Philips DVDR-9000-H Service Manual

HDD & DVD Recorder
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
DVDR9000H/10/75/97
Contents Page
1 Technical Specifications and Connection
Facilities 2
2 Safety Information, General Notes & Lead
Free Requirements 5
3 Directions for Use 7
4 Mechanical Instructions 10
5 Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software 14
6 Block Diagrams,Waveforms, Wiring Diagram 131
Overall block diagram 131
Wiring diagram 132
Waveforms of Analog Board 133
Waveforms of Digital Board 134
Waveforms of HDMI Board 135
Test Points Overview for Analog Board 136
Test Points Overview for Front Left Board 137
Test Points Overview for Front Right Board 138
Test Points Overview for
Front AV_INPUT Board 139
Test Points Overview for Digital Board 140
Test Points Overview for HDMI Board 141
Test Points Overview for IR Blaster Board 142
©
Copyright 2005 Philips Consumer Electronics B.V. Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
Contents Page
7 Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layout 143
Analog Circuit Diagrams 143
Analog Layout Diagrams 153
PCB Front Circuit Diagrams 155
PCB Front Layout Diagrams 158
Digital Circuit Diagrams 161
Digital Layout Diagrams 172
HDMI Circuit Diagrams 174
IR Blaster Board Circuit Diagrams 178
IR Blaster Board Layout Diagrams 179
DTTM Circuit Diagrams 180
DTTM Component Diagrams 186
8 Alignments & Test Procedures 189
9 Circuit and IC description 190
Circuit Description 190
IC Description 199
10 Exploded view & Service parts list 238
Exploded View of the set 238
Service parts list 239
11 Revision List 240
Published by KC-TE 0547 AV Systems Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3139 785 31681
Version 1.1
EN 2
1.
3139 785 31681
Technical Specifi
cations and Connection Facilities
1. Technical Specifi cations and Connection Facilities
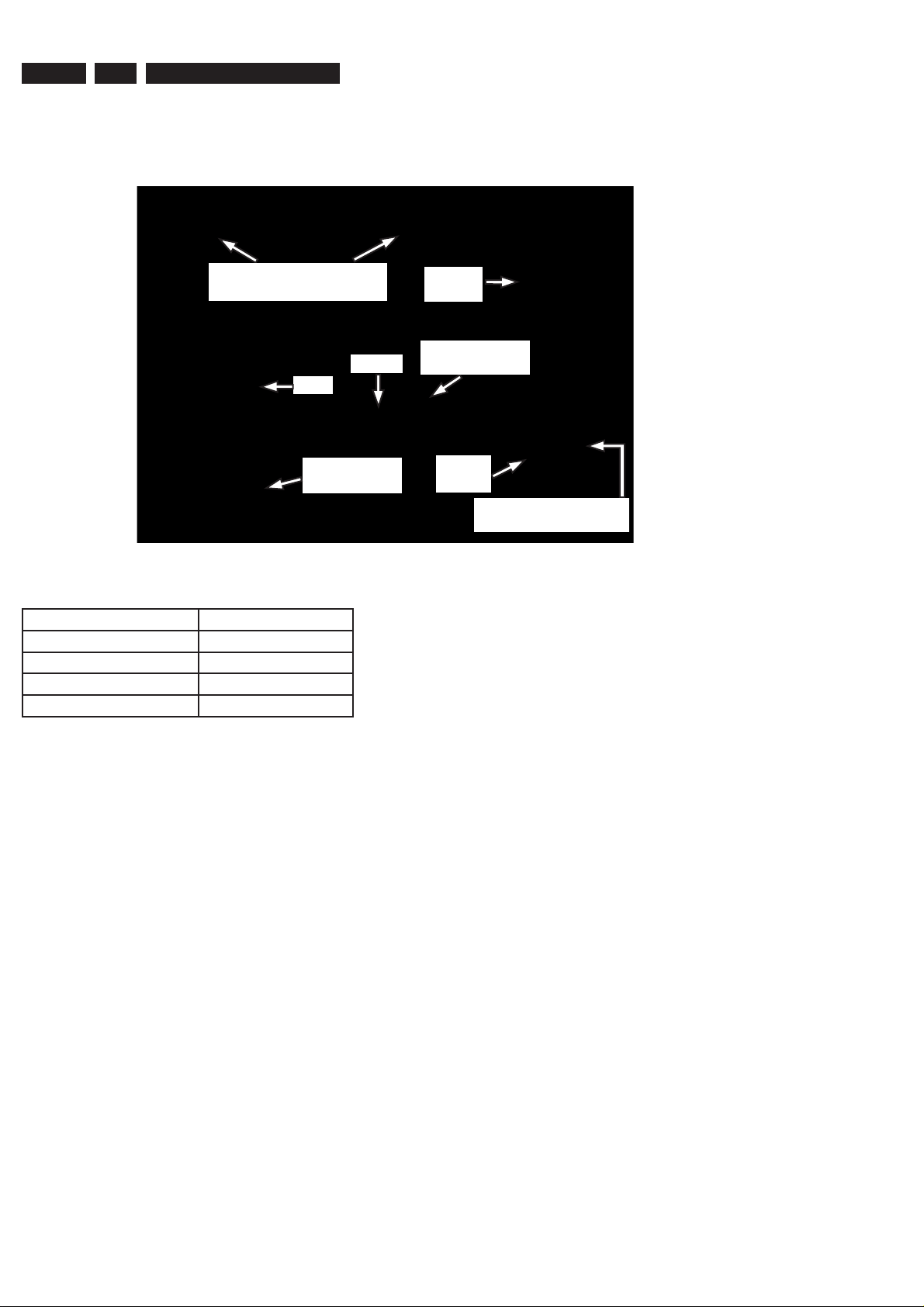
1.1 PCB Locations
Front Boards
(Behind the Front Plate)
HDD
PSU Board
(Below HDD)
1.2 Read / Write Speed
Type of Disc (Function) Disc Rotation Speed
Read Speed CD 7X CAV
Read Speed DVD 4X CAV
Write Speed DVD+R/+RW 2.4X ZCAV
Write Speed DVD-R/-RW 2X
1.3 General:
Mains voltage : 200V – 240V
Mains frequency : 50 Hz
Power consumption (record) : 51 W
Standby Power Consumption : < 5 W
Eco standby : < 3 W
DTTM
Digital
Board
Analog Board
(Below DTTM)
HDMI
Board
IR Blaster Board
(Below HDMI Board)
1.4.1.4 Video Performance:
Channel 25 / 503,25 MHz,
Test pattern: PAL BG PHILIPS standard test pattern,
RF Level 74dBV, Measured on SCART 1
Frequency response : 0.1 MHz – 4 MHz ± 3dB
Group delay (0.1 MHz - 4.4 MHz) : 0 nsec ± 150 nsec
1.4.1.5 Audio Performance:
Audio Performance Analogue - HiFi:
Frequency response at SCART 1
(L+R) output : 100 Hz – 12 kHz / 0 ±
3dB
S/N Ratio (20Hz – 20kHz)
unweighted : 50dB
Harmonic distortion (1 kHz, ± 25
kHz deviation) : 1.5%
1.4 RF Tuner
1.4.1 RF Tuner (Analogue)
1.4.1.1 System
PAL B/G, PAL D/K, SECAM L/L’, PAL I
1.4.1.2 RF - Loop Through:
Frequency range : 45 MHz – 860 MHz
Gain: (ANT IN - ANT OUT) : -6dB to 0dB
1.4.1.3 Receiver:
PLL tuning with AFC for optimum reception
Frequency range : 45.25 MHz – 857 MHz
Sensitivity at 40dB S/N
(video unweighted) : 60dBV at 75
Audio Performance NICAM:
Frequency response at SCART 1
(L+R) output : 40 Hz – 15 kHz / 0 ±
3dB
S/N Ratio (20Hz – 20kHz)
unweighted : 60dB
Harmonic distortion (1kHz, ± 25
kHz deviation) : 0.5%
1.4.1.6 Tuning
Automatic Search Tuning
Scanning time without RF signal : 3min. typical
Stop level (vision carrier) : 37dB/V
Maximum tuning error of a recalled
program : ± 100 kHz
Maximum tuning error (drift) during
operation : ± 100 kHz
Tuning Principle:
Automatic B, G, I, DK and L/L’ detection
Manual selection in “STORE” mode

Technical Specifi
cations and Connection Facilities
3139 785 31681
1.
EN 3
1.4.2 RF Tuner (Digtal Terrestial)
1.4.2.1 DVB - T - Tuner
Frequency range : 49-861MHz
Gain (ANT IN – ANT OUT) : -1 dB to 3 dB
Auto Search scanning time
(without Antenna input signal) : 40 sec typical
1.4.2.2 DVB-T- Video Performance
DVB-T – RF antenna signal IN ; Video performance measured
at Rear Cinch Audio Out:
- S/N(Unweighted,5MHz-BW limitation,
SC trap ON) : 52dB
- Frequency response 0.1
to 4.8 MHz : +1/-5dB
- Y/Chroma delay : 55ns
1.4.2.3 DVB-T- Audio Performance
DVB-T – RF antenna signal IN ; Audio performance measured
at Rear Cinch Audio Out:
- S/N(A-weighted,
22kHz-BW limited) : 88dB
- Frequency response 20Hz
to 20kHz : ± 1dB
- THD + Noise (at 1 kHz) : 85dB
- THD + noise (ratio) for 16Hz
to 20kHz : 65dB
- Channel Separation (at 1kHz) : 100dB
1.5 Analog Inputs / Outputs
1.5.1 SCART 1 (Connected to TV)
Pin Signals:
1 Audio-out R 1.8V RMS
2 Audio-in R
3 Audio-out L 1.8V RMS
4 Audio GND
5 Blue / Chroma GND
6 Audio-in L
7 Blue-out 0.7Vpp ± 0.1V into 75
8 Function switch < 2V = TV
> 4.5V / < 7V = asp. Ratio 16:9 DVD
> 9.5V / < 12V = asp. Ratio 4:3 DVD
9 Green GND
10 P50 control not use
11 Green out 0.7Vpp ± 0.1V into 75
12 NC
13 Red / Chroma GND
14 Fast switch GND
15 Red-out / 0.7Vpp ± 0.1V into 75
Chroma-out 300mVpp ± 3dB
16 Fast switch
RGB / CVBS
or Y out < 0.4V into 75 = CVBS
>1V / < 3V into 75 = RGB
17 Y/CVBS-out GND
18 CVBS-in GND
19 CVBS-out / Y-out 1Vpp ± 0.1V into 75
20 CVBS-in
21 Shield
1.5.2 SCART 2 (Connected to AUX)
Pin Signals:
1 Audio-out R 1.8V RMS
2 Audio-in R
3 Audio-out L 1.8V RMS
4 Audio GND
5 Blue / Chroma GND
6 Audio-in L
7 Blue-in
8 Function switch
9 Green GND
10 NC
11 Green-in
12 NC
13 Red / Chroma GND
14 Fast switch GND
15 Red-in /
Chroma-in
16 Fast switch
RGB / CVBS or Y in
17 CVBS-out GND
18 Y / CVBS-in GND
19 CVBS-out 1Vpp ± 0.1V into 75
20 CVBS-in / Y-in
21 Shield
1.5.3 Audio/Video Front Input Connectors
Audio - Cinch
Input voltage : 2.2Vrms
Input impedance : > 10k
Video - Cinch
Input voltage : 1Vpp ± 3dB
Input impedance : 75
Video - YC (Hosiden)
According to IEC 933-5
Superimposed DC-level on pin 4 (load = 100k)
< 2.4V is detected as 4:3 aspect ratio
> 3.5V is detected as 16:9 aspect ratio
Input voltage Y : 1Vpp ± 3dB
Input impedance Y : 75
Input voltage C : 300mVpp ± 3dB
Input impedance C : 75
1.5.4 Out 1
Component Video Cinch Y/Pb/Pr
according EIO-770-I-A, EIA-770-2
Audio - Cinch
Output voltage : 2.2Vrms max.
Output impedance : > 10k
1.5.5 Out 2
Audio - Cinch
Output voltage : 2Vrms max.
Output impedance : > 10k
Video - Cinch
Output voltage : 1Vpp ± 3dB
Output impedance : 75
Video - YC (Hosiden)
According to IEC 933-5
Superimposed DC-level on pin 4 (load > 100k)
< 2.4V is detected as 4:3 aspect ratio
> 3.5V is detected as 16:9 aspect ratio
Output voltage Y : 1Vpp ± 3dB
Input impedance : 75
Output voltage C : 300mVpp ± 3dB
Input impedance : 75

EN 4
1.
3139 785 31681
Technical Specifi
cations and Connection Facilities
1.6 Digital Inputs / Outputs
1.6.1 Digital Output
Digital Audio – Coaxial / Optical
LCM : according IEC 60958
MPEG 1, MPEG 2, AC3 : according IEC 61937
DTS : according IEC 61937 +
addendum
1.6.2 HDMI Output
Type A connector (19 pins)
1.6.3 Digital Video Input (IEEE 1394)
Implementation Standard according:
IEEE Std 1394-1995
IEC61883 - Part1
IEC61883 - Part 2 SD-DVCR (02-01-1997)
Specifi cation of consumer use digital VCR’s using 6.3mm
magnetic tape – dec.1994
Mechanical connection according to Annex of IEC 61883-1
1.6.4 G-Link (for IR-remote transmitting device)
Output voltage : 5 ± 0.5V (high level)
0.4 ± 0.3V (low level)
Output impedance : 150
1.9 Dimensions and Weight
Height of feet : 5.5mm
Apparatus tray closed : WxDxH:435x390x89mm
Apparatus tray open : WxDxH:435x525x89mm
Weight without packaging : approx. 7.1 ± 0.5kg
Weight with packaging : approx. 8.5kg
1.10 Laser Output Power & Wavelength
1.10.1 DVD
Output power during reading : 0.8mW
Output power during writing : 20mW
Wavelength : 650nm
1.10.2 CD
Output power : 0.3mW
Wavelength : 780nm
1.7 Video Performance
All outputs loaded with 75
SNR measurements over full bandwidth without weighting.
1.7.1 SCART (RGB)
SNR : 55dB on all output
Bandwidth : 4.8MHz -3dB
1.8 Audio Performance
1.8.1 Cinch Output Rear
Output voltage 2 channel mode : 2Vrms ± 2dB
Channel unbalance (1kHz) : < 0.22dB
Crosstalk 1kHz : > 100dB
Crosstalk 16Hz-20kHz : > 87dB
Frequency response 20Hz-20kHz : ± 0.5dB
Signal to noise ratio (unweighted) : > 85dB
Dynamic range 1kHz : > 83dB
Distortion and noise 1kHz : > 83dB
Distortion and noise 16Hz-20kHz : > 75dB
Intermodulation distortion : > 70dB
Mute : > 95dB
1.8.2 Scart Audio
Output voltage 2 channel mode : 1.6Vrms ± 2dB
Channel unbalance (1kHz) : < 1dB
Crosstalk 1kHz : > 85dB
Crosstalk 16Hz-20kHz : > 70dB
Frequency response 20Hz-20kHz : ± 0.5dB
Signal to noise ratio (unweighted) : > 80dB
Dynamic range 1kHz : > 75dB
Distortion and noise 1kHz : > 75dB
Distortion and noise 16Hz-20kHz : > 50dB
Intermodulation distortion : > 70dB
Mute : > 80dB
Safety Information, General Notes & Lead Free Requirements
3139 785 31681
2.
2. Safety Information, General Notes & Lead Free Requirements
EN 5
2.1 Safety
Instructions
2.1.1 General Safety
Safety regulations require that during a repair:
• Connect the unit to the mains via an isolation transformer.
• Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol ,
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type)
may increase risk of fi re or electrical shock hazard.
Safety regulations require that after a repair, you must return
the unit in its original condition. Pay, in particular, attention to
the following points:
• Route the wires/cables correctly, and fi x them with the
mounted cable clamps.
• Check the insulation of the mains lead for external
damage.
• Check the electrical DC resistance between the mains
plug and the secondary side:
1. Unplug the mains cord, and connect a wire between
the two pins of the mains plug.
2. Set the mains switch to the ‘on’ position (keep the
mains cord unplugged!).
3. Measure the resistance value between the mains
plug and the front panel, controls, and chassis
bottom.
4. Repair or correct unit when the resistance
measurement is less than 1 M.
5. Verify this, before you return the unit to the customer/
user (ref. UL-standard no. 1492).
6. Switch the unit ‘off’, and remove the wire between the
two pins of the mains plug.
2.1.2 Laser Safety
This unit employs a laser. Only qualifi ed service personnel
may remove the cover, or attempt to service this device (due
to possible eye injury).
2.2 Warnings
2.2.1 General
• All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
electrostatic discharges (ESD, ). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are at the same potential as the mass
of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools at this same potential.
Available ESD protection equipment:
– Complete kit ESD3 (small tablemat, wristband,
connection box, extension cable and earth cable)
4822 310 10671.
– Wristband tester 4822 344 13999.
• Be careful during measurements in the live voltage
section. The primary side of the power supply, including
the heatsink, carries live mains voltage when you
connect the player to the mains (even when the
player is ‘off’!). It is possible to touch copper tracks and/
or components in this unshielded primary area, when
you service the player. Service personnel must take
precautions to prevent touching this area or components
in this area. A ‘lightning stroke’ and a stripe-marked
printing on the printed wiring board, indicate the primary
side of the power supply.
• Never replace modules, or components, while the unit is
‘on’.
2.2.2 Laser
• The use of optical instruments with this product, will
increase eye hazard.
• Only qualifi ed service personnel may remove the cover or
attempt to service this device, due to possible eye injury.
• Repair handling should take place as much as possible
with a disc loaded inside the player.
• Text below is placed inside the unit, on the laser cover
shield:
Laser Device Unit
Type : Semiconductor laser
GaAlAs
Wavelength : 650 nm (DVD)
: 780 nm (VCD/CD)
Output Power : 20 mW
(DVD+RW writing)
: 0.8 mW
(DVD reading)
: 0.3 mW
(VCD/CD reading)
Beam divergence : 60 degree
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
Figure 2-1
Note: Use of controls or adjustments or performance of
procedure other than those specifi ed herein, may result in
hazardous radiation exposure. Avoid direct exposure to beam.
CAUTION VISIBLE AND INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN AVOID EXPOSURE TO BEAM
ADVARSEL SYNLIG OG USYNLIG LASERSTRÅLING VED ÅBNING UNDGÅ UDSÆTTELSE FOR STRÅLING
ADVARSEL SYNLIG OG USYNLIG LASERSTRÅLING NÅR DEKSEL ÅPNES UNNGÅ EKSPONERING FOR STRÅLEN
VARNING SYNLIG OCH OSYNLIG LASERSTRÅLNING NÄR DENNA DEL ÄR ÖPPNAD BETRAKTA EJ STRÅLEN
VARO ! AVATTAESSA OLET ALTTIINA NÄKYVÄLLE JA NÄKYMÄTTÖMÄLLE LASER SÄTEILYLLE. ÄLÄ KATSO SÄTEESEEN
VORSICHT SICHTBARE UND UNSICHTBARE LASERSTRAHLUNG WENN ABDECKUNG GEÖFFNET NICHT DEM STRAHL AUSSETSEN
DANGER VISIBLE AND INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN AVOID DIRECT EXPOSURE TO BEAM
ATTENTION RAYONNEMENT LASER VISIBLE ET INVISIBLE EN CAS D’OUVERTURE EXPOSITION DANGEREUSE AU FAISCEAU
Figure 2-2

EN 6
2.
3139 785 31681
Safety Information, General Notes & Lead Free Requirements
2.3 Lead Free Requirement
Information about Lead-free produced sets
Philips CE is starting production of lead-free sets from
1.1.2005 onwards.
INDENTIFICATION:
Regardless of special logo (not always indicated)
One must treat all sets from 1 Jan 2005 onwards, according
next rules.
Example S/N:
Bottom line of typeplate gives a 14-digit S/N. Digit 5&6 is the year, digit 7&8 is
the week number, so in this case 1991 wk 18
So from 0501 onwards = from 1 Jan 2005 onwards
• Special information for BGA-ICs:
Do not re-use BGAs at all.
• For sets produced before 1.1.2005 (except products of
• On our website www.atyourservice.ce.Philips.com you
BGA-de-/soldering (+ baking instructions)
Heating-profi les of BGAs and other ICs used in Philips-sets
You will fi nd this and more technical information within the
For additional questions please contact your local repair-helpdesk.
- always use the 12nc-recognizable soldering temperature
profi le of the specifi c BGA (for de-soldering always use the
lead-free temperature profi le, in case of doubt)
- lead free BGA-ICs will be delivered in so-called ‘dry-
packaging’ (sealed pack including a silica gel pack) to
protect the IC against moisture. After opening, dependent
of MSL-level seen on indicator-label in the bag, the
BGA-IC possibly still has to be baked dry. (MSL=Moisture
Sensitivity Level). This will be communicated via AYS-
website.
2004), containing leaded solder-alloy and components,
all needed spare-parts will be available till the end of the
service-period. For repair of such sets nothing changes.
fi nd more information to:
“magazine”, chapter “workshop news”.
Important note: In fact also products of year 2004 must be treated in this way as long as you
avoid mixing solder-alloys (leaded/ lead-free). So best to always use SAC305 and the higher
temperatures belong to this.
Due to lead-free technology some rules have to be respected by the
workshop during a repair:
• Use only lead-free solder alloy Philips SAC305 with order
• Use only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free
o To reach at least a solder-temperature of 400°C,
o To stabilize the adjusted temperature at the solder-tip
o To exchange solder-tips for different applications.
• Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature around 360°C
• Mix of lead-free solder alloy / parts with leaded solder alloy
• Use only original spare-parts listed in the Service-Manuals.
code 0622 149 00106. If lead-free solder-pate is required,
please contact the manufacturer of your solder-equipment.
In general use of solder-paste within workshops should be
avoided because paste is not easy to store and to handle.
solder alloy. The solder tool must be able
– 380°C is reached and stabilized at the solder joint.
Heating-time of the solder-joint should not exceed ~ 4 sec.
Avoid temperatures above 400°C otherwise wear-out of
tips will rise drastically and fl ux-fl uid will be destroyed. To
avoid wear-out of tips switch off un-used equipment, or
reduce heat.
/ parts is possible but PHILIPS recommends strongly to
avoid mixed solder alloy types (leaded and lead-free).
If one cannot avoid or does not know whether product is
lead-free, clean carefully the solder-joint from old solder
alloy and re-solder with new solder alloy (SAC305).
Not listed standard-material (commodities) has to be
purchased at external companies.
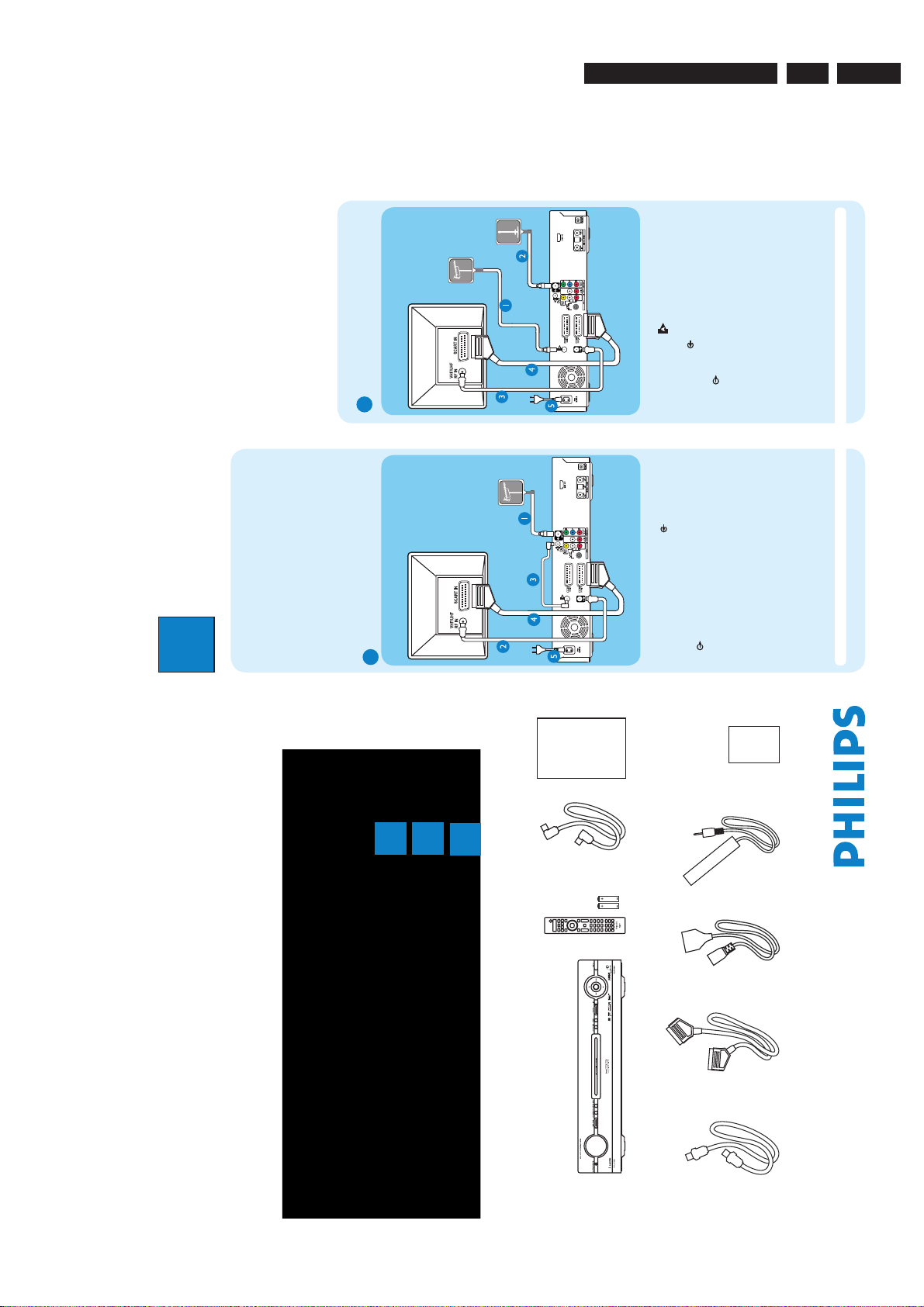
)%%%7%1MBZFS3FDPSEFS %7%3)
2VJDL4UBSU(VJEF
$POOFDU
4FUVQ
&OKPZ
8IBUTJOUIFCPY
)%%%7%1MBZFS3FDPSEFS
3'DPBYJBMDBCMF
3FNPUF$POUSPM
BOECBUUFSJFT
6TFS.BOVBM4DBSUDBCMF
5VOFSJOUFSMJOLDBCMF
2VJDL4UBSU(VJEF
1PXFSDBCMF (-*/,DBCMF
USBOTNJUUFS
Directions For Use
$POOFDU
4UBSUXJUIUIFA#BTJDDPOOFDUJPO
*GZPVIBWFB7$3GPMMPXUIFJOTUSVDUJPOTGPSA$POOFDUJPOXJUI7$3PSTJNJMBSEFWJDF
*GZPVIBWFBTFUUPQCPYGPMMPXUIFJOTUSVDUJPOTGPSA$POOFDUJPOXJUITFUUPQCPY
#BTJD$POOFDUJPO
"
#FGPSF$POOFDUJOH
6OQMVHUIFBOUFOOBDBCMFUIBUJTDVSSFOUMZDPOOFDUFEUP
ZPVS57
*GZPVIBWFPOMZBTJOHMFPGGBJSBOUFOOBGPMMPXA#
DPOOFDUJPO
*GZPVIBWFCPUIUIFPGGBJSBOUFOOBBOEEJHJUBMUFSSFTUSJBM
BOUFOOBGPMMPXA#DPOOFDUJPO
$POOFDUJOH
( %JTDPOOFDUUIFBOUFOOBDBCMFGSPNZPVS57BOE
DPOOFDUJUUPUIF"/5&//" TPDLFUPOUIJT
SFDPSEFS
2 6TFUIFTVQQMJFE3'DPBYJBMDBCMFUPDPOOFDUUIF57
TPDLFUPOUIJTSFDPSEFSUPUIF"OUFOOB*OTPDLFU
POUIF57
1 6TFUIFTVQQMJFE5VOFSJOUFSMJOLDBCMFUPDPOOFDU
UIFUXPA"TPDLFUTPOUIJTSFDPSEFS
* 6TFUIFTVQQMJFETDBSUDBCMFUPDPOOFDUUIF
&955057*0TDBSUTPDLFUPOUIJTSFDPSEFSUP
UIF4$"35*/TPDLFUPOZPVS57
" 1MVHJOUIFQPXFSDBCMFGSPNUIFSFDPSEFSUPBO"$
QPXFSPVUMFU
( %JTDPOOFDUUIFBOUFOOBDBCMFGSPNZPVS57BOE
DPOOFDUJUUPUIF
TPDLFUPOUIJTSFDPSEFS
2 $POOFDUUIFJOEPPS%7#5BOUFOOBDBCMFUPUIF
"/5&//" TPDLFUPOUIJTSFDPSEFS
2 6TFUIFTVQQMJFE3'DPBYJBMDBCMFUPDPOOFDUUIF
57
TPDLFUPOUIJTSFDPSEFSUPUIF"OUFOOB*O
TPDLFUPOUIF57
* 6TFUIFTVQQMJFETDBSUDBCMFUPDPOOFDUUIF
&955057*0TDBSUTPDLFUPOUIJTSFDPSEFSUP
UIF4$"35*/TPDLFUPOZPVS57
" 1MVHJOUIFQPXFSDBCMFGSPNUIFSFDPSEFSUPBO"$
QPXFSPVUMFU
#
$POOFDUJOHXJUIEJHJUBMUFSSFTUSJBM
BOUFOOB
#
'SPNBOPGGBJS
BOUFOOBPSDBCMFCPY
5FMFWJTJPOSFBS
5FMFWJTJPOSFBS
'SPNBOPGGBJS
BOUFOOBPSDBCMFCPY
1IJMJQT3FDPSEFSSFBS
1IJMJQT3FDPSEFSSFBS
'SPNEJHJUBM
UFSSFTUSJBM
BOUFOOB
/PUF4FFUIFBDDPNQBOZJOHVTFSNBOVBMGPSPUIFSQPTTJCMFDPOOFDUJPOTFH)%.*$PNQPOFOU7JEFP
3139 785 31681
3.
3. Directions For Use
The following except of the Quick Use Guide serves as an introduction to the set.
The Complete Direction for the Use can be downloaded in different languages from the internet site of Philips Customer care Center:
www.p4c.philips.com
EN 7
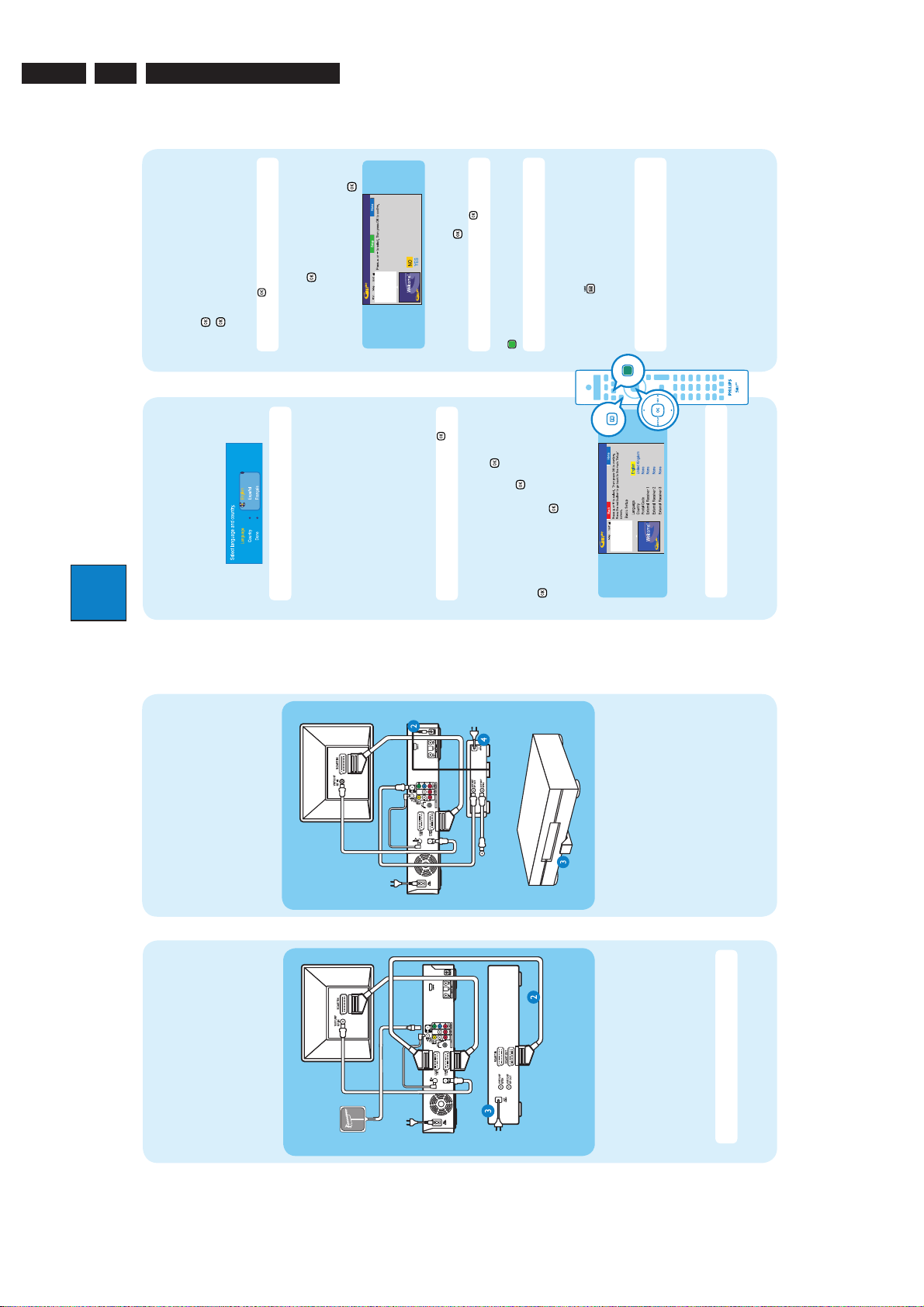
EN 8
6HWXS([WHUQDO5HFHLYHU
+DVWKH([WHUQDO5HFHLYHUFKDQJHGWR
3URJUDPPH1XPEHU"
*8,'(
3.
3139 785 31681
UPHPUPUIFOFYUTDSFFO4FMFDU
Directions For Use
UPUSZB
*OTUBMMUIFTFUUPQCPY
%
4FUVQ
'JOEJOHUIFWJFXJOHDIBOOFM
"
/PUF1SFTT
QSFTT
*GZPVEPOPUIBWFBTFUUPQCPYTLJQA%BOEHPUPA&
( 1SFTTTEPXOUPTFMFDUA&YUFSOBM3FDFJWFSBOE
2 1SFTT BHBJOUPDPOUJOVF
5IFSFDPSEFSXJMMEJTQMBZA*4570/
:PVTIPVMETFFUIF\&"4:4&561^NFOV
( 1SFTTT45"/%#:0/POUIFSFDPSEFS
2 4XJUDIPOUIF57
\/POF^JGOPOFPGUIFFOUSJFTBSFBQQMJDBCMF
CSBOEOBNFPGUIFDPOOFDUFETFUUPQCPY
1 4FMFDUUIFUZQFPGSFDFQUJPOTFSWJDFQSPWJEFSBOE
/PUF*GDPOOFDUFEUPZPVS7$3NBLFTVSFJUJT
UVSOFEPGGCFGPSFQSPDFFEJOH
UPQCPYJTDPOOFDUFEFHA&95GPS&95"69*0
TPDLFUBOEQSFTT
* 4FMFDUUIFSFDPSEFSTPDLFUUISPVHIXIJDIZPVSTFU
OVNCFSPOUIFTFUUPQCPY
" 5VSOPOZPVSTFUUPQCPYBOETFMFDUDIBOOFM
+ 3FBEUIFJOTUSVDUJPOTPOUIF57BOEQSFTT
SFNPUFDPOUSPMSFQFBUFEMZPS"74&-&$5CVUUPO
1 *GOPUQSFTTUIF$IBOOFM%PXOCVUUPOPOUIF57T
4UBSUCBTJDTFUVQ
VOUJMZPVTFFUIFNFOV5IJTJTUIFDPSSFDUWJFXJOH
DIBOOFMGPSUIFSFDPSEFS
#
6TFUIFSFDPSEFSTSFNPUFDPOUSPMBOEGPMMPXUIFPO
TDSFFOJOTUSVDUJPOTUPDPNQMFUFUIFJOTUBMMBUJPO
QSPHSBNNFOVNCFSBTEJTQMBZFEPOUIF57TFMFDU
\:FT^JOUIFNFOVBOEQSFTT
, *GUIFTFUUPQCPYIBTTXJUDIFEUPUIFTBNF
UPHP
UPUIFOFYUTDSFFO
/PUF4FMFDU\%POF^JOUIFNFOVBOEQSFTT
UIF57TIBQF
( 4FMFDUUIFEFTJSFENFOVMBOHVBHFZPVSDPVOUSZBOE
CVUUPOUPFYJU
/PUF*GOPUTFMFDU\/P^BOEQSFTT
EJHJUBMUVOFSSBEJP
2 "DUJWBUFBVUPNBUJDDIBOOFMTFBSDIGPSBOBMPHVFBOE
/PUF5PTXJUDIUIF(6*%&1MVTTZTUFNTIPTU
EJGGFSFOUDPEF
- :PVSTFUUPQCPYJTOPXJOTUBMMFE1SFTTUIFHSFFO
TFMFDU\$POUJOVF^BOEQSFTT
1 $IFDLUIFEBUFBOEUJNFBOEQSFTT
* 5PDPOUJOVFXJUIUIF(6*%&1MVTJOTUBMMBUJPO
-PBEUIF57MJTUJOHEBUB
DIBOOFMNBOVBMMZHPUP\)PTU$IBOOFM4FUVQ^
&
( 1SFTT(6*%& UPFYJU(6*%&1MVTTZTUFN
8BJUVOUJMUIFSFDPSEFSIBTGJOJTIFEJOJUJBMJTJOH
0UIFSXJTFTFMFDU\%POPUJOTUBMMOPX^BOEQSFTT
*OTUBMMUIF(6*%&1MVTTZTUFN
UIFTZTUFNUIFOQSFTT BHBJO
/PUF*GZPVUVOFUPZPVS)PTU$IBOOFMCFGPSFHPJOH
-FBWFUIFSFDPSEFSJOATUBOECZNPEFBOEUVSOAPO
UIFTFUUPQCPYPWFSOJHIUUPDPMMFDUUIF57MJTUJOH
EBUBUIJTNBZUBLFVQUPIPVST
$
UPATUBOECZNPEFUIJTSFDPSEFSXJMMTUBSUEPXOMPBEJOH
UIF57MJTUJOHTEBUBJNNFEJBUFMZ
UIFTPVSDFBOEQSPHSBNNFOVNCFSTBSFNBUDIJOH
GPSBMMDIBOOFMT
2 $IFDLUIF\&EJUPS^TDSFFOUIFOFYUEBZUPFOTVSF
/PUF*GOPPSXSPOHQPTUBMDPEFJTFOUFSFEJUXJMM
DBVTFOP(6*%&1MVT&1(TFSWJDFJOGPSNBUJPO
MBOHVBHFDPVOUSZBOEFOUFSUIFQPTUBMDPEFPGZPVS
BSFB
( 'PMMPXUIFPOTDSFFOJOTUSVDUJPOTUPTFMFDUZPVS
5FMFWJTJPOSFBS
$POOFDUJPOXJUITFUUPQCPY
:PVSOFX1IJMJQT3FDPSEFSQSPWJEFTB(-*/,
USBOTNJUUFSXIJDIBMMPXTZPVUPDPOUSPMUIFUVOFSPGUIF
TFUUPQCPYTBUFMMJUFSFDFJWFSDBCMF57CPYUISPVHI
UIF(6*%&1MVTTZTUFN:PVDBOSFDPSEUIF57
QSPHSBNNFTUIBUBSFSFDFJWFEUISPVHIUIFTFUUPQCPY
#FGPSF$POOFDUJOH
$POOFDUJPOXJUI7$3PS
TJNJMBSEFWJDF
"
:PVSOFX1IJMJQT3FDPSEFSSFQMBDFTUIF7$3GPSZPVS
$POOFDUJOH
5FMFWJTJPOSFBS
$POOFDUJOH
'SPNBOPGGBJS
SFDPSEJOHOFFET'JSTUVOQMVHBMMUIFDPOOFDUJPOTGSPN
ZPVS7$3
#
BOUFOOBPSDBCMFCPY
4FU5PQ#PYSFBS
5PTPVSDF
1IJMJQT3FDPSEFS
SFBS
4FUUPQCPY
1PTJUJPOJOHPG(-*/,
USBOTNJUUFS
7$3PSTJNJMBS
EFWJDFSFBS
(-*/,USBOTNJUUFS
UIJTSFDPSEFSCFGPSFZPVQSPDFFEUPTUFQCFMPX
"CPWFJMMVTUSBUJPOTIPXOUIFDPOOFDUJPOXJUIPVU
UIFEJHJUBMUFSSFTUSJBMBOUFOOB
TPDLFUPOUIJTSFDPSEFS
UPQCPYJOTVDIBXBZUIBUJUDBOBDRVJSFUIFTJHOBM
( 'PMMPXTUFQUPPGA#BTJDDPOOFDUJPOUPDPOOFDU
( 'PMMPXTUFQUPPGA#BTJDDPOOFDUJPOUPDPOOFDU
2 $POOFDUUIFTVQQMJFE(-*/,DBCMFUPUIF(-*/,
UIJTSFDPSEFSCFGPSFZPVQSPDFFEUPTUFQCFMPX
"CPWFJMMVTUSBUJPOTIPXOUIFDPOOFDUJPOXJUIPVU
UIFEJHJUBMUFSSFTUSJBMBOUFOOB
2 6TFBOPUIFSTDBSUDBCMFOPUTVQQMJFEUPDPOOFDU
CSPBEDBTUFECZUIFUSBOTNJUUFS
1 1MBDFUIF(-*/,USBOTNJUUFSJOGSPOUPGZPVSTFU
* $POOFDUUIFQPXFSDBCMFGSPNUIFTFUUPQCPYUP
UIF&95"69*0TDBSUTPDLFUPOUIJTSFDPSEFSUP
/PUF*OUIJTTFUVQUIF7$3DBOOPUSFDPSE57
UIF4$"35065TPDLFUPOZPVS7$3
QPXFSPVUMFU
1 $POOFDUUIFQPXFSDBCMFGSPNUIF7$3UPBO"$
BO"$QPXFSDBCMF
QSPHSBNNFT
6TJOHUIF(6*%&1MVTTZTUFN
.BLFTVSFUIBUUIFBOBMBHVFUVOFSJOTUBMMBUJPOBOE57
MJTUJOHEBUBEPXOMPBEJTDPNQMFUFE
3FDPSE57QSPHSBNNFT
( 1SFTT(6*%&
Directions For Use
PGBMMUIFBWBJMBCMFDIBOOFMTBOEDIPPTFGSPNUIFSF
/PUF1SFTTUIFZFMMPX CVUUPOUPTFFBOPWFSWJFX
2 1SFTTTEPXOUPTFMFDUB57DIBOOFM
/PUF1SFTT PS UPHPEJSFDUMZUPBEBZCFGPSF
PSUIFOFYUEBZ57MJTUJOHT
QSPHSBNNF
1 1SFTTW3&1-":PS/&95XUPTFMFDUB57
* 1SFTTUIFSFE CVUUPOUPTFUUIFIJHIMJHIUFE
/PUF:PVDBOTUPSFVQUPQSPHSBNNFTGPS
QSPHSBNNFGPSSFDPSEJOH
3139 785 31681
SFDPSEJOH
*8,'(
3.
EN 9
¥,POJOLMJKLF1IJMJQT/7
"MMSJHIUTSFTFSWFE
/$
XXXQIJMJQTDPDN
'SPNUIFIBSEEJTL
4UBSUQMBZCBDL
"
TUPSBHF
$POUFOUTJOUIFUFNQPSBSZ)%%
3FDPSEUPIBSEEJTL
"
( 1SFTT)%%#3084&3 UIFOQSFTT/&95X
UIFIBSEEJTLTUPSBHF
( 1SFTT*/'0 UPTFFXIBUJTUFNQPSBSJMZTUPSFEJO
'SPNBEJTD
VOUJMZPVTFFUIF\5*5-&4^BOE\*/'0^NFOVT
2 1SFTTSVQPSTEPXOUPTFMFDUBUJUMF
1 1SFTT 1-":UPTUBSUQMBZCBDL
/PUF5IFUJUMFXJMMCFNBSLFEJOSFEBOEUIF
SFDPSEJOHXJMMPOMZUBLFFGGFDUXIFOZPVUVSOPGGUIF
XBOUUPSFDPSE
2 1SFTTSVQPSTEPXOUPDIPPTFUIFUJUMFZPV
SFDPSEFS
1 1SFTT 3&$03%UPSFDPSEUIFUJUMF
-PBEBEJTDBOEDMPTFUIFEJTDUSBZ
#
( )PMEEPXO 4501VOUJMUIFEJTDUSBZPQFOT
$VSSFOU57QSPHSBNNF
/PUF5PTFUUIFSFDPSEJOHUJNFQSFTT SFQFBUFEMZ
SFDPSEVQUPIPVST
#
( 1SFTT 3&$03%UPTUBSUSFDPSEJOH*UDBO
NFOV4FMFDU\%JTD5SBZ^BOEQSFTT/&95XVOUJM
ZPVTFFUIF\5*5-&4^\53"$,4^PS\1)050
30--4^NFOVEFQFOEJOHPOUIFEJTDUZQF
2 1SFTT)%%#3084&3 UPHPUPUIFEJTD
UPFYUFOEUIFSFDPSEJOHUJNFJONJOVUFJODSFNFOUT
VQUPIPVST*G(6*%&1MVTTZTUFNJTBWBJMBCMF
A3FDPSEQSPHSBNJTEJTQMBZFEBOEUIFDVSSFOU
QSPHSBNNFXJMMCFSFDPSEFE
2 1SFTT 4501UPTUPQUIFSFDPSEJOHJNNFEJBUFMZ
1 1SFTTSVQPSTEPXOUPTFMFDUBUJUMF
* 1SFTT 1-":UPTUBSUQMBZCBDL
/FFEIFMQ
(6*%&1MVTTZTUFN
(PUPXXXFVSPQFHVJEFQMVTDPN
6TFS.BOVBM
4FFUIFVTFSNBOVBMUIBUDBNFXJUIZPVS1IJMJQT3FDPSEFS
0OMJOF
(PUPXXXQIJMJQTDPNTVQQPSU
&OKPZ
/PUF8IFOUIFSFDPSEFSJTUVSOFEPOUIF
QSPHSBNNFZPVBSFXBUDIJOHXJMMCFTUPSFEJOUIF
UFNQPSBSZIBSEEJTLTUPSBHF8IFOZPVTXJUDIUIF
SFDPSEFSUPBOPUIFSJOQVUTJHOBMFH$".PSUP
CFUXFFOBOBMPHVFBOEEJHJUBMUVOFSUIFOQSFTT
8BUDI57m1BVTFMJWF57
:PVS1IJMJQT3FDPSEFSBMMPXTZPVUPDPOUSPMUIF57
QSPHSBNNF:PVDBO1"64&JUBTJGZPVXFSFJODPOUSPM
$)UPTFMFDUB57QSPHSBNNF
PGUIFMJWFCSPBEDBTU
( 5VSOPOZPVSSFDPSEFSBOEQSFTT56/&3UPTXJUDI
2 1SFTT 1"64&UPTVTQFOEJU
1 1SFTT 1-":UPDPOUJOVF
TUBOECZNPEFUIFQSPHSBNNFXJMMCFFSBTFE
* 1SFTT56/&3UPSFUVSOUPUIFMJWFCSPBEDBTU
)FMQUFYUJOGPSNBUJPOCBS
5IFIFMQUFYUCBSMPDBUFEBUUIFCPUUPNPGUIFTDSFFOJT
TUBUF
QSPWJEJOHUIFJOGPSNBUJPOPO
l SFNPUFDPOUSPMLFZTUIBUDBOCFVTFEBUUIFDVSSFOU
l CSJFGJOGPSNBUJPOPGUIFTFMFDUFEJUFN
EN 10
4.
3139 785 31681
Mechanical Instructions
4. Mechanical Instructions
Note: The position numbers given here refers to the
Exploded view on chapter 10.
4.1 Dismantling of the DVD Tray cover manually
1) Insert a screw-driver into the slot provided at the bottom
of the set and push in the direction as shown in
picture 4-1 to unlock before sliding the Tray cover
assembly 910 out.
Figure 4-1
2) Remove the Tray cover assembly 910 as shown in
Figure 4-2.
3) Remove 2 screws to loosen the Bracket Loader 191 and
uncatch the Dust cover assembly 902.
4) Remove 4 screws to loosen the Cover of the Basic
Engine to reach Service position Figure 4-4.
Figure 4-4: Basic Engine Service position
4.3 Dismantling of the HDD / PSU Board
1) Remove 4 screws to loosen the HDD assembly
1009+192+222 as shown in Figure 4-5.
Figure 4-2
4.2 Dismantling of the Basic Engine (Drive D4.3)
1) Remove 9 screws to loosen Top cover 210.
2) Remove 4 screws to loosen the Basic Engine assembly
1008+191+902 as shown in Figure 4-3.
Figure 4-3
Figure 4-5: Digital Board
Mechanical Instructions
3139 785 31681
4.
EN 11
2) Remove 4 screws 285 to separate the Bracket HDD
192 and Bracket HDD suspension 222 from the HDD as
shown in Figure 4-6.
Note: Screws 285 are special type of screws that must be
replaced only with those specifi ed in the Service Parts list on
Chapter 10.
Figure 4-6
4) Service position for PSU Board is given in Figure 4-8.
Insulation Sheet
Figure 4-8: PSU Board Service Position
4.4 Dismantling of the Digital Board
1) Remove 4 screws to loosen the Digital Board 1004 as
shown in Figure 4-9.
3) Remove 4 screws to loosen the PSU Board 1007 as
shown in Figure 4-7.
Figure 4-7
Figure 4-9
EN 12
4.
3139 785 31681
Mechanical Instructions
2) Service position for Digital Board is given in Figure
4-10.
Insulation Sheet
Figure 4-10: Digital Board Service Position
4.5 Dismantling of the DTTM, HDMI, IR Blaster
and Analog Boards
1) Remove 4 screws and 3 catches the HDMI board (1x)
and DTTM board (2x) as shown in Figure 4-11.
2) Remove 8 screws to loosen the Analog Board (3x) and
IR Blaster board (2x) + bracket 193 assembly (3x) as
shown in Figure 4.12.
Figure 4-12
3) Remove 9 screws on the Rear Panel to remove the
Analog Board as shown in Figure 4.13.
Note: It may be necessary to loosen the Digital Board
because the cable from the Front Panel is sandwiched
between the Digital and Analog Boards.
Figure 4-11
Figure 4-13
Mechanical Instructions
4) Service Position is achieved by placing the Analog Board
in the vertical position as shown in Figure 4-14.
Insulation Sheet
Insulation Sheet
Figure 4-14: HDMI and Analog Boards Service Position
4.6 Dismantling of the Front Panel assembly
3139 785 31681
4.
EN 13
1) Remove the DVD Tray cover assembly 910 as given in
step 4-1.
2) Loosen the Digital Board 1004 as given in step 4-4.
There are 2 cables below the Digital Board that are
tapped to the Bottom plate 182 that must be released in
order to dismantle the Front Panel assembly.
3) Loosen the DTTM and IR Blaster Boards (see step 4.5) to
disconnect the 2 cables
4) Loosen 4 screws + 4 catches (top) and 4 screws + 2
catches (bottom) to pull the Front Panel assembly
towards the front away from the Bottom chassis 178.
5) Service position is achieved by placing the Front Panel
assembly by the side & reconnecting the 3 cables.
Figure 4-15: Front Board Service position

EN 14
5.
3139 785 31681
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
5. Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
5.1 Firmware Upgrading
A. Preparation to upgrade fi rmware:
1. Unzip the zip-archive fi le
2. Start the CD Burning software and create a new CD project (data disc) with the following settings:
File system: Joliet
Format: MODE 2: CDROM XA
Recording mode: SINGLE SESSION (TRACK-AT-ONCE), FINALIZED CD
Note: Long fi le name is necessary for the preparation of the upgrade disc
3. Place the content of the zip-archive into the root directory of the new CD project.
4. Burn the data onto a blank CDR or CD-RW
B. Procedure to apply the fi rmware upgrade:
1. Hold the <Record> + <Open/Close> buttons down and Power up the set.
2. The tray opens and set will display:
FORCE DL −>…. PUT DSC
3. Insert the prepared Upgrade CDROM and close the tray.
4. The set will display:
INIT DSC −> ………. DOWNLOAD −>……….
The whole process takes less than 15 minutes
Note: Do not press any buttons or interrupt the mains supply during the upgrading process, otherwise the set may becomes
defective.
5. When the upgrade is completed the tray will open automatically and the set will display:
REMOVE
6. Close the tray and the set will display:
DONE
C. How to read out the fi rmware version to confi rm set has been upgraded:
1. Power up the set.
2. Press <System> button on the Remote control and select {Setup} option
3. Press <Right> button to select {System}
4. The set will prompt you about clearing the Time Shift Buffer
5. Select {Yes} and press <OK> button
6. Press <Down> button several times to select {Version info}
7. Press <OK> button
8. The TV connected to the set will display:
DIF05_3/493AN SV11205
BE 43.2.13 ASP3,9,1,10FP
DTTM HW:01020102 DTTM
SW:00040200
SIT9000-FF3F-S3_F540
20051020-1815 pro sxcplusint
EPG:3.04 DPMS:P_DPM
9. Press <System> button to exit
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
Diagnostic Software
3139 785 31681
5.
EN 15
Due to the complexity of the DVD recorder, the time to find a
defect in the recorder can become long. To reduce this time,
the recorder has been equipped with Diagnostic and Service
software (DS). The DS offers functionality to diagnose the
DVDR hardware and tests the following:
• Interconnections between components
• Accessibility of components
• Functionality of the audio and video paths
This functionality can be accessed via several interfaces:
1. End user/Dealer script interface
2. Command Interface
5.2 End User/Dealer Script Interface
5.2.1 Description
The End user/Dealer script interface gives a diagnosis on a
stand alone DVD recorder. During this mode, a number of
hardware tests (nuclei) are automatically executed to check if
the recorder is faulty. The diagnosis is simply a "fail" or "pass"
message. If the message "FAIL" appears on the display, there
is apparently a failure in the recorder. If the message "PASS"
appears, the nuclei in this mode have been executed
successfully. There can be still a failure in the recorder
because the nuclei in this mode don't cover the complete
functionality of the recorder.
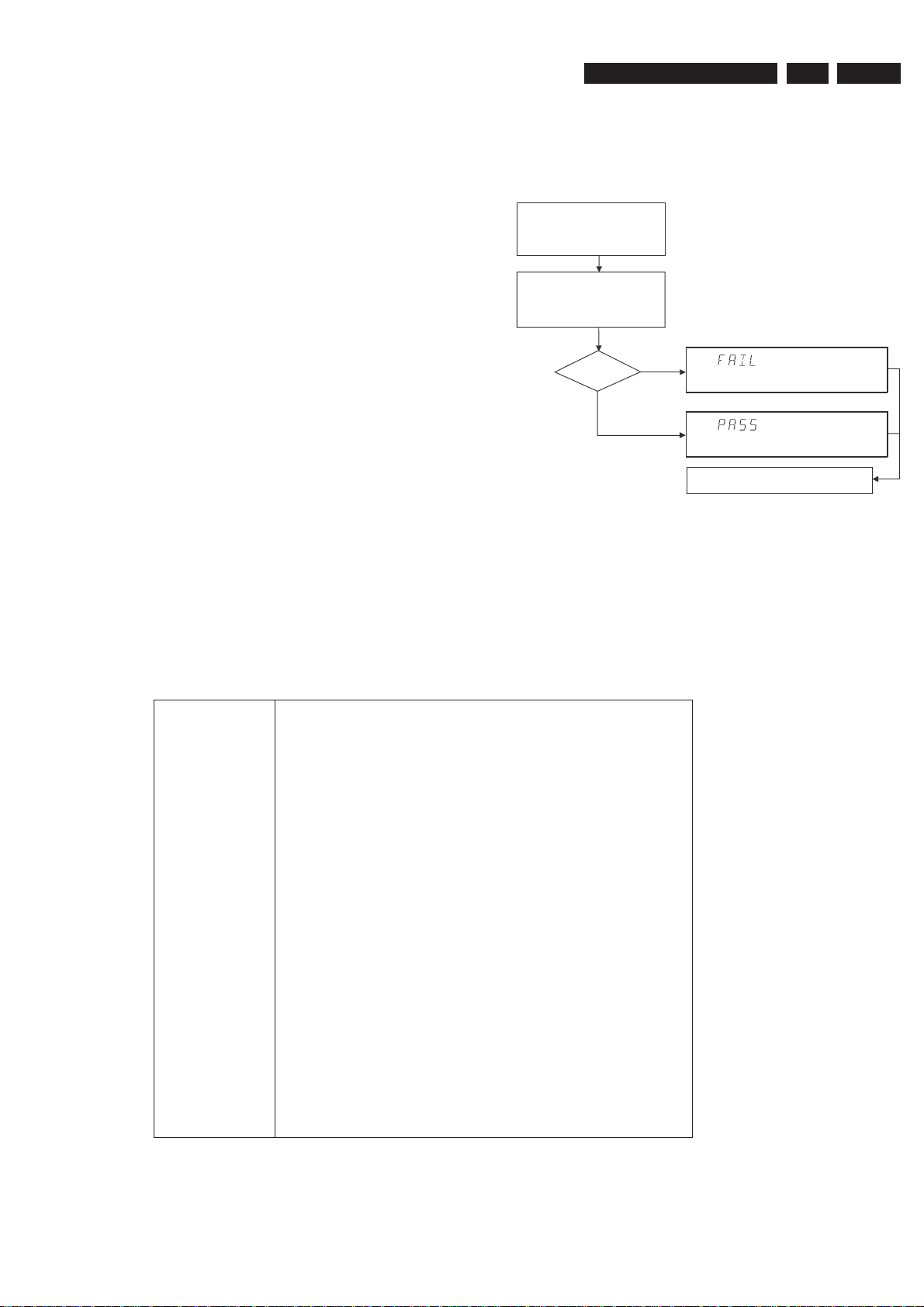
5.2.2 Structure
Unplug the power cord
Hold key <PLAY> pressed
while you plug the recorder
During the test, the display will show
the a sequence of nuclei under test
SET O.K.?
NO
YES
To exit DEALER SCRIPT, unplug the power cord
Figure 5-1
The End use/Dealer script executes all diagnostic nuclei that
do not need any user interaction and are meaningful on a
standalone DVD recorder.
TR 18029_001
120304
5.2.3 Contents
Included tests: 1.DS_ANAB_COM MUN ICATIONECHO_NU C
2.DS_DCB_COMMUNICATIONECHO_NUC
3. DS_BROM_COMMUNICATION_NUC
4. DS_SYS_SETTINGSDISPLAY_NUC
5. DS_CHR_DEVTYPEGET_NUC
6. DS_CHR_INT_PIC_NUC
7. DS_CHR_DMA_NUC
8. DS_BROM_WRITEREAD_NUC
9. DS_NVRAM_COMMUNICATION_NUC
10. DS_NVRAM_WRITEREAD_NUC
11. DS_SDRAM_WRITEREADFAST_NUC
12. DS_FLASH_WRITEREAD_NUC
13.DS_FLASH_CHECKSUMPROGRAM_NUC
14.DS_SYS_HARDWAREVERSIONGET_NUC
15. DS_VIP_DEVTYPEGET_NUC
16. DS_VIP_COMMUNICATION_NUC
17. DS_DVIO_LINKDEVTYPEGET_NUC
18. DS_DVIO_PHYDEVTYPEGET_NUC
19. DS_DVIO_LINKCOMMUNICATION_NUC
20. DS_DVIO_PHYCOMMUNICATION_NUC
21.DS_PSCAN_COMMUNICATIONDENC_NUC
22.DS_PSCAN_COMMUNICATIONDEINTERLACER_NUC
23. DS_BE_COMMUNICATIONECHO_NUC
24.DS_ANAB_COMMUNICATIONIICNVRAM_NUC
25.DS_ANAB_COMMUNICATIONIICTUNER_NUC
26.DS_ANAB_COMMUNICATIONIICSOUNDPROCESSOR_NUC
27.DS_ANAB_COMMUNICATIONIICAVSELECTOR_NUC
28. DS_ANAB_CHECKSUMPROGRAM_NUC
EN 16
5.
3139 785 31681
5.3 Player Script Interface
Virgin mode
5.3.1
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
5.4.2 Error Handling
If you want that the recorder starts up in Virgin mode, follow this
procedure:
• Unplug the recorder
• plug the recorder again while you keep the STAND BY/ON
key pressed
• the set starts up in Virgin mode.
5.4 Menu and Command Mode Interface
5.4.1 Nuclei Numeration
Each nucleus has a unique number of four digits. This number
is the input of the command mode.
[ XX YY ]
Nucleus number
Nucleus group number
Figure 5-3
Group number Group name
0 Scripts
1 Codec (e.g. Chrysalis, Leco)
2 Boot EEPROM
3NVRAM
4 SDRAM
5 Flash
6 Video Input Processor
7DVIO
8 Progressive Scan
9 Basic Engine
10* Display and Control Board
11* Analogue Board
12 System
13 Electronic Program Guide Board
14* PCMCIA
15 HDMI
16 Analogue Slave Processor
17 Analogue Board EEPROM
18 Video Matrix
19 Audio Matrix
20 Front End
21 Hard Disk
22 Di
23* USB
* Not applicable for DVDR9000H Range
gital Terrestrial Tuner Module
CL 06532152_012.eps
051200
Each nucleus returns an error code. This code contains six
numerals, which means:
[ XX YY ZZ ]
Error code
Nucleus number
Nucleus group number
Figure 5-4
The nucleus group numbers and nucleus numbers are the
same as above.
5.4.3 Command Mode Interface
Set-Up Physical Interface Components
Hardware required:
• Service PC
• one free COM port on the Service PC
• special cable to connect DVD recorder to Service PC
The service PC must have a terminal emulation program (e.g.
Hyperterminal) installed and must have a free COM port (e.g.
COM1). Activate the terminal emulation program and check
that the port settings for the free COM port are: 19200 bps, 8
data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit and no flow control. The free COM
port must be connected via a special cable to the RS232 port
of the DVD recorder. This special cable will also connect the
test pin, which is available on the connector, to ground (i.e.
activate test pin).
Code number of PC interface cable: 3122 785 90017
Activation of Diagnostic Software
1. Pull the mains cord from the recorder and reconnect it
again (reboot).
2. The next welcome message will appear on the PC:
Welcome screen D&S program
Figure 5-5
Now, the prompt 'DS:>' will appear. The diagnostic software is
now ready to receive commands. The commands that can be
given are the numbers of the nuclei. If you see above shown
screen, continue with paragraph 'Nuclei Codes'.
CL 06532152_013.eps
051200
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
3139 785 31681
5.
EN 17
3. It is possible that the next messages will appear when
starting the DVD+RW for the first time
Error messages D&S program
Figure 5-6a
Error messages D&S program
Enter "Y" to program a safe string. With this automatically
generated string the board will work in principle but it has to be
checked if all board settings were detected correctly.
Diversity String Input
4. Execute nucleus 1226 to enter the string. Please see
chapter 8 for details
Nucleus 1226 execution with string
Figure 5-7
5. To check if the hardware info is filled correctly, you can
execute nucleus 1228.
Nucleus 1228 info example
Figure 5-6b
In these cases, the boot EEPROM of the Digital Board does not
contain the required string with the hardware information. To
update the Digital Board with the correct string, nucleus 1226
must be executed.
See next section 'Diversity String Input'.
There can also be the next error message.
Figure 5-8
6. Exit the 'Terminal' program.
Figure 5-6c
7. Reboot the DVD recorder to allow the software to start.
EN 18
Command overview Digital Board
Below you will find an overview of the nuclei, their numbers,
and their error codes. This overview is preliminary and subject
to modifications.
Note: AV3 in the overview includes also the AV3.5 drive.
Codec Host Controller (CHR)
5.
3139 785 31681
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name
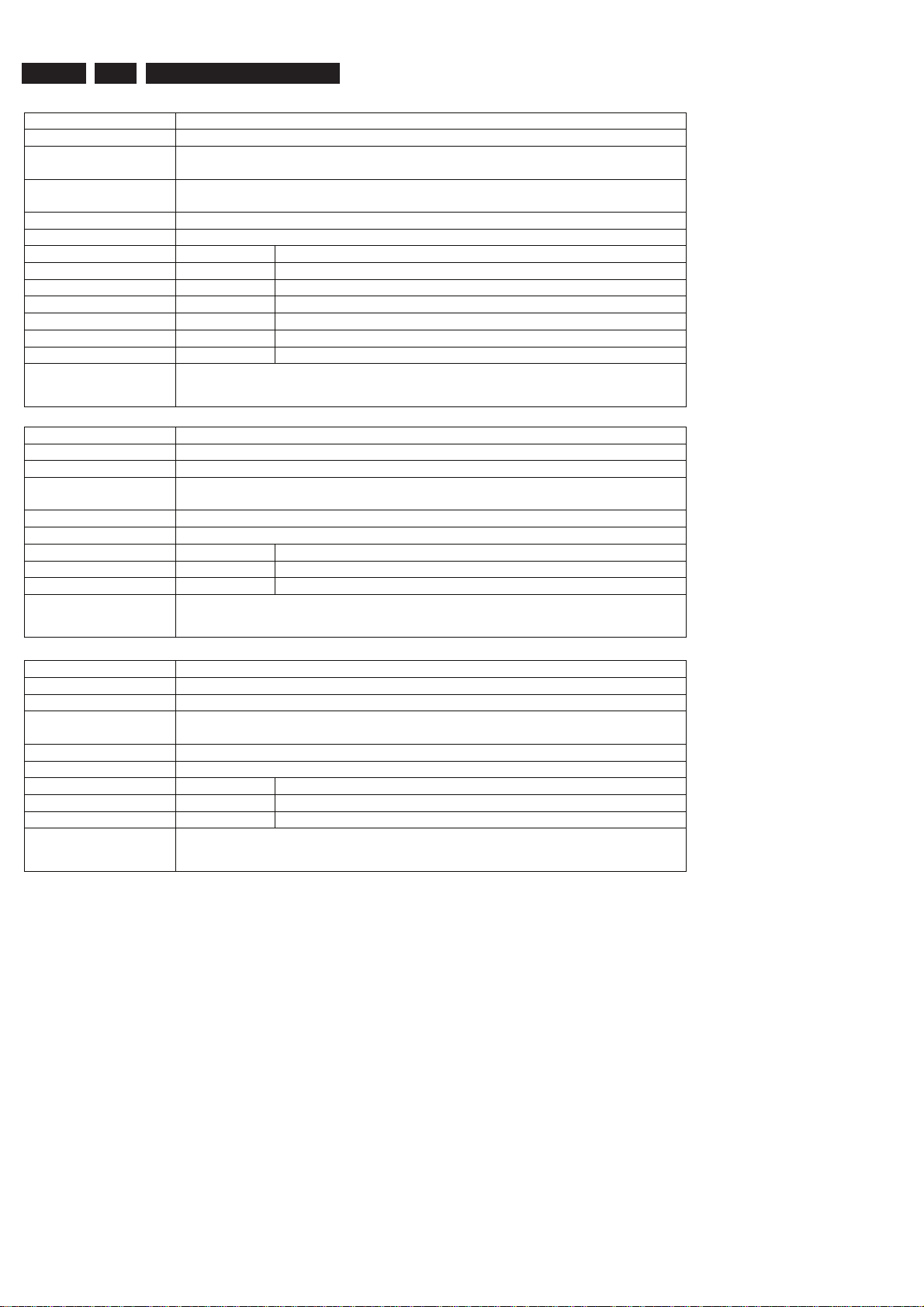
DS_CHR_DevTypeGet
Nucleus Number 100
Description Retrieves the device id, the module ids and revisions of the Codec and returns
them to the stdout port.
Technical - Determine the codec id by means of comparing version ids of the modules.
- Read the module-id register of every module and display it to the user.
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
10000 Getting the information succeeded
10001 Wrong codec id detected
Example
DS:> 100
010000:
Device ID 7100
Codec ID PNX7100_C
F-BCU (0x0102) 1.0 INTC (0x011d) 1.0 PCI-XIO(0x0113) 1.0
SIF (0x013b) 1.0 EJTAG (0x0104) 0.1 S-BCU (0x0102) 1.0
BOOT (0x010a) 1.0 CONFIG (0x013f) 1.1 RESET (0x0123) 1.0
DEBUG (0x0116) 0.0 UART0 (0x0107) 0.1 UART1 (0x0107) 0.1
UART2 (0x0107) 0.1 UART3 (0x0107) 0.1 I2C0 (0x0105) 0.1
I2C1 (0x0105) 0.1 GPIO (0x013c) 1.0 SYNC (0x013a) 1.0
DISP0 (0xa015) 1.12 DISP1 (0xa00f) 1.1 OSD (0x0136) 0.1
SPU (0xa00e) 0.0 MIXER (0x0137) 1.0 DENC (0x0138) 1.0
CCIR (0x0139) 1.0 VDEC (0x0133) 0.2 PARSER (0xa00d) 0.0
DV (0xa00c) 0.0 BEI (0xa00a) 0.1 IDE (0xa009) 0.1
SGDX (0xa008) 1.0 BYTE (0xa00b) 0.1 OUTPUT (0xa003) 1.0
ACOMP (0xa000) 1.0 VFE (0xa001) 0.1 VCOMP (0xa002) 1.0
SCR (0x0000) 0.0 SIFF (0xa011) 0.1 WMD (0xa010) 0.0
AUDIO0 (0xa015) 1.12 AUDIO1 (0xa00f) 1.1 PSCAN (0xa018) 0.1
Test OK @
Nucleus Name
DS_CHR_TestImageOn
Nucleus Number 101
Description Generates a test-image of a selected video standard on selected video output
on the digital board. When no input is given, the default values will be used (see
user input description below). Make sure to use the proper nuclei to route the
video signal on the analogue board to get the video signal to the proper output.
Note: Although a DTT has a Chrysalis C3, the codec IC may never use the
YUV functionality of the internal DENC. This is specified by the hardware. The
digital boards for DTT do have a YUV-matrix. The signals from this YUV-matrix
are not routed to the regular video output connector but to the progressive scan
output connector.
Technical - Validate the user input.
- Initialise the SYNC module.
- Initialise the DISPLAY module.
- Initialise the MIXER module.
- Initialise the DENC module.
- Set the selected video standard.
- Generate the selected test image in memory.
- Start the DISPLAY module.
- Start the MIXER module.
- Start the DENC module according to the selected test image id.
Execution Time 6 seconds.
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
3139 785 31681
User Input The user has to decide which test image, video standard and video output must
be used: < Test image id > < Video standard > < Video output >
Test image id:
0 VERTICAL_COLOURBAR (default)
1 HORIZONTAL_COLOURBAR
2WHITE
3 YELLOW
4 CYAN
5 GREEN
6 MAGENTA
7 RED
8 BLUE
9 BLACK
10 GRAY
11 TEST_IMAGE_FOR_PROGRESSIVE_SCAN
Video standard:
PAL Standard PAL 50 Hz (default)
NTSC Standard NTSC 60 Hz
Video output:
ALL CVBS and YC and RGB DACs are enabled (default)
CVBS CVBS DAC is enabled
YC Y and C DAC is enabled
RGB CVBS, R, G, and B DACs are enabled
YUV Y, U, and V DACs are enabled
PSCAN Progressive scan is enabled.
5.
EN 19
Error Number Description
10100 Generating the test image succeeded.
10101 Invalid input was provided.
10102 The Codec SYNC-module cannot be initialised.
10103 The Codec MIXER-module cannot be initialised.
10104 The Codec VPP-module cannot be initialised.
10105 The Codec DENC-module cannot be initialised.
10106 The digital board hardware information is corrupt
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 101
010100:
Test OK @
DS:> 101 0 pal cvbs
010100:
Test OK @
DS:> 101 4 ntsc yc
010100:
Test OK @
DS_CHR_TestImageOff
Nucleus Number 102
Description Switches the test-image off.
Technical - Stop the DENC module.
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
10200 Stopping the test image generation succeeded
10201 The Codec DENC-module failed.
Example
DS:> 102
010200:
Test OK @
EN 20
5.
3139 785 31681
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name
DS_CHR_SineOn
Nucleus Number 103
Description Generate an audio sine signal on the audio output of the digital board.
Note: Left channel 6kHz, right channel 12 kHz sine. Make sure to route the
signal first.
Technical - De-mute the analogue board
- Set fifo parameters for audio
- Set the volume
- Set the I2S outputs and configuration paths
- Set the decoder mode
- Configure the audio decoder
- Put the AC3 audio in the fifo
- Send ‘prepare’ command to the audio decoder
- Send ‘play’ command to the audio decoder
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
10300 The sine signal was successfully generated
10301 The analogue board could no t be de-muted
10302 The audio decoder did not initialise
10303 The dsp2 (DUET) of the audio decoder did not configure
10304 The dsp1 (PALM) of the audio decoder did not configure
10305 There was a delay-error before starting
10306 Wrong input was given to the decoder function
10307 Wrong input was given to the decoder function @@@@@
10308 The audio decoder did not get into the ‘prepared’ state
Example
DS:> 103
010300:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name
DS_CHR_SineOff
Nucleus Number 104
Description Stop generating the audio sine signal
Technical - Reset the audio block of the Codec
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
10400 Switching off the audio sine signal succeeded
10401 Failed to reset the audio decoder
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 104
010400:
Test OK @
DS_CHR_SineBurst
Nucleus Number 105
Description Generate an audio sine signal on the audio output of the digital board for 4
seconds.
Note: Left channel 6kHz, right channel 12 kHz sine with some known hick-ups
Technical - Call the DS_CHR_SineOn nucleus
- Delay for 4 seconds
- Call the DS_CHR_SineOff nucleus
Execution Time 4 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
10500 The sine signal burst was successfully generated
10501 The delay did not succeed during the burst
10502 The audio sine could not be generated
Example
DS:> 105
010500:
Test OK @
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
3139 785 31681
5.
EN 21
Nucleus Name
DS_CHR_MuteOn
Nucleus Number 106
Description Mute the audio outputs of the digital bo ard
Technical - Send the ‘Mute’ command to the audio decoder
- Activate the ‘audio mute’ PIO pin
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input “PIO” to just use the PIO pin mute. When muting using this, also de-mute using
this as this works ‘paired’.
Error Number Description
10600 Muting the audio succeeded
10601 Muting the audio through the PIO-pin failed
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 106
010600:
Test OK @
DS:> 106 PIO
010600:
Test OK @
DS_CHR_MuteOff
Nucleus Number 107
Description De-mute the audio outputs of the digital board
Technical - Send the ‘DeMute’ command to the audio decoder
- Deactivate the ‘audio mute’ PIO pin
Execution Time “PIO” to just use the PIO pin de-mute. Only de-mute using this when you muted
using the PIO parameter, as this works ‘’paired.
User Input None
Error Number Description
10700 De-muting the audio succeeded
10701 De-muting the audio through the PIO-pin failed
Example
DS:> 107
010700:
Test OK @
DS:> 107 PIO
010700:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name
DS_CHR_DvLedOn
Nucleus Number 108
Description Check the connection to the DV-LED on the digital board by switching it on
Technical - Write to the PIO pin to light the DV LED
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
10800 Switching the DV-LED on succeeded
10801 Switching the DV-LED on failed
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 108
010800:
Test OK @
DS_CHR_DvLedOff
Nucleus Number 109
Description Switch off the DV-LED on the digital board
Technical - Write to the PIO pin to switch off the DV LED
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
10900 Switching the DV-LED off succeeded
10901 Switching the DV-LED off failed
Example
DS:> 109
010900:
Test OK @
EN 22
5.
3139 785 31681
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name
DS_CHR_MacroVisionOn
Nucleus Number 110
Description Turn on MacroVision.
Technical - Set some registers of the DENC module in the Codec.
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
11000 Turning on MacroVision succeeded
11001 Turning on MacroVision failed
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 110
011000:
Test OK @
DS_CHR_MacroVisionOff
Nucleus Number 111
Description Turn off MacroVision.
Technical - Set some registers of the DENC module in the Codec.
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
11100 Turning off MacroVision succeeded
11101 Turning off MacroVision failed
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 111
011100:
Test OK @
DS_CHR_Peek
Nucleus Number 112
Description Peek a value on a specified address
Technical - Check the user input
- Read out the address specified
- Check whether the address to be read is aligned on 4 bytes
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input The address to peek on
Error Number Description
11200 Peeking on the specified address succeeded
11201 Peeking on the specified address failed, wrong user input
11202 Peeking on the specified address failed due to misalignment
Example
DS:> 112 0xa0700000
011200: Value read = 0x000001BD
Test OK @
Nucleus Name
DS_CHR_Poke
Nucleus Number 113
Description Poke a value on a specified address
Technical - Check the user input
- Change the value on the address specified
- Check whether the address to be modified is aligned on 4 bytes
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input The address to poke and the value: <address><value>
Error Number Description
11300 Poking the specified address succeeded
11301 Poking the specified address failed, wrong user input
11302 Poking the specified address failed due to misalignment
Example
DS:> 113 0xa0700000 0xaabbccdd
011300:
Test OK @
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
3139 785 31681
5.
EN 23
Nucleus Name
DS_CHR_INT_PICInterrupts
Nucleus Number 114
Description Test all interrupts of the priority interrupt controller
Technical - Install interrupt handlers
- Generate interrupts
- Test whether all interrupts were received
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input Error Number Description
11400 Testing all the PIC interrupts succeeded
11401 Testing all the PIC interrupts failed
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 114
011400:
Test OK @
DS_CHR_DMA_TestDMA
Nucleus Number 115
Description Test the memory to memory DMA transfer
Technical - Create a block with known data in memory
- Copy this block to the consecutive area using 3 different DMAs
- Check whether all DMAs transferred the data properly
Execution Time Less than 2 seconds.
User Input Error Number Description
11500 The testing of the DMAs succeeded
11501 The initialisation of the DMAs failed for one or more DMA
11502 One or more DMAs failed the test
Example
DS:> 115
011500:
Test OK @
Boot EEPROM (BROM)
Nucleus Name
DS_BROM_Communication
Nucleus Number 200
Description Check the communication between the IIC controller of the Codec and the boot
EEPROM
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Read something from the EEPROM
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
20000 The data is properly read so the commu nication is OK
20001 The IIC bus was not accessible
20002 There was a timeout reading the device
20003 The IIC acknowledge was not received
20004 An IIC-bus error occurred
20005 The IIC bus initialisation failed
20006 An unexpected IIC error occurred
Example
DS:> 200
020000:
Test OK @
EN 24
5.
3139 785 31681
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name
DS_BROM_WriteRead
Nucleus Number 201
Description Check whether the Boot EEPROM can be written to and read from
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Write something to the EEPROM
- Read from the same location and check whether it is the same as written
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
20100 The write-read test succeeded
20101 The write-read test failed
20102 An IIC-bus error occurred
20103 There was a timeout reading the device
20104 The IIC bus was not accessible
20105 The IIC acknowledge was not received
20106 Got unknown IIC bus error
20107 The IIC bus initialisation failed
Example
Non Volatile RAM (NVRAM)
Nucleus Name
DS:> 201
020100:
Test OK @
DS_NVRAM_Communication
Nucleus Number 300
Description Check the communication between the IIC controller of the Codec and the
NVRAM EEPROM
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Read from a location in the NVRAM EEPROM device
Important note:
This nucleus only checks the physical connection between the Codec and IIC
EEPROM. If no EEPROM is mounted this test will fail. However other NVRAM
nuclei might still work because the software will store NVM data into flash
memory
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
30000 Something is properly read so the communication is OK
30001 The IIC bus was not accessible
30002 There was a timeout reading the device
30003 The IIC acknowledge was not received
30004 The communication with the device failed
30005 The IIC bus initialisation failed
Example
DS:> 300
030000:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name
DS_NVRAM_WriteRead
Nucleus Number 301
Description Check whether the EEPROM can be written to and read from
Technical - Initialise IIC
- If no IIC EEPROM was found then initialise flash memory to use NVM
pages
- Backup data from location to modify
- Write to location and read it back again
- Write back the backed up data to the location to leave the NVRAM as
found
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
30100 The write-read test succeeded
30101 The IIC bus could not be initia lised
30102 There was an NVRAM IO error
30103 The value could not be read back from the NVRAM
Example
DS:> 301
030100:
Test OK @
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
3139 785 31681
5.
EN 25
Nucleus Name
DS_NVRAM_Clear
Nucleus Number 302
Description Make the EEPROM empty, containing all zeroes.
Technical - Initialise IIC
- If no IIC EEPROM was found then initialise flash memory to use NVM
pages
- Read the DVID and diversity string from NVM (either EEPROM or Flash)
- Create a memory block filled with zeroes
- Write this block to the NVRAM (either EEPROM or Flash)
- Write back the Read the DVID and diversity string to NVM (either
EEPROM or Flash)
Important note:
The Hardware Diversity Information and unique identification number
(IEE1394-specific) of the Digital Video proc essing part is NOT cleared by this
nucleus!
Execution Time 16 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
30200 The clearing of the NVRAM succeeded
30201 There was an IIC error
30202 Clearing the NVRAM failed
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 302
030200:
Test OK @
DS_NVRAM_Modify
Nucleus Number 303
Description Modifies one or more locations in NVRAM and updates the checksum of the
section modified
Technical - Initialise IIC
- If no IIC EEPROM was found then initialise flash memory to use NVM
pages
- Decode user input
- Modify the NVRAM as indicated
- Validate the NVRAM by calculating the checksum and storing it
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input 1. The location that must be modified
i.e. "ALL" "BOOT" "DIAGNOSTICS" "DOWNLOAD" "CONFIG"
"RECORDER" or no string if an offset from the base address of the
NVRAM is required
2. The offset and data which to put on the selected loc ation
<offset> <length> <data>
Error Number Description
30300 Modifying the NVRAM contents succeeded
30301 Unable to initialise NVM
30302 Modifying the NVRAM contents failed
30303 length out of range
30304 unable to decode length
30305 offset out of range
30306 unable to decode offset
30307 unknown location specifie d
30308 no location is specified
30309 number of values incorrect
30310 There was an IIC error
Example
DS:> 303 DIAGNOSTICS 5 1 0x5a
030300: Section is modified successfully
Test OK @
EN 26
5.
3139 785 31681
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name
DS_NVRAM_Read
Nucleus Number 304
Description Read out one or more locations in the NVRAM
Technical - Initialise IIC
- If no IIC EEPROM was found then initialise flash memory to use NVM
pages
- Decode user input
- Read from the NVRAM and return this info to the user
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input 1. The location which must be read
i.e. "ALL" "BOOT" "DIAGNOSTICS" "DOWNLOAD" "CONFIG"
"RECORDER" or no string if an offset from the base address of the
NVRAM is required
2. The offset and number of bytes to read
<offset> <length>
Error Number Description
30400 Value read
30401 Unable to initialise NVM
30402 Reading the NVRAM contents failed
30403 Length out of range
30404 Unable to decode length
30405 Offset out of range
30406 Unable to decode offset
30407 Unknown location specified
30408 No location is specified
Example
304 DIAGNOSTICS 0 6
030400: Value read = 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x5A
Test OK @
SDRAM (SDRAM)
Nucleus Name
DS_SDRAM_WriteRead
Nucleus Number 400
Description Check all data lines, address lines and memory locations of the SDRAM
Technical - Test the data b us
- Test the address bus
- Test the integrity of the device itself (memory locations)
Execution Time 11 seconds for 32 Mb
23 seconds for 64 Mb
User Input None
Error Number Description
40000 The write-read test succeeded
40001 The data bus contains an error
40002 The address bus contains an error
40003 The SDRAM itself contains an error
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 400
040000:
Test OK @
DS_SDRAM_WriteReadFast
Nucleus Number 401
Description Check all data lines and address lines of the SDRAM
Technical - Test the data b us
- Test the address bus
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
40100 The write-read test succeeded
40101 The data bus contains an error
40102 The address bus contains an error
Example
DS:> 401
040100:
Test OK @
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
3139 785 31681
5.
EN 27
Nucleus Name
DS_SDRAM_Write
Nucleus Number 402
Description Write to a specific un-cached memory address
Technical - Decode the us er input and check its ranges and alignment on 4 bytes
- Write the data to the SDRAM
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input 1. The location that must be modified
(SDRAM starts at address 0xA0000000)
2. The value to put on the selected location
Error Number Description
40200 Writing to the SDRAM succeeded
40201 Writing to the SDRAM failed; Wrong user input
40202 Address is not dividable by 4
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 402 0xa1000010 0xad112222
040200:
Test OK @
DS_SDRAM_Read
Nucleus Number 403
Description Read from a specific un-cached memory address
Technical - Decode the us er input and check the ranges
- Read from the SDRAM and return this info to the user
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input The location from which the data must be read
(SDRAM starts at address 0xA0000000)
Error Number Description
40300 Reading from the SDRAM succeeded
40301 Reading from the SDRAM failed; Wrong user input
40302 Address is not dividable by 4
Example
DS:> 403 0xa1000010
040300: Value read = 0xAD112222
Test OK @
Nucleus Name
DS_SDRAM_DmaWriteRead
Nucleus Number 404
Description Write a pattern to the entire SDRAM using DMA and check the data
Technical - Check if the Stack pointer is not in the write range
- Clear a 64kb block and then fill it with a pattern
- Initialise the DMA controller and write the data to the SDRAM
- Then check if all the data was written correctly (except descriptor tables)
- Repeat the process 4 times with 4 different patterns
Execution Time 24 seconds
User Input None.
Error Number Description
40400 Writing to the SDRAM succeeded
40401 Stack area definition ERROR!
40402 DMA controller could not be initialised.
40403 Not all data was transferred correctly
Example
DS:> 404
040400:
Test OK @
EN 28
FLASH (FLASH)
5.
3139 785 31681
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name
DS_FLASH_DevTypeGet
Nucleus Number 500
Description Get the device (revision) type information of the FLASH ICs. (type,
manufacturer, device ID and size)
Technical - Set the timing for the flash writing
- Write a command sequence to determine device type information
- Return the information to the user
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
50000 Getting the information from the FLASH succeeded
50001 Getting the information from the FLASH failed
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 500
050000: Found FLASH memory:
NOR AMD 29DL640G 8MB,NOR AMD 29DL640G 8MB
Test OK @
DS_FLASH_WriteRead
Nucleus Number 501
Description Check whether the FLASH can be written to and read from
Technical - Find the test segment in flash
- Read the data into SDRAM
- Modify the data
- Write this data from SDRAM to FLASH and verify it by reading back again
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input None
Error Number Description
50100 The FLASH write-read test succeed ed
50101 The test segment could not be found
50102 All bits in the TEST region are filled with 0 (region exhausted)
50103 The Write Read test failed
50104 The Write Failed
Example
DS:> 501
050100:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name
DS_FLASH_Read
Nucleus Number 502
Description Read from a specific memory address in FLASH
Technical - Decode the user input and check the ranges and whether the address is
aligned on 4 bytes
- Read the data and return this to the user
Execution Time Less than 1 second.
User Input The location from which data must be read
(FLASH starts at address 0xB8000000)
Error Number Description
50200 Reading the FLASH succeeded
50201 Reading the FLASH failed; Wrong user input
50202 Address is not dividable by 4
Example
DS:> 502 0xb8000000
050200: Value read = 0x3C08A000
Test OK @
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
3139 785 31681
5.
EN 29
Nucleus Name
DS_FLASH_ChecksumProgram
Nucleus Number 503
Description Check the checksum of the application partitions by recalculating and
comparing partition checksums
Technical - Determine the number of segments
- Find the application in each segment and determine its checksum
- Check whether the checksums stored match the newly calculated
Execution Time 6 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
50300 The checksum is valid, the test succeeded
50301 The checksum is invalid
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 503
050300:
BootCode checksum is: 0xBABE5B6F, which is correct
Diagnostics checksum is: 0xBABEBAFF, which is correct
Download checksum is: 0xBABEEDBF, which is correct
Application checksum is: 0xBABE8EEC, which is correct
Test OK @
DS_FLASH_CalculateChecksum
Nucleus Number 504
Description Calculate the checksum over all memory addresses. Used to check entire
FLASH contents
Technical - Run the check sum calculation algorithm on all flash memory addresses
Execution Time 6 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
50400 Calculating the checksum over all addresses succeeded
Example
DS:> 504
050400: The Checksum = 0xBABE30A4
Test OK @
Nucleus Name
DS_FLASH_CalculateChecksumFast
Nucleus Number 505
Description Calculate a checksum over a selected number of address locations
Technical - Run the check sum calculation algorithm on a selected number of flash
memory addresses
Execution Time 6 seconds
User Input None
Error Number Description
50500 Calculating the checksum over selected addresses succeeded
Example
Video Input Processor (VIP)
Nucleus Name
DS:> 505
050500: The Checksum = 0xBABEB064
Test OK @
DS_VIP_DevTypeGet
Nucleus Number 600
Description Get the device (revision) type information of the VIP IC
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Read out the device (revision) type information of the VIP IC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
60000 Getting the information from the VIP succeeded
60001 The IIC bus initialisation failed
60002 The was an error getting the information from the VIP
60003 Type not according to t ype stored in HW diversity string
Example
DS:> 600
060000: Found SAA7118
Test OK @
EN 30
5.
3139 785 31681
Firmware Upgrading & Diagnostic Software
Nucleus Name
DS_VIP_Communication
Nucleus Number 601
Description Check the communication between the IIC controller of the Codec and the VIP
IC
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Read data from a location in the VIP
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
60100 Communicating with the VIP succeeded
60101 The IIC bus was not accessible
60102 There was a timeout reading the device
60103 The IIC acknowledge was not received
60104 The communication with the device failed
60105 The IIC bus initialisation failed
Example
Nucleus Name
DS:> 601
060100:
Test OK @
DS_VIP_ClockOutputOn
Nucleus Number 602
Description Switch the clock output on
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Set the clock output through IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
60200 Switching the clock output on succeeded
60201 Switching the clock output on faile d
Example
DS:> 602
060200:
Test OK @
Nucleus Name
DS_VIP_ClockOutputOff
Nucleus Number 603
Description Switch the clock output off
Technical - Initialise IIC
- Reset the clock output through IIC
Execution Time Less than 1 second
User Input None
Error Number Description
60300 Switching the clock output off succeeded
60301 Switching the clock output off failed
Example
DS:> 603
060300:
Test OK @
 Loading...
Loading...