Philips 74hc hct5555 DATASHEETS

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines
74HC/HCT5555
Programmable delay timer with
oscillator
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06
September 1993

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Programmable delay timer with oscillator 74HC/HCT5555
FEATURES
• Positive and negative edge
triggered
• Retriggerable or non-retriggerable
• Programmable delay
minimum: 100 ns
maximum: depends on input
frequency and division ratio
• Divide-by range of 2 to 2
24
• Direct reset terminates output
pulse
• Very low power consumption in
triggered start mode
• 3 oscillator operating modes:
– RC oscillator
– Crystal oscillator
– External oscillator
• Device is unaffected by variations
in temperature and VCC when using
an external oscillator
• Automatic power-ON reset
• Schmitt trigger action on both
trigger inputs
• Direct drive for a power transistor
• Low power consumption in active
mode with respect to TTL type
timers
• High precision due to digital timing
• Output capability: 20 mA
• ICC category: MSI.
APPLICATIONS
• Motor control
• Attic fan timers
• Delay circuits
• Automotive applications
• Precision timing
• Domestic appliances.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT5555 are high-speed
Si-gate CMOS devices and are pin
compatible with low power Schottky
TTL (LSTTL). They are specified in
compliance with JEDEC standard
no. 7A.
• retriggerable/non-retriggerable
monostable
• automatic power-ON reset
• output control logic
• oscillator control logic
• overriding asynchronous master
reset (MR).
The 74HC/HCT5555 are precision
programmable delay timers which
consist of:
• 24-stage binary counter
• integrated oscillator (using external
timing components)
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; T
= 25 °C; tr = tf = 6 ns.
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS TYP. UNIT
t
PHL/tPLH
C
I
C
PD
propagation delay CL = 15 pF;
A,
B to Q/Q2424ns
MR to Q/
RS to Q/
Q1920ns
Q2628ns
VCC= 5 V
input capacitance 3.5 3.5 pF
power dissipation
notes 1 and 2 23 36 pF
capacitance per buffer
Notes
1. C
is used to determine the dynamic power dissipation (PD in µW):
PD
PD = CPD x V
2
x fi + Σ(CL x V
CC
2
x fo) where:
CC
fi = input frequency in MHz
fo = output frequency in MHz
Σ(CL x V
2
x fo) = sum of outputs.
CC
CL = output load capacitance in pF
VCC = supply voltage in V
2. For HC the condition is VI = GND to V
CC
For HCT the condition is VI= GND to VCC− 1.5 V.
ORDERING INFORMATION
EXTENDED TYPE
NUMBER
PINS PIN POSITION MATERIAL CODE
PACKAGE
74HC/HCT5555N 16 DIL plastic SOT38Z
74HC/HCT5555D 16 SO16 plastic SOT109A
September 1993 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Programmable delay timer with oscillator 74HC/HCT5555
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
RS 1 clock input/oscillator pin
R
TC
C
TC
A 4 trigger input (positive-edge
B 5 trigger input (negative-edge
RTR 6 retriggerable/non-retriggerable
RTR/
Q 7 pulse output (active LOW)
GND 8 ground (0 V)
Q 9 pulse output (active HIGH)
S
− S
0
3
OSC CON 14 oscillator control
MR 15 master reset input (active
V
CC
2 external resistor connection
3 external capacitor connection
triggered)
triggered)
input (active HIGH/active LOW)
10, 11,
programmable input
12, 13
HIGH)
16 positive supply voltage
handbook, halfpage
RS
1
R
2
TC
C
3
TC
A
4
B
RTR/
RTR
Q
GND
5555
5
6
7
8
MGA642
Fig.1 Pin configuration.
V
16
CC
MR
15
OSC
14
CON
S
13
3
S
12
2
S
11
1
S
10
0
Q
9
handbook, halfpage
X / Y CTRDIVm
10
1
11
2
12
4
13
8
2
RX
3
CX
14
16G17
1
17
6
4
5
15
R
I = 0
! G
0
Y = 0
15
Y = 15
+
&
1
CT = 0
S
R
Fig.2 IEC logic diagram.
[T]
CT = m R
V16
MGA643
9
7
September 1993 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Programmable delay timer with oscillator 74HC/HCT5555
2 3 10 11 12 13
handbook, full pagewidth
1
14
15
4
5
6
RS
OSC
CON
POWER-ON
MR
A
B
RTR/RTR
RESET
R
TC
SSSS
C
012
TC
CP
24 - STAGE COUNTER
CD
MONOSTABLE
CIRCUITRY
3
OUTPUT
STAGE
Q
Q
MGA644
9
7
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The oscillator configuration allows the
design of RC or crystal oscillator
circuits. The device can operate from
an external clock signal applied to the
RS input (RTC and CTC must not be
connected). The oscillator frequency
is determined by the external timing
components (RT and CT), within the
frequency range 1 Hz to 4 MHz
(32 kHz to 20 MHz with crystal
oscillator).
In the HCT version the MR input is
TTL compatible but the RS input has
CMOS input switching levels. The RS
input can be driven by TTL input
levels if RS is tied to VCC via a pull-up
resistor.
The counter divides the frequency to
obtain a long pulse duration. The
24-stage is digitally programmed via
the select inputs (S0 to S3). Pin S3 can
also be used to select the test mode,
which is a convenient way of
functionally testing the counter.
The “5555” is triggered on either the
positive-edge, negative-edge or both.
• Trigger pulse applied to input A for
positive-edge triggering
Fig.3 Functional diagram.
• Trigger pulse applied input
B for
negative-edge triggering
• Trigger pulse applied to inputs A
and B (tied together) for both
positive-edge and negative
triggering.
The Schmitt trigger action in the
trigger inputs, transforms slowly
changing input signals into sharply
defined jitter-free output signals and
provides the circuit with excellent
noise immunity.
The OSC CON input is used to select
the oscillator mode, either
continuously running (OSC CON =
HIGH) or triggered start mode (OSC
CON = LOW). The continuously
running mode is selected where a
start-up delay is an undesirable
feature and the triggered start mode
is selected where very low power
consumption is the primary concern.
The start of the programmed time
delay occurs when output Q goes
HIGH (in the triggered start mode, the
previously disabled oscillator will
start-up). After the programmed time
delay, the flip-flop stages are reset
and the output returns to its original
state.
An internal power-on reset is used to
reset all flip-flop stages.
The output pulse can be terminated
by the asynchronous overriding
master reset (MR), this results in all
flip-flop stages being reset. The
output signal is capable of driving a
power transistor. The output time
delay is calculated using the following
formula (minimum time delay is
100 ns):
1
division ratio (s).×
-- f
i
Once triggered, the output width may
be extended by retriggering the
gated, active HIGH-going input A or
the active LOW-going input
B. By
repeating this process, the output
pulse period (Q = HIGH, Q = LOW)
can be made as long as desired. This
mode is selected by RTR/RTR =
HIGH. A LOW on RTR/RTR makes,
once triggered, the outputs (Q, Q)
independent of further transitions of
inputs A and B.
September 1993 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Programmable delay timer with oscillator 74HC/HCT5555
Q
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
dbook, full pagewidth
CP
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
Q
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
CP
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
CD
Q
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
Q CP
CP
CP
MGA655
Q
Q
CD
Q
TC
2
3
S
CON
S
RS
RTCC
OSC
0
1
S
S
September 1993 5
Fig.4 Logic diagram.
CC
V
MR
RTR
A
RTR/
B

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Programmable delay timer with oscillator 74HC/HCT5555
TEST MODE
Set S3 to a logic LOW level, this will divide the 24 stage counter into three, parallel clocking, 8-stage counters. Set S0,
S1 and S2 to a logic HIGH level, this programs the counter to divide-by 28 (256). Apply a trigger pulse and clock in 255
pulses, this sets all flip-flop stages to a logic HIGH level. Set S3 to a logic HIGH level, this causes the counter to divide-by
224. Clock one more pulse into the RS input, this causes a logic 0 to ripple through the counter and output Q/Q goes from
HIGH-to-LOW level. This method of testing the delay counter is faster than clocking in 224 (16 777 216) clock pulses.
FUNCTION TABLE
INPUTS OUTPUTS
MR A
HXXLH
L↑X one HIGH level
LX↓one HIGH level
Notes
1. H = HIGH voltage level
L = LOW voltage level
X = don't care
↑ = LOW-to-HIGH transition
↓ = HIGH-to-LOW transition.
BQQ
one LOW level
output pulse
output pulse
output pulse
one LOW level
output pulse
September 1993 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Programmable delay timer with oscillator 74HC/HCT5555
DELAY TIME SELECTION
SELECT INPUTS OUTPUT Q/Q (FREQUENCY DIVIDING)
S
3
LLLL2
LLLH2
LLHL2
LLHH2
LHLL2
LHLH2
LHHL2
LHHH2
S
2
S
1
S
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
BINARY DECIMAL
2
4
8
16
32
64
128
256
..... .
HLLL2
HLLH2
HLHL2
HLHH2
HHLL2
HHLH2
HHHL2
HHHH2
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
131 072
262 144
524 288
1 048 576
2 097 152
4 194 304
8 388 608
16 777 216
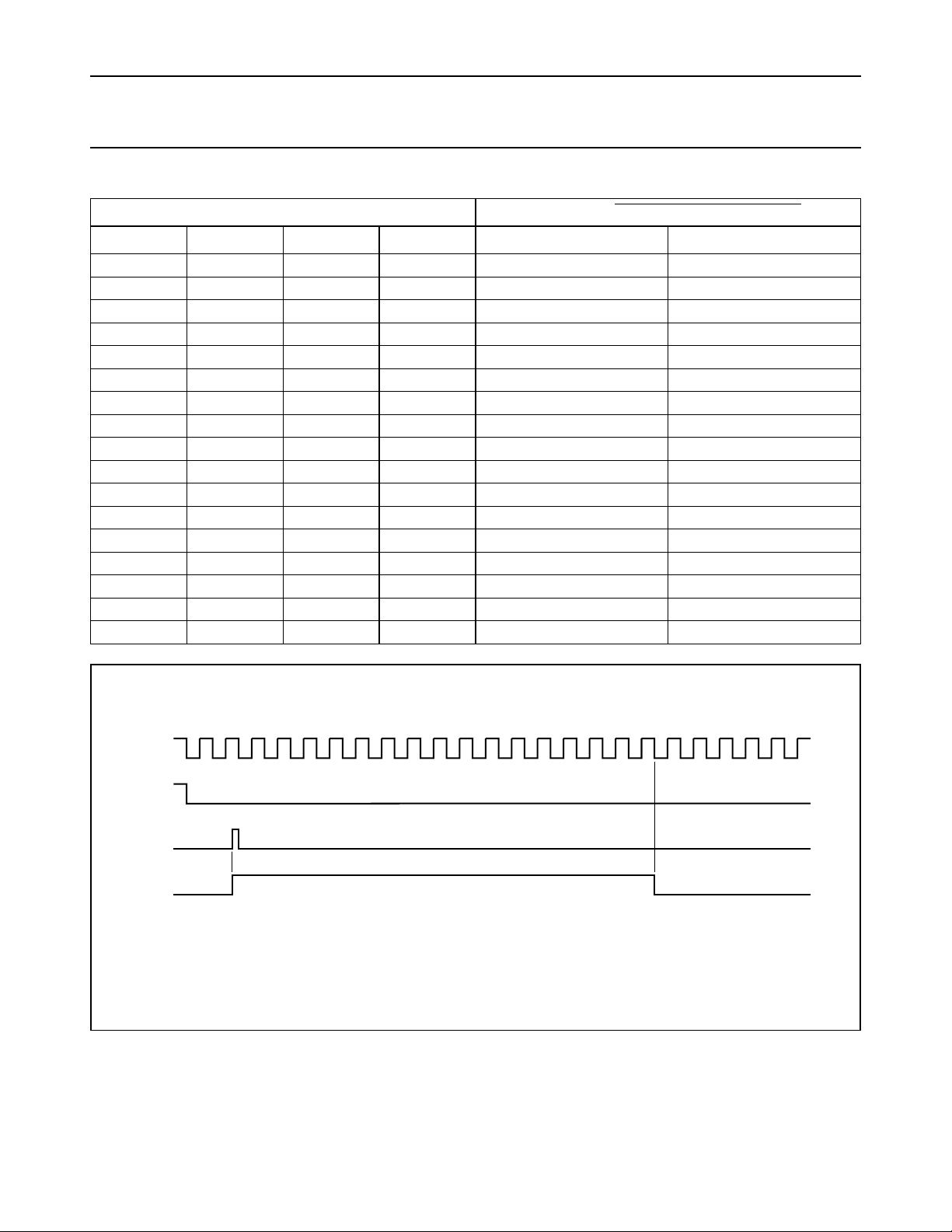
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
handbook, full pagewidth
RS
MR
A
Q
Timing example shown for S3, S2, S1, S0 = 0011 (binary 24, decimal 16).
Fig.5 Timing diagram.
September 1993 7
MGA649
 Loading...
Loading...