Philips 74hc hct175 DATASHEETS
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines
74HC/HCT175
Quad D-type flip-flop with reset;
positive-edge trigger
Product specification
Supersedes data of December 1990
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06
1998 Jul 08
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quad D-type flip-flop with reset; positive-edge trigger 74HC/HCT175
FEATURES
• Four edge-triggered D flip-flops
• Output capability: standard
• ICC category: MSI
The 74HC/HCT175 have four edge-triggered, D-type
flip-flops with individual D inputs and both Q and
outputs.
The common clock (CP) and master reset (MR) inputs load
and reset (clear) all flip-flops simultaneously.
The state of each D input, one set-up time before the
LOW-to-HIGH clock transition, is transferred to the
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT175 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices
and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL
corresponding output (Qn) of the flip-flop.
All Qn outputs will be forced LOW independently of clock
or data inputs by a LOW voltage level on the MR input.
(LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC
standard no. 7A.
The device is useful for applications where both the true
and complement outputs are required and the clock and
master reset are common to all storage elements.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; T
=25°C; tr=tf= 6 ns
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
t
PHL
t
PLH
f
max
C
C
I
PD
propagation delay CL= 15 pF; VCC=5 V
CP to Q
MR to Q
n
n
, Q
n
propagation delay
CP to Q
MR to Q
n
n
, Q
n
maximum clock frequency 83 54 MHz
input capacitance 3.5 3.5 pF
power dissipation capacitance per flip-flop notes 1 and 2 32 34 pF
Q
TYPICAL
UNIT
HC HCT
17 16 ns
15 19 ns
17 16 ns
15 16 ns
Notes
1. C
is used to determine the dynamic power dissipation (PD in µW):
PD
PD=CPD× V
2
× fi+ ∑ (CL× V
CC
2
× fo) where:
CC
fi= input frequency in MHz
fo= output frequency in MHz
∑ (CL× V
2
× fo) = sum of outputs
CC
CL= output load capacitance in pF
VCC= supply voltage in V
2. For HC the condition is VI= GND to V
CC
For HCT the condition is VI= GND to VCC− 1.5 V
1998 Jul 08 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quad D-type flip-flop with reset; positive-edge trigger 74HC/HCT175
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
74HC175N;
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
DIP16 plastic dual in-line package; 16 leads (300 mil); long body SOT38-1
PACKAGE
74HCT175N
74HC175D;
SO16 plastic small outline package; 16 leads; body width 3.9 mm SOT109-1
74HCT175D
74HC175DB;
SSOP16 plastic shrink small outline package; 16 leads; body width 5.3 mm SOT338-1
74HCT175DB
74HC175PW;
TSSOP16 plastic thin shrink small outline package; 16 leads; body width 4.4 mm SOT403-1
74HCT175PW
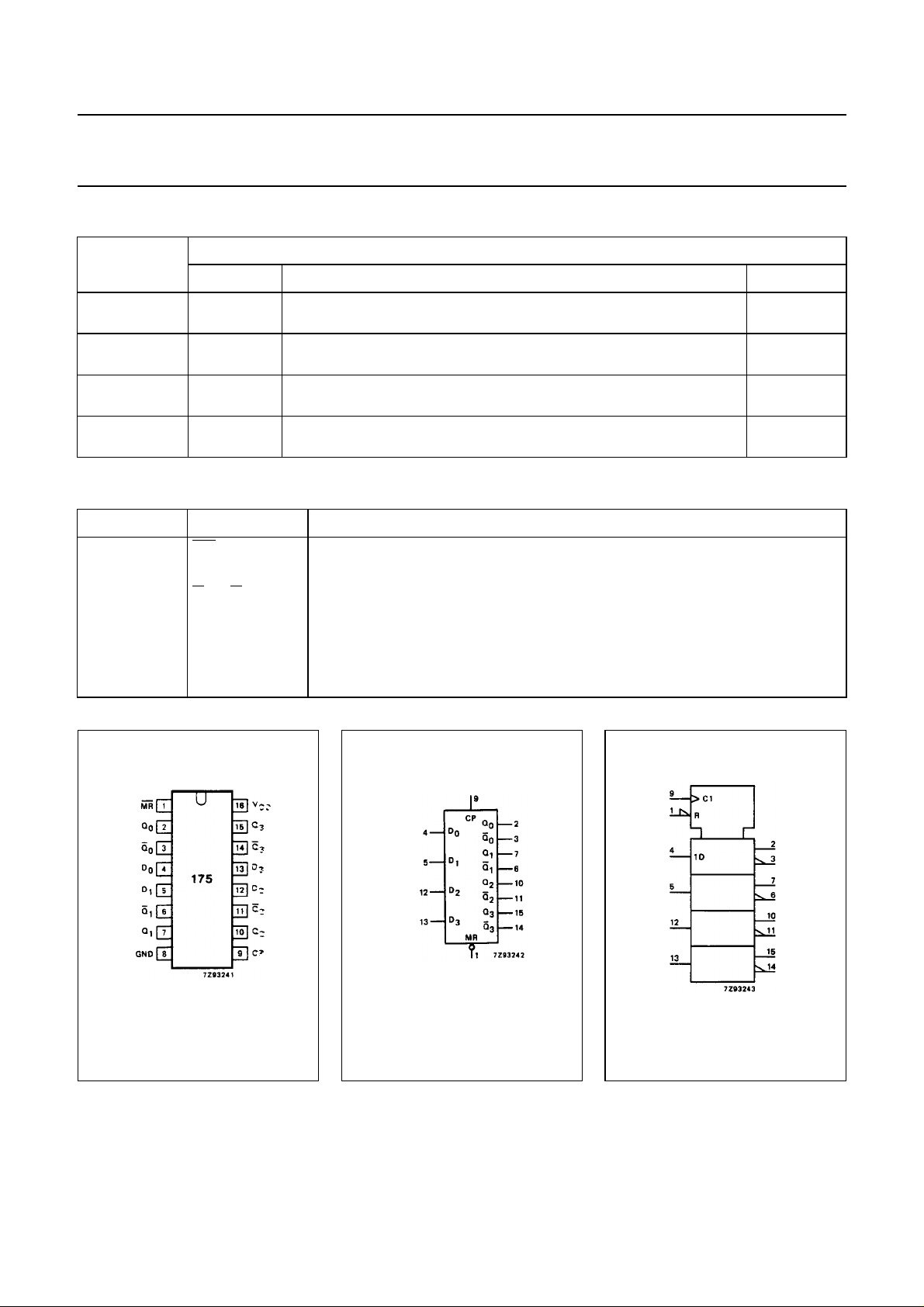
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NO. SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
1
2, 7, 10, 15 Q
3, 6, 11, 14
4, 5, 12, 13 D
MR master reset input (active LOW)
to Q
0
Q0 to Q
to D
0
3
3
3
flip-flop outputs
complementary flip-flop outputs
data inputs
8 GND ground (0 V)
9 CP clock input (LOW-to-HIGH, edge-triggered)
16 V
CC
positive supply voltage
Fig.1 Pin configuration. Fig.2 Logic symbol. Fig.3 IEC logic symbol.
1998 Jul 08 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Quad D-type flip-flop with reset; positive-edge trigger 74HC/HCT175
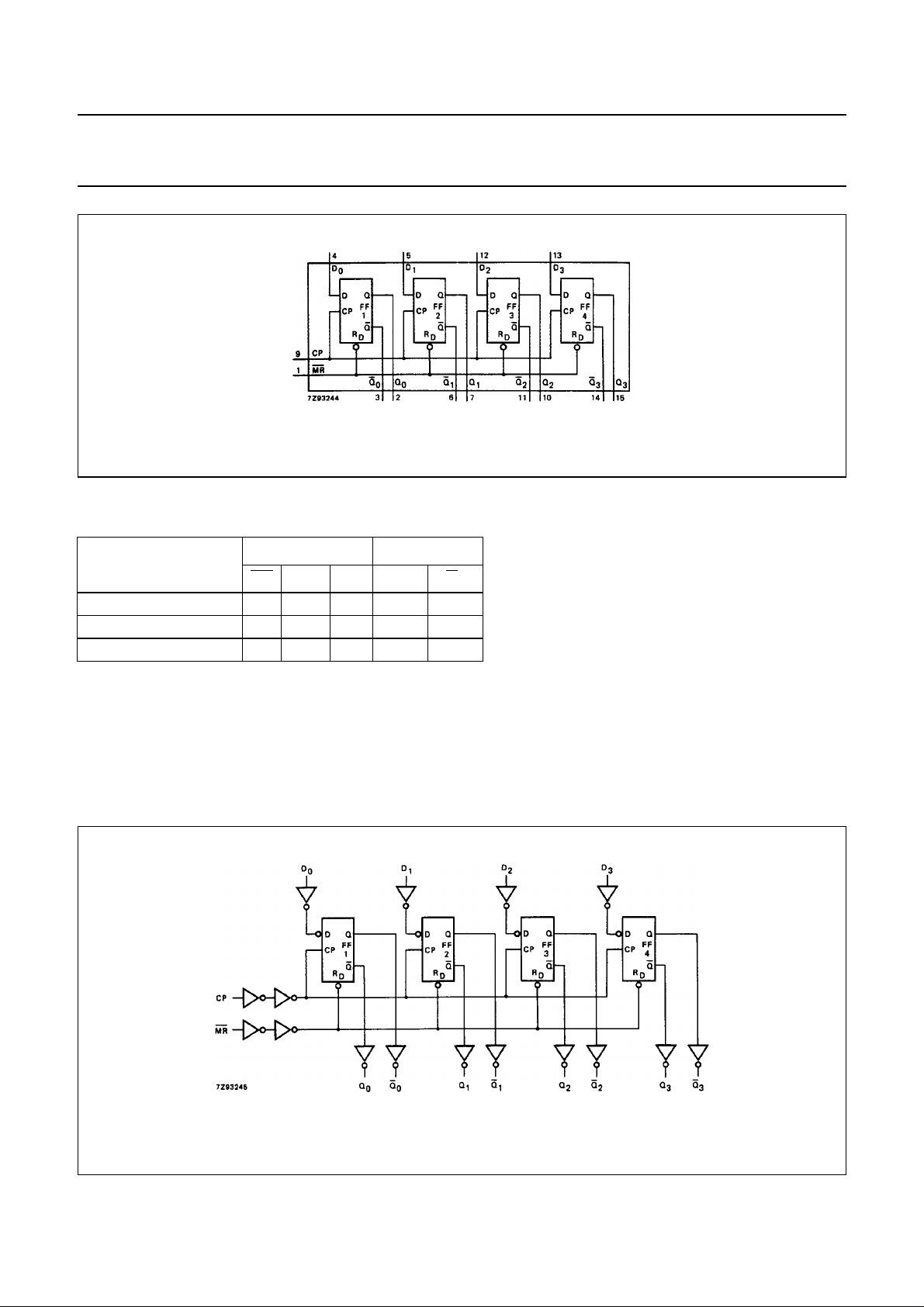
Fig.4 Functional diagram.
FUNCTION TABLE
OPERATING MODES
INPUTS OUTPUTS
MR CP D
Q
n
Q
n
n
reset (clear) L X X L H
load “1” H ↑ hH L
load “0” H ↑ ILH
Note
1. H = HIGH voltage level
h = HIGH voltage level one set-up time prior to the LOW-to-HIGH CP transition
L = LOW voltage level
I = LOW voltage level one set-up time prior to the LOW-to-HIGH CP transition
↑ = LOW-to-HIGH CP transition
X = don’t care
Fig.5 Logic diagram.
1998 Jul 08 4
 Loading...
Loading...