Philips BST80 Datasheet
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
DATA SH EET
BST80
N-channel enhancement mode
vertical D-MOS transistor
Product specification
Supersedes data of April 1995
File under Discrete Semiconductors, SC13b
1997 Jun 20
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
N-channel enhancement mode
vertical D-MOS transistor
FEATURES
• Low drain-source on-state resistance
• Direct interface to C-MOS, TTL, etc.
• High-speed switching
• No secondary breakdown.
APPLICATIONS
• Thin and thick film circuits
• Relay, high-speed and line transformer drivers.
DESCRIPTION
N-channel enhancement mode vertical D-MOS transistor
in a SOT89 package.
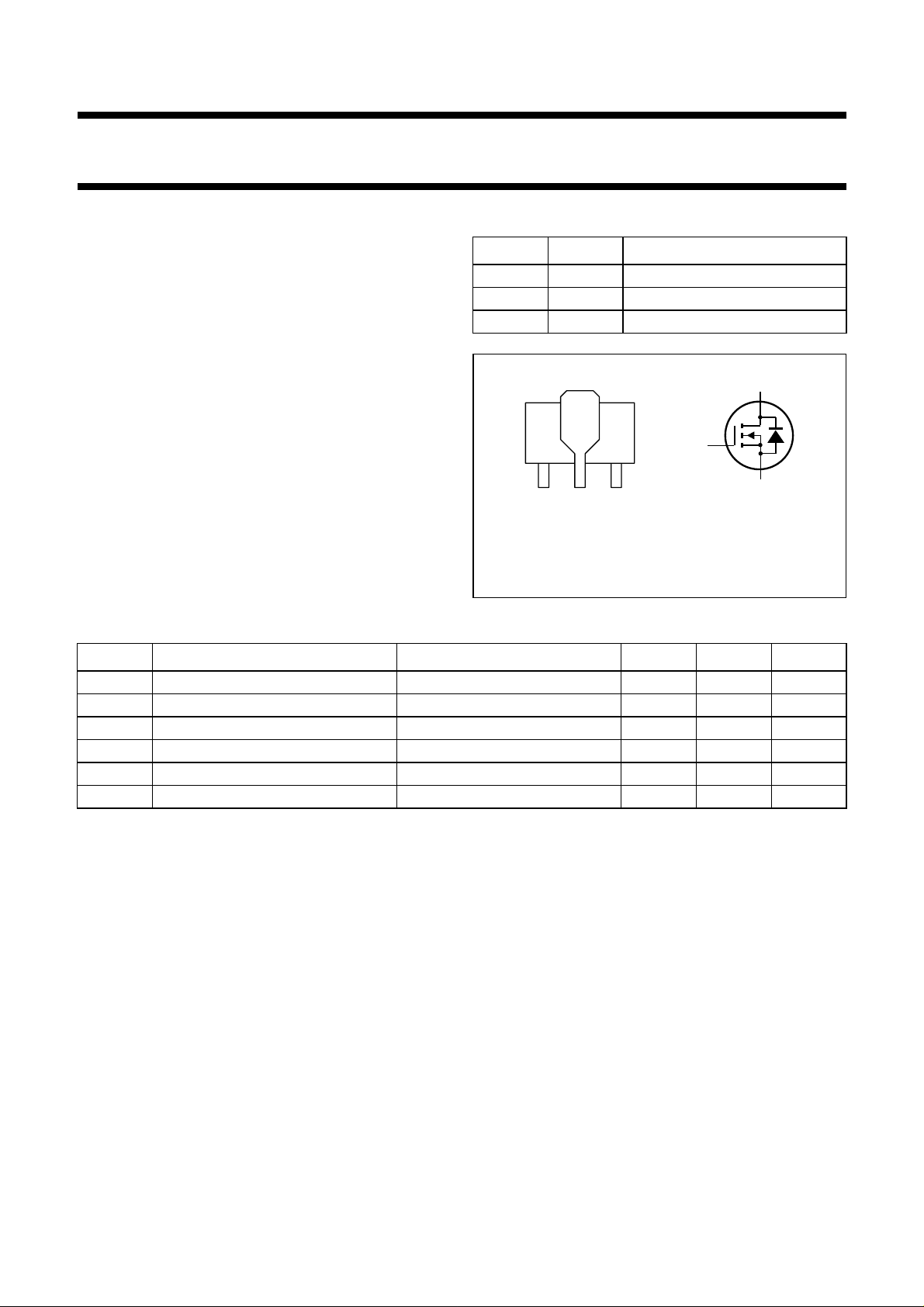
PINNING - SOT89
PIN SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
1 s source
2 d drain
3 g gate
handbook, halfpage
g
123
Bottom view
Marking code: KM
MAM355
Fig.1 Simplified outline and symbol.
BST80
d
s
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DS
V
GSO
I
D
P
tot
R
DSon
y
forward transfer admittance ID= 500 mA; VDS=15V 300 − mS
fs
drain-source voltage (DC) − 80 V
gate-source voltage (DC) open drain −±20 V
drain current (DC) − 500 mA
total power dissipation T
≤ 25 °C − 1W
amb
drain-source on-state resistance ID= 500 mA; VGS=10V 2 3 Ω
1997 Jun 20 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
N-channel enhancement mode
BST80
vertical D-MOS transistor
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DS
V
GSO
I
D
I
DM
P
tot
T
stg
T
j
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th j-a
Note to the Limiting values and Thermal characteristics
1. Device mounted on a ceramic substrate; area 2.5 cm
drain-source voltage (DC) − 80 V
gate-source voltage (DC) open drain −±20 V
drain current (DC) − 500 mA
peak drain current − 1A
total power dissipation T
≤ 25 °C; note 1 − 1W
amb
storage temperature −65 +150 °C
junction temperature − 150 °C
thermal resistance from junction to ambient note 1 125 K/W
2
; thickness 0.7 mm.
CHARACTERISTICS
=25°C unless otherwise specified.
T
j
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
(BR)DSS
V
GSth
I
DSS
I
GSS
R
DSon
forward transfer admittance ID= 500 mA; VDS=15V − 300 − mS
y
fs
C
iss
C
oss
C
rss
drain-source breakdown voltage VGS= 0; ID=10µA80−−V
gate-source threshold voltage VDS=VGS; ID= 1 mA 1.5 − 3.5 V
drain-source leakage current VDS= 60 V; VGS=0 −−1µA
gate leakage current VDS= 0; VGS= ±20 V −−±100 nA
drain-source on-state resistance VGS= 10 V; ID= 500 mA − 23Ω
input capacitance VDS= 10 V; VGS= 0; f = 1 MHz − 45 60 pF
output capacitance VDS= 10 V; VGS= 0; f = 1 MHz − 30 45 pF
reverse transfer capacitance VDS= 10 V; VGS= 0; f = 1 MHz − 812pF
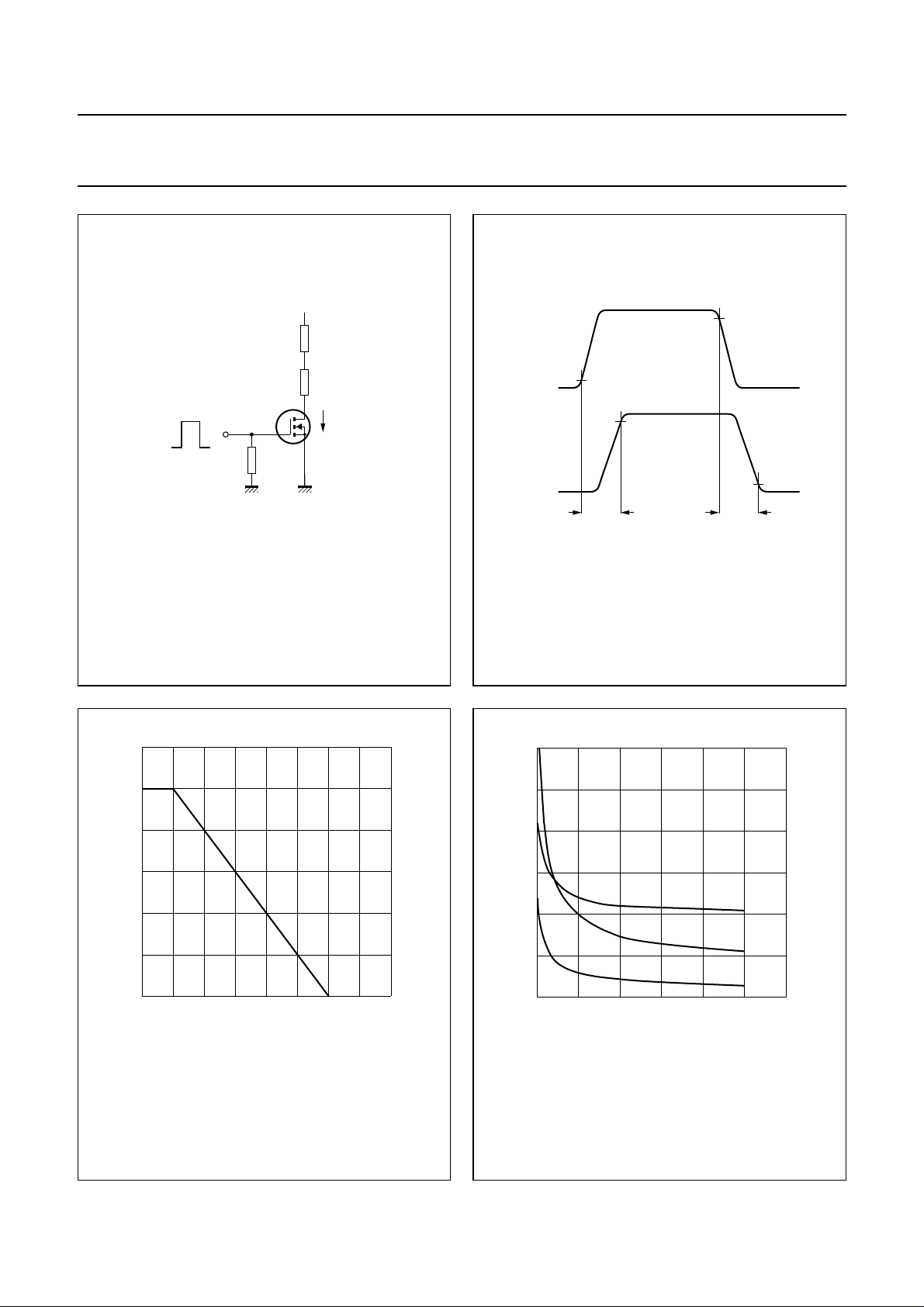
Switching times (see Figs 2 and 3)
t
on
turn-on time VGS= 0 to 10 V; VDD=50V;
−−10 ns
ID= 500 mA
t
off
turn-off time VGS=10to0V; VDD=50V;
−−15 ns
ID= 500 mA
1997 Jun 20 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
N-channel enhancement mode
vertical D-MOS transistor
handbook, halfpage
10 V
0 V
50 Ω
V = 50 V
DD
I
D
MSA631
handbook, halfpage
INPUT
OUTPUT
10 %
t
on
90 %
90 %
t
off
BST80
10 %
MBB692
1.2
handbook, halfpage
P
tot
(W)
0.8
0.4
0
0 200
Fig.2 Switching times test circuit.
MLC697
50 100 150
T ( C)
amb
Fig.3 Input and output waveforms.
120
handbook, halfpage
C
(pF)
80
40
0
o
0
VGS= 0; f= 1 MHz; Tj=25°C.
(1) C
.
iss
(2) C
.
oss
(3) C
.
rss
10 20 30
MDA176
(1)
(2)
(3)
VDS (V)
Fig.4 Power derating curve.
1997 Jun 20 4
Fig.5 Capacitance as a function of drain-source
voltage; typical values.
 Loading...
Loading...