Philips SCN68562C2A52, SCN68562C2N48, SCN68562C4A52, SCN68562C4N48 Datasheet

SCN68562
Dual universal serial communications
controller (DUSCC)
Product specification
IC19 Data Handbook
1995 May 01
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN68562Dual universal serial communications controller (DUSCC)
2
1995 May 01 853-0831 15179
DESCRIPTION
The Philips Semiconductors SCN68562 Dual Universal Serial
Communications Controller (DUSCC) is a single-chip MOS-LSI
communications device that provides two independent,
multi-protocol, full-duplex receiver/transmitter channels in a single
package. It supports bit-oriented and character-oriented (byte count
and byte control) synchronous data link controls as well as
asynchronous protocols. The SCN68562 interfaces to the 68000
MPUs via asynchronous bus control signals and is capable of
program-polled, interrupt driven, block-move or DMA data transfers.
The operating mode and data format of each channel can be
programmed independently.
Each channel consists of a receiver, a transmitter, a 16-bit
multifunction counter/timer, a digital phase-locked loop (DPLL), a
parity/CRC generator and checker, and associated control circuits.
The two channels share a common bit rate generator (BRG),
operating directly from a crystal or an external clock, which provides
16 common bit rates simultaneously. The operating rate for the
receiver and transmitter of each channel can be independently
selected from the BRG, the DPLL, the counter/timer, or from an
external 1X or 16X clock, making the DUSCC well suited for
dual-speed channel applications. Data rates up to 4Mbits per
second are supported.
The transmitter and receiver each contain a four-deep FIFO with
appended transmitter command and receiver status bits and a shift
register. This permits reading and writing of up to four characters at
a time, minimizing the potential of receiver overrun or transmitter
underrun, and reducing interrupt or DMA overhead. In addition, a
flow control capability is provided to disable a remote transmitter
when the FIFO of the local receiving device is full.
Two modem control inputs (DCD and CTS) and three modem
control outputs are provided. These inputs and outputs can be
optionally programmed for other functions.
FEA TURES
General Features
•Dual full-duplex synchronous/asynchronous receiver and
transmitter
•Multiprotocol operation
– BOP: HDLC/ADCCP, SDLC, SDLC loop, X.25 or X.75 link level,
etc.
– COP: BISYNC, DDCMP
– ASYNC: 5–8 bits plus optional parity
•Four character receiver and transmitter FIFOs
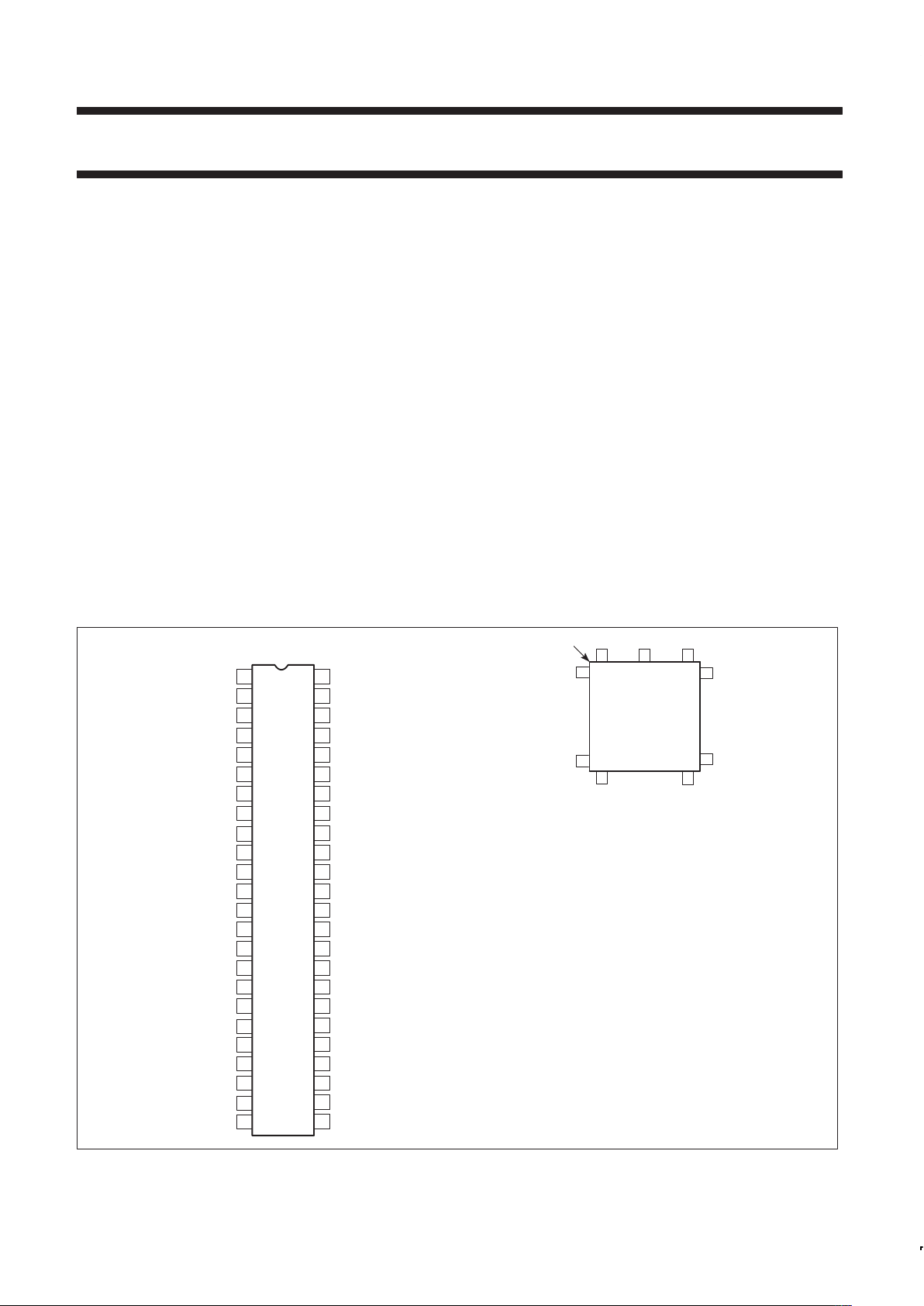
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
28
27
26
25
21
22
23
24
IACKN
A3
A2
A1
RTxDAKBN/
IRQN
RESETN
RTSBN/
TRxCB
RTxCB
DCDBN/
TxDAKBN/
RTxDRQBN/
TxDRQBN/
CTSBN/LCBN
D7
D6
D5
D4
DTACKN
DTCN
GND
CSN
DONEN
D3
D2
D1
D0
CTSAN/LCAN
TxDRQAN/
RTxDRQAN/
TxDAKAN/
TxDA
DCDAN/
RTxCA
TRxCA
RTSAN/
X2/IDCN
X1/CLK
RTxDAKAN/
A6
A5
A4
V
DD
N PACKAGE
GPI1BN
SYNOUTBN
SYNIBN
RxDB
TxDB
GPI2BN
GPO1BN
GPO2BN/RTSBN
R/WN
GPO2AN/RTSAN
GPO1AN
GPI2AN
Rxda
SYNIAN
SYNOUTAN
GPI1AN
DIP
Pin Function Pin Function
1 IACKN 27 CSN
2 A3 28 R/WN
3 A2 29 DONEN
4A1 30D3
5 RTxDAKBN/ 31 D2
GPI1BN 32 D1
6 IRQN 33 D0
7NC 34NC
8 RESETN 35 CTSAN/LCAN
9 RTSBN/ 36 TxDRQAN/
SYNOUTBN GPO2AN/RTSAN
10 TRxCB 37 RTxDRQAN/
11 RTxCB GPO1AN
12 DCDBN/ 38 TxDAKAN/
SYNIBN GPI2AN
13 NC 39 TxDA
14 RxDB 40 RxDA
15 TxDB 41 NC
16 TxDAKBN/ 42 DCDAN/
GPI2BN SYNIAN
17 RTxDRQBN/ 43 RTxCA
GPO1BN 44 TRxCA
18 TxDRQBN/ 45 RTSAN/
GPO2BN/RTSBN SYNOUTAN
19 CTSBN/LCBN 46 X2/IDCN
20 D7 47 X1/CLK
21 D6 48 RTxDAKAN/
22 D5 GPI1AN
23 D4 49 A6
24 DTACKN 50 A5
25 DTCN 51 A4
26 GND 52 V
DD
1
46
20
33
47
34
21
8
PLCC
7
TOP VIEW
INDEX
CORNER
A PACKAGE
SD00222
Figure 1. Pin Configurations

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN68562Dual universal serial communications controller (DUSCC)
1995 May 01
3
•0 to 4MHz data rate
•Programmable bit rate for each receiver and transmitter selectable
from:
– 16 fixed rates: 50 to 38.4k baud
– One user-defined rate derived from programmable
counter/timer
– External 1X or 16X clock
– Digital phase-locked loop
•Parity and FCS (frame check sequence LRC or CRC) generation
and checking
•Programmable data encoding/decoding: NRZ, NRZI, FM0, FM1,
Manchester
•Programmable channel mode: full- and half-duplex, auto-echo, or
local loopback
•Programmable data transfer mode: polled, interrupt, DMA, wait
•DMA interface
– Compatible with the Philips Semiconductors SCB68430 Direct
Memory Access Interface (DMAI) and other DMA controllers
– Single- or dual-address dual transfers
– Half- or full-duplex operation
– Automatic frame termination on counter/timer terminal count or
DMA DONE
•Interrupt capabilities
– Daisy chain option
– Vector output (fixed or modified by status)
– Programmable internal priorities
– Maskable interrupt conditions
•Multi-function programmable 16-bit counter/timer
– Bit rate generator
– Event counter
– Count received or transmitted characters
– Delay generator
– Automatic bit length measurement
•Modem controls
– RTS, CTS, DCD, and up to four general I/O pins per channel
– CTS and DCD programmable autoenables for Tx and Rx
– Programmable interrupt on change of CTS or DCD
•On-chip oscillator for crystal
•TTL compatible
•Single +5V power supply
Asynchronous Mode Features
•Character length: 5 to 8 bits
•Odd or even parity, no parity, or force parity
•Up to two stop bits programmable in 1/16-bit increments
•1X or 16X Rx and Tx clock factors
•Parity, overrun, and framing error detection
•False start bit detection
•Start bit search 1/2-bit time after framing error detection
•Break generation with handshake for counting break characters
•Detection of start and end of received break
•Character compare with optional interrupt on match
•Transmits up to 4Mbs and receive up to 2Mbps data rates
Character-Oriented Protocol Features
•Character length: 5 to 8 bits
•Odd or even parity, no parity, or force parity
•LRC or CRC generation and checking
•Optional opening PAD transmission
•One or two SYN characters
•External sync capability
•SYN detection and optional stripping
•SYN or MARK line-fill on underrun
•Idle in MARK or SYNs
•Parity, FCS, overrun, and underrun error detection
BISYNC Features
– EBCDIC or ASCII header, text and control messages
– SYN, DLE stripping
– EOM (end of message) detection and transmission
– Auto transparent mode switching
– Auto hunt after receipt of EOM sequence (with closing PAD
check after EOT or NAK)
– Control character sequence detection for both transparent and
normal text
Bit-Oriented Protocol Features
•Character length: 5 to 8 bits
•Detection and transmission of residual character: 0–7 bits
•Automatic switch to programmed character length for 1 field
•Zero insertion and deletion
•Optional opening PAD transmission
•Detection and generation of FLAG, ABORT, and IDLE bit patterns
•Detection and generation of shared (single) FLAG between
frames
•Detection of overlapping (shared zero) FLAGs
•ABORT, ABORT-FLAGs, or FCS FLAGs line-fill on underrun
•Idle in MARK or FLAGs
•Secondary address recognition including group and global
address
•Single- or dual-octet secondary address
•Extended address and control fields
•Short frame rejection for receiver
•Detection and notification of received end of message
•CRC generation and checking
•SDLC loop mode capability
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN68562Dual universal serial communications controller (DUSCC)
1995 May 01
4
ORDERING INFORMATION
VCC = +5V +5%, TA = 0°C to +70°C
DESCRIPTION
Serial Data Rate = 4Mbps Maximum
DWG #
48-Pin Plastic Dual In-Line Package (DIP) SCN68562C4N48 SOT240-1
52-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC) Package SCN68562C4A52 SOT238-3
NOTE: See SCN26562/SCN68562 User’s Guide for detailed description of all the features.
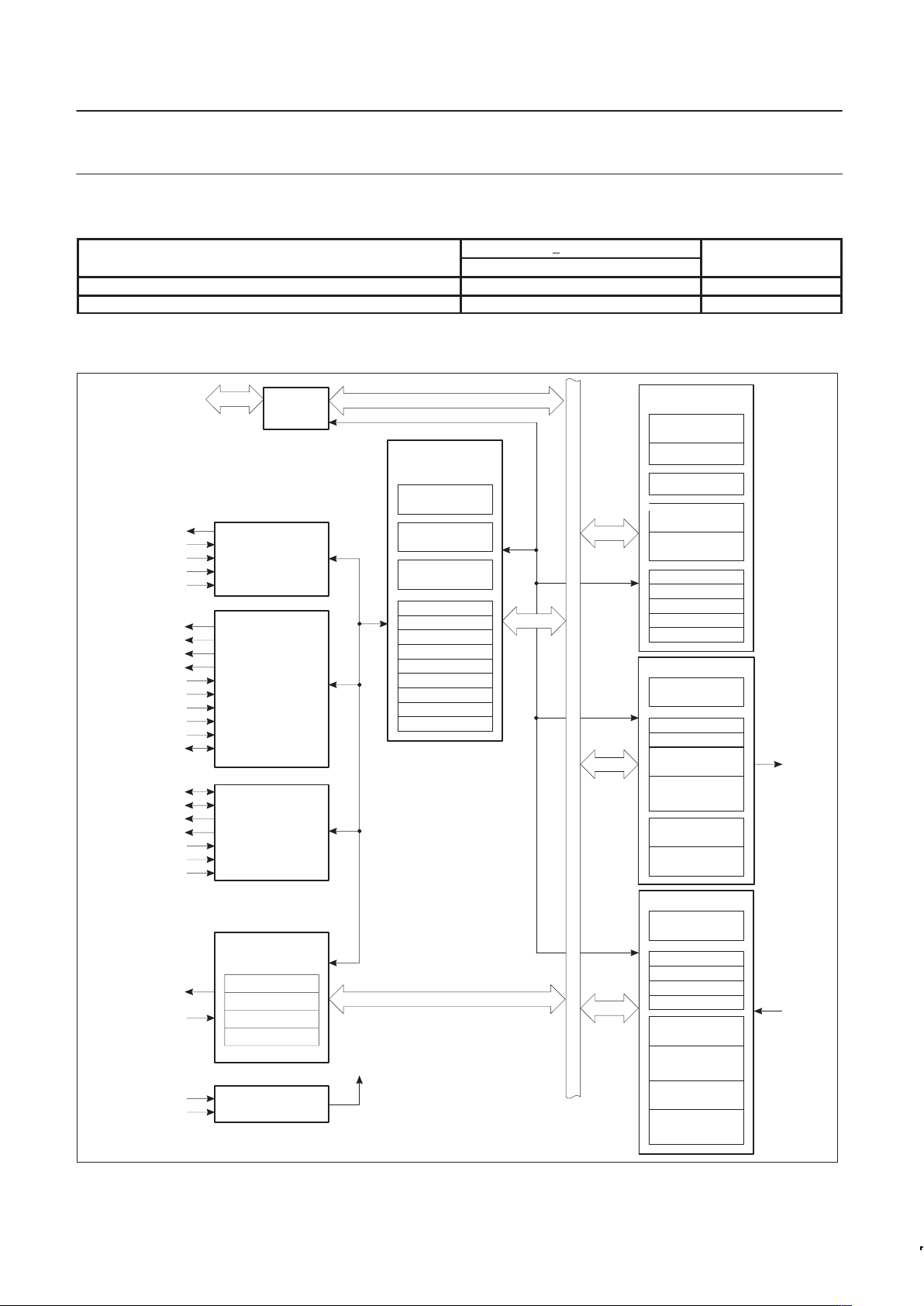
BLOCK DIAGRAM
CHANNEL MODE
AND TIMING A/B
CTCRA/B
CTPRHA/B
CTPRLA/B
INTERNAL BUS
DPLL CLK
MUX A/B
DPLL A/B
BRG
COUNTER/
TIMER A/B
C/T CLK
MUX A/B
CTHA/B
CTLA/B
TRANSMIT A/B
TRANS CLK
MUX
TPRA/B
TTRA/B
TX SHIFT
REG
CRC
GEN
TRANSMIT
4 DEEP
FIFO
SPEC CHAR
GEN LOGIC
RECEIVER A/B
RPRA/B
RTRA/B
S1RA/B
RCVR CLK
MUX
S2RA/B
RCVR
SHIFT REG
RECEIVER
4 DEEP
FIFO
CRC
ACCUM
BISYNC
COMPARE
LOGIC
TxD A/B
RxD A/B
INTERFACE/
OPERATION
CONTROL
ICTSRA/B
GSR
CMR1A/B
ADDRESS
DECODE
DMA
CONTROL
CMR2A/B
OMRA/B
R/W
DECODE
CCRA/B
PCRA/B
RSRA/B
TRSRA/B
ICRA/B
IERA/B
IVR
IVRM
INTERRRUPT
CONTROL
OSCILLATOR
SPECIAL
FUNCTION
PINS
DMA INTERFACE
MPU
INTERFACE
BUS
BUFFER
D0-D7
DTACKN
RWN
A1-A6
CSN
RESETN
RTxDRQAN/GPO1AN
RTxDRQBN/GPO1BN
TxDRQAN/GPO2AN
TxDRQBN/GPO2BN
RTxDAKAN/GPI1AN
RTxDAKBN/GPI1BN
TxDAKAN/GPI2AN
TxDAKBN/GPI2BN
DTCN
DONEN
TRxCA/B
RTxCA/B
RTSBN/SYNOUTBN
RTSAN/SYNOUTAN
CTSA/BN
DCDBN/SYNIBN
DCDAN/SYNIAN
IRQN
IACKN
X1/CLK
X2/IDCN
DUSCC
LOGIC
CONTROL
SD00223
Figure 2. Block Diagram
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN68562Dual universal serial communications controller (DUSCC)
1995 May 01
5
PIN DESCRIPTION
In this data sheet, signals are discussed using the terms ‘active’ and ‘inactive’ or ‘asserted’ and ‘negated’ independent of whether the signal is
active in the High (logic 1) or Low (logic 0) state. N at the end of a pin name signifies the signal associated with the pin is active-Low (see
individual pin description for the definition of the active level of each signal.) Pins which are provided for both channels are designated by A/B
after the name of the pin and the active-Low state indicator, N, if applicable. A similar method is used for registers provided for both channels:
these are designated by either an underline or by A/B after the name.
MNEMONIC
DIP
PIN NO.
TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
A1 – A6 4-2,
45-47
I Address Lines: Active-High. Address inputs which specify which of the internal registers
is accessed for read/write operation.
D0 – D7 31-28,
21-18
I/O Bidirectional Data Bus: Active High, 3-State. Bit 0 is the LSB and bit 7 is the MSB. All
data, command, and status transfers between the CPU and the DUSCC take place over
this bus. The data bus is enabled when CSN is Low, during interrupt acknowledge cycles
and single-address DMA acknowledge cycles.
R/WN 26 I Read/Write: A High input indicates a read cycle and a Low input indicates a write cycle
when a cycle is initiated by assertion of the CSN input.
CSN 25 I Chip Select: Active-Low input. When Low, data transfers between the CPU and the
DUSCC are enabled on D0 – D7 as controlled by the R/WN and A1 – A6 inputs. When
CSN is High, the DUSCC is isolated from the data bus (except during interrupt
acknowledge cycles and single-address DMA transfers) and D0 – D7 are placed in the
3-State condition.
DTACKN 22 O Data Transfer Acknowledge: Active-Low, 3-State. DTACKN is asserted on a write cycle
to indicate that the data on the bus has been latched, and on a read cycle or interrupt
acknowledge cycle to indicate valid data is on the bus. The signal is negated when
completion of the cycle is indicated by negation of the CSN or IACKN input, and returns to
the inactive state (3-State) a short period after it is negated. In a single address DMA
mode, data is latched with the falling edge of DTCN. DTACKN is negated when
completion of the cycle is indicated by the assertion of DTCN or negation of DMA
acknowledge inputs (whichever occurs first), and returns to the inactive state (3-State) a
short period after it is negated. When negated, DTACKN becomes an open-drain output
and requires an external pull-up resistor.
IRQN 6 O Interrupt Request: Active-Low, open-drain. This output is asserted upon occurrence of
any enabled interrupting condition. The CPU can read the general status register to
determine the interrupting condition(s), or can respond with an interrupt acknowledge cycle
to cause the DUSCC to output an interrupt vector on the data bus.
IACKN 1 I Interrupt Acknowledge: Active-Low. When IACKN is asserted, the DUSCC responds by
placing the contents of the interrupt vector register (modified or unmodified by status) on
the data bus and asserting DTACKN. If no active interrupt is pending, DTACKN is not
asserted.
X1/CLK 43 I Crystal or External Clock: When using the crystal oscillator, the crystal is connected
between pins X1 and X2. If a crystal is not used, and external clock is supplied at this
input. This clock is used to drive the internal bit rate generator, as an optional input to the
counter/timer or DPLL, and to provide other required clocking signals.
X2/IDCN 42 O Crystal or Interrupt Daisy Chain: When a crystal is used as the timing source, the
crystal is connected between pins X1 and X2. This pin can be programmed to provide and
interrupt daisy chain active-Low output which propagates the IACKN signal to lower priority
devices, if no active interrupt is pending. This pin should be grounded when an external
clock is used on X1 and X2, is not used as an interrupt daisy chain output.
RESETN 7 I Master Reset: Active-Low. A low on this pin resets the transmitters and receivers and
resets the registers shown in Table 1 of the CDUSCC Users’ Guide. Reset in
asynchronous, i.e., no clock is required.
RxDA, RxDB 37, 12 I Channel A (B) Receiver Serial Data Input: The least significant bit is received first. If
external receiver clock is specified for the channel, the input is sampled on the rising edge
of the clock.
TxDA, TxDB 36, 13 O Channel A (B) Transmitter Serial Data Output: The least significant bit is transmitted
first. This output is held in the marking (High) condition when the transmitter is disabled or
when the channel is operating in local loopback mode. If external transmitter clock is
specified for the channel, the data is shifted on the falling edge of the clock.
RTxCA, RTxCB 39, 10 I/O Channel A (B) Receiver/Transmitter Clock: As an input, it can be programmed to
supply the receiver, transmitter, counter/timer, or DPLL clock. As an output, can supply the
counter/timer output, the transmitter shift clock (1X), or the receiver sampling clock (1X).
The maximum external receiver/transmitter clock frequency is 4MHz.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SCN68562Dual universal serial communications controller (DUSCC)
1995 May 01
6
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
MNEMONIC
DIP
PIN NO.
TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
TRxCA, TRxCB 40, 9 I/O Channel A (B) Transmitter/Receiver Clock: As an input, it can supply the receiver,
transmitter, counter/timer, or DPLL clock. As an output, it can supply the counter/timer
output, the DPLL output, the transmitter shift clock (1X), the receiver sampling clock (1X),
the transmitter BRG clock (16X), The receiver BRG clock (16X), or the internal system
clock (X1/2). The maximum external receiver/transmitter clock frequency is 4MHz.
CTSA/BN, LCA/BN 32, 17 I/O Channel A (B) Clear-To-Send Input or Loop Control Output: Active-Low. The signal
can be programmed to act as an enable for the transmitter when not in loop mode. The
DUSCC detects logic level transitions on this input and can be programmed to generate an
interrupt when a transition occurs. When operating in the COP loop mode, this pin
becomes a loop control output which is asserted and negated by DUSCC commands.
This output provides the means of controlling external loop interface hardware to go on-line
and off-line without disturbing operation of the loop.
DCDA/BN,
SYNIA/BN
38, 11 I Channel A (B) Data Carrier Detected or External Sync Input: The function of this pin is
programmable. As a DCD active-Low input, it acts as an enable for the receiver or can be
used as a general purpose input for the DCD function, the DUSCC detects logic level
transitions on this input and can be programmed to generate an interrupt when a transition
occurs. As an active-Low external sync input, it is used in COP modes to obtain character
synchronization without receipt of a SYN character. This mode can be used in disc or
tape controller applications or for the optional byte timing lead in X.21.
RTxDRQA/BN,
GPO1A/BN
34, 15 O Channel A (B) Receiver/T ransmitter DMA Service Request or General Purpose
Output: Active-Low. For half-duplex DMA operation, this output indicates to the DMA
controller that one or more characters are available in the receiver FIFO (when the
receiver is enabled) or that the transmit FIFO is not full (when the transmitter is enabled).
For full-duplex DMA operation, this output indicates to the DMA controller that data is
available in the receiver FIFO. In non-DMA mode, this pin is a general purpose output that
can be asserted and negated under program control.
TxDRQA/BN,
GPO2A/BN,
RTSA/BN
33, 16 O Channel A (B) Transmitter DMA Service Request, General Purpose Output, or
Request-to-Send: Active-Low. For full-duplex DMA operation, this output indicates to the
DMA controller that the transmit FIFO is not full and can accept more data. When not in
full-duplex DMA mode, this pin can be programmed as a general purpose or a Request-to
-Send output, which can be asserted and negated under program control (see Detailed
Operation).
RTxDAKA/BN,
GPI1A/BN
44, 5 I Channel A (B) Receiver/Transmitter DMA Acknowledge or General Purpose Input:
Active-Low. For half-duplex single address DMA operation, this input indicates to the
DUSCC that the DMA controller has acquired the bus and that the requested bus cycle
(read receiver FIFO or load transmitter FIFO) is beginning. For full-duplex single address
DMA operation, this input indicates to the DUSCC that the DMA controller has acquired
the bus and that the requested read receiver FIFO bus cycle is beginning. Because the
state of this input can be read under program control, it can be used as a general purpose
input when not in single address DMA mode.
TxDAKA/BN,
GP12A/BN
35, 14 I Channel A (B) Transmitter DMA Acknowledge or General Purpose Input: Active-Low.
When the channel is programmed for full-duplex single address DMA operation, this input
is asserted to indicate to the DUSCC that the DMA controller has acquired the bus and
that the requested load transmitter FIFO bus cycle is beginning. Because the state of this
input can be read under program control, it can be used as a general purpose input when
not in full-duplex single address DMA mode.
DTCN 23 I Device Transfer Complete: Active-Low. DTCN is asserted by the DMA controller to
indicate that the requested data transfer is complete.
DONEN 27 I/O Done: Active-Low, open-drain. See Detailed Operation for a description of the function of
this pin.
RTSA/BN,
SYNOUTA/BN
41, 8 O Channel A (B) Sync Detect or Request-to-Send: Active-Low. If programmed as a sync
output, it is asserted one bit time after the specified sync character (COP or BISYNC
modes) or a FLAG (BOP modes) is detected by the receiver. As a Request-to-Send
modem control signal, it functions as described previously for the TxDRQN/RTSN pin.
V
DD
48 I +5V + 10% power input.
GND 24 I Signal and power ground input.
 Loading...
Loading...