Philips rm440 DATASHEETS

HT RM440 Family
HITAG™ Proximity Reader Module
Hardware
Revision 2.0
November 1996Product Specification

Proximity Reader Module HT RM440 Rev. 2.0 November 1996
Table of Contents
1. Introduction 5
2. System Overview 6
2.1. Transponders 6
2.2. Host 6
2.3. I/O - Functions 6
2.4. Connecting the Antenna 7
2.5. Behaviour with Several Transponders 7
3. Specifications 8
3.1. Electrical Specifications 8
3.1.1. Power Supply 8
3.1.2. Modulation 8
3.1.2.1. Read/Write Device ⇒ Transponder 8
3.1.2.2. Transponder ⇒ Read/Write Device 8
3.1.3. Interface 8
3.1.4. Metallic Environment, Interferences 9
3.1.5. Distance between Two Antennas 9
3.1.6. Temperature Range 9
3.2. Mechanical Specifications 10
3.2.1. Mechanical Dimensions 10
3.2.2. Pin Assignment 11
3.2.3. Pin Function Description 13
3.2.4. SubD Pin Description 13
3.2.5. Power supply connector 13
4. Description of the Reader Module Functions 14
4.1. Block Diagram 14
4.1.1. EEPROM 14
4.1.2. Micro Controller 14
4.1.3. Interface: Micro Controller - HOST 14
4.1.4. Line driver 14
4.1.5. Transmitter and Receiver 15
4.1.6. Antenna 15
4.1.7. Filtering of Power Supply 15
4.1.8. I/O Functions 15
5. Postal Approval 16
6. Connection of the Reader Module 17
Htrm440.doc/HS Page 2 of 27

November 1996 Rev. 2.0 Proximity Reader Module HT RM440
6.1. Building HITAG Proximity Antennas 17
6.1.1. Basics 17
6.1.2. Antenna Coil 18
6.1.3. Measuring the Inductance 19
6.1.4. Antenna Cable Length 19
6.1.5. Antenna Tuning 19
6.1.6. Determining the Serial Resistance of the Antenna 20
6.1.7. Checking the Antenna Voltage Û
L
20
6.1.8. Procedure for Practical Antenna Design 21
6.1.9. Reference Antennas 23
6.2. Possible Sources of Errors by Connecting the HITAG Proximity Reader Module 24
7. Security Considerations 25
7.1. Operating Security 25
7.1.1. Anticollision Mode 25
7.1.2. Monitoring the Supply Voltage 25
7.1.3. Antenna Rupture, Antenna Short Circuit 25
7.2. Data Privacy 26
8. Ordering Information 27
Author : Ulrich Brändle
Page 3 of 27 Htrm440.doc/HS
Proximity Reader Module HT RM440 Rev. 2.0 November 1996
Definitions
Data sheet status
Objective specificationThis data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specificationThis data sheet contains preliminary data; s upplementary data may be
published later.
Product specification This data sheet c ontains final produc t spec ifications .
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Max imum Rating Syst em (IEC 134).
Stress above one or more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at thes e or at any other c onditions
above those given in the Characteristics s ection of the specific ation is not implied. Ex posure to
limiting values for extended periods may affect devic e reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
Life support applications
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where
malfunction of these products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips
Semiconductors´ customers using or selling these products for use in such applications do so on
their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any damages resulting from
such improper use or sale.
Htrm440.doc/HS Page 4 of 27

November 1996 Rev. 2.0 Proximity Reader Module HT RM440
1. Introduction
- is the name of one of the universal and powerful product lines of our 125 kHz family.
Th e co nta ctle ss pr ox imity r ead /wr ite s yst em th at w or ks w ith p ass ive t rans po nder s is s uit able fo r
various applications. Inductive coupling helps you to achieve reading ranges up to 200 mm and the
use of cryptography guarantees highest data security.
The HITAG Proximity Reader Mo dule provides you wit h a universal, cost -effect ive, small and
complete reader unit.
It enables communication with the transponders of the 125 kHz family, i. e. M ikro n’s HIT AG 1,
HITAG 2 and µEM(H400x) (Read Only) transponders in proximit y app licat ions , an d t he Ph ilips
PCF793x family which underlines the particular universality of the reader.
Easy integration and application of the HITAG Proximity Reader Module is due to:
• small size
• uncomplicated interfaces
Page 5 of 27 Htrm440.doc/HS

Proximity Reader Module HT RM440 Rev. 2.0 November 1996
2. System Overview
Th e fo llo win g d ra win g sh o ws th e H IT AG Pr o ximit y Re ad er Mo d ule as pa rt o f a co mple t e R ad io
Frequency Identification (RFID) system.
2.1. Transponders
Th e H IT AG Pr o ximit y Re ad er Mo d ule ca n co mmu nic at e wit h Mik ro n’ s H I TAG 1 an d H I TA G 2
transponders as well as with further 125kHz transponders as e.g. t he µEM(H400x) and the Philips
PCF793x family. Y o u us e so ft w a r e c o mma nd s to s w it ch t he d ev ice fr o m be ing u se d as r e ad / wr it e
device for HITAG tr ansponders to a r ead device for µ EM(H400x) transpo nders or a read/write
device for the PCF793x and the other way round.
2.2. Host
The connection to the host (e.g.: µC or PC) is a serial interface on RS232 level (version
HT RM440/AIE) for data transmission. Optionally wired interface drivers for RS422 (version
HT RM440/BIE) and RS485 (version HT RM440/CIE) are integrated on t he HITAG Proximit y
Reader Module.
2.3. I/O - Functions
Tw o lin e s of th e H IT A G P rox imity R e a d e r M od u le ar e w ire d a s inpu ts fr om e . g. s w itc h e s , two a s
outputs to drive LEDs.
On the read/write device space is reserved to co nnect three LEDs as well as to connect e.g. two
switches.
Htrm440.doc/HS Page 6 of 27

November 1996 Rev. 2.0 Proximity Reader Module HT RM440
2.4. Connecting the Antenna
There is space reserved on the HITAG Pro ximit y R ea d e r Modu le for tunin g c a p ac itor s to tu n e the
antenna in case there is no tuning capacity used on the antenna itself.
The antenna has to be mounted in the following way:
*) TX2 is used as GND
C is used for tu ning the antenna. For more det ailed information please see Chapter 6. 1 (Building
HITAG Proximity Antennas).
2.5. Behaviour with Several Transponders
If several HITAG transponders arrive simultaneously within the communication field of the ant enna of a H IT AG P rox imity Re ade r Mo du le, the "st ro nger " t ran spo nde r ( the nea rer o ne) ta kes
over or - under special circumstances - no co mmunication takes place. If the transponders arrive
into the field one after the other, communication is established with the first one, all the other
transponders are ignored.
Nevertheless it is possible to mute t ransponders, so t hat several HITAG transponder s can be accessed sequentially.
Th is e nsu r e s t h at no t w o ( o r s ev er a l) H IT A G tr a ns p o nd e r s w ill e ve r b e pr o c e ss e d ( a bo v e a ll w r it ten to!) accidentally at the same time.
Page 7 of 27 Htrm440.doc/HS
Proximity Reader Module HT RM440 Rev. 2.0 November 1996
3. Specifications
3.1. Electrical Specifications
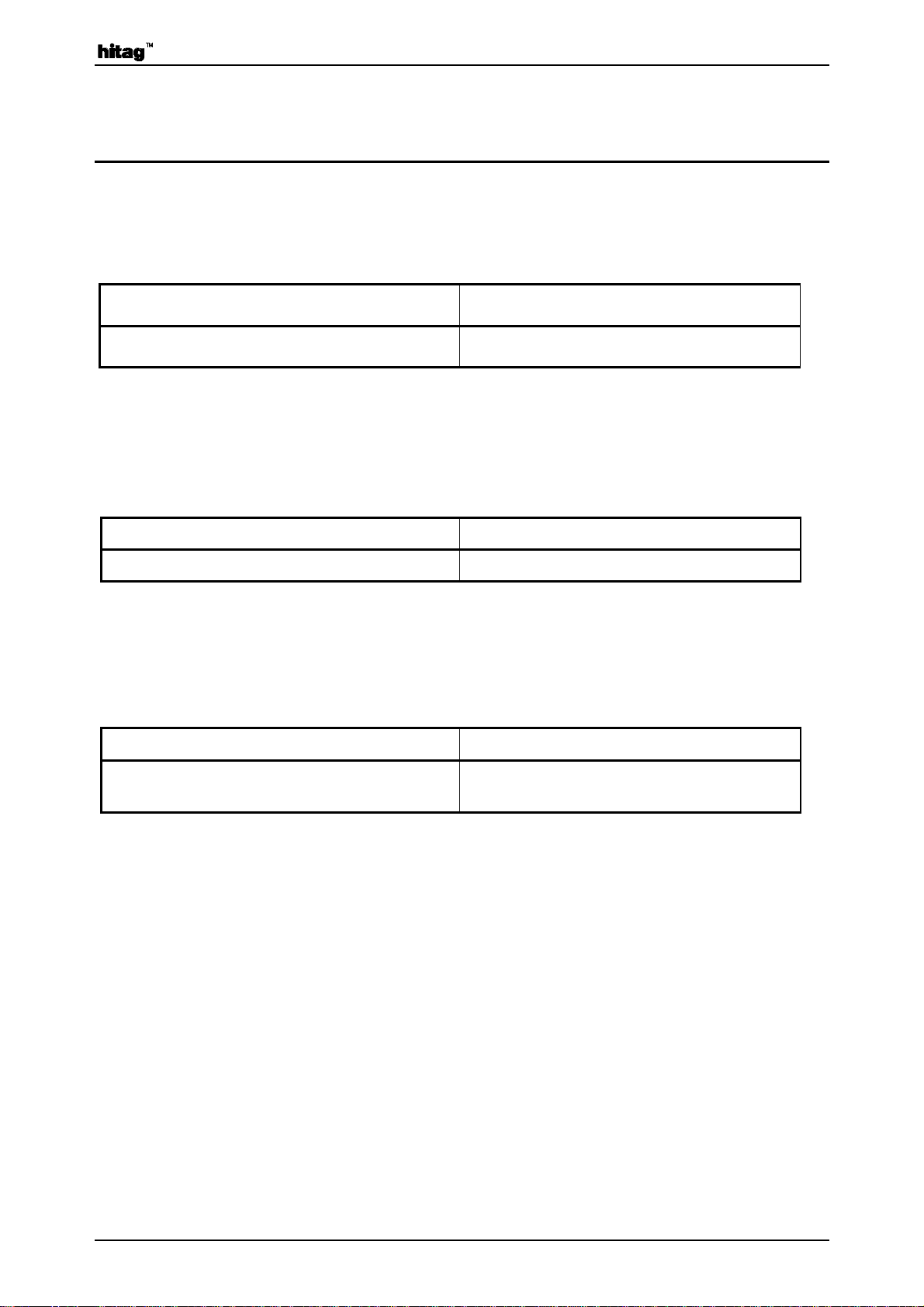
3.1.1. Power Supply
Power Supply Supply Current
9 - 16 VDC 150 mA max.
3.1.2. Modulation
3.1.2.1. Read/Write Device
Type of Modulation Modulation Ratio
amplitude shift keying (ASK) 100 %
That means the carrier is periodically blanked completely, the information is located in the intervals between the pauses.
3.1.2.2. Transponder ⇒ Read/Write Device
Type of Modulation Modulation Ratio
amplitude shift keying (ASK) depending on the distance between
⇒ Transponder
transponder and read/write device
3.1.3. Interface
An interface driver for RS232 (version HT RM440/AIE) is integrated on the HITAG Proximit y
Reader Module.
Optionally drivers are RS422 (version HT RM440/BIE) and RS485 (version HT RM440/CIE)
Htrm440.doc/HS Page 8 of 27

November 1996 Rev. 2.0 Proximity Reader Module HT RM440
3.1.4. Metallic Environment, Interferences
Th e co mmunic atio n r ange is impa ired by met allic e nviro nment and elec tr oma gnet ic int er fere nces
(e.g.: monitors, keyboards). Therefore, you should keep a distance of at least the antenna´s diameter to me tallic su rfaces or loops as well as to electro magnetic interferences. If this is not possible, you have to take pr eventive measures such as using ferrites or shielding for transponder and
antenna.
3.1.5. Distance between Two Antennas
In order t o be able to op erat e t wo systems side by side without negative influence on communication ranges, you must place the antennas at a minimum distance of four times the antenna diameter. If you place them at a closer distance be sure to use suitable shielding or synchronisation.
3.1.6. Temperature Range
-25° C to +85° C (operating)
-40° C to +85° C (storage)
Page 9 of 27 Htrm440.doc/HS
 Loading...
Loading...