Philips SAA7372GP-M1, SAA7372GP-M1-C Datasheet

DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1995 Dec 06
File under Integrated Circuits, IC01
1998 Feb 26
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
SAA7372
Digital servo processor and
Compact Disc decoder (CD7)

1998 Feb 26 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
6 PINNING
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 Decoder part
7.1.1 Principle operational modes of the decoder
7.1.2 Decoding speed and crystal frequency
7.1.3 Lock-to-disc mode
7.1.4 Standby modes
7.2 Crystal oscillator
7.3 Data slicer and clock regenerator
7.4 Demodulator
7.4.1 Frame sync protection
7.4.2 EFM demodulation
7.5 Subcode data processing
7.5.1 Q-channel processing
7.5.2 EIAJ 3 and 4-wire subcode (CD graphics)
interface
7.5.3 V4 subcode interface
7.6 FIFO error corrector
7.6.1 Flags output (CFLG)
7.6.2 C2FAIL
7.7 Audio functions
7.7.1 De-emphasis and phase linearity
7.7.2 Digital oversampling filter
7.7.3 Concealment
7.7.4 Mute, full-speed, attenuation and fade
7.7.5 Peak detector
7.8 DAC interface
7.9 EBU interface
7.9.1 Format
7.10 KILL circuit
7.11 Audio features off
7.12 The VIA interface
7.13 Spindle motor control
7.13.1 Motor output modes
7.13.3 Loop characteristics
7.13.4 FIFO overflow
7.14 Servo part
7.14.1 Diode signal processing
7.14.2 Signal conditioning
7.14.3 Focus servo system
7.14.4 Radial servo system
7.14.5 Off-track counting
7.14.6 Defect detection
7.14.7 Off-track detection
7.14.8 High level features
7.14.9 Driver interface
7.15 Microcontroller interface
7.15.1 Microprocessor interface (4-wire bus mode)
7.15.2 Microcontroller interface (I2C-bus mode)
7.15.3 Summary of functions controlled by
registers 0 to F
7.15.4 Summary of servo commands
7.15.5 Summary of servo command parameters
8 LIMITING VALUES
9 OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
10 OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
(SUBCODE INTERFACE TIMING)
11 OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
(I2S-BUS TIMING)
12 OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
(MICROCONTROLLER INTERFACE TIMING)
13 APPLICATION INFORMATION
14 PACKAGE OUTLINE
15 SOLDERING
15.1 Introduction
15.2 Reflow soldering
15.3 Wave soldering
15.4 Repairing soldered joints
16 DEFINITIONS
17 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
18 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
1998 Feb 26 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
1 FEATURES
• CD ROM mode
• Single and double-speed modes
• Lock-to-disc mode
• Full error correction strategy, t = 2 and e = 4
• Full CD graphics interface
• All standard decoder functions implemented digitally on
chip
• FIFO overflow concealment for rotational shock
resistance
• Digital audio interface (EBU), audio and data
• 2 and 4 times oversampling integrated digital filter,
including f
s
mode
• Audio data peak level detection
• Kill interface for DAC deactivation during digital silence
• All TDA1301 (DSIC2) digital servo functions, plus extra
high-level functions
• Low focus noise
• Improved playability on ABEX TCD-721R, TCD-725 and
TCD-714 discs
• Automatic closed loop gain control available for focus
and radial loops
• Pulsed sledge support
• Microcontroller loading LOW
• High-level servo control option
• High-level mechanism monitor
• Communication may be via TDA1301/SAA7345
compatible bus or I
2
C-bus
• On-chip clock multiplier allows the use of 8.4672 MHz
crystal.
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA7372 is a single chip combining the functions of a
CD decoder IC and digital servo IC. The decoder part is
based on the SAA7345 (CD6) with an improved error
correction strategy. The servo part is based on the
TDA1301T (DSIC2) with improvements incorporated,
extra features have also been added.
Supply of this Compact Disc IC does not convey an implied
license under any patent right to use this IC in any
Compact Disc application.
3 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
supply voltage 3.4 5.0 5.5 V
I
DD
supply current n = 1 mode − 49 − mA
f
xtal
crystal frequency 8 8.4672 35 MHz
T
amb
operating ambient temperature −10 − +70 °C
T
stg
storage temperature −55 − +125 °C
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA7372 QFP64 plastic quad flat package; 64 leads (lead length 1.6 mm);
body 14 × 14 × 2.7 mm
SOT393-1
1998 Feb 26 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
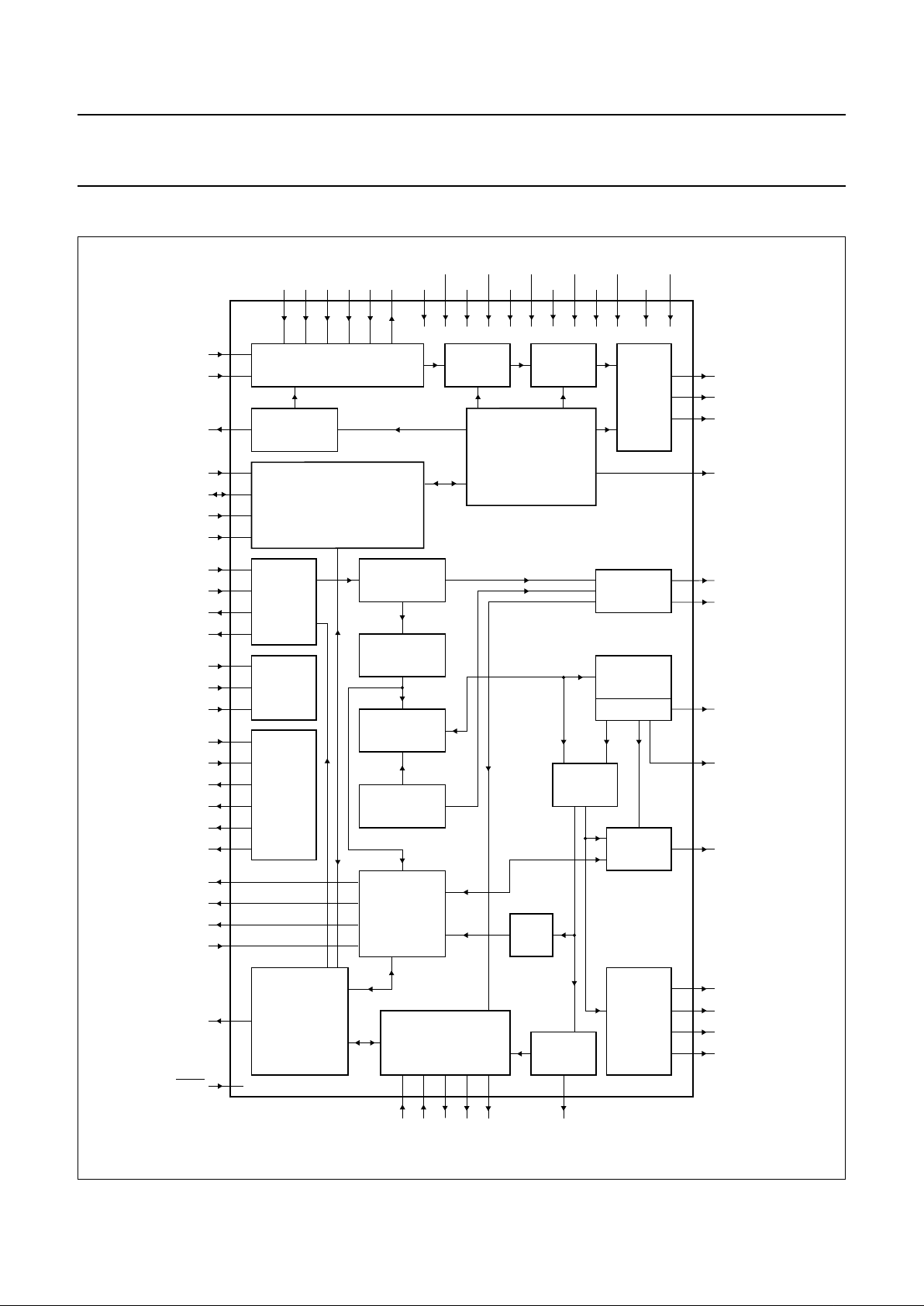
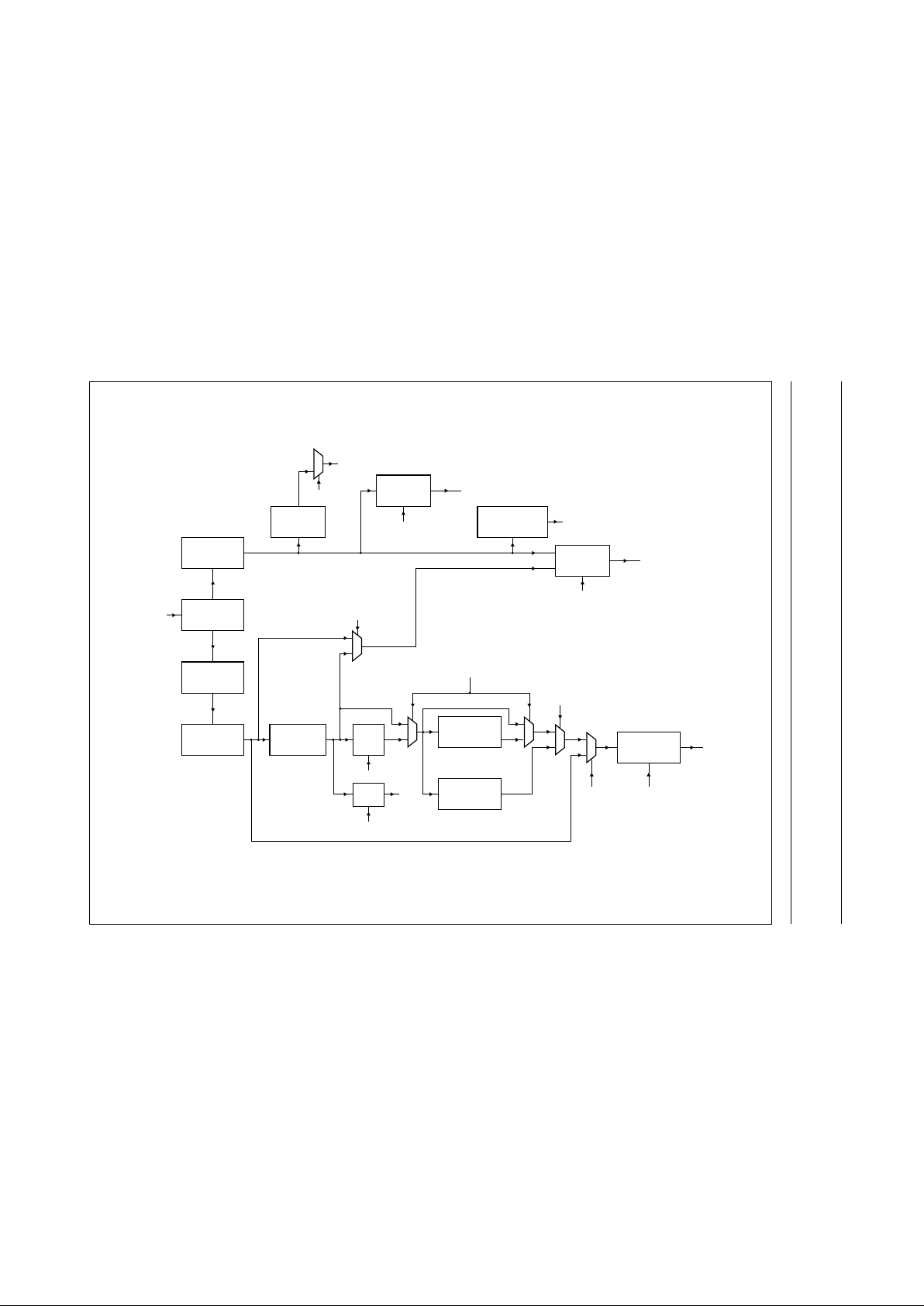
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Fig.1 Block diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
DECODER
MICRO-
CONTROLLER
INTERFACE
VERSATILE PINS
INTERFACE
SUBCODE
PROCESSOR
KILL
PEAK
DETECT
SERIAL DATA
INTERFACE
TIMING
TEST
ADC
V
ref
GENERATOR
FRONT END
DIGITAL
PLL
MOTOR
CONTROL
AUDIO
PROCESSOR
EBU
INTERFACE
ERROR
CORRECTOR
MICROCONTROLLER
INTERFACE
PRE-
PROCESSING
CONTROL
FUNCTION
CONTROL
PART
EFM
DEMODULATOR
SRAM
RAM
ADDRESSER
OUTPUT
STAGES
FLAGS
6
8
9
11
52
51
53
54
15
17
14
18
20
23
29
13
21
22
24
25
50
35
36
38
37
58
57
62 63 42 41 40 43
3 4 5 7 10 1 12 16 2 19 32 39 49 56 30 47 59
26
27
28
64
33
34
61
60
31
48
46
45
44
V
RL
V
RH
I
ref
R2
SCL
SDA
RAB
SILD
HFIN
HFREF
ISLICE
TEST1
TEST2
TEST3
SELPLL
CRIN
CROUT
CL16
CL11
CL4
SBSY
SFSY
SUB
RCK
STATUS
RESET
R1
D1 D2 D3 D4
I
refT
V
SSA1VSSA3VDDA2VSSD2VSSD4VDDD2(P)
V
SSA2VDDA1VSSD1VSSD3VDDD1(P)VDDD3(C)
V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 KILL
EF
DATA
WCLK
SCLK
DOBM
C2FAIL
MOTO2
MOTO1
LDON
SL
FO
RA
CFLG
SAA7372
MGC973

1998 Feb 26 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
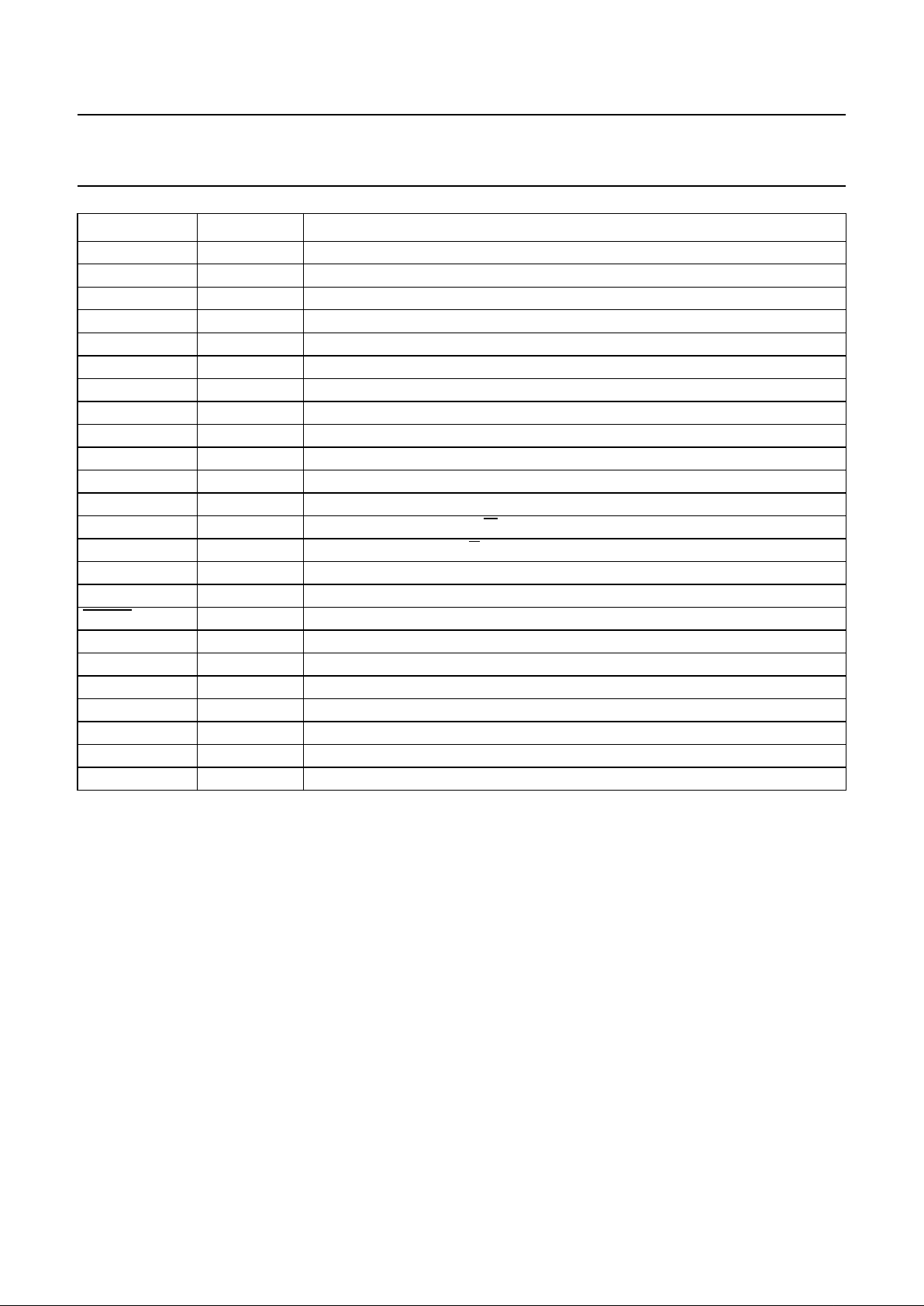
6 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
V
SSA1
1
(1)
analog ground 1
V
DDA1
2
(1)
analog supply voltage 1
D1 3 unipolar current input (central diode signal input)
D2 4 unipolar current input (central diode signal input)
D3 5 unipolar current input (central diode signal input)
V
RL
6 reference voltage input for ADC
D4 7 unipolar current input (central diode signal input)
R1 8 unipolar current input (satellite diode signal input)
R2 9 unipolar current input (satellite diode signal input)
I
refT
10 current reference output for ADC calibration
V
RH
11 reference voltage output from ADC
V
SSA2
12
(1)
analog ground 2
SELPLL 13 selects whether internal clock multiplier PLL is used
ISLICE 14 current feedback output from data slicer
HFIN 15 comparator signal input
V
SSA3
16
(1)
analog ground 3
HFREF 17 comparator common mode input
I
ref
18 reference current output pin (nominally 0.5VDD)
V
DDA2
19
(1)
analog supply voltage 2
TEST1 20 test control input 1; this pin should be tied LOW
CRIN 21 crystal/resonator input
CROUT 22 crystal/resonator output
TEST2 23 test control input 2; this pin should be tied LOW
CL16 24 16.9344 MHz system clock output
CL11 25 11.2896 or 5.6448 MHz clock output (3-state)
RA 26 radial actuator output
FO 27 focus actuator output
SL 28 sledge control output
TEST3 29 test control input 3; this pin should be tied LOW
V
DDD1(P)
30
(1)
digital supply voltage 1 for periphery
DOBM 31 bi-phase mark output (externally buffered; 3-state)
V
SSD1
32
(1)
digital ground 1
MOTO1 33 motor output 1; versatile (3-state)
MOTO2 34 motor output 2; versatile (3-state)
SBSY 35 subcode block sync output (3-state)
SFSY 36 subcode frame sync output (3-state)
RCK 37 subcode clock input
SUB 38 P-to-W subcode output bits (3-state)
V
SSD2
39
(1)
digital ground 2
V5 40 versatile output pin 5
1998 Feb 26 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
Note
1. All supply pins must be connected to the same external power supply voltage.
V4 41 versatile output pin 4
V3 42 versatile output pin 3 (open-drain)
KILL 43 kill output (programmable; open-drain)
EF 44 C2 error flag; output only defined in CD ROM modes and 1f
s
modes (3-state)
DATA 45 serial data output (3-state)
WCLK 46 word clock output (3-state)
V
DDD2(P)
47
(1)
digital supply voltage 2 for periphery
SCLK 48 serial bit clock output (3-state)
V
SSD3
49
(1)
digital ground 3
CL4 50 4.2336 MHz microcontroller clock output
SDA 51 microcontroller interface data I/O line (open-drain output)
SCL 52 microcontroller interface clock line input
RAB 53 microcontroller interface R/
W and load control line input (4-wire bus mode)
SILD 54 microcontroller interface
R/W and load control line input (4-wire-bus mode)
n.c. 55 not connected
V
SSD4
56
(1)
digital ground 4
RESET 57 power-on reset input (active LOW)
STATUS 58 servo interrupt request line/decoder status register output (open-drain)
V
DDD3(C)
59
(1)
digital supply voltage 3 for core
C2FAIL 60 indication of correction failure output (open-drain)
CFLG 61 correction flag output (open-drain)
V1 62 versatile input pin 1
V2 63 versatile input pin 2
LDON 64 laser drive on output (open-drain)
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION

1998 Feb 26 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
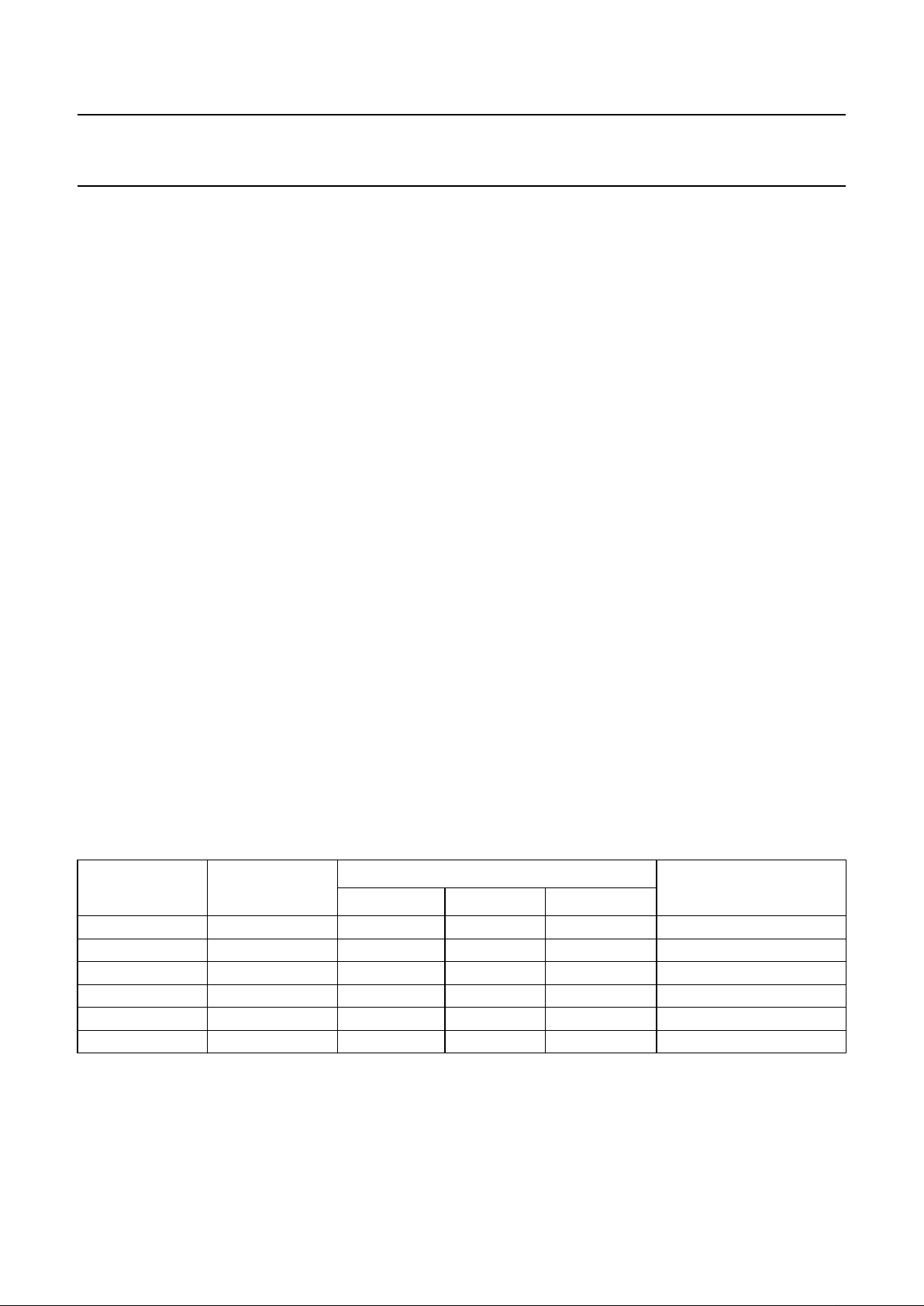
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
handbook, full pagewidth
SAA7372
MGC974
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
V
SSA1
V
DDA1
D1
D2
D3
V
RL
D4
R1
R2
I
refT
V
RH
V
SSA2
SELPLL
ISLICE
HFIN
V
SSA3
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
SCLK
V
DDD2(P)
WCLK
DATA
EF
KILL
V3
V4
V5
V
SSD2
SUB
RCK
SFSY
SBSY
MOTO2
MOTO1
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
HFREF
I
ref
V
DDA2
TEST1
CRIN
CROUT
TEST2
CL16
CL11
RA
FO
SL
TEST3
V
DDD1(P)
DOBM
V
SSD1
LDONV2V1
CFLG
C2FAIL
V
DDD3(C)
STATUS
RESET
V
SSD4
n.c.
SILD
RAB
SCL
SDA
CL4
V
SSD3
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
1998 Feb 26 8
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 Decoder part
7.1.1 P
RINCIPLE OPERATIONAL MODES OF THE DECODER
The decoding part can operate at different disc speeds,
single-speed (n = 1) and double-speed (n = 2). The factor
‘n’ is called the overspeed factor.
A simplified data flow through the decoder part is
illustrated in Fig.6.
7.1.2 D
ECODING SPEED AND CRYSTAL FREQUENCY
The SAA7372 is a multi-speed decoding device, with an
internal phase-locked loop (PLL) clock multiplier.
Depending on the crystal frequency used and the internal
clock settings (selectable via register B), two playback
speeds shown in Table 1 are possible, where ‘n’ is the
overspeed factor.
An internal clock multiplier is present, controlled by
SELPLL, and should only be used if an 8.4672 MHz
crystal, ceramic resonator or external clock is present.
7.1.3 L
OCK-TO-DISC MODE
For high speed CD-ROM applications, the SAA7372 has a
special mode, the lock-to-disc mode. This allows Constant
Angular Velocity (CAV) disc playback with varying input
data rates from the inside-to-outside of the disc. In the
lock-to-disc mode, the FIFO is blocked and the decoder
will adjust its output data rate to the disc speed. Hence, the
frequency of the I2S-bus clocks (WCLK and SCLK) are
dependent on the disc speed. In the lock-to-disc mode
there is a limit on the maximum variation in disc speed that
the SAA7372 will follow. Disc speeds must always be
within 25 to 100% range of their nominal value. The
lock-to-disc mode is enabled/disabled by register E.
7.1.4 S
TANDBY MODES
The SAA7372 may be placed in two standby modes
selected by register B (it should be noted that the device
core is still active)
Standby 1: “CD-STOP” mode. Most I/O functions are
switched off.
Standby 2: “CD-PAUSE” mode. Audio output features
are switched off, but the motor loop, the motor output
and the subcode interfaces remain active. This is also
called a “Hot Pause”.
In the standby modes the various pins will have the
following values;
MOTO1 and MOTO2: put in high-impedance, PWM
mode (standby 1 and reset, operating in standby 2). Put
in high-impedance, PDM mode (standby 1 and reset,
operating in standby 2).
SCL, SDA, SILD and RAB: no interaction. Normal
operation continues.
SCLK, WCLK, DATA, EF, CL11 and DOBM: 3-state in
both standby modes. Normal operation continues after
reset.
CRIN, CROUT, CL16 and CL4: no interaction. Normal
operation continues.
V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, CFLG and C2FAIL: no interaction.
Normal operation continues.
Table 1 Playback speeds
Notes
1. The CL11 output is always a 5.6448 MHz clock if a 16.9344 MHz external clock is used and SELPLL = 0.
2. Data capture performance is not optimized for these options.
REGISTER B SELPLL
CRYSTAL FREQUENCY (MHz)
CL11 FREQUENCY
(MHz)
(1)
33.8688 16.9344 8.4672
00xx 0 n = 1 −− 11.2896
00xx 1 −−n = 1 11.2896
01xx 0 − n=1 − 5.6448
10xx 0 n = 2 −− 11.2896
10xx 1 −−n = 2 11.2896
11xx 0 − n=2
(2)
− 5.6448
1998 Feb 26 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
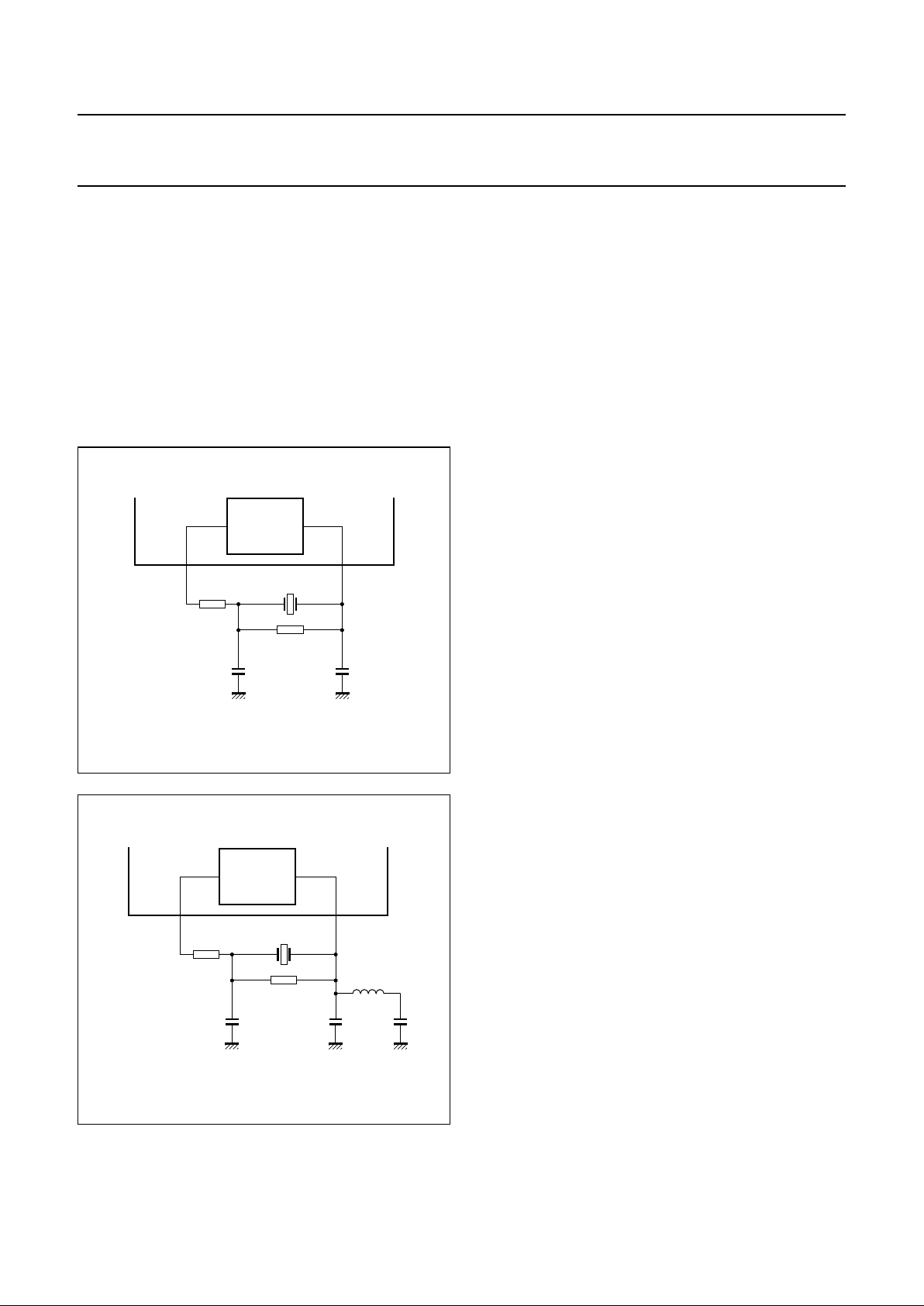
7.2 Crystal oscillator
The crystal oscillator is a conventional 2 pin design
operating between 8 and 35 MHz. This oscillator is
capable of operating with ceramic resonators also with
both fundamental and third overtone crystals. External
components should be used to suppress the fundamental
output of the third overtone crystals as shown in Figs 3
and 4. Typical oscillation frequencies required are 8.4672,
16.9344 or 33.8688 MHz depending on the internal clock
settings used and whether or not the clock multiplier is
enabled.
Fig.3 8.4672 MHz fundamental configuration.
8.4672 MHz
CRINCROUT
SAA7372
22 pF22 pF
330 Ω
100 kΩ
OSCILLATOR
MGC975
Fig.4 33.8688 MHz overtone configuration.
OSCILLATOR
33.8688 MHz
CRIN
CROUT
SAA7372
3.3 µH
1 nF10 pF10 pF
330 Ω
100 kΩ
MGC983
7.3 Data slicer and clock regenerator
The SAA7372 has an integrated slice level comparator
which can be clocked by the crystal frequency clock, or
8 times the crystal frequency clock (if SELPLL is set HIGH
while using an 8.4672 MHz crystal, and register 4 is set
to 0xxx). The slice level is controlled by an internal current
source applied to an external capacitor under the control
of the Digital Phase-Locked Loop (DPLL).
Regeneration of the bit clock is achieved with an internal
fully digital PLL. No external components are required and
the bit clock is not output. The PLL has two registers
(8 and 9) for selecting bandwidth and equalization.
For certain applications an off-track input is necessary.
This is internally connected from the servo part (its polarity
can be changed by the foc_parm1 parameter), but may be
input via the V1 pin if selected by register C. If this flag is
HIGH, the SAA7372 will assume that its servo part is
following on the wrong track and will flag all incoming HF
data as incorrect.

1998 Feb 26 10
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
Fig.5 Data slicer showing typical application components (for n = 1).
47 pF
22 nF
2.2 kΩ
HFIN
HFREF
I
ref
ISLICE
22 kΩ
100 nF
2.2 nF
HF
input
crystal
clock
DQ
DPLL
1/2V
DD
V
SSA
V
SS
V
SSA
MGA368 - 1
V
DD
100 µA
100 µA
7.4 Demodulator
7.4.1 F
RAME SYNC PROTECTION
A double timing system is used to protect the demodulator
from erroneous sync patterns in the serial data. The
master counter is only reset if:
• A sync coincidence detected; sync pattern occurs
588 ±1 EFM clocks after the previous sync pattern
• A new sync pattern is detected within ±6 EFM clocks of
its expected position.
The sync coincidence signal is also used to generate the
PLL lock signal, which is active HIGH after 1 sync
coincidence found, and reset LOW if during 61
consecutive frames no sync coincidence is found.
The PLL lock signal can be accessed via the SDA or
STATUS pins selected by register 2 and 7.
Also incorporated in the demodulator is a Run Length 2
(RL2) correction circuit. Every symbol detected as RL2 will
be pushed back to RL3. To do this, the phase error of both
edges of the RL2 symbol are compared and the correction
is executed at the side with the highest error probability.
7.4.2 EFM
DEMODULATION
The 14-bit EFM data and subcode words are decoded into
8-bit symbols.
1998 Feb 26 11
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
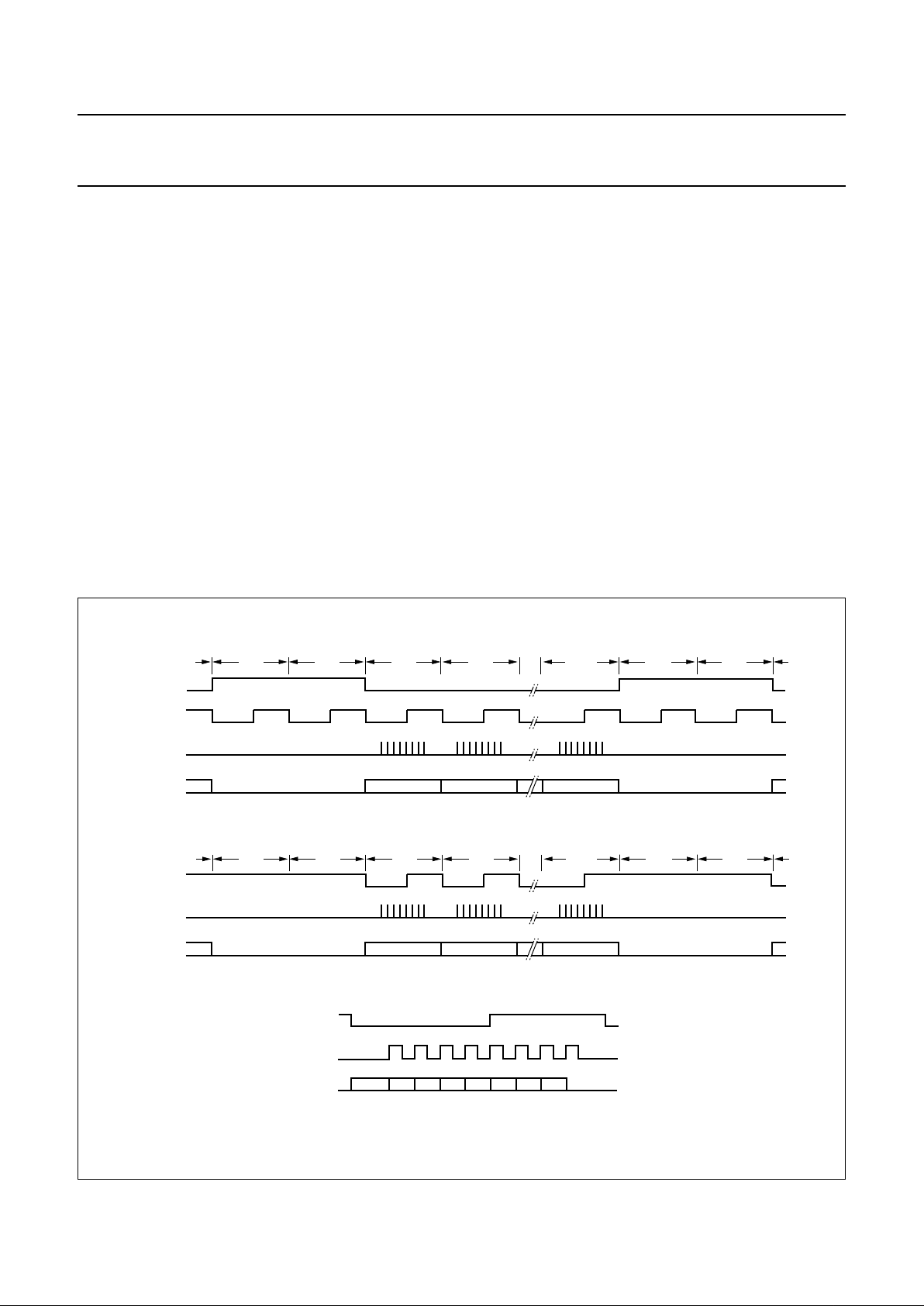
handbook, full pagewidth
SUBCODE
PROCESSOR
DIGITAL PLL AND
DEMODULATOR
FIFO
ERROR
CORRECTOR
FADE/MUTE/
INTERPOLATE
DIGITAL
FILTER
PHASE
COMPENSATION
DE-EMPHASIS
FILTER
KILL
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
I2S-BUS
INTERFACE
SCLK
WCLK
DATA
EF
reg 3
reg C
reg 3
reg F
reg A
1
0
1 : reg 3 ≠ 101x
0 : reg 3 = 101x
0 : reg D = xx01
0 : reg A = xx1x
1 : reg A = xx0x
(CD-ROM modes)
V4 SUBCODE
INTERFACE
MICROCONTROLLER
INTERFACE
CD GRAPHICS
INTERFACE
EBU
INTERFACE
SBSY
SFSY
SUB
DOBM
V4
SDA
output from
data slicer
1 : reg 3 = xx10
(1fs mode)
0 : reg 3 ≠ xx10
1 : no pre-emphasis detected
OR reg D = 01xx (de-emphasis signal at V5)
0 : pre-emphasis detected
AND reg D ≠ 01xx
KILL
V3
MBG418
Fig.6 Simplified data flow of decoder functions.
1998 Feb 26 12
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
7.5 Subcode data processing
7.5.1 Q-
CHANNEL PROCESSING
The 96-bit Q-channel word is accumulated in an internal
buffer. The last 16 bits are used internally to perform a
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). If the data is good, the
SUBQREADY-I signal will go LOW. SUBQREADY-I can
be read via the SDA or STATUS pins, selected via
register 2. Good Q-channel data may be read from SDA.
7.5.2 EIAJ 3
AND 4-WIRE SUBCODE (CD GRAPHICS)
INTERFACES
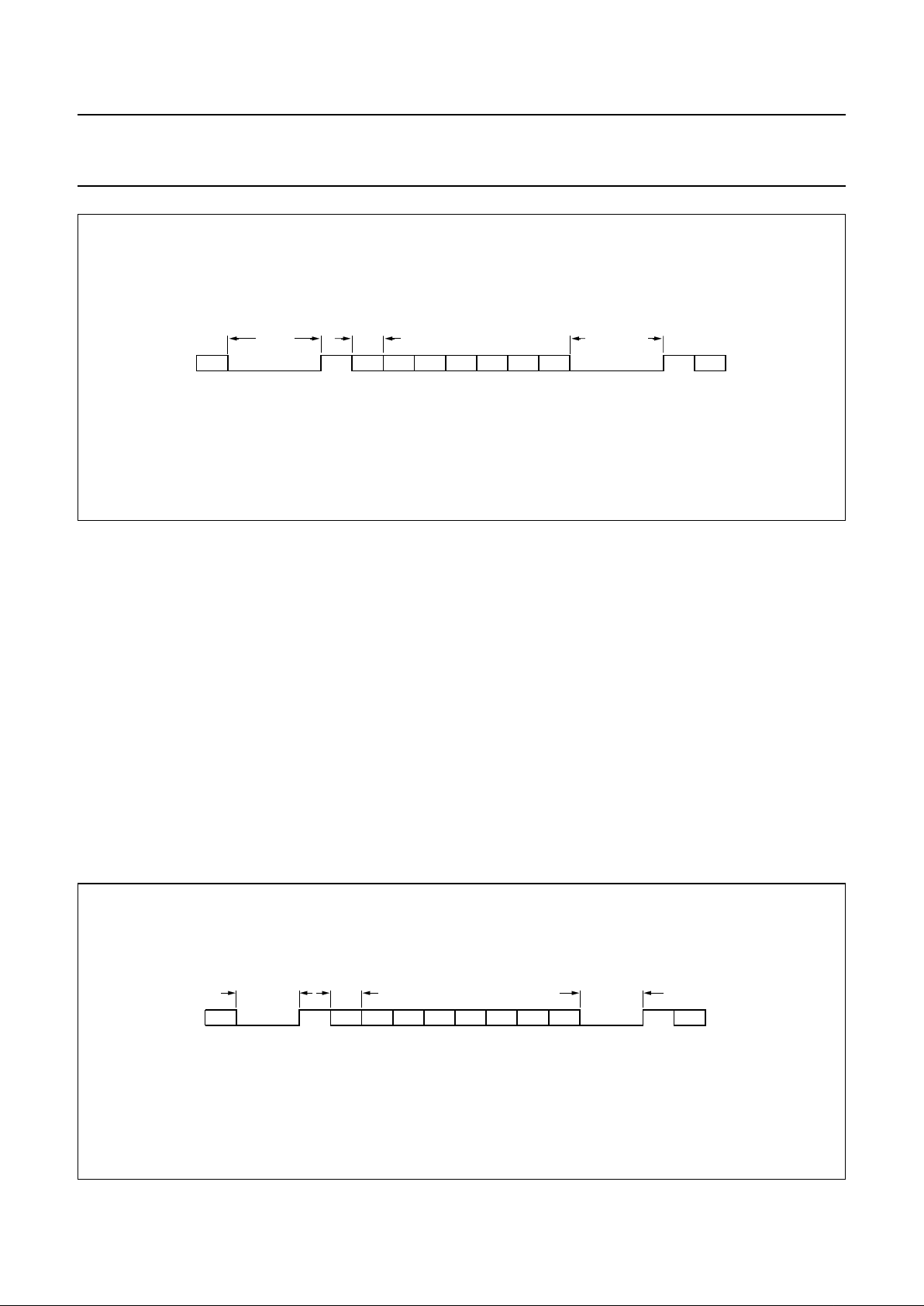
Data from all the subcode channels (P-to-W) may be read
via the subcode interface, which conforms to
EIAJ CP-2401. The interface is enabled and configured as
either a 3-wire or 4-wire interface via register F. The
subcode interface output formats are illustrated in Fig.7,
where the RCK signal is supplied by another device such
as a CD graphics decoder.
7.5.3 V4
SUBCODE INTERFACE
Data of subcode channels, Q-to-W, may be read via pin V4
if selected via register D. The format is similar to RS232
and is illustrated in Fig.8. The subcode sync word is
formed by a pause of (200/n) µs minimum. Each subcode
byte starts with a logic 1 followed by 7 bits (Q-to-W). The
gap between bytes is variable between (11.3/n) µs and
(90/n) µs.
The subcode data is also available in the EBU output
(DOBM) in a similar format.
Fig.7 EIAJ subcode (CD graphics) interface format.
handbook, full pagewidth
SBSY
SFSY
RCK
SUB
SFSY
RCK
SUB
SFSY
RCK
SUB
EIAJ 4-wire subcode interface
EIAJ 3-wire subcode interface
SF0 SF1
SF2 SF3 SF97 SF0 SF1
P-W P-W P-W
P-W P-W P-W
PQRSTUVW
MBG410
SF0 SF1 SF2 SF3 SF97 SF0 SF1
1998 Feb 26 13
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
Fig.8 Subcode format and timing on pin V4.
n = disc speed
W96 1QRSTUVW 1Q
200/n µs
min
11.3/n
µs
11.3/n µs min
90/n µs max
MBG401
7.6 FIFO and error corrector
The SAA7372 has a ±8 frame FIFO. The error corrector is
a t = 2, e = 4 type, with error corrections on both C1
(32 symbol) and C2 (28 symbol) frames. Four symbols are
used from each frame as parity symbols. This error
corrector can correct up to two errors on the C1 level and
up to four errors on the C2 level.
The error corrector also contains a flag processor. Flags
are assigned to symbols when the error corrector cannot
ascertain if the symbols are definitely good. C1 generates
output flags which are read after (de-interleaving) by C2,
to help in the generation of C2 output flags.
The C2 output flags are used by the interpolator for
concealment of uncorrectable errors. They are also output
via the EBU signal (DOBM) and the EF output with I
2
S-bus
for CD ROM applications.
7.6.1 F
LAGS OUTPUT (CFLG)
The flags output pin CFLG (open-drain) shows the status
of the error corrector and interpolator and is updated every
frame (7.35 × n kHz). In the SAA7372 chip a 1-bit flag is
present on the CFLG pin as illustrated in Fig.9. This signal
shows the status of the error corrector and interpolator.
The first flag bit, F1, is the absolute time sync signal, the
FIFO-passed subcode sync and relates the position of the
subcode sync to the audio data (DAC output). This flag
may also be used in a super FIFO or in the synchronization
of different players. The output flags can be made
available at bit 4 of the EBU data format (LSB of the 24-bit
data word), if selected by register A.
Fig.9 Flag output timing diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F1F8
11.3/n
µs
33.9/n µs
33.9/n µs
MBG425
n = disc speed.

1998 Feb 26 14
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
Table 2 Output flags
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 DESCRIPTION
0xxxxxxxno absolute time sync
1xxxxxxxabsolute time sync
x00xxxxxC1 frame contained no errors
x01xxxxxC1 frame contained 1 error
x10xxxxxC1 frame contained 2 errors
x11xxxxxC1 frame uncorrectable
x x x 0 0 x x 0 C2 frame contained no errors
x x x 0 0 x x 1 C2 frame contained 1 error
x x x 0 1 x x 0 C2 frame contained 2 errors
x x x 0 1 x x 1 C2 frame contained 3 errors
x x x 1 0 x x 0 C2 frame contained 4 errors
x x x 1 1 x x 1 C2 frame uncorrectable
xxxxx00xno interpolations
xxxxx01xat least one 1 sample interpolation
xxxxx10xat least one hold and no interpolations
xxxxx11xat least one hold and one 1 sample interpolation
7.6.2 C2FAIL
The C2FAIL pin indicates that invalid data has occurred on
the I2S-bus interface. However, due to the structure of the
corrector it is impossible to determine which byte has
failed. C2FAIL will go LOW for (140/n) µs when invalid
data is detected, this data may then occur (15/n) ms before
or after the pin is activated.
7.7 Audio functions
7.7.1 D
E-EMPHASIS AND PHASE LINEARITY
When pre-emphasis is detected in the Q-channel
subcode, the digital filter automatically includes a
de-emphasis filter section. When de-emphasis is not
required, a phase compensation filter section controls the
phase of the digital oversampling filter to ≤±1° within the
band 0 to 16 kHz. With de-emphasis the filter is not phase
linear.
If the de-emphasis signal is set to be available at V5,
selected via register D, then the de-emphasis filter is
bypassed.
7.7.2 D
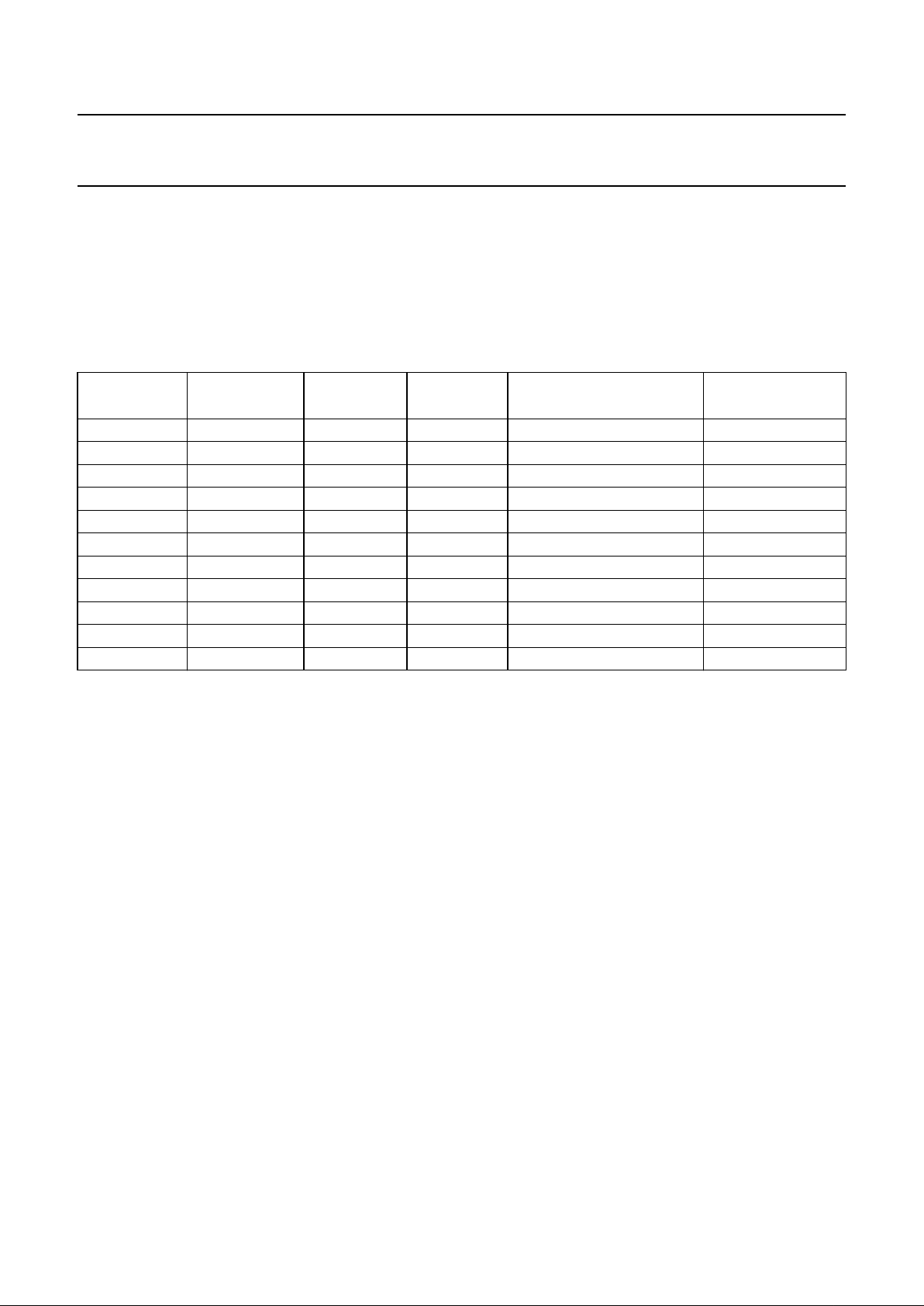
IGITAL OVERSAMPLING FILTER
The SAA7372 contains a 2 to 4 times oversampling IIR
filter. The filter specification of the 4 times oversampling
filter is given in Table 3.
These attenuations do not include the sample-and-hold at
the external DAC output or the DAC post filter. When using
the oversampling filter, the output level is scaled −0.5 dB
down, to avoid overflow on full-scale sine wave inputs
(0 to 20 kHz).
Table 3 Filter specification
PASS BAND STOP BAND ATTENUATION
0 to 9 kHz −≤0.001 dB
19 to 20 kHz −≤0.03 dB
− 24 kHz ≥25 dB
− 24 to 27 kHz ≥38 dB
− 27 to 35 kHz ≥40 dB
− 35 to 64 kHz ≥50 dB
− 64 to 68 kHz ≥31 dB
− 68 kHz ≥35 dB
− 69 to 88 kHz ≥40 dB
1998 Feb 26 15
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
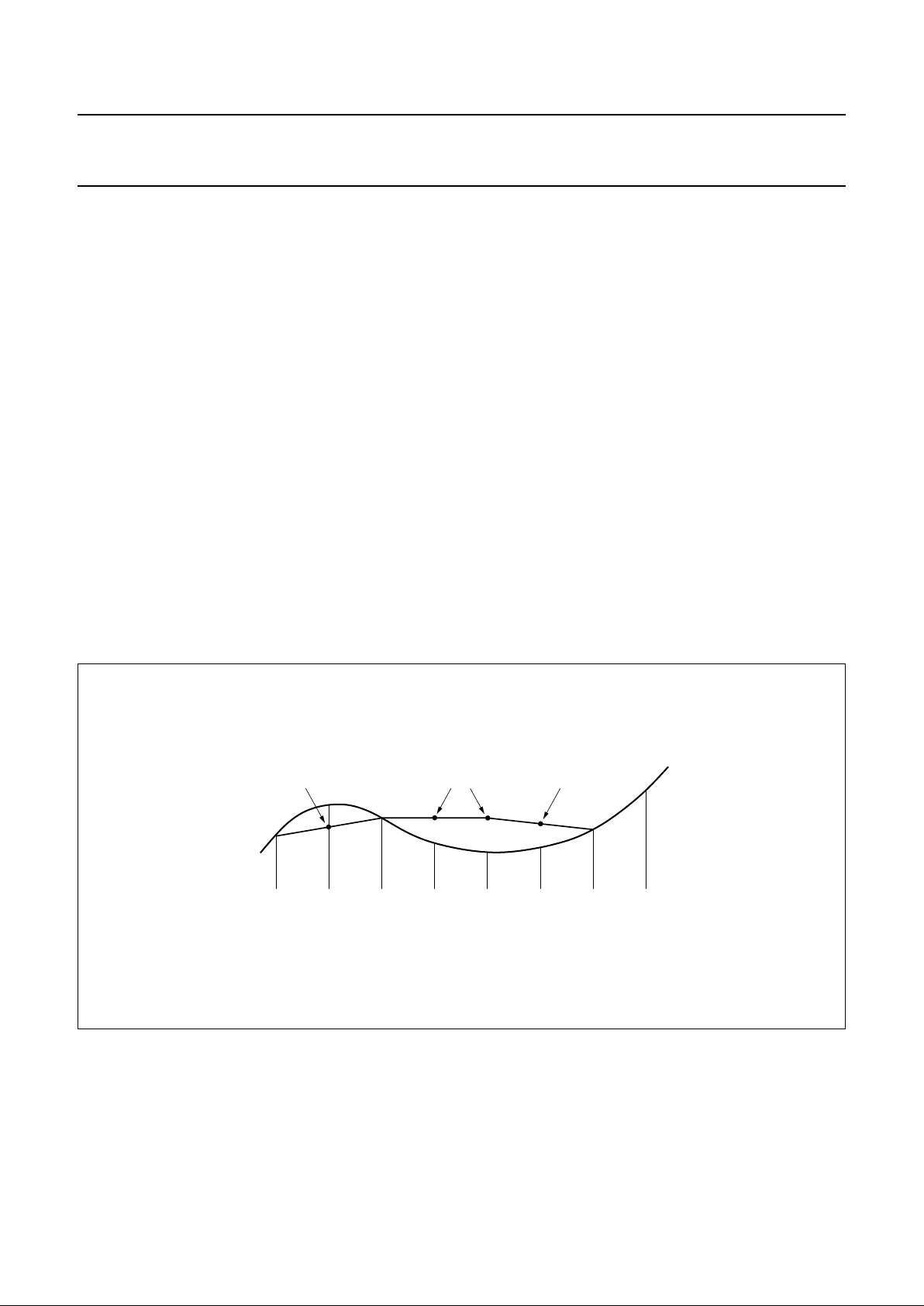
7.7.3 CONCEALMENT
A 1 sample linear interpolator becomes active if a single
sample is flagged as erroneous but cannot be corrected.
The erroneous sample is replaced by a level midway
between the preceding and following samples. Left and
right channels have independent interpolators. If more
than one consecutive non-correctable sample is found, the
last good sample is held. A 1 sample linear interpolation is
then performed before the next good sample (see Fig.10).
In CD ROM modes (i.e. the DAC interface is selected to be
in a CD ROM format) concealment is not executed.
7.7.4 M
UTE, FULL SCALE, ATTENUATION AND FADE
A digital level controller is present on the SAA7372 which
performs the functions of soft mute, full scale, attenuation
and fade; these are selected via register 0:
Mute: signal reduced to 0 in a maximum of 128 steps;
(3/n) ms.
Attenuate: signal scaled by −12 dB.
Full scale: ramp signal back to 0 dB level. From mute
takes (3/n) ms.
Fade: activates a 128 stage counter which allows the
signal to be scaled up/down by 0.07 dB steps
128 = full scale.
120 = −0.5 dB (i.e. full scale if oversampling filter
used).
32 = −12 dB.
0 = mute.
7.7.5 P
EAK DETECTOR
The peak detector measures the highest audio level
(absolute value) on positive peaks for left and right
channels. The 8 most significant bits are output in the
Q-channel data in place of the CRC bits. Bits 81 to 88
contain the left peak value (bit 88 = MSB) and
bits 89 to 96 contain the right peak value (bit 96 = MSB).
The values are reset after reading Q-channel data via
SDA.
Fig.10 Concealment mechanism.
Interpolation Hold Interpolation
MGA372
OK Error OK Error Error Error OK OK
1998 Feb 26 16
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
7.8 DAC interface
The SAA7372 is compatible with a wide range of digital-to-analog converters (DACs). Eleven formats are supported and
are given in Table 4. Figures 11 and 12 show the Philips I2S-bus and the EIAJ data formats respectively. When the
decoder is operated in lock-to-disc mode, the SCLK frequency is dependent on the disc speed factor ‘d’. All formats are
MSB first and fs is (44.1 × n) kHz. The polarity of the WCLK and the data can be inverted; selectable by register 7. It
should be noted that EF is only a defined output in CD ROM and 1fs modes.
Table 4 DAC interface formats
Note
1. In this mode the first 16 bits contain data, but if any of the fade, attenuate or de-emphasis filter functions are activated
then the first 18 bits contain data.
REGISTER 3
SAMPLE
FREQUENCY
NUMBER OF
BITS
SCLK (MHz) FORMAT INTERPOLATION
1010 f
s
16 2.1168 × n CD ROM (I2S-bus) no
1011 f
s
16 2.1168 × n CD ROM (EIAJ) no
1110 f
s
16/18
(1)
2.1168 × n Philips I2S-bus; 16/18 bits
(1)
yes
0010 f
s
16 2.1168 × n EIAJ 16 bits yes
0110 f
s
18 2.1168 × n EIAJ 18 bits yes
0000 4f
s
16 8.4672 × n EIAJ 16 bits yes
0100 4f
s
18 8.4672 × n EIAJ 18 bits yes
1100 4f
s
18 8.4672 × n Philips I2S-bus; 18 bits yes
0011 2f
s
16 4.2336 × n EIAJ 16 bits yes
0111 2f
s
18 4.2336 × n EIAJ 18 bits yes
1111 2f
s
18 4.2336 × n Philips I2S-bus; 18 bits yes

1998 Feb 26 17
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
LEFT CHANNEL DATA (WCLK NORMAL POLARITY)
SCLK
15 14
15 1410DATA
WCLK
LSB error flag MSB error flag LSB error flag MSB error flag
EF
(CD-ROM
AND Ifs MODES ONLY)
01
MBG424
Fig.11 Philips I2S-bus data format (16-bit word length shown).
SCLK
17
170DATA
WCLK
0
LEFT CHANNEL DATA
MSB error flag LSB error flag MSB error flag
MBG423
EF
(CD-ROM
AND Ifs MODES ONLY)
Fig.12 EIAJ data format (18-bit word length shown).

1998 Feb 26 18
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Digital servo processor and Compact Disc
decoder (CD7)
SAA7372
7.9 EBU interface
The bi-phase mark digital output signal at pin DOBM is in
accordance with the format defined by the IEC958
specification. Three different modes can be selected via
register A:
• DOBM pin held LOW
• Data taken before concealment, mute and fade (must
always be used for CD ROM modes)
• Data taken after concealment, mute and fade.
7.9.1 FORMAT
The digital audio output consists of 32-bit words
(‘subframes’) transmitted in bi-phase mark code (two
transitions for a logic 1 and one transition for a logic 0).
Words are transmitted in blocks of 384. Table 5 gives the
formats.
Table 5 Format
Table 6 Description of Table5
FUNCTION BITS DESCRIPTION
Sync 0 to 3 −
Auxiliary 4 to 7 not used; normally zero
Error flags 4 CFLG error and interpolation flags when selected by register A
Audio sample 8 to 27 first 4 bits not used (always zero). 2’s compliment. LSB = bit 12, MSB = bit 27
Validity flag 28 valid = logic 0
User data 29 used for subcode data (Q-to-W)
Channel status 30 control bits and category code
Parity bit 31 even parity for bits 4 to 30
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
Sync The sync word is formed by violation of the bi-phase rule and therefore does not contain any data.
Its length is equivalent to 4 data bits. The 3 different sync patterns indicate the following situations:
sync B: start of a block (384 words), word contains left sample; sync M: word contains left sample
(no block start) and sync W: word contains right sample.
Audio sample Left and right samples are transmitted alternately.
Validity flag Audio samples are flagged (bit 28 = 1) if an error has been detected but was uncorrectable. This
flag remains the same even if data is taken after concealment.
User data Subcode bits Q-to-W from the subcode section are transmitted via the user data bit. This data is
asynchronous with the block rate.
Channel status The channel status bit is the same for left and right words. Therefore a block of 384 words contains
192 channel status bits. The category code is always CD. The bit assignment is given in Table 7.
 Loading...
Loading...