
...
•·
'
HFGenerator 100kHz-110MHz
PM5324
9452 053 240.l
9499 450 05411
73050l/ l/Ol

PHILIPS
Operating manual
HFGenerator 100 kHz-110MHz PM5324
9452 053 240.1
9499 450 CJS4l l
730501 /l/01

2
Important
In correspondence concerning this instrument please quote the type number and the serial number as given
on the type plate at the rear of the instrument.
© N.V. PHILIPS' GLOEILAMPENFABBIEKEN · EINDHOVEN - THE NETHERLANDS· 1973

3
Contents
1. GENERAL
4
1.1. INTRODUCTION
4
1.2. TECHNICAL
5
1.2.1. HF-Generator
5
1.2.2.
Modulation
5
1.2.3.
Calibration
6
1.2.4.
Supply
6
1.2.5.
Temperature range
7
1.2.6. Mechanical data
7
1.3. ACCESSORIES
7
1.3.1.
Included as standard
7
1.3.2.
Optional
7
1.4. DESCRIPTION OF THE BLOCK DIAGRAM
8
2.
DIRECTIONS FOR USE
10
2.1.
INSTALLATION
10
2.1.1.
Position
10
2.1.2. Connection to the mains
10
2.1.3.
Earthing
10
2.2.
OPERATION
11
2.2.1. Switching on
I
'l
2.2.2. Adjusting the frequency
11
2.2.3.
Adjusting the mode
11
2.2.4. Application
11
2.2.4.1. Unmodulated HF·signal generator
2.2.4.2. Amplitude-modulated (AM)
HF-signalgenerator
i .."'
2.2.4.3. Frequency-modulated (FM)
HF-signalgenerator
13
2.2.4.4.
Wobble generator
13
2.2.4.5.
Calibration
i
4
2.2.4.6. 1 kHz-Generator
·1.1
3.
LIST OF PARTS
15

4
1. GENERAL
1.1. Introduction
AM-FM-Generator PM 5324 produces unmodulated and modulated HF-Signals. It is very useful in radio-servicing
and in technical education.
The frequency range is from 0.1 MHz to 110 MHz in 9 sub-ranges.
Fine adjustment of the frequency is effected on a large, illuminated, easv-to-read linear scale. The range which
is in use and the scale to be read is indicated by means of LEDs. The output voltage is electronically stabilised
and is continuously adjustable.
The AM-FM-Generator may also be used in the frequency range from 150 MHz to 220 MHz, e.g. in band Ill
as a test generator for television sets, or as a generator in the frequency range for taxi-transmission.
With an internal X·tal oscillator the frequency of the generator can be checked and, if necessary, adjusted.

5
1.2. Technical data
General
- Alternative voltages are stated as r.m.s. values.
- Only values with tolerances and or numerical values are guaranteed.
- Deviations (in% or ppm) apply to the adjusted value.
- Temperature coefficients apply within temperature range.
- All specifications are met after a warming-up time of30minutes.
1.2.1. HF-GENERATOR
Frequency range
0.1 MHz up to 110 MHz
9
ranges:
0.1 ...
0.3 MHz
0.3 ...
1 MHz
1
...
3
MHz
3
...
10
MHz
10 ... 30
MHz
30
... BO
MHz
75
110 MHz
0.4
0.5
MHz
10.3 11.1MHz
Scale
Accuracy
Long-term stability
6 linear, illuminated scales
<
1.5%in the ranges 0.1 ...80MHz
<1
%
in range
75
110 MHz
<0.5
%
in range 0.4
0.5
MHz
<
0.2
%
in range 10.3 11.lMHz
<0.1
%
on calibrated points
<0.1
%
at:
~ nominal operating conditions
- mains voltage variations +10%,-15
%
- measured over7hours
Temperature coefficient
,,;;;5.2.10-4;oc
Output
HF
OUT
Frequencv-respor se
Connection : BNC connector
Output voltage:
50 mV into 75
~L,atunmodulated signal
O.lMHz ... 110 MHz
;;;;;3c1s
0.4 MHz...
0.5 MHz ( <
0_2
dB
10.3 MHz... 11
MHz
f
;;?-
60 dB,
continuous
for frequencies<
15 MHz; ;;,,
60 dB
Attenuator
1.2.2. MODULATION
Modes
unmodulated : all ranges
AM : all ranges
FM : range
75 ...
110 MHz and 10.3 ... 11.1 MHz
Wobble
: ranges
75 ...
110 MHz, 0.4 ... 0.5 MHz and
10.3 ... 11.1 MHz
Modulation frequency: 1 kHz (sine wave)
Modulation depth : 30
%
AM, internal

6
AM, external
FM, internal
FM, external
Wobble
1 kHz Output
Sweep output
1.2.3.CALIBRATION
Frequency
Error
Frequency distance of the calibration points
Zero beat indication
1.2.4. SUPPLY
Nominal mains voltage
Mains voltage deviation
Frequency
Consumption
Input· : via BNC connector LF IN
Modulation depth : > 70
%
Modulation coefficient : 0.2 V/10%AM
3 dB-Band width : 20 Hz ··- 20 kHz
Input impedance : 10 kn
Modulation frequency: 1 kHz (sine wave)
Sweep (Llf) : 25 kHz, at 10.7 MHz and 97 MHz
(dependent on freque.ncy)
Input : via BNC connector LF IN
Sweep (ll.t) : 75 kHz, at 10.7 MHz and 97 MHz
Modulation coefficient : 0.2 V/7.5 kHz at 10.7 MHz and
97 MHz (dependent on frequency)
: 20 Hz ·-· 60 kHz
: 10 kn
3
dB-Band width
Input impedance
Wobbulating sweep (2tif):
range 0.4 MHz 0.5 MHz, 0 ... 40 kHz at 450 kHz
range 10.3 MHz 11.3 MHz, 0 ... 600 kHz at rn.7 MHz
Wobble frequency: 25 Hz (sawtooth)
BNC connector; combined with sweep output
Voltage : 2 V
Frequency :1kHz (sine wave)
Impedance :1kD
BNC connector; combined with 1 kHz output
Voltage : 10 Vp-p
Frequency : 25 Hz (saw
tooth]
Impedance :1kD
10 MHz }
1 MHz
0.1 MHz
<0.02
%
spectrum with at least 10 harmonics
for every frequency
Range :
Distance
0.1 ...
0.3 MHz
0.1 MHz
0.3 ...
1
MHz
0.1
MHz
3
MHz 1
MHz
3
...
10
MHz 1
MHz
10
30 MHz 10 MHz
30
... 80
MHz 10 MHz
75
... 110
MHz
10
MHz
0.4 ....
0.5 MHz
0. 1
MHz
10.3 ...J11.1 MHz
'
0.1 MHz
By moving coil instrument, illuminated when button CAL.
is pressed
220
v
Also possible 110 V, 128 V, 202 V and 233 V
+10%,-15
%
48 ... 60 Hz
11W,13VA

1.2.5. TEMPERATURE RANGE
Reference temperature
Temperature tolerance range
Storage temperature
1.2.6. MECHANICAL DATA
Dimensions
Weight
1.3. Accessories
1.3.1. INCLUDED AS STANDARD
- Mains cable
- Directions for use
1.3.2.OPTIONAL
- Coax
cable
BNc-2
x 4 mm
PM9072
- Coax
cable
BNC-BNC,
75.nPM 9075
- Impedance transformer PM9537
7
+25
°c
+5
°c ...
+40
°c
-40
°c ...
+70
°c
Height : 192
mm
Width : 287
mm
Depth : 290 mm
5 kg

8
1.4. Description of the block diagram
The frequency of the generator is determined
by
an HF-oscillator the amplitude of which is electronically
stabilised. Frequency rs.1ges are selected with push-button MHz. With in the selected range the frequency can
be adjusted continuously by control F REOUENCY.
A frequency-modulator provides voltage-controlled frequency modulation ot the HF-oscillator· e.g. for
wobbulating purposes· in the ranges 75 MHz ...
110
MHz, 0.4 MHz ... 0.5 MHz and
10.3
MHz ...
11.1
MHz
(/\IVV).
In the amplitude-modulator the amplitude of the HF-signal can be modulated in all frequency ranges and the
HF-signal blanked during fly-back at mode WOB
VV).
The HF-output stage amplifies the power of the HF-signal, the amplitude of which is adjustable continuously
with attenuator HF AMPLITUDE.
The output signal is available at connector HF OUT; the output impedance amounts to 75
n.
If button CAL. is pressed an X.tal controlled calibration oscillator produces harmonics to check the
calibration of the scale. The markers are at a distance of10MHz,1MHz or
0.1
MHz, depending on the
selected frequency range.
In the mixer the signals of the HF-output stage and of the calibration oscillator are mixed. The low-frequency
signal which is obtained at approximately equal frequencies of both signals is amplified, limited, rectified and
indicated by a moving coil meter. If the HF-frequency control is set at a calibration frequency, the indicator,
at exactly equal frequencies, indicates a sharp, limited minimum between two tull scales. (Fig.
l).
A 1 k+iz-sine wave signal, produced by a 1 kHz oscillator, is used for amplitude· or frequency modulation
and selected by push-buttons AM or FM. The1kHz signal is also available at connector1kHz/SWEEP OlJT
if button WOB has not been depressed. If button AM EXT. or FM EXT. has been depressed the HF-signal can
be modulated by an external signal supplied to connector LF IN.
If button WOB has been depressed, a saw-tooth signal, produced by a saw-tooth generator, is supplied to the
frequency modulator. The sweep of the frequency can be adjusted by potentiometer SWEEP WIDTH. At the
same time the saw-tooth signal with constant amplitude is available at connector1kHz/SWEEP OUT.
A square-wave pulse derived from the saw-tooth signal blanks the output stage dur mg tlv-back.
The supply section delivers two stabilised direct voltages
(-12
V and
-18
VI and an alternating voltage for
illumination of the scale.

9
1HF<1CAL.
t
HF>fCAL.
Fig. 1. Zero beat indication
I
M~zIIF~EQUENCY \ \c~L
I
J
HF AM,F'LITUDE
I
I I I I
I I I I
~-·-··----··-:-·--~-.-.-·-..··-:-··-··-·-··-·11-:-·..--,
I
r---,----t----1-------,
r--------------,
1
1
I I I
I I I
INDICATOR
I
I
I
I
DISPLAYUNIT
I I
CALIBRATION MIXER
l I
I FOR
THE
I I
OSCILlATOR /
l ,
: I
APPLIED
I
I
DECIMAL LIMITER
I
I
I
I
SCALE
I I
DIVIDER RECTIFIER
I ,
I I I I •
: I I I I
I
I
l I I I .
AMPLITUD£- I
I
F'REOUENCV MODULATOR/ HF·OUTPUT
HF
• i.o:IJLATOR BLANKING AMPLWIER ATTENUATOR 0U1
' GATE
i
i
I
1kHzJSWEEP
....,1-==--__,3 __,
our'f]_ ' '
~--1---
--;-~----.:::r.:::--------:..
I
I
LI
J
WEEPSIGNAl,I~ - IB
v
FM EXT lkHz
1 ---
!kHz BLANKING _17
v
~OWER
1
I
GENERATOR PULSE. SUPPLV I
i=i
IN
lF
GENERATOR . OV
y
IN!l I :
~,A-M-EXT-./~1-kH~z
t-·-- - -
1
I
j
I
I .
• I
_j
L.·-··-·----··- ..
·-··-·-··---··-··-··-··-1-..
I I
I I
I l
[:@.'EEPWIDTH/
I
POWER
I
POWEP
Fig.2. Block diagram

10
2. DIRECTIONS f'OR USE
2.1. Installation
2.1.1. POSITION
The instrument may be used in any position except on its rear end. Make sure that the instrument is not
exposed to excessive heat.
2.1.2. CONNECTION TO THE MAINS
The instrument must have a.c. supply only. On delivery, it is set for a mains voltage of 220 V. Setting for a
different mains voltage is done as follows:
- Remove the left screw of the handle bar and take oft the left side-plate.
- Change the primary connections of the mains transformer according to Fig. 3, a diagram of which is in the
inside of side-plate.
- Change the mains voltage indication-plate at the rear.
- Refit the handle bar.
- Connect up the instrument.
2.1.3. EARTHING
The instrument must be earthed in accordance with the local safety regulations. The mains cable supplied is
provided with an earth core which is connected to the earth contacts of the mains plug. If the instrument is
connected to a mains socket with earth contacts, the cabinet isautomatically earthed.
The circuit earth of the instrument and the chassis-connection of the BNC-connectors are at chassis potential.
Earthing the instrument via the chassis-connection of the BNC-connectors is not permitted.
r
s
L4
i2
~i
v
.-220V-+-?
Fig. 3. Changingtheprimary connections of the mains transformer

11
2.2.
Operation
2.2.1.
SWITCHING ON
- Connect the instrument to a mains socket with earthing contacts.
- Switch on by means of switch POWER; the scale illumination lights up and a white field in the button-cap
shows that the mains switch is on.
2.2.2.
ADJUSTING THE
FREQUENCY
- Select the required frequency range with one of the range buttons MHz; the corresponding range-scale is
indicated by a LED at the left side of the scale window.
- Adjust to nominal frequency with potentiometer FREQUENCY.
2.2.3.
ADJUSTING THE
MODE
The mode isselectedbydepressing one of the6buttons in the left row of buttons.
If
no button has been pressed the generator supplies an unmodulated HF-signal with the adjusted frequency
and amplitude.
Buttons CAL., AM/EXT., AM/1 kHz, FM/EXT. and
FM/1
kHz unlock each other automatically, thus only
one button can be depressed at a time.
Button WOB. may be unlocked by pressing the button a second time, independently of the other buttons.
The mode-buttons may be combined with the frequency-range buttons according the table given below.
Range button
Mode button
(selectable)
(MHz)
CAL
AM
FM WOB
0.1 - 0.3
x
x
0.3 _ 1
x
x
3
x
x
3
- 10
x
x
10
- 30
x
x
30
- 80
x
x
75
- 110
x
x
x x
0.4 - 0.5
x
x x
10.3- , 1.,
x x
x
x
extra
WOB+AM
x
x
x
2.2.4. APPLICATION
2.2.4.1. Unmodulated
HF·signal
generator
- Depress the required range button MHz.
- The selected range scale is indicated by a LED.
- Set the pointer at the required frequency by means of potentiometer FREQUENCY.
Not marked frequency values should be interpolated between two marks.
- If necessary, calibrate the frequency at the nearest calibratlon-mark according to sub-para 2.2.4.5.
- Unlock the mode-buttons (left row of buttons).
- Apply the HF-signal, available at BNC connector HF OUT, across a cable to the object to be measured (see
accessories, chapter 1.3.).
- Adjust the required output voltage with potentiometer HF AMPLITUDE.

12
Fig. 4. Front view
Fig. 5. Rear view

13
2.2.4.2. Amplitude-modulated (AMI HF-signal generator
Internal
- Preliminary adjustment according to chap. 2.2.4. 1..
- Press button AM/1 kHz. The HF·signal is modulated in amplitude by 30%at an internal frequency of1kHz.
- For indications on checking and adjusting, see the individual checking and adjusting procedures for the
object to be measured or chapter 2.3 ..
External
- Preliminary adjustment according to chap. 2.2.4.1 ..
- Pressbutton AM/EXT.
- Supply the modulation voltage to connector LF IN; maximum 16 V peak-peak, maximum d.c. level ±12 V.
- External modulation frequency 20 Hz ... 20 kHz.
- Adjust the modulation depth by the amplitude of the modulation voltage; voltage necessary 0.2 V /10
%
ampIitude·modulation.
2.2.4.3. Frequencv-modulated (FM) HF·signal generator
Internal
- Press buttons 75 · 110 or 10.3 · 11.1 MHz.
The selected range scale is indicated by a LEO.
- Set the pointer at the required frequency by potentiometer FREOUENCY.
Not marked frequency values should be interpolated between two marks.
- It necessary, calibrate the frequency at the nearest calibratlon-rnark according to sub-para 2.2.4.5 ..
- Press button FM/1 kHz; the HF-signalismodulated in frequency by1kHz and a frequency sweep of about
25 kHz.
- Apply the signal, available at BNC connector HF OUT, across a cable to the object to be measured.
Isse accessories, chapter 1.3.).
- Adjust the required output voltage by means of potentiometer
HF
AMPLITUDE.
Note
When using harmonics the frequency sweep is multiplied by ~he order-number of the harmonics.
External
- Preliminary adjustment according to chap. 2.2.4.3 ..
- Press button FM/EXT.
- Supply the modulation voltage to
BNC
connector LF
IN;
maximum input voltage
70 V peakpeak.
- Adjust the external modulation frequency; 20 Hz ... 60 kHz.
- Adjust the modulation sweep with the external voltage; necessary voltage 0.2 V/7.5 kHz sweep (maximum
sweep75kHz).
- If
necessary, supply a multiplex-signal to
BNC
connector LF IN
2.2.4.4. Wobble generator
- Pressrange·button 75 ... 110 or 10.3 ... 11.1 MHz.
The selected range-scale is indicated by a LED.
- Set the pointer to the required frequency by potentiometer FREQUENCY.
Not marked frequency values should be interpolated.
- Press button WOB.
- Connect BNC-connector 1 kHz/SWEEP OUT to the X·input of an oscilloscope.
- Adjust the X-amplitude of the oscilloscope.
- Apply the wobbulated signal across a cable to the object to be tested.

14
- Set the band-pass curve at the middle of the picture with potentiometer FREQUENCY.
- Adjust the height of the band-pass curve with potentiometer HF AMPLITUDE.
- Adjust the width of the band-pass curve with potentiometer SWEEP WIDTH.
- Check the band-pass curve; if necessary, correct it. The effect of an adjustment can be determined
immediately on the band-pass curve.
Note
When using harmonics the frequency sweep is multiplied by the order number of the harmonics.
Determining the band width
By defined shifting in the horizontal direction the band width (at 70%of the height of the picture) can be
determined as follows:
- Position the point of intersection, e.g. of the right edge of the band-pass curve and a fictitions horizontal
line at 70%of the height of the curve on a prominent point on the graticule by means of potentiometer
FREQUENCY.
- Read the frequency at the scale and note the value.
- Shift the band-pass curve horizontally with potentiometer FREQUENCY so that the second edge is
positioned at the same flctitions point of intersection (at 70%of the height of the picture) asinthe first
adjustment.
- Read the frequency; the difference between the two frequencies is the band width.
Note
Use a d.c. indicator (oscilloscope or meter) so that the base line is horizontal and undistorted at a large
wobbu Iating-sweep.
2.2.4.5. Calibration
The calibration points are indicated on the scale by the symbolYor
A .
A moving coil meter, which is
illuminated at calibration mode, serves as indicator.
Checking
If a very accurate HF-signal, e.g. of 21.5 MHz is needed, this can be checked as follows:
- Switch on the instrument and wait at least 30 minutes for it to warm up.
- Depress range-button 10 - 30 MHz; the diode alongside the top scale will light up.
- Depress button CAL.; the indicator will light up. If necessary, unlock button WOB..
- Set the scale pointer to that calibration mark ( V at mark .2) which is nearest to the nominal value of 21.5 MHz.
- Set the scale pointer exactly on the minimum which lies between two full-scale deflections of the indicator.
- Check, that the line of the scale pointer corresponds to the calibration mark.
Calibration
If the line of the scale pointer is not exactly over the calibration mark calibrate as follows:
- Set the scale pointer exactly on the calibration mark.
- Hold the largest knob of control FREQUENCY with one hand.
- Adjust the smaller knob - against the resistance of the slipping clutch - to obtain the required minimum
(zero beat) between two maxima.
- Release the large button.
- Adjust for exact zero beat.
- Check that the line of the scale pointer corresponds to tHe calibration mark. Repeat the calibration procedure,
if necessary.
2.2.4.6. 1 kHz-Generator
- Release all push-buttons, especially button WOB.
- The 1 kHz-signal, with an amplitude of 2
Vr.m.s .•
is available at BNC-connector 1 kHz/SWEEP OUT.
15
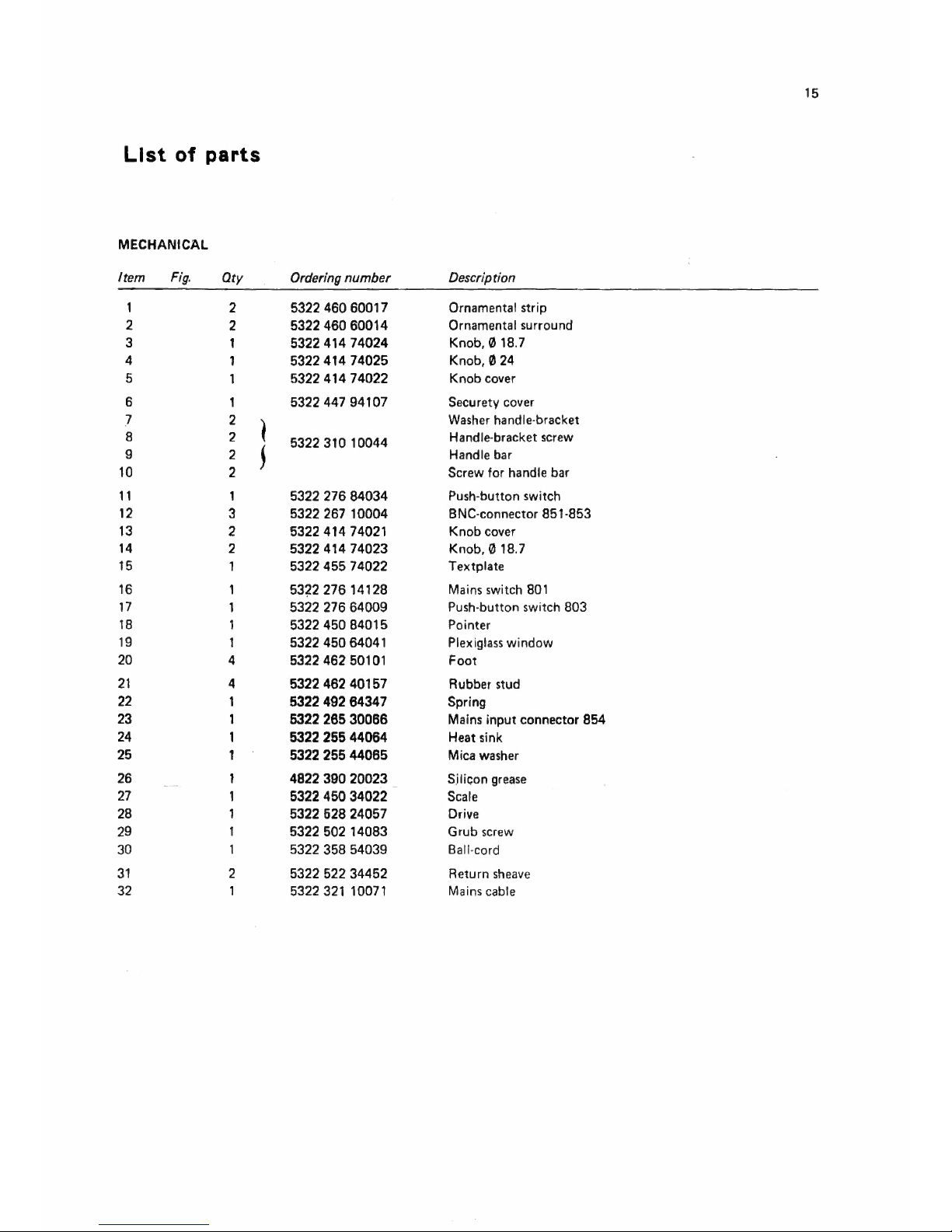
List of parts
MECHANICAL
Item Fig.
Qty
Ordering number
Description
2 5322 460 60017
Ornamental strip
2
2
5322 460 60014
Ornamental surround
3
1 5322 414 74024
Knob, 0 18.7
4
1
5322 414 74025 Knob, 0 24
5
1
5322 414 74022
Knob cover
6
1 5322 447 94107
Securety cover
7
2
l
Washer handle-bracket
8
2
5322 310 10044
Handle-bracket screw
9
2
j
Handle bar
10
2 Screw for handle bar
11
1
5322 276 84034
Push-button switch
12
3
5322 267 10004
BNC-connector 851-853
13
2 5322 414 74021
Knob cover
14
2
5322414 74023 Knob, 0 18.7
15
1 5322 455 74022
Textplate
16
1
53?2 276 14128
Mains switch 801
17
1 5322 276 64009
Push-button switch 803
18
1
5322 450 84015
Pointer
19
1 5322 450 64041 Plexiglass window
20
4
5322 462 50101 Foot
21
4
5322 462 40157 Rubber stud
22
1
5322 492 6434 7 Spring
23
1
5322 265 30066 Mains input connector 854
24
1
5322 255 44064 Heat sink
25
1 5322 256 44065
Mica washer
26
1
4822 390 20023 Silicon grease
--~
27
1
5322 450 34022 Scale
28 1
5322 628 24057
Drive
29
1
5322 502 14083
Grub screw
30
1
5322 358 54039 Ball-cord
31 2
5322 522 34452 Return sheave
32 1 5322 321 10071 Mains cable
16
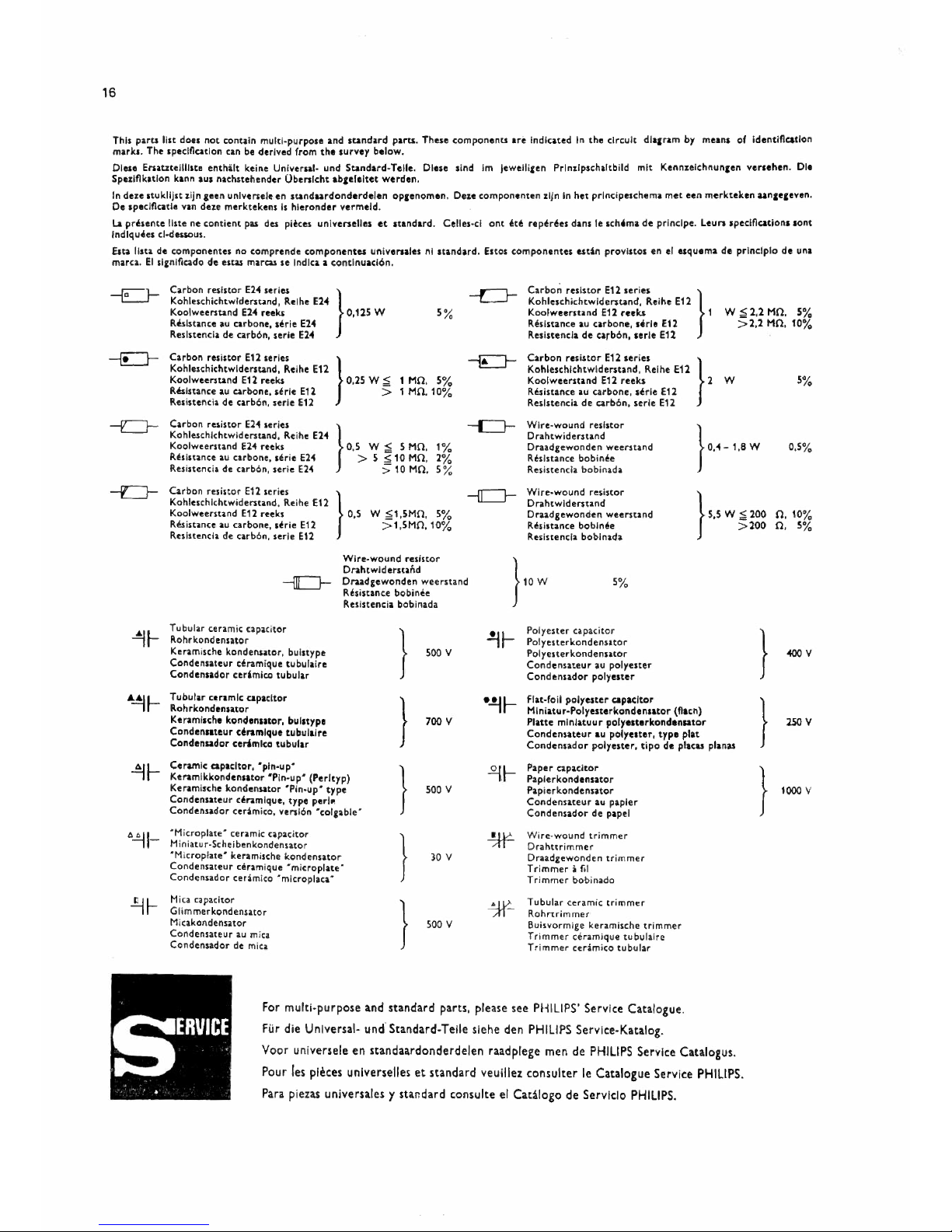
This parts list does not contain multi-purpose and standard parts. These components are Indicated In the circuit dla1rambymeans of ldentlflcitlon
marks. The specification can be derived from the survey below.
Dlese ErnuteJlllste enthalt keine Universal- und Standard-Telle. Dlese slnd Im jewell!gen Prlnilpschaltbild mlt Kenn:i:eichnuncen versehen, Die
Spe:i:lflkatlon kann aus nachstehnder Oberslcht ab1eleltet werden.
In deze stuklljst 1ijn geen unlversele en standurdonderdelen opgenomen. Deze componenten zljn In het prlnclpeschema met een merkteken aan1e1even.
De speclflcatla van
deze
merktekens Is hleronder vermeld.
La preHnte line ne contient pas des pieces unlverselles et standard. Celles-cl ont ete reperees dans le sch•ma de prlnclpe. Leurs speclncatlons sont
lndlquees cl-desseus.
Esta lista de componentes no comprende componentes unJversales nl standard. Estos componentes esttn provlstos en el esquema de princlplo de una
marca. El slgnlficado de estas marcas se lndica a conrtnuactcn.
-E}-
Carbon reslstcr El<H•lu }
-LJ-
C•• boO ~"00' E\l series }
Kohle"hichtwldersund, Reihe E2'4 Kohleschichtwlderstand, Reihe E12
Koolweerstand E2'4reeks 0,125 W
5%
Koolweersnnd E12 reeks 1
W ;:i:i2,2MO.
5%
Resistance au carbone, sl!rie E24 Resistance au carbone, sirie E12
>2,2 MO. 10%
Reslstenda de carbon, serle E2'4
fl.esistencia de carbon, serle E1l
--le}-
Carbon ml•~• E12 serles }
~
c••
boo mb•o' "'"''" }
Kohleschichtwiderstand, Reihe
E12
Kohleschichtwlderstand, Reihe E12
Koolweerstand E1l reeks
0,25 W;;;;:
1 Mn, 5% Koolweerstand E12 reeks
2
w
5%
Reslsnnce au carbone, drie E12 > 1MO.10%
Resistance au carbone, serle E12
Resistencia de carb6n, serte E12
Reslstencia de carb6n, serie E12
-C}--
Carbon reslstor El< "''" }
-ro-
Wire-wound resistor
}'·'- i.e
w
Kohleschichtwlderstand, Reihe EH
Drahtwiderstand
Koolweerstand EH reeks 0,5 W ;;;;: 5 MO, 1%
Draadgewonden weerstand
0,5%
Resistance au carbone, serie El-4 > 5 ~ 10 Mn, 2%
Resistance bobini!e
Resistencia de carbon, serie E24
>
10 MO. 5
%
Resistenda bobinada
~
Carbon resistor "'"''" }
--{C}-
Wire-wound resistor
Kohleschlchtwiderstand, Reihe E12
Drahtwlderstand
Koolweerstand E12reeks 0,S
W ~1,5MO,
5%
Draadgewonden weerstand
l
w '""
n, 10%
Resistance au carbone, st!rie E12
>1,SMn.10% Resistance boblnee
>200
n,
5%
Resistencla de carb6n, serle E12
Resistencla bobinada
Wire-wound resistor
Drahtwidersund
Draadgewonden weerstand
Rbistance boblnee
Resistencia bobinada
5%
~a-
Tubular ceramic capacitor
}
fl.ohrkondenntor
Keramische kondenntor, buistype
Condensateur ct!ramique tubulalre
Condensador cerimlco tubular
"'..!Jl--
Tubular ceramic capacitor
}
Rohrkondensator
Keramlsche konden11tor, buluype
Condensateur ceramlque tubulalre
Condensador cerimlco tubular
~l--
Ceramic capacitor, "pin-up·
}
Keramikkondenntot •Pin-up• (Perltyp)
Keramische kondensator "Pin-up• type
Condensateur ceramique, type perl~
Condensador cerimico, versl6n ·colgabie"
6-11-
'Micropiate" ceramic capacitor
}
Hin
iatu
r-Schei benkondensator
'Hlcrop!ate• keramische kondensator
Condensateur ceramique "mlcroplate "
Condensador ceramico "rnlcroplaca"
.!JI-
Hica capaclter
}
Gfimmerkondensator
Micakondensator
Condensateur au mica
Condensador de mica
500
v
Polyester capacitor
Poiyesterkondensator
Polyesterkondenntor
Condensateur au polyester
Condenudor polyester
"°°
v
}
700
v
flat-foil polyester capacitor
Mlniatur-Polyesterkondenutor (fiach)
Platte mlnlatuur polyesterkondensator
Condensateur au polyester, type plat
Condensador polyester, tipo de placas planas
250V
}
500
v
Paper capacitor
Paplerkendensatcr
Papierkondenntor
Condensateur au papier
Condensadot de papel
1000
v
}
30
v
Wire-wound trimmer
Drahttrimmer
Draadgewonden trimmer
TrimmeriIii
Trimmer bobinado
500
v
Tubular ceramic trimmer
R.ohrtrimmer
Buisvormige keramische trimmer
Trimmer ceramique tubulaire
Trimmer eerarntce tubular
For multi-purpose and standard parts, please see PHILIPS' Service Catalogue.
Fi.ir die Universal-
und
Standard-Telle slehe den PHILIPS
Servtce-Katalog.
Voor universele en standaardonderdelen raadplege men de PHILIPS Service Catalogus.
Pour !es pieces unlverselles et standard veulllez consulter le Catalogue Service PHILIPS.
Para piezas universalesystandard consulte el Catalogo de Servlclo PHILIPS.

17
Resistors
Item Orderingnumber
Vafue (fl)
%
Type
Description
601 5322 105 40007
75
25 0.1
w
HF-voltagedivider
602
5322 101 24012 22 k
Potentiometer
Unit 1
606 5322 116 50253 324
k
1
MR30
Metal film
607 5322 100 10088 220
k
20 0.1
w
Potentiometer
608
4822 100 10107 470 k
20
0.1
w
Potentiometer
609 5322 100 10088
220 k
20
0.1
w
Potentiometer
610 5322 116 54328
51
k 2
CR25
Carbon
612 5322 100 10036
4.7 k
20
0.1
w
Potentiometer
614 5322 116 50524
3 k 2
CR25 Carbon
616 5322 116 54328
51 k
2
CR25 Carbon
623 5322 116 54202
7.5 k 2
CR25 Carbon
626 5322 116 50095 510 k 2
CR25 Carbon
628 5322 116 54207 1 k 2
CR25 Carbon
630 5322 116 50752 1.5 k
2
CR25 Carbon
631
5322 100 10036
4.7 k 20
0.1
w
Potentiometer
663
5322 116 54188
1
M 1
MR30
Metal film
665 5322 116 54327 10 k
1 MR25
Metal film
666 5322 116 50726
36.5 k
1
MR25 Metal film
667 5322 116 50897 18.2 k
1 MR25 Metal film
668 5322 116 50666 73.2 k
1 MR25 Metal film
669 5322 116 50446 66.5 k 1
MR25 Metal film
Unit 2
601 5322 116 50524
3
k 2
CR25
Carbon
602
5322 116 54148 9.1 k
2
CR25
Carbon
603 5322 116 50859 91
k
2
CR25
Carbon
604 5322 116 54293 4.7 k
2
CR25 Carbon
605 5322 116 64147
3.9 k
2 CR25 Carbon
606 5322 116 54079 36 k 2
CR25
Carbon
607
5322 116 50872
62
k
2
CR25 Carbon
611 5322 11650747
l
k 2
CR25
Carbon
612 5322 116 50603
360 k
2
CR25
Carbon
614 5322 116 54405
750 k
2 CR25 Carbon
615
5322 116 54343
5.1 k
2
CR25 Carbon
616 5322 116 50747 1
k
2 CR25
Carbon
617 5322 116 50603
360
k
2
CR25
Carbon
621 5322 116 50309
24
k
2
CR25 Carbon
623
5322 116 54191
30
k
2
CR25
Carbon
624
5322 116 54171
2.2 k
2
CR25
Carbon
625 5322 116 54089
6.2 k 2
CR25
Carbon
629 5322 116 54343 5.1 k
2
CR25
Carbon
632
4822 100 10035 10 k 20 0.1
w
Potentiometer
635
5322 116 54001 15
k
1
MR25 Metal film
636
5322 116 54202 7.5 k 1
MR25
Metal film
638 4822 100 10029
2.2 k 20 0.1
w
Potentiometer
18
Capacitors
Item
Orderingnumber
Value
%
v
Description
581
5322 122 70069
100
pF
10
350
Lead feed-through
582
5322 122 70069 100
pF
10
350
Lead feed-through
583
4822 , 22 70063 2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
584 4822 122 70063 2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
585
4822 122 70063 2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
586
4822 , 22 70063 2.2
nF
-20/+50 400
Feed-through
587 4822 122 70063 2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed· through
588
4822 122 70063 2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
589 4822 122 70063
2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
590
4822 122 70063
2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
591 4822 122 70063
2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed· through
592
4822 122 70063
2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
593
4822 122 70063
2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
594 4822 122 70063
2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
595 4822 122 70063
2.2
nF
-20/+50
400
Feed-through
Unit 1
596
5322 125 14009
Tuning
501 4822 125 50045 2...22
pF
100
Trimmer
503
4822 125 50045 2...22
pF
100
Trimmer
505
4822 125 50045 2...22
pF
100
Trimmer
507
4822 ,25 50045
2...22
pF
100
Trimmer
508 4822 122 31072 4.7
pF
±0.25
p
100
Ceramic
509 4822 122 31177
470
pF
2
100
Ceramic
510
4822 125 50045 2...22
pF
100
Trimmer
511 4822 122 31061 18
pF
2 100
Ceramic
512 4822 125 60045
2...22
pF
100
Trimmer
514 4822 125 60045 2...22
pF
100
Trimmer
515 4822 122 31061
18
pF
2 100
Ceramic
516
4822 125 60045
2...22
pF
100
Trimmer
518 4822 125 50017 5.5...65
pF
100
Trimmer
5-19
4822 122 31081 100
pF
2
100
Ceramic
520
4822 12231056 12
pF
2 100
Ceramic
521 4822 122 31177
470
pF
2 100
Ceramic
522
4822122 31165 300
pF
2
100
Ceramic
523 5322 122 10107
100
nF
-20/+80
30
Ceramic
524 5322 121 40197
1
µF
20
100
Polyester
525
5322 122 30103
22
nF
-20/+100 40
Ceramic
526
5322 122 30103
22
nF
-20/+100
40
Ceramic
527
4822 122 31211
100
pF
5 400
Ceramic
528 5322 122 10107
100
nF
-20/+80 30
Ceramic
529
5322 12230103
22
nF
-20/+100
40
Ceramic
530
4822 124 20461
47
µF
10
Electrolytic
531 5322 122 30103
22
nF
-20/+100
40
Ceramic
532
5322 122 30103
22
nF
-20/+100 40
Ceramic
533
5322 122 30103 22
nF
-20/+100 40
Ceramic
534 4822 124 20475
10
µF
25
Electrolytic
535
5322 122 30109 1.5
pF
0.25 p
100
Ceramic
536 5322 122 30103
22
nF
-20/+100 40
Ceramic
537 5322 122 10107
100
nF
-20/+80
~o
Ceramic
538 4822 125 50017
5.5...65
pF
100
Trimmer
539
4822 122 31177
470
pF
2
100
Ceramic
19
Item
Orderingnumber Value
%
v Description
540
5322 122 10107 100
nF -20/+80 30 Ceramic
541 5322 122 30103
22 nF
-20/+100
40
Ceramic
542
4822 125 50045 2...22 pF
100 Trimmer
543
4822 122 31063 22
pF
2
100
Ceramic
544 4822 122 31175 1 nF 10
100 Ceramic
545 4822 122 31081
100 pF
2 63
Ceramic
546 5322 122 10107
100
nF
-20/+80 30
Ceramic
547
4822 122 31207
68
pF
10
400 Ceramic
548 4822 122 31207
68
pF
10
400 Ceramic
549 5322 122 10107 100 nF
-20/+80
30 Ceramic
550 4822 122 31207 68
pF
10
400 Ceramic
551 4822 12231165
300
pF
2
100 Ceramic
552
5322 121 40323 100 nF 10
100 Polyester
553 5322 124 24063 1
µF
63
Electrolytic
554
5322 122 10107 100
nF
-20/+80 30
Ceramic
555 4822 124 20476
22
µF
25
Electrolytic
556 4822 124 20461
47 µF
10 Electrolytic
557
5322 122 30103 22
nF
-20/+100
40
Ceramic
558
4822 124 20476 22
µF 25 Ceramic
559 4822 121 40045 22
nF
10
250
Polyester
560
5322 122 10107 100
nF -20/+80 30 Ceramic
561 4822 121 40232 220 nF 20 100
Polyester
562
5322 122 10107
100 nF -20/+80
30
Ceramic
563
4822 122 31211 100 pF
5
400
Ceramic
564 5322 122 30103
22
nF -20/+100
40
Ceramic
565 4822 124 20461 47 µF
10
Electrolytic
566
4822 122 31072 47 pF
2
100 Ceramic
567
4822 124 20463
100
µF
10
Electrolytic
568
5322 122 30103
22
nF -20/+100 40 Ceramic
Unit 2
501 5322 121 40283
3.3µF
10 100 Polyester
502 4822 124 20461 47 µF
10 Electrolytic
503
4822 124 20514
1000
µF
6.3 Electrolytic
504
4822 124 20461
47
µF
10
Electrolytic
505 5322 124 24063 1
µF
63 Electrolytic
506
5322 121 40323
100
nF
10 100
Polyester
507
5322 121 40323
100 nF
10
100 Polyester
508 5322 124 24063
1
µF
63 Electrolytic
509 4822 124 20461
47
µF
10 Electrolytic
510 5322 124 24063
1
µF
63 Electrolytic
511 4822 124 20529
1000
µF
25
Electrolytic
512
4822 124 20529 1000
µF
25
Electrolytic
513
4822 121 50414
3
nF
5 63 Polyester
514 4822 124 20476
22
µ.F
25
Electrolytic
515 4822 122 31175 1
nF 10
100
Ceramic
516 4822 122 31175
1 nF 10 100
Ceramic
20
Miscellaneous
Item
Orderingnumber
Description
391
532221664112
Unit l; printed wiring board
392
5322 216 64113
Unit 2; printed wiring board
393
5322 216 64114
Unit 3; printed wiring board
751
5322 146 24059
Mainstransformer
752
5322 242 74036
Quartz crystal 10 MHz
761
5322 156 14019
Ll, Coil
3.56 rnH
762
5322 156 14021
L2, Coil 366
µH
763 5322 156 14022
L3, Coil
35.6
µH
764
5322 156 14023
L4, Coit
3.66 µH
765
5322 156 14024
L5, Coil 0.3
µH
766
5322 157 44001 L6, Coit
767
5322 15744002 L7, Coil
168
5322 156 14025 LS, Coil
1.58 mH
769
5322 156 14026
L9, Coil
0.94 µH
770
5322 158 14044
Coil
1.5 mH
771
5322 158 10278
Coil 1 mH
772
5322 158 14065
Coil 47 mH
811
5322 13444072 Lamp, 40 rnA
812
5322 134 44072
La[11p,40 mA
813
5322 134 44072 L.amp,40 mA
815 5322 344 6404, Indicator 120µA, Ri=1500
i1
Semi-conductors
Diodes
Type
Orderingnumber
Qty
Location
88106
5322 130 30769 5 Unit 1: 401, 402, 403, 411, 412
BAX13
632213040182
6
Unit 1: 404, 405, 406, 407, 408, 410
AA119
6322 ,30 40229
1 Unit 1: 409
BA217
4822 130 30703 4 Unit 1:413, 414, 415
Unit 2: 402:
BA216
5322 130 30702
1
Unit 2: 401
BZX79-C5V1
5322 130 30767
1
Unit 2: 404
BY164
5322 130 30414 1
Unit 2: 405
fV1V50
5322 13034259
6
Unit 3. 491, 492, 493, 494, 495, 496
Transistors
Type
Orderingnumber Oty
Location
BD135
5322 130 40645
1
311
80136
5322 130 40712
1 314
BFX89 5322 130 40542
8 Unit 1: 301, 302, 304, 308, 309, 310, 311, 312
BFW10
5322 130 40443
1
Unit 1: 303
BF254
5322 130 44117
2
Unit 1: 305, 306
BC238C
5322 13044198
5 Unit 1: 307, 314, 315
Unit 2: 304, 306
BC238
5322 13040758
4
Unit 1: 313
Unit 2: 305, 307, 312
BC308
5322 130 44119
3
Unit 2: 301, 302, 313
21
Integrated circuits
Type
Orderingnumber
Oty Location
FJH131/7400
5322 209 84 143 1
Unit 1: 321
SN7490N 5322 209 84114
2
Unit 1: 322, 323
TAA310A 5322 209 84361
1
Unit1:324
CA3086 5322 209 84111
1 Unit 2: 321
SN72741P
5322 209 84 163
2
Unit 2: 322, 323

22
QUALITY REPORTING
CODING SYSTEM FOR FAILURE DESCRIPTION
The following information ismeant for Philips service workshops only and serves as a guide for exact reporting of
service repairs and maintenance routines on the workshop charts.
For full details reference is made to Information Gl (Introduction) and Information Cd 689 (Specific information for
Test and Measuring Instruments).
LOCATION
ITID
Unit number
e.g. OOOAor 0001 (for unit A or 1; not OOUA
orOOUl)
or: Type number of an accessory (only if delivered
with the equipment)
e.g.
9051or9532 (forPM9051 orPM9532)
or: Unknown/Not applicable
0000
CATEGORY
0
0 Unknown, not applicable (fault not present,
intermittent or disappeared)
Software error
2 Readjustment
3 Electrical repair (wiring, solder joint, etc.)
4 Mechanical repair (polishing, filing, rernachining, etc.)
S
Replacement
6 Cleaning and/ or lubrication
7 Operator error
8 Missing items (on pre-sale test)
9 Environmental requirements are not met
COMPONENT /SEQUENCE NUMBER
1111111
Enter the identification as used in the circuit diagram,
e.g.:
GR1003 Diode GRI003
TS0023 Transistor TS23
ICOIOI
RO .
co .
BO .
LA .
VL. ..
SK .
BU .
TO .
LO .
XO .
CB .
RE .
ME .
BA .
TR .
Integrated circuit
ICIO!
Resistor, potentiometer
Capacitor, variable capacitor
Tube, valve
Lamp
Fuse
Switch
Connector, socket, terminal
Transformer
Coil
Crystal
Circuit block
Relay
Meter, indicator
Battery
Chopper
Parts not identified in the circuit diagram:
990000
990001
990002
990003
990004
990005
990006
990007
990008
990009
990099
Unknown,lNot applicable
Cabinet or rack (text plate, emblem, grip,
rail, graticule, etc.)
Knob (incl. dial knob, cap, etc.)
Probe (only if attached to instrument)
Leads and associated plugs
Holder (valve, transistor, fuse, board, etc.)
Complete unit (p.w. board, h.t. unit, etc.)
Accessory (only those without type number)
Documentation (manual, supplement, etc.)
Foreign object
Miscellaneous
 Loading...
Loading...