Page 1

Colour Television Chassis
LC4.9E
AB
For manual LGE plasma panel see: 3122 785 15590
E_14710_000.eps
240604
Contents Page Contents Page
1. Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis
Overview 2
2. Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes 5
3. Directions for Use 7
4. Mechanical Instructions 8
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 11
6. Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and
Waveforms
Wiring Diagram 21
Block Diagram Supply 22
Block Diagram Video 23
Block Diagram Audio 24
Testpoint Overview SSB (Top Side) 25
Block Diagram IBO Zapper 26
Testpoint Overview IBO Zapper (Bottom Side) 27
I2C Overview 28
Supply Voltage Overview 29
7. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts Diagram PWB
SSB: Tuner and IF (B1)30 53-62
SSB: Hercules (B2)31 53-62
SSB: Sync Interface (B3)32 53-62
SSB: Audio Delay line (Reserved) (B4)33 53-62
SSB: Audio Processing (B5)34 53-62
SSB: DC-DC Converter (B6)35 53-62
SSB: Diversity Tables B1-B6 (B1-6) 36
SSB: Scaler (B7)37 53-62
SSB: Scaler Supply (B8)38 53-62
SSB: Scaler Interface (B9)39 53-62
SSB: SDRAM (B10)40 53-62
SSB: Flash / Control (B11)41 53-62
SSB: HDMI (N.A.) (B12)42 53-62
SSB: MUX Sync Interface (B13)43 53-62
SSB: Digital I/O (B14)44 53-62
SSB: Analog I/O (B15)45 53-62
©
Copyright 2005 Philips Consumer Electronics B.V. Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
SSB: Top Connectors (B16)46 53-62
SSB: Side Connectors (B17)47 53-62
SSB: ADC (B18)48 53-62
SSB: Columbus (B19)49 53-62
SSB: EPLD (B20)50 53-62
SSB: EPLD (B21)51 53-62
SSB: Diversity Tables B9-B21 (B9-21)52
PDP Audio Amplifier Panel (C)63 64
Side I/O Panel (D)65 64
Control Board (E)67 68
LED Panel (J)69 70
IBO Zapper: Mojo (K1) 71 78-79
IBO Zapper: Flash Memory (K2) 72 78-79
IBO Zapper: Power Supply (K3) 73 78-79
IBO Zapper: Interface (K4) 74 78-79
IBO Zapper: Analog Back End (K5) 75 78-79
IBO Zapper: Front End (K6) 76 78-79
IBO Zapper: Common Interface (K7) 77 78-79
8. Alignments 81
9. Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data
Sheets 85
Abbreviation List 87
IC Data Sheets 90
10. Spare Parts List 92
11. Revision List 99
Published by BB 0568 TV Service Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3122 785 15670
Page 2

EN 2 LC4.9E AB1.
Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
1. Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
Index of this chapter:
1.1 Technical Specifications
1.2 Connection Overview
1.3 Chassis Overview
Notes:
• Figures can deviate due to the different set executions.
• Specifications are indicative (subject to change).
1.1 Technical Specifications
1.1.1 Vision
Display type : Plasma
Screen size : 42” (107 cm), 16:9
Resolution (HxV pixels) : 852 x 480
Contrast ratio :
- 42PF5520D/10 : 10,000:1
- 42PF7520D/10 : 13,000:1
Light output (cd/m
Viewing angle (HxV degrees) : 160x160
Tuning system : PLL
Reception standards : Analogue &
TV Colour systems : PAL B/G, D/K, I
Video playback : PAL B/G; SECAM L/L’
Supported computer formats : VGA (640x480)
Supported video formats : 640x480i - 1fH
Presets/channels : 100 presets
Tuner bands : VHF
1.1.2 Sound
Sound systems : FM-mono
Maximum power (W
2
) : 1500
: digital terrestrial TV
: (DVB-T)
: SECAM B/G, D/K, L/L’
: NTSC M/N 3.58, 4.43
: VGA (720x400)
: VGA (720x480)
: MAC (640x480)
: MAC (832x624)
: SVGA (800x600)
: XVGA (1024x768)
: WXGA (1280x768)
: WXGA (1280x960)
: WXGA (1280x1024)
: 720x576i - 1fH
: 640x480p - 2fH
: 720x576p - 2fH
: 852x480p - 2fH
: 1920x1080i - 2fH
: UHF
: S-band
: Hyper-band
: FM-stereo B/G
: NICAM B/G, D/K, I, L
: AV Stereo
) : 2 x 15
RMS
Power consumption
- Normal operation (W) : ≈ 450
- Stand-by (W) : < 2
Dimensions (WxHxD cm) : 124x68x10.4
Weight (kg) : 42
1.2 Connection Overview
Note: The following connector colour abbreviations are used
(acc. to DIN/IEC 757): Bk= Black, Bu= Blue, Gn= Green, Gy=
Grey, Rd= Red, Wh= White, and Ye= Yellow.
1.2.1 Side I/O connections
AudioS-Video Video
LR
E_14710_005.eps
210404
Figure 1-1 Side I/O connections
S-Video (Hosiden): Video Y/C - In
1 -Ground Y Gnd H
2 -Ground C Gnd H
3 - Video Y 1 V
4 - Video C 0.3 V
Cinch: Video CVBS - In, Audio - In
Ye -Video CVBS 1 V
Wh - Audio L 0.5 V
Rd - Audio R 0.5 V
Mini Jack: Audio Head phone - Out
Bk - Head phone 32 - 600 ohm / 10 mW ot
1.2.2 Rear Connections
DVI
18
916
17
24
C1 C2
C3 C4
C5
Audio In
AUDIO
DVIDVI -I
Figure 1-2 Rear I/O
/ 75 ohm j
PP
/ 75 ohm j
PP
/ 75 ohm jq
PP
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
DATA
EXT 2 EXT 1
EXT 2 UART I2CEXT 1
AERIAL IN
SPDIFPCMCIA
ComPair
F_15660_001.eps
280705
1.1.3 Miscellaneous
Power supply:
- Mains voltage (V
) : 220 - 240
AC
- Mains frequency (Hz) : 50 / 60
Ambient conditions:
- Temperature range (°C) : +5 to +40
- Maximum humidity : 90% R.H.
Aerial - In
- - IEC-type (EU) Coax, 75 ohm D
Mini Jack: Audio - In
1 - Ground Gnd H
2 - Audio L 0.5 V
3 - Audio R 0.5 V
Service connector (ComPair)
1 - SDA-S I
2
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
C Data (0 - 5 V) jk
Page 3
Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
EN 3LC4.9E AB 1.
2 - SCL-S I2C Clock (0 - 5 V) j
3 - Ground Gnd H
Service connector (UART)
1 - UART_TX Transmit k
2 - Ground Gnd H
3 - UART_RX Receive j
DVI-I: Digital/Analogue Video - In
18
916
17
C1 C2
C5
24
C3 C4
E_06532_004.eps
050404
Figure 1-3 DVI-I connector
1-D2- j
2-D2+ j
3 - Shield Gnd H
4-D4- j
5-D4+ j
6 - DDC_SCL DDC clock k
7 - DDC_SDA DDC data jk
8 - V-sync 0 - 5 V j
9-D1- j
10 - D1+ j
11 - Shield Gnd H
12 - D3- j
13 - D3+ j
14 - +5V j
15 - Ground Gnd H
16 - HPD Hot Plug Detect j
17 - D0- j
18 - D0+ j
19 - Shield Gnd H
20 - D5- j
21 - D5+ j
22 - Shield Gnd H
23 - CLK+ j
24 - CLK- j
C1 - Video Red 0.7 V
C2 - Video Green 0.7 V
C3 - Video Blue 0.7 V
/ 75 ohm j
PP
/ 75 ohm j
PP
/ 75 ohm j
PP
C4 - H-sync 0 - 5 V j
C5 - Ground Gnd H
15 - Video Red 0.7 V
16 - Status/FBL 0 - 0.4 V: INT
/ 75 ohm j
PP
1 - 3 V: EXT / 75 ohm j
17 - Ground Video Gnd H
18 - Ground FBL Gnd H
19 - Video Terr. CVBS 1 V
20 - Video CVBS/Y 1 V
21 - Shield Gnd H
/ 75 ohm k
PP
/ 75 ohm j
PP
EXT2: Video Y/C - in, CVBS - In/Out, Audio - In/Out
21
20
E_06532_001.eps
2
1
050404
Figure 1-5 SCART connector
1 - Audio R 0.5 V
2 - Audio R 0.5 V
3 - Audio L 0.5 V
4 - Ground Audio Gnd H
/ 1 kohm k
RMS
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
/ 1 kohm k
RMS
5 - Ground Blue Gnd H
6 - Audio L 0.5 V
7-n.c.
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
8 - Function Select 0 - 2 V: INT
4.5 - 7 V: EXT 16:9
9.5 - 12 V: EXT 4:3 j
9 - Ground Green Gnd H
10 - n.c.
11 - n.c.
12 - n.c.
13 - Ground Red Gnd H
14 - Ground Gnd H
15 - YC/C - in 0.7 V
16 - n.c.
/ 75 ohm j
PP
17 - Ground Video Gnd H
18 - Ground Gnd H
19 - Video Mon. CVBS 1 V
20 - YC/Y - in 0.7 V
/ 75 ohm k
PP
/ 75 ohm j
PP
21 - Shield Gnd H
EXT1: Video RGB - In, CVBS - In/Out, Audio - In/Out
21
20
E_06532_001.eps
2
1
050404
Figure 1-4 SCART connector
1 - Audio R 0.5 V
2 - Audio R 0.5 V
3 - Audio L 0.5 V
4 - Ground Audio Gnd H
/ 1 kohm k
RMS
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
/ 1 kohm k
RMS
5 - Ground Blue Gnd H
6 - Audio L 0.5 V
7 - Video Blue 0.7 V
8 - Function Select 0 - 2 V: INT
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
/ 75 ohm j
PP
4.5 - 7 V: EXT 16:9
9.5 - 12 V: EXT 4:3 j
9 - Ground Green Gnd H
10 - n.c.
11 - Video Green 0.7 V
12 - n.c.
/ 75 ohm j
PP
13 - Ground Red Gnd H
14 - Ground Gnd H
Page 4
EN 4 LC4.9E AB1.
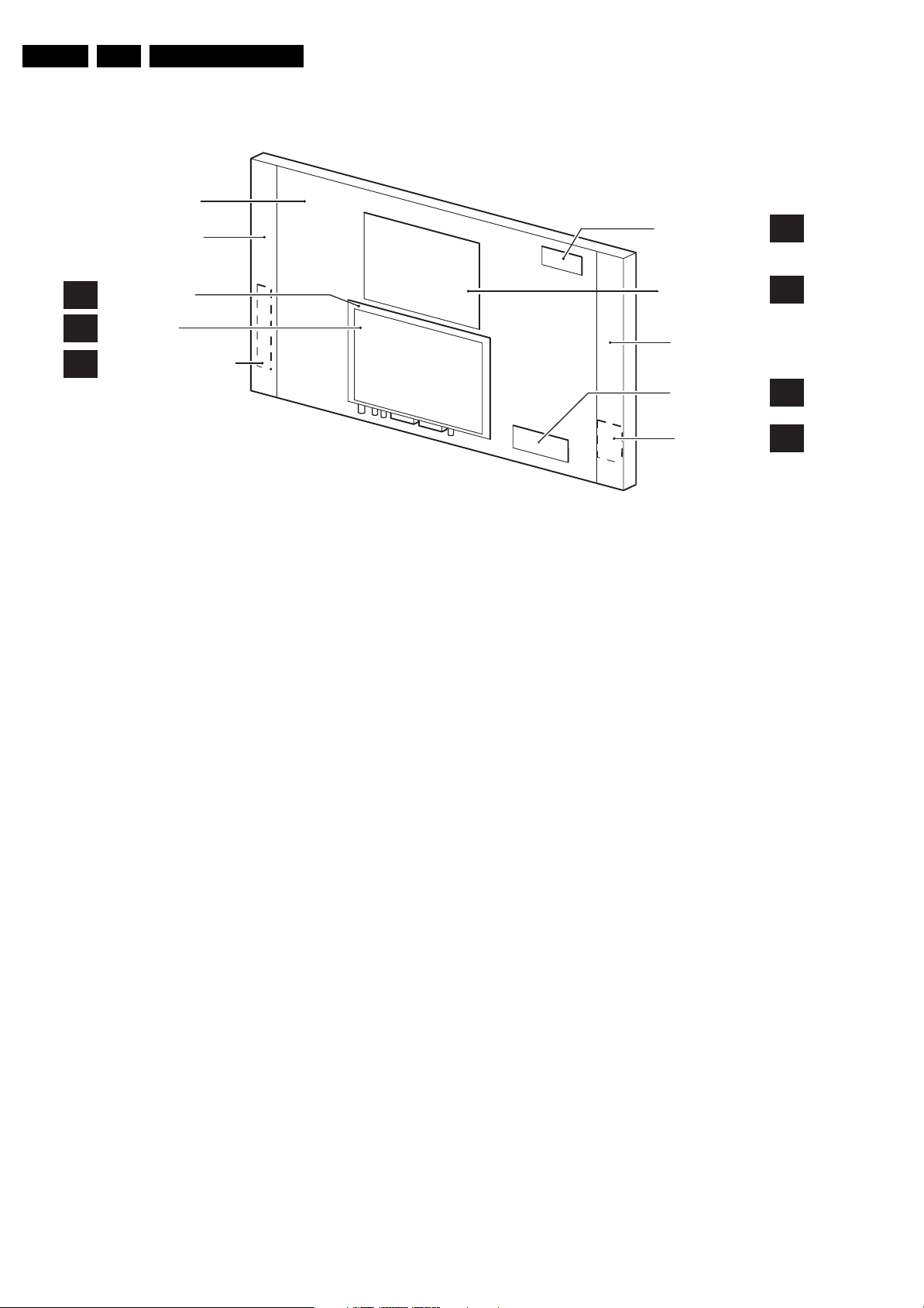
1.3 Chassis Overview
PLASMA
DISPLAY PANEL
LOUDSPEAKER
COMPARTMENT
Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
PDP AUDIO
AMPLIFIER PANEL
C
SMALL SIGNAL
B
BOARD
IBO ZAPPER
K
KEYBOARD CONTROL
E
PANEL
Figure 1-6 PWB locations
POWER SUPPLY
PANEL
LOUDSPEAKER
COMPARTMENT
IR & LED PANEL
SIDE I/O PANEL
F_15670_001.eps
A
J
D
010805
Page 5

Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
2. Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
EN 5LC4.9E AB 2.
Index of this chapter:
2.1 Safety Instructions
2.2 Warnings
2.3 Notes
2.1 Safety Instructions
Safety regulations require the following during a repair:
• Connect the set to the Mains (AC Power) via an isolation
transformer (> 800 VA).
• Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol h,
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type) may
increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard.
Safety regulations require that after a repair, the set must be
returned in its original condition. Pay in particular attention to
the following points:
• Route the wire trees correctly and fix them with the
mounted cable clamps.
• Check the insulation of the Mains (AC Power) lead for
external damage.
• Check the strain relief of the Mains (AC Power) cord for
proper function.
• Check the electrical DC resistance between the Mains (AC
Power) plug and the secondary side (only for sets that have
a Mains (AC Power) isolated power supply):
1. Unplug the Mains (AC Power) cord and connect a wire
between the two pins of the Mains (AC Power) plug.
2. Set the Mains (AC Power) switch to the "on" position
(keep the Mains (AC Power) cord unplugged!).
3. Measure the resistance value between the pins of the
Mains (AC Power) plug and the metal shielding of the
tuner or the aerial connection on the set. The reading
should be between 4.5 Mohm and 12 Mohm.
4. Switch "off" the set, and remove the wire between the
two pins of the Mains (AC Power) plug.
• Check the cabinet for defects, to prevent touching of any
inner parts by the customer.
2.3 Notes
2.3.1 General
• Measure the voltages and waveforms with regard to the
chassis (= tuner) ground (H), or hot ground (I), depending
on the tested area of circuitry. The voltages and waveforms
shown in the diagrams are indicative. Measure them in the
Service Default Mode (see chapter 5) with a colour bar
signal and stereo sound (L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated
otherwise) and picture carrier at 475.25 MHz for PAL, or
61.25 MHz for NTSC (channel 3).
• Where necessary, measure the waveforms and voltages
with (D) and without (E) aerial signal. Measure the
voltages in the power supply section both in normal
operation (G) and in stand-by (F). These values are
indicated by means of the appropriate symbols.
• The semiconductors indicated in the circuit diagram and in
the parts lists, are interchangeable per position with the
semiconductors in the unit, irrespective of the type
indication on these semiconductors.
2.3.2 Schematic Notes
• All resistor values are in ohms, and the value multiplier is
often used to indicate the decimal point location (e.g. 2K2
indicates 2.2 kohm).
• Resistor values with no multiplier may be indicated with
either an "E" or an "R" (e.g. 220E or 220R indicates 220
ohm).
• All capacitor values are given in micro-farads (µ= x10
nano-farads (n= x10
• Capacitor values may also use the value multiplier as the
decimal point indication (e.g. 2p2 indicates 2.2 pF).
• An "asterisk" (*) indicates component usage varies. Refer
to the diversity tables for the correct values.
• The correct component values are listed in the Spare Parts
List. Therefore, always check this list when there is any
doubt.
-9
), or pico-farads (p= x10
-12
-6
),
).
2.2 Warnings
• All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
electrostatic discharges (ESD w). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are connected with the same potential as
the mass of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools also at this same potential. Available
ESD protection equipment:
– Complete kit ESD3 (small tablemat, wristband,
connection box, extension cable and earth cable) 4822
310 10671.
– Wristband tester 4822 344 13999.
• Be careful during measurements in the high voltage
section.
• Never replace modules or other components while the unit
is switched "on".
• When you align the set, use plastic rather than metal tools.
This will prevent any short circuits and the danger of a
circuit becoming unstable.
2.3.3 Rework on BGA (Ball Grid Array) ICs
General
Although (LF)BGA assembly yields are very high, there may
still be a requirement for component rework. By rework, we
mean the process of removing the component from the PWB
and replacing it with a new component. If an (LF)BGA is
removed from a PWB, the solder balls of the component are
deformed drastically so the removed (LF)BGA has to be
discarded.
Device Removal
As is the case with any component that, is being removed, it is
essential when removing an (LF)BGA, that the board, tracks,
solder lands, or surrounding components are not damaged. To
remove an (LF)BGA, the board must be uniformly heated to a
temperature close to the reflow soldering temperature.
A uniform temperature reduces the risk of warping the PWB. To
do this, we recommend that the board is heated until it is certain
that all the joints are molten. Then carefully pull the component
off the board with a vacuum nozzle. For the appropriate
temperature profiles, see the IC data sheet.
Area Preparation
When the component has been removed, the vacant IC area
must be cleaned before replacing the (LF)BGA.
Removing an IC often leaves varying amounts of solder on the
mounting lands. This excessive solder can be removed with
either a solder sucker or solder wick. The remaining flux can be
removed with a brush and cleaning agent.
Page 6

EN 6 LC4.9E AB2.
Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
After the board is properly cleaned and inspected, apply flux on
the solder lands and on the connection balls of the (LF)BGA.
Note: Do not apply solder paste, as this has been shown to
result in problems during re-soldering.
Device Replacement
The last step in the repair process is to solder the new
component on the board. Ideally, the (LF)BGA should be
aligned under a microscope or magnifying glass. If this is not
possible, try to align the (LF)BGA with any board markers.
So as not to damage neighbouring components, it may be
necessary to reduce some temperatures and times.
More Information
For more information on how to handle BGA devices, visit this
URL: www.atyourservice.ce.philips.com (needs subscription,
not available for all regions). After login, select “Magazine”,
then go to “Workshop Information”. Here you will find
Information on how to deal with BGA-ICs.
2.3.4 Lead-free Solder
Philips CE is producing lead-free sets (PBF) from 1.1.2005
onwards.
Identification: The bottom line of a type plate gives a 14-digit
serial number. Digits 5 and 6 refer to the production year, digits
7 and 8 refer to production week (in example below it is 1991
week 18).
To avoid wear-out of tips, switch “off” unused equipment or
reduce heat.
• Mix of lead-free soldering tin/parts with leaded soldering
tin/parts is possible but PHILIPS recommends strongly to
avoid mixed regimes. If this cannot be avoided, carefully
clear the solder-joint from old tin and re-solder with new tin.
• Use only original spare-parts listed in the Service-Manuals.
Not listed standard material (commodities) has to be
purchased at external companies.
• Special information for lead-free BGA ICs: these ICs will be
delivered in so-called "dry-packaging" to protect the IC
against moisture. This packaging may only be opened
shortly before it is used (soldered). Otherwise the body of
the IC gets "wet" inside and during the heating time the
structure of the IC will be destroyed due to high (steam-)
pressure inside the body. If the packaging was opened
before usage, the IC has to be heated up for some hours
(around 90°C) for drying (think of ESD-protection!).
Do not re-use BGAs at all!
• For sets produced before 1.1.2005, containing leaded
soldering tin and components, all needed spare parts will
be available till the end of the service period. For the repair
of such sets nothing changes.
In case of doubt whether the board is lead-free or not (or with
mixed technologies), you can use the following method:
• Always use the highest temperature to solder, when using
SAC305 (see also instructions below).
• De-solder thoroughly (clean solder joints to avoid the
mixing of two alloys).
E_06532_024.eps
230205
Figure 2-1 Serial number example
Regardless of the special lead-free logo (which is not always
indicated), one must treat all sets from this date onwards
according to the rules as described below.
P
b
Figure 2-2 Lead-free logo
Due to lead-free technology some rules have to be respected
by the workshop during a repair:
• Use only lead-free soldering tin Philips SAC305 with order
code 0622 149 00106. If lead-free solder paste is required,
please contact the manufacturer of your soldering
equipment. In general, use of solder paste within
workshops should be avoided because paste is not easy to
store and to handle.
• Use only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free
soldering tin. The solder tool must be able:
– To reach a solder-tip temperature of at least 400°C.
– To stabilise the adjusted temperature at the solder-tip.
– To exchange solder-tips for different applications.
• Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature of around
360°C - 380°C is reached and stabilised at the solder joint.
Heating time of the solder-joint should not exceed ~ 4 sec.
Avoid temperatures above 400°C, otherwise wear-out of
tips will increase drastically and flux-fluid will be destroyed.
Caution: For BGA-ICs, you must use the correct temperature
profile, which is coupled to the 12NC. For an overview of these
profiles, visit the website www.atyourservice.ce.philips.com
(needs subscription, but is not available for all regions).
You will find this and more technical information within the
"Magazine", chapter "Workshop information".
For additional questions please contact your local repair help
desk.
2.3.5 Practical Service Precautions
• It makes sense to avoid exposure to electrical shock.
While some sources are expected to have a possible
dangerous impact, others of quite high potential are of
limited current and are sometimes held in less regard.
• Always respect voltages. While some may not be
dangerous in themselves, they can cause unexpected
reactions that are best avoided. Before reaching into a
powered TV set, it is best to test the high voltage insulation.
It is easy to do, and is a good service precaution.
Page 7

3. Directions for Use
You can download this information from the following websites:
http://www.philips.com/support
http://www.p4c.philips.com
Directions for Use
EN 7LC4.9E AB 3.
Page 8
EN 8 LC4.9E AB4.
Mechanical Instructions
4. Mechanical Instructions
Index of this chapter:
4.1 Cable Dressing
4.2 Service Positions
4.3 Assy/Panel Removal
4.4 Set Re-assembly
4.1 Cable Dressing
Notes:
• Figures below can deviate slightly from the actual situation,
due to the different set executions.
• Follow the disassembling instructions in described order.
4.2 Service Positions
For easy servicing of this set, there are a few possibilities
created:
• The buffers from the packaging (see figure "Rear cover").
• Foam bars (created for service).
• Aluminium service stands (created for Service).
4.2.1 Foam Bars
E_06532_018.eps
Figure 4-2 Foam bars
Figure 4-1 Cable dressing
170504
F_15660_007.eps
280705
The foam bars (order code 3122 785 90580 for two pieces) can
be used for all types and sizes of Flat TVs. By laying the TV
face down on the (ESD protective) foam bars, a stable situation
is created to perform measurements and alignments.
By placing a mirror under the TV, you can monitor the screen.
4.2.2 Aluminium Stands
E_06532_019.eps
170504
Figure 4-3 Aluminium stands (drawing of MkI)
Page 9
The aluminium stands (order code 3122 785 90480) can be
mounted with the back cover removed or still left on. So, the
stand can be used to store products or to do measurements. It
is also very suitable to perform duration tests without taking
much space, without having the risk of overheating, or the risk
of products falling. The stands can be mounted and removed
quick and easy with use of the delivered screws that can be
tightened and loosened manually without the use of tools. See
figure above.
Note: Only use the delivered screws to mount the monitor to
the stands.
4.3 Assy/Panel Removal
4.3.1 Rear Cover
3
3
4
3
3
4
3
Figure 4-4 Rear cover
1
2
3
4
4
F_15420_034.eps
Mechanical Instructions
3
3
3
070605
EN 9LC4.9E AB 4.
1
F_15660_010.eps
280705
Figure 4-6 DVI-I & SPDIF connector screws
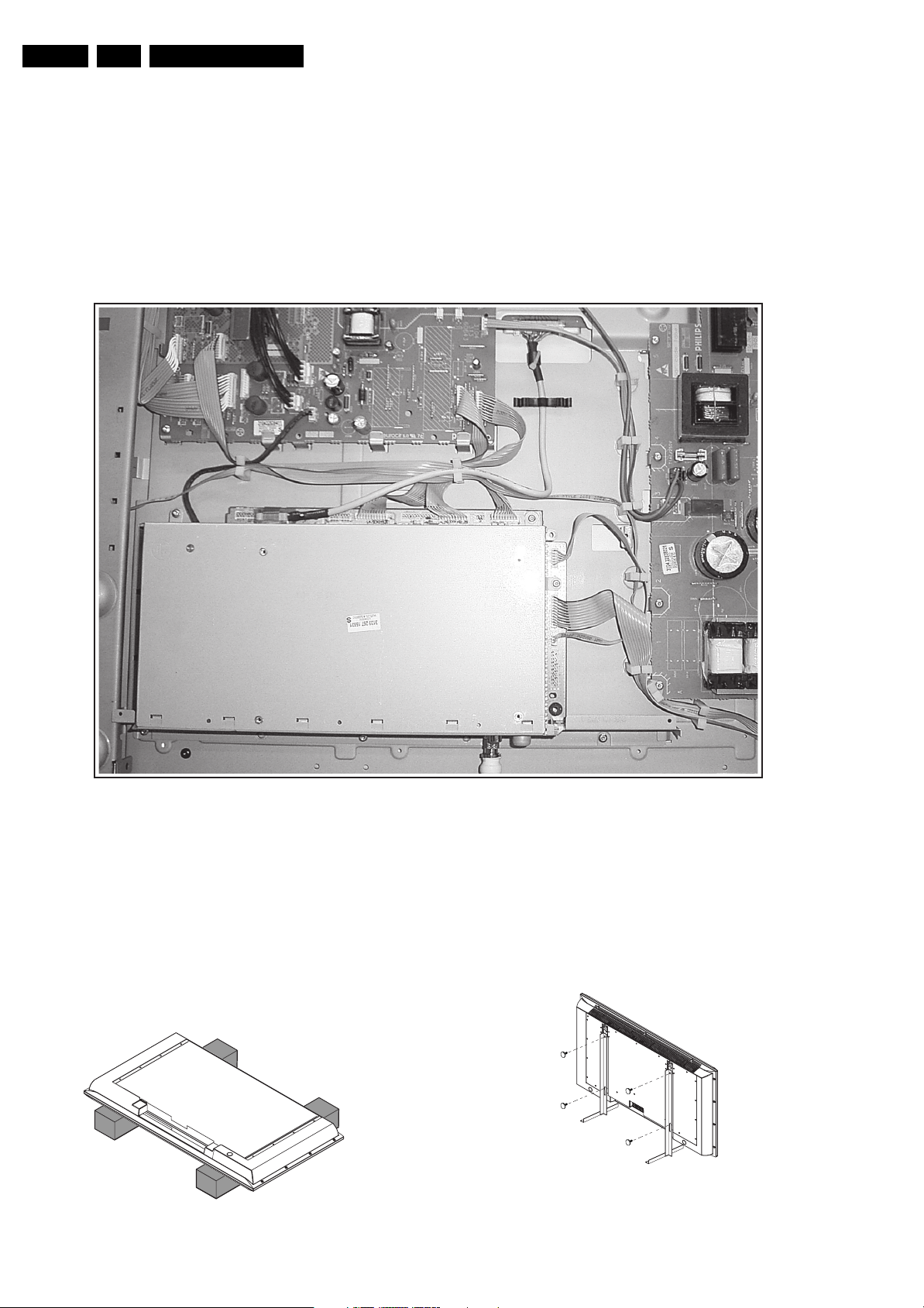
1. Very cautiously disconnect the LVDS cable (1) from the
SSB panel (see Figure “Cover shield”). Notice that this
cable is very fragile.
2. Unplug the black cable coming from the IBO zapper/SSB
board from the Audio/STBY board (see Figure “Cover
shield”).
3. Remove all other cables (2) from the IBO zapper/SSB
board (see Figure “Cover shield”).
4. Remove the 5 fixation screws that connect the top
shielding with the bottom shielding, and also the 2 fixation
screws that connect it with the rear connector plate, see
Figure “Cover shield”.
5. Remove the fixation screws from the DVI-I connector and
from the SPDIF connector, see Figure “DVI-I & SPDIF
connector screws (1)”.
6. Remove the upper part of the shield (with the IBO zapper
attached to it) from the lower part of the shield (on which
the SSB board is located), by unhooking it from its
brackets. Be careful not to damage the LVDS connector on
the SSB board, see Figure “Cover shield”.
7. Finally, remove the IBO zapper (attached to the top
shielding with 4 screws), and the SSB board (attached to
the lower shielding with 2 screws), see Figure “IBO zapper
& SSB board”.
Warning: Disconnect the mains power cord before you remove
the rear cover.
1. Remove the screws that secure the rear cover (see Figure
“Rear cover screws”); these are:
a) 4 x big torx screws (1) for securing the stand/wall mount;
b) 5 x small torx screws (2) near the rear I/O panel;
c) 22 x small torx screws (3) that secure the loudspeaker
compartments [6 of these screws are in sunken holes (4) ]
and along the edges of the rear cover.
2. Lift the rear cover from the cabinet cautiously. Make sure
that wires and other internal components are not damaged
during cover removal.
4.3.2 Cover Shield for IBO-zapper & SSB
1
2
3
F_15660_008.eps
280705
3
Figure 4-7 IBO-zapper & SSB
Figure 4-5 Cover shield
F_15660_009.eps
280705
Page 10

EN 10 LC4.9E AB4.
4.4 Set Re-assembly
To re-assemble the whole set, execute all processes in reverse
order.
Notes:
• While re-assembling, make sure that all cables are placed
and connected in their original positions. See Figure "Cable
dressing". Be careful with the fragile LVDS cable.
• For a complete description of the Plasma panel, see the
LGE plasma panel Service Manual (12nc is listed on the
frontpage).
Mechanical Instructions
Page 11
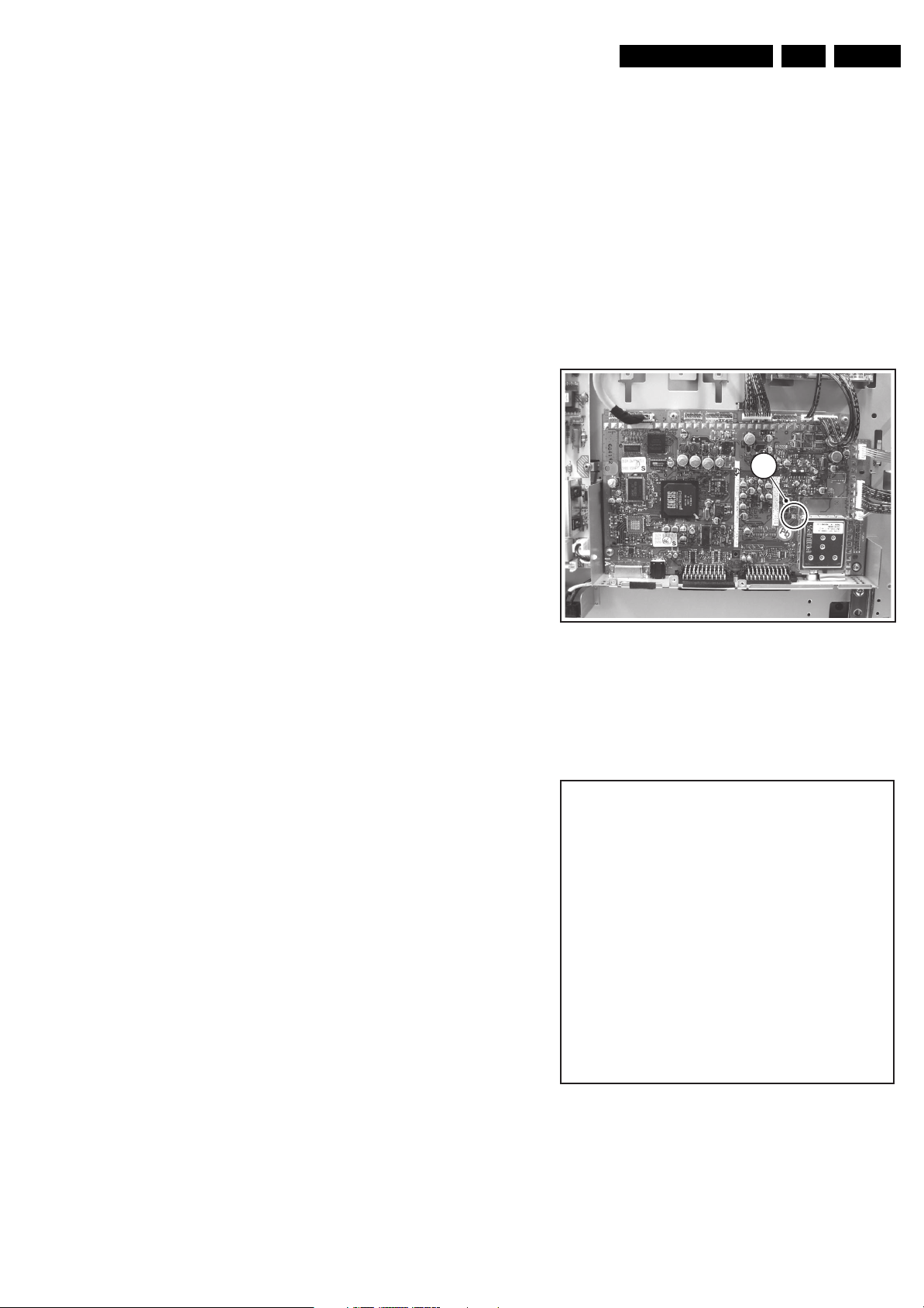
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 11LC4.9E AB 5.
Index of this chapter:
5.1 Test Points
5.2 Service Modes
5.3 Problems and Solving Tips Related to CSM
5.4 Service Tools
5.5 Error Codes
5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure
5.7 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
5.1 Test Points
This chassis is equipped with test points in the service printing.
In the schematics test points are identified with a rectangle box
around Fxxx or Ixxx.
Perform measurements under the following conditions:
• Television set in Service Default Alignment Mode.
• Video input: Colour bar signal.
• Audio input: 3 kHz left channel, 1 kHz right channel.
5.2 Service Modes
Service Default mode (SDM) & Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
offers several features for the service technician, while the
Customer Service Mode (CSM) & Digital Customer Service
Mode (DCSM) are used for communication between the call
centre and the customer.
This chassis also offers the option of using ComPair, a
hardware interface between a computer and the TV chassis. It
offers the possibilities of structured troubleshooting, error code
reading, and software version readout for all chassis.
Minimum requirements for ComPair: a Pentium processor, a
Windows OS, and a CD-ROM drive (see also paragraph
"ComPair").
5.2.1 Service Default Mode (SDM)
Purpose
• To create a predefined setting for measurements to be
made.
• To override software protections.
• To start the blinking LED procedure.
• To inspect the error buffer.
• To check the life timer.
How to Enter
To enter SDM, use one of the following methods:
• Press the following key sequence on the remote control
transmitter: “062596” directly followed by the MENU button
(do not allow the display to time out between entries while
keying the sequence).
• Short "Service" jumpers on the TV board during cold start
and apply mains (see Figure "Service jumpers"). Then
press the mains button (remove the short after start-up).
Caution: Entering SDM by shorting "Service" jumpers will
override the +8V-protection. Do this only for a short period.
When doing this, the service-technician must know exactly
what he is doing, as it could damage the television set.
• Or via ComPair.
1
F_15270_053.eps
180505
Figure 5-1 Service jumpers
After entering SDM, the following screen is visible, with SDM in
the upper right corner of the screen to indicate that the
television is in Service Default Mode.
00035 LC4XEP1 1.14/S4XGNV 1.17 SDM
ERR 0 0 0 0 0
OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
Specifications
• Tuning frequency: 475.25 MHz.
• Colour system: PAL-BG.
• All picture settings at 50% (brightness, colour contrast,
hue).
• Bass, treble, and balance at 50 %; volume at 25 %.
• All service-unfriendly modes (if present) are disabled. The
service unfriendly modes are:
– Timer / Sleep timer.
– Child / parental lock.
– Blue mute.
– Hotel / hospital mode.
– Auto shut off (when no “IDENT” video signal is
received for 15 minutes).
– Skipping of non-favourite presets / channels.
– Auto-storage of personal presets.
– Auto user menu time-out.
– Auto Volume Levelling (AVL).
Figure 5-2 SDM menu
F_15430_039.eps
080605
Page 12
EN 12 LC4.9E AB5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
How to Navigate
Use one of the following methods:
• When you press the MENU button on the remote control,
the set will switch on the normal user menu in the SDM
mode.
• On the TV, press and hold the VOLUME DOWN and press
the CHANNEL DOWN for a few seconds, to switch from
SDM to SAM and reverse.
How to Exit
Switch the set to STANDBY by pressing the mains button on
the remote control transmitter or the television set.
If you turn the television set off by removing the mains (i.e.,
unplugging the television) without using the mains button, the
television set will remain in SDM when mains is re-applied, and
the error buffer is not cleared.
5.2.2 Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
Purpose
• To change option settings.
• To display / clear the error code buffer.
• To perform alignments.
Specifications
• Operation hours counter (maximum five digits displayed).
• Software version, Error codes, and Option settings display.
• Error buffer clearing.
• Option settings.
• AKB switching.
• Software alignments (Tuner, White Tone, Geometry &
Audio).
• NVM Editor.
• ComPair Mode switching.
How to Enter
To enter SAM, use one of the following methods:
• Press the following key sequence on the remote control
transmitter: “062596" directly followed by the OSD/
STATUS/INFO(I+) button (do not allow the display to time
out between entries while keying the sequence).
• Or via ComPair.
After entering SAM, the following screen is visible, with SAM in
the upper right corner of the screen to indicate that the
television is in Service Alignment Mode.
00035 LC4XEP1 1.14/S4XGNV 1.17 SAM
ERR 0 0 0 0 0
OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
. Clear Clear ?
. Options
. Tuner
. White Tone
. Audio
. NVM Editor
. SC NVM Editor
. ComPair Mode On
Figure 5-3 SAM menu
F_15430_040.eps
080605
Menu Explanation
1. LLLLL. This represents the run timer. The run timer counts
normal operation hours, but does not count standby hours.
2. AAABCD-X.Y. This is the software identification of the
main microprocessor:
– A= the project name (LC04.x).
– B= the region: E= Europe, A= Asia Pacific, U= NAFTA,
L= LATAM.
– C= the software diversity:
• Europe: T= 1 page TXT, F= Full TXT, V= Voice
control.
• LATAM and NAFTA: N= Stereo non-dBx, S=
Stereo dBx.
• Asian Pacific: T= TXT, N= non-TXT, C= NTSC.
• ALL regions: M= mono, D= DVD, Q= Mk2.
– D= the language cluster number.
– X= the main software version number (updated with a
major change that is incompatible with previous
versions).
– Y= the sub software version number (updated with a
minor change that is compatible with previous
versions).
3. EEEEE-F.GG. This is the software identification of the
Scaler:
– EEEEEE= the scaler sw cluster
– F= the main sw version no.
– GG= the sub-version no.
4. SAM. Indication of the Service Alignment Mode.
5. Error Buffer. Shows all errors detected since the last time
the buffer was erased. Five errors possible.
6. Option Bytes. Used to set the option bytes. See “Options”
in the Alignments section for a detailed description. Seven
codes are possible.
7. Clear. Erases the contents of the error buffer. Select the
CLEAR menu item and press the MENU RIGHT key. The
content of the error buffer is cleared.
8. Options. Used to set the option bits. See “Options” in the
Alignments section for a detailed description.
9. Tuner. Used to align the tuner. See “Tuner” in the
Alignments section for a detailed description.
10. White Tone. Used to align the white tone. See “White
Tone” in the Alignments section for a detailed description.
11. Audio. No audio alignment is necessary for this television
set.
12. NVM Editor. Can be used to change the NVM data in the
television set. See table “NVM data” further on.
13. SC NVM Editor. Can be used to edit Scaler NVM.
14. ComPaIr. Can be used to switch on the television to In
System Programming (ISP) mode, for software uploading
via ComPair.
Caution: When this mode is selected without ComPair
connected, the TV will be blocked. Remove the AC power
to reset the TV.
How to Navigate
• In SAM, select menu items with the MENU UP/DOWN keys
on the remote control transmitter. The selected item will be
highlighted. When not all menu items fit on the screen, use
the MENU UP/DOWN keys to display the next / previous
menu items.
• With the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys, it is possible to:
– Activate the selected menu item.
– Change the value of the selected menu item.
– Activate the selected submenu.
• In SAM, when you press the MENU button twice, the set
will switch to the normal user menus (with the SAM mode
still active in the background). To return to the SAM menu
press the MENU or STATUS/EXIT button.
• When you press the MENU key in while in a submenu, you
will return to the previous menu.
Page 13

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 13LC4.9E AB 5.
How to Store SAM Settings
To store the settings changed in SAM mode, leave the top level
SAM menu by using the POWER button on the remote control
transmitter or the television set.
How to Exit
Switch the set to STANDBY by pressing the mains button on
the remote control transmitter or the television set.
If you turn the television set “off” by removing the mains (i.e.,
unplugging the television) without using the mains button, the
television set will remain in SAM when mains is re-applied, and
the error buffer is not cleared.
5.2.3 Customer Service Mode (CSM)
Purpose
The Customer Service Mode shows error codes and
information on the TV’s operation settings. The call centre can
instruct the customer (by telephone) to enter CSM in order to
identify the status of the set. This helps the call centre to
diagnose problems and failures in the TV set before making a
service call.
The CSM is a read-only mode; therefore, modifications are not
possible in this mode.
How to Enter
To enter CSM, press the following key sequence on the remote
control transmitter: “123654” (do not allow the display to time
out between entries while keying the sequence).
Upon entering the Customer Service Mode, the following
screen will appear:
1 00035 LC4XEP1 1.14/S4XGNV 1.17 CSM
2 CODES 0 0 0 0 0
3 OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
4
5
6 NOT TUNED
7 PAL
8 STEREO
9 CO 50 CL 50 BR 50
0 AVL Off
8. Displays the detected Audio (e.g. stereo/mono).
9. Displays the picture setting information.
10. Displays the sound setting information.
How to Exit
To exit CSM, use one of the following methods:
• Press the MENU, STATUS/EXIT, or POWER button on the
remote control transmitter.
• Press the POWER button on the television set.
5.2.4 Digital Customer Service Mode (DCSM)
Purpose
The Digital Customer Service Mode shows error codes and
information on the IBO Zapper module operation settings. The
call centre can instruct the customer to activate DCSM by
telephone and read off the information displayed. This helps
the call centre to diagnose problems and failures in the IBO
Zapper module before making a service call.
The DCSM is a read-only mode; therefore, modifications are
not possible in this mode.
How to activate
To activate the DCSM, put the television in its digital mode (via
the A/D button on the remote control).
1. Press the “Digital” Menu button on the remote control to
activate the digital user menu (“Setup”).
2. Activate the “Information” sub menu ( via the “down” and
“right” cursor buttons).
3. In the “Information” sub menu, press the following buttons
on the remote control to activate the DCSM:
“GREEN RED YELLOW 9 7 5 9”. Then, the “Service menu”
will appear (see figures below).
Menu explanation
F_15430_040.eps
080605
Figure 5-4 CSM menu
Menu Explanation
1. Indication of the decimal value of the operation hours
counter, Software identification of the main microprocessor
(see "Service Default or Alignment Mode" for an
explanation), and the service mode (CSM = Customer
Service Mode).
2. Displays the last five errors detected in the error code
buffer.
3. Displays the option bytes.
4. Displays the type number version of the set.
5. Reserved item for P3C call centres (AKBS stands for
Advanced Knowledge Base System).
6. Indicates the television is receiving an "IDENT" signal on
the selected source. If no "IDENT" signal is detected, the
display will read "NOT TUNED"
7. Displays the detected Colour system (e.g. PAL/NTSC).
Figure 5-5 DCSM menu - 1
E_14970_040.eps
090904
Page 14

EN 14 LC4.9E AB5.
Figure 5-6 DCSM menu - 2
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5.3 Problems and Solving Tips Related to CSM
5.3.1 Picture Problems
Note: The problems described below are all related to the TV
settings. The procedures used to change the value (or status)
of the different settings are described.
Picture too Dark or too Bright
If:
• The picture improves when you press the AUTO PICTURE
button on the remote control transmitter, or
• The picture improves when you enter the Customer
E_14970_041.eps
100904
E_14970_042.eps
090904
Service Mode,
Then:
1. Press the AUTO PICTURE button on the remote control
transmitter repeatedly (if necessary) to choose
PERSONAL picture mode.
2. Press the MENU button on the remote control transmitter.
This brings up the normal user menu.
3. In the normal user menu, use the MENU UP/DOWN keys
to highlight the PICTURE sub menu.
4. Press the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to enter the PICTURE
sub menu.
5. Use the MENU UP/DOWN keys (if necessary) to select
BRIGHTNESS.
6. Press the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to increase or
decrease the BRIGHTNESS value.
7. Use the MENU UP/DOWN keys to select PICTURE.
8. Press the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to increase or
decrease the PICTURE value.
9. Press the MENU button on the remote control transmitter
twice to exit the user menu.
10. The new PERSONAL preference values are automatically
stored.
Figure 5-7 DCSM menu - 3
1. Hardware version: This indicates the version of the IBO
Zapper module hardware.
2. Application SW: The application software version.
3. NOR Version: The NOR Flash image software version
4. Digital Frequency: The digital frequency that the set is
tuned to.
5. Bit Error Rate: The error rate measured before the error
correction algorithm circuitry. (this value gives an
impression of the received signal)
6. Tuner AGC: Tuner AGC value.
7. COFDM Lock: Indication if COFDM decoder is locked.
8. AFD Status: Status of the Active Picture Format
Descriptor.
9. Terrestrial Delivery System Parameters:
– Bandwidth: Bandwidth of the received signal.
– Constellation Pattern: Displays the signal
constellation.
– Alpha Value: Displays the Alpha Value.
– FEC Scheme: Displays the Forward Error Correcting
Scheme
– Guard Interval: Displays the value for the Guard
Interval.
– Transmission Mode: Displays the Transmission
Mode.
10. Audio Comp Type: Type of detected audio stream.
11. MHEG Present: Indicates if MHEG is present or not.
12. CIM Card Present: Indicates if CIM card is present or not.
How to exit
Press the BLUE button on the Remote Control to exit DCSM.
White Line around Picture Elements and Text
If:
The picture improves after you have pressed the AUTO
PICTURE button on the remote control transmitter,
Then:
1. Press the AUTO PICTURE button on the remote control
transmitter repeatedly (if necessary) to choose
PERSONAL picture mode.
2. Press the MENU button on the remote control transmitter.
This brings up the normal user menu.
3. In the normal user menu, use the MENU UP/DOWN keys
to highlight the PICTURE sub menu.
4. Press the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to enter the PICTURE
sub menu.
5. Use the MENU UP/DOWN keys to select SHARPNESS.
6. Press the MENU LEFT key to decrease the SHARPNESS
value.
7. Press the MENU button on the remote control transmitter
twice to exit the user menu.
8. The new PERSONAL preference value is automatically
stored.
Snowy Picture
Check CSM line 6. If this line reads “Not Tuned”, check the
following:
• Antenna not connected. Connect the antenna.
• No antenna signal or bad antenna signal. Connect a proper
antenna signal.
• The tuner is faulty (in this case line 2, the Error Buffer line,
will contain error number 10). Check the tuner and replace/
repair the tuner if necessary.
Page 15

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 15LC4.9E AB 5.
Black and White Picture
If:
• The picture improves after you have pressed the AUTO
PICTURE button on the remote control transmitter,
Then:
1. Press the AUTO PICTURE button on the remote control
transmitter repeatedly (if necessary) to choose
PERSONAL picture mode.
2. Press the MENU button on the remote control transmitter.
This brings up the normal user menu.
3. In the normal user menu, use the MENU UP/DOWN keys
to highlight the PICTURE sub menu.
4. Press the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to enter the PICTURE
sub menu.
5. Use the MENU UP/DOWN keys to select COLOR.
6. Press the MENU RIGHT key to increase the COLOR value.
7. Press the MENU button on the remote control transmitter
twice to exit the user menu.
8. The new PERSONAL preference value is automatically
stored.
Menu Text not Sharp Enough
If:
• The picture improves after you have pressed the AUTO
PICTURE button on the remote control transmitter,
Then:
1. Press the AUTO PICTURE button on the remote control
transmitter repeatedly (if necessary) to choose
PERSONAL picture mode.
2. Press the MENU button on the remote control transmitter.
This brings up the normal user menu.
3. In the normal user menu, use the MENU UP/DOWN keys
to highlight the PICTURE sub menu.
4. Press the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys to enter the PICTURE
sub menu.
5. Use the MENU UP/DOWN keys to select PICTURE.
6. Press the MENU LEFT key to decrease the PICTURE
value.
7. Press the MENU button on the remote control transmitter
twice to exit the user menu.
8. The new PERSONAL preference value is automatically
stored.
Specifications
ComPair consists of a Windows based fault finding program
and an interface box between PC and the (defective) product.
The ComPair interface box is connected to the PC via a serial
(or RS-232) cable.
For this chassis, the ComPair interface box and the TV
communicate via a bi-directional service cable via the service
connector(s).
The ComPair faultfinding program is able to determine the
problem of the defective television. ComPair can gather
diagnostic information in two ways:
• Automatically (by communicating with the television):
ComPair can automatically read out the contents of the
entire error buffer. Diagnosis is done on I
ComPair can access the I
ComPair can send and receive I
2
C/UART bus of the television.
2
2
C/UART level.
C/UART commands to
the microcontroller of the television. In this way, it is
possible for ComPair to communicate (read and write) to
devices on the I
2
C/UART buses of the TV-set.
• Manually (by asking questions to you): Automatic
diagnosis is only possible if the microcontroller of the
television is working correctly and only to a certain extent.
When this is not the case, ComPair will guide you through
the faultfinding tree by asking you questions (e.g. Does the
screen give a picture? Click on the correct answer: YES /
NO) and showing you examples (e.g. Measure test-point I7
and click on the correct oscillogram you see on the
oscilloscope). You can answer by clicking on a link (e.g.
text or a waveform picture) that will bring you to the next
step in the faultfinding process.
By a combination of automatic diagnostics and an interactive
question / answer procedure, ComPair will enable you to find
most problems in a fast and effective way.
How To Connect
This is described in the chassis faultfinding database in
ComPair.
Caution: It is compulsory to connect the TV to the PC as
shown in the picture below (with the ComPair interface in
between), as the ComPair interface acts as a level shifter. If
one connects the TV directly to the PC (via UART), ICs will be
blown!
TO
UART SERVICE
CONNECTOR
TO
I2C SERVICE
CONNECTOR
5.4 Service Tools
5.4.1 ComPair
Introduction
ComPair (Computer Aided Repair) is a service tool for Philips
Consumer Electronics products. ComPair is a further
development on the European DST (service remote control),
which allows faster and more accurate diagnostics. ComPair
has three big advantages:
1. ComPair helps you to quickly get an understanding on how
to repair the chassis in a short time by guiding you
systematically through the repair procedures.
2. ComPair allows very detailed diagnostics (on I
is therefore capable of accurately indicating problem areas.
You do not have to know anything about I
yourself because ComPair takes care of this.
3. ComPair speeds up the repair time since it can
automatically communicate with the chassis (when the
microprocessor is working) and all repair information is
directly available. When ComPair is installed together with
the Force/SearchMan electronic manual of the defective
chassis, schematics and PWBs are only a mouse click
away.
2
C level) and
2
C commands
PC VCR I2CPower
9V DC
E_06532_021.eps
180804
Figure 5-8 ComPair interface connection
How To Order
• ComPair order codes (EU/AP/LATAM):
• Starter kit ComPair32/SearchMan32 software and
ComPair interface (excl. transformer): 3122 785 90450.
• ComPair interface (excl. transformer): 4822 727 21631.
• Starter kit ComPair32 software (registration version): 3122
785 60040.
• Starter kit SearchMan32 software: 3122 785 60050.
• ComPair32 CD (update): 3122 785 60070 (year 2002),
3122 785 60110 (year 2003 onwards).
• SearchMan32 CD (update): 3122 785 60080 (year 2002),
3122 785 60120 (year 2003), 3122 785 60130 (year 2004).
• ComPair firmware upgrade IC: 3122 785 90510.
Page 16
EN 16 LC4.9E AB5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
• Transformer (non-UK): 4822 727 21632.
• Transformer (UK): 4822 727 21633.
• ComPair interface cable: 3122 785 90004.
• ComPair interface extension cable: 3139 131 03791.
• ComPair UART interface cable: 3122 785 90630.
Note: If you encounter any problems, contact your local
support desk.
5.4.2 LVDS Tool
Introduction
This service tool (also called “ComPair Assistant 1“) may help
you to identify, in case the TV does not show any picture,
whether the Small Signal Board (SSB) or the display of a Flat
TV is defective.
Furthermore it is possible to program EPLDs with this tool
(Byteblaster). Read the user manual for an explanation of this
feature.
Since 2004, the LVDS output connectors in our Flat TV models
are standardised (with some exceptions). With the two
delivered LVDS interface cables (31p and 20p) you can cover
most chassis (in special cases, an extra cable will be offered).
When operating, the tool will show a small (scaled) picture on
a VGA monitor. Due to a limited memory capacity, it is not
possible to increase the size when processing high-resolution
LVDS signals (>= 1280x768). Generally this tool is intended to
determine if the SSB is working or not. Thus to determine if
LVDS, RGB, and sync signals are okay.
How to Connect
Connections are explained in the user manual, which is
delivered with the tool.
Note: To use the LVDS tool, you must have ComPair release
2004-1 (or later) on your PC (engine version >= 2.2.05).
For every TV type number and screen size, one must choose
the proper settings via ComPair. The ComPair file will be
updated regularly with new introduced chassis information.
How to Order
• LVDS tool (incl. two LVDS cables: 31p and 20p):
3122 785 90671.
• Service Manual LVDS tool:
3122 785 00810.
• LVDS cable 20p (for Telra 14-inch):
3122 785 90810.
• LVDS cable 30p (for LC4.3):
3122 785 90820.
• LVDS cable 41p-to-31p for CA1 (dual -> single LVDS):
3122 785 90830.
5.5 Error Codes
The error code buffer contains all errors detected since the last
time the buffer was erased. The buffer is written from left to
right. When an error occurs that is not yet in the error code
buffer, it is displayed at the left side and all other errors shift one
position to the right.
5.5.1 How to Read the Error Buffer
You can read the error buffer in 3 ways:
• On screen via the SAM (if you have a picture).
Examples:
– ERROR: 0 0 0 0 0 : No errors detected
– ERROR: 6 0 0 0 0 : Error code 6 is the last and only
detected error
– ERROR: 9 6 0 0 0 : Error code 6 was detected first and
error code 9 is the last detected (newest) error
• Via the blinking LED procedure (when you have no
picture). See “The Blinking LED Procedure”.
•Via ComPair.
5.5.2 How to Clear the Error Buffer
The error code buffer is cleared in the following cases:
• By using the CLEAR command in the SAM menu:
– To enter SAM, press the following key sequence on the
remote control transmitter: “062596” directly followed
by the OSD/STATUS button (do not allow the display
to time out between entries while keying the
sequence).
– Make sure the menu item CLEAR is highlighted. Use
the MENU UP/DOWN buttons, if necessary.
– Press the MENU RIGHT button to clear the error
buffer. The text on the right side of the “CLEAR” line will
change from “CLEAR?” to “CLEARED”
• If the contents of the error buffer have not changed for 50
hours, the error buffer resets automatically.
Note: If you exit SAM by disconnecting the mains from the
television set, the error buffer is not reset.
5.5.3 Error Codes
In case of non-intermittent faults, write down the errors present
in the error buffer and clear the error buffer before you begin
the repair. This ensures that old error codes are no longer
present.
If possible, check the entire contents of the error buffer. In
some situations, an error code is only the result of another error
and not the actual cause of the problem (for example, a fault in
the protection detection circuitry can also lead to a protection).
Table 5-1 Error code overview
Error Device Error Description Check Item Diagram
0 Not applicable No Error
1 Not applicable Mis-match of TV
2 Not applicable - - 3 Not applicable - - 4 Genesis Scaler
Flash-ROM
5 Scaler supply
7752
6 Not applicable General I2C error 1102, 7L04, 7M00 B1 + B18
7ADC I
8 Scaler EEPROM I
9 Hercules
EEPROM
10 Tuner I2C error while
11 Columbus I
12 Not applicable - - -
Hercules SW and
Scaler SW
I2C error while
communicating with
the Genesis Scaler
and/or Flash-ROM
is faulty/empty
+5V protection 7752 B6
2
C error 7L04 B18
2
C error while
communicating with
the Scaler
EEPROM
2
C error while
I
communicating with
the Hercules
EEPROM (NVM for
TV).
Remark: when the
Hercules EEPROM
is defective, the
Hercules should
operate with its
default values.
communicating with
the PLL tuner
2
C error while
communicating with
the 2D/3D
combfilter
Columbus
--
7801
7B01
7C01 B11
7207 B2
1102, F102, F104,
F107
7M00 B19
B7 + B8
B10
+ B19
B1
Page 17
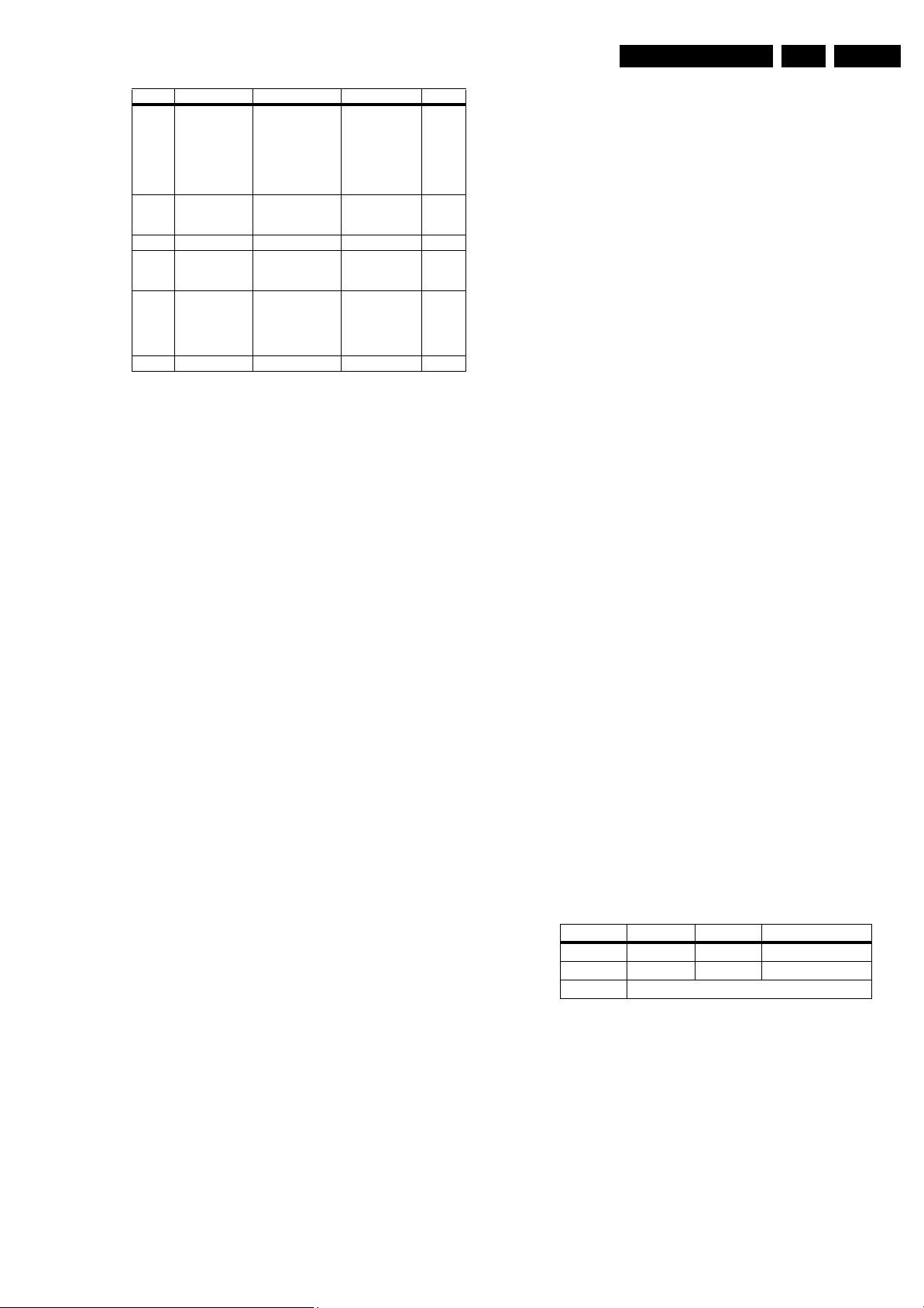
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 17LC4.9E AB 5.
Error Device Error Description Check Item Diagram
13 HDMI Panellink
Receiver/
Decoder
14 Scaler SDRAM Read-write error
15 Not applicable - - 16 EPLD I2C error while
17 Digital Module
(only on Digital
sets)
18 Not applicable - - -
I2C error while
communicating with
the iBoard HDMI
Panellink Receiver/
Decoder (only in
NAFTA and AP
sets)
with the Scaler
SDRAM
communicating with
EPLD
2
I
C error while
communicating with
the Digital Module
(only on Digital
sets)
7D03 B12
7B01 B10
7N02 B20 +
Digital Module
(only on Digital
sets)
(only in
NAFTA
and AP
sets)
B21
5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure
Using this procedure, you can make the contents of the error
buffer visible via the front LED. This is especially useful when
there is no picture.
When the SDM is entered, the front LED will blink the contents
of the error-buffer:
• The LED blinks with as many pulses as the error code
number, followed by a time period of 1.5 seconds, in which
the LED is off.
• Then this sequence is repeated.
Any RC5 command terminates this sequence.
Example of error buffer: 12 9 6 0 0
After entering SDM, the following occurs:
• 1 long blink of 5 seconds to start the sequence,
• 12 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds,
• 9 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds,
• 6 short blinks followed by a pause of 1.5 seconds,
• 1 long blink of 1.5 seconds to finish the sequence,
• The sequence starts again with 12 short blinks.
5.7 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
Notes:
• It is assumed that the components are mounted correctly
with correct values and no bad solder joints.
• Before any fault finding actions, check if the correct options
are set.
5.7.1 NVM Editor
In some cases, it can be handy if one directly can change the
NVM contents. This can be done with the “NVM Editor” in SAM
mode. With this option, single bytes can be changed.
Caution:
• Do not change the NVM settings without
understanding the function of each setting, because
incorrect NVM settings may seriously hamper the
correct functioning of the TV set!
• Do not change the Scaler NVM settings, as this will
hamper the DVI functionality of the TV set!
• Always note down the existing NVM settings, before
changing the settings. This will enable you to return to the
orgininal settings, if the new settings turn out to be
incorrect.
Table 5-2 NVM editor overview
Hex Dec Description
.ADR 0x000A 10 Existing value
.VAL 0x0000 0 New value
.Store Store?
Page 18
EN 18 LC4.9E AB5.
Table 5-3 NVM Default values (option bit settings through NVM Editor in SAM Mode)
Byte Nr. Bit Feature/Mode Description
Byte 0
174(dec)
0 QSS (LSB) Mode of quasi split sound amplifier 1 1
1 FMI Connection of output of QSS amplifier 1 1
2 HCO EHT tracking mode 0 0
3 HP2 Synchronization of OSD/Text display 1 1
4 FSL Forced slicing level for vertical sync 1 1
5 TFR DC transfer ratio of luminance signal 1 1
6 OSVE Black current measuring in overscan 0 0
7 MVK (MSB) (For Future Usage, as defined by software) 0 0
Total Dec Values 59 59
Total Hex Values 3B 3B
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
42PF7520D/10
42PF5520D/10
Byte 1
175(dec)
Byte 2
176(dec)
Byte 3
177(dec)
0 PSE PSE 0 0
1OPC OPC 0 0
2PRIS PRIS 0 0
3 CONTINUOUS FACTORY Continuous factory mode 0 0
4 WHITE PATTERN ON Last color pattern status in factory mode 0 0
5 SDM MODE Service default mode on/off 0 0
6 SAM MODE Service Align mode on/off 0 0
7 SVMA Scavm On / Off 0 0
Total Dec Values 0 0
Total Hex Values 00 00
0 MUTE STATUS Mute status 0 0
1 TUNER AUTO MODE Auto mode 1 1
2 CABLE MODE Cable/Antenna mode 0 0
3 LAST POWER MODE Last power status of the set 1 1
4 CHILD LOCK MODE Child lock enabled 0 0
5 SURF MODE Surf mode on/off 0 0
6 FACTORY MODE Factory mode on 0 0
7 PSNS For PAL color enhancement in ES4 1 1
Total Dec Values 138 138
Total Hex Values 8A 8A
0 RADIO/TV MODE Radio mode or TV mode 0 0
1 WAKE-UP MODE WAKE-UP MODE 0 0
2 HOTEL MODE TV in Hotel mode 0 0
3 HOTEL KBD LOCK Keyboard locked 0 0
4HBL HBL 0 0
5 BLS Blue stretch mode 1 1
6SL SL 0 0
7 CFA0 Comb filter On/Off 1 1
Total Dec Values 160 160
Total Hex Values A0 A0
Byte 4
178(dec)
0 Signal Strength Signal Strength Switch in MK2 0 0
1LPG LPG 0 0
2 DVD TRAY LOCK Lock/Unlock DVD tray 0 0
3 SCRSAVER MODE Screen saver mode 1 1
4 BKS Black Stretch Mode 1 1
5 BSD Black Stretch Depth 1 1
6 CRA0 Coring on SVM 1 1
7 PIP QSS PIP QSS 0 0
Total Dec Values 120 120
Total Hex Values 78 78
Page 19
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Byte Nr. Bit Feature/Mode Description
Byte 5
179(dec)
Byte 6
180(dec)
0 FFI Fast Filter 0 0
1 NNR No red reduction during blue stretch 1 1
2 MUS NTSC matrix 1 1
3 GAM Gamma control 1 1
4 CBS Control sequence of beam current limiting 0 0
5 LLB Low level of beam current limiter 0 0
6 DSA Dynamic skin tone angle area 1 1
7 DSK Dynamic skin tone angle on/ off 0 0
Total Dec Values 78 78
Total Hex Values 4E 4E
0 LTI status LTI last status 1 1
1 Inc_Life_Time Inc_Life_Time 0 0
2 PC_Mode PC_Mode 0 0
3 HD_Mode HD_Mode 0 0
4 Tact_Switch Tact_Switch 0 0
5 Set_In_Special_Stby Set_In_Special_Stby 0 0
6 Hotel_OSDDisplay Hotel_OSDDisplay 0 0
7 Hotel_MonitorOut Hotel_MonitorOut 0 0
Total Dec Values 1 1
Total Hex Values 01 01
42PF7520D/10
42PF5520D/10
EN 19LC4.9E AB 5.
Byte 7
181(dec)
5.7.2 Load Default NVM Values
In case a blank NVM is placed or when the NVM content is
corrupted, default values can be downloaded into the NVM.
(For empty NVM replacement, short the SDM with a jumper
and apply the mains voltage. Remember to remove the jumper
after the reload is completed). After the default values are
downloaded, it will be possible to start up and to start aligning
the TV set. This is no longer initiated automatically; to initiate
the download the following action has to be performed:
1. Switch “off” the TV set by disconnecting the AC Power
2. Short circuit the SDM jumpers (keep short-circuited).
3. Press P+ or Ch+ on the local keyboard (and keep it
4. Switch on the TV set via the AC Power plug.
5. Keep pressing the P+/Ch+ button until the set has started
Alternative method:
1. Go to SAM.
2. Select NVM Editor (not SC NVM Editor).
3. Select ADR (address) to 1 (dec).
4. Change the VAL (value) to 170 (dec).
5. Store the value.
6. Disconnect the mains plug and wait for a few seconds.
7. Reconnect the mains plug and wait until the set goes into
8. Restart the set.
0 Hotel_IconMode Hotel_IconMode 0 0
1DBE DBE 1 1
2SD SD 0 0
3 Set_in_PC_Sleep_Mode Set_in_PC_Sleep_Mode 0 0
4 Reserved Reserved 0 0
5 Reserved Reserved 0 0
6 Reserved Reserved 0 0
7 Reserved Reserved 0 0
Total Dec Values 2 2
Total Hex Values 02 02
plug.
pressed).
up and the SDM is shown.
its standby mode (red LED lights up).
5.7.3 Tuner and IF
No Picture in RF Mode, but there is a Noise Raster
1. Check whether picture is present in AV. If not, go to Video
processing troubleshooting section.
2. If present, check if the Option settings are correct.
3. Check if all the supply voltages are present (3.3/5/8/12/33
V).
4. Check if the I
5. Manually store a known channel and check if there is IF
output at Tuner pin 11.
6. Check the tuning DC voltage at pin 2 of the Tuner. The DC
voltage should vary according to the frequency/channel
being chosen.
7. If the tuning voltage is OK, check the tuner output, pin 11.
8. If it has no output, the Tuner may have a defect. Change
the Tuner.
Sound in Picture Problem for L' System (rolling horizontal lines)
1. Check whether AGC L' in SAM mode is set to 0.
2. If yes, align the set to correct value.
Required System is not Selected Correctly
Check whether a Service jumper (#4204 & 4205, 0805 size) is
present. If yes, remove it.
2
C lines are working correctly (3.3 V).
Page 20

EN 20 LC4.9E AB5.
5.7.4 Video Processing
No Power
1. Check +12 V and 3V3 at position 1J02.
2. If no supply, check the connector 1J02.
3. If it is correct, check the power supply board.
Power Supply is Correct, but no Green LED
1. Check if the connectors 1K00 are properly inserted.
2. If they are inserted correctly, check if the 3V3 is present.
No Picture Display (blank screen with correct sound output)
1. Check whether the user menu is visible.
2. If the user menu is OK, activate teletext mode.
3. If teletext is OK, the problem is in the ADC (B18) &
Columbus 3D combfilter (B19), if present (depending on
model, see also paragraph “Teletext Path” in chapter 9).
4. If the user menu is not visible, check if the LCD panel
backlight is ON.
5. If the backlight is OFF, the problem is in the power supply
board or LCD panel. Also check pin 12 (LAMP_ON_OFF)
of 1J02. It should be HIGH during normal operation.
Note: For faultfinding purposes, it is important to know the
following: in Pixel Plus and Digital Crystal Clear models, which
have an ADC (B18) and Columbus 3D combfilter (B19), the
digital input of the scaler is used for the digital video path
(Hercules output), whereas the analogue RGB input (analogue
input of the scaler) is only used for teletext. This means that no
mixed mode (video plus teletext simultaneously) is possible. If
there is sound and teletext, but no video and user menu (blank
screen), the digital path (Hercules - ADC - Columbus - Scaler)
is faulty. If there is sound but no teletext, the back-end part
(Scaler - LCD panel) is faulty. In Crystal Clear models, which
do not have an ADC and Columbus, the RGB path (analogue
input of scaler) is used for both video and teletext.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
No TV, but PC is Present
1. Check if Hsync_SDTV and Vsync_SDTV are present at pin
1 & pin13 of 7E03.
2. If they are present, check teletext output.
3. If there is no teletext output, the IC TDA150xx may be
defect.
5.7.5 Power Supply
In case the power supply does not work, check (apart from the
obvious fuse-check) if the oscillators in IC7001 and IC7U01 are
working. If not, replace the ICs.
Page 21
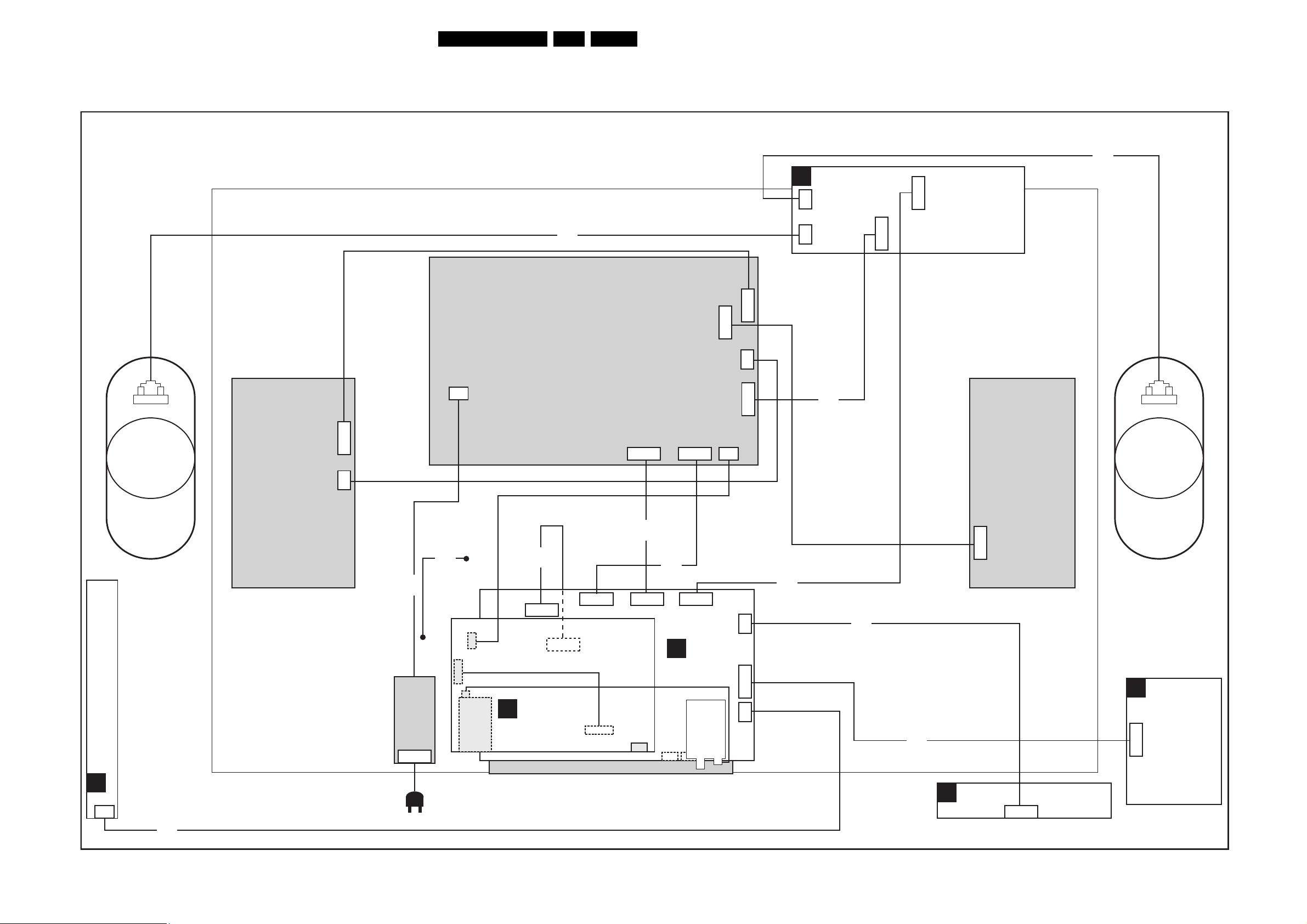
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
6. Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Wiring Diagram
21LC4.9E AB 6.
8736
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
C
9P
2P3
1736
1M52
CONTROL BOARD
E
1M01
3P
RIGHT
SPEAKER
8101
8735
CN07
2P3
1735
10P
CN06
8P
7P
1M02
PDP POWER SUPPLY
4P
1K00
CN308
2P3
P5
10P
10P 11P
P6
4P
8103
8199
AC INLET
8900
1500
32P
1301
Tu ne r
3P
K
8150
31P
1J04
3P
LVDS
CONNECTOR
IBO ZAPPER
11P
1J01
32P
1G03
1402
3P
10P
1J00
8146
1107
3P
B
1M461M03
1101
3P
9P
1J04
SSB
Tu ne r
1M10
4P
1M02
1K00
1K04
1K02
7P
8152
6P
11P
3P
8102
8120
8136
LED PANEL
J
INVERTERINVERTER
LEFT
SPEAKER
8P
P1
SIDE I/O
D
11P
1M36
6P
0345
F_15670_002.eps
010805
Page 22
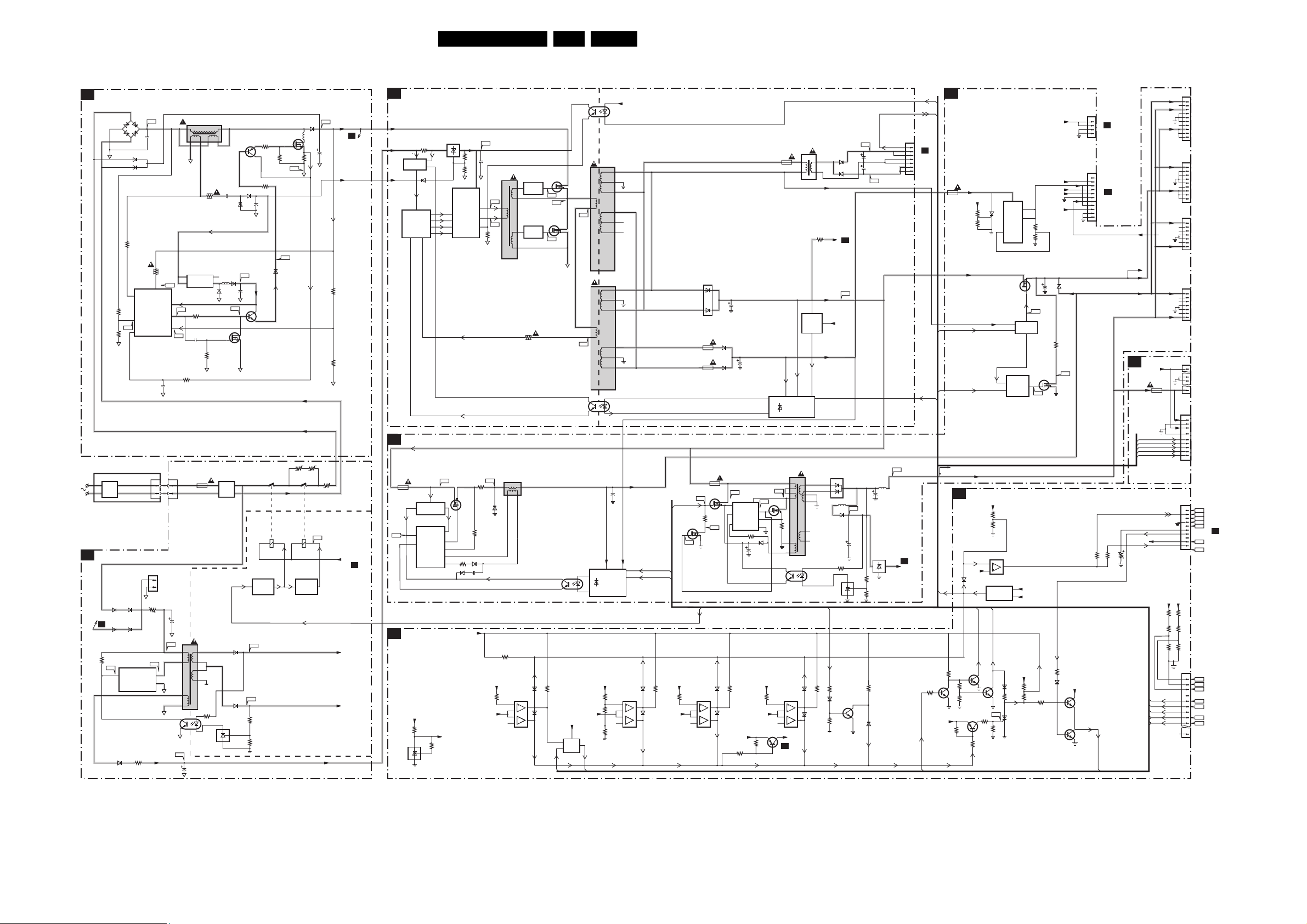
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram Supply
SUPPLY 42” FHP
PRECONDITIONER
A5
6600
3
GBU8J
MAINS FILTER UNIT
MAINS
FILTER
FILTERS STANDBY
A2
400V-HOT
A
A5
3507
I508
F601
1
416
+
-
2603
2
6606
6605
3660
7650
MC33368
LINE
7
ZC
CONTROL
3605
5
MULT
I618
CS
3651
6
2
1
1M05
1
2
6513
6512
BYG10
BYG10
3506
6510
6511
BYG10
BYG10
CONTROL
7500
I510
TNY256
4
ENABLE
DRAIN
SOURCE
6503
3508
RS1G
5600
7661
3668
MC34063AD
8
7
I622
16
12
VCC
F610
11
GATE
3
VFB
I629
3666
2666
0308
2
1
SECOND
STANDBY
+t
2503
5500
F500
236
5
7-8
4
1
4
7501
TCET1102
3
I504
+25V-HOT +25V-HOT
2505
PRECONDITIONER
1246
3663
1
DC TO DC
2
CONVERTOR
3641
2640
3640
1400
T6.3A
7
8
9
3501
1
7502
TS2431
2
14
7608
2663
6661
6660 2664
F609
6665
5660
2662
6663
I625
7641
D
7640
G
BSN20
S
5005
5401
5402
MAINS
FILTER
7460
ACTIVATING
- STANDBY SUPPLY -
6504
F502
RS1G
6505
F503
SB34
3505
1
2
3503
3
BIAS
3610
3608
12
43
STW26NM50
6641
1450
7610
G
3611
F604
F608
+t
6611
5612
D
S
3614
AC3 100-230VAC2
AC5 100-230VAC1
3450
3451
0
0
+t
12
1460
43
7465
7470
ACTIVATING
DELAY
22LC4.9E AB 6.
LLC SUPPLY
A6
HOT
- LLC-CONVERTER -
F600
400V-HOT
A2
A
400V-HOT
2616
SW25V-HOT
3680
3671
400V-HOT
- BIAS-SUPPLY -
25V-HOT
7090 :
7092
PROT
SW25V-HOT
7017
7018
SOFT
START
CURRENT
PROTECTION
AUX-SUPPLY
A7
70-90V
7093
LM317T
3092
6095
+
7001
MC34067P
3
6
8
7
CONTROL
F001
BIAS
3095
2053
3096
15
VCC
F003
14
OA
12
OB
F004
10
FI
3011
7007
5001
4
2
10
11
14
13
7020
HIGH
SIDE
DRIVE
7008,
7021, 7012
LOW
SIDE
DRIVE
3050
STU16NB501
G
I038
F005
BZG03
G
I057
- VA-SUPPLY -
5121
G
S
7117
PSMN035
I107
3118
3117
61133113
21146111
VS_UNSW
1
2
3
4
6120
VS PROTECTION
3308
70-90V
3300
7308 A+B
7
6
2V5
5
4
7120
TCET1102
3312
6312
1
6313
2
VSAGO
7110
CONTROL
7112
TEA1507
1
VCC
3
CTRL
CONTROL
3304
1
3
2
VCC &
DRAIN
DRAIN
DRIVER
SENCE
DEMAG
3324
I101
2V5
D
8
6
5
2
4
+5V_STBY_SW
3452
0
-t
HOT
COLD
F411
+9V_STBY_SW
A3
SUPPLY_ON
+9V_STBY
+5V_STBY_SW
COLD
HOT
1110
TA5
I105
PROTECTIONS
A3
2V5 CIRCUIT
+5V_STBY_SW
7304
TL43IC2
HOT COLD
+5V_STBY_SW
4
1
7005
D
S
7006
D
S
41
32
TCET1102
TCET1102
7003
3
6
I083
3
6
I083
7002
HOT COLD
2
3
5002
5004
1
4
3
2
VA
VA
ADJ.
VS-SUPPLY
16
14
12
11
10
9
6044
STTH2003C
VS_UNSW
70-90V
VCC_GO
A3
A3
G
I220
7202
BSN20
I213
D
S
3
1
1083
F2,5A
1082
F2,5A
A3
SUPPLY-ON
1200
BSN304
G
3202
T2A
7200
I208
6021
BYU28
6045
BYU28
S
2
D
1
3
4
2020
- VCC SUPPLY -
I214
7212
TEA1507
VCC
CTRL
DEMAG
16
14
12
11
10
9
VA
2121
A3
+30V
VSA_CONTROL
VRA
VA PROTECTION VCC PROTECTION 12V PROTECTION
VCC
6321
6322
3320
2V5
7330 A+B
7
6
5
4
1
2
6333
6334
+5V_STBY_SW
3388
+9V_STBY
7375
7376
VSA-
CONTROL
LOGIC
VA
3311
7308 C+D
11
13
10
3313
2V5
9
14
8
3317
VSA CONTROL
A7
AUX-SUPPLY
A7
LATCH
A3
DC_PROT
VSND_POS
GND_SND
VSND_NEG
F140
DC_PROT
A3
1002
TO 1002
7
6
C
5
PDP AUDIO
4
3
2
1
+30V
+12V_OVP
3345
3346
VCC
PROTECTIONS
+9V_STBY_SW
3360
3363
5
6
+2.5V
ref
6378
7326
7327
A7
VCC_GO
+12V SUPPLY
7260
L4973
6348
CONTROL
12
VS- SWITCHED
7050
PSMN035
VB
SWITCH
LOGIC
SEQUENCE
DISCHARGE
7366-2
7
DETECTION
CIRCUIT
A6
LATCH
1200
T2A
V.S._UNSW
70-90V
POK
A3
VSA-CONTROL
A3
VRS
A3
A3
A3
+8V6
POK
A7
7,8
3
2
D
S
G
SWITCH ON
LOGIC
VS
+5V_STBY_SW
+8V6
+8V6 UNDER
VOLTAGE PROT.
+5V_STBY_SW
3345
3346
I200
G
I202
+9V_STBY
VTUN
2021
D
S
VCEGO LATCH DC_PROT
OVERVOLTAGE
3353
+5V_STBY_SW
VCEGO
A2
3349
3350
7352
3354
7341
3341
3342
+5V_STBY_SW
7351
6347
3345
7348
3346
3347
3391
F343
7004
3344
3343
+12V
+8V6
6142
BYD33D
3053
I201
7052
IRFR18N15D
STANDBY
STANDBY
3390
6366
+5V_STBY_SW
1M10
TO 1M10
1
2
AL
3
AMBIENT
4
LIGHT
0323
11
10
9
+12V
VA
TO 1M46
8
7
B21
6
VCC
SSB
5
4
3
2
1
VCC
VS
VS
FITER STANDBY
A2
+3V3_STBY_SW
VCC
A3
A3
A3
A3
A3
- ERROR LOGGING -
t
3372
3355
3356
7391
7393
SUPPLY_ON
A2
2x
2x
A2
A3
A2
A3
F_15670_003.eps
- AUDIO SUPPLY -
VTUN
F293
2292
6291
2294
6292
6225
3228
3358
6364
3364
F294
A7
F016
F116
2230
7227
TL431CZ
5225
2225
FAN CONTROL
7230
L4940
3224
3225
3361
7362
6362
2
5229
6230
6291
D458L20U
5290
1084
4
2
F1A
3
1
VB
3072
VS_UNSW
70-90V
VS
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
5220
+30V
VRS
FEEDBACK
3
14
13
12
1
11
18
16
124
7220
TCET1102
A6
DC_PROT
333833333321
6340
13
6341
14
2022
7010,7011
CONTROL
1
3
I236
2
4
7217
8
I216
PSMN070
DRAIN
DRIVE
SENCE
3214
D
G
6
S
5
3218
GND
6211
2210
5
7
3
+12V
3332
7330 C+D
11
10
2V5
9
8
7389
+12V_OVP
3389
A7
VA
VCC
VS
VCC
VS
VA
VCC
VAVA
VCC
1004
T2A
VRA
VRS
VCEGO
VSAGO
PFCGO
POR
STANDBY
+9V_STBY_SW
POWER_OK
VA V S
3396
3397
3316
PFCGO
VCEGO
VSAGO
0323
NC
NC
10
0333
NC
0342
NC
NC
NC
0352
NC
NC
NC
0306
0311
0319
10
3302
3303
3305
0307
VSK
VAK
VRS
VRA
11
13
15
20
NC
010805
1
2
3
4
TO
5
CN23
6
PDP
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
TO
5
CN33
6
PDP
7
8
9
1
2
3
TO
4
CN42
5
PDP
6
7
1
2
3
TO
4
CN52
5
PDP
6
7
1
3
TO
4
CN6
PDP
6
1
2
3
4
TO
5
CN11
6
PDP
7
8
9
1
F300
2
F301
3
F302
4
F304
5
TO 1M03
F305
6
B21
7
8
SSB
9
F309
F310
1
I900
2
I943
3
I901
5
7
I903
TO
9
CN7
I904
PDP
I905
I906
Page 23

Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram Video
VIDEO
TUNER & VIF
B1
RF
IN
RF
OUT
SCART ANALOG IO
B15
1G02
1
21
SCART 2
1G01
1
21
SCART 1
1G03
FROM 1500
K5
BACK END
See also
Block giagram
IBO-ZAPPER
For DVB
Sets Only
SIDE AV
D
VIDEO
IN
5
SVHS
1102
UV1318SD
20
15
STATUS_2
8
19
20
19
16
15
11
7
STATUS_1
8
DMM1_CVBS_IN
8
14
12
10
1002
1001
1
3
4
2
+5SW_a
67
TUNER
4
5
SCL
SDA
7G05
EF
SC1_CVBS_IN
7G03
EF
SC1_FBL_IN
CVI_Pr_IN
CVI_Y_IN
CVI_Pb_IN
DMMI_R_Pr_IN
DMMI_G_Y_IN
DMMI_B_Pb_IN
+VTUN
Y
C
IF-TER
11
1
3311
B2
B2
1M36
2
4
1104
2106
2
F108
1106
2
SC2_Y_IN
FRONT_Y_CVBS_IN
SC2_C_IN
FRONT_C_IN
DMMI_CVBS_IN
SC2_CVBS_MON_OUT
AV2_DMMI_SW
B2
SC2_AV3_Y_IN
SC1_CVBS_RF_OUT
SC1_FBL_IN
DMMI_FBL_IN
CVI_Pr_IN
DMMI_R_Pr_IN
CVI_Y_IN
DMMI_G_Y_IN
CVI_Pb_IN
DMMI_B_Pb_IN
DMMI_RGB_SM
B2
DMM1_CVBS_IN
SC2_AV3_Y_IN
AV2_DMMI_SW
B2
SC2_Y_IN_1
SIDE CONNECTIONS
B17
1K04
2
4
7
VIF1
8
VIF2
RF_AGC
SIF1
7
SIF2
8
2
1
12
13
3
5
2
4
9
7
12
14
19
17
5
3
7G10
7G09
7G07
HERCULES
B2
7217
TDA15021H
24
25
31
DC
29
30
14
15
4
9
B2
SC1_FBL_IN_1
3
SC1_CV1_DMMI_R_Pr_IN
8
SC1_CV1_DMMI_G_Y_IN
13
SC1_CV1_DMMI_B_Pb_IN
18
9,10,11,20
7G08
4
10,11
AC
AGC
Detect
SC2_AV3_C_IN
SC2_OUT_SW
SC2_Y_IN_1
SC1_CVBS_IN
EF
Sound
Traps
QSS Mixer
AM Demod.
7219
14
7206
EF
CVBS1
QSS/FM
AM
13
12
B2
B13
B13
B13
23LC4.9E AB 6.
SYNC INTERFACE
B3
7208
EF
RO
85
G_OSD
Vertical &
East-West
Geometry
Sync Sep
H-OSC
H-Shift
H-Drive
CVBS/Y
B_OSD
Fast Blanking
RO
GO
BO
VDRB
HOUT
GO
86
BO
87
22
67
7436-2
1
7436-1
3
HISTO-
B18
GRAM
7L01
EF
7L02
EF
DIGITAL IO
B14
C5
C1 C2
18
916
DVI-D
CONNECTOR
RGB Matrix
Blue & Black
Strech
UOUT
Skin Tone
U/V Tint
Saturation
Peaking
SCAVEM
U/V Delay
VOUT
Gamma Corr.
YUV
YUV in/out
H/V
VIN
UIN
N.C.
INTF_V_OUT
INTF_U_OUT
INTF_Y_OUT
R_OSD
YIN
Video
Switch
+
Control
59
64
51
52
48
58
55
43
c
cvbs/y
HERCULES
Dig. 2H/4H
Combfilter
Yint
Y Delay Adj.
Chrome
Uint
PAL/NTSC/
SECAM
Decoder &
Vint
Baseband
Delay
RGB/Pr Pb Insert
INSSW3
R/Pr-3
G/Y3
B/Pb-3
77 78 79 80
SC1_R_CVI_Pr_IN
SC1_B_CVI_Pb_IN
SC1_G_CVI_Y_IN
SC1_FBL_IN_1
B15
B13
B13
B13
SAT
SCAVEM
on text
YUV Interface
YOU T
74 75 76 70 71 72
7209
SDA
2
4
SCL
EF
EF
1F00
27
26
25
28
10
11
14
15
17
18
23
24
16
8
1
2
6
7
9
EF
Vsync_SDTV
Hsync_SDTV
7L04
MST9883C
30
31
54
A/D
CONV.
43
48
56
57
H_PC
V_PC
+5VSWI
7210
7L03
C3 C4
24
17
MUX-SYNC INTERFACE
B13
F624
F625
F626
B13
B13
B13
B14
B14
B13
B14
B3
B14
B13
B14
B3
SC1_CV1_DMMI_R_Pr_IN
B15
SC1_CV1_DMMI_G_Y_IN
B15
SC1_CV1_DMMI_B_Pb_IN
B15
B13
B13
B13
B13
B13
R_SDTV
G_SDTV
B_SDTV
SC1_R_CVI_Pr_IN
SC1_G_CVI_Y_IN
SC1_B_CVI_Pb_IN
BINA|Pb
GINA|YINA
RINA|Pr
Vsync_SDTV
V_PC
H_PC
Hsync_SDTV
COL_Di(1-7)
COL_YA(1-7)
BINA|Pb
GINA|YINA
RINA|Pr
7E01
27
3
7
25
1
5
11
15
1
1
2
12
13
7E00
13
1
3
5
2
12
7E02
7E03
B10
B19
14
15
4
R_PR-ADC
17
G_Y-ADC
14
B_PB-ADC
11
12
14
2
19
15
5
14
1
10,11
SDRAM
7B01
K4D263238F
SDRAM
1Mx32x4
COLUMBUS
(Dig. PAL/NTC Comb)
7M00
T6TU5XBG
COLUMBUS
DIGITAL COMB
FILTER
7M01
MSM56V16
DRAM
512Kx16x2
SC1_R_CVI_Pr_IN
SC1_G_CVI_Y_IN
SC1_B_CVI_Pb_IN
RX2+IN
SCL_DVI
SDA_DVI
RX1+IN
RX0+IN
RXC+IN
HOTPLUG
PC_HD_DET
7604
SD_HD_SEL
+2V5_DDR
COL_A
RX2-IN
RX1-IN
RX0-IN
RXC-IN
8
4
95
COL_D
AVSYNC
AHSYNC
SOG
R_PR+
G_Y+
B_PB+
FSDATA
FSADDR
COL_Do(1-7)
COL_YB(1-7)
B2,B13
B2,B13
B2,B13
B7
SCALER
C3
D2
C2
B2
L3
L4
B10
A10
N4
N3
B9
A9
B8
A8
AL
B6
AE10
7801
GM1501
ANALOG
INPUT
PORT
FRAME
STORE
CONTROL
DVI/HDMI
INPUT
PORT
SCALER
GRAPHIC
ZOOM
OUT BLENDER
OSD CONTROLLER
BRIGHTNESS/CONTRAST/HUE/SAT
VIDEO
ZOOM
UART
INTERFACE
MICRO
CONTROLLER
INTERNAL
RAM
EXTERNAL
ROM
INTERFACE
DISPLAY
TIMING
GEN.
B11
OCMDATA
OCMADDR
AE16
AF16
AE15
AF15
AE14
AF14
AF12
AF11
AF13
AE12
FLASH/CONTROL
7C00
MX29LV040QC
FLASH
ROM
512Kx8
4N03
TXB0TXB0+
TXB1TXB1+
TXB2TXB2+
TXB3TXB3+
TXBCTXBC+
OR
7N04
THC63LVDF84B
TXB0+
TXB0TXB1+
INTERFACE
TXB1-
RECEIVER
TXB2+
TXB2TXB3+
TXB3TXBC+
TXBC-
7N02
EP1C12F256C8N
SD_HD_SEL H H H H H H
PC_HD_DET H H H H L H
RGB|CVI_HDA_SEL L H L L L L
4N01
4N07
4N05
4N11
4N09
4N15
4N13
4N19
4N17
Only for sets with
PIXEL PLUS
LVD S
RGB
EPLD
PIXEL+
PROCESSOR
LVDSAn
LVDSAp
LVDSBn
LVDSBp
LVDSCn
LVDSCp
LVDSDn
LVDSDp
LVDSCLKn
LVDSCLKp
7P02
THC63LVDM83R
LVD S
TRANSMITTER
RGB
OR
LVDS_VCC
LVDSALVDSA+
LVDSBLVDSB+
LVDSCLVDSC+
LVDSD-
LVDSD+
LVDSCLK-
LVDSCLK+
LVDS_VCC
LVDSALVDSA+
LVDSBLVDSB+
LVDSCLVDSC+
LVDSDLVDSD+
LVDSCLK-
LVDSCLK+
LVDSAn
LVDSAp
LVDSBn
LVDSBp
LVDSCn
LVDSCp
LVDSDn
LVDSDp
LVDSCLKn
LVDSCLKp
1P07
1
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
24
25
26
21
22
1P06
1
11
10
12
14
13
15
19
18
20
27
26
28
22
21
23
HDPCSide-AVEXT2EXT1TV
F_15670_004.eps
010805
TO DISPLAY (LC4.8 LC4.9)TO DISPLAY (LC4.3)
Page 24
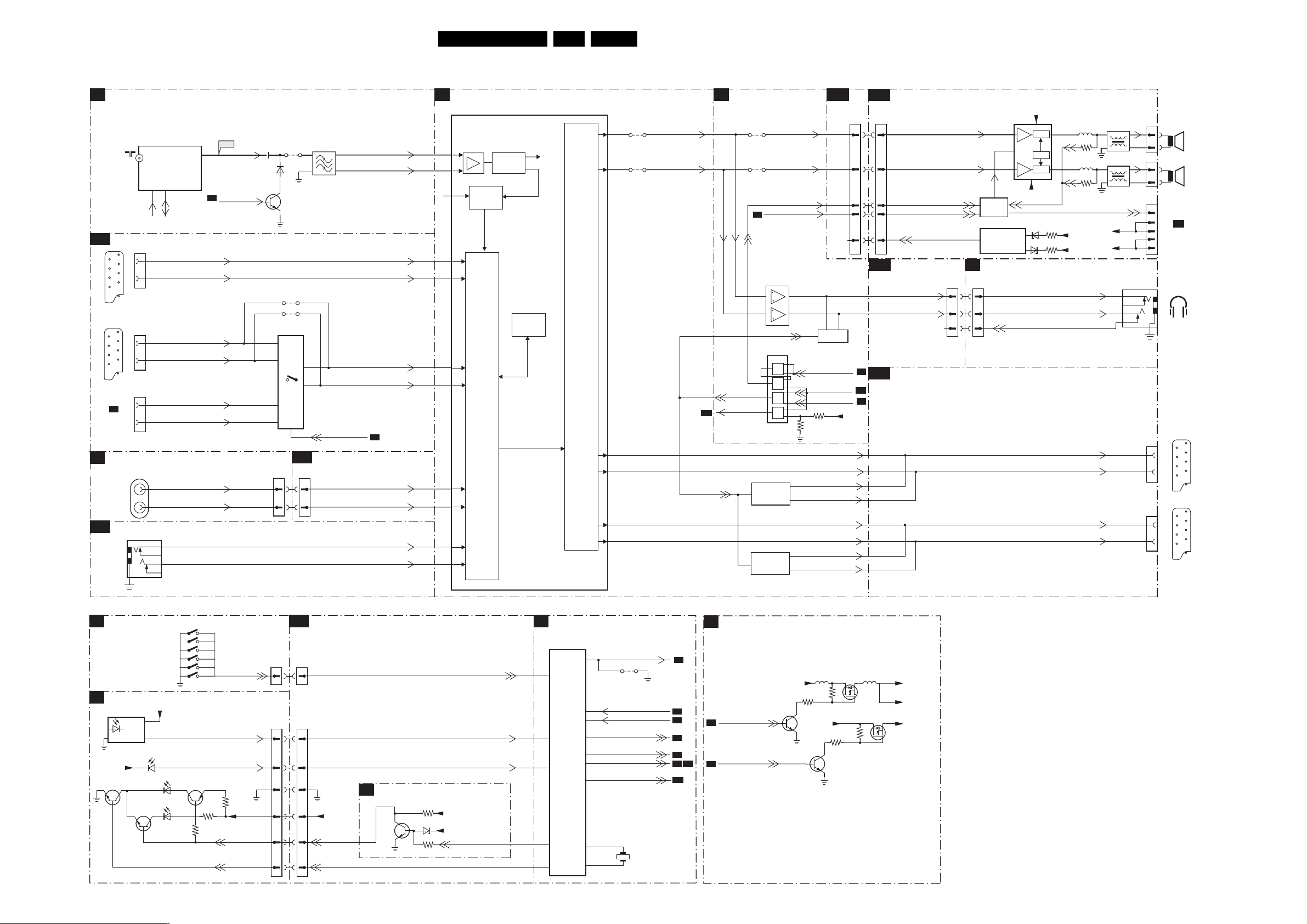
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram Audio
AUDIO
TUNER & IF
B1
1102
UV1318S
RF IN
SCART ANALOG IO
B15
1
21
EXT 1
SCART 1
1
21
EXT 2
SCART 2
FROM 1500
K5
BACK END
(Only for
DVB sets)
CONNECTOR
SIDE I/0
D
AUDIO
L/R IN
DIGITAL IO
B14
PC
AUDIO
IN
1F01
1G01
1G02
1G03
DMMI
1002
6
2
6
2
6
4
IFOUT
TUNER
4
5
SCL
SDA
SC1_COMP_AV1_L_IN
SC1_COMP_AV1_R_IN
SC2_L_IN
SC2_R_IN
DMMI_L_IN
DMMI_R_IN
2
2
4
3
7
11
B2
L
R
F108
IF-TER
SEL_IF_SDM
2106
7101
*Only for
DVB Set
13
1
12
2
1M36
4110
6104
4G11
4G12
7G07*
74HC4053D
14
15
10,11
B17
1K04
66
88
1106
7
2
8
3
SC1_COMP_AV1_L_IN
SC1_COMP_AV1_R_IN
AV2_DMMI_SW
SIDE CONNECTORS
FRONT_L_IN
FRONT_R_IN
SC2_L_IN
SC2_R_IN
B2
AudioIN2L
AudioIN2R
SIF1
SIF2
HERCULES
B2
7217
TDA15021H
29
30
33
34
35
56
57
49
50
53
54
AD Conv.
Std Stereo
Decoder
AUDI O
SELECT
ADC/DAC
QSS Mixer
AM Demod.
AM
QSS/FM
I2S
Processor
AUDI O
CONTROL
Vol/Treb/
Bass
Features
DACs
24LC4.9E AB 6.
AUDIO PROCESSING
B5
4212
60
61
62
63
36
37
4211
AUDOUTLSL
AUDOUTLSR
B16
OUT_MUTE
4618
4219
OUT_MUTE
POR_AUDIO
AUDIO-L
AUDIO-R
SOUND-ENABLE_1
POR_AUDIO
B5
7601
TS482ID
2
1
7
6
OUT_MUTE
7602
74HC08PW
2
3
&
1
&
6
5
9
8
&
10
12
&
13
7202
MUTE
7201
MUTE
3629
B16
N.C.
7606
MUTE
RES
SOUND_ENABLE
POWER_DOWN
EXT_MUTE
3628
+5V
SC2_L_MON_OUT
SC2_R_MON_OUT
SC2_L
SC2_R
SC1_L_RF_OUT
SC1_R_RF_OUT
SC1_L
SC1_R
1J04
(1M52)
11
33
88
99
77
B2
B16
B2
AUDIO
SA3
1739
SOUND-ENABLE
POR-CLASSD
PROT_AUDIOSUPPLY
SIDE
B17
CONNECTORS
HP_LOUT
HP_ROUT
SCART ANALOGUE IO
B15
N.C.
AUDIO-L
AUDIO-R
7701:7707
1K04
10 10
11 11
77
SOUND
ENABLE
7709/7710
PROT, CIRCUIT
SIDE I/O
D
1M36
+16V+19V
7700
TDA7490
AUDI O
SUPPLY
10
18
4,22
PWM
stby-mute
6
OSC
PWM
2,24
-16V-19V
PROT1
6703
6702
SOUND L-HEADPHONE-OUT
SOUND R-HEADPHONE-OUT
DETECT
SC2_L_MON_OUT
SC2_R_MON_OUT
3
23
3764
-16 V-19V
3761
+16 V+19V
SC1_L_RF_OUT
SC1_R_RF_OUT
5701
3718
5702
3717
5731
5730
DCPROT
+16 V+19V
-16 V-19V
1010
2
3
5
1736
1735
1M02
1G02-1
1G01-1
1
3
1
3
7
6
5
2
1
HEADPHONE
3
1
3
1
Speaker L
15W/8Ω
Speaker R
15W/8Ω
TO 1002
SA
SUPPLY
EXT 2
SCART 2
EXT 1
SCART 1
1
21
1
21
CONTROL
CONTROL BOARD
E
LED PANEL
J
1040
2
GND
OUT
+5V2-STBY
7052
+5V2-STBY
VS
6070
7051
Channel+
3
1
Channel-
Menu
Volume+
Volume-
Power
6050
6051
Green
Red
7062
3063
1703
1704
1705
1702
1701
1706
3051
KEYBOARD
RC
LIGHT-SENSOR
3061
+5V2-STBY
LED1
LED2
B17
(1M01)
1M01
22
0345
33
11
22
55
44
66
SIDE CONNECTORS
1K02
1K00
+3V3STBY
LED_SEL
PC-TV-LED
SYNC INTERFACE
B3
7430
3431
6F00
3432
RES
KEYBOARD
LIGHT_SENSOR
+3v3STBY
+5VSW
ITV_IR_SW_RESET
HERCULES
B2
7217
TDA15021H
120
HERCULES
IR
97
115
123
107
114
116
119
102
111
122
127
10
11
SEL_IF_SDM
4022
SERVICE
SDM
STATUS_1
STATUS_2
EXT_MUTE
SOUND-ENABLE
SC_STANDBY
AV2 _DMMI_SW
1202
B3
B3
B5
B5
B15
B1
B15B6
DC-DC CONVERTER
B6
PAN EL-PWR-CTL
B8
SC_STANDBY
B2
+12VSW
7755
5756 5754
3758
3755
+3V3STBY
3759
7756
7754
3750
7758
LVDS_VCC
PAN_VCC
+3V3SW
F_15420_024.eps
150605
Page 25
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Testpoint Overview SSB (Top Side)
F101 C1
F114 C2
F102 D2
F115 D2
F103 C1
F116 D2
F104 D2
F117 D2
F105 D1
F201 A2
F106 D2
F202 A2
F107 C1
F203 A2
F108 C2
F204 B3
F109 C2
F205 B2
F110 B2
F206 B2
F111 B2
F207 B2
F112 B2
F208 B2
F113 B2
F209 B2
3139 123 6093.1
F210 C2
F211 A2
F212 A2
F213 A2
F214 A2
F215 A2
F216 B3
F218 A2
F219 A2
F220 A3
F221 A3
F222 B2
F223 B2
F224 A2
F225 A3
F226 A3
F227 C3
F228 A3
F229 B2
F230 A3
F231 A2
F232 B3
F233 B3
F234 B3
F235 B3
F236 C3
F237 B2
F238 B2
F239 B2
F240 B2
F241 B3
F242 B2
F243 B2
F244 B2
F245 A2
F246 B2
F247 A2
F248 B2
F249 B2
F250 B3
F501 A2
F502 A2
F503 A2
F504 A2
F505 A3
F601 A1
F602 A2
F603 A1
F604 A2
F605 A2
F700 A6
F701 A5
F710 A5
F736 A3
F737 A3
F738 A3
F743 B3
F754 A5
F755 A6
F800 B7
F801 B6
F802 C5
F803 B5
F804 B5
F900 C5
F901 C5
F902 C6
F903 C5
F904 C6
F905 B6
F906 B6
F907 B5
F908 C5
F909 C5
F910 C6
FB01 B7
FC00 B5
FC01 B5
FC02 B5
FC03 B5
FC04 B5
FC05 C5
FC06 B5
FC07 B4
FC08 B5
FC09 B5
FC10 B4
FD00 C7
FD01 D7
FD02 D7
FD03 D7
FD04 C7
FD05 C6
FD06 C6
FD07 C7
FD08 C7
FD09 C7
FD10 C7
FD11 D7
FD12 C7
FD13 C7
FD14 C7
FD15 C7
FD16 C7
FD17 B6
FE00 C5
FE01 C5
FE02 C4
FE03 B5
FE04 D5
FE05 C5
FE06 D5
FE07 B7
FE08 C4
FE09 C5
FE10 C4
FE11 C5
FE12 C5
FE13 C5
FF00 D6
FF01 D6
FF02 D4
FF03 D7
FF04 D7
FF05 D7
FF06 D6
FF07 D6
FF08 D3
FF09 D7
FF10 D6
FF11 D6
FF12 D6
FF13 D6
FG00 D4
FG01 D4
FG02 D3
FG03 D4
FG04 D3
FG05 D3
FG06 D3
FG07 D3
FG08 D3
FG09 D3
FG10 D2
FG11 D3
FG12 D2
FG13 D2
FG14 D6
FG15 D5
FG16 D6
FG17 D6
FG18 D5
FG19 D5
FG20 D5
FG21 D5
FG22 D5
FG23 D4
FG24 D3
FG25 D3
FG26 D5
FG27 D5
FG28 D5
FG30 D5
FG32 D3
FG33 D3
FG34 D3
FG35 D3
FG36 D4
FG37 D3
FG38 D3
FG39 D4
FG40 D7
FG41 D3
FG42 D4
FG43 D4
FG44 D4
FG45 D4
FG47 D4
FG48 D4
FG49 D4
FG50 D4
FG51 C2
25LC4.9E AB 6.
FG53 D4
FG54 D4
FG56 D4
FJ00 A7
FJ01 A5
FJ02 A4
FJ03 A5
FJ04 A5
FJ05 A4
FJ06 A4
FJ07 A5
FJ08 A4
FJ09 A2
FJ10 A2
FJ11 A4
FJ12 A2
FJ13 A2
FJ14 A2
FJ15 A7
FJ16 A7
FJ17 A7
FJ18 A7
FJ19 A7
FJ20 A7
FJ21 A5
FJ22 A5
FJ23 A5
FJ24 A5
FJ25 A5
FJ26 A5
FK00 B1
FK01 B1
FK02 B1
FK03 B1
FK04 B1
FK05 B1
FK06 B1
FK07 C1
FK08 C1
FK09 C1
FK10 B1
FK11 A1
FM01 C4
FM02 C4
FM03 C4
FM04 C4
FM05 C4
FN01 A6
FN02 A6
FN03 A6
FN04 A7
FN05 A7
FN06 A7
FN07 A7
FN08 A7
FN09 A7
FN10 A7
FN11 B6
FN12 A6
FN13 A6
FN14 A6
FN15 A6
FN16 A6
FN17 A6
FN18 B6
FN19 B5
FN20 A7
FN21 A7
FN22 A7
FN23 A7
FN24 A6
FN25 B6
FN26 A7
FN27 A7
FN28 A7
FN29 A7
FN30 A7
FN31 A7
FN32 A7
FN33 A7
FN34 A7
FN35 A7
FP01 A6
FP02 A6
FP03 A6
FP04 A6
FP05 A6
FP06 A6
FP07 A6
FP08 A7
FP09 A7
FP10 A7
FP11 A7
FP12 A7
FP13 A6
FP14 A7
FP15 A6
FP16 A6
FP17 A7
I101 D2
I102 C2
I103 C2
I104 C2
I105 C2
I106 C2
I107 C2
I108 C2
I109 C2
I110 C2
I111 C1
I112 D2
I113 D2
I201 A2
I202 A2
I203 B2
I204 B2
I205 B2
I206 B2
I207 B2
I208 B2
I209 B2
I210 A3
I211 A3
I212 A3
I213 A2
I214 B2
I215 A2
I216 B2
I217 B3
I218 A3
I219 B3
I220 B3
I221 A2
I222 A2
I223 A2
I224 A3
I225 A2
I226 B2
I227 B2
I228 B3
I229 B2
I230 A3
I231 B2
I232 A2
I233 B2
I234 B2
I235 B2
I236 B2
I237 B2
I238 A2
I239 A3
I240 A3
I241 A2
I242 A2
I243 A3
I244 B3
I246 A3
I247 A3
I248 A3
I254 C3
I255 B3
I256 B3
I257 B3
I258 B2
I259 B3
I262 B2
I264 A2
I265 B3
I266 B3
I267 B3
I268 B3
I269 A2
I270 B3
I271 A3
I272 B3
I273 C3
I274 A1
I275 A3
I277 A3
I278 A3
I283 B3
I284 B3
I285 B3
I288 B3
I289 A2
I290 A2
I291 A2
I292 A2
I293 A2
I294 A2
I297 A1
I298 B3
I430 A1
I440 B3
I443 B3
F_15430_038.eps
180405
I449 A3
I450 A3
I451 A3
I452 A3
I453 A1
I454 A1
I501 A3
I502 A3
I503 A2
I504 A2
I505 A2
I602 A1
I603 A2
I604 A1
I605 A2
I606 A2
I607 A1
I608 A1
I610 A1
I611 B1
I612 A1
I613 A1
I614 A1
I615 A1
I616 A1
I617 A2
I618 A1
I619 A1
I705 A3
I706 A4
I708 A5
I709 A5
I710 A4
I711 A4
I712 A4
I713 A4
I714 A4
I715 A4
I716 A4
I731 A4
I732 A3
I733 A3
I734 A3
I735 A3
I736 A3
I740 B3
I741 B3
I742 B3
I747 A5
I748 A5
I749 A5
I750 A6
I751 A5
I752 A5
I753 A5
I754 A5
I755 A5
I756 A6
I757 A5
I758 A5
I759 A5
I760 A6
I800 C6
I801 C5
I802 B5
I803 B5
I804 B6
I805 B5
I806 B5
I807 B5
I808 B5
I809 B5
I810 B5
I811 C7
I812 C6
I813 B7
I815 C6
I816 C6
I817 C6
I818 C4
I819 B5
I820 B6
I821 B5
I822 B5
I900 B7
I901 B6
I902 C6
I903 C6
I904 B6
I905 B6
I906 C5
IA00 C6
IA03 B4
IA05 C6
IA06 C6
IA07 C6
IA08 B5
IA09 B6
IB02 B7
IB03 B7
ID00 C7
ID01 D7
ID02 C7
ID03 C7
ID04 C7
ID05 C7
ID06 C7
ID07 C7
ID08 C7
ID09 C7
ID10 C7
ID11 C7
ID12 C7
ID13 C6
ID14 C6
ID15 C7
ID16 C7
ID17 C7
ID18 C7
ID19 C7
ID20 C7
ID21 C7
ID22 C6
IE00 D4
IE01 C4
IE02 D5
IE03 C6
IE04 C5
IE05 C5
IE06 C4
IE07 C4
IE08 C4
IE09 C5
IE10 C5
IE11 C5
IE12 C5
IE13 D5
IE14 D4
IE15 D4
IE16 C4
IE17 C4
IE18 C4
IE19 D5
IE20 D5
IE21 D5
IE22 D5
IE23 C5
IE24 C5
IE25 D5
IE26 D5
IE27 C5
IE28 C4
IE29 C4
IE30 C4
IE31 C5
IE32 C5
IE33 C5
IE34 C5
IE35 D5
IE36 C5
IE37 C5
IF00 D7
IF01 D7
IF02 D7
IF03 D7
IF04 D6
IF05 D6
IF06 D7
IF07 D7
IF08 D7
IF11 D6
IF12 D6
IF13 D7
IF14 D7
IF15 D6
IF17 D7
IF20 D7
IF21 D4
IF22 D6
IF23 D6
IG00 D4
IG01 D4
IG02 D4
IG03 D4
IG04 D3
IG05 D3
IG06 D3
IG07 D3
IG08 D3
IG09 D3
IG10 D3
IG11 D3
IG12 D3
IG13 D2
IG14 D6
IG15 D5
IG16 D6
IG17 D5
IG18 D6
IG19 D5
IG20 D6
IG21 D5
IG23 D5
IG24 D5
IG25 D5
IG26 D5
IG27 D4
IG28 D3
IG29 D3
IG30 D3
IG40 D5
IG42 D5
IG43 D4
IG46 D5
IG47 D5
IG49 D4
IG50 D4
IG52 D5
IG53 D5
IG54 D5
IG55 D5
IG56 D5
IG57 D5
IG58 D5
IG59 D4
IG60 D3
IG61 D2
IG62 D2
IG63 D3
IG64 D3
IG67 D3
IG69 D3
IG73 D4
IG75 D5
IG76 D6
IG78 D5
IG79 D5
IG80 D5
IJ01 A3
IJ02 A3
IJ03 A4
IJ04 A3
IJ05 A3
IJ06 A3
IJ07 A3
IJ08 A3
IJ09 A3
IJ10 A3
IJ11 A3
IJ12 A3
IJ13 A3
IK00 A1
IK01 A1
IK02 A1
IK03 A1
IK16 A1
IK17 B1
IK18 B1
IL01 B3
IL02 B3
IL03 B3
IL04 B3
IL05 B3
IL06 B3
IL07 B3
IL08 B3
IL09 B3
IL10 B4
IL11 B4
IL12 B4
IL13 B4
IL14 B4
IL15 B4
IL16 C3
IL17 B3
IL18 B3
IL19 B4
IM00 C4
IM01 C3
IM03 B4
IM04 B4
IM06 B4
IM07 B4
IM08 B4
IM09 B4
IM10 B3
IM11 C3
IN01 A6
IN02 A6
IN03 A6
IN04 A6
IN05 A6
IN06 A6
IN07 B6
IN08 A6
IN09 A6
IN10 A6
IN11 A6
IN12 A6
IN13 B6
IN14 A6
IN15 B6
IN16 A7
IN17 A7
IN18 A7
IN19 A6
Page 26
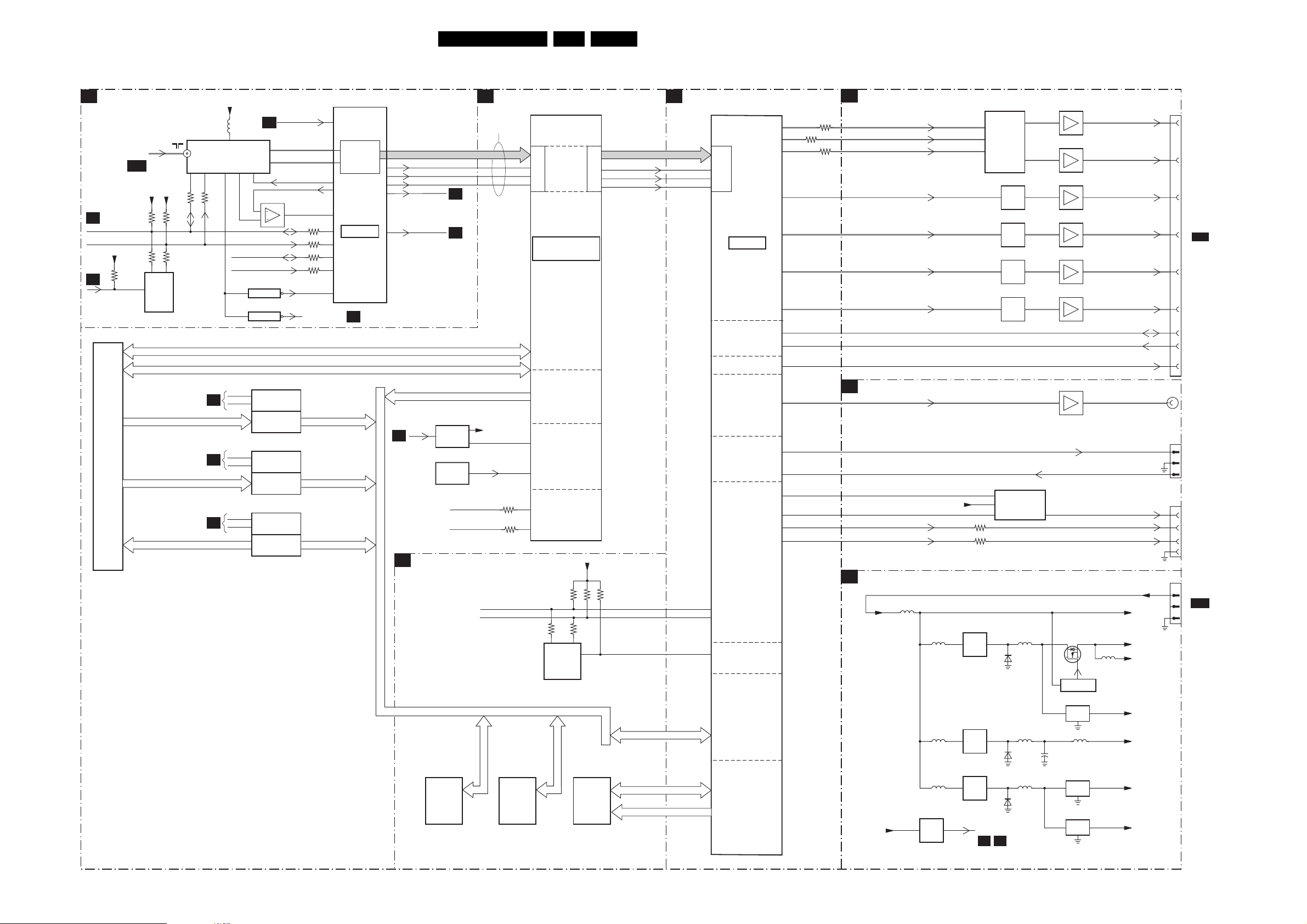
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram IBO Zapper
IBO - ZAPPER PANEL
FRONT END
K6
1600
+5V+5V
3627
3633
TD1316L
9
3607
3606
8
K7
K7
K7
TUNER
B2B
K6
I2C_TDA_SDA
I2C_TDA_SCL
+5V
K1
3634
DSP_EEPROM_WP
68P PCMCIA
CONNECTOR
13435
68
FROM
MAIN
3626
3612
7
M24C256
EEPROM
RF-IN
56
7602
+5VClean
5602
11
TUNER
10 5 13
AGC
XTAL
7601-1
LM393D
2
3
I2C_LOCAL_SDA
I2C_LOCAL_SCL
7605
74AHC1GU04GW
2
INVERTER
7606
74AHC1GU04GW
2
INVERTER
A_MD (0-7) + A_MDO (0-7)
CONTROL LINES
7701
74LVC573ADB
7702
74LVC573ADB
7703
74LVC245A
RESET_FE-N
K1
14
15
CONTROL
LATCH
CONTROL
LATCH
CONTROL
BUS
TRANS
CEIVER
IF-AGC
AGC-TUN
1
COMB-OUT
4
4
IF1
IF2
3630
3631
3625
3629
X-IN
4MHz_MOJO
MIU_ADDR (0-7)PCMCIA-A (0-7)
MIU_ADDR (8-14)PCMCIA-A (8-14)
MIU_DATA (0-7)PCMCIA-D (0-7)
7600
TDA10046HT
9
62
61
2
1
21
4
COFMD
3
8
6
54
COFDM
CHANNEL
DECODER
K1
38
TDA_DATA (0-7)
TDA_CLK
37
TDA_VALID
36
TDA_SYNC
35
UNCOR
33
FE_LOCK
25
MIU_ADDR (15-24)
K7
VCCEN
FLASH MEMORY
K2
K7
K1
7705
ST890C
3
CURRENT
SWITCH
7704
FXO-31FT
OSC
27MHz
I2C_LOCAL_SCL 31
I2C_LOCAL_SDA 30
7200
M29W32ODT
EEPROM
NOR
FLASH
COMMON INTERFACE
K7
MPEG
8
PCMCIA_5V
FAULT
6
3700
3701
I2C_LOCAL_SDA
I2C_LOCAL_SCL
MIU BUS
7201
M58LWO32A
NOR
FLASH
(optional)
7700
STV0700
TS
TS
50
INTER
IN
48
FAC E
49
PCMCIA
CONTROLLER
UCSG
12
INTERRUPT
MANAGEMENT
35
ICC
INTERFACE
3209
5
7203
M24Z64
EEPROM
8KX8
TS
OUT
+5V
3207
3206
3210
6
7
7202
KUS281632D
SYNC
DRAM
4x2Mx16
26LC4.9E AB 6.
TS_DATA (0-7)
TS_CLK
63
TS_SYNC
62
TS_VALID
61
3211
user_EEPROM_WP
K1
SDRAM_DATA
SDRAM_ADDR
MOJO
185
7100
PNX8316HS
TS
29
IN
30
28
7
6
AV
MOJO
I2C
GPIO
AV
GPIO
I2C
GPIO
MIU
SDRAM
202
203
204
172
165
163
167
180
8
9
206
198
199
201
200
ANALOG BACK END
K5
3135
3134
3133
15
14
MOJO_I2S_OUT_SD
MOJO_I2S_OUT_SCK
MOJO_I2S_OUT_WS
INTERFACE
K4
USB_OVRCUR
POWER SUPPLY
K3
+3V3
C_CVBS
USB_PWR
USB_DM
USB_DP
+12V
G/Y
B/Pb
R/Pr
TV_IRQ
SPDIF
5309
+5V_USB
5301
5304
5306
73006
NCP303LSN30
POWER
12
ON
RESET
7502
UDA1334ATS
3
1
2
2
7
1
3420
3421
7300
MC34063AP1
26
SUPPLY
7303
MC34063AP1
26
SUPPLY
7305
MC34063AP1
SUPPLY
RESET_n
K1 K2
16
AUDIO
DAC
14
5511
5511
FILTER
FILTER
5512
FILTER
5513
FILTER
5514
FILTER
7403
LM3525
Power Switch and
Over-current
Protection
5300
6300
5303
6303
5305
6304
2311
6,8
TXDO
RXDO
7500
7501
7503
7504
7507
7507
7508
7508
7509
7510
7505
7506
7402
EF
7311
7309
7310
CONTROL
7302
LD1117V18
IN OUT
COM
5307
7307
LD1117V50
IN OUT
COM
7308
LD1117V50
IN OUT
COM
CVBS_VCR
GREEN/Y
BLUE/U
RED/V
I2C_TV_SDA
I2C_TV_SCL
TV_IRQ
VBUS
USB_D-
USB_D+
5302
R1
L1
1401
1403
+12V
+12V_A
+3V3
+3V3
CLEAN
+1V8FE
+1V2_MOJO
+5V
+5V
CLEAN
F_15660_006.eps
280705
1500
12
10
14
1402
1301
4
6
8
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
TO 1G03
B15
SSB
SPDIF
OUT
UART
CONN.
FOR
COMPAIR
ONLY
USB
CONNECTOR
(Optional)
TO X220
PSU
Page 27

Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Testpoint Overview IBO Zapper (Bottom Side)
27LC4.9E AB 6.
3139 123 5906.2
F_15270_063.eps
200505
Page 28
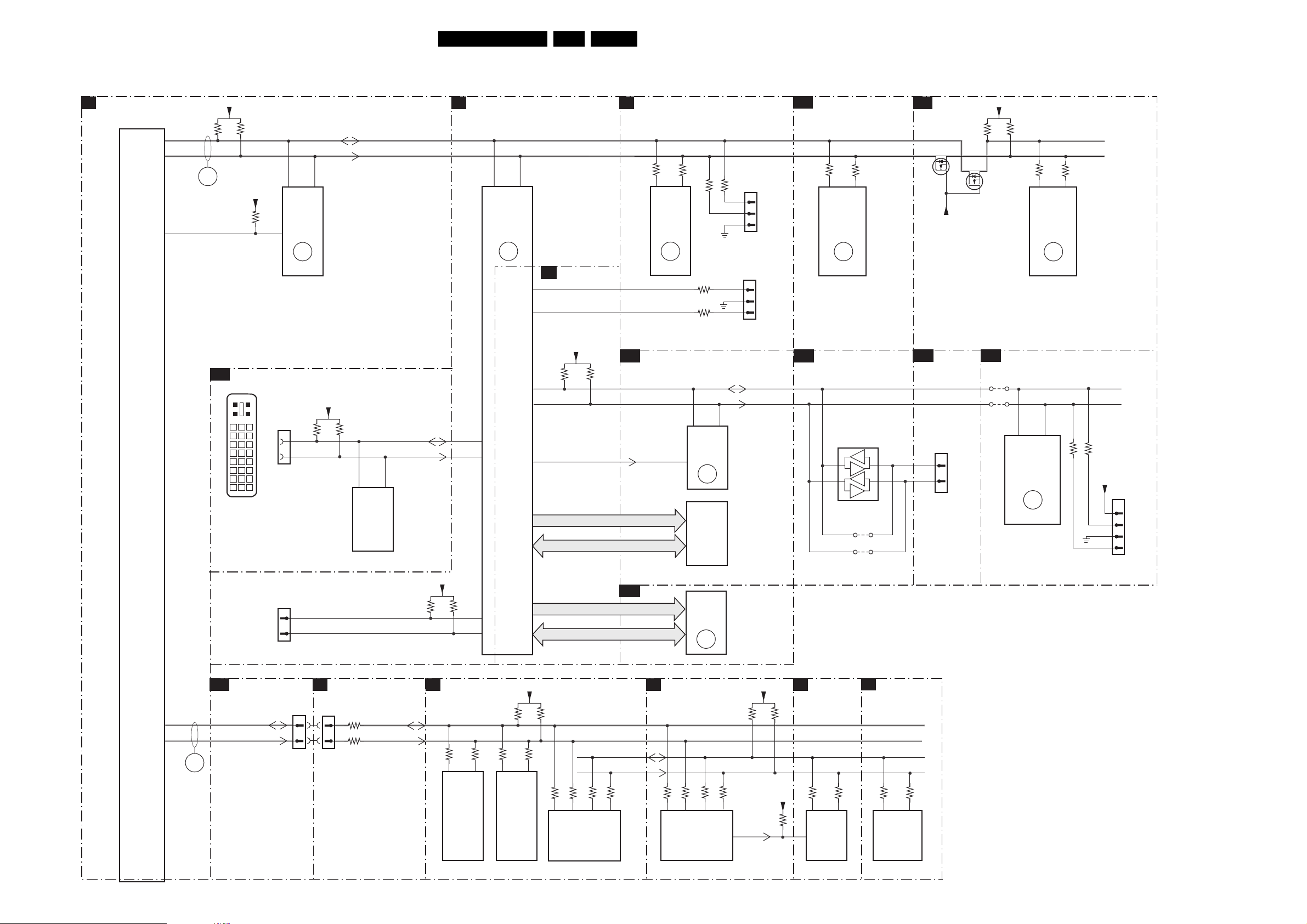
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
I2C Overview
28LC4.9E AB 6.
I²C
B2
HERCULUS
7217
TDA15021H
HERCULES
PROCESSOR
SET
109
108
104
+3V3STBY
3232
3233
ERR
6
NVM_WP_HERC
DIGITAL IO
B14
C1 C2
18
DVI-D
CONNECTOR
SCART ANALOGUE IO
B15
+3V3STBY
3249
C5
C3 C4
24
916
17
56
M24C16
EEPROM
7
1F00
7
6
1802
2
1
JTAG
I2C
SDA
SCL
7207
NVM
ERR
9
DCC_5V
3F18
JTAG_TDI_SDA
JTAG_CLK_SCL
IBO ZAPPER
ANALOG BACKEND
K5
3F17
SDA_DVI
SCL_DVI
6
5
7F03
M24C02
EEPROM
256x8
(Only For DVB Sets)
+3V3IO
3838
K6
SCALER
B8
3837
AF7
AD6
FRONT END
N3
N4
N1 N2
7801
GM1501H
SCALER
ERR
4
ADDRESS
DATA
ADDRESS
DATA
+5V
SCALER
B7
M1
M2
3818
P3
P4
NVM_WP_SCALER
AF5
+3V3SW
OCMADDR
FSADDR
3817
OCMDATA
FSDATA
TUNER & IF
B1
3102
(5108)
UART_TX
UART_RX
FLASH / CONTROL
B11
SDRAM
B10
K1
3101
(5107)
54
1102
UV1318S
TUNER
ERR
10
3122
3123
56
7C01
M24C32
7
EEPROM
7C00
MX29LV040
FLASH ROM
7B01
K4D263238F
SDRAM
MOJO
3125
SDA_IO
SCL_IO
ERR
8
ERR
14
1101
3124
SDA
SCL
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
COMPAIR
1107
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
UART
COLUMBUS
B19
3M14
3M15
A15 B15
1
2
3
1
2
3
B9
+5V
K2
7M00
T6TU5XBG
COLUMBUS
CTRL
ERR
11
SCALER INTERFACE
7A00
PCA9515ADP
3
2
4A01
4A00
FOR
PDP ONLY
MEMORY
RES
K7
6
7
MEMORY
B18
B21
ADC
7L07
+3V3SWB
EPLD
1P07
(1G50)
31
30
TO
DISPLAY
7L06
+3V3SWB
3L36
EPLD
B20
4N21
4N22
3L37
3L19
57 56
7L04
MST9883C
ANALOG
INTERFACE
R2
T2
7N02
EP1C12F256C8N
EPLD
BANK 4
ERR
16
ERR
3L20
7
3N47
3N46
+3V3SW
1N02
1
2
SDA
3
4
SCL
FOR
DEVELOPMENT
USE ONLY
112
113
ERR
17
SW_I2C_SDA
SW_I2C_SCL
1G03
1500
1
2
3513
1
2
3512
I2C_TV_SDA
I2C_TV_SCL
3607
3605
98
1600
TD1316L
TUNER
DIGITAL
3632
M24C256
EEPROM
3627
3626
3625
3631
3
7600
TDA10046
COFDM
I2C_local_SDA
I2C_local_SCL
3629
6
8
3147
9
3144
3146
7
8
7100
PNX8316HS
MOJO
3143
6
185
3633
6
5
7602
3630
4
CHANNEL DECODER
3207
WP
3206
+5V
3625
3209
7
5
7203
M24C64
EEPROM
3210
3701
6
3700
30
7700
ST70700
PCMCIA
CONTROLLER
31
F_15270_041.eps
280705
Page 29
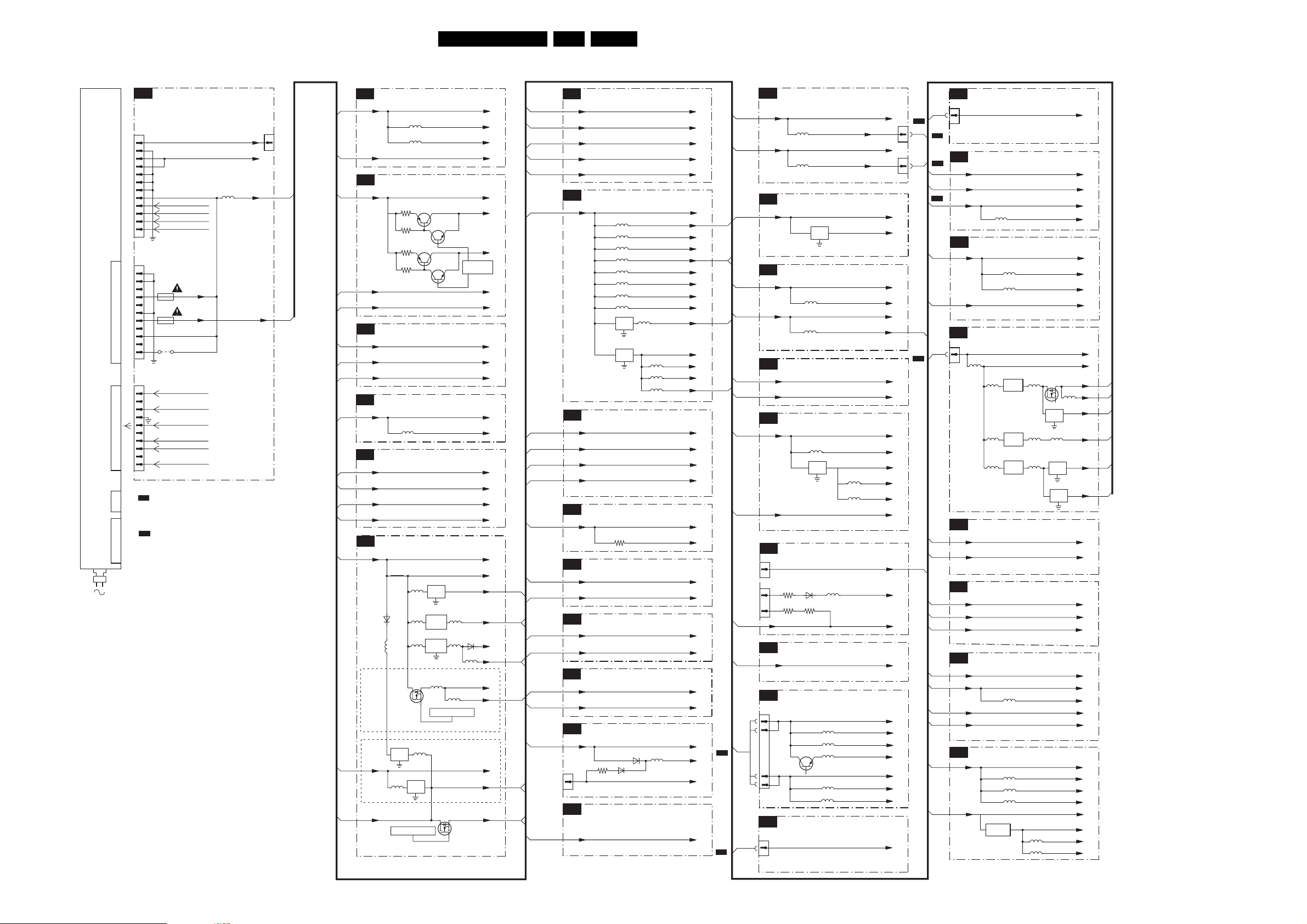
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Supply Voltage Overview
SUPPLY LINE OVERVIEW
SUPPLY
PAN E L
(PSU)
1M46
1M03
1M10
1M02
TOP CONNECTORS
B16
1J02
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
RES
1J01
(1M46)
1
2
3
N.C
.
1J07
4
5
N.C
.
6
1J08
7
8
N.C
.
9
10
N.C
.
4J01
11
1J00
(1M03)
1
2
N.C
.
3
4
5
6
N.C
.
7
8
9
N.C
.
10
TO 1301
K3
POWER
SUPPLY
TO 1M02
C
AUDI O
AMPLIFIER
MFD SUPPY
POWER_DOWN
STANDBY
BACKLIGHT_CTRL
LAMP_ON_OFF
UFD SUPPY
+12VUFD
+5V_UFD
UFD CONTROL
BACKLIGHT_CTRL
LAMP_ON_OFF
FAN_SPEED
STANDBY
PROTECT_AUD
POWER_UP_O
K
5J03
1J03
VP
+3V3STBY
+12VUNREG
+5V_UFD
29LC4.9E AB 6.
TUNER & IF
B1
5753
5754
5733
5700
+5VSW
+5VSW_a
+5VSW_b
+3V3STBY
+3V3STBY
+1V8_A
+1V8_B
HERCULES
+5VSW
+8VSW_TV
+3V3STBY
+3V3SW
+5VSW
+5VSWI
+5VD
+3V3SW
+3V3STBY
+5VSW
+5V
+12VUNREG
+12VSW
+8VSW_TV
+5VSWI
6735
+VTUN
+5VSW
5737
(Only LCD)
PAN+VCC
LVDS_VCC
(Only UFD)
+5V
+3V3STBY
+3V3SW
B8
B8
B6
B8
B8
B6
B16
B16
B6
B6
B8
B8
B6
B6
B22
B6
B6
B6
B6
B2
B4,B9,B13,
B14,B19
B1,B2,B3,
B15,B17
B21
B1,B2,B3,
B5,B9,B17
B3,B5,B7,
B8,B9,B11
B12,B13,
B19,B20,
B21
B6
1
N.C.
B16
B16
B6
B6
B6
B5,B6,B9
B16
B6
B6
B6
B6
B16
B6
B16
B16
B16
N.C.
+5VSW
5102
5103
+3V3STBY
HERCULES
B2
+3V3STBY
3265
7215
3264
3263
7217
3262
+5VSW
+8VSW_TV
SYNC INTERFACE
B3
+3V3STBY
+3V3SW
+5VSW
AUDIO DELAY LINE (RESERVED)
B4
+5VSWI
5501
AUDIO PROCESSING
B5
+3V3SW
+3V3STBY
+5VSW
(Only UFD)
+5V
DC-DC CONVERTER
B6
+12VUNREG
7738
5738
IN OUT
7752
5752
DC/DC
5730
7754
5712
COM
7708
IN OUT
COM
SC_STANDBY
Converter
7730
+5V
+3V3STBY
6708
5709
7710
IN OUT
5704
7216-1
7216-2
COM
PWR
REG
5757
PANEL-PWR-CTL
7758
SCALER
B7
+1V8_CORE
+2V5_DDR
+3V3SW
+3V3_IO
+3V3_PLL
SCALER
B8
+3V3SW
5900
5901
5902
5903
5904
5905
5906
5907
7900
IN OUT
COM
7901
IN OUT
COM
SCALER INTERFACE
B9
+3V3SW
+3V3STBY
+5VSWI
+5V
SDRAM
B10
+2V5_DDR
3B01
FLASH / CONTROL
B11
+3V3_IO
+3V3SW
HDMI (Not for EUR Sets)
B12
+3V3SW
+5VHDMI
MUX-SYNC INTERFACE
B13
+3V3SW
+5VSWI
DIGITAL IO (Only for EUR Sets)
B14
+5VSWI
6F00
6F01
3F20
1F00
1
DVI
SCART ANALOGUE IO (Only for EUR Sets)
B15
+5VSW
5908
5909
5910
5911
5F03
+1V8_CORE
+2V5_DDR
+3V3SW
+3V3_IO
+3V3_PLL
+3V3SW
3V3_PLL
3V3_ADC
3V3_DVI
3V3_IO
3V3_LBADC
3V3_LVDSA
3V3_LVDSB
3V3_LVDS
+2V5_DDR
+1V8
+1V8_ADC
+1V8_DV1
+1V8_CORE
+3V3SW
+3V3STBY
+5VSWI
+5V
+2V5_DDR
FSVREF
+3V3_IO
+3V3SW
+3V3SW
+5VHDMI
+3V3SW
+5VSWI
+5VSWI
DDC_5V
DVI_5V
+5VSW
1M02
PSU
1K01
B17
B16
B19
B6
B6
B6
B8
B6
B6
B6
B6
B6
B7
B7,
B11,B20
B7,B10
B7
HDMI
VGA
SIDE CONNECTORS
B17
+3V3STBY
5K00
+5VSW
5K01
ADC
B18
+5VSWIA
7K05
IN OUT
COM
COLUMBUS
B19
+3V3SW
5M03
+5VSWI
5M04
EPLD
B20
+3V3SW
+3V3-IO
EPLD
B21
+3V3SW
5P01
7P01
IN OUT
COM
LVDS_VCC
DIGITAL IO (Not for EUR Sets)
B22
1Q03
18
1870
9
10
+5VSWI
B23
C
1M02
1
2
5
6
D
1M36
7
+5VSW
6Q16
3Q16
3Q17
5Q16
3Q18
CINCH ANALOGUE (Not for EUR Sets)
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
5708
5714
5701
7702
5705
5709
SIDE I/0
+3V3STBY_1
+5VSW_1
5P02
5P03
+3V3STBY
1K00
+5VSW
1K01
+5VSWIA
+3V3SWB
+3V3SW
+3V3SWA
+5VSWI
+5VSWIA
+3V3SW
+3V3-IO
+3V3SW
+3V3-IO
1V5
1V5-PLL
1V5-INT
LVDS_VCC
+5VSW
DDC_5V
+5VSWI
+5VSW
-19-16V
-19-16VS1
-19-16VS2
VDDOPAMP
+19-16V
+19-16VS1
+19-16VS2
+5VSW
LED PANEL
J
0345
K3
K3
K3
K3
K3
B18
K3
B12
K3
K3
K3
K3
K3
K3
K3
K3
K3
5
0345
J
1M16
K1
D
+1V2_MOJO
1540
J
(ONLY FOR DVB SET)
K2
(ONLY FOR DVB SET)
K3
1301
1
(ONLY FOR DVB SET)
K4
(ONLY FOR DVB SET)
K5
+3V3clean
(ONLY FOR DVB SET)
K6
(ONLY FOR DVB SET)
K7
(ONLY FOR DVB SET)
MOJO
3V3clean
+3V3
5100
FLASH MEMORY
+3V3
5201
5200
+5V
POWER SUPPLY
5309
5301
5304
5306
7300
MC34063AP1
6
SUPPLY
7303
MC34063AP1
6
SUPPLY
7305
MC34063AP1
6
SUPPLY
INTERFACE
+3V3
+5V_USB
ANALOG BACK END
+3V3
+5V
FRONT END
+1V8FE
+3V3
5801
+5V
+5Vclean
COMMON INTERFACE
+3V3
5703
5704
5702
+5V
7705
1
CURRENT
SWITCH
5300
2
5303
2
5305
2
7
5700
5701
1K00
B17
5
7
1M10
PSU
N.C.
7311
7P01
IN OUT
COM
5307
7P01
IN OUT
COM
7P01
IN OUT
COM
PCMCIA_AVCC
+5V2-STBY
+1V2_MOJO
3V3clean
+3V3
+3V3_MOJO
+3V3
+3V3_NOR48
+3V3_NOR48
+5V
+12V
+12V_A
+3V3
3V3clean
5302
+1V8FE
+1V2_MOJO
+5V
+5Vclean
+3V3
+5V_USB
+3V3
+3V3clean
+5V
+1V8FE
+3V3
+3V3_FE
+5V
+5Vclean
+3V3
+3V3_STV
+3V3_CORE
+3V3_BUF
+5V
PCMCIA_5V
PCMCIA_VPP
F_15670_005.eps
K1,K2,K4,
K5,K6,K7
K1,K5
K6
K1
K2,K5,
K6,K7
K6
010805
Page 30
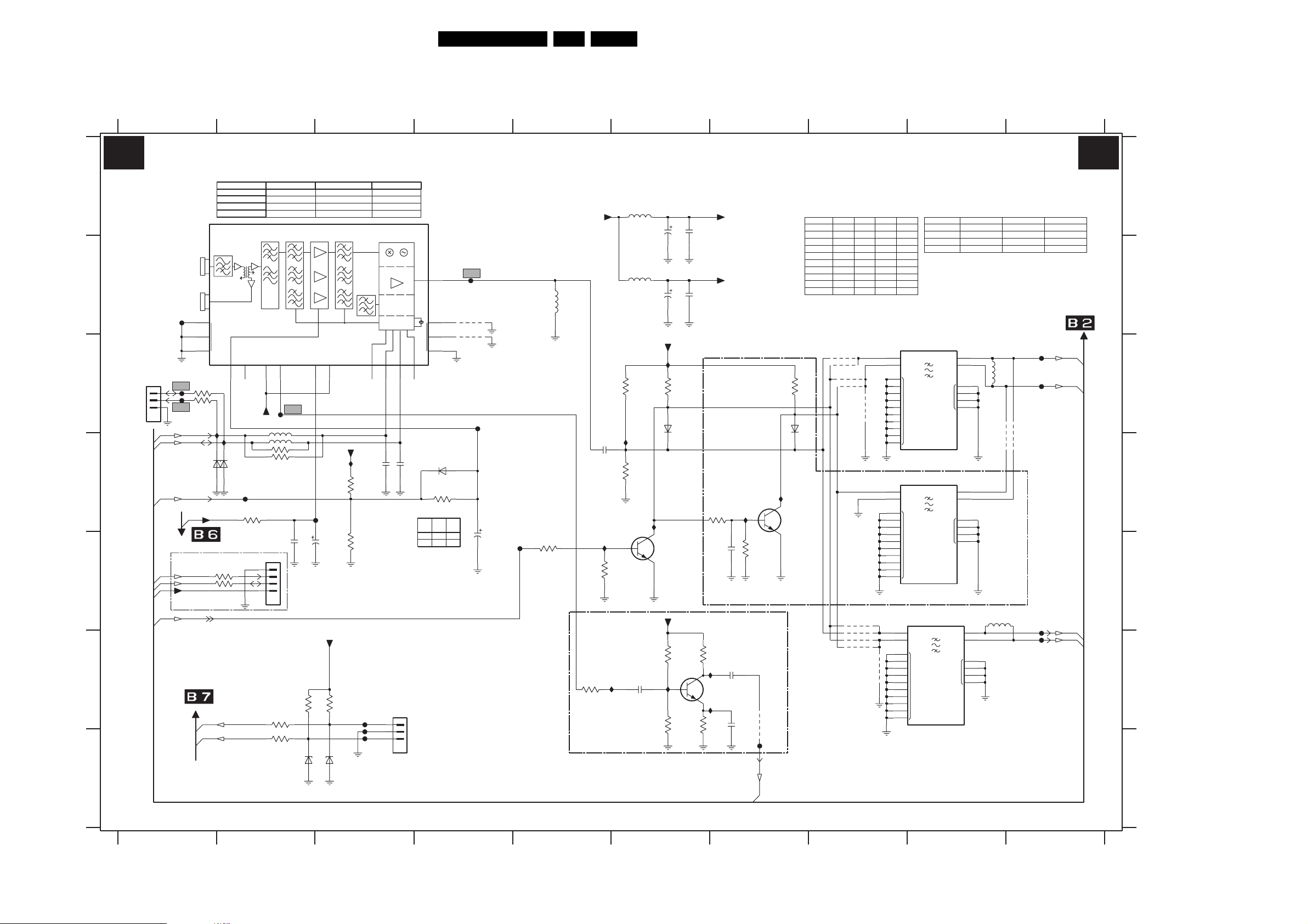
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
7. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
SSB: Tuner and IF
30LC4.9E AB 7.
12345678910
TUNER & IF
B1 B1
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
3139 123 6093.1
STANDARD SD2
UV1318S/AI H N3
UV1318SI/AI C H3
UV1316E/A I H4
UV1338/A F SH4
TRACK
PRE-FIL
FILTER
1102
UV1318ST/AIH-MK3
RF
IN
*
EUROPE
CHINA
AP(PAL)
NA/LA/AP(NTSC)
PRE-FIL
BOOSTER
SPLITTER
RF
OUT
F101
12
13
MT
14
NC1
SERVICE
COMPAIR
1101
1
2
3
45
3124
F102
100R
3125
F104
100R
SCL
SDA
RF_AGC
SCL
SDA
+3V3STBY
SEL_IF_SDM
FROM SCALER
AGC1
I112
I113
6101 6102
BZX384-C6V8BZX384-C6V8
+VTUN
For ITV Only
3126
100R
3127
100R
UART_TX
UART_RX
TU2
1V7
F106
3105
1K0
NC
5VSW_a
5107
5108
3102
3101
NC2
0V
6
10
F103
RES
RES
100R
100R
1103
1
2
3
4
56
100R3122
6106
12345678910
UV1318SD/A CPHN 3
GAIN
CTRL
PRE-AMP
5V7
33V
933V
F107
2108
2107
2u2
47n
50V
3120
10K
BZX384-C6V8
BZX384-C6V8
IDTV SD2
-
-
-
TRACK
FILTER
5V3
5VSW_a
+3V3STBY
3121
10K
6107
UR1316S/A I H3
UR1316S/A I H3
UR1316S/A I H3
UR1336/A F I S H3
INTMED
FILTER
AS3
I101
22p
3103
10K
3106
RES
F115
F116
F1173123 100R
FM RADIO SD2
MIX-OSC
IF AMP
AGC
DET
PLL
SCL4SDA5
5V3
2V6
2V6
21052104
22p
SERVICE
UART
1107
45
IFOUT
MT
ADC8
1
2
3
NC
*
3104
61030R-
11
15
16
17
6103
BAS316
3104
10K
Non-
EU EU
10K
Yes
10n
I103
5102
3107
6K8
3109
2K2
6u8
5103
6u8
5VSW_b
2101
100u
16V
2113
100u
16V
I102
3108
2K2
6104
1SS356
+5VSW
F108
0V
4115
RES
4116
RES
F105
IF-TER
5101
390n
2106
*
*
2109
22u
16V
F109
3111
22K
I104
3112
18K
7101
BC847BW
0V
I105
0V
2102
10n
2103
10n
3113
22K
1u0
2114
5VSW_a
5VSW_b
I106
3114
47K
EU AP CHINA NAFTA
**
4102
YY Y
4103
--
4104
--
4106
Y
4110
YYYYY
4111
4113
--
4107
------
4108
4102
4103
3110
2K2
6105
1SS356
4104
4105
OFWK3955L
I110
7102
BC847BW
*
*
*
*
-Y
--
-----Y
--
4106
--
Y
Y
Y
Y
2
3
1105
1
4
5
6
9
10
13
14
15
18
2
3
1
4
5
6
9
10
13
14
15
18
--
--
-Y
--
--
--
--
I1
I2
GND
*
I1
I2
GND
NAFTA OFWM1967L
1104
OFWK3953L
*
38M9
38M
1104
OFWK3953LEUROPE
OFWK7265LAP
OFWK3956LCHINA
7
O1
8
O2
11
12
NC
16
17
7
O1
8
O2
11
12
NC
16
17
OFWK9355L
5105
RES
**
4107
1105
--
--
-- --
F110
VIF1
F111
VIF2
4108
OFWK9656L
OFWK9361L
OFWK9352L
FOR -/93 ONLY
3115
I111
2110
1n0
+5VSW
I107
3116
100K
3118
150K
3117
820R
I108
7103
BFS20
I109
3119
560R
2111
1n0
2112
1n0
4114
F114
4109
4110
4111
4112
EUROPE & AP
PAL-MUTLI
ONLY
2
*
3
*
1
4
*
5
6
4113
9
10
13
14
15
18
OFWK9656L
I
ISWI
GND
1106
40M4
RES
*
NC
5106
7
O1
8
O2
11
12
16
17
SIF1
SIF2
F112
F113
FOR FM RADIO ONLY
SSIF
1106
F_15430_001.eps
140405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1101 C1
1102 A1
1103 E2
1104 C9
1105 D8
1106 E9
1107 F3
2101 A6
2102 A6
2103 B6
2104 D3
2105 D3
2106 D5
2107 E2
2108 E3
2109 D4
2110 F6
2111 F7
2112 F7
2113 B6
2114 E7
3101 D2
3102 D2
3103 D3
3104 D4
3105 D2
3106 E3
3107 C6
3108 C6
3109 D6
3110 C7
3111 E5
3112 E5
3113 D7
3114 E7
3115 F5
3116 F6
3117 F7
3118 F6
3119 F6
3120 F3
3121 F3
3122 F2
3123 G2
3124 C1
3125 C1
3126 E1
3127 E1
4102 C8
4103 C8
4104 C8
4105 C8
4106 C8
4107 D9
4108 D10
4109 E8
4110 F8
4111 F8
4112 F8
4113 F8
4114 F7
4115 B4
4116 C4
5101 B5
5102 A6
5103 B6
5105 C9
5106 E9
5107 D2
5108 D2
6101 D1
6102 D2
6103 D4
6104 C6
6105 C7
6106 G2
6107 G3
7101 D6
7102 D7
7103 F6
F101 B1
F102 C1
F103 C2
F104 C1
F105 C4
F106 D2
F107 D3
F108 B4
F109 E5
F110 C10
F111 C10
F112 E10
F113 F10
F114 G7
F115 F3
F116 G3
F117 G3
I101 D3
I102 C6
I103 D6
I104 E5
I105 D6
I106 D7
I107 F6
I108 F7
I109 F7
I110 D7
I111 F6
I112 C1
I113 D2
Page 31

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
31LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Hercules
123456789101112
HERCULES
B2 B2
AUDIO PROCESSING
A
B
OUT_MUTE
C
RESERVED
D
E
F
G
H
3139 123 6093.1
B15/B23
SC2_CVBS_MON_OUT
B7
123456789101112
B5
HETV
(15W)
3203
3202
3206
3205
B5
7201-1 PUMH7
B5
0V
+5VSW
B13
B13
B13
F210
SC2_OUT_SW
B15 / B23
AUDOUTLSR
MTV
(5W)
5K6
820R
5K6
10K
5K6
820R
5K6
10K
AUDOUTLSL
PUMH77201-2
INTF_V_OUT
INTF_Y_OUT
INTF_U_OUT
3250
100R
R_SDTV
B_SDTV
G_SDTV
7219
RES
MDX
14
15
4
SC2_L
SC1_L
SC1_R
SC2_R
Const_R_OUT
5218
F201
3V9
7202-1
PUMH7
3228
3244
3289
I246
2203
10u
16V
3256
0R
3259
330R
+5VSW
RES
RES
RES
6
3291
13
11
RES
1
2
10
3293
3
5
9
3V9
3V9
7209
BC847BW
7208
BC847BW
RES RES RES
3255
0R
3258
330R
2291
16
VDD
G4
1
2
4X1
4X2
VEEVSS
7
8
B15
B15
Const_L_OUT
SC2_L_MON_OUT
SC2_R_MON_OUT
F202
F204
F203
7202-2
PUMH7
RES
RES
RES
7210
BC847BW
3257
0R
3260
330R
RES
150R3282
3292
2290 4u712
RES
3294
2V5
7216-2
BC847BS
2280
4u7
3201 100R
2281
4u7
3204
100R
Const_L_OUT
Const_R_OUT
3V9
7203-1
PUMH7
F220
F221
I218
42094207 4208
4206
3262
22K
2V1
3
5
4
+8VSW_TV
*
I289
I290
I292
I293
7214
BCP69-25
3202
1u0
2201
I291
7204-2
BC857BS
I294
2202
1u0
7205-2
BC857BS
7203-2
3V9
PUMH7
3251
100R
3252
100R
3253
100R
+8VSW_TV
+5VSW
ES10.3B RESET (RESERVED)
3254
I242
1K0
+3V3STBY
3263
3R9
3264
22K
2V8
3
7216-1
BC847BS
2
2
4
1V9
2208
1u0
+8VSW_TV
3V9
I243
1
50V
*
3203
7204-1
BC857BS
+8VSW_TV
3205
I247
I248
+1V8_B
3265
3R9
2V
11
6
1V9
+8VSW_TV
*
7205-1
BC857BS
GND
+1V8_A
+1V8_B
6201
BAS321
7211
BC847BW
2V7
3
7215
BCP69-25
2
4211
*
3206
+3V3STBY
5206
2234 220n
5207
2235
220n
F227
+3V3STBY
+3V3STBY
+3V3STBY
+1V8_A
2u22206
RES
2205
4
F230
F231
2209
16V10u
4212
+5VSW
GND1
I221
+1V8_B
+1V8_A
3280
1R0
3267 5K6
2207
220n
+1V8_A
+1V8_B
I201
I202
2230
5204
2231 220n
5205
2232
2233
5208
5209
5210
2238
5211
2239 100n
5212
2240 220n
5213
2241
2242
2243
5K63266
B1
B15/B23
SEL_IF_SDM
AV2_DMMI_SW
100R
3296
100n
100n
10u 16V
220n2236
220n2237
220n
220n
100n
10u
16V
F232
4201
2258 10u
SC1_G_CVI_Y_IN
B13
+5VSW
+5VSW
5201
5202
2210 220n
10u
I219
RES
2228 100n
2229
82
VP3
47
F222
VP2
15
F223
VP1
110
F224
VDDP_3.3
I220
69
VDDCOMB
3
VDDC4
124
I222
VDDC3
100
VDDC2
117
F225
VDDC1
F226
96
VDDADC_1.8
4
I223
VDDA3_3.3
94
F228
VDDA2_3.3
88
I224
VDDA1
93
VDDA_1.8
45
F229
VCC8V
8V
2244 100n
2246
F233
F234
F235
4202
4203
4215
4213
4214
SC1_B_CVI_Pb_IN
SC1_CVI_DMMI_B_Pb_IN
SC1_CVI_DMMI_G_Y_IN
SC1_FBL_IN_1
SC1_CVI_DMMI_R_Pr_IN
SC1_R_CVI_Pr_IN
B15/B23
B15/B23
B15/B23
B13
B13
B15/B23
CVBS_COMB
B1
B1
SSIF
RF_AGC
MAIN_OUTR
680R
3207
7217
MAIN_OUTL
10n2211
I203
2V4
AGCOUT
AGC2SIF
463153
100n2245
100n
100R3268
I227
2u2
2247
2285
100n
100R
100R
100R
3208
3209
3210
I285
I288
I284
626360
AUDOUTLSL
AUDOUTHPL
AUDOUTHPR
SSIF
AUDIOIN2L
AUDIOIN2R
54565749503435
I254
50V
SC2_L_IN_1
AudioIN2L
AudioIN2R
B12/B14
B12/B14
B15/B23
3286
B15
B15
SC1_L_RF_OUT
SC1_R_RF_OUT
F206
F205
100R
100R
100R
*EMC
3212
3213
1n0
1n02216
3211
*EMC
2214
I205
I283
I204
0V
363733
61
AVL
AUDOUTSL
AUDOUTSR
AUDOUTLSR
AUDIOIN3R
AUDIOIN4L
AUDIOIN4R
AUDIOIN3L
F236
F239
F237
F238
2248
RES
FRONT_L_IN
FRONT_R_IN
SC2_R_IN_1
SC1_COMP_AV1_L_IN
B17
B17
B15/B23
B15/B23
100R
2288
RES
+5VSW
100n
330R
2218
2219
3216
CVBS_COMB
1201
SFSKA
3215
330R
4M5
2V2
RES
1V6
7206
BC857B
3214
680R
85
86
87
BO
RO
GO
SSIF
SWO
REFO
REFIN
AUDIOIN5L
AUDIOIN5RBBCLIN
PBIN3
YIN3
G
79
80
78
I256
I257
I255
I230
RES
RES
F240
1n0
3271
2250
3270
2249
+3V3STBY
RES
SC1_COMP_AV1_R_IN
B15/B23
3285
0R
5217
RES
RES
I244
3217 1K0
CVBSO
PRIN3
I228
2287
RES
83
10u2251 25V
I206
2
GND
3
100K
RES
3218
2220
I207
44
43
PIP
DVBO
FMRO
BLKIN
C2C4CVBS2
84
595255
I258
100n2252
F241
SC2_AV3_C_IN
B15/B23
B15
16V
100u
2221
+5VSW
F250
SC1_CVBS_RF_OUT
1
I
F209
5203
SANDCASTLE
O
RES
100R
47K
I208
3287
3220
3219
F207
F208
66
21
AVL
EWD
IFVO
DVBO
FMRO
FBISO
PROCESSOR
HERCULES
TDA15021H/N1A11
C3
Y2
Y3
CVBS3
58
I229
I231
100n
100n2253
2254
2255 100n
2286 100n
F243
F242
CVBS_COMB
SC2_Y_IN_1
SC1_CVBS_IN
B15/B23
B15/B23
B3
HOUT
RES
3290
RES
RES
3288
3283
I209
I298
67
48
CSY
IFVO
HOUT
Φ
VIDEO
SIGNAL
CVBS4
DECBG
Y4
5164201438
F248
F244
16V
10u
100n
2256
2257
RES
3284
F212
SVO
DECDIG
I232
I233
100n
2259
B4
I2SDI1
106
O
CVBSI
I2SDI1
DECSDEM
DECV1V8
EHTO
32
118
10u2260
3295 100K
2262 10u
B4
I2SDO1
105
I2SDO1
INSSW3
77
I259
39K
3281
50V
B4
B5
I2SCLK
EXT_MUTE
104
103
I2SDO2
IREF
27
17
I235
I234
6n8
3272 4K7
2263
10V
10V2265
470n
1u0
2264
100R
3222
3V2
I210
102
I2SWS
I2SCLK
PH1LF
PH2LF
16
I236
1K0
3273
I262
100n
B15/B17
IR
+3V3STBY
100p
I297
10R
I211
3223
1u0
100R
I278
2224
3227 3225 4K7
I277
979899
INT0
P0<0:5>
PLLIFRSECPLL
41
422930
19
I237
I226
390R3274
220n
2267
2u2 50V2268
2266
B7
B7
TV_IRQ
TV_SC_COM
I275
100R
2223
3226
+3V3STBY
4K7
3224
I212
RES
F211
3V1
126
INT2T0INT1
SIFIN1
DVBAGC
SIFAGC
1V9
B1
B17
+3V3STBY
PC-TV-LED
I274
2K2
3230 10K
3231
3232 3K3
3229 4K7
0V
3V2
107
127
128
T1
RX
SIFIN2
DVBIN1
1V9
SIF2
SIF1
B1
B8
B8
B5
+3V3STBY
SCL
+3V3STBY
SDA
SOUND_ENABLE
3K3
3233
+3V3STBY
I273
3V2
108
109
111
TX
SCL
SDA
P1<0:7>
VGUARD
VIFIN1
SWIO
DVBIN2
24
25
13
1V9
1V9
I264
100R
3276 75R
3275
F245
5214 1m0
DMMI_RGB_SW
VIF1
VIF2
B1
B1
B15/B23
B23
B15/
B23
B15/
+3V3STBY
+3V3STBY
+3V3STBY
4K7
4K73236
SW_I2C_SDA
SW_I2C_SCL
3235 4K7
3234
+3V3STBY
RES
RES
RES
4205
4204
FOR SERVICE
3237
F213
0V
3V2
123
112
113
114
122
PWM4
PWM3
PWM2
PWM1
PWM0
TPWM
P2<0:5>
VREF_POS_HPR
VREF_POS_LSL
VREF_POS_LSR+HPR
VIFIN2
+3V3STBY
VREFAD
VREF_NEG_HPL+HPR
VREF_NEG_LSL+HPL
86957
91
I238
I239
16V
16V
100u
100n2272
2271
2270 100n
2269 470u
+3V3STBY
RES
2275 8p2
B15
B15
B17
+3V3STBY
STATUS_1
STATUS_2
LIGHT_SENSOR
2225
3240 1K0 1%
I241
100R
F215
F214
3239
3238 100R
0V
0V
I225
I213
115
116
119
120
ADC3
ADC1
ADC0
ADC2
VREFAD_NEG
VREFAD_POS
VSC
XTALIN
90
26
89
10
1V4
I240
F246
220n2273
2274 150n
5216
1202
24M576
2276 8p2
B8
B17
KEYBOARD
1n0
3n3
2226
I215
I214
39
QSSO
P3<0:3>
UIN
XTALOUT
11
70
1V4
RES
RES
2283
2282
RES
RES
B9
B6/B15/ B23
SC_STANDBY
INTF_U_OUT
100R
I272
3241
10K
3242
F216
657175
SVM
UOUT
AMOUT
AUDEEM
YIN
YSYNC
VIN
727473
I265
2277 100n
1K5
RES
2284
3277
INTF_Y_OUT
B18
B3/B18
B18
B3
B3/B15/B17/B23
VSYNC
INTF_V_OUT
F218
ITV_IR_SW_RESET
+3V3STBY
I271
I270
NVM_WP_HERC
3247
3248
+3V3STBY
RES
220K
4K7
3245
2293
3243 4K7
I266
3246
POWER_DOWN_BOLTON_P50
I216
76
22
23
VDRB
VDRA
YOUT
VOUT
SWO1
INSSW2
VSSP2
VSSCOMB
VSSC4
VSSC3
VSSC2
VSSC1|P
VSSADC
VSSA1
GNDA
GND3
GND2
GND1
GNDIF
2292
100n
2278
27p
5215
47u
0V
3279
Y_NOTCH
B7
1n0
2227
100R
100R
I217
F247
1
68
2
125
101
121
95
12
92
81
40
18
28
F249
I267
8V
7218
BC847BW
100R
I268
7207
M24C16-WMN6
3V2
7
2V9
6
5
2V8
I269
GND1
3278
68K
4K73249
WC
SCL
6204 BAT54 COL
2279 100n
+3V3STBY
(2Kx8)
EEPROM
+8VSW_TV
3V2
8
Φ
ADR
4
BAT54 COL
6206
RES
6205
POWER_DOWN
POWER-DOWN_BOLT-ON
B6/B7
B15/B23
1
0
2
1
3
2SDA
F219
F_15430_002.eps
150405
G
1201 B7
3215 B6
5209 D5
1202 G10
3216 A6
2201 A3
3217 B7
2202 B3
3218 B7
2203 D2
3219 B7
2205 G4
3220 B7
2206 G4
3222 B8
2207 F5
3223 B8
2208 G4
3224 B8
2209 G4
3225 B8
2210 B5
2211 B6
2214 B6
2216 B6
2218 A7
2219 A7
2220 B7
2221 A7
2223 B8
2224 C8
2225 B10
2226 C10
2227 B11
2228 C5
2229 C5
2230 D5
2231 D5
2232 D5
2233 D5
2234 D4
2235 D4
2236 D5
2237 D5
2238 E5
2239 E5
2240 E5
2241 E5
2242 E5
2243 E5
2244 E5
2245 E5
2246 F5
2247 F6
2248 G6
2249 G6
2250 F7
2251 F7
2252 F7
2253 F7
2254 F7
2255 F7
2256 F8
2257 F8
2258 G5
2259 G8
2260 F8
2262 G8
2263 F8
2264 G8
2265 G8
2266 G8
2267 F8
2268 G8
2269 F9
2270 F9
2271 F9
2272 F9
2273 F10
2274 F10
2275 G9
2276 G10
2277 F10
2278 F11
2279 F11
2280 A3
2281 B3
2282 F10
2283 F10
2284 F10
2285 F6
2286 F7
2287 H7
2288 H6
2290 F3
2291 F2
2292 E11
2293 C10
3201 A3
3202 A4
3203 A4
3204 B3
3205 B4
3206 B4
3207 B6
3208 B6
3209 B6
3210 B6
3211 B6
3212 B6
3213 B6
3214 B7
3226 B9
3227 C8
3228 D2
3229 C9
3230 B9
3231 B9
3232 B9
3233 B9
3234 B9
3235 B9
3236 B9
3237 C9
3238 C10
3239 C10
3240 B10
3241 B10
3242 C10
3243 C10
3244 D2
3245 C10
3246 C11
3247 B11
3248 B11
3249 A11
3250 D2
3251 D3
3252 D3
3253 D3
3254 F3
3255 E2
3256 E2
3257 E3
3258 E2
3259 E2
3260 E3
3262 F3
3263 F3
3264 F4
3265 F4
3266 F4
3267 F4
3268 F5
3270 F7
3271 F7
3272 F8
3273 F8
3274 F8
3275 F9
3276 F9
3277 F10
3278 F11
3279 G11
3280 E4
3281 F8
3282 F3
3283 B8
3284 B8
3285 G6
3286 H6
3287 B7
3288 B7
3289 D2
3290 B8
3291 F2
3292 F2
3293 G2
3294 G2
3295 F8
3296 B5
4201 F5
4202 F5
4203 F5
4204 C9
4205 C9
4206 F3
4207 E2
4208 E2
4209 E3
4211 A4
4212 B4
4213 F5
4214 F5
4215 F5
5201 B5
5202 B5
5203 B7
5204 D5
5205 D5
5206 D4
5207 D4
5208 D5
A
B
C
D
E
F
H
5210 D5
5211 E5
5212 E5
5213 E5
5214 G9
5215 F10
5216 F10
5217 H7
5218 F2
6201 E4
6204 C11
6205 C11
6206 C12
7201-1 B1
7201-2 C2
7202-1 C2
7202-2 C3
7203-1 C3
7203-2 C3
7204-1 A4
7204-2 A3
7205-1 B4
7205-2 B4
7206 B6
7207 B11
7208 D2
7209 D2
7210 D3
7211 F4
7214 G3
7215 G4
7216-1 G3
7216-2 G3
7217 C6
7218 F11
7219 F2
F201 B2
F202 B2
F203 B3
F204 B3
F205 B6
F206 B6
F207 C7
F208 C7
F209 B7
F210 F1
F211 C9
F212 C8
F213 C10
F214 C10
F215 C10
F216 C10
F218 A11
F219 B12
F220 D3
F221 D3
F222 D5
F223 D5
F224 D5
F225 D5
F226 D5
F227 D4
F228 E5
F229 E5
F230 G4
F231 G4
F232 F5
F233 F5
F234 F5
F235 F5
F236 F6
F237 F6
F238 F6
F239 F6
F240 F6
F241 G7
F242 G7
F243 G7
F244 F8
F245 F9
F246 F10
F247 D11
F248 F8
F249 E11
F250 A7
I201 A5
I202 B5
I203 B6
I204 B6
I205 B6
I206 A7
I207 C7
I208 B7
I209 C8
I210 C8
I211 B8
I212 B9
I213 C10
I214 C10
I215 C10
I216 C10
I217 C11
I218 D3
I219 C5
I220 D5
I221 D5
I222 D5
I223 D5
I224 E5
I225 C10
I226 F8
I227 F6
I228 F7
I229 F7
I230 F7
I231 F7
I232 F8
I233 F8
I234 F8
I235 F8
I236 F8
I237 F8
I238 F9
I239 F9
I240 F10
I241 B10
I242 F4
I243 C4
I244 B7
I246 D2
I247 D4
I248 D4
I254 F6
I255 F6
I256 E7
I257 E7
I258 E7
I259 F8
I262 F8
I264 F9
I265 F10
I266 F10
I267 F11
I268 G11
I269 C11
I270 B11
I271 B10
I272 B10
I273 C9
I274 A9
I275 A9
I277 C8
I278 C8
I283 B6
I284 B6
I285 B6
I288 B6
I289 A3
I290 A3
I291 A4
I292 B3
I293 B3
I294 B3
I297 B8
I298 C7
Page 32

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
32LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Sync Interface
123456789
B3 B3
A
B
C
D
SYNC INTERFACE
TO SIDE CONNECTORS
LED_SEL
4438
RES
4440
COL_HREF
H_DELAY
I454
3458
100R
+3V3STBY
3431
1K0
7430
PDTC114ET
0V
7436-3
74LVC14APW
5
+3V3SW
14
7
+5VSW
3V1
6430
BZX384-C2V7
I453
6431
1N4148
I430
6
3432
9
RES
3463
RES
+3V3SW
14
7
7436-4
74LVC14APW
8
ITV_IR_SW_RESET
3459
H_1FH
100R
+3V3STBY
3451
4K7
HOUT Hsync_SDTV
VSYNC
I443
I440
74LVC14APW
3453
100R
3455
100R
1
3
7436-1
4436
RES
+3V3SW
14
7
4437
RES
+3V3SW
14
7
2
7436-2
74LVC14APW
4
3454
100R
3456
100R
SC1_CVBS_RF_OUT
&
Vsync_SDTV
I449
I450
1440
1
2
3
4
5
67
BM05B-SRSS-TBT
A
B
C
D
1440 D9
1441 E9
2447 E8
2448 E9
2449 E4
3431 A3
3432 B3
3451 A5
3453 B6
3454 B7
3455 C6
3456 C7
3458 D2
3459 D4
3461 E2
3462 E4
3463 C4
4436 A6
4437 B6
4438 D2
4439 E2
4440 D2
4441 E2
5431 E8
6430 A3
6431 B3
7430 B3
7436-1 A6
7436-2 C7
7436-3 D3
7436-4 D4
7436-5 E4
7436-6 E3
I430 B3
I440 C6
I443 B5
I449 D8
I450 D8
I451 E9
I452 E9
I453 B3
I454 B2
E
3139 123 6093.1
+3V3SW+3V3SW
(NC)
I452
S3B-PH-SM4-TB
1441
1
2
3
45
COL_VA
Vsync_SDTV
4439
RES
4441
3461
100R
2447
10p
5431
I451
2448
10p
2449
7436-6
74LVC14APW
14
13
12
7
7436-5
74LVC14APW
11
100n
14
7
3462
10
V_1FH
100R
+12VSW
FOR ITV ONLY
F_15430_003.eps
140405
123456789
E
Page 33

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
SSB: Audio Delay line (Reserved)
33LC4.9E AB 7.
12345678910
B4 B4
AUDIO DELAY LINE (RESERVED)
+5VSWI
5501 1u0
F501
+5VD
A
+5VD
B
C
D
E
F
+5VD
+5VD
COUNTER
COUNTER
7501
M74HC590T
14
EN3
13
C2
2V3
12
G1
11
1+
2V3
10
CT=0
5V3
14
EN3
13
C2
12
G1
5V3
11
1+
2V3
10
CT=0
5V3
7503
M74HC590T
VCC
CTR8
(CT=255)Z4
GND
+5VD
16
VCC
CTR8
(CT=255)Z4
GND
16
2D 3
8
2D 3
8
100n2501
4
5V3
15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2503 100n
5V3
4
15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2V5
7502
5V3
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
*
4504
CY62256LL-70ZC
RAM
32kx8
0
2425261234
21
23
RES
RES
4506
4505
0
A
32k-1
5
1110987654321
678
2EN
14
13
12
222827
9
10
+5VD
2502
9
100n
F502
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
9
I503
4501
I504
4502
I505
*
4503
4504
4503
LCD PDP
NYY
*
N
11121315161718
A
A,1D
2C1
G2
20
2V3
19
14
+5VD
2505
100n
20
5V3
1
EN
11
C1
2
1D
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
10
4507
4508
4509
4510
4511
4512
4513
4514
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
2V6
F504
F505
F503
2506
330p
2507
470p
I501
2V3
+5VD
3501
470R
7504
BC847BW
0V2
I502
2508
82p
3502
47K
2509
82p
2V3
LATCH
7505
74HC573PW
1
11
2V6
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
EN
C1
1D
5V3
+5VD
2504
100n
20
2V3
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
10
LATCH
7506
74HC573PW
2V5
2V5
2V5
2V5
2V5
2V5
2V5
I2SDI1
I2SDO1
I2SCLK
A
B
C
D
E
F
2501 A2
2502 B2
2503 D2
2504 B8
2505 B9
2506 C10
2507 D10
2508 F6
2509 F7
3501 F6
3502 F6
4501 E2
4502 F2
4503 F2
4504 F3
4505 F3
4506 F3
4507 C9
4508 C9
4509 C9
4510 C9
4511 C9
4512 C9
4513 C9
4514 C9
5501 A1
7501 A1
7502 B3
7503 F1
7504 F6
7505 B7
7506 B8
F501 A2
F502 B2
F503 C10
F504 D10
F505 F10
I501 F5
I502 F6
I503 E2
I504 E2
I505 F2
3139 123 6093.1
1234567
F_15430_004.eps
140405
8910
Page 34

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
34LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Audio Processing
123456789
B5 B5
A
B
C
D
E
F
3139 123 6093.1
AUDIO PROCESSING
FROM HERCULES
AUDOUTLSL
AUDOUTLSR
AUDIO-L
AUDIO-R
SOUND_ENABLE
HP_DET_R_DC
POWER_DOWN
EXT_MUTE
OUT_MUTE
+5VSW
3626
10K
3627
22K
4613
ITV ONLY
4601
RES
I613
2616
2u2
4618
RES
2617
2u2
4619
RES
7602-1
74HC08PW
I606
I607
I614
6601
BZX384-C3V3
F601
F602
1
2
10
4611
+3V3SW
4616
14
7
14
7
7605
PDTA143ET
I615
5V
RES
4612
+5V
RES
7602-3
74HC08PW9
4621
2619
47u
+3V3STBY
4617
3V3
3
8
+5VSW
RES
4620
5V2
RES
I605
4605
RES
1K0
1K0
I604
4604
RES
10V
2612
1u0
4609
3632
39R
4610
3633
39R
3605 22K
I608
2603
1u0
2608
1u0
+5V
3628
RES
3629
RES
I617
0V
3623
47K
I610
7602-2
74HC08PW
4
5
12
13
3630
470R
3631
470R
HPIC_LIN
2604
470p
HPIC_RIN
2609
470p
14
7
14
7
3604
22K
2605
1u0
3609
22K
2610
1u0
6
7602-4
74HC08PW
11
3610
100K
3611
100K
0V
I618
0V
7606-1
BC847BS
7606-2
BC847BS
F603
F604
F605
2611
100u
16V
3625
3K3
I612
2V6
2
2V6
3
2V6
6
2V6
5
+5VSW
3V4
7601-1
TS482IDT
2V6
84
5V3
22K3612
7601-2
TS482IDT
2V6
84
5V3
I611
3V2
7607
BC847BW
4606
RESERVED FOR UFD
1
7
3615
10K
+3V3SW
HPIC_LOUT
HPIC_ROUT
+5VSW
2614
100n
3620
10K
4603
4614
RES
4615
RES
I602
I603
3.2 TO 4.3V
4602
2613
1u0
10V
RESERVED FOR UFD
7604
BC847BW
I619
3619
10K
BC847BW
I616
3621
RES
7603
3618
22K
470u
+3V3STBY
2615
16V470u
**
2618
16V
**
SOUND_ENABLE_1
3617
+3V3STBY
3616
HP_LOUT
HP_ROUT
POR_AUDIO
F_15430_005.eps
140405
A
B
C
D
E
F
2603 A5
2604 A6
2605 B6
2608 B5
2609 B6
2610 B6
2611 B6
2612 E9
2613 C8
2614 B8
2615 A8
2616 A4
2617 B4
2618 B8
2619 F5
3604 A6
3605 A7
3609 B6
3610 B6
3611 B6
3612 B7
3615 C7
3616 E9
3617 C9
3618 C8
3619 D8
3620 E8
3621 E8
3623 F5
3625 C6
3626 D2
3627 D2
3628 D5
3629 E5
3630 E5
3631 F5
3632 A9
3633 B9
4601 D2
4602 C8
4603 F8
4604 A9
4605 B9
4606 C7
4609 A9
4610 B9
4611 B4
4612 B4
4613 D2
4614 F8
4615 F8
4616 C4
4617 C5
4618 A4
4619 B4
4620 E5
4621 E5
6601 E4
7601-1 A7
7601-2 B7
7602-1 C4
7602-2 C5
7602-3 D5
7602-4 D6
7603 E8
7604 D8
7605 E4
7606-1 E6
7606-2 F6
7607 C7
F601 A4
F602 B4
F603 A6
F604 B6
F605 B6
I602 A8
I603 B8
I604 A9
I605 B9
I606 C4
I607 C4
I608 A5
I610 B5
I611 C7
I612 C6
I613 E3
I614 E4
I615 E4
I616 E8
I617 F5
I618 A6
I619 D8
123456789
Page 35

SSB: DC-DC Converter
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
35LC4.9E AB 7.
1234567891011
DC-DC CONVERTER
B6 B6
FOR LCD ONLY
FROM SCALER
PANEL-PWR-CTL
7755
PDTC114ET
F755
(0V)
0V6
SUPPLY TO SCALER
+12VSW
5752
1R0
10u
2753
16V470u
GND
SUP_GND3
SUP_GND3
FROM HERCULES
SC_STANDBY
3V1
3753
2754
RES
0V
+5VSWI
37523751
1R0
+3V3STBY
5758
RES
3758
15K
I760
I751
I752
I753
1%1K0
3759
1K0
7756
PDTC114ET
+12VSW
5755
RES
I756
3755
10K 100n
11V7
6
11V7
5
1V2
3750
22K
I748
FOR UFD ONLY
5756
SI2301BDS-T1-E3
11V5
2751
FOR UFD ONLY
7752
MC34063AD
DCOL8
IS7
VCC
CIN_NEG
3754
1%3K3
2755
4n7
I747
2750
2u2
7754
3761
100R
2761
1u0
25V
2
1
6V8
100R
1u0
25V
IPK
OSC
22u16V
I757
SS = 4V9
5757
3
7753
5759
L4940D2T12
RES
I759
13
2759
RES
COM
OUTIN
RES
2
3760
2760
QRS
REFERENCE
REGULATOR
I754
+3V3STBY
3V2
2762
123
567
7758
SI9433BDY-T1-E3
SI4433DY
8
3V2
4
I749
I750
SWC 1
SWE 2
TIMC 3
GND
1751
RES
PAN_VCC
2752
47u
16V
11V7
SUP_GND3
4
SUP_GND3
67
5
4
3
2
1
I758
2756
470p
SUP_GND3
I755
5700
RES
5753
220u
SUP_GND3
5754
10u
2757
16V470u
F700
27012700
100p
3734
2K2
6751
SS14
TO SCALER CELL
F754
5V4
2758
+3V3SW
LVDS_VCC
11V5
+5VSWI
16V470u
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
3139 123 6093.1
FROM TOP CONNECTORS
+12VUNREG
+5V
+12VUNREG
FOR UFD ONLY
3708
6708
SS24
5709
10u
2710 2711
10u
SUP_GND2
10K
I710
10u
SUP_GND2
6709
SS14
6K8
7710
I711
L5973D
3
INH
2
SYNC
NC
SUP_GND2
GND GND_HS
SUP_GND2 SUP_GND2
2704
10u
8
7
27083709
RES
F701
+12VSW
16V
I706
2706
5704
16V10u
I709
I708
2709
47u 16V
NC
6
VREFVCC
Φ
OUT
FB
COMP
9
1
5
4
7708
LF33CPT
1
2
CTRL NC
I712
I714
I715
SUP_GND2
COM
6712
SS36
OUTIN
3
5712
33u
5
4
NC
SUP_GND2
2714
220p
2715
22n
SUP_GND2
I713
I716
3716
4K7
SUP_GND2 SUP_GND2
3712
5K6
1%
3713
3K3
1%
2713
470u
5713
10u
+3V3STBY
F710
2716
16V
470u
16V
SUPPLY TO TUNER & HERCULES
32V9
F736
+VTUN
22u
F737
F738
F743
2737
470u 16V
TO TUNER CELL
6736
BZX384-C33
TO HERCULES CELL
+5VSW
+8VSW_TV
POWER_DOWN
B5
B7
B16
+12VSW
+12VUNREG
BZX384-C8V2
5738
6740
+12VSW
1
2738
47u 16V
3740
1K5
5730
10u
SUP_GND1
COM
I731
2730
10u
25V
SUP_GND1
OUTIN
2
3741
1K5
2733
220p
SUP_GND1 SUP_GND1
7738
L78M08CDT
3
2739
47u 16V
I741I740
2741
220n
2734
22n
3736
4K7
I705
+3V3STBY
7741
BC847BW
8
4
3
7
SUP_GND1
SUP_GND1
3742
15K
7730
L5970D
VCC
COMP5FB
INH
SYNC
VREF
GND
3743
22K
I742
OUT
3732
7742
BC847BW
6735
2735
470p
2736
35V
SUP_GND1
SUP_GND1
5V2
8V
1
2
6
3733
I732
1%1K0
I733
7735
BC817-25
I734
6733
5733
220u
3K3
1%
SS14
SUP_GND1
3735
1K0
SUP_GND1
I736
SUP_GND1
SUP_GND1
2731
470u
5735
1m0
5737
10u
BAV99
I735
SUP_GND1
16V
FOR UFD ONLY
1234567891011
TO EPLD
TO LIPSYNC
F_15430_006.eps
150405
A
B
C
D
G
1751 A10
2700 B11
2701 B11
2704 A3
2706 B3
2708 C3
2709 C3
2710 C2
2711 C2
2713 D5
2714 D4
2715 D4
2716 D6
2730 E2
2731 G5
2733 F2
2734 E3
2735 F6
2736 E6
2737 G6
2738 G2
2739 G3
2741 G3
2750 F9
2751 B9
2752 B10
2753 E8
2754 E8
2755 F9
2756 E10
2757 E11
2758 E11
2759 B9
2760 B9
2761 G9
2762 F9
3708 B2
3709 C3
3712 D5
3713 D5
3716 D5
3732 F4
3733 F4
3734 D11
3735 F5
3736 F3
3740 G2
3741 G2
3742 G3
3743 G4
3750 F9
3751 D8
3752 D8
3753 E8
3754 E9
3755 B9
3758 B8
E
3759 F8
3760 B9
3761 F9
5700 B11
5704 B4
5709 C2
5712 C4
5713 C5
5730 E2
5733 F5
5735 F5
F
5737 F5
5738 F1
5752 D8
5753 E11
5754 E11
5755 A9
5756 A9
5757 A9
5758 A8
5759 B9
6708 C2
6709 C2
6712 D4
6733 F5
6735 E6
6736 E6
6740 G2
6751 E11
7708 B4
7710 C3
7730 E3
7735 E5
7738 F2
7741 G3
7742 G4
7752 D9
7753 B10
7754 A9
7755 B8
7756 G8
7758 F10
F700 B11
F701 A3
F710 B6
F736 E6
F737 F6
F738 F6
F743 G6
F754 E11
F755 C8
I705 E3
I706 B3
I708 B3
I709 B3
I710 C2
I711 C2
I712 C4
I713 C5
I714 C4
I715 D4
I716 D5
I731 E2
I732 F4
I733 E5
I734 F5
I735 E5
I736 F5
I740 G2
I741 G3
I742 G4
I747 B9
I748 F8
I749 A10
I750 A10
I751 D8
I752 E8
I753 E8
I754 E9
I755 D10
I756 B9
I757 A9
I758 D10
I759 B9
I760 B8
Page 36

SSB: Diversity Tables B1-B6
TUNER & IF
B1
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
HERCULES
B2
36LC4.9E AB 7.
SYNC INTERFACE
B3
AUDIO WITHOUT AMPLIFIER
B5
DC DC CONVERTER
B6
Item
AP - non China
Europe
NAFTA/LT
1102
1102
1102
1102
1102
1104
1104
1104
1104
1105
1106
1106
1106
3101
3102
3104
3104
3107
3108
3109
3110
3111
3112
3113
3114
4102
4103
4104
4106
4107
4108
4110
4111
4113
5101
5101
5102
5102
5107
5107
5108
5108
6103
6105
7101
7102
V
V
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV V
VV V
VV
VVVV
VV VVV
VV VVV
VV VVV
VV VVV
VV VVV
VVVVV
VV
VV VV
VV VVV
VV
VVV
VV VVV
VVVV V
V
V
VV
VV VVV
AP - DVB
V
VV
V
V
VV
VV
Europe - DVB
China
V
TUN V+U PLL IEC BGDKM B
TUN V+U PLL IEC BGHIL B
TUNER UV1338/A F S H-4
TUNER UV1316E/A I H-4
TUNER UV1318SD/A CP H N-4
FIL SAW SM 38MHZ9 OFWK3953L R
V
FIL SAW SM 38MHZ OFWM3956L R
FIL SAW SM 45MHZ75 OFWM1967L R
FIL SAW SM 38MHZ9 OFWK7265L R
V
FIL SAW SM 38MHZ OFWK3955L R
FIL SAW SM 38MHZ9 OFWK9656L R
V
FIL SAW SM 38MHZ OFWK9352L R
FIL SAW SM 38MHZ9 OFWK9361L R
RST SM 0603 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 10K PM5COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 6K8 PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 2K2 PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 2K2 PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0603 2K2 PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 22K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 18K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0603 22K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
FXDIND SM 0805 0U39 PM10 COL R
FXDIND SM 0805 0U68 PM10 COL R
FXDIND SM 0805 12U PM10 COL R
V
FXDIND SM 1008 6U8 PM5 COL R
FXDIND 0603 100MHZ 600R COL R
RST SM 0603 100R PM5 COL
FXDIND 0603 100MHZ 600R COL R
RST SM 0603 100R PM5 COL
DIO SIG SM BAS316 (COL) R
V
DIO SIG SM 1SS356 (RHM0) R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
V
Description
Item
LC4.3A AB (DVB-T)
LC4.3E AB/LC4.8E AB/LC4.9E AB (DVB-T)
LC4.3U/L
LC4.3E/LC4.8E/LC4.9E
LC4.3E W/O 3D COMB FILTER
LC4.3A - CHINA
VV VVVV
2203
2229
2244
2245
2246
2255
2286
2289
2289
2290
2291
2292
3250
3251
3252
3253
3255
3256
3257
3258
3259
3260
3270 RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
3282
3285
3286
3291
3292
3292
3293
3294
3295
3296
4206
4213
4214
4215
5218
6206
7208
7209
7210
7217
7217
7219
V
VV VV
VV VV
VV VV
VVVV VV
VVVV VV
V
VV VV
VV V
VVVV VV
VVVV VV
V
V
V
VV V
VV VVVV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV V
VV
VV VV V
VV V
V
V
V VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
V
VV
VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
V VVVV
VV
LC4.3A - AP (non-China)
ELCAP SM 16V 10U PM20 COL R
CER2 0805 X5R 6V3 10U PM10 R
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0805 Y5V 10V 4U7 P8020 R
RST SM 0603 150R PM5 COL
CER2 0805 Y5V 10V 4U7 P8020 R
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 1K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 1K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 1K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 150R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 12K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0805 JUMP. 0R05 COL R
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
IND FXD 1206 EMI 100MHZ 120R R
DIO SIG SM BAT54 SOD323 COL R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
IC SM TDA15011H/N1BD0 (PHSE) Y
IC SM TDA15021H/N1B91 (PHSE) Y
IC SM 74HC4053D (PHSE) R
Description
Item
26/32PFxxxx - AP/NAFTA/LT
VVV
2449
3432
VVV
3458
VVV
3459
VVV
3461
VVV
3462
4436
4437
VVV
4440
VVV
4441
VVV
6430
6431
VVV
7436
VVV
EU & AP DVB sets
LC4.3E/LC4.9x/LC4.8x/LC4.3A-China
26PF4310/10
V
V
V
Description
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
RST SM 0402 2K7 PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
DIO REG SM PDZ2.4B (PHSE) R
DIO SIG SM 1N4148WS (VISH) R
IC SM 74LVC14APW (PHSE) R
Item
2612
2613
2616
2617
3615
3616
3617
3618
3619
3620
3623
3625
3627
3628
3629
3630
3630
3631
3631
3632
3633
4601
4602
4603
4606
4609
4610
4611
4612
4613
4614
4615
4616
4617
4618
4619
4620
4621
7603
7604
7607
26/32PF
37/42/50PF
V
CER2 0603 Y5V 10V 1U COL
V
CER2 0603 Y5V 10V 1U COL
V
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 2U2 PM10 R
V
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 2U2 PM10 R
V
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 1K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 1K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 22K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 47K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 3K3 PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 22K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 22K PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 330R PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 470R PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 330R PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 470R PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 RC31 39R PM5 R
V
RST SM 0402 RC31 39R PM5 R
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
V
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
V
Description
Item
26/32PF LCD
2701
VV V
2706
VVVV
2709
VVVV
2710
VVVV
2711
VVVV
2713
VVVV
2714
VVVV
2715
VVVV
2741
VVVV
2751
VV V
2752
VV V
2760
VV V
2761
VVVV
3708
VVVV
3709
VVVV
3712
VVVV
3713
VVVV
3716
VVVV
3740
VVVV
3741
VVVV
3742
VVVV
3743
VVVV
3755
VV V
3758
VV V
3760
VV V
3761
VVVV
5700
VV V
5704
VVVV
5709
VVVV
5712
VVVV
5713
VVVV
5756
VV V
5757
VV V
6708
VVVV
6709
VVVV
6712
VVVV
6740
VVVV
7708
VVVV
7710
VVVV
7741
VVVV
7742
VVVV
7754
VV V
7755
VV V
37/42PF LCD
42/50PF PDP
DVB PDP 42PF
DVB LCD 37PF
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
ELCAP SM 16V 10U PM20 COL R
ELCAP SM 16V 47U PM20 COL R
CER2 1210 Y5V 25V 10U P8020 R
CER2 1210 Y5V 25V 10U P8020 R
ELCAP SM SEV 16V 470U PM20 R
CER2 0402 X7R 50V 220P COL
CER2 0402 X7R 16V 22N PM10 R
CER2 0603 X7R 10V 220N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
ELCAP SM 16V 47U PM20 COL R
CER2 1206 X7R 25V 1U PM10 R
CER2 1206 X7R 25V 1U PM10 R
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 6K8 PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 RC22H 5K6 PM1 R
RST SM 0603 RC22H 3K3 PM1 R
RST SM 0402 4K7 PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 1K5 PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 1K5 PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 15K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 22K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 15K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
IND FXD 1206 EMI 100MHZ 120R R
IND FXD SM 1206 10U PM20 R
IND FXD SM 7032 10U PM20 R
IND FXD SM 12565 33U PM20 R
INDFXD SM 10145 10U PM20 R
IND FXD 1206 EMI 100MHZ 120R R
IND FXD 1206 EMI 100MHZ 120R R
DIO REC SS24 COL R
DIO REC SS14 COL R
DIO REC SS36 COL R
DIO REG SM PDZ8.2B (PHSE) R
IC SM LF33CPT (ST00) R
IC SM E-L5973D (ST00) R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
FET POW SM SI2301BDS-E3(VISH)R
TRA SIG SM PDTC114ET (COL) R
Description
F_15270_069.eps
230505
Page 37

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
37LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Scaler
1234567891011121314
SCALER
B7 B7
+2V5_DDR
F800
2800
A
100u16V
I813
FROM SDRAM
#RESET
B
FROM SDRAM
FSVREF
C
FSDATA(21)
FSDATA(11)
FSDATA(10)
FSDATA(19)
FSDATA(14)
FSDATA(18)
FSDATA(16)
D
E
F
G
FSDATA(15)
FSDATA(5)
FSDATA(6)
FSDATA(4)
FSDATA(3)
TO COLUMBUS
FROM SYNC INTERFACE
COL_YB(1:8)
COL_Do(1:7)
H
FROM HDMI
I
FROM MUX-SYNC INTF
3139 123 6093.1
2802
2801
100n
28042803
100n 100n
100n
100n100n
28082807
28062805
100n100n
100n100n
3800
10K
2813
2814
100n
100n
3801-4 22R4
3801-3 22R
3801-2 22R
3801-1 22R18
3802-2 2 7
3802-1 22R18
3803-4
3803-3
3803-2
3803-1 22R
3805-4 22R
3805-1 22R18
3806-4
3807-3 22R
3807-2
3807-1 22R
3808-4 4 5
5
36
27
45
22R3802-4
22R3802-3 3 6
22R
22R45
22R36
22R27
18
18
22R3804-1
27
22R3804-2
36
22R3804-3
5
22R3804-4 4
45
22R3805-3 3 6
22R3805-2 2 7
18
22R3806-1
27
22R3806-2
22R3806-3 3 6
22R45
22R3807-4
45
36
22R27
18
27
22R3808-2
36
22R3808-3
22R
8
22R3808-1 1
FSDATAU0FSDATA(0)
FSDATAU1FSDATA(1)
FSDATAU2FSDATA(2)
FSDATAU29FSDATA(29)
FSDATAU26FSDATA(26)
FSDATAU7FSDATA(7)
FSDATAU25FSDATA(25)
FSDATAU24FSDATA(24)
FSDATAU21
FSDATAU11
FSDATAU10
FSDATAU19
FSDATAU14
FSDATAU18
FSDATAU16
FSDATAU15
FSDATAU17FSDATA(17)
FSDATAU20FSDATA(20)
FSDATAU12FSDATA(12)
FSDATAU13FSDATA(13)
FSDATAU23FSDATA(23)
FSDATAU22FSDATA(22)
FSDATAU9FSDATA(9)
FSDATAU8FSDATA(8)
FSDATAU5
FSDATAU6
FSDATAU4
FSDATAU3
FSDATAU30FSDATA(30)
FSDATAU31FSDATA(31)
FSDATAU27FSDATA(27)
FSDATAU28FSDATA(28)
+3V3SW
3819
RES
FSDATAU0
FSDATAU1
FSDATAU2
FSDATAU3
FSDATAU4
FSDATAU5
FSDATAU6
FSDATAU7
FSDATAU8
FSDATAU9
FSDATAU10
FSDATAU11
FSDATAU12
FSDATAU13
FSDATAU14
FSDATAU15
FSDATAU16
FSDATAU17
FSDATAU18
FSDATAU19
FSDATAU20
FSDATAU21
FSDATAU22
FSDATAU23
FSDATAU24
FSDATAU25
FSDATAU26
FSDATAU27
FSDATAU28
FSDATAU29
FSDATAU30
FSDATAU31
3820 10K
COL_DE
V_1FH
H_1FH
HDMI_CbCr(0)
HDMI_CbCr(1)
HDMI_CbCr(2)
HDMI_CbCr(3)
HDMI_CbCr(4)
HDMI_CbCr(5)
HDMI_CbCr(6)
HDMI_CbCr(7)
COL_YB(1)
COL_YB(2)
COL_YB(3)
COL_YB(4)
COL_YB(5)
COL_YB(6)
COL_YB(7)
COL_YB(8)
COL_Do(1)
COL_Do(2)
COL_Do(3)
COL_Do(4)
COL_Do(5)
COL_Do(6)
COL_Do(7)
I800
I816
COL_Do(8)_INV
3840
22R
F801
3839
100R
28102809
100n100n
+2V5_DDR
K1
M3
M4
R4
J24
K26
W25
W24
E24
E25
E26
G26
G24
H26
H24
J25
T26
R25
P24
P26
N24
N26
M25
L24
L25
M26
M24
N25
N23
P25
R26
R24
K24
J26
H25
G23
G25
F24
F25
F26
I812
I818
I815
28122811
AA23
AB23
AC23
RESET_
IR0|GPIO_29
IR1|GPIO_28
EXTCLK|GPI_02
FSVREF1
FSVREFVSS1
FSVREF2
FSVREFVSS2
FSDATA0
FSDATA1
FSDATA2
FSDATA3
FSDATA4
FSDATA5
FSDATA6
FSDATA7
FSDATA8
FSDATA9
FSDATA10
FSDATA11
FSDATA12
FSDATA13
FSDATA14
FSDATA15
FSDATA16
FSDATA17
FSDATA18
FSDATA19
FSDATA20
FSDATA21
FSDATA22
FSDATA23
FSDATA24
FSDATA25
FSDATA26
FSDATA27
FSDATA28
FSDATA29
FSDATA30
FSDATA31
B17
VCLAMP|GPIO_31
D20
VDV|VSOG|GPIO07
B20
VODD|HSOUT|GPIO_06
C20
VVS|GPIO_05
D19
VHS_CSYNC|GPIO_04
A23
VGRN0|GPIO_G02_B0
C22
VGRN1|GPIO_G02_B1
B22
VGRN2|GPIO_G02_B2
A22
VGRN3|GPIO_G02_B3
D21
VGRN4|GPIO_G02_B4
C21
VGRN5|GPIO_G02_B5
B21
VGRN6|GPIO_G02_B6
A21
VGRN7|GPIO_G02_B7
C19
VRED0|GPIO_G01_B0
B19
VRED1|GPIO_G01_B1
A19
VRED2|GPIO_G01_B2
D18
VRED3|GPIO_G01_B3
C18
VRED4|GPIO_G01_B4
B18
VRED5|GPIO_G01_B5
A18
VRED6|GPIO_G01_B6
C17
VRED7|GPIO_G01_B7
B25
VBLU0|GPIO_G03_B0
A25
VBLU1|GPIO_G03_B1
D24
VBLU2|GPIO_G03_B2
C24
VBLU3|GPIO_G03_B3
B24
VBLU4|GPIO_G03_B4
A24
VBLU5|GPIO_G03_B5
C23
VBLU6|GPIO_G03_B6
B23
VBLU7|GPIO_G03_B7
Y23
W23
T23
V23
R23
GM1501-LF-BD
+2V5_DDR +1V8_CORE
7801-12
P23
M23
SYSTEM
VSSA18_DLL
K25
7801-6
GM1501-LF-BD
VIDEO
SVHSYNC|GPIO_02
SVVSYNC|GPIO_01
SVDV|VCOAST|GPIO_03
SVDATA7|GPIO_G00_B7
SVDATA6|GPIO_G00_B6
SVDATA5|GPIO_G00_B5
SVDATA4|GPIO_G00_B4
SVDATA3|GPIO_G00_B3
SVDATA2|GPIO_G00_B2
SVDATA1|GPIO_G00_B1
SVDATA0|GPIO_G00_B0
J23
L23
F23
E23
H23
FS_2.5FS_2.5
FSADDR0
FSADDR1
FSADDR2
FSADDR3
FSADDR4
FSADDR5
FSADDR6
FSADDR7
FSADDR8
FSADDR9
FSADDR10
FSADDR11
FSBKSEL0
FSBKSEL1
MSTR_SCL|GPI_03
MSTR_SDA|GPI_04
SVCLK|GPI_0
SVODD|GPIO_00
VCLK|GPI_01
K23
FSDQM0
FSDQM1
FSDQM2
FSDQM3
FSCKE
FSWE
FSCAS
FSRAS
FSCLKn
FSCLKp
FSDQS
D16
C14
D14
C15
D15
C16
VDDA18_DLL
AD25
AD26
AC24
AC25
AB26
AA24
AA25
AA26
Y24
AB25
AC26
AB24
Y25
Y26
T25
U25
U26
T24
W26
V26
V25
V24
U23
U24
L26
P4
P3
B14
A14
A17
A15
B15
A16
B16
I817
A20
FSADDRU0
FSADDRU1
FSADDRU2
FSADDRU3
FSADDRU4
FSADDRU5
FSADDRU6
FSADDRU7
FSADDRU8
FSADDRU9
FSADDRU10
FSADDRU11
FSBKSELU0
FSBKSELU1
FSDQMU0
FSDQMU1
FSDQMU2
FSDQMU3
FSCKEU
FSWEU
FSCASU
FSRASU
3818 10K
FROM MUX-SYNC INTF
3823
RES
HDMI_VHS
HDMI_VVS
100R3822
COL_CLKASB
COL_CLKASA
4801
TO SDRAM
FSADDRU3
FSADDRU2 FSADDR(2)
FSADDRU1 FSADDR(1)
FSADDRU0 FSADDR(0)
FSADDRU8 FSADDR(8)
FSADDRU7 FSADDR(7)
FSADDRU6 FSADDR(6)
FSADDRU5 FSADDR(5)
FSADDRU4
FSADDRU9
FSADDRU11
FSADDRU10
FSDQMU0
FSDQMU1
FSDQMU2
FSDQMU3
FSWEU
FSCASU
FSRASU
FSCKEU
FSBKSELU0
FSBKSELU1
3809-4 4 5
3809-3
3810-2 22R
3810-4 4 5
3811-4 22R45
3812-1
3812-4 22R
3813-3
3814 22R
3815 22R
22R
22R36
22R3809-2 2 7
8
22R3809-1 1
18
22R3810-1
27
36
22R3810-3
22R
6
22R3811-3 3
22R3811-2
27
18
22R3811-1
22R18
22R3812-3 3 6
45
22R3812-2 2 7
22R3813-1 1 8
22R3813-2 2 7
22R36
22R3813-4 4 5
FSADDR(3)
FSADDR(4)
FSADDR(9)
FSADDR(11)
FSADDR(10)
FSDQM(0)
FSDQM(1)
FSDQM(2)
FSDQM(3)
FSWE
FSCAS
FSRAS
FSCKE
FSBKSEL(0)
FSBKSEL(1)
FSCLK-
FSCLK+
22R
+3V3SW
3816
SCL_IO
SDA_IO
10K3817
FSDQS
TO SCALER INTRF
TO FLASH CONTROL
TO HDMI
TO EPLD
FROM HDMI
HDMI_VCLK
HDMI_VDV
HDMI_Y(7)
HDMI_Y(6)
HDMI_Y(5)
HDMI_Y(4)
HDMI_Y(3)
HDMI_Y(2)
HDMI_Y(1)
HDMI_Y(0)
FROM COLUMBUS
TO HDMI
AV3_HDMI-AUDIO_SEL
FROM DIGITAL-IO
(CINCH)
RESERVED
FROM ANALOG-IO
(CINCH)
TO FLASH / CONTROL
TO FLASH / CONTROL
TO EPLD
TO DIGITAL-IO
(SCART)
1234567891011121314
+3V3_PLL
F802
2815
16V
22u
OCMADDR(0)
OCMADDR(1)
OCMADDR(2)
OCMADDR(3)
OCMADDR(4)
OCMADDR(5)
OCMADDR(6)
OCMADDR(7)
OCMADDR(8)
OCMADDR(9)
OCMDATA(0)
OCMDATA(1)
OCMDATA(2)
OCMDATA(3)
OCMDATA(4)
OCMDATA(5)
OCMDATA(6)
OCMDATA(7)
HDMI_HOTPLUG_RESET
PIXEL+_RESET
(RESERVED FOR CINCH ONLY)
CVI_VGA_SEL
3831 100R
POWER_UP_OK
3833 10R
HOT_PLUG
100R3832
PDP_GO_UP
VS_ON
2816
100n100n
+3V3_PLL
2823
22p
36
3825-3
3825-2 2 7
3825-1 1
36
3826-3
3826-1 1 8
45
3825-4
27
3826-2
45
3826-4
+3V3_IO
3830
RES
I819
I820
I821
SD_HD_SEL
28182817
100n
8
10K
2819
100n
H3
VDDA33_SDDS
G3
TCLK
H2
AA1
AA2
AA3
Y1
Y2
Y3
W1
W2
W3
V1
AD4
AF3
AE3
AD3
AF2
AE2
AD2
AF1
AE1
AD1
I802
AC1
AC2
I803
AC3
AB1
AB2
AB3
AD23
GPIO_G04_B0|DOBLU2
AD24
GPIO_G04_B1|DOBLU3
AE24
GPIO_G04_B2|DOBLU4
AF24
GPIO_G04_B3|DOBLU5
AF25
GPIO_G04_B4|DOBLU6
AF26
GPIO_G04_B5|DOBLU7
AE25
GPIO_G04_B6|DOBLU8
AE26
GPIO_G04_B7|DOBLU9
NC
AD21
GPIO_G05_B0|DOGRN2
AD22
GPIO_G05_B3|DOGRN5
AC18
GPIO_G06_B0|DORED2
AD18
GPIO_G06_B1|DORED3
AE18
GPIO_G06_B2|DORED4
AF18
GPIO_G06_B3|DORED5
AE8
GPIO_G07_B0|DERED2
AF8
GPIO_G07_B1|DERED3
AC9
GPIO_G07_B2|DERED4
AD9
GPIO_G07_B3|DERED5
AE9
GPIO_G07_B4|DERED6
AF9
GPIO_G07_B5|DERED7
AD10
GPIO_G07_B6|DERED8
AE10
GPIO_G07_B7|DERED9
7801-11
J3
F4
G1
GM1501-LF-BD
CLK-SYN
VDDA33_FPLL
VDDA33_RPLL
VDDA33_DDDS
VSSA33_DDDSH4VSSA33_FPLL
VSSA33_RPLL
VSSA33_SDDS
J2
F3
GM1501-LF-BD
OCMADDR0
OCMADDR1
OCMADDR2
OCMADDR3
OCMADDR4
OCMADDR5
OCMADDR6
OCMADDR7|GPIO_18
OCMADDR8|GPIO_G11_B0
OCMADDR9|GPIO_G11_B1
GM1501-LF-BD
OCMDATA0
OCMDATA1
OCMDATA2
OCMDATA3
OCMDATA4
OCMDATA5
OCMDATA6
OCMDATA7
OCMDATA8|GPIO_G10_B0
OCMDATA9|GPIO_G10_B1
OCMDATA10|GPIO_G10_B2
OCMDATA11|GPIO_G10_B3
OCMDATA12|GPIO_G10_B4
OCMDATA13|GPIO_G10_B5
OCMDATA14|GPIO_G10_B6
OCMDATA15|GPIO_G10_B7
OCM_DATA
GM1501-LF-BD
H1
J1
F2
VDDD33_PLL
VDDD33_SDDS
VDDD33_DDDS
XTAL
ACS_RSET_HD
VSSD33_DDDSG2VSSD33_PLL
VSSD33_SDDS
K4
J4
7801-4
OCM-ADR
OCMADDR10|GPIO_G11_B2
OCMADDR11|GPIO_G11_B3
OCMADDR12|GPIO_G11_B4
OCMADDR13|GPIO_G11_B5
OCMADDR14|GPIO_G11_B6
OCMADDR15|GPIO_G11_B7
OCMADDR16|GPIO_19
OCMADDR17|GPIO_20
OCMADDR18|GPIO_21
OCMADDR19|GPIO_22
7801-5
OCM_TIMER1|PWM3|GPIO_13
OCM_UDI|GPIO_27
OCM_UDO|GPIO_26
OCM_INT1|GPIO_30
OCM_INT2|GPI_10
OCM_WE_
OCM_RE_
OCM_CS0_|GPIO_23
OCM_CS1_|GPIO_24
OCM_CS2_|GPIO_25
ROM_CS_|GPI_9
7801-9
GPIO
GPIO_G08_B0|JTAG_CLK|DORED0
GPIO_G08_B1|JTAG_MODE|DORED1
GPIO_G08_B2|JTAG_TDI|DOGRN0
GPIO_G08_B3|DVS|DOGRN1
GPIO_G08_B4|JTAG_TDO|DOBLU0
GPIO_G08_B5|JTAG_RESET|DOBLU1
GPIO_G09_B0|DERED0
GPIO_G09_B1|DERED1
GPIO_G09_B2|DEGRN0
GPIO_G09_B3|DEGRN1
GPIO_G09_B4|DEBLU0
GPIO_G09_B5|DEBLU1
GPIO_14|DHS
GPIO_15|DVS
GPIO_16|DEN
2820
100n
D25
M2
M1
L2
L1
R3
R2
T4
P1
P2
R1
G4
K2
V2
V3
V4
U1
U2
U3
U4
T1
T2
T3
100n
+3V3_PLL
I801
3824
3K3
I804
I805
V-CHIP_INT
I806
I807
I808
AD6
I809
AE6
AF6
NC
I810
AE7
AF7
I822
AD8
AE4
SC2|AV2_SIDE_SW
AF4
AC5
AD5
AE5
AF5
AF17
AD16
AD7
28222821
100n
2824
22p
1801
14M31818
SMD-49
(RESERVED)
10K3827
3828 10K
10K3829
3834 10K
10K3835
3836 10K
NVM_WP_SCALER
TO ANALOG-IO
/
(SCART) (CINCH)
OCMADDR(10)
OCMADDR(11)
OCMADDR(12)
OCMADDR(13)
OCMADDR(14)
OCMADDR(15)
OCMADDR(16)
OCMADDR(17)
OCMADDR(18)
OCMADDR(19)
TO SCALER INTRF
BU_LHT_ADJ1
UART_RX
UART_TX
POWER_DOWN
#OCM_WE
#OCM_RE
+3V3SW
#ROM_CS
JTAG_CLK_SCL
JTAG_TDI_SDA
RGB|CVI_HDA_SEL
TV_SC_COM
TV_IRQ
SC2_OUT_SW
Y_NOTCH
+3V3_IO
3837
3838
10K 10K
PC_HD_SEL
TO HERCULES
TO TUNER
TO DC-DC CONVERTER
FOR SW TESTING
F803
F804
+3V3_IO
B3B-PH-SM4-TBT(LF)
(RES)
1802
I811
45
3
2
1
TO MUX-SYNC INTF
TO FLASH / CONTROL
3841
10K
COL_RST
TO COLUMBUS
F_15430_007.eps
140405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
1801 B12
1802 G14
2800 A1
2801 A1
2802 A1
2803 A1
2804 A2
2805 A2
2806 A2
2807 A2
2808 A2
2809 A3
2810 A3
2811 A3
2812 A3
2813 B2
2814 B3
2815 A9
2816 A9
2817 A10
2818 A10
2819 A10
2820 A12
2821 A12
2822 A12
2823 A10
2824 A12
3800 B3
3801-1 C1
3801-2 C1
3801-3 C1
3801-4 C1
3802-1 C1
3802-2 C1
3802-3 C1
3802-4 C1
3803-1 D1
3803-2 D1
3803-3 C1
3803-4 C1
3804-1 D1
3804-2 D1
3804-3 D1
3804-4 D1
3805-1 D1
3805-2 D1
3805-3 D1
3805-4 D1
3806-1 D1
3806-2 E1
3806-3 E1
3806-4 E1
3807-1 E1
3807-2 E1
3807-3 E1
3807-4 E1
3808-1 E1
3808-2 E1
3808-3 E1
3808-4 E1
3809-1 B6
3809-2 B6
3809-3 B6
3809-4 B6
3810-1 B6
3810-2 B6
3810-3 B6
3810-4 B6
3811-1 C6
3811-2 C6
3811-3 C6
3811-4 C6
3812-1 C6
3812-2 C6
3812-3 C6
3812-4 C6
3813-1 C6
3813-2 D6
3813-3 D6
3813-4 D6
3814 D6
3815 D6
3816 D6
3817 D6
3818 E6
3819 F2
3820 F1
3822 G5
3823 F5
3824 B12
3825-1 F9
3825-2 F9
3825-3 F9
3825-4 F9
3826-1 F9
3826-2 F9
3826-3 F9
3826-4 F9
3827 F13
3828 F13
3829 F13
3830 H10
3831 I9
3832 I9
3833 I9
3834 G13
3835 G13
3836 G13
3837 G14
3838 G14
3839 G3
3840 I3
3841 H14
4801 H5
7801-11 A11
7801-12 A4
7801-4 C11
7801-5 E11
7801-6 F4
7801-9 G11
F800 A1
F801 B3
F802 A9
F803 G14
F804 G14
I800 G2
I801 B12
I802 F10
I803 F10
I804 E12
I805 E12
I806 F12
I807 F12
I808 F12
I809 G12
I810 G12
I811 G14
I812 F3
I813 A1
I815 G3
I816 G2
I817 H5
I818 F3
I819 I10
I820 I10
I821 I10
I822 G12
Page 38

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
38LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Scaler Supply
1234567891011
SCALER
B8 B8
GM1501-LF-BD
A1
NC
C5
NC
D5
NC
7801-3
GM1501-LF-BD
ADC
LBADC_IN1
LBADC_IN2
LBADC_IN3
LBADC_RETURN
LBADC_GND
+3V3_LVDS
+3V3_LVDSA
+3V3_LVDSB
100n
7801-14
NC
AC17
NC
K3
NC
NCNC
F1
NC
+3V3_LBADC
C13D13
LBADC_33
2945
22u 16V 100n
2950
16V22u
29572956
100n
2946
100n
2951
100n
2958
100n
2947
2952
100n
2959
100n
2948
100n
A
SUPPLY FOR SCALER
B
C
D
E
F
G
3139 123 6093.1
+3V3SW
5900
5901
5902
5903
5904
F900
5905
5906
5907
+3V3SW
+3V3SW
7900
LF25CDT
13
OUTIN
COM
2900
I901
100n
2903
100n
2
7901
LD1086D2T18
32
OUTIN
COM
1
+3V3_PLL
+3V3_ADC
+3V3_DVI
+3V3_IO
+3V3_LBADC
+3V3_LVDSA
+3V3_LVDSB
+3V3_LVDS
I900
1n0
+1V8
I902
2904
16V47u
+3V3_IO
F901
2905
2906
100u
16V
I905
5908
29022901
16V470u
5909
5910
5911
+2V5_DDR
+1V8_ADC
+1V8_DVI
+1V8_CORE
TO DIGITAL-IO (SCART ONLY)
100n100n
+3V3_IO +1V8_CORE
A13
K14
K15
K13
K12
B13
SCL_DVI
SDA_DVI
RXC+IN
RXC-IN
RX0+IN
RX0-IN
RX1+IN
RX1-IN
RX2+IN
RX2-IN
HD_FILTER
29082907
100n
AC8
AC10
D_GND
L10
L12
3900 3K3
AC6
L13
AC4
L14
2909
AB4
IO_3.3
L15
I904
AA4
L17
Y4
M10
AC16
C26
C25
W4
M11
100n100n
D23
M12
2930
29112910
D22
D17
M13
M14
M15
F903
100n100n
OEXTR
PWM0|GPIO_10
PWM1|GPIO_11
2912
100n100n
M17
N10
N11
M16
29322931
7801-7
GM1501-LF-BD
CTRL
2913 2914
100n
N12
N13
2933
100n100n
N4
N3
A6
B6
A8
B8
A9
B9
A10
B10
B11
PPWR|GPIO_08
PBIAS|GPIO_09
DCLK|GPIO_17
PWM2|GPIO_12
2915
100n
100n
7801-13
GM1501-LF-BD
SUPPLY
D_GND D_GND
P11
P12
N14
N15
N16
DVI_SCL|GPI_07
DVI_SDA|GPI_08
RXCp
RXCn
RX0p
RX0n
RX1p
RX1n
RX2p
RX2n
REXT
P13
N17
P10
+1V8_DVI
D6D8D9
D10
DVI_1.8 DVI_3.3
GM1501-LF-BD
DVI_GND
A7
A11B5B7
I906
FROM DC-DC CONVERTER
A26
B26
AC7
NC
I903
D26
+1V8_CORE
2916
100n
P14
P15
P16
U17
U11
U16
P17
R10
R11
+3V3_DVI
C10
C11
U10
R12
T17
R13
C6C8C9
2917
100u
16V
T16
CORE_1.8
R14
DVI
7801-2
D7
D11
C7
ADC
TO COLUMBUS HERCULES
PANEL-PWR-CTL
LAMP_ON_OFFFAN_SPEED
BU_LHT_ADJ2
&
(RES)
TO TOP CONN.
F902
2918
2919
100n
L11
L16
T11
K11
K16
K17
K10
R15
R16
R17
T10
TO MUX-SYNC INTERFACE
U12
T12
T13
T14
T15
F904
2934 2938
2935
16V47u
AVSYNC
AHSYNC
SCL
SDA
SOG
R_PR+
R_PR-
G_Y+
G_Y-
B_PB+
B_PB-
2927 2928
2926
2939
100n100n
100n100n
29252924
KEYBOARD
100n
100n100n
4900
RES
29212920
100n100n
U13
U14
U15
AD15
100n100n
29232922
100n100n
29372936
100n
2929
100n
100n
2942
100n
7801-10
GM1501-LF-BD
2940
47u 16V
(RES)
(RES)
2941
100n
C12
B12
A12
D12
DISPLAY PWR
F905
+3V3STBY
3901
RES
3902
RES
3903
2953
100n
100R
100R3904
2954
100n
AD19
AC19
AC20
AC13
AC14
AC15
AD17
L3
L4
N2
N1
C3
D2
D1
C2
C1
B2
B1
LVDSA_GND_1
LVDSA_GND_2
LVDSA_GND_3
LVDSB_GND_1
LVDSB_GND_2
LVDSB_GND_3
VSSD33_LVDS
+1V8_ADC
F908
A3
A4
ADC_1.8
AVSYNC
AHSYNC
VGA_SCL|GPI_05
VGA_SDA|GPI_06
SOG
REDp
REDn
GREENp
GREENn
BLUEp
BLUEn
ADC_AGND ADC_DGND
E1E2E4
C4
D4
VDDD33_LVDS
LVDSA_3.3_3
LVDSA_3.3_2
LVDSA_3.3_1
LVDSB_3.3_3
LVDSB_3.3_2
LVDSB_3.3_1
7801-1
GM1501-LF-BD
ANA-IN
F910
+3V3_ADC
B3
ADC_3.3
A5
AE17
F906
AC22
AC21
AD20
F907
AC12
AD13
AD12
F909
2955
22u 16V
A2D3E3
B4
1234567891011
2949
100n
F_15430_008.eps
150405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
2900 D1
2901 D2
2902 D2
2903 E1
2904 E2
2905 A4
2906 A4
2907 A4
2908 A4
2909 A4
2910 A5
2911 A5
2912 A5
2913 A5
2914 A6
2915 A6
2916 A6
2917 A7
2918 A7
2919 A7
2920 A7
2921 A7
2922 A8
2923 A8
2924 A8
2925 A8
2926 A9
2927 A9
2928 A9
2929 A9
2930 C5
2931 C5
2932 C5
2933 C5
2934 C7
2935 C7
2936 C7
2937 C8
2938 C8
2939 C8
2940 B9
2941 B10
2942 C9
2945 D10
2946 D11
2947 D11
2948 D11
2949 D11
2950 D10
2951 D11
2952 D11
2953 E8
2954 E8
2955 E10
2956 E10
2957 E10
2958 E11
2959 E11
3900 F4
3901 E8
3902 E8
3903 F8
3904 F8
4900 B9
5900 A1
5901 B1
5902 B1
5903 B1
5904 B1
5905 C1
5906 C1
5907 C1
5908 C2
5909 D2
5910 E2
5911 E2
7801-1 F9
7801-10 C9
7801-13 B6
7801-14 A10
7801-2 C6
7801-3 B10
7801-7 F5
7900 C1
7901 D1
F900 B2
F901 A4
F902 A7
F903 C5
F904 C7
F905 D10
F906 D10
F907 D10
F908 E9
F909 E10
F910 G9
I900 C2
I901 E1
I902 E2
I903 G6
I904 F4
I905 C4
I906 E6
Page 39

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
39LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Scaler Interface
123456789
SCALER INTERFACE
B9 B9
7801-8
GM1501-LF-BD
A
B
C
ACp|GPIO_G06_B6|DORED8
ACn|GPIO_G06_B7|DORED9
A3p|GPIO_G06_B4|DORED6
A3n|GPIO_G06_B5|DORED7
A2p|GPIO_G05_B1|DOGRN3
A2n|GPIO_G05_B2|DOGRN4
A1p|GPIO_G05_B4|DOGRN6
A1n|GPIO_G05_B5|DOGRN7
A0p|GPIO_G05_B6|DOGRN8
A0n|GPIO_G05_B7|DOGRN9
SHIELD5|DEBLU5
SHIELD4|DEBLU2
SHIELD3|DEGRN5
SHIELD2|DEGRN4
SHIELD1|DEGRN3
SHIELD0|DEGRN2
BCp|DEGRN8
BCn|DEGRN9
B3p|DEGRN6
B3n|DEGRN7
B2p|DEBLU3
B2n|DEBLU4
B1p|DEBLU6
B1n|DEBLU7
B0p|DEBLU8
B0n|DEBLU9
LVDS
AE20
AF20
AE19
AF19
AE21
AF21
AE22
AF22
AE23
AF23
AD14
AE13
AE11
AD11
AC11
AF10
AE12
AF13
AF11
AF12
AF14
AE14
AF15
AE15
AF16
AE16
TO SCALER
RESERVED
NC
TO EPLD
TXBC+
TXBC-
TXB3+
TXB3-
TXB2+
TXB2-
TXB1+
TXB1-
TXB0+
TXB0-
BU_LHT_ADJ1
IA07 IA05
4A02
RES
BACKLIGHT CONTROL
5V DC 5V PWM 3V3 DC 3V3 PWM
3A03
390R
390R
-
-
-
1K
-
Y
-
-
Y
0R
10K
-
1u
3A02
1K0
3A03
RES
1
7A01
SI2301DS-T1
4A03
RES
+5VSWI
3
2
3A04
1K0
3A05
RES
IA06
3A05
3A04
7A01
4A03
3A06
2A03
3A06
10K
10K
1u
IA00
1K
Y
-
-
2A03
1u0
BACKLIGHT_DIM
-
-
-
-
Y
0R
-
BACKLIGHT_CTRL
TO TOP CONNECTORS
FROM EPLD
A
B
C
2A00 E3
2A01 F2
2A02 F2
2A03 C7
2A12 F6
2A13 E8
3A00 E2
3A01 E2
3A02 C5
3A03 C6
3A04 C6
3A05 C6
3A06 C7
3A07 E2
3A08 E2
3A10 F6
3A11 E7
3A13 E8
3A14 E9
4A00 F3
4A01 F3
4A02 B6
4A03 D6
4A04 F4
4A05 F6
4A06 F8
5A00 E3
6A01 F8
7801-8 A2
7A00 E4
7A01 C6
7A02 F6
7A03 E8
IA00 C7
IA03 F6
IA05 B8
IA06 C7
IA07 B6
IA08 E3
IA09 E3
D
E
F
3139 123 6093.1
TO EPLD
2A13
100n
+3V3STBY
7A03
BC847BW
4A06
3A13
10K
+5V
6A01
3A14
4K7
BZX384-C3V9
STANDBY
F_15430_009.eps
FOR PDP ONLY
+3V3SW
3A08
3A07
10K
10K
IA08
SDA_DMA_BUS1_DISP SDA_IO
SCL_DMA_BUS1_DISP
2A02
2A01
100p100p
3A00
68R
3A01
68R
IA09
7 SCL1
1
NC (PDP)
2A00
100n
+3V3SW
5A00
8
7A00
PCA9515ADP
VCC
3SDA06 SDA1
SCL0 2
RES
RES
5EN
NC
GND
4
4A00
4A01
4A04
SCL_IO
BUF_ENABLE
FROM HERCULES
SC_STANDBY
FOR UFD ONLY
BC847BW
IA03
3A10
10K
2A12
10n
7A02
4A05
+3V3STBY
3A11
4K7
123456789
D
E
F
140405
Page 40

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
40LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: SDRAM
12345678
SDRAM
B10 B10
A
B
C
D
E
F
+2V5_DDR
2B01
47u
16V
2B02
47u
6.3V
100n
2B042B03
100n100n
TO/FROM SCALER
FSRAS
FSCAS
FSWE
FSCLK+
FSCLKFSCKE
FSDQM(0)
FSDQM(1)
FSDQM(2)
FSDQM(3)
FSBKSEL(0)
FSBKSEL(1)
FSADDR(0)
FSADDR(1)
FSADDR(2)
FSADDR(3)
FSADDR(4)
FSADDR(5)
FSADDR(6)
FSADDR(7)
FSADDR(8)
FSADDR(9)
FSADDR(10)
FSADDR(11)
2B062B05
FSVREF
100n100n
IB03
IB02
2B082B07
+2V5_DDR
3B01
FB01
3B02
100n100n
10K
1%
10K
1%
K4D263238F-UC50
1%3B03 150R
2B102B09
100n
7B01
28
26
25
55
54
53
23
56
24
57
29
30
31
32
33
34
47
48
49
50
51
45
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
93
52
2B11
2B12
100n 100n
2B18
22u
16V
2B17
100n
5816
153565962958
VREF
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
CKE
0
1
2
3
0
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
NC
RFU
MCL
CK
CK
DM
BA
A
SDRAM
1M X 32 X 4
VSS VSSQ
85
46
66
100n
14225967737986
VDDQVDD
Φ
5
11196270768292
2B142B13
+2V5_DDR
D
D
99
NC
DQS
2B15
100n100n
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
100
2B16
100n
TO/FROM SCALER
FSDATA(0)
FSDATA(1)
FSDATA(2)
FSDATA(3)
FSDATA(4)
44
87
8827
89
90
91
97
98
1
3
4
6
7
60
61
63
64
68
69
71
72
9
10
12
13
17
18
20
21
74
75
77
78
80
81
83
84
94
FSDATA(5)
FSDATA(6)
FSDATA(7)
FSDATA(8)
FSDATA(9)
FSDATA(10)
FSDATA(11)
FSDATA(12)
FSDATA(13)
FSDATA(14)
FSDATA(15)
FSDATA(16)
FSDATA(17)
FSDATA(18)
FSDATA(19)
FSDATA(20)
FSDATA(21)
FSDATA(22)
FSDATA(23)
FSDATA(24)
FSDATA(25)
FSDATA(26)
FSDATA(27)
A
B
C
D
E
F
2B01 A1
2B02 A1
2B03 A1
2B04 A1
2B05 A2
2B06 A2
2B07 A2
2B08 A3
2B09 A3
2B10 A3
2B11 A3
2B12 A4
2B13 A4
2B14 A4
2B15 A5
2B16 A5
2B17 B4
2B18 B4
3B01 B3
3B02 B3
3B03 C2
7B01 C3
FB01 B3
IB02 C2
IB03 C2
G
3139 123 6093.1
FSDATA(28)
FSDATA(29)
FSDATA(30)
FSDATA(31)
FSDQS
F_15430_010.eps
140405
12345678
G
Page 41

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
41LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Flash / Control
1234567
FLASH / CONTROL
B11 B11
+3V3_IO
+3V3_IO
10K
10K
10K
10K
5C00
A
B
C
D
E
TO SCALER
OCMADDR(0)
OCMADDR(1)
OCMADDR(2)
OCMADDR(3)
OCMADDR(4)
OCMADDR(5)
OCMADDR(6)
OCMADDR(7)
OCMADDR(8)
OCMADDR(9)
OCMADDR(10)
OCMADDR(11)
OCMADDR(12)
OCMADDR(13)
OCMADDR(14)
OCMADDR(15)
OCMADDR(16)
OCMADDR(17)
OCMADDR(18)
#OCM_RE
#OCM_WE
#ROM_CS
NVM_WP_SCALER
SCL_IO
SDA_IO
M29W040B-55K1
+3V3SW
3C00
10K
0V
FC01
3V2
FC02
3V2
FC03
7
6
5
7C00
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
27
26
23
25
4
28
29
3
2
30
1
24
31
22
WC
SCL
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
OE
WE
CE
2C02
100n
FC00
3216
ROM
512Kx8
[FLASH]
0
A
512K-1
DQ
+3V3SW
3V2
8
M24C32-WMN6
Φ
(4Kx8)
EEPROM
4
ADR
2C00
100n
2C01
16V10u
13
0
14
15
17
18
19
20
21
7
7C01
1
0
2
1
3
2SDA
OCMDATA(0:7)
OCMDATA(0)
OCMDATA(1)
OCMDATA(2)
OCMDATA(3)
OCMDATA(4)
OCMDATA(5)
OCMDATA(6)
OCMDATA(7)
TO SCALER
1C00
SKQR
2
4
For Software
Development
only - (RES)
OCMADDR(0:19)
OCMADDR(0)
OCMADDR(1)
OCMADDR(2)
OCMADDR(3)
OCMADDR(4)
OCMADDR(5)
OCMADDR(6)
OCMADDR(7)
OCMADDR(8)
OCMADDR(9)
OCMADDR(10)
OCMADDR(11)
OCMADDR(12)
OCMADDR(15)
OCMADDR(16)
OCMADDR(18)
OCMADDR(17)
OCMADDR(14)
OCMADDR(13)
OCMADDR(19)
1
3
FC04
2C03
100n
3C01
10K
3C06-1 10K
3C06-2 10K
3C06-3
3C06-4 10K45
3C08-2 10K
3C08-1 10K
3C08-3 10K
3C08-4 10K
3C09-2 2 7
3C10-1 10K18
3C10-2 10K2
3C10-3 10K
3C10-4 10K
+3V3SW
3V2
5
1
MR
VCC
SUB
2
18
27
36
45
27
18
36
45
18
36
45
7C02
PST596J
VOUT
GND
3
7
10K36
10K3C07-1 1 8
10K3C07-2 2 7
10K3C07-3
10K3C07-4
10K3C09-1
10K
10K3C09-3 3 6
10K3C09-4 4 5
4
3V20V
FC05
36
183C04-1
3C04-4 4 5
3C04-3
3C04-2 2 7
3C02
1K0
#RESET
3C03
RES
3C05 10K
3C11
3C12
3C13
3C14
3C15
+3V3_IO
3C17
3C16-4
45
FC06
3C19
RES RES RES
TO SCALER
RES
RES
RES
RES
RES
10K
10K
3C16-3
36
FC08
FC07
&
&
TO COLUMBUS
3C18
10K
3C16-2
3C16-1
27
18
FC09
3C213C20
TO HDMI
FC10
A
B
C
D
E
1C00 E4
2C00 A3
2C01 A3
2C02 E2
2C03 E5
3C00 E2
3C01 E5
3C02 E6
3C03 E6
3C04-1 A6
3C04-2 A6
3C04-3 A6
3C04-4 A6
3C05 A6
3C06-1 B5
3C06-2 B5
3C06-3 B5
3C06-4 B5
3C07-1 B5
3C07-2 B5
3C07-3 B5
3C07-4 B5
3C08-1 B5
3C08-2 B5
3C08-3 C5
3C08-4 C5
3C09-1 C5
3C09-2 C5
3C09-3 C5
3C09-4 C5
3C10-1 C5
3C10-2 C5
3C10-3 C5
3C10-4 C5
3C11 A6
3C12 A6
3C13 A6
3C14 B6
3C15 B6
3C16-1 B7
3C16-2 B7
3C16-3 B6
3C16-4 B6
3C17 B6
3C18 B7
3C19 C6
3C20 C7
3C21 C7
5C00 A3
7C00 A2
7C01 E3
7C02 E5
FC00 A3
FC01 E2
FC02 E2
FC03 E2
FC04 E4
FC05 E6
FC06 C6
FC07 C6
FC08 C7
FC09 B7
FC10 B7
3139 123 6093.1
1234567
F_15430_011.eps
140405
Page 42

SSB: HDMI (N.A.)
2D00 A3
2D01 C2
2D02 C3
2D03 F4
2D04 F4
2D05 F4
2D06 F4
2D07 A5
2D08 B5
2D09 B5
2D10 B5
2D11 B5
2D12 A5
2D13 B5
2D14 B5
2D15 B5
2D16 B5
2D17 A6
123456789101112131415
2D18 B6
2D19 B6
2D20 A7
2D21 B6
2D22 B6
2D23 A7
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2D24 B7
2D25 B7
2D26 B7
2D27 A8
2D28 B8
2D29 B8
2D30 B8
2D31 B8
2D32 E11
2D33 E11
2D34 E12
2D35 E12
2D36 G11
2D37 H11
2D38 G12
2D39 G12
2D40 G12
2D41 H13
2D44 F14
2D45 G14
3D00 A2
3D01 A3
3D02 A3
3D03 C2
3D04 C2
3D05 C4
3D06 C4
3D07 D4
3D08 D4
3D09 C5
3D10 C5
3D11 F4
3D12 F4
3D15-1 B11
3D15-2 B11
3D15-3 C11
3D15-4 C11
3D16-1 C11
3D16-2 C11
3D16-3 C11
3D16-4 C11
3D17-1 C11
3D17-2 D11
3D17-3 D11
3D17-4 D11
3D18-1 D11
3D18-2 D11
3D18-3 D11
3D18-4 D11
3D19 E12
3D20 E12
3D21-1 G9
3D21-2 G9
3D21-3 F9
42LC4.9E AB 7.
3D21-4 F9
3D22 G9
3D23 G9
3D24 G11
3D25 H11
3D26 G12
3D27 H13
3D30 F14
3D31 F14
3D32 G14
3D33 G14
3D34 H11
3D35 H12
4D00 F13
4D01 F13
5D00 A5
5D01 A6
5D02 A6
5D03 A7
5D04 A7
7D00 A2
7D01 D3
7D02 D4
7D03 C5
7D04 E11
7D05 F13
FD00 B3
FD01 C2
FD02 C2
FD03 C2
FD04 D2
FD05 G2
FD06 G2
FD07 A5
FD08 A6
FD09 A6
FD10 A6
FD11 A7
FD12 F9
FD13 E11
FD14 E12
FD15 F10
FD16 E13
FD17 H7
ID00 C3
ID01 D3
ID02 D4
ID03 D4
ID04 F5
ID05 F5
ID06 F5
ID07 G5
ID08 G10
ID09 G11
ID10 G12
ID11 G12
ID12 H12
ID13 H12
ID14 H12
ID15 F13
ID16 E13
ID17 E13
ID18 F14
ID19 G14
ID20 F14
ID21 G14
ID22 F4
B12 B12
FROM SCALER
A
B
C
HDMI
SCL_IO
SDA_IO
7D00
M24C02-WMN6
1
0
2
ADR
1
3
2 SDA
FROM DIGITAL-IO (CINCH ONLY)
DOC_SDA
DOC_SCL
+5VHDMI
D
RXC-
RXC+
RX0-
E
F
G
TO MUX-SYNC INTF
H_HDMI
V_HDMI
RX0+
RX1-
RX1+
RX2-
RX2+
COMP
PLLIN
H
3139 123 6093.1
(NOT APPLICABLE IN EUROPE SET)
+3V3SW+3V3SW
84
Φ
(256x8)
EEPROM
FD01
FD02
FD03
FD05
FD06
SCL
3D03
3D04
5D00
22u
3D01
3D00
4K7
4K7
FD00
7
WC
6
5
0R
ID00
0R
2D02
2D01
FD04
1n0
10n
3D02
4K7
ID01
7D01
BSN20
2D00
100n
+3V3SW
FLASH/CONTROL
3D05 3D06
100R 100R
+3V3SW
7D02
BSN20
2D05 47n
FROM
3D07
10u2D03
10n2D04
10u2D06
#RESET
4K7
ID22
ID02
ID03
3D12
3K9
+3V3SW+3V3SW
3D11
100R
3D08
4K7
6.3V
100n
2D09 2D252D14
1n0
2D10
1n0
1n02D11
3D10
390R
7D03
SII9993CTG100
72
RESET
3D09
27
MCLKIN
33R
26
MCLKOUT
74
CSCL
75
CSDA
77
DSCL
76
DSDA
83
RXC-
84
RXC+
86
RX0-
87
RX0+
91
RX1-
92
RX1+
96
RX2-
97
ID04
ID05
ID06
ID07
RX2+
9
RSET
8
COMP
24
PLLIN
25
PLLOUT
81
EXT-RES
33
HSYNC
34
VSYNC
FD07
2D122D07
2D132D08
2D15
2D16
828993
858890
AGND
6.3V
100n
1n0
1n0
1n0
5D01
22u
95
17
94
+3V3SW
5D02
5D03
FD10FD08 FD09
2D17 10u
2D18 100n
40
VCCAVCC
164165
98
64
2D20 10u
100n
2D21
1n0
2D221n02D19
PLLIN
100
80
23
Φ
PVCC2
PVCC1
HDMI
PANELLINK
RECEIVER
GND PGND OGND
99
DACGND
DACGNDR
2
5
79
22
FD17
+3V3SW
FD11
COMP
11411
DACVCC
DACGNDG
13
10
6
DACGNDB
+3V3SW
5D04
22u
2D23
6.3V
100n
1n0
2D26
1n0
21
DACVCCB
DACVCCR
DACVCCG
2845576678
2D27
2D28 100n2D24
475667
OVCC1
RSVDL
RSVDO
101
22u
6.3V
1n02D29
1n02D30
1n02D31
NC
Q
ANRPR
ANGY
ANBPB
SPDIF
SDO
SCK
ODCK
GND_HS
TO SCALER
2D41
10n
HDMI_Y(0:7)
HDMI_CbCr(0:7)
ID17
FD16
ID16
FOR SET W/O HDMI
7D05
HEF4053B
6
13
1V6
12
0V
11
0V
1
1V7
2
0V
10
3
NC
5
NC
9
4D00
4D01
+3V3SW
16
VDD
MDX
G4
1
2
4X1
4X2
VEE VSS
7
3V3
8
+3V3SW
3D30 3D31
ID20
14
1V7
ID21
15
1V7
3D32 3D33
4
NC
TO DIGITAL-IO (CINCH ONLY)
AV3_LEFT
AV3_HDMI-AUDIO_SEL
AV3_RIGHT
RESRES
2D44
ID18
1u0
2D45
ID19
1u0
RESRES
FROM SCALER
TO HERCULES
AudioIN2R
AudioIN2L
HDMI_VDV
HDMI_VCLK
HDMI_CbCr(0)
HDMI_CbCr(1)
HDMI_CbCr(2)
HDMI_CbCr(3)
HDMI_CbCr(4)
HDMI_CbCr(5)
HDMI_CbCr(6)
HDMI_CbCr(7)
11
7
16
2D40
1u0
ID11
3D26
100K
3D35
HDMI_Y(0)
HDMI_Y(1)
HDMI_Y(2)
HDMI_Y(3)
HDMI_Y(4)
HDMI_Y(5)
HDMI_Y(6)
HDMI_Y(7)
ID15
10V
3D27
100R
8
33R3D15-1 1
27
18
36
45
1
BCK
2
WS
3
DATAI
6
SYSCLK
8
MUTE
9
DEEM
10
PCS
14
VOL
3D25
100R
33R3D15-2
33R
33R
33R18
33R27
33R3D16-3 3 6
5
33R3D16-4 4
33R27
33R3D17-3 3 6
33R3D17-4 4 5
33R18
7
2D32
47u 6.3V
2D33
100n
VDDA13VDDD
DIGITAL
INTERFACE
DE-EMPHASIS
INTERPOLATION
NOISE SHAPER
VSSA15VSSD
2D37
10n
+3V3SW
3D19
FD13
FD14
FILTER
DAC
5
2D38
3D20
1R01R0
47u
4
DAC
VREF-DAC
ID10
6.3V47u
2D34
6.3V
2D35
100n
SFOR0
SFOR1
12
2D39
100n
ID12
ID13
ID14
AUDIO DAC
VOR
3D15-33 6
3D15-44 5
3D16-1
3D16-2
3
4
NC
18
73
19
20
70
0
69
1
68
2
63
3
62
4
61
5
60
6
59
7
58
8
55
9
54
10
53
11
52
12
51
13
50
14
49
15
48
16
44
17
43
18
42
19
39
20
38
21
37
22
36
23
7
12
NC
15
29
SPDIF
(NC)
30
31
WS
32
35
DE
46
71
INT
NC
FD12
3D21-4 33R45
3D21-3
36
3D21-22 7
18
3D22
FD15
33R
33R
33R3D21-1
33R
33R3D23
3D17-1 33R
3D17-2
3D18-1
3D18-2 33R2
3D18-3 33R
3D18-4 33R
7D04
UDA1334BT/N2
ID08
2D36
1u0
ID09
3D24
100K
3D34 100K
100K
F_15430_012.eps
123456789101112131415
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
140405
Page 43

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
43LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: MUX Sync Interface
1234567891011
B13 B13
MUX-SYNC INTERFACE
+5VSWI
5E02
A
1
5
11
4u7
4u7
4u7
15p2E38
7E05-1
7E05-3
7E05-5
IE05
IE06
IE07
FE09
FE10
FE11
FE12
FE13
+3V3SW
14
IE17
IE29
IE30
14
7
14
7
7
16
18
20
2
0V6
1
2V7
14
0V8
15
12
0V4
11
2V7
4
5
3E24
3E25
3E26
3E27
3E28
3E29
3E30
74LVC14APW
3
2
74LVC14APW
9
6
74LVC14APW
13
10
FROM HERCULES
B
FROM ANALOG-IO
C
FROM DIGITAL-IO
D
E
SYNC INTERFACE
F
(SCART)
G
3139 123 6093.1
56R3E00
56R3E01
56R3E02
R_SDTV
G_SDTV
B_SDTV
(SCART) (CINCH)
FE00
FE01
FE02
/
4u7
100R3E31
100R3E33
100R3E34
2E00
2E01
2E02
BZX384-C2V7
BZX384-C2V7
SC1_CVI_DMMI_R_Pr_IN
SC1_CVI_DMMI_G_Y_IN
SC1_CVI_DMMI_B_Pb_IN
RINA|Pr
GINA|YINA
BINA|Pb
(SCART) (CINCH)
/
Hsync_SDTV
H_PC
Vsync_SDTV
V_PC
FROM DIGITAL-IO
/
(CINCH)
3E32 100R
12
2E33
2E34
2E35
IE09
6E00
IE11
6E02
IE13
4u7
IE14
4u7
IE15
4u7
4u7
4u7
IE18
RES
4E10
IE10
6E01
BZX384-C2V7
IE12
6E03
BZX384-C2V7
47K3E50
IE16
3E53 47K
+5VSWI
47K3E52
3E51 47K
47K3E54
3E55 47K
7E03
74HC4053D
6
13
12
11
1
2
10
3
5
9
SD_HD_SEL
3V2
47K
3E06
+3V3SW
VDD
MDX
G4
1
2
4X1
4X2
VEE VSS
7
47K
3E07
16
4E11
RES
5E03
8
47K3E08
3E09
3E10
3E11
2E31
14
15
4
+5VSWI
47K
47K
47K
100n
FROM ADC
COL_Di(8)
5E00
7E00
ADG733BRU
12
S1A
13
S1B
2
S2A
1
S2B
5
S3A
3
S3B
VSS
3E37
22R
RESERVED
IE00
16
VDD
Φ
EN
A0
A1
A2
D1
D2
D3
GND
7
8
7E04-5
74LVC14APW
11
2E03
100n
10K3E12
6
11
10
RGB|CVI_HDA_SEL
9
FE03
SC1_R_CVI_Pr_IN
14
SC1_G_CVI_Y_IN
15
SC1_B_CVI_Pb_IN
4
RES
RES
RES
4E13
4E14
4E12
74LVC14APW
3E35
100R
3E36
100R
74LVC14APW
14
10
COL_Di(8)_INV COL_Do(8)
7
TO HERCULES
7E04-1
1
7E04-3
5
+3V3SW
3E13 330R
3E14
3E15 330R
FROM SCALER
3V2
IE19
IE21
TO SCALER
14
7
14
7
3E49
22R
HD_FILTER
3
2
9
6
13
330R
SD_HD_SEL
0V
IE03
7E04-2
74LVC14APW
14
7
7E04-4
74LVC14APW
14
7
7E04-6
74LVC14APW
14
7
3456
2E32
100n
3E16
4E03
12
4
8
3E19
56R
3E20
56R
3E21
56R
3E22
100K
9
23
22
26
25
27
2
1
3
6
5
7
20
21
TO SCALER
PC_HD_SEL
+5VSWI
DISABLE
THROUGH
MUXSEL
GSR1
RINA|YINA
RINB|YINB
GSG1
GINA|UINA
GINB|UINB
GSB1
BINA|VINA
BINB|VINB
RFC
VFC
1u0
2E04
2E05
2E06 2E16
3E183E17
330R
330R330R
I_PC_HD_SEL
0V
RES
3V2
IE25
2E07
33p
IE26
2E09
33p
2E11
33p
2E13
1u0
3E39
100R
3E38
100R
IE28
1u0
1u0
2E08
4u7
2E10
4u7
2E12
4u7
33p
IE27
AHSYNC
IE24
AVSYNC
COL_Do(8)_INV
IE37
3E232E14
820R
IE35
IE36
IE01
IE02
FE04
IE20
IE22
IE23
IE04
FE05
7891011
5E01
FE06
181512
VCC
Φ
ROUT|YOUT
GOUT|UOUT
BOUT|VOUT
GND
161310
19
24
VCC
GND_HS
29
30
FROM HDMI
I_PC_HD_SEL
2E17
2E18
2E19
2E20 47u
NC1
NC2
NC3
FE07
H_HDMI
100n
100n
100n
100n
6.3V
7E01
SM5301BS-G
4
8
28
17
R-PR-ADC
14
G-Y-ADC
11
B-PB-ADC
2E21
2E22
2E23
2E37 15p
2E39 15p
74LVC14APW
3E41
100R
74LVC14APW
3E42
100R
74LVC14APW
3E43
100R
IE08
5V4
VDD
SPST
SWITCH
NC
S1
D1
S2
D2
S3
D3
S4
D4
GND_HS
39R
22R
39R
22R
39R
22R
7E05-2
7E05-4
7E05-6
13
Φ
21
IE32
IE34
14
7
14
7
14
7
2E15
100n
NC
IN1
IN2
IN3
IN4
GND
2E24 100n470R
2E26 100n
2E27 100n
2E30
2E36
100n
4
8
12
7E02
ADG781BCP
3
100n2E25
100n2E28
100n2E29
100n
3V3
10
19
17
IE33
6
8
PC_HD_SEL
3V2
FE08
9
7
TO SCALER
SOG
R_PR+
R_PR-
G_Y+
G_Y-
B_PB+
B_PB-
IE31
3E44
HDMI_VVSV_HDMI
100R
3E45
HDMI_VHS
100R
3E46
(NC)
100R
TO SCALER
F_15430_013.eps
140405
A
B
C
D
E
G
F
2E00 C2
2E01 C2
2E02 C2
2E03 B5
2E04 B7
2E05 B7
2E06 B7
2E07 C7
2E08 C7
2E09 C7
2E10 C7
2E11 D7
2E12 D7
2E13 D7
2E14 D7
2E15 A10
2E16 B8
2E17 B8
2E18 B8
2E19 B8
2E20 B8
2E21 A9
2E22 B9
2E23 B9
2E24 C10
2E25 C10
2E26 C10
2E27 C10
2E28 C10
2E29 D10
2E30 D10
2E31 E3
2E32 E6
2E33 C2
2E34 C2
2E35 D2
2E36 E10
2E37 B9
2E38 B9
2E39 B9
3E00 A2
3E01 A2
3E02 A2
3E06 C3
3E07 C3
3E08 C3
3E09 C3
3E10 C3
3E11 C3
3E12 C5
3E13 B6
3E14 B6
3E15 B6
3E16 B6
3E17 B6
3E18 B7
3E19 C6
3E20 C6
3E21 D6
3E22 D6
3E23 D7
3E24 C10
3E25 C10
3E26 C10
3E27 C10
3E28 C10
3E29 D10
3E30 D10
3E31 E2
3E32 F2
3E33 F2
3E34 F2
3E35 E5
3E36 F5
3E37 G4
3E38 F6
3E39 E6
3E41 E9
3E42 F9
3E43 G9
3E44 E11
3E45 F11
3E46 G11
3E49 G5
3E50 C3
3E51 C3
3E52 C3
3E53 D3
3E54 D3
3E55 D3
4E03 B6
4E10 E2
4E11 G3
4E12 D5
4E13 D5
4E14 D5
5E00 B4
5E01 B8
5E02 A10
5E03 E3
6E00 F2
6E01 F2
6E02 F2
6E03 F2
7E00 B4
7E01 B8
7E02 A10
7E03 E3
7E04-1 E5
7E04-2 E6
7E04-3 F5
7E04-4 F6
7E04-5 G5
7E04-6 G6
7E05-1 E9
7E05-2 E10
7E05-3 F9
7E05-4 F10
7E05-5 G9
7E05-6 G10
FE00 B2
FE01 B2
FE02 B2
FE03 C5
FE04 C7
FE05 D7
FE06 B8
FE07 D8
FE08 B11
FE09 C9
FE10 C9
FE11 C9
FE12 C9
FE13 D9
IE00 B4
IE01 B7
IE02 B7
IE03 D6
IE04 D7
IE05 A9
IE06 B9
IE07 B9
IE08 A10
IE09 E2
IE10 F2
IE11 F2
IE12 F2
IE13 C3
IE14 C3
IE15 C3
IE16 C3
IE17 A10
IE18 D2
IE19 C6
IE20 C7
IE21 D6
IE22 C7
IE23 D7
IE24 F7
IE25 C7
IE26 C7
IE27 E7
IE28 G6
IE29 A10
IE30 A10
IE31 E11
IE32 C10
IE33 C11
IE34 D10
IE35 B7
IE36 B7
IE37 B7
Page 44

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
44LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Digital I/O
12345678910
DIGITAL IO
B14 B14
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
RGB/COMPONENT VIDEO
INPUT
1F00-4
YKF45-7005
C125 C2 26
IF12
IF13
C327 C4 28
31
29
30
DVI INPUT
ROW_A
1F00-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
YKF45-7005
ROW_B
1F00-2
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
DVI CONNECTOR
YKF45-7005
ROW_C
1F00-3
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
YKF45-7005
FF00
FF01
FF03
FF04
FF05
FF06
FF07
FF08
IF06
IF07
FF09
FF10
FF11
IF08
FF12
FF13
FF02
32
IF15
3F28
3F29
DVI_5V
2F11
330p 330p
100R
100R
2F12
3F20
3F21
2F00
RES
2F02
RES
2F05
RES
5F00
3F00
75R
5F01
3F10
1R0
3F09
75R
5F02
3F11
75R
DDC_5V
2F07
5V
100n
(256x8)
EEPROM
ADR
2F09
330p
8
Φ
4
1R03F19
2F10
M24C02-WMN6
0
1
2SDA
IF01
1K0
1
2
3
2F08
330p
100R
7F03
SCL
100p
2F04
100p
WC
DDC_5V
3F17
IF00
3F16
7
0V
5V
5V
10K
6
5
6F01
3F22
3F23
BAS316
10K
1K0
IF02
10K
BAS316
6F00
5F03
3F18
10K
+5VSWI
IF03
IF21
DDC_5V
TO MUX-SYNC INTERFACE
IF11
RINA|Pr
IF17IF14
GINA|YINA
H_PC
IF20
BINA|Pb
V_PC
SCL_DVI
SDA_DVI
RX2-IN
RX2+IN
RX1-IN
RX1+IN
HOT_PLUG
RX0-IN
RX0+IN
RXC+IN
RXC-IN
TO SCALER
PC AUDIO IN
YKB21-5101A
TO SCALER
1F01
To HERCULES
5
4
IF05
2
IF04
3
7
8
1
S001
S002
3F25 10K
3F24
10K
IF23
2F13
180p
IF22
2F14
180p
2F16 2u2
3F26
15K
3F27
15K
AudioIN2L
AudioIN2R
2u22F15
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1F00-1 D1
1F00-2 E1
1F00-3 F1
1F00-4 B1
1F01 A7
2F00 A2
2F02 B2
2F04 B3
2F05 C2
2F07 C3
2F08 E2
2F09 E2
2F10 E3
2F11 F2
2F12 F2
2F13 B9
2F14 B9
2F15 B9
2F16 B9
3F00 A2
3F09 B2
3F10 B3
3F11 C2
3F16 D4
3F17 D4
3F18 D4
3F19 E2
3F20 F2
3F21 F2
3F22 F3
3F23 F3
3F24 B8
3F25 B8
3F26 B9
3F27 B9
3F28 E2
3F29 E2
5F00 A3
5F01 B3
5F02 C3
5F03 F4
6F00 F4
6F01 F3
7F03 D2
FF00 D1
FF01 E1
FF02 E1
FF03 E1
FF04 E1
FF05 E1
FF06 E1
FF07 F1
FF08 F1
FF09 F1
FF10 F1
FF11 G1
FF12 G1
FF13 G1
IF00 D3
IF01 F2
IF02 F4
IF03 F5
IF04 B8
IF05 B8
IF06 F1
IF07 F1
IF08 G1
IF11 A6
IF12 B1
IF13 B1
IF14 B2
IF15 B2
IF17 B6
IF20 C6
IF21 F5
IF22 B9
IF23 B9
S001 B8
S002 B8
3139 123 6093.1
1234567
F_15430_014.eps
140405
8910
Page 45

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
45LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Analog I/O
123456789101112131415
B15 B15
A
Audio-R_out
Audio-L_out
B
Function_Sw
C
D
Terr_CVBS_out
E
F
Audio-R_out
G
H
I
J
Audio-L_out
Function_Sw
RGB-R/YC-C_in
Video/YC-Y_in
SCART ANALOGUE IO
Audio-R_in
Audio-L_in
RGB-B_in
RGB-G_in
RGB-R_in
RGB-BL_in
Video_in
Audio-R_in
Audio-L_in
RGB-B_in
RGB-G_in
CVBS_out
SCART 1
1G01-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
HR-AR0761S-2
MT
1G01-2
23
22
HR-AR0761S-2
SCART 2
1G02-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
HR-AR0761S-2
MT
1G02-2
23
22
HR-AR0761S-2
FG02
FG24
FG25
FG16
FG19
6G05
BZX384-C3V9
6G06
BZX384-C3V9
S015
S016
FG10
BZX384-C3V9
6G09
BZX384-C3V9
FG26
S028
FG27
S029
FG28
S030
S031
S032
FG30
FG00
FG01
2G02
S012
RES
FG03
FG04
FG05
FG06
FG07
FG08
FG09
FG11
FG12
S023
BZX384-C3V9
FG14
FG15
6G10
BZX384-C3V9
FG22
S035
FG23
S036
S011
S013
BZX384-C3V9
6G04
S020
S021
S022
6G086G07
FG18
FG21
6G03
BZX384-C3V9
S019 S018
EMC
RES
2G52
FG17
FG20
EMC
RES
2G53
2G01
RES
2G03
RES
S034
S033
S014
S017
3G30
S024
S025
S026
S027
2G04
RES
3G13
91R
3G14
91R
27K3G26
6G00
3G00
RES
3G01
4G00
RES
4G01
3G04
3G05 10K
3G15 100R
3G12
91R
3G17
3G27
6K8
3G29
3G28
75R
68R
3G31
75R
RES
2G48
RES
2G49
RES
2G50
RES
2G51
RES
3G45
75R
6G01
RES
150R
10K
150R
100R3G16
100R
330R
IG11
100R3G33
3G37
3G38
RES
RES
4G05
4G06
3G42 10K
3G51
3G53
68R
3G58
100R
3G57
75R
IG00
2G05
330p
IG01
2G06
180p 15K
IG04
2G09
330p
IG05
2G10
180p
+5VSW
7G03
BC847BW
5V2
1V8
3G32
1K0
150R
10K
150R3G41
27K
3G46
100R
3G09
RES
7G05
BC847BW
IG24
3G54
1K0
IG43
2G28
4u7
3G60
47K
3G02
220K
3G03
3G06
220K
3G07
15K
2V5
2G18
330p
2G19
180p
2G22
330p
2G23
180p
3G52
6K8
IG40
5V2
3V
+5VSW
3G59
47K
IG12
IG14
IG15
IG18
IG19
+5VSW
2G07 10u
*
2G08
2G11
*
2u22G12
4G26
5G00
RES
2G16
RES
2G20 10u
3G39
220K
3G40
15K
3G43
220K
3G44
15K
3V7
16V
2u2
10u
16V
2G21
2G24 10u
2G26
4u7
3G55
RES
IG25
3G56
RES
2G17
RES
16V
2u2
16V
2u22G25
3G08
1K0
3G34
1K0
IG02
IG03
IG23
IG26
IG27
IG16
IG17
IG20
IG21
IG42
4G18
+5VSW
3G48
47K
3G47
47K
SC2_CVBS_MON_OUT
SC1_COMP_AV1_R_IN
SC1_COMP_AV1_L_IN
SC2_CVBS_MON_OUT
K
3139 123 6093.1
123456789101112131415
TO HERCULES
SC1_R
SC1_R_RF_OUT
SC1_L
SC1_L_RF_OUT
IG06
CVI_Pb_IN
IG07
CVI_Y_IN
IG08
CVI_Pr_IN
IG09
STATUS_1
IG10
SC1_CVBS_RF_OUT
IG13
SC1_CVBS_IN
FG13
SC2_R
SC2_R_MON_OUT
SC2_L
SC2_L_MON_OUT
STATUS_2
SC2_Y_IN
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B13
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
IG49
SC1_CVI_DMMI_R_Pr_IN
CVI_Pb_IN
CVI_Y_IN
SC2_AV3_C_IN
FROM SIDE CONNECTOR
FRONT_C_IN
SC2_C_IN
FRONT_Y_CVBS_IN
FROM SCALER
SC2|AV2_SIDE_SW
0V
AV2_DMMI_SW
SC2_L_IN
DMMI_L_IN
AV2_DMMI_SW
DMMI_RGB_SW
SC2_R_IN
DMMI_R_IN
DMMI_CVBS_IN
SC1_FBL_IN
SC1_FBL_IN_1
DMMI_FBL_IN
DMMI_RGB_SW
CVI_Pr_IN
DMMI_R_Pr_IN
DMMI_R_IN
DMMI_L_IN
DMMI_R_Pr_IN
DMMI_FBL_IN
SC2_AV3_Y_IN
IG73
IG76
2G56
4u7
+5VSW
2G55
4u7
3G99
47K
+5VSW
IG78
3S03
47K
IG75
4G20
2G65
4u7
3S00
47K
RESERVED FOR DMMI
3G63
3G64
RES
3G66 3G67
+5VSW
4G14
4G15
3S01
150R
4G19
3G96
47K
+5VSW
IG79
47K
3G92
47K
3G93
4G21
2G66
4u7
SC2_Y_IN
IG47
3G94
47K
3G95
47K
+5VSW
2G302G29
10u
10K
10K
2G64
2u2
15K
3G68
15K
IG56
2u22G63
2G31
2G32
4G09
4G10
10K3G65+5VSW
100n 3
100n
74HC4053D
6
13
IG50
12
11
1
IG52
2
10
IG53
5
IG54
9
IG55
VDD
G4
1
2
4X1
4X2
VEE VSS
7
4G11
4G12
4G13
16
MDX
8
7G07
100n
16V
3G69
47K
IG57
IG58
3G70
47K
2G33
220n
6G02
BAS316
14
15
4
RESERVED FOR DMMI
IG28
5G01
3G72
3G74
3G73
10K
47K
47K
100R
3G75
1u02G36
3G76
100R
2G37 4u7 2G41 4u7
3G77
47K
+5VSW
IG80
7G10
74HC4053D
4G22
16
VDD
MDX
6
G4
13
1
12
2
11
4X1
4X2
1
2
10
3
5
9
VEE VSS
7
8
3G78
47K
IG60
IG61
IG62
IG63
+5VSW
IG46
14
15
2G34
10u
16V
IG29
5G02
4
2G47
100n
2G35
100n
7G09
ADG734BRU
16
VDD
Φ
SPDT
11
SWITCH
1
IN1
IN3
S1A
D1
S1B
IN2
S2A
D2
S2B
GND VSS
6
4G16
4G17
12
S3A
13
D3
14
S3B
20
IN4
19
S4A
18
D4
17
S4B
15
NC
5
3G90
2
3
4
10
9
8
7
RESERVED FOR DMMI
IG64
IG67
IG69
2G38
1u0
TO HERCULES
3G88
3G91
75R
75R75R
3G79
47K
3G89
47K
3G83
100R
3G84
100R
B2
B2
B2
B2
B17/B5
B2/B6
B2
IG30
3G82
3G81
3G80
47K
47K
47K
2G39
2G40 4u7
3G87
3G86
3G85
47K
47K
47K
SW_I2C_SDA
SW_I2C_SCL
POWER-DOWN_BOLT-ON
SC2_L_MON_OUT
SC2_R_MON_OUT
SC2_CVBS_MON_OUT
IR
HP_DET_R_DC
SC_STANDBY
ITV_IR_SW_RESET
7G08
BC847B
3G71
560R
IG59
1u0
DMMI_B_Pb_IN
DMMI_G_Y_IN
2G43
1n0
SC2_Y_IN_1
SC2_L_IN_1
SC2_R_IN_1
SC1_CVI_DMMI_G_Y_IN
SC1_CVI_DMMI_B_Pb_IN
FG32
FG33
FG34
FG35
FG36
FG37
FG38
FG39
FG41
FG42
FG43
FG44
FG45
FG47
FG48
FG49
FG50
+3V3STBY
FG51
FG53
FG54
FG56
2G46
2G45
1n0
1n0
TO MUX-SYNC INTF
1G03
FG40
NC
NC
NC
3334
AF732L-N2G1A
F_15430_015.eps
TO HERCULES
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
DMMI CONNECTOR
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
140405
1G01-1 A1
1G01-2 E1
1G02-1 F1
1G02-2 J1
1G03 G15
2G01 A3
2G02 A2
2G03 B3
2G04 B3
2G05 A3
A
2G06 B3
2G07 A4
2G08 A4
2G09 B3
2G10 B3
2G11 B4
2G12 B4
2G16 E4
2G17 E5
2G18 G4
2G19 G4
2G20 G5
B
2G21 G4
2G22 H4
2G23 H4
2G24 G5
2G25 H4
2G26 I5
2G28 J4
2G29 B11
2G30 B11
2G31 C11
2G32 C11
C
2G33 C13
2G34 D11
2G35 D11
2G36 F9
2G37 F9
2G38 F12
2G39 E13
2G40 E13
2G41 F13
2G43 I14
2G45 I14
2G46 I14
D
2G47 J11
2G48 G3
2G49 G3
2G50 H3
2G51 H3
2G52 F2
2G53 K2
2G55 I8
2G56 J8
2G63 B10
2G64 C10
2G65 K9
E
2G66 I9
3G00 A3
3G01 A3
3G02 A4
3G03 B4
3G04 B3
3G05 B3
3G06 B4
3G07 B4
3G08 J5
3G09 I4
F
3G12 C3
3G13 C3
3G14 D3
3G15 C3
3G16 C3
3G17 D3
3G26 D2
3G27 D3
3G28 E3
3G29 E3
3G30 E3
3G31 F3
G
3G32 E4
3G33 F3
3G34 E5
3G37 G3
3G38 G3
3G39 G4
3G40 G4
3G41 G3
3G42 H3
3G43 H4
3G44 H4
3G45 I3
H
3G46 I3
3G47 I6
3G48 I6
3G51 H3
3G52 H4
3G53 J3
3G54 J4
3G55 I5
3G56 J5
3G57 K3
3G58 J3
I
3G59 J4
3G60 K4
3G63 B9
3G64 C9
3G65 B11
3G66 C9
3G67 C10
3G68 C10
3G69 B12
3G70 C12
3G71 C14
3G72 D10
J
3G73 D10
3G74 D10
3G75 E9
3G76 F9
3G77 F10
3G78 F10
3G79 D12
3G80 D13
3G81 D13
3G82 D13
3G83 E12
3G84 F12
K
3G85 F13
3G86 F13
3G87 F13
3G88 H12
3G89 F12
3G90 H11
3G91 H12
3G92 J9
3G93 K9
3G94 I9
3G95 I9
3G96 I9
3G99 I8
3S00 J9
3S01 G9
3S03 J8
4G00 A3
4G01 B3
4G05 G3
4G06 G3
4G09 B11
4G10 B11
4G11 D12
4G12 D12
4G13 D12
4G14 E9
4G15 F9
4G16 G11
4G17 G11
4G18 J5
4G19 H9
4G20 K9
4G21 I9
4G22 K10
4G26 E4
5G00 E4
5G01 D10
5G02 I11
6G00 F3
6G01 K3
6G02 B13
6G03 B2
6G04 C2
6G05 A2
6G06 B2
6G07 F2
6G08 F2
6G09 G2
6G10 G2
7G03 E4
7G05 J4
7G07 B11
7G08 B13
7G09 E11
7G10 J10
FG00 A2
FG01 A2
FG02 B1
FG03 B2
FG04 B2
FG05 C2
FG06 C2
FG07 C2
FG08 D2
FG09 E2
FG10 D2
FG11 E2
FG12 F2
FG13 F6
FG14 G2
FG15 G2
FG16 G1
FG17 G2
FG18 H2
FG19 H1
FG20 I2
FG21 H2
FG22 J2
FG23 J2
FG24 C1
FG25 C1
FG26 G2
FG27 H2
FG28 H2
FG30 I2
FG32 G14
FG33 G14
FG34 G14
FG35 G14
FG36 G14
FG37 H14
FG38 H14
FG39 H14
FG40 H15
FG41 H14
FG42 H14
FG43 H14
FG44 H14
FG45 H14
FG47 I14
FG48 I14
FG49 I14
FG50 I14
FG51 I14
FG53 I14
FG54 I14
FG56 I14
IG00 A4
IG01 A4
IG02 A5
IG03 B5
IG04 B4
IG05 B4
IG06 C6
IG07 C6
IG08 D6
IG09 D6
IG10 D6
IG11 E3
IG12 E4
IG13 E6
IG14 G4
IG15 G4
IG16 G5
IG17 G5
IG18 G4
IG19 H4
IG20 G5
IG21 H5
IG23 H5
IG24 J4
IG25 J5
IG26 J5
IG27 K5
IG28 D10
IG29 E11
IG30 F12
IG40 I4
IG42 I5
IG43 J4
IG46 I11
IG47 K9
IG49 B8
IG50 B11
IG52 C11
IG53 C11
IG54 C11
IG55 C11
IG56 D10
IG57 B13
IG58 B13
IG59 D14
IG60 E11
IG61 F11
IG62 F11
IG63 F11
IG64 E12
IG67 F12
IG69 F12
IG73 I8
IG75 I9
IG76 J8
IG78 J9
IG79 K9
IG80 I10
S011 A2
S012 B2
S013 B2
S014 B2
S015 C2
S016 C2
S017 C3
S018 C2
S019 D2
S020 E2
S021 E2
S022 E2
S023 F2
S024 G3
S025 G3
S026 H3
S027 H2
S028 G2
S029 H2
S030 H2
S031 H2
S032 I2
S033 I2
S034 I2
S035 J2
S036 K2
Page 46

SSB: Top Connectors
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
46LC4.9E AB 7.
12345678
TOP CONNECTORS
B16 B16
A
B
C
D
E
F
3139 123 6093.1
FOR UFD ONLY
(1M03)
1J00
1
IJ01
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
UFD CONTROL
(1M46)
1J01
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
UFD SUPPLY
1J02
TO/FROM PSU
(SUPPLY FOR LCD)
B12P-PH-K-S(LF)
1J03
B3B-PH-K-S(LF)
3
2
1
(+18V / +24V)
TO/FROM 1003 OF
CLASS-D AUDIO AMP
POR
IJ02
IJ03
IJ04
TEMP_SENSOR (NC)
IJ05
IJ06
NC
IJ07
FJ00
FJ01
(NC)
FJ02
5V(NC)
FJ03
FJ04
+33V_TUN(NC)
FJ05
NC
1
GND_AUDIO
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
FJ08
FJ09
GND_AUDIO
1
FROM SCALER INTERFACE
(NC)
LAMP_ON_OFF_1
5J05
STANDBY_1
POWER_UP_OK_1 POWER_UP_OK
RES
2J16
5J04
3V2
5J03
1n02J35
2J02 1n0
1J07
1J08
4J01
+12V_UFD
T3A
+5V_UFD
VP
FJ06
FJ07
IJ08
IJ09
IJ10
IJ11
VP
GND_AUDIO
1n0
2J31
2J03
1n0
RES
4J02
2J30 1n0
RES
3J06
RES
2J33
+3V3STBY
POWER_DOWN
100p2J17
100p
100p
2J19
2J18
RES
RES
RES
2J20
2J34
TO DC-DC CONVERTER
+5V
11V6
+12VUNREG
68R3J05
68R3J03
68R3J04
100p
2J22
FAN_SPEED
PROTECT_AUD
BACKLIGHT_CTRL
LAMP_ON_OFF
100p
2J23
2J21 100p
2345678
FROM SCALER
IJ12
FROM SCALER
FROM SCALER INTERFACE
STANDBY
3V1
3V2
IJ13
PROTECT_AUD
FROM SCALER
FROM AUDIO
FROM EPLD
AUDIO-L
AUDIO-R
SOUND_ENABLE_1
3V3
POR_AUDIO
3V3
B_LT_PWM
G_LT_PWM
R_LT_PWM
B_RT_PWM
G_RT_PWM
R_RT_PWM
B_LB_PWM
G_LB_PWM
R_LB_PWM
B_RB_PWM
G_RB_PWM
R_RB_PWM
2J26
5J01
5J02
2J27 2J28
100p
100p100p
100p2J04
100p2J05
100p
2J10
2J11 100p
FJ10
FJ12
FJ13
FJ14
2J29
100p
100p2J07
2J06 100p
100p2J12
2J08 100p
100p2J14
2J13 100p
RESERVED
FJ11
AUDIO-SW (NC)
2J36
1n0
FJ15
FJ16
FJ17
FJ18
FJ19
FJ20
100p2J09
FJ21
FJ22
FJ23
FJ24
FJ25
FJ26
2J15 100p
(1M52)
1J04
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
B9B-PH-K-S(LF)
1J05
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
B7B-PH-K-S(LF)
1J06
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
B7B-PH-K-S(LF)
TO/FROM 1002 OF
AMBIENT LIGHT
AMBIENT LIGHT
1J00 B1
1J01 C1
1J02 D1
1J03 F1
1J04 B8
1J05 C8
1J06 E8
1J07 C2
1J08 C2
2J02 F2
A
2J03 F2
2J04 D6
2J05 D7
2J06 D7
2J07 D7
2J08 D7
2J09 D7
2J10 E6
2J11 E7
2J12 E7
2J13 E7
2J14 E7
B
2J15 E7
2J16 C2
2J17 F3
2J18 F2
2J19 F3
2J20 C3
2J21 F3
CLASS-D AUDIO AMPLIFIER
2J22 F3
2J23 F3
2J26 C6
2J27 C7
C
2J28 C7
2J29 C7
2J30 F2
2J31 D2
2J33 C2
2J34 C3
2J35 F2
(TOP)
2J36 C7
3J03 E3
3J04 E3
3J05 E3
3J06 B3
D
4J01 D2
4J02 C2
5J01 B7
5J02 B7
5J03 E2
5J04 C2
5J05 B3
FJ00 C1
FJ01 C1
FJ02 C1
(BOTTOM)
E
FJ03 C1
FJ04 C1
FJ05 D1
FJ06 E2
FJ07 E2
FJ08 F1
FJ09 F2
FJ10 B7
FJ11 B8
FJ12 B7
FJ13 B7
FJ14 C7
FJ15 C7
F
FJ16 C7
FJ17 D7
FJ18 D7
FJ19 D7
FJ20 D7
FJ21 E7
F_15430_016.eps
140405
FJ22 E7
FJ23 E7
FJ24 E7
FJ25 E7
FJ26 E7
IJ01 B1
IJ02 B1
IJ03 B1
IJ04 B1
IJ05 B1
IJ06 B1
IJ07 B1
IJ08 E2
IJ09 E2
IJ10 E2
IJ11 E2
IJ12 B4
IJ13 E4
Page 47

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
47LC4.9E AB 7.
SSB: Side Connectors
12345678
1 2345678
B17 B17
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
FOR DISC/ ARCH CABINET
RES
1K04
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
3139 123 6093.1
SIDE CONNECTORS
FK00
FK02
FK03
FK04
FK05
FK06
FK07
FK10
4K06
4K07
RESERVED
+3V3STBY_1
+3V3STBY_1
RES
+5VSW_1
FRONT_Y_CVBS_IN_1
FRONT_C_IN_1
FRONT_L_IN_1
+5VSW_1
FRONT_R_IN_1
HP_LOUT_1
HP_DET_R_DC_1
HP_ROUT_1
1K03
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
TO/FROM 1304
OF SIDE I/O
(1M06)
1K01
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
FK01
3V3
3V3
4K02
RES
PC-TV-LED_1
LED_SEL_1
LIGHT_SENSOR_1
3K00
100R
2K02
10p
3K01
100R
2K04
10p
3K02
10K
2K06
5K01
1u0
2K19
1n0
3K05
10K
2K10
100p
3K07
*
39R
2K13
**
100p
3K08
68R
2K15
100p
3K09
*
39R
2K16
**
100p
2K20
1n0
IK17
IR_1
2K03
10p
2K05
10p
2K07100p
100p
IK18
2K11
100p
2K14
100p
2K17
100p
3K03
15K
3K06
15K
+5VSW
2K12
ITV_IR_SW_RESET
2K08
2u2
2u2
+3V3STBY
LED_SEL
KEYBOARD
FRONT_Y_CVBS_IN
FRONT_C_IN
UFD
*
2K13
10p
2K14
10p
2K16
10p
2K17
10p
3K07
10R
3K09
10R
HP_LOUT
HP_DET_R_DC
HP_ROUT
PC-TV-LED
IR
LIGHT_SENSOR
FRONT_L_IN
FRONT_R_IN
2K01
100p
100p
2K22
2K21
KEYBOARD
3K11
5K00 1u0
5K02 1u0
3K12
3K13
100p
100p
2K24
2K23
68R
68R
68R
2K00
1n01n0
IK16
100p
2K25
100p
2K26
4K01
4K03
4K04
4K05
100p
2K27
RES
RES
100p
2K28
IK00
IK01
IK02
IK03
TO/FROM 1540 OF
PC-TV-LED_1
+3V3STBY_1
LED_SEL_1
IR_1
LIGHT_SENSOR_1
TOP/SIDE KEYBOARD
FK08
FK09
2K18
100p
B3B-PH-K-S(LF)
1
2
3
FK11
1K02
IR/ LED
1K00
(1M21)
6
5
4
3
2
1
B6B-PH-K
(1M01)
F_15430_017.eps
140405
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
1K00 A8
1K01 D1
1K02 E8
1K03 A1
1K04 D1
2K00 B7
2K01 B6
2K02 C3
2K03 C3
2K04 D3
2K05 D3
2K06 D3
2K07 D3
2K08 D4
2K10 E3
2K11 E3
2K12 E4
2K13 F3
2K14 E3
2K15 F3
2K16 F3
2K17 F3
2K18 E8
2K19 E3
2K20 E3
2K21 B6
2K22 B6
2K23 B6
2K24 B6
2K25 B7
2K26 B7
2K27 B7
2K28 B7
3K00 C3
3K01 C3
3K02 D3
3K03 D3
3K05 E3
3K06 E3
3K07 E3
3K08 F3
3K09 F3
3K11 A7
3K12 A7
3K13 B7
4K01 A7
4K02 F2
4K03 A7
4K04 A7
4K05 A7
4K06 B1
4K07 B1
5K00 A7
5K01 D3
5K02 A7
FK00 E1
FK01 E1
FK02 E1
FK03 E1
FK04 E1
FK05 E1
FK06 E1
FK07 E1
FK08 E8
FK09 E8
FK10 E1
FK11 B8
IK00 A8
IK01 A8
IK02 A8
IK03 B8
IK16 A7
IK17 D3
IK18 E3
12345678
1 2345678
Page 48

SSB: ADC
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
48LC4.9E AB 7.
123456789
ADC
B18 B18
A
TO HERCULES
B
C
D
E
FROM HERCULES
F
3139 123 6093.1
INTF_V_OUT
CVBS_COMB
INTF_Y_OUT
FROM SYNC INTERFACE
INTF_U_OUT
Hsync_SDTV
Vsync_SDTV
IL06
SDA
SCL
4L03
RES
4L02
12345678
+5VSWIA
3L12
1K0
2L36
RES
IL05
3L06
IL04
0R
7L05
LD1117DT33
32
OUTIN
COM
1
+5VSWIA
3L01
RES
3L00
1K0
+5VSWIA
3L07
3L09
RES
3L13
3L15
2L35
RES
RES
7L02
BC847BW
+5VSWIA
RES
1V5
RES
3L11
150R
1V5
3L03
RES
3L10
330R
5V4
7L03
BC847BW
0V9
+3V3SWB
2
7L06
BSN20
1
3L16
3L36
3K3
+3V3SWB
0R
IL16
2L30
5V4
7L01
BC847BW
0V9
2L38
5L03 10u
2L37
68p
5L04
3
3V3
16V10u
4L04
RES
RES
10u
3L17
150R
+3V3SWB
1
+3V3SWB
3L04
0R
3L35
220R
23
7L07
BSN20
3L37
3K3
3L38
0R
IL09
3L05
150R
2L39
82p
3L33
220R
2L17
47n
RES
4L00
RES
4L01
3L19
3L08
RES
4L05
+5VSWIA
3L39
RES
7L08
RES
+3V3SWB
5L00
IL17
150R
150R3L20
3L34
3L21 2K2
2L15
3L23
3L24
2L20
2L21 100n
82n 2K72L18 3L18
2L19 8n2
2L29
IL07
0R
2K23L22
RES
RES
2K2
100n
2L31
100u
16V
10u16V
2L13 47n
2L26
IL08
2L22
10u
9883(MSTAR)
220n
2L32
100u
16V
CLAMP_ADC
AD9985KSTZ
IL01
IL02
IL03
+3V3SWB +3V3SWB
5L01
IL18
2L23
2L24
100n
100n
7L04
394245465152596211
54
RAIN
48
GAIN
43
BAIN
30
HSYNC
31
VSYNC
49
SOGIN
38
CLAMP
29
COAST
58
REF_BYPASS
37
MIDSCV
33
FILT
57
SDA
56
SCL
55
A0
1
20
5L02
IL19
2223697879
VD VDD PVD
ANALOG INTERFACE FOR
Φ
262734
FLAT PANEL DISPLAY
GND
2425283236
21
4041444750
53606163681080
35
RED
GREEN
BLUE
DATACK
HSOUT
VSOUT
SOGOUT
2L03
2L02
10u 100n
10u 100n
IL10
77
0
IL11
76
1
IL12
75
2
74
3
73
4
72
5
71
6
70
7
IL13
9
0
IL14
8
1
IL15
7
2
6
3
5
4
4
5
3
6
2
7
19
0
18
1
17
2
16
3
15
4
14
5
13
6
12
7
67
66
64
65
2L04
100n
100n
2L08
2L092L07
100n 100n
3L25-1
3L25-2 22R
3L25-3 22R
3L25-4 22R
3L26-1 22R
3L26-2
3L26-3 22R
3L27-4
3L27-3 22R
3L27-2 22R
3L27-1
3L28-4 22R
3L28-3 22R
3L28-2 22R
3L28-1 22R
3L30 22R
2L05
100n
22R3L31
2K23L32
22R
22R
22R
22R
2L06
2L112L10
100n
2L27
10u 16V
2L33 2L34
100n
100n
COL_Di(8)
2L28
COL_CLKASA
COL_HREF
16V10u
COL_Di(1:7)
COL_Di(1)
COL_Di(2)
COL_Di(3)
COL_Di(4)
COL_Di(5)
COL_Di(6)
COL_Di(7)
COL_YA(1:8)
COL_YA(1)
COL_YA(2)
COL_YA(3)
COL_YA(4)
COL_YA(5)
COL_YA(6)
COL_YA(7)
COL_YA(8)
TO SCALER
COL_CLKASA
SYNC INTF
9
TO COLUMBUS
COL_HREF
COL_VACOL_VA
F_15430_018.eps
140405
A
B
C
D
E
F
2L02 A7
2L03 A7
2L04 A7
2L05 A8
2L06 A8
2L07 B7
2L08 B7
2L09 B7
2L10 B8
2L11 B8
2L13 C4
2L15 D4
2L17 E3
2L18 E4
2L19 E4
2L20 D4
2L21 D4
2L22 B5
2L23 B5
2L24 B5
2L26 C4
2L27 A8
2L28 B9
2L29 B4
2L30 A3
2L31 E4
2L32 E5
2L33 B8
2L34 B8
2L35 B2
2L36 E1
2L37 C3
2L38 C3
2L39 C3
3L00 B2
3L01 B2
3L03 B2
3L04 B3
3L05 B3
3L06 C1
3L07 C2
3L08 C3
3L09 C2
3L10 C2
3L11 C2
3L12 E1
3L13 D2
3L15 E2
3L16 E2
3L17 E3
3L18 E4
3L19 F3
3L20 F3
3L21 C4
3L22 D4
3L23 D4
3L24 D4
3L25-1 C7
3L25-2 C7
3L25-3 C7
3L25-4 C7
3L26-1 C7
3L26-2 C7
3L26-3 C7
3L27-1 D7
3L27-2 D7
3L27-3 D7
3L27-4 D7
3L28-1 D7
3L28-2 D7
3L28-3 D7
3L28-4 D7
3L30 E7
3L31 E7
3L32 E7
3L33 B3
3L34 C4
3L35 E3
3L36 E2
3L37 E3
3L38 C3
3L39 C4
4L00 D3
4L01 D3
4L02 C1
4L03 C1
4L04 C3
4L05 C4
5L00 B4
5L01 A5
5L02 A6
5L03 C3
5L04 C3
7L01 B3
7L02 C2
7L03 E2
7L04 C5
7L05 A2
7L06 F2
7L07 F3
7L08 C3
IL01 C5
IL02 C5
IL03 C5
IL04 B1
IL05 C1
IL06 E1
IL07 C4
IL08 C4
IL09 E3
IL10 C7
IL11 C7
IL12 C7
IL13 D7
IL14 D7
IL15 D7
IL16 A3
IL17 B4
IL18 A5
IL19 B6
Page 49

SSB: Columbus
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
49LC4.9E AB 7.
123456789101112
B19 B19
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
COLUMBUS
+3V3SW
+5VSWI
5M03
5M04
+3V3SWA
FROM FLASH/
CONTROL
+3V3SWA
5M02
FROM SCALER
#RESET
FM01
3M53 47R
FM02
FM03
3M55 47R
FM04
3M57 47R
FM05
2M65
100n
2M67
100n
2M00 100n
100u
2M68
100u
16V
47R3M54
47R3M59
3M58
10K
3V2
2M66
16V
5V3
2M02 100n
2M01 100n
COL_RST
+3V3SWA
10K
10K
3M52
3M56
+3V3SWA
2M03 100n
10K
3M50
3M51
10K
+5VSWIA
100n2M04
2M33
3M10
3M11 4K7
4M06
3M12
FROM ADC
100n2M06
2M05 100n
4M17
4M04
RES
100p
RES
4M05
RES
4M16
RES
COL_DQM
COL_RAS
COL_CAS
COL_CLK
COL_WE
COL_A0
COL_A1
COL_A2
COL_A3
COL_A4
COL_A5
COL_A6
COL_A7
COL_A8
COL_A9
COL_A10
COL_A11
COL_CLKASA
COL_YA(1:8)
COL_VA
COL_HREF
COL_Di(1:7)
100n2M08
100n2M07
G15
H15
H14
G14
A7
D15
F15
E15
E14
F14
A8
F1
H3
B8
3M13
4K7
+3V3SWA
3M79
4M00
4M01
4M02
4M03
3M89
22R
0R
0R
N8
N11
N14
COLUMBUS_CTRL
C10N4N12
P13
N13P2P14
IM03
IM04
IM06
IM07
IM08
3K3
2M11 100n
VSS
7M17
RES
3M00
RES
COL_Di(1)
COL_Di(2)
COL_Di(3)
COL_Di(4)
COL_Di(5)
COL_Di(6)
COL_Di(7)
C4
C12
B2
C3
3M26
3M90 22R
G3
M3
L13
G13
VDDS
C6
C13
D13C9M13
C5
N3
COL_YA(1)
COL_YA(2)
COL_YA(3)
COL_YA(4) COL_WE
COL_YA(5)
COL_YA(6)
COL_YA(7)
COL_YA(8)
COL_Di(8)_INV
100n
16V
100n
2M09
2M10
2M31 100u
7M00-2
COLUMBUS
RESET
CLKSEL
CLKEXT
A0IIC
656SEL
TCK
TDI
TDO
TMS
TRST
TST1
TST2
TST3
BISTEN
3M87
L14
DQM
K15
RAS_
K14
CAS_
J14
CLK
J15
WE_
P6
A0
R6
A1
P5
A2
R5
A3
R1
A4
R2
A5
R3
A6
P3
A7
R4
A8
P4
A9
R7
A10
P7
A11
H1 G1
CLKASA
B13
WEA / DAVA
B7
YA0 / Di9
B9
YA1
A9
YA2
B10
YA3
A10
YA4
B11
YA5
A11
YA6
B12
YA7
A12
YA8
A13
VA
A14
HREF
A2
UVA0 / Di0
B3
UVA1 / Di1
A3
UVA2 / Di2
B4
UVA3 / Di3
A4
UVA4 / Di4
B5
UVA5 / Di5
A5
UVA6 / Di6
B6
UVA7 / Di7
A6
UVA8 / Di8
100n2M12
C8C7D3
J3
B14E3F3
F13
+3V3SWA
0R
656
Decod
K3
N6
N9
E13
C11
H13
VDDC
J13
K13L3N5N7N10R9R11
COLUMBUS_IO
MUX
MUX
100n
2M13
3M86
RES
3D Comb
Memory
Interface
100n
2M14
AVD
AVS
SNDA
SNCL
SNRST
SDA
SCL
NC_2
NC_3
SWAN 3D
2M15 100n
Noise Reduct
MUX
656
Encod
2M17 100n
2M16 100n
N1
P1
C14
D14
C15
A15
B15
D4
N2
7M00-1
COLUMBUS
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15
DQ16
CLKASB
WEB / DAVB
YB0 / Do9
UVB0 / Do0
UVB1 / Do1
UVB2 / Do2
UVB3 / Do3
UVB4 / Do4
UVB5 / Do5
UVB6 / Do6
UVB7 / Do7
UVB8 / Do8
100n2M18
2M19 100n
5M01
IM11
3M78 1K0
3M15 100R
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQ8
DQ9
YB1
YB2
YB3
YB4
YB5
YB6
YB7
YB8
4M08
4M09
100u
2M56
100R3M14
R12
R10
R13
R14
R15
N15
M14
M15
G2
M2
M1
L2
L1
K2
K1
J2
J1
H2
16V
P12
P11
P10
P15
L15
A1
F2
E2
E1
D2
D1
C2
C1
B1
P9
P8
R8
IM01
100n
2M20
+3V3SWA
3M01-1
3M01-3 68R
3M01-4
3M02-1 68R
3M02-2 68R
3M02-3 68R
3M02-4
3M03-4
3M03-3
3M03-2 68R
3M03-1
3M04-4 68R
3M04-3 68R
3M04-2 68R
3M04-1 1 8
3M06-1
3M06-2 2 7
3M06-3 3 6
3M06-4
3M07-1 22R1
3M07-3 3 6
3M07-4 22R
2u2
2M21
18
68R
27
68R3M01-2
36
45
68R
18
27
36
45
68R
45
68R
36
68R
27
18
68R
45
6
3
7
2
68R
22R3M88
COL_CLKASB
IM00
IM10
RES
3M28
3M293M27
3M08-1
3M08-2 22R27
3M08-4 22R4
3M09-2
3M09-3
COL_Do(8)
3V2
22R18
22R
22R
22R45
8
27
22R3M07-2
22R
45
RES
22R18
22R3M08-3 3 6
5
18
22R3M09-1
22R27
22R36
7M03
LF15ABDT
13
OUT IN
1V5
COM
2
2M22
100n
100n2M24
FROM HERCULES
SDA
SCL
TO SCALER
COL_DE
COL_YB(1)
COL_YB(2)
COL_YB(3)
COL_YB(4)
COL_YB(5)
COL_YB(6)
COL_YB(7)
COL_YB(8)
COL_Do(1)
COL_Do(2)
COL_Do(3)
COL_Do(4)
COL_Do(5)
COL_Do(6)
COL_Do(7)
IM09
COL_DQ1
COL_DQ2
COL_DQ3
COL_DQ4
COL_DQ5
COL_DQ6
COL_DQ7
COL_DQ8
COL_DQ9
COL_DQ10
COL_DQ11
COL_DQ12
COL_DQ13
COL_DQ14
COL_DQ15
COL_DQ16
TO/FROM SYNC INTERFACE
5M00
+3V3SWA
2M23
100u
16V
Hsync_SDTV
2M32
100u
16V
COL_A0
COL_A1
COL_A2
COL_A3
COL_A4
COL_A5
COL_A6
COL_A7
COL_A8
COL_A9
COL_A10
COL_A11
+3V3SWA
COL_CLK
COL_RAS
COL_CAS
+5VSWIA
+5VSWIA
+3V3SWA
5M05
2M27
2M25
2M26 2M30
100n
100n
3M16 4K7
3M68
15K
2M60
1n0
3M71
2K7
2M62
1n0
2M28
100n
100n
25
7
1
VDD
21
0
22
1
23
2
24
3
27
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
A11
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
7M14-1
74HCT221D
16
VCC
GND
7M15-1
74HCT221D
16
VCC
GND
CLK
8
8
A
26
512K-1
VSS
0
50
13
4
13
43
28
29
30
31
32
20
19
35
34
18
17
16
15
4M10
+5VSWIA
1
2
3
R
14
CX
15
CX|RX
+5VSWIA
1
2
R
14
CX
15
CX|RX
133844
VDDQ
Φ
DRAM
512K X 16 X 2
MSM56V16160F-7T3
VSSQ
4
10
+5VSWIA
3M69
10K
2M61
1n0
CLAMP_ADC
TO ADC
41
2M29
100n
100n
7M01
33
NC
37
2
1
3
2
5
3
6
4
8
5
9
6
11
7
12
D
8
39
9
40
10
42
11
43
12
45
13
46
14
48
15
49
16
36
U
DQM
14
L
47
COL_DQ1
COL_DQ2
COL_DQ3
COL_DQ4
COL_DQ5
COL_DQ6
COL_DQ7
COL_DQ8
COL_DQ9
COL_DQ10
COL_DQ11
COL_DQ12
COL_DQ13
COL_DQ14
COL_DQ15
COL_DQ16
COL_DQM
RESERVED
+5VSWIA
7M14-2
16
74HCT221D
VCC
9
10
11
R
6
CX
7
CX|RX
GND
5
H_DELAY
12
8
H
3139 123 6093.1
123456789101112
F_15430_019.eps
150405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
2M00 E2
2M01 E2
2M02 E3
2M03 E3
2M04 E3
2M05 E3
2M06 E3
2M07 E3
2M08 E3
2M09 E4
2M10 E4
2M11 E5
2M12 E5
2M13 E6
2M14 E6
2M15 E6
2M16 E6
2M17 E6
2M18 E7
2M19 E7
2M20 E7
2M21 E7
2M22 E8
2M23 E8
2M24 F7
2M25 A9
2M26 A10
2M27 A10
2M28 A10
2M29 A11
2M30 A11
2M31 E4
2M32 A9
2M33 F3
2M56 E7
2M60 F9
2M61 F11
2M62 G9
2M65 A2
2M66 A2
2M67 B2
2M68 B2
3M00 A4
3M01-1 B7
3M01-2 B7
3M01-3 B7
3M01-4 B7
3M02-1 B7
3M02-2 B7
3M02-3 B7
3M02-4 B7
3M03-1 B7
3M03-2 B7
3M03-3 B7
3M03-4 B7
3M04-1 C7
3M04-2 C7
3M04-3 C7
3M04-4 C7
3M06-1 C7
3M06-2 C7
3M06-3 C7
3M06-4 C7
3M07-1 C7
3M07-2 D7
3M07-3 D7
3M07-4 D7
3M08-1 D7
3M08-2 D7
3M08-3 D7
3M08-4 D7
3M09-1 D7
3M09-2 D7
3M09-3 E7
3M10 F3
3M11 F3
3M12 G3
3M13 H3
3M14 G7
3M15 G7
3M16 C9
3M26 C4
3M27 D4
3M28 C7
3M29 D7
3M50 G3
3M51 G3
3M52 G3
3M53 G2
3M54 G2
3M55 G2
3M56 G2
3M57 G2
3M58 G2
3M59 G2
3M68 E9
3M69 E11
3M71 F9
3M78 F7
3M79 A5
3M86 A6
3M87 A5
3M88 C8
3M89 C5
3M90 E4
4M00 B5
4M01 B5
4M02 B5
4M03 B5
4M04 F3
4M05 F3
4M06 F3
4M08 F7
4M09 F7
4M10 D10
4M16 F3
4M17 F3
5M00 E8
5M01 F7
5M02 E2
5M03 A2
5M04 A2
5M05 A10
7M00-1 A7
7M00-2 F4
7M01 B11
7M03 E8
7M14-1 E10
7M14-2 E11
7M15-1 F10
7M17 A4
FM01 G2
FM02 G2
FM03 G2
FM04 G2
FM05 G2
IM00 C8
IM01 E7
IM03 C5
IM04 C5
IM06 C5
IM07 C5
IM08 D5
IM09 E8
IM10 C8
IM11 F7
Page 50

SSB: EPLD
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
50LC4.9E AB 7.
123456789101112
EPLD
B20 B20
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
3139 123 6093.1
+3V3-IO
2N01 100n
26
DATA
378
VCC
Φ
SCD
GND
4
EPCS4SI8
CS_
DCLK
ASDI
+3V3-IO
1u02N03
33K
100n
2N02
3N07
IN08
33K
3N10
5
IN09
7N03-2
LVDSAp
4N02
FN26
4N01
LVDSAn
4N04
FN27
4N03
BC847BS
LVDSBp
4N06
FN28
4N05
LVDSBn
4N08
FN29
4N07
LVDSCp
4N10
FN30
TO EPLD
FOR NON-
PIXEL+ SETS
TO SCALER
INTERFACE
TXB0+
TXB0-
TXB1+
TXB1-
TXB2+
TXB2-
TXB3+
TXB3-
TXBC+
TXBC-
123456789101112
7N01
4N09
10K
IN06
3N08
3
4
LVDSCn
4N12
FN31
4N11
1
5
2N04 1n0
LVDSDp
FN32
2
4N14
4N13
+3V3-IO
10K
3N01
IN01
IN02
IN04
LVDSDn
4N16
FN33
4N15
10K
3N03 10K
3N02
6
7N03-1
BC847BS
1
LVDSCLKp
4N18
FN34
4N17
IN03
LVDSCLKn
4N20
FN35
4N19
+3V3-IO
10K3N04
3N05 10K
IN05
IN10
3N21 100R
100R3N22
3N23 100R
100R3N24
3N25 100R
7N02-1
3N06 10K
FN01
IN11
3N09
1K0
H2
K4
G4
K3
J3
J2
K13
J13
H3
J4
EP1C12F256C8
CONTROL
DATA0
DCLK
CSO
ASDO
0
MSEL
1
CONF_DONE
STATUS
CONFIG
CE
LVDS IN
5N02
100n2N05
IN14
100n2N06
IN07
FN25
3N26
4K7
31
404856
VCC
10
RA+
9
11 38
16
15
20
19
18
17
25
26
RA-
RB+
RB-
RC+
RC-
RD+
RD-
RCLK+
RCLK-
PDWN
CLKOUT
8
LCD PANEL
INTERFACE
RECEIVER
4
14
21
Φ
SCAN
CLK
3N11
47R
+3V3SW
5N03
2N09
100n
13
LVDSVCC
Φ
GNDLVDSGND PLLGND
283644
52
TDI
TDO
TCK
TMS
CEO
+3V3SW+3V3SW
IN13
PLLVCC
22
0
1
2
3
5N04
H14
H15
J14
J15
H4
G1
H1
G16
H16
IN12
2N08
7N04
THC63LVDF84B
0
1
2
3
RA
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
RB
4
5
6
0
1
2
RC
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
RD
3
4
5
6
24 23
+3V3-IO+3V3-IO+3V3-IO
10K
10K
FOR DEBUGGING
FN09
2N15
100p
TO SCALER
B21
+3V3-IO
FN08
FN10
3N28
180R
SDA_IO
SCL_IO
1N01
RES
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
FN18
FN19
LVDS_PWR_DWN
PIXEL+_RESET
IN19
6N01
LED_OUT
TLMG3100
4N21
4N22
FN20
+3V3SW
1N02
B4B-PH-SM4-TBT(LF)
Φ
BANK 4
100R
IO_65
IO_66
IO_67
IO_68
IO_69
IO_70
IO_71
IO_72
IO_73
IO_74
IO_75
IO_76
IO_77
IO_78
IO_79
IO_80
IO_81
IO_82
IO_83
IO_84
IO_85
IO_86
IO_87
IO_88
3N46
3N47 100R
7N02-5
EP1C12F256C8
R2
IO_41
T2
IO_42
R3
IO_43
P4
IO_44
R4
IO_45
T4
IO_46
R5
IO_47
P5
IO_48
M5
IO_49
M6
IO_50
N5
IO_51
N6
IO_52
P6
IO_53
R6
IO_54
M7
IO_55
T6
IO_56
R7
IO_57
P7
IO_58
N7
IO_59
R8
IO_60
T8
IO_61
M8
IO_62
N8
IO_63
P8
IO_64
M10
R10
T11
N10
P10
R11
P11
N11
N12
M11
M12
P12
R12
T13
R13
R14
P13
T15
R15
R9
T9
P9
N9
M9
IN15
IN16
IN17
IN18
3N29
100R
3N31
3N32
3N33 100R
3N34
3N35
3N37
3N38
3N39
3N40
3N41
3N42
3N43
3N44
3N45
BACKLIGHT_DIM
2N16
100p
100R3N30
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R3N36
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
1
FOR DEVELOPMENT
2
USE ONLY
3
4
56
B_LT_PWM
G_LT_PWM
R_LT_PWM
B_RT_PWM
G_RT_PWM
R_RT_PWM
B_LB_PWM
G_LB_PWM
R_LB_PWM
B_RB_PWM
G_RB_PWM
R_RB_PWM
FN21
FN22
100p
100p
100p
2N18
2N17
TO SCALER INTERFACE
TO TOP CONN.
FN23
FN24
100p
BM05B-SRSS-TBT
2N20
2N19
B_IN(7)
B_IN(0)
G_IN(5)
B_IN(4)
R_IN(6)
B_IN(6)
B_IN(1)
PARITY_IN
DE_IN
B_IN(5)
VS_IN
B_IN(3)
HS_IN
B_IN(2)
5N01
RES
IO_20
IO_19
IO_18
IO_17
IO_16
IO_15
IO_14
IO_13
IO_12
IO_11
IO_10
IO_9
IO_8
IO_7
IO_6
IO_5
IO_4
IO_3
IO_2
IO_1
RES
2N14
FN04
FN05
FN06
FN07
H5
F1
G2
E1
F2
G3
F3
D1
E2
D2
E3
F5
E4
D3
F4
G5
B1
C2
C3
D4
3N12 10K
3N13
27
29
30
32
33
35
3712
39
43
45
46
47
51
53
54
55
34
41
42
49
50
100n2N07
100n
1
3
5
6
7
2
CLK_REF
3N19 10K
FN03
FN11
FN12
FN13
FN14
FN15
FN16
FN17
3N14
FN02
47R
3N20
3
1N05
14M31818
R_IN(0)
R_IN(1)
R_IN(2)
R_IN(3)
R_IN(4)
R_IN(5)
G_IN(0)
G_IN(1)
G_IN(2)
G_IN(3)
G_IN(4)
G_IN(5)
B_IN(0)
B_IN(1)
B_IN(2)
B_IN(3)
B_IN(4)
B_IN(5)
HS_IN
VS_IN
DE_IN
R_IN(6)
R_IN(7)
G_IN(6)
G_IN(7)
B_IN(6)
B_IN(7)
PARITY_IN
+3V3-IO
5N05
OC
4
2
R_IN(1)
R_IN(2)
R_IN(0)
R_IN(5)
R_IN(7)
G_IN(1)
G_IN(0)
G_IN(3)
G_IN(7)
R_IN(3)
R_IN(4)
G_IN(2)
G_IN(6)
G_IN(4)
2N10
100n
3N15
47R
3N16
47R
3N17
47R
47R
3N18
RES
RES
2N12
2N11
2N13
1
3N27
47R
7N02-2
EP1C12F256C8
N4
IO_40
P3
IO_39
P2
IO_38
R1
IO_37
L4
IO_36
K5
IO_35
N3
IO_34
M4
IO_33
L5
IO_32
M3
IO_31
N2
IO_30
M2
N1
M1
L2
L1
K1
L3
K2
J1
IO_29
IO_28
IO_27
IO_26
IO_25
IO_24
IO_23
IO_22
IO_21
BANK 1
Φ
CLKUSR
INIT_DONE
1N03
1
2
3
4
5
67
RES
F_15430_020.eps
150405
A
B
C
D
E
G
H
F
1N01 A9
1N02 D11
1N03 F12
1N05 D5
2N01 A2
2N02 C1
2N03 C2
2N04 C2
2N05 D4
2N06 D4
2N07 D5
2N08 D5
2N09 D5
2N10 D6
2N11 B7
2N12 B7
2N13 B7
2N14 B7
2N15 B8
2N16 E11
2N17 F11
2N18 F11
2N19 F11
2N20 F11
3N01 A3
3N02 A3
3N03 A3
3N04 A3
3N05 A3
3N06 A3
3N07 C2
3N08 C2
3N09 B4
3N10 C2
3N11 C4
3N12 A5
3N13 A5
3N14 A5
3N15 B6
3N16 B6
3N17 B6
3N18 B6
3N19 C5
3N20 C5
3N21 E3
3N22 E3
3N23 E3
3N24 F3
3N25 F3
3N26 D4
3N27 D6
3N28 F8
3N29 E11
3N30 E11
3N31 E11
3N32 E11
3N33 E11
3N34 E11
3N35 E11
3N36 E11
3N37 E11
3N38 F11
3N39 F11
3N40 F11
3N41 F11
3N42 F11
3N43 F11
3N44 F11
3N45 F11
3N46 D10
3N47 D10
4N01 D2
4N02 D2
4N03 D2
4N04 D2
4N05 D2
4N06 D2
4N07 D2
4N08 D2
4N09 D2
4N10 D2
4N11 D2
4N12 D2
4N13 D2
4N14 D2
4N15 D3
4N16 D3
4N17 D3
4N18 D3
4N19 D3
4N20 D3
4N21 D9
4N22 D9
5N01 A8
5N02 D4
5N03 D4
5N04 D5
5N05 C6
6N01 F9
7N01 A2
7N02-1 A4
7N02-2 D7
7N02-5 D10
7N03-1 C3
7N03-2 C2
7N04 D5
FN01 B4
FN02 B6
FN03 C5
FN04 A8
FN05 B8
FN06 B8
FN07 B8
FN08 B8
FN09 B8
FN10 B8
FN11 D5
FN12 E5
FN13 E5
FN14 F5
FN15 F5
FN16 F5
FN17 G5
FN18 D9
FN19 D9
FN20 F9
FN21 F11
FN22 F11
FN23 F11
FN24 F12
FN25 F4
FN26 D2
FN27 D2
FN28 D2
FN29 D2
FN30 D2
FN31 D2
FN32 D2
FN33 D3
FN34 D3
FN35 D3
IN01 B3
IN02 B3
IN03 B3
IN04 B3
IN05 B3
IN06 C2
IN07 D4
IN08 C2
IN09 C2
IN10 B3
IN11 B4
IN12 C5
IN13 D5
IN14 D4
IN15 D11
IN16 D11
IN17 D11
IN18 D11
IN19 F9
Page 51

SSB: EPLD
6
B
D
A
A
B
B
C
D
E
E
D
E
E
E
F
F
F
F
G
G
D
E
D
D
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
D
E
A
B
C
D
D
D
3
4
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
D
D
D
D
E
E
F
F
G
A
D
B
B
B
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
51LC4.9E AB 7.
1234567891011
EPLD
B21 B21
A
B
2P15
100u
16V
C
D
E
F
G
3139 123 6093.1
+3V3SW
FP01
PARITY_OUT
HS_OUT
VS_OUT
DE_OUT
B(5)
B(4)
B(6)
B(3)
B(2)
G(5)
B(1)
B(7)
B(0)
CLK_OUT
G(7)
1
2P16
100n
7P01
LF15ABDT
OUTIN
COM
2
N13
P14
P15
R16
N15
N16
K12
K14
L12
N14
M13
M14
L13
M15
M16
L14
L15
L16
K16
K15
J16
H12
+1V5
FP03
3
2P17
2u2
LVDS OUT
7N02-4
EP1C12F256C8
IO_89
IO_90
IO_91
IO_92
IO_93
IO_94
IO_95
IO_96
IO_97
IO_98
IO_99
IO_100
IO_101
IO_102
IO_103
IO_104
IO_105
IO_106
IO_107
IO_108
IO_109
IO_110
Φ
BANK 3
IO_111
IO_112
IO_113
IO_114
IO_115
IO_116
IO_117
IO_118
IO_119
IO_120
IO_121
IO_122
IO_123
IO_124
IO_125
IO_126
IO_127
IO_128
IO_129
IO_130
IO_131
5P01
5P02
5P03
G14
G13
G15
F16
F14
F13
F15
E16
E15
D16
D15
E14
F12
E13
D14
H13
G12
B16
C15
C14
D13
2u22P01
2P18 2u2
2u2
2P22
100n2P02
2P19 100n
100n
2P23
100n
2P03
100n
2P20
100n2P24
FP04
2P25
100n2P04
100n
2P21
100n
2P05 100n
100n2P26
100n
2P07 100n
2P06
+1V5-PLL
100n
100n
2P28
2P27
R(1)
G(6)
G(2)
G(1)
R(2)
R(5)
G(0)
R(7)
R(6)
R(0)
R(3)
R(4)
G(3)G(4)
100n
2P08
100n
2P29
B20
FP02
100n2P10
2P11 100n
2P09 100n
FP05
+1V5-INT
100n2P30
(H=NORMAL)
LVDS_PWR_DWN
CLK_OUT
R(0)
R(1)
R(2)
R(3)
R(4)
R(5)
G(0)
G(1)
G(2)
G(3)
G(4)
G(5)
B(0)
B(1)
B(2)
B(3)
B(4)
B(5)
HS_OUT
VS_OUT
DE_OUT
R(6)
R(7)
G(6)
G(7)
B(6)
B(7)
PARITY_OUT
100n2P12
2P13 100n
FP06
FP07
FP08
FP09
FP10
FP11
FP12
FP13
FP14
2P14 100n
+3V3-IO
3P01
4K7
1234
EAGLE INTERFACE
7N02-3
+3V3-IO
N.C.
47R3P03
B15
A15
B14
C13
B13
A13
B12
C12
E12
E11
E9
D12
D11
C11
B11
A11
B10
C10
D10
A9
B9
D9
C9
E10
C8
2P32
2P33
100n
IO_132
IO_133
IO_134
IO_135
IO_136
IO_137
IO_138
IO_139
IO_140
IO_141
IO_142
IO_143
IO_144
IO_145
IO_146
IO_147
IO_148
IO_149
IO_150
IO_151
IO_152
IO_153
IO_154
IO_155
IO_156
100n2P31
100n
1
32
17
31
51
52
54
55
56
3
4
6
7
11
12
14
15
19
20
22
23
24
27
28
30
50
2
8
10
16
18
25
EP1C12F256C8
Φ
BANK 2
DEV_CLR
LVDS TRANSMITTER
5P04
2P34 100n
9
26
VCC
RS
PDWN
R|F
CLKIN
0
TA
6
0
TB
6
0
TC
6
0
TD
6
GND LVDS GND PLL GND
5
13212953364349
D8
IO_157
E8
IO_158
A8
IO_159
B8
IO_160
D7
IO_161
C7
IO_162
B7
IO_163
A6
IO_164
E7
IO_165
B6
IO_166
C6
IO_167
D6
IO_168
D5
IO_169
E6
IO_170
E5
IO_171
C5
IO_172
B5
IO_173
A4
IO_174
B4
IO_175
C4
IO_176
B3
IO_177
A2
IO_178
B2
IO_179
DEV_OE
+3V3SW
5P05
44
LVDS VCC PLL VCC
56
N.C.
5P06
7P02
THC63LVDM83R
+
TCLK
-
+
TA
-
+
TB
-
+
TC
-
+
TD
-
33
35 34
C1
G6
P1
A14
F10
F7
A3
P16
K11
C16
T3
L7
L10
T14
A7
A10
G8
G10
H7
H9
J8
J10
K7
K9
T7
T10
H6
H11
1
1P01
4
DLW21S
DLW21S
1
1P02
4
DLW21S
1
1P03
4
DLW21S
1
1P04
4
DLW21S
1
1P05
4
+1V5-INT
+1V5-PLL
2P35
LVDSCLKp
39
LVDSCLKn
40
47
LVDSAp
LVDSAn
48
LVDSBp
45
LVDSBn
46
LVDSCp
41
LVDSCn
42
LVDSDp
37
LVDSDn
38
+3V3-IO
100n
FROM EPLD
7 8 9 10 11
BANK1
BANK2
BANK3
BANK4
VCCINT
PLL1
PLL2
2
3
2
3
2
3
2
3
2
3
7N02-6
EP1C12F256C8
Φ
POWER
VCCIO
GNDA
VCCA
GNDG
FROM SCALER INTERFACE
10p
2P36
10p
2P37
10p
2P38
10p
2P39
10p
2P40
10p
2P41
10p
2P42
10p
2P43
10p
2P44
10p
2P45
GND
PLL1
PLL2
PLL1
PLL2
LVDSCLK+
LVDSCLK-
A1
A16
A5
A12
F6
F8
F9
F11
G7
G9
G11
H8
H10
J7
J9
K6
K8
K10
L6
L8
L9
L11
T1
T5
T12
T16
J6
J11
J5
J12
LVDSA+
LVDSA-
LVDSB+
LVDSB-
LVDSC+
LVDSC-
LVDSD+
LVDSD-
FOR MFD ONLY
FOR UFD ONLY
SDA_DMA_BUS1_DISP
SCL_DMA_BUS1_DISP
+3V3SW
+3V3SW
LVDSD+
LVDSD-
LVDSCLK+
LVDSCLK-
LVDSC+
LVDSC-
LVDSB+
LVDSB-
LVDSA+
LVDSA-
+3V3SW
+3V3SW
+3V3SW
3P04
4P09
4P10
*
4P01
4P02
RES
100R3P05
100R
4P03
4P04
4P05
4P06
4P07
4P08
RES
LVDS_VCC
26"/32"
16X9
YES
23"
15X9
-
-
-
+3V3SW
FROM DC-DC CONVERTER
FOR LCD ONLY
4P01
*
4P02
*
LVDS_OPT
(NC)
(NC)
LVDS_VCC
NC
FP15
FP16
FP17
LVDS_OPT
CTRL_DISP2
CTRL_DISP1
VDISP_2
VDISP2
FI-WE31P-HFE-E1500
1P06
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
TO LCD PANEL (TIMING CONTROL)
25
26
27
28
29
30
32
31
0-1453230-3
(1G50)
1P07
3233
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
TO PLASMA PANEL (TIMING CONTROL)
6
5
4
3
2
1
F_15430_021.eps
150405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1P01
1P02
1P03
1P04
1P05
1P06
1P07
2P01
2P02
2P03
2P04
2P05
2P06
2P07
2P08
2P09
2P10
2P11
2P12
2P13
2P14
2P15
2P16
2P17
2P18
2P19
2P20
2P21
2P22
2P23
2P24
2P25
2P26
2P27
2P28
2P29
2P30
2P31
2P32
2P33
2P34
2P35
2P36
2P37
2P38
2P39
2P40
2P41
2P42
2P43
2P44
2P45
3P01
3P03
3P04
3P05
4P01
4P02
4P03
4P04
4P05
4P06
4P07
4P08
4P09
4P10
5P01
5P02
5P03
5P04
5P05
5P06
7N027N027N027P01
7P02
FP01
FP02
FP03
FP04
FP05
FP06
FP07
FP08
Page 52

SSB: Diversity Tables B9-B21
+
+
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
Y
R
R
MUX-SYNC INTERFACE
B9
Item
LC4.3x
LC4.8x
LC4.9x
V
VV
VV
VV
V
V
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
V
V
VV
VV
VV
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
2A00
2A01
2A02
2A03
2A12
2A13
3A00
3A01
3A02
3A06
3A06
3A07
3A07 RST SM 0402 68R PM5 COL
3A08
3A10
3A11
3A13
3A14
4A03
4A04
4A05
4A06
5A00
6A01
7A00
7A02
7A03
Description
CER2 0603 X7R 16V 100N COL
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
CER2 0603 Y5V 10V 1U COL
CER2 0402 X7R 16V 10N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
RST SM 0402 68R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 68R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 1K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 10K PM5COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 560R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL R
DIO REG SM BZX384-C3V9 COL R
IC SM PCA9515ADP (PHSE) R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
TRA SIG SM BC847BW (COL) R
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
MUX-SYNC INTERFACE
B13
Teletext)
ITEM
2E00
2E01
2E02
2E04
2E05
2E06
3E06
3E07
3E08
3E13
3E14
3E15
3E16
3E17
3E18
AP/EU/AP-DVB (with Teletext)
EU-DVB (with Teletext)
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
DESCRIPTION
NAFTA/LT & China (non-
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 4U7 PM10 R
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 4U7 PM10 R
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 4U7 PM10 R
CER2 0402 X5R 6V3 1U PM20 R
CER2 0402 X5R 6V3 1U PM20 R
CER2 0402 X5R 6V3 1U PM20 R
RST SM 0402 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 330R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 330R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 330R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 330R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 330R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 330R PM5 COL
ANALOG I/O SCART
B15
Item
26/32PF
VV
1G01
1G01
VV
1G02
1G02
1G03
2G29
2G30
2G31
2G32
2G33
2G34
2G35
2G36
2G37
2G38
2G39
2G40
2G41
2G43
2G45
2G46
2G63
2G64
2G65
2G65
2G66
2G66
3G63
3G64
3G65
3G66
3G67
3G68
3G69
3G70
3G71
3G72
3G73
3G75
3G76
3G77
3G79
3G81
3G83
3G84
3G86
3G88
3G89
3G92
3G93
3G94
3G95
4G09
4G11
4G12
4G13
4G14
4G15
4G16
4G17
4G18
4G19
4G22
5G01
6G02
7G07
7G08
7G09
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
DVB.T 26/32PF
37/42PF
DVB.T 37/42PF
SOC EURO H 21P F BK R-GRND B
VV
SOC EURO H 21P F SHD R-GRND Y
SOC EURO H 21P F BK R-GRND B
VV
SOC EURO H 21P F SHD R-GRND Y
CON H 32P F 0.50 SM FPC 0.3 R
ELCAP SM 16V 10U PM20 COL R
CER2 0603 X7R 16V 100N COL
CER2 0603 X7R 16V 100N COL
V
CER2 0603 Y5V 25V 100N COL
CER2 0603 Y5V 16V 220N COL
ELCAP SM 16V 10U PM20 COL R
CER2 0603 Y5V 25V 100N COL
CER2 0603 Y5V 10V 1U COL
RST SM 0603 330R PM5 COL
CER2 0603 Y5V 10V 1U COL
CER2 0603 Y5V 10V 1U COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 330R PM5 COL
CER2 0603 X7R 50V 1N COL
CER2 0603 X7R 50V 1N COL
CER2 0603 X7R 50V 1N COL
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 2U2 PM10 R
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 2U2 PM10 R
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 4U7 PM10 R
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 4U7 PM10 R
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 4U7 PM10 R
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 4U7 PM10 R
RST SM 0603 10K PM5COL
RST SM 0603 10K PM5COL
RST SM 0603 10K PM5COL
V
RST SM 0603 150R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 15K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 15K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 560R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 10K PM5COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 75R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 47K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
FXDIND 0603 100MHZ 120R COL R
DIO SIG SM BAS316 (COL) R
IC SM 74HC4053D (PHSE) R
TRA SIG SM BC847B (COL) R
IC SM ADG734BRUZ (ANA0) R
Description
52LC4.9E AB 7.
SIDE CONNECTORS
B16
Item
LC4.3x - CINCH
1J00
1J01
1J02
1J03
1J07
1J08
2J31
3J03
3J04
4J01
5J04
B17
Item
1K00
1K01
1K03
1K04
2K15
3K08
4K02
4K06
5K01
B18
Item
3L38
4L05
5L04
LC4.3E - SCART
VV
VV
VV V
VV V
SIDE CONNECTORS
LC4.3x - ME5 styling
LC4.3x - Arch Styling
VVV
V
V
VV
VV
V
VV V
ADC
non-DVB sets with 3D Comb Filter
DVB sets with 3D Comb Filter
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
LC4.9x - PDP
LC4.8x - LCD
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
LC4.8x - LCD
LC4.9x - PDP
VV
VV
Description
Description
CON V 10P M 2.00 PH B
CON V 11P M 2.00 PH B
CON V 12P M 2.00 PH B
CON V 3P M 2.00 PH B
FUSE SM T 3A 125V UL R
FUSE SM F 630MA 50V UL R
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
RST SM 0402 68R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 68R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
IND FXD 1206 EMI 100MHZ 120R R
Description
CON V 6P M 2.00 PH B
CON V 12P M 2.00 PH B
CON V 20P F 1.25 FFC 0.3 B
CON V 11P M 2.00 PH B
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
RST SM 0402 68R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
FXDIND SM 0603 1U PM10 COL R
B20 B21
Item
1N02
1N05
1P06
1P07
2N01
2N02
2N03
2N04
2N05
2N06
2N07
2N08
2N09
2N10
2N11
2N12
2N13
2N14
2N15
2N16
2P01
2P02
2P03
2P04
2P05
2P06
2P07
2P08
2P09
2P10
2P11
2P12
2P13
2P14
2P15
2P16
2P17
2P18
2P19
2P20
2P21
2P22
2P23
2P24
2P25
2P26
2P27
2P28
2P29
2P30
2P31
2P32
2P33
2P34
2P35
3N01
3N02
3N03
3N04
3N05
3N06
3N07
3N08
3N09
3N10
3N11
3N12
3N13
3N14
3N15
3N16
PIXEL PLUS&
+LEXIP htiw 3.4CL
+LEXIP non 3.4CL
VV V
VV V
VV
VVV
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
+LEXIP non 9.4CL/8.4CL
L
E
X
IP h
t
i
w
82/0237FP24
9.
4
CL/8
.4C
L
Description
CON V 4P M 2.00 SM PH R
OSC XTL SM 14M31818 15P OC R
CON V 30P M 1.25 SM 1453230 R
CON H 31P F 1.25 SM FI-WE R
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 X5R 6V3 1U PM20 R
CER2 0402 X7R 50V 1N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
CER1 0402 NP0 50V 100P COL
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 2U2 PM10 R
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
ELCAP SM 16V 100U PM20 COL R
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 2U2 PM10 R
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 2U2 PM10 R
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0603 X5R 6V3 2U2 PM10 R
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
CER2 0402 Y5V 16V 100N COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 33K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 1K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 33K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47R PM5 COL
+LEXIP non 9.4CL/8.4CL
LEXIP htiw 9.4CL/8.4CL
+
+LEXIP non 3.4CL
LEXIP
82/0237FP24
htiw
3
.
4C
Item
3N17
3N18
3N19
3N20
3N21
3N22
3N23
3N24
3N25
3N26
3N27
3N28
3N29
3N30
3N31
3N32
3N33
3N34
3N35
3N46
3N47
3P01
3P03
3P04
3P04
3P05
3P05
4N01
4N02
4N03
4N04
4N05
4N06
4N07
4N08
4N09
4N10
4N11
4N12
4N13
4N14
4N15
4N16
4N17
4N18
4N19
4N20
4N21
4N22
4P01 RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
4P02 RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
4P07
5N01
5N02
5N03
5N04
5N05
5P01
5P02
5P03
5P04
5P05
5P06
6N01
7N01
7N02
7N03
7N04
7P01
7P02
L
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
VV V
RST SM 0402 47R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 10K PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 4K7 PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47R PM5 COL
RST SM 0603 180R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 4K7 PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 47R PM5 COL
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0402 100R PM5 COL
V
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
RST SM 0402 JUMP. 0R05 COL
V
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
FXDIND 0805 100MHZ 30R COL
LED VS SM TLMG3100 (VISH) R
IC SM EPCS4SI8N (ALT0) R
IC SM EP1C12F256C8N (ALT0)
TRA SIG SM BC847BS (PHSE) R
IC SM THC63LVDF84B (THIN)
IC SM LF15ABDT (ST00) R
IC SM THC63LVDM83R (THIN)
Description
F_15270_070.eps
240505
Page 53

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Top Side Overview)
1101 D2
2109 D1
2282 B3
2701 A6
2803 B6
2823 C5
2922 C6
2945 B6
2B07 B7
1104 B1
2110 C2
2111 C2
2112 C2
2113 C2
2114 C2
2201 A2
2202 A2
2219 B2
2220 B2
2225 A2
2227 A2
2239 A3
2252 B3
2253 B2
2254 B2
2273 A3
2280 A2
2281 A2
2283 B3
2284 B3
2292 B3
2293 B2
2449 C3
2603 A1
2604 A1
2605 A2
2608 A2
2609 A1
2610 A2
2612 A2
2613 A1
2614 A2
2616 A1
2617 A1
2619 A2
2700 A6
1106 B1
1107 D2
1751 A5
1802 B6
1C00 C5
1N01 A7
1N02 B7
1N03 A7
1N05 A7
2101 C1
2102 C1
2103 C2
2104 D1
2105 D1
2106 C2
2107 C1
2108 C1
3139 123 6093.1
2708 A5
2710 A4
2711 A4
2714 A5
2715 A5
2730 A4
2733 A3
2734 A3
2735 A3
2741 B3
2750 A5
2751 A6
2759 A5
2760 A5
2761 A5
2762 A5
2801 B6
2802 B6
2804 B6
2805 B6
2806 B6
2807 B6
2808 C6
2809 C6
2810 C6
2811 C6
2812 C6
2813 B6
2814 B6
2816 C5
2817 C5
2818 C5
2819 C5
2820 C5
2821 C5
2822 C5
2824 C5
2900 B7
2905 B5
2906 B5
2907 B5
2908 B5
2909 B5
2910 B5
2911 B5
2912 B5
2913 B5
2914 C6
2915 C6
2916 C6
2918 C5
2919 C5
2920 C6
2921 C6
2923 B6
2946 B6
2924 B6
2947 B6
2925 B6
2948 B6
2926 B6
2949 B6
2927 B5
2950 B5
2928 B5
2951 B6
2929 B5
2952 B6
2930 C5
2953 C5
2931 C5
2954 C5
2932 C5
2955 C5
2933 C5
2956 C5
2935 C5
2957 C5
2936 C5
2958 C5
2937 C5
2959 C5
2938 C5
2A03 C6
2939 C5
2B03 B7
2941 C6
2B04 B7
2942 C5
2B06 B7
Part 1
F_15430_028a.eps
F_15430_028c.eps
2B08 B7
2B09 B7
2B10 B7
2B11 B7
2B12 B7
2B13 B7
2B14 B7
2B15 B7
2B16 B7
2C00 B5
2C01 B5
2C02 B5
2C03 B5
2D00 C7
2D01 D7
2D02 D7
2D08 C7
2D09 C7
Part 3
2D10 C7
2D11 C7
2D13 C7
2D14 C7
2D16 C7
2D18 C7
2D19 C7
2D28 C7
2D29 C7
2D30 C7
2D33 C7
2D35 C7
2D36 C7
2D37 C7
2D39 C7
2D40 C7
2D44 C7
2D45 C7
2E24 C5
2E25 C5
2E26 C5
2E27 C5
2E28 C5
2E29 C5
2E30 C5
2E31 C5
2E32 C4
2E36 D4
2E37 C5
2E38 C5
2E39 C5
2G01 D4
2G02 D4
2G03 D3
2G04 D3
2G05 D4
2G06 D4
2G08 D4
2G09 D4
2G10 D3
2G12 D3
2G16 D2
2G17 D2
2G18 D6
2G19 D5
2G21 D5
2G22 D5
2G23 D5
2G25 D5
2G26 D5
2G28 D4
2G45 D4
2G46 D4
2G48 D6
2G49 D5
2G50 D6
2G51 D5
2G52 D2
2G53 D5
2K00 A1
2K01 A1
2K02 B1
2K03 B1
2K04 B1
2K05 B1
2K06 B1
2K07 B1
2K08 B1
2K10 B1
2K11 B1
2K12 B1
2K13 B1
2K14 B1
2K15 B1
2K16 C1
2K17 C1
2K18 C1
2K19 B1
2K20 B1
2K21 A1
2K22 A1
2K23 A1
2K24 A1
2K25 A1
2K26 A1
2K27 A1
2K28 A1
2L07 B4
2L08 B4
2L09 B4
2L10 B3
2L11 B4
2L13 B3
2L15 B3
2L17 B3
2L18 B3
2L19 B4
2L23 B4
2L24 B4
2L26 B3
2L33 B4
2L34 B4
2L35 B3
2L36 B3
2L37 B3
2L38 B3
2L39 B3
2M24 C3
2M25 C4
2M26 C3
2M65 B4
2M67 B3
2N01 A6
2N02 A6
2N03 A6
2N04 A6
2N05 A6
2N06 A6
2N07 B6
2N08 B6
2N09 B6
2N10 A7
2N11 A7
2N12 A7
2N13 A7
2N14 A7
2N15 A7
2N16 A6
2N17 A7
2N18 A7
2N19 A7
2N20 A7
2P01 A6
53LC4.9E AB 7.
2P02 A6
2P03 A6
2P04 A6
2P05 A6
2P06 A6
2P07 A6
2P08 A6
2P09 A6
2P10 A6
2P11 A6
2P12 A6
2P13 A6
2P14 A6
2P16 A6
2P17 A6
2P18 A6
2P19 A6
2P20 A6
2P21 A6
2P22 A6
2P23 A6
2P24 A6
2P25 A6
2P26 A6
2P27 A6
2P28 A6
2P29 A6
2P30 A6
2P31 A7
2P32 A7
2P33 A7
2P34 A7
2P35 A7
3101 D1
3102 D1
3103 D2
3104 D2
3105 C1
3106 D2
3107 C2
3108 C2
3109 C2
3110 C2
3111 C2
3112 C2
3113 C2
3114 C2
3115 C1
3116 C2
3117 C2
3118 C2
3119 C2
3120 D2
3121 D2
3122 D2
3123 D2
3124 D1
3125 D1
3201 A2
3202 A2
3203 A2
3204 A2
3205 A2
3206 A2
3208 B3
3209 B3
3210 B3
3211 B3
3212 B2
3213 B2
3218 B2
3219 B2
3220 B2
3228 B3
3229 A2
3232 A2
3233 A2
3237 A2
3238 A2
3239 A2
3240 A2
3241 A2
3243 A2
3246 A2
3247 A2
3248 A2
3249 A2
3250 A3
3251 A3
3252 A3
3253 A3
3254 A2
3255 B3
3256 A3
3257 A3
3258 B3
3259 A3
3260 A3
3275 A2
3276 A2
3283 B2
3284 B2
3287 B3
3288 B3
3289 B3
3290 B2
3296 A2
3431 A1
3432 A1
3451 B3
3453 B3
3454 B3
3455 B3
3456 B3
3458 B3
3625 B1
3626 B1
3627 B1
3628 A1
3629 A1
3630 A2
3631 A1
3632 A1
3633 A2
3708 A5
3709 A5
3712 A4
3713 A4
3716 A5
3732 A3
3733 A3
3735 A3
3736 A3
3740 B3
3741 B3
3742 B3
3743 B3
3750 A5
3755 A5
3758 A6
3759 A5
3760 A5
3761 A5
3800 B5
3817 B5
3818 B5
3820 C6
3822 C6
3823 C6
3824 C5
3825 B5
3826 B5
3827 B5
3459 B3
3461 C3
3462 C3
3463 B3
3604 A1
3605 A1
3609 A1
3610 A2
3611 A2
3612 A2
3615 B1
3616 A2
3617 A1
3618 A1
3619 A1
3620 A1
3621 A1
3623 A1
F_15430_028b.eps
F_15430_028d.eps
Part 2
Part 4
3828 B5
3829 B5
3830 B5
3831 B5
3832 B5
3833 B5
3834 B5
3835 B5
3836 B5
3837 B5
3838 B5
3839 C6
3840 C6
3841 B6
3900 B6
3901 B5
3902 B5
3903 B5
3904 B5
3A02 C6
3A03 C6
3A04 C6
3A05 C6
3A06 C6
3C00 B5
3C01 B5
3C02 C5
3C03 C5
3C04 B5
3C05 B4
3C06 B4
3C07 B4
3C08 B4
3C09 B4
3C10 B4
3C11 B4
3C12 B5
3C13 B5
3C14 B5
3C15 B4
3C16 B5
3C17 B4
3C18 B4
3C19 B4
3C20 B5
3C21 B5
3D00 C7
3D01 C7
3D02 C7
3D03 D7
3D04 D7
3D11 C7
3D19 C7
3D21 C7
3D22 C6
3D23 C7
3D24 C7
3D25 C7
3D26 C7
3D27 C7
3D30 C7
3D31 C7
3D32 C7
3D33 C7
3D34 C7
3D35 C7
3E01 D4
3E02 C4
3E24 C5
3E25 C5
3E26 C5
3E27 C5
3E28 C5
3E29 C5
3E30 C5
3E31 C5
3E32 C5
3E33 C5
3E34 C5
3E35 C5
3E36 C5
3E37 C4
3E38 C5
3E39 C5
3E41 D5
3E42 C5
3E43 C4
3E44 C5
3E45 C5
3E46 C4
3E49 C4
3E51 D4
3E54 D4
3G00 D4
3G01 D4
3G02 D4
3G03 D4
3G04 D3
3G05 D3
3G06 D3
3G07 D3
3G08 D5
3G09 D5
3G12 D3
3G13 D3
3G14 D3
3G15 D3
3G16 D3
3G17 D3
3G26 D3
3G27 D3
3G28 D3
3G29 D3
3G30 D3
F_15430_025.eps
180405
3G31 D2
3G32 D2
3G33 D2
3G34 D2
3G37 D6
3G38 D5
3G39 D6
3G40 D5
3G41 D5
3G42 D5
3G43 D6
3G44 D5
3G45 D5
3G46 D5
3G47 D5
3G48 D5
3G51 D5
3G52 D5
3G53 D5
3G54 D5
3G55 D5
3G56 D5
3G57 D5
3G58 D4
3G59 D4
3G60 D4
3K00 B1
3K01 B1
3K02 B1
3K03 B1
3K05 B1
3K06 B1
3K07 B1
3K08 B1
3K09 C1
3K11 A1
3K12 A1
3K13 A1
3L00 B3
3L01 B3
3L03 B3
3L04 B3
3L05 B3
3L06 B3
3L08 B3
3L10 B3
3L11 B3
3L12 B3
3L13 B3
3L15 B3
3L16 B3
3L17 B3
3L18 B3
3L19 B3
3L20 B3
3L21 B4
3L22 B4
3L23 B3
3L24 B4
3L25 B4
3L26 B4
3L27 B4
3L28 B4
3L30 B3
3L31 B3
3L32 B3
3L33 B3
3L34 B3
3L35 B3
3L36 B3
3L37 B3
3L38 B3
3L39 B3
3M00 B4
3M01 C4
3M02 C4
3M03 C4
3M04 C4
3M06 C3
3M07 C3
3M08 C3
3M09 C3
3M10 C4
3M11 C4
3M14 B4
3M15 C4
3M27 B3
3M29 C3
3M50 C4
3M51 C4
3M52 C4
3M53 C4
3M54 C4
3M55 C4
3M56 C4
3M57 C4
3M58 C4
3M59 C4
3M78 C4
3M79 B4
3M86 B4
3M87 B4
3N01 A6
3N02 A6
3N03 A6
3N04 A6
3N05 A6
3N06 A6
3N07 A6
3N08 A6
3N09 A6
3N10 A6
3N11 A6
3N12 A6
3N13 A6
3N14 A6
3N15 A7
3N16 A7
3N17 A7
3N18 A7
3N19 A6
3N20 A6
3N26 B6
3N27 A6
3N28 A7
3N29 A6
3N30 A7
3N31 A7
3N32 A7
3N33 A7
3N34 A7
3N35 A7
3N42 A7
3N43 A7
3N44 A7
3N45 A7
3N46 B7
3N47 B7
3P01 A6
3P03 A6
3S01 D4
4102 C2
4103 C2
4104 C2
4105 C2
4106 C2
4109 C2
4110 C2
4111 C2
4112 C2
4113 C2
4114 C2
4115 C2
4116 C2
4204 C3
4207 B3
4208 A3
4209 A3
4211 A2
4212 A2
4436 B3
4437 B3
4438 B3
4439 B3
4440 B3
4441 C3
4501 A2
4502 A2
4503 A2
4504 A2
4505 A2
4506 A2
4601 A1
4602 A1
4603 A2
4604 A1
4605 A2
4606 B1
4609 A1
4610 A2
4611 A1
4612 A1
4613 B1
4614 A1
4615 A1
4618 A1
4619 A1
4801 C6
4A02 C6
4A03 C6
4D00 C7
4D01 C7
4E03 D5
4E10 C5
4E11 C5
4G00 D4
4G01 D3
4G05 D6
4G06 D5
4G19 D4
4G26 D2
4K01 A1
4K02 C1
4K03 A1
4K04 A1
4K05 A1
4K06 B1
4K07 B1
4L00 B4
4L01 B4
4L02 B3
4L03 B3
4L04 B3
4L05 B3
4M00 C4
4M01 C4
4M02 C4
4M03 C4
4M05 C4
4M06 C4
4M08 C4
4M09 C4
4M10 C4
4N21 B6
4N22 B6
4P09 A6
4P10 A6
5101 C2
5102 C2
5103 C2
5105 B2
5106 B2
5107 D1
5108 D1
5211 A3
5214 A2
5216 A3
5700 A6
5704 A5
5709 A4
5713 A5
5730 A4
5733 A4
5735 A3
5738 A3
5755 A5
5756 A5
5757 A5
5758 A5
5759 A5
5901 C5
5902 C6
5903 B5
5904 C5
5905 B6
5906 B6
5907 B6
5908 B7
5909 C5
5910 C5
5911 C6
5C00 B5
5E03 C5
5G00 D2
5K00 A1
5K01 B1
5K02 A1
5L03 B3
5L04 B3
5M00 B4
5M01 C3
5M03 B4
5M04 B3
5N01 A7
5N02 A6
5N03 B6
5N04 B6
5N05 A7
5P01 A6
5P02 A6
5P03 A6
5P04 A7
5P05 A7
5P06 A7
6101 D1
6102 D1
6103 D2
6104 C2
6105 C2
6106 D2
6107 D2
6204 A2
6205 A2
6206 A2
6430 A1
6431 A1
6601 A1
6709 A4
6712 A4
6733 A4
6740 B3
6E00 C5
6E01 C5
6E02 C5
6E03 C5
6G00 D2
6G01 D5
6G07 D5
6G08 D5
6G09 D5
6G10 D5
6N01 A7
7101 C2
7102 C2
7103 C2
7201 A2
7202 A2
7203 A2
7204 A2
7205 A2
7207 A2
7208 B3
7209 A3
7210 A3
7211 A2
7217 B2
7430 A1
7436 C3
7601 A1
7602 A1
7603 A2
7604 A1
7605 A1
7606 A1
7607 B1
7708 A5
7710 A4
7730 A4
7735 A3
7738 A3
7741 B3
7742 B3
7753 A5
7754 A5
7755 A6
7756 A5
7758 A5
7900 B7
7A01 C6
7C01 B5
7C02 C5
7D00 C7
7D04 C7
7D05 C7
7E03 C5
7E04 C5
7E05 C5
7G03 D3
7G05 D5
7L01 B3
7L02 B3
7L03 B3
7L04 B4
7L06 C3
7L07 C3
7L08 B3
7M00 C4
7M01 C4
7M17 B4
7N01 A6
7N03 A6
7P01 A6
Page 54

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Top Side Part 1)
54LC4.9E AB 7.
Part 1
F_15430_025a.eps
180405
Page 55

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Top Side Part 2)
55LC4.9E AB 7.
Part 2
F_15430_025b.eps
180405
Page 56

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Top Side Part 3)
56LC4.9E AB 7.
Part 3
F_15430_025c.eps
180405
Page 57

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Top Side Part 4)
57LC4.9E AB 7.
Part 4
F_15430_025d.eps
180405
Page 58

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Bottom Side Overview)
2709 A3
2502 A6
2276 A6
2262 B6
2245 B5
2231 A6
2209 A6
1102 C6
1103 B6
1105 B7
1201 B6
1202 A6
1440 B5
1441 A5
1801 C3
1F00 D1
1F01 D2
1G01 D5
1G02 D3
1G03 D4
1K04 B7
1J00 A5
1J01 A3
1J02 A4
1J03 A6
1J04 A6
1J05 A1
1J06 A3
1J07 A4
1J08 A3
1K00 A7
1K01 B7
1K02 C7
1K03 C7
1P01 A1
1P02 A1
1P03 A1
1P04 A1
1P05 A1
1P06 A1
1P07 A1
2203 A5
2205 B6
2206 B6
2207 B6
2208 A6
2210 B5
2211 B6
2214 B6
2216 B6
2218 B5
2221 B6
2223 A5
2224 A5
2226 B6
2228 B6
2229 B6
2230 B6
Part 1
F_15430_024a.eps
3139 123 6093.1
2232 B5
2233 B5
2234 A6
2235 A6
2236 A5
2237 A5
2238 A6
2240 A5
2241 A5
2242 B6
2243 B6
2244 B5
2246 B5
2247 B6
2248 B6
2249 B6
2250 A5
2251 B5
2255 B6
2256 B6
2257 B6
2258 A6
2259 B6
2260 A6
2264 B6
2265 B6
2266 B6
2267 B6
2268 B6
2269 A6
2270 A6
2271 A5
2272 A5
2274 B6
2275 A6
2278 B5
2279 B5
2285 A6
2286 B6
2287 B6
2288 B5
2290 C5
2291 B5
2447 A5
2448 A5
2501 A5
2277 B5
2263 B6
Part 3
F_15430_024c.eps
2503 A5
2504 A6
2505 A6
2506 A6
2507 A6
2508 A5
2509 A5
2611 A7
2615 A7
2618 A6
2704 A4
2706 A4
2713 A4
2716 A3
2731 A4
2736 A5
2737 A4
2738 A5
2739 A5
2752 A3
2753 A3
2754 A3
2755 A3
2756 A3
2757 A3
2758 A3
2800 C2
2815 C3
2901 B1
2902 B1
2903 C4
2904 C3
2917 C2
2934 C3
2940 C3
2A00 B3
2A01 B2
2A02 B2
2A12 B4
2A13 B3
2B01 B1
2B02 B1
2B05 B1
2B17 B1
2B18 B1
2D03 D1
2D04 C1
2D05 C1
2D06 D1
2D07 C1
2D12 C1
2D15 C1
2D17 C1
2D20 D1
2D21 C1
2D22 C1
2D23 D1
2D24 C1
2D25 C1
2D26 C1
2D27 C1
2D31 C1
2D32 C1
2D34 D2
2D38 C1
2D41 C1
2E00 D3
2E01 D4
2E02 D4
2E03 D3
2E04 D3
2E05 D3
2E06 C3
2E07 D3
2E08 D3
2E09 C3
2E10 D3
2E11 C3
2E12 C3
2E13 C3
2E14 C3
2E15 C4
2E16 C3
2E17 C3
2E18 C3
2E19 C3
2E20 C3
2E21 C3
2E22 C4
2E23 C4
2E33 C4
2E34 D4
2E35 C4
2F00 D2
2F02 D1
2F04 D2
2F05 D2
2F07 D1
2F08 D1
2F09 D1
2F10 D1
2F11 D1
58LC4.9E AB 7.
2F12 D1
2F13 D2
2F14 D2
2F15 D2
2F16 D2
2G07 D4
2G11 D4
2G20 D2
2G24 D2
2G29 D4
2G30 D4
2G31 D3
2G32 D3
2G33 D3
2G34 D5
2G35 D5
2G36 D5
2G37 D5
2G38 D5
2G39 D5
2G40 D5
2G41 D5
2G43 D5
2G47 D3
2G55 D2
2G56 D2
2G63 D4
2G64 D3
2G65 D3
2G66 D3
2J02 A4
2J03 A6
2J04 A1
2J05 A1
2J06 A1
2J07 A1
2J08 A1
2J09 A1
2J10 A3
2J11 A3
2J12 A3
2J13 A3
2J14 A3
2J15 A3
2J16 A5
2J17 A5
2J18 A5
2J19 A5
2J20 A5
2J21 A5
2J22 A5
2J23 A5
2J27 A6
2J28 A6
2J29 A6
2J30 A4
2J31 A3
2J33 A5
2J34 A5
2J35 A5
2J36 A6
2L02 B5
2L03 B5
2L04 B5
2L06 B5
2L20 B5
2L21 B4
2L22 B5
2L27 B5
2L28 B4
2L29 B5
2L30 B5
2L31 B5
2L32 B4
2M00 C4
2M01 C4
2L05 B5
2J26 A6
Part 2
F_15430_024b.eps
2M02 C4
2M03 C4
2M04 C4
2M05 C4
2M06 C4
2M07 C4
2M08 C4
2M09 C4
2M10 C4
2M11 C4
2M12 C4
2M13 C4
2M14 C4
2M15 C4
2M16 C4
2M17 C4
2M18 C4
2M19 C4
2M20 B4
2M21 B4
2M22 B4
2M23 B4
2M27 C4
2M28 C4
2M29 C4
2M30 C4
2M31 C4
2M32 C4
2M33 C4
2M56 C4
2M60 C5
2M61 C4
2M62 C5
2M66 B4
2M68 B5
2P15 A2
2P36 A1
2P37 A1
2P38 A1
2P40 A1
2P41 A1
2P42 A1
2P43 A1
2P44 A1
2P45 A1
3126 B6
3127 B6
3207 B6
3214 B6
3215 B5
3216 B5
3222 A5
3223 A5
3224 A5
3225 A5
3226 A5
3227 A5
3230 A6
3231 A6
3234 A6
3235 A6
3236 A6
3242 B5
3245 B6
3262 B6
3263 B6
3264 B6
3265 B6
3266 B6
3267 B6
3268 B5
3270 A5
3271 B5
3272 B6
3273 B6
3244 B5
3217 B5
2P39 A1
Part 4
F_15430_024d.eps
3274 B6
3277 B5
3278 B5
3279 B5
3280 B6
3281 B6
3282 C5
3285 B6
3286 B5
3291 B5
3292 C5
3293 B5
3294 C5
3295 B6
3501 A5
3502 A5
3734 A3
3751 A3
3752 A3
3753 A3
3754 A3
3801 C1
3802 C2
3803 B2
3804 B2
3805 B2
3A01 B2
3806 B2
3A07 B2
3807 C1
3A08 B2
3808 C1
3A10 B4
3809 B2
3A11 B3
3810 B2
3A13 B3
3811 B2
3A14 B3
3812 B2
3B01 B1
3813 B2
3B02 B1
3814 B2
3B03 B1
3815 B2
3D05 C1
3816 C2
3D06 C1
3819 C2
3D07 C1
3A00 B2
F_15430_024.eps
180405
3D08 C1
3D09 C2
3D10 C1
3D12 C1
3D15 C2
3D16 C2
3D17 C2
3D18 C2
3D20 C2
3E00 C4
3E06 D4
3E07 D4
3E08 D3
3E09 C3
3E10 D4
3E11 D4
3E12 C4
3E13 D3
3E14 C3
3E15 C3
3E16 D3
3E17 C3
3E18 C3
3E19 D3
3E20 D3
3E21 C3
3E22 C3
3E23 C3
3E50 C4
3E52 C4
3E53 C4
3E55 C4
3F00 D2
3F09 D1
3F10 D2
3F11 D2
3F16 D1
3F17 D1
3F18 D1
3F19 D1
3F20 D1
3F21 D1
3F22 D1
3F23 D1
3F24 D2
3F25 D2
3F26 D2
3F27 D2
3F28 D1
3F29 D1
3G63 D4
3G64 D3
3G65 D4
3G66 D3
3G67 D3
3G68 D4
3G69 D3
3G70 D3
3G71 D3
3G72 D5
3G73 D5
3G74 D5
3G75 D5
3G76 D5
3G77 D5
3G78 D5
3G79 D5
3G80 D5
3G81 D5
3G82 D5
3G83 D5
3G84 D5
3G85 D5
3G86 D5
3G87 D5
3G88 D5
3G89 D5
3G90 D4
3G91 D4
3G92 D3
3G93 D3
3G94 D3
3G95 D3
3G96 D2
3G99 D2
3J03 A5
3J04 A5
3J05 A5
3J06 A5
3L07 B5
3L09 B5
3M12 C4
3M13 C4
3M16 C4
3M26 C4
3M28 C5
3M68 C5
3M69 C5
3M71 C5
3M88 C4
3M89 C5
3M90 C4
3N21 B2
3N22 B2
3N23 B2
3N24 B2
3N25 B2
3N36 A2
3N37 A2
3N38 A2
3N39 A2
3N40 A2
3N41 A2
3P04 A1
3P05 A1
3S00 D2
3S03 D2
4107 B6
4108 B6
4201 B5
4202 B5
4203 B5
4205 C5
4206 C5
4213 B5
4214 B5
4215 B5
4507 A6
4508 A6
4509 A6
4510 A6
4511 A6
4512 A6
4513 A6
4514 A6
4616 A7
4617 A7
4620 A7
4621 A7
4900 B3
4A00 B3
4A01 B3
4A04 B4
4A05 B4
4A06 B3
4E12 C3
4E13 C4
4E14 C4
4G09 D4
4G10 D4
4G11 D4
4G12 D3
4G13 D3
4G14 D5
4G15 D5
4G16 D5
4G17 D5
4G18 D4
4G20 D3
4G21 D3
4G22 D3
4J01 A4
4J02 A5
4M04 C4
4M16 C4
4M17 C4
4N01 A2
4N02 A1
4N03 B2
4N04 A1
4N05 A2
4N06 A1
4N07 A2
4N08 A1
4N09 A2
4N10 A1
4N11 A2
4N12 A1
4N13 A2
4N14 A1
4N15 A2
4N16 A1
4N17 A2
4N18 A1
4N19 A2
4N20 A1
4P01 A1
4P02 A1
4P03 A1
4P04 A1
4P05 A1
4P06 A1
4P07 A1
4P08 A1
5201 B6
5202 B5
5203 A6
5204 A6
5205 B5
5206 A6
5207 A6
5208 A6
5209 A5
5210 A6
5212 A5
5213 A5
5215 B5
5217 B6
5218 B5
5431 A5
5501 A6
5712 A4
5737 A4
5752 A3
5753 A3
5754 A3
5900 B3
5A00 B2
5D00 C1
5D01 C1
5D02 C1
5D03 D2
5D04 D1
5E00 D4
5E01 C3
5E02 C4
5F00 D2
5F01 D1
5F02 D1
5F03 D1
5G01 D5
5G02 D3
5J01 A6
5J02 A6
5J03 A4
5J04 A4
5J05 A5
5L00 B4
5L01 B4
5L02 B4
5M02 C4
5M05 C4
6201 B6
6708 A4
6735 A5
6736 A5
6751 A3
6A01 B3
6F00 D1
6F01 D1
6G02 D3
6G03 D5
6G04 D5
6G05 D5
6G06 D5
7206 B5
7214 B6
7215 B5
7216 B6
7218 B5
7219 C5
7501 A6
7502 A6
7503 A6
7504 A5
7505 A6
7506 A6
7752 A3
7801 B2
7901 C4
7A00 B3
7A02 B3
7A03 B3
7B01 B1
7C00 B3
7D01 C1
7D02 C1
7D03 C1
7E00 C4
7E01 C3
7E02 C4
7F03 D1
7G07 D3
7G08 D3
7G09 D5
7G10 D3
7L05 C5
7M03 B4
7M14 C5
7M15 C5
7N02 A2
7N04 B2
7P02 A1
Page 59

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Bottom Side Part 1)
59LC4.9E AB 7.
Part 1
F_15430_024a.eps
180405
Page 60

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Bottom Side Part 2)
60LC4.9E AB 7.
Part 2
F_15430_024b.eps
180405
Page 61

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Bottom Side Part 3)
61LC4.9E AB 7.
Part 3
F_15430_024c.eps
180405
Page 62

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Small Signal Board (Bottom Side Part 4)
62LC4.9E AB 7.
Part 4
F_15430_024d.eps
180405
Page 63

PDP Audio Amplifier Panel
0001 A15
1736 A13
1738 G13
1M02 A13
1M06 A14
1M52 E14
2700 A3
2701 B10
2702 H11
2703 A7
2704 A7
2705 B10
2706 A3
2707 C5
2708 F9
2709 A6
2710 A7
2711 A2
2712 A10
2713 A4
2714 G14
2715 A10
2716 A10
2717 A8
2718 B5
2719 A4
2720 B5
2721 B6
2722 B4
2723 B8
2724 H10
2725 H10
2726 B4
2727 C9
2728 H10
2729 H10
2731 C91735 C12
2732 C10
2733 G9
2736 D10
2737 D10
2739 D6
2740 F11
2741 E6
2742 G11
2743 E5
2744 E3
1234
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2745 B7
2746 C7
2747 C2
2748 C2
2749 C3
2750 G9
2751 F4
2752 G5
2754 D15
2756 G7
2757 G7
2758 G5
2759 G11
2760 G6
2761 G1
2762 G2
2763 H5
2764 E8
2766 H11
2767 H11
2768 H5
2770 A15
2771 H6
2772 G2
2773 G3
2774 G3
2775 H5
2776 A6
2778 E9
2779 E8
2780 A10
2782 F8
2783 G8
2788 H8
2789 D10
2790 G15
2791 D14
2793 H1
2794 H3
2795 H3
2796 H3
2797 H4
2798 H4
2799 H9
3700 A2
3701 A10
3702 C2
3703 A2
3704 A10
3705 A5
3706 A4
3707 A8
3708 A10
3709 A3
3710 B8
3711 B9
3712 B3
3713 C13
3714 B4
63LC4.9E AB 7.
3715 B8
3716 C10
3717 C5
3718 C2
3719 C2
3720 D10
3721 C3
3722 A3
3723 A3
3724 C2
3726 D4
3727 D6
3728 D4
3729 D2
3730 D1
3731 D3
3732 E4
3733 E6
3734 E4
3735 F5
3736 F3
3737 F3
3738 F5
3739 F9
3740 F15
3741 G10
3742 G14
3743 G5
3744 G5
3745 G11
3746 G13
3747 G5
3748 G152755 G2
3749 G5
3750 G2
3751 H13
3752 H14
3753 H11
3754 G4
3755 H5
3756 H5
3757 G3
3758 G2
3759 G7
3760 E2
3761 H11
3762 H9
3763 H7
3764 A10
3765 D10
3766 H10
3767 H9
3768 G10
3769 H8
3770 H2
3771 H3
3772 H2
3773 H23725 D2
3774 H2
3775 H9
3776 H9
3777 D3
3778 D10
3999 A15
5700 A10
5701 D14
5702 C10
5704 G9
5705 A7
5706 G10
5708 C7
5709 E9
5714 H8
6700 D13
6702 D5
6703 E3
6704 G13
6705 H13
7700-1 C4
7700-2 A4
7701 A7
7702 C14
7705 D5
5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
7706 D3
7707 D2
7708 E6
7709 E5
7710 E4
7711 F5
7712 G6
7713 G6
7714 F8
7715 G15
7716 G14
7717 H14
7718-1 G2
7718-2 G4
7719-1 H6
7719-2 H6
7720 H15
9700 E12
9701 E12
9702 E12
9703 E13
9704 G12
9705 H12
9706 G7
9707 H7
9708 H7
9709 G14
F700 A12
F701 A12
F702 A11
F703 B13
F704 A13
F705 B13
F706 B12
F707 C12
F708 C12
F709 C11
F710 E13
F711 E14
F712 E13
F713 D15
F714 F13
F715 F13
F716 F13
F717 F13
F718 F13
F719 G12
F720 G12
F721 G12
F722 H8
F723 H8
F724 H6
F725 G7
F726 A7
F727 A5
F728 B6
F729 C5
F730 D6
F731 B8
F733 H4
F734 A15
F735 A14
F740 A12
F741 A12
F742 A13
F743 B13
F744 C7
F745 C12
F747 E8
F748 G3
F749 G12
F750 G7
I700 G13
I701 H13
I702 G11
I703 A2
I704 A3
I705 A3
I706 A4
I707 C3
I708 D4
I709 D5
I710 A4
I711 G10
I712 A9
I713 C2
I714 C2
I715 A8
I716 A10
I717 D2
I718 A8
I719 A10
I720 B8
I721 B4
I722 C9
I723 B4
I724 B9
I725 C8
I726 B10
I727 D10
I728 G9
I729 D13
I730 D3
I731 G7
I732 D14
I733 D10
I734 D3
I735 H7
I736 D2
I737 D2
I738 D3
I739 D4
I740 E4
I741 G11
I742 E3
I743 F3
I744 F5
I745 F6
I746 F9
I747 G10
I748 G15
I749 G1
I750 G3
I751 G14
I752 G5
I753 G5
I754 G5
I755 G2
I756 G4
I757 G5
I758 H11
I759 H5
I760 H14
I761 H4
I762 H9
I763 H5
I764 H3
I765 H15
I766 G1
I767 H3
I768 H10
I769 H11
I770 H3
I771 H1
I772 H2
I773 H10
I774 G10
I775 C9
I776 B10
I777 A11
C C
PDP AUDIO AMPLIFIER
AUDIO-L
A
B
AUDIO-R
C
D
SOUND-ENABLE
C (4x)
POR
DC-PROT
DC
AUDIO-C
I766
E
F
G
H
3104 313 6056.4
1
2761
2793
120p
VDD2
VSS2
2757
2704
13
BOOT1
BOOT2
10
F725
2K2
OUT1
DIAG
OUT2
470u 25V
3759
2K2
100n
F750
25V
470u
12
11
2745
220n
2746
-19-16VS1
+19-16VS2
-19-16VS2
I731
-19-16VS2
5705
+19-16V
2710
-19-16VS1
220n
6
7
3
9706
9707
F731
-19-16V
I720
2764
7714
TDA8925ST
1
2
4
9
15
17
16
14
F722
I715
2717
2723
I725
2782
220n
SW1
REL1
EN1
STAB
POWERUP
SW2
REL2
EN2
2783
220n
2788
25V 470u
3707
39K
1u0
3710
39K
1u0
F747
100V22u
5
VDD1
CLASS-D
AMPLIFIER
VSS1
8
2779
F723
Φ
5714
I718
3715
5R6
220n
VDD2
VSS2
3769
13
BOOT1
OUT1
DIAG
BOOT2
OUT2
10
-19-16VS2
3775
120K
5R6
+19-16VS1
+19-16VS1
I724
I775
2778
12
11
2799
470p
25V470u
6
7
3
3776
I712
5709
2708
220n
18K
2727
560p
2731
560p
5700
33u
3764
100K
I726
3711
5R6
I776
+19-16VS1
-19-16VS1
I722
5702
33u
3765
100K
+19-16V
-19-16VS2
I746
3739
39K
1u0
2750
I747
1u0
2733
3768
I728
39K
5704
I711
33u
2724
3767
100K
2725
3762
22R
I762
I719
I733
5706
33u
I768
I773
2712
470n
I716
2780
470n
47R
3708
2701
560p
2705
560p
470n
2732
I727
2789
470n
47R
3720
+19-16VS2
470n
470n
2728
3701
3778
3704
100K
47R
47R
I774
+19-16VS2
2729
470n
2715
+19-16VS1
-19-16VS1
3716
100K
2736
3741
5R6
3766
100K
15n
470n
470n
2716
2737
I777
15n
15n
2740
560p
2742
I702
I741
560p
3745
100K
2759
470n
2766
470n
2767
I758
2702
470n
3753
I769
22R
3761
100K
F709
+19-16VS2
-19-16VS2
15n
C (4x)
DC
C (4x)
DC
C (4x)
DC
C (4x)
DC
DC-PROT
AUDIO-C
AUDIO-L
AUDIO-R
PROT-AUDIOSUPLLY
SOUND-ENABLE
POR
PROT-AUDIOSUPLLY
F721
SW1
REL1
EN1
STAB
POWERUP
SW2
REL2
EN2
I735
F726
220n
2703
5
VDD1
Φ
CLASS-D
AMPLIFIER
VSS1
8
F744
5708
1
2756
22u 100V
-19-16VS2
3763
9708
3n9
+19-16VS1
I742
1
47K
3737
I743
3757
2719
470n
I710
2713
I706
4n7
3706
3K9
I721
2722
470n
2726
4n7
3714
3K9
I739
3
7710
BC847BW
2
3754
470R
I756
5
6
8K2
2798
2797
560p
560p
5
6
7700-2
LM393PT
84
I723
7700-1
LM393PT
3732
22K
7718-2
LM833D
I761
84
3
2
3728
15K
BC857BW
7
F733
84
3726
15K
I708
I740
3734
7711
2751
VDDOPAMP
7
2718
1
6702
BZX384-C39
22K
2743
2
3
47u 25V
2752
120p
3749
10K
2775
39n
-19-16VS1
100n
100n
2707
I709
1
1
1n0
3735
1
I744
3743
I752 I753
3K3
2758
I757
1u0
2763
220p
2768
470n
3755
3K9
I759
3756
8K2
F727
3705
3717
F729
3
2
3
7709
BC847BW
2
270K
3738
100K
3747
I763
3709
4K7
3722
2711
2755
100n
2772
100n
120K
I705
3723
I704
2744
2796
470n
3771
470R
2n7
2700
I707
2749
I730
3777
I734
100n
2773
1u0
2794
1u0
3K9
3n9
1K0
3
7706
BC847BW
2
6703
2706
3712
4K7
3731
1K0
BZX384-C3V3
3736
47K
I750
2774
1u0
-19-16VS2
+19-16VS2
I770
I764
1u0
3721
470R
1
I738
I767
2795
220p
8K2
3703
I703
3700
560R
3719
2747
1u0
3725
3
2
47K
47K
3
7707
BC847BW
2
3774
100K
3729
120K
I714
1n5
2748
3724
1K0
I717
47K
84
7718-1
1
LM833D
3770
10K
8K2
3702
I713
3718
560R
+19-16VS1
I736
I737
3730
1
22K
22K
3760
VDDOPAMP
I749
3750
330R
I755
2762
1u0
1u0
22K
3758
3773
-19-16VS2
I772
3K3
3772
I771
2K2
2K2
7705
BC847BW
+19-16VS1
47K
I754
2
3
VDDOPAMP
100V22u
2721
2720
3727
BC857BW
2
1
3744
100K
84
+19-16VS1
-19-16VS1
100n
10K
7708
1
3
7712
BC847BW
2
2760
100n
1
LM393PT
7719-1
2771
100n
2739
3
F728
100n
-19-16VS2
6
5
2776
22u 100V
TDA8925ST
-6V7
-19-16V
F730
5K6
2741
3733
-19-16VS1
I745
7713
BC847BW
F724
LM393PT
7719-2
84
2709
220n
7701
1
2
4
9
15
17
16
14
-19-16VS1
220p
3
2
7
F707
F720
9704
9705
F700
F701F702
F745
F708
F719F748
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
F740
F741
B3B-PH-K
-19-16V
+19-16V
F706
1735
3
2
1
B3B-PH-K
+19-16V
9700
9701
9702
F717
+19-16V
1738
F749
B3B-PH-K
TO
CENTER
SPEAKER
-19-16V
1736
3
2
1
F742
F704
F743
F705
1V2
TO
RIGHT
SPEAKER
9703
F710
F712
F716
F718
3
2
1
TO
LEFT
SPEAKER
1M02
1
2
F703
3
4
5
6
7
B7B-PH-K
3713
I729
6700
F714
F715
6704
I700
3746
3751
I701
6705
3K3
2791
BZX384-C15
F711
4V7
0V3
BZX384-C10
3742
100K
2K2
2K2
3752
10K
BZX384-C10
F735
1M06
0V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
B7B-EH-A
7702
BC847BW
1
220n
B9B-PH-K
1M52
2714
3
2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
I751
9709
100u 16V
TO 1M02
SUPPLY
I732
BP2.x / FTP2.x
1
I760
14 15
3999
1K0
PDP
5701
TO 1M52
SSB
I748
3
7716
BC847BW
2
2
7717
BC847BW
2754
1
2770
F713
3740
100K
F734
GND screw
10n
OR
22u 100V
OR
1
3
I765
0001
1
TO
SDI
SUPPLY
VDDOPAMP
TO 1J04
SSB
LC4.x
3
7715
BC847BW
2
3748
100K
3
1
7720
BC847BW
2
F_15430_055.eps
2790
100n
140605
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
Page 64

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
64LC4.9E AB 7.
Layout PDP Audio Amplifier Panel (Top Side)
3104 313 6056.4
F_15400_062.eps
090505
0001 C1
1735 E1
1736 E1
1738 B1
1M02 C1
1M06 C1
1M52 B1
2704 D1
2714 C1
2715 E1
2720 D1
2728 B1
2736 E1
2746 D1
2751 B1
2754 C1
2756 A1
2764 A1
2766 B1
2776 D1
2778 A1
2788 A1
3753 B1
3762 A1
5700 E1
5702 E1
5704 A1
5705 D1
5706 A1
5708 D1
5709 B1
5714 A1
7701 D1
7714 A1
9704 B1
9705 B1
9708 A1
9715 E1
9716 B1
9721 A1
9723 B1
9724 A1
9725 A1
9726 C1
9727 A1
9728 B1
9730 B1
9731 A1
9732 A1
9733 A1
9734 A1
9735 B1
9739 D1
9740 D1
9741 E1
9742 D1
9744 D1
9745 D1
9747 E1
9749 A1
9774 A1
9797 C1
9798 B1
9799 B1
9801 C1
9804 C1
9805 C1
9810 C1
9811 C1
Layout PDP Audio Amplifier Panel (Bottom Side)
2700 D1
2701 D1
2702 B1
2703 E1
2705 D1
2706 D1
2707 C1
2708 A1
2709 E1
2710 E1
2711 D1
2712 E1
2713 D1
2716 E1
2717 D1
2718 C1
2719 C1
2721 E1
2722 C1
2723 D1
2724 B1
2725 B1
2726 C1
2727 E1
2729 B1
2731 E1
2732 E1
2733 A1
2737 E1
2739 E1
2740 A1
2741 E1
2742 A1
2743 B1
2744 B1
2745 D1
2747 C1
2748 C1
2749 C1
2750 A1
2752 A1
2755 A1
2757 A1
2758 A1
2759 B1
2760 A1
2761 A1
2762 A1
2763 A1
2767 B1
2768 A1
2770 B1
2771 A1
2772 A1
2773 A1
2774 A1
2775 A1
2779 A1
2780 E1
2782 A1
2783 A1
2789 E1
2790 D1
2791 C1
2793 A1
2794 A1
2795 A1
2796 A1
2797 A1
2798 A1
2799 A1
3700 C1
3701 E1
3702 C1
3703 D1
3704 E1
3705 D1
3706 D1
3707 D1
3708 E1
3709 C1
3710 D1
3711 D1
3712 C1
3713 C1
3714 C1
3715 D1
3716 E1
3717 D1
3718 C1
3719 C1
3720 E1
3721 C1
3722 D1
3723 D1
3724 B1
3725 B1
3726 E1
3727 E1
3728 E1
3729 B1
3730 B1
3731 B1
3732 B1
3733 E1
3734 B1
3735 B1
3736 C1
3737 B1
3738 B1
3739 A1
3104 313 6056.4
9800
F_15400_063.eps
090505
3740 C1
3741 A1
3742 C1
3743 A1
3744 A1
3745 B1
3746 C1
3747 A1
3748 D1
3749 A1
3750 A1
3751 D1
3752 D1
3754 A1
3755 A1
3756 A1
3757 A1
3758 A1
3759 A1
3760 B1
3761 B1
3763 A1
3764 E1
3765 E1
3766 A1
3767 A1
3768 A1
3769 A1
3770 A1
3771 A1
3772 A1
3773 A1
3774 A1
3775 A1
3776 A1
3777 B1
3778 E1
3999 A1
5701 C1
6700 C1
6702 E1
6703 B1
6704 C1
6705 D1
7700 C1
7702 C1
7705 E1
7706 B1
7707 B1
7708 B1
7709 B1
7710 B1
7711 B1
7712 B1
7713 B1
7715 C1
7716 C1
7717 D1
7718 A1
7719 A1
7720 D1
9700 C1
9701 C1
9702 B1
9703 C1
9706 A1
9707 A1
9709 C1
9710 D1
9711 E1
9712 D1
9713 D1
9748 D1
9757 D1
9758 D1
9759 D1
9760 D1
9761 D1
9762 D1
9763 D1
9764 D1
9765 D1
9766 D1
9768 D1
9770 D1
9775 A1
9776 A1
9777 A1
9778 A1
9779 A1
9780 A1
9781 A1
9782 A1
9783 A1
9784 A1
9785 A1
9786 A1
9787 A1
9788 A1
9789 A1
9790 C1
9792 A1
9793 A1
9795 D1
9796 B1
9800 B1
9801 C1
9802 B1
9803 C1
9806 B1
9807 C1
9808 C1
9809 C1
9812 C1
9813 C1
9814 C1
Page 65

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
65LC4.9E AB 7.
Side I/O Panel
123456789
JAGUAR ONLY
SIDE I/O
D D
F001
A
B
C
D
E
F
3104 313 6008.4
C
2010
2008
1101
1102
1106
GND_AUD
1108
GND_AUD
22n
GNDB
22n
GNDB
1109
1111
1110
2
1001
1002-1
YELLOW
1002-2
WHITE
1002-3
RED
1010
Y / CVBS
134
5
F003
1
2
F004
9004
645
I001
9005
978
I003
F007
5
4
2
F008
F009
3
7
F019
8
1
GNDB
GND_AUD
F002
F005
F006
GNDB
123456
I009
I002
I010
GNDB
GNDB
GNDB
6000
6002
6003
6004
6005
6006
6007
PDZ6.8-B
I004
PDZ6.8-B
PDZ6.8-B
PDZ6.8-B
PDZ6.8-B
GND_AUD
PDZ6.8-B
PDZ6.8-B
GND_AUD
6010
PDZ6.8-B
I014
PDZ6.8-B
6008
I013
PDZ6.8-B
6009
6001
6011
GNDB
PDZ6.8-B
GNDB
PDZ6.8-B
3004
2004
2006
I007
I005
75R
680p
680p
75R
3000
F020
3010
GND_AUD
3013
GND_AUD
33K
33K
9011
9010
9009
9008
3009
1K0
3012
1K0
2005
2007
I008
I006
100p
100p
3020
3016
10K
GNDB
10K
3011
2011
2009
3K9
10n
GNDB
10n
GNDBGNDB
TO 1H01
VIPER
2K2
3008
2003
RES
1u0
F025
9003
1H01
OR
1M60
1
2
3
4
56
F022
F021
F023
F024
F012
F014
F016
5000
1050
DLW31S
F013
1112
1005
F015
F017
56
1
2
3
4
USB
CONNECTOR
TO 1M36
1M36
GNDB
1M37
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
B11B-PH-SM3-TBT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
12
SSB EMGT
OR
TO 1M36
SCART 3
OR
TO 1M36
SSB JAGUAR
F010
3999
150R
F011
I011
9006
F018
GNDB
9007
I012
GND_AUD
789
EMGT
F_15420_008.eps
030605
A
B
C
D
E
F
1001 B2
1002-1 B1
1002-2 C1
1002-3 D1
1005 A8
1010 E1
1050 A7
1101 A3
1102 B3
1106 C3
1108 D3
1109 E3
1110 F3
1111 E3
1112 A7
1H01 A6
1M36 B8
1M37 B8
2003 C5
2004 C3
2005 C4
2006 D3
2007 D4
2008 F2
2009 F5
2010 E2
2011 E5
3000 A4
3004 B3
3008 C5
3009 C4
3010 C4
3011 C5
3012 D4
3013 D4
3016 F5
3020 E5
3999 F9
5000 A7
6000 A3
6001 A3
6002 B3
6003 B3
6004 C3
6005 C3
6006 D3
6007 D3
6008 F3
6009 F3
6010 E3
6011 F3
9003 C6
9004 C2
9005 D2
9006 F7
9007 F8
9008 F4
9009 F4
9010 E4
9011 E4
F001 A2
F002 A2
F003 B2
F004 C2
F005 C2
F006 D2
F007 E2
F008 E2
F009 E2
F010 F8
F011 F9
F012 A6
F013 A7
F014 A6
F015 A7
F016 A6
F017 A7
F018 F7
F019 F2
F020 B4
F021 C6
F022 C6
F023 C6
F024 E6
F025 E6
I001 C2
I002 C3
I003 D2
I004 A3
I005 F4
I006 F4
I007 E4
I008 E4
I009 B3
I010 D3
I011 F7
I012 F8
I013 F3
I014 E3
Page 66

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
66LC4.9E AB 7.
Layout Side I/O Panel (Top Side)
1001 B1
1002 A1
1005 A1
1010 A1
1050 A1
1H01 A1
1M36 B1
1M37 B1
5000 A1
Layout Side I/O Panel (Bottom Side)
2003 A1
2004 A1
2005 A1
2006 A1
2007 A1
2008 A1
2009 A1
2010 A1
2011 A1
3000 B1
3004 B1
3008 A1
3009 A1
3010 A1
3011 A1
3012 A1
3013 A1
3016 A1
3020 A1
3999 B1
6000 B1
6001 B1
6002 B1
6003 B1
6004 A1
6005 A1
6006 A1
6007 A1
6008 A1
6009 A1
6010 A1
6011 A1
9003 A1
9004 A1
9005 A1
9006 A1
9007 B1
9008 A1
9009 A1
9010 A1
9011 A1
3104 313 6008.4
F_15420_009.eps
060605
3104 313 6008.4
F_15420_010.eps
060605
Page 67

Control Board
1701 A1
1702 A1
1703 A2
1704 A2
1705 A1
1706 A3
1M01 A4
3002 C2
3003 C2
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
3004 C1
3005 C1
3006 C1
3007 C1
3008 C1
3009 C2
3999 C4
9001 C3
9002 C1
9003 C2
F001 A4
F002 A4
F003 C4
F004 C4
I006 C1
I007 C1
I008 C1
I009 C2
I010 C2
I100 B1
I101 B1
I102 B1
I103 B2
I104 B2
67LC4.9E AB 7.
I105 B3
Personal Notes:
A
B
C
123
4
CONTROL BOARD
E E
1M01
F001
3999
10K
1
2
3
F004F003
1701
VOLUME-
I100
3006
9002
SKQNAB
390R
1702
VOLUME+
3005
3007
SKQNAB
100R
100R
I102
I008 I009I007I006
1705
MENU
3004
3008
1704
SKQNAB
I103I101 I104
1K0
1K0
SKQNAB
CHANNEL-
1K0
3003
3009
100R
1703
CHANNEL+
3002
I010
9003
SKQNAB
680R
KEYBOARD
1706
ON / OFF
I105
9001
F002
SKQNAB
A
B
C
D
3104 313 6071.2
D
F_15420_011.eps
030605
1234
E_06532_012.eps
131004
Page 68

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
68LC4.9E AB 7.
Layout Control Board (Top Side)
1701 -- 1702 -- 1703 -- 1704 -- 1705 -- 1706 -- 1M01 --
3104 313 6071.2
F_15420_012.eps
Layout Control Board (Bottom Side)
3002 -- 3003 -- 3004 -- 3005 -- 3006 -- 3007 -- 3008 -- 3009 -- 3999 -- 9001 -- 9002 -- 9003 --
3104 313 6071.2
F_15420_013.eps
060605
060605
Page 69

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
69LC4.9E AB 7.
LED Panel
12345678910
11 12 13 14
LED PANEL
J J
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
3104 313 6074.3
123456
TO 1M20
SSB
JL2.x / LC4.x
OR
TO 1M20
EXTERNALS
FTx2.x / Bx2.x
TO 1M01
CONTROL
BOARD
TO 0345
TOP CONTROL
I010
COM-SND
STATUS-POWER
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1
2
3
1M01
45
+8V
1M20
14
+5V2-STBY
3094
10K
9093
3091
9110
9112
9114
9116
9118
9119
F010
F011
F012
F015
F017
F013
F014
F016
F018
F021
9083
0345
1
2
3
4
5
6
78
I093
I011
10K
3092
7092
BC847BW
F084
F086
9082
+5V2-STBY
10K
3096
10K
+8V
+5V2-STBY
2014
F083
I012
F089
I094
10K
3093
9111
9113
9115
9117
3030
7032
BC847BW
3011
100R
100n
I013
9081
+5V2-STBY
4K7
I039
9015
KEYBOARD
COM-SND
9016
9017
9012
LED1
LIGHT-SENSOR
LED2
KEYBOARD
LIGHT-SENSOR
KEYBOARD
BLACKLIGHT-TC
LED1
LED2
RC
RC
"LED DIMMING"
9031
6030
BAS316
6031
BAS316
I047
I033
3031
100K
3032
180K
I040
2030
3063
I064
LED1
I048
3033
1K0
10u 16V
"GREEN"
"BLUE" or
+8V
+5V2-STBY
3062
3061
330R
I062
7062
BC857B
6060
(RES)
9063
I061
7061
3064
100R
(RES)
3056
BC847BW
10K
I038
BC857BW
7030
3034
1K0
10K
STATUS-POWER
560R
9011
I095
I063
SML512BC4T
3035
LED1
9064
9065
9062
(RES)
+5V2-STBY
4K7
I037
9056
3036
+5V2-STBY
2R2
I049
BCP53
7031
I054
2R2
3037
BLACKLIGHT-TC
9066
LED1
3053
LED2
I051
10K
3054
I052
100R
"RED"
+5V2-STBY
3051
330R
(RES)
9053
7051
BC847BW
10K
3055
7052
BC847BW
TSOP34836YA1
3052
OPT_LED
6051
1040
+8V
560R
I053
12
SML512BC4T
I065
VS
OUT
GND
9052
9054
9041
9040
RC
+5V2-STBY
I046
3040
330R
I044
9043
6K8
2040
3042
3041
100u 16V
I045
10K
I043
I042
9042
I041
"IR RECEIVER"
78910
EMC HOLE
9120
LIGHT-SENSOR
9122
3078
11 12 13 14
00020001
EMC HOLE
9121
I071
2M2
+5V2-STBY
9070
6070
9072
9071
TEMD5000
F038
2
I075
3
4M7
3070
3999
10K
2070
470n
3071
4M7
84
I073
2071
LM358P
7070-1
+8V
10u 16V
F039
1
"LIGHT SENSOR"
I026
3074
+8V
10K
84
3077
5
6
I074
1K0
3K3
3072
7070-2
LM358P
3073
3K3
I076
7
I072
3075
4K7
LIGHT-SENSOR
3K3
3076
F_15420_014.eps
030605
0001 A10
0002 A11
0345 D2
1040 F9
1M01 C2
1M20 A2
2014 C4
2030 G5
A
2040 F9
2070 F12
2071 G12
3011 A4
3030 G4
3031 G5
3032 G5
3033 G5
3034 G6
3035 G6
3036 G7
3037 G7
B
3040 F9
3041 G9
3042 F9
3051 B8
3052 B8
3053 C8
3054 C8
3055 C8
3056 D6
3061 B6
3062 B6
C
3063 D5
3064 D5
3070 G11
3071 F12
3072 G13
3073 G13
3074 F13
3075 F14
3076 G14
3077 G12
3078 G11
3091 G2
D
3092 F2
3093 F3
3094 F2
3096 G3
3999 B12
6030 G4
6031 G4
6051 C8
6060 C6
6070 G11
7030 G6
7031 G7
E
7032 G4
7051 C8
7052 D8
7061 D6
7062 C6
7070-1 F12
7070-2 G13
7092 F2
9011 C6
9012 B4
9015 A4
F
9016 A4
9017 A4
9031 G4
9040 G9
9041 F9
9042 G9
9043 F9
9052 C9
9053 C8
9054 D9
9056 D7
9062 D7
G
9063 D6
9064 B7
9065 B7
9066 D7
9070 F11
9071 F11
9072 G11
9081 E4
9082 E3
9083 D3
9093 G2
9110 D2
H
9111 D4
9112 D2
9113 D4
9114 E2
9115 E4
9116 E2
9117 E4
9118 E2
9119 E2
9120 B10
9121 B11
9122 F11
F010 A3
F011 A3
F012 A3
F013 B3
F014 B3
F015 A3
F016 B3
F017 B3
F018 B2
F021 C3
F038 B12
F039 B12
F083 D3
F084 D3
F086 E3
F089 E3
I010 F2
I011 G2
I012 E3
I013 E4
I026 F12
I033 G4
I037 G7
I038 G6
I039 G4
I040 G5
I041 G9
I042 G9
I043 F9
I044 F9
I045 F9
I046 E9
I047 G4
I048 G5
I049 G7
I051 D8
I052 C8
I053 B9
I054 D7
I061 D6
I062 C6
I063 D7
I064 D5
I065 C9
I071 F11
I072 F14
I073 G12
I074 G12
I075 F12
I076 F13
I093 F2
I094 F3
I095 C6
Page 70

Layout LED Panel
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
1040 -3031 -3032 -3033 -3055 -3056 -3070 -6030 -6031 -6051 -6060 -6070 -7030 -7031 -7052 -7062 -9011 -9031 -9054 -9056 -9066 -9110 -9112 -9114 -9116 -9118 -9119 -9120 --
0345 -1M01 -1M20 -2014 -2030 -2040 -2070 -2071 -3011 -3030 -3034 -3035 -3036 -3037 -3040 -3041 -3042 -3051 -3052 -3053 -3054 -3061 -3062 -3063 -3064 -3071 -3072 -3073 -3074 -3075 -3076 -3077 -3078 -3091 -3092 -3093 -3094 -3096 -3999 -7032 -7051 -7061 -7070 -7092 -9012 -9015 -9016 -9017 -9040 -9041 -9042 -9043 -9052 -9053 -9062 -9063 -9064 -9065 -9070 -9071 -9072 -9081 -9082 -9083 -9093 -9111 -9113 -9115 -9117 -9121 -9122 --
70LC4.9E AB 7.
Personal Notes:
3104 313 6074.3
F_15420_015.eps
060605
3104 313 6074.3
F_15420_016.eps
060605
E_06532_012.eps
131004
Page 71

IBO Zapper: Mojo
12345
MOJO
K1
A
K1, K2, k7
MIU_WEN
K2
NOR_RYBY
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
3139 123 5906.2
RESET_n
K2, K3
4MHz_MOJO
K6
TS_DATA(0)
K7
TS_DATA(1)
K7
TS_DATA(2)
K7
TS_DATA(3)
K7
TS_DATA(4)
K7
TS_DATA(5)
K7
TS_DATA(6)
K7
TS_DATA(7)
K7
K5
MOJO_I2S_OUT_SD
MOJO_I2S_OUT_SCK
K5
MOJO_I2S_OUT_WS
K5
K4
SPDIF
K5
MOJO_SYSCLK
I2C_LOCAL_SCL
K2, K6, K7
K2, K6, K7
I2C_LOCAL_SDA
I2C_TV_SCL
K5
I2C_TV_SDA
K5
USB_OVRCUR
K4
USB_PWR
K4
USB_DM
K4
USB_DP
K4
123456
3135
3133
3134
7100-2
PNX8316HS
0
1
2
3
TS_DATA
4
5
6
7
SD_OUT
SCK_OUT
WS_OUT
SPDIF
FSCLK
4101
3
10K
F135
OPTION
1
(TS)
7100-3
PNX8316HS
(AV)
2
7104
BSN20
20
2V2
21
2V2
22
2V2
23
2V2
24
2V2
25
2V2
26
2V2
27
2V2
1V
202
22R
0V
203
22R
204
1V6
22R
206
100R3142
3164
205 165
22R
F136
3148
OPTION
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
RES
3114
TS_SYNC
TS_STROBE
3
10K
3145
+3V3_MOJO
TS_VAL
CVBS
CVBS
CVBS
4100
+3V3
Y
C
Y
B
G
Y
R
C
7103
BSN20
+3V3_MOJO
1
OPTION
10K
3138
10K
TS_SYNC
0V
30
TS_CLK
29
1V6
TS_VALID
28
1V3
168
C_CVBS
0V
172
170
B|Pb
0V
163
G|Y
0V
R|Pr
0V
167
F133
F134
2
I100
I101
10K
10K
3149
3150
+3V3_MOJO+3V3_MOJO
10K3119
+3V3
10K3115
3117
3100
100R3143
100R3144
100R
100R
10K3116
10K
10K
+1V2_MOJO
RES
+1V2_MOJO
PCST0_1
DSU_CLK DSU_CLK
PCST0_2
6
4V6
SCL0
7
4V6
SDA0
8
3V3
SCL1
3V3
9
SDA1
36
SC0_DA
198
USB_OVRCUR
39
SC0_OFF
+3V3
+3V3
+3V3
+3V3
4102
4104
K7
K7
K7
K5
K5
K5
K5
3146
3147
RESET_n
5103
100MHz
1V2clean
2133
10u
PCST0_0
FOR DEV. ONLY
(I2C-USB-SCO)
5101
100MHz
5102
100MHz
7100-6
PNX8316HS
157
160
AVSS_PLL
AVDD_PLL
DSU_CLK
186
312033R
SC0_CMDVCC
USB_PWR
1V2
159
XTAL_OUT
DSU_TPC1
187
312133R
USB_DP
USB_DM
SC0_CCK
SC0_RST
0V
158
XTAL_IN
3V3
2100
2101
2102
71LC4.9E AB 7.
6 7 8 9 10 11 12
MOJO_TCK
RESETN
PCST1
195 4
312633R
33R 3127
10u
10u
10u
37
199
200
201
40
38
MOJO_TRST
0V
3V3
3
TCK
197
196
33R 3125
MOJO_TMS
3V3
2
TRST
PCST0
12012
189
188
312433R
33R 3123
1
TMS
0
194
312233R
MOJO_TDO
F125
DSU_TPC0
SYS_RESETN
I104
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
1V2_CORE
+3V3_MOJO
CONFIGURABLE
MOJO_TDI
33R
3139
3V2
3V2
208
207
TDI
TDO
7100-8
PNX8316HS
(JTAG-ETAG-SYS)
5
3101
10K
2112 100n
100n2113
100n2114
100n
2115
2116 100n
100n2103
100n
2104
100n
2105
100n
2106
100n
2107
100n
2108
100n
2109
100n
2110
2111 100n
2132
10u 16V
2131
16V10u
2130
16V10u
4105
4110
4106
4107
4109
+3V3_MOJO
1V2
3V3
5100
+3V3
F105
F108
F114
F109
F111
F106
F107
F110
F112
F113
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TRST
JTAG_TMS
STV_TDI
10046_TDO
3113
RES
MOJO_TRST
MOJO_TDI
10046_TDO
MOJO_TMS
MOJO_TCK
RESET_n
PCST0_0
PCST0_1
PCST0_2
TPCI
PCST1_0
PCST1_1
PCST1_2
41
78
119
VDDC
134
191
10
43
60
76
94
VDDP
111
130
161
190
MOJO_TRST
MOJO_TDI
10046_TDO
MOJO_TMS
MOJO_TCK
RESET_n
PCST0_2
2122
RES
FTSH-114-01-L-DV
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
7100-1
PNX8316HS
(PWR)
PCST0_0
PCST0_1
DSU_CLK
ROW_1
1100-1
FTSH-114-01-L-DV
VSSC
VSSP
AVDD
IDUMP
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
ROW_2
1100-2
2
4
6
8
0
1
2
1
2
42
79
120
135
192
11
44
61
77
95
112
131
162
193
175
169
164
171
166
174
173
78
1
34
56
78
9
11 12
13
15 16
17 18
19
1101
FTR
FOR DEV.
ONLY
2119
2120
2121
I105
1V2
3140
9 1011121314
+3V3clean
1%
1K2
100n
100n
100n
F138
2
10
14
20
+3V3_MOJO
3112
F122
10K
DSW_n
K2
SDRAM_DATA(0)
SDRAM_DATA(1)
K2
K2
SDRAM_DATA(2)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(3)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(4)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(5)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(6)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(7)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(8)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(9)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(10)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(11)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(12)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(13)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(14)
K2
SDRAM_DATA(15)
K6
RESET_FE_n
RESET_STV
K7
user_EEPROM_WP
K2
dsp_EEPROM_WP
K6
FE_LOCK
K6
NOR_RYBY
K2
NOR_WP
K2
STV_INT
K7
STV_A25
K7
RS232_DSR
CTSN0
RTSN0
RXD0
K4
TXD0
K4
DCD0
K2, K7
MIU_DATA(0)
K2, K7
MIU_DATA(1)
K2, K7
MIU_DATA(2)
MIU_DATA(3)
K2, K7
MIU_DATA(4)
K2, K7
K2, K7
MIU_DATA(5)
K2, K7
MIU_DATA(6)
K2, K7
MIU_DATA(7)
K2
MIU_DATA(8)
K2
MIU_DATA(9)
K2
MIU_DATA(10)
MIU_DATA(11)
K2
MIU_DATA(12)
K2
K2
MIU_DATA(13)
MIU_DATA(14)
K2
MIU_DATA(15)
K2
MIU_RDY
K7
NOR_CS
K2
STV_CS
K7
K2, K7
MIU_OEN
MIU_WEN
K2, K7
0V
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
2V6
0V
2V3
2V9
2V5
0V
2V5
2V3
2V3
0V
2V3
3V3
0V
4V6
3V3
3V3
0V
0V
0V
0V
3V3
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
10K
3163
3157-1
3157-3
3158-1
3158-3
8 33R
3156-1
3156-3
3159-1
3159-3
8
3157-2
3157-4
3158-22733R
3158-4
3156-2
3156-4
3159-2
3160
33R
3161
3V3
33R
3V3
3162
33R
18
36
1
36
18
36
1
36
27
45
45
27 33R
45
27
45
3V3
3V3
3V3
113
114
115
116
117
118
121
122
132
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
31
32
185
33
34
35
45
46
47
48
49
12
13
14
15
16
33R
69
67
33R
33R
65
63
33R
59
33R
57
33R
55
33R
53
33R
68
33R
66
64
33R
62
33R
58
56
33R
54
33R3159-4
52
109
74
73
72
71
70
108
106
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
IR_IN
IR_OUT
PWM
VS
VPP
C4
C8
SC1_DA
SC1_CMDVCC
SC1_RST
SC1_OFF
SC1_CCK
CTS0
RTS0
RX0
TX0
DCD0
PLL_OUTX0
0V
0
0V
1
0V
2
0V
3
0V
4
0V
5
0V
6
0V
7
0V
8
0V
9
0V
10
0V
11
0V
12
0V
13
0V
14
0V
15
MIU_RDY
MIU_CS_N0
MIU_CS_N1
MIU_CS_N2
MIU_CS_N3
MIU_OE_N
MIU_WEN
MIU_MASK0
PNX8316HS
(SDRAM)
SDRAM_DATA
PIO <0:15>
MIU_DATA
7100-4
SDRAM_ADDR
7100-7
PNX8316HS
(GPIO)
7100-5
PNX8316HS
(MIU)
DQM0
DQM1
CAS
RAS
CKE
HSCKB
VCXO_CLOCK
BOOT <0:3>
ITU_OUT
ITU_CLOCK
PIO <16:27>
MIU_ADDR
MIU_MASK1
MIU_LBA
MIU_BAA
MIU_CLK
WE
DTR0
13 14
0V
153
0
0V
154
1
0V
155
2
156
0V
3
0V
149
4
148
0V
5
0V
147
6
0V
146
7
0V
145
8
144
0V
9
0V
152
10
0V
143
11
0V
142
12
0V
150
13
0V
151
14
2V1
138
3V1
133
3V
140
2V9
141
3V
139
3V3
137
1V5
136
DTR0
17
0V
F129
UART1_RX
0V
18
RX1
3V3
19
TX1
0V
PIO19|ITU_OUT0|BOOT0
176
0
177
3V3
3V3
PIO21|ITU_OUT2|BOOT2
178
179
I103
180
3V2
181
182
F132
183
0V
184
DSW_I2C_enable
0V
75
80
3V3
0V
81
82
3V3
3V3
83
3V3
84
3V3
85
0V
86
0V
87
3V3
88
0V
89
0V
90
3V3
91
0V
92
3V3
93
0V
96
0V
97
3V3
98
3V3
99
3V3
100
3V3
101
3V3
102
0V
103
0V
104
0V
105
107
110
50
51
PIO20|ITU_OUT1|BOOT1
PIO22|ITU_OUT3|BOOT3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
UART1_TX
+3V3_MOJO
3151
RES
10K
10K
3154
7105
BSN20
F131
2
RES
3130 10K
3128
3131 10K
4108
3132
1
3155
10K
SDRAM_ADDR(10)
SDRAM_ADDR(11)
SDRAM_ADDR(12)
SDRAM_ADDR(13)
SDRAM_ADDR(14)
3141
10K
B2B-PH-K
F137
3
10K
MIU_ADDR(0)
MIU_ADDR(1)
MIU_ADDR(2)
MIU_ADDR(3)
MIU_ADDR(4)
MIU_ADDR(5)
MIU_ADDR(6)
MIU_ADDR(7)
MIU_ADDR(8)
MIU_ADDR(9)
MIU_ADDR(10)
MIU_ADDR(11)
MIU_ADDR(12)
MIU_ADDR(13)
MIU_ADDR(14)
MIU_ADDR(15)
MIU_ADDR(16)
MIU_ADDR(17)
MIU_ADDR(18)
MIU_ADDR(19)
MIU_ADDR(20)
MIU_ADDR(21)
MIU_ADDR(22)
MIU_ADDR(23)
MIU_ADDR(24)
SDRAM_ADDR(0)
SDRAM_ADDR(1)
SDRAM_ADDR(2)
SDRAM_ADDR(3)
SDRAM_ADDR(4)
SDRAM_ADDR(5)
SDRAM_ADDR(6)
SDRAM_ADDR(7)
SDRAM_ADDR(8)
SDRAM_ADDR(9)
SDRAM_DQM0
SDRAM_DQM1
SDRAM_CAS
SDRAM_RAS
SDRAM_WE
SDRAM_CKE
SDRAM_CLK
1106
10K
10K3136
10K3129
10K3137
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
1
2
OPTION
+3V3
+3V3
OPTION
+3V3
OPTION
TV_IRQ
K5
OPTION
+3V3
+3V3
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
K2, K7
F_15270_054.eps
190505
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
1100-1 D8
1100-2 D8
1101 B9
1106 D14
2100 F6
2101 F6
2102 G6
2103 G6
2104 G6
2105 G6
2106 G6
2107 G6
2108 H6
2109 H6
2110 H6
2111 H6
2112 F6
2113 F6
2114 F6
2115 G6
2116 G6
2119 H9
2120 H9
2121 H9
2122 C8
2130 I7
2131 I7
2132 H7
2133 C5
3100 A4
3101 E6
3112 E9
3113 C7
3114 A3
3115 A4
3116 A4
3117 A4
3119 A4
3120 E5
3121 E5
3122 E6
3123 E6
3124 E6
3125 E6
3126 E6
3127 E6
3128 E14
3129 F14
3130 E14
3131 E14
3132 F14
3133 G1
3134 G1
3135 F1
3136 E14
3137 F14
3138 A3
3139 C6
3140 I9
3141 D14
3142 G1
3143 G4
3144 H4
3145 H2
3146 H4
3147 H4
3148 I2
3149 I3
3150 I3
3151 F13
3154 G13
3155 G14
3156-1 G11
3156-2 H11
3156-3 G11
3156-4 H11
3157-1 G11
3157-2 H11
3157-3 G11
3157-4 H11
3158-1 G11
3158-2 H11
3158-3 G11
3158-4 H11
3159-1 G11
3159-2 H11
3159-3 H11
3159-4 H11
3160 I11
3161 I11
3162 I11
3163 G11
3164 G1
4100 H3
4101 H2
4102 A4
4104 A4
4105 B7
4106 B7
4107 B7
4108 F14
4109 C7
4110 B7
5100 I7
5101 F5
5102 F5
5103 C5
7100-1 F8
7100-2 E2
7100-3 F2
7100-4 A12
7100-5 G12
7100-6 H5
7100-7 D12
7100-8 D7
7103 H3
7104 H2
7105 F13
F105 A7
F106 A7
F107 A7
F108 A7
F109 A7
F110 A7
F111 A7
F112 A7
F113 A7
F114 A7
F122 E9
F125 B6
F129 E13
F131 E13
F132 F13
F133 G3
F134 H3
F135 H2
F136 H2
F137 F14
F138 A10
I100 H4
I101 H4
I103 F13
I104 E6
I105 I9
Page 72

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
IBO Zapper: Flash Memory
72LC4.9E AB 7.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
K2
12345
FLASH MEMORY
100n
100n
2210
2209
114
VDD VDDQ
0
1
2
3
4
5
A
6
7
8
9
10
11
0
BA
1
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
VSS
28 41 54 6
I202
100n
100n
2208
2213
27 3 9
Φ
SYNC
DRAM
4x2Mx16
100n
2207
43
VSSQ
12 46 52
2212
100n
100n
2211
49
NC
D
10
11
12
13
14
15
DQM
U
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
L
2206
0V
36
40
2
1V3
4
1V3
5
1V
7
1V3
8
1V3
10
1V2
11
0V
13
1V4
42
1V3
44
1V3
45
1V
47
1V4
48
1V4
50
1V3
51
0V7
53
1V2
15
39
10u
SDRAM_ADDR(12)
SDRAM_DATA(0)
SDRAM_DATA(1)
SDRAM_DATA(2)
SDRAM_DATA(3)
SDRAM_DATA(4)
SDRAM_DATA(5)
SDRAM_DATA(6)
SDRAM_DATA(7)
SDRAM_DATA(8)
SDRAM_DATA(9)
SDRAM_DATA(10)
SDRAM_DATA(11)
SDRAM_DATA(12)
SDRAM_DATA(13)
SDRAM_DATA(14)
SDRAM_DATA(15)
3V3
SDRAM_DQM0
2V2
SDRAM_DQM1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(0)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(1)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(2)
K1
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(3)
SDRAM_ADDR(4)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(5)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(6)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(7)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(8)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(9)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(10)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(11)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(13)
K1
SDRAM_ADDR(14)
K1
SDRAM_CLK
K1
SDRAM_CKE
K1
SDRAM_RAS
K1
SDRAM_CAS
K1
SDRAM_WE
K1
+3V3
3V
3V
3V
5202
100MHz
7202
K4S281632F
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
1V5
3V3
23
24
25
26
29
30
31
32
33
34
22
35
20
21
38
37
19
18
17
16
67
5201
+3V3
100MHz
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(1)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(2)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(3)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(4)
MIU_ADDR(5)
K1, K7
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(6)
MIU_ADDR(7)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(8)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(9)
K1, K7
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(10)
MIU_ADDR(11)
K1, K7
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(12)
MIU_ADDR(13)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(14)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(15)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(16)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(17)
K1, K7
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(18)
MIU_ADDR(19)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(20)
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(22)
K1, K7
K1, K7
MIU_ADDR(21)
+3V3_NOR48
K1
MIU_ADDR(20)
K1, K7
RESET_n
K1, K3
MIU_WEN
K1, K7
MIU_OEN
K1, K7
NOR_CS
K1
NOR_RYBY
3200
F201
I205
4201
4202
4203
OPTION
3K3
OPTION
4204
4200
3V2
25
0V
24
23
3V2
22
3V2
21
3V2
3V2
20
0V
19
18
0V
3V2
8
0V
7
6
0V
3V2
5
4
0V
3
3V2
2
0V
0V
1
3V2
48
17
0V
3V2
16
3V2
9
3V2
10
15
3V2
12
3V2
11
3V2
I204
3V2
3V2
3V2
+3V3_NOR48
28
26
47
8 9 10 11 12
+3V3_NOR48
I201
2203
10u
7200
M29W320DT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
A
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
RB
RP
WE
OE
CE
BYTE
37
EPROM
4Mx8/2Mx16
0
32M-1
2/4/8MB
NOR
FLASH
27 46
2204
100n
D
VPP/WP_
K1, K7
OPTION
K1
+5V
2
3
5V
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K3
M24C64-WMN6
1
E0
E1
E2
7203
MIU_DATA(0)
MIU_DATA(1)
MIU_DATA(2)
MIU_DATA(3)
MIU_DATA(4)
MIU_DATA(5)
MIU_DATA(6)
MIU_DATA(7)
MIU_DATA(8)
MIU_DATA(9)
MIU_DATA(10)
MIU_DATA(11)
MIU_DATA(12)
MIU_DATA(13)
MIU_DATA(14)
MIU_DATA(15)
4205
3205
10K
4215
OPTION
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
MIU_ADDR(22)
+3V3_NOR48
NOR_WP
K1, K7
+3V3_NOR48
3212
470R
4214
K1
+5V
NOR_WP
OPTION
0V
29
0
0V
31
1
33
0V
2
35
0V
3
38
0V
4
0V
40
5
42
0V
6
44
0V
7
30
0V
8
0V
32
9
34
0V
10
0V
36
11
0V
39
12
0V
41
13
43
0V
14
0V
45
15
A-1
0V
13
NC
I206
14
3V2
5200
+3V3
100MHz
2201
10u
M58LW032C90N1
MIU_ADDR(1)
MIU_ADDR(2)
MIU_ADDR(3)
MIU_ADDR(4)
MIU_ADDR(5)
MIU_ADDR(6)
MIU_ADDR(7)
MIU_ADDR(8)
MIU_ADDR(9)
MIU_ADDR(10)
MIU_ADDR(11)
MIU_ADDR(12)
MIU_ADDR(13)
MIU_ADDR(14)
MIU_ADDR(15)
MIU_ADDR(16)
MIU_ADDR(17)
MIU_ADDR(18)
MIU_ADDR(19)
MIU_ADDR(20)
MIU_ADDR(21)
I203
MIU_WEN
NOR_CS
MIU_OEN
RESET_n
I209
I210
3204
3203
470R
470R
5203
100MHz
2214
100n
5V
8
Φ
(8Kx8)
EEPROM
SYSTEM
0
EEPROM
1
ADR
I2C ADDRESS=A8
2SDA
VSS
4
+3V3_NOR48
16V
7201
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
20
19
18
17
13
12
11
10
8
7
6
5
4
15
55
14
54
16
29
31
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
VPP
W
E
G
RP
L
K
WC
SCL
I200
93743
VDD
Φ
2/4/8MB
NOR
FLASH
0
A
2048k-1
D
VSS
214842
+5V
10K
F200
7
WC_
6
SCL
SDA
13 14
0001 H1
0002 H1
0003 H2
0004 H2
K2
2200
100n
2202
100n
2205
100n
MIU_ADDR(22)
1
VDDQVSSQ
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
RB
R
+5V
3206
3211
I207
4V6
100R
4V6
5
30
32
56
33
35
38
40
44
46
493
51
34
36
39
41
45
47
50
52
53
2
3K3
I208
3210
4V6
I211
3202
470R
+5V
3K3
3207
4212
I2C_LOCAL_SCL
I2C_LOCAL_SDA
3209
100R
MIU_ADDR(23)
MIU_ADDR(24)
MIU_DATA(0)
MIU_DATA(1)
MIU_DATA(2)
MIU_DATA(3)
MIU_DATA(4)
MIU_DATA(5)
MIU_DATA(6)
MIU_DATA(7)
MIU_DATA(8)
MIU_DATA(9)
MIU_DATA(10)
MIU_DATA(11)
MIU_DATA(12)
MIU_DATA(13)
MIU_DATA(14)
MIU_DATA(15)
NOR_RYBY
4213
user_EEPROM_WP
K1, K6, K7
K1, K6, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
+3V3_NOR48
3201
470R
+3V3_NOR48
K1
0005 H3
0006 H4
0007 H4
0008 H5
0009 H5
0010 H6
0011 H6
0012 G7
A
0013 G8
0014 G9
0015 G9
0016 G10
0017 G10
0018 G11
2200 A13
2201 A12
2202 A13
2203 A8
2204 A9
B
2205 B13
2206 D5
2207 E4
2208 E4
2209 E4
2210 E4
2211 E4
2212 E4
2213 E4
2214 F11
3200 D6
3201 D14
C
3202 D13
3203 E11
3204 E12
3205 D9
3206 F12
3207 F13
3209 F13
3210 F13
3211 F12
3212 C11
4200 D7
4201 D7
D
4202 C7
4203 D7
4204 D7
4205 C9
4212 F13
4213 D13
4214 D11
4215 D9
5200 A12
5201 A8
5202 D3
E
5203 E11
7200 B8
7201 B12
7202 E3
7203 F11
F200 F12
F201 D6
I200 A12
I201 A8
I202 D4
I203 C12
I204 D7
F
I205 D6
I206 D9
I207 F12
I208 F13
I209 D12
I210 D12
I211 D13
G
0001
TYPE
H
3139 123 5906.2
1
0003
0002
TYPE
TYPE
MECHANICAL 3.5MM HOLE
0004
TYPE
0005
HEATSINK
HEATSINK
00070006
HEATSINKHEATSINK
00090008
HEATSINKHEATSINK
00110010
HEATSINK
0012
HEATSINK
HEATSINK
00140013
HEATSINK
HEATSINK
00160015
HEATSINKHEATSINK
00180017
HEATSINK
H
F_15270_055.eps
190505
234567891011121314
Page 73

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
73LC4.9E AB 7.
IBO Zapper: Power Supply
1234567891011
2323
6300
5V1
2308
470p
SS14
I314
2300
470p
SUPPLY_GND
SUPPLY_GND
RES
3326
10K
SUPPLY_GND
2312
100n
5300
47u
470n
2324
2304
SUPPLY_GND
I321
5303
470n
2325
I327
2311
SUPPLY_GND
K3 K3
A
F301
B
1301
1
2
3
B3B-PH-K
+12V
F309
I328
2333
10n
5309
2334
100n
100u
2335
+12V_A
16V
+12V
F302
630mA
1304
FROM 1220 OF
C
D
+3V3
+5V
POWER SUPPLY BOARD
F306
F305
I301
I302
I306
SUPPLY_GND
SUPPLY_GND
SUPPLY_GND
5304
10u
E
5301
10u
SUPPLY_GND
SUPPLY_GND
3301
2301
3314
2309
330u
330u
F300
1R0
I316
I322
1R0
1R0
3303
SUPPLY_GND
1R0
3312
SUPPLY_GND
2303
2310
3302
3311
4n7
4n7
I318
N.C N.C
11V3
I323
OPTION OPTION
1R0
3300
F308
1R0
3313
8 DCOL
11V3
7IS
11V3
6
5 CIN_NEG
1V2
3306
1%
1K0
MC34063AP1
8 DCOL
11V3
7IS
6
VCC
5 CIN_NEG
1V3
3317
3K3
2336
4n7
3315
1K0
7300
MC34063AP1
VCC
1K8
100R
7303
IPK
OSC
3304
1%
2329
4n7
3307
1%
SUPPLY_GND
IPK
OSC
3332
75R
SRQ
SRQ
REFERENCE
REGULATOR
SUPPLY_GND
REFERENCE
REGULATOR
1SWC
2SWE
3V3
3TIMC
0V7
4GND
SUPPLY_GND
1SWC
2SWE
3TIMC
0V7
4GND
SUPPLY_GND
POWER SUPPLY
F
POWER ON RESET
7305
3323
3331
8 DCOL
11V3
7
6
1V3
5 CIN_NEG
1V2
1%
820R
1%
100R
MC34063AP1
IS
VCC
3K9
3322
2331
1SWC
SRQ
6V5
2SWE
IPK
OSC
REFERENCE
REGULATOR
1%
4n7
0V7
3TIMC
4GND
SUPPLY_GND
2313
470p
I324
2326
SUPPLY_GND
470n
3318
2315
SUPPLY_GND
330u
F315
1R0
3321
2316
SUPPLY_GND
4n7
1R0
I326
OPTION
SUPPLY_GND
1R0
1R0
3319
3320
I325
3316
1K0
7306
NCP303LSN30
3V3
F312
2
INP
5
CD
2V9
33n
2314
1
OUTP
NC
GND
4
3V3
3
4
12
SKQTLB
1303
3
RESET_n
K1, K2
5306
10u
G
+3V3
H
FOR DEV. ONLY
I
OPTION
3330
1m0 16V
100u
470u 16V
5305
2318
SUPPLY_GND
1K8
4302
100u
16V470u
I310
2
3333
47K
7311
SI2314EDS
I317
3V2
3
3V2
OPTION
2321
100n
6303
SS14
6306
S1D
RES
I330
6305
RES
I331
2305
100n
OPTION
2322
100n
6304
SS14
F316
2327
100n
2328
S1D
2V6
A
TL431CZ
2337
3
LD1117V18
6V5
IN OUT
100n
3139 123 5906.2
123456789
10 11
12 13
3
7310
R
1V9
K
1
3329
47K
1N4148
6307
16V10u
1
11V2
2
7301
OUTIN
COM
1
SUPPLY_GND
4303
RES
SUPPLY_GND
7307
LD1117V50
COM
7312
BC847B
3V2
10K
3334
2320
100n
2
1V8
100u
2306
5307
10u
7302
LD1117V
32
OUTIN
COM
1
5V
OUTIN
GND
7308
LD1117V50
32
OUTIN
6V5
COM
1
12 13
+12V
5302
3324
10u
+12V
7309
BC857B
1K0
3325
10V6
100K
I312
I313
F303
+3V3
(446mA)
F304
+3V3clean
(193mA)
2302
25V
100u
F307
F310
16V470u
2330
2332
2317
5V
100u
25V100u
2319
F313
F317
F314
100u
+1V8FE
(197mA)
+5V_USB
(500mA)
+1V2_MOJO
+5V
(367mA)
+5Vclean
(180mA + 180mA)
3327
11V3
33R
(230mA)
F_15270_056.eps
190505
100K
3328
1301 B1
F314 I13
1303 H3
F315 G7
1304 B6
F316 H11
2300 B10
F317 F13
2301 B7
I301 D2
2302 C13
I302 D1
2303 C8
I306 D1
2304 C11
I310 A11
I312 A13
2305 F11
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
2306 C12
2308 D10
2309 E7
2310 E8
2311 E11
2312 A11
2313 G10
2314 H2
2315 H7
2316 H8
2317 H12
2318 H11
2319 I13
2320 C12
2321 D11
2322 G11
2323 A11
2324 B10
2325 D10
2326 H11
2327 H11
2328 I11
2329 C9
2330 E12
2331 H9
2332 F13
2333 B2
2334 B3
2335 B3
2336 E9
2337 B11
3300 A7
3301 A7
3302 A8
3303 A7
3304 B9
3306 C8
3307 C9
3311 D8
3312 D7
3313 D7
3314 D7
3315 E9
3316 G3
3317 E9
3318 G7
3319 G7
3320 G7
3321 G8
3322 H9
3323 H8
3324 A12
3325 A13
3326 A11
3327 A13
3328 B13
3329 A12
3330 A11
3331 I8
3332 E9
3333 B11
3334 C12
4302 F11
4303 E12
5300 B11
5301 B7
5302 C12
5303 D11
5304 D6
5305 H11
5306 H6
5307 E12
5309 B3
6300 A10
6303 D11
6304 G11
6305 F11
6306 E11
6307 B12
7300 A9
7301 C12
7302 F12
7303 C9
7305 F9
7306 G2
7307 H12
7308 I12
7309 A13
7310 A12
7311 B11
7312 B12
F300 A7
F301 B5
F302 B5
F303 B13
F304 C13
F305 C1
F306 C1
F307 C12
F308 D7
F309 B2
F310 E12
F312 H2
F313 H13
I313 B13
I314 B10
I316 B7
I317 B11
I318 B8
I321 D11
I322 D7
I323 E8
I324 G11
I325 H7
I326 H8
I327 E11
I328 B2
I330 F11
I331 F11
Page 74

IBO Zapper: Interface
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
74LC4.9E AB 7.
123
456
7891011
INTERFACE
K4 K4
A
B
C
D
E
F
UART CON
FOR
COMPAIR ONLY
1402
1
2
3
S3B-PH-K
6401
ESD Protection
F414
F415
6403
BZX384-C8V2
4414
3414
3415
4415
BZX384-C8V2
2415
330p
100R
100R
TXD0
RXD0
2414
330p
K1
K1
K1
K1
USB_OVRCUR
K1
USB_PWR
SPDIF
F409
F410
2416
I420 I418
3409
10K
RES
3424
RES
4402
RES
2411
100n
3403
10K
I402
+3V3
I403
+5V_USB
3V3
0V
5V1
560R
7
2
1
3404
LM3525MY
7403
LM3525MX-H
OUTIN
FLG
EN
COM
3
3405
1K0
I416
3406
1K0
6
8
4
5
NC
4V5
1V6
I404
2403
100n
3V3
5420
+3V3
7402
BC847B
1V
3411
180R
2405
100n
I419
2406
3407
68R
SPDIF OUTPUT
1401
I417
2412
100n
VBUS
USB_DM
K1
USB_DP
K1
6.3V100u
I405
I406
3408
RES
I421
3420
3421
5401
100MHz
6400
BZX384-C5V1
33R
33R
2413
100n
15K
F424
F407
F408
USB_DUSB_D+
34233422
15K
1400
F420
F421
F422
F423
1
2
3
YKC21-3416
1403
56
5401-032-100-70
1
2
3
4
USB
A
B
C
D
E
F
1400 B10
1401 B11
1402 B3
1403 F11
2403 E7
2405 F7
2406 F8
2411 B6
2412 B8
2413 B9
2414 C4
2415 C4
2416 F5
3403 E6
3404 B6
3405 B7
3406 B7
3407 B8
3408 B9
3409 E6
3411 B7
3414 B4
3415 C4
3420 F9
3421 F9
3422 F10
3423 F10
3424 F5
4402 F5
4414 B4
4415 C4
5401 B9
5420 F7
6400 B9
6401 C3
6403 C4
7402 B7
7403 E6
F407 B10
F408 B10
F409 F5
F410 F5
F414 B4
F415 C4
F420 F10
F421 F10
F422 F10
F423 F10
F424 F10
I402 F6
I403 F6
I404 E7
I405 F9
I406 F9
I416 B7
I417 B8
I418 B6
I419 B8
I420 B6
I421 B9
G
3139 123 5906.2
12345678910
G
F_15270_057.eps
200505
11
Page 75

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
IBO Zapper: Analog Back End
75LC4.9E AB 7.
123456789101112 13
K5 K5
ANALOG BACK END
+12V_A
2544
100n
5528
A
I524
I501
VOUTL
DEEM
VDDD
2502
100n
5502
1V6
12
1V6
14
1V6
16
9
F501
2511
100n
+3V3
I515
2512
3507
1K5
16V47u
4507
UDA1334ATS
0V6
1V
I507
10
I509
11
7
I510
1V6
3504
3508
2R2
2R2
2504
100n
7502
3V3 3V3
13 4
Φ
1
BCK
VDDA
DAC
6
3
2
8
SYSCLK
PLL1
DATAI
PLL0
0
SFOR
1
WS
MUTE
VREF_DAC
VSSA
15 5
VOUTR
CLKOUT
VSSD
+3V3clean
B
MOJO_I2S_OUT_SCK
K1
K1
MOJO_SYSCLK
MOJO_I2S_OUT_SD
K1
F500
F503
C
MOJO_I2S_OUT_WS
K1
F502
D
+12V_A
I544
E
3519
2520
22p
5511
I532
2u2
75R
2523
390p
2522
390p
3547
5504
I538
2521
75R
22p
3560
27K
2550
220n
2551
1u0
I548
F
2524
75R
2537
22p
5512
2u2
75R
2525
390p
390p
2526
2527
22p
2531
390p
2532
5514
5513
2u2
390p
22p
2u2
2538
I534
390p
2530
3533
75R
I535
3539
390p
75R
5507
5508
I533
75R
3530
I528
2535
22p
I531
2536
22p
5505
2539
220n
K1
G
C_CVBS
K1
K1
K1
G|Y
B|Pb
R|Pr
I520
I521
I522
I523
3520
H
3521
I
75R
3522
3557
6503
2V1
100K
BAS316
F512
I503
2506
2507
1V5
3528
10R
2543
16V47u
68K
3502
2501
I502
2V7
I506
1u0
33K
3506
I508
4n7
I543
1K0
3559
3558
7V7
I545
7V
7512
BC847B
3561
270R
I549
4503
3562
150R
I541
2529
22p
3534
I526
3535
2540
220n
I500
3501
100p
3505
3517
1K5
680R
BC857B
7511
220K
3V9
220K
I529
820R
8V2
7501
BC847B
2V1
820R
I513
2514
2515
11V6
3500
3503
1K0
I546
+12V_A
3532
1K0
1u0
I518
7505
BC847B
3V8
2500
1u0
8V8
7500
BC857B
3V8
I504
I505
2505
1u0
1K0
3509
3514
2508
1u0
8V8
7503
BC857B
3V8
I514
I516
2513
1K0
1u0
+12V_A
4506
3572
150R
100n
2558
2557
11V6
3548
10u 16V
4505
7507
BC847B
I537
560R
3569
68R
3566
I550
27K
220n
2553
2554
1u0
2V5
I511
68K
100p
2503
3510
3511
820R
8V2
I512
2V7
7504
BC847B
2V1
I517
33K
3516
3515
4n7
3V3
560R
3537
220K
3538
220K
+12V_A
11V6
7506
BC847B
3540
820R
3V1
3V1
560R
+12V_A
3563
6504
I552
2V1
100K
BAS316
3527
75R
3526
75R
I547
1K0
3565
3564
I551
7V
7514
BC847B
1V5
I554
3568
150R
3567
270R
4504
680R
7V7
BC857B
7513
I553
K1
I2C_TV_SDA
K1
I2C_TV_SCL
K1
TV_IRQ
2534
22p
2533
22p
+12V_A
3571
150R
11V6
3V2
7510
BC847B
2V6
3556
560R
2555
16V10u
I542
3513 100R
3523
2556
100n
3570
68R
2510
100p
F506
F505
F507
F519
F521
F514
F517
F516
CVBS_VCR
BLUE|U
100R3512
75R
2528
2509
100p
22p
F518
3139 123 5906.2
123456789101112 13
1500
SDA
SCL
IRQ
R1
L1
RED|V
F509
F_15270_058.eps
33 34
AF732L-N2G1A
200505
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
5512 G3
1500 C13
2500 A7
5513 H3
5514 I3
2501 A6
5528 A5
2502 B3
6503 E5
2503 C7
6504 G8
2504 B3
7500 A6
2505 B7
2506 B5
7501 B6
2507 C5
7502 B3
2508 C8
7503 C7
2509 B12
2510 B12
2511 C4
2512 C4
2513 D8
2514 D6
2515 D6
2520 E3
2521 F4
2522 F3
2523 F3
2524 G3
2525 G3
2526 G3
2527 H3
2528 B11
2529 G5
2530 H3
2531 H2
2532 I3
2533 D10
2534 B10
2535 H4
2536 I4
2537 I2
2538 I3
2539 H5
2540 I5
2543 A5
2544 A4
2550 E5
2551 E5
2553 G8
2554 G8
2555 G10
2556 G11
2557 E8
2558 E8
3500 A6
3501 A6
3502 A5
3503 B6
3504 A3
3505 B6
3506 B5
3507 C5
3508 B3
3509 C7
3510 C6
3511 C7
3512 A11
3513 A11
3514 D7
3515 D6
3516 D7
3517 D6
3519 F2
3520 G2
3521 H2
3522 I2
3523 A11
3526 D9
3527 B9
3528 A5
3530 G4
3532 H6
3533 H3
3534 H6
3535 H6
3537 I6
3538 I6
3539 I3
3540 I7
3547 F3
3548 F7
3556 G10
3557 E5
3558 E5
3559 E6
3560 E4
3561 E6
3562 F5
3563 F8
3564 F9
3565 F9
3566 G8
3567 G9
3568 H9
3569 E8
3570 G11
3571 F10
3572 D7
4503 F6
4504 H9
4505 E8
4506 D7
4507 C2
5502 A4
5504 E4
5505 G5
5507 H4
5508 I4
5511 E3
7504 D7
7505 H6
7506 I7
7507 E7
7510 G10
7511 E6
7512 E5
7513 G9
7514 G9
F500 B2
F501 C4
F502 C2
F503 C2
F505 A12
F506 A12
F507 A12
F509 E13
F512 D5
F514 E13
F516 D13
F517 B13
F518 G11
F519 H12
F521 I12
I500 A6
I501 A3
I502 B6
I503 B5
I504 B7
I505 B7
I506 B6
I507 C2
I508 B5
I509 C2
I510 C2
I511 C7
I512 C7
I513 C6
I514 D7
I515 C4
I516 D8
I517 D7
I518 D6
I520 G2
I521 G2
I522 G2
I523 G2
I524 A3
I526 H6
I528 H4
I529 I6
I531 I4
I532 E3
I533 G4
I534 H3
I535 I3
I537 E7
I538 E4
I541 G5
I542 G10
I543 D5
I544 E5
I545 E5
I546 E6
I547 F9
I548 E5
I549 F5
I550 F8
I551 F9
I552 G8
I553 G9
I554 G9
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
Page 76

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
76LC4.9E AB 7.
IBO Zapper: Front End
12
34567
8 9 10 11 12 13
FRONT END
K6 K6
A
B
C
D
E
K6
COMP_OUT
F
G
I2C_TDA_SDA
I2C_TDA_SCL
H
I
RESERVED
dsp_EEPROM_WP
K1
3139 123 5906.2
1600
TD1316/SPHP
RF
IN
LB
OSC
OSC
MB
OSC
1 DC-PWR
NC
234
HB
PLL
33
5
PLL8SCL9SDA
5V
7
100R
3606
84
Φ
(32Kx8)
EEPROM
3607
2635
5V
100R
+5Vclean
3611
3616
OPTION
100n
SDA
680K
100K
2632
4607
10p
+5V
2K7
3626
3632
100R
5
F603
6
5AGC
11 VTUN
3V2
OPTION
+5Vclean
4606
+5Vclean
OPTION
3620
3623
3634
470R
4610
5V
I601
5602
2622
4K7
4K7
+5V
M24256-BWMN6
F613
16V47u
100n
2623
I605
I616
5603
7602
1
0
2
12E
3
7
WC
6
SCL
EEPROM
16
MT
17
F600
+5V
3612
2630
+5V
OPTION
+5Vclean
2626
7601-1
4K7
8
LM393D
1
2V2
4
100n
+5Vclean
7601-2
8
LM393D
5
6
4
100n
3V3
3613 100K
3
I632
2
3V3
7
12345
TUNER
18
MT
19
14 IF-1
1V3
F606
100K
F604
F611
13 IF-AGC
OPTION
15 IF-2
74AHC1GU04GW
3636
74AHC1GU04GW
3640
2628
1601
AT-49
4MHz
33p
2633
4MHz
390R
+3V3
4MHz_MOJO
330R
4605
I631
F608
+3V3FE
I2C_LOCAL_SDA
I2C_LOCAL_SCL
F610
+3V3
K1
3625
3629
3630
3631
2615
K1
RESET_FE_n
2V3
3621
33R
3645
10K
100R
100R
100R
100R
2617
100n
3V2
I614
3608
10K
I604
2V8
1V3
1V5
1V5
0V7
0V6
100n
TDA10046AHT
3V2
F609
4V6
4V6
5V
5V
2607
42
22
VDDI18_2VDDI18_2
VDDI18_3VDDI18_3
VSS540VSS5
100n
VSS4
29
5600
2610
5
VDDI18_1
VDDI18_1
VSS3VSS324VSS4
+1V8FE
2611
100n
100n
2612
19
34
47
VDDE33_1VDDE33_1
VDDE33_2VDDE33_2
VDDE33_3VDDE33_3
TDO20TDO
TDI17TDI
TMS16TMS
JTAG
TCKTCK
MPEG-TS (SERIAL)
TRST14TRST
ENSERI13ENSERI
S_DOS_DO
S_OCLKS_OCLK
S_DENS_DEN
S_PSYNC
S_PSYNC
MPEG-TS (SERIAL)
S_UNCORS_UNCOR
DO038DO0
DO139DO1
DO241DO2
DO343DO3
DO4DO4
DO546DO5
DO648DO6
DO749DO7
OCLK37OCLK
DEN36DEN
MPEG-TS (PARALLEL)
PSYNC35PSYNC
UNCOR33UNCOR
SACLK51SACLK
VSS17VSS1
VSS215VSS2
+1V8FE
+3V3FE
+3V3FE
7600
9
54
55
23
25
26
8
4
3
12
CLR_CLR_
AGC_TUN1AGC_TUN
AGC_IF2AGC_IF
VIP62VIP
VIM61VIM
XINXIN
XOUT
XOUT
GPIO021GPIO0
GPIO1GPIO1
GPIO2GPIO2
GPIO3
GPIO3
SADDR011SADDR0
SADDR110SADDR1
SDA
SDA
SCL6SCL
SDA_TUNSDA_TUN
SCL_TUNSCL_TUN
TESTTEST
60
VDD33_ADCVDD33_ADC
VDDA33_ADCVDDA33_ADC
100n
2608
2609
100n
50
53
57
5964
VDDI18_4VDDI18_4
VDDA18_PLL
VDDA18_PLL
VDDA18_OSCVDDA18_OSC
VDD18_PLL_ADCVDD18_PLL_ADC
COFDM
CHANNEL DECODER
I2C
VSS645VSS6
VSS_PLL_ADCVSS_PLL_ADC
58
VSS752VSS7
VSSA_ADCVSSA_ADC56VSSA_OSCVSSA_OSC
63
3614
100K
680K
680K
7605
2
1V3
7606
2
1V3
100n
NC
1
NC
1
+5Vclean
3609
2631
100n
33p
2634
3637
220K
3641
220K
3V2
5
4
1
1V6
3
3V2
5
4
1
1V6
3
+5Vclean
4K7
I607
3615
1K0
3617
220R
3610
2629
100n
4K7
3638
330R
3642
330R
I633
3639
I634
3643
K6
FE_LOCK
K1
K1, K2, K7
K1, K2, K7
2625
100n
F607
COMP_OUT
678910
2618
44
100n
100n
32
31
30
28
27
1V7
2613
18
2V2
2V2
2V2
2V2
2V2
2V2
2V2
2V2
1V3
0V
0V
2614
100n
47u 16V
+3V3FE
16V47u
100n
2619
0V
0V
2V4
0V
2V4
3622-3 33R
3624-4 33R
3624-3 3 6
3624-2
3644-1 1
3644-2
3644-3
3644-4
I628
I629
2621
2620
100n
3635
33R
4533R3622-4
36
27
33R3622-2
183622-1 33R
45
33R
33R27
33R3624-1 1 8
33R
8
33R
27
33R
36
33R
45
I615
I618
I619
I620
I621
I622
I623
I624
I625
I626
I627
I603
10
12
14
16
18
20
ROW_2
1603-2
2
4
6
8
FTSH
10046_TDO
STV_TDO
JTAG_TMS
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TRST
TDA_DAT(0)
TDA_DAT(1)
TDA_DAT(2)
TDA_DAT(3)
TDA_DAT(4)
TDA_DAT(5)
TDA_DAT(6)
TDA_DAT(7)
TDA_CLK
TDA_VALID
TDA_SYNC
TDA_DAT(0)
TDA_DAT(1)
TDA_DAT(2)
TDA_DAT(3)
TDA_DAT(4)
TDA_DAT(5)
TDA_DAT(6)
TDA_DAT(7)
UNCOR
K1, K7
K1, K7
K1, K7
+3V3
K1
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K6
K7
K7
UNCOR
K7
K6
K7
TDA_VALID
K7
K7
K7
TDA_SYNC
K7
K7
K7
K7
TDA_CLK
11 12 13
5601
ROW_1
1603-1
FTSH
10 XTAL
12 IF-OUT
1V3
I602
I606
2627
100n
F605
3618
3619
100K
+5V
2K7
3627
F612
3633
100R
+3V3FE
100n
2624
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
F_15270_059.eps
200505
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
1600 A2
1601 F6
1603-1 H13
1603-2 H12
2607 D10
2608 D9
2609 D9
2610 D10
2611 D10
2612 D10
2613 D11
2614 D11
2615 D8
2617 D8
2618 D10
2619 D11
2620 D11
2621 D11
2622 D3
2623 D4
2624 E13
2625 D7
2626 E2
2627 E5
2628 F6
2629 F7
2630 F1
2631 F6
2632 F5
2633 G5
2634 G6
2635 H4
3606 C4
3607 C4
3608 E8
3609 E6
3610 E6
3611 E4
3612 E1
3613 E2
3614 E6
3615 E6
3616 F4
3617 F6
3618 F5
3619 F5
3620 G3
3621 G8
3622-1 G11
3622-2 G11
3622-3 G11
3622-4 G11
3623 G3
3624-1 G11
3624-2 G11
3624-3 G11
3624-4 G11
3625 G8
3626 G5
3627 G5
3629 G8
3630 H8
3631 H8
3632 H5
3633 H5
3634 I3
3635 E11
3636 C6
3637 C6
3638 C7
3639 C7
3640 D6
3641 D6
3642 D7
3643 D7
3644-1 G11
3644-2 H11
3644-3 H11
3644-4 H11
3645 G8
4605 E7
4606 E3
4607 E5
4610 I3
5600 C10
5601 D13
5602 D3
5603 H4
7600 E8
7601-1 E2
7601-2 F2
7602 H4
7605 C6
7606 D6
F600 C2
F603 D3
F604 F5
F605 F5
F606 F5
F607 F7
F608 F7
F609 F8
F610 G7
F611 H5
F612 H5
F613 I3
I601 D4
I602 C5
I603 H12
I604 E8
I605 E4
I606 E5
I607 E6
I614 G8
I615 G12
I616 G4
I618 G12
I619 G12
I620 G12
I621 G12
I622 G12
I623 G12
I624 G12
I625 G12
I626 H12
I627 H12
I628 H11
I629 H11
I631 E7
I632 E2
I633 C7
I634 D7
Page 77

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
77LC4.9E AB 7.
IBO Zapper: Common Interface
1234
K7 K7
COMMON INTERFACE
A
B
C
D
E
K2, K6, K7
K2, K6, K7
K6
K6
K6
K6
K6
K6
K6
K6
K6
K6
K6
K7
K7
K7
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
I2C_LOCAL_SCL
I2C_LOCAL_SDA
TDA_CLK
TDA_SYNC
TDA_VALID
TDA_DAT(0)
TDA_DAT(1)
TDA_DAT(2)
TDA_DAT(3)
TDA_DAT(4)
TDA_DAT(5)
TDA_DAT(6)
TDA_DAT(7)
TS_CLK
TS_SYNC
TS_VALID
TS_DATA(0)
TS_DATA(1)
TS_DATA(2)
TS_DATA(3)
TS_DATA(4)
TS_DATA(5)
TS_DATA(6)
TS_DATA(7)
3702-3
3702-2
3702-1
3703-1
3703-2
3703-3
3703-4
3705-1
3705-2
3705-3
3705-4
3700
3701
33R
33R
33R
33R
33R
33R
33R
33R
33R
33R
33R
F
G
H
+3V3_STV
10K
I766
5V
I770
3713
+3V3_STV
3710
2K0
3709
1n0
10K
I767
PCMCIA_5V
10u
2707
VCCEN
I
CURRENT
SWITCH
3V2
7705
ST890C
+5V
5V
1
J
2
8
10K
3711
3
I772
0V
IN1
IN2
FAULT_
ON_
7
OUT1
6
OUT2
5
SET
0V
GND
4
K
L
5703
+3V3
M
5704
+3V3
I777
+3V3_STV
10u
2709
2713
2710
100n
2708
100n
100n
2711
I778
+3V3_CORE
10u
2712
100n
+5V
7704
FXO-31FT
4
1
VDD
3
GND
27M0
2
F700
2714
K1
RESET_STV
K1
STV_INT
+3V3_STV
MIU_OEN
K2, K7
MIU_WEN
K2, K7
K1
STV_CS
K7
K2, K7
MIU_RDY
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(15)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(16)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(17)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(18)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(19)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(20)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(21)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(22)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(23)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(24)
STV_A25
K1
N
5678910
K1
K6
K1, K6
K1, K6
K1, K6
PCMCIA
STV_TDO
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TMS
JTAG_TRST
10
8
TDO
TRST_
GND-TSI39GND-TSO
52
CONTROLLER
MICLKA
MISTRTA
MIVALA
MDIA0
MDIA1
MDIA2
MDIA3
MDIA4
MDIA5
MDIA6
MDIA7
MOCLKA
MOSTRTA
MOVALA
MDOA0
MDOA1
MDOA2
MDOA3
MDOA4
MDOA5
MDOA6
MDOA7
MICLKB
MISTRTB
MIVALB
MDIB0
MDIB1
MDIB2
MDIB3
MDIB4
MDIB5
MDIB6
MDIB7
MOCLKB
MOSTRTB
MOVALB
MDOB0
MDOB1
MDOB2
MDOB3
MDOB4
MDOB5
MDOB6
MDOB7
CD1A_
CD2A_
CD1B_
CD2B_
RDY|IRQA_
RDY|IRQB_
RSTA
RSTB
WAITA_
WAITB_
REG_
WE_
IORD_
IOW_R
OE_
CE1A_
CE1B_
CE2A_
CE2B_
VCCEN
DATOE_
DATDIR
ADOE_
ADLE
GND-PROC
86
9
110
3727 47R
0V
92
0V
105
3729 47R
0V
94
0V
96
3731 47R
0V
0V
99
103
0V
3733
107
0V
3734-2
112
0V
3734-3
114
0V
0V
116
3734-4
2V8
118
127
3739 47R
0V
125
0V
1
0V
3741 47R
3
0V
5
3743 47R
0V
74
0V
76
3745 47R
0V
0V
78
80
3747 47R
0V
84
0V
108
91
104
4K7
3752
93
95
98
102
106
111
113
115
117
126
124
128
2
4
73
75
77
79
83
72
3V2
7
3V2
71
3V2
6
3V2
101
5V
100
5V
120
0V
119
122
5V
121
5V
3V2
123
3V2
97
89
3V2
90
3V2
88
3V2
82
3V2
81
87
3V2
85
70
0V
0V
69
0V
68
67
0V
0V
66
A_MICLK
K7
A_MISTRT
47R3728
47R3730
47R3732
47R
47R3734-1
18
47R
27
47R
36
47R
45
47R3738
47R3740
47R3742
47R3744
47R3746
47R3748
A_MIVAL
A_MOCLK
A_MOSTRT
A_MOVAL
I768
I769
I773
I776
K7
K7
A_MDI(0)
A_MDI(1)
A_MDI(2)
A_MDI(3)
A_MDI(4)
A_MDI(5)
A_MDI(6)
A_MDI(7)
K7
K7
K7
A_MDO(0)
A_MDO(1)
A_MDO(2)
A_MDO(3)
A_MDO(4)
A_MDO(5)
A_MDO(6)
A_MDO(7)
10K
10K
10K
10K
10K
10K
3720
3716
3717
3715
3722
3718
7700
STV0700
32
SA0
33
SA1
31
4V6
100R
100R
3712
SCL
30
SDA
4V6
50
MICLK
1V6
49
0V
MISTRT
48
2V2
MIVAL
40
2V2
MDI0
41
2V2
MDI1
2V2
42
MDI2
2V2
43
MDI3
2V2
44
MDI4
2V2
45
MDI5
1V3
46
MDI6
2V2
MDI7
47
1V5
63
MOCLK
62
0V
MOSTRT
61
1V3
MOVAL
53
2V2
MDO0
54
2V2
MDO1
2V2
55
MDO2
2V2
56
MDO3
2V2
57
MDO4
2V2
58
MDO5
2V2
59
MDO6
2V2
MDO7
60
I764
2V3
4700
2V5
F701
35
CLK
F702
0V
34
RESET
3V2
12
EXTINT
14
3V2
INT
10K
17
3V2
RD|DIR
16
3V2
WR|STR
18
3V2
CS
I775
15
3V2
WAIT|ACK
19
0V
A15
20
0V
A16
21
A17
3V2
22
3V2
A18
23
3V2
A19
24
3V2
A20
25
3V2
A21
26
A22
0V
27
0V
A23
28
A24
0V
29
0V
A25
13
EXTCS
+3V3_CORE
+3V3_STV
11
65
TCK
TMS
INTERFACE
TS INTERFACE
INTERRUPTS
MANAGEMENT
UCSG
VCC-TSO
VCC-CORE36VCC-PROC
VCC-TSI
64
109
51
STV_TDI
38
TDI
2
I C
GND-CORE37GND-DVB2
10K
10K
3719
3721
11
A_|CD1
A_|CD2
A_|RDY|IRQ
A_RESET
A_|WAIT
PCMCIA_|REG
PCMCIA_|WE
PCMCIA_|IORD
PCMCIA_|IOWR
PCMCIA_|OE
A_|CE1
A_|CE2
VCCEN
|DATOE
DATDIR
|ADOE
ADLE
+3V3_STV
PCMCIA_5V
MIU_ADDR(0:24)
3139 123 5906.2
12345
6
78
9 1011121314
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
+3V3_BUF
11
2D0
3D1
4D2
5D3
6D4
8D6
1OE_
11
2D0
3D1
4D2
5D3
6D4
7D5
8D6
9D7
2700
100n
7701
20
OE_1
EN
VCC
C1
19Q0
0V
1D
D57
D79
GND
10
+3V3_BUF
2701
7702
100n
20
EN
VCC
C1
Q0 19
1D
GND
10
3V2
20
VCC
3EN1
3EN2
19
G3
2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
GND
10
PCMCIA_A(7)
18Q1
3V2
PCMCIA_A(6)
17Q2
3V2
PCMCIA_A(5)
16Q3
3V2
PCMCIA_A(4)
15Q4
3V2
PCMCIA_A(3)
14Q5
0V
PCMCIA_A(2)
3V2
13Q6
PCMCIA_A(1)
12Q7
3V2
PCMCIA_A(0)
0V
PCMCIA_A(8)
18Q1
PCMCIA_A(9)
3V2
17Q2
0V
PCMCIA_A(10)
16Q3
0V
PCMCIA_A(11)
15Q4
3V2
PCMCIA_A(12)
14Q5
0V
PCMCIA_A(13)
13Q6
3V2
PCMCIA_A(14)
12Q7
0V
1
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
3723-1
2715
100p
27
18
45
36
33R3725
33R3726
33R3723-4 4 5
33R3723-3 3 6
33R3723-2
33R
33R3724-4
33R3724-3
33R3724-2 2 7
33R3724-1 1 8
DATDIR
|DATOE
PCMCIA_D(7)
PCMCIA_D(6)
PCMCIA_D(5)
PCMCIA_D(4)
PCMCIA_D(3)
PCMCIA_D(2)
PCMCIA_D(1)
PCMCIA_D(0)
PCMCIA_A(0:14)
PCMCIA_D(3)
PCMCIA_D(4)
PCMCIA_D(5)
PCMCIA_D(6)
PCMCIA_D(7)
PCMCIA_D(0)
PCMCIA_D(1)
PCMCIA_D(2)
A_|IOIS16
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
PCMCIA_D(0:7)
K7
PCMCIA_A(10)
K7
PCMCIA_A(11)
PCMCIA_A(9)
PCMCIA_A(8)
PCMCIA_A(13)
PCMCIA_A(14)
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
PCMCIA_A(12)
PCMCIA_A(7)
PCMCIA_A(6)
PCMCIA_A(5)
PCMCIA_A(4)
PCMCIA_A(3)
PCMCIA_A(2)
PCMCIA_A(1)
PCMCIA_A(0)
+3V3_STV
A_|CE1
PCMCIA_|OE
PCMCIA_|WE
A_|RDY|IRQ
PCMCIA_AVCC
PCMCIA_VPP
A_MIVAL
A_MICLK
68p PCMCIA
CONNECTOR
1700-B
1700-A
ROW_B
ROW_A
GND1
I700
I702
I704
I706
I708
I710
CE1
I712
A10
I714
I716
A11
I718
I720
I722
A13
I724
A14
I726
WE|P
I728
RDY|BSY
I730
VCC1
I731
VPP1
I732
A16
I734
A15
I736
A12
I738
I740
I742
I744
I746
I748
I750
I752
I754
I756
I758
I760
WP|IOIS16
GND2
I763
4K7
3751
3708
10K
PCMCIA_5V
PCMCIA_5V
ICME68H-D1121NS
5700
5701
GND3
1
35
CD1
D3
36
2
D11
D4
37
3
D12
D5
38
4
D13
D6
39
5
D14
D7
40
6
D15
41
7
CE2
8
42
OE
VS1
9
43
IORD
10
44
IOWR
A9
45
11
A17
A8
46
12
A18
13
47
A19
48
14
A20
49
15
A21
50
16
VCC2
17
51
VPP2
18
52
A22
53
19
A23
54
20
A24
55
21
A25
A7
56
22
A6
VS2
57
23
A5
RESET
24
58
A4
WAIT
25
59
INPACK
A3
60
26
REG
A2
61
27
BVD2|SPKR
A1
28
62
A0
BVD1|STSCHG
63
29
D8
D0
64
30
D9
D1
65
31
D10
D2
66
32
CD2
67
33
GND4
68
34
7172
ICME68H-D1121NS
100n
2703
2702
100n
100n
2705
LATCH
74LVC573ADB
3749
33R
K7
K7
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
|ADOE
ADLE
MIU_ADDR(7)
MIU_ADDR(6)
MIU_ADDR(5)
MIU_ADDR(4)
MIU_ADDR(3)
MIU_ADDR(2)
MIU_ADDR(1)
MIU_ADDR(0)
0V
3V2
3750
33R
0V
3V2
3V2
3V2
3V2
0V
3V2
3V2
LATCH
74LVC573ADB
+3V3_BUF
MIU_DATA(7)
MIU_DATA(6)
MIU_DATA(5)
MIU_DATA(4)
MIU_DATA(3)
MIU_DATA(2)
MIU_DATA(1)
MIU_DATA(0)
0V
0V
3V2
0V
0V
3V2
0V
3V2
100n
2704
7703
74LVC245A
0V
18
0V
17
0V
16
0V
15
0V
14
0V
13
0V
12
0V
11
MIU_ADDR(8)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(9)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(10)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(11)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(12)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(13)
K1, K2
MIU_ADDR(14)
K1, K2
K2, K7
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K1, K2
K7
K7
BUS TRANSCEIVER
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
+3V3
I779
5702
+3V3_BUF
10u
2706
15
16
17 18 19 20
I762
PCMCIA_VPP
PCMCIA_AVCC
F703 F704
3999
68R
PROCESS CHIP
I701
I703
I705
I707
I709
I711
I713
I715
I717
I719
I721
I723
I725
I727
I729
I733
I735
I737
I739
I741
I743
I745
I747
I749
I751
I753
I755
I757
I759
I761
A_MDI(0:7)
A_MDO(0:7)
PCMCIA_|IORD
PCMCIA_|IOWR
PCMCIA_AVCC
A_MOCLK
A_RESET
A_|WAIT
A_|INPACK
PCMCIA_|REG
A_MOVAL
A_MOSTRT
+3V3_STV
10K
3704
A_|CD1
A_MDO(3)
A_MDO(4)
A_MDO(5)
A_MDO(6)
A_MDO(7)
A_|CE2
A_|VS1
A_MISTRT
PCMCIA_VPP
A_MDO(0)
A_MDO(1)
A_MDO(2)
A_|CD2
10K
3706
10K
3707
+3V3_STV
+3V3_STV
F_15270_060.eps
20
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
A_MDI(0)
A_MDI(1)
A_MDI(2)
A_MDI(3)
K7
K7
A_MDI(4)
A_MDI(5)
A_MDI(6)
A_MDI(7)
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
K7
200505
1700-A D18
I770 J2
1700-B D18
I772 J1
2700 C14
I773 J9
2701 E14
I775 K5
I776 K9
2702 G18
I777 L2
2703 G18
I778 M2
2704 H12
I779 J13
2705 H18
2706 K13
2707 J3
A
2708 M2
2709 M2
2710 M2
2711 M2
2712 M2
2713 M2
2714 I3
2715 J14
3700 B4
3701 B4
3702-1 D4
3702-2 D4
B
3702-3 D4
3703-1 E4
3703-2 E4
3703-3 E4
3703-4 E4
3704 D19
3705-1 E4
3705-2 E4
3705-3 F4
3705-4 F4
3706 G19
3707 G19
C
3708 G17
3709 I3
3710 J2
3711 J1
3712 J4
3713 J2
3715 I9
3716 I9
3717 I9
3718 I9
3719 I10
D
3720 I10
3721 I10
3722 I9
3723-1 I14
3723-2 I14
3723-3 I14
3723-4 I14
3724-1 I14
3724-2 I14
3724-3 I14
3724-4 I14
3725 I14
E
3726 I14
3727 B8
3728 C8
3729 C8
3730 C8
3731 C8
3732 C8
3733 C8
3734-1 C8
3734-2 D8
3734-3 D8
3734-4 D8
F
3738 D8
3739 D8
3740 D8
3741 E8
3742 E8
3743 E8
3744 E8
3745 E8
3746 E8
3747 F8
3748 F8
G
3749 C12
3750 D12
3751 G17
3752 F8
3999 K19
4700 I5
5700 G18
5701 H18
5702 J13
5703 L1
5704 M1
7700 A5
H
7701 C13
7702 E13
7703 H13
7704 H4
7705 J2
F700 I4
F701 I5
F702 I5
F703 K18
F704 K19
I700 D17
I701 D19
I
I702 D17
I703 D19
I704 D17
I705 D19
I706 D17
I707 D19
I708 D17
I709 D19
I710 E17
I711 E19
I712 E17
J
I713 E19
I714 E17
I715 E19
I716 E17
I717 E19
I718 E17
I719 E19
I720 E17
I721 E19
I722 E17
I723 E19
I724 E17
K
I725 E19
I726 E17
I727 E19
I728 E17
I729 E19
I730 E17
I731 E17
I732 E17
I733 E19
I734 E17
I735 E19
I736 F17
L
I737 F19
I738 F17
I739 F19
I740 F17
I741 F19
I742 F17
I743 F19
I744 F17
I745 F19
I746 F17
I747 F19
M
I748 F17
I749 F19
I750 F17
I751 F19
I752 F17
I753 F19
I754 F17
I755 F19
I756 F17
I757 F19
I758 F17
I759 F19
N
I760 F17
I761 F19
I762 F19
I763 F17
I764 I5
I766 J2
I767 J3
I768 J9
I769 J9
Page 78

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout IBO Zapper (Top Side)
78LC4.9E AB 7.
3139 123 5906.2
F_15270_061.eps
200505
Page 79

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout IBO Zapper (Bottom Side)
79LC4.9E AB 7.
3139 123 5906.2
F_15270_062.eps
200505
Page 80

Personal Notes:
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
80LC4.9E AB 7.
Page 81

8. Alignments
Index of this chapter:
8.1 General Alignment Conditions
8.2 Hardware Alignments
8.3 Software Alignments
Note: Figures below can deviate slightly from the actual
situation, due to the different set executions.
General: The Service Default Mode (SDM) and Service
Alignment Mode (SAM) are described in chapter 5. Menu
navigation is done with the Cursor Up, Down, Left or Right keys
of the remote control transmitter.
8.1 General Alignment Conditions
Perform all electrical adjustments under the following
conditions:
Mains voltage and frequency: 100-240 V / 50/60 Hz.
Allow the set to warm up for approximately 10 minutes.
Test probe: Ri > 10 MΩ; Ci < 2.5 pF.
8.2 Hardware Alignments
Alignments
EN 81LC4.9E AB 8.
There are no hardware alignments foreseen for the plasma-TV.
8.3 Software Alignments
With the software alignments of the Service Alignment Mode
(SAM) the geometry, white tone and tuner (IF) can be aligned.
To store the data: Use the RC button Menu to switch to the
main menu and next, switch to ‘Stand-by’ mode.
Page 82

EN 82 LC4.9E AB8.
8.3.1 SAM Menu
Alignments
00035 LC4XEP1 1.14/S4XGNV 1.17 SDM
ERR 0 0 0 0 0
OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
00035 LC4XEP1 1.14/S4XGNV 1.17 SAM
ERR 0 0 0 0 0
OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
. Clear Clear ?
. Options
. Tuner
. White Tone
. Audio
. NVM Editor
. SC NVM Editor
. Test Pattern
. ComPair Mode On
1 00035 LC4XEP1 1.14/S4XGNV 1.17 CSM
2 CODES 0 0 0 0 0
3 OP 000 057 140 032 120 128 000
4
5
6 NOT TUNED
7 PAL
8 STEREO
9 CO 50 CL 50 BR 50
0 AVL Off
SAM SAM
. OP1 0 . Delta Cool Red -3
. OP2 57 . Delta Cool Green -1
. OP3 140 . Delta Cool Blue 5
. OP4 32
. OP5 120
. OP6 128
. OP7 0
SAM SAM
. IFPLL 32 . Normal Red 32
. AGC 30 . Normal Green 35
. AGCL' 255 . Normal Blue 41
SAM SAM
. Cool . Delta Warm Red 2
. Normal . Delta Warm Green -3
. Warm . Delta Warm Blue -13
SAM
. QSS Off
. FMI On
. NICAM Alignment 63
. Lip Sync Off
. DBE Off
8.3.2 Tuner Adjustment
AGC (RF AGC Take Over Point)
• Activate the SAM menu.
• Go to the sub-menu Tuner.
• Select the AGC sub-menu.
• Adjust the AGC value to AGC = 27.
• Adjust the AGC L’ value to AGC L’ = 27 (Europe only).
• Adjust the IFPLL value to IFPLL = 32 (Europe only).
• Switch the set to standby to store the data.
SAM
.ADR 0x0000 0
.VAL 0x0000 0
.Store Store ?
SAM
.ADR 0x0000 0
.VAL 0x0000 0
.Store Store ?
Figure 8-1 Overview SAM menu.
8.3.3 DCXO (Digital Xtal Oscillator) Alignment (for NICAM sets only)
• Input a Colour bar signal with a colour subcarier frequency
• Select as a signal source EXT1 or AV1.
• Go to the SAM menu and select Audio.
• Activate DCXO Alignment and wait until this process has
• Check if the NICAM audio reception is OK, if not: repeat the
• Switch the set to standby to store the data.
F_15430_042.eps
080605
of 4.43 MHz on SCART1 or SCART2.
finished (DONE).
procedure.
Page 83

Alignments
EN 83LC4.9E AB 8.
8.3.4 ADC Gain and Grey Scale Alignment
The table below shows a number of NVM settings used for
each model of TV set. Be sure to use the correct editor in the
SAM menu (NVM Editor or SC NVM Editor), because the first
one is used for the Hercules NVM, and the second one for the
SCALER (SC) part of the TV set. For further important NVM
settings, see also the other NVM tables elsewhere in this
manual.
Caution:
• Do not change the NVM settings without
understanding the function of each setting, because
incorrect NVM settings may seriously hamper the
correct functioning of the TV set!
• Do not change the Scaler NVM settings, as this will
hamper the DVI functionality of the TV set!
• Always note down the existing NVM settings, before
changing the settings. This will enable you to return to the
orgininal settings, if the new settings turn out to be
incorrect.
Table 8-1 ADC gain and grey scale alignment
SDTV ADC Gain settings: Use the NVM Editor in SAM to set these
Setting
NVM_ADC_GAIN_R 006 143 143 075 - 155
NVM_ADC_GAIN_G 007 191 191 200 - 250
NVM_ADC_GAIN_B 008 143 143 075 - 155
SDTV Greyscale settings: Use the SC NVM Editor in SAM to set these
Setting
ADC_RED_OFFSET2 338 080 080 050 - 110
ADC_GRN_OFFSET2 339 080 080 050 - 110
ADC_BLU_OFFSET2 340 080 080 050 - 110
ADC_RED_GAIN 341 154 154 045 - 095
ADC_GRN_GAIN 343 154 154 045 - 095
ADC_BLU_GAIN 345 154 154 045 - 095
Setting
ADC_RED_OFFSET2 325 080 080 040 - 090
ADC_GRN_OFFSET2 326 080 080 040 - 090
ADC_BLU_OFFSET2 327 080 080 040 - 090
ADC_RED_GAIN 328 154 154 180 - 270
ADC_GRN_GAIN 330 154 154 180 - 270
ADC_BLU_GAIN 332 154 154 180 - 270
Setting
ADC_RED_OFFSET2 351 064 064 050 - 090
ADC_GRN_OFFSET2 352 082 082 050 - 090
ADC_BLU_OFFSET2 353 064 064 050 - 090
ADC_RED_GAIN 354 159 159 120 - 200
ADC_GRN_GAIN 356 144 144 120 - 200
ADC_BLU_GAIN 358 147 147 120 - 200
values in the Hercules NVM
These models are with ADC
& Columbus 3D Combfilter
Hercules NVM
Address
(decimal value)
42PF7520D/10
values in the Scaler NVM
Scaler NVM
Address
(decimal value)
PC Greyscale settings
Scaler NVM
Address
(decimal value)
HD Greyscale settings
Scaler NVM
Address
(decimal value)
These models are with ADC
& Columbus 3D Combfilter
42PF7520D/10
These models are with ADC
& Columbus 3D Combfilter
42PF7520D/10
These models are with ADC
& Columbus 3D Combfilter
42PF7520D/10
42PF5520D/10
42PF5520D/10
42PF5520D/10
42PF5520D/10
Settings
Range
(decimal
value)
Settings
Range
(decimal
value)
Settings
Range
(decimal
value)
Settings
Range
(decimal
value)
8.3.5 Sound
• For NICAM sets: see paragraph 8.3.3.
• For other sets: No adjustments needed for sound.
8.3.6 Options
Options OP1...OP7 in the SAM menu can be used for quickly
restoring 64 features or settings of the HERCULES part of the
TV set to their orginal default factory values (8 groups of 8
features/settings each). When the decimal value of one option
byte OP1...OP7 is changed (see the first table below) then a
group of 8 bits, representing 8 HERCULES options or features,
is changed as well (see the second table below for a detailed
description of the features or settings that are changed).
The second table shows which option byte (OP1...OP7)
represents which group of 8 option bits. Each bit (0...7)
switches a particular HERCULES feature or setting ON or OFF,
depending on its value (1 or 0).
It is also possible to change the features or settings mentioned
in the second table directly at bit level, by means of the NVM
Editor in the SAM menu. In the NVM Editor, first the correct
NVM address (ADR) has to be entered, then the correct value
(VAL, 1 or 0) for each bit (see second table), and finally the
settings have to be stored (STORE). For quickly restoring the
HERCULES part of the TV set to its original factory settings,
however, it is more convenient to simply enter the default
factory settings OP1...OP7 that are given in the first table
below. How to do this, is described in the next paragraph.
How to Change an Option Byte
As has been explained above, an Option byte (OP) represents
a number of different HERCULES options. Changing these
bytes directly makes it possible to set all HERCULES options
very fast. All options are controlled via seven option bytes.
Select the option byte (OP1.. OP7) with the Menu Up/ Down
keys, and enter the new (decimal) value. For the correct
Factory Default settings, see the first table below. For more
detailed information, see the second table.
Leaving the Option submenu saves the changes in the Option
Byte settings. Some changes will only take effect after the set
has been switched “off” and “on” with the AC power switch (cold
start).
Table 8-2 Option codes OP1...OP7
Option table for quickly restoring the HERCULES to its
Options (can be changed only via the SAM
Factory Default settings
42PF7520D/10
OP1 152 152
OP2 37 101
OP3 79 15
OP4 241 241
OP5 252 252
OP6 27 27
OP7 19 19
menu)
Model number
Total decimal value
for each option per
model number
How to Change Options at Bit Level
If you wish to know which features or settings of the
HERCULES are changed via OP1...OP7, or if you want to
change each option or feature bit by bit, use the more detailed
table below.
Note: the table below contains only part of the NVM settings
that can be changed. A second range of settings and features
can be found in Chapter 5 of this manual, in table NVM Default
values. The settings mentioned there can only be changed via
the NVM editor. For further settings, see also the table “ADC
Gain and Grey scale alignment” elsewhere in this manual.
42PF5520D/10
Page 84

EN 84 LC4.9E AB8.
Alignments
Table 8-3 Option codes in detail, at bit level
Option byte & bit table for restoring the TV set to its original Factory Default settings via the NVM Editor in the SAM menu
OP1 Description of feature/option to be switched ON or OFF
bit 7 (msb) OP_PHILIPS_TUNER 11
bit 6 OP_FM_RADIO 00
bit 5 OP_LNA 00
bit 4 OP_ATS // for EU 11
bit 3 OP_ACI 11
bit 2 OP_UK_PNP 00
bit 1 OP_VIRGIN_MODE 00
bit 0 (lsb) OP_CHINA 00
OP2
bit 7 (msb) OP_SC 00
bit 6 OP_IBEX 11
bit 5 OP_CHANNEL_NAMING 11
bit 4 OP_LTI (Lum Transcient Improvmt) 00
bit 3 OP_TILT 00
bit 2 OP_FINE_TUNING 11
bit 1 OP_PIP_PHILIPS_TUNER 00
bit 0 (lsb) OP_HUE 11
OP3
bit 7 (msb) OP_EW_FUNCTION 00
bit 6 OP_PIXEL_PLUS 10
bit 5 OP_PIP_SPLITTER // temp 00
bit 4 OP_SPLITTER // temp 00
bit 3 OP_VIRTUAL_DOLBY 11
bit 2 OP_WIDE_SCREEN 11
bit 1 OP_WSSB 11
bit 0 (lsb) OP_OP_ME5 // OP_ME5 - 5/6 local buttons implementation 11
OP4
bit 7 (msb) OP_LIP_SYNC 11
bit 6 OP_HD 11
bit 5 OP_ULTRA_BASS 11
bit 4 OP_DELTA_VOLUME 11
bit 3 OP_TAIWAN_KOREA 00
bit 2 OP_VOLUME_LIMITER 00
bit 1 OP_STEREO_DBX 00
bit 0 (lsb) OP_STEREO_NICAM_2CS 11
OP5
bit 7 (msb) OP_AV1 11
bit 6 OP_AV2 11
bit 5 OP_AV3 11
bit 4 OP_CVI 11
bit 3 OP_SVHS2 11
bit 2 OP_SVHS3 11
bit 1 OP_HOTEL_MODE 00
bit 0 (lsb) OP_SIMPLY_FACTORY=OP_BTSC_AVSTEREO 00
OP6
bit 7 (msb) OP_PERSONAL_ZAPPING 00
bit 6 OP_SMART_SURF 00
bit 5 OP_FMTRAP 00
bit 4 OP_COMBFILTER 11
bit 3 OP_ACTIVE_CONTROL 11
bit 2 OP_VIDEO_TEXT 00
bit 1 OP_LIGHT_SENSOR 11
bit 0 (lsb) OP_TWIN_TEXT 11
OP7
bit 7 (msb) OP_TIME_WIN1 00
bit 6 OP_DVB_USB = OP_MALAY 00
bit 5 OP_AMBILIGHT 00
bit 4 OP_COLUMBUS 11
bit 3 OP_DUMMY6 00
bit 2 OP_DUMMY7 00
bit 1 OP_WEST_EU 11
bit 0 (lsb) OP_MULTI_STANDARD_EUR 11
Total DEC Value 152 152
Total HEX Value 98 98
Total DEC Value 101 101
Total HEX Value 65 65
Total DEC Value 79 15
Total HEX Value 4F 0F
Total DEC Value 241 241
Total HEX Value F1 F1
Total DEC Value 252 252
Total HEX Value FC FC
Total DEC Value 27 27
Total HEX Value 1B 1B
Total DEC Value 19 19
Total HEX Value 03 03
42PF7520D/10
Model number
42PF5520D/10
Page 85

Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
9. Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
EN 85LC4.9E AB 9.
Index of this chapter:
9.1 Introduction
9.2 IBO Zapper Module
9.3 Block diagram IBO Zapper Module
9.4 PNx83xx MOJO
9.5 Front End
9.6 Back End
9.7 IBOLink Interface
9.8 Control Interface
9.9 UART Interface
9.10 Power Supply IBO Zapper Module
9.11 Abbreviation List
9.12 IC Data Sheets
9.1 Introduction
The Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) TV sets/models
discussed in this manual are a combination of a standard TV
set and an IBO zapper module. For a description of the original
TV sets (without an IBO zapper module), see the LC4.9E AA
manual, order code 3122 785 15432. The table below shows
9.3 Block diagram IBO Zapper Module
ni FH
FI golana
ni FH
FI golana C2I CGA
FI latigid ni FI
RENUT dirbyh
6131DT
renut C2I CGA
the original models of TV sets on which the IBO zapper models
are based, together with the various picture qualities globally
available (the Crystal Clear version is not applicable to the TV
sets discussed in this manual).
Table 9-1 TV Models and Picture Quality
IBO Zapper Model Original TV Model Picture quality
42PF7520D/10 42PF7320/10
Pixel Plus
42PF5520D/10 42PF5320/10 Digital Crystal Clear
N.a. N.a. Crystal Clear
9.2 IBO Zapper Module
The “IBO Zapper” module is meant to receive, process, and
transfer Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial (DVB-T) signals
to the internal TV interface for audio, video, and control. The
“IBO Zapper” is intended for use in combination with an
analogue TV chassis.
eludom reppaZOBI
tuo ST
GATJGATJ
i ST
n
MDFOC
64001
2I
2I
C
C
L
NOC
ORT
.I.C
A0070VTS
tuo ST
UP
F/I
C
-AICMCP
rotcennoc
HSAL
F
+
hctaL
viec
r
narT
e
s
BM 4
hctiw
s A/D
CGA
QRI
FEH+XUM
GAT
JE
D
TS inI2C0SmCard1SmCard0
C2I
MORPEE
)sgnittes resu(
L
MA
ATX
UIM
M
E
XU
ed
M
GEP
UPC
RDS
SPDIF I2S Analog Video Out
R
CSED
oid
uA-1GEPM
ed
r
oc
ediV-2
o
redoced
DSO
OJOM
xx38xnp
RI BSU 1C2I TESER 232SR
MA
RDS
BM 6
1
ua latigid
oi
d
oidua
a
CAD
rp
ro
Y
d
golan
:4:
4( BGR
cnysSBVC
R,L o
ua
i
T( yrami
)V
:
+ )4
)4:4:4( rPbP
:)RCV( yradnuces
C2I
/nO rewo
P
ffO
V21
5
V
USP
232SR/LTT
Figure 9-1 Block Diagram IBO zapper module
SBV
C
32S
2
R
E_14970_036.eps
020605
Page 86

EN 86 LC4.9E AB9.
Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
9.4 PNx83xx MOJO
The MOJO is a source decoder chip targeted for very low cost
application in integrated digital televisions.The device contains
all hardware and software to be able to decode and display
MPEG2 transport streams, including:
• Descrambling
• Demultiplexing
• Audio / video decompression
• Video encoding.
• Overlay graphics provisions
Some features of the MOJO are:
• 32-bit PR1910 core operating at 120 MHz.
• 16-bit memory and peripheral interface to connect ROM,
NOR Flash and various peripherals.
• Sixteen external interrupt inputs shared with PIO lines.
• Several embedded peripheral units with physical interfaces
to:
– Two UART (RS-232) data ports
–Two I
– Two smart-card reader interfaces
– One Integrated Conditional Access Module interface
• Supports parallel and serial transport stream input
interfaces
2
C master / slave transceivers
9.5 Front End
The front end of the “IBO Zapper” module is almost identical to
the “IBO+” module as used in the A10E with the exception that
the Transport Streams that come from the COFDM
demodulator are now fed through the PCMCIA controller first.
The PCMCIA controller receives encrypted Transport Streams
from the COFDM demodulator. Via the PCMCIA card, these
encrypted Transport Streams are decrypted, and transported
to the MOJO.
9.6 Back End
The MOJO is the main building block of the back-end of the
“IBO Zapper” module. The IC decodes the MPEG-2 stream into
analogue video and digital audio.
9.6.1 Transport Stream Input
The Transport Stream input is according to MPEG2 standard.
In the “IBO Zapper”, only 8-bit parallel is supported. The used
TS names are TDA_DATA.
9.6.2 Video Outputs
The MOJO has two analogue video outputs:
• Primary (TV): YUV + RGB
• Secundary (VCR): CVBS
The primary MOJO output is used as input for the TV display
and is fed either to the Hercules YUV/RGB input (pins 78/79/
80), for teletext insertion purposes, or directly to the analogue
Scaler input D2/C2/B2. The signal path is as follows:
switch 7G09 chooses between the SCART1 input signal and
the YUV/RGB output of the MOJO. The signal selected by
switch 7G09 is passed on to one group of the inputs of switch
7E00. The other group of inputs of this switch is connected to
the three analogue input pins of the DVI-D connector. The
output signal of switch 7E00 is passed on to the Hercules input,
pins 78/79/80 and to the Scaler input D2/C2/B2 via switch 7E01
in the MUX-SYNC interface. This switch chooses between the
MOJO output signal and the Hercules output signal, which is
used for SDTV signals (analogue terrestrial TV reception via
the analogue receiving part). The Hercules output is not only
used for SDTV signals, but also for MOJO output signals that
were first sent to the Hercules input for e.g. teletext reinsertion
purposes before they are passed on to the Scaler.
The secundary MOJO output, which delivers CVBS signals, is
used for monitoring purposes or for recording via the SCART 2
output of the TV set. The signal path of the secundary MOJO
output is as follows:
the CVBS/VCR signal coming from the MOJO is sent to the
Hercules video switch input, pin 58, via switch 7G07. The
signal then appears on one of the outputs of the Hercules video
switch, pin 48, and is passed on via switches 7219 and 7G10
to pin 19 of SCART 2, which is the CVBS/monitor output.
For further details, see the manuals of the original TV sets on
which the various models of IBO zappers are based.
9.6.3 Audio Outputs
The MOJO has two audio output interfaces:
• SPDIF Out: The SPDIF sound output goes directly to a
connector on the back of the module.
• I2S Out: This digital sound output is fed through a DAC and
the analogue L/R signals are directely fed into the
Hercules.
9.7 IBOLink Interface
The IBOLink™ approach is such that the conventional TV
microcontroller is re-used when digital functionality is added. In
principle, the TV can still operate without the bolt-on module.
The IBOLink™ software is added to the TV-set software, and is
operating as a software bridge.
9.8 Control Interface
The “IBO Zapper” is connected as a slave I2C device, The I2C
bus should be +5V tolerable and operating at 100kHz(MAX).
The “IBO Zapper” module slave address is 0xE4 (similar to
IBO+) but is configurable via IBOLink.
All communication from digital module to Television chassis
has to be initiated via an active low hardware interrupt line from
the digital module.
9.9 UART Interface
The UART interfaces (Universal Asynchronous Receiver And
Transmitter) are serial interfaces, which are used to transfer
data and commands between two devices.
The “IBO Zapper” system uses an UART interface for serial
communication with a pc for:
• Diagnostic SW for Service or Production
• SW uploading for Service or Development
9.10 Power Supply IBO Zapper Module
The “IBO Zapper” module operates from a single 12V supply
provided by the TV chassis. All other voltages that the module
needs are derived from the +12V. The module has four
different physical power states:
• “Off” State.
• “Passive Standby”.
• “Active Standby”.
• “On” State.
9.10.1 Off State
The set is powered off via the main power switch. The module
is not powered.
Page 87

Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
EN 87LC4.9E AB 9.
9.10.2 Passive Standby State
The set is in standby mode. The module is in off state.
9.10.3 Active Standby State
The set is in “Semi-Standby” mode. All the circuits in the set,
except the audio output and the LCD display are powered up
and fully active. The set appears to be in normal standby mode
for the customer.
The module is in “On” or “Logical Standby” state.
• On state. In this state the module can perform the following
pre-programmed functions:
– VCR (digital program) records
– EPG updates
– Over-the-air software download signaling detection
and software downloads
• Logial Standby state. In this state only over-the-air
software download signaling detection and software
downloads can be performed.
9.10.4 On State
The set is fully functional and the module is powered up. The
module is in “On” or “Logical Standby” state.
• On state. In this state all system functionality is available or
the module is in software downloading process.
• Logial Standby state. In this state only over-the-air
software download signaling detection and software
downloads can be performed.
9.11 Abbreviation List
0/6/12 SCART switch control signal on A/V
board. 0 = loop through (AUX to TV), 6
= play 16:9 format, 12 = play 4:3
format
1080i 1080 visible lines, interlaced
1080p 1080 visible lines, progressive scan
2CS 2 Carrier Sound (or 2 Channel Stereo)
480i 480 visible lines, interlaced
480p 480 visible lines, progressive scan
ACI Automatic Channel Installation:
algorithm that installs TV channels
directly from a cable network by
means of a predefined TXT page
ADC Analogue to Digital Converter
AFC Automatic Frequency Control; Control
signal used to tune and lock to the
correct frequency
AGC Automatic gain control (feedback)
signal to the tuner. This circuit ensures
a constant output amplitude
regardless of the input amplitude
AM Amplitude Modulation; A "data
encoding to a carrier" method, such
that the carrier amplitude is
proportional to the data value
AP or A/P Asia Pacific
AR Aspect Ratio: 4 by 3 or 16 by 9
ASD Automatic Standard Detection
AV External Audio Video
B-SC1-IN Blue SCART1/EXT1 in
B-SC2-IN Blue SCART2/EXT2 in
B-TXT Blue TeleteXT
B/G Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 5.5 MHz. B= VHF-
band, G= UHF-band
BOCMA Bimos one Chip Mid-end Architecture:
video and chroma decoder
C-FRONT Chrominance front input
CBA Circuit Board Assembly (also called
PCB or PWB)
CL Constant Level: audio output to
connect with an external amplifier
CLUT Colour Look-Up Table
COLUMBUS COLour LUMinance Baseband
Universal Subsystem. IC performing
noise reduction and 2D/3D comb
filtering
ComPair Computer aided rePair. A tool for
diagnosing a TV through a PC
controlled interface
CSM Customer Service Mode
CVBS Composite Video and Blanking Signal;
A single video signal that contains
luminance, colour, and timing
information
CVBS-EXT CVBS signal from external source
(VCR, VCD, etc.)
CVBS-INT CVBS signal from internal Tuner
CVBS-MON CVBS monitor signal
CVBS-TER-OUT CVBS TERrestrial OUTput signal
DAC Digital to Analogue Converter
DBE Dynamic Bass Enhancement: extra
low frequency amplification
DFU Directions For Use: Owner's manual
DNR Dynamic Noise Reduction / Digital
Noise Reduction; Noise reduction
feature of the set
DRAM Dynamic RAM; dynamically refreshed
RAM
DSP Digital Signal Processing
DST Dealer Service Tool; Special remote
control designed for dealers to enter
Page 88

EN 88 LC4.9E AB9.
Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
e.g. service mode (a DST-emulator is
available in ComPair)
DTS Digital Theatre System; A multi-
DVB Digital Video Broadcast; A method of
DVB-T DVB-Terrestrial; HDTV standard for
DVD Digital Versatile Disc
EEPROM Electrically Erasable and
EPG Electronic Program Guide: system
EU Europe
EXT EXTernal (source), entering the set by
FBL Fast BLanking; DC signal
FBL-SC1-IN Fast blanking signal for SCART1 in
FBL-SC2-IN Fast blanking signal for SCART2 in
FBL-TXT Fast Blanking Teletext
FM Field Memory; A memory chip that is
FMR Radio receiver that can receive the FM
FRC Frame Rate Converter
FRONT-C Front input chrominance (SVHS)
FRONT-DETECT Control line for detection of
FRONT-Y_CVBS Front input luminance or CVBS
G-SC1-IN Green SCART1/EXT1 in
G-SC2-IN Green SCART2/EXT2 in
G-TXT Green teletext
H H_sync to the module
HA Horizontal Acquisition; horizontal sync
HD High Definition
HP HeadPhone
I Monochrome TV system. Sound
2
I
C Integrated IC bus
2
I
S Integrated IC Sound bus
IC Integrated Circuit
IF Intermediate Frequency
Interlaced Scan mode where two fields are used
IR Infra Red
IRQ Interrupt ReQuest
Last Status The settings last chosen by the
LATAM LATin AMerica
LC04 Philips chassis name for LCD TV 2004
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
channel surround sound format,
similar to Dolby Digital
transmitting digital audio and video,
based on MPEG2
the EU
Programmable Read Only Memory
used by broadcasters to transmit TV
guide information (= NexTView)
SCART or by cinches (jacks)
accompanying RGB signals. To blank
the video signal when it is returning
from the right side of the screen to the
left side. The video level is brought
down below the black video level
capable of storing one or more TV
picture fields / Frequency Modulation;
A technique that sends data as
frequency variations of a carrier signal
Band 87.5 - 108 MHz
headphone insertion, Service Mode
jumper, power failure detection
(SVHS)
pulse
carrier distance is 6.0 MHz. VHF- and
UHF-band
to form one frame. Each field contains
half the number of the total amount of
lines. The fields are written in "pairs",
causing line flicker.
customer and read and stored in RAM
or in the NVM. They are called at startup of the set to configure it according
to the customer's preferences
project
LED Light Emitting Diode; A semiconductor
diode that emits light when a current is
passed through it
LINE-DRIVE Horizontal (line) deflection drive signal
(for the Line transistor)
L/L' Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 6.5 MHz. L' is Band
I, L is all bands except for Band I
LS LoudSpeaker
LVDS Low Voltage Differential Signalling,
data transmission system for high
speed and low EMI communication.
M/N Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 4.5 MHz. M= 525
lines @ 60 Hz, N= 625 lines @ 50 Hz
MOSFET Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field
Effect Transistor
MPEG Motion Pictures Experts Group. An
ISO/IEC body that has given its name
to an image compressing scheme for
moving video
MSP Multi-standard Sound Processor: ITT
sound decoder
MUTE MUTE Line
NC Not Connected
NICAM Near Instantaneously Companded
Audio Multiplexing; This is a digital
sound system, mainly used in Europe
NTSC National Television Standard
Committee. Colour system used
mainly in North America and Japan.
Colour carrier NTSC M/N = 3.579545
MHz, NTSC 4.43 = 4.433619 MHz
(this is a VCR norm, it is not
transmitted off-air)
NVM Non Volatile Memory; IC containing
data such as alignment values, preset
stations
O/C Open Circuit
ON/OFF LED On/Off control signal for the LED
OSD On Screen Display
PAL Phase Alternating Line. Colour system
used mainly in Western Europe
(colour carrier = 4.433619 MHz) and
South America (colour carrier PAL M =
3.575612 MHz and PAL N = 3.582056
MHz)
PC Personal Computer
PCB Printed Circuit Board (or PWB)
PIG Picture In Graphic
PIP Picture In Picture
PLL Phase Locked Loop. Used, for
example, in FST tuning systems. The
customer can directly provide the
desired frequency
Progressive Scan Scan mode where all scan lines are
displayed in one frame at the same
time, creating a double vertical
resolution.
PWB Printed Wiring Board (also called PCB
or CBA)
RAM Random Access Memory
RC Remote Control transmitter
RC5 or 6 Remote Control system 5 or 6, the
signal from the remote control receiver
RGB Red, Green, and Blue colour space;
The primary colour signals for TV. By
mixing levels of R, G, and B, all colours
(Y/C) are reproduced
RGBHV Red, Green, Blue, Horizontal sync,
and Vertical sync
ROM Read Only Memory
SAM Service Alignment Mode
SC SandCastle: two-level pulse derived
from sync signals
Page 89

Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
SC-IN SCART in
SC-OUT SCART out
S/C Short Circuit
SCART Syndicat des Constructeurs
d'Appareils Radiorécepteurs et
Téléviseurs; This is a 21-pin connector
used in EU, that carries various audio,
video, and control signals (it is also
SCL Serial CLock Signal on I
called Péritel connector)
SD Standard Definition
SDA Serial DAta Signal on I
SDRAM Synchronous DRAM
SECAM SÉquence Couleur Avec Mémoire;
Colour system mainly used in France
and East Europe. The chroma is FM
modulated and the R-Y and B-Y
signals are transmitted line
sequentially. Colour carriers=
4.406250 MHz and 4.250000 MHz
SIF Sound Intermediate Frequency
SMPS Switched Mode Power Supply
SND SouND
SNDL-SC1-IN Sound left SCART1 in
SNDL-SC1-OUT Sound left SCART1 out
SNDL-SC2-IN Sound left SCART2 in
SNDL-SC2-OUT Sound left SCART2 out
SNDR-SC1-IN Sound right SCART1 in
SNDR-SC1-OUT Sound right SCART1 out
SNDR-SC2-IN Sound right SCART2 out
SNDR-SC2-OUT Sound right SCART2 out
SOPS Self Oscillating Power Supply
S/PDIF Sony Philips Digital InterFace; This is
a consumer interface used to transfer
digital audio
SRAM Static RAM
STBY STandBY
SVHS Super Video Home System
SW Software or Subwoofer or Switch
THD Total Harmonic Distortion
TXT Teletext; TXT is a digital addition to
analogue TV signals that contain
textual and graphical information (25
rows x 40 columns). The information is
transmitted within the first 25 lines
during the Vertical Blank Interval (VBI)
uP Microprocessor
VA Vertical Acquisition
VL Variable Level out: processed audio
output towards external amplifier
VCR Video Cassette Recorder
VGA Video Graphics Array; 640x480 (4:3)
WD Watch Dog
WYSIWYR What You See Is What You Record:
record selection that follows main
picture and sound
XTAL Quartz crystal
Y Luminance signal
Y/C Y consists of luminance signal,
blanking level and sync; C consists of
chroma (colour) signal
YPbPr This is a scaled version of the YUV
colour space. Y= Luminance, Pb/Pr=
Colour difference signals B-Y and R-Y,
other amplitudes w.r.t. to YUV
YUV Colour space used by the NTSC and
PAL video systems. Y is the luminance
and U/V are the colour difference
signals
2
C bus
2
C bus
EN 89LC4.9E AB 9.
Page 90

EN 90 LC4.9E AB9.
9.12 IC Data Sheets
This section shows the internal block diagrams and pin layouts
of ICs that are drawn as "black boxes" in the electrical diagrams
(with the exception of "memory" and "logic" ICs).
9.12.1 Diagram K1, PNx83xx (IC7100)
Block Diagram
Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
16 bit@133 MHz
EJTAG, DSU
Priority int ctrl
Clock, Reset
Power down
I2C-unit1
I2C-unit2
GPIO
Infrared
Boot
CPU PR1910
Fast PI-Bus@120 MHz
PI Bridge DMA
Slow PI-Bus (60 MHz)
MPEG system processor
Video decoder
Audio decoder
Background color
Display
MIU
SDRAM interface
3L PVD
suB
Central Data Unit
suB
2
L PV
D
USB host
RS232-UART0
RS232-UART1
ISO7816-UART
Graphics (OSD)
Cursor
Mixer unit
DENC
Analog video
RGB, Y,C,CVBS
Figure 9-2 PNx831x architecture and data paths
CCIR
CCIR-656
E_14970_043.eps
020605
Page 91

Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
9.12.2 Diagram K6, TDA10046 (IC7600)
Block Diagram
EN 91LC4.9E AB 9.
VIM
VIP
SACLK
XIN
XOUT
SCL_TUN
SDA_TUN
SCL
SDA
SADDR(1:0)
ANALOG
A
D
C
Fsamp
PLL
O
S
C
spare inputs
Interface
I2C
ACI
Filtering
AGC_IF
DIGITAL FRONT-END
AND OFDM
DEMODULATION
Digital
AGC
FFT
2K/8K
Coarse
Time
Estimator
Dynamic
TimeShift
CHANNEL ESTIMATION
AND CORRECTION
OFDM Spectrum
CPE
calculation
Partial
Channel
Estimation
Time
Interpolation
Frequency
Interpolation
AGC_TUN
∆Σ
Dual AGC
10
Carrier
Recovery
Time
Recovery
∆Σ
DSP CORE
SYNCHRONISATION
GPIO(3:0)
MPEG-TS
(parallel)
MPEG-TS
(serial)
∆Σ
∆Σ
MPEG2
Output
Interface
∆Σ
∆Σ
Frequency, Time, Frame Recovery
FFT Window positioning
TPS decoding
Descrambler RS decoder Demapper
CPT_UNCOR
Outer
Forney
Deinterleaver
VBER
Viterbi
Decoder
CBER
Bit
Deinterleaver
CHANNEL DECODER
Figure 9-3 Internal blockdiagram TDA10046
Confidence
Calculation
Confidence
Channel
Correction
(I,Q)
Inner
Frequency
Deinterleaver
E_14970_044.eps
020605
Page 92

EN 92 LC4.9E AB10.
10. Spare Parts List
Spare Parts List
Set Level
Various
1004 8204 000 78181 PDP S42SD-YD07
1004
h 9322 224 88682 PDP PDP42V7A062
1012 3104 328 39571 LED panel LC04SD2
8102 3104 311 03601 Cable 7p/400/7p
8102 3104 311 07241 Cable 7P/1000/7P
8103 3104 311 06511 Cable 10p/280/10p
8103 3104 311 07391 Cable 10P/220/10P
h 3104 311 07421 Cable 6P/680/6P
8120
8146 3104 311 08621 Cable 11P/220/11P
8150 3104 311 08831 Cable 31P/300/31P
8150 3104 311 10493 Cable 31P/220/31P
h 3104 311 09921 Cable 9P/680/9P
8152
h 3104 311 07911 Cable ring/180/ring
8900
Set Level
Various
1014 3104 328 39561 Side control LC04SD2
1116 3104 328 40501 Side I/O Assy LC04SD2
8101 3104 311 10751 Cable 3P/1K7/3P
8136 3104 311 10733 Cable 11P/1K/11P
8735 3104 311 10601 Cable 2P3/1400/POSI
8736 3104 311 10591 Cable 2P3/1000/POSI
b
5213 2441 257 30020 Loudspeaker 8Ω 10W
5214 2441 257 30020 Loudspeaker 8Ω 10W
Small Signal Board [B]
Various
0605 3104 317 08961 Hercules SW for
0605 3104 317 08972 Hercules SW for
0605 3104 337 00011 Hercules SW for
0610 3104 317 09052 Scaler SW for 42PF7320
0610 3104 317 09062 Scaler SW for 42PF5320
0610 3104 337 00021 Scaler SW for 50PF7320
0620 3104 317 08881 DDC SW for 42PF7320
0620 3104 317 08891 DDC SW for 42PF5320
0620 3104 317 08901 DDC SW for 50PF7320
0635 3104 317 09141 EPLD SW for 42PF7320
0635 3104 337 00031 EPLD SW for 50PF7320
1062 2422 549 00148 Socket 3p m
h 2422 549 00151 Socket 3p m
1062
1101 2422 025 18749 Connector 3p m
1102 3139 147 19801 Tuner UV1318S/A IH -3
1104 2422 549 44372 SAW 38.9MHz K3953L
1106 2422 549 44369 SAW 38.9MHz K9656L
1107 2422 025 18749 Connector 3p m
1202 2422 543 01414 Xtal 24.576MHz
1801 2422 543 01133 Xtal 14.32MHz 20pF
1F00 2422 033 00515 Socket DVI-I 29p f
1F01 2422 026 05703 Socket 1P f
1G01 2422 025 18959 Socket 21P f shd
1G02 2422 025 18959 Socket 21P f shd
1J00 2422 025 10771 Connector 10p m
1J01 2422 025 10655 Connector 11p m
1J04 2422 025 10769 Connector 9p m
h 2422 086 11081 Fuse T3A 125V
1J07
1J08
h 2422 086 11105 Fuse F630mA 50V
1K00 2422 025 08149 Connector 6p m
1K02 2422 025 10768 Connector 3p m
1K04 2422 025 10655 Connector 11p m
1N01 2422 025 17274 Connector 10p m
42PF7320 (check Prod.
Survey)
42PF5320 (check Prod.
Survey)
50PF7320 (check Prod.
Survey)
(check Prod. Survey)
(check Prod. Survey)
(check Prod. Survey)
(check Prod. Survey)
(check Prod. Survey)
(check Prod. Survey)
(check Prod. Survey)
(check Prod. Survey)
1N02 2422 025 18779 Connector 4P m
1N05 2722 171 08825 Xtal 14.31818Mhz 15pF
1P01 2422 549 45325 Bead 67Ω at 100MHz
1P02 2422 549 45325 Bead 67Ω at 100MHz
1P03 2422 549 45325 Bead 67Ω at 100MHz
1P04 2422 549 45325 Bead 67Ω at 100MHz
1P05 2422 549 45325 Bead 67Ω at 100MHz
1P07 2422 025 18427 Connector 31p f
8321 3104 311 08731 Cable POSI/100/POSI
g
2101 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2102 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V 0603
2103 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V 0603
2104 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2105 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2106 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V 0603
2107 3198 024 44730 47nF 50V 0603
2109 5322 124 41945 22µF 20% 35V
2113 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2203 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2206 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2207 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2208 4822 124 12084 1µF 20% 50V
2209 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2210 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2211 2020 552 96628 10nF 10% 16V 0402
2214 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2216 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2218 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2221 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2223 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2225 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2226 3198 035 03320 3.3nF 5% 50V 0402
2227 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2228 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2230 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2231 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2232 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2233 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2234 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2235 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2236 4822 126 14076 220nF +80/-20% 25V
2237 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2238 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2239 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2240 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2241 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2242 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2243 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2244 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2245 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2246 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2250 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2251 2020 552 96656 10µF 20% 25V 1210
2252 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2253 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2254 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2255 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2256 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2257 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2258 2020 552 96637 10µF 10% 6.3V 0805
2259 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2260 2020 552 96637 10µF 10% 6.3V 0805
2262 4822 124 12082 10µF 20% 50V
2263 3198 035 26820 6.8nF 10% 16V 0402
2264 3198 017 44740 470nF 10V 0603
2265 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2266 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2267 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2269 2020 012 00003 470µF 16V 20% SMD
2270 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2271 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2272 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2273 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2274 3198 017 31540 150nF 10V 0603
2277 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2280 2020 552 00027 4.7µF 2% 6.3V 0603
2281 2020 552 00027 4.7µF 2% 6.3V 0603
h 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2285
2286 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2289
h 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
2290
h 2222 240 59872 4.7µF 5% 10V 0805
h 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2291
2449 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2501 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2502 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2503 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2504 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2505 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2506 3198 035 03310 330pF 5% 50V 0402
2507 3198 035 04710 470pF 50V 0402
2508 2238 869 15829 82pF 5% 50V 0402
2509 2238 869 15829 82pF 5% 50V 0402
2603 2020 552 96834 1µF 20% 6.3V 0402
2604 3198 035 04710 470pF 50V 0402
2605 2020 552 96834 1µF 20% 6.3V 0402
2608 2020 552 96834 1µF 20% 6.3V 0402
2609 3198 035 04710 470pF 50V 0402
2610 2020 552 96834 1µF 20% 6.3V 0402
2611 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2612 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2614 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2615 2020 012 00003 470µF 16V 20% SMD
2618 2020 012 00003 470µF 16V 20% SMD
2704 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2706 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2709 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2710 2020 552 96656 10µF 20% 25V 1210
2711 2020 552 96656 10µF 20% 25V 1210
2713 2020 012 00028 470µF 20% 16V
2714 3198 035 02210 220pF 5% 50V 0402
2715 2020 552 96455 22nF 10% 16V 0402
2716 2020 012 00028 470µF 20% 16V
2730 2020 552 96656 10µF 20% 25V 1210
2731 2020 012 00003 470µF 16V 20% SMD
2733 3198 035 02210 220pF 5% 50V 0402
2734 2238 787 16641 22nF 10% 16V 0402
2735 3198 035 04710 470pF 50V 0402
2736 2022 031 00308 22µF 20% 35V
2737 2020 012 00003 470µF 16V 20% SMD
2738 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2739 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2741 4822 126 13879 220nF +80-20% 16V
2750 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2753 2020 012 00003 470µF 16V 20% SMD
2755 3198 035 14720 4.7nF 5% 25V 0402
2756 3198 035 04710 470pF 50V 0402
2757 2020 012 00003 470µF 16V 20% SMD
2758 2020 012 00003 470µF 16V 20% SMD
2761 2020 552 96671 1µF 10% 25V
2762 4822 124 23237 22µF 6.3V
2800 2020 021 91557 100µF 20% 16V
2801 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2802 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2803 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2804 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2805 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2806 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2807 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2808 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2809 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2810 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2811 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2812 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2813 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2814 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2815 5322 124 41945 22µF 20% 35V
2816 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2817 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2818 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2819 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2820 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2821 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2822 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2823 4822 126 14519 22pF 5% 50V 0402
2824 4822 126 14519 22pF 5% 50V 0402
2900 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2901 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2902 2020 021 00046 470µF 20% 16V
2903 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2904 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2905 2020 021 91557 100µF 20% 16V
2906 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2907 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2908 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2909 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2910 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2911 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2912 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2913 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2914 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2915 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2916 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2917 2020 021 91557 100µF 20% 16V
2918 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2919 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
Page 93

Spare Parts List
EN 93LC4.9E AB 10.
2920 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2921 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2922 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2923 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2924 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2925 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2926 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2927 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2928 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2929 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2930 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2931 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2932 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2933 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2934 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2935 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2936 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2937 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2938 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2939 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2940 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2941 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2942 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2945 5322 124 41945 22µF 20% 35V
2946 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2947 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2948 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2949 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2950 5322 124 41945 22µF 20% 35V
2951 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2952 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2953 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2954 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2955 5322 124 41945 22µF 20% 35V
2956 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2957 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2958 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2959 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2A00 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2A01 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2A02 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2A12 2020 552 96628 10nF 10% 16V 0402
2A13 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B01 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2B02 4822 124 11131 47µF 6.3V
2B03 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B04 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B05 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B06 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B07 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B08 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B09 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B10 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B11 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B12 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B13 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B14 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B15 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B16 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B17 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2B18 5322 124 41945 22µF 20% 35V
2C00 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2C01 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2C02 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2C03 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E00 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E01 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E02 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E03 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E04 2020 552 96834 1µF 20% 6.3V 0402
2E05 2020 552 96834 1µF 20% 6.3V 0402
2E06 2020 552 96834 1µF 20% 6.3V 0402
2E07 4822 126 14324 33pF 5% 50V 0402
2E08 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E09 4822 126 14324 33pF 5% 50V 0402
2E10 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E11 4822 126 14324 33pF 5% 50V 0402
2E12 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E13 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2E14 4822 126 14324 33pF 5% 50V 0402
2E15 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E16 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E17 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E18 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E19 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E20 4822 124 11131 47µF 6.3V
2E21 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E22 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E23 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E24 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E25 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E26 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E27 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E28 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E29 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E30 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E31 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E32 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2E33 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E34 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E35 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2E36 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2F04 2020 552 94427 100pF 5% 50V
2F07 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2F08 4822 126 14241 330pF 0603 50V
2F09 4822 126 14241 330pF 0603 50V
2F10 2020 552 94427 100pF 5% 50V
2F11 4822 126 14241 330pF 0603 50V
2F12 4822 126 14241 330pF 0603 50V
2F13 4822 126 14508 180pF 5% 50V 0603
2F14 4822 126 14508 180pF 5% 50V 0603
2F15 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2F16 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2G05 4822 126 14241 330pF 0603 50V
2G06 4822 126 14508 180pF 5% 50V 0603
2G07 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2G08 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2G09 4822 126 14241 330pF 0603 50V
2G10 4822 126 14508 180pF 5% 50V 0603
2G11 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2G12 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2G18 4822 126 14241 330pF 0603 50V
2G19 4822 126 14508 180pF 5% 50V 0603
2G20 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2G21 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2G22 4822 126 14241 330pF 0603 50V
2G23 4822 126 14508 180pF 5% 50V 0603
2G24 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2G25 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2G26 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2G28 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2G47 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2G55 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2G56 2020 552 00005 4.7µF 10% 6.3V 0603
2J02 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2J03 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2J17 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2J18 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J19 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J21 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J22 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J23 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J26 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J27 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J28 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J29 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J30 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2J31 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2J35 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2K00 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2K01 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2K02 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2K03 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2K04 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2K05 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2K06 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K07 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K08 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2K10 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K11 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K12 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2K13 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K14 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K16 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K17 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K18 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K19 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2K20 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2K21 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K22 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K23 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K24 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K25 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K26 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K27 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2K28 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2L02 2020 552 96637 10µF 10% 6.3V 0805
2L03 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L04 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L05 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L06 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L07 2020 552 96637 10µF 10% 6.3V 0805
2L08 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L09 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L10 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L11 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L13 3198 035 74730 47nF 5% 16V 0402
2L17 3198 035 74730 47nF 5% 16V 0402
2L20 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L21 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L22 2020 552 96637 10µF 10% 6.3V 0805
2L23 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L24 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L26 2020 552 96718 220nF 10% 6.3V 0402
2L27 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2L28 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2L29 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2L30 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2L31 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2L32 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2L33 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L34 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2L37 4822 126 14524 68pF 5% 50V 0402
2L39 2238 869 15829 82pF 5% 50V 0402
2M00 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M01 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M02 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M03 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M04 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M05 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M06 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M07 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M08 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M09 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M10 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M11 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M12 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M13 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M14 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M15 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M16 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M17 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M18 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M19 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M20 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M21 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2M22 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M23 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2M24 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M25 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M26 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M27 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M28 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M29 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M30 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M31 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2M32 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2M56 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2M65 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M66 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2M67 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2M68 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2N01 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2N02 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2N03 2020 552 96834 1µF 20% 6.3V 0402
2N04 2020 552 96618 1nF 10% 50V 0402
2N05 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2N06 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2N07 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2N08 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2N09 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2N10 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2N11 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2N12 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2N13 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2N14 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2N15 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2N16 2238 869 15101 100pF 5% 50V 0402
2P01 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2P02 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P03 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P04 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P05 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P06 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P07 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P08 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P09 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P10 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P11 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P12 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P13 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P14 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P15 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2P16 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P17 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2P18 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2P19 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P20 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P21 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P22 2020 552 00035 2.2µF 6.3V 10% 0603
2P23 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P24 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
Page 94

EN 94 LC4.9E AB10.
Spare Parts List
2P25 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P26 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P27 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P28 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P29 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P30 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P31 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P32 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P33 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P34 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P35 3198 035 71040 100nF 10% 16V 0402
2P36 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2P37 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2P38 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2P39 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2P40 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2P41 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2P42 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2P43 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2P44 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
2P45 2238 869 15109 10pF 5% 50V 0402
f
3103 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3104 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3105 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3107 4822 051 30682 6.8Ω 5% 0.062W
3108 4822 051 30222 2.2kΩ 5% 0.062W
3109 4822 051 30222 2.2kΩ 5% 0.062W
3111 4822 051 30223 22kΩ 5% 0.062W
3112 4822 051 30183 18kΩ 5% 0.062W
3120 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3121 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3122 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3123 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3124 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3125 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3207 3198 031 06810 680Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3208 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3209 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3210 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3211 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3212 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3213 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3214 3198 031 06810 680Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3215 3198 031 02710 270Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3216 4822 117 13597 330Ω 5% 0402 0.01W
3217 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3218 4822 117 11297 100kΩ 5% 0.1W
3219 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3220 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3222 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3223 3198 031 01090 10Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3224 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3225 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3226 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3227 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3229 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3230 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3231 4822 117 13602 2.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3232 3198 031 03320 3.3kΩ 5% 0402
3233 3198 031 03320 3.3kΩ 5% 0402
3234 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3235 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3236 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3238 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3239 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3240 2322 704 61002 1kΩ 1%
3241 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3242 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3243 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3245 3198 031 02240 220kΩ 5% 0.1W 0402
3246 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3247 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3248 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3249 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3250 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3251 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3252 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3253 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3255 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3256 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3257 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3258 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3259 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3260 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3262 4822 117 13601 22kΩ 5% 0402
3263 2322 702 70398 3.9Ω 5% 0603
3264 4822 117 13601 22kΩ 5% 0402
3265 2322 702 70398 3.9Ω 5% 0603
3266 3198 031 05620 5.6kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3267 3198 031 05620 5.6kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3268 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3272 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3273 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3274 3198 031 03910 390Ω 1% 0402
3275 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3276 3198 031 07590 75Ω 5% 0402
3277 3198 031 01520 1.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
h 4822 117 11151 1Ω 5%
3280
3281 3198 031 03930 39kΩ 5% 0402
3285 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3286 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3292
h 3198 031 01230 12kΩ 5% 0402
h 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3294
h 4822 117 11297 100kΩ 5% 0.1W
3295
3431 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3451 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3453 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3454 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3455 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3456 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3458 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3459 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3461 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3462 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3501 4822 117 13543 470Ω 5% 0402
3502 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3604 4822 117 13601 22kΩ 5% 0402
3605 4822 117 13601 22kΩ 5% 0402
3609 4822 117 13601 22kΩ 5% 0402
3610 4822 117 11297 100kΩ 5% 0.1W
3611 4822 117 11297 100kΩ 5% 0.1W
3612 4822 117 13601 22kΩ 5% 0402
3616 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3617 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3619 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3620 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3628 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3629 4822 117 13601 22kΩ 5% 0402
3630 4822 117 13602 2.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3631 4822 117 13602 2.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3632 2322 705 70569 56Ω 5% 0402
3633 2322 705 70569 56Ω 5% 0402
3708 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3709 3198 031 06820 6.8kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3712 5322 117 13031 5.6kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3713 2322 704 63302 3.3kΩ 1% 0603
3716 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3732 2322 704 61002 1kΩ 1%
3733 2322 704 63302 3.3kΩ 1% 0603
3734 4822 117 13602 2.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3735 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3736 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3740 3198 031 01520 1.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3741 3198 031 01520 1.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3742 3198 031 01530 15kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3743 4822 117 13601 22kΩ 5% 0402
3750 4822 117 13601 22kΩ 5% 0402
3751 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3752 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3753 2322 704 61002 1kΩ 1%
3754 2322 704 63302 3.3kΩ 1% 0603
3759 3198 031 01230 12kΩ 5% 0402
3761 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3800 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3801 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3802 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3803 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3804 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3805 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3806 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3807 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3808 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3809 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3810 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3811 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3812 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3813 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3814 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3815 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3816 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3817 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3818 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3820 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3822 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3824 3198 031 03320 3.3kΩ 5% 0402
3825 3198 031 11030 4 x 10kΩ 5% 1206
3826 3198 031 11030 4 x 10kΩ 5% 1206
3827 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3828 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3829 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3831 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3832 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3833 3198 031 01090 10Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3834 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3835 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3836 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3837 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3838 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3839 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3840 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3841 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3900 3198 031 03320 3.3kΩ 5% 0402
3901 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3902 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3903 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3904 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3A00 3198 031 06890 68Ω 5% 0402
3A01 3198 031 06890 68Ω 5% 0402
3A07 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3A08 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3A10 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3A11 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3A13 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3A14 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3B01 4822 117 12706 10kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3B02 4822 117 12706 10kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3B03 2322 704 61501 150Ω 1% 0603
3C00 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3C01 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3C02 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3C04 3198 031 11030 4 x 10kΩ 5% 1206
3C05 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3C06 3198 031 11030 4 x 10kΩ 5% 1206
3C07 3198 031 11030 4 x 10kΩ 5% 1206
3C08 3198 031 11030 4 x 10kΩ 5% 1206
3C09 3198 031 11030 4 x 10kΩ 5% 1206
3C10 3198 031 11030 4 x 10kΩ 5% 1206
3C16 3198 031 11030 4 x 10kΩ 5% 1206
3C17 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3C18 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3E00 2322 705 70569 56Ω 5% 0402
3E01 2322 705 70569 56Ω 5% 0402
3E02 2322 705 70569 56Ω 5% 0402
3E06 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E07 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E08 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E09 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E10 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E11 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E12 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3E13 4822 117 13597 330Ω 5% 0402 0.01W
3E14 4822 117 13597 330Ω 5% 0402 0.01W
3E15 4822 117 13597 330Ω 5% 0402 0.01W
3E16 4822 117 13597 330Ω 5% 0402 0.01W
3E17 4822 117 13597 330Ω 5% 0402 0.01W
3E18 4822 117 13597 330Ω 5% 0402 0.01W
3E19 2322 705 70569 56Ω 5% 0402
3E20 2322 705 70569 56Ω 5% 0402
3E21 2322 705 70569 56Ω 5% 0402
3E22 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3E23 3198 031 08210 820Ω 5% 0.5W
3E24 4822 117 13543 470Ω 5% 0402
3E25 2322 705 70399 39Ω 5% 0402
3E26 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3E27 2322 705 70399 39Ω 5% 0402
3E28 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3E29 2322 705 70399 39Ω 5% 0402
3E30 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3E31 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E32 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E33 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E34 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E35 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E36 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E37 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3E38 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E39 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E41 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E42 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E43 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E44 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E45 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3E49 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3E50 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E51 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E52 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E53 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E54 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3E55 3198 031 04730 47Ω 5% 0402
3F00 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3F09 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3F10 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3F11 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3F16 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F17 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F18 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F19 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3F20 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
Page 95

Spare Parts List
EN 95LC4.9E AB 10.
3F21 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F22 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F23 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F24 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F25 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F26 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F27 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3F28 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3F29 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3G00 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3G01 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G02 4822 117 12891 220kΩ 1%
3G03 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G04 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3G05 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G06 4822 117 12891 220kΩ 1%
3G07 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G08 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3G12 2122 118 06408 91Ω 5% 0603
3G13 2122 118 06408 91Ω 5% 0603
3G14 2122 118 06408 91Ω 5% 0603
3G15 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3G16 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3G17 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3G26 4822 051 30273 27kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G27 4822 051 30682 6.8Ω 5% 0.062W
3G28 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3G29 4822 051 30331 330Ω 5% 0.062W
3G30 4822 051 30689 68Ω 5% 0.063W 0603
3G31 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3G32 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G33 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3G34 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G37 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3G38 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G39 4822 117 12891 220kΩ 1%
3G40 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G41 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3G42 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G43 4822 117 12891 220kΩ 1%
3G44 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G45 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3G46 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3G47 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3G48 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3G51 4822 051 30273 27kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G52 4822 051 30682 6.8Ω 5% 0.062W
3G53 4822 051 30689 68Ω 5% 0.063W 0603
3G54 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3G57 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3G58 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3G59 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3G60 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3G96 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3G99 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3J05 3198 031 06890 68Ω 5% 0402
3K00 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3K01 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3K02 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3K03 3198 031 01530 15kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3K05 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3K06 3198 031 01530 15kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3K07 2322 705 70399 39Ω 5% 0402
3K09 2322 705 70399 39Ω 5% 0402
3K11 3198 031 06890 68Ω 5% 0402
3K12 3198 031 06890 68Ω 5% 0402
3K13 3198 031 06890 68Ω 5% 0402
3L00 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3L04 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3L05 3198 031 01510 150Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3L06 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3L10 4822 117 13597 330Ω 5% 0402 0.01W
3L11 3198 031 01510 150Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3L12 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3L16 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3L17 3198 031 01510 150Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3L19 3198 031 01510 150Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3L20 3198 031 01510 150Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3L21 4822 117 13602 2.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3L22 4822 117 13602 2.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3L24 4822 117 13602 2.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3L25 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3L26 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3L27 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3L28 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3L30 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3L31 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3L32 4822 117 13602 2.2kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3L33 4822 117 13596 220Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3L34 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3L35 4822 117 13596 220Ω 5% 0.01W 0402
3L36 3198 031 03320 3.3kΩ 5% 0402
3L37 3198 031 03320 3.3kΩ 5% 0402
3M01 2350 035 10689 4 x 68Ω 5%
3M02 2350 035 10689 4 x 68Ω 5%
3M03 2350 035 10689 4 x 68Ω 5%
3M04 2350 035 10689 4 x 68Ω 5%
3M06 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3M07 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3M08 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3M09 2350 035 10229 4 x 22Ω 5% 1206
3M11 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3M13 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3M14 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3M15 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3M16 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3M26 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3M27 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3M50 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3M51 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3M52 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3M53 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3M54 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3M55 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3M56 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3M57 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3M58 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3M59 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3M78 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3M79 3198 031 03320 3.3kΩ 5% 0402
3M87 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3M89 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3M90 3198 031 02290 22Ω 5% 0.1W 0402
3N01 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N02 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N03 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N04 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N05 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N06 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N07 4822 051 30333 33kΩ 5% 0.062W
3N08 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N09 4822 117 13548 1kΩ 5% 0402
3N10 4822 117 13603 33kΩ 5% 0402
3N11 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3N12 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N13 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N14 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N15 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3N16 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3N17 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3N18 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3N19 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3N20 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3N21 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N22 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N23 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N24 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N25 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N26 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3N27 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3N28 4822 051 30181 180Ω 5% 0.062W
3N29 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N30 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N31 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N32 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N33 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N34 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N35 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N46 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3N47 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3P01 3198 031 04720 4.7kΩ 5% 0402
3P03 4822 117 13546 47Ω 5% 0402
3P04 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3P04 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3P05 4822 117 13545 100Ω 1% 0402
3P05 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
3S00 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3S03 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
4211 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4212 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4440 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4441 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4501 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4502 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4504 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4511 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4801 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4A04 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4J01 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4K04 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4K05 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4L02 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M00 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M01 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M02 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M03 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M05 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M08 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M09 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M10 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M16 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4M17 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N01 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N02 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N03 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N04 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N05 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N06 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N07 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N08 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N09 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N10 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N11 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N12 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N13 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N14 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N15 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N16 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N17 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N18 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N19 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N20 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N21 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4N22 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
4P07 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
b
5101 3198 018 33970 0.39µF 10% 0805
5103 4822 157 71334 0.68µH 5% 1008
5107 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
5108 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
5201 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5202 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5203 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5204 2422 549 42896 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5205 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5206 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5207 2422 549 42896 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5208 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5209 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5210 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5211 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5212 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5213 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5214 2422 536 00667 1000µF 20% 7032
5216 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
h 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5218
5501 3198 018 31080 1µF 10% 0805
5704 4822 157 63635 10µF 20% 1206
5709 2422 535 94134 10µH 20% 0805
5712 2422 536 00339 33µ 20%
5713 2422 535 94995 10µF 20% 10145
5730 2422 535 94134 10µH 20% 0805
5733 2422 536 00689 220µF 20%
5735 2422 536 00667 1000µF 20% 7032
5737 2422 535 94134 10µH 20% 0805
5738 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5752 2422 535 94134 10µH 20% 0805
5753 2422 536 00689 220µF 20%
5754 2422 535 94134 10µH 20% 0805
5900 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5901 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5902 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5903 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5904 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5905 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5906 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5907 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5908 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5909 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5910 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5911 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5A00 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5C00 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5E00 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5E01 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5E02 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5E03 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5F00 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5F01 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5F02 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5F03 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5G02 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5J01 2422 549 42896 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5J02 2422 549 42896 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5J03 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5J04 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5L00 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5L01 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5L02 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
Page 96

EN 96 LC4.9E AB10.
Spare Parts List
5M00 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5M01 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5M02 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5M03 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5M04 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5M05 2422 549 45333 Bead 120Ω 100MHz
5N01 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5N02 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5N03 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5N04 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5N05 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5P01 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5P02 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5P03 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5P04 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5P05 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5P06 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
d
6101 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6102 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6103 4822 130 11397 BAS316
6104 4822 130 11525 1SS356
6204 4822 130 80622 BAT54
6205 4822 130 80622 BAT54
6430 9340 548 42115 PDZ2.4B
6431 9965 000 20150 1N4148WS SOD-323
6601 4822 130 10838 UDZ3.3B
6708 3198 010 10720 SS24
6709 9322 128 70685 SMSS14
6712 3198 010 10730 SS36
6733 9322 128 70685 SMSS14
6735 5322 130 34337 BAV99
6736 9340 548 71115 PDZ33B
6740 4822 130 10837 UDZS8.2B
6751 9322 128 70685 SMSS14
6E01 9322 102 64685 UDZ2.7B
6E03 9322 102 64685 UDZ2.7B
6F00 4822 130 11397 BAS316
6F01 4822 130 11397 BAS316
6G03 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6G04 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6G05 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6G06 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6G07 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6G08 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6G09 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6G10 4822 130 11416 PDZ6.8B
6N01 9322 085 77685 TLMG3100
ce
7101 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7201 9340 550 49115 PUMH7
7202 9340 550 49115 PUMH7
7206 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7207 9322 214 45668 M24C16-WMN6P
7208 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7209 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7210 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7214 9339 693 90135 BCP69-25
7215 9339 693 90135 BCP69-25
7216 9340 425 20115 BC847BS
7217 9352 780 22557 TDA15021H/N1B91
h 4822 209 60792 74HC4053D
7219
7430 4822 130 11155 PDTC114ET
7436 9352 607 39118 74LVC14APW
7501 9322 199 16668 M74HC590T
7502 9322 201 05671 CY62256LL-70ZC
7503 9322 199 16668 M74HC590T
7504 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7505 9351 870 00118 74HC573PW
7506 9351 870 00118 74HC573PW
7601 9322 183 05668 TS482ID
7602 9351 742 70118 74HC08PW
7603 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7604 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7605 9340 310 50215 PDTA143ET
7606 9340 425 20115 BC847BS
7708 9322 139 16668 LF33CPT
7710 9322 202 34668 L5973D
7730 9322 191 07668 IC SM L5970D
7735 4822 130 42804 BC817-25
7738 9322 163 24668 L78M08CDT
7741 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7742 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7752 5322 209 90529 MC34063AD
7756 4822 130 11155 PDTC114ET
7758 9322 212 14668 SI4423DY
7801 9322 219 57671 GM1501H-LF-BD
For SW see item 0605
7900 9322 142 88668 LF25CDT
7901 9322 189 19668 LD1086D2T18
7A00 9352 759 98118 PCA9515ADP
7A02 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7A03 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7B01 9322 214 42671 K4D263238F-QC50
7C00 9322 205 12671 MX29LV040QC-70G
7C01 9322 206 23668 M24C32-WMN6P
7C02 9322 215 39685 PST596JN
7E00 9322 195 23668 ADG733BRU
7E01 9322 199 80668 SM5301BS-G
7E02 9322 199 56668 ADG781BCP
7E03 4822 209 60792 74HC4053D
7E04 9352 607 39118 74LVC14APW
7E05 9352 607 39118 74LVC14APW
7F03 9322 206 24668 M24C02-WMN6P
7G03 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7G05 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7G10 4822 209 60792 74HC4053D
7L01 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7L02 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7L03 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7L04 9322 212 77672 MST9883C-LF-110
7L05 4822 209 17398 LD1117DT33
7L06 9965 000 04199 BSN20
7L07 9965 000 04199 BSN20
7M00 9322 204 76671 T6TU5XBG-0001
7M01 9322 206 19672 MSM56V16160F-7T3-FG
7M03 9322 170 14668 LF15ABDT
7N01 9322 210 01668 EPCS4SI8N
7N02 9322 217 35671 EP1C12F256C8N
7N03 9340 425 20115 BC847BS
7N04 9322 210 59668 THC63LVDF84B
7P01 9322 170 14668 LF15ABDT
7P02 9322 201 03668 THC63LVDM83R
For SW see item 0610
For SW see item 0620
For SW see item 0635
PDP Audio [C]
Various
1735 4822 267 10918 Connector 3p
1736 2422 025 10768 Connector 3p m
1M02 4822 267 10618 Connector 7p
1M06 2422 025 11244 Connector 7p m
1M52 2422 025 10769 Connector 9p m
g
2700 4822 126 14247 1.5nF 50V 0603
2701 4822 126 14249 560pF 10% 50V 0603
2703 2020 552 96683 220nF 10% 50V
2704 4822 124 11767 470µF 20% 25V
2705 4822 126 14249 560pF 10% 50V 0603
2706 5322 126 11579 3.3nF 10% 63V
2707 2222 580 15649 100nF 10% 50V 0805
2709 2020 552 96683 220nF 10% 50V
2710 2020 552 96683 220nF 10% 50V
2711 2022 552 05679 1µF 10% 16V 0805
2712 4822 126 14583 470nF 10% 16V 0805
2713 4822 126 13193 4.7nF 10% 63V
2715 4822 121 51252 470nF 5% 63V
2716 3198 017 31530 15nF 20% 50V 0603
2717 2022 552 05679 1µF 10% 16V 0805
2718 2222 580 15649 100nF 10% 50V 0805
2719 4822 126 14583 470nF 10% 16V 0805
2720 2020 021 91431 22µF 20% 100V
2721 2222 580 15649 100nF 10% 50V 0805
2722 4822 126 14583 470nF 10% 16V 0805
2723 2022 552 05679 1µF 10% 16V 0805
2726 4822 126 13193 4.7nF 10% 63V
2727 4822 126 14249 560pF 10% 50V 0603
2731 4822 126 14249 560pF 10% 50V 0603
2732 4822 126 14583 470nF 10% 16V 0805
2736 4822 121 51252 470nF 5% 63V
2737 3198 017 31530 15nF 20% 50V 0603
2739 2222 580 15649 100nF 10% 50V 0805
2741 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2743 3198 016 31020 1nF 25V 0603
2744 2222 580 15649 100nF 10% 50V 0805
2745 2020 552 96683 220nF 10% 50V
2746 4822 124 11767 470µF 20% 25V
2747 2022 552 05679 1µF 10% 16V 0805
2748 4822 126 14247 1.5nF 50V 0603
2749 5322 126 11579 3.3nF 10% 63V
2751 4822 124 40433 47µF 20% 25V
2754 2020 021 91431 22µF 20% 100V
2770 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2776 2020 021 91431 22µF 20% 100V
2780 4822 126 14583 470nF 10% 16V 0805
2789 4822 126 14583 470nF 10% 16V 0805
2791 4822 126 13879 220nF +80-20% 16V
f
3700 4822 051 30561 560Ω 5% 0.062W
3701 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3702 3198 021 38220 8.2kΩ 5% 0.062W 0603
3703 3198 021 38220 8.2kΩ 5% 0.062W 0603
3704 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3705 4822 051 30222 2.2kΩ 5% 0.062W
3706 4822 051 30682 6.8Ω 5% 0.062W
3707 4822 051 30393 39kΩ 5% 0.062W
3708 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3709 4822 051 30272 2.7kΩ 5% 0.062W
3710 4822 051 30393 39kΩ 5% 0.062W
3711 2322 762 60568 5.6Ω 5% 5% 2512
3712 4822 051 30272 2.7kΩ 5% 0.062W
3713 4822 051 30332 3.3Ω 5% 0.062W
3714 4822 051 30682 6.8Ω 5% 0.062W
3715 2322 762 60568 5.6Ω 5% 5% 2512
3716 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3717 4822 051 30222 2.2kΩ 5% 0.062W
3718 4822 051 30561 560Ω 5% 0.062W
3719 4822 051 30124 120kΩ 5% 0.062W
3720 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3721 4822 051 30471 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3722 4822 051 30124 120kΩ 5% 0.062W
3723 4822 051 30471 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3724 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3725 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3726 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3727 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3728 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3729 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3730 4822 051 30223 22kΩ 5% 0.062W
3731 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3732 4822 051 30223 22kΩ 5% 0.062W
3733 4822 051 30562 5.6kΩ 5% 0.063W 0603
3734 4822 051 30223 22kΩ 5% 0.062W
3735 4822 117 12889 270kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3736 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3737 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3738 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3760 4822 051 30223 22kΩ 5% 0.062W
3764 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3765 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3777 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3778 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3999 4822 051 30472 4.7Ω 5% 0.062W
9710 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9711 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9712 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9713 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9748 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9757 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9758 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9759 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9760 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9761 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9762 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9763 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9764 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9765 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9766 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9768 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9770 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9790 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9795 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9796 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9806 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9807 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
9808 4822 051 20008 Jumper 0805
b
5700 2422 536 00942 33µH 20%
5701 4822 157 11716 Bead 30Ω at 100MHz
5702 2422 536 00942 33µH 20%
5705 4822 157 11411 Bead 80Ω at 100MHz
5708 4822 157 11411 Bead 80Ω at 100MHz
d
6700 4822 130 11522 UDZ15B
6702 9322 150 18685 BZX384-C47
6703 4822 130 10838 UDZ3.3B
Page 97

Spare Parts List
EN 97LC4.9E AB 10.
ce
7700 9322 202 89668 LM393P
7701 9352 729 65112 TDA8925ST/N1
7702 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7705 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7706 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7707 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7708 3198 010 42320 BC857BW
7709 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7710 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7711 3198 010 42320 BC857BW
7712 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7713 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
LED Panel [J]
Various
0345 2422 025 18741 Connector 6p m
1040 9322 206 81667 TSOP34836YA1
g
2040 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
f
3040 4822 117 13597 330Ω 5% 0402 0.01W
3051 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3061 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3063 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
3078 3198 031 02250 2.2MΩ 5% 0.1W 0402
9012 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9041 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9042 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9062 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9066 4822 117 13606 10kΩ 5% 0.01W 0402
9070 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9081 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9082 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9111 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9112 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9115 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
9122 4822 117 13605 Jumper 0402
d
6051 9322 218 97685 SML-310VTK
6060 9322 134 46685 SML-310MT
6070 9322 140 63685 TEMD5000
ce
7051 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7052 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7062 4822 130 60373 BC856B
IBO Zapper Panel [K]
Various
0188 3139 124 62521 IDTV BRACKET
0315 3139 120 41531 SCR T10 SERR ST ZN
1301 2422 025 10768 Connector 3p m
1304 4822 252 51187 19398E1(0,500A)
1401 4822 267 31729 Connector cinch 1p
1402 4822 267 10459 Connector 3p
1403 2422 025 18799 Socket USB 4p f
1500 2422 025 18872 Connector 32p f
1600 3112 297 13381 TUNER TD1316/SPHP
1700 2422 033 00364 Connector smartcard
8301 3139 110 27701 Cable 03P/480/03P
8500 3139 131 06221 Cable 32P/400/32P
8600 3139 131 05451 Cable 340
g
2100 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2101 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2102 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2103 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2104 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2105 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2106 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2107 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
M3X8
2108 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2109 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2110 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2111 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2112 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2113 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2114 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2115 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2116 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2119 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2120 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2121 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2130 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2131 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2132 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2133 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2203 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2204 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2206 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2207 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2208 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2209 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2210 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2211 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2212 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2213 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2214 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2300 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2301 4822 124 40849 330UF 20% 16V
2302 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2304 2020 021 91506 1000µF 20% 16V
2305 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2306 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2308 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2309 4822 124 40849 330UF 20% 16V
2311 2020 021 91687 470µF 20% 16V
2313 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2314 3198 017 33330 33nF 20% 16V 0603
2315 4822 124 40849 330UF 20% 16V
2317 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2318 2020 021 91687 470µF 20% 16V
2319 2020 021 91634 100µF 25V
2320 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2324 3198 017 44740 470nF 10V 0603
2325 3198 017 44740 470nF 10V 0603
2326 3198 017 44740 470nF 10V 0603
2327 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2328 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2329 4822 126 13193 4.7nF 10% 63V
2330 2020 021 91687 470µF 20% 16V
2331 4822 126 13193 4.7nF 10% 63V
2332 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2333 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V 0603
2334 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2335 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2336 4822 126 13193 4.7nF 10% 63V
2337 4822 124 11947 10µF 20% 16V
2337 4822 124 22652 2.2µF 20% 50V
2403 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2405 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2406 3198 032 27190 100µF 6.3V
2411 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2412 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2413 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2500 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2501 2020 552 94427 100pF 5% 50V
2502 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2503 2020 552 94427 100pF 5% 50V
2504 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2505 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2506 4822 124 12084 1µF 20% 50V
2507 4822 126 13193 4.7nF 10% 63V
2508 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2509 2020 552 94427 100pF 5% 50V
2510 2020 552 94427 100pF 5% 50V
2511 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2512 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2513 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2514 4822 124 12084 1µF 20% 50V
2515 4822 126 13193 4.7nF 10% 63V
2520 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2521 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2522 4822 126 14315 390pF 5% 50V 0603
2523 4822 126 14315 390pF 5% 50V 0603
2524 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2525 4822 126 14315 390pF 5% 50V 0603
2526 4822 126 14315 390pF 5% 50V 0603
2527 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2528 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2529 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2530 4822 126 14315 390pF 5% 50V 0603
2531 4822 126 14315 390pF 5% 50V 0603
2532 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2533 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2534 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2535 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2536 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2537 4822 126 14315 390pF 5% 50V 0603
2538 4822 126 14315 390pF 5% 50V 0603
2539 4822 126 13879 220nF +80-20% 16V
2540 4822 126 13879 220nF +80-20% 16V
2543 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2544 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2550 4822 126 13879 220nF +80-20% 16V
2551 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2553 4822 126 13879 220nF +80-20% 16V
2554 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V 0603
2555 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2556 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2607 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2608 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2609 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2610 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2611 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2612 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2613 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2614 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2615 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2617 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2618 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2619 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2620 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2621 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2622 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2623 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2624 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2625 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2626 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2627 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2628 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2629 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2630 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2631 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2632 4822 122 33741 10pF 10% 50V
2700 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2701 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2702 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2703 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2704 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2705 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2706 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2707 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2708 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2709 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2710 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2711 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2712 2238 586 59812 100nF 20% 50V 0603
2713 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2714 5322 126 11578 1nF 10% 50V 0603
2715 2020 552 94427 100pF 5% 50V
f
3100 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3101 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3112 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3116 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3117 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3119 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3128 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3130 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3131 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3133 9965 000 23109 22Ω 5% 0603
3134 9965 000 23109 22Ω 5% 0603
3135 9965 000 23109 22Ω 5% 0603
3137 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3138 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3139 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3140 5322 117 13036 1.2kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3141 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3142 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3143 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3144 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3146 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3147 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3151 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3154 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3156 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3157 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3158 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3159 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3160 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3161 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3162 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3163 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3200 4822 051 30332 3.3Ω 5% 0.062W
3205 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
Page 98

EN 98 LC4.9E AB10.
Spare Parts List
3206 4822 051 30332 3.3Ω 5% 0.062W
3207 4822 051 30332 3.3Ω 5% 0.062W
3209 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3210 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3211 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3300 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3301 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3303 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3304 5322 117 13046 1.8kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3306 2322 704 61002 1kΩ 1%
3307 2322 704 61001 100Ω 1% 0603
3312 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3313 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3314 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3315 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3316 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3317 2322 704 63302 3.3kΩ 1% 0603
3318 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3319 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3320 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3321 3198 021 31080 1Ω 5% 0603
3322 5322 117 13042 3.9kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3323 5322 117 13057 820Ω 1% 0.063W 0603
3324 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3325 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3326 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3327 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3328 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3330 3198 021 31820 1.8kΩ 5% 0.062W 0603
3331 2322 704 61001 100Ω 1% 0603
3332 5322 117 13055 75Ω 1% 0.063W 0603
3333 4822 051 30273 27kΩ 5% 0.062W
3333 4822 117 12925 47kΩ 1% 0.063W 0603
3334 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3334 4822 051 30333 33kΩ 5% 0.062W
3403 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3404 4822 051 30561 560Ω 5% 0.062W
3405 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3406 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3407 4822 051 30689 68Ω 5% 0.063W 0603
3411 4822 051 30181 180Ω 5% 0.062W
3420 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3421 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3422 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3423 4822 051 30153 15kΩ 5% 0.062W
3500 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3501 4822 117 12968 820Ω 5% 0.62W
3502 4822 051 30683 68kΩ 5% 0.062W
3503 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3504 4822 117 13613 2.2Ω 5% 0603
3505 4822 117 12968 820Ω 5% 0.62W
3506 4822 051 30333 33kΩ 5% 0.062W
3507 4822 051 30152 1.5Ω 5% 0.062W
3508 4822 117 13613 2.2Ω 5% 0603
3509 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3510 4822 051 30683 68kΩ 5% 0.062W
3511 4822 117 12968 820Ω 5% 0.62W
3512 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3513 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3514 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3515 4822 051 30333 33kΩ 5% 0.062W
3516 4822 117 12968 820Ω 5% 0.62W
3517 4822 051 30152 1.5Ω 5% 0.062W
3519 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3520 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3521 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3522 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3523 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3526 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3527 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
h 5322 117 11726 10Ω 5%
3528
3530 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3532 4822 051 30561 560Ω 5% 0.062W
3533 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3534 4822 117 12891 220kΩ 1%
3535 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3537 4822 117 12891 220kΩ 1%
3538 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3539 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3540 4822 051 30561 560Ω 5% 0.062W
3547 4822 051 30759 75Ω 5% 0.062W
3548 4822 051 30561 560Ω 5% 0.062W
3557 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3558 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3559 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3560 4822 051 30273 27kΩ 5% 0.062W
3561 4822 051 30271 270Ω 5% 0.062W
3562 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3563 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3564 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3565 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3566 4822 051 30273 27kΩ 5% 0.062W
3567 4822 051 30271 270Ω 5% 0.062W
3568 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3570 4822 051 30689 68Ω 5% 0.063W 0603
3571 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3606 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3607 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3608 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3609 4822 051 30472 4.7Ω 5% 0.062W
3610 4822 051 30472 4.7Ω 5% 0.062W
3612 4822 051 30472 4.7Ω 5% 0.062W
3613 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3614 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3615 4822 051 30102 1kΩ 5% 0.062W
3618 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3619 4822 117 13632 100kΩ 1% 0603 0.62W
3621 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3622 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3623 4822 051 30472 4.7Ω 5% 0.062W
3624 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3625 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3626 4822 051 30272 2.7kΩ 5% 0.062W
3627 4822 051 30272 2.7kΩ 5% 0.062W
3629 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3630 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3631 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3635 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3636 4822 051 30684 680kΩ 5% 0.062W
3637 4822 117 12891 220kΩ 1%
3638 4822 051 30331 330Ω 5% 0.062W
3639 4822 051 30391 390Ω 5% 0.062W
3640 4822 051 30684 680kΩ 5% 0.062W
3641 4822 117 12891 220kΩ 1%
3642 4822 051 30331 330Ω 5% 0.062W
3643 4822 051 30331 330Ω 5% 0.062W
3644 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3645 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3700 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3701 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3702 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3703 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3704 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3705 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3707 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3708 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3709 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3710 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3711 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3712 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3713 2322 704 62002 2kΩ 1%
3715 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3716 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3717 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3718 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3719 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3720 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3721 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3722 4822 051 30103 10kΩ 5% 0.062W
3723 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3724 3198 031 13390 4X 33Ω 5% 1206
3725 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3726 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3727 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3728 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3729 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3730 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3731 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3732 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3733 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3734 4822 117 13573 4 x 47Ω 5%
3738 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3739 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3740 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3741 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3742 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3743 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3744 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3745 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3746 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3747 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3748 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3749 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3750 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3751 4822 051 30472 4.7Ω 5% 0.062W
3752 4822 051 30472 4.7Ω 5% 0.062W
b
5100 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5101 4822 157 11717 Bead 50Ω at 100MHz
5102 4822 157 11717 Bead 50Ω at 100MHz
5103 4822 157 11717 Bead 50Ω at 100MHz
5201 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5202 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5203 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5300 2422 536 00491 47µ
5301 4822 157 10452 10µH 10%
5302 2422 535 94639 10µH 20%
5303 2422 536 00548 100µ
5304 4822 157 10452 10µH 10%
5305 2422 536 00548 100µ
5306 4822 157 10452 10µH 10%
5307 2422 535 94639 10µH 20%
5309 3198 018 90050 Bead 1kΩ at 100MHz
5401 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5420 2422 549 44197 Bead 220Ω at 100MHz
5502 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5504 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5505 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5507 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5508 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5511 3198 018 52280 2.2µF 10% 1008
5512 3198 018 52280 2.2µF 10% 1008
5513 3198 018 52280 2.2µF 10% 1008
5514 3198 018 52280 2.2µF 10% 1008
5528 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5600 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5601 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5602 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5700 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5701 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5702 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5703 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
5704 4822 157 11499 Bead 60Ω at 100MHz
d
6300 9322 128 70685 SMSS14
6303 9322 128 70685 SMSS14
6304 9322 128 70685 SMSS14
6307 9965 000 20150 1N4148WS SOD-323
6400 9340 548 52115 PDZ5.1B
6401 4822 130 10837 UDZS8.2B
6403 4822 130 10837 UDZS8.2B
6503 4822 130 11397 BAS316
6504 4822 130 11397 BAS316
ce
7100 9352 744 74557 SM PNX8316HS/C102
7200 9322 206 20668 M29W320DT70N6F
7202 9322 213 88668 K4S281632F-TC60
7203 9322 130 41668 M24C64-WMN6
7300 4822 209 60059 MC34063AP1
7301 9322 184 19687 LD1117V18
7302 9322 216 98687 LD1117V
7303 4822 209 60059 MC34063AP1
7305 4822 209 60059 MC34063AP1
7306 9322 165 15685 NCP303LSN30
7307 9322 202 15687 LD1117V50
7308 9322 202 15687 LD1117V50
7309 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7310 3198 010 70510 TL431CZ
7311 9322 214 70685 SM SI2314EDS-E3
7312 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7402 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7403 9322 150 49668 LM3525M-H
7500 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7501 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7502 9352 668 39118 SM UDA1334ATS/N2
7503 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7504 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7505 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7506 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7507 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7510 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7511 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7512 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7513 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7514 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7600 9352 732 45557 TDA10046AHT/C1
7601 5322 209 70225 LM393D
7605 9352 630 16165 SM 74AHC1GU04GW
7606 9352 630 16165 SM 74AHC1GU04GW
7700 9322 172 92671 CIMAX 2.0
7701 9352 190 10118 74LVC573ADB
7702 9352 190 10118 74LVC573ADB
7703 9352 115 40118 74LVC245APW
7704 2722 171 08821 XTL 27MHz 50pF
7705 9322 175 13668 ST890CD
Page 99

11. Revision List
Manual xxxx xxx xxxx.0
• First release.
Revision List
EN 99LC4.9E AB 11.
 Loading...
Loading...