Philips SAB9083H Datasheet
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAB9083
Multistandard Picture-In-Picture
(PIP) controller
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 1999 Feb 18
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1999 Nov 12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multistandard Picture-In-Picture (PIP)
controller
FEATURES
• Double window Picture-In-Picture (PIP) in interlaced or
non-interlaced mode at 8-bit resolution
• Internal 1-Mbit DRAM
• Three 8-bit Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) (7-bit
performance) with clamp circuit for each acquisition
channel
• One PLL which generatesthe line-locked clocks for the
subchannel
• One PLL which generates the line-locked clocks for the
main and display channels
• Three 8-bit Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs)
• Linear zoom in both horizontal and vertical directions for
the subchannel
• Linear zoom in horizontal direction for the main channel
• Three multistandard PIP modes are available.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAB9083 is a multistandard PIP controller which can
be used in double window applications. The SAB9083
inserts one or two live video signals with reduced size into
another live video signal. The incoming video signals are
expected to be analog baseband signals.
SAB9083
The conversion to the digital environment is done on chip
with ADCs. Processing and storage of the video data is
done entirely in the digital domain. The conversion back to
the analog domain is done by means of DACs. Internal
clocks are generated by PLLs which lock on to the applied
horizontal and vertical syncs.
The main input channel is compressed horizontally by a
factor of two and directly fed to the output. After
compression, a horizontal expansion of two is possible for
the main channel.
The subchannel is also compressed horizontally by a
factor of two but stored in memory before it is fed to the
outputs.
The SAB9083 can also create three multistandard PIP
modes, one with three PIPs placed in a column (MP3) and
two with two columns of three PIPs (MP6, MP6S).
The reduction factors of these PIPs are horizontal1⁄4 and
vertical1⁄3. In the first two modes, the column(s) can be
placed on the left or right side of the screen.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
V
I
DDD
I
DDA
DDD
DDA
digital supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
analog supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
digital supply current − 50 − mA
analog supply current 140 165 210 mA
PLL
f
clk(sys)
B
loop
t
jitter
system clock frequency 1792 × f
HSYNC
− 28 − MHz
loop bandwidth − 4 − kHz
short term stability peak-to-peak jitter for 64 µs −−4ns
ζ damping factor − 0.7 −
ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAB9083H QFP100 plastic quad flat package; 100 leads (lead length 1.95 mm);
body 14 × 20 × 2.8 mm
SOT317-2
1999 Nov 12 2
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1999 Nov 12 3
handbook, full pagewidth
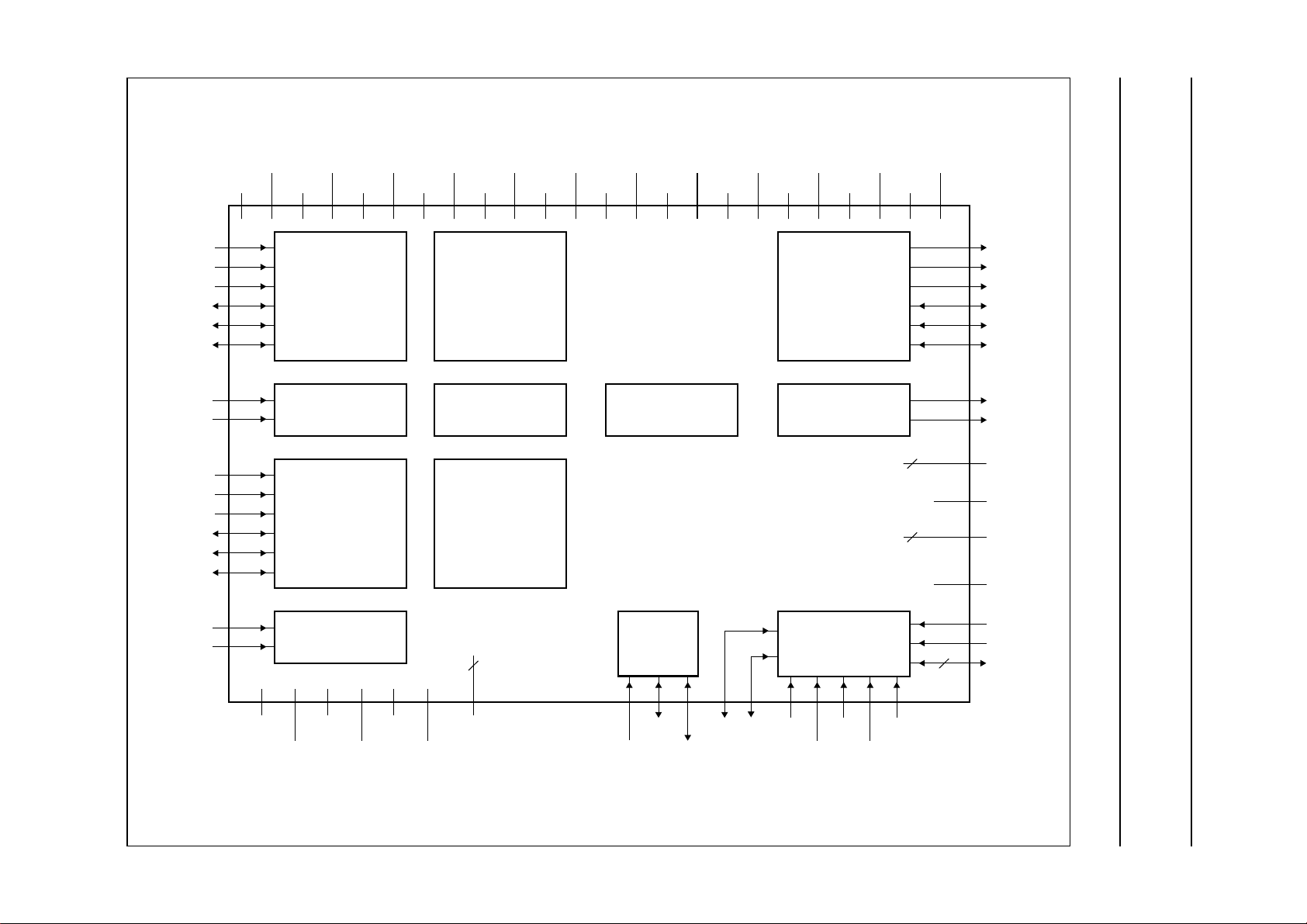
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multistandard Picture-In-Picture (PIP)
controller
V
bias(SA)
V
ref(T)(SA)
V
ref(B)(SA)
SHSYNC
SVSYNC
V
bias(MA)
V
ref(T)(MA)
V
ref(B)(MA)
DHSYNC
DVSYNC
SU
SV
SY
MU
MY
MV
V
DDA(MF)
79
81
83
84
82
80
87
72
2
98
100
97
99
1
94
70
V
V
SSA(MA)
V
DDA(MA)
34
89
DDA(SP)
V
SSA(SP)
V
DDA(DA)
56
CLAMP AND ADC
PLL AND CLOCK
GENERATOR
CLAMP AND ADC
PLL AND CLOCK
GENERATOR
90 91 92 95
V
SSA(DP)
V
SSA(DA)
V
DDA(DP)
V
DDD(DA)
714
V
DDD(MA)
V
SSD(DA)
V
SSD(MA)
V
SSD(P1)
15 16
96
V
DDD(RP)
V
DDD(P1)
17 20
HORIZONTAL
AND
VERTICAL
FILTER
LINE MEMORY INTERNAL DRAM
HORIZONTAL
FILTER
19
21 to 29, 31,
52 to 60
n.c.
V
DDD(RL)
V
SSD(RL)
V
39 40
V
DDD(RM)
SSD(RM)
41 42
POR
CONTROL
75
V
SSD(RP)
2
I
C-BUS
SDA
V
DDD(P2)
61 64
V
SSD(P2)
V
SSD(D)
65 66
V
DDA(SA)
V
DDD(D)
67 76
DAC AND BUFFER
DISPLAY
CONTROL
V
SSA(SA)
SAB9083
TEST
CONTROL
73 88 93 44 43 45 46 47
74
T7
T6
SCL
TCBD TCBR
TCLKTMTCBC
V
DDA(SF)
77 78
V
SSD(SA)
V
DDD(SA)
85 86
18, 19
2
48 to 51
4
62, 63
32 to 37
MGL584
8
DY
10
DV
12
DU
9
V
bias(DA)
11
V
ref(T)(DA)
13
V
ref(B)(DA)
69
PKOFF
68
FBL
V
SSD(T1)
and
V
SSD(T2)
30
V
SSD(T3)
V
SSD(T4)
to
V
SSD(T7)
V
SSD(T8)
and
V
SSD(T9)
71
DCLK
38
TC
6
T5 to T0
SAB9083
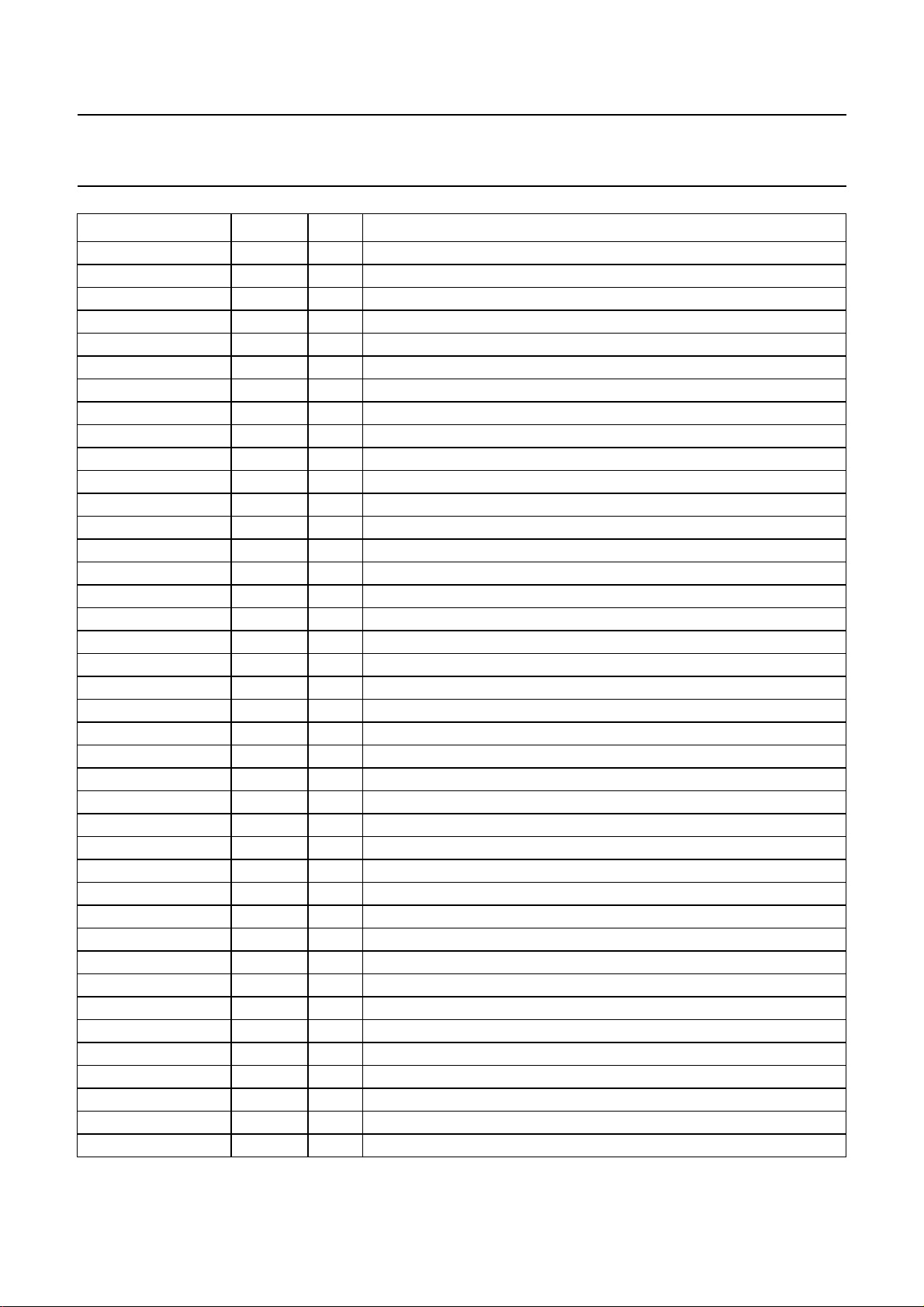
Fig.1 Block diagram.
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multistandard Picture-In-Picture (PIP)
controller
PINNING
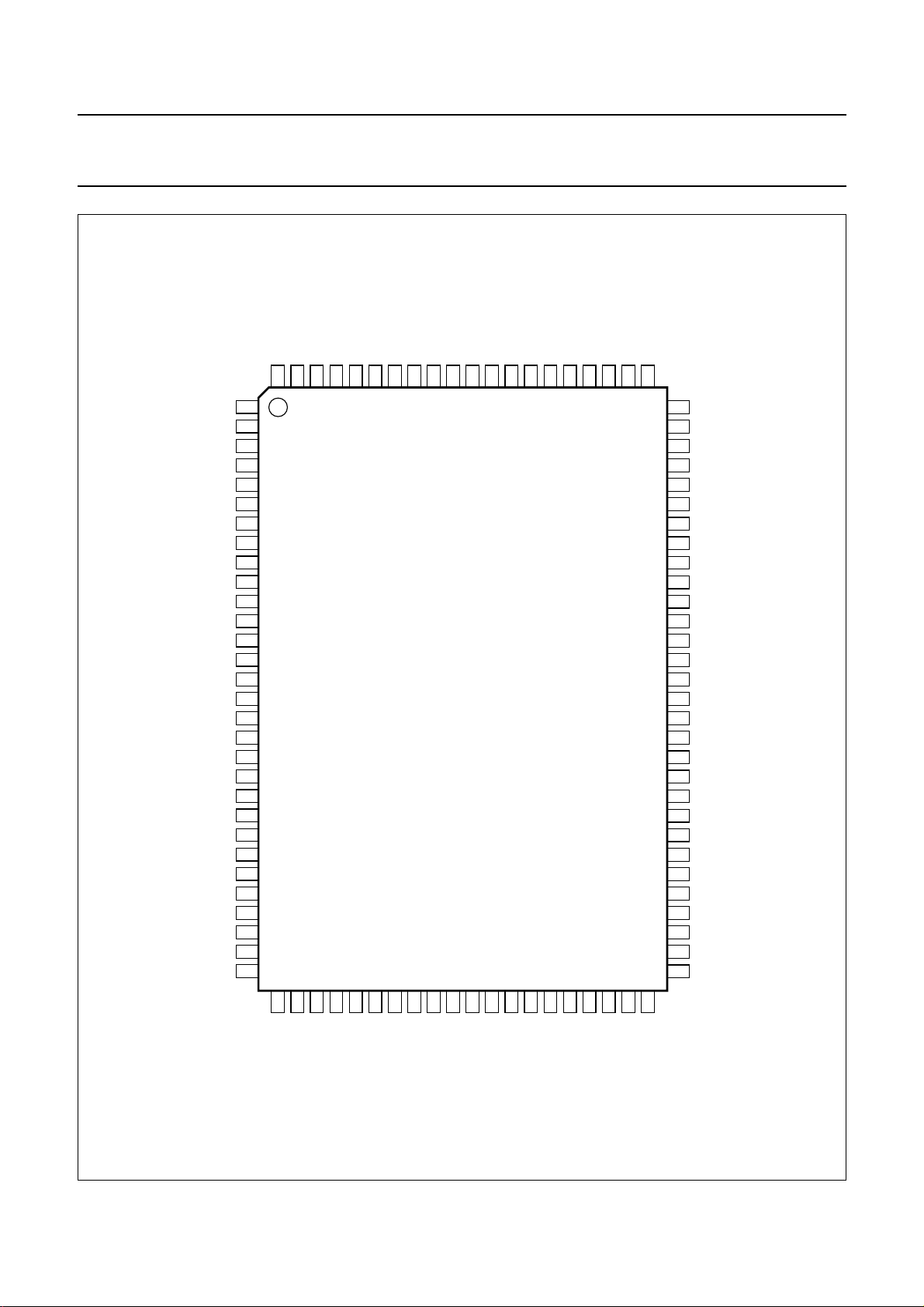
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
V
ref(B)(MA)
MU 2 I analog U input for main channel
V
DDA(MF)
V
SSA(MA)
V
DDA(MA)
V
DDA(DA)
V
SSA(DA)
DY 8 O analog Youtput of DAC
V
bias(DA)
DV 10 O analog V output of DAC
V
ref(T)(DA)
DU 12 O analog U output of DAC
V
ref(B)(DA)
V
DDD(DA)
V
SSD(DA)
V
SSD(P1)
V
DDD(P1)
V
SSD(T1)
V
SSD(T2)
V
DDD(RP)
n.c. 21 to 29 − not connected
V
SSD(T3)
n.c. 31 − not connected
T5 32 I/O test data input/output bit 5 (CMOS levels)
T4 33 I/O test data input/output bit 4 (CMOS levels)
T3 34 I/O test data input/output bit 3 (CMOS levels)
T2 35 I/O test data input/output bit 2 (CMOS levels)
T1 36 I/O test data input/output bit 1 (CMOS levels)
T0 37 I/O test data input/output bit 0 (CMOS levels)
TC 38 I test control input (CMOS levels)
V
DDD(RL)
V
SSD(RL)
V
SSD(RM)
V
DDD(RM)
TCLK 43 I test clock input (CMOS levels)
TM 44 I test mode input (CMOS levels)
TCBD 45 I test control block data input (CMOS levels)
TCBC 46 I test control block clock input (CMOS levels)
TCBR 47 I test control block reset input (CMOS levels)
V
SSD(T4)
to V
SSD(T7)
1 I/O analog bottom reference voltage for main channel ADCs
3 S analog supply voltage for main channel front-end buffers
4 S analog ground for main channel ADCs
5 S analog supply voltage for main channel ADCs
6 S analog supply voltage for DACs
7 S analog ground for DACs
9 I/O input/output analog bias reference voltage for DACs
11 I/O input/output analog top reference voltage for DACs
13 I/O analog bottom reference voltage for DACs
14 S digital supply voltage for DACs
15 S digital ground for DACs
16 S digital ground for periphery
17 S digital supply voltage for periphery
18 S digital ground for test
19 S digital ground for test
20 S digital supply voltage for memory periphery
30 S digital ground for test
39 S digital supply voltage for memory logic
40 S digital ground for memory logic
41 S digital ground for memory core
42 S digital supply voltage for memory core
48 to 51 S digital ground for test
SAB9083
1999 Nov 12 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multistandard Picture-In-Picture (PIP)
SAB9083
controller
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
n.c. 52 to 60 − not connected
V
SSD(RP)
V
SSD(T8)
V
DDD(P2)
V
SSD(P2)
V
SSD(D)
V
DDD(D)
and V
SSD(T9)
FBL 68 O fast blanking control signal output (CMOS levels; +5 V tolerant)
PKOFF 69 O peak off control signal output (CMOS levels; +5 V tolerant)
DVSYNC 70 I vertical sync display channel input (CMOS levels; +5 V tolerant)
DCLK 71 I test clock input (28 MHz; CMOS levels)
SVSYNC 72 I vertical sync for subchannel input (CMOS levels; +5 V tolerant)
SCL 73 I/O input/output serial clock (I
SDA 74 I/O input/output serial data/acknowledge output (I
POR 75 I power-on reset input (CMOS levels; pull-up resistor connected to V
V
DDA(SA)
V
SSA(SA)
V
DDA(SF)
SU 79 I analog U input for subchannel
V
ref(B)(SA)
SV 81 I analog V input for subchannel
V
ref(T)(SA)
SY 83 I analog Y input for subchannel
V
bias(SA)
V
SSD(SA)
V
DDD(SA)
SHSYNC 87 I horizontal sync input for subchannel (V
T6 88 I/O test data input/output bit 7 (CMOS levels)
V
DDA(SP)
V
SSA(SP)
V
SSA(DP)
V
DDA(DP)
T7 93 I/O test data input/output bit 6 (CMOS levels)
DHSYNC 94 I horizontal sync input for display channel (V
V
DDD(MA)
V
SSD(MA)
V
bias(MA)
MY 98 I analog Y input for main channel
V
ref(T)(MA)
MV 100 I analog V input for main channel
61 S digital ground for memory periphery
62 and 63 S digital ground for test
64 S digital supply voltage for periphery
65 S digital ground for periphery
66 S digital ground for digital core
67 S digital supply voltage for digital core
2
C-bus; CMOS levels; +5 V tolerant)
2
C-bus; +5 V tolerant)
76 S analog supply voltage for subchannel ADCs
77 S analog ground for subchannel ADCs
78 S analog supply voltage for subchannel front-end buffers and clamps
80 I/O input/output analog bottom reference voltage for subchannel ADCs
82 I/O input/output analog top reference voltage for subchannel ADCs
84 I/O analog bias reference voltage for subchannel ADCs
85 S digital ground for subchannel ADCs
86 S digital supply voltage for subchannel ADCs
i<VSHSYNC
)
89 S analog supply voltage for subchannel PLL
90 S analog ground for subchannel PLL
91 S analog ground for display channel PLL
92 S analog supply voltage for display channel PLL
i<VDHSYNC
)
95 S digital supply voltage for main channel ADCs
96 S digital ground for main channel ADCs
97 I/O analog bias reference voltage for main channel ADCs
99 I/O analog top reference voltage for main channel ADCs
DD
)
1999 Nov 12 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multistandard Picture-In-Picture (PIP)
controller
handbook, full pagewidth
ref(T)(MA)
bias(MA)VSSD(MA)VDDD(MA)
V
MY
V
99989796959493929190898887868584838281
DHSYNCT7V
V
ref(B)(MA)
V
DDA(MF)
V
SSA(MA)
V
DDA(MA)
V
DDA(DA)
V
SSA(DA)
V
bias(DA)
V
ref(T)(DA)
V
ref(B)(DA)
V
DDD(DA)
V
SSD(DA)
V
SSD(P1)
V
DDD(P1)
V
SSD(T1)
V
SSD(T2)
V
DDD(RP)
V
SSD(T3)
MU
DY
DV
DU
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
MV
100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
DDA(DP)VSSA(DP)VSSA(SP)VDDA(SP)
T6
SAB9083
DDD(SA)VSSD(SA)Vbias(SA)
SHSYNC
V
SY
ref(T)(SA)
V
SV
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
V
ref(B)(SA)
SU
V
DDA(SF)
V
SSA(SA)
V
DDA(SA)
POR
SDA
SCL
SVSYNC
DCLK
DVSYNC
PKOFF
FBL
V
DDD(D)
V
SSD(D)
V
SSD(P2)
V
DDD(P2)
V
SSD(T9)
V
SSD(T8)
V
SSD(RP)
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
V
SSD(T7)
SAB9083
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
T5T4T3T2T1
n.c.
T0
TC
DDD(RL)
V
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
1999 Nov 12 6
SSD(RL)
SSD(RM)
V
V
TCLK
DDD(RM)
V
TM
TCBD
TCBC
TCBR
50
MGL585
SSD(T4)VSSD(T5)VSSD(T6)
V
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multistandard Picture-In-Picture (PIP)
controller
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Acquisition
The internal pixel rate is 28 MHz for the Y, U and V
channels. It is expected that the bandwidth of the input
signals will be limited to 4.5 MHz for the Y input and
1.125 MHz for the U and V inputs. Inset synchronisation is
achieved via the acquisition HSYNC and VSYNC pins of
the main channel. The display is driven by the main
channel clock.
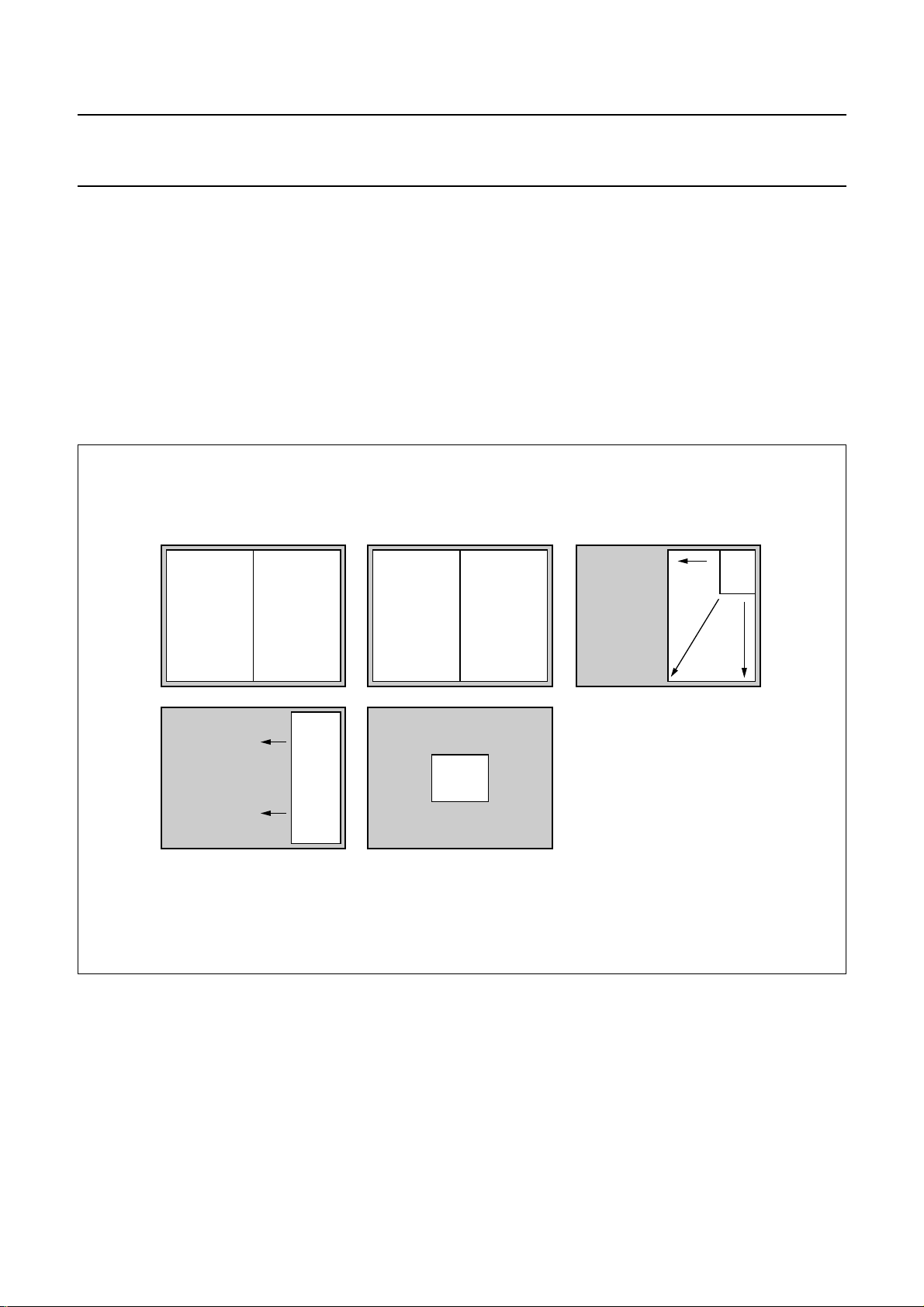
PIP modes
handbook, full pagewidth
SAB9083
The starting-point of the acquisition can be controlled with
the acquisition fine positioning added to a system
constant. With a nominal input f
signals, 1408 samples (active video) are acquired and
processed by the SAB9083. Here, the nominal input
f
results in a nominal system clock frequency of
HSYNC
1792 × f
(approximately 28 MHz).
HSYNC
and standard NTSC
HSYNC
SUB
MAIN SUB
MAIN
SUB
REPLAY
MAIN
Fig.3 PIP modes.
MGM810
1999 Nov 12 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Multistandard Picture-In-Picture (PIP)
controller
handbook, full pagewidth
S0
S1
S2
S0
S2
S4
S1
S3
S5
MAIN
S0
S1
S2
MAIN
S0
S1
S2
MAIN
MAIN
S0
S2
S4
SAB9083
S1
S3
S5
S0
S1
S2
S0
S2
S4
S1
S3
S5
S0
S2
S4
S0
S2
S4
MAIN
S1
S3
S5
S1
S3
S5
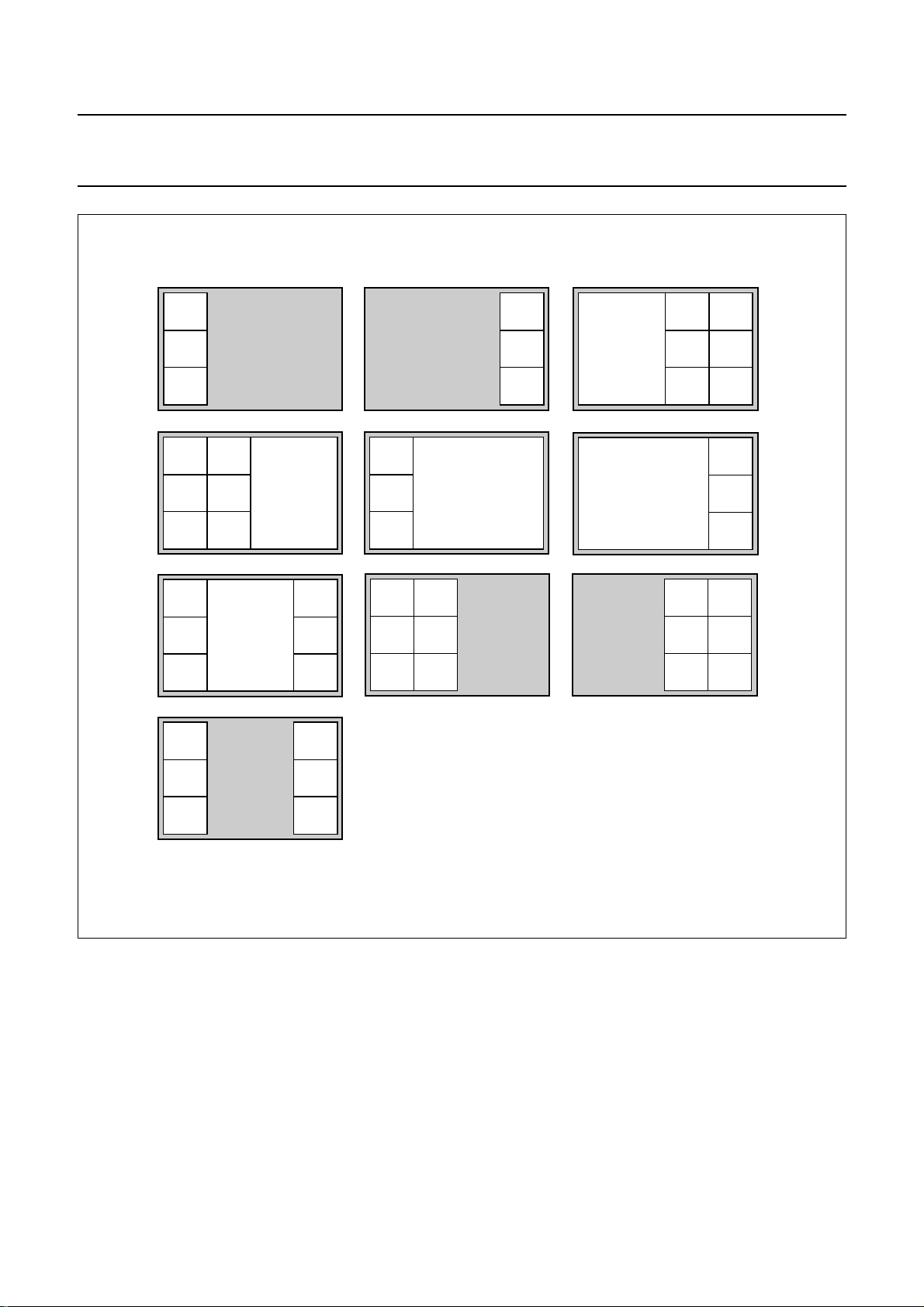
Fig.4 Multistandard PIP modes.
I2C-bus description
The I2C-bus provides bidirectional 2-line communication
between different ICs. The SDA line is the serial data line
and the SCL the serial clock line. Both lines must be
connected to a positive supply via a pull-up resistor when
connected to the output stages of a device.
Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not
busy. The SAB9083 has the I2C-bus address 2CH. Valid
subaddresses are 00H to 18H, register 15H (except bits 7
and 6) and registers 16H to 18H are reserved for future
extensions.
S0
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
MGL587
2
I
C-bus control is according to the I2C-bus protocol: first, a
START sequence must be put on the I2C-bus Then, the
I2C-bus address of the circuit must be sent, followed by a
subaddress. After this sequence, the data of the
subaddresses must be sent. An auto-increment function
gives the option of sending data of the incremented
subaddresses until a STOP sequence is sent. Table 1
gives an overview of the I2C-bus addresses. The data bits
that are not used should be set to zero.
1999 Nov 12 8
 Loading...
Loading...