Page 1

1
CL 96532047_013.eps
270599
Colour Television Chassis
L9.2A
AA
Contents Page
1. Technical Specifications 2
2. Safety- and maintenance instructions, 3
warnings and notes. 4
3. Directions for use 5
4. Mechanical instructions 14
5. Service modes, faultfinding and repair tips 15
6. Faultfinding trees 21
Supply voltage diagram 25
Blockdiagram 26
Testpointsoverview and oscillograms 27
Electrical diagram’s en PWB’s Diagram PWB
7.
Power supply (Diagram A1) 28 34/37
Diversity table A1 29
Horizontal deflection (Diagram A2) 30 34/37
Vertical deflection (Diagram A3) 31 34/37
Synchronisation (Diagram A4) 31 34/37
Tuner en video IF (TDA 8844) (Diagram A5) 32 34/37
Diversity table A5 33
Video processing (Diagram A6) 38 34/37
Control (Diagram A7) 39 34/37
Front control (Diagram A8) 40 34/37
Smart sound & mono amplifier (Diagram A10) 41 34/37
Front cinch and headphone (Diagram A11) 42 34/37
Rear IO Cinches (Diagram A12) 43 34/37
CRT Panel (Diagram B) 44 45
BTSC decoder (Diagram C1) 46 48
BTSC Audio amplifier (Diagram C2) 47 48
ITT Audio decodering (Diagram D1) 49 45
ITT Audio amplifier (Diagram D2) 50 45
Side AV panel (Diagram E) 51 51
8. Alignments 53
9. Circuit description new circuits and 56
list of abbreviations 61
10. Spareparts list 64
Copyright reserved 1999 Philips Consumer Electronics B.V. Eindhoven, The
Netherlands. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means,
electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of
Philips.
Published by JvR 9965 Service PaCE Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification 5 4822 727 21705
Page 2
GB 2 L9.2A1.
Technical Specifications
1. Technical Specifications
1.1 Specifications
Mains voltage : 150V - 276Vac;
Mains frequency : 50 - 60Hz
Maximum power consumption :
• 14" : 40W +/- 10%
• 20" : 56W +/- 10%
• 21" : 58W +/- 10%
Standby power consumption : 10W +/- 10%
Max. Antenne-input :
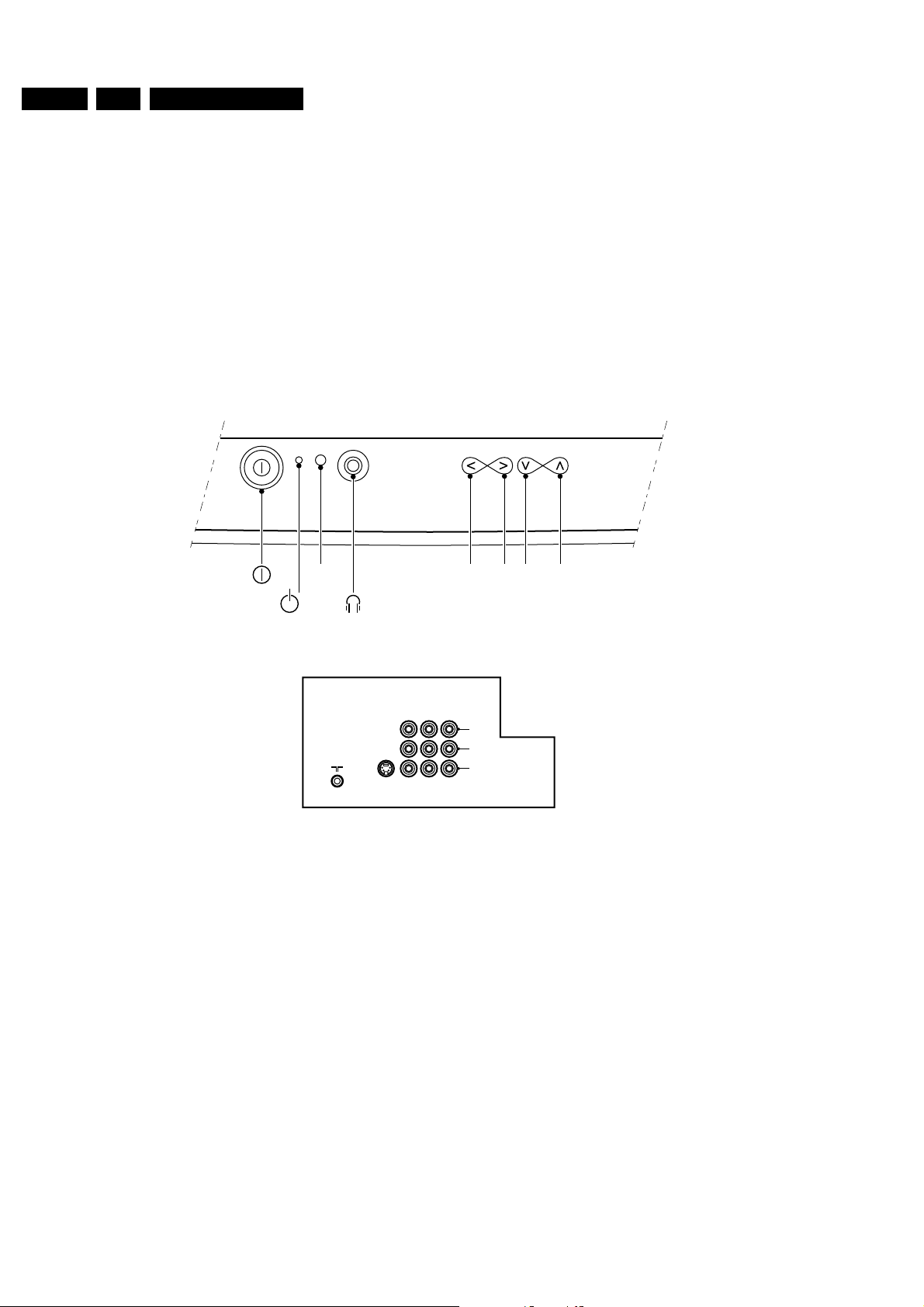
1.2 Specification of the terminal sockets
IR
Red
Off air : 100dBV
On air : 90dBV
Audio output :
• Stereo : 2 * 3W; 2 * 1W
• Mono : 2 * 2W; 4W; 3W; 2W; 1W
Tuners :
• UV 1316/AI-2 (PAL)
• UV 1316/AIU-2 (PAL)
• UV 1356C/AI (PAL)
++
--
ChannelVolume
CL 86532104_011.eps
080299
1.3 Specification of the terminal sockets
1.3.1 Inputs (AV1, AV2 and Side AV)
- Cinch CVBS (yellow) (1Vpp +/- 3dB 75Ω)
- Cinch Audio R (red) (0.2-2VRMS 10kΩ)
- Cinch Audio L (white) (0.2-2VRMS 10kΩ)
1.3.2 Outputs (MONITOR out)
- Cinch CVBS (yellow) (1Vpp +/- 3dB 75Ω)
- Cinch Audio R (red) (0.5VRMS < 1kΩ)
- Cinch Audio L (white) (0.5VRMS < 1kΩ)
1.3.3 Headphone
- Jack 8-600 (4mW)
1.3.4 SVHS
S-Video
q
q
q
q
q
q
t
IN OUTIN
Video
L
Audio
R
CL 86532104_069.AI
290399
1 - Ground
2 - Ground
3 - Y (1Vpp +/- 3dB 75Ω)
4 - C (0.3Vpp +/- 3dB 75Ω)
v
v
p
p
Page 3
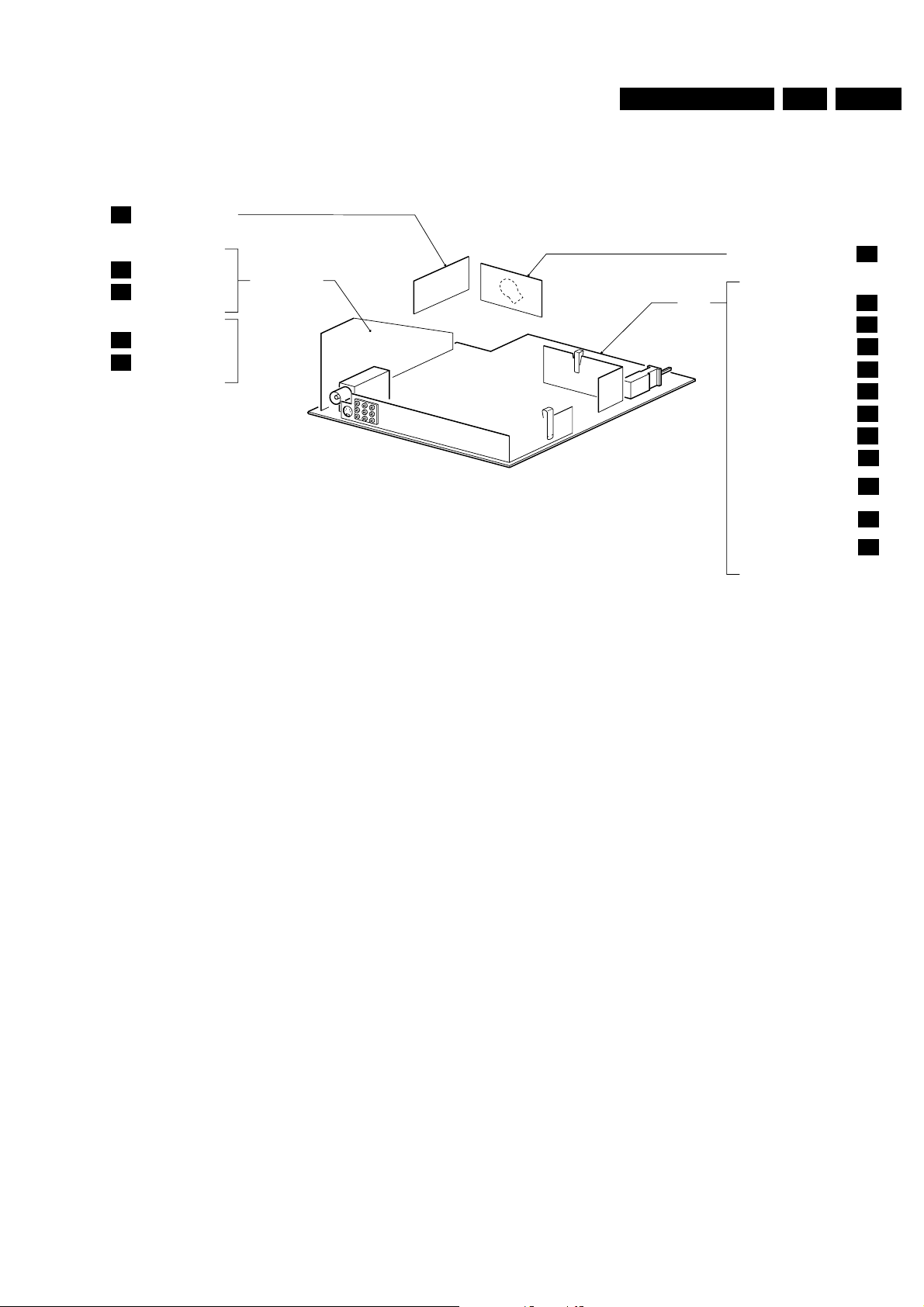
Safety instructions, maintenance instruction, warnings and Notes
1.4 PCB location drawing
GB 3L9.2A 2.
E
D1
D2
C1
C2
SIDE AV PANEL
ITT AUDIO DECODING
ITT AUDIO AMPLIFIER
BTSC DECODER
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
OR
AUDIO PANEL
MAIN
CRT PANEL
POWER SUPPLY
LINE DEFLECTION
FRAME DEFLECTION
SYNCHRONISATION
TUNER VIDEO IF
VIDEO PROCESSING
CONTROL
FRONT CONTROL
SMART SOUND +
MONO SOUND AMPLIFIER
FRONT CINCH +
HEADPHONE
REAR I/O CINCHES
CL 96532047_014.eps
B
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A10
A11
A12
270599
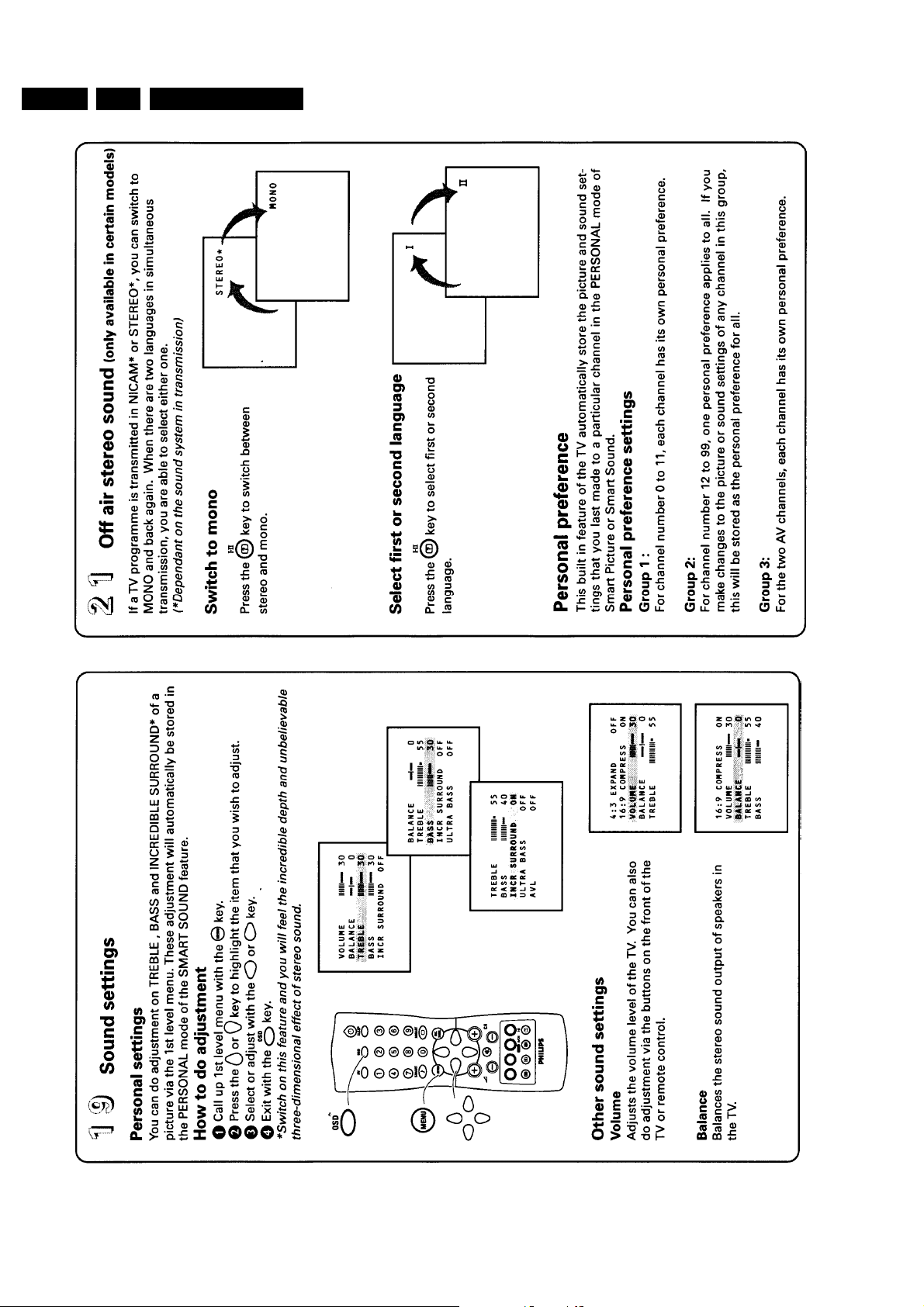
2. Safety instructions, maintenance instruction, warnings and Notes
2.1 Safety instructions for repairs h?????????
h?????????
h?????????h?????????
1. Safety regulations require that during a repair:
– The set should be connected to the mains via an
isolating transformer;
– Safety components, indicated by the symbol h,
should be replaced by components identical to the
original ones;
– When replacing the CRT, safety goggles must be
worn.
2. Safety regulations require that after a repair the set must
be returned in its original condition. In particular attention
should be paid to the following points.
– As a strict precaution, we advise you to resolder the
solder joints through which the horizontal deflection
current is flowing, in particular ('general repair
instruction'):
• All pins of the line output transformer (LOT);
• Fly-back capacitor(s);
• S-correction capacitor(s);
• Line output transistor;
• Pins of the connector with wires to the deflection
coil;
• Other components through which the deflection
current flows.
• Note:
• This resoldering is advised to prevent bad
connections due to metal fatigue in solder joints
and is therefore only necessary for television sets
older than 2 years.
– The wire trees and EHT cable should be routed
correctly and fixed with the mounted cable clamps.
– T he insulation of the mains lead should be checked for
external damage.
2.2 Maintenance instruction
– The mains lead strain relief should be checked for its
function in order to avoid touching the CRT, hot
components or heat sinks.
– The electrical DC resistance between the mains plug
and the secondary side should be checked (only for
sets which have a mains isolated power supply). This
check can be done as follows:
• Unplug the mains cord and connect a wire
between the two pins of the mains plug;
• Set the mains switch to the "on" position (keep the
mains cord unplugged!);
• Measure the resistance value between the pins of
the mains plug and the metal shielding of the tuner
or the aerial connection on the set. The reading
should be between 4.5 MΩ and 12 M
Ω
• Switch off the TV and remove the wire between the
two pins of the mains plug.
– The cabinet should be checked for defects to avoid
touching of any inner parts by the customer.
It is recommended to have a maintenance inspection carried
out by a qualified service employee. The interval depends on
the usage conditions:
– When the set is used under normal circumstances, for
example in a living room, the recommended interval is 3 to
5 years.
– When the set is used in circumstances with higher dust,
grease or moisture levels, for example in a kitchen, the
recommended interval is 1 year.
– The maintenance inspection contains the following actions:
• Execute the above mentioned 'general repair
instruction'.
Page 4
GB 4 L9.2A2.
• Clean the power supply and deflection circuitry on the
• Clean the picture tube panel and the neck of the picture
Safety instructions, maintenance instruction, warnings and Notes
chassis.
tube.
2.3 Warnings
1. ESD
2. All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
3. Available ESD protection equipment:
4. In order to prevent damage to ICs and transistors, all high-
5. Together with the deflection unit and any multipole unit, the
6. Be careful during measurements in the high-voltage
7. Never replace modules or other components while the unit
8. When making settings, use plastic rather than metal tools.
9. Wear safety goggles during replacement of the picture
w
electrostatic discharges (ESD). Careless handling during
repair can reduce life drastically. When repairing, make
sure that you are connected with the same potential as the
mass of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools also at this same potential.
– Complete kit ESD3 (small table mat, Wristband,
Connection box, Extension cable and Earth cable)
4822 310 10671
– Wristband tester 4822 344 13999
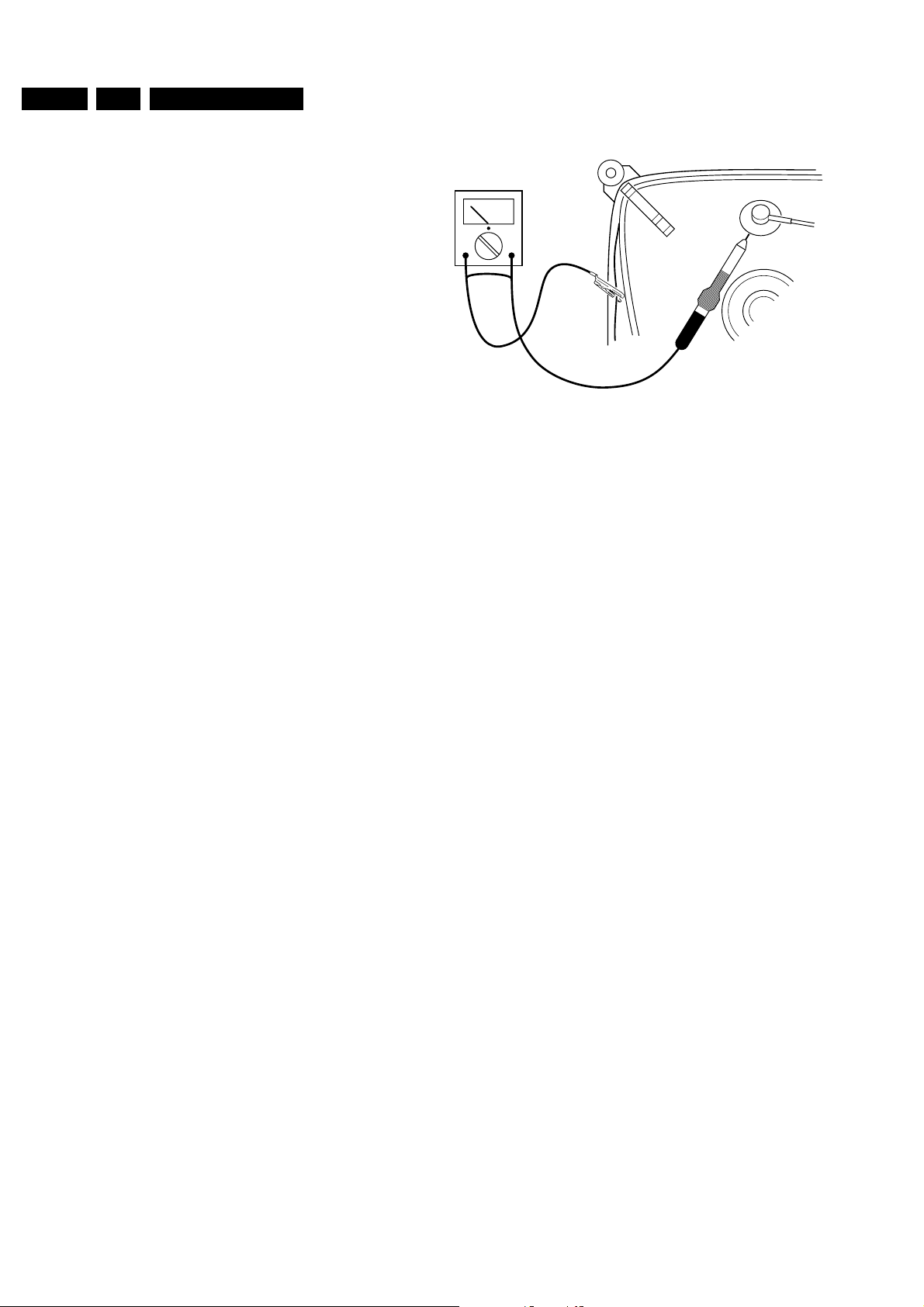
voltage flashovers must be avoided. In order to prevent
damage to the picture tube, the method shown in Fig. 2.1
should be used to discharge the picture tube. Use a highvoltage probe and a multimeter (position DC-V). Discharge
until the meter reading is 0V (after approx. 30s).
flat square picture tubes used form an integrated unit. The
deflection and the multipole units are set optimally at the
factory. Adjustment of this unit during repair is therefore not
recommended.
section and on the picture tube.
is switched on.
This will prevent any short circuits and the danger of a
circuit becoming unstable.
tube.
V
CL 26532098/042
140792
Figure 2-1
2.4 Notes
The direct voltages and oscillograms should be measured with
regard to the tuner earth (v), or hot earth (u) as this is called.
The direct voltages and oscillograms shown in the diagrams
are indicative and should be measured in the Service Default
Mode (see chapter 8) with a colour bar signal and stereo sound
(L:3 kHz, R:1 kHz unless stated otherwise) and picture carrier
at 475.25 MHz.
Where necessary, the oscillograms and direct voltages are
measured with (D) and without aerial signal (E). Voltages in
the power supply section are measured both for normal
operation (G) and in standby (F). These values are indicated
by means of the appropriate symbols.
The picture tube PWB has printed spark gaps. Each spark gap
is connected between an electrode of the picture tube and the
Aquadag coating.
The semiconductors indicated in the circuit diagram and in the
parts lists are completely interchangeable per position with the
semiconductors in the unit, irrespective of the type indication
on these semiconductors.
Page 5
Directions for use
3. Directions for use
GB 5L9.2A 3.
Page 6
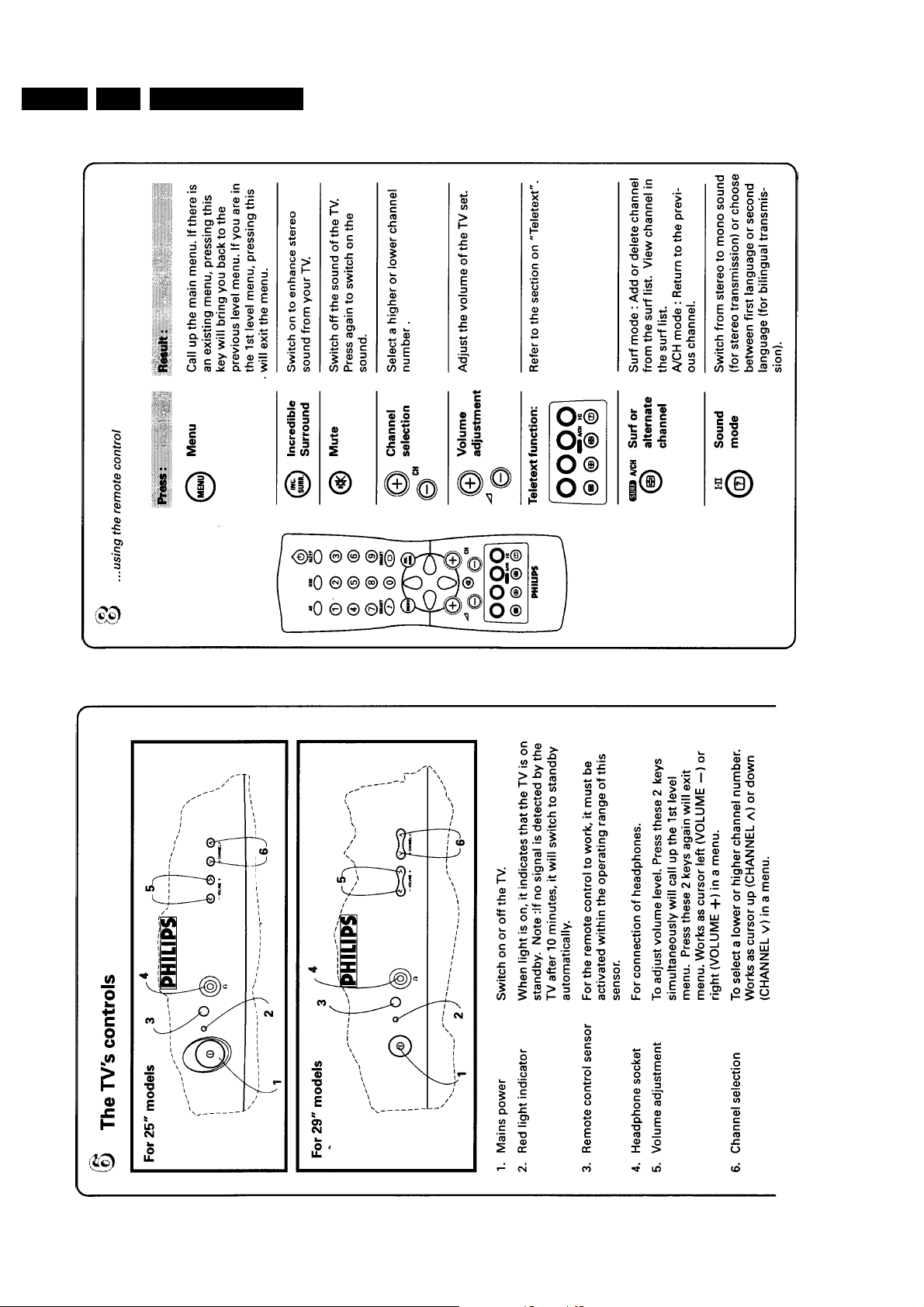
GB 6 L9.2A3.
Directions for use
Page 7
Directions for use
GB 7L9.2A 3.
Page 8
GB 8 L9.2A3.
Directions for use
Page 9
Directions for use
GB 9L9.2A 3.
Page 10
GB 10 L9.2A3.
Directions for use
Page 11
Directions for use
GB 11L9.2A 3.
Page 12

GB 12 L9.2A3.
Directions for use
Page 13

Directions for use
GB 13L9.2A 3.
Page 14

GB 14 L9.2A4.
Mechanical instructions
4. Mechanical instructions
4.1 Service positions
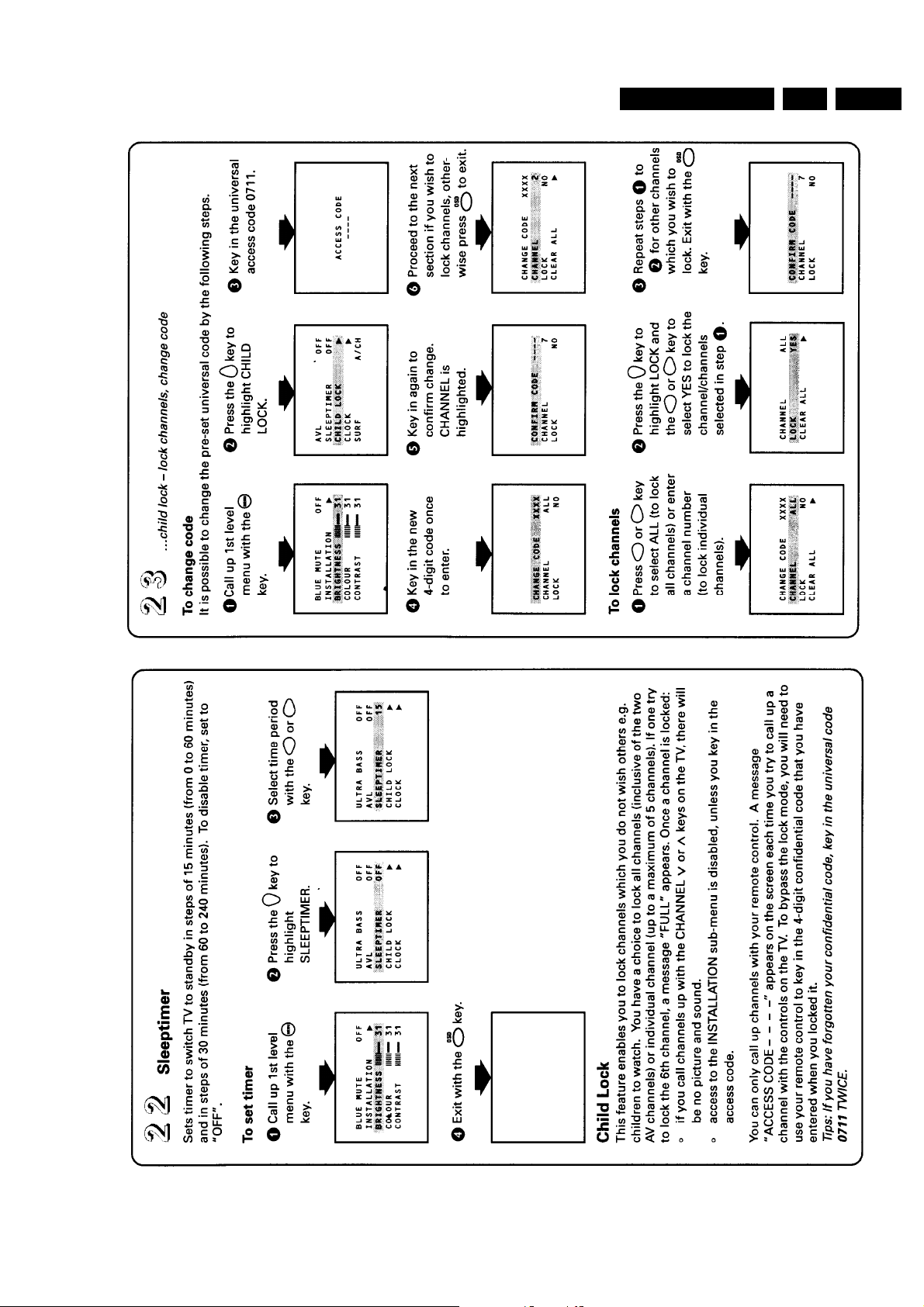
See figure 4.2 for the service position.
Disconnect the connecting cable feeding the right-hand and the
left-hand speaker, also disconnect the degaussing cable.
1
11
The mono-carrier is removed by pushing the two centre clips at
both chassis brackets outwards and pulling the panel forward.
A B
Figure 4-2
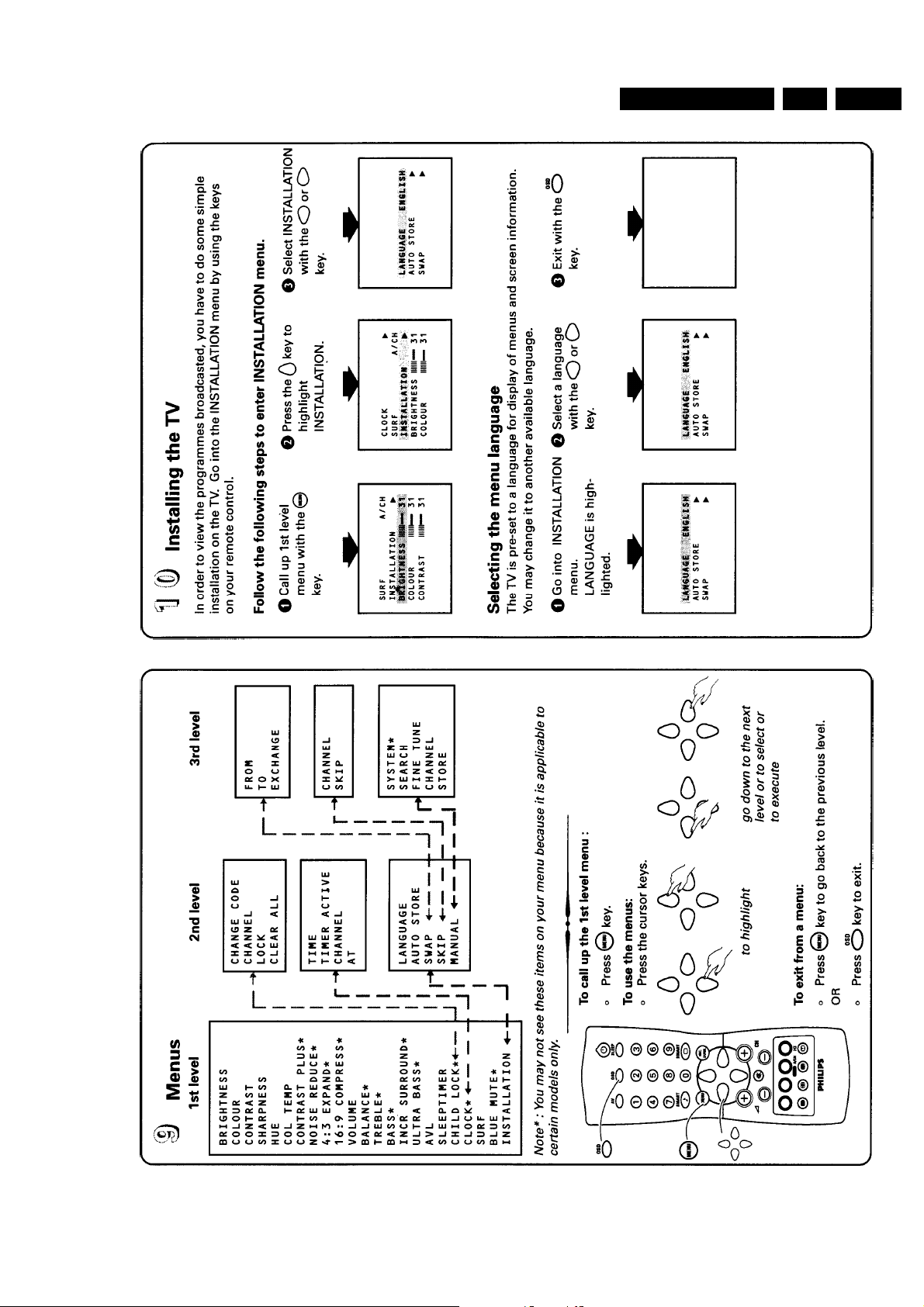
5. Service Modes, fault finding and repair tips
In this chapter the following paragraphs are included:
5.1 Test points
5.2 Service Modes and Dealer Service Tool (DST)
5.3 The menus and submenus
5.4 Error code buffer and error codes
5.5 The "blinking LED" procedure
5.6 Trouble shooting tips
5.7 Customer service mode ( CSM )
5.8 ComPair
5.9 Ordering compare
5.1 Test points
The L9 chassis is equipped with test points in the service
printing. These test points are referring to the functional blocks:
• A1-A2-A3, etc.: Test points for the Smart Sound + Mono
Sound amplifier ( A10 ), BTSC decoder (C1), Audio
amplifier (C2), ITT panel ( D1) and Sound amplifier ( D2 )
• C1-C2-C3, etc.: Test points for the control circuit ( A7 ) and
the front control ( A8 )
• F1-F2-F3, etc.: Test points for the frame deflection circuit (
A3 )
• I1-I2-I3, etc.: Test points for the Tuner Video IF circuit ( A5 )
• L1-L2-L3, etc.: Test points for the Line deflection circuit (
A2 )
• P1-P2-P3, etc.: Test points for the power supply ( A1 )
• S1-S2-S3, etc.: Test points for the synchronisation circuit (
( A4 )
• V1-V2-V3, etc.: Test points for the video processing circuit
/ CRT panel( A6 ) / CRT panel ( B )
Measurements are performed under the following conditions:
• Video: colour bar signal;
• audio: 3kHz left, 1kHz right
5.2 Service modes and Dealer Service Tool (DST)
For easy installation and diagnosis the dealer service tool
(DST) RC7150 can be used. When there is no picture (to
access the error code buffer via the OSD), DST can enable the
functionality of displaying the contents of the entire error code
buffer via the blinking LED procedure, see also paragraph 5.5.
The ordering number of the DST (RC7150) is 4822 218 21232.
5.2.1 Installation features for the dealer
The dealer can use the RC7150 for programming the TV-set
with presets. 10 Different program tables can be programmed
into the DST via a GFL TV-set (downloading from the GFL to
the DST; see GFL service manuals) or by the DST-I (DST
interface; ordering code 4822 218 21277). For explanation of
the installation features of the DST, the directions for use of the
CL 96532047_015.eps
280599
Page 15

Service Modes, fault finding and repair tips
LLLL L90BBC X.Y SDM
OP VALUE
OB1 OB2 OB3 OB4 OB5 OB6 OB7
ERR xx xx xx xx xx
CL 86532104_015.eps
160299
SDM
SDM
TV LOCK
INSTALLATION
BRIGHTNESS
COLOUR
CONTRAST
llllll
llllll
llllll
31
31
31
......
......
......
MENU
GB 15L9.2A 5.
DST are recommended (For the L9 chassis, download code X
should be used).
5.2.2 Diagnose features for service
L9 sets can be put in two service modes via the RC7150. These
are the Service Default Mode (SDM) and the Service Alignment
Mode (SAM).
5.2.3 Service Default Mode (SDM)
The purpose of the SDM is:
• provide a situation with predefined settings to get the same
measurements as in this manual
• override 5V protections in case of short circuiting pin 0228
and pin 0224 at A7.
• start the blinking LED procedure
• Setting of options controls
• Inspect the error buffer
Entering the SDM:
• By transmitting the "DEFAULT" command with the RC7150
Dealer Service Tool (this works both while the set is in
normal operation mode or in the SAM)
• Standard RC sequence 062596 followed by the key
"MENU"
• By shorting pin 0228 and 0224 on the mono-carrier ( A7 )
while switching on the set. After switching on the set the
short-circuit can be removed. ( Caution!! Override of 5V
protections ).
Exit the SDM:
Switch the set to Standby or press EXIT on the DST (the error
buffer is also cleared).
Note: When the mains power is switched off while the set is in
SDM, the set will switch to SDM immediately when the mains
is switched on again. ( The error buffer will not be cleared ).
The SDM sets the following pre-defined conditions:
• Pal sets: tuning at 475.25 PAL (BTSC sets tuning of
channel 3 at 61,25MHz)
• Volume level is set to 25% (of the maximum volume level).
• Other picture and sound settings are set to 50%.
The following functions are "ignored" in SDM since they
interfere with diagnosing/repairing a set. "Ignoring" means that
the event that is triggered is not executed, the setting remains
unchanged.
• (Sleep)Timer
• Blue mute
• Auto switch off
• Hotel or Hospitality Mode
• Child lock or Parental lock
• Skipping, blanking of "Not favourite" present/channels
• Automatic storing of Personal Preset settings
• Automatic user menu time-out
All other controls operate normally.
5.2.4 Special functions in SDM
Access to normal user menu
Pressing the "MENU" button on the remote control will enter the
normal user menu ( TV lock, Installation, Brightness, colour
and contrast ) while "SMD" remains displayed in top of screen).
Pressing the "MENU" key again will return to the last SDM
status.
Error buffer
Pressing the "OSD" button on the remote control shows all
OSD (incl. error buffer).
Access to SAM
By pressing the "CHANNEL DOWN" and "VOLUME DOWN"
buttons on the local keyboard simultaneously or pressing
"ALIGN" on theDST
DST, the set switches from SDM to SAM
In the SDM the following information is displayed on the
screen:
Figure 5-3 Service Default Mode screens and structure
Explanation notes/references:
1. (1) "LLLL" Operation hours timer (hexadecimal)
2. (2) Software identification of the main micro controller
(L90BBC X.Y)
• L90 is the chassis name for L9
• BBC is 2 letter and 1 digit combination to indicate the
software type and the supported languages:
• X = (main version number)
• Y = (subversion number) BB = (range specification )
3. (3) "SDM" To indicate that the TV set is in the service
default mode
4. (4) "OP" Options Code which exists of 2 characters. It is
possible to change each option code
5. "VALUE" The value of the selected option ( ON/OFF or a
combination of 2 letters )
6. "XXX" Value of the options bytes ( OB1 .. OB7)
7. "ERR" The last five detected errors; The left most number
indicates the most recent error detected.
The MENU UP or MENU DOWN command can be used to
select the next/previous option; The MENU LEFT and MENU
RIGHT command can be used to change the option value.
Remark: When the option-code RC = OFF, the P+ and the Pkey have the same functions as the MENU UP/DOWN keys
while the VOL+ and the VOL- key have the same function as
the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys. When the option RC = OFF it is
not possible to change the channel preset or to adjust the
volume when in SAM/SDM menu. Using a L9 remote control,
option-code RC = ON, the P+, P-, VOL- and VOL+ can be used
to change the preset and/or to adapt the volume, while the
menu-cursor keys are used to select the option and to change
its value.
For an extended overview of the option codes see Chapter 8 Options
5.2.5 Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
The purpose of the SAM is to do tuning adjustments, align the
white tone, adjust the picture geometry and do sound
adjustments.
For recognition of the SAM, "SAM" is displayed at the top of the
right side of the screen
Entering SAM:
• By pressing the "ALIGN" button command withon the
RC7150 Dealer Service Tool
Page 16

GB 16 L9.2A5.
Service Modes, fault finding and repair tips
• By pressing the "CHANNEL DOWN" and "VOLUME
DOWN" key on the local keyboard simultaneously when
the set is in SDM
• Standard RC sequence 062596 followed by the key "OSD"
• By shorting pin 0225 and 0226 on the mono-carrier ( A7 )
while switching on the set. After switching on the set the
short-circuit can be removed. ( Caution!! Override of 5V
protections ).
Exit the SAM:
Switch the set to standby or press EXIT on the DST (the error
buffer is cleared).
Note: When the mains power is switched off while the set is in
SAM, the set will switch to SAM immediately when the mains is
switched on again. ( The error buffer will not be cleared ).
In the SAM the following information is displayed on the screen:
Figure 5.4 Service Alignment Mode screens and structure
Access to normal user menu
Pressing the "MENU" button on the remote control will enter the
normal user menu ( TV lock, installation, brightness, colour and
SAM
TV LOCK
INSTALLATION
31
BRIGHTNESS
COLOUR
CONTRAST
llllll
llllll
llllll
......
......
......
31
31
contrast ) while "SAM" remains displayed in top of screen.
Pressing the "MENU" key again will return to the last SAM
status.
Pressing the "OSD" button of the remote control shows only
"SAM" in the top of screen
Access to SDM
Pressing the "DEFAULT" button on the DST
SAM menu control
Menu items (AKB, VSD, Tuner, White tone, Geometry and
Audio) can be selected with the MENU Up or MENU DOWN
key. Entry into the selected items (sub menus) is done by the
MENU LEFT or MENU RIGHT key. The selected item will be
highlighted.
With the cursor LEFT/RIGHT keys, it is possible to increase/
decease the value of the selected item.
SAM
AKB
VSD
TUNER
WHITE TONE
GEOMETRY
AUDIO
L90 BBC X.Y
SOUND
MENU
SAMAAABBC X.Y
SAM
MENU
MENU
MENU
L90 BBC X.Y
TUNER
IF-PLL
IF-PLL POS
AFA
AFB
L90 BBC X.Y
NORMAL RED
L90 BBC X.Y
SAM
64
192
1
1
SAM
40
SAM
A-FM
AT
STEREO
232
4
15
Figure 5-4 Service Alignment Mode screens and structure
MENU
VAM
55
CL 86532104_016.eps
040599
Page 17

Service Modes, fault finding and repair tips
GB 17L9.2A 5.
5.3 The menus and submenus
5.3.1 Tuner sub menu
The tuner sub menu contains the following items:
• IF_PLL : PLL Alignment for all PAL/SECAM
systems, excluding SECAM-LL'
• IF_PLL POS : PLL Alignment for SECAM-LL'
• IF_PLL OFFSET : Default value = 48 ; Do not align
• AFW : AFC Window
• AGC : AGC take-over point
• YD : Default value = 12 ; Do not align
• CL : Default value = 4 ; Do not align
•AFA
•AFB
The items AFA and AFB can not be selected, they are for
monitoring purposes only.
The commands MENU UP and MENU DOWN are used to
select the next/previous item.
The commands MENU LEFT and MENU RIGHT are used to
increase/decrease the value of the selected item. The changed
values will be send directly to the related hardware.
The item values are stored in NVM if this sub menu is left.
5.3.2 White tone sub menu
The commands MENU UP and MENU DOWN are used to
select the next/previous item.
The commands MENU LEFT and MENU RIGHT are used to
increase/decrease the value of the selected item. The changed
values will be send directly to the related hardware.
The item values are stored in NVM if this sub menu is left.
The white tone sub menu contains the following items:
• NORMAL RED
• NORMAL GREEN
• NORMAL BLUE
• DELTA COOL RED
• DELTA COOL GREEN
• DELTA COOL BLUE
• DELTA WARM RED
• DELTA WARM GREEN
• DELTA WARM BLUE
OSD is kept to a minimum in this menu, in order to make white
tone alignment possible.
The Contrast Plus feature (black stretch) is set to OFF when
the white tone submenu is entered.
5.3.3 Audio sub menu
The tuner sub menu contains the following items:
• A-FM : Default value = 232 ; Do not align
• AT : Default value = 4 ; Do not align
• STEREO : Default value = 15 ; Do not align
• DUAL : Default value = 12 ; Do not align
The sound adjustments sub menu are not available in Mono
sets.
The presence of an item in the menu strongly depends on the
selected soundboard (option SB).
5.3.4 Geometry sub menu
The geometry sub menu contains the following items:
• VAM : Vertical amplitude
• VSL : Vertical slope
• SBL : Service blanking
• HSH : Horizontal shift
• H60 : Default value = 10 ; Do not align
• V60 : Default value = 12 ; Do not align
• VSC : Vertical S correction
• VSH : Vertical shift
5.4 Error code buffer and error codes
5.4.1 Error code buffer
The error code buffer contains all errors detected since the last
time the buffer was erased. The buffer is written from left to
right.
• when an error occurs that is not yet in the error code buffer,
the error is written at the left side and all other errors shift
one position to the right
• the error code buffer will be cleared in the following cases:
1. exiting SDM or SAM with the "Standby" command on
the remote control
2. transmitting the commands "EXIT" with the DST
(RC7150)
3. transmitting the commands "DIAGNOSE-9-9-OK" with
the DST.
• The error buffer is not reset by leaving SDM or SAM with
the mains error buffer is not switch.
Examples:
• ERROR: 0 0 0 0 0 : No errors detected
• ERROR: 6 0 0 0 0 : Error code 6 is the last and only
detected error
• ERROR: 5 6 0 0 0 : Error code 6 was first detected and
error code 5 is the last detected (newest) error
5.4.2 Error codes
In case of non-intermittent faults, clear the error buffer before
starting the repair to prevent that "old" error codes are present.
If possible check the entire content of the error buffers. In some
situations an error code is only the RESULT of another error
code (and not the actual cause).
Note: a fault in the protection detection circuitry can also lead
to a protection.
a. Error 0 = No error
b. Error 1 = X-ray ( Only for USA sets )
c. Error 2 = High beam current protection
High beam protection active; set is switched to protection;
error code 2 is placed in the error buffer; the LED will blink
2 times ( repeatedly ).
As the name implies, the cause of this protection is a too
high beam current (bright screen with flyback lines). Check
whether the +160V supply to the CRT panel is present. If
the voltage is present, the most likely cause is the CRT
panel or the picture tube. Disconnect the CRT panel to
determine the cause. If the +160V voltage is not present,
check R3416 and D6409 ( Horizontal Deflection - A2 )
EW protection:
If this protection is active, the cause could be one of the
following items;
horizontal deflection coil 5445
S-correction capacitor 2407
flyback capacitor 2434
line output stage
short circuit of flyback diode 6434
EW power-transistor 7402 or driver-transistor 7400
d. Error 3 = Vertical / Frame protection
There are no pulses detected at pin 37 of the main
microprocessor 7600 ( panel A7 ).
If this protection is active, the causes could be one of the
following items;
IC 7460 is faulty ( A3 )
Open circuit of vertical deflection coil
Vlotaux +13V not present and/or Vlotaux -13V not present
Resistor 3463
Transitor 7609 is defect ( A7 )
e. Error 4 = Sound processor ( IC7803 ) I2C error (
MSP3415D )
Sound processor does not respond to the micro controller
f. Error 5 = Bimos ( IC7250 ) start-up error ( POR bit )
Page 18

GB 18 L9.2A5.
Service Modes, fault finding and repair tips
Bimos start-up register is corrupted or the I2C line to the
Bimos is always low or no supply at pin 12 of the Bimos).
This error is usually detected during start-up and hence will
prevent the set from starting up.
g. Error 6 = Bimos (TDA884x ) I2C error
Note that this error may also be reported as a result of error
codes 4 (in that case the Bimos might not be the actual
problem)
h. Error 7 = General I2C error. This will occur in the following
cases:
SCL or SDA is shorted to ground
SCL is shorted to SDA
SDA or SCL connection at the micro controller is open
circuit.
i. Error 8 = Microprocessor ( IC7600 ) internal RAM error ( A7
)
The micro controller internal RAM test indicated an error of
the micro controller internal memory (tested during startup);
j. Error 9 = EEPROM Configuration error ( Checksum error );
EEPROM is corrupted.
k. Error 10 = I2C error EEP R O M . NV mem ory (EEPROM)
does not respond to the micro controller
l. Error 11 = I2C error PLL tuner. Tuner is corrupted or the
I2C line to the Tuner is low or no supply voltage present at
pin 9, pin 6 or pin 7 of the tuner.
m. Error 12 = Black current loop instability protection. The
black current could not be stabilised. The possible cause
could be a defect in one or more of the RGB amplifiers,
RGB guns or RGB driving signals.
5.5 The "blinking LED" procedure
The contents of the error buffer can also be made visible
through the "blinking LED" procedure. This is especially useful
when there is no picture. There are two methods:
• When the SDM is entered, the LED will blink the number of
times, equal to the value of the last (newest) error code
(repeatedly).
• With the DST all error codes in the error buffer can be
made visible. Transmit the command: "DIAGNOSE x OK"
where x is the position in the error buffer to be made visible
x ranges from 1, (the last (actual) error) to 5 (the first error).
The LED will operate in the same way as in point 1, but now
for the error code on position x.
Example:
Error code position 1 2 3 4 5
Error buffer 8 9 5 0 0
• after entering SDM: blink (8x) - pause - blink (8x) - etc.
• after transmitting "DIAGNOSE- 2- OK" with the DST blink
(9x) - pause - blink (9x) - etc.
• after transmitting "DIAGNOSE- 3- OK" with the DST
blink(5x) - pause - blink(5x) - etc.
• after transmitting "DIAGNOSE- 4- OK" with the DST
nothing happens
5.6 TROUBLE SHOOTING TIPS
In this paragraph some trouble shooting tips for the deflection
and power supply circuitry are described. For detailed
diagnostics, check the fault finding tree or use COMPAIR.
5.6.1 THE DEFLECTION CIRCUIT:
1. Measure the +VBATT ( 95V) is present across 2551 ( A2 Line deflection ). If the voltage is not present, disconnect
coil 5551. (Horizontal deflection stage is disconnected). If
the voltage is present then the problem might be caused by
the deflection circuit. Possibilities:
• Transistor 7402 is faulty
• The driver circuit around transistor 7400 is faulty
• No horizontal drive signal coming from the BIMOS
7250-D pin 40 ( A4 - Synchronisation )
• Timer-IC 7607 or transitor 7608 is defect ( A7 -
Control )
2. Note: If the Collector of 7402 is shorted to the Emitter, hickup noise can be heard from the power supplyIn this case
the E/W protection is disabled.is correctly working ( a
parabolic picture )
3. Also take note of protection circuits in the line output stage.
If any of these circuits are activated, the set will shut down.
Depending on the protection, the led will blink according to
the fault defined. In order to determine which protection
circuit is active, isolation of each separate circuit is
necessary. These protection circuits are:
• High beam current protection ( LED blinks repetitively
2 times ) - CRT panel ( B )
• Vertical protection ( LED blinks repetitively 3 times ) -
Vertical deflection ( A3 )
5.6.2 THE POWER SUPPLY
To trouble shoot the L9.2A SMPS, first check the Vaux voltage
on C2561. If this voltage is not present, check fuse F1572 and
D6560. If F1572 or D6560 is not open circuit, the problem might
be caused on the primary side of the switching supply. Check
the output of the bridge rectifier on C2508 for approximately
300V DC at an input voltage of 230Vac. If this voltage is
missing, check the bridge diodes 6502 .. 6505 and the fuse
1500. If fuse F1500 is found open, check MOSFET 7518 to
make sure that there is no short circuit present and check
R3518. If the 300V DC is present on C2508, check for a startup voltage of approx. 13V on pin 1 of IC7520. If no start-up
voltage is present, check if R3510 is open or zener 6510 is a
short-circuit. It is necessary to have a feedback signal from the
hot primary side of switch mode transformer T5545 at pin 1 and
pin 2 for the power supply to oscillate. If the start-up voltage of
13V is present on pin 1 of IC7520 and the supply is not
oscillating, check R3529 and D6540.
Check for a drive signal at the gate of MOSFET 7518, square
wave signal - P1. Check pin 3 of IC7520 and R3525.
To determined whether OVP is active, check the presence of
Vaux at C2561.
5.6.3 Customer Service Mode (CSM)
All L9 sets are equipped with the "Customer Service Mode"
(CSM). CSM is a special service mode that can be activated
and deactivated by the customer, upon request of the service
technician/dealer during a telephone conversation in order to
identify the status of the set. This CSM is a 'read only' mode,
therefore modifications in this mode are not possible.
Entering the Customer Service Mode. The Customer Service
Mode can be switched on by pressing simultaneously the
button (MUTE) on the remote control and any key on the
control buttons (P+, P-, VOL +, VOL -) on the TV for at least 4
seconds.
When the CSM is activated:
• picture and sound settings are set to nominal levels
• "Service unfriendly modes" are ignored
Exit the Customer Service Mode.
The Customer Service Mode will switch off after:
• pressing any key on the remote control handset (except
"P+" or "P-")
• switching off the TV set with the mains switch.
All settings that were changed at activation of CSM are set
back to the initial values
5.6.4 The Customer Service Mode information screen
The following information is displayed on screen:
Page 19

Service Modes, fault finding and repair tips
I7 B7502
1V / div DC
10µs / div
GB 19L9.2A 5.
Text "CSM" on the first line
• Line number for every line (to make CSM language
independent)
• Operating hours
• Software version L90BBC X.Y)
• Text "CSM" on the first line
• Error buffer contents
• Option code information
• Configuration information
• Service unfriendly modes
1 HHHH L90BBC-X.Y CSM
2 CODES xx xx xx xx xx
3 OP xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx
4 SYS: xxxxxxxxxxx
5 NOT TUNED
6 TIMER
7 LOCKED
8 (HOSPITAL) (HOTEL)
9 VOL LIM <value>
CL 86532104_014.eps
080299
Figure 5-5 Screen lay-out Customer Service Mode
SYS: xxxxxx = xxxxxx is the SYSTEM THAT IS SET FOR THIS
PRESET
NOT TUNED = no ident signal present
TIMER = (SLEEP) TIMER is actived
LOCKED = Channel/preset locked via parental lock, child lock
HOTEL = HOTEL mode activated; HOSPITAL = HOSPITAL
mode activated
VOL LIM = Volume limiter activated and set to the adjusted
value
The ComPair fault finding program is able to determine the
problem of the defective television. ComPair can gather
diagnostic information in 2 ways:
1. Communication to the television (automatic)
2. Asking questions to you (manually)
ComPair combines this information with the repair information
in its database to find out how to repair the L9.2A.
Automatic information gathering
Reading out the error buffer, ComPair can automatically read
out the contents of the entire error buffer.
Diagnosis on I2C level. ComPair can access the I2C bus of the
television. ComPair can send and receive I2C commands to
the micro controller of the television. In this way it is possible for
ComPair to communicate (read and write) to devices on the
I2C busses of the L9.2A.
Manual information gathering
Automatic diagnosis is only possible if the micro controller of
the television is working correctly and only to a certain extend.
When this is not the case, ComPair will guide you through the
fault finding tree by asking you questions and showing you
examples. You can answer by clicking on a link (e.g. text or an
waveform pictures) that will bring you to the next step in the
faultfinding process.
A question could be: Do you see snow? (Click on the correct
answer)
YES / NO
An example can be: Measure testpoint I7 and click on the
correct oscillogram you see on the oscilloscope
5.6.5 Exit
Any key (RC or local keyboard) except "channel up" / "channel
down" (standby switched to standby, mains OFF switches set
off, other keys switch to normal operation)
5.7 ComPair
5.7.1 Introduction
Compair (Computer Aided Repair) is a service tool for Philips
Consumer Electronics products. ComPair is a further
development on the DST service remote control allowing faster
and more accurate diagnostics. ComPair has three big
advantages:
• ComPair helps you to quickly get an understanding how to
repair the L9.2A in short time by guiding you step by step
through the repair procedures.
• ComPair allows very detailed diagnostics (on I2C level)
and is therefore capable of accurately indicating problem
areas. You do not have to know anything about I2C
commands yourself; Compair takes care of this.
• ComPair speeds up the repair time since it can
automatically communicate with the L9.2A (when the micro
processor is working) and all repair information is directly
available. When ComPair is installed together with the
SearchMan L9.2A electronic manual, schematics and
PCBs are only a mouse-click away.
ComPair consists of a Windows based fault finding program
and an interface box between PC and the (defective) product.
The ComPair interface box is connected to the PC via a serial
or RS232 cable. In case of the L9.2A chassis, the ComPair
interface box and the L9.2A communicate via an I2C cable (bidirectional) and via infra red communication (uni-directional;
from ComPair interface box to L9.2A)
Figure 5-6
By a combination of automatic diagnostics and an interactive
question/answer procedure, ComPair will enable you to find
most problems in a fast and effective way.
Additional features
Beside fault finding, ComPair provides some additional
features like:
• Uploading/downloading of presets
• Managing of preset lists
• Emulation of the Dealer Service Tool
5.7.2 SearchMan (Electronic Service Manual)
If both ComPair and SearchMan are installed, all the
Schematics and PCBs of the faulty set are available when
clicking on the hyper-link of a schematic or a PCB in ComPair
Example: Measure the DC-voltage on capacitor C2568 (
Schematic/Panel ) at the Monocarrier.
Clicking on the PCB hyper-link, automatically shows the PCB
with a high-lighted capacitor C2568. Clicking on the schematic
hyper-link, automatically shows the position of a high-lighted
capacitor at the schematic.
5.7.3 Connecting the ComPair interface
The ComPair Browser software should be installed and setup
before connecting ComPair to the L9.2A. (See the ComPair
Browser Quick Reference Card for installation instructions.)
Page 20

GB 20 L9.2A5.
Service Modes, fault finding and repair tips
Connect the RS232 interface cable to a free serial
1.
(COMM) port on the PC and the ComPair interface PC
connector (connector marked with "PC").
Place the ComPair interface box straight in front of the
2.
television with the infrared window (marked "IR")
directed to the television LED. The distance between
ComPair interface and television should be between
0.3 and 0.6 meter. (Note: make sure that (also) in the
service position, the ComPair interface infra red
window is pointed to the standby LED of the television
set (no objects should block the infra red beam)
Connect the mains adapter to the connector marked
3.
"POWER 9V DC" on the ComPair interface
Switch the ComPair interface OFF
4.
Switch the television set OFF with the mains switch
5.
Remove the rear cover of the television set
6.
Connect the interface cable (4822 727 21641) to the
7.
connector on the rear side of the ComPair interface
that is marked "I2C" (See Figure 5.8)
Connect the other end of the interface cable to the
8.
ComPair connector on the monocarrier (see figure 5.9)
Plug the mains adapter in the mains outlet and switch
9.
ON the interface. The green and red LEDs light up
together. The red LED extinguishes after approx. 1
second (the green LED remains lit).
Start-up Compair and select "File" menu, "Open...:;
10.
select "L9.2A Fault finding" and click "OK"
Click on the icon (fig 5.7) to switch ON the
11.
communication mode (the red LED on the Compair
interface wil light up)
The set has now started up in ComPair mode. Follow the
instruction in the L9.2A fault finding tree to diagnose the set.
Note that the OSD works but that the actual user control is
disabled
5.7.4 Preset installation
Presets can be installed in 2 ways with the L9.2A.
• Via infra red
– only sending TO the television
– the rearcover does NOT have to be removed
Click on "File" "Open" and select "TV - use ComPair as DST"
to use infra red
• Via cable
– sending TO the television and reading FROM the
television
– the rearcover has to be removed
Click on "File" "Open" and select "L9.2A fault findi ng" to use the
cable
Presets can be installed via menu "Tools", "Installation",
"Presets".
5.8 Ordering ComPair
Compair order codes:
• Starterkit ComPair+SearchMan software + ComPair
interface (excluding transformer): 4822 727 21629
• ComPair interface (excluding transformer): 4822 727
21631
• ComPair transformer (continental) Europe: 4822 727
21632
• ComPair transformer United Kingdom: 4822 727 21633
• Starterkit ComPair software: 4822 727 21634
• Starterkit SearchMan software: 4822 727 21635
• Starterkit ComPair+SearchMan software: 4822 727 21636
• Compair CD (update): 4822 727 21637
• SearchMan CD (update): 4822 727 21638
• ComPair interface cable (for L9): 4822 727 21641
MAIN PANEL COMPONENT VIEW
Switch on the television set with the mains switch
12.
When the set is in standby. Click on "Start-up in
13.
ComPair mode from standby" in the ComPair L9.2A
fault finding tree, otherwise continue.
Figure 5-7
PC VCR I2CPower
Figure 5-8
9V DC
86532027_003.EPS
050898
13
0267
COMPAIR
1000
TUNER
Figure 5-9
HOT GROUND
BORDER
0231
CL 96532028_013a.eps
220499
Page 21

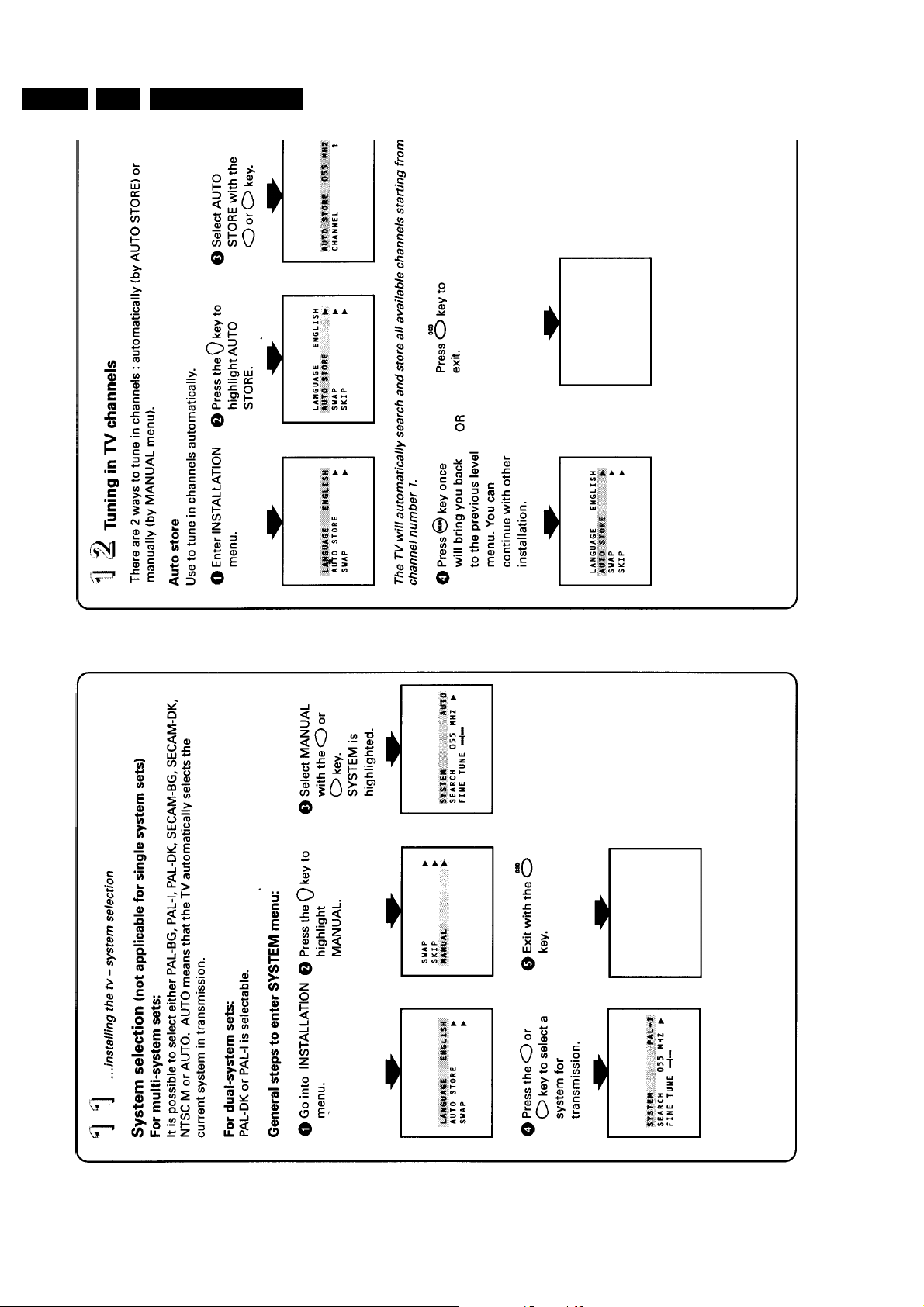
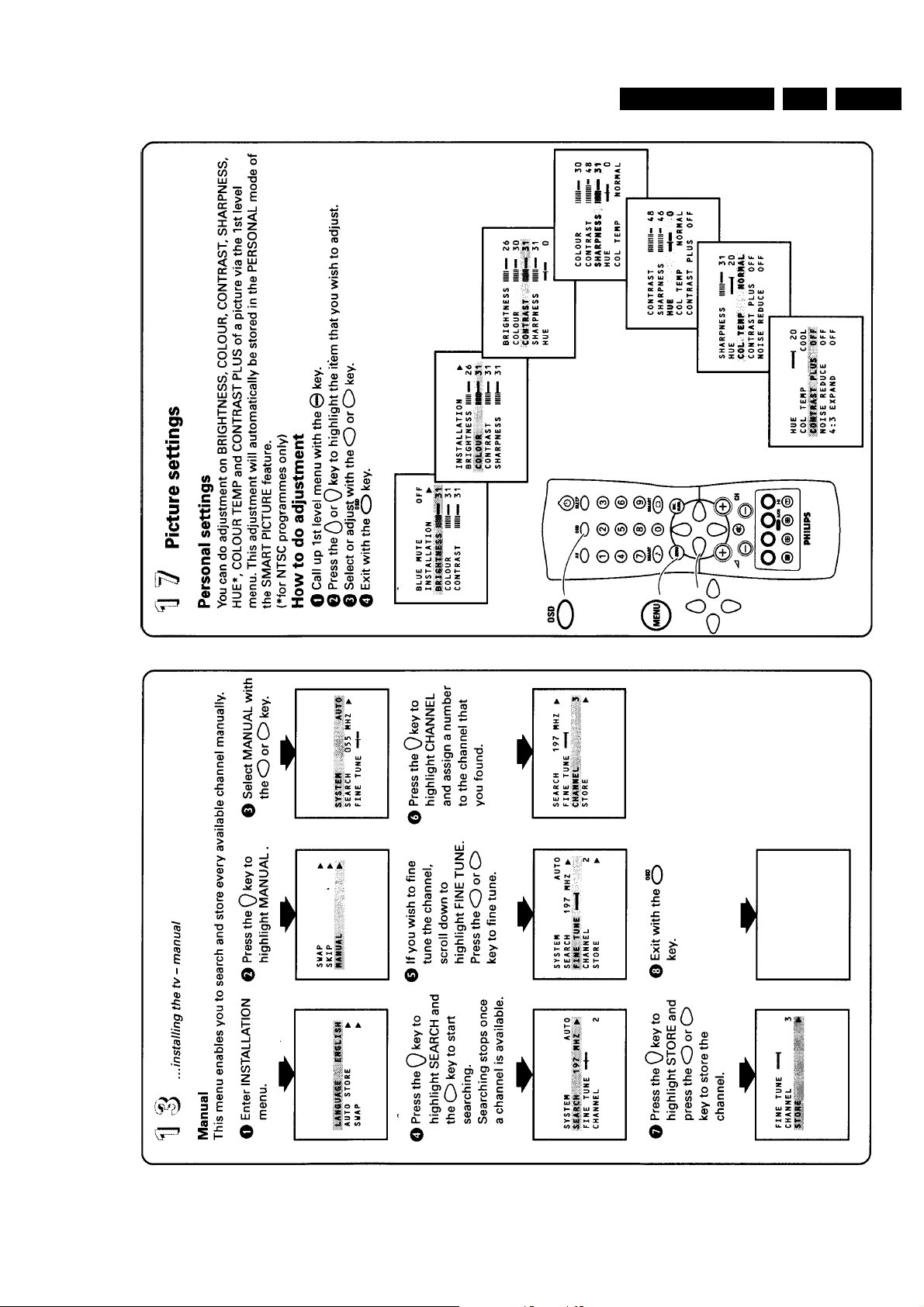
Alignments
8. Alignments
GB 53L9.2A 8.
General: the Service Default Mode (SDM) and Service
Alignment Mode (SAM) are described in chapter 5.
8.1 Alignment conditions
All electrical adjustments should be performed under the
following conditions:
• Supply voltage : 220V - 240V ( 10% )
• Warm-up time: 10 minutes
• The voltages and oscillograms are measured in relation to
the tuner earth.
• Test probe: Ri > 10MΩ Ci < 2,5 pF.
8.1.1 Selection of the SDM-menu
• By transmitting the "DEFAULT" command with the RC7150
Dealer Service Tool (this works both while the set is in
normal operation mode or in the SAM)
• Standard RC sequence 062596 ( within OSD time-out )
MENU
• By shorting test-point 0228 and 0224 on the mono-carrier
while switching on the set. After switching on the set the
short-circuit can be removed. ( Caution!! Override of 5V
protections ).
8.1.2 Selection of the SAM-menu
• By transmitting the "ALIGN" command with the RC7150
Dealer Service Tool
• By pressing the "CHANNEL DOWN" and "VOLUME
DOWN" key on the local keyboard simultaneously when
the set is in SDM
• Standard RC sequence 062596 ( within OSD time-out )
OSD
• By shorting test-point 0225 and 0226 on the mono-carrier
while switching on the set. After switching on the set the
short-circuit can be removed. ( Caution!! Override of 5V
protections ).
• The alignment of the VG2 has been completed; Switch the
set to Standby. The values adapted at the BRIGHTNESSand the CONTRAST-menu during the alignment, will
change back again to their default values.
8.2.2 Focusing
Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) with Circle and Small
Squares pattern and connect to aerial input with RF signal
amplitude - 10mv. Adjusted with focusing potentiometer
(positioned at LOT 5545 ) for maximum sharpness of the
picture.
8.2.3 Adjustment of the Power Supply
• Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) with Circle and Small
Squares pattern and connect to aerial input with RF signal
amplitude - 10mv.
• Switch on the set.
• Select the 300Vdc voltage range when using a normal
multi-meter.
• Connect the DC multi-meter to capacitor 2409.
• Adjust potentiometer R3540 till the DC multi-meter
indicates 95V.
8.3 SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT
8.3.1 Geometry adjustments
• Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) with Circle and Small
Squares pattern on 475.25 MHz for PAL/SECAM and
connect to aerial input with RF signal amplitude - 10mV,
France select L'-signal.
• First enter the SDM mode to set the tuner at 475.25 MHz.
• Enter the SAM mode and then select GEOMETRY with the
up/down keys buttons on the RC the respective items can
be selected. Use the left/right buttons to adjust the selected
items to correct the picture geometry as stated below.
8.2 Electrical Alignments
8.2.1 VG2
• Use a pattern generator to display a normal black picture.
• Program the pattern generator with a frequency of 475.25
MHz for PAL/SECAM or 61.25MHz for BTSC
• Switch on the TV set.
• Select the SDM-MENU. The tuner is set to a frequency of
475.25 MHz for PAL/SECAM or 61.25MHz for BTSC.
• Select the" SAM-MENU".
• Press the "MENU" key on the RC to leave the SAM-MENU
and go to the normal user menu ( "SAM" remains
displayed at the top of the screen). Select with the MENU
UP/DOWN command the sub-menu BRIGHTNESS.
Change the default value from 31 to 50 with the MENU
LEFT/RIGHT keys. Select the CONTRAST sub-menu and
change the value from 31 to 0.
• Leave the normal user menu to return to the SAM-MENU,
by pressing the MENU key on the RC.
• Select sub-menu VSD and change the value from 0 to 1 by
pressing the MENU LEFT key. CAUTION!! Depending on
the position of the VG2 potentio-meter, the screen will turn
completely black because the Vertical Scan has been
disabled.
• Adjust with VG2 potentiometer (positioned at LOT 5545)
the blue line at the middle of the screen till this line is just
not visible.
Vertical Amplitude and Position
• Select Vertical Slope "VSL" and shift the test pattern to the
top. The text VSL and its value should be above the upper
half of the screen
• Select Service Blanking "SBL" and set it to 1. The lower
half of the picture will be blanked.
• Press the up button once to select Vertical Slope "VSL".
Now align "VSL" to start the blanking exactly at the
horizontal white line at the centre of the test circle. "VSL"
has the correct value now and should not be changed
anymore.
• Press the down button once to select "SBL" and set it back
to 0. The full picture reappears.
• Now select Vertical Amplitude "VAM" and align the picture
height to the top of the screen, so that the top horizontal
line just disappears. This corresponds with an over scan of
approx. 6%.
• Select Vertical Shift "VSH" and align for vertical centring of
the picture on the screen.
• Repeat the last two steps if necessary.
Select Vertical S-correction "VSC" to align the top/bottom
squares till they have the same size as the squares in the
middle of the screen.
Horizontal Amplitude and Phase
• Select Horizontal Shift "HSH" to horizontally centre the
picture on the screen
Page 22

GB 54 L9.2A8.
Alignments
To go back to the main SAM-menu , press the MENU key on
the RC.
To leave the SAM-menu and store the alignments in the NVN,
press the STANDBY-key on the RC.
8.3.2 AGC
Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) with colour bar pattern
and connect to aerial input with RF signal amplitude - 10mV
and set frequency for PAL/SECAM to 475.25 MHz or
61.25MHz for BTSC.
• Select the" SAM-MENU.
• Select at the TUNER sub-menu the option AFW and select
the lowest value.
• Select the AGC subsub-menu
• Connect a DC multi-meter at pin 1 of the tuner IC 1000.
• Adjusting the AGC until the voltage at pin 1 of the tuner is
1.0V +/- 0.1V.
• The value can be incremented or decremented by pressing
the right/left MENU-button on the RC.
• Switch the set to standby.
8.3.3 IF-PL L / IF -PLL POS
Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) with colour bar pattern
and connect to aerial input with RF signal amplitude - 10mV
and set frequency for PAL/SECAM to 475.25 MHz or
61.25MHz for BTSC.
• Select the " SAM-MENU".
• Select at the TUNER sub-menu the option AFW and select
the lowest value.
Within the TUNER-menu we now have two options : IF-PLL
and IF-PLL POS.
The IF-PLL option is used for all PAL/SECAM signal excluding
SECAM L',
The IF-PLL POS option is used for only the SECAM L' signal
For the IF-PLL option the following should be done:
• Select at the TUNER menu the IF-PLL subsubmenu
• Adjust the IF-PLL value until the AFA becomes "1" and
AFB alternates between "0" and "1"
• Switch the set to Standby or go to the IF-PLL POS menu.
For the IF-PLL POS option the following should be done:
• Change the signal at the pattern generator from PAL to
SECAM and select the L'-signal.
• Select at the TUNER menu the IF-PLL POS subsubmenu.
• Adjust the IF-PLL POS value until the AFA becomes "1"
and AFB alternates between "0" and "1"
• Switch the set to Standby or go to the IF-PLL menu.
8.3.4 Tuner options CL, YD and IF-PLL OFFSET
NO ADJUSTMENTS NEEDED FOR THESE ALIGNMEN TS .
The tuner option code IF-PLL-OFFSET is only used in
combination with sets with the TDA8845 BiMOS (IC7250).
(Typically this is for Secam LL'). The default values for these
option codes are:
• CL : 4
• YD : 12
• IF-PLL-OFFSET : 48
8.3.5 White tone
• Connect a pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) and set it to
colour bar and circle pattern.
• Set frequency for PAL 475.25MHz or 61.25MHz for BTSC
with RF signal amplitude - 10mv and connect to tuner
(aerial) input
• Enter the SAM -MENU.
• Enter into WHITE TONE menu, select item NORMAL,
DELTAWARM, or DELTACOOL depending on the item
which has to be aligned. Only one of the three items (R, G
or B) will be displayed on the screen.
The default values for the colour temperature as displayed in
the table below:
NORMAL 11500K R = 40 G = 40 B = 40
(DELTA)COOL 13500K R = -2 G = 0 B = 6
(DELTA)WARM 8500K R = 2 G = 0 B = -7
Switch the set to standby.
8.3.6 Audio
NO ADJUSTMENTS NEEDED FOR SOUN D.
The default values for the audio alignments as displayed in the
table below:
AUDIO Alignment Options
A-FM 232
AT 4
STEREO 15
DUAL 15
8.4 Options
Options are used to control the presence / absence of certain
features and hardware. There are two ways to change the
option settings. The various option configurations and the
descriptions of the two character-codes are explained below.
Changing a single option:
A single option can be selected with the MENU UP/DOWN
keys and its setting can be changed with the MENU LEFT/
RIGHT keys.
Changing multiple options by changing option byte values:
Option bytes make it possible to set very fast all options. An
option byte represents a number of different options. All options
of the L9 are controlled via 7 option bytes. Select the option
byte (OB1, OB2, OB3, OB4, OB5, OB6 or OB7) and key in the
new value.
Changes in the options and option bytes settings are saved
when the set is switched to standby. Some changes will only
take affect after the set has been switched OFF and ON with
the mains switch (cold start).
The following options in SDM can be identified:
OP OPTION (ON=enabled / present) Explanation / Remark
AC Alternate Channel Alternate channel function (SWAP between last presets)
enabled
AM Animated men u
2X External 2
AO Audio out Default value is OFF
AS Auto startup/Micro controller startup Default value is ON (ON = start-up via micro controller, OFF =
auto start-up BiMOS)
AT Automatic Tuni ng System (AT S)
Page 23

Alignments
GB 55L9.2A 8.
BM Blue Mute (ON = enabled) Enabled: blue mute background in case of no video ident /poor
BS BiMOS standby mode Default value = ON
BT Bass/Treble Control Menu controls for BASS and TREBLE available when enabled
C8 Maximum Program ( ON = 80 programmes ) C8 is OFF : Maximum of 100 programs
CD Auto Cable Detect Default value = OFF (Not applicable for European sets)
CI Auto matic Channel Installation (ACI)
CK Clock (Volatile) Clock function available when enabled
CL Child Lock Menu item Child lock/Parental control when enabled
CP Contrast Plus Menu item Contrast Plus available when enabled
CT Colour Temperature Menu item Colour Temperature available when enabled
CX 16:9 Compress Menu item 16:9 compress when enabled
DM Demo Mode Demonstration of TV functions on screen when enabled
DP Slider Bar Value Display Slider bar value displayed when enabled
DU Dual I/II Possibility of language selection when enabled
DV Delta Volume (Delta) Volume is stored separately for channel 0..40 and
EW East-West Control East-West Alignment in SAM GEOMETRY menu available
EX 4:3 Expand 4:3 expand mode available when enabled
FV Favourite page Favourite TXT-page feature present when enabled
FQ Frequency display Frequency displayed when enabled
GM Games Mode Optimisation of setting for games possible when enabled
HS Hospital Mode Possibility to block the local keyboard when enabled
HT Hotel Mode Possibility to pre-select the channel numbers when enabled
IS Incredible Surround Incredible surround function available when enabled
LV Automatic Volume Leveller (AVL) Menu item AVL available when enabled
NI No Ident Auto Standby Set switches to standby after 10min. when NI enabled
NR Noise Reduction Menu item Noise Reduction available when enabled
RC (*) Separate preset/volume control on remote control (ON =
separate control (A8 RC); OFF = combined control (L7
RC))
SB Sound Board (Set the sound hardware configuration) MA = Mono ALL
SP Smart Picture Smart picture command is processed when enabled
SS Smart Sound Smart sound command is processed when enabled
ST Sound system s supported SS = BG, I, DK, M
SY Systems supported SS = Single system without NTSC Playback
TN Tuner (OFF: Philips tuner; ON: Alps tuner) Default value = OFF
TW Channel Select Time Window (OFF: 2 seconds; ON: 5
seconds)
UB Ultra Bass Ultra bass function available when enabled
VI Virgin Mode OSD at very first installation when enabled
VL Volume Limiter Menu item Volume Limiter available when enabled
VM Video Mute Screen blanking during channel switching when enabled
WE Europe West (ON: Western Europe; OFF: other)
signal conditions
external sources when enabled; OFF = not available
when enabled
See note below table. Default value is OFF
ND = Stereo/2CS/Nicam
IT = German 2CS
AD = BG/I, BG/DK, I/DK
SP = Single system with NTSC Playback
AD = Dual Mono
ED = Europe Tri Mono
EF = Europe Full Multi
EL = Europe Full Multi with LL’
Time interval for entering a second digit for channel selection
Page 24

GB 56 L9.2A9.
XS External Source Colour Select External source colour selection available when enabled
XT External 1 External 1 source input available when enabled
Circuit description new circuits
(*) Remark: When option RC = OFF, the P+ and the P- key on
the remote control have the same functions as the MENU UP/
DOWN keys while the VOL+ and the VOL- key have the same
function as the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys. When RC=OFF, it is
not possible to change the channel preset or to adjust the
volume in SAM/SDM with the remote control.
RC = OFF for use with L7-based remote control (only cursor
keys). RC = ON for use with A8-based remote control (cursor
keys, P+/P- and Volume+/Volume-).
8.5 Option bits/bytes
Option bytes
OB1 bits 8, 7, ..., 1: DP, FQ, AM, HS, HT, DM, GM, VI
OB2 bits 8, 7, ..., 1: CK, CL, AT, CI, (res), (res), SS, SP
9. Circuit description new circuits
Power supply (diagram A1)
9.1 Introduction
9.1.1 General
The switch mode power supply (SMPS) is mains isolated. The
control IC7520 (MC44603A) produces pulses for driving FET
7518. Power supply regulation is achieved by using duty cycle
control at a fixed frequency of nominal 40 kHz in normal
operation. In stand-by, slow-start and overload situations the
SMPS runs at frequencies other than 40 kHz.
Basic characteristics of this SMPS :
• Mains Isolated flyback Converter type
• Input range : 90 - 276 Volts AC
• Secondary Sensing by Opto-coupler
• IC7520 is Featured with Slow-Start circuitry
• Protection Circuits
• Degaussing circuit
9.1.2 Output voltages
• Audio Supply ( +16.5V ) for the AUDIO AMPLIFIER (
Diagram A12 )
• Mains Supply ( +140V ) for the HORIZONTAL
DEFLECTION stage (A2) and the CRT discharge circuit
(A3)
• Vaux ( +11.3V ) for the Video IF (A5), Video processing
(A6) and Control circuit (A7)
OB3 bits 8, 7, ..., 1: RC, WE, (res), (res), TW, AC, C8, VM
OB4 bits 8, 7, ..., 1: TN, FV,XT,2X, XS, CD, BM, NI
OB5 bits 8, 7, ..., 1: EX, CX, NR, CP, CT, EW, BS, AS
OB6 bits 8, 7, ..., 1: BT, IS, VL, DV, UB, LV, DU, AO
OB7 bits 8, 7, ..., 1: ST, ST, SB, SB, SB, SY, SY, SY
An option byte value is calculated in the following way:
value "option bit 1" x 1 =
value "option bit 2" x 2 =
value "option bit 3" x 4 =
value "option bit 4" x 8 =
value "option bit 5" x 16 =
value "option bit 6" x 32 =
value "option bit 7" x 64 =
value "option bit 8" x 128 =
Total : value "option byte" =
controlling the duty cycle of the SMPS in this way the
(VBATT is controlled.
• During T-off, FET 7518 is switched off and therefore does
not conduct. The energy is now transferred to the
secondary side of the transformer and then supplied to the
load via the secondary diodes (D6550, D6560 and
D6570,D6590). The current through the secondary side of
the transformer decreases until it reaches zero.
• During T-dead FET 7518 does not conduct .The voltage at
the drain of the FET decays and eventually reaches the
input voltage of approximately 300V.
9.2 Primary side
9.2.1 Mains input and degaussing
• Mains voltage: this voltage is filtered by L5500 and L5502,
rectified by a diode bridge rectifier 6505 and then
smoothed by C2508 which provides a DC input voltage of
300V DC for an ac input voltage of 230V.
• Degaussing : R3503 is a PTC. When switching "on" the set,
the PTC is cold and has a low-ohmic value. Relay 1580 is
activated while the Reset signal, coming from the (P is
present. This allows a very high degaussing current at
initial power on. The PTC will then heat up due to the high
current involved and becomes high-ohmic which reduces
the degaussing-current. During normal operation, the
degaussing current is zero, because relay 1580 is open
due to the absence of the (P - Reset signal.
9.1.3 The switching periods of TS7518
The power supply duty cycle is dependent on the T-on of FET
7518. The FET is driven by pin 3 of IC7520. This I C controls the
secondary voltage (VBATT via opto-coupler 7581 and
regulator 7570. The switching period of TS7518 can be divided
into three main phases: Duty cycle T-on, T-off and T-dead.
• During T-on, FET 7518 conducts.
• Energy is stored in the primary winding (2-5) of transformer
T5545 by using a linear increasing primary current. The
slope depends on the rectified mains-voltage present
across C2508. The T-on period is varied to provide
regulation of the drive waveform at pin 3 of IC7520. By
9.2.2 Start up and take over
• Start-up : The start-up circuitry consisting of 3510, 3530
and 3529 use the voltage coming from the 230V AC mains
to start-up IC7520 via the supply pin 1. The output drive
waveform (pin 3) is blocked by using the ICs internal logic
until the voltage on pin 1 reaches 14.5 Volts however with
less than 14.5 volts on Pin 1 the IC only consumes 0.3mA.
Once pin 1 reaches the 14.5 Volts threshold, IC7520 will
start up (FET 7518 will conduct) and pin 1 sinks a typical
supply current of about 17 mA. This supply current cannot
be delivered by the start-up circuitry, so a take-over circuit
must be present. If take-over does not occur then the
voltage on pin 1 will decrease below 9V and IC7520 will
switch off. The supply begins a new Start-up cycle, see top
Page 25

Circuit description new circuits
GB 57L9.2A 9.
of this paragraph. This cycle will repeat itself and can be
noticed by an audible hick-up sounding noise.
• Take for IC7520: During start-up a voltage across winding
8 - 9 is gradually built up. At the moment the voltage across
winding 8 - 9 reaches approx. (14.5 Volts, D6540 start
conducting and takes over the supply voltage Vpin 1 of
IC7520 (take over current is approx. 17mA).
Note: This power supply is a SMPS (= Switched Mode Power
Supply) and not a SOPS (= Self Oscillating Power Supply).
9.3 Control circuitry
9.3.1 IC7520 control mechanisms
IC7520 controls the T-on time of FET 7518 in four different
ways:
• "Secondary-output-sensing" controls the secondary
output voltages via the feedback voltage pin 14
• "Primary current sensing" control due to the mains voltage
via the current sense voltage pin 7
• "Demagnetization control" prevents the transformer T5545
from going into saturation via the so-called "DEMAG"
function at pin 8
• Mains voltage control via R3514 and R3516
9.3.2 Secondary voltage sensing (pin 14 of IC7520)
When the output voltage +VBATT increases (due to a reduction
in the load ) the current through the led in the opto-coupler 7581
will increase due to the fact that the series-resistor in regulator
7570 decreases. An increase in opto-coupler led-current
(7581) results in a decrease in the Vce of transistor 7581,
therefore the voltage across capacitor 2576 increases. This will
reduce the on-time of FET 7518 due to an increase of the
voltage present on pin 14.
In the event of an increase of the load (decrease of output
voltage +VBATT ), the control circuit will work in the opposite
way to the explanation above.
9.3.3 Primary sensing (pin 7 of IC7520)
The current sense voltage at pin 7 is used to measure the
primary current through FET7518. The primary current is
converted into a voltage by R3518. R3514. 3516. couples a
part of the main voltage to the same pin 7 of IC 7520 by dividing
this sample of the voltage.
Hence the higher the input voltage the more the primary current
is limited. In this way the maximum output power of the powersupply is limited.
9.3.4 Demagnetization control (pin 8 of IC7520)
Winding 8 - 9 has the same polarity as the secondary winding
that supplies the load. When FET 7518 is turned off the voltage
at winding 9 becomes positive. The power supply transfers the
stored energy at the secondary side. Until the transformer is
demagnetized the voltage on the winding remains positive. At
the moment that the energy is fully transferred to the load, the
voltage at pin 9 of the transformer becomes negative.
Additionally with a certain dead time the voltage at control pin
8 of IC 7520 also drops below zero which releases the output
buffer (pin 3) and a new cycle starts.
too high which is detected by pin 7. As a result the primary
current is limited to its maximum value and the secondary
voltages will drop. The voltage at pin 1, which is coupled with
the output voltage, will also drop. When the voltage at pin 1
drops below the 9V, IC7520 will stop functioning and the output
voltage will rapidly drop to zero.
Via start-up circuitry 3510, 3530 and 3529 the voltage
originating from the 230V AC mains is used to start-up IC7520
via the supply pin 1. As soon as this voltage reaches the 14.5V,
IC7520 starts functioning. If the load is still too much or the
output is short-circuited the same cycle will happen again. This
fault condition can be clearly identified as the power supply will
be loudly tripping.
9.3.6 Slow-start
As soon as Vpin 1 > 14.5V the SMPS will start-up. During the
slow-start procedure both the frequency and the duty cycle will
be built up slowly. The duty cycle will initially slowly increase
commencing with the absolute lowest possible duty cycle. The
maximum duty cycle is determined by C2530 at pin 11 of
IC7520, as C2530 is uncharged at start-up.
9.3.7 Standby mode
In standby mode the SMPS switches to the so-called "reduced
frequency mode" and runs at about 20 kHz. During standby the
SMPS only has to deliver a minimal level of output power. The
minimal load threshold level is determined by R3532 at pin 12.
In the L9 chassis the SMPS does not have a burst mode in
standby but only a reduced frequency mode of about 20 kHz as
stated above. In normal operation mode the internal oscillator
is around 40 kHz. This frequency is controlled by C2531 at pin
10 of IC7520 and by R3537 at pin 16 of IC7520. In standby
mode the frequency of operation is determined by R3536 at pin
15 of IC7520.
9.3.8 Protections
Over voltage protection of the secondary voltages.
After start-up the supply voltage pin 1 will be "taken over" by
winding 8 - 9. Pin 1 of IC 7520 is used to detect an over voltage
situation on the secondary side of the transformer. If this
voltage exceeds 17V (typically the output buffer is disabled,
and IC 7520 goes into over voltage protection and a complete
restart sequence is required. Check in this case IC7520,
IC7581 and the secondary voltage +VBATT ( +140V ).
REMARK: In the event of the over voltage situation remaining
present, the SMPS will go in protection, start up cycle,
protection, etc. The standby led on the front of the set starts
flashing.
Under voltage protection of the secondary voltages
If the supply voltage at pin 1 of IC 7520 drops below 9V
because of a short-circuit or excessive load, the drive pulse
present at pin 3 will be disabled and IC7520 will switch off the
complete SMPS. Capacitor C2450 is charged up via start-up
resistors 3510, 3530 and 3529, however once the voltage
exceeds 14.5V start up threshold, the SMPS will once again
commence a re start cycle.
In the event of the under voltage situation remaining, the SMPS
will again go in protection mode, start up cycle, protection, etc.
and so the cycle repeats. This effect is highly audible.
9.3.5 Peak current limiting
An internal clamp at pin 7 allows peak current limiting to be
achieved . This pin can never exceed 1V DC and so the
maximum primary current through FET 7518, and also the
maximum output power is determined. In case of an output
being short-circuited or loaded excessively, the I-prim becomes
9.4 Audio processing
The following systems are available:
• BASIC : MONO/AV STEREO ( M,BG, I and DK : single or
dual system )
Page 26

GB 58 L9.2A9.
• 2CS : FM STEREO / FM MONO ( all standards 4.5, 5.5, 6.5
MHz )
• BTSC : MONO/STEREO/STEREO-AP
MONO/AV STEREO, BTSC DBX incorporating 2CS (two
carrier stereo) use a TDA8841/42 BIMOS device (built-in Mono
FM Demodulator circuit).
The Audio Module incorporates for each system a different
multi digital sound processor.
• MONO /AV STEREO: BSP3505 & TDA884x
• NICAM / 2CS: MSP3415D
• BTSC: TDA8841, TDA9851 and HEF4052
These IC's have an incorporate digital audio processing for
volume, bass, treble, balance, mute, spatial sound, incredibl e
sound, smart sound and source selection (SIF-signal, EXT1 or
EXT2).
9.4.1 MONO / AV STEREO
This set does have the digital sound processor BSP3505,
IC7833.
MONO/AV STEREO
7250-A
48
IF
49
TDA 8844
15
AUDIO OUT
7803
58
52 53 49 50
EXT. 1
AUDIO
BSP3505
Figure 9-10 “MONO / AV STEREO SETS”
The video IF output is present at pin 11 of t he tuner 1000. T his
signal goes through a sound SAW filter and is fed to the BIMOS
via pins 48 and 49, where the signal is demodulated. . At pin 6
of BIMOS IC 7250-A, the SIF signal is fed to another SAW
filter. Signal Duall/Mono selects either SAW filter 1001 or SAW
filter 1002.
The system hardware configuration, option code SY, is set at
AD - Dual Mono for a Dual configuration, while option code SY
is set at SS for the Mono configuration ( BG,I, DK, M ). Via
Duall/Mono, a signal coming from the Micro-processor IC7600,
is possible to switch between two Mono configurations (BG/DK
or BG/I or DK/I).
This signal goes back to pin 1 of the BIMOS , for further
demodulation. The demodulated FM signal or the REAR I/O
audio signal, ExtAudioMono at pin 2, is switched by the BIMOS
and is present at pin 15.
The signal at pin 15 is fed to pin 55 of IC 7833 - BSP3505 - at
panel D1. IC 7833 performs source selection as well as audio
processing such as volume, bas, treble, balance, tone control
and spatial stereo. The audio output from IC 7833, pin 28 and
pin 29, is fed to the power amplifier IC 7950 or IC7951. Pin 36
and 37 pass the same selected signal through to the Audiocinches.
Signal Volume enables the output of the sound amplifier.
EXT. 2
AUDIO
LEFT OUT
28
29
RIGHT OUT
36
37
REAR
Circuit description new circuits
7250-A
48
TDA 8844
IF
49
Audio signals coming from the frontpanel are connected to pin
49/50 of IC7803 for the Ext1Audio signals, while pin 52/53 of IC
7861 are used for the Ext2Audio signals. IC 7803 performs
source selection as well as audio processing such as volume,
balance, tone control, mute, spatial stereo, incredible surround
sound and SMART sound. The audio output from IC 7803, pin
28 and pin 29, is fed to the power amplifier IC 7953 or IC7954.
Pin 36 and 37 pass the same selected signal through to the
audio-cinches. Signal Volume enables the output of the sound
amplifier.
7953/7954
3
5
+
R
16
-
R
13
-
L
12
+
L
9
9.4.3 BTSC
The SIF signal from the BIMOS are passed through a high pass
filter and are then fed back into pin 7 of IC 7861 (TDA9851) for
further demodulation. This signal is present at pin 6 of BIMOS
IF
- TDA8841.
7250-A
48
49
CL 96532047_018.eps
020699
Audio signals coming from the rear I/O panel are connected to
pin 5/14 of IC7802 for the Ext1Audio signals. The audio output
from IC 7802, performs the source selection via signal EXT 1 /
2. It is possible to switch between the demodulated BTSC
signal on the FRONT/EXT signal. Pin 3 and pin 13, are fed to
the power amplifier IC 7954. Signal Volume enables the output
of the sound amplifier.
9.5 Tuner and Video IF (see circuit diagram A5)
9.5.1 Introduction:
15
TDA 8841
7803
(SIF)
6
58
52 53 49 50
EXT. 1
AUDIO
MSP3415
Figure 9-11 “2CS”
"BTSC"
7861
SIF
76
TDA 9851
Figure 9-12 “BTSC”
2CS
EXT. 2
AUDIO
12(L)
13(R)
FRONT
EXT1 Audio L
28
29
36
37
LEFT OUT
RIGHT OUT
EXT 1/2
7802
1
5
HEF
4052
12
14
FRONT
EXT1 Audio R
REAR
BASS TREBLE
3
SMART
SOUND
13
7953/7954
3
5
CL 96532047_019.eps
7954
4
2
6
8
CL 96532047_026.eps
+
R
8
-
R
10
-
L
11
+
L
13
020699
16
13
12
9
250599
9.4.2 2CS
It is used on some cable television networks.
The diagram below indicates the AUDIO path for 2CS.
The CVBS + SIF signals present at pin 6 from BIMOS, TDA8844-, are passed through a high pass filter and are then
fed back into pin 58 of IC 7803 (MSP3415D) for further
demodulation. All variants of 2CS are demodulated in this IC.
In Figure 9.13 a simplified block diagram of the video path is
shown. The main item in the block diagram shown in Fig.9.13
is the video processor item 7250. The IC performs the following
functions, video IF demodulation, chroma processing and RGB
processing. Additionally synchronisation processing, mono IF
audio demodulation and audio selection takes place.
One version of video processor is used:
• TDA8844 N2 for SW CENELEC BG/DK, CENELEC I
NICAM, CENELEC BG NICAM
For a detailed block diagram of the TDA8844/8845 see Figure
9.12.
Page 27

Circuit description new circuits
GB 59L9.2A 9.
9.5.2 Tuner
The PLL tuner (item 1000) is digitally controlled via the I2Cbus. The tuner is suitable to receive off-air, S-(cable) and hyper
band channels.
Tuner pin description:
• Pin 1: AGC, Automatic gain control voltage input (0.3 -
4.0V)
• Pin 2: VT, tuning voltage input (not connected)
• Pin 3: AS, address select (not connected)
• Pin 4: SCL, IIC-bus serial clock
• Pin 5: SDA, IIC-bus serial data
• Pin 6: not connected
• Pin 7: Vs, PLL supply voltage +5V
• Pin 8: not connected
• Pin 9: Vst, tuning voltage +33V
• Pin 10: ground
• Pin 11: IF, asymmetrical IF output
Note: The +5V supply voltage and the +33V tuning voltage is
derived from the line output stage, see diagram A2).
9.5.3 IF band pass filter (SAW FILTER)
Between the tuner output and the video IF input of the video
processor the IF band pass filtering take place. Filter 5002 is
tuned at 40.4MHz and serves as an extra suppression of the
neighbour channel. For the IF band pass filtering SAW filters
are used (item 1003 or 1004). 5 Types of SAW filters are used
depending of the version of the set.
9.5.4 Video IF
General: Video IF-demodulation is achieved in combination
with reference circuit L5006 connected at pin 3 and 4 of
IC7250-A. The AGC control for the tuner is applied via pin 54
of IC7250-A. Internally the IC uses the top sync level as a
reference for AGC control. The AGC adjustment can be
readjusted via the SAM (service alignment menu). C2201
connected to pin 53 determines the time constant of the AGC.
The Base band CVBS signal is present at pin 6 of IC7250-A
(normal amplitude 3.2Vpp). From here the signal is fed via
transistor 7266 to the sound trap filters and then on to the video
source selection circuit.
The main functions of the video IF part are (see also figure 9.5):
• IF- amplifier
• PLL-demodulator
• Video buffer
•AFC
• IF-AGC
• Tuner AGC
9.5.5 IF- amplifier
The IF-amplifier incorporates symmetrical inputs (pins 48 and
49). By using IIC bus control (IFS) the AGC attenuation can be
adjusted by up to -20db.
Remark: If the BIMOS is replaced the AGC value should be
adjusted as part of the repair process. (see software alignment
adjustments).
9.5.6 PLL-demodulator
The IF-signal is demodulated with the assistance of the PLL
detector. The video IF-demodulator can handle both negative
and positively modulated IF signals; selection is achieved via
the IIC bus (bit MOD).
9.5.7 Video buffer
The video buffer is present to provide a low ohmic video output
with the required signal amplitude. Additionally, it provides
protection against (pin 6) the occurrence of noise peaks. The
video buffer stage also contains a level shifter and a gain stage
for both the positive and negative video modulation formats, so
that the correct video amplitude and DC level are always
present at pin 6 regardless of the input signal.
9.5.8 Video-IF AGC
An AGC system controls the gain of the IF amplifier such that
the video output amplitude is constant. The demodulated video
signal is supplied, via a low pass filter inside the I C to an AGC
detector. External AGC de coupling is provided by capacitor
2201 at pin 53. The AGC detector voltage directly controls the
IF amplification stages.
9.5.9 The tuner AGC
Tuner AGC is provided to reduce the tuner gain and thus the
tuner output voltage when receiving to strong RF signal. The
tuner AGC starts working when the video-IF input reaches a
certain input level. This level can be adjusted via the IIC bus.
The tuner AGC signal is applied to the tuner via the open
collector output pin 54 of the BIMOS.
9.5.10 AFC
The AFC output information is available for search tuning. The
AFC output is available via the I2C bus ( AFA and AFB signals).
For alignment purposes it is displayed in the TUNER submenu
of the SAM (See chapter 8).
Figure 9-13 “BIMOS”
9.6 Video Signal Processing (see circuit diagram
A6)
9.6.1 Introduction:
The video signal processing can be divided in the following
parts:
• CVBS/Y/C input selection
• Luminance and chrominance signal processing
• PAL/NTSC and SECAM demodulation /Auto system
manager
• YUV/RGB processing/ black stretcher
• Second RGB insertion
• RGB processing
• Black current calibration loop
• Beaming current limiting
Above mentioned processing circuits are integrated in the TVprocessor (parts B and C). The surrounding components are
for the adaptation of the selected application. The I2C bus is
used for defining and controlling the signals.
Page 28

GB 60 L9.2A9.
Circuit description new circuits
IC 7250-4A
34 5
TDA 8845
AFC
48
49
54
55
56 15
IF AMPLIFIER
+
PLL VIDEO DEMO.
AGC
53
SOUND
AMPL.
AGC
VIDEO
AMPL.
IF
1
OR
IC 7250-4A
34 5
TDA 8844
AFC
48
49
54
53
IF AMPLIFIER
+
PLL VIDEO DEMO
AGC
1
LIMITER
AUDIO
FM DEMO.
VIDEO
AMPL.
PLL-
AMPL.
+
MUTE
2
TDA 8844/8845
Y
U
V
OSD/TXT/SCART
PROCESSING
+SWITCH
SOUND
SIF
(to sound proc..)
YC/CVBS EXT
YC/CVBS EXT
YC/CVBS EXT
CVBS_MON
V_PATH1.PPT
20/3/98
TUNER
CVBS + SIF
SOUND
TRAP
BPF
CVBS_INT
CVBS_EXT
SWITCH
IF
48/49 25
6
IF
13
17
TDA884X
CHROMA
PROCESSING
30 29 28 27 31
Figure 9-14 “VIDEOPATH”
9.6.2 CVBS/Y/C selection
The input switches are used for selection of the input signal.
Three input signals can be selected:
• Pin 13: terrestrial CVBS input.
• Pin 17: external AV1 input.
• Pin10/11: external AV2-Y, CVBS/C input
When pin 11 is in the CVBS input mode then pin 10 is not used.
When pin 11 is in the Y/C input mode then both pins are used
and the CHROMA filter in the Y signal path is switched off.
9.6.3 Luminance / Chroma signal processing
Once the signal source has been selected, CHROMA filter
calibration is performed. The received colour burst-sub-carrier
frequency is used for the calibration. Correspondingly, the
CHROMA band-pass filter for PAL/NTSC processing or the
cloche filter for SECAM processing is switched on. Pins 34, 35
have the crystals connected to them. These crystals are used
for multi-purpose calibration of the burst sub-carrier. The
selected luminance signal is then supplied to the Horizontal
and Vertical synchronisation processing circuits and to the
luminance processing circuits. In the Luminance processing
block, the luminance signal is applied to the CHROMA trap.
This trap is switched on or off depending upon on the colour
burst detection of the CHROMA calibration circuit. Before the
AFC
QSS MIXER
SOUND
AM DEM.
AFC
RGBFBL
242326
RGB
MATRIX
CL 86532104_017.eps
VIDEO-
BASEBAND
OUTPUT
+
VIDEO-
BASEBAND
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
VOLUME
CONTROL
3238
38
7250-4B
TDA 8844/45
13
17
6
10
11
7250-4C
TDA 8844/45
27
Y
31
U
32
V
7250-4D
TDA 8844/45
Y
43
50
VIDEO IDENT
CD MATRIX
SATURATION
CONTROL
SKIN
SYNC.
SEPARATOR
VERT.
SYNC.
SEPARATOR
2
6
55
+
15
TINT
+
+
Y (TO SYNC PART)
LUM.
DELAY
PEAKING
CORING
CHROMA
BANDPASS
RGB
MATRIX
+
BLACK
STRETCH
+
RGB1
INPUT
41 42 37
VCO
+
CONTROL
52514439
PAL/NTSC/
DEMODULATOR
169 36353433
78
CONTROL
R
G
OUTPUT
B
2223 24 25 26
HORIZONTAL
OUTPUT
VERTICAL
OUTPUT
E/W
OUTPUT
SECAM
IIC BUS
RGB
CALIB.
CATH.
28
INPUT SELECT
Y + CHROMA
29
BASE-
PROCESSING
BAND
DELAY
30
LINE
21
R
20
G
RGB
19
B
OUTPUT
18
40
46
SYNC
47
45
CL 86532104_021.EPS
220299
luminance signal is applied to pin 28 of the TV-processor the
signal is applied to a "peaking" and "coring" circuit. In these
circuits the sharpness and noise level of the signal can be
influenced via the remote control (control menu in the user
menu ).
21
R
20
G
TO CRT
19
B
9.6.4 PAL, NTSC and SECAM demodulation via the Auto system
manager
The colour decoder circuit detects whether the signal is a PAL
or NTSC signal. The result is made known to the auto system
manager. The base-band delay line is activated when a PAL or
SECAM signal is detected. For the SECAM colour standard a
reference voltage is generated at pin16 of the TV-processor.
160299
Connected at Pin 9 of the TV-processor, is the band-gap decoupling circuit, which consists of (2214,2215). The band-gap
circuit provides a very stable and temperature independent
reference voltage. It ensures optimal performance of the TVprocessor and is used by almost all functional blocks inside the
processor. The Y signal and the demodulator outputs R-Y and
B-Y are present at pin 28, 29, 30 of the TV-processor. The auto
system manager identifies PAL, NTSC and SECAM colour
standards and is controllable via the IIC bus. Connected on pin
36 of the TV-processor is the Loop Filter for the phase detector
The filter chosen provides an optimal transient response, which
ensures both an optimum for noise bandwidth and colour
acquisition time.
9.6.5 YUV / RGB processing/ black stretching
The signal Y, R-Y and B-Y present on pins 27, 31, 32 of the TVprocessor are used as the input signals for the colour decoding
section of the BiMOS (IC7520-C). The YUV processor enables
the colour saturation control and also converts the Y, B-Y and
B-Y signals to the R, G, B signal format via the colour matrix
circuit. The black stretcher circuit , initial stage of the matrix
circuit, extends the Grey signal level towards the actual black
level. The amount of extension depends upon the difference
between actual black level and the darkest part of the incoming
video signal level. This feature is fully integrated. The user can
switch this circuit on or off by using the Contrast Plus option in
the user menu.
Page 29

Circuit description new circuits
GB 61L9.2A 9.
9.6.6 Second RGB insertion
Pins 23, 24, 25 are used as the inputs for the second R, G, B
signals insertion. Pin 26 of the TV-processor is the input for the
insertion control signal which is called "FBL". When the FBL
signal level becomes higher than 0.9V (but less than 3V) the R,
G, B signals at pins 23,24,25 are inserted into the picture by
using the internal switches incorporated in the TV-processor.
This second insertion possibility is used for insertion of the on
screen display signals , TXT or R. G. B signals from the CINCH
socket..
9.6.7 RGB processing
The RGB processing circuit enables the picture parameters to
be adjusted by using a combination of the user menus and the
remote control. Additionally automatic gain control for the RGB
signals via cut-off stabilisation is achieved in this functional
block..
The block also inserts the cut off point "measuring pulses" into
the RGB signals during vertical retrace period.. From outputs
19,20 and 21 the RGB signals are then applied to the output
amplifiers on the CRT panel.
9.6.8 Black current calibration loop
The black current calibration loop ensures that the white
balance at low signal levels and low light white balance is
skipped. By means of the inserted measuring pulses, the black
current calibration loop, tracks the beam current feed back of
the RGB signals at the cathodes of the picture tube. As a result
of this calibration, the individual black level of the RGB output
signals is shifted to a level which allocates around 10uAof
beam current to each of the RGB signals. Pin 18 (BC_info) of
the BIMOS is used as the feed back input from the CRT base
panel.
9.6.9 Beam current limiting
A beam current limiting circuit inside the BiMOS handles the
contrast and brightness control for the RGB signals. This
prevents the CRT tube being over driven, which may cause
serious damage in the line output stage. The reference used for
this purpose is the DC voltage on Pin 22 (BLCIN) of the TVprocessor. Contrast and brightness reduction of the RGB
output signals is therefore proportional to the voltage present
on this pin. Contrast reduction starts when the voltage on pin
22 is lower than 3.0 V. Brightness reduction starts when the
voltage on pin 22 is less than 2.0 V.
The voltage on pin 22 is normally 3.3V (limitor not active). To
enable correct operation however, an external adaptation to
the circuit is required for the correct functioning of the limiting
function. This is connected to Pin 22, the circuit therefore
ensures that correct peak white limiting and the average beam
current limiting takes place. Components 6212, 2227, 3253,
3246 are for the average beam current limiting and the items
connected to 7263 are for the peak white limiting. As a
reference for the average beam current control the signal
EHT_info is used. This signal is a measurement of the picture
contents. It is filtered by 3253, 2227. As the time constant of
the filter is much bigger than the frame period time, the DC at
the anode of 6212 represents the average value of the picture
content. Via 6212 and 2226 the DC voltage at pin 22 is slowly
'clamped'. For peak white limiting transistor 7263 is utilised.
When peak white occurs, the DC voltage at the base of 7263
drops rapidly. 7263 starts conducting, which provides a path to
discharge the capacitor 2226 very fast. The voltage bias at the
base of 7263 is fixed via voltage divider 3251 and 3249. The
RGB output signals are applied to the CRT panel via connector
0243. Via diodes 6263, 6264 and 6265 and series resistor
3253, the RGB signals are also connected to the
CRT_discharge signal. The level of this signal is only high
during the time the set is switched off. And id due to the
cathodes of the CRT are driven fully negative. That means that
the beam current is increased. and consequently the CRT
quickly discharged.
9.6.10 CRT panel (see circuit diagram B)
On the CRT panel the output amplifiers for the RGB signals (
IC T7330, DA6107Q) are located. Via the outputs 9, 8 and 7 of
the IC the cathodes of the CRT are driven. The supply voltage
for the IC is +200VA and is derived from the line output stage.
9.7 List of abbreviations
2CS 2 Carrier Stereo
A/P Asia Pacific; schematic/PCB
information (only) applicable for Asia
Pacific sets
AFC Automatic Frequency Control
AQUADAG Aquadag coating on the (outside of
the) picture tube
AudioOutR Audio signal at Right output channel.
AudioOutL/Mono Audio signal at Left output channel /
Mono output channel.
AV_MUTE Signal to mute the sound on the Audio-
out of Cinch / Scart (Combined with
RBG_Blanking)
Ext2Fun_SW
(AV_Mute/
Ext2Fun_SW) S witching signal from Scart2 to micro
controller indicating the presence and
type of signal on Scart2. (no signal /
CVBS 16:9 / CVBS 4:3)
AV Audio Video signal
AVL Automatic Volume Level
B_TXT_OSD Blue TXT or OSD signal from uC to the
video controller IC7250 (BIMOS)
BASS Control signal for BASS
BCI Beam Current information
BTSC Broadcast Television Standard
Committee; sound standard for
America and Asia Pacific
Buzzer Buzzer (only used in L9-ITV)
CRT DISCHARGE Fast drop of VBATT during after switch
off the set. Which result in EHT voltage
reducing to less than 18 kv within 5
sec.
CTI Colour Transient Improvement
CVBS Colour Video Blanking
Synchronisation. Video signal
containing colour, black/white,
blanking and synchronisation
information.
CVBS_EXT CVBS external = CVBS signal form
external source (VCR, DVD etc.)
CVBS_INT CVBS internal = CVBS signal from the
tuner
CVBS_MON CVBS monitor (CVBS) signal to Cinch
or Scart
CVBS_Terr CVBS Terrestrial output signal
CVBS_TXT CVBS for TXT processing in micro
controller
Din Digital input signal only used in L9-
ITV)
Dout Digital output signal (only used in L9-
ITV)
DBX Dynamic Bass Expander (only used
for BTSC sound system)
DNR Dynamic Noise Reduction
EAR Earth (ground layer)
Page 30

GB 62 L9.2A9.
Circuit description new circuits
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable
Read Only Memory (also called NVM;
non-volatile memory)
EHT-INFO Extra high tension information; Beam
current related signal from CRT to
BIMOS.
Ext1 B RGB External 1 Blue input signal.
Ext1 FB RGB External 1 Fast-blanking input
signal.
Ext1 G RGB External 1 Green input signal.
Ext1 R RGB External 1 Red input signal.
Ext1 Video RGB External 1 Video input signal.
Ext2 AudioL/Mono External 2 Audio Left input signal /
Mono input signal.
Ext Audio/Mono External Audio input signal / Mono
input signal.
Ext2 AudioR External 2 Audio Right input signal.
Ext2C Exterial 2 SVHS Chrominance (C)
input signal.
Ext2Video/Y External 2 Video input signal or SVHS
Luminance (Y) input signal.
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
EURO Euro pe; schematic/P CB information
(only) applicable for European sets
EWD_dyn Dynamic East-West correction to
compensate for variations in EHT
EWDRIVE East-West drive correction
FB_TXT_OSD Fast blanking signal from micro
controller to IC7250 (BIMOS) for
inserting or displaying TXT and OSD
information (generated by the micro
processor)
Filament Filament (heater voltage) from LOT t o
CRT
FBL Fast Blanking
FFBL Full screen Fast Blanking
FM/AM/
Ext_VC_AudioMono FM, AM or external mono signal from
BiMOS to audio processor input (only
used in Mono and Nicam L sets)
Front/Ext1AudioL Front audio Left input signal / External
1 Audio Left input signal.
Front/Ext1AudioR Front audio Right input signal /
External 1 Audio Right input signal.
GND Ground
GND_LOT Ground of LOT
G_TXT_OSD Green TXT or OSD signal from micro
processor to the video controller
IC7250 (BIMOS)
HD Horizontal pulse derivation
HDRIVE Horizontal output drive
HEW_protn Switching signal to (de)activate the
XRAY protection which is measured
via pin 50 of the BIMOS (only for USA
sets)
Hflybk Horizontal flyback pulse used to
monitor the horizontal oscillator
IF Intermediate Frequency signal from
the tuner
12C (or IIC) 2 Wire communication protocol
between micro controller and
integrated circuits
IC Integrated Circuit
I/O Input/Output
INT Audio internal output
IR Output signal from infrared receiver to
micro controller.
KeyBd1 Local keyboard control signal to micro
controller
KeyBd2 Local keyboard control signal to micro
controller (In protection mode KeyBd2
is Ground)
KeyBd3 Local keyboard control signal to micro
controller
L- Power amplifier output to headphone
and speaker
L+ Power amplifier output to speaker
LED LED control signal from micro
controller to LED
LATAM Latin America; schematic/PCB
information (only) applicable for Latin
American (incl. Brazilian) sets
LeftOut Audio Left signal output
LTI Luminance Transient Improvement (=
steepness)
MainAudioL/Mono Audio Left/Mono signal to input power
amplifier
MainAudioR Audio Right signal to input power
amplifier
MON Audio monitor output
NICAM Near Instantaneous Companded
Audio Muliplex (digital audio)
NR Noise Reduction
NTSC NTSC colour system
OSD On Screen Display
P0Sys1/AM Switching signal with several
functions:
BiMOS crystal
selection (only for
Latam sets) Selection of AM or FM signal (used in
combination with P1Sys2/
AMFM_ExtSel) (only for Europe)
Sys2/AMFM_ExtSel Switching signal with several
functions: BIMOS crystal selection
(only for Latam sets) Selection of
internal AM/FM signal or an external
signal (used in combination with
P0Sys1/AM)
LLp/Mtrap Switching signal with several
functions: M-trap (sound filtering)
switching (only for A/P Pal Multi sets)
BiMOS crystal selection (only for
Latam sets), Selection of L or L'
system (only for Europe sets)
Dual/Mono Switching signal to select the sound
filter in dual-system Mono sets (BG/I,
BG/DK or I/DK).
ScartPin8/SVHS Switching signal from I/O to micro
controller with several functions:
Scart1 I/O: detects signal type
connected to Scart 1 (no signal, 16:9
signal, 4:3 signal) (only for Europe)
Cinch I/O: detects signal type
connected to cinch: SVHS or CVBS
(not for Europe)
BassSw Bass switching signal (only for some
mono sets)
TrebleSw Treble switching signal (only for some
mono sets)
Ext1/2 Used in L9-ITV sets (Hotel TV)
stbyon+protn Signal from E-W and LOT output to
micro controller to (de)activate the
protection mode
Mute/Volume Audio mute / Volume control signal pin
POR/CLK Power on reset (only used in L9-ITV
sets)
R- Power amplifier output " R- " to
speaker
R+ Power amplifier output " R+ " to
headphone and speaker
RAM Random Access Memory
RESET Reset signal to micro controller
RF_AGC Automatic gain control signal from
BiMOS output to tuner input.
RGB Red-Green-Blue
Page 31

Circuit description new circuits
GB 63L9.2A 9.
RGB_Blanking Red Green Blue Blanking signal
RightOut Audio right signal output
R_TXT_OSD Red TXT or OSD signal from uC to the
ROM Read Only Memory
SAM Service Alignmen t Mode. Service
SAP Second audio program (only for USA
SCL Clock line of the I2C-bus
SCL2 2nd Clock line of the IIC-bus (only
SDA Data line of the I2C-bus
SDA2 2nd Data line of the I2C-bus (only
SDM Service Default Mode. Service mode
SIF Sound IF signal for FM audio
SMPS Switching Mode Power Supply
STANDBY Switching signal from micro controller;
SW_OUT Selected Output signal from source
SYNC Synchronisation
TBD To Be Defined
TREBLE Control signal for treble
TXT Teletext
µ
C Micro controller
USA United States; schematic/PCB
V_TUNE Tuning voltage for tuner
Vdrive - Negative Vertical drive pulse signal
Vdrive + Positive Vertical drive pulse signal
VD Vertical pulse derivation
VFL Vertical flyback pulse used to inform
Vflybk Vertical flyba ck pulse
VG2 Voltage on grid 2 of the picture tube
VideoOut CVBS output signal
VOLUME Control signal (from micro controller,
XRAY-PROT XRAY protection (only for USA sets)
YC Luminance (Y) and Chrominance (C)
(combined with AV_MUTE)
video controller IC7250 (BIMOS)
mode for alignments and error buffer
display
& A/P sets)
used in L9-ITV sets)
used in L9-ITV sets)
with predefined settings for waveform
and voltage measurements, error
buffer display and option (byte)
setting.
demodulator
"low" for standby (power supply will be
switched to stand-by mode), "high" for
normal operation
information (only) applicable for North
American sets
the micro controller that flyback is
occurring. This is critical for the correct
OSD and TXT
(screen control)
but on DC level via RC network) for
sound processing in sound IC
Page 32

GB 64 L9.2A10.
10. Spare parts list
Spare parts list
Mono Carrier [A]
Various
0127 3122 358 721 41 F US E HOLDE R CLIC K
0130 3139 123 21331 INSULATING PLATE
0139 4822 492 70788 IC fixation
0189 3139 124 24322 PCB RELIEF BRACKET
4822 265 20723 Conn. 2p
0211
h
0218 4822 265 10481 CINCH CONNECTOR 2P
0223 4822 265 10495 Cinch block
0224 4822 267 10676 Conn. 1p
0228 4822 267 10676 Conn. 1p
0229 4822 267 31673 Headphone plug
0230 4822 267 31673 Headphone plug
4822 276 14024 Mains switch
0231
h
4822 267 31014 HEADPHONE SOCKET
0232
h
0234 4822 267 10928 Conn. 5p
0267 4822 267 31673 Headphone plug
4822 210 10841 Tuner UV1316/A
1000
h
1001 4822 242 10314 filter 5,5MHz
1002 4822 242 10316 filter 6,5MHz
1003 4822 242 10357 SAW filter OFWK2960M
1200 4822 242 10315 ce r. filt er 5,5 /5,7 /6,5 MHz
1200 4822 242 81712 filter 5,5/5,74MHz
1201 4822 242 81301 filter 6,5MHz
1201 4822 242 81572 filter 6,0MHz
1203 4822 242 81978 filter 4,5MHz
1205 4822 242 10695 cr ystal 4.4 336 19 MH z
1208 4822 242 10776 cr ystal 3.5 795 45 MH z
4822 070 34002 fuse (4A)
1500
h
4822 071 51002 fuse (1A)
1571
h
1572
4822 252 11194 fuse (0,800A)
h
1600 4822 242 10694 cr ystal 12.000MHz
1680 4822 276 13775 SWITCH
1681 4822 276 13775 SWITCH
1682 4822 276 13775 SWITCH
1683 4822 276 13775 SWITCH
g
2001 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2002 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2003 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2004 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2005 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2006 4822 126 13695 82pF 1% 63V
2008 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2009 4822 122 33926 12pF 50V
2010 5322 122 33861 120pF 10% 50V
2011 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2012 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2013 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2110 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2111 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2112 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2113 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2114 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2115 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2135 4822 126 14043 1µF 20% 16V
2136 4822 126 14043 1µF 20% 16V
2137 4822 126 13482 470nF 20% 16V
2172 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2173 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2174 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2176 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2177 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2201 4822 124 21913 1µF 20% 63V
2202 5322 126 10465 3.9nF 10% 50V
2203 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2205 4822 126 13838 100nF 50V 20%
2206 4822 122 33127 2.2nF 10% 63V
2207 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2210 4822 126 13482 470nF 20% 16V
2211 4822 126 13482 470nF 20% 16V
2212 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2213 4822 126 13482 470nF 20% 16V
2214 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2215 4822 124 22652 2.2µF 20% 50V
2216 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2217 4822 126 13689 18pF 1% 63V
2218 5322 122 31866 6.8nF 10% 63V
2220 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2221 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2222 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2223 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2224 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2225 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2226 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2227 4822 051 20008 jumper (0805)
2227 4822 126 13482 470nF 20% 16V
2228 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2229 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2230 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2231 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2232 4822 122 33127 2.2nF 10% 63V
2233 4822 124 21913 1µF 20% 63V
2234 5322 126 10223 4.7nF 10% 63V
2236 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2237 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2238 4822 126 13486 15pF 2% 63V
2239 5322 121 42386 100nF 5% 63V
2240 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2241 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2242 4822 124 21913 1µF 20% 63V
2243 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2244 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2248 4822 126 13486 15pF 2% 63V
2250 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2253 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2255 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2313 4822 122 33216 270pF 5% 50V
2323 4822 122 33172 390pF 5% 50V
2331 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
4822 126 14588 2.2nF 10% 1KV
2341
h
2342 4822 121 43526 47nF 5% 250V
2343 4822 121 43526 47nF 5% 250V
2400 4822 121 43526 47nF 5% 250V
2401 4822 121 43526 47nF 5% 250V
2402 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2403 4822 122 31169 1.5nF 10% 500V
4822 126 14237 470pF 10% R 2KV
2405
h
2406
4822 126 13866 4.7nF 10% 1KV
h
4822 121 70434 11nF 5% 1.6KV
2407
h
4822 121 70617 10nF 5% 1.6KV
2407
h
2407
4822 121 70637 8.2nF 5% 1600V
h
2408 4822 122 30103 22nF 20% 63V
2409 4822 124 11575 47µF 20% 160V
2410 4822 124 11767 470µF 20% 25V
2411 4822 124 40255 100µF 20% 63V
2412 4822 121 51385 33nF 20% 100V
2413 4822 124 11845 22µF 20% 250V
2414 4822 124 81145 1000µF 20% 16V
2415 4822 124 81145 1000µF 20% 16V
4822 126 11503 820pF 10% 2KV
2416
h
4822 126 12263 220pF 10% 2KV
2416
h
4822 126 13864 330pF 10% 2KV
2416
h
2417 4822 124 11767 470µF 20% 25V
2418 4822 126 13482 470nF 20% 16V
2420 4822 121 10781 470nF 5% 250V
2420 4822 126 14097 680nF 5% 250V
2431 4822 124 12438 2.2µF 20% 100V
2432 4822 124 81188 100µF 20% 25V
2460 5322 122 32268 470pF 10% 50V
2461 5322 126 10184 820P 5% 50V
2462 5322 122 32268 470pF 10% 50V
2463 5322 121 42386 100nF 5% 63V
2464 4822 124 40255 100µF 20% 63V
2465 5322 121 42386 100nF 5% 63V
2466 4822 121 42408 220nF 5% 63V
2467 5322 121 42386 100nF 5% 63V
2470 5322 126 10223 4.7nF 10% 63V
4822 126 13589 470nF 275V
2500
h
4822 126 14153 2.2nF 10% 1KV
2502
h
4822 126 14153 2.2nF 10% 1KV
2504
h
2505
4822 126 14153 2.2nF 10% 1KV
h
2508 4822 124 12415 220µF 20% 400V
4822 126 13517 820pF 10% 1000V
2509
h
2510
4822 126 13517 820pF 10% 1000V
h
2517 5322 122 32331 1nF 10% 100V
4822 126 13337 220pF 10% 1KV
2518
h
2518
4822 126 14149 330pF 10% 1KV
h
2520 4822 126 13695 82pF 1% 63V
2521 4822 122 33891 3.3nF 10% 63V
2521 5322 126 10223 4.7nF 10% 63V
2522 4822 122 33891 3.3nF 10% 63V
2522 5322 126 10223 4.7nF 10% 63V
2524 5322 122 32268 470pF 10% 50V
2529 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2530 4822 124 22776 1µF 50V
2531 4822 126 14587 560pF 2% 50V
2533 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2534 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2537 5322 121 42386 100nF 5% 63V
2540 4822 124 81188 100µF 20% 25V
2541 4822 121 10686 4.7nF 10% 50V
4822 126 14049 1.5nF 20% 250V
2545
h
4822 126 14152 680pF 10% 1KV
2550
h
2551 4822 124 42336 47µF 20% 160V
2560 5322 122 31647 1nF 10% 63V
2561 4822 124 81145 1000µF 20% 16V
2570 4822 122 33127 2.2nF 10% 63V
2571 4822 124 12417 2200µF 20% 25V
2572 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2600 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2601 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2604 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2605 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2606 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2607 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2608 4822 121 43897 1nF 5% 400V
2609 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2610 4822 121 42687 3.3nF 10% 63V
2611 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2612 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2613 4822 126 13695 82pF 1% 63V
2614 4822 126 13695 82pF 1% 63V
2615 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2616 5322 122 32658 22pF 5% 50V
2617 5322 122 32658 22pF 5% 50V
2618 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2619 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2620 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2621 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2622 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2623 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2624 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2625 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2651 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2675 4822 126 13482 470nF 20% 16V
2680 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2697 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2950 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2951 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2952 4822 122 33127 2.2nF 10% 63V
2953 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2954 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2955 4822 124 11767 470µF 20% 25V
2971 4822 121 51252 470nF 5% 63V
2972 4822 126 12105 33nF 5% 50V
2973 5322 121 42386 100nF 5% 63V
2974 4822 121 51379 82nF 5% 63V
2975 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
f
3000 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3001 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3002 4822 116 52244 15k 5% 0.5W
3003 4822 116 52238 12k 5% 0.5W
3004 4822 116 52243 1k5 5% 0.5W
3013 4822 051 20008 jumper (0805)
3014 4822 051 20392 3k9 5% 0.1W
3015 4822 116 83933 15k 1% 0.1W
3016 4822 117 10361 680Ω 1% 0.1W
3021 4822 117 10361 680Ω 1% 0.1W
3026 4822 051 20562 5k6 5% 0.1W
3027 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3110 4822 117 11927 75Ω 1% 0.1W
3112 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3113 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3114 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3115 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3117 4822 051 20008 jumper (0805)
3120 4822 117 11927 75Ω 1% 0.1W
3121 4822 117 10353 150Ω 1% 0.1W
3122 4822 117 13579 220k 1% 0.1W
3124 4822 117 10353 150Ω 1% 0.1W
3125 4822 117 13579 220k 1% 0.1W
3127 4822 051 20008 jumper (0805)
3128 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3140 4822 116 83874 220k 5% 0.5W
3141 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3145 4822 116 52228 680Ω 5% 0.5W
3146 4822 051 20334 330k 5% 0.1W
3147 4822 051 20391 390Ω 5% 0.1W
Page 33

Spare parts list
GB 65L9.2A 10.
3152 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3153 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3156 4822 116 83876 270Ω 5% 0.5W
3157 4822 116 83876 270Ω 5% 0.5W
3200 4822 117 10361 680Ω 1% 0.1W
3201 4822 116 83881 390Ω 5% 0.5W
3202 4822 051 20155 1M5 5% 0.1W
3203 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3204 4822 117 10353 150Ω 1% 0.1W
3205 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3206 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
4822 052 10338 3Ω3 5% 0.33W
3207
h
3208 4822 051 20829 82Ω 5% 0.1W
3210 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3211 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3212 4822 116 83883 470Ω 5% 0.5W
3213 4822 051 20561 560Ω 5% 0.1W
3214 4822 116 83868 150Ω 5% 0.5W
3218 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3219 4822 116 52226 560Ω 5% 0.5W
3221 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3222 4822 051 20561 560Ω 5% 0.1W
3223 4822 117 11927 75Ω 1% 0.1W
3224 4822 117 11927 75Ω 1% 0.1W
3225 4822 117 10837 100k 1% 0.1W
3228 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3243 4822 117 12955 2k7 1% 0.1W
3246 4822 116 83933 15k 1% 0.1W
3247 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3248 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3257 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3258 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3259 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3260 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3265 4822 051 20105 1M 5% 0.1W
3266 4822 116 83933 15k 1% 0.1W
3268 4822 051 20333 33k 5% 0.1W
3269 4822 051 20393 39k 5% 0.1W
3272 4822 051 20273 27k 5% 0.1W
3273 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3274 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3275 4822 117 13579 220k 1% 0.1W
3276 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3277 4822 051 20008 ju mp er (08 05)
3278 4822 051 20008 ju mp er (08 05)
3279 4822 053 11331 330Ω 5% 2W
3280 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3311 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3312 4822 117 13577 330Ω 1% 1.25W
3313 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3314 4822 053 12183 18k 5% 3W
4822 052 10221 220Ω 5% 0.33W
3316
h
3317 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
3321 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3322 4822 117 13577 330Ω 1% 1.25W
3323 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3324 4822 053 12183 18k 5% 3W
4822 052 10221 220Ω 5% 0.33W
3326
h
3327 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
3331 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3332 4822 117 13577 330Ω 1% 1.25W
3333 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3334 4822 053 12183 18k 5% 3W
4822 052 10221 220Ω 5% 0.33W
3336
h
3337 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
3341 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
4822 052 10102 1k 5% 0.33W
3347
h
3348 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
3349
4822 052 10128 1Ω2 5% 0.33W
h
4822 052 10128 1Ω2 5% 0.33W
3350
h
3400 4822 053 12472 4k7 5% 3W
3402 4822 050 12709 27Ω 1% 0.4W
3403 4822 116 52289 5k6 5% 0.5W
3404
4822 117 13671 12k 5% 0.33W
h
4822 052 10472 4k7 5% 0.33W
3405
h
4822 052 10472 4k7 5% 0.33W
3406
h
3407 2322 195 63471 470Ω 5% 3W
3407 4822 117 12172 220Ω 5% 3W
4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3411
h
3411
4822 052 10228 2Ω2 5% 0.33W
h
4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3412
h
3414 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3414 4822 051 20182 1k8 5% 0.1W
3414 4822 117 11449 2k2 1% 0.1W
3415 4822 050 21003 10k 1% 0.6W
3415 4822 116 52244 15k 5% 0.5W
4822 052 11398 3Ω9 5% 0.5W
3416
h
4822 052 11108 1Ω 5% 0.5W
3417
h
3420 4822 117 11927 75Ω 1% 0.1W
3421 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3423 4822 050 21003 10k 1% 0.6W
3424 4822 117 11507 6k8 1% 0.1W
3425 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3431 4822 117 13579 220k 1% 0.1W
3432 4822 117 11149 82k 1% 0.1W
3433 4822 117 13579 220k 1% 0.1W
3434 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3435 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3436 4822 116 52256 2k2 5% 0.5W
3440 4822 050 21003 10k 1% 0.6W
3441 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3460 4822 050 22202 2k2 1% 0.6W
3461 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3462 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
4822 052 10158 1Ω5 5% 0.33W
3463
h
3464 4822 050 22202 2k2 1% 0.6W
3465 4822 050 23308 3Ω3 1% 0.6W
3465 4822 050 24708 4Ω7 1% 0.6W
3465 4822 050 26808 6Ω8 1% 0.6W
3466 4822 050 23308 3Ω3 1% 0.6W
3466 4822 050 24708 4Ω7 1% 0.6W
3466 4822 050 25608 5Ω6 1% 0.6W
3467 4822 116 83872 220Ω 5% 0.5W
3468 4822 116 83872 220Ω 5% 0.5W
3470 4822 116 52251 18k 5% 0.5W
3471 4822 051 20391 390Ω 5% 0.1W
3472 4822 116 52256 2k2 5% 0.5W
3473 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3474 4822 053 12229 22Ω 5% 3W
3501 4822 117 12181 470Ω 20% 0.5W
4822 053 21225 2M2 5% 0.5W
3502
h
3504 4822 117 12728 9Ω 200V S 100R
3506 4822 116 82776 2Ω2
3509 4822 117 12654 100Ω 5% 5W
3510 4822 117 12647 33k 5% 3W
3512 4822 117 10965 18k 1% 0.1W
3513 4822 117 13579 220k 1% 0.1W
3517 4822 050 21003 10k 1% 0.6W
3518 2120 106 90549 0Ω27 5%
3520 4822 117 11149 82k 1% 0.1W
3521 4822 116 52219 330Ω 5% 0.5W
3524 4822 051 20008 jumper (0805)
4822 052 10229 22Ω 5% 0.33W
3525
h
3528 4822 116 83868 150Ω 5% 0.5W
3529 4822 050 24708 4Ω7 1% 0.6W
3530 4822 116 52276 3k9 5% 0.5W
3532 4822 117 11507 6k8 1% 0.1W
3534 4822 117 13579 220k 1% 0.1W
3536 4822 051 20273 27k 5% 0.1W
3537 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3538 4822 116 52304 82k 5% 0.5W
3539 4822 116 52244 15k 5% 0.5W
3540 4822 100 12156 4k7 30%
3541 4822 053 11479 47Ω 5% 2W
4822 053 21475 4M7 5% 0.5W
3542
h
3570 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3600 4822 116 52213 180Ω 5% 0.5W
3601 4822 116 83881 390Ω 5% 0.5W
3602 4822 116 83883 470Ω 5% 0.5W
3603 4822 116 52263 2k7 5% 0.5W
3605 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3606 4822 051 20561 560Ω 5% 0.1W
3607 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3608 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3609 4822 117 11454 820Ω 1% 0.1W
3610 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3611 4822 051 20822 8k2 5% 0.1W
3612 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3613 4822 051 20332 3k3 5% 0.1W
3614 4822 051 20332 3k3 5% 0.1W
3615 4822 117 11454 820Ω 1% 0.1W
3616 4822 117 12167 8k2 X 12
3617 4822 116 90885 8k2X6
3618 4822 051 20822 8k2 5% 0.1W
3619 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3620 4822 050 12403 24k 1% 0.4W
3622 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3623 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3624 4822 117 13649 2k2 5% 7X
3625 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3626 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3627 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3628 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3629 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3630 4822 116 83884 47k 5% 0.5W
3631 4822 117 13579 220k 1% 0.1W
3632 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3633 4822 116 52264 27k 5% 0.5W
3634 4822 051 20562 5k6 5% 0.1W 0805
3636 4822 117 11449 2k2 1% 0.1W
3639 4822 117 10353 150Ω 1% 0.1W
3640 4822 117 12521 68Ω 1% 0.1W
3641 4822 117 12521 68Ω 1% 0.1W
3642 4822 117 12521 68Ω 1% 0.1W
3643 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3644 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3647 4822 116 52202 82Ω 5% 0.5W
3648 4822 116 52202 82Ω 5% 0.5W
3649 4822 116 52202 82Ω 5% 0.5W
3650 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3651 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3652 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3653 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3654 4822 051 20105 1M 5% 0.1W
3655 4822 116 52234 100k 5% 0.5W
3670 4822 051 20392 3k9 5% 0.1W
3670 4822 117 11449 2k2 1% 0.1W
3680 4822 117 10361 680Ω 1% 0.1W
3682 4822 116 52303 8k2 5% 0.5W
3683 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3684 4822 051 20332 3k3 5% 0.1W
3685 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3950 4822 051 20273 27k 5% 0.1W
3953 4822 051 20332 3k3 5% 0.1W
3971 4822 117 11504 270Ω 1% 0.1W
3972 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3973 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3974 4822 117 11507 6k8 1% 0.1W
3975 4822 051 20562 5k6 5% 0.1W
3976 4822 051 20182 1k8 5% 0.1W
3977 4822 051 20182 1k8 5% 0.1W
3978 4822 117 11383 12k 1% 0.1W
3979 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
4xxx 4822 051 10008 0Ω 5% 0.25W
4xxx 4822 051 20008 0Ω 5% 0.25W
b
5002 3139 128 22371 COIL
5004 3198 018 18270 820N 10%
5202 4822 157 11867 5.6µH 5%
5341 4822 157 71401 27µH
5342 4822 526 10704 100mH
5404 4822 157 11869 33µH 10%
5404 4822 157 11894 56µH 10%
5405 4822 157 52392 27µH
5405 4822 157 71401 27µH
5406 2422 535 94864 Linearity coil
5408 4822 157 11213 22µH
5408 4822 157 50965 15µH 10%
5408 4822 157 71403 15µH
5410 4822 157 71401 27µH
5444 2422 531 02321 Line drive trafo
5445 3128 138 20661 LOT
5445 3128 138 20671 LOT
5545 2422 531 02312 FLYBACK TRANSFORMER
5545 2422 531 02313 FLYBACK TRANSFORMER
4822 157 10476 DMF-2820H
5500
h
5502 4822 526 10704 100mH
5516 4822 157 60171 Bead EMI 100Mhz 83R
5521 4822 157 62552 2.2µH
5540 4822 157 11835 4.7µH 5%
5550 4822 157 60171 Bead EMI 100Mhz 83R
5551 4822 157 71401 27µH
5552 4822 526 10704 100mH
5570 4822 526 10704 100mH
5571 4822 157 50961 22µH
5573 4822 157 60171 Bead EMI 100Mhz 83R
5603 4822 157 11139 6.8µH 5%
5604 4822 157 11895 4.7µH 10%
d
6007 4822 130 34142 BZX79-B33
6010 5322 130 34955 BA482
6111 4822 130 34278 BZX79-B6V8
6116 4822 130 34278 BZX79-B6V8
6161 4822 130 34278 BZX79-B6V8
6212 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6213 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6214 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6215 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6217 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6218 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6219 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6311 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6321 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6331 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6341 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6342 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6343 4822 130 11666 BZX284-C8V2
6400 4822 130 30621 1N4148
Page 34

GB 66 L9.2A10.
Spare parts list
6401 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6402 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6404 4822 130 32896 BYD33M
6405 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6406 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6409 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6410 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6412 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6413 4822 130 34197 BZX79-B12
6414 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6415 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6418 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6419 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6431 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6432 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6435 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6460 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6461 4822 130 34142 BZX79-B33
6502 4822 130 31083 BYW55
6503 4822 130 31083 BYW55
6504 4822 130 31083 BYW55
6505 4822 130 31083 BYW55
6507 4822 130 31393 BYT52J
6507 4822 130 42606 BYD33J
6508 4822 130 31393 BYT52J
6508 4822 130 42606 BYD33J
6537 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6540 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6550 4822 130 10218 BY229X-800
6560 4822 130 10871 SBYV27-200
6570 4822 130 10256 EGP20DL-5300
6600 4822 130 11366 BZX284-C3V9
6601 4822 130 10852 BZX284-C6V8
6612 4822 130 34278 BZX79-B6V8
6669 4822 130 34233 BZX79-B5V1
6953 4822 130 10756 BZX284-C2V7
ce
7010 4822 209 90008 L78M05CP
7116 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7118 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7206 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7250 4822 209 16775 TDA8842/N2/S1
7252 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7253 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7256 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7265 4822 130 40981 BC337-25
7266 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7311 4822 130 41782 BF422
7312 4822 130 41782 BF422
7313 4822 130 41646 BF423
7321 4822 130 41782 BF422
7322 4822 130 41782 BF422
7323 4822 130 41646 BF423
7331 4822 130 41782 BF422
7332 4822 130 41782 BF422
7333 4822 130 41646 BF423
7400 4822 130 41782 BF422
7401 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7402 4822 130 11575 BUT11APX
7431 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7460 4822 209 13176 TDA9302H
7469 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7518 4822 130 10806 STP6NA60FI
7520 4822 209 15684 MC44603AP
7600 4822 209 17537 SAA5563/M2A/0018
7600 4822 209 17538 SAA5542PS/M2A/0017
7600 9352 636 28112 IC SAA5563PS/M2/0037
7601 4822 209 15546 ST24W08B6
7602 4822 130 41109 BD135-16
7605 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7607 5322 209 60154 NE555D
7608 4822 209 73852 PMBT2369
7609 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7610 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7611 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7612 4822 130 41109 BD135-16
7620 4822 130 40959 BC547B
7621 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7680 4822 218 12055 TSOP2836UH1
7951 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7952 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7953 4822 209 90462 TDA7056B/N1
7955 4822 130 60511 BC847B
7956 4822 130 60373 BC856B
CRT[B]
Various
4822 267 20466 Conn. 9p
0254
h
4822 255 70293 CRT socket 14" ANS
0254
h
1015 3139 178 03401 CRT PANEL 14 "
1015 3139 178 03391 CRT PANEL 20"
1015 3139 177 19321 CRT PANEL 21"
g
2313 4822 122 33216 270pF 5% 50V
2323 4822 122 33172 390pF 5% 50V
2331 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
4822 126 14588 2.2nF 10% 1KV
2341
h
2342 4822 121 43526 47nF 5% 250V
2343 4822 121 43526 47nF 5% 250V
f
3311 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3312 4822 117 13577 330Ω 1% 1.25W
3313 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3314 4822 053 12183 18k 5% 3W
4822 052 10221 220Ω 5% 0.33W
3316
h
3317 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
3321 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3322 4822 117 13577 330Ω 1% 1.25W
3323 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3324 4822 053 12183 18k 5% 3W
4822 052 10221 220Ω 5% 0.33W
3326
h
3327 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
3331 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3332 4822 117 13577 330Ω 1% 1.25W
3333 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3334 4822 053 12183 18k 5% 3W
4822 052 10221 220Ω 5% 0.33W
3336
h
3337 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
3341 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
4822 052 10102 1k 5% 0.33W
3347
h
3348 4822 052 11152 1k5 5% 0.5W
4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3349
h
3349
4822 052 10128 1Ω2 5% 0.33W
h
4822 052 10158 1Ω5 5% 0.33W
3349
h
4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3350
h
3350
4822 052 10128 1Ω2 5% 0.33W
h
4822 052 10158 1Ω5 5% 0.33W
3350
h
b
5341 4822 157 51157 3.3µH
5341 4822 157 71401 27µH
5341 4822 158 10604 6.8 µH
5342 4822 526 1070 4 100mH z
d
6311 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6321 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6331 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6341 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6342 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6343 4822 130 11666 BZX284-C8V2
ce
7311 4822 130 41782 BF422
7312 4822 130 41782 BF422
7313 4822 130 41646 BF423
7321 4822 130 41782 BF422
7322 4822 130 41782 BF422
7323 4822 130 41646 BF423
7331 4822 130 41782 BF422
7332 4822 130 41782 BF422
7333 4822 130 41646 BF423
Sound[D]
Various
0239 4822 267 11052 Conn. 17P
0240 4822 267 11052 Conn. 17P
0248 4822 267 31673 HEADPHONE PLUG
1801 4822 242 10769 cr ystal 18.432MHz
g
2801 5322 122 32658 22pF 5% 50V
2804 4822 122 33926 12pF 50V
2805 5322 126 10225 1P5 5%
2806 5322 126 10225 1P5 5%
2807 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2808 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2809 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2810 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2814 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2815 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2820 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2821 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2822 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2823 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2824 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2825 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2827 4822 124 40769 4.7µF 20% 100V
2828 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2829 4822 124 40769 4.7µF 20% 100V
2830 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2831 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2835 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2836 4822 126 13838 100nF 20% 50V
2837 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2838 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2841 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2842 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2950 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2951 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2952 4822 122 33891 3.3nF 10% 63V
2953 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2954 5322 121 42386 100nF 5% 63V
2955 4822 124 11767 470µF 20% 25V
2958 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2959 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2960 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2961 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2962 4822 122 33891 3.3nF 10% 63V
2963 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
2965 4822 126 14076 220nF 20% 25V
f
3807 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3808 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3809 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3810 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3811 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
4822 052 10688 6Ω8 5% 0.33W
3812
h
3950 4822 051 20273 27k 5% 0.1W
3953 4822 051 20332 3k3 5% 0.1W
4xxx 4822 051 10008 0Ω 5% 0.25W
4xxx 4822 051 20008 0Ω 5% 0.25W
b
5801 4822 157 50965
5811 4822 157 51462 10µH 10%
5812 4822 157 51462 10µH 10%
5813 4822 157 51462 10µH 10%
5814 4822 157 53139 4.7µH
d
6801 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6802 4822 130 34382 BZX79-B8V2
6953 5322 130 31504 BZX79-B3V3
ce
7803 4822 209 17461 MSP3415D-PP-A2
7953 4822 209 13646 TDA7057AQ/N2
7956 4822 130 60373 BC856B
Side AV [E]
Various
0021 3139 124 26931 SIDE AV Bracket
0250 4822 265 11606 Conn. 3P
Page 35

Spare parts list
0251 4822 267 31673 HEADPHONE PLUG
0253 4822 267 31673 HEADPHONE PLUG
g
2171 4822 126 13512 330pF 10% 50V
2172 4822 126 13512 330pF 10% 50V
f
3150 4822 116 83884 47k 5% 0.5W
3151 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3152 4822 116 83884 47k 5% 0.5W
3153 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
GB 67L9.2A 10.
 Loading...
Loading...