
Philips Semiconductors FAST Products Product specification
74F8965/74F89669-Bit address/data Futurebus transceiver, ADT
1
December 19, 1990 853 1526 01320
FEATURES
• 9–bit transceiver (both directions)
• Drives heavily loaded backplanes with
equivalent load impedances down to
10 ohms
• High drive (100mA) open collector
drivers on B port
• Reduced voltage swing (1V to 2V)
produces less noise and reduces
power consumption
• High speed operation enhances
performance of backplane buses and
facilitates incident wave switching
• Compatible with IEEE 896 futurebus
standards and IEEE 1194 BTL standard
• Built–in precision band–gap reference
provides accurate receiver thresholds
and improved noise immunity
• Controlled output ramp and multiple
GND pins minimize ground bounce
• Glitch–free power up/power down
operation
• Guaranteed skew of less than 2ns
DESCRIPTION
The 74F8965 and 74F8966 are 9–bit
bidirectional latchable transceivers and are
intended to provide the electrical interface to
a high performance wired–OR bus. The B
port inverting drivers are low–capacitance
open collector with controlled ramp and are
designed to sink 100mA from 2 volts. The B
port inverting receivers have a precision band
gap references for improved noise margins.
The B port interfaces to ’Backplane
Transceiver Logic’ (BTL). BTL features a
reduced (1V to 2V) voltage swing for lower
power consumption and a series diode on
the drivers to reduce capacitive loading.
Incident wave switching is employed, therefore BTL propagation delays are short. Although the voltage swing is much less for
BTL, so is its receiver threshold region,
therefore noise margins are excellent.
BTL offers low power consumption, low
ground bounce, EMI and crosstalk, low
capacitive loading, superior noise margin and
low propagation delays. This results in a high
bandwidth, reliable backplane.
The 74F8965 and 74F8966 A ports have TTL
3–state drivers and TTL receivers.
The B ports have standard BTL I/O with
100mA current sink capability. The B–to–A
path is a simple inverted buffered path. When
going from A–to–B the user may choose between a buffered path or a latching function.
The 74F8966 also has an idle arbitrator/multiple competitors output. The IAMC
output
compares, using a wired–OR configuration,
the data on the bus to the latched data presented to the bus. If the bus data matches the
data presented by the 74F8966 then IAMC
is
high. If the data doesn’t match then IAMC
goes low.
TYPE
TYPICAL PROPAGATION DELAY TYPICAL SUPPLY CURRENT( TOTAL)
74F8965 3.5ns 80mA
74F8966 3.5ns 80mA
ORDERING INFORMATION
ORDER CODE
DESCRIPTION COMMERCIAL RANGE
V
CC
= 5V ±10%, T
amb
= 0°C to +70°C
44–pin PLCC N74F8965A, N74F8966A
INPUT AND OUTPUT LOADING AND FAN OUT TABLE
PINS DESCRIPTION
74F (U.L.)
HIGH/LOW
LOAD VALUE
HIGH/LOW
A0 – A8 TTL data inputs 1.0/0.033 20µA/20µA
B0 – B8 Data inputs with threshold circuitry 5.0/0.167 100µA/100µA
OEA, OEB0, OEB1
Output enable inputs 1.0/0.167 20µA/100µA
LS Latch select (active low) (’F8965) 1.0/0.167 20µA/100µA
IAREQ Idle arbitration request (active low) (’F8965) 1.0/0.167 20µA/100µA
LE Latch enable input (active low) 1.0/0.167 20µA/100µA
A0 – A8 3–state TTL outputs 150/40 3mA/24mA
B0 – B8 Open collector BTL outputs OC/166.7 OC/100mA
IAMC
Idle arbitration/multiple competitors output (’F8966)
OC/80 OC/48mA
Notes to input and output loading and fan out table
1. One (1.0) FAST unit load is defined as: 20µA in the high state and 0.6mA in the low state.
2. OC = Open collector.
Philips Semiconductors FAST Products Product specification
74F8965/74F8966
9-Bit address/data Futurebus transceiver, ADT
December 19, 1990
2
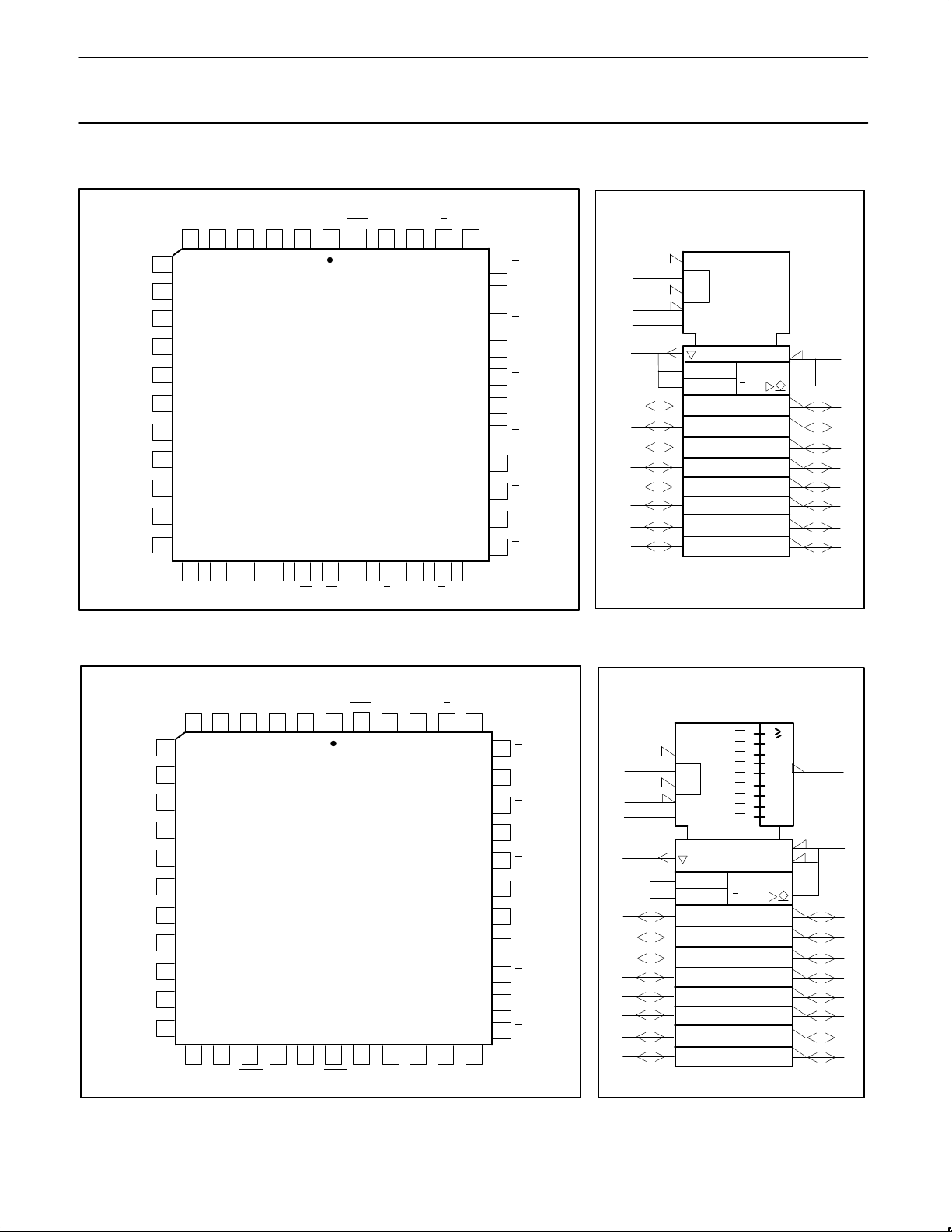
PIN CONFIGURATION PLCC IEC/IEEE SYMBOL
74F8965
6 5 4 3 2 1
39
38
37
36
35
34
13
12
11
10
9
8
2422 23212019
44
33
18
7
A0
LOGIC
GND
A1 OEA OEB0 OEB
1
A8
2826 2725
43 42 41 40
B
0
32
31
30
29
17
16
15
14
LOGIC GND
A2
LOGIC GND
A3
LOGIC GND
A4
A5
LOGIC GND
A6
LOGIC GND
A7
LE
B8 B7
B1
BUS GND
B2
BUS GND
B3
BUS GND
B
4
BUS GND
B5
BUS GND
B
6
74F8965
41
2
C4
EN5
4D
39
37
35
33
31
29
27
25
MUX
1
3
LOGIC
V
CC
BUS
V
CC
BUS
GND
BUS
GND
LOGIC
GND
LOGIC
GND
LOGIC
V
CC
LS BUS
V
CC
BUS
GND
BUS
GND
6
8
10
12
13
15
17
19
23
1
44
22
2
1
1
1
4
&
EN3
G1/V2
PIN CONFIGURATION PLCC IEC/IEEE SYMBOL
74F8966
74F8966
6 5 4 3 2 1
39
38
37
36
35
34
13
12
11
10
9
8
2422 23212019
44
33
18
7
A0
LOGIC
GND
A1 OEA OEB0OEB
1
A8
2826 2725
43 42 41 40
B0
32
31
30
29
17
16
15
14
LOGIC GND
A2
LOGIC GND
A3
LOGIC GND
A4
A5
LOGIC GND
A6
LOGIC GND
A7
LE
B8 B7
B
1
BUS GND
B2
BUS GND
B3
BUS GND
B
4
BUS GND
B5
BUS GND
B
6
LOGIC
V
CC
BUS
V
CC
BUS
GND
BUS
GND
LOGIC
GND
IAMC
LOGIC
V
CC
IREQ BUS
V
CC
BUS
GND
BUS
GND
41
2
C4
EN5
4D
39
37
35
33
31
29
27
25
MUX
1
3
6
8
10
12
13
15
17
19
23
1
44
22
2
1
1
1
4
&
EN3
G1/V2/EN6
7 Z10
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
1
20
N7
Philips Semiconductors FAST Products Product specification
74F8965/74F8966
9-Bit address/data Futurebus transceiver, ADT
December 19, 1990
3
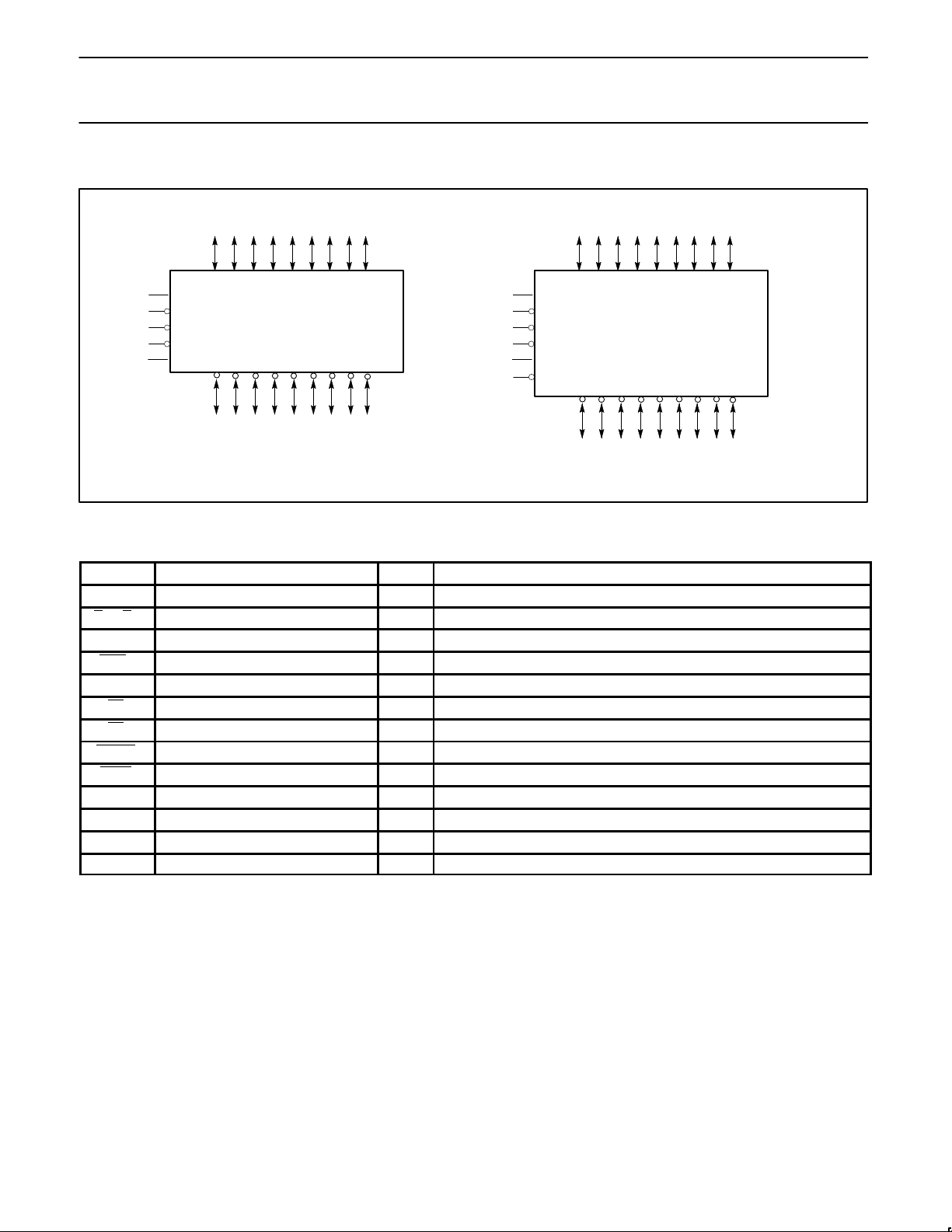
LOGIC SYMBOL
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8
Logic VCC = Pin 3, 21
Logic GND = Pin 5, 7, 9, 11, 14, 16, 18, 20
74F8965
1
44
23
22
2
OEB0
OEB1
LS
LE
OEA
4 6 8 10 12 13 15 17 19
B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8
41 39 37 35 33 31 29 27 25
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8
74F8966
1
44
23
22
2
20
OEB0
OEB1
IAREQ
LE
OEA
IAMC
4 6 8 10 12 13 15 17 19
B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8
41 39 37 35 33 31 29 27 25
Logic VCC = Pin 3, 21
Logic GND = Pin 5, 7, 9, 11, 14, 16, 18
PIN DESCRIPTION
SYMBOL PINS TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
A0 – A8 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 13, 15, 17, 19 I/O Data inputs/TTL 3–state outputs
B0 – B8 41, 39, 37, 35, 33, 31, 29, 27, 25 I/O Data inputs / open collector outputs, high current drives.
OEB0 1 Input Output enable input. Enables the B outputs when high.
OEB1 44 Input Output enable input. Enables the B outputs when low.
OEA 2 Input Output enable input. Enables the A outputs when high.
LE 22 Input Latch enable input. Enables latch when low.
LS 23 Input Latch select input. Selects latch when low (74F8965).
IAREQ 23 Input Idle arbitration request input (74F8966).
IAMC 20 Output Idle arbitration/multiple competitors output (open collector output) (74F8966).
Bus GND 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42 Ground Bus ground (0V)
Logic GND 5, 7, 9, 11, 14, 16, 18, 20 (74F8965) Ground Logic ground (0V)
Bus V
CC
24, 43 Power Positive supply voltages
Logic V
CC
3, 21 Power Positive supply voltages

Philips Semiconductors FAST Products Product specification
74F8965/74F8966
9-Bit address/data Futurebus transceiver, ADT
December 19, 1990
4
LOGIC DIAGRAM FOR 74F8965
D
E
Q
41
39
37
35
33
31
29
27
25
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
4
6
8
10
12
13
15
17
19
OEB0
OEB1
1
44
B0
B
1
B
2
B3
B
4
B
5
B
6
B
7
B
8
D
E
Q
D
E
Q
D
E
Q
D
E
Q
D
E
Q
D
E
Q
D
E
Q
D
E
Q
LS
LE
OEA
23
22
2
Logic VCC = Pin 3, 21
Logic GND = Pin 5, 7, 9, 11, 14, 16, 18, 20
TTL levels
BTL levels
 Loading...
Loading...