Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA8303
TDA8303A
Small signal combination IC for
black/white TV
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
July 1992
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
FEATURES
• Video IF amplifier with synchronous demodulator
• Automatic gain control (AGC) detector suitable for
negative modulation
• AGC tuner
• Automatic frequency control (AFC) circuit with
sample-and-hold
• Video preamplifier
• Sound IF amplifier and demodulator
• DC volume control or separate supply for starting the
horizontal oscillator
• Audio preamplifier
• Horizontal synchronization circuit with two control loops
• Vertical synchronization (divider system) and sawtooth
generation with automatic amplitude adjustment for 50
and 60 Hz
• Transmitter identification (mute)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8303/TDA8303A combines all small signal
functions (except the tuner) which are required for a
monochrome television receiver. For a complete black and
white receiver only the output stages for video, sound,
horizontal and vertical deflection and a tuner have to be
added.
The TDA8303 is for applications with npn tuners and the
TDA8303A for pnp tuners.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Video IF amplifier, demodulator and video amplifier
Each of the three AC-coupled IF stages permits the
omission of DC feedback and possesses a control range
in excess of 20 dB. An additional advantage is the
symmetry of the amplifier which results in a less critical
application.
The IF amplifier is followed by a passive synchronous
demodulator providing a regenerated carrier signal. This is
limited by a logarithmic limiter circuit prior to its application
to the demodulator. The limiter has a very low differential
phase shift which results in good differential gain and
phase figures.
The video amplifier also contains a white spot inverter and
a noise clamp which limits interference pulses to a point
below the peak sync level. This circuit is more effective
than a noise inverter and results in an improved picture
stability, with respect to interference.
AFC-circuit
The reference signal for the AFC circuit is obtained from
the demodulator tuned circuit. In this way only one tuned
circuit needs to be applied and only one adjustment has to
be carried out. The disadvantage with this method is that
the frequency spectrum of the signal fed to the detector is
determined by the SAW filter characteristic. This spectrum
is asymmetrical with respect to the picture carrier so that
the AFC output voltage is dependent on the video signal.
To overcome this video frequency dependency of the AFC
output, the demodulator output is followed by a
sample-and-hold circuit which samples during the sync
level of the signal. This means that only the carrier signal
is available to the AFC and it will not be affected by the
video information.
At very weak input signals the drive signal of the AFC
circuit will contain substantial noise. This noise has an
asymmetrical frequency spectrum causing an offset in the
AFC output voltage. This effect can be minimized by
applying a notch in the demodulator tuned circuit. The
sample-and-hold circuit is followed by an amplifier with
high output impedance, therefore the steepness of the of
the AFC control voltage is dependent on the load
impedance.
TDA8303
TDA8303A
ORDERING INFORMATION
EXTENDED TYPE
NUMBER
TDA8303 28 DIL plastic SOT117
TDA8303A 28 DIL plastic SOT117
Note
1. SOT117-1; 1996 December 3.
July 1992 2
PINS PIN POSITION MATERIAL CODE
PACKAGE
(1)
(1)
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
P
I
P
I
start
Video
V
8-9(RMS)
G
8-9
S/N signal-to-noise ratio input signal =
V
18(p-p)
Sound
V
12(RMS)
AMS AM suppression at V
THD total harmonic distortion − 0.5 − %
positive supply voltage (pin 7) 9.5 12 13.2 V
supply current (pin 7) 90 125 160 mA
start current (pin 11) note 1 − 6.5 9 mA
IF sensitivity (RMS value) at 38.9 MHz;
20 40 65 µV
note 2
IF gain control range − 74 − dB
− 57 − dB
10 mV
AFC output voltage swing
10.5 − 11.5 V
(peak-to-peak value)
AF output signal (RMS value) note 3 400 600 800 mV
= 50 mV − 58 − dB
I
Sync
V
25
I
27
V
22
required sync pulse amplitude note 4 200 −−mV
required input current during flyback pulse 0.1 − 2mA
coincidence detector output voltage
in synchronized condition − 9.7 − V
in no signal condition − 1.5 − V
V
22
V
22(p-p)
vertical feedback for DC voltage 2.9 3.3 3.7 V
vertical feedback for AC voltage
− 1.2 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
Notes to the quick reference data
1. Pin 11 has a double function. When during switch-on a current of 9 mA is supplied to this pin, it is used to start the
horizontal oscillator. The main supply can then be obtained from the horizontal deflection stage. When no current is
supplied to this pin it can be used as a volume control.
2. On set AGC.
3. The output signal is measured at ∆f = 7.5 kHz and maximum volume control.
4. The minimum value is obtained by connecting a 1.8 kΩ resistor and a 470 nF capacitor in series between the video
output and pin 25. The slicing level can be varied by changing the value of this resistor (higher resistance value
results in a larger value of the minimum sync pulse amplitude). The slicing level is independent of the video
information.
July 1992 3
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white
TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
July 1992 4
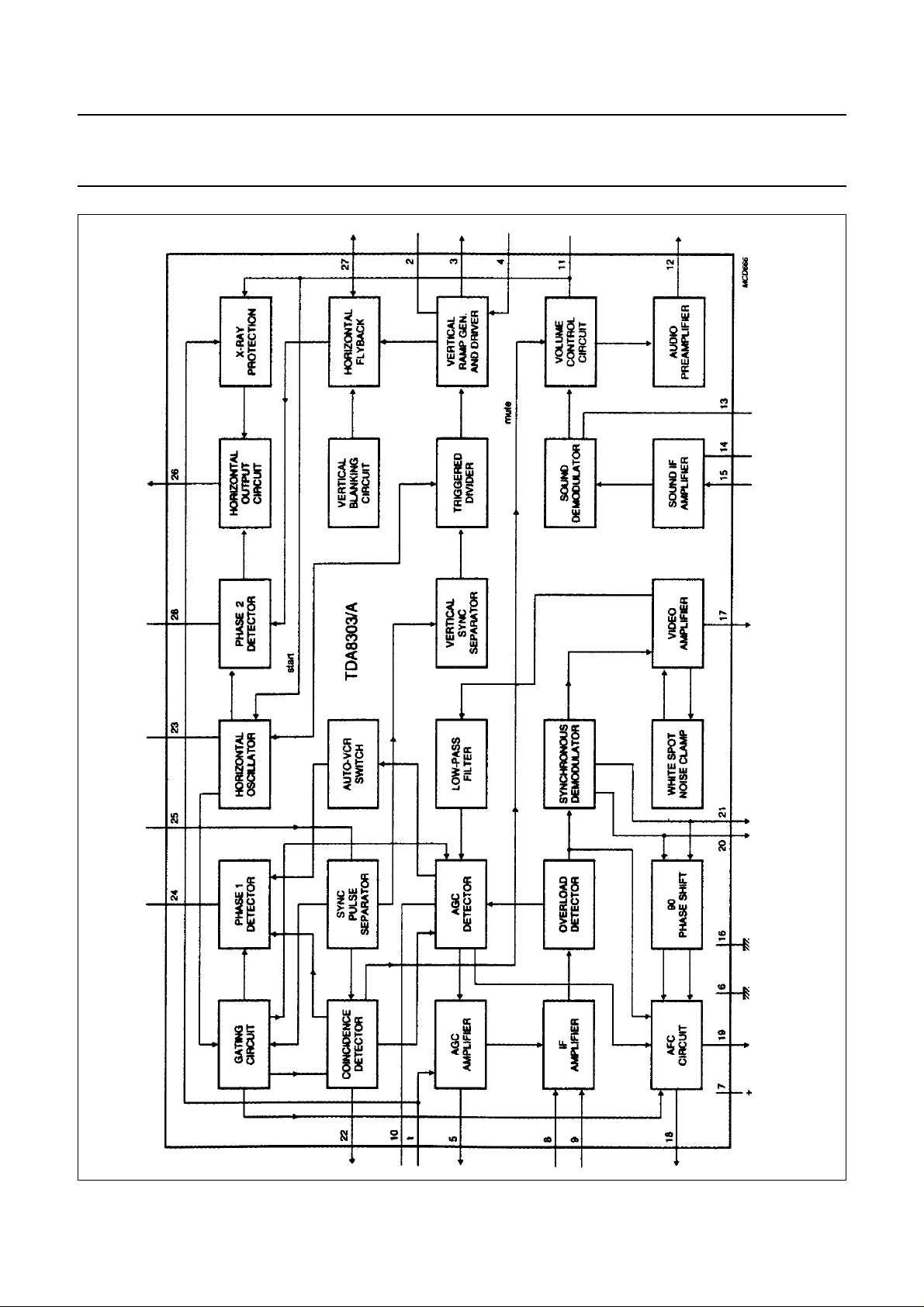
Fig.1 Block diagram
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white
TV
PINNING
PIN DESCRIPTION
1 AGC take-over
2 vertical ramp generator
3 vertical drive
4 vertical feedback
5 tuner AGC
6 ground
7 supply voltage input
8 video IF input
9 video IF input
10 IF AGC
11 volume control/start horizontal oscillator
12 audio output
13 sound demodulator
14 sound IF decoupling
15 sound IF input
16 ground (for some critical parts)
17 video amplifier output
18 AFC output
19 AFC S/H, AFC switch
20 video demodulator tuned circuit
21 video demodulator tuned circuit
22 coincidence detector
23 horizontal oscillator
24 phase 1 detector
25 sync separator input
26 horizontal drive output
27 horizontal flyback input
28 phase 2 detector
TDA8303
TDA8303A
Sound circuit
The sound quality of the TDA8303/TDA8303A compared
with the predecessors has been improved at weak signal
conditions. The improvement has been achieved by the
new IF amplifier which is less sensitive for radiation from
the sound IF amplifier and by change of the ground and
supply connections in the IC. When out-of-sync condition
is detected by the coincidence detector the sound output
is muted. When no mute is required the minimum voltage
level on pin 22 should be clamped to a high level of 5 V.
At this level the gating of the AGC is switched off and the
phase 1 detector has a high output current for reliable
catching of a new transmitter.
Vertical synchronization
The TDA8303/TDA8303A embodies a synchronized
divider system for generating the vertical sawtooth at pin 2
having several advantages and features such as:
• The vertical frequency is alignment free. The divider
automatically adapts to a vertical frequency of 50 Hz or
60 Hz including automatic amplitude correction and its
operating modes offer maximum
interference/disturbance protection.
• A discriminator-window checks the accuracy of the
vertical trigger pulse. Internally clock pulses are
generated by doubling the line frequency. The divider
operates in the 60 Hz mode when the trigger pulse
appears before count 576, otherwise the 50 Hz mode
will be active.
• The divider system operates with two different reset
windows for maximum interference/disturbance
protection. The windows are activated via an up/down
counter. The counter increases its counter-value by 1 for
each time the separated vertical sync pulse appears
within the selected window, otherwise the counter value
is decreased by 1.
AGC circuit
The AGC circuit of the TDA8303/TDA8303A is a top-sync
detector. The video signal coming from the video amplifier
passes a 2nd order low-pass filter before it is compared
with an internal reference level. The comparator stage is
gated when the horizontal oscillator is synchronized with
the video signal, such that interference pulses outside the
gating time have no influence on the gain control.
July 1992 5
Modes of operation
Large search window: divider ratio between 488 and 576.
This mode is valid for the following conditions:
• Divider is looking for a new transmitter
• Divider ratio found does not comply with the narrow
window specification limits
• Up/down counter value of the divider system, operating
in the narrow window mode, drops below count 10
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
Narrow window mode: divider ratio between 522 and 528
(60 Hz); or 622 and 628 (50 Hz).
• The divider system switches over to narrow window
mode when the up/down counter has reached his
maximum value of 15 approved vertical sync pulses
• When the divider operates in the narrow window mode
and a vertical sync pulse is missing within the window,
the divider is reset at the end of that window and the
counter value is decreased by 1
• At a counter value below 10 the divider system switches
over to the large window mode
• The divider system also generates an anti-top-flutter
pulse which inhibits the phase 1 detector during the
vertical sync pulse. The pulse width is dependent on the
divider mode. For the large window mode the start is
generated at the reset of the divider. In the narrow
window mode the anti-top-flutter pulse starts at the
beginning of the first equalizing pulse. The
anti-top-flutter pulse ends at count 10 for the 50 Hz
mode and count 12 for the 60 Hz mode
VCR switch
An extra time constant switch in the horizontal phase
detector makes an external VCR switch redundant. The
time constant is automatically switched depending on the
signal strength of the IF input (pins 8/9) and the
coincidence detector.
When a strong signal is detected (V
circuit is synchronized the time constant of the phase
detector is optimum for VCR playback, a fast time constant
during the vertical retrace to correct head errors of the
VCR and during scan a sufficient time constant to correct
fluctuations of the horizontal sync
During weak signal and synchronized conditions the time
constant is enlarged and the phase detector is gated. This
> 2.2 mV) and the
8/9
ensures a stable display which is not disturbed by the
noise in the video signal. When the circuit is not
synchronized the time constant is fast and not gated to
ensure a short catching time.
Combination of DC volume control and start-up feature
Pin 11 of the IC can be used as a DC volume control or as
a start-up feature of the horizontal oscillator/output circuit
dependent on the application.
Volume control is achieved by connecting a 4.7 kΩ
potentiometer or a DC voltage of 0 to 3 V to pin 11. When
a current of 9 mA is supplied to pin 11 the volume control
is set to a fixed output signal level and the circuit will
generate drive pulses for the horizontal deflection and the
main supply can be derived from the deflection.
Application when external video signals require synchronization
The input to the sync separator is externally available via
pin 25. For normal application the video output signal at pin
17 is AC-coupled to the sync separator input. It is possible
to interrupt this connection and drive the sync separator
from other sources.
When external signals are applied to the sync separator
the connections between the two parts must be
interrupted. This can be achieved by connecting pin 22 to
ground, which results in the following conditions:
• AGC detector is not gated
• Mute circuit not active, sound channel remains switched
on
• Phase detector 1 has an optimum time constant for
external video sources and is not gated
TDA8303
TDA8303A
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134)
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
P
tot
T
stg
T
amb
July 1992 6
supply voltage (pin 7) − 13.2 V
total power dissipation − 2.3 W
storage temperature range −55 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature range −25 +65 °C
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
CHARACTERISTICS
= 12 V;T
V
P
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply (pin 7)
V
P
I
P
I
11
V
11
V
11
IF Amplifier (pins 8 and 9)
V
8-9(RMS)
V
8-9(RMS)
R
8-9
C
8-9
G
8-9
∆V
17
V
8-9
Video Amplifier (note 5)
V
17
V
17
V
17
V
17
V
17
Z
17
I
17
I
source
B bandwidth of demodulated output signal 5 7 − MHz
G
17
ϕ differential phase note 8 − 2 5 deg.
NL video non linearity note 9 − 25%
= 25 °C; carrier 38.9 MHz negative modulation, unless otherwise specified
amb
supply voltage range 9.5 12 13.2 V
supply current no input 90 125 160 mA
start current (pin 11) note 1 − 6.5 9 mA
start voltage horizontal oscillator 9.5 −−V
start protection level I11 = 12 mA −−16.5 V
input sensitivity (RMS value) at 38.9 MHz;
25 40 65 µV
note 2
input sensitivity (RMS value) at 45.75 MHz;
25 40 65 µV
notes 2 and 25
differential input resistance note 3 − 1300 −Ω
differential input capacitance note 3 − 5 − pF
gain control range − 74 − dB
output signal expansion for 46 dB input signal
note 4 − 1 − dB
variation
maximum input signal 100 170 − mV
zero signal output level note 6 − 5.4 − V
peak sync level 2.3 2.5 2.7 V
video output signal amplitude note 7 2.3 2.65 3.0 V
white spot threshold level − 5.7 − V
white spot insertion level − 3.8 − V
video output impedance − 25 −Ω
internal bias current of npn emitter follower
1.4 1.8 − mA
output transistor
maximum source current (pin 17) 10 −−mA
differential gain note 8 − 48%
intermodulation note 10
1.1 MHz; blue 50 60 − dB
1.1 MHz; yellow 50 60 − dB
3.3 MHz; blue 55 65 − dB
3.3 MHz; yellow 55 65 − dB
July 1992 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
S/N signal-to-noise ratio 10 mV input
signal
S/N signal-to-noise ratio end of gain
control range
V
17
V
17
residual carrier signal − 210mV
residual 2nd harmonic of carrier signal − 210mV
Tuner AGC
V
8-9(RMS)
minimum starting point for tuner take−over
(RMS value)
V
8-9(RMS)
maximum starting point for tuner take−over
(RMS value)
I
5
V
5
I
L
∆V
I
V
1
maximum tuner AGC output swing V5 = 3 V 4 −−mA
output saturation voltage I5 = 2 mA −−300 mV
leakage current (pin 5) −−1µA
input signal variation complete tuner control 0.2 2 4 dB
minimum voltage tuner take−over −−1V
AFC circuit
I
19
I
O
I
LO
V
18
I
18
AFC sample-and-hold switch-off current 0.1 −−mA
output current (pin 19) V19 = 0 V − 0.1 0.3 mA
output leakage current (pin 19) −−2µA
AFC output voltage swing notes 18 and 19 10.5 − 11.5 V
available output current 0.2 −−mA
control slope − 100 − mV/kHz
V
O
R
O
V
18
output voltage (pin 18) AFC off 5.5 6 6.5 V
AFC output resistance − 40 − kΩ
output voltage swing notes 25 and 26 − 11 − V
control slope notes 25 and 26 − 80 − mV/kHz
V
18
output voltage shift with respect to
notes 25 and 26 −−2−V
VI= 10 mV(RMS)
50 57 − dB
50 62 − dB
−−0.2 mV
100 150 − mV
July 1992 8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Sound circuit (note 12)
V
15
R
15
C
15
input limiting voltage V
input resistance − 2.6 − kΩ
input capacitance − 6 − pF
AMS AM suppression note 13 53 58 − dB
V
12(RMS)
V
12(RMS)
AF output signal (RMS value) note 14 400 600 800 mV
AF output signal when pin 11 is used as a
starting pin or connected to V
P
(RMS value)
Z
12
AF output impedance − 25 100 Ω
THD total harmonic distortion note 15 − 0.5 2 %
RR ripple rejection volume control
V
12
V
12
output voltage when muted − 2.5 − V
output level shift due to muting volume control
S/N signal-to-noise ratio note 16 − 47 − dB
V
11
I
11
V
12
voltage with pin 11 disconnected − 6 − V
current with pin 11 short-circuited to ground − 1 − mA
temperature dependence of the output signal
amplitude
= −3 dB − 400 800 µV
O(max)
∆f = 50 kHz 500 900 1500 mV
− 35 − dB
−20 dB;
fk= 100 Hz
−−0.5 dB
−20 dB
T
= 20 to 65
amb
− 2.5 − dB
°C;
−30 dB volume
control and
voltage of pin 11
fixed;
note 17
Volume control (note 17; see Fig.8)
R
11
OSS suppression of output signal during mute
external control resistor note 17 − 4.7 − kΩ
60 66 − dB
condition
Horizontal synchronization circuit (see Fig.9)
SYNC SEPARATOR
V
25
I
25
required sync pulse amplitude note 20 200 750 − mV
input current (pin 25) V25> 5 V − 8 −µA
= 0 V − 10 − mA
V
25
FIRST CONTROL LOOP
±∆f PLL holding range − 1500 2000 Hz
±∆f PLL catching range 600 1500 − Hz
control sensitivity to oscillator note 21 see Fig.10
V
8-9
IF input signal at which the time constant is
strong-to-weak − 2.2 − mV
switched (RMS value)
July 1992 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
SECOND CONTROL LOOP (POSITIVE EDGE)
δt
d
------δt
o
t
d
PHASE ADJUSTMENT (VIA SECOND CONTROL LOOP)
α maximum allowed phase shift −±2−µs
H
ORIZONTAL OSCILLATOR
f
fr
∆f spread with fixed external components −−4%
∆ffrfrequency variations with supply voltage from
∆f
T
∆f
fr
∆f frequency variation when only noise is
ORIZONTAL OUTPUT (PIN 26; OPEN COLLECTOR)
H
V
26
V
OL
I
sink
t
r
t
f
HORIZONTAL FLYBACK INPUT (PIN 27)
I
27
COINCIDENCE DETECTOR
V
22
V
22
V
22
V
22
V
22
V
22
t
d
V
22
I
22
control sensitivity note 22 − 100 −
control range − 25 −µs
control sensitivity − 25 −µA/µs
free running frequency R = 34.3 kΩ;
− 15625 − Hz
C = 2.7 nF
−−2%
9.5 to 13.2 V
frequency variation with temperature note 25 −−1.6 − Hz/°C
maximum frequency deviation at start of
−−10 %
horizontal output
note 25 −−500 Hz
received
output limiting voltage −−16.5 V
LOW level output voltage I
= 10 mA − 0.2 0.5 V
sink
maximum sink current 10 −−mA
duty factor of output signal − 46 − %
rise time of output pulse − 260 − ns
fall time of output pulse − 100 − ns
required input current during flyback pulse 0.01 − 1.0 mA
voltage for in-sync condition − 9.8 − V
voltage for no-sync condition no signal − 1.5 − V
switching level to the phase detector from fast
6.2 6.7 7.2 V
to slow
hysteresis slow to fast − 0.6 − V
switching level to activate the mute function
2.5 2.8 3.1 V
(transmitter identification)
hysteresis mute function − 2 − V
delay of mute release after transmitter
−−300 µs
insertion
allowable load on pin 22 −−10 µA
external video mode −−0.7 V
current at pin 22 V22 = 0 V −−0.8 mA
July 1992 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Vertical circuit (note 24)
V
ERTICAL RAMP GENERATOR
I
2
I
2
V
2(p−p)
t interlace timing of the internal pulses 30 32 34 µs
V
ERTICAL OUTPUT
I
3
V
3
VERTICAL FEEDBACK INPUT
V
4
V
4(p−p)
I
4
∆t
p
input current during scan −−2µA
discharge current during retrace − 0.8 − mA
sawtooth amplitude (peak-to-peak value) − 1.9 − V
available output current V3 = 4 V −−3mA
maximum available output voltage I3 = 0.1 mA 4.4 5 − V
DC input voltage 2.9 3.3 3.7 V
AC input voltage (peak-to-peak value) − 1 − V
input current −−12 µA
internal pre-correction to sawtooth − 3 − %
deviation amplitude 50/60 Hz −−4%
temperature dependency of the amplitude T
amb
= 20 to
−−2%
65 °C
Notes to the characteristics
1. Pin 11 has a double function. When during switch-on a current of 9 mA is supplied to this pin, it is used to start the
horizontal oscillator. The main supply can then be obtained from the horizontal deflection stage. When no current is
supplied to this pin it can be used as a volume control.
2. On set AGC.
3. The input impedance has been chosen such that a SAW filter can be employed.
4. Measured with 0 dB = 450 µV.
5. Measured at 10 mV RMS top sync input signal.
6. Projected zero point; i.e. with switched demodulator.
7. White 10% of the top sync amplitude.
8. Measured according to the test line illustrated by Fig.2. The differential gain is expressed as a percentage of the
difference in peak amplitudes between the largest and smallest value relative to the subcarrier amplitude at blanking
level. The differential phase is defined as the difference in degrees between the largest and smallest phase angle.
The differential gain and phase are measured with a DSB signal.
9. This figure is valid for the complete video signal amplitude (peak white-to-black); see Fig.3. The non−linearity is
expressed as a percentage of the maximum deviation of a luminance step from the mean step, with respect to the
mean step.
10. The test set−up and input conditions are illustrated by Fig.4. The figures are measured at an input signal of 10 mV
RMS.
11. Measured with a source impedance of 75Ω.
V
black-to-white
The signal-to-noise ratio = 20
12. The sound circuit is measured (unless otherwise specified) with an input signal of V
O
-----------------------------------------------------------log
V
nRMS()
atB=5MHz
of 50 mV RMS, a carrier
15
frequency of 5.5 MHz at a ∆f of 27.5 kHz. The QL of the demodulator tuned circuit is 16 and the volume control is
July 1992 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
connected to the supply. The reference circuit must be tuned in such a way that the output is symmetrical clipping at
maximum volume.
13. The test set-up is illustrated by Fig.6. The AM rejection curve (typical) is illustrated by Fig.7.
14. The output signal is measured at a ∆f = 7.5 kHz and maximum volume control.
15. The demodulator tuned circuit must be tuned at minimum distortion.
16. Weighted noise, measured in accordance with CCIR 468.
17. See also note 1. The volume can be controlled by using a potentiometer connected to ground (value 4.7 kΩ) or by
means of a variable direct voltage. In the latter event the relatively low input impedance must be taken into account.
18. The AFC control voltage is obtained by multiplying the IF output signal (which is also used to drive the synchronous
demodulator) with a reference carrier. This reference carrier is obtained from the demodulator tuned circuit via a 90
degree phase shift network.The IF output signal has an asymmetrical frequency spectrum with respect to the carrier
frequency. To avoid problems due to this asymmetrical signal the AFC circuit is followed by a sample-and-hold circuit
which samples during the sync level. As a result the AFC output voltage contains no video information. The specified
control slope decreases when the AFC output is loaded with two resistors between the voltage supply and ground.
19. At very weak input signals the drive signal for the AFC circuit will have a high noise content. This noise input has an
asymmetrical frequency spectrum which will cause an offset of the AFC output voltage. The characteristics given for
weak signals are measured with a SAW filter (OFW 1956) connected in front of the IC input signal such that the input
signal of the IC is 150 µV RMS.
20. The minimum value is obtained by connecting a 1.8 kΩ resistor between pins 17 and 25. The slicing level can be
varied by changing the value of this resistor (higher resistor value results in larger value of the minimum sync pulse
amplitude). The slicing level is independent of the video information.
21. Frequency control is obtained by supplying a correction current to the oscillator RC network via a resistor connected
between the phase 1 detector output and the oscillator network. The oscillator can be adjusted to the correct
frequency by short circuiting the sync separator bias network (pin 25) to the voltage supply. To avoid the need of a
VCR switch the time constant of the phase detector at strong input signals is sufficiently short to obtain a stable
picture during VCR playback. During the vertical retrace period the time constant is even shorter so that the
head−errors of the VCR are compensated at the beginning of scan. During conditions of weak signal (information
derived from the AGC circuit) the time constant is increased to obtain a better noise immunity.
22. This figure is valid for an external load impedance of 82 kΩ between pin 28 and the phase adjustment potentiometer.
23. The functions in-sync/out-of-sync and transmitter identification have been combined on pin 22. The capacitor is
charged during the sync pulse and discharged during the time difference between gating (6.5 µs) and the sync pulse.
24. The vertical scan is synchronized by means of a divider system. Therefore no frequency adjustment is required for
the ramp generator. The divider detects whether the incoming signal has a vertical frequency of 50 or 60 Hz and
corrects the vertical amplitude.
25. These figures are based on test samples.
26. Measured at an input signal amplitude of 150 µV RMS (pin 18).
July 1992 12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
handbook, full pagewidth
MLA667
17.5%
100%
95%
30%
TDA8303
TDA8303A
handbook, full pagewidth
MBC211
Fig.2 Video output signal.
100%
86%
72%
58%
44%
30%
µs
646056524844403632221210 26
Fig.3 EBU test signal waveform (line 330).
July 1992 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
handbook, full pagewidth
SC
33.4 MHz
PC
38.9 MHz
Σ
CC
34.5 MHz
ATTENUATOR
TEST
CIRCUIT
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
gain setting adjusted
for blue or yellow
MLA666
TDA8303
TDA8303A
handbook, full pagewidth
Input signal conditions
SC = Sound carrier
CC = Chrominance carrier
PC = Picture carrier
All with respect to top sync level
Value at 1.1 MHz : 20 log
Value at 3.3MHz: 20 log
13.2 dB
30 dB
SC CC PC
BLUE
V
at 4.4 MHz
O
-------------------------------------at 1.1 MHz
V
O
V
at 4.4 MHz
O
--------------------------------------
V
at 3.3 MHz
O
3.6 dB+
3.2 dB
13.2 dB
30 dB
SC CC PC
YELLOW
10 dB
MBC213
Fig.4 Test set-up intermodulation.
July 1992 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
Fig.5 Signal-to-noise ratio as a function of the
input voltage (0 dB = 100 mV).
Fig.6 Test set-up AM suppression.
July 1992 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
Fig.7 AM suppression.
Fig.8 Volume control characteristics.
July 1992 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
Fig.9 Timing diagram.
July 1992 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
Table 1 Switching levels coincidence detector
CONDITION
V
22
> 6.7 V
V
22
and
strong signal 11.3 7.6
weak signal 1.3 1.3
1 < V
< 5.7 V
22
and
strong signal 11.3 7.6
weak signal 11.3 7.6
V
< 0.7 11.3 7.6
22
T2 - T1 T3 = SCAN
CONTROL SENSITIVITY
HORIZONTAL OSCILLATOR (kHz/µS)
TDA8303
TDA8303A
Fig.10 Switching levels coincidence detector.
Fig.11 Anti-top-flutter pulse.
July 1992 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
Fig.12 Application diagram.
July 1992 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
PACKAGE OUTLINE
handbook, full pagewidth
DIP28: plastic dual in-line package; 28 leads (600 mil)
D
seating plane
L
Z
28
e
b
b
15
TDA8303
TDA8303A
SOT117-1
M
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
1
c
(e )
1
M
H
pin 1 index
1
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
A
A
A
UNIT
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
max.
mm
1 2
min.
max.
b
1.7
1.3
0.066
0.051
b
1
0.53
0.38
0.020
0.014
cD E weM
0.32
0.23
0.013
0.009
(1) (1)
36.0
35.0
1.41
1.34
14.1
13.7
0.56
0.54
E
14
(1)
L
3.9
3.4
M
15.80
15.24
0.62
0.60
H
E
17.15
15.90
0.68
0.63
0.252.54 15.24
0.010.10 0.60
e
1
0.15
0.13
Z
max.
1.75.1 0.51 4.0
0.0670.20 0.020 0.16
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT117-1
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
051G05 MO-015AH
REFERENCES
July 1992 20
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
92-11-17
95-01-14
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Small signal combination IC for black/white TV
TDA8303
TDA8303A
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when through-hole and
surface mounted components are mixed on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is not always suitable for
surface mounted ICs, or for printed-circuits with high population densities. In these situations reflow soldering is often
used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in our
“IC Package Databook”
Soldering by dipping or by wave
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is 260 °C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact with the
joint for more than 5 seconds. The total contact time of successive solder waves must not exceed 5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the temperature within the permissible limit.
Repairing soldered joints
Apply a low voltage soldering iron (less than 24 V) to the lead(s) of the package, below the seating plane or not more
than 2 mm above it. If the temperature of the soldering iron bit is less than 300 °C it may remain in contact for up to
10 seconds. If the bit temperature is between 300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
(order code 9398 652 90011).
). If the printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling may
stg max
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
July 1992 21
 Loading...
Loading...