Philips TDA9332H-N2, TDA9331H-N1, TDA9330H-N2, TDA9330H-N1 Datasheet
DATA SH EET
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 1998 Oct 22
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
2000 May 08
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TDA933xH series
I
2
C-bus controlled TV display
processors

2000 May 08 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
FEATURES
Available in all ICs:
• Can be used in both single scan (50 or 60 Hz) and
double scan (100 or 120 Hz) applications
• YUV input and linear RGB input with fast blanking
• Separate OSD/text input with fast blanking or blending
• Black stretching of non-standard luminance signals
• Switchable matrix for the colour difference signals
• RGBcontrolcircuitwithContinuousCathodeCalibration
(CCC), plus white point and black level offset
adjustment
• Blue stretch circuit which offsets colours near white
towards blue
• Internal clock generation for the deflection processing,
which is synchronized by a 12 MHz ceramic resonator
oscillator
• Horizontal synchronization with two control loops and
alignment-free horizontal oscillator
• Slow start and slow stop of the horizontal drive pulses
• Low-power start-up option for the horizontal drive circuit
• Vertical count-down circuit
• Vertical driver optimized for DC-coupled vertical output
stages
• Vertical and horizontal geometry processing
• Horizontal and vertical zoom possibility and vertical
scroll function for application with 16 : 9 picture tubes
• Horizontal parallelogram and bow correction
• I2C-bus control of various functions
• Low dissipation.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA933xH series are display processors for
‘High-end’ television receivers which contain the following
functions:
• RGB control processor with Y, U and V inputs, a linear
RGBinput for SCART orVGA signals with fastblanking,
a linear RGB input for OSD and text signals with a fast
blanking or blending option and an RGB output stage
withblack current stabilization, which isrealizedwith the
CCC (2-point black current measurement) system.
• Programmable deflection processor with internal clock
generation, which generates the drive signals for the
horizontal, East-West (E-W) and vertical deflection.
The circuithasvariousfeaturesthatareattractiveforthe
application of 16 : 9 picture tubes.
• Thecircuitcan be used in both singlescan(50 or 60 Hz)
and double scan (100 or 120 Hz) applications.
In addition to these functions, the TDA9331H and
TDA9332H have a multi-sync function for the horizontal
PLL, with a frequencyrange from 30 to 50 kHz(2fHmode)
or 15 to 25 kHz (1fHmode), so that the ICs can also be
used to display SVGA signals.
The supply voltage of the ICs is 8 V. They are each
contained in a 44-pin QFP package.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA9330H QFP44 plastic quad flat package; 44 leads (lead length 1.3 mm);
body 10 × 10 × 1.75 mm
SOT307-2
TDA9331H
TDA9332H
2000 May 08 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
SURVEY OF IC TYPES
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
IC VERSION VGA MODE DAC OUTPUT
TDA9330H no I
2
C-bus controlled
TDA9331H yes proportional to VGA frequency
TDA9332H yes I
2
C-bus controlled
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
P
supply voltage − 8.0 − V
I
P
supply current (VP1plus VP2) − 50 − mA
Input voltages
V
i(Y)(b-w)
luminance input signal (black-to-white value) − 1.0/0.315 − V
V
i(U)(p-p)
U input signal (peak-to-peak value) − 1.33 − V
V
i(V)(p-p)
V input signal (peak-to-peak value) − 1.05 − V
V
i(RGB)(b-w)
RGB input signal (black-to-white value) − 0.7 − V
V
i(Hsync)
horizontal sync input (HD) − TTL − V
V
i(Vsync)
vertical sync input (VD) − TTL − V
V
i(IIC)
I2C-bus inputs (SDA and SCL) − CMOS 5 V − V
Output signals
V
o(RGB)(b-w)
RGB output signal amplitude (black-to-whitevalue) − 2.0 − V
I
o(hor)
horizontal output current −− 10 mA
I
o(ver)(p-p)
vertical output current (peak-to-peak value) − 0.95 − mA
I
o(EW)
E-W drive output current −− 1.2 mA
2000 May 08 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I
2
C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
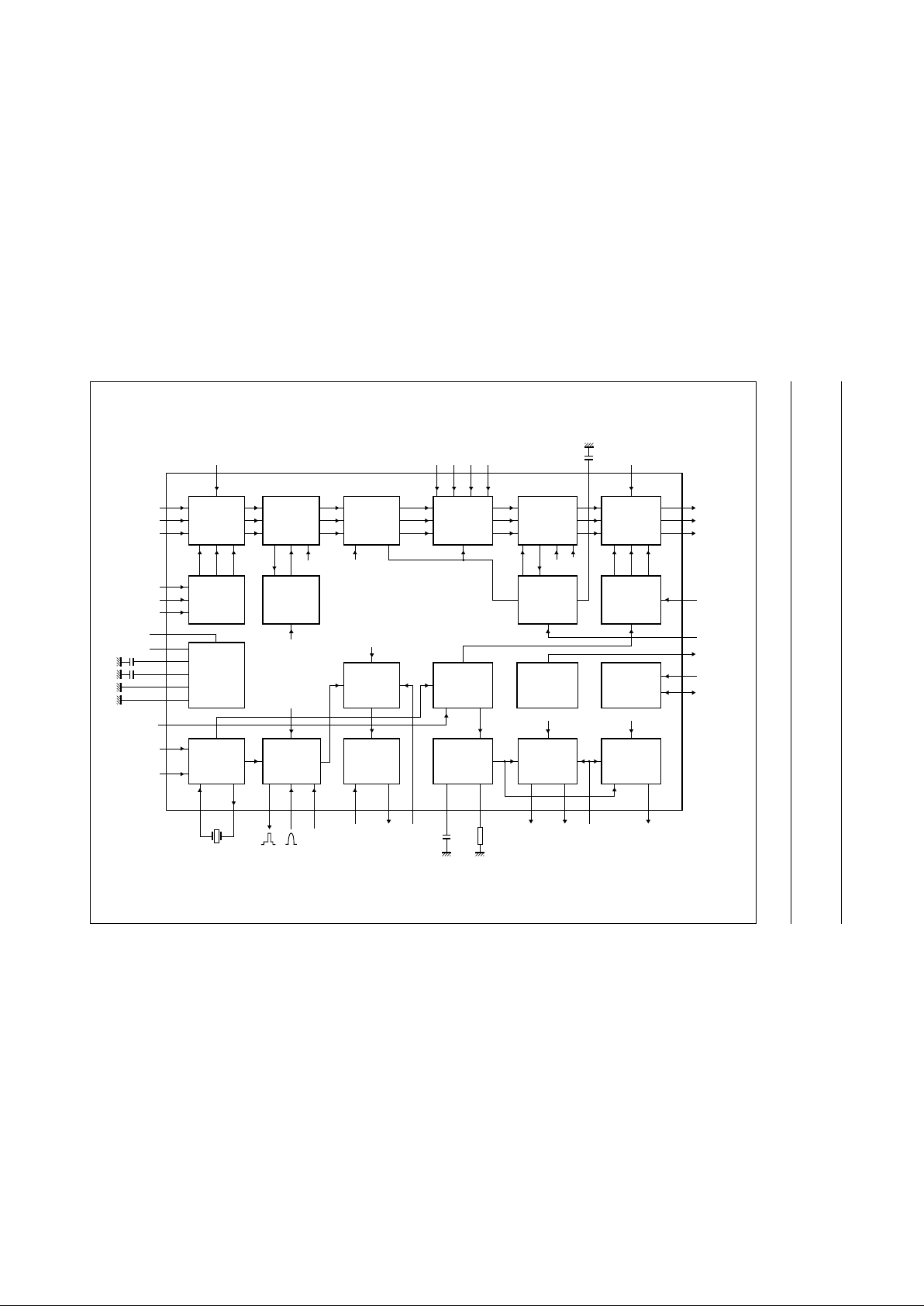
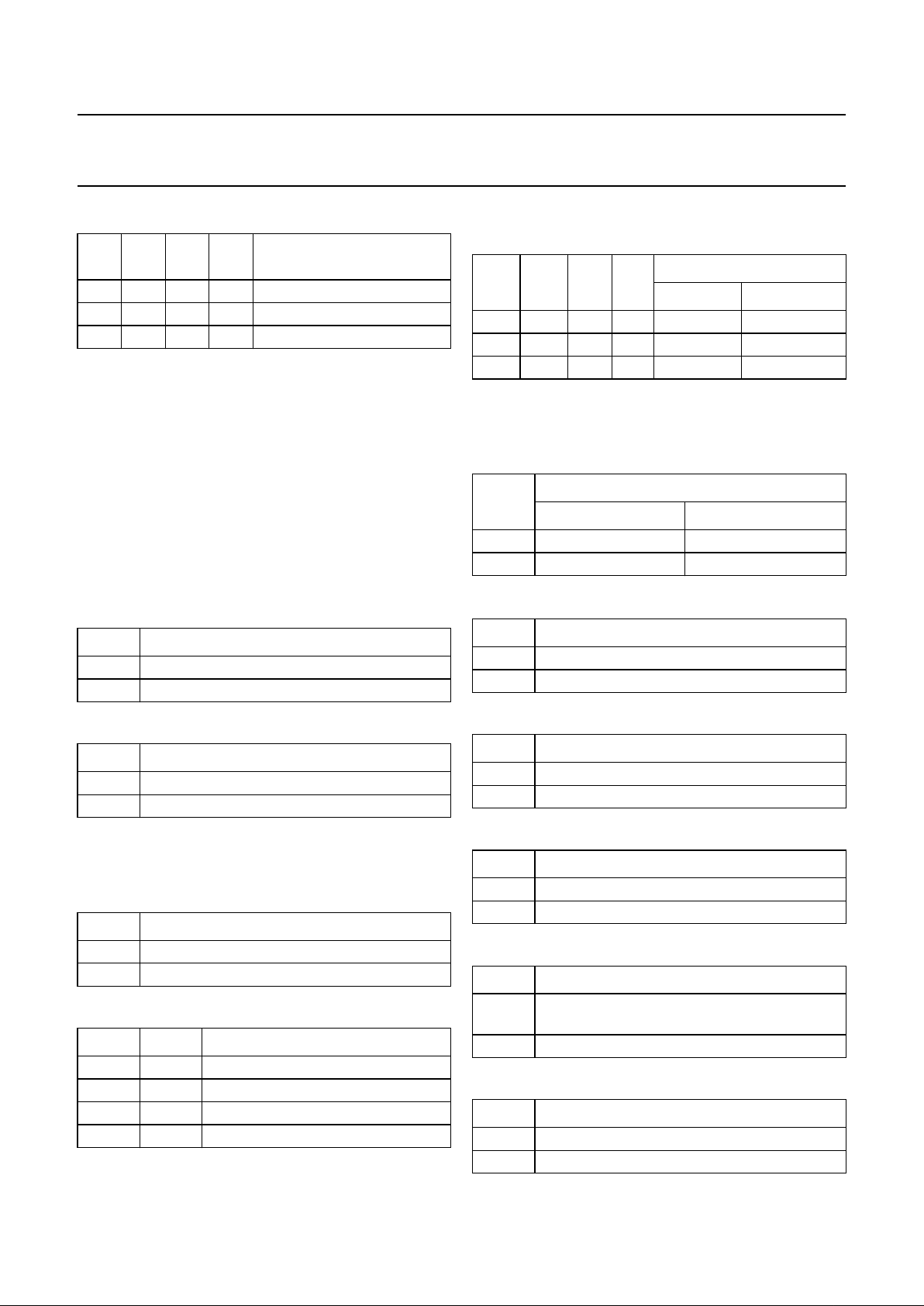
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
MGR445
SWITCH
Y
Y
U V
SAT
CONTR
U
V
SATURATION
CONTROL
COLOUR
DIFFERENCE
MATRIX
R
G
B
CONTRAST
CONTROL
R
G
B
RGB
INSERTION
R
GG
B
BRI
white
point
WHITE POINT
AND
BRIGHTNESS
CONTROL
R
B
OUTPUT
AMPLIFIER
AND
BUFFER
BLUE STRETCH
40
41
42
28
27
26
YIN
UIN
VIN
RGB-YUV
MATRIX
BLACK
STRETCH
PWL
AND
BEAM
CURRENT
LIMITER
CONTINUOUS
CATHODE
CALIBRATION
44
30
31
32
RI1
GI1
BI1
SUPPLY
H-SHIFT
SOFT
START/STOP
LOW-POWER
START-UP
H/V DIVIDER
19 × 6-BIT DACs
2 × 4-BIT DACs
I2C-BUS
TRANSCEIVER
10
43
11
25
18
6
19
17
7
39
DEC
BG
GND1
GND2
23
V
P1
DEC
VD
V
P2
CLOCK
GENERATION
AND
1st LOOP
20
21 13 14 22
PHASE-2
LOOP
HORIZONTAL
OUTPUT
15 16
VSC I
ref
RAMP
GENERATOR
1 24
VERTICAL
GEOMETRY
3
E-W
GEOMETRY
GEOMETRY CONTROL
24
12
HSEL
33
29
38373635
34
TDA933xH
BL1
FBCSO
BL2GI2RI2
PWL
BI2
BCL
BO
GO
RO
BLKIN
DACOUT
SDA
SCL
VDOA
589
VDOB EWOEHTIN
XTALI
XTALO
LPSU
FLASH
HOUT
SCO
HFB
DPC
H
D
V
D
Fig.1 Block diagram.
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to forcelandscapepagestobe rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2000 May 08 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
VDOA 1 vertical drive output A
VDOB 2 vertical drive output B
EWO 3 E-W output
EHTIN 4 EHT compensation input
FLASH 5 flash detection input
GND1 6 ground 1
DEC
VD
7 digital supply decoupling
HOUT 8 horizontal output
SCO 9 sandcastle pulse output
SCL 10 serial clock input
SDA 11 serial data input/output
HSEL 12 selection of horizontal frequency
HFB 13 horizontal flyback pulse input
DPC 14 dynamic phase compensation
VSC 15 vertical sawtooth capacitor
I
ref
16 reference current input
V
P1
17 positive supply 1 (+8 V)
DEC
BG
18 band gap decoupling
GND2 19 ground 2
XTALI 20 crystal input
XTALO 21 crystal output
LPSU 22 low-power start-up supply
V
D
23 vertical sync input
H
D
24 horizontal sync input
DACOUT 25 DAC output
VIN 26 V-signal input
UIN 27 U-signal input
YIN 28 luminance input
FBCSO 29 fixed beam current switch-off input
RI1 30 red 1 input for insertion
GI1 31 green 1 input for insertion
BI1 32 blue 1 input for insertion
BL1 33 fast blanking input for RGB-1
PWL 34 peak white limiting decoupling
RI2 35 red 2 input for insertion
GI2 36 green 2 input for insertion
BI2 37 blue 2 input for insertion
BL2 38 fast blanking/blending input for RGB-2
V
P2
39 positive supply 2 (+8 V)
RO 40 red output

2000 May 08 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
GO 41 green output
BO 42 blue output
BCL 43 beam current limiting input
BLKIN 44 black current input
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
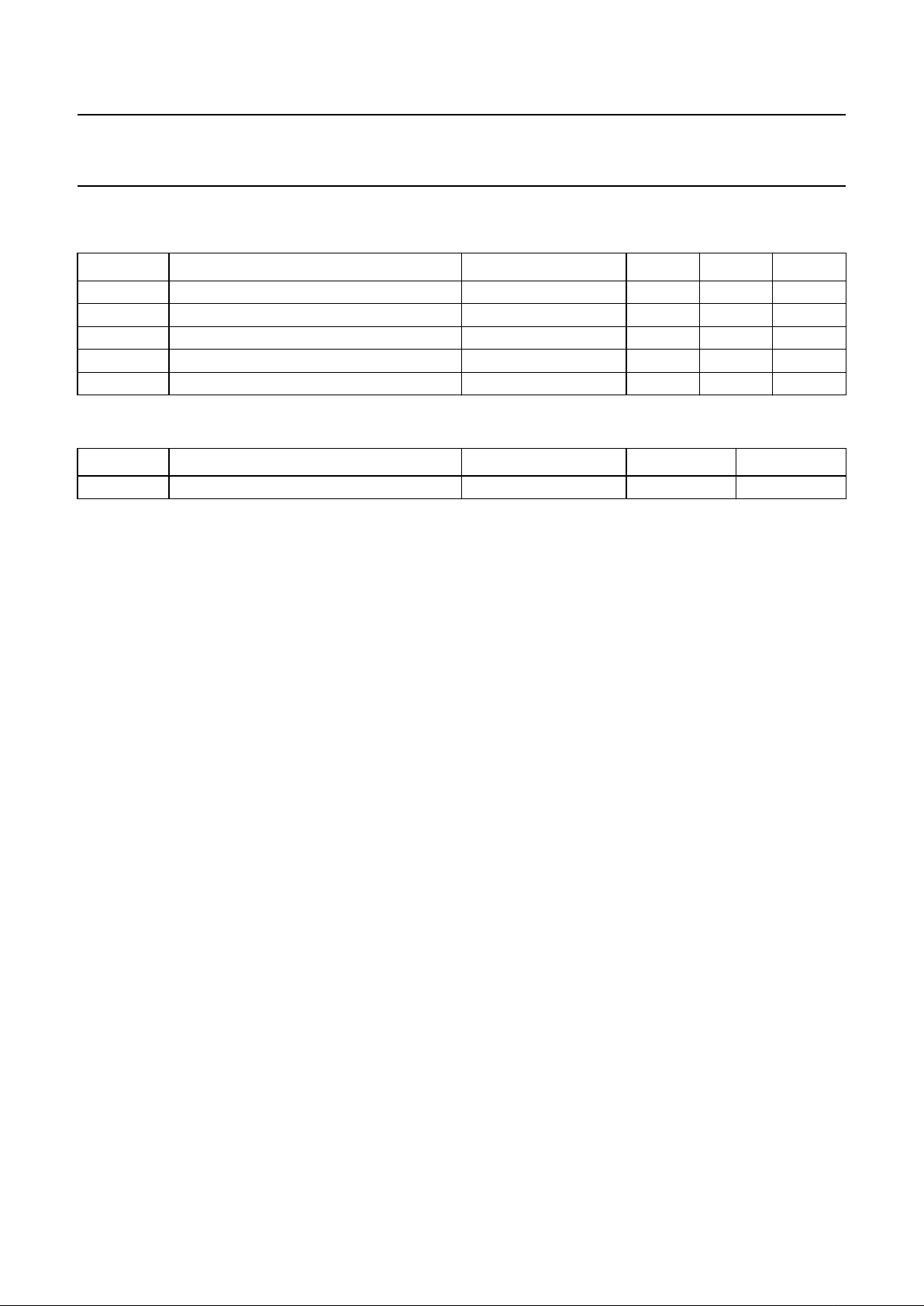
handbook, full pagewidth
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
12
13
14
15
16
17
181920
21
22
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
TDA933xH
MGR446
BL1
BI1
GI1
RI1
YIN
UIN
VIN
DACOUT
H
D
V
D
VDOA
VDOB
EWO
EHTIN
FLASH
GND1
HOUT
SCO
SDA
FBCSO
BCL
BO
GO
RO
V
P2
BL2
GI2
RI2
PWL
BLKIN
BI2
HFB
DPC
VSC
I
ref
V
P1
DEC
BG
XTALI
XTALO
LPSU
HSEL
GND2
DEC
VD
SCL
Fig.2 Pin configuration.

2000 May 08 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
RGB control circuit
INPUT SIGNALS
The RGB control circuit of the TDA933xH contains three
sets of input signals:
• YUV input signals, which are supplied by the input
processor or the feature box. Bit GAI can be used to
switch the luminance input signal sensitivity between
0.45 V (p-p) and 1.0 V (b-w). The nominal input signals
for U and V are 1.33 V (p-p) and 1.05 V (p-p),
respectively. These input signals are controlled on
contrast, saturation and brightness.
• The first RGB input is intended for external signals
(SCARTin 1fHandVGA in 2fHapplications),which have
an amplitude of 0.7 V (p-p) typical. This input is also
controlled on contrast, saturation and brightness.
• The second RGB input is intended for OSD and teletext
signals. The required input signals havean amplitude of
0.7 V (p-p). The switching between the internal signal
and the OSD signal can be realized via a blending
function or via fast blanking. This input is only controlled
on brightness.
Switchingbetween the various sources canberealized via
the I2C-bus and by fast insertion switches. The fast
insertion switches can be enabled via the I2C-bus.
The circuit contains switchable matrix circuits for the
colour difference signals so that the colour reproduction
can be adapted for PAL/SECAM and NTSC. For NTSC,
two different matrices can be chosen. In addition, a matrix
for high-definition ATSC signals is available.
OUTPUT AMPLIFIER
The output signal has an amplitude of approximately
2 V (b-w) at nominal input signals and nominal settings of
the controls. The required ‘white point setting’ of the
picture tube can be realized by means of three separate
gain settings for the RGB channels.
To obtain an accurate biasing of the picture tube, a CCC
circuit has been developed. This function is realized by a
2-point black level stabilization circuit.
Byinsertingtwotestlevelsforeachgunandcomparing the
resulting cathode currents with two different reference
currents,the influence of thepicture tube parameters such
as the spread in cut-off voltage can be eliminated.
This 2-point stabilization is based on the principle that the
ratio between the cathode currents is coupled to the ratio
between the drive voltages according to:
The feedback loop makes the ratio between cathode
currents I
k1
and Ik2 equal to the ratio between the
reference currents (which are internally fixed)by changing
the (black) level and the amplitude of the RGB output
signals via two converging loops. The system operates in
such a way that the black level of the drive signal is
controlled to thecut-off point of the gun. In this way, a very
good grey scale tracking is obtained. The accuracy of the
adjustmentof the black level isonly dependent on the ratio
ofinternalcurrents and these can be madeveryaccurately
in integrated circuits. An additional advantage of the
2-point measurement is that the control system makes the
absolute value of Ik1 and Ik2 identical to the internal
reference currents. Because this adjustment is obtained
by adapting the gain of the RGB control stage, this control
stabilizes the gain of the complete channel (RGB output
stage and cathode characteristic). As a result, this 2-point
loop compensates for variations in the gain figures during
life.
An important property ofthe 2-point stabilizationis that the
offset and the gain of the RGB path are adjusted by the
feedback loop. Hence, the maximum drive voltage for the
cathode is fixed by the relationship between the test
pulses, the reference current and the relative gain setting
of the three channels. Consequently, the drive level of the
CRT cannot be adjusted by adapting the gain of the RGB
output stage. Because different picture tubes may require
different drive levels, the typical ‘cathode drive level’
amplitudecan be adjusted bymeans of an I2C-bussetting.
Depending on the selected cathode drive level, the typical
gain of the RGB output stages can be fixed, taking into
account the drive capability of the RGB outputs
(pins 40 to 42). More details about the design are given in
the application report (see also Chapter “Characteristics”;
note 11).
The measurement of the high and the low currents of the
2-point stabilization circuit isperformed in two consecutive
fields. The leakage current is measured in each field. The
maximum allowable leakage current is 100 µA.
For extra flexibility, it also possible to switch the CCC
circuit to 1-point stabilization with the OPC bit. In this
mode, only the blacklevel at theRGB outputs is controlled
by the loop. The cathode drive level setting has no
influence on the gain in thismode. This level should be set
to the nominal value to get the correct amplitude of the
measuring pulses.
I
k1
I
k2
------ -
V
dr1
V
dr1
-----------
γ
=

2000 May 08 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
Via the I2C-bus, an adjustable offset can be made on the
black level of red and green channels with respect to the
level that is generated by the black current control loop.
These controls can be used to adjust the colour
temperature of the dark part of the picture, independent of
the white point adjustment.
When the TV receiver is switched on, the black current
stabilization circuit is directly activated and the RGB
outputs are blanked. The blanking is switched off as soon
as the loop has stabilized (e.g. the first time that bit BCF
changes from 1 to 0, see also Chapter “Characteristics”;
note 15). This ensures that the switch-on time is reduced
to a minimum and is only dependent on the warm-up time
of the picture tube.
The black current stabilization system checks the output
levelof the three channels andindicateswhether the black
level of the lowest RGB output of the IC is in a certain
window (WBC bit), below or above this window (HBC bit).
This indication can be read from the I2C-bus and can be
used for automatic adjustment of voltage Vg2 during the
production of the TV receiver.
When a failure occurs in theblack current loop (e.g. due to
an open circuit), statusbit BCF is set.This information can
be used to blank the picture tube to avoid damage to the
screen.
The control circuit contains an average beam current
limiting circuit and a peak white level (PWL) circuit. The
PWL detects small white areas in the picture that are not
detected by the average beam current limiter. The PWL
can be adjusted via the I2C-bus. A low-pass filter is placed
in front of the peak detector to prevent it from reacting to
short transients in the video signal. The capacitor of the
low-pass filter is connected externally so that the set
maker can adapt the time constant as required. The IC
also contains a soft clipper that limits the amplitude of the
shorttransientsintheRGBoutputsignals.Inthisway,spot
blooming on, for instance, subtitles is prevented. The
differencebetween the PWL and thesoftclipping level can
be adjusted via the I2C-bus in a few steps.
The vertical blanking is adapted to the vertical frequency
of the incoming signal (50 or 100 Hz or, 60 or 120 Hz).
When the flyback time of the vertical output stage is
greater than the 60 Hz blanking time, the blanking can be
increased to the same value as that of the 50 Hz blanking.
This can be set by means of bit LBM.
When no video is available, it is possible to insert a blue
background. This feature can be activated via bit EBB.
Synchronization and deflection processing
HORIZONTAL SYNCHRONIZATION AND DRIVE CIRCUIT
The horizontal drive signal is obtained from an internal
VCO which runs at a frequency of 440 times (2fHmode) or
880 times (1fHmode) the frequency of the incoming H
D
signal. The free-running frequency of this VCO is
calibrated by a crystal oscillator which needs an external
12 MHz crystal or ceramic resonator as a reference. It is
also possible to supply an external reference signal to the
IC (in this case, the external resonator should be
removed).
The VCO is synchronized to the incoming horizontal H
D
pulse (applied from the feature box or the input processor)
by a PLL with an internal time constant. The frequency of
thehorizontaldrive signal (1fHor2fH)isselected by means
of a switching pin, which must be connected to ground or
left open circuit.
For HDTV applications, it is possible to change the
free-running frequency of the horizontal drive output from
31.2 kHz to 33.7 kHz by means of bit HDTV.
For safety reasons, switching between 1fH and 2f
H
modes is only possible when the IC is in the standby
mode.
For the TDA9331H and TDA9332H, it is also possible to
set the horizontal PLL to a ‘multi-sync’ mode by means of
bit VGA. In this mode, the circuit detects the frequency of
theincomingsyncpulses and adjusts the centre frequency
of the VCO accordingly by means of an internal
Digital-to-Analog-Converter (DAC). The frequency range
in this mode is 30 to 50 kHz at the output.
The polarities of the incoming HD and VD pulses are
detected internally. The detected polarity can be read out
via status bits HPOL and VPOL.
The horizontal drive signal is generated by a second
control loop which compares the phase of the reference
signal (applied from the internal VCO) with the flyback
pulse. The time constant of this loop is set internally. The
IC has a dynamic horizontal phase correction input, which
can be used to compensate phase shifts that are caused
by beam current variations. Additional settings of the
horizontal deflection (which are realized via the second
loop) are the horizontal shift and horizontal parallelogram
and bow corrections (see Chapter “Characteristics”;
Fig.16). The adjustments are realized via the I2C-bus.
When no horizontal flyback pulse is detected during three
consecutive line periods, status bit NHF is set (output
status byte 01-D3; see Table 3).

2000 May 08 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
The horizontal drive signal is switched on and off via the
so-called slow-start/slow-stop procedure. This function is
realizedby varying the tonof the horizontal drive pulse. For
EHT generators without a bleeder, the IC can be set to a
‘fixed beam current mode’ via bit FBC. In this case, the
picture tube capacitance is discharged with a current of
approximately 1 mA. The magnitude of the discharge
current is controlled via the black current feedback loop.
If necessary, the discharge current can be enlarged with
the aid of an external currentdivision circuit. With the fixed
beam current option activated, it is still possible to have a
black screen during switch-off. This can be realized by
placing the vertical deflectionin an overscan position. This
mode is activated via bit OSO.
An additional mode of the IC is the ‘low-power start-up’
mode.This mode is activated when asupplyvoltageof 5 V
is supplied to the start-up pin.
The required current for this mode is 3 mA (typ.). In this
condition, the horizontal drive signal has the nominal t
off
and the ton grows gradually from zero to approximately
30% of the nominal value. This results in a line frequency
of approximately 50 kHz (2fH) or 25 kHz (1fH). The output
signal remains unchanged until the main supply voltage is
switched on and the I2C-bus data has been received. The
horizontal drive then gradually changes to the nominal
frequency and duty cycle via the slow-start procedure.
TheICcanonlybeswitched on and to standby mode when
both standby bits (STB0 and STB1) are changed. The
circuit will not react when only one bit changes polarity.
The IC has a general purpose bus controlled DAC output
with a 6-bit resolution and with an output voltage range
between 0.2 to 4 V. In the TDA9331H, the DC voltage on
this output is proportional to the horizontal line frequency
(only in VGA mode). This voltage can be used to control
the supply voltage of the horizontal deflection stage, to
maintain constant picture width for higher line frequencies.
VERTICAL DEFLECTION AND GEOMETRY CONTROL
The drive signals for the vertical and E-W deflection
circuits are generated by a vertical divider, which derives
its clock signal from the line oscillator. The divider is
synchronized by the incoming VDpulse, generated by the
input processor or the feature box. The vertical ramp
generator requires an external resistor and capacitor; the
tolerances for these components must be small. In the
normal mode, the vertical deflection operates in constant
slope and adapts its amplitude, depending on the
frequency of the incoming signal (50 or 60 Hz, or
100 or 120 Hz). When the TDA933xH is switched to the
VGA mode, the amplitude of the vertical scan is stabilized
andindependent of the incomingvertical frequency. In this
mode, the E-W drive amplitude is proportional to the
horizontalfrequency so that the correctiononthe screen is
not affected.
The vertical drive is realized by a differential output
current. The outputs must be DC-coupled to the vertical
output stage (e.g. TDA8354).
The vertical geometry can be adjusted via the I2C-bus.
Controls are possible for the following parameters:
• Vertical amplitude
• S-correction
• Vertical slope
• Vertical shift (only for compensation of offsets in output
stage or picture tube)
• Vertical zoom
• Verticalscroll (shifting the picture inthevertical direction
when the vertical scan is expanded)
• Vertical wait, an adjustable delay for the start of the
vertical scan.
Withregardtothevertical wait, the following conditions are
valid:
• In the 1fHTV mode, the start of the vertical scan is fixed
and cannot be adjusted with the vertical wait
• In the 2fH TV mode, the start of the vertical scan
depends on the value of the Vertical Scan Reference
(VSR) bus bit. If VSR = 0, the start of the vertical scan is
related to the end of the incoming VDpulse. If VSR = 1,
it is related to the start. In both cases, the start of the
scan can be adjusted with the vertical wait setting
• In the multi-sync mode (TDA9331H and TDA9332H
both in 1fHmode and 2fHmode), the start of the vertical
scan is related to the start of the incoming VDpulse and
can be adjusted with the vertical wait setting.
The minimum value for the vertical wait setting is 8 line
periods. If the setting is lower than 8, the wait period will
remain at 8 line periods.
The E-W drive circuit has a single-ended output. The E-W
geometry can be adjusted on the following parameters:
• Horizontal width with increased range because of the
‘zoom’ feature
• E-W parabola/width ratio
• E-W upper corner/parabola ratio
• E-W lower corner/parabola ratio
• E-W trapezium.

2000 May 08 10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
The IC has an EHT compensation input which controls
both the vertical and the E-W output signals. The relative
control effect on both outputs can be adjusted via the
I2C-bus (sensitivity of vertical correction is fixed; E-W
correction variable).
Toavoiddamagetothe picture tube in the event of missing
or malfunctioning vertical deflection, a vertical guard
function is available at the sandcastle pin (pin SCO). The
vertical guard pulse from the vertical output stage
(TDA835x) should be connected to the sandcastle pin,
which acts as a current sense input. If the guard pulse is
missing or lasts too long, bit NDF is set in the status
register and the RGB outputs are blanked. If the guard
function is disabled via bit EVG, only NDF status bit NHF
is set.
TheICalsohasinputsforflashandovervoltageprotection.
More details about these functions are given in Chapter
“Characteristics”; note 43.
I
2
C-BUS SPECIFICATION
The slave address of the IC is given in Table 1. The circuit
operates up to clock frequencies of 400 kHz. Valid
subaddresses: 00 to 1F, subaddress FE is reserved for
test purposes. The auto-increment mode is available for
subaddresses.
Table 1 Slave address (8C)
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 R/W
10001101/0

2000 May 08 11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
Table 2 Input control bits
Notes
1. For zero parallelogram and bow correction use register value 7 DEC.
2. See Chapter “Characteristics”; note 47.
3. Bit VGA is not available in the TDA9330H.
FUNCTION
SUBADDRESS
(HEX)
DATA BYTE
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
RGB processing-1 00 MAT EBB SBL RBL BLS BKS IE1 IE2
RGB processing-2 01 MUS FBC OBL AKB CL3 CL2 CL1 CL0
Wide horizontal blanking 02 HBL TFBC GAI STB0 HB3 HB2 HB1 HB0
Horizontal deflection 03 HDTV VSR 0 STB1 POC PRD VGA
(3)
ESS
Vertical deflection 04 OPC VFF LBM DIP OSO SVF EVG DL
Brightness 05 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Saturation 06 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Contrast 07 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point R 08 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point G 09 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
White point B 0A 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Peak white limiting 0B 0 0 SC1 SC0 A3 A2 A1 A0
Horizontal shift 0C 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Horizontal parallelogram
(1)
0D 0000A3A2A1A0
E-W width 0E 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W parabola/width 0F 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W upper corner/parabola 10 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W trapezium 11 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
E-W EHT compensation sensitivity 12 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical slope 13 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical amplitude 14 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
S-correction 15 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical shift 16 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical zoom 17 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical scroll 18 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Vertical wait 19 0 0 0 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
DAC output
(2)
1A 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Black level offset R 1B 0000A3A2A1A0
Black level offset G 1C 0000A3A2A1A0
Horizontal timing 1D 0 0 0 HDCL LBL3 LBL2 LBL1 LBL0
E-W lower corner/parabola 1E 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Horizontal bow
(1)
1F 0000A3A2A1A0

2000 May 08 12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
Table 3 Output status bits
FUNCTION
SUBADDRESS
(HEX)
DATA BYTE
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Output status bytes 00 POR FSI SL XPR NDF IN1 IN2 WBC
01 N2 ID2 ID1 ID0 NHF BCF FLS NRF
02 X X X X X HPOL VPOL HBC
Input control bits
Table 4 Colour difference matrix
Table 5 Enable ‘blue-back’
Table 6 Service blanking
Table 7 RGB blanking
Table 8 Blue stretch
Table 9 Black stretch
Table 10 Enable fast blanking RGB-1
Table 11 Enable fast blanking RGB-2
Table 12 Fixed beam current switch-off
Table 13 Blending function on OSD; note 1
Note
1. When bit OBL is set to 1, the blending function is
always activated, independent of the setting of bit IE2.
Table 14 Black current stabilization
MAT MUS MATRIX POSITION
00 PAL
0 1 ATSC
1 0 NTSC Japan
1 1 NTSC USA
EBB MODE
0 blue-black switched off
1 blue-black switched on
SBL SERVICE BLANKING MODE
0 off
1on
RBL RGB BLANKING
0 not active
1 active
BLS BLUE STRETCH MODE
0 off
1on
BKS BLACK STRETCH MODE
0 off
1on
IE1 FAST BLANKING
0 not active
1 active
IE2 FAST BLANKING
0 not active
1 active
FBC MODE
0 switch-off with blanked RGB outputs
1 switch-off with fixed beam current
OBL MODE
0 OSD via fast blanking
1 OSD via blending function
AKB OPC MODE
0 0 2-point control
0 1 1-point control
1 − not active
2000 May 08 13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
Table 15 Cathode drive level (15 steps; 3.6 V/step)
Note
1. The given values are valid for the following conditions:
a) Nominal CVBS input signal.
b) Settings for contrast and white point nominal.
c) Black and blue stretch switched off.
d) Gain of output stage such that no clipping occurs.
e) Beam current limiting not active.
f) Gamma of picture tube is 2.25.
g) The tolerance on these values is approximately
±3V.
Table 16 RGB blanking mode
Table 17 Picture tube discharge time
Note
1. See Chapter “Characteristics”; Fig.15
Table 18 Gain of luminance channel
Table 19 Standby
Table 20 Position of wide blanking (14 steps; 1f
H
mode
0.29 µs/step; 2f
H
mode 0.145 µs/step)
Note
1. See Chapter “Characteristics”; note 13.
Table 21 Horizontal free-running frequency in TV mode
Table 22 Vertical scan reference in 2f
H
TV mode
Table 23 Synchronization mode
Table 24 Overvoltage input mode
Table 25 Multi-sync mode
Table 26 Extended slow start mode
CL3 CL2 CL1 CL0
SETTING OF CATHODE
DRIVE AMPLITUDE
(1)
0000 41V(b-w)
1000 70V(b-w)
1111 95V(b-w)
HBL MODE
0 normal blanking (horizontal flyback)
1 wide blanking
TFBC MODE
0 18.6 ms
1 25 ms
GAI MODE
0 normal gain [V
28
= 1 V (b-w)]
1 high gain [V
28
= 0.45 V (p-p)]
STB0 STB1 CONDITION
0 0 horizontal drive off
0 1 no action
1 0 no action
1 1 horizontal drive on
HB3 HB2 HB1 HB0
TIMING OF BLANKING
(1)
1fH MODE 2fH MODE
0000−2.03 µs −1.015 µs
0111 0µs0µs
111−2.03 µs 1.015 µs
HDTV
FREQUENCY
1f
H
MODE 2fH MODE
0 15.65 kHz 31.3 kHz
1 16.85 kHz 33.7 kHz
VSR VERTICAL SCAN REFERENCE
0 end of V
D
pulse
1 start of V
D
pulse
POC MODE
0 synchronization active
1 synchronization not active
PRD OVERVOLTAGE MODE
0 detection mode
1 protection mode
VGA MODE
0
horizontal frequency fixed by internal
reference
1 multi-sync function switched on
ESS EXTENDED SLOW START MODE
0 not active
1 active

2000 May 08 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
Table 27 Long blanking mode
Table 28 Vertical free-running frequency in TV mode
Table 29 De-interlace phase
Table 30 Switch-off in vertical overscan
Table 31 Select vertical frequency
Table 32 Enable vertical guard (RGB blanking)
Table 33 Interlace
Table 34 Soft clipping level
Table 35 Clamp pulse timing
Note
1. See Chapter “Characteristics”; note 13.
Table 36 Start line blanking (15 steps; 2 line locked clock
period per step; 1 line period is 440 LLC pulses)
Note
1. See Chapter “Characteristics”; note 13.
Output status bits
Table 37 Power-on reset
Table 38 Field frequency indication
Table 39 Phase 1 (ϕ
1
) lock indication
LBM BLANKING MODE
0 adapted to standard (50 or 60 Hz)
1 fixed in accordance with 50 Hz standard
VFF FREQUENCY
0 50 Hz (SVF = 0) or 100 Hz (SVF = 1)
1 60 Hz (SVF = 0) or 120 Hz (SVF = 1)
DIP PHASE
0
delay of 1st field (start of synchronized V
D
pulse coincides with H-flyback) with 0.5 H
1 delay of 2nd field with 0.5 H
OSO MODE
0 switch-off undefined
1 switch-off in vertical overscan
SVF MODE
0 vertical frequency is 50 or 60 Hz
1 vertical frequency is 100 or 120 Hz
EVG VERTICAL GUARD MODE
0 not active
1 active
DL STATUS
0 interlace
1 de-interlace
SC1 SC0
VOLTAGE DIFFERENCE
BETWEEN SOFT CLIPPING AND
PWL
0 0 0% above PWL
0 1 5% above PWL
1 0 10% above PWL
1 1 soft clipping off
HDCL MODE
(1)
0 normal timing
1 HDTV timing
LBL3 LBL2 LBL1 LBL0
START LINE
BLANKING
(1)
0000 +14 LLC
0111 normal
1111 −16 LLC
POR MODE
0 normal
1 power-down
FSI FREQUENCY
0 50 or 100 Hz
1 60 or 120 Hz
SL INDICATION
0 not locked
1 locked

2000 May 08 15
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
Table 40 X-ray protection
Table 41 Output of vertical guard
Table 42 Indication of RGB-1 insertion
Table 43 Indication of RGB-2 insertion
Table 44 Indication of output black level inside/outside
Vg2 alignment window
Note
1. See Chapter “Characteristics”; note 16.
Table 45 IC identification
Table 46 Mask version indication
Table 47 Condition of horizontal flyback
Table 48 Indication of failure in black current circuit
Table 49 Indication of flash detection
Table 50 Locking of reference oscillator to crystal
oscillator
Table 51 Indication of output black level below or above
the middle of Vg2 alignment window
Note
1. See Chapter “Characteristics”; note 16.
Table 52 Polarity of H
D
input pulse
Table 53 Polarity of V
D
input pulse
XPR OVERVOLTAGE
0 no overvoltage detected
1 overvoltage detected
NDF VERTICAL OUTPUT STAGE
0OK
1 failure
IN1 RGB INSERTION
0no
1yes
IN2 RGB INSERTION
0no
1yes
WBC CONDITION
(1)
0 black current stabilization outside window
1 black current stabilization inside window
ID2 ID1 ID0 IC VERSION
0 0 0 TDA9330H
0 0 1 TDA9332H
0 1 1 TDA9331H
N2 MASK VERSION
0 N1 version
1 N2 version
NHF CONDITION
0 flyback pulse present
1 flyback pulse not present
BCF CONDITION
0 normal operation
1 failure in black current stabilization circuit
FLS CONDITION
0 no flash-over detected
1 flash-over detected
NRF CONDITION
0 reference oscillator is locked
1 reference oscillator is not locked
HBC CONDITION
(1)
0 black current stabilization below window
1 black current stabilization above window
HPOL POLARITY
0 positive
1 negative
VPOL POLARITY
0 positive
1 negative
2000 May 08 16
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
supply voltage − 9.0 V
T
stg
storage temperature −25 +150 °C
T
amb
ambient temperature 0 70 °C
T
sol
soldering temperature for 5 s − 260 °C
T
j
junction temperature − 150 °C
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 60 K/W
QUALITY SPECIFICATION
In accordance with
“SNW-FQ-611E-part E”
.
ESD protection
All pins are protected against ESD by internal protection
diodes, and meet the following specification:
• Human body model (R = 1.5 kΩ; C = 100 pF):
all pins > ±3000 V
• Machine model (R = 0 Ω; C = 200 pF):
all pins > ±300V.
Latch-up performance
At an ambient temperature of 50 °C all pins meet the
following specification:
• Positive stress test: I
trigger
≥ 100 mA
or V
pin
≥ 1.5 × V
CC(max)
• Negative stress test: I
trigger
≤−100 mA
or V
pin
≤−0.5 × V
CC(max)
.
At an ambient temperature of 70 °C, all pins meet the
specification as mentioned above, with the exception of
pin 32, which can withstand a negative stress current of at
least 50 mA.
2000 May 08 17
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV display processors
TDA933xH series
CHARACTERISTICS
VP=8V; T
amb
=25°C; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
M
AIN SUPPLY; PINS 17 AND 39
V
P1
supply voltage 7.2 8.0 8.8 V
V
POR
power-on reset voltage level note 1 5.8 6.1 6.5 V
I
P1
supply current pin 17 plus pin 39 44 50 58 mA
pin 17 − 22 − mA
pin 39 − 28 − mA
P
tot
total power dissipation − 400 − mW
L
OW-POWER START-UP; PIN 22
V
P2
supply voltage note 2 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
I
P2
supply current − 3.0 4.5 mA
RGB control circuit
LUMINANCE INPUT; PIN 28
V
i(Y)(b-w)
luminance input voltage
(black-to-white value)
GAI = 0 − 1.0 1.5 V
Z
i
input impedance 10 −−MΩ
C
i
input capacitance −− 5pF
I
i(Y)(clamp)
input current during clamping −25 0 +25 µA
U/V INPUTS; PINS 27 AND 26
V
i(U)(p-p)
U input signal amplitude
(peak-to-peak value)
− 1.33 2.0 V
V
i(V)(p-p)
V input signal amplitude
(peak-to-peak value)
− 1.05 1.6 V
Z
i
input impedance 10 −−MΩ
C
i
input capacitance −− 5pF
I
i(UV)(clamp)
input current during clamping −20 0 +25 µA
RGB-1 INPUT (SCART/VGA);PINS 30 TO 32; note 3
V
i(b-w)
input signal amplitude
(black-to-white value)
− 0.7 1.0 V
∆V
o
difference between black level of
YUV and RGB-1 signals at the
outputs
−− 10 mV
Z
i
input impedance 10 −−MΩ
C
i
input capacitance −− 5pF
I
i(clamp)
input current during clamping −25 0 +25 µA
∆t
d
delay difference for the three
channels
note 5 − 0 − ns
 Loading...
Loading...