INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAA8110G
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1997 Jun 13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
FEATURES
• High precision digital processing with 9 or 10 bit input
• Different types of CCDs (PAL, NTSC and CIF)
(progressive, interlaced and non-interlaced)
• Black offset preprocessing (including optical black offset
control)
• RGB-separation (with contour and white clip signals
generation)
• RGB-processing (colour space matrix, black control,
knee and gamma)
• RGB-to-YUV conversion (including down-sampling
filters)
• White balance control
• Y -processing (contour processing, false colour detector ,
filters and noise reduction)
• UV-processing (false colour correction and noise
reduction)
• Digital output formatter (including CIF-formatter, DTV2,
D1)
• Analog output preprocessing (including
PAL/NTSC-encoder and DACs)
• Measurement engine (prepared for auto-exposure and
auto-white balance features)
• Miscellaneous functions (e.g. switched mode power
supply pulse generator, control DAC)
• VH-reference and window timing
• Serial interface (selectable I2C-bus or 80C51 UART
interface)
• Mode control (including power management).
APPLICATIONS
• Desktop video applications
• Surveillance systems
• Video-phone systems.
SAA8110G
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA8110G is designed for desktop video applications
(teleconferencing, video grabbing), surveillance and
video-phone systems.
The SAA8110G may be applied together with an analog
front-end (TDA8786 including CDS/AGC/ADC), a timing
generator and a microcontroller as shown in
Figs 18 and 19. Other configurations are also possible.
The CCD-sensor can be of PAL, NTSC or CIF type (with
complementary mosaic colour filter). The maximum
number of active pixels is limited to 800 samples/line.
The 10-bits digital input may have a pixel frequency of up
to 14.318 MHz.
The SAA8110G output data is available in a digital and an
analog output format. Two digital output formats are
selectable: DTV2 (CCIR-601 at the input pixel frequency)
and D1 (CCIR-656 at twice the input pixel frequency). It is
also possible to generate the CIF and QCIF formats as
subsets from the processed CCD-image. The analog
output is available in one of four formats: RGB, YUV, YC
or CVBS. The SAA8110G includes a digital
PAL/NTSC-encoder and 3 DACs for this purpose.
Two types of serial interface are selectable: a fast 400 kHz
2
C-bus interfaceor a 80C51 UART interface (with bit rates
I
from 1 Mbit/s up to 3.75 Mbit/s depending on the system
clock used). The power dissipation of the SAA8110G can
be optimized for each application using the built-in power
management function.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
SAA8110G LQFP80 plastic low profile quad flat package; 80 leads; body 12 × 12 × 1.4 mm SOT315-1
1997 Jun 13 2
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
SAA8110G
cameras
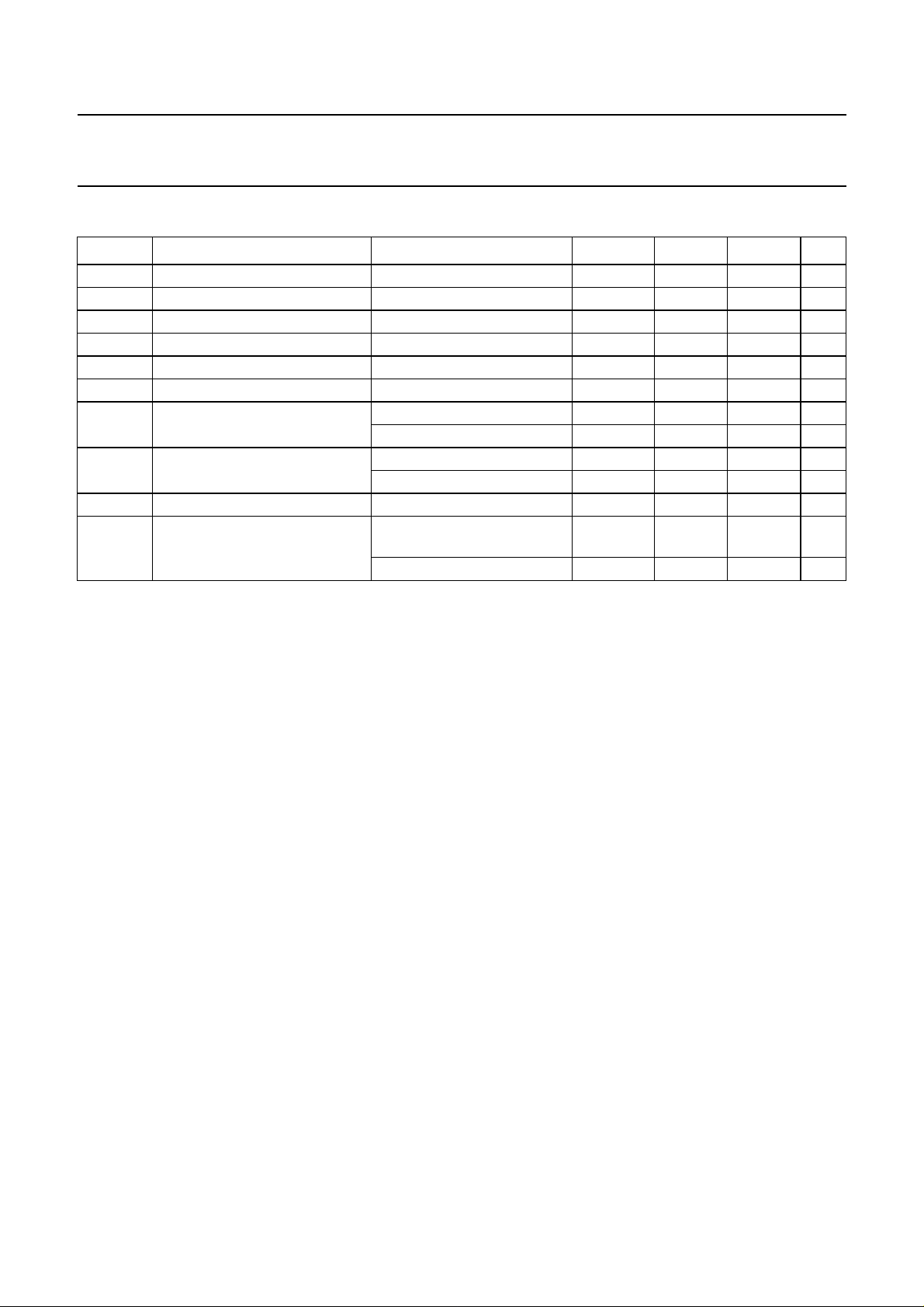
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DDD
V
DDA
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
I
DDD(tot)
I
DDA(tot)
T
amb
I
DMD
digital supply voltage 3 5 5.25 V
analog supply voltage 3 5 5.25 V
LOW level digital input voltage 0 − 0.3V
HIGH level digital input voltage 0.6V
DDD
− V
DDD
DDD
V
V
LOW level digital output voltage IOL = −20 µA −−0.5 V
HIGH level digital output voltage IOH = 20 µAV
total digital supply current f
total analog supply current f
= 14.3 MHz; V
clk
f
= 14.3 MHz; V
clk
= 14.3 MHz; V
clk
f
= 14.3 MHz; V
clk
=5V − 180 200 mA
DDD
= 3.3 V − 80 100 mA
DDD
=5V − 30 40 mA
DDA
= 3.3 V − 22 35 mA
DDA
− 0.1 −−V
DDD
operating ambient temperature 0 − 75 °C
supply current in digital output
mode
f
= 14.3 MHz; V
clk
note 1
= 14.3 MHz; V
f
clk
=5V;
DDD
= 3.3 V − 85 − mA
DDD
− 185 − mA
Note
1. When digital mode is selected, V
supply pins can be connected to ground.
DDA
1997 Jun 13 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
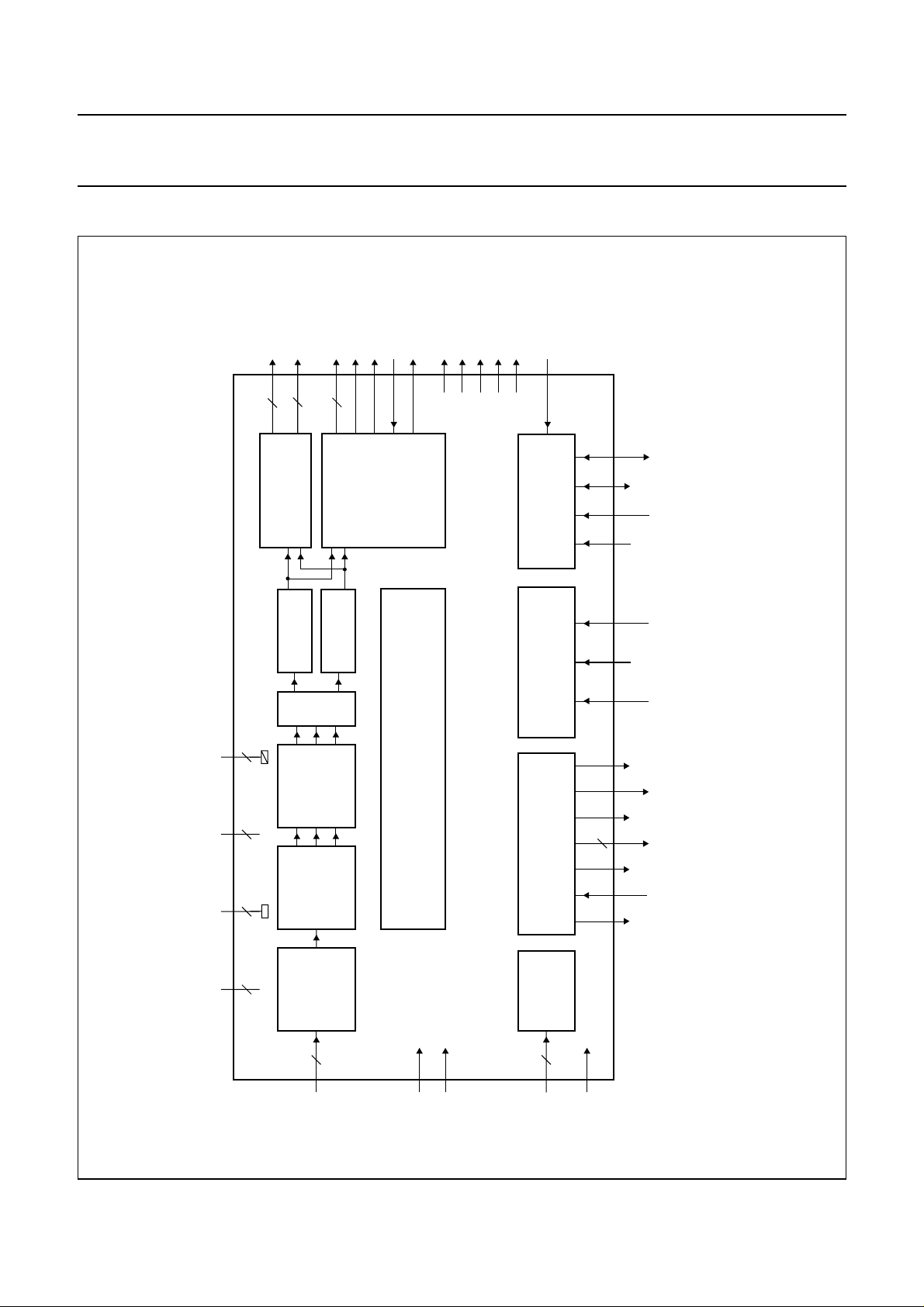
BLOCK DIAGRAM
OUT3 to OUT1
DECOUPL
Y0 to Y7
70 to 63
61 to 54
DIGITAL
OUTPUT
UV0 to UV7
35, 37, 39
FORMATTER
RBIAS
44
43
OUTPUT
ANALOG
PREPROCESSING
OUT
XINX
80
79
V DACs
ENCODER
PAL/NTSC-
OUT
OUT
LLC
FI
HREF
VSYNC
4950485251
CREF/PXQ
SIS
28
C
2
I
SNERT/
SELECT
C
2
SNERT/I
INTERFACE
73 77 75 74
MGK158
SDA
RES
A1/SN
SAA8110G
DA
A0/SN
CL
SCL/SN
ull pagewidth
SSA(CD)
SSA(OB)
SSA(BG)
V
V
V
DDA(BG)
DDA(DC)
DDA(CD)
DDA(O1)
DDA(O2)
V
V
V
DDD(C2)
DDD(C3)
V
V
V
DDA(O3)
V
DDD(P1)
DDD(P2)
V
V
V
SSD(C1)VSSD(C2)VSSD(C3)VSSD(C4)VSSD(P1)VSSD(P2)
V
DDD(C1)
V
19, 34,
42
45, 41, 22,
40, 38, 36
6, 17, 76,
78, 53, 71
1, 29,72,
46, 62
Y-
UV-
PROCESSING
TO
YUV
RGB
RGB
PROCESSING
RGB
(INCL. LINE
SEPARATION
PRE-
OFFSET
PROCESSING
PROCESSING
MEMORIES)
SAA8110G
MEASUREMENT ENGINE
IN
FI
IN
IN
HSYNC
345
TIMING AND CONTROL
VH-REFERENCE WINDOW
23 24 18
26,
27
FUNCTIONS
MISCELLANEOUS
20 21 25
MODE
CONTROL
VSYNC
SCLKCDAC
STROBE
SDATA
P0, P1
SMP
RBIAS
OUT
CDAC
Fig.1 Block diagram.
47
7 to 16
CCD9toCCD0
2
CLK1
CLK2
1997 Jun 13 4
31 to 33
T2, T1, T0
30
RESET
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN I/O DESCRIPTION
V
DDD(C1)
CLK1 2 I system- or pixel clock
VSYNC
HSYNC
FI
V
IN
IN
IN
SSD(C1)
CCD9 7 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 9 (MSB)
CCD8 8 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 8
CCD7 9 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 7
CCD6 10 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 6
CCD5 11 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 5
CCD4 12 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 4
CCD3 13 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 3
CCD2 14 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 2
CCD1 15 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 1
CCD0 16 I (preprocessed) AD-converted CDD-signal bit 0 (LSB)
V
SSD(C2)
SCLK 18 O serial clock to TDA8786
V
SSA(CD)
CDAC
OUT
CDAC
RBIAS
V
DDA(CD)
SDATA 23 O serial data to TDA8786
STROBE 24 O strobe to TDA8786
SMP 25 O switch mode pulse for DC-DC
P0 26 O quasi-static control output pin 0
P1 27 O quasi-static control output pin 1
SIS 28 I SNERT/I
V
DDD(C2)
RESET 30 I reset input
T2 31 I test mode control signal bit 2
T1 32 I test mode control signal bit 1
T0 33 I test mode control signal bit 0
V
SSA(OB)
OUT3 35 O output buffer 3 (R, V or CVBS)
V
DDA(O3)
OUT2 37 O output buffer 2 (B, U or C)
V
DDA(O2)
OUT1 39 O output buffer 1 (G or Y)
V
DDA(O1)
1 I digital supply 1 for digital core and CLK1 related peripherals
3 I vertical synchronization input
4 I horizontal synchronization input
5 I field identification signal input
6 I digital ground 1 for digital core and CLK1 related peripherals
17 I digital ground 2 for digital core and CLK1 related peripherals
19 I analog ground for control DAC
20 O output control DAC
21 I pin to connect external bias resistor for control DAC
22 I analog supply for control DAC
2
C-bus select input signal
29 I digital supply 2 for digital core and CLK1 related peripherals
34 I analog ground for the three output buffers
36 I analog supply for output buffer OUT3
38 I analog supply for output buffer OUT2
40 I analog supply for output buffer OUT1
SAA8110G
1997 Jun 13 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
SYMBOL PIN I/O DESCRIPTION
V
DDA(DC)
V
SSA(BG)
DECOUPL 43 O pin to be used for external decoupling of band gap
RBIAS 44 O external bias resistor connection for band gap
V
DDA(BG)
V
DDD(P1)
CLK2 47 I output clock (CLK2 frequency is 2 × CLK1 frequency)
FI
OUT
VSYNC
OUT
HREF 50 O horizontal reference output for YUV-port
CREF/PXQ 51 O clock/pixel qualifier output for YUV-port
LLC 52 O line-locked system clock output
V
SSD(P1)
UV7 54 O multiplex chrominance UV bit 7 (MSB)
UV6 55 O multiplex chrominance UV bit 6
UV5 56 O multiplex chrominance UV bit 5
UV4 57 O multiplex chrominance UV bit 4
UV3 58 O multiplex chrominance UV bit 3
UV2 59 O multiplex chrominance UV bit 2
UV1 60 O multiplex chrominance UV bit 1
UV0 61 O multiplex chrominance UV bit 0 (LSB)
V
DDD(P2)
Y7 63 O luminance Y or multiplexed YUV bit 7 (MSB)
Y6 64 O luminance Y or multiplexed YUV bit 6
Y5 65 O luminance Y or multiplexed YUV bit 5
Y4 66 O luminance Y or multiplexed YUV bit 4
Y3 67 O luminance Y or multiplexed YUV bit 3
Y2 68 O luminance Y or multiplexed YUV bit 2
Y1 69 O luminance Y or multiplexed YUV bit 1
Y0 70 O luminance Y or multiplexed YUV bit 0 (LSB)
V
SSD(P2)
V
DDD(C3)
A1/SN
RES
A0/SN
DA
SDA 75 I I
V
SSD(C3)
SCL/SN
V
X
X
CL
SSD(C4)
IN
OUT
41 I analog supply for analog core of triple DAC
42 I analog ground for to band gap
45 I analog supply for band gap
46 I digital supply 1 for CLK2 related peripherals
48 O field identification output pulse
49 O vertical synchronization output
53 I digital ground 1 for CLK2 related peripherals
62 I digital supply for CLK2 related peripherals
71 I digital ground 2 for to CLK2 related peripherals
72 I digital supply 3 for digital core and CLK1 related peripherals
73 I I2C-bus address select pin A1 or SNERT reset input
74 I I2C-bus address select pin A0 or SNERT data input/output
2
C-bus data input/output
76 I digital ground 3 for digital core and CLK1 related peripherals
77 I I2C-bus clock/SNERT clock input
78 I digital ground 4 for digital core and CLK1 related peripherals
79 I input crystal oscillator for subcarrier lock applications
80 O output crystal oscillator for subcarrier lock applications
SAA8110G
1997 Jun 13 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
handbook, full pagewidth
V
DDD(C1)
VSYNC
HSYNC
V
SSD(C1)
V
SSD(C2)
V
SSA(CD)
CDAC
CLK1
FI
CCD9
CCD8
CCD7
CCD6
CCD5
CCD4
CCD3
CCD2
CCD1
CCD0
SCLK
OUT
OUTXINVSSD(C4)
X
80
79
78
1
2
3
IN
4
IN
5
IN
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
SCL/SNCLV
77
SSD(C3)
SDA
76
75
A0/SNDAA1/SN
74
RES
73
V
72
DDD(C3)VSSD(P2)
Y0
71
70
SAA8110G
Y1
69
Y2
68
Y3
67
Y4
66
Y5
65
Y6
64
Y7
63
SAA8110G
DDD(P2)
V
UV0
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
UV1
UV2
UV3
UV4
UV5
UV6
UV7
V
SSD(P1)
LLC
CREF/PXQ
HREF
VSYNC
OUT
FI
OUT
CLK2
V
DDD(P1)
V
DDA(BG)
RBIAS
DECOUPL
V
SSA(BG)
V
DDA(DC)
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
P0
P1
RBIAS
CDAC
SDATA
DDA(CD)
V
SMP
STROBE
SIS
RESET
DDD(C2)
V
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
1997 Jun 13 7
31
T2
32
T1
33
T0
34
35
OUT3
SSA(OB)
V
36
37
OUT2
DDA(O3)
V
38
39
OUT1
DDA(O2)
V
40
DDA(O1)
V
MGK151
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Black offset preprocessing
The input data is clamped within the optical black pixel
area of the CCD. The size of the digital clamp window is
16 pixels by 128 lines (i.e. TDA8786). It is possible to
differentiate black levels for odd/even lines, pixels and
fields. This comes in addition to the analog preprocessing
clamp which is active on the clamp pulse generated by the
external timing circuit. The analog clamp is included in the
TDA8786.
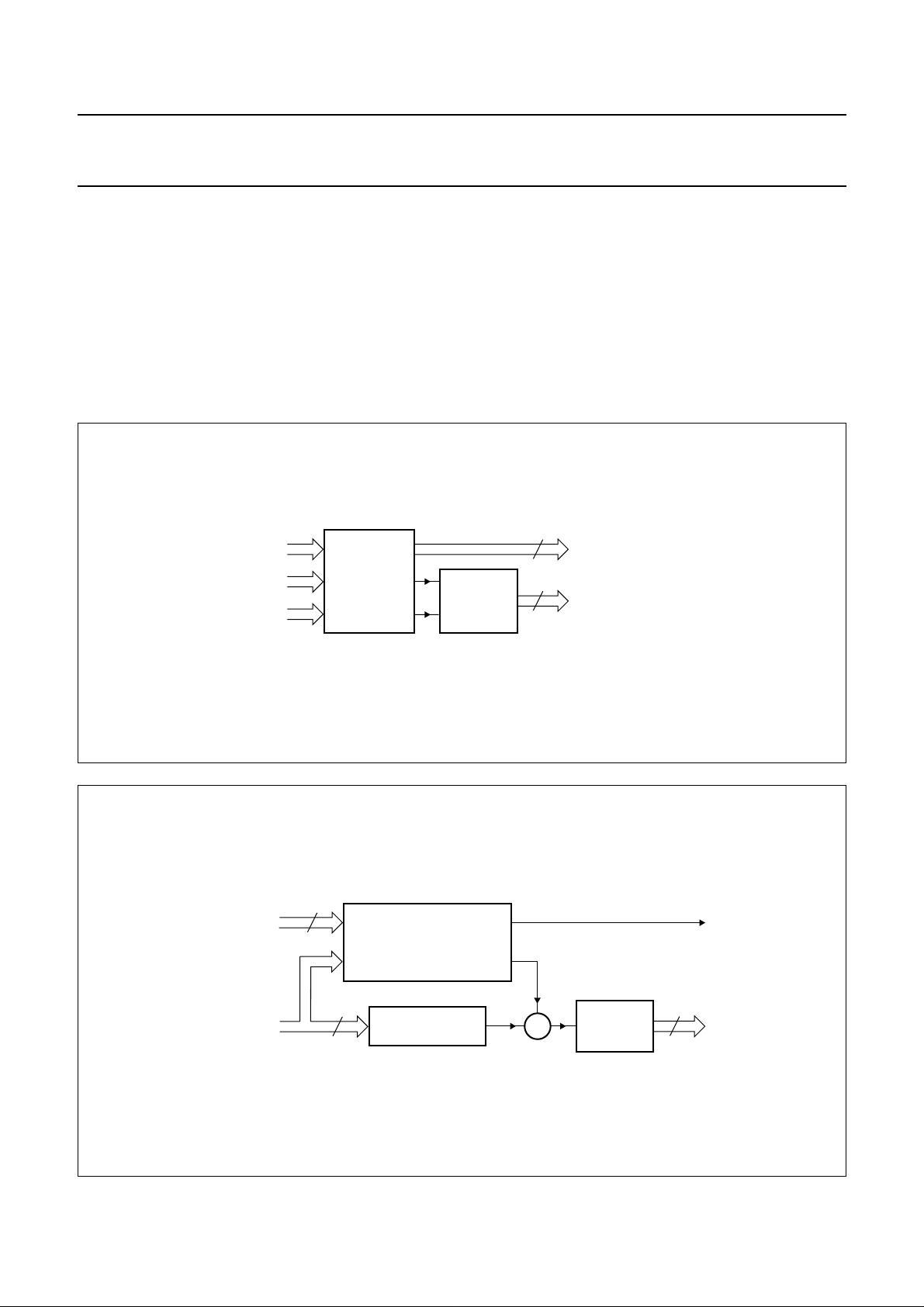
RGB separation
PAL/NTSC sensors generate interlaced data adding offset
in the complementary colour pixels. The RGB separation
block with its two line memories generates the three
components Y, 2R − G, and 2B − G for each input data
corresponding to a pixel value of the CCD. Then the
triplet R, G, B is derived. This block also delivers some
contour and white clip information.
SAA8110G
RGB processing
The RGB processing includes several features:
• Colour space matrix depending on CCD type to be
suitable with different sensor colour filters
• Gain correction for R and B signals for white balance
control
• Black offset
• Adjustable knee
• Adjustable gamma function.
The knee function is applied to all three RGB signals.
Its shape is continuously adjustable by changing the slope
and the knee offset point.
To compensate for the non-linear response of display
devices, a gamma correction is applied to R, G and B
signals. It may be adjustable from linear to a 0.35 power
coefficient.
handbook, full pagewidth
handbook, full pagewidth
CCD inputs
R
G
B
COLOUR
MATRIX
LINE
MEMORY
RGB
LINE
MEMORY
10
COLOUR
SEPARATION
Fig.3 RGB separation diagram.
R
gainRblack
×
G
+
black
3 ×
KNEE
+
B
gainBblack
×
+
R
G
B
white clip
vertical contour
MGK153
R
3 ×
GAMMA
G
B
MGK154
Fig.4 RGB processing.
1997 Jun 13 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
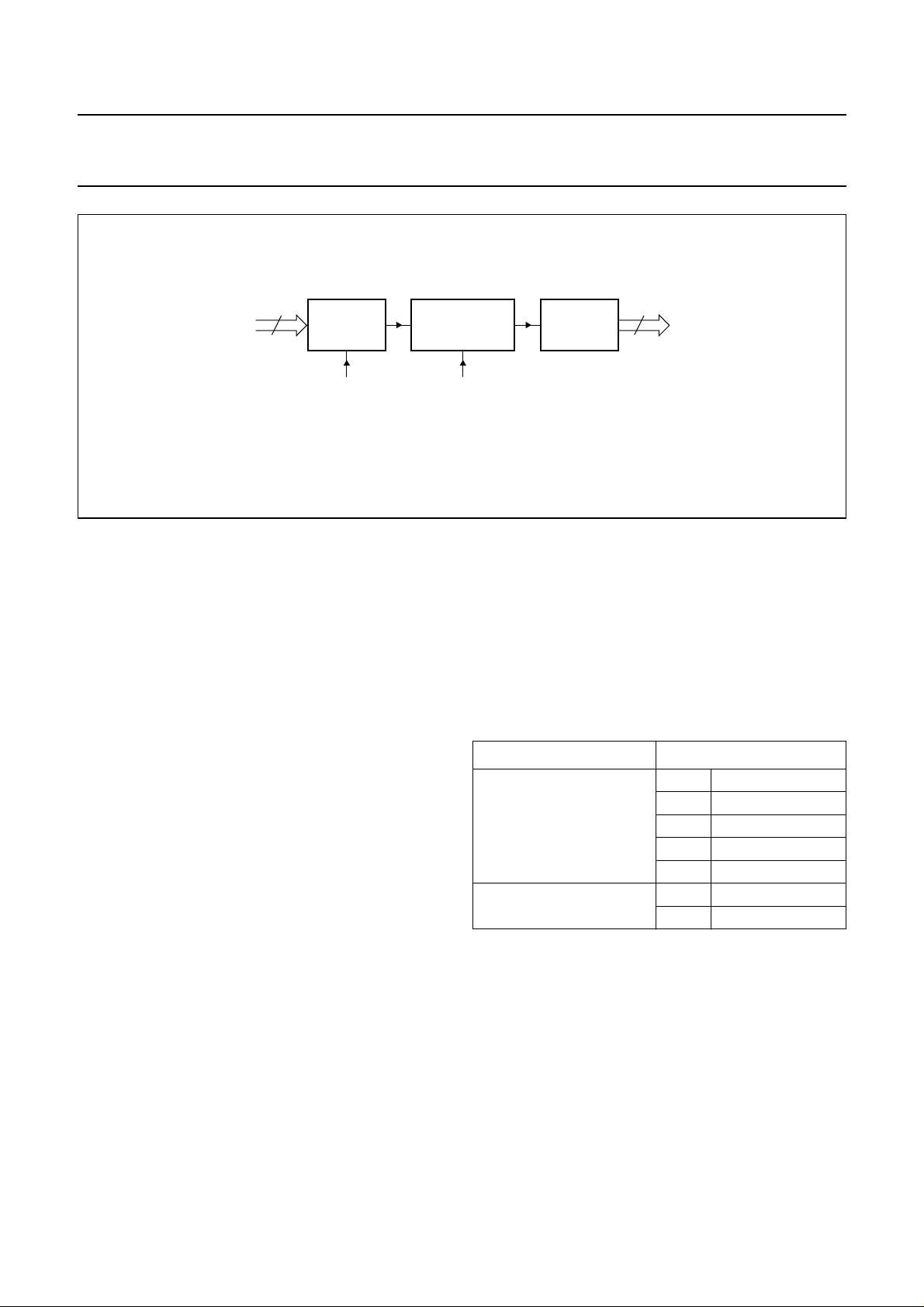
RGB-to-YUV block
After RGB processing, the channels are separated in a
luminance and two colour difference path:
Y = 0.299 R + 0.597 G + 0.114 B, U = 0.49 (B − Y) and
V = 0.88 (R − Y) . It also contains two down-sampling
filters for U and V signals.
Y-processing
The luminance component includes several features:
handbook, full pagewidth
R
G
B
CONVERSION
MATRIX
SAA8110G
• Contour correction allowing an increase of the
luminance transitions for a sharper picture
• Black stretch function for contrast enhancement in dark
scenes
• False colour detector used by the UV-processing block
to enable the colour killer
• Filters and noise reduction by coring (only in the high
frequency part of the signal).
9
Y
(0 to 511)
DOWN-
SAMPLING
& MUX
8
UV
(−128 to 127)
MGK155
handbook, full pagewidth
(from RGB-separation)
vertical contour
(−512 to 511)
(0, 0.5 to 255.5)
Fig.5 RGB-to-YUV conversion.
10
CONTOUR PROCESSING
FALSE COLOUR DETECTION
Y
9
AND
BLACK STRETCH
+
NOISE
REDUCTION
false colour
8
Y
MGK156
Fig.6 Y processing.
1997 Jun 13 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
handbook, full pagewidth
(−127 to 128)
UV-processing
The chrominance component includes several features:
• Noise reduction for high frequencies
• False colour correction: a colour killer cuts the false
colour components in the UV signals
• UV-gain control used to set the correct UV levels for
PAL/NTSC encoding.
As the colour filter saturation levels may be different in the
CCD, the white clip is used in the UV-processing to
suppress colour errors in case of high exposure.
Digital output formatter
This block contains several features:
• Generation of a synchronous clock LLC (twice the clock
frequency)
• Generation of three synchronization signals (HREF,
CREF and VS)
• Synchronization of the output data to the output clock
LLC
• Generation of a CIF/QCIF output format for several type
of sensors (see Table 1)
• Selection of the required digital output format (8-bit
multiplexed YUV standard D1/CCIR 656, including the
generator of SAV/EAV codes or 16-bit multiplexed YUV
4:2:2 standard DTV2/CCIR601).
UV
8
NOISE
REDUCTION
false colour
(from Y-processing)
FALSE COLOUR
CORRECTION
(from RGB-separation)
Fig.7 UV-processing.
SAA8110G
UV GAIN
CONTROL
white clip
Moreover, using a high resolution PAL and NTSC CCDs,
it is possible to generate the following formats by means of
cutting or down-sampling.
• CIF 352 × 288 at 25 frame/second and CIF 352 × 240 at
30 frame/second
• QCIF 176 × 144 at 25 frame/second and QCIF
176 × 120 at 30 frame/second.
Table 1 CIF/QCIF output format for different sensor
types
INPUT FORMAT OUTPUT FORMAT
PAL/NTSC-sensor CIF ‘full screen’
CIF QCIF ‘full screen’
8
UV
(−127 to 128)
MGK157
CIF ‘zoom-by-2’
QCIF ‘full screen’
QCIF ‘zoom-by-2’
QCIF ‘zoom-by-4’
QCIF ‘zoom-by-2’
Note that the D1 frequency data rate is twice the DTV2
frequency data rate.
1997 Jun 13 10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for
cameras
handbook, full pagewidth
HSYNC
VSYNC
FI
IN
VSYNC
FI
OUT
CSYNC
BLANK
BURST
521523525246810121418205225241357911131519212223
IN
IN
OUT
SAA8110G
MGK159
handbook, full pagewidth
HSYNC
IN
VSYNC
IN
FI
IN
VSYNC
OUT
FI
OUT
CSYNC
BLANK
BURST
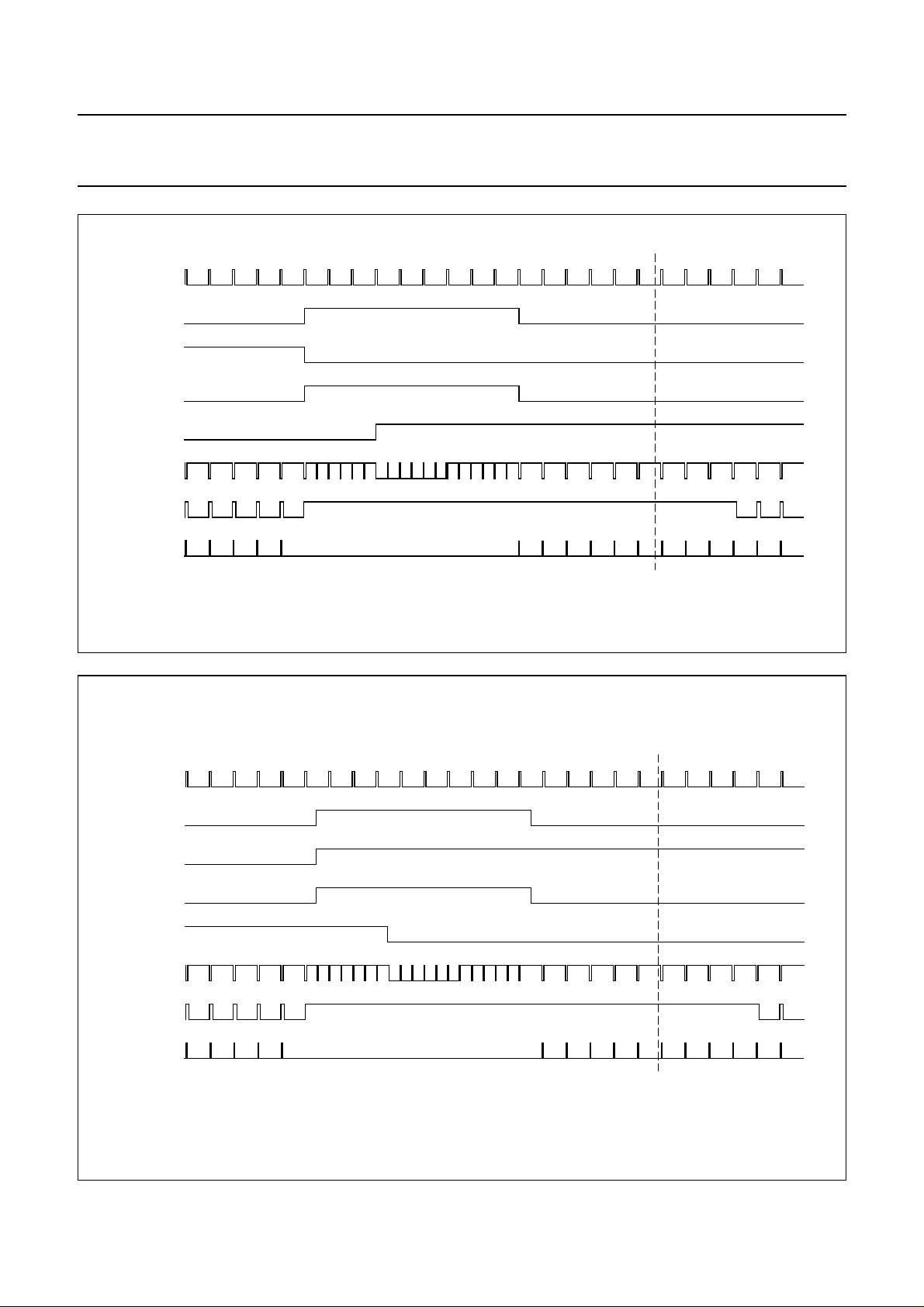
Fig.8 Vertical timing NTSC odd field.
258 260 262 264 266 268 270 272 274 276 280 282259 261 263 265 267 269 271 273 275 277 281 283 284 285
MGK160
Fig.9 Vertical timing NTSC even field.
1997 Jun 13 11
 Loading...
Loading...