Philips P83C654FHA, P83C654FBB, P83C654IFB, P80C652FHP, P80C652FBP Datasheet
...
87C654
CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
Product specification 1996 Aug 16
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
IC20 Data Handbook

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
87C654CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
2
1996 Aug 16 853–1689 17192
DESCRIPTION
The 87C654 Single-Chip 8-Bit Microcontroller
is manufactured in an advanced CMOS
process and is a derivative of the 80C51
microcontroller family. The 87C654 has the
same instruction set as the 80C51. Two
versions of the derivative exist:
83C654—16k bytes mask programmable
ROM
87C654—EPROM version
This device provides architectural
enhancements that make it applicable in a
variety of applications for general control
systems. The 87C654 contains a non-volatile
16k × 8 EPROM, a volatile 256 × 8 read/write
data memory, four 8-bit I/O ports, two 16-bit
timer/event counters (identical to the timers of
the 80C51), a multi-source, two-priority-level,
nested interrupt structure, an I
2
C interface,
UART and on-chip oscillator and timing
circuits. For systems that require extra
capability, the 87C654 can be expanded
using standard TTL compatible memories
and logic.
The device also functions as an arithmetic
processor having facilities for both binary and
BCD arithmetic plus bit-handling capabilities.
The instruction set consists of over 100
instructions: 49 one-byte, 45 two-byte and 17
three-byte. With a 16MHz crystal, 58% of the
instructions are executed in 0.75µs and 40%
in 1.5µs. Multiply and divide instructions
require 3µs.
FEATURES
•80C51 central processing unit
•16k × 8 EPROM expandable externally to
64k bytes
•256 × 8 RAM, expandable externally to
64k bytes
•Two standard 16-bit timer/counters
•Four 8-bit I/O ports
•I
2
C-bus serial I/O port with byte oriented
master and slave functions
•Full-duplex UART facilities
•Power control modes
– Idle mode
– Power-down mode
•Five package styles
•Extended temperature range
•OTP package available
•Two speed ranges
– 16MHz
– 20MHz
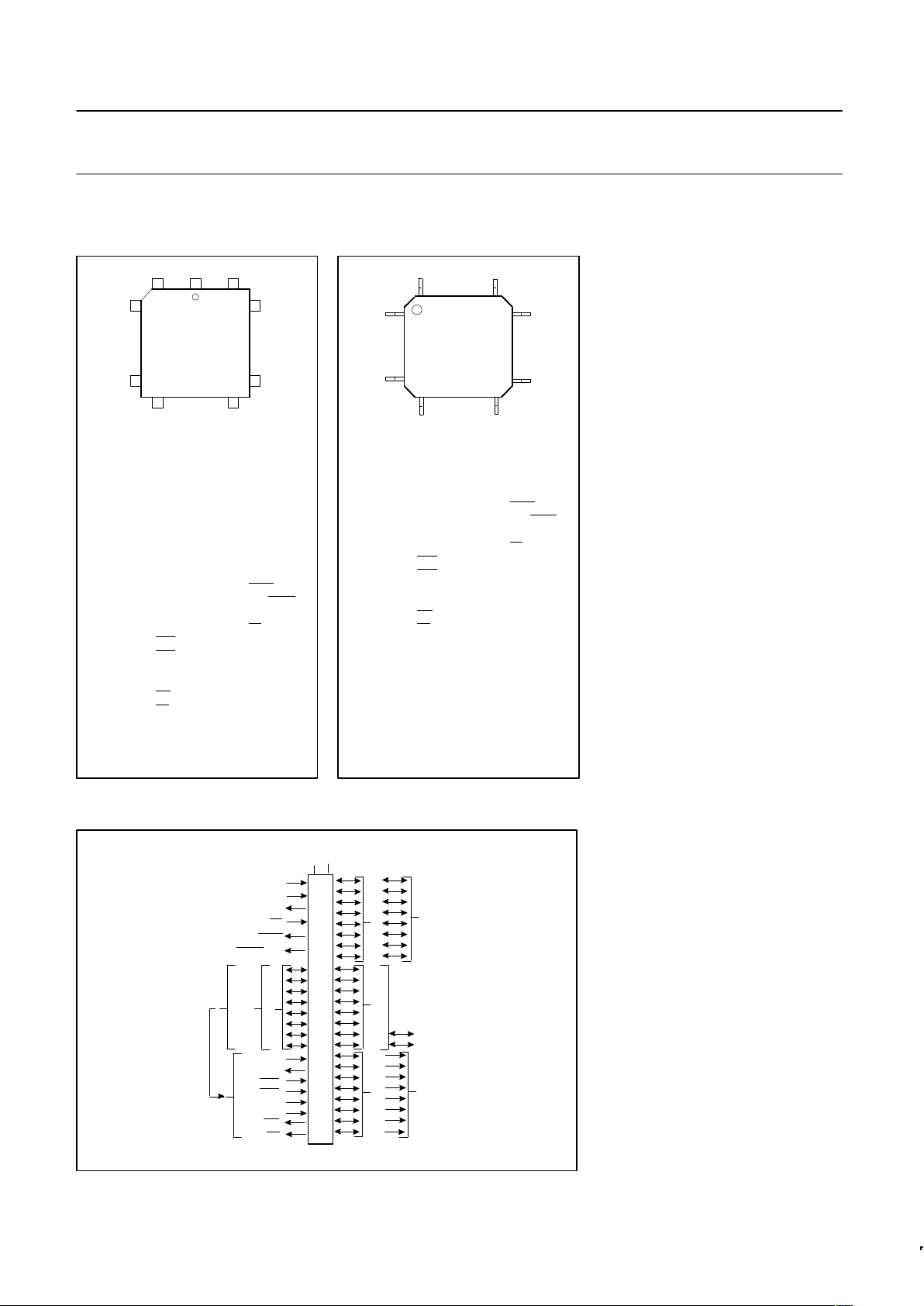
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P1.5
SCL/P1.6
RST
RxD/P3.0
TxD/P3.1
INT0
/P3.2
INT1
/P3.3
T0/P3.4
T1/P3.5
SDA/P1.7
WR/P3.6
RD
/P3.7
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
P2.0/A8
P2.1/A9
P2.2/A10
P2.3/A11
P2.4/A12
P2.5/A13
P2.6/A14
P2.7/A15
PSEN
ALE/PROG
EA/V
PP
P0.7/AD7
P0.6/AD6
P0.5/AD5
P0.4/AD4
P0.3/AD3
P0.2/AD2
P0.1/AD1
P0.0/AD0
V
CC
CERAMIC
AND
PLASTIC
DUAL
IN-LINE
PACKAGE
CERAMIC
AND PLASTIC
LEADED
CHIP
CARRIER
6 1 40
7
17
39
29
18 28
PLASTIC
QUAD
FLAT
PACK
44
34
1
11
33
23
12 22
SU00259
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
87C654CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
1996 Aug 16
3
CERAMIC AND PLASTIC LEADED
CHIP CARRIER PIN FUNCTIONS
LCC
6 1 40
7
17
39
29
18 28
Pin Function
1 NC*
2 P1.0
3 P1.1
4 P1.2
5 P1.3
6 P1.4
7 P1.5
8 P1.6/SCL
9 P1.7/SDA
10 RST
11 P3.0/RxD
12 NC8
13 P3.1/TxD
14 P3.2/INT0
15 P3.3/INT1
16 P3.4/T0
17 P3.5/T1
18 P3.6/WR
19 P3.7/RD
20 XTAL2
21 XTAL1
22 V
SS
Pin Function
23 NC8
24 P2.0/A8
25 P2.1/A9
26 P2.2/A10
27 P2.3/A11
28 P2.4/A12
29 P2.5/A13
30 P2.6/A14
31 P2.7/A15
32 PSEN
33 ALE/PROG
34 NC8
35 EA
/V
PP
36 P0.7/AD7
37 P0.6/AD6
38 P0.5/AD5
39 P0.4/AD4
40 P0.3/AD3
41 P0.2/AD2
42 P0.1/AD1
43 P0.0/AD0
44 V
CC
SU00260
* DO NOT CONNECT
PLASTIC QUAD FLAT PACK
PIN FUNCTIONS
Pin Function
1 P1.5
2 P1.6/SCL
3 P1.7/SDA
4 RST
5 P3.0/RxD
6 NC*
7 P3.1/TxD
8 P3.2/INT0
9 P3.3/INT1
10 P3.4/T0
11 P3.5/T1
12 P3.6/WR
13 P3.7/RD
14 XTAL2
15 XTAL1
16 V
SS
17 NC*
18 P2.0/A8
19 P2.1/A9
20 P2.2/A10
21 P2.3/A11
22 P2.4/A12
Pin Function
23 P2.5/A13
24 P2.6/A14
25 P2.7/A15
26 PSEN
27 ALE/PROG
28 NC*
29 EA
/V
PP
30 P0.7/AD7
31 P0.6/AD6
32 P0.5/AD5
33 P0.4/AD4
34 P0.3/AD3
35 P0.2/AD2
36 P0.1/AD1
37 P0.0/AD0
38 V
CC
39 NC*
40 P1.0
41 P1.1
42 P1.2
43 P.13
44 P1.4
PQFP
44 34
1
11
33
23
12 22
SU00261
* DO NOT CONNECT
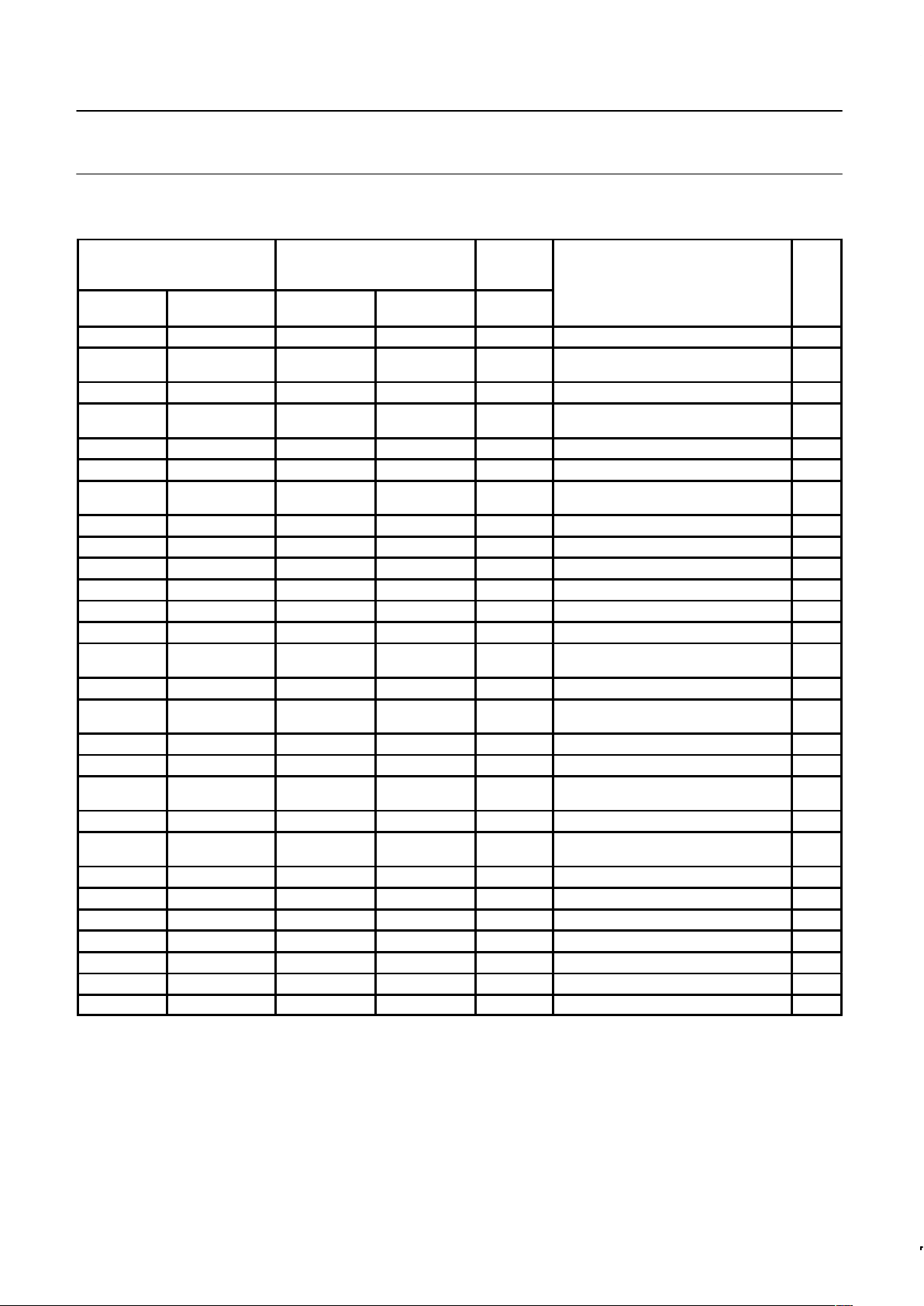
LOGIC SYMBOL
PORT 0
PORT 1PORT 2
PORT 3
ADDRESS AND
DATA BUS
ADDRESS BUS
VSSV
CC
ALTERNATE
FUNCTIONS
RST
XTAL1
XTAL2
VPP/EA
PROG/ALE
PSEN
RxD
TxD
INT0
INT1
T0
T1
WR
RD
SCL
SDA
SU00262
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
87C654CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
1996 Aug 16
4
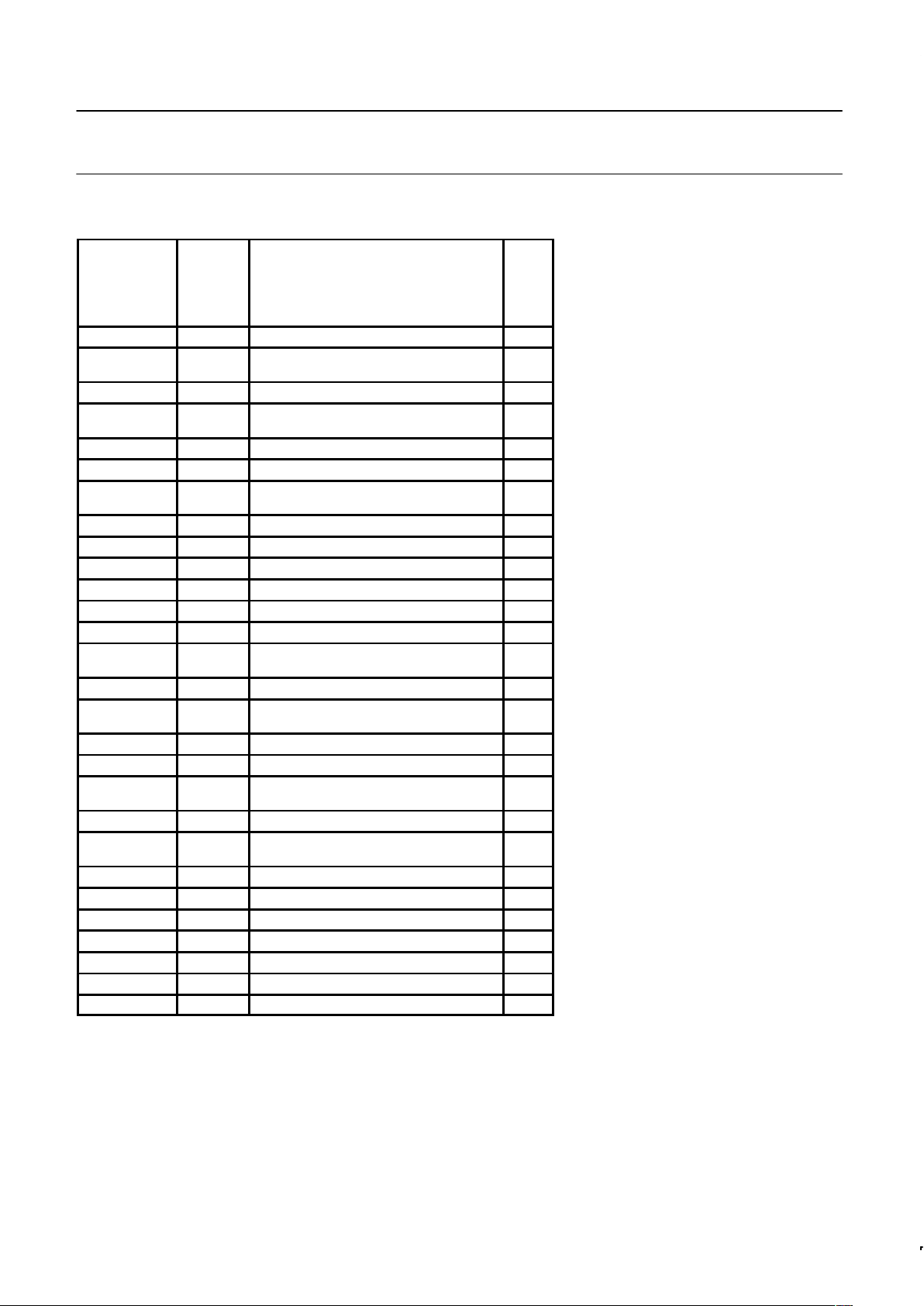
ORDERING INFORMATION
PHILIPS PART
ORDER NUMBER
PART MARKING
PHILIPS NORTH AMERICA
PART ORDER NUMBER
TEMPERATURE
RANGE °C
ROMless ROM ROMless ROM Drawing
Number
AND PACKAGE FREQ
MHz
P80C652FBP P83C654FBP/xxx S80C652FBPN S83C654FBPN SOT129-1 0 to +70, Plastic Dual In-line Package 16
0 to +70, Ceramic Dual In-line Package
w/Window
16
P80C652FBA P83C654FBA/xxx S80C652FBAA S83C654FBAA SOT187-2 0 to +70, Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier 16
P80C652FBB P83C654FBB/xxx S80C652FBBB S83C654FBBB SOT307-2
4
0 to +70, Plastic Quad Flat Pack 16
P80C652FFP P83C654FFP/xxx S80C652FFPN S83C654FFPN SOT129-1 –40 to +85, Plastic Dual In-line Package 16
P80C652FFA P83C654FFA/xxx S80C652FFAA S83C654FFAA SOT187-2 –40 to +85, Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier 16
P80C652FFB P83C654FFB/xxx S80C652FFBB S83C654FFBB SOT307-2
4
–40 to +85, Plastic Quad Flat Pack 16
P80C652FHP P83C654FHP/xxx S80C652FHPN S83C654FHPN SOT129-1 –40 to +125, Plastic Dual In-line Package 16
P80C652FHA P83C654FHA/xxx S80C652FHAA S83C654FHAA SOT187-2 –40 to +125, Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier 16
P80C652FHB P83C654FHB/xxx S80C652FHBB S83C654FHBB SOT307-2
4
–40 to +125, Plastic Quad Flat Pack 16
P80C652IBP P83C654IBP/xxx S80C652IBPN S83C654IBPN SOT129-1 0 to +70, Plastic Dual In-line Package 24
P80C652IBA P83C654IBA/xxx S80C652IBAA S83C654IBAA SOT187-2 0 to +70, Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier 24
P80C652IBB P83C654IBB/xxx S80C652IBBB S83C654IBBB SOT307-2
4
0 to +70, Plastic Quad Flat Pack 24
P80C652IFP P83C654IFP/xxx S80C652IFPN S83C654IFPN SOT129-1 –40 to +85, Plastic Dual In-line Package 24
P80C652IFA P83C654IFA/xxx S80C652IFAA S83C654IFAA SOT187-2 –40 to +85, Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier 24
P80C652IFB P83C654IFB/xxx S80C652IFBB S83C654IFBB SOT307-2
4
–40 to +85, Plastic Quad Flat Pack 24
NOTES:
1. For full specification, see the 87C652 data sheet.
2. 87C654 frequency range is 3.5MHz – 16MHz or 3.5MHz – 24MHz.
3. xxx denotes the ROM code number.
4. SOT311 replaced by SOT307-2.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
87C654CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
1996 Aug 16
5
TEMPERATURE
RANGE °C
EPROM Drawing
Number
AND PACKAGE FREQ
MHz
S87C654-4N40 SOT129-1 0 to +70, Plastic Dual In-line Package 16
S87C654-4F40 0590B 0 to +70, Ceramic Dual In-line Package
w/Window
16
S87C654-4A44 SOT187-2 0 to +70, Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier 16
S87C654-4K44 1472A 0 to +70, Ceramic Leaded Chip Carrier
w/Window
16
S87C654–4B44 SOT307-2 0 to +70, Plastic Quad Flat Pack 16
S87C654-5N40 SOT129-1 –40 to +85, Plastic Dual In-line Package 16
S87C654-5F40 0590B –40 to +85, Ceramic Dual In-line Package
w/Window
16
S87C654-5A44 SOT187-2 –40 to +85, Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier 16
S87C654-5B44 SOT307-2 –40 to +85, Plastic Quad Flat Pack 16
S87C654–7N40 SOT129-1 0 to +70, Plastic Dual In-line Package 20
S87C654–7F40 0590B 0 to +70, Ceramic Dual In-line Package
w/Window
20
S87C654–7A44 SOT187-2 0 to +70, Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier 20
S87C654–7K44 1472A 0 to +70, Ceramic Leaded Chip Carrier
w/Window
20
S87C654–8N40 SOT129-1 –40 to +85, Plastic Dual In-line Package 20
S87C654–8F40 0590B –40 to +85, Ceramic Dual In-line Package
w/Window
20
S87C654–8A44 SOT187-2 –40 to +85, Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier 20
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
87C654CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
1996 Aug 16
6
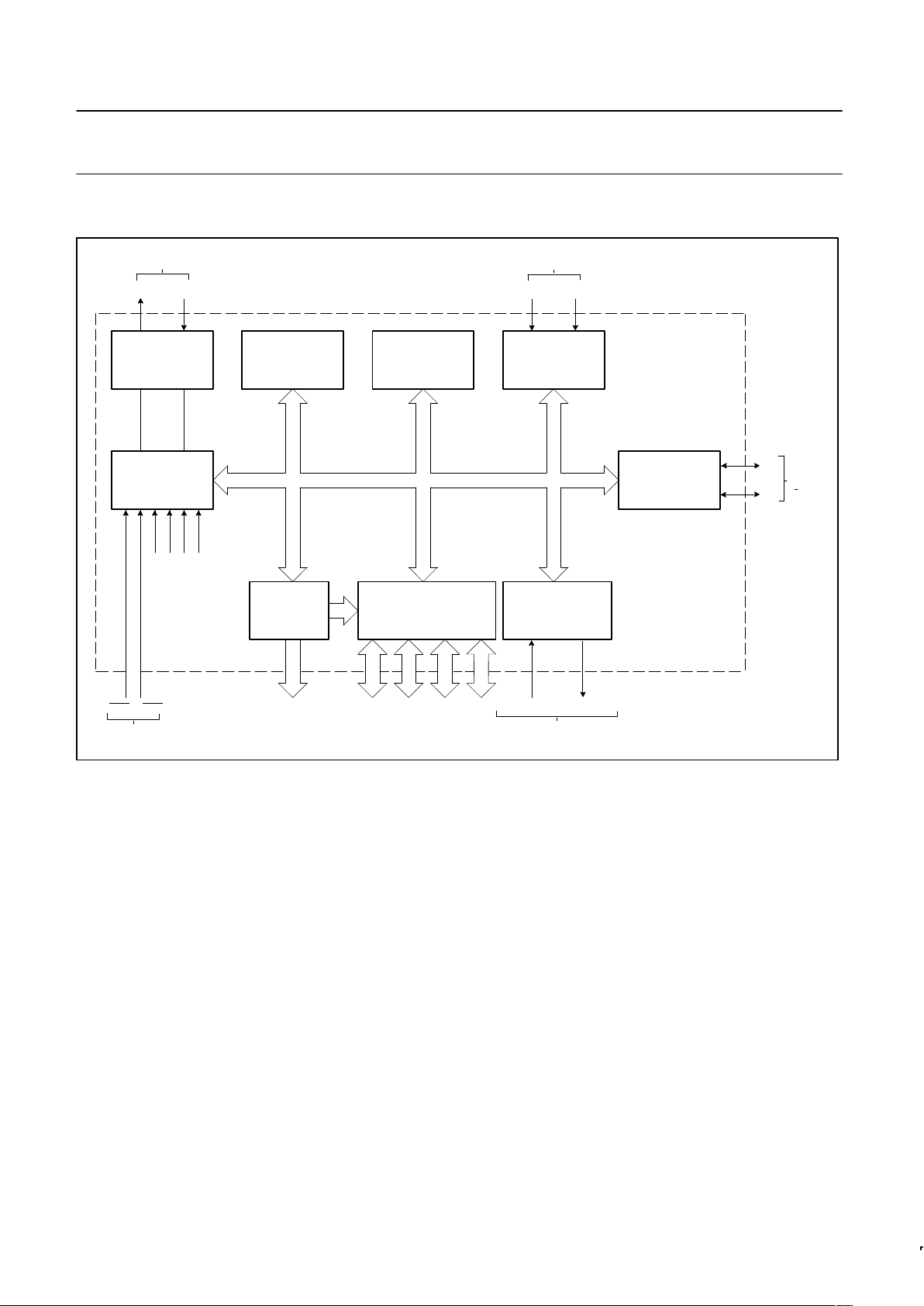
BLOCK DIAGRAM
64K BYTE BUS
EXPANSION
CONTRTOL
PROG SERIAL PORT
FULL DUPLEX UART
SYNCHRONOUS SHIFT
PROGRAMMABLE I/O
CPU
OSCILLATOR
AND
TIMING
PROGRAM
MEMORY
DATA
MEMORY
(256 x 8 RAM)
TWO 16-BIT
TIMER/EVENT
COUNTERS
I
2
C SERIAL I/O
SDA
SCL
SHARED
WITH
PORT 1
T0 T1
COUNTERS
XTAL2 XTAL1
FREQUENCY
REFERENCE
INTERNAL
INTERRUPTS
INT0
INT1
EXTERNAL
INTERRUPTS
CONTROL
PARALLEL PORTS,
ADDRESS/DATA BUS
AND I/O PINS
SERIAL IN SERIAL OUT
SHARED WITH
PORT 3
(16K x 8
EPROM)
SU00271

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
87C654CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
1996 Aug 16
7
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
PIN NUMBER
MNEMONIC
DIP LCC QFP TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
V
SS
20 22 16 I Ground: 0V reference.
V
CC
40 44 38 I Power Supply: This is the power supply voltage for normal, idle, and power-down
operation.
P0.0–0.7 39–32 43–36 37–30 I/O Port 0: Port 0 is an open-drain, bidirectional I/O port. Port 0 pins that have 1s written to them
float and can be used as high-impedance inputs. Port 0 is also the multiplexed low-order
address and data bus during accesses to external program and data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s. Port 0 also outputs the code
bytes during program verification in the 87C654. External pull-ups are required during
program verification.
P1.0–P1.7 1–8 2–9 40–44,
1–3
I/O Port 1: Port 1 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups, except P1.6 and P1.7
which are open drain. Port 1 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the internal
pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 1 pins that are externally pulled low will
source current because of the internal pull-ups. (See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
IL
).
Port 1 also receives the low-order address byte during program memory verification.
Alternate functions include:
P1.6 7 8 2 I/O SCL: I2C-bus serial port clock line.
P1.7 8 9 3 I/O SDA: I2C-bus serial port data line.
P2.0–P2.7 21–28 24–31 18–25 I/O Port 2: Port 2 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 2 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 2 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the internal
pull-ups. (See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
IL
). Port 2 emits the high-order address byte
during fetches from external program memory and during accesses to external data memory
that use 16-bit addresses (MOVX @DPTR). In this application, it uses strong internal
pull-ups when emitting 1s. During accesses to external data memory that use 8-bit
addresses (MOV @Ri), port 2 emits the contents of the P2 special function register.
P3.0–P3.7 10–17 11,
13–195,7–13
I/O Port 3: Port 3 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 3 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 3 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the pull-ups.
(See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
IL
). Port 3 also serves the special features of the 80C51
family, as listed below:
10 11 5 I RxD (P3.0): Serial input port
11 13 7 O TxD (P3.1): Serial output port
12 14 8 I INT0 (P3.2): External interrupt
13 15 9 I INT1 (P3.3): External interrupt
14 16 10 I T0 (P3.4): Timer 0 external input
15 17 11 I T1 (P3.5): Timer 1 external input
16 18 12 O WR (P3.6): External data memory write strobe
17 19 13 O RD (P3.7): External data memory read strobe
RST 9 10 4 I Reset: A high on this pin for two machine cycles while the oscillator is running, resets the
device. An internal diffused resistor to V
SS
permits a power-on reset using only an external
capacitor to V
CC
.
ALE/PROG 30 33 27 I/O Address Latch Enable/Program Pulse: Output pulse for latching the low byte of the
address during an access to external memory. In normal operation, ALE is emitted at a
constant rate of 1/6 the oscillator frequency, and can be used for external timing or clocking.
Note that one ALE pulse is skipped during each access to external data memory. This pin is
also the program pulse input (PROG
) during EPROM programming.
PSEN 29 32 26 O Program Store Enable: The read strobe to external program memory. When the 87C654 is
executing code from the external program memory, PSEN
is activated twice each machine
cycle, except that two PSEN
activations are skipped during each access to external data
memory. PSEN
is not activated during fetches from internal program memory.
EA/V
PP
31 35 29 I External Access Enable/Programming Supply Voltage: EA must be externally held low to
enable the device to fetch code from external program memory locations 0000H and 3FFFH.
If EA
is held high, the device executes from internal program memory unless the program
counter contains an address greater than 3FFFH. This pin also receives the 12.75V
programming supply voltage (V
PP
) during EPROM programming.
XTAL1 19 21 15 I Crystal 1: Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock generator
circuits.
XTAL2 18 20 14 O Crystal 2: Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier.
NOTE:
To avoid “latch-up” effect at power-on, the voltage on any pin at any time must not be higher than V
CC
+ 0.5V or VSS – 0.5V, respectively.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
87C654CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
1996 Aug 16
8
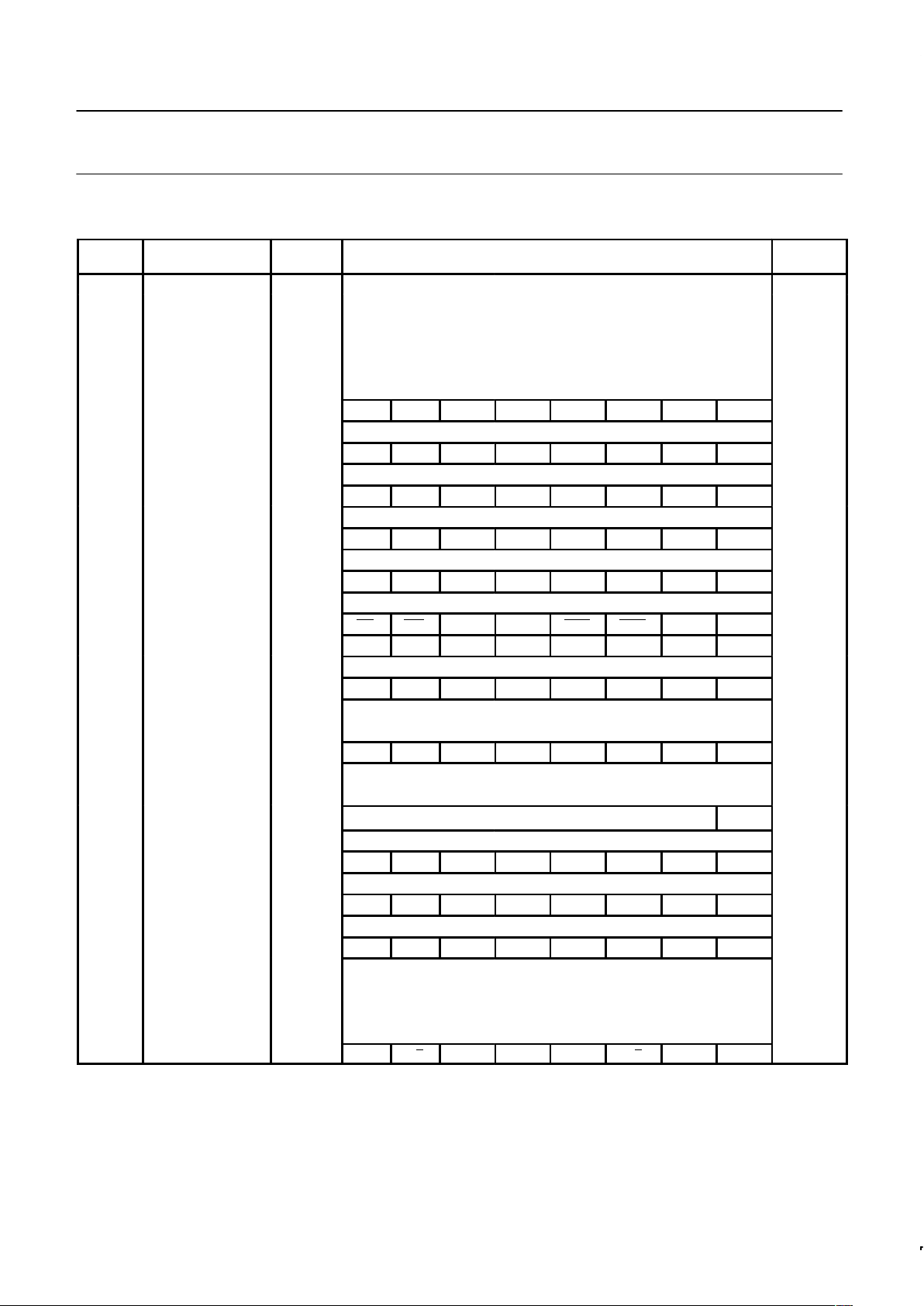
Table 1. 8XC652/654 Special Function Registers
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
DIRECT
ADDRESS
BIT ADDRESS, SYMBOL, OR ALTERNATIVE PORT FUNCTION
MSB LSB
RESET
VALUE
ACC* Accumulator E0H E7 E6 E5 E4 E3 E2 E1 E0 00H
B* B register F0H F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0 00H
DPTR:
DPH
DPL
Data pointer
(2 bytes)
Data pointer high
Data pointer low
83H
82H
00H
00H
AF AE AD AC AB AA A9 A8
IE*# Interrupt enable A8H EA ES1 ES0 ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0 0x000000B
BF BE BD BC BB BA B9 B8
IP*# Interrupt priority B8H – PS1 PS0 PT1 PX1 PT0 PX0 xx000000B
87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80
P0* Port 0 80H AD7 AD6 AD5 AD4 AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0 FFH
97 96 95 94 93 92 91 90
P1*# Port 1 90H SDA SCL FFH
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
P2* Port 2 A0H A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 FFH
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
P3* Port 3 B0H RD WR T1 T0 INT1 INT0 TXD RXD FFH
PCON# Power control 87H SMOD – – – GF1 GF0 PD IDL 0xxx0000B
9F 9E 9D 9C 9B 9A 99 98
S0CON*# Serial 0 port control 98H SM0 SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI 00H
S0BUF# Serial 0 data buffer 99H xxxxxxxxB
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
PSW* Program status word D0H CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 P 00H
S1DAT# Serial 1 data DAH 00H
SP Stack pointer 81H 07H
S1ADR# Serial 1 address DBH
SLAVE ADDRESS
GC 00H
S1STA# Serial 1 status D9H SC4 SC3 SC2 SC1 SC0 0 0 0 F8H
DF DE DD DC DB DA D9 D8
S1CON*# Serial 1 control D8H CR2 ENS1 STA STO SI AA CR1 CR0 00000000B
8F 8E 8D 8C 8B 8A 89 88
TCON* Timer control 88H TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0 00H
TH1 Timer high 1 8DH 00H
TH0 Timer high 0 8CH 00H
TL1 Timer low 1 8BH 00H
TL0 Timer low 0 8AH 00H
TMOD Timer mode 89H GATE C/T M1 M0 GATE C/T M1 M0 00H
* SFRs are bit addressable.
# SFRs are modified from or added to the 80C51 SFRs.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
87C654CMOS single-chip 8-bit microcontroller
1996 Aug 16
9
OSCILLATOR
CHARACTERISTICS
XTAL1 and XTAL2 are the input and output,
respectively, of an inverting amplifier. The
pins can be configured for use as an on-chip
oscillator, as shown in the Logic Symbol.
To drive the device from an external clock
source, XTAL1 should be driven while XTAL2
is left unconnected. There are no
requirements on the duty cycle of the
external clock signal, because the input to
the internal clock circuitry is through a
divide-by-two flip-flop. However, minimum
and maximum high and low times specified in
the data sheet must be observed.
Reset
A reset is accomplished by holding the RST
pin high for at least two machine cycles (24
oscillator periods), while the oscillator is
running. To insure a good power-on reset, the
RST pin must be high long enough to allow
the oscillator time to start up (normally a few
milliseconds) plus two machine cycles. At
power-on, the voltage on V
CC
and RST must
come up at the same time for a proper
start-up.
Idle Mode
In the idle mode, the CPU puts itself to sleep
while all of the on-chip peripherals stay
active. The instruction to invoke the idle
mode is the last instruction executed in the
normal operating mode before the idle mode
is activated. The CPU contents, the on-chip
RAM, and all of the special function registers
remain intact during this mode. The idle
mode can be terminated either by any
enabled interrupt (at which time the process
is picked up at the interrupt service routine
and continued), or by a hardware reset which
starts the processor in the same manner as a
power-on reset.
Power-Down Mode
In the power-down mode, the oscillator is
stopped and the instruction to invoke
power-down is the last instruction executed.
Only the contents of the on-chip RAM are
preserved. A hardware reset is the only way
to terminate the power-down mode. The
control bits for the reduced power modes are
in the special function register PCON. Table 2
shows the state of the I/O ports during low
current operating modes.
I2C SERIAL
COMMUNICATION—SIO1
The I2C serial port is identical to the I2C
serial port on the 8XC552. The operation of
this subsystem is described in detail in the
8XC552 section of this manual.
Note that in both the 8XC652/4 and the
8XC552 the I
2
C pins are alternate functions
to port pins P1.6 and P1.7. Because of this,
P1.6 and P1.7 on these parts do not have a
pull-up structure as found on the 80C51.
Therefore P1.6 and P1.7 have open drain
outputs on the 8XC652/4.
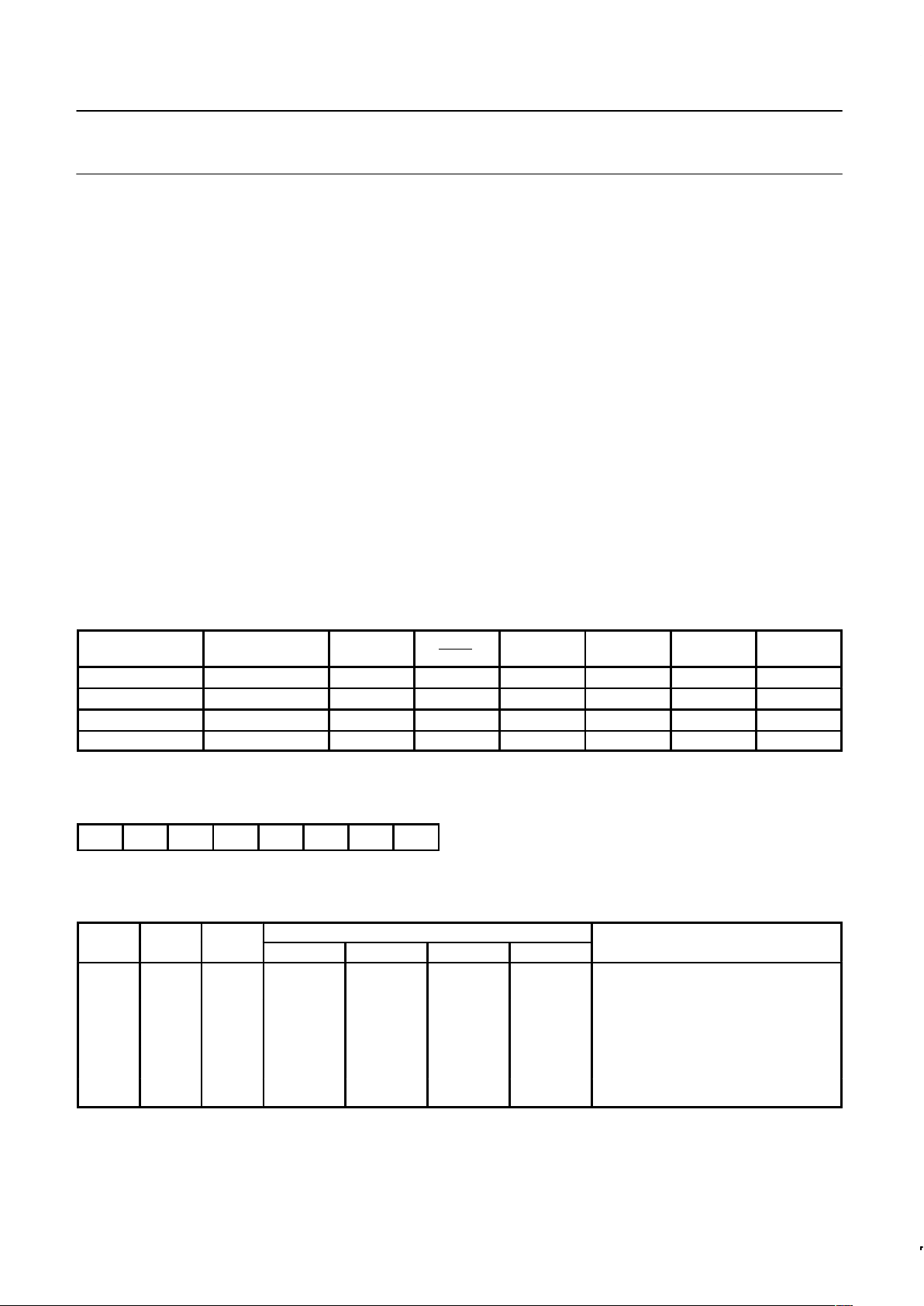
Table 2. External Pin Status During Idle and Power-Down Mode
MODE
PROGRAM
MEMORY
ALE PSEN PORT 0 PORT 1 PORT 2 PORT 3
Idle Internal 1 1 Data Data Data Data
Idle External 1 1 Float Data Address Data
Power-down Internal 0 0 Data Data Data Data
Power-down External 0 0 Float Data Data Data
Serial Control Register (S1CON) – See Table 3
S1CON (D8H)
CR2 ENS1 STA STO SI AA CR1 CR0
Bits CR0, CR1 and CR2 determine the serial clock frequency that is generated in the master mode of operation.
Table 3. Serial Clock Rates
BIT FREQUENCY (kHz) AT f
OSC
CR2 CR1 CR0
6MHz 12MHz 16MHz 20MHz f
OSC
DIVIDED BY
0 0 0 23 47 62.5 78 256
0 0 1 27 54 71 89
1
224
0 1 0 31.25 62.5 83.3 104
1
192
0 1 1 37 75 100 125
1
160
1 0 0 6.25 12.5 17 21 960
1 0 1 50 100 133
1
166
1
120
1 1 0 100 200
1
267
1
334
1
60
1 1 1 0.25 < 62.5
0 to 255
0.5 < 62.5
0 to 254
0.65 < 55.6
0 to 253
0.81 < 69.4
0 to 253
96 × (256 – (reload value Timer 1))
(Reload value range: 0 – 254 in mode 2)
NOTES:
1. These frequencies exceed the upper limit of 100kHz of the I
2
C-bus specification and cannot be used in an I2C-bus application.
 Loading...
Loading...