43
test modes
275 Ω
bit ACK
2
(I
C-bus acknowledge)
275 Ω
40 µA
1 kΩ
MGR868
V
CC
MGR867
44
1999 Apr 14 47
MGR869
Page 48

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
16 PACKAGE OUTLINE
QFP44: plastic quad flat package; 44 leads (lead length 1.3 mm); body 10 x 10 x 1.75 mm
c
y
X
A
33 23
34
pin 1 index
44
1
22
Z
E
e
H
E
E
w M
b
p
12
11
A
2
A
A
1
detail X
SOT307-2
(A )
3
θ
L
p
L
w M
b
e
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
mm
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT307-2
A
max.
2.10
0.25
0.05
1.85
1.65
UNIT A1A2A3bpcE
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
p
D
H
D
0.40
0.20
0.25
0.14
0.25
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
Z
D
B
0 2.5 5 mm
scale
(1)
(1) (1)(1)
D
10.1
9.9
REFERENCES
eH
10.1
9.9
12.9
0.8 1.3
12.3
1999 Apr 14 48
v M
H
v M
D
A
B
E
12.9
12.3
LL
p
0.95
0.55
0.15 0.10.15
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
Z
D
1.2
0.8
Zywv θ
E
1.2
0.8
o
10
o
0
ISSUE DATE
95-02-04
97-08-01
Page 49

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
17 SOLDERING
17.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount packages
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
our
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface
mount IC packages. Wave soldering is not always suitable
for surface mount ICs, or for printed-circuit boards with
high population densities. In these situations reflow
soldering is often used.
17.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
infrared/convection heating in a conveyor type oven.
Throughput times (preheating, soldering and cooling) vary
between 100 and 200 seconds depending on heating
method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C. The top-surface temperature of the
packages should preferable be kept below 230 °C.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
• For packages with leads on four sides, the footprint must
be placed at a 45° angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
17.3 Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
for surface mount devices (SMDs) or printed-circuit boards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
1999 Apr 14 49
17.4 Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Page 50

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
17.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering methods
PACKAGE
WAVE REFLOW
(1)
BGA, SQFP not suitable suitable
SOLDERING METHOD
HLQFP, HSQFP, HSOP, HTSSOP, SMS not suitable
(3)
PLCC
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO not recommended
(2)
(3)(4)
(5)
suitable
suitable
suitable
Notes
1. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods”
.
2. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering as a solder joint between the printed-circuit board and heatsink
(at bottom version) can not be achieved, and as solder may stick to the heatsink (on top version).
3. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
4. Wave soldering is only suitable for LQFP, TQFP and QFP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.8 mm;
it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
5. Wave soldering is only suitable for SSOP and TSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.65 mm; it is
definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
1999 Apr 14 50
Page 51

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Audio processor with head amplifier for VHS hi-fi TDA9605H
18 DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
19 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
20 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
Purchase of Philips I
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
2
C COMPONENTS
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips I2C patent to use the
1999 Apr 14 51
Page 52

Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. +61 2 9805 4455, Fax. +61 29805 4466
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. +43 1 60 101 1248, Fax. +43 1 60 1011210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 20 0733, Fax. +375 172 200773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 68 9211, Fax. +359 268 9102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 9430087
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +8522319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Sydhavnsgade 23, 1780 COPENHAGEN V,
Tel. +45 33 29 3333, Fax. +45 33 29 3905
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615 800, Fax. +358 96158 0920
France: 51 Rue Carnot, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 4099 6161, Fax. +33 14099 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 2353 60, Fax. +49 40 2353 6300
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Band Box Building, 2nd floor,
254-D, Dr. Annie BesantRoad, Worli, MUMBAI 400 025,
Tel. +91 22 493 8541, Fax.+91 22493 0966
Indonesia: PT Philips Development Corporation, Semiconductors Division,
Gedung Philips, Jl. Buncit Raya Kav.99-100, JAKARTA 12510,
Tel. +62 21 794 0040 ext.2501, Fax. +6221 7940080
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax.+353 17640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax.+972 3649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Piazza IV Novembre 3,
20124 MILANO, Tel. +39 2 6752 2531, Fax. +39 2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku,
TOKYO 108-8507, Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 7574880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381, Fax +9-5800 9430087
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 4027 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Pakistan: see Singapore
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC,MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +632 817 3474
Poland: Ul. Lukiska 10, PL 04-123 WARSZAWA,
Tel. +48 22 612 2831, Fax.+48 22612 2327
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax.+7 095755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 319762,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. +27 11 470 5911, Fax.+27 11470 5494
South America: Al. Vicente Pinzon, 173, 6th floor,
04547-130 SÃO PAULO, SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax.+55 11821 2382
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 93 301 6312, Fax.+34 93301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 5985 2000, Fax. +46 85985 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2741 Fax. +41 1 488 3263
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2886, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. +90 212 279 2770, Fax. +90 212 282 6707
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +38044 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 181 730 5000, Fax.+44 181754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 9430087
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 62 5344, Fax.+38111 635777
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors,
International Marketing & Sales Communications, Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218,
5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
© Philips Electronics N.V. 1999 SCA63
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
Printed in The Netherlands 545004/750/01/pp52 Date of release: 1999Apr 14 Document order number: 9397 750 04687
 Loading...
Loading...