Philips TDA9321H-N2, TDA9321H-N1 Datasheet

DATA SH EET
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1998 Dec 16
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TDA9321H
I
2
C-bus controlled TV input
processor

1998 Dec 16 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
FEATURES
• Multistandard Vision IF (VIF) circuit with Phase-Locked
Loop (PLL) demodulator
• Sound IF (SIF) amplifier with separate input for single
reference Quasi Split Sound (QSS) mode and separate
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) circuit
• AM demodulator without extra reference circuit
• Switchable group delay correction circuit which can be
used to compensate the group delay pre-correction of
the B/G TV standard in multistandard TV receivers
• Several (I
2
C-bus controlled) switch outputs which can
be used to switch external circuits such as sound traps,
etc.
• Flexible source selection circuit with 2 external
CVBS inputs, 2 Luminance (Y) and Chrominance (C)
(or additional CVBS) inputs and 2 independently
switchable outputs
• Comb filter interface with CVBS output and Y/C input
• Integrated chrominance trap circuit
• Integrated luminance delay line with adjustable delay
time
• Integrated chrominance band-pass filter with switchable
centre frequency
• Multistandard colour decoder with 4 separate pins for
crystal connection and automatic search system
• PALplus helper demodulator
• Possible blanking of the helper signals for PALplus and
EDTV-2
• Internal baseband delay line
• Two linear RGB inputs with fast blanking; the
RGB signals are converted to YUV signals before they
are supplied to the outputs; one of the RGB inputs can
also be used as YUV input
• Horizontal synchronization circuit with switchable time
constant for the PLL and Macrovision/subtitle gating
• Horizontal synchronization pulse output or clamping
pulse input/output
• Vertical count-down circuit
• Vertical synchronization pulse output
• Two-level sandcastle pulse output
• I
2
C-bus control of various functions
• Low dissipation.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA9321H (see Fig.1) is an input processor for
‘High-end’ television receivers. It contains the following
functions:
• Multistandard IF amplifier with PLL demodulator
• QSS-IF amplifier and AM sound demodulator
• CVBS and Y/C switch with various inputs and outputs
• Multistandard colour decoder which can also decode the
PALplus helper signal
• Integrated baseband delay line (64 µs)
• Sync processor which generates the horizontal and
vertical drive pulses for the feature box
(100 Hz applications) or display processor
(50 Hz applications).
The supply voltage for the TDA9321H is 8 V.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA9321H QFP64 plastic quad flat package; 64 leads (lead length 1.95 mm);
body 14 × 20 × 2.8 mm
SOT319-2
1998 Dec 16 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
P
supply voltage (pins VP1and VP2) 7.2 8.0 8.8 V
I
P
supply current (pins VP1and VP2) − 120 − mA
Input signals
V
i(VIF)(rms)
VIF amplifier sensitivity (RMS value) − 35 −µV
V
i(SIF)(rms)
SIF amplifier sensitivity (RMS value) − 30 −µV
V
i(CVBS/Y)(p-p)
CVBS or Y input signal (peak-to-peak value) − 1.0 − V
V
i(C)(p-p)
chrominance input signal (burst amplitude)
(peak-to-peak value)
− 0.3 − V
V
i(RGB)(p-p)
RGB input signal (peak-to-peak value) − 0.7 − V
Output signals
V
o(VIFO)(p-p)
demodulated CVBS output signal (peak-to-peak value) − 2.5 − V
V
o(CVBSPIP)(p-p)
CVBS output signal for Picture-In-Picture
(peak-to-peak value)
− 1.0 − V
V
o(CVBSTXT)(p-p)
CVBS output signal for teletext (peak-to-peak value) − 2.0 − V
I
o(TAGC)
tuner AGC output current 0 − 5mA
V
o(QSS)(rms)
QSS output signal (RMS value) − 100 − mV
V
o(AM)(rms)
demodulated AM sound output signal (RMS value) − 500 − mV
V
o(V)(p-p)
−V output signal (peak-to-peak value) − 1.05 − V
V
o(U)(p-p)
−U output signal (peak-to-peak value) − 1.33 − V
V
o(Y)(b-w)
Y output signal (black-to-white value) − 1.0 − V
V
o(hor)
horizontal pulse output − 5 − V
V
o(ver)
vertical pulse output − 5 − V
V
o(sc)(p-p)
subcarrier output signal (peak-to-peak value) − 250 − mV

1998 Dec 16 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I
2
C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
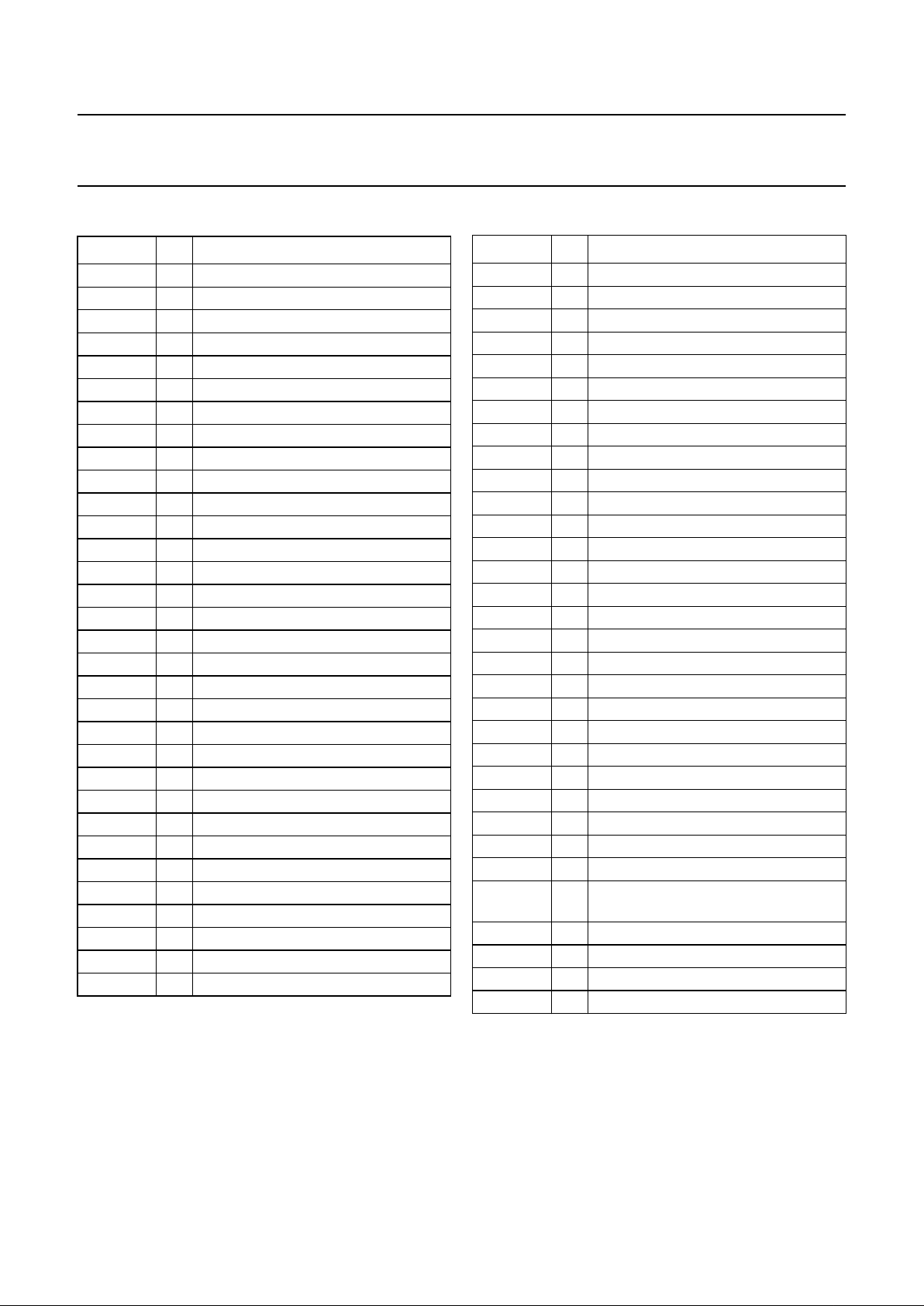
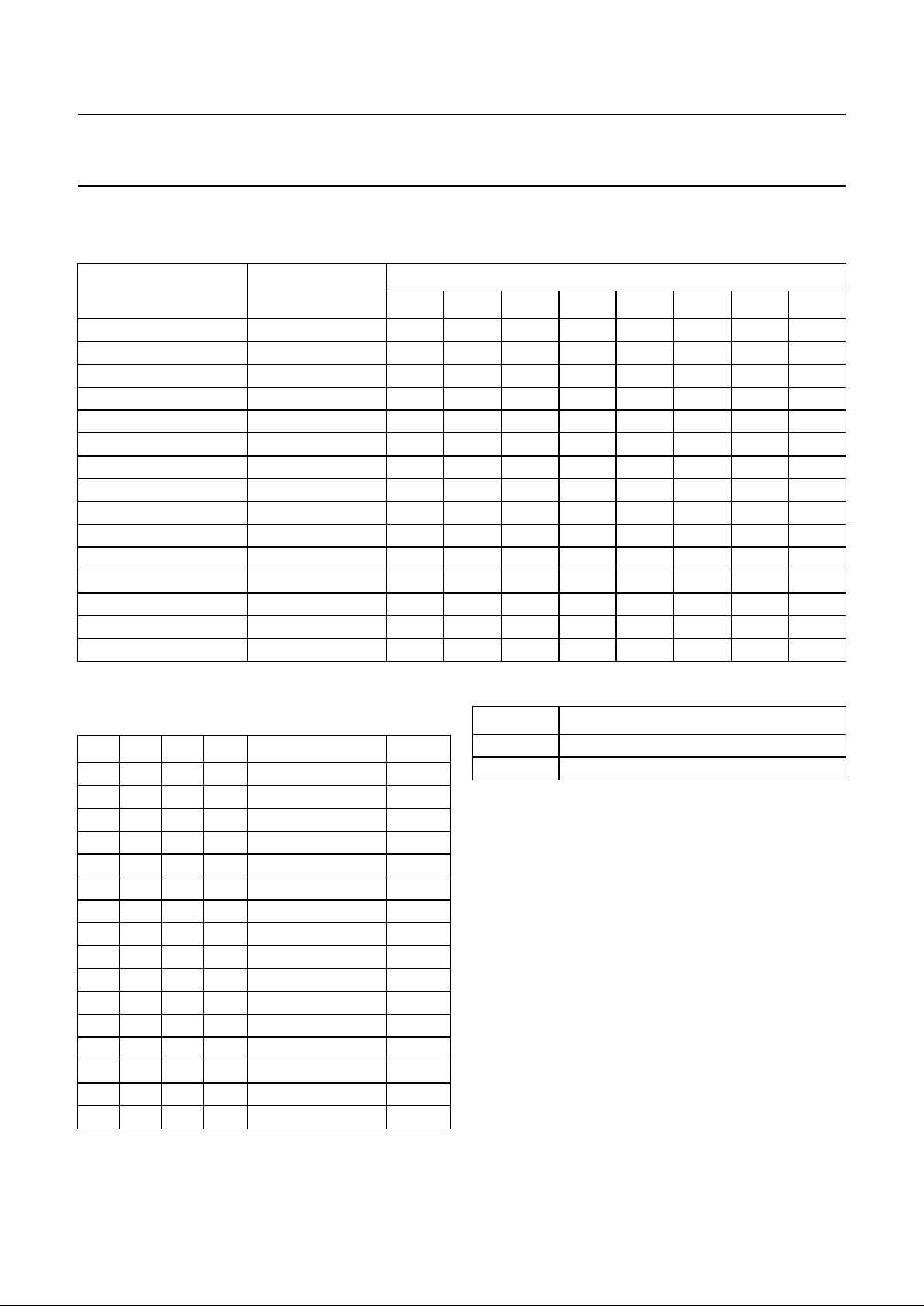
BLOCK DIAGRAM
MGR473
a
ndbook, full pagewidth
32
8
7
10
12
13
62
VIFVCO2
VIFVCO1
TAGC
AFC TOP
mute
Y/CVBS
helper
hue
f
sc
switch control
VIF AMPLIFIER
AND PLL
DEMODULATOR
AGC/AFC
VIDEO AMPLIFIER
MUTE
SUPPLY
PULSE
GENERATOR
SOUND
TRAP
GROUP DELAY
CORRECTION
VIDEO SWITCHES
AND
CONTROL
VIFO
GDI
GDO
48
AS
24
C4
23
CVBS/Y4
22
SW1
21
C3
20
CVBS/Y3
19
SW0
18
CVBS2
17
AV2
16
CVBS1
15
AV1
14
CVBS
int
64
VIF1 VIF2
DEC
VIF
VCO AND
HORIZONTAL
PLL
VIDEO
IDENTIFICATION
IDENT
SYNC
SEPARATOR
AUTOMATIC
CHROMINANCE
CONTROL
CLOCHE
FILTER
VERTICAL
DIVIDER
SYNC
IN-LOCK
DETECTOR
FILTER
TUNING
I2C-BUS
TRANSCEIVER
Y-DELAY
Y-delay
RGB2
VO
Y-SWITCH
AND TRAPS
SECAM
DECODER
RGB MATRIX
Y/U/V
SWITCH
BASEBAND
DELAY LINE
PAL(NTSC)/
SECAM SWITCH
Y/C
DETECTOR
BANDPASS
FILTER
subcarrier
COMB FILTER
PAL/NTSC
PLL
HUE CONTROL
SYSTEM
IDENTIFICATION
PAL/NTSC
DEMODULATOR
63
SIF AMPLIFIER
AGC
QSS MIXER
AM DEMODULATOR
1
SIF1
60
HA/CLP59SCO
61
VA
46
SCL47SDA
36
37
GI1RI138BI139RGB1
64
SIF2
DEC
SIF
11
33
V
P1
5
QSS/AM
45
VP2DEC
DIG
35
DEC
BG
VIFPLL
VERTICAL
SYNC
SEPARATOR
58
40
BI2
43
GI2
42
RI2
41
53
51
UO
V
U
VU
B-YR-Y
Y
Y
Y
50
YO
49
DEC
SEC
PH1LF
5756555430
REFO
29
CCF28YCF27SYS2
25
SYS1
26
CVBSCF
32
CVBSPIP
34
CVBSTXT
52
LFBP
XTALD
XTALC
XTALB
XTALA
44
GND3
31
GND2
9
GND1
TDA9321H
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1998 Dec 16 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
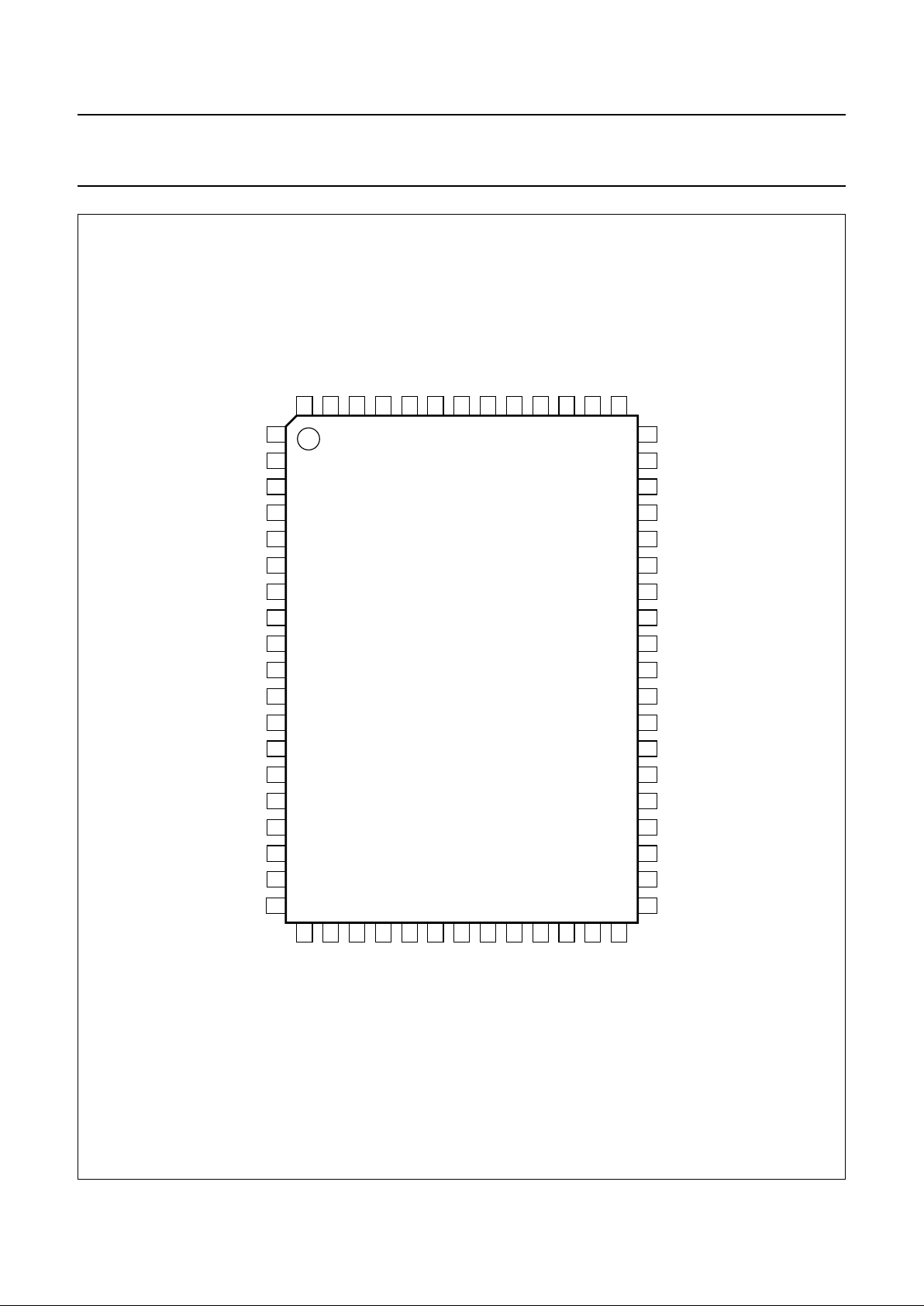
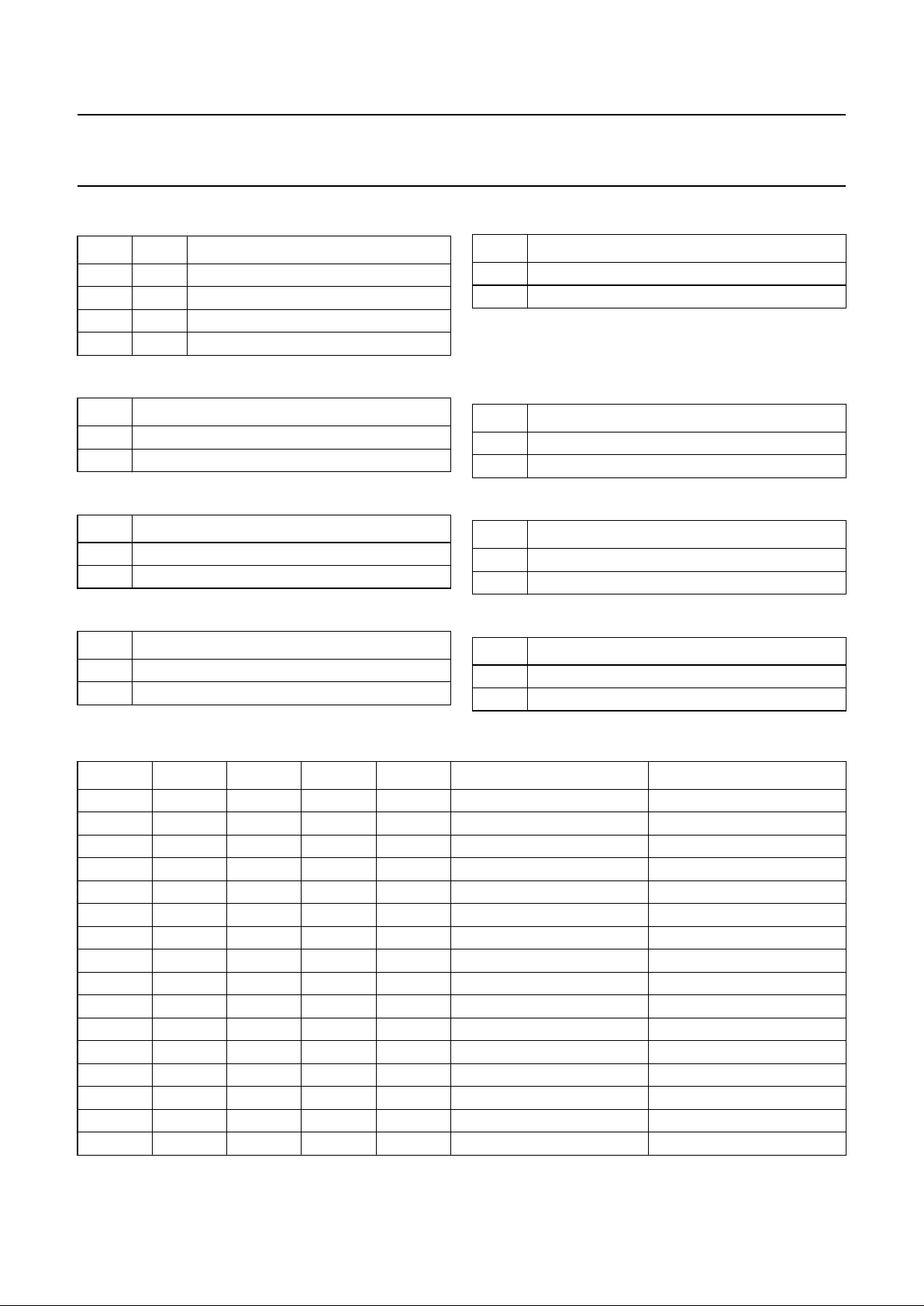
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
DEC
SIF
1 SIF AGC decoupling
VIF1 2 VIF input 1
VIF2 3 VIF input 2
DEC
VIF
4 VIF AGC decoupling
QSS/AM 5 combined QSS and AM sound output
VIFPLL 6 VIF PLL filter
VIFVCO1 7 VIF VCO tuned circuit 1
VIFVCO2 8 VIF VCO tuned circuit 2
GND1 9 main supply ground
VIFO 10 VIF output
V
P1
11 positive supply 1 (+8 V)
GDI 12 group delay correction input
GDO 13 group delay correction output
CVBS
int
14 internal CVBS input
AV1 15 AV input 1
CVBS1 16 CVBS input 1
AV2 17 AV input 2
CVBS2 18 CVBS input 2
SW0 19 switch output bit 0 (I
2
C-bus)
CVBS/Y3 20 CVBS or luminance input 3
C3 21 chrominance input 3
SW1 22 switch output bit 1 (I
2
C-bus)
CVBS/Y4 23 CVBS or luminance input 4
C4 24 chrominance input 4
SYS1 25 system output 1 for comb filter
CVBSCF 26 CVBS output for comb filter
SYS2 27 system output 2 for comb filter
YCF 28 luminance input from comb filter
CCF 29 chrominance input from comb filter
REFO 30 reference output (subcarrier)
GND2 31 digital supply ground
CVBSPIP 32 CVBS output for Picture-In-Picture
DEC
DIG
33 digital supply decoupling
CVBSTXT 34 CVBS output for teletext
DEC
BG
35 band gap decoupling
RI1 36 red input 1
GI1 37 green input 1
BI1 38 blue input 1
RGB1 39 RGB insertion input 1
RGB2 40 RGB insertion input 2
RI2 41 red input 2
GI2 42 green input 2
BI2 43 blue input 2
GND3 44 ground 3
V
P2
45 positive supply 2 (+8 V)
SCL 46 serial clock input (I
2
C-bus)
SDA 47 serial data input/output (I
2
C-bus)
AS 48 address select input (I
2
C-bus)
YO 49 luminance output
UO 50 U-signal output
VO 51 V-signal output
LFBP 52 loop filter burst phase detector
DEC
SEC
53 SECAM PLL decoupling
XTALA 54 crystal A (4.433619 MHz)
XTALB 55 crystal B (3.582056 MHz)
XTALC 56 crystal C (3.575611 MHz)
XTALD 57 crystal D (3.579545 MHz)
PH1LF 58 phase 1 loop filter
SCO 59 sandcastle pulse output
HA/CLP 60 horizontal pulse output or clamp pulse
input/output
VA 61 vertical pulse output
TAGC 62 tuner AGC output
SIF1 63 SIF input 1
SIF2 64 SIF input 2
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
1998 Dec 16 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
handbook, full pagewidth
TDA9321H
MGR474
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
DEC
SIF
VIF1
VIF2
DEC
VIF
QSS/AM
VIFPLL
VIFVCO1
VIFVCO2
GND1
VIFO
V
P1
GDI
GDO
CVBS
int
AV1
CVBS1
AV2
CVBS2
SW0
VO
UO
YO
AS
SDA
SCL
V
P2
GND3
BI2
GI2
RI2
RGB2
RGB1
BI1
GI1
RI1
DEC
BG
CVBSTXT
DEC
DIG
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
SIF2
SIF1
TAGCVAHA/CLP
SCO
PH1LF
XTALD
XTALC
XTALB
XTALA
DEC
SEC
LFBP
CVBS/Y3
C3
SW1
CVBS/Y4
C4
SYS1
CVBSCF
SYS2
YCF
CCF
REFO
GND2
CVBSPIP

1998 Dec 16 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Vision IF amplifier
The VIF amplifier contains 3 AC-coupled control stages
with a total gain control range which is higher than 66 dB.
The sensitivity of the circuit is comparable with that of
modern IF-ICs.
The video signal is demodulated by a PLL carrier
regenerator. This circuit contains a frequency detector and
a phase detector. During acquisition the frequency
detector will tune the VCO to the correct frequency.
The initial adjustment of the oscillator is realized via the
I
2
C-bus. The switching between SECAM L and L’ can also
be realized via the I2C-bus. After lock-in the phase
detector controls the VCO so that a stable phase
relationship between the VCO and the input signal is
achieved. The VCO operates at twice the IF frequency.
The reference signal for the demodulator is obtained by
means of a frequency divider circuit. To get a good
performance for phase modulated carrier signals the
control speed of the PLL can be increased by bit FFI.
The AFC output is obtained by using the VCO control
voltage of the PLL and can be read via the I2C-bus.
For fast search tuning systems the window of the AFC can
be increased with a factor 3. The setting is realized with
bit AFW.
The AGC detector operates on top-sync and
top-white-level. The demodulation polarity is switched via
the I2C-bus. The AGC detector time constant capacitor is
connected externally; this is mainly because of the
flexibility of the application. The time constant of the AGC
system during positive modulation is rather long, this is to
avoid visible variations of the signal amplitude. To improve
the speed of the AGC system a circuit has been included
which detects whether the AGC detector is activated every
frame period. When, during 3 field periods, no action is
detected the speed of the system is increased. For signals
without peak white information the system switches
automatically to a gated black level AGC. Because a black
level clamp pulse is required for this mode of operation the
circuit will only switch to black level AGC in the internal
mode.
The circuits contain a video identification (ident) circuit
which is independent of the synchronization circuit.
Therefore search tuning is possible when the display
section of the receiver is used as a monitor. However, this
ident circuit cannot be made as sensitive as the slower
sync ident circuit (bit SL). It is recommended to use both
ident outputs to obtain a reliable search system. The ident
output is supplied to the tuning system via the I2C-bus.
The input of the ident circuit is connected to pin 14
(see Fig.3). This has the advantage that the ident circuit
can also be made operative when a scrambled signal is
received (descrambler connected between pins 10
and 14). A second advantage is that the ident circuit can
be used when the VIF amplifier is not used (e.g. with
built-in satellite tuners). The video ident circuit can also be
used to identify the selected CBVS or Y/C signal.
The switching between the 2 modes can be realized with
bit VIM.
The TDA9321H contains a group delay correction circuit
which can be switched between the BG and a flat group
delay response characteristic. This has the advantage that
in multistandard receivers no compromise has to be made
for the choice of the SAW filter. Both the input and output
of the group delay correction circuit are externally
available so that the sound trap can be connected
between the VIF output and the group delay correction
input. The output signal of the correction circuit can be
supplied to the internal video processing circuit and to the
external SCART plug.
The IC has several (I
2
C-bus controlled) output ports which
can be used to switch sound traps or other external
components.
When the VIF amplifier is not used the complete VIF
amplifier can be switched off with bit IFO.
Sound circuit
The SIF amplifier is similar to the VIF amplifier and has a
gain control range of approximately 66 dB. The AGC
circuit is related to the SIF carrier levels (average level of
AM or FM carriers) and ensures a constant signal
amplitude to the AM demodulator and the QSS mixer.
The single reference QSS mixer is realized by a multiplier.
In this multiplier the SIF signal is converted to the
intercarrier frequency by mixing it with the regenerated
picture carrier from the VCO. The mixer output signal is
supplied to the output via a high-pass filter for attenuation
of the residual video signals. With this system a high
performance hi-fi stereo sound processing can be
achieved.
The AM sound demodulator is realized by a multiplier.
The modulated SIF signal is multiplied in phase with the
limited SIF signal. The demodulator output signal is
supplied to the output via a low-pass filter for attenuation
of the carrier harmonics.

1998 Dec 16 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
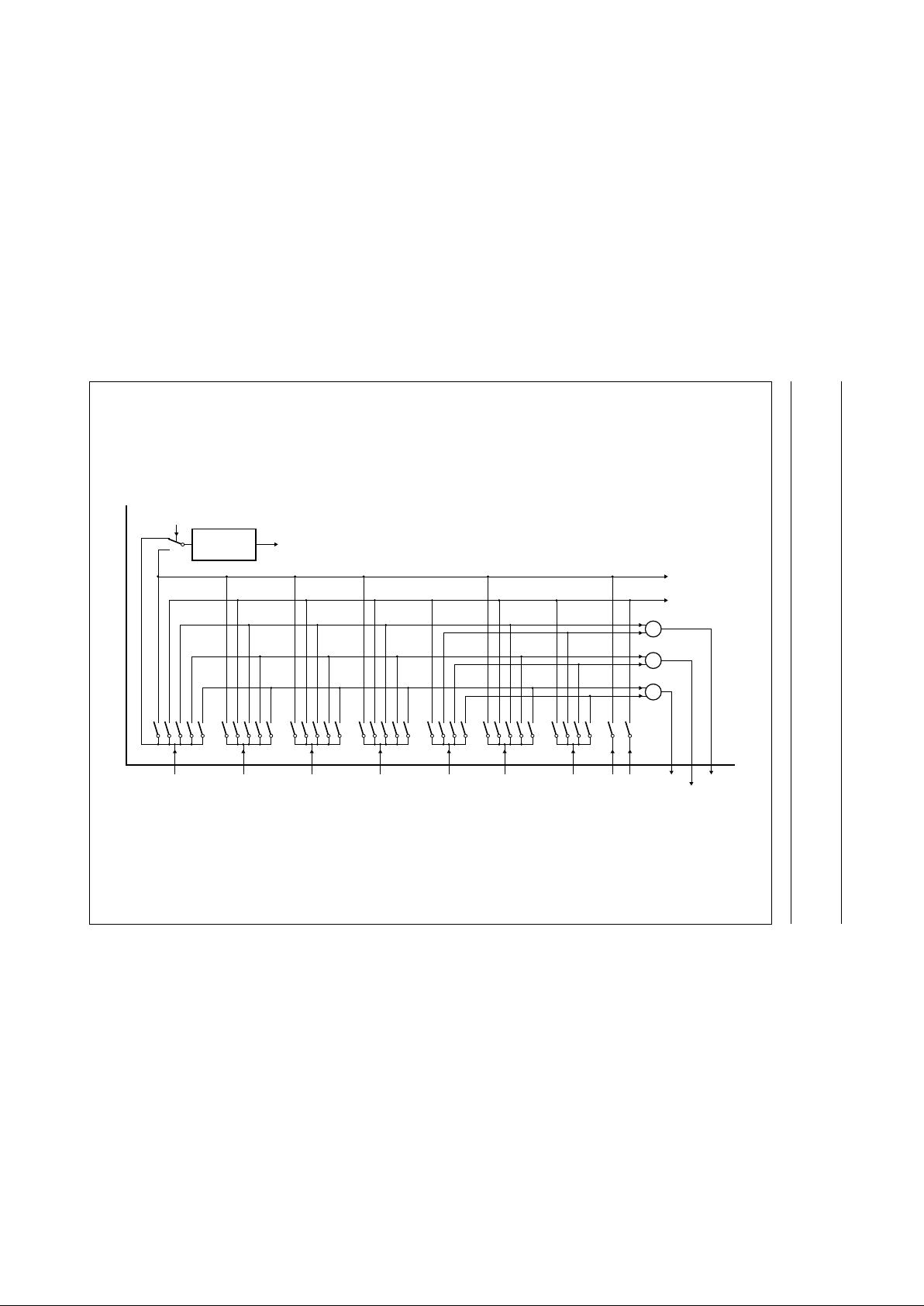
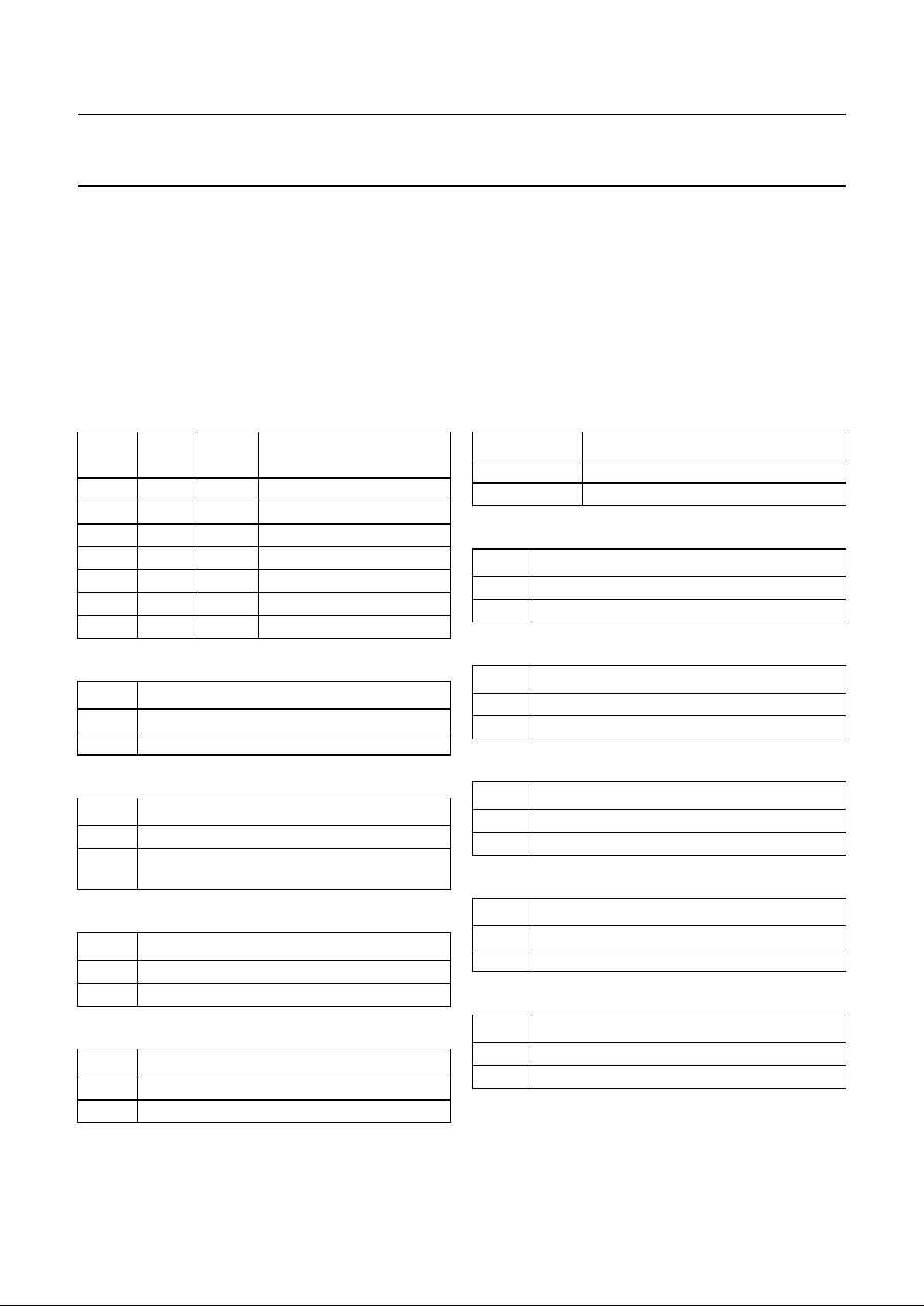
Video switches
The circuit has 3 CVBS inputs (1 internal and 2 externals)
and 2 Y/C inputs. The Y/C inputs can also be used as
additional CVBS inputs. The switch configuration is given
in Fig.3. The various sources can be selected via the
I2C-bus.
The circuit can be set in a mode in which it automatically
detects whether a CVBS or a Y/C signal is supplied to the
Y/C inputs. In this mode the TV-standard identification first
takes place on the added Y/CVBS and the C input signal.
Then both chrominance input signal amplitudes are
checked once and the input signal with the highest burst
signal amplitude is selected. The result of the detection
can be read via the I
2
C-bus.
The IC has 2 inputs (AV1 and AV2) which can be used to
read the status levels of pin 8 of the SCART plug.
The information is available in the output status byte 02 in
bits D0 to D3.
The 3 outputs of the video switches (CVBSCF, CVBSTXT
and CVBSPIP) can be independently switched to the
various input signals. The names are just arbitrary and it is,
for instance, possible to use the CVBSCF signal to drive
the comb filter and the teletext decoder in parallel and to
supply the CVBSTXT signal to the SCART plug (via an
emitter follower).
For comb filter interfacing the circuit has the CVBSCF
output, a 3rd Y/C input, a reference signal output REFO
and 2 control pins (SYS1 and SYS2) which switch the
comb filter to the standard of the incoming signal (as
detected by the ident circuit of the colour decoder). When
a signal is recognized which can be combed and the comb
filter is enabled by bit ECMB the Y/C signals coming from
the comb filter are automatically selected. This is indicated
via bit CMB in output status byte 02 (D5). For signals
which cannot be combed (such as SECAM or
black-to-white signals) the Y/C signals coming from the
comb filter are not selected.
Chrominance and luminance processing
The circuits contain a chrominance band-pass, a SECAM
cloche filter and a chrominance trap circuit. The filters are
realized by means of gyrator circuits and they are
automatically calibrated by comparing the tuning
frequency with the crystal frequency of the decoder.
The luminance delay line is also realized by means of
gyrator circuits. The centre frequency of the chrominance
band-pass filter is switchable via the I
2
C-bus so that the
performance can be optimized for ‘front-end’ signals and
external CVBS signals.
The luminance output signal which is derived from the
incoming CVBS or Y/C signal can be varied in amplitude
by means of a separate gain setting control via the I
2
C-bus
control bits GAI1 and GAI0. The gain variation which can
be realized with these bits is −1to+2dB.
Colour decoder
The colour decoder can decode PAL, NTSC and SECAM
signals. The PAL/NTSC decoder contains an
alignment-free crystal oscillator with 4 separate pins for
crystal connection, a killer circuit and two colour difference
demodulators. The 90° phase shift for the reference signal
is produced internally.
Because it is possible to connect 4 different crystals to the
colour decoder, all colour standards can be decoded
without external switching circuits. Which crystals are
connected to the decoder must be indicated via the
I
2
C-bus. The crystal connection pins which are not used
must be left open-circuit.
The horizontal oscillator is calibrated by means of the
crystal frequency of the colour PLL. For a reliable
calibration it is very important that the crystal indication
bits XA to XD are not corrupted. For this reason
bits XA to XD can be read in the output bytes so that the
software can check the I2C-bus transmission.
The IC contains an Automatic Colour Limiting (ACL) circuit
which is switchable via the I2C-bus and prevents
oversaturation occuring when signals with a high
chrominance-to-burst ratio are received. The ACL circuit is
designed such that it only reduces the chrominance signal
and not the burst signal. This has the advantage that the
colour sensitivity is not affected by this function. The ACL
function is mainly intended for NTSC signals but it can also
be used for PAL signals. For SECAM signals the ACL
function should be switched off.
The SECAM decoder contains an auto-calibrating PLL
demodulator which has two references: the 4.43 MHz
subcarrier frequency which is obtained from the crystal
oscillator which is used to tune the PLL to the desired
free-running frequency and the band gap reference to
obtain the correct absolute value of the output signal.
The VCO of the PLL is calibrated during each vertical
blanking period, when the IC is in search or SECAM mode.
The circuit can also decode the PALplus helper signal and
can insert the various reference signals: set-ups and
timing signals which are required for the PALplus decoder
ICs.
The baseband delay line (TDA4665 function) is integrated.
1998 Dec 16 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I
2
C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
handbook, full pagewidth
MGR475
TDA9321H
14 16 18 20 21 23 28 2924
CVBSCF
26
+
CVBSTXT
34
CVBSPIP
32
+
+
to luminance/sync
processing
to chrominance
processing
VIDEO
IDENTIFICATION
VIM
ident
CVBS
int
CVBS1 CVBS2 C3 CVBS/Y4CVBS/Y3 C4 YCF CCF
Fig.3 Video switches and interfacing of video ident.

1998 Dec 16 10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
RGB switch and matrix
The IC has 2 RGB inputs with fast switching. The switching
of the various sourcing is controlled via the I2C-bus and the
condition of the switch inputs can be read from the I2C-bus
status bytes. If the RGB signals are not synchronous with
the selected decoder input signal, an external clamp pulse
has to be supplied to the HA/CLP input. The IC must be set
in this mode via the I2C-bus. In that case the vertical pulse
is suppressed by switching the VA output in a
high-impedance off-state.
When an external RGB signal is mixed with the internal
YUV signal it is necessary to switch-off the PALplus
demodulation. To detect the presence of a fast blanking a
circuit is added which forces bits MACP and HD to zero if
a blanking pulse is detected in 2 consecutive lines. This
system is chosen to prevent switching-off at every spike
which is detected on the fast blanking input.
The IC has the possibility to use the RGB1 input as YUV
input. This function can be enabled by means of bit YUV in
subaddress 0A (D3). When switched to the YUV input the
input signals must have the same amplitude and polarity
as the YUV output signals. The Y signal has to be supplied
to the GI1 input, the U signal to the BI1 input and the
V signal to the RI1 input.
Synchronization circuit
The sync separator is preceded by a controlled amplifier
which adjusts the sync pulse amplitude to a fixed level.
These pulses are fed to the slicing stage which operates at
50% of the amplitude. The separated sync pulses are fed
to the phase detector and to the coincidence detector. This
coincidence detector is used to detect whether the line
oscillator is synchronized and can also be used for
transmitter identification. This circuit can be made less
sensitive with bit STM. This mode can be used during
search tuning to avoid the tuning system stopping at very
weak input signals. The PLL has a very high statical
steepness so that the phase of the picture is independent
of the line frequency.
For the horizontal output pulse 2 conditions are possible:
• An HA pulse which has a phase and width which is
identical to the incoming horizontal sync pulse
• A clamp pulse (CLP) which has a phase and width which
is identical to the clamp pulse in the sandcastle pulse.
The HA/CLP signal is generated by means of an oscillator
which is running at a frequency of 440 × f
hor
. Its frequency
is divided by 440 to lock the first loop to the incoming
signal. The time constant of the loop can be forced by the
I2C-bus (fast or slow).
If required the IC can select the time constant depending
on the noise content of the incoming video signal.
The free-running frequency of the oscillator is determined
by a digital control circuit which is locked to the reference
signal of the colour decoder. When the IC is switched on
the HA/CLP is suppressed and the oscillator is calibrated
as soon as all subaddress bytes have been sent. When the
frequency of the oscillator is correct the HA/CLP signal is
switched on again. When the coincidence detector
indicates an out-of-lock situation the calibration procedure
is repeated.
The VA pulse is obtained via a vertical count-down circuit.
The count-down circuit has various windows depending on
the incoming signal (50 or 60 Hz standard or
non-standard). The count-down circuit can be forced in
various modes via the I
2
C-bus. To obtain short switching
times of the count-down circuit during a channel change
the divider can be forced in the search window by means
of bit NCIN.
I
2
C-BUS SPECIFICATION
The slave address of the IC is given in Table 1. Bit A1 is
controlled via pin AS. When pin AS is connected to
pin GND2 it is at logic 0 and when connected to VP2 it is at
logic 1. When pin AS is left open-circuit it is connected to
ground via an internal pull-up resistor. The circuit operates
at clock frequencies of up to 400 kHz.
Table 1 Slave address bits
Start-up procedure
Read the status bytes until bit POR = 0 and send all
subaddress bytes. It is advised to check the I
2
C-bus
transmission by reading the output status bits SXA
to SXD. This ensures a good operation of the calibration
system of the horizontal oscillator. The horizontal output
signal is switched on when the oscillator is calibrated.
Each time before the data in the IC is refreshed, the status
bytes must be read. If bit POR = 1, then the procedure
mentioned above must be carried out to restart the IC.
When this procedure is not carried out the horizontal
frequency may be incorrect after power-up or after a power
dip.
The valid subaddresses are 00 to 0E. Subaddresses
FE and FF are reserved for test purposes. Auto-increment
mode is available for the subaddresses.
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 R/W
100011/011/0
1998 Dec 16 11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
Inputs and outputs
Table 2 Input status bits
FUNCTION
SUBADDRESS
(HEX)
DATA BYTE
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Colour decoder 0 00 CM3 CM2 CM1 CM0 XD XC XB XA
Colour decoder 1 01 MACP HOB HBC HD FCO ACL CB BPS
Luminance 02 0 0 GAI1 GAI0 YD3 YD2 YD1 YD0
Hue control 03 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Spare 04 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Synchronization 0 05 FORF FORS FOA FOB 0 VIM POC VID
Synchronization 1 06 0 0 0 0 BSY HO EMG NCIN
Spare 07 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Video switches 0 08 0 0 0 ECMB DEC3 DEC2 DEC1 DEC0
Video switches 1 09 0 PIP2 PIP1 PIP0 0 TXT2 TXT1 TXT0
RGB switch 0A 0 0 0 0 YUV ECL IE2 IE1
Output switches 0B 0 0 0 0 0 0 OS1 OS0
Vision IF 0C FFI IFO GD MOD AFW IFS STM VSW
Tuner takeover 0D 0 0 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Adjustment IF-PLL 0E L’FA A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
INPUT CONTROL BITS
Table 3 Colour decoder mode
CM3 CM2 CM1 CM0 DECODER MODE XTAL
0 0 0 0 PAL/NTSC/SECAM A
0 0 0 1 PAL/NTSC A
0010PAL A
0 0 1 1 NTSC A
0 1 0 0 SECAM A
0 1 0 1 PAL/NTSC B
0110PAL B
0 1 1 1 NTSC B
1 0 0 0 PAL/NTSC/SECAM A/B/C/D
1 0 0 1 PAL/NTSC C
1010PAL C
1 0 1 1 NTSC C
1 1 0 0 PAL/NTSC A/B/C/D
1 1 0 1 PAL/NTSC D
1110PAL D
1 1 1 1 NTSC D
Table 4 Crystal indication
Note
1. When a comb filter is used, the various crystals must
be connected to the IC as indicated in the pinning
diagram. This is required because the ident system
switches automatically to the comb filter when a signal
is identified which can be combed (correct
combination of colour standard and crystal frequency).
For applications without comb filter only the crystal on
pin XTALA is important (4.43 MHz); to pins XTALB to
XTALD an arbitrary 3.5 MHz crystal can be connected.
XA to XD CONDITION
0 crystal not present
1 crystal present; note 1

1998 Dec 16 12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
Table 5 Motion Adaptive Colour Plus (MACP)
Note
1. The black set-up will only be present in a norm sync
condition.
Table 6 Helper output blanking (PALplus/EDTV-2)
Note
1. X = don’t care.
Table 7 PALplus helper demodulation active
Note
1. Black and helper set-up will only be present in a norm
sync condition.
Table 8 Forced colour on
Table 9 Automatic colour limiting
MACP MODE
0 internal 4.43 MHz trap used
1 external MACP chrominance filtering used;
4.43 MHz trap bypassed and black set-up
200 mV; note 1
HOB HBC SNR BLANKING
0X
(1)
X
(1)
off
10X
(1)
on
110off
111on
HD CONDITIONS
0off
1 on; PALplus mode with helper set-up 400 mV
and black set-up 200 mV; note 1
FCO MODE
0 not active
1 active
ACL COLOUR LIMITING
0 not active
1 active
Table 10 Chrominance band-pass centre frequency
Table 11 Bypass of chrominance baseband delay line
Table 12 Gain luminance channel
Table 13 Y-delay adjustment; note 1
Note
1. For an equal delay of the luminance and chrominance
signal the delay must be set at a value of 280 ns
(YD3 to YD0 = 1011). This is only valid for a CVBS
signal without group delay distortions.
Table 14 Forced field frequency
Note
1. When switched to this mode the divider will directly
switch to forced 60 Hz only.
CB CENTRE FREQUENCY
0f
c
1 1.1 × f
c
BPS DELAY LINE MODE
0 active
1 bypassed
GAI1 GAI0 GAIN SETTING
00−1dB
010dB
1 0 +1 dB
1 1 +2 dB
YD0 to YD3 Y-DELAY
YD3 YD3 × 160 ns +
YD2 YD2 × 160 ns +
YD1 YD1 × 80 ns +
YD0 YD0 × 40 ns
FORF FORS FIELD FREQUENCY
0 0 auto (60 Hz when line not
synchronized)
0 1 forced 60 Hz; note 1
1 0 keep last detected field frequency
1 1 auto (50 Hz when line not
synchronized)
1998 Dec 16 13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
Table 15 Phase 1 (ϕ1) time constant; see also Table 57
Table 16 Video ident mode
Table 17 Synchronization mode
Table 18 Video ident mode
FOA FOB MODE
0 0 normal
0 1 slow
1 0 slow or fast
1 1 fast
VIM MODE
0 ident coupled to internal CVBS (pin 14)
1 ident coupled to selected CVBS
POC MODE
0 active
1 not active
VID VIDEO IDENT MODE
0 ϕ
1
loop switched-on and off
1 not active
Table 19 Blanked sync on pin YO
Note
1. Except for PALplus with black set-up.
Table 20 Condition of horizontal output
Table 21 Enable ‘Macrovision/subtitle’ gating
Table 22 Vertical divider mode
BSY CONDITIONS
0 unblanked sync; note 1
1 blanked sync
HO CONDITIONS
0 clamp pulse available on pin HA/CLP
1 horizontal pulse available on pin HA/CLP
EMG MODE
0 disable gating
1 enable gating
NCIN VERTICAL DIVIDER MODE
0 normal operation
1 switched to search window
Table 23 Video switch control
ECMB
(1)
DEC3 DEC2 DEC1 DEC0 SELECTED SIGNAL SIGNAL TO COMB
0000X
(2)
CVBS
int
CVBS
int
00010CVBS1 CVBS1
00011CVBS2 CVBS2
00100CVBS3 CVBS3
00101Y3/C3 Y3 + C3
00110CVBS4 CVBS4
00111Y4/C4 Y4 + C4
01100AUTO Y3/C3; note 3 CVBS3 or Y3 + C3
01110AUTO Y4/C4; note 3 CVBS4 or Y4 + C4
1000X
(2)
YCF/CCF CVBS
int
10010YCF/CCF CVBS1
10011YCF/CCF CVBS2
10100YCF/CCF CVBS3
10110YCF/CCF CVBS4
11100AUTO COMB3; note 4 CVBS3 or Y3 + C3
11110AUTO COMB4; note 4 CVBS4 or Y4 + C4
1998 Dec 16 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
I2C-bus controlled TV input processor
TDA9321H
Notes
1. When bit ECMB = 1 the subcarrier frequency is present on pin 30. The YCF and CCF signals coming from the comb
filter are only switched on when a signal is received that can be combed.
2. X = don’t care.
3. AUTO YC means the decoder switches between CVBS and Y/C depending on the presence of the burst signal on
these signals.
4. AUTO COMB means the decoder switches to Y/C mode if the burst is present on the C input and to the comb filter
output if the burst is present on the CVBS signal.
Table 24 Video switch outputs
Table 25 Enable YUV input (on RGB1 input)
Table 26 External RGB clamp mode
Table 27 Enable fast blanking RGB1
Table 28 Enable fast blanking RGB2
TXT2
PIP2
TXT1
PIP1
TXT0
PIP0
OUTPUT SIGNAL TXT
OUTPUT SIGNAL PIP
00−CVBS
int
0 1 0 CVBS1
0 1 1 CVBS2
1 0 0 CVBS3
101Y3+C3
1 1 0 CVBS4
111Y4+C4
YUV MODE
0 RGB1 input active
1 YUV input active
ECL MODE
0 off; internal clamp pulse used
1 on; external clamp pulse has to be supplied to
pin HA/CLP
IE1 FAST BLANKING
0 not active
1 active
IE2 FAST BLANKING
0 not active
1 active
Table 29 Output switches OS0 and OS1
Table 30 Fast filter IF-PLL
Table 31 IF circuit not active
Table 32 Group delay correction
Table 33 Modulation standard
Table 34 AFC window
OS0; OS1 CONDITIONS
0 output = LOW
1 output = HIGH
FFI CONDITIONS
0 normal time constant
1 fast time constant
IFO MODE
0 normal operation of IF amplifier
1 IF amplifier switched off
GD GROUP DELAY CHARACTERISTIC
0 flat
1 according to BG standard
MOD MODULATION
0 negative
1 positive
AFW AFC WINDOW
0 normal
1 enlarged
 Loading...
Loading...