
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
74LV4799
Timer for NiCd and NiMH chargers
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1998 Apr 07
IC24 Data Handbook
1998 Apr 20
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74L V4799Timer for NiCd and NiMH chargers
FEA TURES
•Wide supply voltage range of 0.9 V to 6 V allows 1 to 4-cell
applications
•10 V allowed on special inputs
•Supports virtually all battery chargers, including switched-mode
power supplies
•On-chip timer calculates the actual capacity of the battery by
measuring the charger time, discharge time and self-discharge time
•Automatic switch-over to trickle charge after completion of the
charge time
•Can be adjusted for use with different types of batteries:
– Charge time: 4 to 16 hours
– Discharge time: 15 minutes to 4.7 hours
– Self-discharge time: 50 to 100 days
•Battery status indication included:
– LED output for charging/full indication
– MOLLI
output for battery-low indication
•LED mode select allows two different methods of indication
•Automatic power-ON reset
•Low-power consumption
•Requires only a few peripheral components
•Very accurate on-chip oscillator
•Scan test facilities included
•I
category: non-standard.
CC
APPLICATIONS
•Time-controlled NiCd and NiMH low-current chargers
•Domestic appliances such as rechargeable battery shavers,
electric toothbrushes etc.
•Portable equipment such as notebook PCs, laptop PCs, camera
flash units etc.
•Personal communications like cordless telephones, personal
mobile radios, pagers, etc.
DESCRIPTION
The 74LV4799 is a low-voltage Si-gate CMOS control IC for battery
management. It consists of:
•17-stage divider
•10-stage up/down counter
•Control logic
•Integrated precision oscillator (using external timing components)
•Automatic power-ON reset
•Scan test facilities
•Battery charging/full indication output (LED)
•Battery-low indication output (MOLLI)
•Open-drain-N outputs for driving the load transistor
Battery management with the 74LV4799 is based on the principle of
time measurement. It measures the charge time, discharge time and
self-discharge time by means of a very accurate on-chip oscillator, a
divider and an up/down counter.
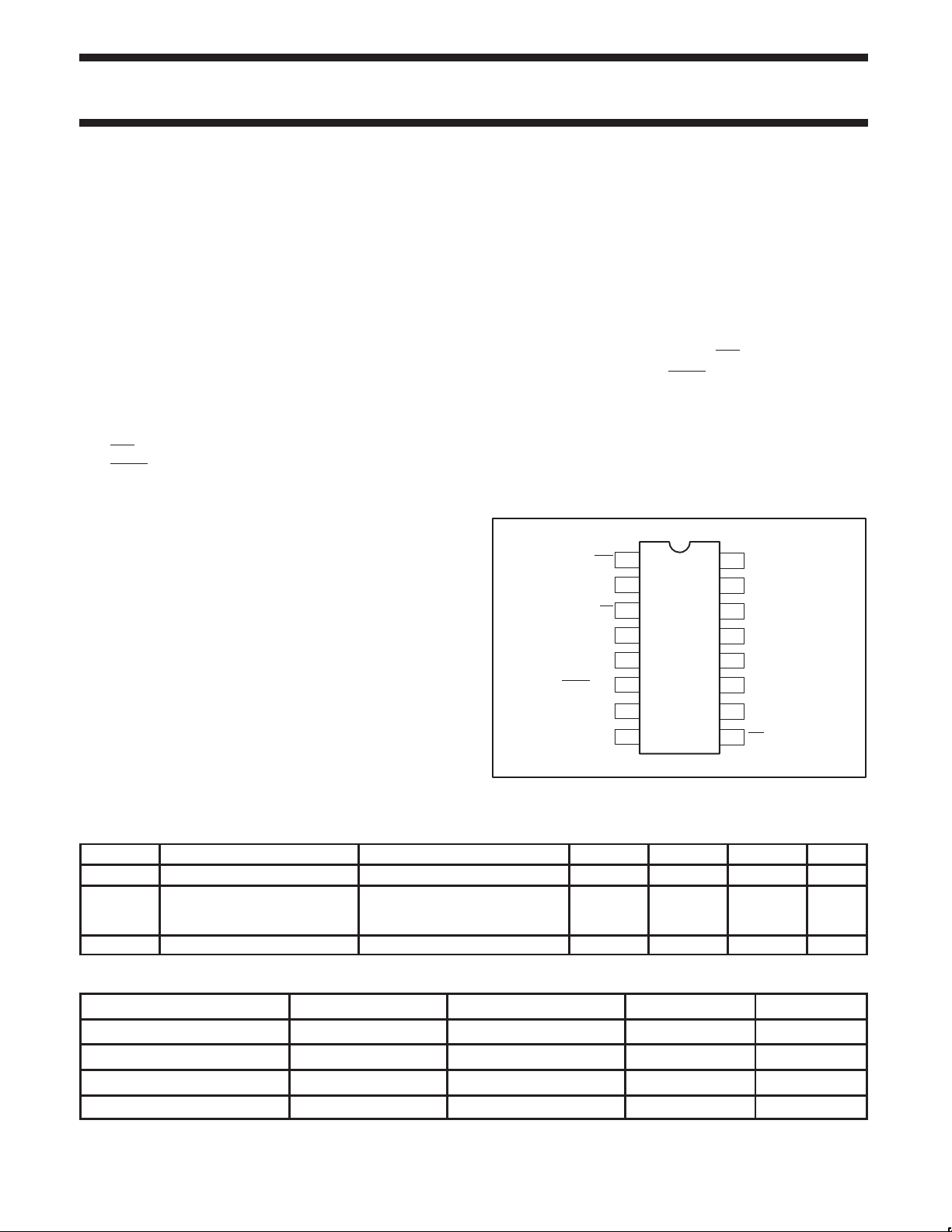
PIN CONFIGURATION
MOLLI
LED
EN
EN
V
PWRS
/SCO
SEL
GND
1
2
3
4
in
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
SV01643
V
CC
SCI
SCAN
I
OSC
R
S
R
D
R
C
DIS
QUICK REFERENCE DA TA
GND = 0V; T
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS TYPICAL TYPICAL TYPICAL UNIT
V
CC
I
CC
f
= 25°C
amb
DC supply voltage 0.9 6.0 V
VCC = 3.3V; self-discharge mode;
= 100 k;
Operating supply current
Oscillator frequency tolerance VCC = 1 to 6 V 7 %
R
s
C
= 220nF
1
36 µA
ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGES TEMPERATURE RANGE OUTSIDE NORTH AMERICA NORTH AMERICA CODE
16-Pin Plastic DIL 0°C to +70°C 74LV4799 N 74LV4799 N SOT38-4
16-Pin Plastic SO 0°C to +70°C 74LV4799 D 74LV4799 D SOT109-1
16-Pin Plastic SSOP Type II 0°C to +70°C 74LV4799 DB 74LV4799 DB SOT338-1
16-Pin Plastic TSSOP Type I 0°C to +70°C 74LV4799 PW 74LV4799PW DH SOT403-1
1998 Apr 20 853-2058 19258
2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74LV4799Timer for NiCd and NiMH chargers
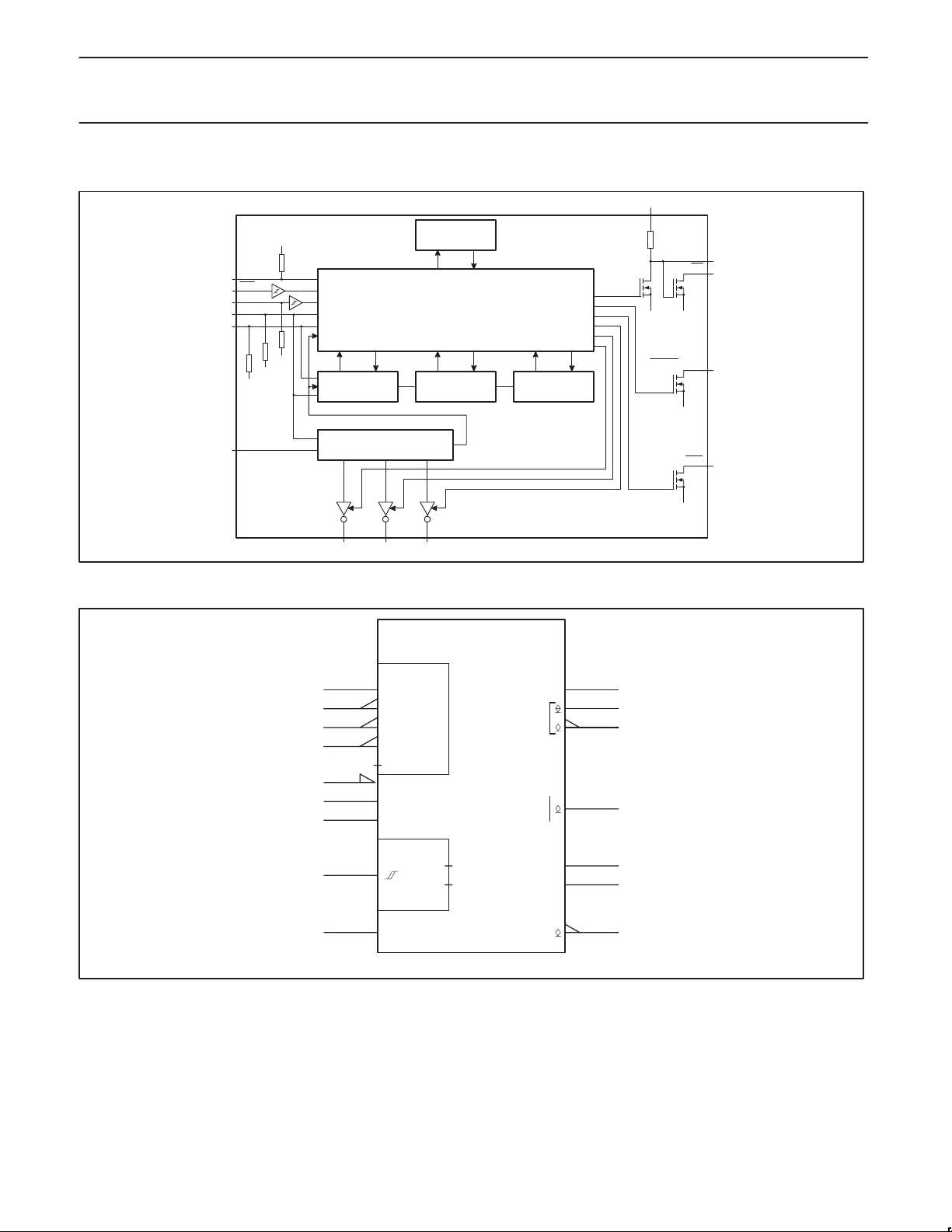
FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM
4
V
GND
in
EN
2
EN
3
GND
V
CC
SEL
7
DIS
9
PWRS
5
SCAN
14
SCI
15
POWER–ON
RESET
CONTROL LOGIC
IEC LOGIC SYMBOL
GND
GND
GND
I
OSC
13
3–STAGE
CP
DIVIDER
OSCILLATOR CP
R
C
10 11
13
12
11
10
9
15
14
5–14 STAGE
DIVIDER
R
R
D
S
12
F
BATT. TIMER
G
IOSC
RS
RD
RC
1
DIS
SCI SCO
SCAN/Z1
MOLLI
10–STAGE
UP/DOWN
COUNTER
U+[1]
EN
MOLLI/SCO
4
2
3
6
GND
LED
GND
SV01644
6
1
1998 Apr 20
I=0
5
7
PWRS
SEL
CT=0
U+[2]
0V
LED
16
8
1
SV01645
3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74LV4799Timer for NiCd and NiMH chargers
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NO. SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
1 LED LED driver output pin (active LOW)
2 EN Enable output (active HIGH)
3 EN Enable output (active LOW)
4 V
in
5 PWRS Power sense input
6 MOLLI/SCO More-or-less-low-indication output (active LOW)/scan test output
7 SEL LED mode select input
8 GND Ground (0 V)
9 DIS Discharge input (active LOW)
10 R
11 R
12 R
13 I
C
D
S
OSC
14 SCAN Scan test mode select input (active HIGH)
15 SCI Scan test input
16 V
CC
External power input
External resistor pin 3-State oscillator output (charge)
External resistor pin 3-State output (discharge)
External resistor pin 3-State output (self-discharge)
Oscillator input
Positive supply voltage
Power On Reset.
An automatic Power On Reset initiates the IC when the battery is
discharged and power is connected to the circuit. The initial
condition is the charge mode in which the counter is reset and
counts from zero up to maximum. At start up, the battery therefore
always receives a full charge cycle. When a partially charged battery
is inserted, it may be over-charged during the first cycle. To guard
against this, simply replace the resistor at the R
pin with an NTC
C
type which is in good thermal contact with the battery. If the
temperature of the battery increases, the frequency of the oscillator
also increases to quickly reach a counter full indication and
switch-over to trickle charge. With a battery that is almost
completely discharged, the POR input can also be activated during
discharge or self-discharge. The counter will then be reset to zero.
This is a correct action while returning to the initial condition.
Power-on sensing.
Because this IC supports virtually all battery chargers, the PWRS input
has a broad input frequency spectrum (active HIGH to 100 kHz). A
pull-down circuit at the PWRS input allows detection of the open state
which corresponds to an inactive charger. A HIGH level on the PWRS
input, or an AC signal up to 100 kHz, enables the charge mode.
Start-up with low battery voltage.
Good start-up, even with an un-charged battery, is assured by using
the V
input. The voltage on the VIN input biases the external
IN
bipolar transistors at the EN or EN
output, even if the IC is not yet
functioning. After the battery has received sufficient charge, the
internal control logic takes over control of the EN and EN outputs.
Charge mode.
This mode is selected when PWRS is active (HIGH or pulsed) and
the discharge input DIS
EN
output is LOW initiating continuous charge of the battery. The
is HIGH. The EN output is HIGH, and the
counter then counts from the zero state up to the maximum value.
The clock frequency is determined by the external capacitor and
resistor connected to the R
output. The counter stops when it
C
reaches its maximum value and the EN and EN
outputs switch over
from the continuous charge to the trickle charge mode.
Trickle charge mode.
At the maximum counter value, it is assumed that the battery is fully
charged. The counter stops and remains on this maximum value.
The EN and EN
outputs switch over from the continues charge to
the trickle charge mode. In the trickle charge mode, the average
charge current is reduced to only compensate the self-discharge of
the battery by using the dedicated duty cycle control. The control is
dedicated because it adjusts the duty cycle in inverse proportion to
the load current, resulting in a fixed charger current irrespective of
the kind of charger (e.g. 4-hour or 16-hour charger). In the trickle
charge mode, the oscillator circuitry alternately generates 4 periods
of R
-C1 time-constant, and 3 periods of the RS -C1 time-constant
C
(See Figure 1).
Discharge mode.
The discharge input (DIS
battery. If DIS
is LOW, the counter counts down. The clock
) is used to detect the discharge of the
frequency is determined by the external capacitor and resistor at the
RD output. If PWRS is inactive (LOW or open), the EN output is
LOW, and the EN
output is in the high impedance OFF-state (no
charge of the battery). This is called the discharge mode. If PWRS is
active, the circuit is in the charge/discharge mode.
Charge/Discharge mode.
If DIS
is LOW and PWRS is active (HIGH or pulsed), the circuit is in
the charge/discharge mode. The counter counts down. The clock
frequency is determined by the external capacitor and resistor tied
at the R
output. The EN output is HIGH, and the EN output is LOW
D
initiating continuous charge of the battery. The battery is therefore
charged and discharged at the same instant, thereby maintaining a
better load condition of the battery.
1998 Apr 20
4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
OPERATING
74LV4799Timer for NiCd and NiMH chargers
Self-discharge mode.
is HIGH and PWRS is inactive (LOW or open), the battery is
If DIS
being neither charged nor discharged. The circuit is in the
self-discharge mode. This mode represents the battery leakage
(self-discharge). The counter counts down. The clock frequency is
determined by the external capacitor and resistor at the R
When the counter reaches the zero state, it stops.
LED mode select.
The LED
charge/full status of the battery. For optimum flexibility, two modes of
operation are built-in.
output drives a battery status LED which indicates the
output.
S
•Mode 1: If SEL is LOW, the LED output is active LOW in the
charge mode, and the LED blinks with a frequency of
about 1 Hz during trickle charge.
•Mode 2: If SEL is HIGH or open, the LED output blinks with a
frequency of about 0.25 Hz in the charge mode, and is
active LOW during trickle charge. In the discharge or
self-discharge mode, the LED
when PWRS is active (HIGH or pulsed). Then, the
battery is charging and discharging simultaneously.
Although the discharge mode is dominant, the LED
output is active when PWRS is also active.
NOTE: The blink frequency depends on the oscillator frequency.
(See application information)
Low indication.
As part of the user interface, the MOLL
battery needs to be charged. MOLLI
Indication (active LOW). The function is as follows: In the discharge
mode, (DIS
reaches the zero state, it stops. If DIS
output gives an output signal of four periods of about one second,
with a 50% duty cycle. This can be used to activate a buzzer. The
MOLLI
PWRS is activated.
Alarm indication.
If an almost completely discharged battery is connected to the
charger, it may not be noticed by the user if the load switch is still
is active LOW), the counter counts down and, when it
output signal of four periods will be interrupted as soon as
output is open except
I output shows when the
stands for More Or Less Low
is switched HIGH, the MOLLI
on. To prevent damaging the battery , an alarm signal on the LED
output will alert the user to switch off the load. The alarm signal is
easily recognized, because the LED
frequency than normal (about 5 Hz instead of 1 Hz). This alarm
indication is only active if the SEL input is HIGH or open. If the SEL
input is LOW, no alarm indication is present, because in many
applications simultaneous charging and discharging is quite
acceptable. (See charge/discharge mode)
Scan test mode.
If the SCAN input (pin 14) is made active HIGH, the circuit is in the
test mode. The tester clock is connected to the I
the scan mode, the on–chip oscillator is bypassed to allow rapid
testing of the divider/counter. The scan test patterns are available on
request. The scan test data is entered serially through the SCI input
(pin 15). The scan out data is present on the MOLLI
(pin 6), which then acts as a scan output.
Remaining energy indication.
The scan test facility can be used as a remaining energy indication
because the value of the counter can be read out at the scan output
(MOLLI
/SCO). This is done by briefly interrupting the normal mode
of operation, putting the circuit in the scan mode, and reading out
the counter value. The circuit then reverts to the normal mode. This
only works correctly with the MOLLI
linked (round coupled loop) and with exactly 49 clock pulses applied
to the I
The serial scan-out data is available on the MOLLI/SCO output. The
value of the counter can be decoded by reading the correct bits.
Details are given later in the section “Application information”.
Output drivers EN and EN
In one-cell battery (low-voltage) applications, the drive from the
ENABLE output (EN
for the external bipolar PNP regulator transistor. The inverse signal has
therefore been made available at the ENABLE output (EN) to drive an
extra bipolar NPN transistor that can provide the base current for the
bipolar PNP regulator transistor as shown in Figure 2.
OSC
input.
) is insufficient to provide the base current directly
output will blink at a higher
/SCO output and SCI input
.
pin (pin 13). In
OSC
/SCO output
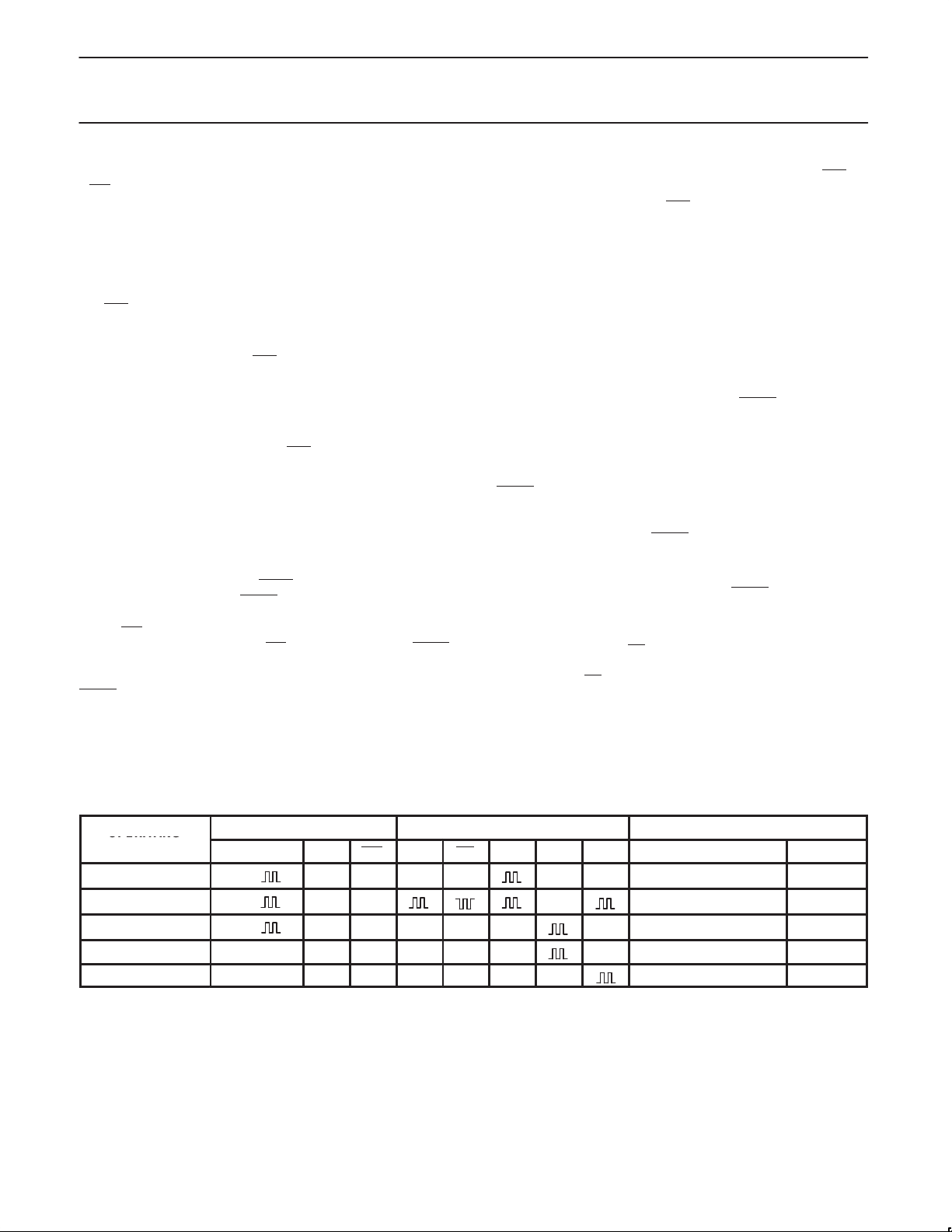
FUNCTION TABLE 1
Charge
Trickle charge
Charge/discharge
Discharge L or open X L L Z Z Z Count down 18 sections ≥ min
Self-discharge L or open X H L Z Z Z Count down 27 sections ≥ min
1998 Apr 20
OPERATING
MODES
INPUTS OUTPUTS DIVIDER/COUNTER
PWRS V
H or
H or
H or
DIS EN EN R
IN
H H H L Z Z Count up 22 sections < max
H H Z Stop max
H L H L Z Z Count down 18 sections ≥ min
5
R
C
R
D
S
MODE VALUE
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
STATUS
Ch
Trickle charge
74LV4799Timer for NiCd and NiMH chargers
FUNCTION TABLE 2
STATUS
INDICATION
arge
PWRS DIS SEL
H or
H or
Charge/discharge
H or
H or
H or H H or open L
Discharge L or open L X Z Z Count down > min
Self-discharge L or open H X Z Z Count down > min
Low L or open ↑ X Z Stop min
Low ↑ ↑ X Z Z
Alarm H or L H or open
INPUTS OUTPUTS COUNTER
(1)
LED MOLLI MODE VALUE
H L L Z Count up < max
H H or open Z Count up < max
L L L Z Count down ≥ min
H L
Z
Z
(2)
Z
Stop max
Stop max
Count up ≥ min
Count down ≥ min
NOTES:
1. Don’t change SEL during operation.
2. The MOLLI
function will be interrupted as soon as PWRS is activated.
H = HIGH voltage level
L = LOW voltage level
Z = high impedance OFF-state
X = don’t care
= pulsed (H/L)
= pulsed (Z/L)
= 4 periods of about one second (Z/L)
↑ = LOW-to-HIGH level transition
Z–state
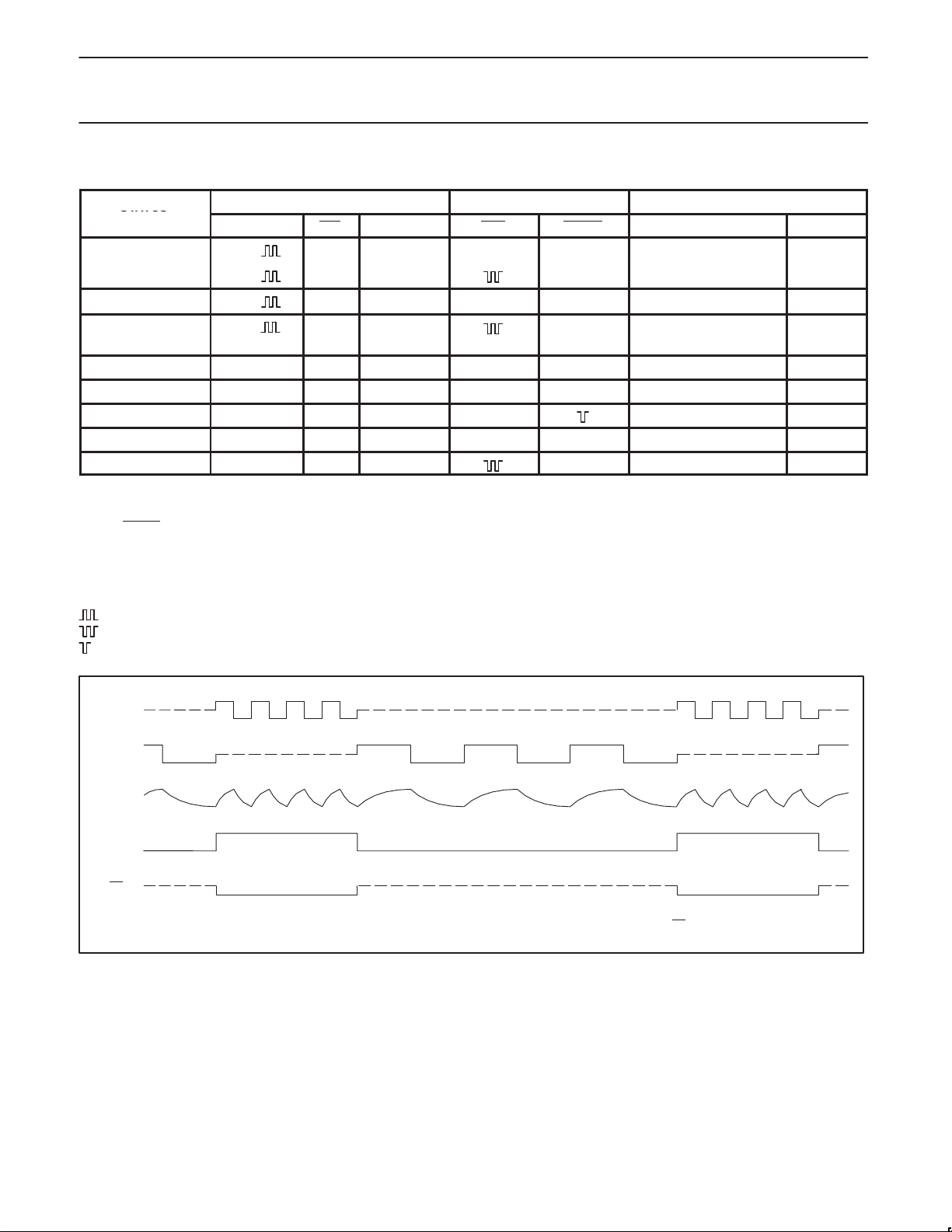
C
S
Operation in the trickle charge mode. The duration of the RC cycle determines the duty cycle of the enable outputs (EN and EN), allowing a dedicated
control. The average trickle charge current will compensate for the self-discharge, independent of the charge current.
Z–state
I
R
R
OSC
EN
EN
Z–state
Z–state
Z–state
SV01646
Figure 1. Trickle charge mode characteristics.
1998 Apr 20
6
 Loading...
Loading...