Philips 74hc hct7030 DATASHEETS

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines
74HC/HCT7030
9-bit x 64-word FIFO register;
3-state
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06
December 1990

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
9-bit x 64-word FIFO register; 3-state 74HC/HCT7030
FEATURES
• Synchronous or asynchronous operation
• 3-state outputs
• Master-reset input to clear control functions
• 33 MHz (typ.) shift-in, shift-out rates with or without flags
• Very low power consumption
• Cascadable to 25 MHz (typ.)
• Readily expandable in word and bit dimensions
• Pinning arranged for easy board layout: input pins
directly opposite output pins
• Output capability: standard
• ICCcategory: LSI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT7030 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS
devices specified in compliance with JEDEC standard
no. 7A.
The 74HC/HCT7030 is an expandable, First-In First-Out
(FIFO) memory organized as 64 words by 9 bits. A 33 MHz
data-rate makes it ideal for high-speed applications. Even
at high frequencies, the I
(f
= 18 MHz; VCC= 5 V produces a dynamic ICCof
max
80 mA). If the device is not continuously operating at f
dynamic is very low
CC
max
then ICCwill decrease proportionally.
With separate controls for shift-in (SI) and shift-out (SO),
reading and writing operations are completely
independent, allowing synchronous and asynchronous
data transfers. Additional controls include a master-reset
input (MR) and an output enable input (OE). Flags for
data-in-ready (DIR) and data-out-ready (DOR) indicate the
status of the device.
Devices can be interconnected easily to expand word and
bit dimensions. All output pins are directly opposite the
corresponding input pins thus simplifying board layout in
expanded applications.
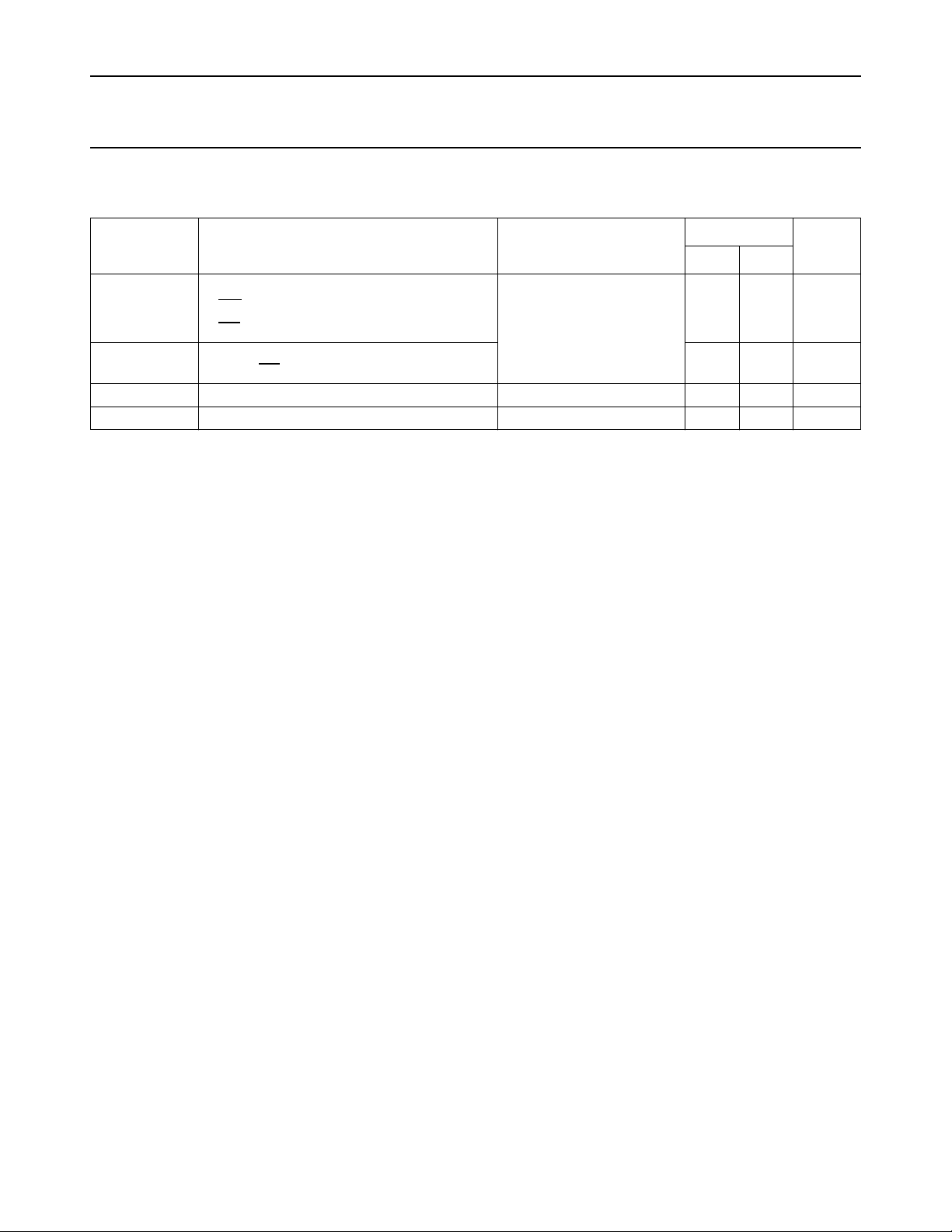
Data outputs (Q
to Q8)
0
As there is no weighting of the outputs, any output can be
assigned as the MSB. The size of the FIFO memory can
be reduced from the 9 × 64 configuration as described for
data inputs. In a reduced format, the unused data output
pins must be left open circuit.
Master-reset (
MR)
When MR is LOW, the control functions within the FIFO
are cleared, and data content is declared invalid. The
data-in-ready (DIR) flag is set HIGH and the
data-out-ready (DOR) flag is set LOW. The output stage
remains in the state of the last word that was shifted out,
or in the random state existing at power-up.
Status flag outputs (DIR, DOR)
Indication of the status of the FIFO is given by two status
flags, data-in-ready (DIR) and data-out-ready (DOR):
DIR = HIGH indicates the input stage is empty and
ready to accept valid data
DIR = LOW indicates that the FIFO is full or that a
previous shift-in operation is not complete
(busy)
DOR = HIGH assures valid data is present at the
,
outputs Q
to Q8(does not indicate that new
0
data is awaiting transfer into the output stage)
DOR = LOW indicates the output stage is busy or
there is no valid data
Shift-in control (SI)
Data is loaded into the input stage on a LOW-to-HIGH
transition of SI. A HIGH-to-LOW transition triggers an
automatic data transfer process (ripple through). If SI is
held HIGH during reset, data will be loaded at the rising
edge of the
Shift-out control (
MR signal.
SO)
INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Data inputs (D
to D8)
0
As there is no weighting of the inputs, any input can be
assigned as the MSB. The size of the FIFO memory can
be reduced from the 9 × 64 configuration, i.e. 8 × 64,
7 × 64, down to 1 × 64, by tying unused data input pins to
V
or GND.
CC
December 1990 2
A LOW-to-HIGH transition of SO causes the DOR flags to
go LOW. A HIGH-to-LOW transition of SO causes
upstream data to move into the output stage, and empty
locations to move towards the input stage (bubble-up).
Output enable (
OE)
The outputs Q0to Q8are enabled whenOE = LOW. When
OE = HIGH the outputs are in the high impedance
OFF-state.
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
9-bit x 64-word FIFO register; 3-state 74HC/HCT7030
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; T
=25°C; tr=tf= 6 ns
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
t
PHL/ tPLH
propagation delay CL= 15 pF; VCC=5 V
MR to DIR and DOR 21 26 ns
f
max
SO to Q
maximum clock frequency
n
SI and SO
C
I
C
P
input capacitance 3.5 3.5 pF
power dissipation capacitance per package notes 1 and 2 660 660 pF
Notes
1. C
is used to determine the dynamic power dissipation (PDin µW):
PD
PD=CPD× V
2
× fi+∑(CL× V
CC
2
× fo) where:
CC
fi= input frequency in MHz
fo= output frequency in MHz
∑ (CL× V
2
× fo) = sum of outputs
CC
CL= output load capacitance in pF
VCC= supply voltage in V
2. For HC the condition is VI= GND to V
CC
For HCT the condition is VI= GND to VCC− 1.5 V
TYPICAL
UNIT
HC HCT
36 40 ns
33 29 MHz
ORDERING INFORMATION
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information”
See
.
December 1990 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
9-bit x 64-word FIFO register; 3-state 74HC/HCT7030
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NO. SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
1, 2, 14 GND ground (0 V)
3 DIR data-in-ready output
4 SI shift-in input (LOW-to-HIGH, edge-triggered)
5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 D
15
24, 23, 22, 21, 20, 19, 18, 17, 16 Q
25 DOR data-out-ready output
26
27
28 V
Note
1. Pin 14 must be connected to GND. Pins 1 and 2 can be left floating or connected to GND, however it is not allowed
to let current flow in either direction between pins 1, 2 and 14.
0
to D
8
parallel data inputs
OE output enable input (active LOW)
0
to Q
8
3-state parallel data outputs
SO shift-out input (HIGH-to-LOW, edge-triggered)
MR asynchronous master-reset input (active LOW)
CC
positive supply voltage
Fig.1 Pin configuration. Fig.2 Logic symbol. Fig.3 IEC logic symbol.
December 1990 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
9-bit x 64-word FIFO register; 3-state 74HC/HCT7030
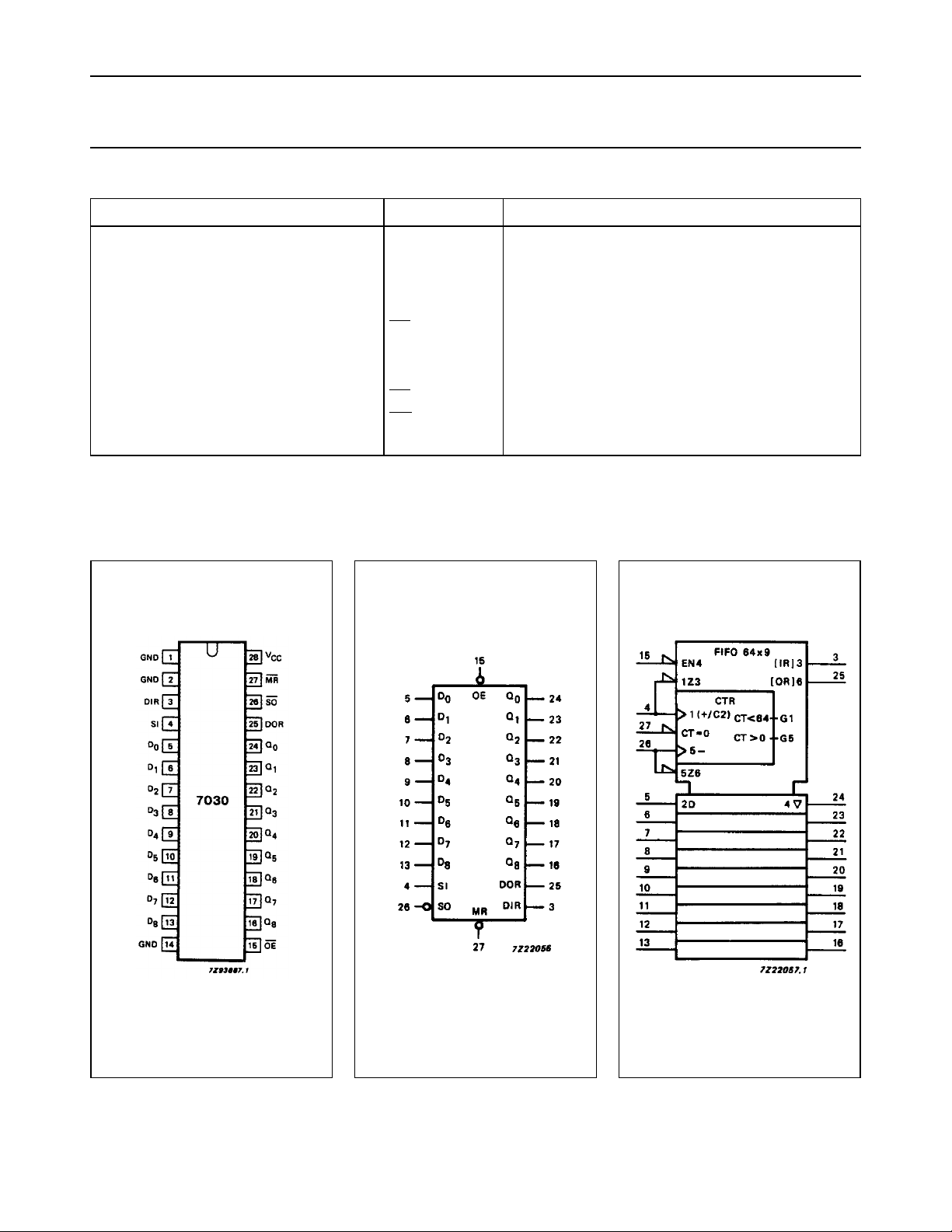
Fig.4 Functional diagram.
APPLICATIONS
• High-speed disc or tape controller
• Video timebase correction
• A/D output buffers
• Voice synthesis
• Input/output formatter for digital filters and FFTs
• Bit-rate smoothing
December 1990 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
9-bit x 64-word FIFO register; 3-state 74HC/HCT7030
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Data input
Following power-up, the master-reset (
LOW to clear the FIFO memory (see Fig.8). The
data-in-ready flag (DIR = HIGH) indicates that the FIFO
input stage is empty and ready to receive data. When DIR
is valid (HIGH), data present at D0to D8can be shifted-in
using the SI control input. With SI = HIGH, data is shifted
into the input stage and a busy indication is given by DIR
going LOW.
The data remains at the first location in the FIFO until SI is
set to LOW. With SI = LOW data moves through the FIFO
to the output stage, or to the last empty location. If the
FIFO is not full after the SI pulse, DIR again becomes valid
(HIGH) to indicate that space is available in the FIFO. The
DIR flag remains LOW if the FIFO is full (see Fig.6). The
SI pulse must be made LOW in order to complete the
shift-in process.
With the FIFO full, SI can be held HIGH until a shift-out
(SO) pulse occurs. Then, following a shift-out of data, an
empty location appears at the FIFO input and DIR goes
HIGH to allow the next data to be shifted-in. This remains
at the first FIFO location until SI again goes LOW (see
Fig.7).
Data transfer
After data has been transferred from the input stage of the
FIFO following SI = LOW, data moves through the FIFO
asynchronously and is stacked at the output end of the
register. Empty locations appear at the input end of the
FIFO as data moves through the device.
MR) input is pulsed
With the FIFO empty, the SO input can be held HIGH until
the SI control input is used. Following an SI pulse, data
moves through the FIFO to the output stage, resulting in
the DOR flag pulsing HIGH and a shift-out of data
occurring. The SO control must be made LOW before
additional data can be shifted out (see Fig.10).
High-speed burst mode
If it is assumed that the shift-in/shift-out pulses are not
applied until the respective status flags are valid, it follows
that the shift-in/shift-out rates are determined by the status
flags. However, without the status flags a high-speed burst
mode can be implemented. In this mode, the
burst-in/burst-out rates are determined by the pulse widths
of the shift-in/shift-out inputs and burst rates of 35 MHz can
be obtained. Shift pulses can be applied without regard to
the status flags but shift-in pulses that would overflow the
storage capacity of the FIFO are not allowed (see Figs 11
and 12).
Expanded format
With the addition of a logic gate, the FIFO is easily
expanded to increase word length (see Fig.17). The basic
operation and timing are identical to a single FIFO, with the
exception of an additional gate delay on the flag outputs. If
during application, the following occurs:
• SI is held HIGH when the FIFO is empty, some
additional logic is required to produce a composite DIR
pulse (see Figs 7 and 18).
•
SO is held HIGH when the FIFO is full, some additional
logic is required to produce a composite DOR pulse (see
Figs 10 and 18).
Data output
The data-out-ready flag (DOR = HIGH) indicates that
there is valid data at the output (Q
master-reset at power-on (MR = LOW) sets DOR to LOW
(see Fig.8). After MR = HIGH, data shifted into the FIFO
moves through to the output stage causing DOR to go
HIGH. As the DOR flag goes HIGH, data can be
shifted-out using the SO control input. With SO = HIGH,
data in the output stage is shifted out and a busy indication
is given by DOR going LOW. When SO is made LOW,
data moves through the FIFO to fill the output stage and an
empty location appears at the input stage. When the
output stage is filled DOR goes HIGH, but if the last of the
valid data has been shifted out leaving the FIFO empty the
DOR flag remains LOW (see Fig.9). With the FIFO empty,
the last word that was shifted-out is latched at the output
Q0to Q8.
December 1990 6
to Q8). The initial
0
Due to the part-to-part spread of the ripple through time,
the flag signals of FIFOAand FIFOBwill not always
coincide and the AND-gate will not produce a composite
flag signal. The solution is given in Fig.18.
The “7030” is easily cascaded to increase the word
capacity and no external components are needed. In the
cascaded configuration, all necessary communications
and timing are performed by the FIFOs. The
intercommunication speed is determined by the minimum
flag pulse widths and the flag delays. The data rate of
cascaded devices is typically 25 MHz. Word-capacity can
be expanded to and beyond 128-words × 9-bits (see
Fig.19).

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
9-bit x 64-word FIFO register; 3-state 74HC/HCT7030
December 1990 7
Fig.5 Logic diagram.
(2) LOW on R input to FF1 to FF64 will set Q output to LOW independent of state on S input.
(see control flip-flops)
(1) LOW on S input of flip-flops FS, FB and FP will set Q output to HIGH independent of state on R input.
 Loading...
Loading...