Philips BLF545 Datasheet
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
DATA SH EET
BLF545
UHF push-pull power MOS
transistor
Product specification
October 1992
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF push-pull power MOS transistor BLF545
FEATURES
• High power gain
• Easy power control
• Good thermal stability
• Gold metallization ensures
excellent reliability
• Designed for broadband operation.
DESCRIPTION
Silicon N-channel enhancement
mode vertical D-MOS push-pull
transistor designed for
communications transmitter
applications in the UHF frequency
range.
The transistor is encapsulated in a
4-lead, SOT268 balanced flange
envelope, with two ceramic caps. The
mounting flange provides the
common source connection for the
transistors.
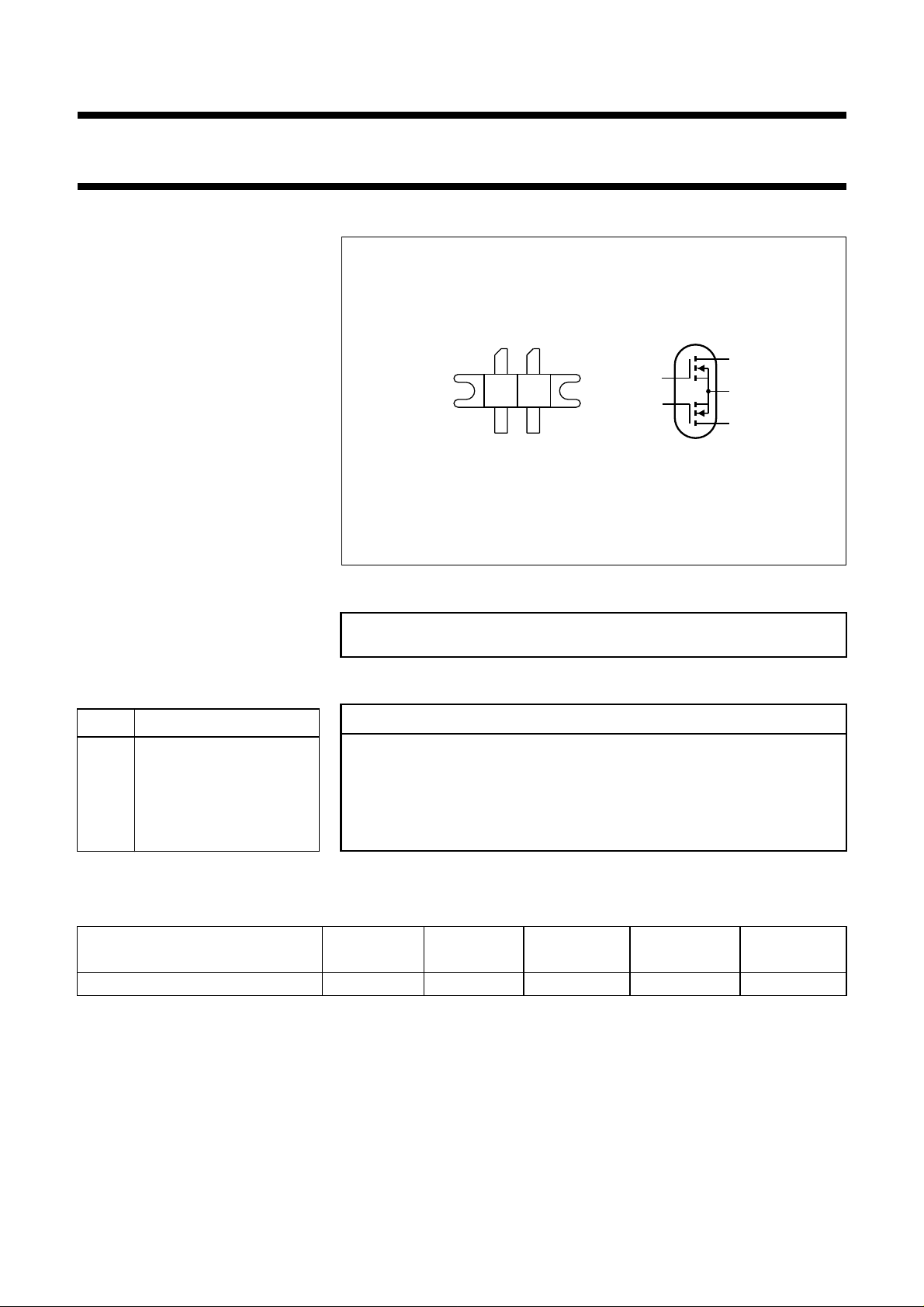
PIN CONFIGURATION
handbook, halfpage
1
2
Top view
4
g
5
3
g
d
s
d
MAM395
Fig.1 Simplified outline and symbol.
CAUTION
The device is supplied in an antistatic package. The gate-source input must
be protected against static charge during transport and handling.
PINNING - SOT268
PIN DESCRIPTION
1 drain 1
2 gate 1
3 gate 2
4 drain 2
5 source
Product and environmental safety - toxic materials
This product contains beryllium oxide. The product is entirely safe provided
that the BeO discs are not damaged. All persons who handle, use or dispose
of this product should be aware of its nature and of the necessary safety
precautions. After use, dispose of as chemical or special waste according to
the regulations applying at the location of the user. It must never be thrown
out with the general or domestic waste.
WARNING
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
RF performance at T
MODE OF OPERATION
= 25 °C in a push-pull common source circuit.
h
f
(MHz)
V
(V)
DS
P
(W)
L
G
P
(dB)
(%)
CW, class-B 500 28 40 > 11 > 50
η
D
October 1992 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF push-pull power MOS transistor BLF545
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134).
Per transistor section unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DS
±V
GS
I
D
P
tot
T
stg
T
j
THERMAL RESISTANCE
drain-source voltage − 65 V
gate-source voltage − 20 V
DC drain current − 3.5 A
total power dissipation up to Tmb=25°C; total device;
− 92 W
both sections equally loaded
storage temperature −65 150 °C
junction temperature − 200 °C
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
R
th j-mb
R
th mb-h
2
10
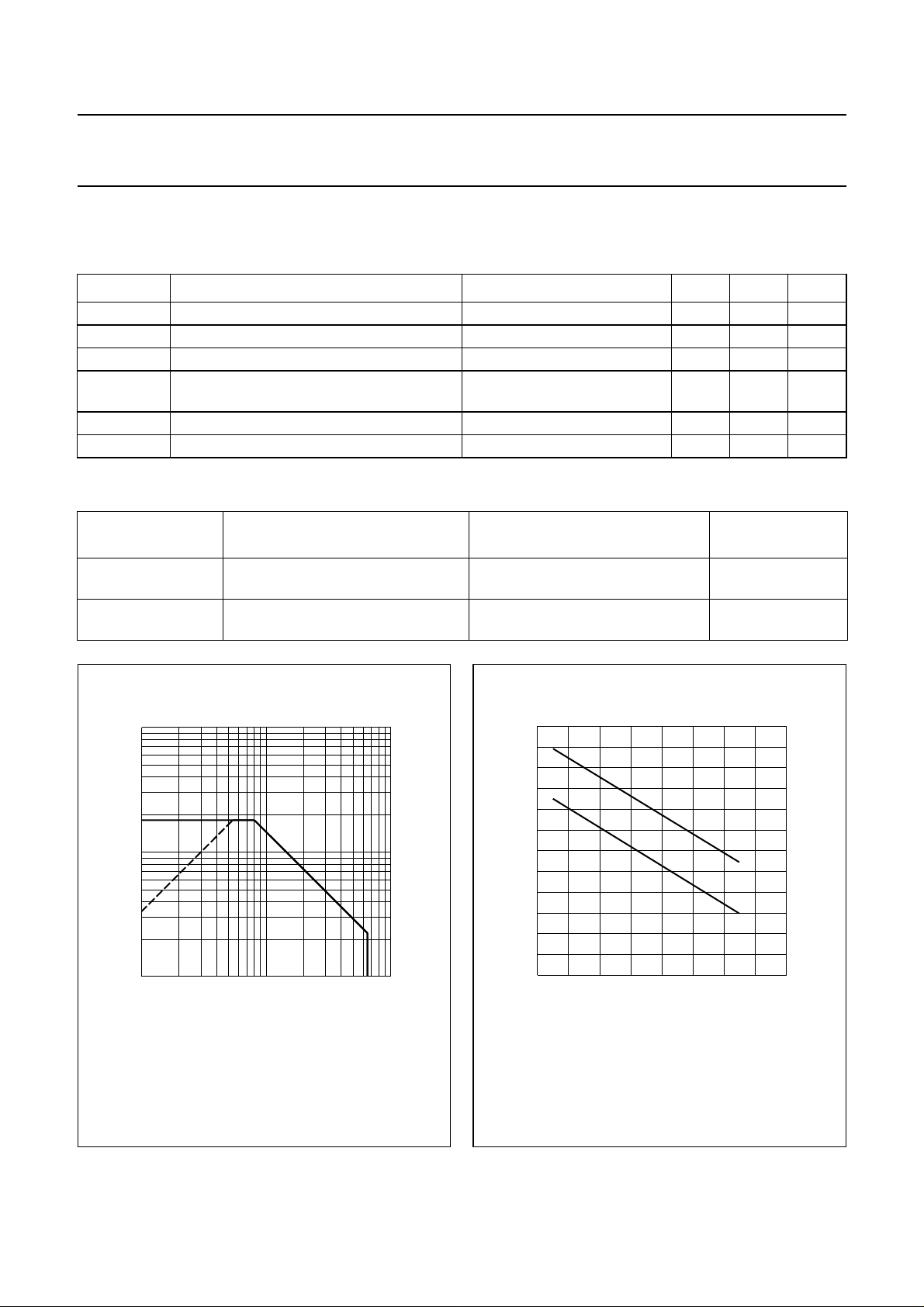
handbook, halfpage
I
D
(A)
10
1
110
thermal resistance from junction to
mounting base
thermal resistance from mounting
base to heatsink
(1)
(2)
VDS (V)
MRA995
total device; both sections equally
loaded
total device; both sections equally
loaded
120
handbook, halfpage
P
tot
(W)
80
40
2
10
0
0
40 80
THERMAL
RESISTANCE
1.9 K/W
0.25 K/W
MBK463
(1)
(2)
Th ( °C)
160
120
(1) Current in this area may be limited by R
(2) Tmb=25°C.
Total device; both sections equally loaded.
DS(on)
.
Fig.2 DC SOAR.
October 1992 3
(1) Short-time operation during mismatch.
(2) Continuous operation.
Total device; both sections equally loaded.
Fig.3 Power/temperature derating curves.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF push-pull power MOS transistor BLF545
CHARACTERISTICS (per section)
T
= 25 °C unless otherwise specified.
j
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
(BR)DSS
I
DSS
I
GSS
V
GS(th)
g
fs
R
DS(on)
I
DSX
C
is
C
os
C
rs
drain-source breakdown voltage VGS= 0; ID = 10 mA 65 −−V
drain-source leakage current VGS= 0; VDS= 28 V −−1mA
gate-source leakage current ±VGS= 20 V; VDS=0 −−1µA
gate-source threshold voltage ID= 40 mA; VDS= 10 V 1 − 4V
forward transconductance ID= 1.2 A; VDS= 10 V 600 900 − mS
drain-source on-state resistance ID= 1.2 A; VGS= 10 V − 0.85 1.25 Ω
on-state drain current VGS= 15 V; VDS= 10 V − 4.8 − A
input capacitance VGS= 0; VDS= 28 V; f = 1 MHz − 32 − pF
output capacitance VGS= 0; VDS= 28 V; f = 1 MHz − 24 − pF
feedback capacitance VGS= 0; VDS= 28 V; f = 1 MHz − 6.4 − pF
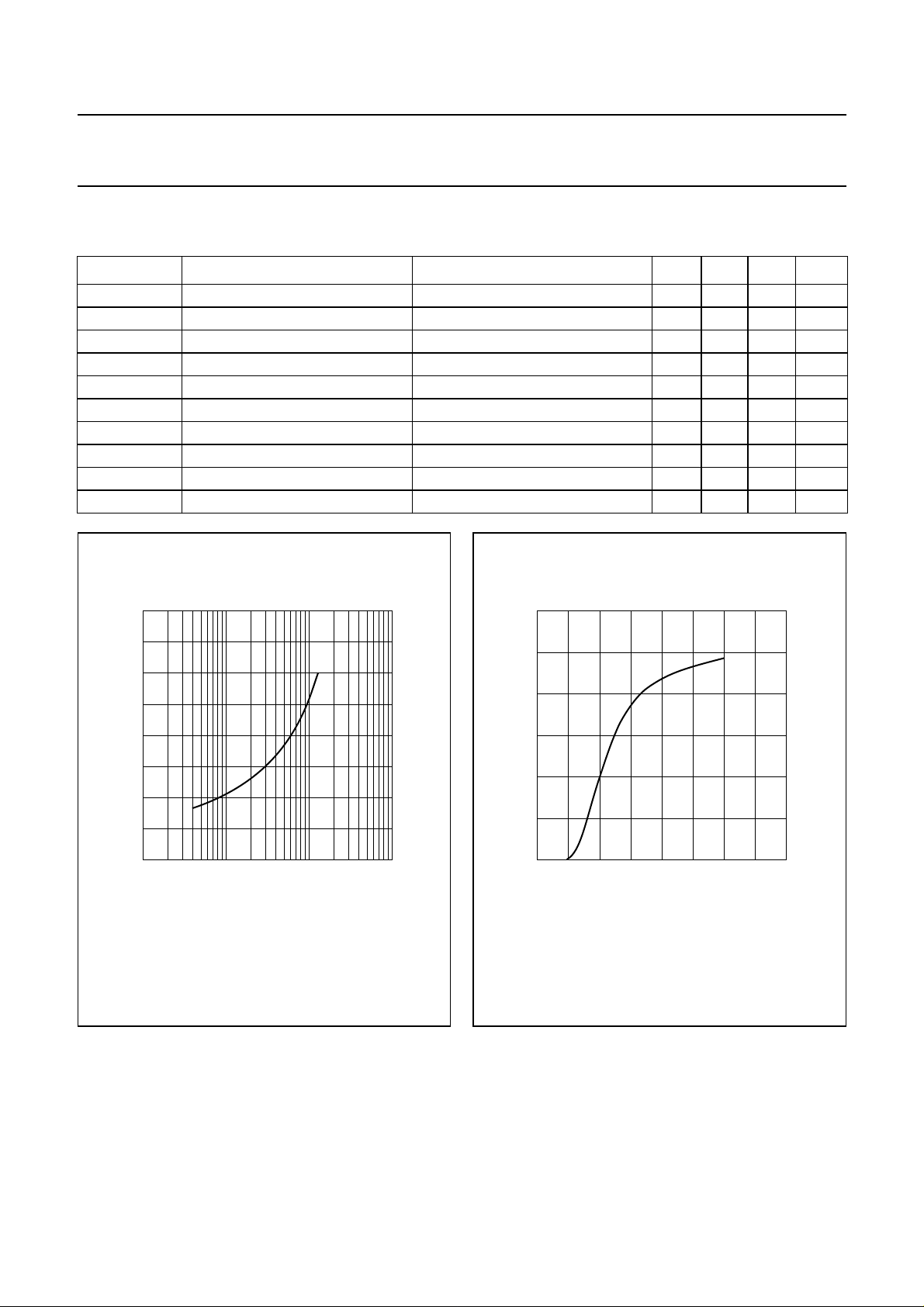
handbook, halfpage
4
T.C
(mV/K)
2
0
−2
−4
10
VDS= 10 V.
−2
−1
10
110
ID (A)
Fig.4 Temperature coefficient of gate-source
voltage as a function of drain current,
typical values per section.
MDA504
handbook, halfpage
6
I
D
(A)
4
2
0
0
VDS= 10 V; Tj= 25 °C.
5
10 20
MDA505
15
V
(V)
GS
Fig.5 Drain current as a function of gate-source
voltage, typical values per section.
October 1992 4
 Loading...
Loading...