Philips BUK207-50X Datasheet
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
TOPFET high side switch BUK207-50X
SMD version of BUK203-50X
DESCRIPTION QUICK REFERENCE DATA
Monolithic temperature and SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. UNIT
overload protected power switch
based on MOSFET technology in a I
L
Nominal load current (ISO) 1.6 A
5 pin plastic surface mount
envelope, configured as a single
high side switch. SYMBOL PARAMETER MAX. UNIT
APPLICATIONS V
BG
Continuous off-state supply voltage 50 V
I
L
Continuous load current 4 A
General controller for driving T
j
Continuous junction temperature 150 ˚C
lamps, motors, solenoids, heaters. R
ON
On-state resistance 220 mΩ
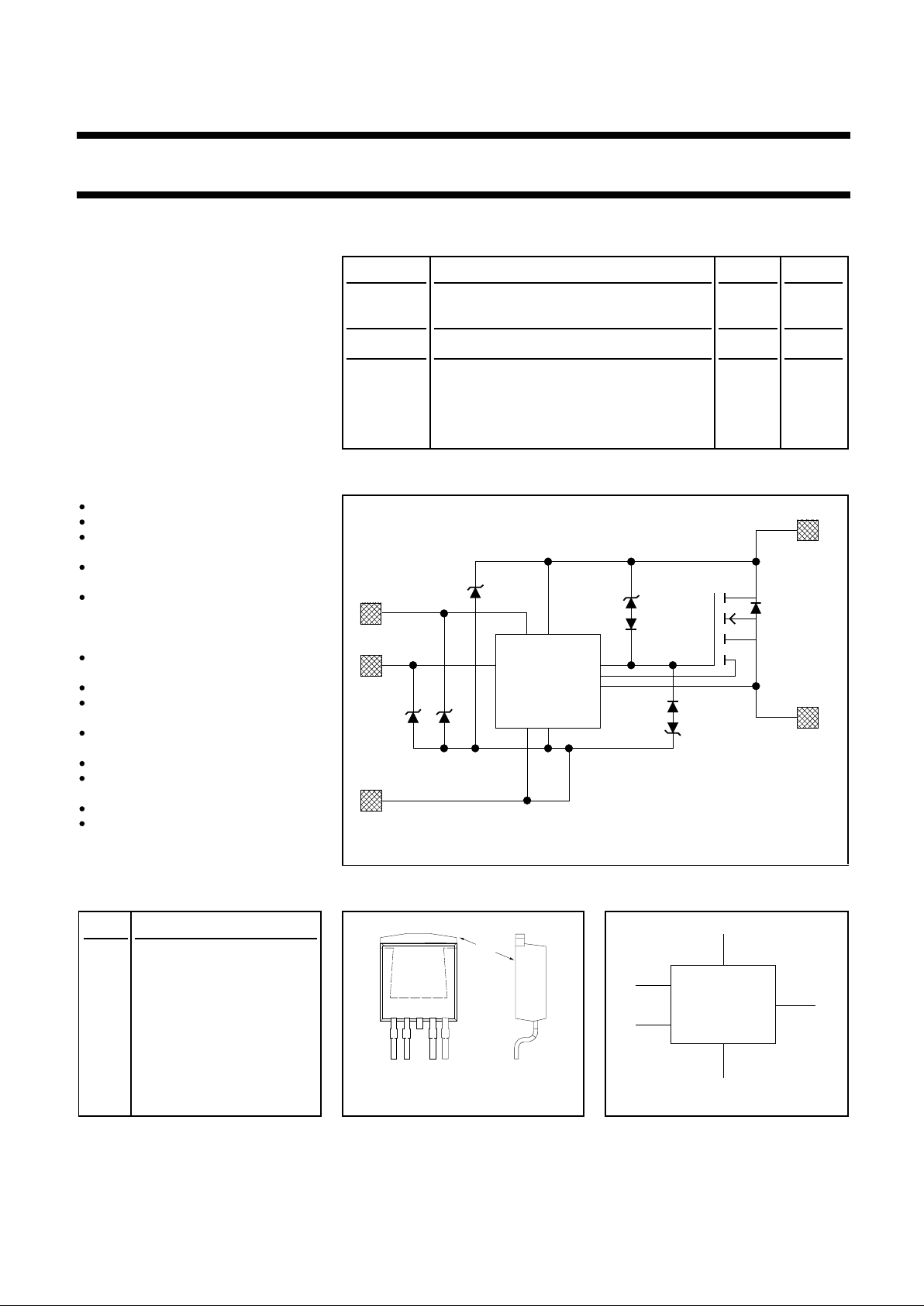
FEATURES FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Vertical power DMOS switch
Low on-state resistance
5 V logic compatible input
with hysteresis
Overtemperature protection self resets with hysteresis
Overload protection against
short circuit load with
output current limiting;
latched - reset by input
High supply voltage load
protection
Supply undervoltage lock out
Status indication for overload
protection activated
Diagnostic status indication
of open circuit load
Very low quiescent current
Voltage clamping for turn off of
inductive loads
ESD protection on all pins
Reverse battery and
overvoltage protection Fig.1. Elements of the TOPFET HSS.
with external ground resistor
PINNING - SOT426 PIN CONFIGURATION SYMBOL
PIN DESCRIPTION
1 Ground
2 Input
3 (connected to mb)
4 Status
5 Load
Fig. 2. Fig. 3.
mb Battery
BATT
LOAD
INPUT
GROUND
STATUS
POWER
MOSFET
CONTROL &
PROTECTION
CIRCUITS
mb
12 45
3
B
G
L
I
S
HSS
TOPFET
July 1996 1 Rev 1.000
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
TOPFET high side switch BUK207-50X
SMD version of BUK203-50X
LIMITING VALUES
Limiting values in accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134)
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
Battery voltages
V
BG
Continuous off-state supply voltage - 0 50 V
Reverse battery voltages
1
External resistors:
-V
BG
Repetitive peak supply voltage RG ≥150 Ω; RI = RS ≥ 4.7 kΩ, - 32 V
δ ≤ 0.1
-V
BG
Continuous reverse supply voltage RG ≥150 Ω; RI = RS ≥ 4.7 kΩ -16V
I
L
Continuous load current T
mb ≤
110 ˚C - 4 A
P
D
Total power dissipation T
mb ≤
25 ˚C - 50 W
T
stg
Storage temperature - -55 175 ˚C
T
j
Continuous junction temperature
2
- - 150 ˚C
T
sold
Lead temperature during soldering - 250 ˚C
Input and status
I
I
Continuous input current - -5 5 mA
I
S
Continuous status current - -5 5 mA
I
I
Repetitive peak input current δ ≤ 0.1 -20 20 mA
I
S
Repetitive peak status current δ ≤ 0.1 -20 20 mA
Inductive load clamping
E
BL
Non-repetitive clamping energy Tmb = 150 ˚C prior to turn-off - 1.4 J
ESD LIMITING VALUE
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
C
Electrostatic discharge capacitor Human body model; - 2 kV
voltage C = 250 pF; R = 1.5 kΩ
THERMAL CHARACTERISTIC
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Thermal resistance
3
R
th j-mb
Junction to mounting base - - 2 2.5 K/W
1 Reverse battery voltage is allowed only with external input and status resistors to limit the currents to a safe value.
2 For normal continuous operation. A higher Tj is allowed as an overload condition but at the threshold T
j(TO)
the over temperature trip operates
to protect the switch.
3 Of the output Power MOS transistor.
July 1996 2 Rev 1.000
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
TOPFET high side switch BUK207-50X
SMD version of BUK203-50X
STATIC CHARACTERISTICS
Tmb = 25 ˚C unless otherwise stated
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Clamping voltages
V
BG
Battery to ground IG = 1 mA 50 55 65 V
V
BL
Battery to load IL = IG = 1 mA 50 55 65 V
-V
LG
Negative load to ground IL = 1 mA 12 17 21 V
Supply voltage battery to ground
V
BG
Operating range
1
-5-40V
Currents VBG = 13 V
I
L
Nominal load current
2
VBL = 0.5 V; Tmb = 85 ˚C 1.6 - - A
I
B
Quiescent current
3
VIG = 0 V; VLG = 0 V - 0.1 2 µA
I
G
Operating current
4
VIG = 5 V; IL = 0 A 1.5 2.2 4 mA
I
L
Off-state load current
5
VBL = 13 V; VIG = 0 V - 0.1 1 µA
Resistances
R
ON
On-state resistance
6
VBG = 13 V; IL = 2 A; tp = 300 µs - 160 220 mΩ
R
ON
On-state resistance VBG = 5 V; IL = 0.5 A; tp = 300 µs - 225 320 mΩ
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Tmb = 25 ˚C; VBG = 13 V
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
I
I
Input current VIG = 5 V 35 60 100 µA
V
IG
Input clamping voltage II = 200 µA678V
V
IG(ON)
Input turn-on threshold voltage - 2.1 2.4 V
V
IG(OFF)
Input turn-off threshold voltage 1.5 1.7 - V
∆V
IG
Input turn-on hysteresis - 0.4 - V
1 On-state resistance is increased if the supply voltage is less than 9 V. Refer to figure 8.
2 Defined as in ISO 10483-1.
3 This is the continuous current drawn from the battery when the input is low and includes leakage current to the load.
4 This is the continuous current drawn from the battery with no load connected, but with the input high.
5 The measured current is in the load pin only.
6 The supply and input voltage for the RON tests are continuous. The specified pulse duration tp refers only to the applied load current.
July 1996 3 Rev 1.000
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
TOPFET high side switch BUK207-50X
SMD version of BUK203-50X
PROTECTION FUNCTIONS AND STATUS INDICATIONS
Truth table for normal, open-circuit load and overload conditions and abnormal supply voltages.
FUNCTIONS TRUTH TABLE THRESHOLD
SYMBOL CONDITION INPUT STATUS OUTPUT MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Normal on-state 1 1 1
Normal off-state 0 1 0
I
L(OC)
Open circuit load
1
1 0 1 30 90 150 mA
Open circuit load 0 1 0
T
j(TO)
Over temperature
2
1 0 0 150 175 - ˚C
Over temperature
3
00 0
V
BL(TO)
Short circuit load
4
1 0 0 9 10.5 12 V
Short circuit load 0 1 0
V
BG(TO)
Low supply voltage
5
X1 0345V
V
BG(LP)
High supply voltage
6
X1 0404550V
For input ‘0’ equals low, ‘1’ equals high, ‘X’ equals don’t care.
For status ‘0’ equals low, ‘1’ equals open or high.
For output switch ‘0’ equals off, ‘1’ equals on.
STATUS CHARACTERISTICS
Tmb = 25 ˚C.
The status output is an open drain transistor, and requires an external pull-up circuit to indicate a logic high.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
SG
Status clamping voltage IS = 100 µA678V
V
SG
Status low voltage IS = 50 µA; VBG = 13 V - 0.7 0.8 V
I
S
Status leakage current VSG = 5 V - 0.1 1 µA
I
S
Status saturation current
7
VSS = 5 V; RS = 0 Ω; VBG = 13 V - 9 - mA
Application information
R
S
External pull-up resistor
8
VSS = 5 V - 100 - kΩ
1 In the on-state, the switch detects whether the load current is less than the quoted open load threshold current. This is for status indication
only. Typical hysteresis equals 25 mA. The thresholds are specified for supply voltage within the normal working range.
2 After cooling below the reset temperature the switch will resume normal operation. The reset temperature is lower than the trip temperature by
typically 10 ˚C.
3 If the overtemperature protection has operated, status remains low to indicate the overtemperature condition even if the input is taken low,
providing the device has not cooled below the reset temperature.
4 After short circuit protection has operated, the input voltage must be toggled low for the switch to resume normal operation.
5 Undervoltage sensor causes the device to switch off. Typical hysteresis equals 0.5 V.
6 Overvoltage sensor causes the device to switch off to protect the load. Typical hysteresis equals 1.1 V.
7 In a fault condition with the pull-up resistor short circuited while the status transistor is conducting.
8 The pull-up resistor also protects the status pin during reverse battery conditions.
July 1996 4 Rev 1.000
 Loading...
Loading...