Philips HEF4516BPB, HEF4516BP, HEF4516BDB, HEF4516BD, HEF4516BU Datasheet
...
DATA SH EET
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC04
January 1995
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
HEF4516B
MSI
Binary up/down counter
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic
Family Specifications HEF, HEC
•The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic
Package Outlines/Information HEF, HEC
January 1995 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Binary up/down counter
HEF4516B
MSI
DESCRIPTION
The HEF4516B is an edge-triggered synchronous
up/down 4-bit binary counter with a clock input (CP), an
up/down count control input (UP/DN), an active LOW
count enable input (CE), an asynchronous active HIGH
parallel load input (PL), four parallel inputs (P0to P3), four
parallel outputs (O0to O3), an active LOW terminal count
output (TC), and an overriding asynchronous master reset
input (MR).
Information on P
0
to P3is loaded into the counter while PL
is HIGH, independent of all other input conditions except
MR which must be LOW. When PL and CE are LOW, the
counter changes on the LOW to HIGH transition of CP.
Input UP/DN determines the direction of the count, HIGH
for counting up, LOW for counting down. When counting
up,TC is LOW when O0and O3are HIGH andCE is LOW.
When counting down, TC is LOW when O0to O3and
CE are LOW. A HIGH on MR resets the counter (O0to
O3= LOW) independent of all other input conditions.
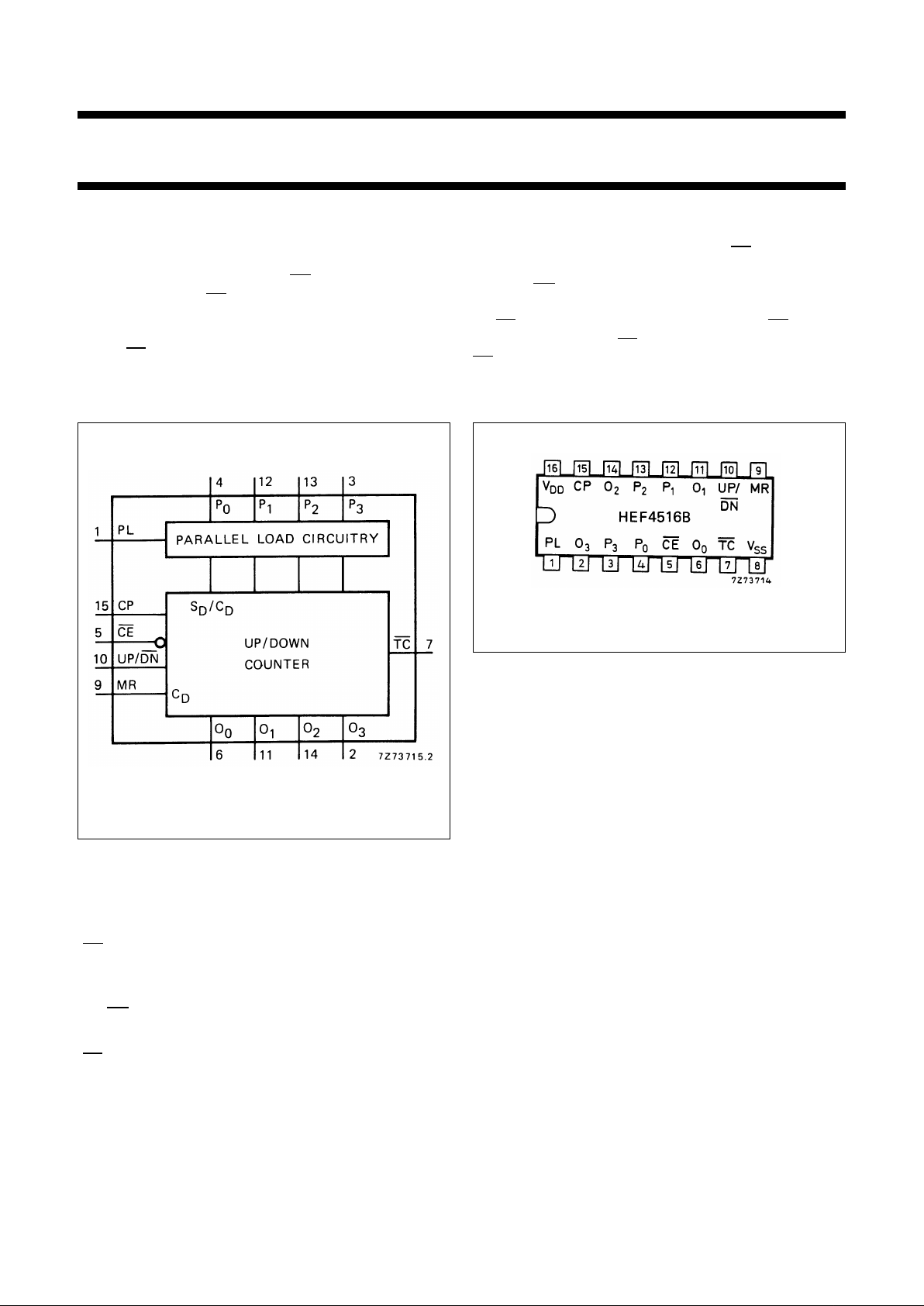
Fig.1 Functional diagram.
HEF4516BP(N): 16-lead DIL; plastic (SOT38-1)
HEF4516BD(F): 16-lead DIL; ceramic (cerdip) (SOT74)
HEF4516BT(D): 16-lead SO; plastic (SOT109-1)
( ): Package Designator North America
Fig.2 Pinning diagram.
PINNING
FAMILY DATA, I
DD
LIMITS category MSI
See Family Specifications
PL parallel load input (active HIGH)
P
0
to P
3
parallel inputs
CE count enable input (active LOW)
CP clock pulse input (LOW to HIGH,
edge triggered)
UP/
DN up/down count control input
MR master reset input
TC terminal count output (active LOW)
O
0
to O
3
parallel outputs
January 1995 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Binary up/down counter
HEF4516B
MSI
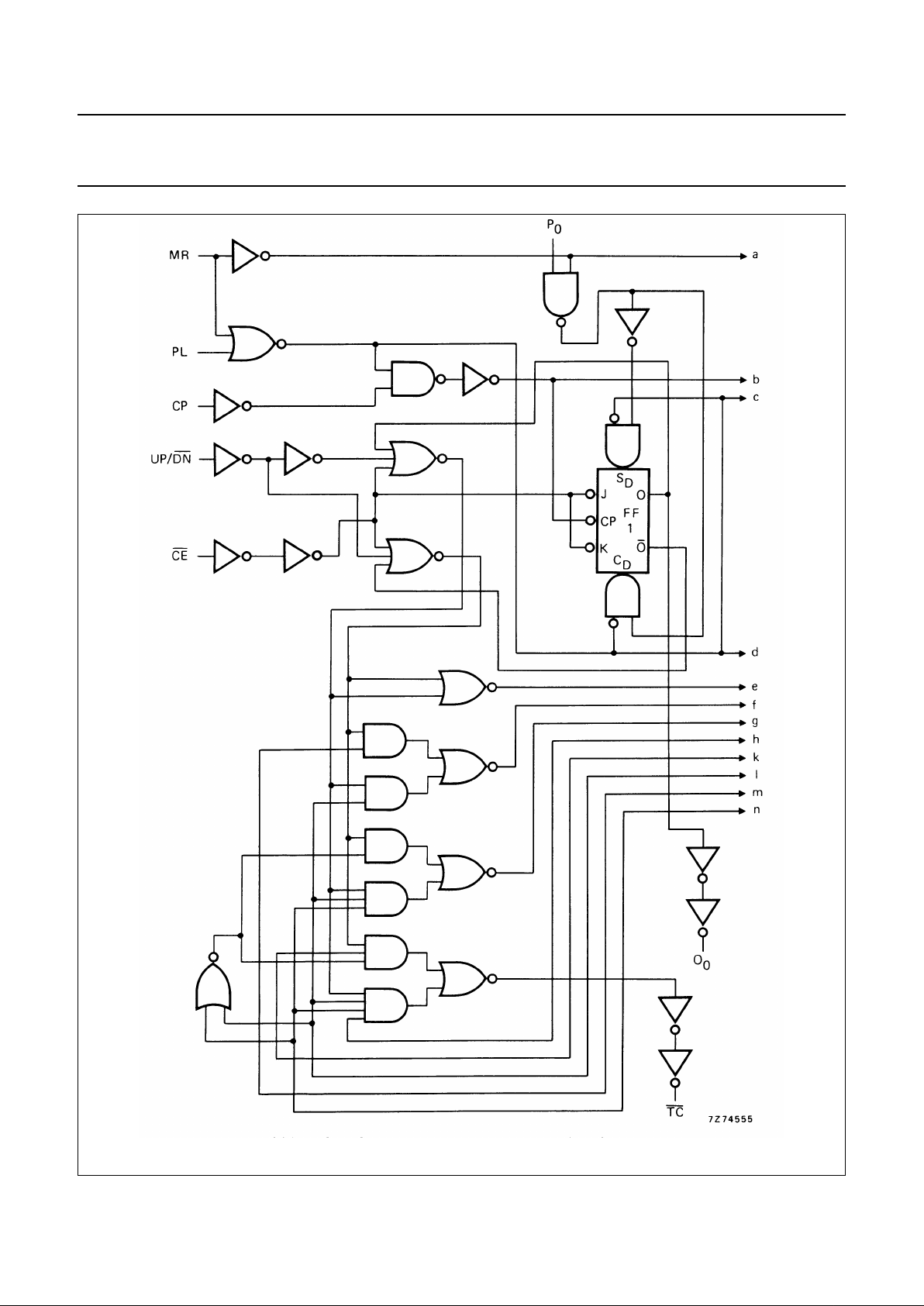
Fig.3 Logic diagram (continued in Fig.4).
 Loading...
Loading...