Philips 74f776 DATASHEETS

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
74F776
Pi-bus transceiver
Product specification
IC15 Data Handbook
1990 Dec 19
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F776Pi–bus transceiver
FEA TURES
• Octal latched transceiver
• Drives heavily loaded backplanes with equivalent load impedances
down to 10 ohms
• High drive (100mA) open collector drivers on B port
• Reduced voltage swing (1 volt) produces less noise and reduces
power consumption
• High speed operation enhances performance of backplane buses
and facilitates incident wave switching
• Compatible with Pi–bus and IEEE 896 Futurebus standards
• Built–in precision band–gap reference provides accurate receiver
thresholds and improved noise immunity
• Controlled output ramp and multiple GND pins minimize ground
bounce
• Glitch–free power up/power down operation
• Multiple package options
• Industrial temperature range available (–40°C to +85°C)
DESCRIPTION
The 74F776 is an octal bidirectional latched transceiver and is
intended to provide the electrical interface to a high performance
wired–OR bus. The B port inverting drivers are low–capacitance open
collector with controlled ramp and are designed to sink 100mA from 2
volts. The B port inverting receivers have a 100 mV threshold region
and a 4ns glitch filter.
The 74F776 B port interfaces to ’Backplane Transceiver Logic’ (BTL).
BTL features a reduced (1V to 2V) voltage swing for lower power
consumption and a series diode on the drivers to reduce capacitive
loading. Incident wave switching is employed, therefore BTL
propagation delays are short. Although the voltage swing is less for
BTL, so is its receiver threshold, therefore noise margins are excellent.
BTL offers low power consumption, low ground bounce, EMI and
crosstalk, low capacitive loading, superior noise margin and low
propagation delays. This results in a high bandwidth, reliable
backplane.
The 74F776 A port has TTL 3–state drivers and TTL receivers with a
latch function. A separate high–level control voltage input (V
provided to limit the A side output level to a given voltage level (such
as 3.3V). For 5.0V systems, V
The 74F776 has a designed feature to control the B output transitions
during power sequencing. There are two possible sequencing, They
are as follows:
1.When LE
the LE
making a maximum of one transition during power–up (or down).
2. If LE = high or OEBn = high then the B outputs will be disabled during
power–up (or down).
= low and OEBn = low then the B outputs are disabled until
circuitry takes control. Then the B outputs will follow the A inputs,
TYPE
74F776 6.5ns 80mA
TYPICAL PROPAGA-
TION DELAY
is simply tied to VCC.
X
TYPICAL SUPPL Y
CURRENT( TOTAL)
) is
X
ORDERING INFORMATION
ORDER CODE
COMMERCIAL RANGE INDUSTRIAL RANGE
DESCRIPTION
28–pin plastic DIP (600 mil) N74F776N I74F776N SOT117-2
28–pin PLCC N74F776A I74F776A SOT261-2
VCC = 5V ±10%, T
= 0°C to +70°C VCC = 5V ±10%, T
amb
= –40°C to +85°C
amb
PKG DWG #
INPUT AND OUTPUT LOADING AND FAN OUT TABLE
PINS DESCRIPTION
A0 – A7 PNP latched inputs 3.5/0.1 17 70µA/70µA
B0 – B7 Data inputs with threshold circuitry 5.0/0.167 100µA/100µA
OEA A output enable input (active high) 1.0/0.033 20µA/20µA
OEB0, OEB1 B output enable inputs (active low) 1.0/0.033 20µA/20µA
LE Latch enable input (active low) 1.0/0.033 20µA/20µA
A0 – A7 3–state outputs 150/40 3mA/24mA
B0 – B7 Open collector outputs OC/166.7 OC/100mA
Notes to input and output loading and fan out table
One (1.0) FAST unit load is defined as: 20µA in the high state and 0.6mA in the low state.
OC = Open collector.
74F (U.L.)
HIGH/LOW
LOAD VALUE
HIGH/LOW
December 19, 1990 853 1121 01321
2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F776Pi–bus transceiver
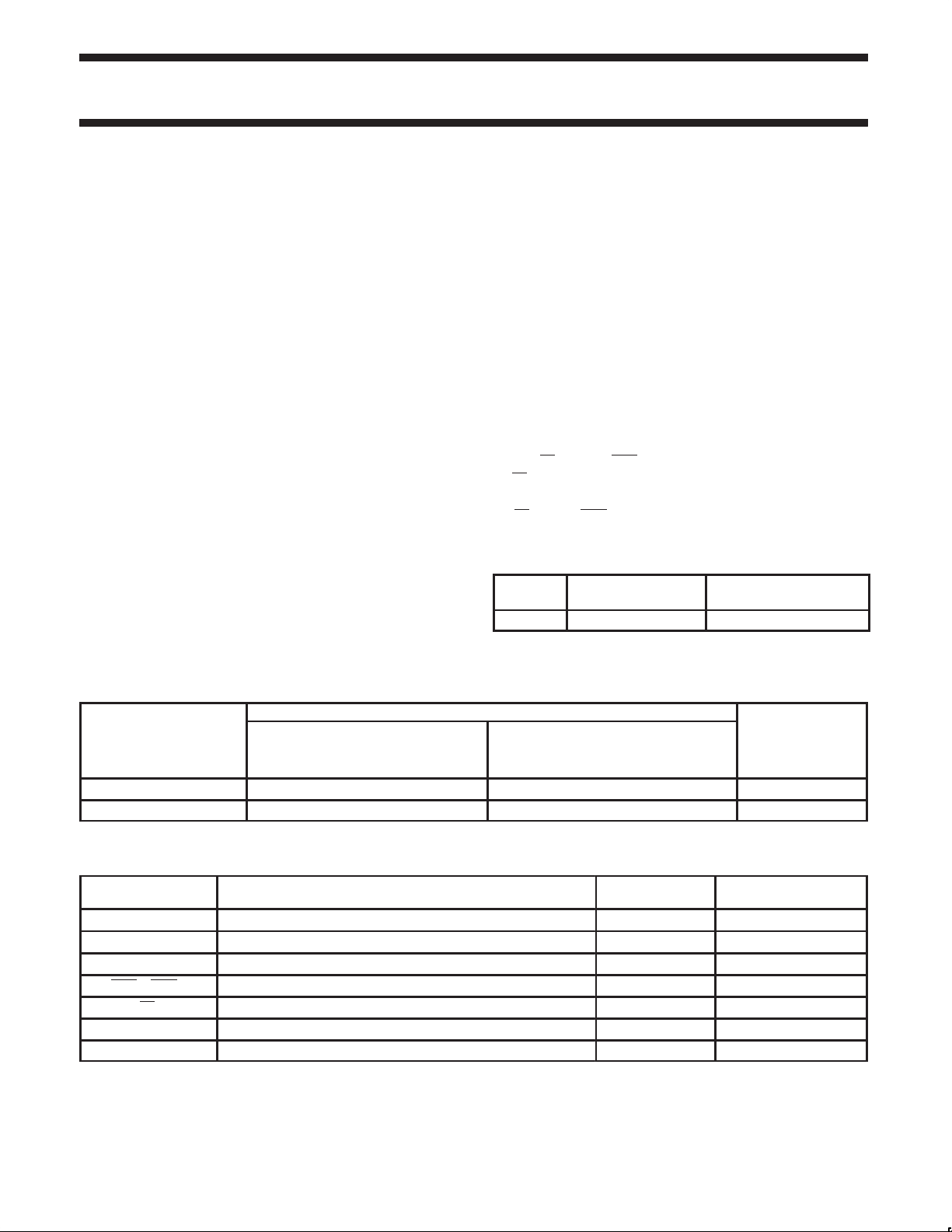
PIN CONFIGURATION
1
V
CC
2
OEA
3
A0
4
GND
5
A1
6
A2
7
A3
8
GND
9
A4
10 19
A5
GND
11
A6
12
A7
13
VX
14 15
PIN CONFIGURA TION PLCC
V
OEAA0GND LE B0 B1
CC
PLCC
A7A6 OEB1
V
X
GND
GND
4 3 2 1 28 27
5
A1
6
A2
7
A3
8
9
A4
A5
10
11
12
16 17151413
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
18
17
16
SF00422
B7
LE
B0
B1
GND
B2
B3
GND
B4
B5
B6
GND
B7
OEB
OEB
26
18
GNDOEB0
1
0
25
GND
24
B2
B3
23
22
GND
21
B4
20
B5
19
B6
SF00423
IEC/IEEE SYMBOL
15
16
28
2
3
5
6
7
9
10
12
13
LOGIC SYMBOL
15
OEB0
2
OEA
28
LE
16
OEB1
VCC = Pin 1, V
GND = Pin 4, 8, 11, 18, 22, 25
= Pin 14
X
&
EN2
EN1
EN3
ID
2
3
35679101213
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7
B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7
27 26 24 23 21 20 19 17
27
26
24
23
21
20
19
17
SF00425
SF00424
PIN DESCRIPTION
SYMBOL PINS TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
A0 – A7 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13 I/O PNP latched input/3–state output (with VX control option)
B0 – B7 27, 26, 24, 23, 21, 20, 19, 17 I/O
OEB0 15 Input Enables the B outputs when both pins are low
OEB1 16 Input
OEA 2 Input Enables the A outputs when high
LE 28 Input Latched when high (a special feature is built in for proper enabling times)
V
X
14 Input Clamping voltage keeping VOH from rising above VX (VX = Vcc for normal use)
December 19, 1990
Data input with special threshold circuitry to reject noise/ open collector output, high
current drive
3
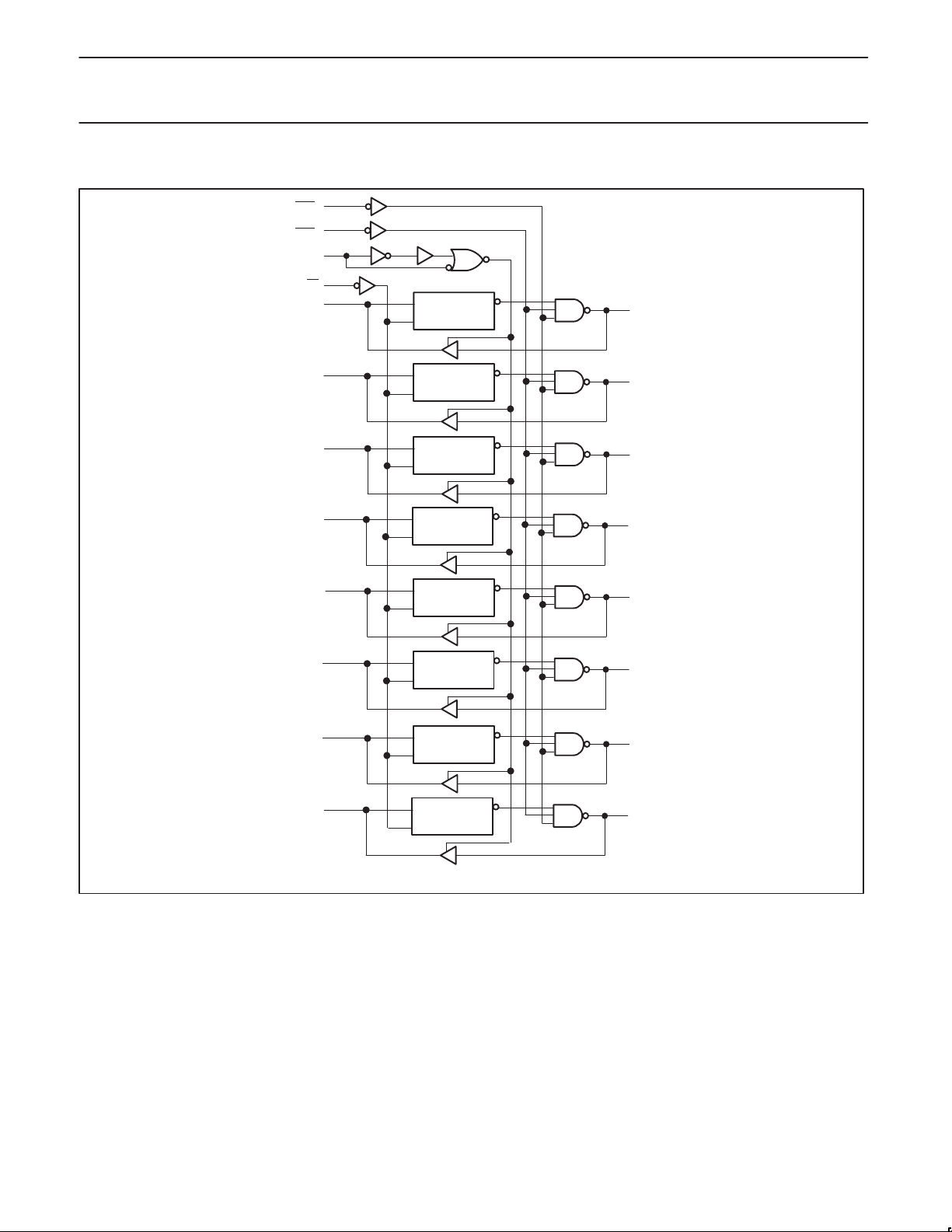
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
74F776Pi–bus transceiver
LOGIC DIAGRAM
15
OEB0
16
OEB
1
2
OEA
28
LE
A0
3
Data
LE
Q
27
B0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
5
6
7
9
10
12
13
Data
LE
Data
LE
Data
LE
Data
LE
Data
LE
Data
LE
Data
LE
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
26
B1
24
B2
23
B3
21
B4
20
B5
19
B6
17
B7
= Pin 1, V
V
CC
GND = Pin 4, 8, 11, 18, 22, 25
= Pin 14,
X
December 19, 1990
SF00426
4
 Loading...
Loading...