Page 1

Page 2
Safety and Troubleshooting Information
Safety Precautions and Maintenance • Troubleshooting • Regulatory Information • Other
Related Information
Safety precautions and maintenance
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
WARNING: Use of controls, adjustments, or procedures other
than those specified in this documentation may result in
exposure to shock, electrical hazards, and/or mechanical
hazards.
Read and follow these instructions when connecting and using your computer monitor:
z Disconnect the monitor from the power supply if the monitor is not to be used for an
extended period of time.
z Do not attempt to remove the back cover, as you will be exposed to a shock hazard. The
back cover should only be removed by qualified service personnel.
z Do not place objects on top of the monitor cabinet, objects could fall into vents or cover
them and prevent proper cooling of the monitor's electronic devices.
z To avoid the risk of shock or permanent damage to the set, do not expose the monitor to
rain or excessive moisture.
z Do not use alcohol or ammonia-based liquid to clean the monitor. If necessary, clean with
a slightly damp cloth. Disconnect the monitor from the power supply before cleaning.
z When positioning the monitor, make sure the power plug and outlet are easily accessible.
z When using the monitor, please make sure to install the swivel base for safety concert.
Consult a service technician if the monitor does not operate normally when operating instructions
of this manual are followed.
Page 3

About This Electronic User's Manual
About This Guide • Other Documents You May Need • Notational Descriptions
About This Guide
This electronic user's guide is intended for anyone who uses the Philips Color Monitor. It describes
the monitor's features, setup, operation and all other information, which is the same exact
information described in our printed version.
The sections are as follows:
● Safety and Troubleshooting Information provides tips and solutions for common problems,
and other related information you may need.
● About This Electronic User's Manual gives overview of what information are included as well
as notation icon descriptions and other documentation you can refer to.
● Product Information gives an overview of the monitor's features and as well as the technical
specifications for this monitor.
● Installing Your Monitor describes the initial setup process and gives an overview of how to
use the monitor.
● On Screen Display provides information on adjusting the settings on your monitor.
● Customer Care and Warranty is a list of worldwide Philips consumer information centers
along with the help desk phone numbers and information on the applicable warranty of your
product.
● Glossary provides more information for technical terms.
● Download allows users to install the entire manual on their hard drive.
● Frequently Asked Questions provides answers to commonly asked questions.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Other Documents You May Need
In addition to this Electronic User's Guide, you may need to refer to the following documentation:
Page 4

● Philips Color Monitor Quick Start Guide which summarizes the steps for setting up the
monitor. This is included with this product.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Notational Descriptions
The following subsections describe notational conventions used in this document.
Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
Throughout this guide, blocks of text may be accompanied by an icon and printed in bold type or in
italic type. These blocks are notes, cautions, and warnings, and they are used as follows:
NOTE: This icon indicates important information and tips that help you make
better use of your computer system.
CAUTION: This icon indicates information that tells you how to avoid either
potential damage to hardware or loss of data.
WARNING: This icon indicates the potential for bodily harm and tells you how
to avoid the problem.
SMART HELP: This icon indicates helpful information when adjusting the On
Screen Display of your monitor.
Some warnings may appear in alternate formats and may be unaccompanied by an icon. In such
cases, the specific presentation of the warning is mandated by regulatory authority.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 5

©2006 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V.
All rights reserved. Reproduction, copying, usage, modifying, hiring, renting, public performance, transmission and/or
broadcasting in whole or in part is prohibited without written consent of Philips Electronics N.V.
Page 6

Product Information
Product Features • Lead-free product • Technical Specifications • Automatic Power
Saving • Physical Specification • Pin Assignment • Product Views
Product Features
Model
109B70 TCO'03 Grey
109B73
109B75
109F71 MPRII Grey
109F72 MPRII Silver/Black
109F76 MPRII Black
109B7/109F7:
z 19-inch (18.0" VIS) Real Flat color monitor with exce lle nt front of screen performance for use
with MACs and PCs
z Autoscan covers horizontal frequencies up to 86 kHz offering a maximum resolution of 1600 x
1200 with flicker free display of 1600 x 1200 at up to 65 Hz
z Real Flat High Contrast CRT with high-resolution 0.25 mm dot pitch (0.21 hdp)
z sRGB for true on screen color representation.
z FCC, CE (in selected countries only) and ISO9241, ISO14001 certified
Regulation
TCO'03
TCO'03
Color
Silver/Black
Black
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Lead-free product
Philips eliminated toxic substances like lead from its displays. Lead-free display helps protect your
health and promotes environmentally sound recovery and disposal of waste from electrical and
electronic equipment. Philips complies with the European Community stringent RoHS Directive
mandating restrictions on hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment. With Philips,
you can be confident that your display device does not harm the environment.
Technical Specifications*
CRT
• Size and deflection 19 inch / 46 cm ; 90° deflection angle
• Dot pitch / Grille pitch 0.25 mm
• Horizontal pitch 0.21 mm
• Tube type
• Phosphor P22
Shadow mask, Real Flat, high contrast, high
brightness, anti-static, anti reflection
Page 7

• Recommended display area 14.0" x 10.4" / 355 x 265 mm
SCANNING
• Horizontal scanning 30 - 86 KHz
• Vertical scanning 50 - 160 Hz
VIDEO
• Video dot rate 180 MHz
• Input impedance
- Video 75 ohm
- Sync 4.7 kOhm
• Input signal levels 0.7 Vpp
• Sync input signal
• Sync polarities Positive and negative
Separate sync
WHITE COLOR TEMPERATURE
Chromaticity CIE coordinates:
• at 9300 degrees K x = 0.283 / y = 0.297
• at 6500 degrees K x = 0.313 / y = 0.329
• at 5500 degrees K x = 0.332 / y = 0.347
sRGB
sRGB is a standard for ensuring correct exchange of colors between different devices (e.g.
digital cameras, monitors, printers, scanners, etc.)
Using a standard unified color space, sRGB will help represent pictures taken by an sRGB
compatible device correctly on your sRGB enabled Philips monitors. In that way, the colors are
calibrated and you can rely on the correctness of the colors shown on your screen.
Important with the use of sRGB is that the brightness and contrast of your monitor is fixed to a
predefined setting as well as the color gamut. Therefore it is important to select the sRGB setting
in the monitor's OSD.
To do so, open the OSD by pressing the OK button on the front of your monitor. Use the down
button to go to Color temperature and press OK again. Then move the down button to go to
sRGB and press OK again.
Exit this OSD.
After this, please don't change the brightness or contrast setting of your monitor. If you change
either of these, the monitor will exit the sRGB mode and go to a color temperature setting of
6500K.
* These information are subject to change without notice.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 8
Automatic Power Saving
If you have VESA's DPMS compliance display card or software installed in your PC, the monitor can
automatically reduce its power consumption when not in use. And if an input from a keyboard, mouse or
other input device is detected, the monitor will automatically "wake up". The following table shows the
power consumption and signaling of this automatic power saving features:
VESA's Mode
Active
Sleep
Switch Off
Power Management Definition
Video
ON
OFF
OFF
H-sync V-sync Power Used
Yes
No
Yes
No
-- --
Typical 70W
< 2W
< 2W
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Physical Specifications
• Dimensions 17.3" x 16.6" x 17.9" / 439 x 422.5 x 457mm
• Weight 22.9 kg
Power
Saving (%)
0 %
99%
99%
LED color
Green
Flashing
Green
Off
• Power supply 100-240 VAC, 60-50Hz
• Temperature
(operating)
• Temperature (storage) -25° to + 60°C / -13° to +140°F
• Relative humidity
(storage)
* Resolution 1024 x 768, standard size, contrast max., brightness 50%, 9300°, full white pattern.
* These information are subject to change without notice.
Pin Assignment
The 15-pin D-sub connector (male) of the signal cable (IBM systems):
0° to 40°C / 32° to 104°F
5% to 95%
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 9

Pin
Assignment
No.
1 Red video input
2 Green video input 10 Sync ground
3 Blue video input 11 Ground
4 Ground 12 Serial data line (SDA)
5 Self test 13 H. Sync
6 Red video ground 14 V. Sync
7 Green video ground 15 Data clock line (SCL)
8 Blue video ground
Pin
Assignment
No.
+5V (Supply from PC for
9
DDC circuit)
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Views
Follow the links to see various views of the monitor and its components.
Front View
Rear View
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 10

Installing your Monitor
Front View • Rear View
Front View
Power button switches your monitor on.
OK button which when pressed will take you to the OSD controls
High Brightness hotkey.
Contrast hotkey. When the "-" button is pressed, the adjustment
controls for the CONTRAST will show up.
Brightness hotkey. When the "+" button is pressed, the
adjustment controls for BRIGHTNESS will show up.
"-" and "+" buttons, are used for adjusting the OSD of your
monitor.
Rear View
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 11
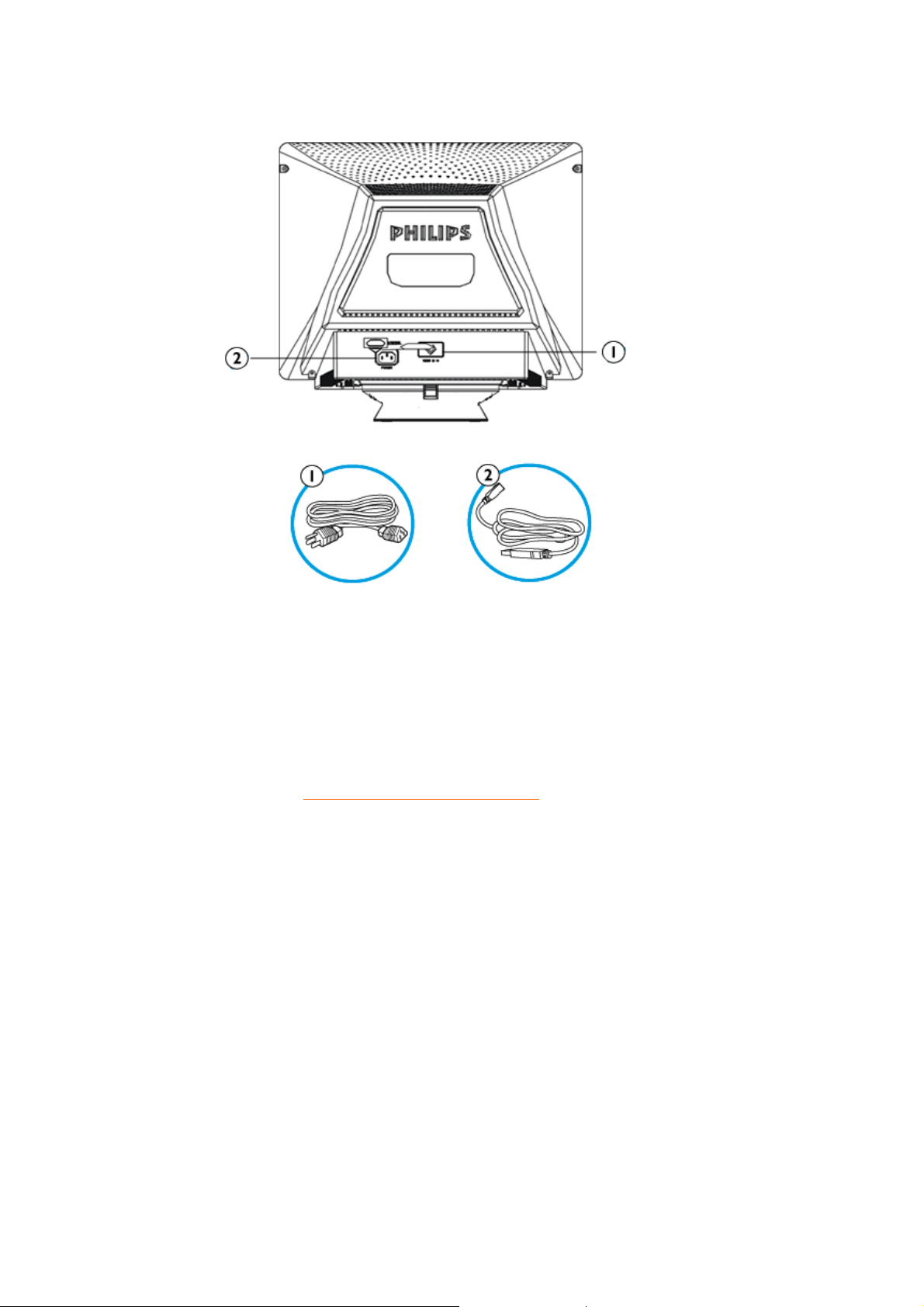
Power in - attach power cable here.
1.
Video In - this is a cable which is already attached to your monitor. Connect
2.
the other end of the cable to your PC.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 12

On-Screen Display
Description of the On-Screen Display • The OSD Tree • The OSD Controls
Description of the On Screen Display
What is the On-Screen Display?
This is a feature in all Philips monitors which allows an end-user to adjust screen performance of
monitors directly through an on-screen instruction window. The user interface provides userfriendliness and ease-of-use when operating the monitor.
Basic and simple instruction on the control keys.
On the front controls of your monitor, once you press the
(OSD) Main Controls window will pop up and you can now start making adjustments to your
monitor's various features. Use the to make your adjustments within.
button, the On Screen Display
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 13

The OSD Tree
Below is an overall view of the structure of the On-Screen Display. You can use this as reference
when you want to later on work your way around the different adjustments.
Your monitor may not include all the items in the OSD tree shown below.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 14

Customer Care & Warranty
PLEASE SELECT YOUR COUNTRY/AREA TO READ THE WARRANTY COVERED:
WESTERN EUROPE:
Austria • Belgium • Cyprus • Denmark • France • Germany • Greece •
Finland • Ireland • Italy • Luxembourg • the Netherlands • Norway • Portugal • Sweden •
Switzerland • Spain • United Kingdom
EASTERN EUROPE: Czech Republic • Hungary • Poland • Russia • Turkey • Bulgaria •
Slovakia • Slovenia
LATIN AMERICA: Antilles • Argentina • Brazil • Chile • Colombia • Mexico • Paraguay •
Peru • Uruguay • Venezuela
NORTH AMERICA: USA & Canada
PACIFIC: Australia • New Zealand
ASIA: Bangladesh • China • Hong Kong • India • Indonesia • Japan • Korea • Malaysia •
Pakistan • Philippines • Singapore • Taiwan • Thailand
AFRICA: Morocco • South Africa
MIDDLE EAST: Dubai • Egypt
Page 15

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does the "Designed for Windows" logo signify?
The "Designed for Windows" logo means your Philips monitor fulfills the requirements and
recommendations of the PC9x (97, 98, or 99) System Design Guide and passes stringent WHQL
tests.
2. What is TCO?
TCO is a Swedish abbreviation for the Swedish Confederation of Professional
Employees.
3. What is MPR?
MPR is a Swedish abbreviation for the Swedish National Board of Measurement
and Testing.
4. What are the differences between MPRII, TCO92, TCO95, TCO99 and
TCO'03?
In the general hierarchy of standards, TCO'03/TCO99 is the highest level of
certification. Next is TCO95, which is "better" than TCO92, which, in turn, is better
than MPRII. Below, we compare the standards in each category.
-TCO 92 Phase out: June 30, 2000
-TCO 95 Will be end December 31, 2003
Emissions:
MPRII: Set low emission rules for visual displays.
TCO92: Imposed more stringent standards than MPRII.
TCO95: Further toughened TCO92 rules.
TCO99: Delineated even more severe standards and test procedures than
TCO95.
TCO'03: Same as TCO99 standard + Testing uncertainty.
Safety:
MPRII: No requirement.
TCO92/95/99/03: All set requirements.
Page 16

Energy Saving:
MPRII: No requirement.
TCO92: Standby mode < 30W, Off mode < 8W
TCO95: Standby mode < 30W, Off mode < 8W
TCO99: Standby mode < 15W, Off mode < 5W
TCO'03:Standby mode < 15W, Off mode < 5W
Visual Ergonomics:
MPRII: No requirement.
TCO92: No requirement.
TCO95: Set ergonomic rules including minimum contrast level, flicker and jitter.
TCO99: Tightened TCO95 rules.
TCO'03: Tighten TCO99 rule for CRT and new requirement of screen color for
TFT LCD Monitors.
Ecology:
MPRII: No requirement.
TCO92: No requirement.
TCO95: Set general ecological standards including recycling preparation,
environmental policy and environmental certification.
TCO99: Further tightened TCO95 norms.
TCO'03:Require the recycling information to users.
5. How do I enable the energy saving function?
Go to 'My Computer' and select 'Control Panel' followed by 'Monitor Control.'
Select "All default selection' and choose your Philips monitor model from the
default driver list. Plug and Play will automatically enable the EPA tick box for
you. In DOS or Windows 3.1, you must first make sure your PC supports power
saving.
6. What is refresh rate?
"Refresh rate" describes the number of times an entire screen is vertically scanned each second.
In other words: If a monitor's refresh rate is 85 Hz, its screen is refreshed - or vertically scanned 85 times per second. A higher the refresh rate means better image stability and less flicker. A high
refresh rate helps users who work long hours in front of a monitor avoid eye fatigue and stress. To
change the refresh rate, go into "Start/Settings / Control Pannel / Display / Properties /
Setting/Advance/Adaptor" Windows settings of the computer, the monitor will automatically adjust
itself to the video card.
Page 17

A
A
7. Why does the picture on the screen appear to flicker?
low refresh rate or electrical interference typically causes flickering in the picture. Possible
solutions include the following:
z Verify that the proper drivers are installed for your video card
z Make sure that all electrical devices (such as mobile phones) are at least
1m from the monitor
z Place the monitor in another physical location away from electrical
interference
z Adjust the refresh rate to 75hz or higher.
8. How do I adjust my monitor's resolution?
vailable resolutions are determined by the capabilities of your video card and graphic driver.
Under Windows '95, you may select the desired available resolution through the 'Display
properties/Settings' menu.
9. How can I adjust the size, position and rotation of my screen?
Depending on the model you own, you can use your CustoMax Software, On
Screen Display (OSD) or control knobs located on the monitor.
10. What if I get lost when making monitor adjustments?
Simply press OK button then select "Reset to factory settings" to restore all
settings.
11 . The Main Menu displays OSD MAIN MENU LOCKED . Pressing the
front control panels hasno effect. How can I unlock this function?
Press and hold the OSD menu key for about 15 seconds until picture displays
"OSD MAIN MENU UNLOCKED"
12. My screen shows NO SYNC INPUT , how can I get rid of this?
Page 18

Check the following for possible solutions:
z Bent pins on the video cable
z Make sure the computer is turned on
z Ensure the VGA Cable is properly connected
z Video card may be not a VESA standard (try the monitor with another
computer)
13. Why does my monitor display "Out of Range"?
The video card installed in your computer may be too high for the monitor 's specifications. Please
contact your computer manufacturer for details on how to lower resolution for your operating
system.
14. What is Moire? Why does my monitor have this wavy phenomenon?
Moire is a natural effect or phenomenon of CRT that has the appearance of a
wavy pattern, which is repetitive and superimposed on the screen as ripple
images. These are a few suggestions to help reduce or minimize the effects:
Some monitors have a Moire cancellation feature, activate it to the on
z
position or adjust the Moire cancellation function via the OSD on the
monitor.
z Change resolution to the recommended standard for the specific monitor
size.
z Change Window viewing pattern/scheme to a pattern where the Moire is
less visible.
z Change horizontal and vertical size to optimize the reduction of the Moire
effect.
15. My monitor appears to be missing one or more colors. How do I correct
this?
z If the OSD menu is also missing a color, please contact service for details
z Set color temperature to 9300 color coordination
Check the video cable for any bent pins
z
z Video card could be defective (try the monitor with another computer).
16. When I degauss my monitor, it makes a loud noise. Is this normal?
Yes, when degaussing your monitor via the OSD, it is normal for the monitor to
make a relatively loud noise. Please be aware that many models will not degauss
Page 19

more than once within any given time period (up to 30 minutes). This is due to
A
the unit having a temperature sensitive resistor. While the unit is degaussing, the
resistor increases in value with heat and once it reaches a certain temperature,
the resistance will rise and prevent voltage from reaching the degaussing coil.
This is what stops the degausser, and this device's resistance will decrease as it
cools back off, enabling the degauss function to operate again. This is an
intentional design and is an industry standard, not just for Philips monitors. Please
be aware that not all models in the Philips range has this manual degauss
function. Some models are built with an auto degauss feature which automatically
degausses the monitor when it is switched on.
17. How do I adjust the picture on the screen?
Please perform the following to correct the picture image:
z Reset your monitor via the OSD menu
z Adjust the Horz (width) and/or Vert size (height) in the OSD
Change monitor timing to work at the recommended resolution
z
18. The edge of the picture on the screen appears to be distorted. How can
I correct this?
Please perform the following to correct the picture image:
z A magnetic or electrical interference typically causes poor geometry in the
picture. Place the monitor in a different physical location
Reset the monitor to the factory preset via the OSD menu
z
z Access the Geometry Menu in the OSD of the Monitor and perform the
necessary adjustments
Change the monitor timing to the recommended resolution
z
19. The picture appears too dim. How can I correct this?
djust Brightness and/or Contrast via the monitor 's OSD.
under Advanced Controls in the monitor 's OSD. Most computers require it to be
set at 0.7V.
Please review the following for possible solutions:
Page 20

z If the OSD menu is also dim, please contact service for repair
Reset the monitor via the OSD menu
z
z Change the color temperature settings to 9300 color coordination via the
OSD menu
Set the Contrast to maximum level (100) and Brightness to middle level (50)
z
Video card could be defective (try the monitor with another computer)
20. How can I increase the color display of my monitor?
The amount of video memory your video card holds determines the amount of colors that can be
displayed on your computer screen. To get the most out of your video card, you will need to either
install the latest drivers onto your computer or upgrade the video cards memory. Please check
with your computer or video card manufacturer for further details.
21. Why is there no picture on my monitor?
z Check the wall socket for power. Verify that there is power by connecting
another product.
z Ensure the power cable is correctly attached to both the wall socket and the
monitor.
z Check that the power button is switched on.
z Unplug the monitor for approx. 1 minute and plug it in again. Switch the
monitor back on.
22. Why is there no picture on my monitor even though the power LED is flashing green?
z Reboot your computer while holding the Ctrl key on your computer. If you
see any picture during the boot procedure, please verify the settings of your
video card (for Windows go to Control Panel and select Display).
Check that the video cable is not damaged, bent or that any of the pins in
z
the connector are damaged (please be aware that some VGA connectors
have one missing pin). If damaged, replace with a new cable.
z Check that the cable is attached correctly to the computer.
z Press any key on the keyboard to wake-up the computer from power saving
mode.
23. Why is there no picture on my monitor even though the power LED is
green?
z Verify the Contrast and Brightness setting of the monitor. First press and
hold the (-) button to increase Contrast and then press and hold the (+)
button to increase Brightness. These buttons are located on the front of
your monitor.
z Try and repeat step 22 above.
Page 21

24. Why does the picture disappear after I press the on/off button quickly?
This is a unique Philips feature designed to preserve the life of your monitor. Please allow 5
seconds between powering off and on your monitor, your picture will then be restored.
Page 22

Glossary
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A
Autoscan
A microprocessor-based feature of Philips Brilliance monitors is able to detect automatically
horizontal and vertical frequencies of input signals with those of the installed video card. An
autoscan monitor can thus operat e wit h a wid e range of video cards. MultiSync, a registered
trademark of NEC, provides a similar function.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
C
CE Mark
CE mark is displayed on products per EMC and LV ( low Voltage Device ) directives in
compliance with European Community safety, EMI and EMS requirements and is compulsory on
products for sale in the European Community.
Color temperature
A way of describing the color of a radiating source in terms of the temperature (in degrees Kelvin)
of a black body radiating with the same dominant frequency as the source.
Most Philips monitors offer the possibility of setting the color temperature to any desired value.
Contrast
The ratio between the brightness of the brightest and darkest parts of a picture. The darkest part
of a picture is set by the brightness of the unexcited phosphor, which is governed by the degree
with which ambient light is reflected. Contrast is therefore reduced in conditions of high ambient
light levels. Black Matrix tubes reflect less ambient light so exhibit higher contrast than other
tubes.
Convergence error
Bean misalignment causing one or more of the three beams passing through the wrong aperture
in the shadow mask and striking a phosphor dot in the wrong triad.
Convergence error is expressed in mm often at two well-defined points on the screen, designated
Page 23
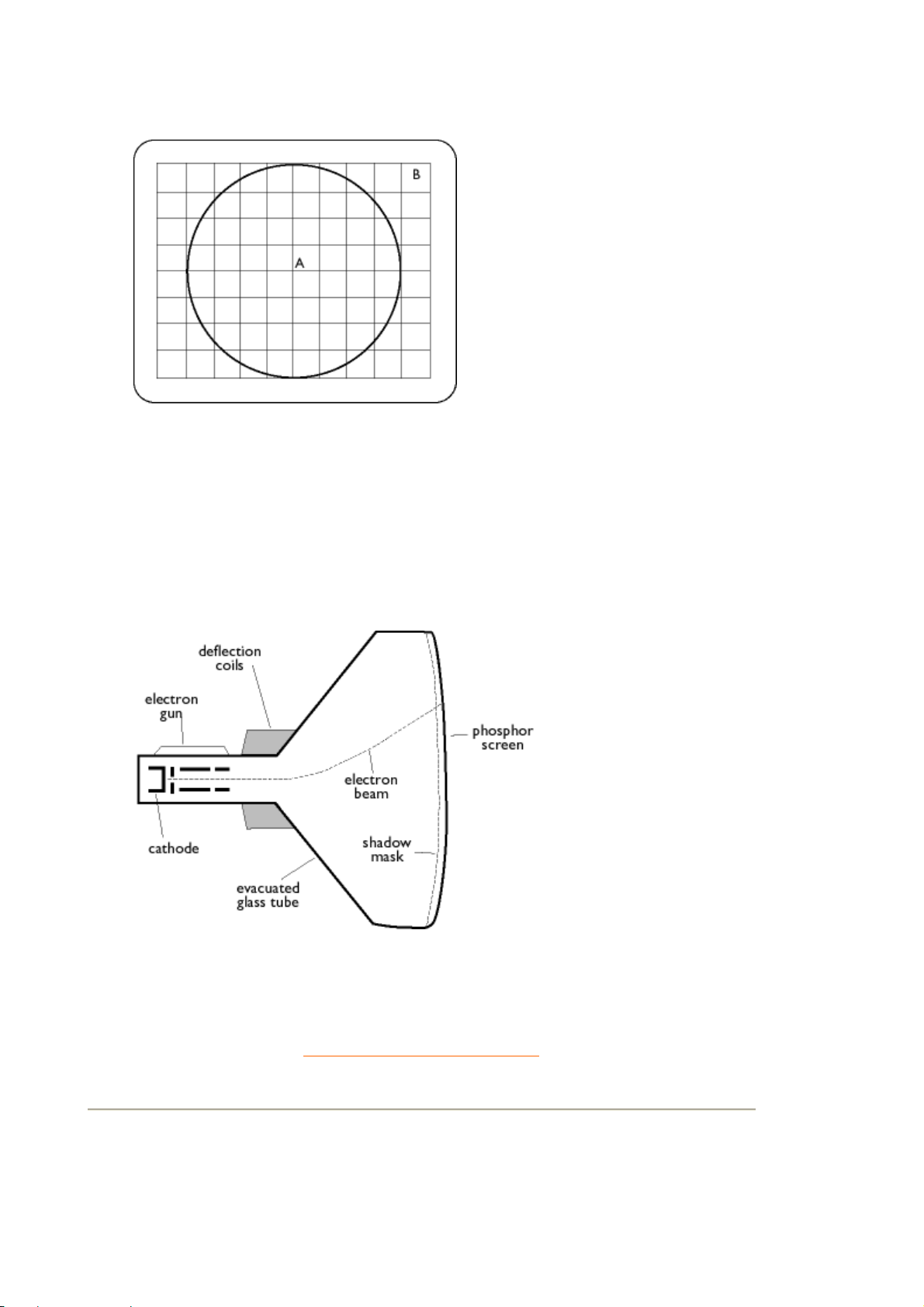
A, B (see figure ). Also known as misconvergen ce .
Points where convergence error is specified
.
CRT
Cathode-ray tube - the general term for all tubes in which one or more electron beams emitted by
a cathode are periodically scanned across a phosphor screen by means of deflection circuitry. A
special form of the cathode-ray tube is the TV and monitor picture tube.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
D
DDC (Display Data Channel)
Page 24

DDC is a communication channel for displays and computers. The DDC feature allows the
monitor controller to be automatically configured to make optimal use of the display without
manual user interaction. DDC is implemented as part of the new Plug & Play approach
introduced into the PC market to increase user friendliness.
The three levels developed for Plug & play are: (1) DDC1, monitor send data to the PC; (2)
DDC2B, PC can request information from monitor; and (3) DDC2Bi which is a two-way
communication - monitor can be addressed and PC or graphics board can give commands to
monitor.
DDC 1/2B
See DDC.
DDC 2Bi
See DDC.
Degaussing
The procedure of demagnetizing the shadow mask and associated metal parts of a picture tube
at switch-on to minimize picture distortion. This is usually accomplished by means of a special
degaussing coil through which a decaying alternating current is passed to generate an alternating
magnetic field that gradually decays to demagnetize the tube. Some monitors offer a manual
degaussing facility that can be activated at any time.
Digital control
Microprocessor-based digital control of picture parameters and video modes for complete control
of picture settings and modes and instant recall of all settings at the push of a button. This is a
very advanced feature that allows the user to switch to any required mode at any instant without
having to spend time readjusting the picture. It is currently available in most Philips monitors.
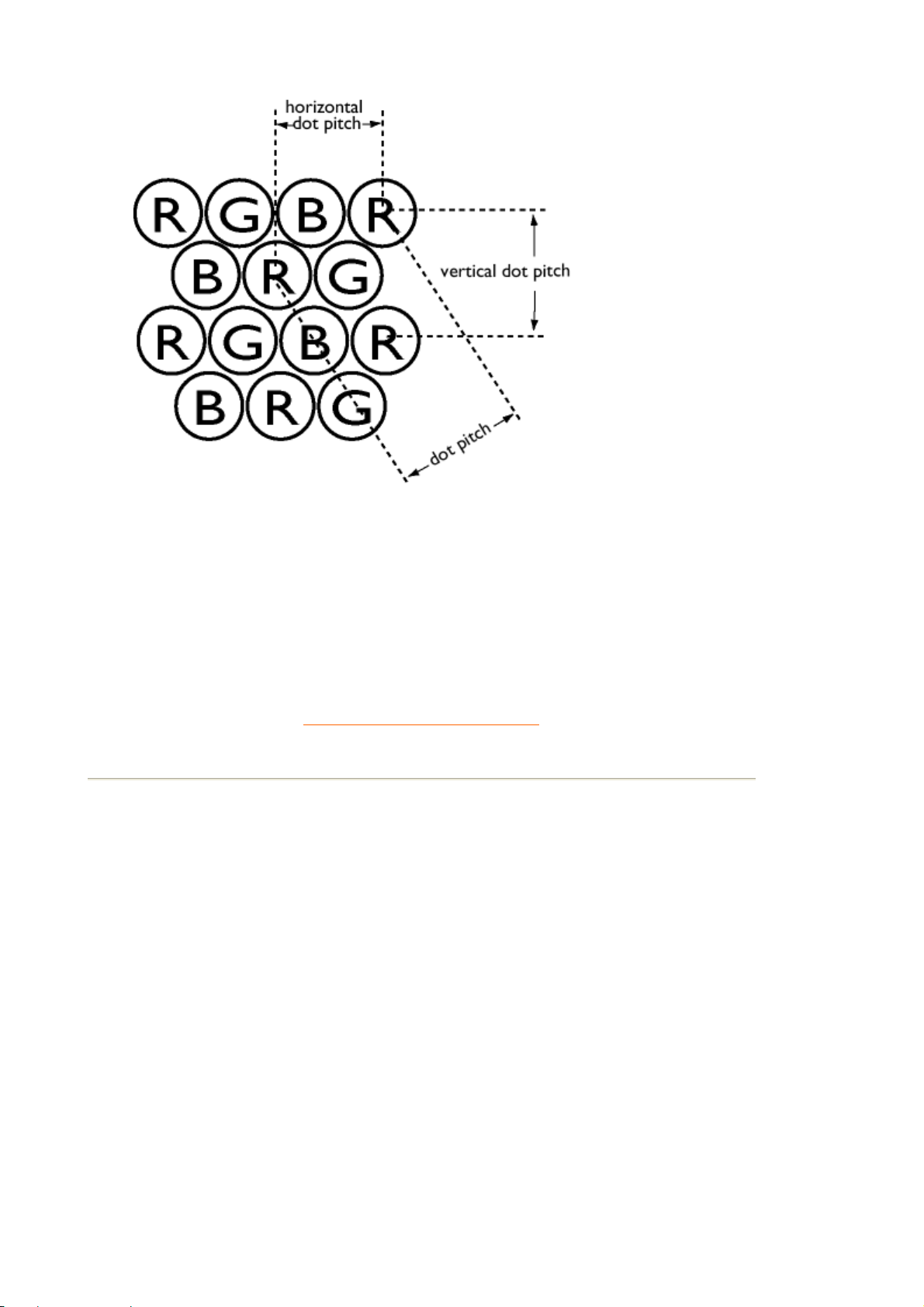
Dot pitch
The shortest distance between two phosphor dots of the same color on the screen. The smaller
the dot pitch, the better the resolution of the monitor.
Page 25
Dot rate
Frequency in MHz of the dot clock. It is a measure of the speed with which data is transferred
between the video card and subsequent processing circuitry.
Also known as video dot rate.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
E
Electromagnetic radiation standards
International standards set to limit electromagnetic emissions from monitors. There are currently
two important standards both derived from regulations originally laid down by Swedish
authorities.
MPR-II
The standard originally proposed by the Swedish National Board of Measurement and Testing. It
set maximum levels of electromagnetic radiation emitted by monitors, and has now been adopted
as a world standard. MPR-II defines maximum permitted electrostatic, magnetic and electric field
levels measured at a distance of 50 cm from the center of the monitor (see table).
TCO
In 1991, the Swedish Tjänstemannens Central Organization (TCO, Swedish confederation of
Professional Employees ) set a standard even more severe than MPR-II, especially for
alternating electric fields (AEF). The TCO standard is more severe since not only are the
permitted field levels reduced compared with MPR-II, but the measuring distance is also reduced
Page 26

(see table).
Electromagnetic radiation standards
EMI (Electrical Magnetic Interference)
The electrical and/or magnetic radiation coming from the working electrical or electronic
equipment.
EMS (Electrical Magnetic Sustainment)
The ability of electrical or electronic equipment to function properly in the environment with
electrical and/or magnetic interference.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
F
Flicker
Very rapid variations in picture intensity caused by the finite time required for the electron beam
to scan a picture onto the screen. Two kinds of flicker occur: line flicker caused by the electron
beam scanning-in each line of the pic tu re; an d frame flicker (or field flicker if the picture is
interlaced) caused by the frame repetition rate of 50 frames/second. Frame flicker is noticeable
with GUI and DTP software (which have a light background), and can be very disturbing,
especially for those who work regularly with displays - contributing to eye strain, headaches,
visual blurring, stress, etc. The problem can, however, be eliminated by increasing the refresh
rate (number of frames/second) of the monitor to a value above around 70 Hz. Sensitivity to
flicker appears to diminish with increasing age.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
H
Hertz
The unit of frequency named after the physicist Heinrich Hertz (1857-1894). 1 hertz (Hz) is equal
to 1 cycle/second.
Horizontal dot pitch
See Dot pitch.
Horizontal scanning frequency
Also called line frequency and expressed in kHz, it is the number of video lines written on the
Page 27
screen every second (from left to right). The higher the horizontal scanning frequency, the better
the resolution (i.e., the higher the resolution and/or the higher the refresh rate).
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
I
INF File
INF file (Information File)
Information (INF) files store information in a specific format. The set-up functions retrieve
information from the INF file to use when performing installation operations. Examples of the type
of information stored in an INF file include INI and registry changes, file names, and locations of
the source files on source media.
L
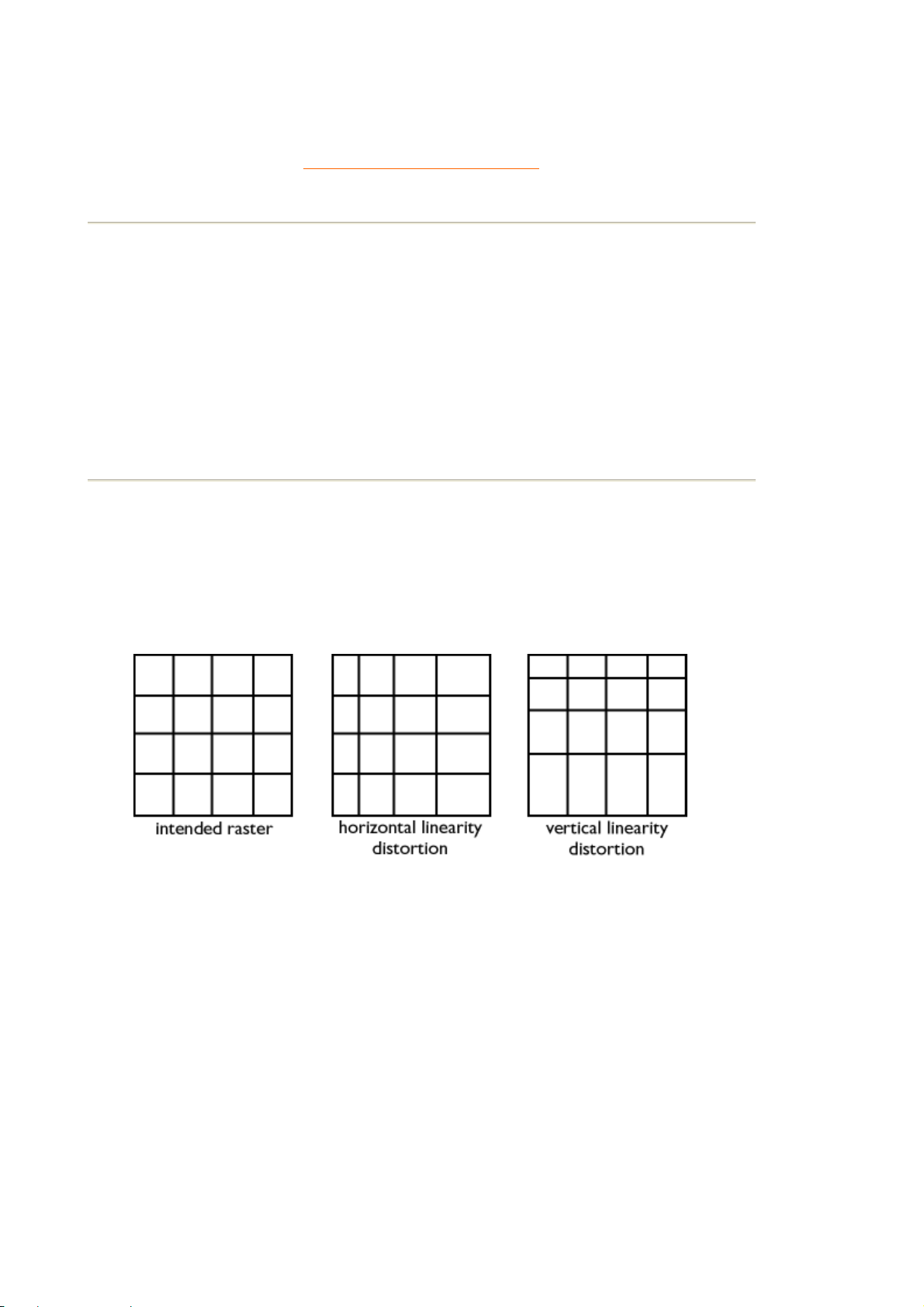
Linearity
The degree to measure the actual location of a pixel on the screen corresponds with its intended
location. ( see figure )
Line frequency
See Horizontal scanning frequency.
Low-emission monitor
A monitor that complies with international standards on radiation.
See Electromagnetic radiation standards.
Page 28

Low-frequency electric and magnetic fields
Alternating fields generated by the deflection yoke. These are subject to increasing attention,
notably by governing authorities, the trade and the press. Although there is no scientific evidence
that monitor emissions are harmful, much effort has gone into reducing emissions on the
principle of better safe than sorry. Currently, there are two areas of interest: very-low frequency
(VLF) electric and magnetic fields extending from 2 kHz to 400 kHz, and extreme low frequency
(ELF) fields extending from 5 Hz to 2 kHz.
See also
Electromagnetic radiation standards
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
.
M
Moiré effect
A fringe pattern arising from the interference between two superimposed line patterns.
In a monitor it comes from the interference between the shadow mask pattern and the video
information (video moiré), and between the shadow mask pattern and the horizontal line pattern
(scan moiré). It shows itself as wavy patterns on the screen and becomes more noticeable as
monitor resolution increases. Since the video signal varies continuously, little can be done about
video moiré. Scan moiré depends on the horizontal scanning frequency and can be alleviated by
appropriate choice of frequency. Autoscan (MultiSync) monitors, which operate over a range of
scanning frequencies, may sometimes exhibit moiré in certain video modes.
MPR
See Electromagnetic radiation standards.
MultiSync monitor
See Autoscan monitor.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
N
Non-interlaced
See Interlaced/non-interlaced.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 29

O
OSD (On Screen Display)
The feature that allows an end user to adjust screen performance and parameters of monitors
directly through an on-screen instruction window. See CustoMax in CrystalClear section.
Overscan
The practice in which areas without useful video information are scanned outside the visible
screen area in order to make maximum use of the screen for display of active video information.
This practice is occasionally necessary because some video cards generate a video pattern that
is smaller than the visible screen area, resulting in an image that is smaller (and less legible) than
it needs to be.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
P
Parallelogram Distortion
See Geometric distortion.
Phosphor
Generic name for the class of substances that exhibit luminescence. To produce a picture on
screen, phosphors are deposited on the inner surface of the picture-tube screen and excited into
luminescence by the electron beam. Typical examples of phosphors are P22 medium shortpersistence phosphor and EBU high-color-saturation phosphor.
Pin-cushion Distortion
See Geometric distortion.
Pixel
Abbreviation for picture element, the smallest element of the picture that can be displayed on the
screen. The smaller the pixel size, the better the resolution of the monitor. Pixel size is
determined by the size of the electron spot on the screen and not necessarily by the phosphor
dot pitch (the size of the triad). Thus, a monitor with a large electron spot covering several triads
can exhibit poor resolution even though its dot pitch is small.
Page 30

Pixel frequency
The number of pixels that can be written in a video line per second.
Pixel rate
See pixel frequency
Plug-and-Play
See DDC. See USB section.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
R
Raster
The area on screen that electron beam can reach.
Refresh rate
See Vertical scanning frequency.
Resolution
The number of pixels that can be displayed on the screen. The resolution is specified as the
number of pixels in a line multiplied by the number of horizontal lines.
See also video graphic adapter.
Rotation function
The feature that allows users to adjust the whole screen rotating to be horizontal.
Because of the magnetic field of earth, the screen of monitor will be tilt when the screen faces
toward the different direction.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 31

S
Screen coatings
Anti-Static coatings
Due to bombardment by beam electrons, monitor screens become electrically charged when in
use. Electrically charged screens surfaces can attract dust particles. An Anti-Static coating is a
conductive coating deposited on the screen (or on a glass panel immediately in front of the
screen) that conducts away the charge and prevents screen dust build-up.
ARAS (Anti-Reflection, Anti-Static) coating
ARAS is one of the most effective anti-reflection/anti-static screen treatments currently available.
It is composed of a multi-layer structure of transparent dielectric material that suppresses
specular reflections by broadband interference effects at the screen surface. Anti-static
properties are provided by a single conductive layer within the multi-layer structure.
With ARAS, the intensity of reflected light is reduced from around 4.5% of the incident light (the
reflectivity of uncoated screens) to less than 0.5%. ARAS also has a major advantage over other
screen treatments: It doesn't diffuse or scatter reflected light, so picture contrast and sharpness
remain completely unimpaired. It's also easy to clean and tough enough to withstand
commercially available cleaning agents.
The ARAS coating reflects only about 0.5% of the incident light.
Page 32

AGRAS (Anti-Glare anti-Reflection Anti-Static) coating
A combined anti-reflection, anti-glare, anti-static coating.
.
Self-test function
A monitor equipped with hardware or software to automatically detect cable connection status.
Shape
Deviation of a reproduced picture from its intended shape. The following types of distortion are
most common:
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
T
TCO
See Electromagnetic radiation standards.
Page 33

Tilt function
See rotation function.
Trapezoid distortion
See Geometrical distortion.
TTL signal
A TTL (Transistor-transistor-logic) signal is a digital signal level for controlling the screen colors.
With TTL driving, the red, green and blue signals can only be switched on or off or provided with
an intensity signal. A TTL-driven monitor can thus display a maximum of 64 colors. Video
standards such as MDA, CGA and EGA are based on TTL level.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
V
Vertical dot pitch
See Dot pitch.
Vertical scanning frequency
Expressed in Hz, this is the number of fields written to the screen every second in interlaced
mode. In non-interlaced mode vertical scanning frequency is the number of frames (complete
pictures) written to the screen every second (also known as refresh rate).
Vertical sync pulses
A train of square shaped waveforms that define the start of a new frame.
VESA
Video Electronic Standards Association, a consortium of manufacturers formed to establish and
maintain industry-wide standards for video cards and monitors. VESA was instrumental in the
introduction of the Super VGA and Extended VGA video graphics standards (see Video graphics
adapters) with a refresh rate of 70 Hz, minimizing flicker and helping to reduce operator eyes
fatigue and stress.
Page 34

Video dot rate
See Dot rate.
Video graphics adapters
A card equipped with a character or graphic generator and video memory, which maps to the
screen. A microprocessor scans video memory and translates bit information from the computer
into displayable video signals for the monitor. These cards comply with various standards that
determine the nature and quality of the display.
VGA (Video Graphics Array), introduced in 1987, was the first analog card. It offered still higher
resolution than EGA: 640 X 480 pixels for graphics and 720 x 400 pixels for text, and a color
palette of 256 colors. VGA could also emulate EGA and CGA.
Super VGA, devised by VESA in 1989, offers a resolution of 800 x 600 pixels.
Extended VGA, introduced by VESA in 1991, offers a top resolution of 1024 x 768 pixels (non-
interlaced) and a refresh rate slightly higher than IBM's XGA 8514A.
High-end, graphics adapters, introduced over the last three years for professional workstations,
offer top resolutions from 1280 x 1024 to 1600 x 1280, horizontal line frequencies up to 90 kHz
and bandwidths up to 200 MHz.
VIS (Viewable Image Size)
The real screen dimensions that users can see measured diagonally. The VIS of a monitor is
always less than the so called screen size of a monitor. For example, the VIS of a 17-inch
monitor is only about 16 inches. It depends on the useful screen size of CRT and the opening of
a monitor's front cabinet.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 35

Download and Print
This page provides an option to read the manual in .pdf format. PDF files can be downloaded into
your hard disk, then viewed and printed with Acrobat Reader or through your browser.
If you do not have Adobe¨ Acrobat Reader installed, click on the link to install the application.
® Acrobat Reader for PC / Adobe® Acrobat Reader for Mac.
Adobe
Download instructions:
To download the file:
1. Click-and-hold your mouse over the icon below. (Win95/98 users right-click)
2. From the menu that appears, choose 'Save Link As...', 'Save Target As...' or 'Download Link to
Disk'.
3. Choose where you would like to save the image; click 'Save' (if prompted to save as either
'text' or 'source', choose 'source').
Printing instructions:
To print the manual:
1. With the manual file open, follow your printer's instructions and print the pages you need.
109B7/109F7.pdf English language manual
Page 36

Troubleshooting
Safety Precautions and Maintenance • Troubleshooting • Regulatory Information
• Other Related Information
Common Problems
Having trouble? Something not working? Before calling for help, try these suggestions.
Having this
problem?
No Picture
(Power LED not lit)
No Picture
(Power LED is flashing
green)
No Picture
(Power LED is green)
Check these items
z Make sure the Power cable is plugged into the power
outlet and back of the monitor.
z Power button in the front of your monitor should be in the
ON position.
z Disconnect the monitor from the power outlet for about
one minute.
z Make sure the computer is turned on.
z Make sure the monitor cable is properly connected to your
computer.
z Check to see if the monitor cable has bent pins.
z The Energy Saving feature may be activated
z Make sure the Brightness and Contrast controls are set
correctly.
z Make sure the monitor cable is properly connected to your
computer.
z Check to see if the monitor cable has bent pins.
z Make sure the computer Power button is on.
Screen doesn't show
when you turn on the
monitor
No color or intermittent
color
Color appears blotchy
Missing one or more
colors
Dim Picture
Picture is too large or
too small.
z Make sure the monitor cable is properly connected to your
computer. (Also refer to the Quick Start Guide).
z Check to see if the monitor cable has bent pins.
z Make sure the computer is turned on.
z If you are using a non-VESA-DDC standard video card,
turn the DDC1 / 2B feature Off.
z The picture may need degaussing.
z Remove any nearby magnetic objects.
z Face the monitor toward the East for the best picture
quality.
z Check the Color Temperature.
z Make sure the monitor cable is properly connected to your
computer.
z Check to see if the monitor cable has bent pins.
z Adjust the Brightness and Contrast controls.
z Check your video card and it's owner's manual
instructions for it may be a non-VESA-DDC Standard
card.
z
Adjust the Horizontal and/or Vertical Size.
z Adjust the Zoom.
Page 37

Edges of the picture
are not square.
Picture has a double
image.
z Adjust the geometry.
z Eliminate the use of a video extension cable and/or video
switch box.
z Face the monitor toward the East for the best picture
quality.
Picture is not sharp.
Unstable Picture
z Check to make sure Moiré is switched off.
z Adjust Sync Input.
z Increase your refresh rate.
Problem with On
Screen Display
For further assistance, refer to the Consumer Information Centers list to contact your local Philips
distributor.
z Refer to the instructions and troubleshooting information
in that chapter.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 38

Regulatory Information
TCO'03 Information • Recycling Information for Customers • Waste Electrical and
Electronic Equipment-WEEE • CE Declaration of Conformity • Commission
Federale de la Communication (FCC Declaration) • EN 55022 Compliance
(Czech Republic Only) • VCCI Class 2 Notice (Japan Only) • MIC Notice (South
Korea Only) • Polish Center for Testing and Certification Notice • North Europe
Information (Nordic Countries) • BSMI Notice (Taiwan Only) • Ergonomie Hinweis
(nur Deutschland) • Philips End-of-Life Disposal • Information for UK only
Safety Precautions and Maintenance • Troubleshooting • Other Related
Information
TCO' 03 Information (For TCO Model Only)
Congratulations!
The display you have just purchased carries the TCO'03
Displays label. This means that your display is designed,
manufactured and tested according to some of the strictest
quality and environmental requirements in the world. This
makes for a high performance product, designed with the
user in focus that also minimizes the impact on our natural
environment.
Some of the features of the TCO'03 Display requirements.
Ergonomics
z Good visual ergonomics and image quality in order to improve the working environment
for the user and to reduce sight and strain problems. Important parameters are luminance,
contrast, resolution, reflectance, colour rendition and image stability.
Energy
Emissions
Ecology
z Energy-saving mode after a certain time-beneficial both for the user and the environment
z Electrical safety
z Electromagnetic fields
z Noise emissions
z The product must be prepared for recyclin g and the manufacturer must have a certified
Page 39

environmental management system such as EMAS or ISO 14 000
z Restrictions on
chlorinated and brominated flame retardants and polymers
heavy metals such as cadmium, mercury and lead.
The requirements included in this label have been developed by TCO Development in cooperation with scientists, experts, users as well as manufacturers all over the world. Since the
end of the 1980s TCO has been involved in influencing the development of IT equipment in a
more user-friendly direction. Our labelling system started with displays in 1992 and is now
requested by users and IT-manufacturers all over the world.
For more information, please visit
www.tcodevelopment.com
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Recycling Information for Customers
Philips establishes technically and economically viable objectives to optimize the environmental
performance of the organization's product, service and activities.
From the planning, design and production stages, Philips emphasizes the important of making
products that can easily be recycled. At Philips, end-of-life management primarily entails
participation in national take-back initiatives and recycling programs whenever possible,
preferably in cooperation with competitors.
There is currently a system of recycling up and running in the European countries, such as The
Netherlands, Belgium, Norway, Sweden and Denmark.
In U.S.A., Philips Consumer Electronics North America has contributed funds for the Electronic
Industries Alliance (EIA) Electronics Recycling Project and state recycling initiatives for end-of-life
electronics products from household sources. In addition, the Northeast Recycling Council
(NERC) - a multi-state non-profit organization focused on promoting recycling market
development - plans to implement a recycling program.
In Asia Pacific, Taiwan, the products can be taken back by Environment Protection
Administration (EPA) to follow the IT product recycling management process, detail can be found
in web site www.epa.gov.tw
For help and service, please contact Consumers Information Center or F1rst Choice Contact
Information Center in each country or the following team of Environmental specialist can help.
Mr. Job Chiu - Environment manager
Philips Electronics Industries (Taiwan) Ltd, Monitor Business Unit
E-mail: job.chiu@philips.com
Tel: +886 (0) 3 454 9839
Mr. Maarten ten Houten - Senior Environmental Consultant
Philips Consumer Electronics
E-mail: marten.ten.houten@philips.com
Tel: +31 (0) 40 27 33402
Ms. Delmer F. Teglas
Page 40

Philips Electronics North America
E-mail: butch.teglas@philips.com
Tel: +1 865 521 4322
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment-WEEE
Attention users in European Union private households
This marking on the product or on its packaging illustrates that, under European
Directive 2002/96/EG governing used electrical and electronic appliances, this product may not
be disposed of with normal household waste. You are responsible for disposal of this equipment
through a designated waste electrical and electronic equipment collection. To determine the
locations for dropping off such waste electrical and electronic, contact your local government
office, the waste disposal organization that serves your household or the store at which you
purchased the product.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
CE Declaration of Conformity
z Philips Consumer Electronics declare under our responsibility that the product is in
conformity with the following standards
- EN60950-1:2001 (Safety requirement of Information Technology Equipment)
- EN55022:1998 (Radio Disturbance requirement of Information Technology Equipment)
- EN55024:1998 (Immunity requirement of Information Technology Equipment)
- EN61000-3-2:2000 (Limits for Harmonic Current Emission)
- EN61000-3-3:1995 (Limitation of Voltage Fluctuation and Flicker)
following provisions of directives applicable
- 73/23/EEC (Low Voltage Directive)
- 89/336/EEC (EMC Directive)
- 93/68/EEC (Amendment of EMC and Low Voltage Directive)
and is produced by a manufacturing organization on ISO9000 level.
z The product also comply with the following standards
- ISO9241-3, ISO9241-7, ISO9241-8 (Ergonomic requirement for Visual Display)
- ISO13406-2 (Ergonomic requirement for Flat panels)
- GS EK1-2000 (GS specification)
- prEN50279:1998 (Low Frequency Electric and Magnetic fields for Visual Display)
- MPR-II (MPR:1990:8/1990:10 Low Frequency Electric and Magnetic fields)
- TCO'03 (Requirement for Environment Labelling of Ergonomics, Energy, Ecology and
Emission,
TCO: Swedish Confederation of Professional Employees) for TCO versions
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 41

Commission Federale de la Communication (FCC Declaration)
Cet équipement a été testé et déclaré conforme auxlimites des appareils
numériques de class B,aux termes de l'article 15 Des règles de la FCC. Ces
limites sont conçues de façon à fourir une protection raisonnable contre les
interférences nuisibles dans le cadre d'une installation résidentielle. CET appareil
produit, utilise et peut émettre des hyperfréquences qui, si l'appareil n'est pas
installé et utilisé selon les consignes données, peuvent causer des interférences
nuisibles aux communications radio. Cependant, rien ne peut garantir l'absence
d'interférences dans le cadre d'une installation particulière. Si cet appareil est la
cause d'interférences nuisibles pour la réception des signaux de radio ou de
télévision, ce qui peut être décelé en fermant l'équipement, puis en le remettant
en fonction, l'utilisateur pourrait essayer de corriger la situation en prenant les
mesures suivantes:
z Réorienter ou déplacer l'antenne de réception.
z Augmenter la distance entre l'équipement et le récepteur.
z Brancher l'équipement sur un autre circuit que celui utilisé par le récepteur.
z Demander l'aide du marchand ou d'un technicien chevronné en radio/télévision.
Toutes modifications n'ayant pas reçu l'approbation des services compétents en
matière de conformité est susceptible d'interdire à l'utilisateur l'usage du présent
équipement.
N'utiliser que des câbles RF armés pour les connections avec des ordinateurs ou périphériques.
CET APPAREIL NUMERIQUE DE LA CLASSE B RESPECTE TOUTES LES EXIGENCES DU
REGLEMENT SUR LE MATERIEL BROUILLEUR DU CANADA.
FCC Declaration of Conformity
Model Number: 109B/F
Trade Name: Philips
Responsible Party: Philips Consumer Electronics North America
P.O. Box 671539
Marietta, GA 30006-0026
1-888-PHILIPS (744-5477)
Declaration of Conformity for Products Marked with FCC Logo,
United States Only
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Page 42

RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
EN 55022 Compliance (Czech Republic Only)
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
VCCI Notice (Japan Only)
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for Interference
(VCCI) for Information technology equipment. If this equipment is used near a radio or television
receiver in a domestic environment, it may cause radio Interference. Install and use the
equipment according to the instruction manual.
Class B ITE
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
MIC Notice (South Korea Only)
Class B Device
Page 43

Please note that this device has been approved for non-business purposes and may be used in
any environment, including residential areas.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Polish Center for Testing and Certification Notice
The equipment should draw power from a socket with an attached protection circuit (a threeprong socket). All equipment that works together (computer, monitor, printer, and so on) should
have the same power supply source.
The phasing conductor of the room's electrical installation should have a reserve short-circuit
protection device in the form of a fuse with a nominal value no larger than 16 amperes (A).
To completely switch off the equipment, the power supply cable must be removed from the power
supply socket, which should be located near the equipment and easily accessible.
A protection mark "B" confirms that the equipment is in compliance with the protection usage
requirements of standards PN-93/T-42107 and PN-89/E-06251.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 44

North Europe Information (Nordic Countries)
A
Placering/Ventilation
VARNING:
FÖRSÄKRA DIG OM ATT HUVUDBRYTARE OCH UTTAG ÄR
LÄTÅTKOMLIGA, NÄR DU STÄLLER DIN UTRUSTNING PÅPLATS.
Placering/Ventilation
ADVARSEL:
SØRG VED PLACERINGEN FOR, AT NETLEDNINGENS STIK OG
STIKKONTAKT ER NEMT TILGÆNGELIGE.
Paikka/Ilmankierto
VAROITUS:
SIJOITA LAITE SITEN, ETTÄ VERKKOJOHTO VOIDAAN TARVITTAESSA
HELPOSTI IRROTTAA PISTORASIASTA.
Plassering/Ventilasjon
ADVARSEL:
NÅR DETTE UTSTYRET PLASSERES, MÅ DU PASSE PÅ
KONTAKTENE FOR STØMTILFØRSEL ER LETTE Å NÅ.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
BSMI Notice (Taiwan Only)
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
T
Ergonomie Hinweis (nur Deutschland)
Page 45

Der von uns gelieferte Farbmonitor entspricht den in der "Verordnung über den Schutz vor
Schäden durch Röntgenstrahlen" festgelegten Vorschriften.
Auf der Rückwand des Gerätes befindet sich ein Aufkleber, der auf die Unbedenklichkeit der
Inbetriebnahme hinweist, da die Vorschriften über die Bauart von Störstrahlern nach Anlage III ¤
5 Abs. 4 der Röntgenverordnung erfüllt sind.
Damit Ihr Monitor immer den in der Zulassung geforderten Werten entspricht, ist darauf zu
achten, daß
1.
2.
3.
Aus ergonomischen Gründen wird empfohlen, die Grundfarben Blau und Rot nicht auf
dunklem Untergrund zu verwenden (schlechte Lesbarkeit und erhöhte Augenbelastung bei
zu geringem Zeichenkontrast wären die Folge).
Der arbeitsplatzbezogene Schalldruckpegel nach DIN 45 635 beträgt 70dB (A) oder weniger.
Reparaturen nur durch Fachpersonal durchgeführt werden.
nur original-Ersatzteile verwendet werden.
bei Ersatz der Bildröhre nur eine bauartgleiche eingebaut wird.
ACHTUNG:
NETZSTECKER UND NETZKABELANSCHLUß LEICHT ZUGÄNGLICH SIND.
BEIM AUFSTELLEN DIESES GERÄTES DARAUF ACHTEN, DAß
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
End-of-Life Disposal
Your new monitor contains materials that can be recycled and reused. Specialized companies
can recycle your product to increase the amount of reusable materials and to minimize the
amount to be disposed of.
Please find out about the local regulations on how to dispose of your old monitor from your local
Philips dealer.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Information for UK only
WARNING - THIS APPLIANCE MUST BE
EARTHED.
Important:
This apparatus is supplied with an
approved moulded 13A plug. To change a
fuse in this type of plug proceed as follows:
Page 46

1. Remove fuse cover and fuse.
2. Fit new fuse which should be a BS 1362
5A,A.S.T.A. or BSI approved type.
3. Refit the fuse cover.
If the fitted plug is not suitable for your
socket outlets, it should be cut off and an
appropriate 3-pin plug fitted in its place.
If the mains plug contains a fuse, this
should have a value of 5A. If a plug without
a fuse is used, the fuse at the distribution
board should not be greater than 5A.
Note: The severed plug must be destroyed
to avoid a possible shock hazard should it
be inserted into a 13A socket elsewhere.
How to connect a plug
The wires in the mains lead are coloured in
accordance with the following code:
BLUE - "NEUTRAL" ("N")
BROWN - "LIVE" ("L")
GREEN & YELLOW - "EARTH" ("E")
1. The GREEN AND YELLOW wire must
be connected to the terminal in the plug
which is marked with the letter "E" or by
the Earth symbol or coloured GREEN or
GREEN AND YELLOW.
2. The BLUE wire must be connected to
the terminal which is marked with the letter
"N" or coloured BLACK.
3. The BROWN wire must be connected to
the terminal which marked with the letter
"L" or coloured RED.
Before replacing the plug cover, make
certain that the cord grip is clamped over
the sheath of the lead - not simply over the
three wires.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 47

Other Related Information
Safety Precautions and Maintenance • Troubleshooting • Regulatory
Information • Information for Users in the U. S. • Information for Users Outside
the U.S
Information for Users in the U. S.
For units set at 115 V :
Use a UL Listed Cord Set consisting of a minimum 18 AWG, Type SVT or SJT three conductor
cord a maximum of 15-feet long and a parallel blade, grounding type attachment plug rated 15 A,
125 V.
For units set at 230 V:
Use a UL Listed Cord Set consisting of a minimum 18 AWG, Type SVT or SJT three conductor
cord a maximum of 15-feet long and a tandem blade, grounding type attachment plug rated 15 A,
250 V.
Information for Users outside the U.S.
For units set at 230 V:
Use a Cord Set consisting of a minimum 18 AWG cord and grounding type attachment plug rated
15 A, 250 V. The Cord Set should have the appropriate safety approvals for the country in which
the equipment will be installed and / or be marked HAR.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 48

The OSD Controls
Description of the On-Screen Display • The OSD Tree
The OSD Controls : Brightness (HotKey)
• Contrast (HotKey) • Language •
Zoom • Adjust Horizontal • Adjust Vertical • Adjust Shape • Adjust Color • Reset
to Factory Settings • Extra Controls • Close Main Controls
BRIGHTNESS
To adjust your screen's brightness, follow the steps below. Brightness is the overall intensity of
the light coming from the screen. A 50% brightness is recommended.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The BRIGHTNESS window appears.
2) Press the or button to adjust the brightness.
3) When the brightness is adjusted to the level desired, press to confirm and the
BRIGHTNESS window will disappear with the new adjustment saved.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
CONTRAST
To adjust your screen's contrast, follow the steps bellow. Contrast is the difference between the
light and dark areas on the screen. A 100% contrast is recommended.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The CONTRAST window appears.
Page 49

2) Press the or button to adjust the contrast.
3) When the contrast is adjusted to the level desired, press to confirm and the CONTRAST
window will disappear with the new adjustment saved.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
LANGUAGE
The ON SCREEN DISPLAY shows its settings in one of eight languages. The default is English,
but you can select French, Spanish, German, Italian, Simplify-Chinese, Korea, or Portuguese.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears. LANGUAGE
should be highlighted.
2) Press the button again. The LANGUAGE window appears.
3) Press the or button until the desired language is highlighted.
Page 50

4) Press the button to confirm your selection and return to MAIN CONTROLS window.
CLOSE MAIN CONTROLS will be highlighted.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
ZOOM
ZOOM increases or decreases the size of the images on your screen. To adjust the ZOOM follow
the steps below.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
2) Press the button until ZOOM is highlighted.
3) Press the button. The ZOOM window appears.
Page 51

4) Press the or button to adjust ZOOM.
5) Press the button to confirm your selection and Press again return to the MAIN
CONTROLS window. CLOSE MAIN CONTROLS will be highlighted.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
ADJUST HORIZONTAL
ADJUST POSITION under ADJUST HORIZONTAL shifts the image on your screen either to the
left or right. Use this feature if your image does not appear centered. ADJUST SIZE under
ADJUST HORIZONTAL expands or controls the image on your screen, pushing it out toward the
left and right sides or pulling it in toward the center.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
2) Press the button until ADJUST HORIZONTAL is highlighted.
3) Press the button. The ADJUST HORIZONTAL window appears. POSITION should be
highlighted.
Page 52

4) Press the or button to move the image to the left or right.
5) When the position is adjusted, press the button to confirm. Press the to highlight
SIZE, press to confirm.
6) To adjust the horizontal size, press the or button.
7) When the size is adjusted, press the button to confirm. Press again to return to MAIN
CNTROLS sindow. CLOSE MAIN CONTROLS will be highlighted.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
ADJUST VERTICAL
ADJUST POSITION under ADJUST VERTICAL shifts the image on your screen either up or
down. Use this feature if your image does not appear centered. ADJUST SIZE under ADJUST
VERTICAL expands or controls the image on your screen, pushing it out toward the top or
bottom or pulling it in toward the center.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
2) Press the button until ADJUST VERTICAL is highlighted.
Page 53

3) Press the button. The ADJUST VERTICAL window appears. POSITION should be
highlighted.
4) Press the or button to move the image up or down.
5) When the position is adjusted, press the button. Press again to return to MAIN
CONTROLS window, or press the to highlight SIZE and to confirm.
6) To adjust the vertical size, press the or button.
Page 54

7) When the size is adjusted, press the button to confirm. Press return to MAIN
CONTROLS window. CLOSE MAIN CONTROLS will be highlighted.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
ADJUST SHAPE
ADJUST SIDE CURVE
ADJUST SIDE CURVE under ADJUST SHAPE allows you to adjust two of the five preset
options. These two options are PINCUSHION and BALANCED pincushion. Note: use these
features only when the picture is not square.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
2) Press the button until ADJUST SHAPE is highlighted.
3) Press the button. The ADJUST SHAPE window appears. ADJUST SIDE CURVE should
be highlighted.
4) Press the button. The SIDE CURVE window appears. PINCUSHION should be
Page 55

highlighted. Press to confirm.
5) To adjust the pincushion, press the or button,press the to confirm.
6) When the pincushion is adjusted, press the button to highlight BALANCED. Press to
confirm.
7) To adjust the balanced pincushion, press the or button.Press to confirm.
8) When the balanced pincushion is adjusted, press the button to return to the ADJUST
SHAPE window. BACK TO MAIN WINDOWS will be highlighted.
9) Press the button to return to the MAIN CONTROLS window, or press the button until
ADJUST SIDE ANGLES is highlighted.
ADJUST SIDE ANGLES
ADJUST SIDE ANGLES under ADJUST SHAPE allows you to adjust two of the five preset
options. These two options are TRAPEZOID and PARALLELOGRAM. Note: use these features
only when the picture is not square.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
Page 56

2) Press the button until ADJUST SHAPE is highlighted.
3) Press the button. The ADJUST SHAPE window appears. ADJUST SIDE CURVE should
be highlighted.
4) Press the button to highlight ADJUST SIDE ANGLES.
5) Press the button. The SIDE ANGLES window appears. TRAPEZOID should be
highlighted, press to confirm.
6) To adjust the trapezoid, press the or button.
Page 57

7) When the trapezoid is adjusted, press the button to confirm. Then to highlight
PARALLELOGRAM, press to confirm.
8) To adjust the parallelogram, highlight parallelogram then to confirm. Press the
or button to adjust..
9) When the parallelogram is adjusted, press the button to confirm. Press again to return
to the ADJUST SHAPE window. BACK TO MAIN WINDOWS will be highlighted.
10) Press the button to return to the MAIN CONTROLS window, or press the button
until ROTATE IMAGE is highlighted.
ROTATE IMAGE
ROTATE IMAGE under ADJUST SHAPE allows you to adjust one of the five preset options.
These two options are PINCUSHION and BALANCED pincushion. Note: use this feature only
when the picture is not square.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
2) Press the button until ADJUST SHAPE is highlighted.
(Not available in all models)
Page 58

3) Press the button. The ADJUST SHAPE window appears. ADJUST SIDE CURVE should
be highlighted.
4) Press the button until ROTATE IMAGE is highlighted.
5) Press the button. The ROTATE IMAGE window appears. ROTATE should be highlighted.
6) To adjust the rotation, press the or button.
7) When the rotation is adjusted, press the button to confirm. Press to return to the
ADJUST SHAPE window. BACK TO MAIN CONTROLS should be highlighted.
8) Press the button to return to MAIN CONTROLS.
Page 59

RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
ADJUST COLOR
Your monitor has three preset options you can choose from. The first option is for GENERAL
USE, which is fine for most applications. The second option is for IMAGE MANAGEMENT, which
includes projects such as desktop publishing, viewing a DVD from your DVD player or pictures
on the World Wide Web, and playing video games. The third option is for PHOTO RETOUCH,
which is for working with pictures you have imported into your computer and want to alter. When
you select one of these options, the monitor automatically adjusts itself to that option. There is
also a fourth option, USER PRESET, which allows you to adjust the colors on your screen to a
setting you desire.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
2) Press the button until ADJUST COLOR is highlighted.
3) Press the button. The ADJUST COLOR window appears.
4) Press the or button to highlight 9300K for GENERAL USE, 6500K for IMAGE
MANAGEMENT, 5500K for PHOTO RETOUCH, or USER PRESET.
Page 60

5) Once you have highlighted GENERAL USE, IMAGE MANAGEMENT, or PHOTO RETOUCH,
press the button to confirm you selection. Press again to return to the MAIN CONTROLS
window. CLOSE MAIN CONTROLS will be highlighted.
6a) If USER PRESET is highlighted, press the button to highlight RED. Next, press the
to confirm. Press or button to adjust the color red.
6b) When finished with RED, press to confirm. Press the button to highlight GREEN.
press to confirm.Next, press the or button to adjust the color green.
6c) When finished GREEN, press to confirm.Then, press button to highlight
BLUE.Press
to confirm. Next, press the or button to adjust the color blue.
6d) When all adjustments are complete, press the button to confirm your adjustments and
return to the MAIN CONTROLS window. CLOSE MAIN CONTROLS will be highlighted.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
RESET TO FACTORY SETTINGS
RESET TO FACTORY SETTINGS returns everything in all the windows to factory presets.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
2) Press the button until RESET TO FACTORY SETTINGS is highlighted.
Page 61

3) Press the button. The RESET TO FACTORY SETTINGS window appears.
4) Press the or button to select YES or NO. NO is the default. YES returns all settings
to their original factory adjustments.
5) Press the button to confirm your selection and press again return to the MAIN
CONTROLS window. CLOSE MAIN CONTROLS will be highlighted.
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
EXTRA CONTROLS
DEGAUSS
EXTRA CONTROLS is a set of three features, including DEGAUSS. Degaussing removes
electromagnetic build up that may distort the color on your screen.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
2) Press the button until EXTRA CONTROLS is highlighted.
Page 62

3) Press the button. The EXTRA CONTROLS window appears. MOIRE will be highlighted.
4) Press the button to highlight DEGAUSS.
5) To degauss your screen, press the button. Your screen will be degaussed, then the MAIN
CONTROLS window will reappear. CLOSE MAIN CONTROLS will be highlighted.
ADJUST MOIRE
EXTRA CONTROLS is a set of three features, including ADJUST MOIRE. Moire is a fringe
pattern arising from the interference between two superimposed line patterns. To adjust your
moire, follow the steps below. Note: Use only if necessary. By activating ADJUST MOIRE,
sharpness can be affected.
1) Press the button on the monitor. The MAIN CONTROLS window appears.
2) Press button until EXTRA CONTROLS is highlighted.
(Not available in all models)
Page 63

3) Press the button. The EXTRA CONTROLS window appears. ADJUST MOIRE will be
highlighted.
4) Press the button. The ADJUST MOIRE window appears. HORIZONTAL will be
highlighted,press to confirm.
5) To adjust the horizontal moire, press the or button.
Page 64

6) When the horizontal moire is adjusted, press to confirm. Press the button to highlight
VERTICAL.
7) To adjust the vertical moire, press to confirm. Then press or button to adjust.
8) When the vertical moire is adjusted, press the to confirm. Press the button to return
to the EXTRA CONTROLS window. BACK TO MAIN CONTROLS will be highlighted.
CLOSE MAIN CONTROLS
RETURN TO TOP OF THE PAGE
Page 65

Your Philips F1rst Choice Warranty
Thank you for purchasing this Philips monitor.
All Philips monitors are designed and manufactured to high standards and deliver
high-quality performance, ease of use and ease of installation. Should you
encounter any difficulties while installing or using this product, please contact the
Philips helpdesk directly to benefit from your Philips F1rst Choice Warranty. This
three-year service warranty entitles you to a swap model on-site if your monitor
turns out to be faulty or defective.Philips aims at a swap within 48 hours of your call
being received.
What is covered?
The Philips F1rst Choice Warranty applies within Andorra, Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Denmark,
France, Germany, Greece, Finland, Ireland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Monaco, the
Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, Switzerland, Spain and the United Kingdom and only for
monitors originally designed, manufactured, approved and/or authorized for usage within these
countries.
Warranty coverage begins as from the day you buy your monitor. For three years thereafter, your
monitor will be swapped by at least an equivalent monitor in case of defects provided for under the
warranty coverage.
The swap monitor remains yours and Philips keeps the defective/original monitor. For the swap
monitor the warranty period remains equal to that of your original monitor, being 36 months as from
the purchase date of your original monitor.
What is excluded?
The Philips F1rst Choice Warranty applies provided the product is handled properly for its intended
use, in accordance with its operating instructions and upon presentation of the original invoice or
cash receipt, indicating the date of purchase, dealer's name and model and production number of
the product.
The Philips F1rst Choice Warranty may not apply if:
●
The documents have been altered in any way or made illegible;
●
The model or production number on the product has been altered, deleted, removed or made
illegible;
Page 66

●
Repairs or product modifications and alterations have been executed by unauthorized service
organizations or persons;
●
Damage is caused by accidents including but not limited to lightning, water or fire, misuse or
neglect;
●
Reception problems caused by signal conditions or cable or antenna systems outside the
unit;
●
Defects caused by abuse or misuse of the monitor;
●
Product requires modification or adaptation to enable it to comply with local or national
technical standards, which apply in countries for which the product was not originally
designed, manufactured, approved and/or authorized. Therefore always check whether a
product can be used in a specific country.
●
Note that products that are not originally designed, manufactured, approved and/or
authorized for usage within the Philips F1rst Choice countries, do not apply to the Philips
F1rst Choice Warranty. In these cases the Philips global warranty terms are valid.
Just a click away
In case of any problems, we advise you to read the operating instructions carefully or go to the
www.
philips.com/support website for additional support.
Just a phone call away
In order to avoid unnecessary inconvenience, we advise you to read the operating instructions
carefully or go to the
www.philips.com/support website for additional support before contacting the
Philips helpdesk.
To solve your problem quickly, please prepare the following details before contacting the Philips
helpdesk:
● Philips type number
● Philips serial number
● Purchase date (copy of purchase may be required)
● PC environment Processor:
❍ 286/386/486/Pentium Pro/Internal memory
❍ Operating system (Windows, DOS, OS/2, MAC)
❍ Fax/Modem/Internet program?
● Other cards installed
Page 67

Having the following information available will also help speed up the process:
● Your proof of purchase indicating: date of purchase, dealer name, model and product serial
number.
● The full address to which the faulty monitor has to be collected and the swap model should
be delivered.
Philips' customer help desks are located worldwide. Click here to access the
F1rst Choice Contact
Information.
Or you can reach us via:
Website:
http://www.philips.com/support
Page 68

Your Guarantee in Central and Eastern Europe
Dear Customer,
Thank you for purchasing this Philips product, which has been designed and manufactured to the
highest quality standards. If, unfortunately, something should go wrong with this product Philips
guarantees free of charge labor and replacement parts during a period of 36 months from date of
purchase.
What is covered?
This Philips Guarantee in Central and Eastern Europe applies within Czech Republic, Hungary,
Slovakia, Slovenia, Poland, Russia and Turkey and only for monitors originally designed,
manufactured, approved and/or authorized for usage within these countries.
Warranty coverage begins as from the day you buy your monitor. For 3 years thereafter, your
monitor will be serviced in case of defects provided for under the warranty coverage.
What is excluded?
The Philips guarantee applies provided the product is handled properly for its intended use, in
accordance with its operating instructions and upon presentation of the original invoice or cash
receipt, indicating the date of purchase, dealer's name and model and production number of the
product.
The Philips guarantee may not apply if:
● the documents have been altered in any way or made illegible;
● the model or production number on the product has been altered, deleted, removed or made
illegible;
● repairs or product modifications and alterations have been executed by unauthorized service
organizations or persons;
● damage is caused by accidents including but not limited to lightning, water or fire, misuse or
neglect.
● Reception problems caused by signal conditions or cable or antenna systems outside the
unit;
● Defects caused by abuse or misuse of the monitor;
● Product requires modification or adaptation to enable it to comply with local or national
technical standards, which apply in countries for which the product was not originally
designed, manufactured, approved and/or authorized. Therefore always check whether a
product can be used in a specific country.
Page 69

Please note that the product is not defective under this guarantee in the case where modifications
become necessary in order for the product to comply with local or national technical standards
which apply in countries for which the product was not originally designed and/or manufactured.
Therefore always check whether a product can be used in a specific country.
Just a click away
In case of any problems, we advise you to read the operating instructions carefully or go to the
www.
philips.com/support website for additional support.
Just a phone call away
In order to avoid unnecessary inconvenience, we advise you to read the operating instructions
carefully before contacting our dealers or Information Centers
In case your Philips product is not working correctly or is defective, please contact your Philips
dealer or directly the
Philips Service and Consumer Information Centers.
Website:
www.philips.com/support
Page 70

Your International Guarantee
Dear Customer,
Thank you for purchasing this Philips product which has been designed and manufactured to the
highest quality standards.
If, unfortunately, something should go wrong with this product Philips guarantees free of charge
labor and replacement parts irrespective of the country where it is repaired during a period of 12
months from date of purchase. This international Philips guarantee complements the existing
national guarantee obligations to you of dealers and Philips in the country of purchase and does not
affect your statutory rights as a customer.
The Philips guarantee applies provided the product is handled properly for its intended use, in
accordance with its operating instructions and upon presentation of the original invoice or cash
receipt, indicating the date of purchase, dealer's name and model and production number of the
product.
The Philips guarantee may not apply if:
● the documents have been altered in any way or made illegible;
● the model or production number on the product has been altered, deleted, removed or made
illegible;
● repairs or product modifications and alterations have been executed by unauthorized service
organizations or persons;
● damage is caused by accidents including but not limited to lightning, water or fire, misuse or
neglect.
Please note that the product is not defective under this guarantee in the case where modifications
become necessary in order for the product to comply with local or national technical standards
which apply in countries for which the product was not originally designed and/or manufactured.
Therefore always check whether a product can be used in a specific country.
In case your Philips product is not working correctly or is defective, please contact your Philips
dealer. In the event you require service whilst in another country a dealer address can be given to
you by the Philips Consumer Help Desk in that country, the telephone and fax number of which can
be found in the relevant part of this booklet.
In order to avoid unnecessary inconvenience, we advise you to read the operating instructions
carefully before contacting your dealer. If you have questions which your dealer cannot answer or
any related question please contact the
Philips Consumer Information Centers or via:
Page 71

International Guarantee
Website: http://www.philips.com
Page 72

Philips F1rst Choice Warranty (USA / Canada)
Thank you for purchasing this Philips monitor.
All Philips monitors are designed and manufactured to high standards and
deliver high-quality performance, ease of use and ease of installation. Should
you encounter any difficulties while installing or using this product, please
contact Philips directly to benefit from your Philips F1rst Choice Warranty. This
three-year service warranty entitles you to a swap model on-site within 48
hours of your call being received within the first year of purchase. If you have
any problems with your monitor within the second or third year of purchase, we
will repair it after it has been sent to the service provider at your expense and
returned to you within five working days, free of charge.
LIMITED WARRANTY (Computer Monitor)
Click here to access the Warranty Registration Card
Three Years Free Labor / Three Years Free Service on Parts / One Year Exchange*
*Product will be exchanged with a new or renewed to original specifications unit within two
business days for the first year. This product must be shipped in at your expense for service during
years two and three.
WHO IS COVERED?
You must have proof of purchase to receive warranty service. A sales receipt or other document
showing that you purchased the product is considered proof of purchase. Attach it to this owner's
manual and keep both nearby.
WHAT IS COVERED?
Warranty coverage begins the day you buy your product. For three years thereafter, all parts will be
repaired or replaced, and labor is free. After three years from the day of purchase, you pay for the
replacement or repair of all parts, and for all labor charges.
All parts, including repaired and replaced parts, are covered only for the original warranty period.
Page 73

When the warranty on the original product expires, the warranty on all replaced and repaired
products and parts also expires.
WHAT IS EXCLUDED?
Your warranty does not cover:
● labor charges for installation or setup of the product, adjustment of customer controls on the
product, and installation or repair of antenna systems outside of the product.
● product repair and/or part replacement because of misuse, accident, unauthorized repair or
other cause not within the control of Philips Consumer Electronics.
● reception problems caused by signal conditions or cable or antenna systems outside the
unit.
● a product that requires modification or adaptation to enable it to operate in any country other
than the country for which it was designed, manufactured, approved and/or authorized, or
repair of products damaged by these modifications.
● incidental or consequential damages resulting from the product. (Some states do not allow
the exclusion of incidental or consequential damages, so the above exclusion may not apply
to you. This includes, but is not limited to, prerecorded material, whether copyrighted or not
copyrighted.)
● a product used for commercial or institutional purposes.
●
the model or production number on the product has been altered, deleted, removed or made
illegible.
Where IS SERVICE AVAILABLE?
Warranty service is available in all countries where the product is officially distributed by Philips
Consumer Electronics. In countries where Philips Consumer Electronics does not distribute the
product, the local Philips service organization will attempt to provide service (although there may be
a delay if the appropriate spare parts and technical manual(s) are not readily available).
Where CAN I GET MORE INFORMATION?
For more information, contact the Philips Customer Care Center by calling (877) 835-1838 (U.S.A.
customers only) or
(919) 573-7855.
Before Requesting Service...
Please check your owner's manual before requesting service. Adjustments of the controls
Page 74

discussed there may save you a service call.
TO GET WARRANTY SERVICE IN U.S.A., PUERTO RICO OR U.S. VIRGIN ISLANDS...
Contact the Philips Customer Care Center phone number listed below for product assistance and
procedures for servicing:
Philips Customer Care Center
(877) 835-1838 or
(919) 573-7855
(In U.S.A., Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands, all implied warranties, including implied warranties
of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, are limited in duration to the duration of this
express warranty. But, because some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied
warranty may last, this limitation may not apply to you.)
TO GET WARRANTY SERVICE IN CANADA...
Please contact Philips at:
(800) 479-6696
Three years free parts and three years free labor will be provided at Philips Canada depot or any
one of its authorized service centers.
(In Canada, this warranty is given in lieu of all other warranties. No other warranties are expressed
or implied, including any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
Philips is not liable under any circumstances for any direct, indirect, special, incidental or
consequential damages, howsoever incurred, even if notified of the possibility of such damages.)
REMEMBER... Please record the model and serial numbers found on the product below.
MODEL # ________________________________________________
SERIAL # ________________________________________________
Page 75

This warranty gives you specific legal rights. You may have other rights which vary from state/
province to state/province.
Before contacting Philips, please prepare the following details so we can solve your problem
quickly.
● Philips type number
● Philips serial number
● Purchase date (copy of purchase may be required)
● PC environment Processor:
❍ 286/386/486/Pentium Pro/Internal memory
❍ Operating system (Windows, DOS, OS/2, MAC)
❍ Fax/Modem/Internet program?
● Other cards installed
Having the following information available will also help speed up the process:
● Your proof of purchase indicating: date of purchase, dealer name, model and product serial
number.
● The full address to which the faulty monitor has to be collected and the swap model should
be delivered.
Just a phone call away
Philips' customer help desks are located worldwide. Within the U.S. you can contact Philips
customer care Monday-Friday from 8:00 AM-9:00 PM Eastern Time (ET) and on Saturdays from
10:00 AM-5:00 PM ET hrs by using one of the contact phone numbers.
For more information on this and more great Philips products visit our website at:
Website:
http://www.philips.com
Page 76

F1rst Choice Contact Information
Country Telephone number Tariff
Austria 0820 901115
0.20
Belgium 070 253 010
0.17
Cyprus 800 92256 Free of Charge
Denmark 3525 8761 Local call tariff
Finland 09 2290 1908 Local call tariff
France 08 9165 0006
0.23
Germany 0180 5 007 532
0.12
Greece 00800 3122 1223 Local call tariff
Ireland 01 601 1161 Local call tariff
Italy 199 404 042
0.25
Luxembourg 26 84 30 00 Local call tariff
The Netherlands 0900 0400 063
0.20
Norway 2270 8250 Local call tariff
Portugal 2 1359 1440 Local call tariff
Spain 902 888 785
0.15
Sweden 08 632 0016 Local call tariff
Switzerland 02 2310 2116 Local call tariff
United Kingdom 0207 949 0069 Local call tariff
Page 77

Consumer Information Centers
Antilles • Argentina • Australia • Bangladesh • Belarus • Brasil • Bulgaria • Canada • Chile •
China • Colombia • Croatia • Czech Republic • Dubai • Estonia • Hong Kong • Hungary •
India• Indonesia • Korea • Latvia • Lithuania • Malaysia • Mexico • Morocco • New Zealand
•
Pakistan • Paraguay • Peru • Philippines • Poland • Russia • Romania • Serbia&Montenegro
•
Singapore • Slovakia • Slovenia • South Africa • Taiwan • Thailand • Turkey • Uruguay •
Ukraine • Venezuela
Eastern Europe
BELARUS
Technical Centre of JV IBA
M. Bogdanovich str. 155
BY - 220040 Minsk
Tel: +375 17 217 33 86
BULGARIA
LAN Service
140, Mimi Balkanska Str.
Office center Translog
1540 Sofia, Bulgaria
tel: +359 2 960 2360
www.lan-service.bg
CZECH REPUBLIC
Xpectrum
Lužná 591/4
CZ - 160 00 Praha 6
Tel: 800 100 697
Email:info@xpectrum.cz
www.xpectrum.cz
Page 78

CROATIA
Renoprom d.o.o.
Mlinska 5, Strmec
HR - 41430 Samobor
+385 1 333 0974
ESTONIA
FUJITSU SERVICES OU
Akadeemia tee 21G
EE-12618 Tallinn
Tel: +372 6519900
www.ee.invia.fujitsu.com
HUNGARY
Serware Szerviz
Vizimolnár u. 2-4
HU - 1031 Budapest
Tel: +36 1 2426331
Email: inbox@serware.hu
www.serware.hu
LATVIA
ServiceNet LV
Jelgavas iela 36
LV-1055 Riga,
Tel: +371 7460399
Email: serviss@servicenet.lv
LITHUANIA
ServiceNet LT
Gaiziunu G. 3
LT – 3009 KAUNAS
Tel: +370 7400088
Email: servisas@servicenet.lt
www.servicenet.lt
Page 79

ROMANIA
Blue Ridge Int'l Computers SRL
115, Mihai Eminescu St., Sector 2
RO - 020074 Bucharest
Tel.:+40 21 2101969
SERBIA&MONTENEGRO
Tehnicom Service d.o.o.
Bulevar Vojvode Misica 37B
YU – 11000 Belgrade
Tel: +381 11 3060 886
SLOVAKIA
Datalan Servisne Stredisko
Puchovska 8
SK - 831 06 Bratislava
Tel: +421 2 49207155
Email: servis@datalan.sk
SLOVENIA
PC HAND
Brezovce 10
SI - 1236 Trzin
Tel: +386 1 530 08 24
Email: servis@pchand.si
POLAND
Zolter
ul.Zytnia 1
PL - 05-500 Piaseczno
Tel:+48 22 7501766
Email: servmonitor@zolter.com.pl
www.zolter.com.pl
Page 80

RUSSIA
Tel: +7 095 961-1111
Tel: 8-800-200-0880
Web-site: www.philips.ru
TURKEY
Türk Philips Ticaret A.S.
Yukari Dudullu Org.San.Bolgesi
2.Cadde No:22
34776-Umraniye/Istanbul
Tel: (0800)-261 33 02
UKRAINE
Comel
Shevchenko street 32
UA - 49030 Dnepropetrovsk
Tel: +380 562320045
www.csp-comel.com
Latin America
ANTILLES
Philips Antillana N.V.Kaminda A.J.E. Kusters 4
Zeelandia, P.O. box 3523-3051
Willemstad, Curacao
Phone: (09)-4612799
Fax : (09)-4612772
ARGENTINA
Vedia 3892 Capital Federal
CP:1430 Buenos Aires
Phone/Fax: (011)-4544 2047
Page 81

BRASIL
Philips da Amazonia Ind. Elet.Ltda.
Rua Verbo Divino, 1400 -Sao Paulo-SP CEP-04719-002
Phone: 11 2121 0203
-São Paulo & 0800-701-0203 - Other Regions without São Paulo City.
CHILE
Philips Chilena S.A.
Avenida Santa Maria 0760
P.O. box 2687Santiago de Chile
Phone: (02)-730 2000
Fax : (02)-777 6730
COLOMBIA
Industrias Philips de Colombia
S.A.-Division de Servicio
CARRERA 15 Nr. 104-33
Bogota, Colombia
Phone: (01)-8000-111001 (toll free)
Fax : (01)-619-4300/619-4104
MEXICO
Consumer Information Centre
Norte 45 No.669
Col. Industrial Vallejo
C.P.02300, -Mexico, D.F.
Phone: (05)-3687788 / 9180050462
Fax : (05)-7284272
PARAGUAY
Av. Rca. Argentina 1780c/ Alfredo Seiferheld
P.O. BOX 605
Phone: (595 21)-664 333
Fax : (595 21)-664 336
Customer Desk:
Phone: 009 800 54 1 0004
Page 82

PERU
Philips Peruana S.A.
Customer Desk
Comandante Espinar 719
Casilla 1841
Limab18
Phone: (01)-2136200
Fax : (01)-2136276
URUGUAY
Rambla O'Higgins 5303 Montevideo
Uruguay
Phone: (598)-619 66 66
Fax : (598)-619 77 77
Customer Desk:
Phone: 0004054176
VENEZUELA
Industrias Venezolanas Philips S.A.
Apartado Postal 1167
Caracas 1010-A
Phone: (02) 2377575
Fax : (02) 2376420
Canada
CANADA
Philips Electronics Ltd.
281 Hillmount Road Markham Ontario,
L6C 2S3
Phone: 800- 479-6696
Fax:905-887-3974
Pacific
Page 83

AUSTRALIA
Philips Consumer Electronics
Customer Care Centre.
Level 1, 65 Epping Rd
North Ryde NSW 2113
Phone: 1300 363 391
Fax:+61 2 9947 0063
NEW ZEALAND
Philips New Zealand Ltd.
Consumer Help Desk
2 Wagener Place, Mt.Albert
P.O. box 1041
Auckland
Phone: 0800 477 999 (Toll Free)
Fax:0800 288 588
Asia
BANGLADESH
Philips Service Centre
100 Kazi Nazrul Islam
Avenue Kawran Bazar C/A
Dhaka-1215
Phone: (02)-812909
Fax : (02)-813062
CHINA
SHANHAI
Rm 1007, Hongyun Building, No. 501 Wuning road,
200063 Shanghai
P.R. China
Phone: 4008 800 008
Fax:21-52710058
Page 84

HONG KONG
Philips Electronics Hong Kong Limited
Consumer Service
Unit A, 10/F. Park Sun Building
103-107 Wo Yi Hop Road
Kwai Chung, N.T.
Hong Kong
Phone: (852) 2619-9663
Fax: (852) 2481 5847
INDIA
Phone: (020)-712 2048 ext 2765
Fax:(020)-712 1558
BOMBAY
Philips India
Customer Relation Centre
Bandbox House
254-D Dr. A Besant Road, Worli
Bombay 400 025
CALCUTTA
Customer Relation Centre
7 justice Chandra Madhab Road
Calcutta 700 020
MADRAS
Customer Relation Centre
3, Haddows Road
Madras 600 006
NEW DELHI
Customer Relation Centre
68, Shivaji Marg
New Dehli 110 015
Page 85

INDONESIA
Philips Group of Companies in Indonesia
Consumer Information Centre
Jl.Buncit Raya Kav. 99-100
12510 Jakarta
Phone: (021)-7940040 Ext 2100
Fax : (021)-7947511 / 7947539
KOREA
Philips Korea Ltd.
Philips House
C.P.O. box 3680
260-199, Itaewon-Dong.
Yongsan-Ku, Seoul 140-202
Phone: 080 600 6600 (Toll Free)
Fax:(02)709 1245
MALAYSIA
After Market Solutions Sdn Bhd,
Philips Authorised Service Center,
Lot 6, Jalan 225, Section 51A,
46100 Petaling Jaya,
Selangor Darul Ehsan,
Malaysia
Phone: (603)-7954 9619/ 7956 3695
Fax:(03)-7954 8504
Customer Careline: 1800-880-180
Page 86

PAKISTAN
Philips Consumer Information Centre
Mbuarak manzil,
39, Garden Road, Saddar,
Karachi-74400
Phone: (9221)-2737 411-16
Fax:(9221)-2721 167
E-Mail:care@philips.com
Web-site:www.philips.com.pk
PHILIPPINES
Philips Electronics&Lighting, Inc.
Consumer Electronics
48F PBCOM Tower
6795 Ayala Avenue cor VA Rufino St.
Salcedo Village
1227 Makati City, PHILS
Phone: (02)-888 0572 , Domestic Toll Free:1-800-10-PHILIPS or 1-800-10-744 5477
Fax:(02)-888 0571
SINGAPORE
Accord Customer Care Solutions Ltd
Authorized Philips Service Center
Consumer Service
620A Lorong 1 Toa Payoh
Singapore 319762
Phone:+65 6882 3999
Fax:+65 6250 8037
TAIWAN
Philips Taiwan Ltd.
Consumer Information Centre
13F, No. 3-1 Yuan Qu St., Nan Gang Dist.,
Taipei, 115, Taiwan
Phone: 0800-231-099
Fax:(02)-3789 2641
Page 87

THAILAND
Philips Electronics Thailand Ltd.
26-28th floor, Thai Summit Tower
1768 New Petchburi Road
Khwaeng Bangkapi, Khet Huaykhwang
Bangkok 10320 Thailand
Phone : (66) 2-652 8652
email:cic Thai@philips.com
Africa
MOROCCO
Philips Electronique Maroc
304,BD Mohamed V
Casablanca
Phone: (02)-302992
Fax : (02)-303446
SOUTH AFRICA
PHILIPS SA (PTY) LTD
Customer Care Centre
195 Main Road
Martindale, Johannesburg
P.O. box 58088
Newville 2114
Phone: +27 (0)11-471 5194
Fax : +27 (0)11-471 5123
Middle East
DUBAI
Philips Middle East B.V.
Consumer Information Centre
P.O.Box 7785
DUBAI
Phone: (04)-3353666
Fax : (04)-3353999
Page 88

It Takes Only A Moment To
PROTECT YOUR INVESTMENT.
Congratulations on investing in a Philips product. It’s an important and intelligent decision that’s sure to reward you
for many years to come. To ensure you’ll get all of the privileges and protection that come with your purchase,
please complete your Warranty Registration Card within the next ten days.
SIMPLY MAIL THE CARD BELOW TO RECEIVE ALL
OF THESE BENEFITS TO WHICH YOU’RE ENTITLED.
WARRANTY VERIFICATION
Your prompt registration verifies your right to protection
under the terms and conditions of your warranty.
OWNER CONFIRMATION
Your completed Warranty Registration Card serves as confirmation
of ownership in the event of product loss or theft.
MODEL REGISTRATION
Returning the attached card right away guarantees you’ll receive
all information and special offers for which your purchase makes you eligible. So please act today!
www.philipsusa.com
DETACH AND MAIL PORTION BELOW.
3135 015 07803 rev. 7/02
Mail This Card Today To Get The Most From Your Purchase!
❏
No, I do not want to receive personalized offers about Philips products or other information from Philips in the future.
Registering your product is an essential step to ensure that you receive all of the benefits you are entitled to as a
Philips customer. So complete the information below in ink, and drop this card in the nearest mailbox.
WARRANTY
REGISTRATION CARD
IMPORTANT - RETURN WITHIN TEN DAYS
Month
Day Year
Page 89

RETURN THE ATTACHED CARD WITHIN
TEN DAYS TO ENSURE YOUR:
✓ Warranty Verification
✓ Owner Confirmation
✓ Model Registration
See Inside For
Valuable
Benefits!
Warranty
Registration Card
PO BOX 1533
DEPOSIT NY 13754-1533
PLEASE
APPLY FIRST
CLASS
STAMP
TIME-DATED
MATERIAL
Please Open
Promptly!
a
!1375415338!
IMPORTANT
 Loading...
Loading...