Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAA6752HS
MPEG-2 video and
MPEG-audio/AC-3 audio encoder
with multiplexer
Product specification
Supersedes data of 2002 Dec 09
2004 Jan 26
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
1.1 Video input and preprocessing
1.2 Video compression
1.3 Audio input
1.4 Audio compression
1.5 Stream multiplexer
1.6 Output interface
1.7 Control domain
1.8 Other features
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 General
2.2 Application fields
3 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
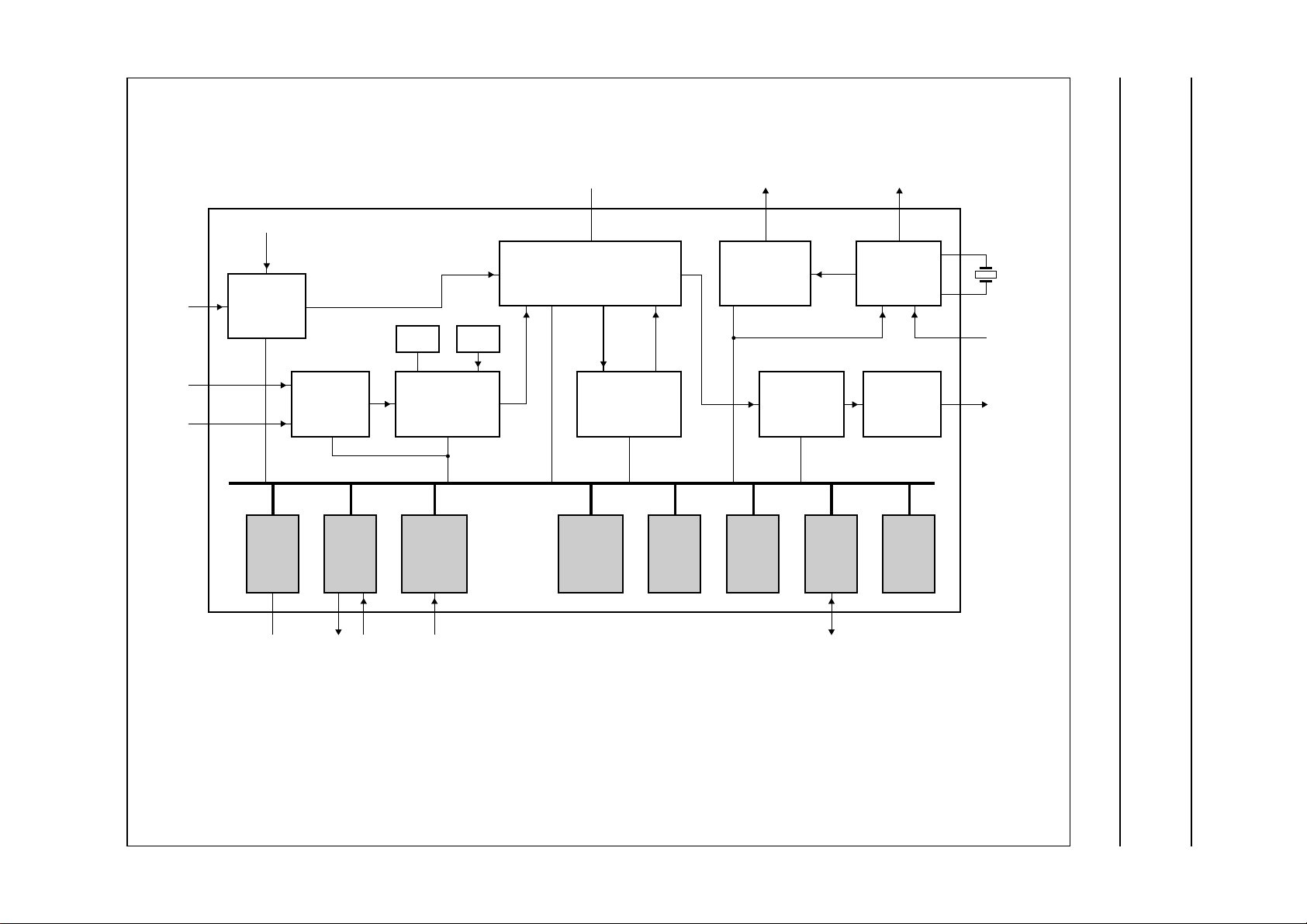
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
6 PINNING
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 System operation
7.2 Digital video input
7.3 Video compression
7.4 Digital audio input
7.5 Audio compression
7.6 SDRAM interface
7.7 Multiplexer
7.8 MPEG stream output port
7.9 Clock generation
7.10 Power control and reset
7.11 I2C-bus interface
7.12 Exception handling
SAA6752HS
8 BOUNDARY SCAN TEST
8.1 Initialization of boundary scan circuit
8.2 Device identification codes
9I
10 LIMITING VALUES
11 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
12 CHARACTERISTICS
13 PACKAGE OUTLINE
14 SOLDERING
14.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
14.2 Reflow soldering
14.3 Wave soldering
14.4 Manual soldering
14.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for
15 DATA SHEET STATUS
16 DEFINITIONS
17 DISCLAIMERS
18 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
2
C-BUS CONTROL AND STATUS
REGISTERS
packages
wave and reflow soldering methods
2004 Jan 26 2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
1 FEATURES
1.1 Video input and preprocessing
• Digital YUVinputaccording to
27 MHz) and
• Support of enhanced
containing decoded VBI data readable via I2C-bus;
Closed Caption (CC), Wide Screen Signalling (WSS)
and copyright information with Copy Generation
Management System (CGMS)
• Processing of non-broadcast video signals from analog
VCR according to IEC 756
• Twovideo clockinput pins forswitching two digitalvideo
sources
•
“ITU-R BT.601”
Standard Interchange Format (SIF)
• 4:2:2to4:2:0 colour format conversion
• Decimation filtering for all format conversions
• Adaptive median filterand motion compensated filter for
input noise reduction.
1.2 Video compression
• Real-time MPEG-2 encoding compliant to Main Profile
at Main Level (MP@ML) for 625 and 525 interlaced line
systems
• Supported resolutions: D1, 2/3D1, 1/2D1 and SIF
• IPB frame, IP frame and I frame only encoding
supported at all modes
• Supported bit rates: up to 25 Mbit/s I-only encoding;
up to 15 Mbit/s IP-only or IBP encoding.
• Variable video bit rate mode for constant picture quality
and constant bit rate mode to gain optimum picture
quality from a fixed channel transfer rate
• Access to bit rate control parameters whilst encoding to
support external real-time control algorithms (e.g.
constrained variable bit rate control)
• Programmable Group Of Pictures (GOP) structure
• Innovative motion estimation with wide search range
• Adaptive quantization
• Motion compensated noise filter.
“ITU-R BT.601”
“ITU-R BT.656”
format conversion to 1/2D1, 2/3D1 and
“ITU-R BT.656”
input format
(8 bits at
SAA6752HS
1.3 Audio input
• Audio inputs: I2S format or EIAJ format (16, 18 or
20 bits), master or slave mode at 32, 44.1 and 48 kHz
• Two digital I2S input ports for selection between two
digital audio sources
• Audio clock generation: 256fs or 384fs (where
fs= 48 kHz) locked to video frame rate (if video is
present and locking is enabled)
• Sample rate conversion to 48 kHz (locked to video
frame rate if enabled) for slave mode operation in all
modes except Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) compliant
bypass.
1.4 Audio compression
• Dolby
• MPEG-1 layer 2 audio encoding at 256 kbit/s or
• Input data bypass for Linear Pulse Code Modulation
• Preamble Pc, Preamble Pd and bit stream information
• Audio mute via I2C-bus control for all modes except
(1) Dolby is a registered trademark of Dolby Laboratories
(2) AC-3 is a registered trademark of Dolby Laboratories
(1)
Digital Consumer Encoding (DDCE) also
known as AC-3
256 kbit/s or 384 kbit/s (only for SAA6752HS/V103)
384 kbit/s
(LPCM) and compressed audio data [MPEG-1,
MPEG-2, Dolby Digital (DD) and Digital Theatre
System (DTS)] according to IEC 61937
captured for identification of modes during bypass of
compressed audio data for MPEG-1, MPEG-2, DD and
DTS according to IEC 61937
DVD-compliant bypass.
Licensing Corporation.
Licensing Corporation.
(2)
2 channel audio encoding at
2004 Jan 26 3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
1.5 Stream multiplexer
• Multiplexingof video and audiostreamsaccording to the
MPEG-2 systems standard (
• Generation and output of MPEG-2 Transport Streams
(TS), MPEG-2 Program Streams (PS), Packetized
Elementary Streams (PES) and Elementary Streams
(ES) compliant to the DVD, D-VHS and DVB standards
• MPEG time stamp (PTS/DTS/SCR/PCR) generation
and insertion (synchronization)
• Insertion of metadata
• Optional generation of empty time slots for subsequent
insertion of application specific data packets
• Optionalinsertion ofuser data inthe GOP headerand in
the picture header
• Optional automatic insertion of Closed Caption data
according to DVD or ATSC standard
• Optional generation of transport streams with variable
bit rate.
1.6 Output interface
• Parallel interface 8-bit master/slave output
• 3-state output port
• Glueless interfacing with IEEE 1394 chip sets (for
example, PDI 1394 L11)
• Data Expansion Bus Interface (DEBI) interface.
1.7 Control domain
• All control done via I2C-bus
• I2C-bus slave transceiver up to 400 kbit/s
• I2C-bus slave address select pin
• Host interrupt flag pin.
1.8 Other features
• Single external clock or single crystal 27 MHz
• Separate 27 MHz system clock output
• Interface voltage 3.3 V
• TTL compatible digital outputs
• Power supply voltage 3.3 and 2.5 V
• Boundary Scan Test (BST) supported
• Power-down mode
• Single SDRAM system memory (16 Mbit@16 bit or
64 Mbit@16 bit).
“ISO 13818-1”
)
SAA6752HS
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 General
Philips Semiconductors’ second generation real time
MPEG-2 encoder, the SAA6752HS, is a highly integrated
single-chip audio and video encoding solution with flexible
multiplexing functionality. With our expertise in two critical
areas for consumer video encoding, noise filtering and
motion estimation, we have pushed the boundaries for
video quality even further, providing enhanced quality for
low bit rates and enabling increased recording times for a
given storage capacity. The SAA6752HS will also enable
a key driver for new consumer digital recording
applications and system cost reduction. By integrating all
audio encoding and multiplexing functionality we will be
moving from a three chip to a one chip system, with cost
efficient design and process technology, thus providing a
truly low cost, high quality encoding system.
The SAA6752HS/V104 is intended for customers whose
application does not require the DDCE function.
The SAA6752HS gives significant advantages to
customers developing digital recording applications:
• Fast time-to-market and low development
resources. By adding a simple external video input
processor IC, an audio analog-to-digital converter, and
an external SDRAM, analog video and audio sources
are compressed into high quality MPEG-2 video and
MPEG-1layer 2 or AC-3 audiostreams,multiplexed into
a single program or transport stream for simple
connection to various storage media or broadcast
media. Hence, making designeffort for our customers a
minimum, as well as removing the need for in-depth
experience in MPEG encoding.
• Low system host resources. All video and audio
encoding algorithms and software arerun onan internal
(1)
MIPS
small amount of communication from the system host
processor to set up and control required encoding
parameters via the I2C-bus.
processor. The SAA6752HS only requires a
2004 Jan 26 4
(1) MIPS is a registered trademark of MIPS Technologies.
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
2.2 Application fields
2.2.1 DVD BASED OPTICAL DISC RECORDERS (DVD+RW,
DVD-RW, DVD-RAM)
Emerging optical disc based recording systems target to
replace the existing consumer recording (VCR) and
playback (DVD and VCD) products. The first generation
recordable DVD based products will want to maximise
recording times for the 4.7 Gbyte storage capacity. For
these systems the SAA6752HS is critical, with its superior
noise filtering and motion estimation, in enabling high
quality at low bit rates.
Playback compatibility with existing DVD decoding
solutions will also be important, which is why the
SAA6752HS provides Dolby digital consumer (AC-3)
audio encoding to allow playback through existing players
implementing DDCE (AC-3) decoding dominant in current
DVD platforms.
The DVD stream is based on MPEG Program Stream
(PS). The SAA6752HS directly outputs MPEG PS
compliant to the DVD standard.
SAA6752HS
2.2.3 DIGITAL VCR (DVHS) RECORDING
A DVHS player records streams based on MPEG
Transport Streams (TS) packedin logical tape tracks. The
SAA6752HS output streams are compliant with DVHS
standard requirements.
2.2.4 VIDEO EDITING/TRANSMISSION/SURVEILLANCE/
CONFERENCING
The SAA6752HS can operate as a stand-alone device in
all the above applications. The SAA6752HS full features
and flexibility allows customers to tailor functionality and
performance to specific application requirements. All
required control settings such as GOP size and bit rate
modes can be selected via the I2C-bus.
2.2.2 HDD BASED TIME SHIFT RECORDING
Hard Disc Drive (HDD) based time-shift systems enable
Personalized TV (PTV) functionality, providingconsumers
with new powers of control over what and when to watch
broadcast content. With the audio and video content
recorded digitally, identification, search and retrieval
becomes a ‘no brainer’ task as compared to traditional
VCR functionality. Combine this with electronic program
guides and intelligent control, and the PTV can also
analyse the viewers watching habits to search for
programs likely to be of interest and automatically
recorded in anticipation of the viewers preferences.
Since HDD recorders are closed systems, the recording
format stream can be proprietary. The SAA6752HS
flexiblemultiplexingformats support a number ofrecording
stream formats for HDD including MPEG Transport
Stream (TS) or MPEG Packetized Elementary Stream
(PES).
2004 Jan 26 5
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
3 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DDP
V
DDCO
V
DDA
I
DD(tot)
P
tot
f
DCXO
f
SDRAM
f
SCL
B output bit-rate 1.5 − 25 Mbit/s
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
T
amb
digital supply voltage (pad cells) 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
digital supply voltage (core) 2.3 2.5 2.7 V
analog supply voltage (oscillator and PLL) 2.3 2.5 2.7 V
total analog plus digital supply current 407 453 525 mA
total power dissipation 0.95 1.16 1.48 W
quartz frequency (digital controlled tuning) 27 × [1 − (200 × 10−6)] 27 27 × [1 + (200 × 10−6)] MHz
SDRAM clock frequency − 108 − MHz
I2C-bus input clock frequency 100 − 400 kHz
HIGH-level digital input voltage 1.7 − 3.6 V
LOW-level digital input voltage −0.5 − +0.7 V
HIGH-level digital output voltage V
− 0.4 − V
DDP
DDP
V
LOW-level digital output voltage 0 − 0.4 V
ambient temperature 0 − 70 °C
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA6752HS/V103
SAA6752HS/V104
(1)(3)
SQFP208 plastic shrink quad flat package; 208 leads (lead length 1.3 mm);
(2)(4)
body 28 × 28 × 3.4 mm; high stand-off height
Notes
1. MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3 audio encoder with multiplexer.
2. MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio encoder with multiplexer, but without AC-3 audio encoder.
3. SAA6752HS/V103 is a replacement of SAA6752HS/V101 with enhanced functionality.
4. SAA6752HS/V104 is a replacement of SAA6752HS/V102 with enhanced functionality.
SOT316-1
2004 Jan 26 6
Page 7
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
f
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 7
16 Mbit @ 16-bit or 64 Mbit @ 16-bit audio clock
system
clock
reference
SDRAM-INTERFACE
STREAM DOMAIN SCHEDULER
digital
video
input
SAA6752HS
VIDEO
FRONT-END
ROMRAM
ull pagewidth
SDRAM
system clock
output
SYSTEM
CLOCK
REFERENCE
CLOCK 27 MHz
external
clock
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
digital
audio
input
I2C-BUS
2
C-bus
I
AUDIO
INTERFACE
GPIO RAM ROM TAP
host interrupt reset boundary scan
AUDIO
COMPRESSION
RESET
CONTROL
VIDEO
COMPRESSION
®
MIPS
CPU
PI-bus
STREAM
MULTIPEXER
Fig.1 Block diagram.
OUTPUT
INTERFACE
STATIC
MEM
DEBUG
ONLY
MHC128
MPEG
output
SAA6752HS
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
6 PINNING
I
max
SYMBOL PIN INPUT/OUTPUT
V
SSP
1 ground − pad ground
SDATA1 2 input − I2S-bus serial data input port 1 with internal pull-down resistor
SCLK1 3 input/output 4 I2S-bus serial clock port 1 with internal pull-down resistor
SWS1 4 input/output 4 I2S-bus word select port 1 with internal pull-down resistor
V
DDP
5 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SDATA2 6 input/output 4 I2S-bus serial data port 2 with internal pull-down resistor
SCLK2 7 input/output 4 I2S-bus serial clock port 2 with internal pull-down resistor
SWS2 8 input/output 4 I2S-bus word select port 2 with internal pull-down resistor
ACLK 9 output 4 audio clock output (256fs or 384fs)
V
SSP
10 ground − pad ground
IDQ 11 input − reserved input with internal pull-down resistor; (recommended
YUV0 12 input − video input signal bit 0 (LSB)
YUV1 13 input − video input signal bit 1
YUV2 14 input − video input signal bit 2
YUV3 15 input − video input signal bit 3
YUV4 16 input − video input signal bit 4
YUV5 17 input − video input signal bit 5
YUV6 18 input − video input signal bit 6
YUV7 19 input − video input signal bit 7 (MSB)
V
SSP
20 ground − pad ground
HSYNC 21 input − horizontal sync input (video) with internal pull-down resistor
VSYNC 22 input − vertical sync input (video) with internal pull-down resistor
FID 23 input − video field identification input (odd/even field) with internal
VCLK1 24 input − video clock input 1 (27 MHz) with internal pull-down resistor
V
SSCO
V
SSCO
V
DDCO
V
DDCO
V
DDP
25 ground − core ground
26 ground − core ground
27 supply − core supply voltage (2.5 V)
28 supply − core supply voltage (2.5 V)
29 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
VCLK2 30 input − video clock input 2 (27 MHz) with internal pull-down resistor
PDOAV 31 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output for audio/video identifier
PDIDS 32 input − parallel stream data input for data strobe [request for packet in
PDOSYNC 33 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output for packet sync
V
SSP
34 ground − pad ground
PDOVAL 35 3-state output 4 parallel stream data valid output with internal pull-up resistor
PDO0 36 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output bit 0 (LSB)
(1)
(mA)
to connect to pin V
DESCRIPTION
)
SSP
pull-down resistor
Data Expansion Bus Interface(DEBI) slave mode] with internal
pull-up resistor
2004 Jan 26 8
Page 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
I
max
SYMBOL PIN INPUT/OUTPUT
PDO1 37 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output bit 1
PDO2 38 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output bit 2
V
DDP
39 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
PDO3 40 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output bit 3
PDO4 41 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output bit 4
PDO5 42 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output bit 5
PDO6 43 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output bit 6
V
SSP
44 ground − pad ground
PDO7 45 3-state output 4 parallel stream data output bit 7 (MSB)
PDIOCLK 46 input/output 4 parallel stream clock input/output
I2CADDRSEL 47 input − I2C-bus address select input with internal pull-up resistor
SD_DQ15 48 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 15 (MSB)
V
DDP
49 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SD_DQ0 50 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 0 (LSB)
SD_DQ14 51 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 14
SD_DQ1 52 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 1
V
SSP
53 ground − pad ground
SD_DQ13 54 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 13
SD_DQ2 55 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 2
SD_DQ12 56 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 12
V
DDP
57 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SD_DQ3 58 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 3
SD_DQ11 59 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 11
SD_DQ4 60 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 4
SD_DQ10 61 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 10
V
SSP
62 ground − pad ground
SD_DQ5 63 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 5
SD_DQ9 64 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 9
SD_DQ6 65 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 6
SD_DQ8 66 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 8
V
DDP
67 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SD_DQ7 68 input/output 8 SDRAM data input/output bit 7
SD_DQM1 69 output 8 SDRAM data mask enable output bit 1
SD_DQM0 70 output 8 SDRAM data mask enable output bit 0 (LSB)
SD_WE 71 output 8 SDRAM write enable output (active LOW)
V
SSP
72 ground − pad ground
SD_CAS 73 output 8 SDRAM column address strobe output (active LOW)
SD_CLK 74 output 8 SDRAM clock output
SD_RAS 75 output 8 SDRAM row address strobe output (active LOW)
SD_CKE 76 output 8 SDRAM clock enable output
(1)
(mA)
DESCRIPTION
2004 Jan 26 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
I
max
SYMBOL PIN INPUT/OUTPUT
V
SSCO
V
SSCO
V
DDCO
V
DDCO
V
DDP
77 ground − core ground
78 ground − core and substrate ground
79 supply − core supply voltage (2.5 V)
80 supply − core supply voltage (2.5 V)
81 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SD_CS 82 output 8 SDRAM chip select output (active LOW)
SD_A13 83 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 13 (bank selection for 64 Mbit)
SD_A9 84 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 9
SD_A8 85 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 8
V
SSP
86 ground − pad ground
SD_A11 87 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 11 (bank selection for 16 Mbit)
SD_A7 88 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 7
SD_A12 89 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 12 (bank selection for 64 Mbit)
SD_A6 90 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 6
V
DDP
91 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SD_A10 92 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 10
SD_A5 93 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 5
SD_A0 94 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 0 (LSB)
SD_A4 95 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 4
V
SSP
96 ground − pad ground
SD_A1 97 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 1
SD_A3 98 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 3
SD_A2 99 output 8 SDRAM address output bit 2
SD_DQM3 100 output 8 reserved (do not connect)
V
DDP
101 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SD_DQM2 102 output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ31 103 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ16 104 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
V
SSP
105 ground − pad ground
SD_DQ30 106 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ17 107 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ29 108 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
V
DDP
109 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SD_DQ18 110 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ28 111 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ19 112 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ27 113 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
V
SSP
114 ground − pad ground
SD_DQ20 115 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ26 116 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
(1)
(mA)
DESCRIPTION
2004 Jan 26 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
I
max
SYMBOL PIN INPUT/OUTPUT
SD_DQ21 117 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ25 118 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
V
DDP
119 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SD_DQ22 120 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ24 121 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
SD_DQ23 122 input/output 8 reserved (do not connect)
EXTCLK 123 input − 27 MHz external clock input with internal pull-up resistor
V
V
SSP
SSA
124 ground − pad ground
125 ground − oscillator analog ground
XTALI 126 analog input − crystal oscillator input (27 MHz); note 2
XTALO 127 analog output − crystal oscillator output (27 MHz)
V
DDA
V
SSCO
V
SSCO
V
DDCO
V
DDCO
V
DDP
128 supply − oscillator analog supply voltage (2.5 V)
129 ground − core ground
130 ground − core ground
131 supply − core supply voltage (2.5 V)
132 supply − core supply voltage (2.5 V)
133 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
TDI 134 input − boundary scan test data input; pin must float or set to HIGH
TMS 135 input − boundary scan test mode select; pin must float or set to HIGH
TCK 136 input − boundary scan test clock; pin must be set to LOW during
TDO 137 3-state output 4 boundary scan test data output; pin not active during normal
V
SSP
138 ground − pad ground
TRST 139 input − test reset input (active LOW), for boundary scan test (with
CLKOUT 140 output 4 27 MHz system clock output
TEST0 141 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect)
TEST1 142 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect)
V
DDP
143 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
TEST2 144 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect)
SDA 145 input/open-drain
output
SCL 146 input/open-drain
output
RESET 147 input − reset input (active LOW); with internal pull-up resistor
V
SSP
148 ground − pad ground
RTS 149 output 4 reserved (do not connect); Universal Asynchronous
(1)
(mA)
DESCRIPTION
during normal operating; with internal pull-up resistor; note 3
during normal operating; with internal pull-up resistor; note 3
normal operating; with internal pull-up resistor; note 3
operating; with 3-state output; note 3
internal pull-up resistor); notes 3 and 4
− I2C-bus serial data input/output
− I2C-bus serial clock input/output
Receiver/Transmitter (UART) request to send output (active
LOW)
2004 Jan 26 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
I
max
SYMBOL PIN INPUT/OUTPUT
CTS 150 input − reserved (recommended connect to pin V
RXD 151 input − reserved (recommended connect to pin V
TXD 152 output 4 reserved (do not connect); UART transmit data
V
DDP
153 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SM_LB 154 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect)
SM_UB 155 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect)
H_IRF 156 3-state output 4 host interrupt flag output; with internal pull-up resistor
V
SSP
157 ground − pad ground
SM_OE 158 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory output enable output
SM_A9 159 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 9
SM_A10 160 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 10
V
DDP
161 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SM_A8 162 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 8
SM_A11 163 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 11
SM_A7 164 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 7
SM_A12 165 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 12
V
SSP
166 ground − pad ground
SM_A6 167 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 6
SM_A13 168 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 13
SM_A5 169 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 5
SM_A14 170 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 14
V
DDP
171 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SM_WE 172 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory write enable output
SM_D7 173 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D8 174 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D6 175 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
V
SSP
176 ground − pad ground
SM_D9 177 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D5 178 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D10 179 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
(1)
(mA)
DESCRIPTION
); UART clear to
DDP
send input; external static memory select input (active LOW);
with internal pull-up resistor
); UART receive
DDP
data; internal boot select input; with internal pull-up resistor
(active LOW)
(active LOW)
(active LOW)
bit 7 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 8 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 6 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 9 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 5 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 10 with internal pull-down resistor
2004 Jan 26 12
Page 13
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
I
max
SYMBOL PIN INPUT/OUTPUT
SM_D4 180 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
V
SSCO
V
SSCO
V
DDCO
V
DDCO
V
DDP
181 ground − internal pre-driver and substrate ground
182 ground − core ground
183 supply − core supply voltage (2.5 V)
184 supply − internal pre-driver supply voltage (2.5 V)
185 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SM_D11 186 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D3 187 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D12 188 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D2 189 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
V
SSP
190 ground − pad ground
SM_D13 191 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D1 192 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D14 193 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_D0 194 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
V
DDP
195 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SM_D15 196 input/output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory data input/output
SM_CS3 197 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory chip select output for
SM_A4 198 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 4
SM_A3 199 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 3
V
SSP
200 ground − pad ground
SM_A2 201 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 2
SM_A15 202 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 15
SM_A1 203 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 1
SM_A16 204 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 16
V
DDP
205 supply − pad ring supply voltage (3.3 V)
SM_A0 206 output 4 reserved (do not connect); static memory address output bit 0
SM_A17 207 output 4 reserved (donot connect);static memory address output bit 17
SM_CS0 208 output 4 reserved (do not connect)
(1)
(mA)
DESCRIPTION
bit 4 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 11 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 3 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 12 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 2 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 13 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 1 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 14 with internal pull-down resistor
bit 0 (LSB) with internal pull-down resistor
bit 15 (MSB) with internal pull-down resistor
external ROM or RAM (active LOW)
(LSB)
(MSB)
2004 Jan 26 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
Notes
1. All input pins, input/output pins (in input mode), output pins (in 3-state mode) and open-drain output pins are limited
to 3.3 V.
2. If used with external clock source the input voltage has to be limited to 2.5 V.
3. In accordance with the
4. Special function of pin TRST:
a) For board designs without boundary scan implementation, pinTRST must be connected to ground.
b) PinTRST provides easy initialization of the internal BST circuit. By applying a LOW level it can be used to force
the internal Test Access Port (TAP) controller to the Test-Logic-Reset state (normal operating) immediately.
“IEEE 1149.1”
handbook, halfpage
standard.
1
208
157
156
SAA6752HS
52
53
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
104
105
MHC129
2004 Jan 26 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 System operation
7.1.1 GENERAL
The SAA6752HS has a multi-processor architecture.
The different processing and control modules are not
lockedto each otherbut run independentlywithin the limits
of the global scheduling. The data transfer between the
processing units is carried out via FIFO memories or the
external SDRAM. The device is configured and the
operation modes are selected via the I2C-bus.
7.1.2 OPERATING MODES
There are five operating modes:
1. Idle. This mode is set after applying a hard reset (i.e.
on power-up). In this mode the SAA6752HS can be
initialized by the host to the required configuration.
Video and audio processing is disabled. A hard reset
always resets the SAA6752HS configuration
parameters back to the default states.
SAA6752HS
2. Stop. In Stop mode, the video and audio input
processing is enabled but the multiplexer output
remains disabled. It is possible to read status
information on the input video and audio signals via
the I2C-bus. The SAA6752HS initialization settings
cannot be modified, except to some specific dynamic
encoding parameters (i.e. bit rate setting).
3. Encode. In this mode, the multiplexer output is
enabled. Like Stop mode, only dynamic encoding
parameters can be modified in this mode.
4. Paused. This mode allows the SAA6752HS to make
seamless transitions. Restarting from Paused mode
will generate a stream output with sequential time
stamps and MPEG buffer model content.
5. Power-down. In this mode, the internal clock is
disabled, sending the SAA6752HS into a
(non-functional) power saving state. A hard reset will
re-initialize the SAA6752HS.
handbook, full pagewidth
Power-
down
HARD RESET
SLEEP
HARD RESET
power
applied
RECONFIGURE
RECONFIGURE
Idle
ENABLE
Stop Encode Paused
START
Fig.3 Mode transition diagram.
STOP
START
START
PAUSE
MHC130
2004 Jan 26 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.1.3 MODE TRANSITION COMMANDS
There are seven mode transition commands:
1. SOFT RESET. Like a hard reset, a soft reset can be
applied in any mode, setting the SAA6752HS back to
Idle mode and resetting all configuration parameters
back to the default settings.
2. RECONFIGURE. This command sets the
SAA6752HS back to Idle mode without resetting the
configuration parameters back to the default settings.
3. ENABLE.This transition setsStopmode, enabling the
video and audio input processing.
4. START. This transition sets Encode mode, enabling
the multiplexer stream output. Note that if the
SAA6752HS is commanded to start from the Idle
mode, then the internal transition isvia the Stop mode.
5. STOP. This command will disable the multiplexer
stream output, setting the SAA6752HS to Stop mode.
Thecurrent GOP and/oraudio frame iscompleted and
an end of sequence bit appended to the stream.
6. PAUSE. A PAUSE transitionwill cause themultiplexer
to complete the current GOP and/or audio frame but
no end of sequence bit is appended. The current
MPEG buffer model contents are saved to provide a
seamless transition on START.
7. SLEEP. This mode disables the internal clock.
8. FORCED RECONFIGURE. A STOP command whilst
in the Encode mode will not work in case the video or
audio input signalis interrupted,because for stopping,
the SAA6752HS tries to finish the current GOP. The
forced reconfigure command allows a mode transition
back to the Idle state, without losing the actual
configuration settings. The forced reconfiguration
performs a soft reset and the automatic internal
reprogramming of the I2C-bus registers. The forced
reconfiguration will take about 200 ms; during the
forcedreconfiguration all registervalues will changeto
their default values before they are reprogrammed.
Please note that outputs, which can be switched to
high-impedance or to input mode, will not be active
during the forced reconfiguration.
The SAA6752HS is not able to process any other
commands during mode transitions. In this event, a get
running mode request will return a busy flag. The
completion of a mode transition can also be flagged as an
event using the host interrupt pin.
SAA6752HS
7.2 Digital video input
7.2.1 GENERAL
The video front-end processes an
compliant video stream for conversion to 4 :2:0 format
(MP@ML). It includes synchronization, digital video signal
processingthroughseveralfilters,subsampling,sliced/raw
VBI data handling, and SDRAM address generation.
The video interface is designed for use with Philips
SAA7114 digital multi-standard decoder or similar video
decoders. The input interface accepts a digital video input
streamaccording to
50 Hz and 720 pixels by 576 lines as well as 525 lines at
60 Hz and 720 pixels by 480 lines are covered. The video
synchronization may either follow
recommendation or can also be supplied by external
signals (HSYNC, VSYNC and FID). The formatter module
performs a colour conversion from 4 :2:2to4:2:0
format. Optionally, also SIF progressive downscaling and
2/3D1, 1/2D1 downscaling may be activated.
The SAA6752HS supports non-standard features of the
SAA711x series of video input processors, such as
hard-wired external synchronization signals (2 and 3-wire
sync), special VCR playback signal streams (IEC 756
subset for VCR playback and still pictures), extraction of
sliced data from the input video stream.
7.2.2 VIDEO FRONT-END CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
The following configuration options can be selected from
the host:
• VIDEOINPUTPORT SELECTION. Two input clockpins
are selectable.
• VIDEOINPUTFORMAT. 525 or625-lineformatscan be
selected.
• VIDEO SYNC FORMAT. Various combinations and
polarities of HSYNC, VSYNC and Field Information
(FID) can be selected as the source of sync signal
processing.
• VIDEO FILTER SETTINGS. Noise pre-filter and
horizontal filters can be enabled and, if the default
coefficients are not suitable for an application, new
coefficients can be set.
• VIDEO FORMAT CONVERSION. Selection of
conversion from D1 to 1/2D1, 2/3D1 or SIF progressive
downscaling.
• VBI DATA EXTRACTION. VBI data extraction of WSS
or CC data can be enabled.
“ITU-R-BT.601”
“ITU-R BT.601/605”
.625 lines standard at
“ITU-R-BT.656”
2004 Jan 26 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.2.3 VIDEO ENCODER STATUS INFORMATION
The following configuration option can be selected from
the host:
• VBI DATA: WSS and CC data can be read back via the
I2C-bus.
7.2.4 DATA INPUT FORMAT
7.2.4.1 Interface definition
The data input interface uses 13 pins, all of which are
inputs (see Table 1). Pins YUV0 to YUV7 carry video and
synchronization data and 3 pins are reserved for control
purposes. Two separate clock inputs allow two different
signal sources to be used. The input clock can be
asynchronous to the SAA6752HS system clock.
Table 1 List of pins data input port
PIN DESCRIPTION
YUV0 to YUV7 video input signal
(synchronous to VCLK)
FID odd/evenfield identification
signal; note 1
HSYNC horizontal synchronization
signal; note 1
VSYNC vertical synchronization
signal; note 1
VCLK1 or VCLK2 video clock signal (from
source 1 or 2)
Note
1. In ITU-T 656 mode sync signals are embedded in the
video data input stream. The external sync signals are
not used.
SAA6752HS
recognized by a sync decoder. This checks the incoming
field (FID), vertical sync and horizontal sync. It is possible
to select either ‘internal synchronization’ (which means
thatSAV/EAV codes inthe ITU 601/656 videostreamsare
used) or externally applied hardware synchronization
signals (which are given by the video input processor).
In the latter case, 3 pin or 2 pin (V-sync and H-sync only)
synchronization can be used.
Using 2 pin synchronization, the FID information is given
by the timing of the transition of the V-sync. If a Vertical
Blanking Interval (VBI) starts during H-sync, the next field
will be the top field, otherwise it will be the bottom field.
A sync filter is used to inhibit sync signal triggering if an
incorrect number of pixels or lines has been input. It also
checks for the correct consecutive fields. The filter works
on three different levels. An H-sync is only accepted after
a predefined number of video cycles, a V-sync is only
accepted after a programmed number of lines and a field
is only accepted if top field follows bottom field or vice
versa.
7.2.5.3 Horizontal and vertical shift
This function is intended for correction in synchronization
of external sync signals if incorrectly timed. The amount of
shift is programmable via the I2C-bus.
7.2.5.4 SAV/EAV decoder
A SAV/EAV decoder extracts the F, V and H bits from the
video timing reference code. The decoder evaluates the
protection bits tobe able tocorrect one bit errors withinthe
codeword.If multiple bit errorsaredetected,theprotection
bits are ignored and the field (F), vertical sync (V) and
horizontal sync (H) bits are directly extracted from the
code.
7.2.5 VIDEO SIGNAL PROCESSING
7.2.5.1 Acquisition of video data
Data is latched with the incoming video clock to provide
robust data capture. Video clock and data is unlocked to
the internal system clock therefore a clock domain bridge
is used. This is performed by oversampling of video clock
and data with 108 MHz.
7.2.5.2 Sync decoding and filtering
To allow selection of the right portion of the video input
stream, synchronization signals from the stream are
2004 Jan 26 17
7.2.5.5 Video format conversion
The SAA6752HS converts the input video input signal to
the formats defined in Table 2 controlled by the I2C-bus
command. A 4 : 2 : 2 to 4 : 2 : 0 colour conversion is
performed as this is a pre-requisite of MPEG MP@ML
encoding.
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
Table 2 Format conversion
MODE
D1 720
2/3D1 480
1/2D1 352; note 1
SIF 352; notes 1 and 2
Notes
1. The 8 pixels at the right edge of the scaled picture are
not encoded.
2. Top field only.
7.2.6 VIDEO FILTERING
7.2.6.1 Adaptive mean filter
The SAA6752HS uses an adaptive mean filter. There are
three different filter modes that can be selected: median,
averaging or no filter.
The median algorithm provides better noise performance
and is well suited to suppress single noise spikes without
degrading the signal edges. The averaging algorithm is a
standard low-pass filter so has greater impact on signal
edges.
The default threshold and gaincoefficients ofthis filtercan
beoverwrittenvia the I2C-bustoallow user optimizationfor
different applications.
7.2.6.2 Horizontal pre-filter/decimation filter
There is ahorizontal filterfor Y and C andthis canoperate
as a pre-filter or decimation filter. It is a symmetrical FIR
filter with up to 8 coefficients programmable via the
I2C-bus.
7.2.6.3 Vertical chrominance filtering
For 4 :2:2to4:2:0 conversion, vertical filtering and
subsampling of the chrominance is performed. The
sequenceofcoefficients is mirrored intopandbottomfield.
This generates the right phases of the chrominance
samples between the luminance samples (a non co-sited
sampling scheme).
PICTURE FORMAT
(PIXEL/LINES)
SAA6752HS
7.2.7 VBI DATA EXTRACTION
The SAA6752HS supports the extraction of WSS and CC
data using two independent VBI data extractor modules.
The data is available via the I2C-bus.
The following VBI data formats are supported: Closed
Caption (CC525 and CC625) and Wide Screen Signalling
(WSS525 and WSS625). For CC525, CC625 and
WSS625 the sliceddata from a video inputprocessor (e.g.
SAA7114, SAA7115 or SAA7118) are extracted from the
digital video input signal and can be read via the I2C-bus.
For WSS525 an internal data slicer is available which
slices the oversampled raw data, which are delivered by
the video input processor. The extracted WSS525 signal
can be read via the I2C-bus.
Optionally the automatic insertion of extracted Closed
Caption data into the user data area of a video stream is
possible (for details see Section 7.3.8).
7.3 Video compression
7.3.1 GENERAL
Compression of video data is performed by the video
compressor block; see Fig.4. The input to this block is the
uncompressed video information pre-processed by the
video front-end and stored in external SDRAM memory.
The output is a compressed video stream, compliant to
MPEG-2Video ElementaryStream (VES) upto slice level.
Controlling information (for example, quantizer step size)
as well as the bit stream for higher layers of the VES is
generated by the embedded MIPS processor of the
SAA6752HS.
The video compressor contains several subblocks. The
MacroBlock Processor (MBP) performs generation of
video ES on macroblock level. Controlling parameters for
this task and MB headers as well as slice headers are
generated by the core control subblock. Bitstream
formatting and concatenation of MBP bitstream and
header information is done by the subblocks pre-packer
and packer.
2004 Jan 26 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.3.2 VIDEO ENCODER CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
The following configuration options can be selected from
the host:
• VIDEO COMPRESSION SETTINGS. I, IP and IPB
encoding with various GOP structures can be selected.
• ENCODER BIT RATE. The bit rate for variable bit rate
or constant bit rate modescan beprogrammed usingbit
rate and quantization control parameters. These
parameterscan be adjustedwhilst encoding, notjustset
at initialization.
• ENCODER PERFORMANCE TUNING. The ability for
the user to tune encoding performance is provided by
allowing control of adaptive quantizationdepth. Alsothe
SAA6752HS allows download of new quantizer matrix
contents.
7.3.3 VIDEO ENCODER STATUS INFORMATION
The following status information is available to the host:
• CURRENT ENCODER BIT RATE. The actual encoded
bit rate, as number of bytes per GOP, is available
allowing the use of constrained variable bit rate
algorithms to fine tune the encoding efficiency.
7.3.4 GOP STRUCTURE
The programmable GOP structure features a reference
frame distance (M) up to 3, and a GOP length (N) of up
to 19.Supported structures arerealclosed GOP(M,N) and
backward predicted closed GOP(M,N). For the use of
B-frames in D1 and 2/3D1 mode a 64 Mbit SDRAM is
needed.
In D1 mode, B-frames will be unidirectional. Backward
predicted closed GOPs may have the first one (M = 2) or
two (M = 3) B-frames referenced inside the GOP
dependent on the I2C-bus register settings. This is
intended for editable applications as GOPs are
independent of each other. Non-editable GOPs allow the
first one (M = 1) or two (M = 2) B-frames to be referenced
to the P-frame in the previous GOP. This is a non-editable
formatbut has optimum encodingefficiency.This structure
is sometimes calledan openGOP. The first one (M = 1) or
two (M = 2) B-frames in the first GOP of a sequence are
always forced backwards predicted.
SAA6752HS
Table 3 GOP
GOP
LENGTH (N)
1I
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Notes
1. Undefined.
2. This GOP structure is defined as a Real Closed GOP
(RCG).
3. This GOP structure is defined as a Backward
Predicted Closed GOP (BPCG) or Non-Editable GOP
(NEG), selectable via the I2C-bus.
REFERENCE FRAME DISTANCE (M)
01 2 3
(1) (1) (1)
(1)
IP
(1)
IPP IBP
(1)
IPPP BIBP
(1)
IPPPP IBPBP
(1)
IPP...PP BIBPBP
(1)
IPP...PP IBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP BIBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP IBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP BIBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP IBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP BIBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP IBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP BIBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP IBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP BIBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP IBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP BIBP...BP
(1)
IPP...PP IBP...BP
(1) (1)
(2) (1)
(3)
IBBP
(2) (1)
(3)
BBIBBP
(2)
IBBPBBP
(3) (1)
(2)
BBI...BBP
(3)
IBBP...BBP
(2) (1)
(3)
BBI...BBP
(2)
IBBP...BBP
(3) (1)
(2)
BBI...BBP
(3)
IBBP...BBP
(2) (1)
(3)
BBI...BBP
(2)
IBBP...BBP
(2)
(3)
(2)
(3)
(2)
(3)
(2)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(2)
2004 Jan 26 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.3.5 BIT RATE CONTROL
The SAA6752HS supports two modes of video bit rate
control: variable bit rate and constant bit rate.
The Variable Bit Rate (VBR) mode is intended for burst
data transfer applications, where the bit rate is allowed to
vary but the image quality should be constant. In this
mode,acombination of three parameterscanbeset:Rvbr,
Qmin_VBR and Qmax_VBR. While aimingat thetarget bit
rate Rvbr, only quantizer scale values within the range
between Qmin_VBR and Qmax_VBR are applied.
Broadeningthis range leadsto greater variationsinpicture
quality but better adherence to Rmax. Constriction of this
range forces a better constancy in picture quality at the
expense of meeting the target bit rate. Note that optimal
control results require reasonable combinations of Rmax,
Qmin_VBR and Qmax_VBR. Furthermore, the maximum
bit rateRmax can beset.If Rmax isreachedin VBR mode,
the CBR algorithmtakes over the control byincreasing the
quantizer scale values temporarily (over Qmax_VBR) to
guarantee that Rmax is never exceeded. Hence, the
closer Rmax and Rvbr are chosen, the more the control in
VBR mode turns to CBR mode behaviour.
SAA6752HS
7.3.7 QUANTIZER MATRIX TABLE DOWNLOAD
The MPEG standard default quantizer matrices can be
overwritten to allow picture encoding optimization.
7.3.8 USER DATA INSERTION
User data insertion of up to 64 bytes is supported on GOP
and picture level.
Different modes can be selected via I2C-bus.
7.3.8.1 External user data insertion (permanently
repeated)
User data is downloaded via the I2C-bus to
subaddresses 73H/76H and the number of inserted user
data bytes is set via subaddresses 74H/75H. In Encode
mode the downloaded user data will be inserted
permanently into the user data area of the video stream.
It is possible to download a new set of user data during
Encodemode. The newdata will berepeatedly inserted as
soon as the download is finished. It is possible to stop the
user data insertion with a special command.
The Constant Bit Rate (CBR) mode is intended for
applications, where a fixed channel rate is provided (e.g.
transmission systems). A tight control of the quantizer
scale is applied to make optimal use of the given
bandwidth. The parameter Rmax specifies the required
constant bit rate.
Independent of thebit rate mode(CBR or VBR),a B-frame
weighting factor (the weighting factor is applied to the
quantization scale) can be applied to further reduce the
bit rate of B-frames. In IP-only GOP structures, every
second P-frame is weighted by this factor generating
‘virtual B-frames’ to simulate a bit rate distribution similar
to IPB sequences. This feature can further improve the
perceptual rate-distortion ratio by taking advantage of the
inertia of the human visual system.
7.3.6 ADAPTIVE QUANTIZATION
Adaptive quantization is an algorithm that uses internal
generated statistics to fine tune the quantizer scale used
for encoding a specific macroblock. For example, the
controller adapts the quantization scalewith respectto the
local complexity distribution within a frame, resulting in a
perceptually smoother picture quality. The amount of fine
tuning can be adjusted by control of the adaptive
quantization depth.
7.3.8.2 External user data insertion (each downloaded
byte inserted only once)
In this mode each downloaded user data byte is inserted
only once into the user data area. If no new user data is
downloaded between two GOP or pictures then no user
data will be inserted. This mode can be used to transmit
more than 64 bytes of user data from the encoder to the
decoder, e.g. 1000 bytes distributed on 15 packets of
64 bytes and one packet of 40 bytes. The host has to
control the insertion and repetition of user data. A host
interrupt 'mode transition completed' is signalled, if not
masked and the bit 9 of the exception status word is set
when the user data have been read by the video encoder.
Then new user data can be downloaded via I2C-bus.
2004 Jan 26 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.3.8.3 Internal Closed Caption user data insertion
compliant to ATSC/NTSC standard
Automatic insertion of Closed Caption data into the user
data 2 area on picture header level compliant to the ATSC
and EIA-708 standard can be selected via the I2C-bus.
Closed Caption data, which is delivered from the video
input processor (e.g. SAA7114) and captured in the video
front-end will be inserted into the user data 2 area (picture
header level) of the video stream. Preconditions are
appropriate settings of the video input processor and the
VBI data extractor in the video front-end. The Closed
Caption user data will be written for both fields. If no valid
Closed Caption data for field 2 is available these data will
be marked as invalid in the stream. At SIF mode only
field 1 Closed Captions can be inserted from the video
input signal and dummy values (80H 80H) will be inserted
for field 2.
If extended data services (XDS data, line 21 field 2) are
inserted, the insertion will be transparent. No modification
of the CGMS-A copy information will be done.
In accordance to EIA-708 the Closed Caption data will
appear in the stream in transport order. If B-frames are
present the user data isre-ordered inthe sameway as the
video frames.
AdvancedTV Closed Captioning(ATVCC)channel packet
data (cc_type 10 or 11) is not supported, because the
inputsignal of theencoderis an analogvideo signal, which
cancarry only NTSC ClosedCaptions,but not ATV Closed
Captions.
No additional user data on picture header level can be
inserted if internal Closed Caption user data insertion
compliant to the ATSC/NTSC standard is active.
SAA6752HS
Closed Caption data, which is delivered from the video
input processor (e.g. SAA7114) and captured in the video
front-end will be inserted into the user data 1 area (GOP
header level) of the video stream. Preconditions are
appropriate settings of the video input processor and the
VBI data extractor in the video front-end. The Closed
Caption user data will be written for both fields. If no valid
Closed Caption data for field 2 is available these data will
be marked as invalid in the stream.
If extended data services (XDS data, line 21 field 2) are
inserted, the insertion will be transparent. No modification
of the CGMS-A copy information will be done.
The Closed Caption data will be inserted for each field of
the GOP in display order. At SIF mode only field 1 Closed
Captions can be inserted from the video input signal and
dummy values (80H 80H) will be inserted for field 2.
The user data is delayed by one GOP period. The first
GOP in the stream carries dummy data marked as invalid.
No additional user data on GOP header level can be
inserted if internal Closed Caption user data insertion
compliant to the DVD standard is active.
The amount of user data depends on the GOP size:
5 bytes header and 3 bytes/field are required. With the
maximum GOP size of 19 this results in
5+19× 2 × 3 = 119 bytes, which is more than the
available array of 64 bytes for GOP user data. Therefore
the64 byte array forpictureuser data isalsoused for GOP
userdata, ifGOP sizes largerthan 9 are selected. Thenall
128 bytes, which are available for user data insertion on
GOP and picture header levelwill beused forthe insertion
of CC data on GOP level. In this case no additional user
data insertion on picture header level is possible.
7.3.8.4 Internal Closed Caption user data insertion
compliant to DVD standard
Automatic insertion of Closed Caption data into the user
data area on GOP header level compliant to the DVD
standard can be selected via I2C-bus.
2004 Jan 26 21
7.3.9 MOTION ADAPTIVE NOISE REDUCTION
The gain and adaptivity can be controlled to optimize
encoding efficiency in case of noisy input sequences, i.e.
off-air reception.
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.3.10 COMPRESSION BLOCK PARTITIONING
Thevideo compression block,shown in Fig.4,containsthe
following sub-modules:
• MacroBlock Processor (MBP). Reads uncompressed
videodata from SDRAMandgenerates the compressed
bitstream on MB level (withoutMB headers).Addresses
for frame buffer (previous frame) access are generated
by the MBP.
• Core control. Performs MB and slice header
generation, base address generation for the current MB
(uncompressed), motion vector candidate generation,
and computation of encoding statistics required by the
CPU for bit rate controlling.
handbook, full pagewidth
to/from SDRAM-IF to SDRAM-IF
SAA6752HS
• Pre-packer (part ofpacking unit). Since the MBPoutput
words are not necessarily fully used (i.e. some output
words may contain unused bits) the pre-packer packs
the output of the MBP in such a way that all words
contain valid bits. This reduces the amount of memory
required for storing the MB data.
• Packer (part of packing unit). Merges header and MB
headers.
from video
front-end
VIDEO COMPRESSION BLOCK
PACKING UNIT
MBP/CPM
PRE-
PACKER
CORE CONTROL
GENERIC INTERFACE
to/from PCI-bus
MEMORY
Fig.4 Video compressor block diagram.
PACKER
MHC131
2004 Jan 26 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.4 Digital audio input
7.4.1 GENERAL
The audio input interface (I2S) accepts serial digital audio
data and supports master and slave mode. The interface
is able to handle 16 to 20 bits audio data with left and right
channel. Audio data with more than 20-bit word width is
accepted as input, but the additional bits are ignored.
7.4.2 AUDIO PORT CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
The following configuration options can be selected from
the host:
• AUDIO INPUT PORT SELECTION. Two digital audio
input ports are selectable.
• AUDIO INPUT FORMAT. Various I2S and EIAJ formats
can be selected.
• AUDIO INPUT MODES. Master or slave mode can be
selected.
• AUDIO CLOCK OUTPUT. An audio clock output
(256 × 48 kHzor 384 × 48 kHz) canbeusedfor external
analog-to-digital converter clocking.
• AUDIO OUTPUT. The second audio interface port can
be configured as output in special applications e.g.
concurrent encoding of audio and video without internal
multiplexing of the two streams.
SAA6752HS
The alternative formats are defined as having the word
select shifted by one clock cycle with respect to the data.
EIAJ and EIAJ alternative format are supported for 16, 18
and 20-bit resolution. I2S and I2S alternative format are
supportedfor 16,18, 20 and24-bit resolution. Inputdata is
truncated to 20 bits internally if 24-bit resolution is applied.
Each of the formats can be applied in master or slave
mode.
When in master mode, theexternal audioanalog-to-digital
convertor must be clocked using the audio clock
generated by the SAA6752HS. This can be set to
256 × 48 kHz or 384 × 48 kHz.
In slave mode an internal sample rate converter converts
theinput sample frequencytoa video framelocked48 kHz
sample frequency.
If video is not present and/or the clock mode is set to
mode 3, the audio clock frequency is locked to the fixed
nominal system frequency (crystal or external). In allother
cases the audio clock will be locked to the video frame
frequency.
7.4.3 INPUT FORMATS
The digital audio input interface can select between two
digital audio input ports via I2C-bus control and is able to
input the following audio formats:
• I2S, see Fig.5
• EIAJ, see Fig.6
• EIAJ alternative format.
2004 Jan 26 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
2
handbook, full pagewidth
S
I
SWS
SCLK
SDATA
MSB LSB MSB LSB MSB
SAA6752HS
1 stereo word
right dataleft data
MHC132
handbook, full pagewidth
EIAJ
SWS
SCLK
SDATA
Fig.5 I2S mode format protocol.
1 stereo word
left data right data
LSB MSB LSB MSB
LSB
MHC133
Fig.6 EIAJ mode format protocol.
2004 Jan 26 24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.4.4 AUDIO INPUT PROCESSING
In order to be able to cope with analog and digital sources, the I2S input ports can be configured as master (analog) or
slave (digital). For the slave mode however, a sample rate converter will be involved, except for DVD-compliant audio
bypass. Table 4 reflects the different configuration possibilities.
Table 4 Audio input processing modes
PROCESSING MODE
(1)
AUDIO CONTENT
FORMAT
MPEG-1 L2 encoding LPCM at 16, 18, 20
or 24 bits
DDC encoding
(6)
LPCM at 16, 18, 20
or 24 bits
LPCM bypass (uncompressed
audio format)
(7)
LPCM at 16, 18, 20
or 24 bits
DVD-compliant audio bypass 16 bits
(5)
(5)
(5)
(8)
INPUT SAMPLE
FREQUENCY (kHz)
MASTER
(2)
SLAVE
(3)(4)
48 32 kHz ±0.1%
44.1 kHz ±0.1%
48 kHz ±0.1%
48 32 kHz ±0.1%
44.1 kHz ±0.1%
48 kHz ±0.1%
48 32 kHz ±0.1%
44.1 kHz ±0.1%
48 kHz ±0.1%
− 48 kHz
(9)
NO. OF
ENCODED
BITS
ENCODED
BIT RATE
(kbit/s)
20 256, 384
20 256, 384
16 −
16 −
Notes
1. Processing modes can be changed when SAA6752HS is in Idle mode.
2. In master mode, the external audio source must use the SAA6752HS audio clock as a clock source.
3. A sample rate conversion process will convert incoming data to a nominal 48 kHz audio frequency that is locked to
V-sync of the video input signal (if present). The sample rate converter is not enabled for DVD-compliant bypass
mode.
4. The sample rate conversion input frequency range has been selected to be compatible withclass 2 SPDIFreceivers.
5. 24-bit input option only applies to I2S input formats, in this event it will be truncated to 20 bits internally in the
SAA6752HS before processing. EIAJ formats are limited to 20 bits maximum.
6. Only for SAA6752HS/V103.
7. In systems that use 16 Mbit SDRAM due to system architecture constraints, LPCM bypass must be restricted to be
used with I and IP video encoding only. There is no constraint if 64 Mbit SDRAM is used.
8. TheIEC 60958 format defines20 bits for anaudiosample, plus 4 auxiliarybits, which canbe used toextendthe word
length. IEC 61937 uses only 16 data bits of each IEC 60958 sub-frame. It depends on the settings of an external
SPDIF to I2S converter if 16, 18, 20 or 24 bits are transferred to the SAA6752HS.
9. For DVD-compliant bypass mode the audio clock must be locked to the video clock externally.
2004 Jan 26 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.5 Audio compression
7.5.1 GENERAL
The digital audio signal from the I2S input port is
compressed according to MPEG-1 layer 2 and DDC
(AC-3) encoding (only for SAA6752HS/V103). The
constant bit rate is programmable via the I2C-bus.
An audio stream with 16 to 20 bits and a sampling
frequency of 48 kHz canbe processed. A higher accuracy
of more than 20 bits is ignored. A bypass mode can be
selected for LPCM for 16-bit data resolution and
compressed audio signals (MPEG-1 layer2, MPEG-2,DD
and DTS) according to IEC 61397 or LPCM. The format of
such compressed inputsis identified and made accessible
via the I2C-bus.
7.5.2 AUDIO ENCODER CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
The following configuration options can be selected from
the host:
• AUDIO PROCESSING MODES. MPEG-1 L2 or DDC
(AC-3) encoding (only for SAA6752HS/V103) modes
can be selected. Two bypass modes are also available:
LPCM bypass and DVD-compliant bitstream bypass.
• AUDIO MUTE. It is possibleto mutethe audiodata prior
to encoding.
7.5.3 AUDIO ENCODER STATUS INFORMATION
The following configuration options can be selected from
the host:
SAA6752HS
• DVD-BYPASS HEADER INFORMATION. Header
information is available to allow the host to determine
the content of the bypassed audio data stream. This
includes information from the Preamble Pc, Preamble
Pd and audio frame headers.
7.5.4 MPEG-1 LAYER 2 ENCODING
MPEG-1 layer 2 encoding can be selected. The available
I2C-bus settings are:
• No pre-emphasis (default setting)
• 50/15 µs (compliant to ISO 11172-3)
• CCITT J.17 (compliant to ISO 11172-3).
7.5.5 DDC ENCODING (ONLY FOR SAA6752HS/V103)
Dolby Digital Consumer (DDC) encoding mode can be
selected. The encoder performance is suitable for
consumer electronic recordable DVD systems.
7.5.6 LPCM BYPASS
16-bit LPCM audio streamscan be bypassed by the audio
encoder module.
7.5.7 DVD-COMPLIANT AUDIO BYPASS
DVD-compliant bypass and pause burst handling is
selectable in accordance to IEC 61937. Preamble Pc,
Preamble Pd and part of the elementary stream header
are captured and made available via the I2C-bus. If any
non DVD-compliant formats are detected then these are
flagged via host interrupt.
Table 5 DVD-compliant audio bypass
MODE BIT RATE SAMPLE FREQUENCY CHANNEL CONFIGURATION
MPEG-1/2 layer 2 without
extension
MPEG-2 layer 2 with
extension
Dolby digital 64 to 448 kbit/s 48 kHz only 1/0, 2/0, 3/0, 2/1, 3/1, 2/2 and 3/2
DTS-1 192 to 1536 kbit/s 48 kHz only stereo or multi-channel up to 5.1
7.6 SDRAM interface
7.6.1 GENERAL
The external SDRAM is used as memory for storing video
and audio information during the compression process.
It is also used as a buffer for the output stream. The
interfacing to and from the functional blocks is done via a
number of internal FIFO memories.
2004 Jan 26 26
64 to 384 kbit/s 48 kHz only mono, stereo or multi-channel up to 7.1
up to 912 kbit/s 48 kHz only mono, stereo or multi-channel up to 7.1
The SAA6752HS will support 16 Mbit@16 bit
(512k × 16 × 2) and 64 Mbit@16 bit (1024k × 16 × 4)
SDRAM devices. The minimum recommended speed of
theSDRAM is 125 MHz.Recommended SDRAMs include
the Samsung K4S641632D-TC/L80 and
K4S161622D-TC/L80 devices.
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.7 Multiplexer
7.7.1 GENERAL
The system stream multiplexer combines compressed
audio and video streams into a single MPEG system
stream. Presentation data is synchronized by the use of
time stamps asspecified in the MPEG systemsstandards.
The multiplexer ensures an MPEG-compliant multiplexing
with respect to buffer maintenance, synchronization and
data alignment. It takes care of the system specific
requirements for D-VHS, DVD, DVB and ATSC.
7.7.2 MULTIPLEXER CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
The following configuration options can be selected from
the host:
• STREAM FORMAT. Selection of audio or video
elementary stream, packetized elementary stream,
programstream or transportstreamoptions and general
system parameters including maximum system bit rate,
number of flushing bytes and PES header IDs.
• TRANSPORT STREAM SYSTEM MODES. In TS
mode, it is possible to set packet IDs and download
system information tables.
7.7.3 MULTIPLEXER STATUS INFORMATION
The following status information can be selected from the
host:
• METABYTES INFORMATION. If selected and in
program stream or pack stream, it is possible to insert
video and audio status information into the stream
outputas special metabytedatapacketsfor later system
processing.
• NUMBER OF BYTES PER GOP. It is possible to read
the current system bit rate of the output stream.
7.7.4 ELEMENTARY STREAM OUTPUT
Video and audio elementary stream outputs can be
selected.
7.7.5 PACKETIZED ELEMENTARY STREAM OUTPUT
Packetized Elementary Stream (PES) outputs can be
selected. There are two options: PES (DVD) and PES
(TS).Variable bit rateis only availablein PES (DVD)mode
and constant bit rate only available in PES (TS) mode.
SAA6752HS
7.7.6 PROGRAM STREAM OUTPUT
Program stream output, intended for storage recording
applications, can be selected. Time slot reservation for
navigation packets is available. Metabytes can be
appended after each pack, see Section 7.7.10.
7.7.7 PACK STREAM OUTPUT
A special mode called pack stream can be selected. This
is a program stream but without the MPEG buffer model
implemented. This minimizes the throughput time of video
and audio data through the SAA6752HS and is intended
for applications where low latency is important. In this
mode no program stream header is inserted.
7.7.8 TRANSPORT STREAM OUTPUT
Transportstream output canbe selected. Thevideo,audio
and PCR (clock) Packet Identifiers (PIDs) can be
programmed. System information tables can be
transferred to the SAA6752HS via the I2C-bus. If transport
stream output is combined with DIO master mode as
output mode then packets are sent in a controlled way, so
that a set-top box can be connected.
7.7.8.1 Transport stream with variable bit rate
Optionally a transportstream without null packets, i.e.with
variable bit rate can be generated. Via subaddress C3H it
is possible to select constant or variable TS bit rate.
At constant TS bit rate mode null packets are delivered at
the multiplexer output to achieve the constant TS bit rate,
even if the video bit rate is variable.
At variable TS bit rate mode no Null Packets are inserted
at the multiplexer output. This mode can be used in
combination with variable video bit rate.
7.7.9 INSERTION OF LEADING NULL BYTES
For some applications it is helpful to deliver leading
flushing bytes before the stream content starts. Null bytes
(00H) will be inserted at the beginning of a stream, if
programmed by subaddress F6H. By default no null bytes
will be delivered.
The video and audio PES IDs can be programmed via the
I2C-bus. Original copy or copyright flags can also be set.
2004 Jan 26 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.7.10 METABYTES DATA
In program stream and pack stream modes, the SAA6752HS can append additional metabyte data packets to the
stream, providing information on sector information for downstream application processing. The video and audio
metabytes format is defined in Tables 6 and 7. The sector and metabytes form a block format, where each sector of
2048 bytes is followed by 16 metabytes containing data on the previous sector.
Table 6 Video metabytes data
BYTE
(HEX)
00 identification 0 to 7 55H; video
01 flags 0 ‘GOP start flag’; indicates that a GOP start code is present in the
02 data length LSB 0 to 7 amount of non-stuffing bytes minus one
03 MSB 0 to 7
04 time stamp LSB 0 to 7 The value of the STC at the moment that the first byte of the first
05 0 to 7
06 0 to 7
07 MSB 0 to 7
08 picture start count 0 to 7 the amount of picture starts in the sector
09 picture types 0 and 1 1st picture type:
0A first picture position LSB 0 to 7 position (in bytes) of the first picture (or GOP or sequence) start
0B MSB 0 to 7
0C second picture position LSB 0 to 7 position (in bytes) of the second picture (or GOP or sequence)
0D MSB 0 to 7
0E GOP header position LSB 0 to 7 position (in bytes) of the GOP start code in the sector, if present,
0F MSB 0 to 7
NAME
LSB/
MSB
BIT DESCRIPTION
sector
1 ‘GOP start header’; indicates that a group of GOPs starts in the
sector
2 ‘sequence end flag’; indicates that a sequence end code is
present in the sector
3 and 4 reserved
5 to 7 undefined
frame arrived at the input. Only 32 bits are used; note 1.
00: I picture
01: P picture
10: B picture
11: invalid type
2 reserved
4 and 5 2nd picture type:
00: I picture
01: P picture
10: B picture
11: invalid type
6 reserved
code in the sector
start code in the sector
else 0000
Note
1. This is the same value as used to generate the PTS and DTS values.
2004 Jan 26 28
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
Table 7 Audio metabytes data
BYTE
(HEX)
00 identification 0 to 7 AAH; audio
01 flags 0 reserved
02 data length LSB 0 to 7 amount of non-stuffing bytes minus one
03 MSB 0 to 7
04 time stamp LSB 0 to 7 The value of the STC at the moment that the first byte of the first
05 0 to 7
06 0 to 7
07 MSB 0 to 7
08 reserved 0 to 7 00
09 frame start count 0 to 7 the amount of frame starts in the sector
0A first frame position LSB 0 to 7 position (in bytes) of the first frame in the sector
0B MSB 0 to 7
0C last frame position LSB 0 to 7 position (in bytes) of the last frame in the sector
0D MSB 0 to 7
0E reserved 0 to 7 00
0F reserved 0 to 7 00
NAME
LSB/
MSB
BIT DESCRIPTION
1 ‘terminated audio flag’; this flag is only set at the end of a
recording session and indicates that this sector is not completely
filled with audio data
2 ‘synchronization flag’; indicates that the audio data in the sector is
related in time to the beginning of a Video Object Unit (VOBU)
3 reserved
4 reserved
5 to 7 audio pack type:
000: MPEG-1 layer 2 or MPEG-2 without extension
010: MPEG-2 with extension
011: DDCE
100: DTS-1 (512 samples/frame)
101: reserved
110: reserved
111: LPCM 16-bit stereo 48 kHz
frame arrived at the input. Only 32 bits are used; note 1.
Note
1. This is the same value as used to generate the PTS value.
2004 Jan 26 29
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.8 MPEG stream output port
7.8.1 GENERAL
The MPEG stream output port connects the SAA6752HS
multiplexer output to the outside world. The parallel
interface performs a parallel output transition of audio and
video data toan externally connected device andsupports
3-bus protocol modes.
7.8.2 OUTPUT PORT CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
The following configuration options can be selected from
the host:
• OUTPUT PROTOCOL. Three output protocols can be
selected: DIO slave mode, DIO master mode and DEBI
slave mode and associated signalling pin polarities.
• OUTPUT DISABLE. Output can be set to
high-impedance if the SAA6752HS is not used in
application.
7.8.3 DATA OUTPUT FORMAT
The data to be transmitted have a width of 8 bits in all
modes. The data output port supports DIO and DEBI bus
protocols. The bus protocol mode is set via an I2C-bus
controlled register. The DEBI protocol provides only a
transmission of 8-bit data block transfer without address
decoding.
SAA6752HS
7.8.4 PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION
Table 8 Output port definitions
PORT I/O DESCRIPTION
PDIDS I Request from external system if
interface is in DEBI slave mode.
PDIOCLK I/O Output clock to the external system if
interface is set to DIO master mode.
Input clock to the SAA6752HS if
interface is set to DIO slave mode.
PDO[7:0] O output data (8-bit parallel)
PDOSYNC O Indicates a first byte of a data packet
(for transport streams in DIO mode).
PDOAV O Indicates when an audio packet is
output (for transport stream).
PDOVAL O Indicates whether currently sent data
is valid.
7.8.4.1 DIO master mode
The PDIOCLK clock for the DIO interface is derived from
the system clock by a division of the 27 MHz clock by 3 or
by 4, generating a data output clocked at 9 or 6.75 MHz.
A PDOVAL signal indicates whether current data at the
output is valid. If the output buffer is empty the PDOVAL
signal will stay LOW. The number of valid pulses indicate
the real number of data transmissions. The signal
PDOSYNC in conjunction with PDOVAL indicates the first
byte of a transport stream packet.
handbook, full pagewidth
OUTPUT INTERFACE
SAA6752HS
PDIOCLK
PDOSYNC
PDOAV
PDO[7:0
PDOVAL
PDIDS
]
Fig.7 DIO master mode protocol.
2004 Jan 26 30
DATA RECEIVER
CLOCK
DSYNC
AUDIO/VIDEO QUALIFIER
DATA
VALID
n.c.
MHC134
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
handbook, full pagewidth
PDIOCLK
PDO[7:0
PDOVAL
]
00 01 BA
SAA6752HS
MHC135
handbook, full pagewidth
PDIOCLK
PDOVAL
]
PDO[7:0
PDOSYNC
Fig.8 Data transfer in DIO master mode.
188 bytes
MHC136
Fig.9 DIO master mode, transport stream packet.
2004 Jan 26 31
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.8.4.2 DIO slave mode
The SAA6752HS can be enabled in a DIO slave mode where the data receiver acts as master. PDO, PDOSYNC and
PDOAV are clocked out by the internal clock; earliest two internal clock cycles e.g. 36 to 58 ns after the falling edge of
the external clock. The external clock PDIOCLK should not exceed a maximum of 9 MHz. The PDOVAL signal still
indicates if data is available in the output buffer. To operate in this mode, the PDIDS request input must be set to logic 1.
handbook, full pagewidth
OUTPUT INTERFACE
SAA6752HS
PDIOCLK
PDOSYNC
PDOAV
PDO[7:0
PDOVAL
PDIDS
DATA RECEIVER
CLOCK
DSYNC
]
'1'
AUDIO/VIDEO QUALIFIER
DATA
VALID
handbook, full pagewidth
PDIOCLK
]
PDO[7:0
PDOVAL
MHC137
Fig.10 DIO slave mode protocol.
10 00 01 BA
MHC138
Fig.11 Data transfer in DIO slave mode.
2004 Jan 26 32
Page 33

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.8.4.3 DEBI slave mode
The SAA6752HS supports DEBI slave mode with a block
transfer of 8-bit data. This can be used for interfacing with
a PCI bridge (for example, an SAA7146A chip set). There
isno addressingphase necessary. Thetransfer starts with
recognition of a PDIDS pulse. The requested data,
PDO[7:0], is transferred when the PDOVAL signal goes
active, indicating that datais available in the output buffer.
In the event of interfacing to an SAA7146A chip set, the
PDOVAL pin is connected to the DTACK_RDY pin and
serves as a handshake. The LDS_RDN and UDS_WRN
signals should be used to generate the PDIDS signal.
handbook, full pagewidth
OUTPUT INTERFACE
SAA6752HS
PDIOCLK
PDOSYNC
PDOAV
PDO[7:0
PDOVAL
PDIDS
SAA6752HS
Note that to operate correctlyto theDEBI transferprotocol
the VALID output signal should be programmed negative
by I2C-bus command and a 3.3 kΩ resistor to V
recommended.
DATA RECEIVER
(SAA7146A)
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
]
AD16IN
DTACK_RDY
LDS_RDN
UDS_WRN
DDP
is
handbook, full pagewidth
PDIDS
PDO[7:0
PDOVAL
MHC139
Fig.12 DEBI slave mode protocol.
]
XX 01 XX 02
MHC140
Fig.13 Data transfer in DEBI slave mode.
2004 Jan 26 33
Page 34

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.9 Clock generation
7.9.1 GENERAL
The SAA6752HS is designed to operate with a single
fundamental 27 MHz crystal or an external 27 MHz clock.
From these clock sources an internal PLL produces the
27 MHz, 54 MHz and 108 MHz frequencies needed for
operation.
It is possible to use a third overtone crystal in combination
with a 9 MHzexternal trap. In this eventClock mode 2and
tuning by the I2C-bus commands are not usable.
7.9.2 CLOCK CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
The following configuration options can be selected from
the host:
• CLOCK MODE. Dependent on the type of application
(i.e. video frame locked, reference clock locked etc.),
three different clock modes are available
• CLOCK SOURCE. The clock can be generated from an
internal crystal controlled clock or an external source.
If from a crystal then a fine tune adjustment is available
SAA6752HS
• CLOCKOUTPUT.It is possible toenableasystemclock
output so that the 27 MHz clock can be used elsewhere
by the user.
7.9.3 CLOCK MODES
The SAA6752HS internal PLL can be configured in three
differentclock modes: Clockmodes 1,2 and 3.Adefinition
of the clock modes is shown in Table 9. The clock modes
are intended for different applications:
• Clock mode 1. System clock reference locked to input
video frame frequency. Intended for applications where
the output stream is recorded directly onto a medium
(i.e. DVD video recorder).
• Clock mode 2. Crystal locked to input video frame
frequency. Intended for applications that require both
recording and direct playback. However it is limited by
the required accuracyof the input video framefrequency
• Clock mode 3. Crystal free-running. Intended for
applications where the output stream is played realtime
directly by a decoder.
To meet the requirements for each clock mode the
conditions specified in Table 10 must be met.
Table 9 Clock modes
CLOCK
MODE
1 DVD-compliant
2 DVD and MPEG-compliant 27 MHz ± video frame
3 MPEG-compliant crystal frequency crystal frequency
Note
1. The stream contents are MPEG-compliant but the time stamps are not synchronized with real time (i.e. dependent
on the accuracy of the video input frame frequency). Playback of such a stream is MPEG-compliant due to the
re-generation of time synchronization.
Table 10 Clock modes requirements
CLOCK
MODE
1 27 MHz ±0.1% 27 MHz ±0.1% nominal − 8% to nominal + 2%
227× (1 ±200 × 10−6) MHz
327× (1 ±30 × 10−6) MHz 27 × (1 ±30 × 10−6) MHz not applicable
Note
1. The nominal video frame frequency is dependent on the video mode set: 525 or 625 lines.
OUTPUT STREAM
TIME-STAMP COMPLIANCE
(1)
CRYSTAL FREQUENCY
(to allow fine tuning via PLL)
SYSTEM FREQUENCY SYSTEM CLOCK REFERENCE FREQUENCY
crystal frequency 27 MHz ± video frame frequency accuracy
27 MHz ± video frame frequency accuracy
frequency accuracy
EXTERNAL
CLOCK FREQUENCY
not applicable nominal × (1 ±200 × 10−6)
INPUT VIDEO FRAME FREQUENCY
(1)
2004 Jan 26 34
Page 35

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
7.9.4 CLOCK MODE 2 AUTO-SWITCH
An auto-switch mode is available if Clock mode 2 is
selected. In this event the PLL will switch to Clock mode 1
or 3 if the conditions for Clock mode 2 are no longer met
(i.e. video frame frequency outside the range
1 ±200 × 10−6). The auto-switch preference is set by an
I2C-bus command during the SAA6752HS initialization.
If auto-switch occurs then a host interrupt can be flagged.
7.9.5 CRYSTAL TUNING
It is possible to tune the crystal frequency by up to
1 ±200 × 10−6 via the I2C-bus. If necessary this can be
usedtoachieve the MPEG-2 accuracy of1 ±20 × 10−6with
standard crystals.
7.9.6 EXTERNAL CLOCK SOURCE
It is possible to use an external system clock. For start-up
before switching to the externalclock inputa crystalhas to
be connected or the external frequency has to be applied
to pin XTALI. The input voltage for this pin must be limited
to 2.5 V. An external clock source cannot be used with
Clock mode 2.
7.9.7 AUDIO CLOCK
A switchable sampling frequency for an audio
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) is generated by the
internal PLL. Two sampling frequencies are selectable:
256 × 48 kHz and 384 × 48 kHz. This clock output can be
used as clock signal for an external audio ADC. The
systemclock reference frequencyas described inTable 9,
is used as reference for the internal PLL generating the
audio clock.
7.10 Power control and reset
7.10.1 GENERAL
An external reset pulse at power-up is needed to start-up
the SAA6752HS. This will start the oscillator and initialize
hardware and firmware. The SAA6752HS can be set to a
power saving sleep mode where all internal clocks are
switched off. In this mode restartingcan only be done by a
hard reset pulse.
SAA6752HS
7.11 I
7.11.1 GENERAL
The I2C-bus interface within the SAA6752HS is a slave
transceiver. It is used for all control settings. The read
mode may be used to read back error or status codes.
The I2C-bus interface is compliantto the I2C-bus standard
at 100 kHz and 400 kHz clock frequency and suitable for
bus line voltage levels of 3.3 V. If an I2C-bus with higher
voltage is used by an application, it is possible to add a
small interface between 3.3 V and a higher voltage level.
Only two MOSFET transistors (e.g. BSN10, BSN20 or
BSS83) are needed. A description of this circuit is
available at
http://www.semiconductors.philips.com/i2c/facts/
Information about the I2C-bus can be found in the
brochure
(order number 9398 393 40011).
7.11.2 SLAVE ADDRESSES
Two write I2C-bus slave addresses (SAD) are available,
40H and 42H (8-bit), dependent on the state of address
select pin I2CADDRSEL. This avoids possible address
conflict of addresses with other devices. A HIGH-level at
the address selection pin will set the device write address
to 42H.
Similarly for read operations there are two slave
addresses: 41H and 43H. A HIGH-level at the address
selection pin will set the device read address to 43H.
7.12 Exception handling
7.12.1 GENERAL
The SAA6752HS is capable of flagging certain events to a
host via a hostinterrupt flag pin H_IRF. Thehost is able to
read back a 16-bit status word via the I2C-bus to identify
the specific event and take action accordingly. Detectable
events include copyright violations, loss of input
synchronization, DVD compliance errors etc.
7.12.2 EXCEPTION CONDITIONS
A list of the SAA6752HS exception conditions, as
indicated by the status word, is defined in Table 11. The
I2C-bus subaddress is 12H (see Table 14).
2
C-bus interface
“The I2C-bus and how to use it”
2004 Jan 26 35
Page 36

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
Table 11 Interrupt status definition
STATUS
WORD BIT
0 video copyright violation SAA6752HS continues encoding; note 1.
1 input video signal not detected or lost SAA6752HS continues encoding but outputs audio ES
2 when a difference between the V-sync period
in I2C-bus settings and in the video input signal
is detected
3 Clock mode 2 out of range If enabled, the SAA6752HS PLL will auto-switch to
4 output bufferoverflow (due to loss of data read
command)
5 video and audio frames out of alignment Ratio between number of generated audio frames and
6 input audio not DVD-compliant (toIEC 61937) SAA6752HS continues encoding but will not include
• incorrect Preamble Pc
• sampling frequency out of range
• bit rate out of range
7 audio format change detected in DVD bypass
mode
8 audio pause burst detected SAA6752HS continues operation.
9 SAA6752HS mode transition complete;
desired operation mode has been reached
if external user data insertion in mode ‘only
once’ is active: insertion of user data has
been finished and the host can send new
user data
10 illegal I2C-bus command SAA6752HS ignores the I2C-bus command.
• I2C-bus command not recognized
• command in invalid mode
• command parameter error
11 general error SAA6752HS will go to Idle mode if time-out is enabled
12 input audio word select signal not detected or
audio stream stopped after exception status
bit 4, 6, 7 or 8
EXCEPTION CONDITION RESPONSE IF EXCEPTION IS DETECTED
packets only; SAA6752HS will resynchronize if video
input is recommenced; notes 2 to 4.
SAA6752HS continues but frames may be lost during
the event.
Clock mode 1 or 3 as programmed.
Stream output stops or corrupted data will be
delivered; reset or forced reconfigure needed to
recover.
number of generated video frames is not nominal; time
stamps remain correct; note 5.
audio packets.
SAA6752HS continues encoding but will not include
audio packets.
SAA6752HS continues operation.
or stop operating if time-out is disabled; in case of the
later a forced reconfigure is recommended.
SAA6752HS continues encoding but outputs video ES
packets only; transition to STOP needed to recover.
2004 Jan 26 36
Page 37

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
STATUS
WORD BIT
13 VBI WSS data has been captured SAA6752HS continues operation.
14 VBI CC data has been captured SAA6752HS continues operation.
15 memory manager resynchronization occurred
after discontinuity in the video input signal
Notes
1. ‘No copy’ flag is only detected if the correct WSS VBI mode is enabled.
2. This error flag detects mismatches between the input video format (525 or 625) and SAA6752HS video setting
(525 or 625). Video syncs out of range are also detected.
3. A loss of video sync is flagged if 10 consecutive syncs are not detected.
4. For stream types which include video mode transitions to encode or idle/stop will not be finished, if no video is
present. A pending mode transition can be stopped by forced reconfigure.
5. In clock mode 1 and 3 this can occur due to discontinuity in the video input signal. In applications, which require an
exactratio between thenumberof generated audioframesand the numberofgenerated video frames,thehost might
start a corrective action. In clock mode 3 this exception can be ignored; it will happen after some encoding time,
because the audio processing is locked to the system frequency and video processing depends on the video input
frequency.
EXCEPTION CONDITION RESPONSE IF EXCEPTION IS DETECTED
SAA6752HS continues operation, but a forced
reconfigure is recommended.
7.12.3 HOST INTERRUPT OPERATION
A LOW level as signalled by the host interface pin
indicates that an exception condition has been detected.
The host interrupt flag pin H_IRF is reset to HIGH by
reading the interrupt status word via the I2C-bus.
7.12.4 INTERRUPT MASKING
It is possible to mask any combination of exception
conditions by setting a 16-bit interrupt mask via the
I2C-bus.
8 BOUNDARY SCAN TEST
The SAA6752HS has built-in logic and 5 dedicated pins to
support boundary scan testing, which allows board testing
without special hardware (nails). The SAA6752HS follows
the
“IEEE Std. 1149.1 - Standard Test Access Port and
Boundary Scan Architecture”
Group (JTAG) chaired by Philips.
The 5 special pins are: Test Mode Select (TMS), Test
Clock (TCK), Test Reset (TRST), Test Data Input (TDI)
and Test Data Output (TDO).
The Boundary Scan Test (BST) functions BYPASS,
EXTEST, SAMPLE, CLAMP and IDCODE are all
supported(see Table 12).Detailson the JTAG BST-TEST
can be found in the specification “
set by the Joint Test Action
IEEE Std. 1149.1”
.
A file containing the detailed Boundary Scan Description
Language (BSDL) description of the SAA6752HS is
available on request.
8.1 Initialization of boundary scan circuit
The Test Access Port (TAP) controller of an IC should be
in the reset state (TEST_LOGIC_RESET), when the IC is
in functional mode. This reset state also forces the
instruction register into a functional instruction such as
IDCODE or BYPASS.
To solve the power-up reset, the standard specifies that
the TAP controller will be forced asynchronously to the
TEST_LOGIC_RESETstate bysetting pin TRST to LOW.
8.2 Device identification codes
A device identification register is specified in
1149.1b-1994
for the specification of the IC manufacturer, the IC part
number and the IC version number. Its biggest advantage
is the possibility tocheck for the correct ICs mounted after
productionand determination ofthe version numberof ICs
during field service.
When the IDCODE instruction is loaded into the BST
instruction register, the identification register will be
connected between TDI and TDO of the IC.
”. It is a 32-bit register which contains fields
“IEEE Std.
2004 Jan 26 37
Page 38

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
The identificationregister willload a componentspecific code duringthe CAPTURE_DATA_REGISTER stateof the TAP
controller and this code can subsequently be shifted out. At board level this code can be used to verify component
manufacturer, type and version number. The device identification register contains 32 bits, numbered 31 to 0, where
bit 31 is the most significant bit (nearest to TDI) and bit 0 is the least significant bit (nearest to TDO); see Fig.14.
Table 12 BST instructions supported by the SAA6752HS
INST DESCRIPTION
BYPASS This mandatory instruction provides a minimum length serial path (1-bit) between TDI and TDO,
when no test operation of the component is required.
EXTEST This mandatory instruction allows testing of off-chip circuitry and board level interconnections.
SAMPLE This mandatory instruction can be used to take a sample of the inputs during normal operation of
the component. It can also be used to preload data values into the latched outputs of the boundary
scan register.
CLAMP This optional instruction is useful for testing, when not all ICs have BST. It addresses the bypass
register, while the boundary scan register is in external test mode.
IDCODE This optional instruction will provide information on the components manufacturer, part number and
version number.
handbook, full pagewidth
TDI
MSB LSB
31
28 27 12
XXXX 0010 1011 0110 0110 0000 0010 101
4-bit
version
code
16-bit part number
E M S
11
11-bit manufacturer
identification
10
1
Fig.14 32 bits of identification code.
TDO
MHC141
2004 Jan 26 38
Page 39

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 39
2
C-BUS CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTERS
9I
Tables 13 to 26 list the I2C-bus instructions intended for functional control and status.
Column M identifies the SAA6752HS modes that are valid for each I2C-bus instruction. The key is:
I - write and/or read valid in Idle mode
P- write and/or read valid in Paused mode
S - write and/or read valid in Stop mode
E - write and/or read valid in Encode mode
All - write and/or read valid in Idle, Encode, Paused and Stop mode.
2
Table 13 I
C-bus control
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
ADR
HEX
00 all soft reset W none none − This command resets the SAA6752HS to its
01 I enable W none none − go to Stop mode from Idle mode
02 I, P, S start W none none − go to Encode mode
03 E stop W none none − go to Stop mode from Encode mode
04 E pause
05 E, P, S reconfigure W none none − go to Idle mode
06 I sleep W none none − go to Power-down mode
07 E, P, S forced
08 I enable system
Note
1. Paused mode transitions are not applicable to transport stream and DIO output mode combination, only transport stream and DEBI output mode
M
combination.
COMMAND
NAME
(1)
reconfigure
time-out
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
default settings.
W none none − go to Paused mode from Encode mode
W none none − Go to Idle mode without completing the
current GOP/audio frame. This is intended for
use in cases similar to no video/audio input
present.
R/W 1 byte disabled Enables SAA6752HS to time-out to Idle mode
bit 0 = 1 enabled
bit 0 = 0 disabled
if STOP to IDLE transition cannot be
completed (i.e. due to no video signal being
present). If a general error event is detected,
the SAA6752HS will automatically switch to
Idle mode via forced reconfigure.
SAA6752HS
Page 40

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 40
Table 14 I
ADR
HEX
10 all get running mode R 1 byte − This command gets the actual running mode
11 all status mask W 2 bytes (16 bits) all 0’s masking of events; see Table 11
12 all interrupt status R 2 bytes (16 bits) − This command allows reading a status
13 all get version
2
C-bus status
M
COMMAND
number
NAME
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
bit 0 = 1 idle
bit 1 = 1 encoding
bit 2 = 1 stopped
bit 3 = 1 paused
bit 4 = 1 reserved
bit 5 = 1 busy flag
bit = 0 event disabled
bit = 1 event enabled
bit = 0 no event detected
bit = 1 event detected
R 12 bytes −−This command allows reading of the current
from the SAA6752HS and is read-only. The
busy flag indicates that the SAA6752HS is
working at a control command. If the busy flag
is set, the SAA6752HS skips all received
2
I
C-bus commands.
register. Reading the status will clear the
status and reset the interrupt assertion pin.
MIPS firmware version number, hardware
number and the audio DSP firmware number.
Each number contains 4 bytes.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
2
Table 15 I
ADR
HEX
20 I bus width and
C-bus SDRAM size
M
COMMAND
NAME
memory size
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
R/W 1 byte 16 bit
bit[1:0] = 00 16 Mbit 16-bit wide
bit[1:0] = 10 64 Mbit 16-bit wide
bit[1:0] = 11 reserved
64 Mbit
bus width of the SDRAM interface and size of
connected SDRAM
SAA6752HS
Page 41

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 41
Table 16 I
ADR
HEX
30 I clock mode R/W 1 byte mode 1
31 I clock source R/W 1 byte crystal
32 I clock auto mode R/W 1 byte mode
33 I enable system
34 all adjust crystal
2
C-bus clock static/dynamic settings
M
COMMAND
NAME
clock output
oscillator
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
R/W 1 byte disable This command outputs the internal crystal
R/W 1 byte −128 to +127 0 adjust the frequency of the oscillator
bit[1:0] = 01 mode 1 mode 1: crystal frequency fixed; SCR
frequency frame locked to V-sync
bit[1:0] = 10 mode 2 mode 2: crystal frequency frame locked to
V-sync
bit[1:0] = 11 mode 3 mode 3: crystal frequency fixed
This command is used to switch from an
bit0=0 crystal clock
bit1=1 external clock
bit[1:0] = 00 mode fixed
bit[1:0] = 01 enable mode 2 and 1
auto-switch
bit[1:0] = 10 enable mode 2 and 3
auto-switch
bit0=0 disabled
bit0=1 enabled
clock
fixed
internal crystal controlled clock source to an
external clock source and vice versa.
This command sets the behaviour of the
SAA6752HS in Clock mode 2 if video sync
cannot be achieved. Either mode 2 is
continued or the SAA6752HS will
automatically switch to mode 1 or mode 3, as
selected.
generated clock (27 MHz) to an output
pin CLKOUT for use in other parts of an
application.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 42

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 42
Table 17 I
ADR
HEX
40 I 625/525 R/W 1 byte 625 defines the input signal either as 625 lines
41 I subsampling type R/W 1 byte D1 specifies the subsampling type; remark: if
42 I video sync format R/W 1 byte 0 defines the incoming video sync sources
43 I video clock select R/W 1 byte video clock 1 defines which external video input clock is
44 I vertical sync
2
C-bus video front-end input interface static settings
M
COMMAND
NAME
timing adjustment
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
bit[1:0] = 00 625
bit[1:0] = 01 525
bit[1:0] = 00 D1
bit[1:0] = 01
bit[1:0] = 10
bit[1:0] = 11 SIF
bit[1:0] = 00 H-sync, V-sync and Field
bit[1:0] = 01 separate H-sync, V-sync
bit[1:0] = 10 separate H-sync and
bit 0 = 0 video clock 1
bit 0 = 1 video clock 2
R/W 2 bytes 0, 0 Remark: If a vertical sync timing
byte 0 0 to 225 defines the number of shifted lines in the
byte 1 0 to 225 defines the number of shifted lines in the
2
/3D1
1
/2D1
Identification (FID)
information coded in the
EAV/SAV bytes complying
to ITU-R BT.656
and FID signals input to
from external source(s)
V-sync signals input to
from external source(s)
or 525 lines
the subsampling type is changed, then the
horizontal shift (address 45H) will be
overwritten with the defaultvalues and the
horizontal filter (addresses 53H, 54H and
55H) will be initialized with appropriate
parameter
used
adjustment different from ‘0’ is used, then
a horizontal shiftof minimum2 pixelsmust
be programmed in subaddress 45H.
top field
bottom field
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 43

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 43
ADR
HEX
45 I horizontal shift R/W 2 bytes 0 to 511 (bits 0 to 8) 0 (D1,2/3D1)
46 I sync polarity R/W byte 000 defines the polarity of the sync signals
47 I disable forced
M
COMMAND
NAME
field toggle
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
defines the number of shifted cycles for
or
8(1/2D1, SIF)
bit 0 = 0 H-sync signal HIGH for
horizontal blanking
bit 0 = 1 H-sync signal LOW for
horizontal blanking
bit 1 = 0 V-sync signal HIGH for
vertical sync
bit 1 = 1 V-sync signal LOW for
vertical sync
bit 2 = 0 FID signal LOW for first
field
bit 2 = 1 FID signal HIGH for first
field
R/W bit 0 = 0 enable forced field toggle 0 If no FID polarity transitions are detected
bit 0 = 1 disable forced field toggle If no FID polarity transitions are detected
everyline; remark: 4 cyclescorrespond to
2 pixels; only multiple of 4 should be
programmed
in the input signal, then an internal toggle
of FID polarity ensures the encoding of
some frames.
in the input signal, then no frames are
encoded.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 44

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 44
Table 18 I
ADR
HEX
50 I, E, P,Snoise pre-filter
51 I, E, P,Snoise pre-filter
52 I, E, P,Snoise pre-filter
53 I, E, P,Shorizontal filter
54 I, E, P,Shorizontal filter
55 I, E, P,Shorizontal filter
2
C-bus video front-end filters static/dynamic settings
M
COMMAND
NAME
off/on
coefficients
thresholds
off/on
coefficients
scaling factor
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
R/W 1 byte off enables ordisablesnoise pre-filterand selects
bit[1:0] = 00 off
bit[1:0] = 01 median filter
bit[1:0] = 10 average filter
R/W 4 bytes 4 × 6 bits; bits 0 to 5 valid 33H,20H,
R/W 3 bytes 3 × 6 bits; bits 0 to 5 valid 10, 15, 20 defines the threshold coefficients for the
R/W 1 byte off enables or disables the horizontal filter by
bit 0 = 0 off
bit0=1 on
R/W 16 bytes array of word (8× 10 bits) first word
R/W 1 byte (4 bits) 0 to 15 8 Defines the scaling factor for the horizontal
16H, 0DH
=256, the
others = 0
the mode for this filter
defines the filter coefficients for the noise
pre-filter
median filter
bypassing
Defines the coefficientsfor the horizontal filter;
the default applies to D1 mode only. When
other subsampling modes are selected the
SAA6752HS automatically overwrites the
horizontal filter coefficients with the
appropriate parameters.
filter; the default applies to D1 mode only.
When other subsampling modes are selected
the SAA6752HS automatically overwrites the
horizontal filter scaling parameter with the
appropriate parameter.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 45

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 45
Table 19 I
ADR
HEX
60 I VBI mode select W 5 bytes −
2
C-bus video front-end VBI data extraction
M COMMAND NAME R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
bit 0 = 0 WSS mode selects between WSS and CC modes
bit 0 = 1 CC mode
bit 8 = 0 data input sliced Selects if the input data is sliced by the
bit 8 = 1 data input unsliced
sliced data sent in case of sliced input data
bit[17:16] data type[3:2] The data type compared with the data type
bit[23:18] SDID, 0 to 63 The SDID compared with the SDID field in
bit[28:24] line number, 0 to 31 line number of data as set bythe video input
bit 29 = 0 top field field dependent on video input processor
bit 29 = 1 bottom field
bit[31:30] data type[1:0] The data type compared with the data type
bit 32 = 1 field qualifiermask SDID match the SDID
bit 33 = 1 field qualifier mask
data type
bit 34 = 1 field qualifier mask field match field
bit 35 = 1 field qualifier mask
line number
bit[39:36] reserved must be set to zero
video input processor (sliced) or by the
SAA6752HS (unsliced).
field in the VBI data header for extraction
decision; bits 3 and 2.
the VBI data header for extraction decision.
processor
setting
field in the VBI data header for extraction
decision; bits 1 and 0.
match data type
match line number
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 46

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 46
ADR
HEX
60 I VBI mode select
61 I WSS data enable R/W 1 byte disabled enables or disables WSS data extraction
62 all WSS read data R 2 bytes −−WSS data and flag indicating valid data
63 I CC data enable R/W 1 byte disabled enables the closed caption data extraction
64 all CC read data R 3 bytes − CC data and flags indicating valid data and
M COMMAND NAME R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
W continued unsliced data − sent in case of unsliced input data
(continued)
bit[20:16] line number for bottom,
0to31
bit[28:24] line number for top,
0to31
bit[37:32] reserved must be set to zero
bit 38 = 1 field qualifier mask
line field 1
bit 39 = 1 field qualifier mask
line field 2
bit[1:0] = 00 disabled
bit[1:0] = 01 enabled
bit[1:0] = 10 enabled without checksum
bit[13:0] WSS data
bit 15 = 0 valid data
bit 15 = 1 invalid or previous data
bit 0 = 0 disabled
bit 0 = 1 enabled
bit[15:0] CC data
bit 16 = 0 top field
bit 16 = 1 bottom field
bit 23 = 0 valid data
bit 23 = 1 invalid data
line number for bottom field as set by the
video input
line number for top field as set by the video
input
match if field = ‘top’ and line = ‘line number’
match if field = ‘bottom’ and
line = ‘line number’
current field
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 47

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 47
ADR
HEX
65 I user data insertion
M COMMAND NAME R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
R/W 1 byte 00H selects the user data insertion mode
mode
bit 0 = 0 always repeated external user data insertion into GOP
bit 0 = 1 only once
bit 1 = 0 always repeated external user data insertion into picture
bit 1 = 1 only once
bit 2 = 0 disabled Internal user data insertion of Closed
bit 2 = 1 enabled
bit 3 = 0 disabled Internal user data insertion of Closed
bit 3 = 1 enabled
bit4=0 − Stop user data insertion into GOP header
bit 4 = 1 stop
bit5=0 − Stop user data insertion into picture header
bit 5 = 1 stop
bit 6 reserved must be set to zero
bit 7 reserved must be set to zero
header (user data 1)
header (user data 2)
Caption data into GOP header user data
area according to DVD standard.
Remark: Only one internal user data
insertion mode can be active at the same
time, either bit2=1 or bit3=1.
Caption data into picture header user data
area according to ATSC/NTSC standard.
Remark: Only one internal user data
insertion mode can be active at the same
time, either bit2=1 or bit3=1.
user data area. This bit can be used in all
operation modes. Setting this bit to logic 1
(= stop) deletes the downloaded GOP user
data and resets bit 2 to ‘disabled’.
user data area. This bit can be used in all
operation modes. Setting this bit to logic 1
(= stop) deletes the downloaded picture
user data and resets bit 3 to ‘disabled’.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 48

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 48
Table 20 I
ADR
HEX
70 I disable video
71 I bit rate mode R/W 1 byte VBR defines the encoding bit rate control mode
72 I GOP definition R/W 2 bytes 0001H:
73 I, E, P,Suser data GOP
74 I, E, P,Snumberofuser data
75 I, E, P,Snumberofuser data
76 I, E, P,Suser data picture
77 I, E, P,Snoise filter
78 I adaptive
2
C-bus video encoder: general
M COMMAND NAME R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
R/W 1 byte enabled Specifies if the video encoder is enabled.
encoder
header
GOP
picture header
header
coefficients
quantization depth
bit 0 = 0 enabled
bit 0 = 1 disabled
bit 0 = 0 VBR
bit 0 = 1 CBR
byte 0 distance (M) (0 to 3)
byte 1 length (N) (0 to 19)
R/W 64 bytes all 0 Specifies the data to be inserted into the
R/W 1 byte 0 Specifies the amount of user data to be
R/W 1 byte 0 Specifies the amount of user data to be
R/W 64 bytes all 0 Specifies the data to be inserted into the
R/W 2 bytes off Defines the noise filter coefficients gain and
byte 0 gain
byte 1 criterion
R/W 1 byte 0 to 128 32 Selects the depth of quantization
M=0;
N=1
If the video encoder is disabled, no video
data will be inserted in the output stream.
(variable or constant bit rate)
Defines the used GOP structure as (N.M),
where ‘N’ is the number of frames per GOP
and ‘M’ is the distance of 2 sequential I- or
P-frames (reference frame distance);
distance = 0 is I-frame coding; see Table 3
for meaningful combinations.
GOP header.
inserted into the GOP header.
inserted into the picture header.
picture header. If internal user data insertion
of Closed Caption data into the GOP header
is active and the GOP size is larger than 9,
then the insertion of user data to the picture
header is not available.
criterion scale.
adaptation; 0 for no adaptation, 128 for
maximum adaptation.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 49

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 49
ADR
HEX
79 I quantizer matrix R/W 2 × 64 bytes array of integers
7A I reserved −− − − −
7B I disable forced
7C I scan select R/W 1 byte 0
7D I quantizer scale
M COMMAND NAME R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
− Specifies the quantizer matrix as 2 tables,
backward prediction
table
(8 × 8 bytes)
R/W 1 byte 0 Applies only for GOP structures starting with
bit 0 = 0 enabled
bit 0 = 1 disabled
bit 0 = 0 alternate scan
bit 0 = 1 zigzag scan
R/W 1 byte 0
bit 0 = 0 logarithmic
bit 0 = 1 linear
each an 8 × 8 array. Data must be
transferred column by column, not row by
row. Theinter Q matrix must be downloaded
first, the intra Q matrix downloaded second;
note 1.
a B-frame: Disabled forced backward
prediction results in non-editable (open)
GOPs with prediction from a former GOP.
Enabled forced backward prediction results
in backward predicted closed GOPs without
prediction from a former GOP.
In all cases the leading B-frames of the very
first GOP structure after start of encoding
are forced to backward prediction.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
Note
1. If no Q matrix is downloaded then the default is the MPEG standard and no Q matrix is inserted into the stream.
SAA6752HS
Page 50

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 50
Table 21 I
ADR
HEX
80 I, E, P,SRvbr R/W 2 bytes − 6000 VBR target bit rate (kbit/s); this applies to
81 I, E, P,SRmax R/W 2 bytes − 9800 CBR mode: Target bit rate (kbit/s);
82 I, E, P,SQmin_VBR R/W 1 byte 1 to 112 4 Minimum Q-scale for external constraints of
83 I, E, P,SQmax_VBR R/W 1 byte 1 to 112 12 Maximum Q-scalefor external constraints of
84 I, E, P,SB-frame weighting R/W 1 byte 32 to 128 128, no
85 I, E, P,Sread bytes per GOP R 4 bytes −−This command reads the number of bytes
Note
1. If the video bit rate Rmax is intended to be changed during the encoding state, the maximum applied value for Rmax has to be set before start of
2
C-bus video encoder: bit rate control (dynamic settings)
M COMMAND NAME R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
VBR mode only; Rvbr must be set to less
than Rmax.
VBR mode: Maximum bit rate (kbit/s);
note 1.
VBR
VBR.
B-frame weighting factor (internally divided
weighting
encoding. I.e. the Rmax value that was valid at start of encoding (coming from stop) is the maximum allowed value for this encoding process.
by 128; i.e. 128 = no effect)
per GOP.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 51

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 51
Table 22 I
ADR
HEX
90 I disable audio
91 I audio input format R/W 1 byte I2S defines the audio input format
92 I audio input mode
93 I audio processing
2
C-bus audio encoder: bit rate control (static settings)
M
COMMAND
NAME
encoder
and port select
mode
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
R/W 1 byte 0 Specifies if the audio encoder is enabled.
bit 0 = 0 enabled
bit 0 = 1 disabled
bit[2:0] = 000 I2S
bit[2:0] = 001 reserved
bit[2:0] = 010 EIAJ 16 bits
bit[2:0] = 011 EIAJ 18 bits
bit[2:0] = 100 EIAJ 20 bits
bit[2:0] = 101 EIAJ alternative format
bit[2:0] = 110 EIAJ alternative format
bit[2:0] = 111 EIAJ alternative format
R/W 1 byte slave,
bit 0 = 0 master mode
bit 0 = 1 slave mode
bit 1 = 0 port 1
bit 1 = 1 port 2
R/W 1 byte MPEG-1L2defines the audio processing mode (see
bit[1:0] = 00 MPEG-1 L2 encode
bit[1:0] = 01 DDC encode (only for
bit[1:0] = 10 LPCM bypass
bit[1:0] = 11 DVD bypass
16 bits
18 bits
20 bits
SAA6752HS/V103)
port 1
If the audio encoder is disabled, no audio data
will be inserted in the output stream.
In master mode, SAA6752HS delivers the bit
clock and word select signal. In slave mode,
SAA6752HS receives the bit clock and word
select signal. Remark: If I2S port 2 is switched
to output mode (VES + AES output stream
mode) then SAA6752HS is fixed to master
mode.
Section 7.5); note 1
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 52

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 52
ADR
HEX
94 I audio encoding
95 I audioclockoutput
96 I audio
Notes
1. In systems that use 16 Mbit SDRAM, due to system architecture constraints, LPCM bypass must be restricted to be used with I and IP video
2. All compressed audio data is 16-bit. In the event of LPCM bypass 20-bit data will be truncated to 16 bits.
M
encoding only. There is no constraint if 64 Mbit SDRAM is used.
COMMAND
NAME
bitrateand output
resolution
frequency
pre-emphasis
mode
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
R/W 1 byte 256 kbit/s
bit 0 = 0 256 kbit/s
bit 0 = 1 384 kbit/s
bit 1 = 0 16-bit
bit 1 = 1 reserved
R/W 1 byte 256 ×
bit 0 = 0 256 × 48 kHz
bit 0 = 1 384 × 48 kHz
R/W 1 byte off selects audio pre-emphasis mode of input
bit[1:0] = 00 off
bit[1:0] = 01 50/15 ms
bit[1:0] = 10 CCITT J17
16-bit
48 kHz
defines the audio encoding bit rate (see
Section 7.5); note 2
selects the output frequency atthe audioclock
mode
signal (valid for MPEG encoding only)
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 53

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 53
Table 23 I
ADR
HEX
A0 E, P, S Preamble Pc R 1 byte I2S Preamble Pc in case of IEC 61937 input (data
A1 E, P, S Preamble Pd R 2 bytes Preamble Pd (16 bits) − Preamble Pd in case of IEC 61937 input
A2 E, P, S audio bit stream
A3 − reserved −− − − −
A4 all audio mute on/off R/W 1 byte 0
2
C-bus audio encoder: bit rate control (dynamic settings)
M
COMMAND
NAME
information
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
bit[4:0] data type
bit[6:5] reserved
bit 7 error flag indicatingvalidity
of burst load
R 8 bytes bit stream information
(4 × 16 bits)
bit 0 = 0 off
bit0=1 on
type), applies to DVD bypass mode only
(payload length); this applies to DVD bypass
mode only
− Part of audio frame header in case of
IEC 61937 input; this applies to DVD bypass
mode only.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 54

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 54
Table 24 I
ADR
HEX
B0 I output stream
B1 I maximum
B2 I number of
2
C-bus multiplexer: general (static settings)
M
COMMAND
NAME
format
system bit rate
flushing bytes
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
R/W 1 byte PS (DVD) Selects the MPEG-2 output format (see
bit[2:0] = 000 ES video (VES) Elementary Stream (ES):
bit[2:0] = 001 ES audio (AES)
bit[2:0] = 010 PES (DVD) Packetized Elementary Stream (PES):
bit[2:0] = 011 PES (TS)
bit[2:0] = 100 PS (DVD) Program Stream (PS):
bit[2:0] = 101 TS Transport Stream (TS):
bit[2:0] = 110 pack stream Pack stream is a special not MPEG-compliant
bit[2:0] = 111 VES + AES VES + AES mode allows VES output from the
R/W 2 bytes <27000; note 1 10080 Maximum target bit rate of the system stream
R/W 2 bytes − 0 Number of flushing bytes appended to the
SAA6752HS output stream formats for details):
Elementary stream output is possible for audio
or video only encoding.
DVD-compliant: PES packets have a limited
size and can be easily multiplexed into a DVD
program stream.
TS-compliant: PES packets have an unlimited
size and can be easily multiplexed into a
transport stream.
PES packets containing audio and video
information are flagged with an audio/video
signal pin. The audio/video polarity of the
signal pin is programmable.
A DVD-compliantprogram stream isgenerated,
but no navigation packs are inserted.
A transport stream is generated.
mode. The MPEG buffer model is not used.
output port at the same time as an SPDIF
formatted AES is output from the 2nd I2S audio
port. For this mode subaddress 92H must be
set to zero.
in kbit/s (= 1000 bit/s) and must be set if TS or
PS or pack stream modes are selected. It is
ignored if ES or PES streams are selected.
stream after a stop.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 55

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 55
ADR
HEX
B3 I video PES ID R/W 8 bits E0H to EFH E0H Stream ID for video PES header; must be set
B4 I audio PES ID R/W 8 bits C0H to DFH C0H Stream ID for audio PES header; must be set
B5 I PES original
B6 I multiplexer
B7 I audio substreamIDR/W 1 byte − 00 audio substream ID; for PS (DVD) or PES
B8 E current system
B9 I enable MPEG
M
COMMAND
NAME
copy and
copyright
special DVD PS
settings
bit rate
end code
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
for TS, PS and PES output.
for TS, PS and PES output.
R/W 1 byte copy, no
bit0=1 original
bit0=0 copy
bit1=1 copyright
bit1=0 no copyright
R/W 1 byte 2 GOPs,
bit[3:0] 1 to 15, number of
GOP/VOBU
bit4=0 metabyte output off Enables/disables the output of metabytes for
bit4=1 metabyte output on
bit[6:5] 0 to 3, time slot
reservation for NAV
packets
bit7=0 inserted Determines if the PES header extension is
bit7=1 not inserted
R 2 bytes −−Current system bit rate of the system stream in
R/W 1 byte disable Enables the MPEG end code (for program
bit0=1 enable
bit0=0 disable
copyright
off,
metabyte,
0 (NAV
packet),
inserted
(PES
header)
Copy and copyright setting in audio and video
PES header.
The number of GOPs per VOBU for PS output.
PS (DVD) and pack stream modes.
Specifies the number of reserved time slots for
navigation packets and DVD recorder data.
inserted into the stream; this applies to
program stream and pack stream modes.
Remark: For DVD-compliance, the PES
header extension must be inserted.
(DVD) only
kbit/s (= 1000 bit/s); applies for PS and TS
modes. The parameter includes the number of
stuffing bytes. During pause mode, this
address will read back the value of the last
GOP before the pause command.
stream only).
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 56

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 56
Note
1. The limit for I-frame only is 27 Mbit/s. For IP or IPB formats the limit is 16 Mbit/s.
2
Table 25 I
C-bus multiplexer: transport stream (static settings)
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
ADR
HEX
C0 I video TS packetIDR/W 2 bytes 0020H to 1FFEH 0100H Packet ID for transport stream packets
C1 I audio TS packetIDR/W 2 bytes 0020H to 1FFEH 0102H Packet ID for transport stream packets
C2 I system
C3 I TS
C4 I clock TS packetIDR/W 2 bytes 0020H to 1FFEH 0104H Packet ID for transport stream packets
M
COMMAND
NAME
information
tables
miscellaneous
R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
containing video data; for TS only.
containing audio data; for TS only.
W 189 bytes
(maximum
value); up to
5 separate tables
R/W 1 byte 00H A discontinuity information table is inserted at
bit0=0 DIT insertion disabled
bit0=1 DIT insertion enabled
bit1=0 constant TS bit rate At constant TS bit rate mode null packets are
bit1=1 variable TS bit rate At variable TS bit rate mode no nullpackets are
first byte is table number
range (0 to 4) + array of
maximum 188 bytes
values
− There are5 different tables followed by anarray
of up to 188 bytes.The tables must be sent one
by one; the size of the tables is not defined but
limited to 188 bytes.
Table 0: Program Association Table (PAT)
Table 1: Program Map Table (PMT)
Table 2: free programmable [e.g. Conditional
Access Table (CAT)]
Table 3: free programmable [e.g. Network
Information Table (NIT)]
Table 4: free programmable [e.g. Selection
Information Table (SIT)]
the beginning of the stream (after a stop of
recording).
delivered at the multiplexer output to achieve
the constant TS bit rate.
inserted at the multiplexer output. This mode
can be used in combination with variable video
bit rate.
containing PCR values; for TS only.
SAA6752HS
Page 57

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2004 Jan 26 57
Table 26 I
ADR
HEX
D0 I R/W 1 byte Defines the output interface in one byte
F6 I insert leading null
2
C-bus output interface
M COMMAND NAME R/W SIZE/POSITION PARAMETER/RANGE DEFAULT DESCRIPTION
(collects all sub parameter bits in one byte).
All states defined are the active states
output protocol bit[1:0] = 00 DIO slave mode DIO slave
bit[1:0] = 01 DIO master mode
bit[1:0] = 10 not applicable
bit[1:0] = 11 DEBI slave mode
data valid pin
polarity
high-impedance
on/off
audio/video pin
polarity
sync pin polarity bit 5 = 0 positive positive
data request pin
polarity
PDO clock
frequency
W 2 bytes number of bytes 00H Defines the number of leading null bytes
bytes
bit 2 = 0 positive positive for the DEBI output protocol negative
bit 2 = 1 negative
bit 3 = 0 off on Selection of high-impedance for output pin.
bit3=1 on
bit 4 = 0 audio HIGH, video LOW audio
bit 4 = 1 audio LOW, video HIGH
bit 5 = 1 negative
bit 6 = 0 negative negative
bit 6 = 1 positive
bit 7 = 0 9 MHz 9 MHz selection of clock frequency for DIO master
bit 7 = 1 6.75 MHz
mode
HIGH,
video
LOW
DIO master mode: SAA6752HS deliversthe
clock signal.
DIO slave mode: SAA6752HS receives the
clock signal.
polarity has to be selected
mode
(00H), which are delivered to the output
before the start of the stream.
Remark: After forced reconfigure command
the default value of 00H will be set.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
SAA6752HS
Page 58

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
10 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DDP
V
DDCO
V
DDA
V
I
V
i
V
O
I
sc
I
lu(prot)
P
tot
T
stg
T
amb
V
es
digital supply voltage for pads −0.5 +4.0 V
digital supply voltage for core −0.5 +2.8 V
analog supply voltage −0.5 +2.8 V
digital input voltage note 1 −0.5 +4.0 V
analog input voltage note 2 −0.5 +2.8 V
digital output voltage note 3 −0.5 V
DDP
+ 0.5 V
short-circuit current of output pads note 4 − 125 mA
latch-up protection current − 100 mA
total power dissipation − 2W
storage temperature −25 +125 °C
ambient temperature 0 70 °C
electrostatic handling voltage note 5 −2000 +2000 V
note 6 −150 +150 V
Notes
1. All pads are not 5 V tolerant.
2. Pins XTALI and XTALO.
3. At V
> 3.7 V only maximum 4.2 V at digital outputs is allowed.
DDP
4. Short-circuit current is only allowed for a short time (<1 s).
5. Human body model: C = 100 pF; R = 1.5 kΩ.
6. Machine model: C = 200 pF; L = 0.75 µH; R = 0 Ω.
11 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air; soldered to a PCB with
28 K/W
supply and ground plane
2004 Jan 26 58
Page 59

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
12 CHARACTERISTICS
V
externally together; grounds V
specified.
DDCO
= 2.5 V, V
= 2.5 V and V
DDA
SSCO
= 3.3 V for the I/O pads; supply voltages V
DDP
, V
SSA
and V
are connected externally together; T
SSP
DDCO
and V
amb
are connected
DDA
=25°C; unless otherwise
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies: pins V
V
DDP
, V
DDP
digital supply voltage
DDCO
and V
DDA
3.0 3.3 3.6 V
(pad cells)
V
DDCO
digital supply voltage
2.3 2.5 2.7 V
(core)
V
DDA
analog supply voltage
2.3 2.5 2.7 V
(oscillator and PLL)
I
DDP
digital supply current
17 25 37 mA
(pad cells)
I
DDCO
digital supply current
390 430 500 mA
(core)
I
DDA
P
tot
analog supply current − 3 − mA
total power dissipation 0.95 1.16 1.48 W
Input: pins YUV0 to YUV7
V
IL
V
IH
V
hys
I
IL
I
IH
C
I
LOW-level input voltage −0.5 − +0.7 V
HIGH-level input voltage 1.7 − V
DDP
V
hysteresis voltage 0.4 −− V
LOW-level input current VIL=V
HIGH-level input current VIH=V
SSP
DDP
−5 −− µA
−−5 µA
input capacitance −−10 pF
Input with pull-up resistor: pins CTS, EXTCLK, I2CADDRSEL, PDIDS, RESET, RXD, TCK, TDI, TMS and TRST
V
IL
V
IH
V
hys
I
pu(L)
LOW-level input voltage −0.5 − +0.7 V
HIGH-level input voltage 1.7 − V
DDP
hysteresis voltage 0.4 −− V
LOW-level pull-up input
VIL=V
SSP
−20 −50 −70 µA
V
current
I
pu(H)
HIGH-level pull-up input
V
DDCO<VIH<VDDP
− 010 µA
current
C
I
input capacitance −−10 pF
Input with pull-down resistor: pins FID, IDQ, HSYNC, SDATA1, VCLK1, VCLK2 and VSYNC
V
IL
V
IH
V
hys
I
pd
C
I
LOW-level input voltage −0.5 − +0.7 V
HIGH-level input voltage 1.7 − V
DDP
V
hysteresis voltage 0.4 −− V
pull-down input current V
DDCO<VIL<VDDP
−20 −50 −70 µA
input capacitance −−10 pF
2004 Jan 26 59
Page 60

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Inputs/outputs with I
V
IL
V
IH
V
hys
V
OL
V
OH
LOW-level input voltage −0.5 − +0.7 V
HIGH-level input voltage 1.7 − V
hysteresis voltage 0.4 −− V
LOW-level output voltage IOL=4mA −−0.4 V
HIGH-level output
voltage
I
sc
I
TL
C
I
C
L
short-circuit current note 1 −55 − +55 mA
3-state leakage current VIH=V
input capacitance −−10 pF
load capacitance −−30 pF
Inputs/outputs with I
SWS1 and SWS2; note 2
V
IL
V
IH
V
hys
V
OL
V
OH
LOW-level input voltage −0.5 − +0.7 V
HIGH-level input voltage 1.7 − V
hysteresis voltage 0.4 −− V
LOW-level output voltage IOL=4mA −−0.4 V
HIGH-level output
voltage
I
sc
I
pd
C
I
C
L
short-circuit current note 1 −55 − +55 mA
pull-down input current V
input capacitance −−10 pF
load capacitance −−30 pF
Inputs/outputs with I
V
IL
V
IH
V
hys
V
OL
V
OH
LOW-level input voltage −0.5 − +0.7 V
HIGH-level input voltage 1.7 − V
hysteresis voltage 0.4 −− V
LOW-level output voltage IOL=8mA −−0.4 V
HIGH-level output
voltage
I
sc
I
TL
C
I
C
L
short-circuit current note 1 −55 − +55 mA
3-state leakage current VIH=V
input capacitance −−10 pF
load capacitance −−30 pF
= 4 mA: pins PDIOCLK, SM_CS0, SM_LB, SM_UB, TEST0, TEST1 and TEST2
max
DDP
IOH= −4mA V
;
DDP
VIL=V
SSP
= 4 mA and pull-down resistor: pins SCLK1, SCLK2, SDATA2, SM_D0 to SM_D15,
max
IOH= −4mA V
DDCO<VIL<VDDP
= 8 mA: pins SD_DQ0 to SD_DQ31; note 2
max
IOH= −8mA V
;
DDP
VIL=V
SSP
− 0.4 − V
DDP
DDP
−5 − +5 µA
DDP
− 0.4 − V
DDP
DDP
−20 −50 −70 µA
DDP
− 0.4 − V
DDP
DDP
−5 − +5 µA
V
V
V
V
V
V
2004 Jan 26 60
Page 61

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
3-state output with I
V
OL
V
OH
I
sc
I
TL
C
L
3-state output with I
V
OL
V
OH
I
sc
I
pu(L)
I
pu(H)
C
L
Output with I
= 4 mA: pins ACLK, CLKOUT, RTS, SM_A0 to SM_A17, SM_CS3, SM_OE, SM_WE, TDO and
max
TXD
V
OL
V
OH
I
sc
I
TL
C
L
Output with I
= 8 mA: pins SD_A0 to SD_A13, SD_CAS, SD_CKE, SD_CLK, SD_CS,
max
SD_DQM0 to SD_DQM3,
V
OL
V
OH
I
sc
C
L
2
I
C-bus interface: pins SCL and SDA; notes 3 and 4
f
SCL
V
IL
V
IH
V
hys
I
I
= 4 mA: pins PDO0 to PDO7, PDOAV and PDOSYNC; note 2
max
LOW-level output voltage IOL=4mA −−0.4 V
HIGH-level output
IOH= −4mA V
− 0.4 − V
DDP
DDP
voltage
short-circuit current note 1 −55 − +55 mA
3-state leakage current VIH=V
VIL=V
DDP
SSP
;
−1 − +1 µA
load capacitance −−30 pF
= 4 mA and pull-up resistor: pin PDOVAL; note 2
max
LOW-level output voltage IOL=4mA −−0.4 V
HIGH-level output
IOH= −4mA V
− 0.4 − V
DDP
DDP
voltage
short-circuit current note 1 −55 − +55 V
LOW-level pull-up input
VIL=V
SSP
−20 −50 −70 µA
current
HIGH-level pull-up input
V
DDCO<VIH<VDDP
− 010 µA
current
load capacitance −−30 pF
LOW-level output voltage IOL=4mA −−0.4 V
HIGH-level output
IOH= −4mA V
− 0.4 − V
DDP
DDP
voltage
short-circuit current note 1 −55 − +55 mA
3-state leakage current VIH=V
VIL=V
DDP
SSP
;
−1 − +1 µA
load capacitance −−30 pF
SD_RAS and SD_WE
LOW-level output voltage IOL=8mA −−0.4 V
HIGH-level output
IOH= −8mA V
− 0.4 − V
DDP
DDP
voltage
short-circuit current note 1 −125 − +125 mA
load capacitance −−30 pF
SCL clock frequency 100 − 400 kHz
LOW-level input voltage −−0.3V
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7V
DDP
hysteresis voltage − 0.05V
− 3.6 V
DDP
DDP
− V
input current −10 − +10 µA
V
V
V
V
V
2004 Jan 26 61
Page 62

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
OL
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
r(I2C)
t
f(I2C)
t
SU;DAT
t
HD;STA
t
SU;STO
Video clock input timing: pins VCLK1 and VCLK2; see Fig.15
T
cy
δ duty factor t
t
r(VCLK)
t
f(VCLK)
Video input data and control timing: pins YUV7 to YUV0, FID, HSYNC and VSYNC; see Fig.15
t
SU;DAT
t
HD;DAT
Video input parameter range
f
i(D)
f
H
f
V
N
al/f
Crystal oscillator: pins XTALI and XTALO; note 10
f
XTAL
f
stab
C
L
V
IL
LOW-level output
3 mA sink current 0 − 0.4 V
voltage; open-drain
SCL LOW time 1.3 −− µs
SCL HIGH time 0.6 −− µs
rise time of both SDA
−−0.3 µs
and SCL
fall time of both SDAand
−−0.3 µs
SCL
data set-up time 100 −− ns
hold time START
0.6 −− µs
condition
set-up time STOP
0.6 −− µs
condition
cycle time 35 37 39 ns
HIGH/Tcy
40 50 60 %
rise time VI= 0.8 to 2 V −−5ns
fall time VI= 2 to 0.8 V −−6ns
data set-up time 6 −− ns
data hold time 3 −− ns
data input frequency rate frame-locked;
25.46 27 28.54 MHz
notes 5 and 6
line frequency 625 lines; note 6 14734 15625 16515 kHz
525 lines; note 6 14837 15734 16631 kHz
field frequency 625 lines;
46 50 50.75 kHz
notes 7 and 8
525 lines;
55 60 60.9 kHz
notes 7 and 8
active lines/field 625 lines;
265 288 311
notes 7 and 9
525 lines;
221 240 259
notes 7 and 9
fundamental frequency note 11 27 ×
(1 −80 × 10−6)
MPEG2 frequency
stability
note 11 27 ×
(1 −30 × 10−6)
27 27 ×
(1+80× 10−6)
− 27 ×
(1+30× 10−6)
load capacitance 8 10 12 pF
LOW-level input voltage if usedwith external
−0.5 − +0.7 V
clock
MHz
MHz
2004 Jan 26 62
Page 63

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
IH
C
shunt
R
s
Crystal oscillator tuning: pins XTALI and XTALO; note 10
N
tune
C
tune(min)
C
tune(max)
f
step
External clock input: pin EXTCLK
f
EXTCLK
δ duty factor t
t
r(EXTCLK)
t
f(EXTCLK)
2
I
C-bus address select input: pin I2CADDRSEL
V
IL
V
IH
Reset input: pin RESET
V
IL
t
start
t
length
t
init
HIGH-level input voltage if usedwith external
1.7 − V
DDA
clock
shunt capacitance −−7pF
serial resistance −−25 Ω
tuning steps −127 − +128
minimum internal tuning
capacitance to V
SSA
maximum internal tuning
N
= 128 − 8 − pF
tune
N
= −127 − 72 − pF
tune
capacitance
crystal frequency offset
14 42 70 Hz
per tuning step
external frequency square wave;
25.7 27.0 28.3 MHz
note 11
HIGH/Tcy
40 50 60 %
rise time VI= 0.7 to 1.7 V −−5ns
fall time VI= 1.7 to 0.7 V −−6ns
LOW-level input voltage
−0.5 − +0.7 V
for I2C-bus addresses
40H and 41H
HIGH-level input voltage
1.7 − V
DDP
for I2C-bus addresses
42H and 43H
LOW-level input voltage
−0.5 − +0.7 V
for active reset
start time of first reset
− 010 µs
pulse after power-on
length of reset pulse
10 −− ms
after power-on and after
sleep
initialization phase after
−−1s
reset pulse until I2C-bus
commands are accepted
V
V
2004 Jan 26 63
Page 64

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
SDRAM interface data, address and control timing: pins SD_DQ31 to SD_DQ0, SD_A13 to SD_A0, SD_CAS,
SD_RAS, SD_WE and SD_OE
T
cy
t
CAS
t
RCD
t
RRD
t
RP
t
WR
t
RSC
t
RAS
t
RC
t
power-up
t
d(C-D)
t
d(C-A)
t
su(D)
t
h(D)
Data output interface timing: pins PDO7 to PDO0, PDIDS, PDOSYNC, PDOAV and PDIOCLK
t
l-o(PDIDS-PDOVAL)
t
l-o(PDIDS-PDO)
t
stab(PDO-PDOVAL)
t
r(PDOVAL-PDO)
t
h(PDO-PDIOCLK)
t
su(PDO-PDIOCLK)
t
i(PDIOCLK)H
t
i(PDIOCLK)L
t
stab(PDIOCLK-PDO)
cycle time f
= 27 MHz − 9.26 − ns
sys
CAS latency time − 3 − clock
cycles
row to column delay time − 3T
activate to activate delay
− 2T
cy
cy
− ns
− ns
time
row precharge time − 3T
write recovery time − 2T
mode register set cycle
− 2T
cy
cy
cy
− ns
− ns
− ns
time
row activate time − 6T
row cycle time − 8T
cy
cy
− ns
− ns
wait time after power-on 500 515 −µs
clock to data output
delay
clock to address output
delay
C
L(SD_CLK)
C
L(SD_DQn)
f
SD_CLK
C
L(SD_CLK)
C
L(SD_An)
f
SD_CLK
= 15 pF;
= 8 pF;
= 108 MHz
= 15 pF;
= 8 pF;
= 108 MHz
2.5 4.0 5.0 ns
2.5 4.0 5.0 ns
data input set-up time 1 −− ns
data input hold time 2.5 −− ns
PDIDS to PDOVAL
DEBI slave mode 0 − 20 ns
low-ohmic time
PDIDS to PDO[7:0]
DEBI slave mode 0 − 20 ns
low-ohmic time
PDO[7:0] data stable to
DEBI slave mode 10 −− ns
falling PDOVAL time
rising
DEBI slave mode 10 −− ns
PDOVAL to PDO[7:0]
high-impedance time
PDO[7:0] data to
PDIOCLK hold time
PDO[7:0] data to
PDIOCLK set-up time
input PDIOCLK HIGH
DIO master mode;
10 −− ns
PDOVAL = 1
DIO master mode;
10 −− ns
PDOVAL = 1
DIO slave mode 55 −− ns
time
input PDIOCLK LOW
DIO slave mode 55 −− ns
time
falling input PDIOCLK to
PDO[7:0] data stable
DIO slave mode;
PDOVAL = 1
36 − 58 ns
time
2004 Jan 26 64
Page 65

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
Notes
1. Short-circuit current is only allowed for a short time (<1 s).
2. The output pins are 3.3 V tolerant when in 3-state mode.
3. Pins SCL and SDA of the I2C-bus interface do not obstruct the SDA and SCL lines if the supply voltage V
switched off.
4. The open-drain outputs are 3.3 V tolerant.
5. Frame-locked input data rate deviation from SAA6752HS crystal clock.
6. Supporting output range of the Philips SAA7114 video input processor.
7. Applies for line frequencies ±2% from nominal.
8. Minimum limit according to IEC 60756; maximum limit because the SAA6752HS may drop frames for V-sync
frequencies greater than 1.5% above nominal.
9. Deviation according to IEC 60756.7. The SAA6752HS will only encode 240 lines (when in 525-line mode) and
288 lines (when in 625-line mode). Therefore any additional lines in a field above these values will not be encoded.
10. Pin XTALO has to be used for connection with a crystal only. Do not use for other purposes.
11. The required stability of the crystal frequencyor externalsystem clockis dependentupon the clock mode used in the
application.
DDP
is
handbook, full pagewidth
VCLK
data and
control
inputs
data and
control
outputs
t
SU;DAT
T
cy
t
HIGH
t
HD;DAT
valid not valid valid
t
OH;DAT
valid not valid valid
t
f(VCLK)
t
LOW
t
r(VCLK)
Fig.15 Clock data timing.
MHC142
1.7 V
1.3 V
0.7 V
1.7 V
0.7 V
2.4 V
0.4 V
2004 Jan 26 65
Page 66

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
13 PACKAGE OUTLINE
SQFP208: plastic shrink quad flat package;
208 leads (lead length 1.3 mm); body 28 x 28 x 3.4 mm; high stand-off height
c
157
y
156
X
A
105
104
Z
E
SAA6752HS
SOT316-1
e
w
b
p
pin 1 index
208
1
w
M
p
D
H
D
0.27
0.17
3.6
3.2
b
0.25
e
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
mm
A
max.
4.1
0.50
0.25
UNIT A1A2A3bpcE
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
Z
(1) (1)(1)
D
28.1
0.20
27.9
0.09
53
52
D
0 5 10 mm
(1)
eHELL
28.1
0.5
27.9
B
scale
H
30.9
30.3
0.75
0.45
A
2
A
A
1
detail X
Zywv θ
p
0.080.21.3 0.08
Z
1.39
1.11
D
E
1.39
1.11
(A )
3
θ
L
p
L
o
8
o
0
H
E
E
M
v
M
A
v
M
B
D
30.9
30.3
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT316-1 MS-029
IEC JEDEC JEITA
REFERENCES
2004 Jan 26 66
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
00-01-25
03-02-25
Page 67

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
14 SOLDERING
14.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
Thistext gives a verybriefinsight to acomplextechnology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface
mount IC packages. Wave soldering can still be used for
certainsurface mount ICs, butitis not suitable forfinepitch
SMDs. In these situations reflow soldering is
recommended.
14.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
tothe printed-circuit boardby screen printing,stencillingor
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Driven by legislation and environmental forces the
worldwide use of lead-free solder pastes is increasing.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
convection or convection/infrared heating in a conveyor
type oven. Throughput times (preheating, soldering and
cooling) vary between 100 and 200 seconds depending
on heating method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 270 °C depending on solder paste material. The
top-surface temperature of the packages should
preferably be kept:
• below 225 °C (SnPb process) or below 245 °C (Pb-free
process)
– for all BGA, HTSSON-T and SSOP-T packages
– for packages with a thickness ≥ 2.5 mm
– for packages with a thickness < 2.5 mm and a
volume ≥ 350 mm3 so called thick/large packages.
• below 240 °C (SnPb process) or below 260 °C (Pb-free
process) for packages with a thickness < 2.5 mm and a
volume < 350 mm3 so called small/thin packages.
Moisture sensitivity precautions, as indicated on packing,
must be respected at all times.
SAA6752HS
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
• Forpackages with leads onfoursides, the footprint must
be placed at a 45° angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering,the packagemust
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time of the leads in the wave ranges from
3 to 4 seconds at 250 °C or 265 °C, depending on solder
material applied, SnPb or Pb-free respectively.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
14.4 Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
14.3 Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
forsurface mount devices (SMDs)orprinted-circuit boards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
2004 Jan 26 67
Page 68

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
14.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering methods
(1)
(3)
, TFBGA,
not suitable suitable
BGA, HTSSON..T
PACKAGE
(3)
, LBGA, LFBGA, SQFP, SSOP..T
USON, VFBGA
DHVQFN, HBCC, HBGA, HLQFP, HSO, HSOP, HSQFP, HSSON,
not suitable
HTQFP, HTSSOP, HVQFN, HVSON, SMS
(5)
PLCC
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO, VSSOP not recommended
CWQCCN..L
(8)
, PMFP
(9)
, WQCCN..L
(8)
not suitable not suitable
Notes
1. Formore detailed informationonthe BGA packagesrefer to the
“(LF)BGAApplication Note
from your Philips Semiconductors sales office.
2. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods”
3. These transparent plastic packages are extremely sensitive to reflow soldering conditions and must on no account
be processed through morethan one soldering cycle or subjected toinfrared reflow soldering with peak temperature
exceeding 217 °C ± 10 °C measured in the atmosphere of the reflow oven. The package body peak temperature
must be kept as low as possible.
4. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering. On versions with the heatsink on the bottom side, the solder
cannot penetrate between the printed-circuit board and the heatsink. On versions with the heatsink on the top side,
the solder might be deposited on the heatsink surface.
5. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
6. Wave soldering is suitablefor LQFP, TQFP and QFP packages with a pitch (e) larger than0.8 mm; it is definitely not
suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
7. Wave soldering is suitable for SSOP, TSSOP, VSO and VSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than
0.65 mm; it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
8. Image sensor packages in principle should not be soldered. They are mounted in sockets or delivered pre-mounted
on flex foil. However, the image sensor package can be mounted by the client on a flex foil by using a hot bar
soldering process. The appropriate soldering profile can be provided on request.
9. Hot bar or manual soldering is suitable for PMFP packages.
SOLDERING METHOD
WAVE REFLOW
(4)
(5)(6)
(7)
suitable
suitable
suitable
”(AN01026); order acopy
(2)
.
2004 Jan 26 68
Page 69

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
SAA6752HS
audio encoder with multiplexer
15 DATA SHEET STATUS
LEVEL
I Objective data Development This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product
II Preliminary data Qualification This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification.
III Product data Production This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips
Notes
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
2. The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was
published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
3. For data sheets describing multiple type numbers, the highest-level product status determines the data sheet status.
DATA SHEET
STATUS
(1)
PRODUCT
STATUS
(2)(3)
development. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the
specification in any manner without notice.
Supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification without
notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible
product.
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time in order
to improve the design, manufacturing and supply. Relevant changes will
be communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change Notification
(CPCN).
DEFINITION
16 DEFINITIONS Short-form specification The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition Limiting values given arein
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
atthese or atanyother conditions abovethosegiven in the
Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
norepresentationor warranty that suchapplicationswillbe
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
17 DISCLAIMERS Life support applications These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expectedto result in personal injury.Philips
Semiconductorscustomersusing or selling theseproducts
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes in the products including circuits, standard cells, and/or software described or contained herein in order to improve design
and/or performance. When the productis infull production
(status ‘Production’), relevant changes will be
communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change
Notification (CPCN). Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these
products, conveys no licence or title under any patent,
copyright, or mask work right to these products, and
makes no representations or warranties that these
products are free from patent, copyright, or mask work
right infringement, unless otherwise specified.
2004 Jan 26 69
Page 70

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 video and MPEG-audio/AC-3
audio encoder with multiplexer
ICs with MPEG-audio/AC-3 audio functionality
Purchase of a Philips ICwith anMPEG-audio and/orAC-3
audio functionality does not convey an implied license
under any patentright to use this IC in anyMPEG-audio or
AC-3 audio application. A license can be obtained via
Philips Intellectual Property & Standards
(Internet at URL http://www.ip.philips.com;
e-mail info.licensing@philips.com).
18 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
Purchase of Philips I2C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms tothe I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
2
C COMPONENTS
SAA6752HS
ICs with MPEG-2 functionality Use of this product in
any manner that complies with the MPEG-2 Standard is
expressly prohibited without a license under applicable
patents in the MPEG-2 patent portfolio, which license is
available from MPEG LA, L.L.C., 250 Steele Street, Suite
300, Denver, Colorado 80206.
2004 Jan 26 70
Page 71

Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
Contact information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com. Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Printed in The Netherlands R04/03/pp71 Date of release: 2004 Jan 26 Document order number: 9397 750 12538
SCA76
 Loading...
Loading...