Page 1
MANUAL
IC-KP-B5-V23
IDENTControl interface
with Interbus interface
FACTORY AUTOMATION
Page 2

IC-KP-B5-V23
With regard to the supply of products, the current issue of the following document is applicable: The
General Terms of Delivery for Products and Services of the Electrical Industry, published by the
Central Association of the Electrical Industry (Zentralverband Elektrotechnik und Elektroindustrie
(ZVEI) e.V.) in its most recent version as well as the supplementary clause: "Expanded reservation
of proprietorship"
Page 3

IC-KP-B5-V23
Contents
1 Introduction......................................................................... 5
2 Declaration of conformity.................................................. 6
2.1 Declaration of conformity ..............................................................................6
3 Safety................................................................................... 7
3.1 Symbols relevant to safety ............................................................................7
3.2 Intended use.................................................................................................7
3.3 General notes on safety.................................................................................7
3.4 Contact protection.........................................................................................8
4 Product Description ........................................................... 9
4.1 Range of application .....................................................................................9
4.2 Device characteristics ...................................................................................9
4.3 Product family...............................................................................................9
4.3.1 R/W heads ...............................................................................................9
4.3.2 Code / data carrier....................................................................................9
4.3.3 Handhelds..............................................................................................10
4.4 Displays and controls..................................................................................11
4.5 Interfaces and connections.........................................................................12
4.6 Delivery package ........................................................................................12
4.7 Connection accessories..............................................................................13
4.7.1 Connection cable for R/W heads and trigger sensors ............................13
4.7.2 Cable connectors for the power supply ..................................................13
5 Installation......................................................................... 14
5.1 Storage and transport .................................................................................14
5.2 Unpacking...................................................................................................14
5.3 EMC concept..............................................................................................14
5.4 Device connection ......................................................................................15
5.4.1 Power supply..........................................................................................15
5.4.2 R/W head and trigger sensors................................................................15
5.4.3 Cable length between control interface and R/W heads .........................16
5.4.4 Ground connection.................................................................................16
5.4.5 INTERBUS connection guide .................................................................17
5.4.6 Cables....................................................................................................18
5.4.7 Cable lengths .........................................................................................18
5.4.8 INTERBUS ring termination....................................................................18
2011-05
3
Page 4

IC-KP-B5-V23
Contents
6 Commissioning ................................................................ 19
6.1 Connection................................................................................................. 19
6.2 Preliminary considerations......................................................................... 19
6.3 Device settings........................................................................................... 20
6.3.1 Operating the device.............................................................................. 21
6.4 Output of the contents of read data carriers on the display......................... 21
6.4.1 Setting the transfer rate.......................................................................... 22
6.4.2 Setting the data hold time ...................................................................... 22
7 Commands........................................................................ 23
7.1 General information on INTERBUS............................................................. 23
7.1.1 Outline of the commands and data on the INTERBUS........................... 23
7.2 General command information ................................................................... 23
7.2.1 Software information .............................................................................. 23
7.3 Command types......................................................................................... 25
7.4 Command overview ................................................................................... 25
7.5 System commands..................................................................................... 28
7.6 Standard read/write commands.................................................................. 39
7.7 Special commands..................................................................................... 45
7.8 Legend....................................................................................................... 71
7.9 Fault/Status messages ............................................................................... 72
8 Technical specifications.................................................. 74
8.1 Dimensions................................................................................................ 74
8.2 General data............................................................................................... 74
9 Troubleshooting ............................................................... 76
9.1 Fault location .............................................................................................. 76
10 ASCII table ........................................................................ 77
4
2011-05
Page 5

IC-KP-B5-V23
Introduction
1 Introduction
Congratulations
You have chosen a device manufactured by Pepperl+Fuchs. Pepperl+Fuchs
develops, produces and distributes electronic sensors and interface modules for
the market of automation technology on a worldwide scale.
Before installing this equipment and put into operation, read this manual carefully.
This manual containes instructions and notes to help you through the installation
and commissioning step by step. This makes sure bring such a trouble-free use of
this product. This is for your benefit, since this:
■ ensures the safe operation of the device
■ helps you to exploit the full functionality of the device
■ avoids errors and related malfunctions
■ avoids costs by disruptions and any repairs
■ increases the effectiveness and efficiency of your plant
Keep this manual at hand for subsequent operations on the device.
After opening the packaging please check the integrity of the device and the
number of pieces of supplied.
Symbols used
The following symbols are used in this manual:
Note!
This symbol draws your attention to important information.
2011-05
Handling instructions
You will find handling instructions beside this symb
Contact
If you have any questions about the device, its functions, or accessories, please
contact us at:
Pepperl+Fuchs GmbH
Lilienthalstraße 200
68307 Mannheim
Telephone: +49 621 776-4411
Fax: +49 621 776-274411
E-Mail: fa-info@pepperl-fuchs.com
ol
5
Page 6

IC-KP-B5-V23
ISO9001
Declaration of conformity
2 Declaration of conformity
2.1 Declaration of conformity
This product was developed and manufactured under observance of the
applicable European standards and guidelines.
Note!
A Declaration of Conformity can be requested from the manufacturer.
The product manufacturer, Pepperl+Fuchs GmbH, D-68307 Mannheim, has a
certified quality assurance system that conforms to ISO 9001.
6
2011-05
Page 7
IC-KP-B5-V23
Safety
3 Safety
3.1 Symbols relevant to safety
Danger!
This symbol indicates a warning about a possible danger.
In case of ignoring the consequences may range from personal injury to death.
Warning!
This symbol indicates a warning about a possible fault or danger.
In case of ignoring the consequences may cause personal injury or heaviest
property damage.
Caution!
This symbol warns of a possible fault.
In case of ignoring the devices and any connected facilities or systems may be
interrupted or fail completely.
3.2 Intended use
The IDENTControl IC-KP-B5-V23 is a control interface
interface for identification systems. The device can be used as a control cabinet
module or for field applications. Besides the INTERBUS connection, suitable
inductive R/W heads, microwave antennas or trigger sensors can be connected.
Wiring suitable for the system design must be used.
3.3 General notes on safety
Only instructed specialist staff may operate the device in accordance with the
operating manual.
User modification and or repair are dangerous and will void the warranty and
exclude the manufacturer from any liability. If serious faults occur, stop using the
device. Secure the device against inadvertent operation. In the event of repairs,
return the device to your local Pepperl+Fuchs representative or sales office.
The connection of the device and maintenance work when live may only be
carried out by a qualified electrical specialist.
The operating company bears responsibility for observing locally applicable
safety regulations.
Store the not used device in the original packaging. This offers the device optimal
protection against impact and moisture.
Ensure that the ambient conditions comply with regulations.
including an INTERBUS
2011-05
7
Page 8
IC-KP-B5-V23
Read head IDENTControl
Safety
Note!
Disposal
Electronic waste is hazardous waste. When disposing of the equipment, observe
the current statutory requirements in the respective country of use, as well as local
regulations.
3.4 Contact protection
Our housings are manufactured using components made partly or completely
from metal to improve noise immunity.
Danger!
Electric shock
The metallic housing components are connected to ground to protect against
dangerous voltages that may occur in the event of a fault in the SELV power
supply!
See chapter 5.4.4
8
2011-05
Page 9

IC-KP-B5-V23
Product Description
4 Product Description
4.1 Range of application
The system is suited for the following applications:
■ Automation
■ Material flow control in production
■ Acquisition of operating data
■ Access control
■ Identification of storage vessels, pallets, work piece carriers, refuse
containers, tanks, containers, etc.
4.2 Device characteristics
■ Up to 4 R/W heads can be connected
■ Alternatively up to 2 R/W heads and 2 trigger sensors can be connected
■ LCD indicator with background illumination
■ Direct operation using 4 function keys
■ LED status indicator for bus communication and R/W heads
4.3 Product family
The IDENTControl brand name represents a complete identification system. The
system consists of an IDENTControl interface including bus interface, inductive
R/W heads (125 kHz and 13.56 MHz) and accompanying code and data carriers
in many different designs. The IDENTControl can be connected to other
identification systems.
The system is equally well suited for use in the switching cabinet and for field use
in IP67. The interface to the controlling fieldbus is integrated into the enclosure
and all connections are implemented as plugs. This enables simple installation
and quick, correct replacement in case of device failure. The consistent EMC
design (metal enclosure, grounding, shielded wires) offers a high degree of noise
immunity. Function buttons are available for parameterization and entering
commands directly into the IDENTControl.
4.3.1 R/W heads
There are different R/W heads available for the IDENTControl in different designs.
You can connect inductive R/W heads (125 kHz and 13.56 MHz) depending on
your particular application.
4.3.2 Code / data carrier
Code / data carrier 125 kHz (inductive)
A wide range of code and data carrier designs are available for this frequency
range, from a 3 mm thin glass tube to a transponder 100 mm in diameter. Data
carriers are available for temperatures up to 300 °C (max. 5 min) in chemical-
esistant housings for installation in metal and in degree of protection IP68/IP69K.
r
IPC02-... code carriers offer 40-bit read only codes. IPC03-... data carriers have
2011-05
9
Page 10

IC-KP-B5-V23
Product Description
928 bits of programmable memory and a non-variable read only code of 32 bits.
With IPC11-... code carriers, you can generate individually definable 40-bit read
only codes, which you can use as permanent read only codes or continually
redefine. The IPC12 data carrier with 64 kBit FRAM memory and a 32 bit read
only code is available for larger volumes of data.
Data carrier 13.56 MHz (inductive)
Data carriers in this frequency range can store large quantities of data and offer a
reading speed superior to that of data carriers from the 125 kHz system. A larger
antenna also achieves a sensing range of up to 300 mm. The R/W heads IQH-*
and IQH1-* from Pepperl+Fuchs are compatible with most existing data carriers
that comply with standard ISO 15693. With the R/W heads IQH2-* you can use
data carriers complying with standard ISO 14443.
The 13.56 MHz technology even allows so-called smart labels (data carriers in
the form of adhesive labels with printed barcode). Currently available data carriers
have a memory capacity of 64 bits of read only code and a maximum of 2 kByte of
programmable memory.
4.3.3 Handhelds
There are various handheld read/write devices availa
(write/read functions, initialization of data carriers).
ble for controlling processes
10
Figure 4.1
Handheld Frequency range
IPT-HH20 125 kHz
IST-HH20 250 kHz
IQT1-HH20 13.56 MHz
IC-HH20-V1 depending on the read/write head
2011-05
Page 11
IC-KP-B5-V23
INTERBUS
CH1
PWR/
ERR
CH2 CH3 CH4
IC-KP-B5-V23
UL
RC
RD
BA
Control
ESC
ESC
Product Description
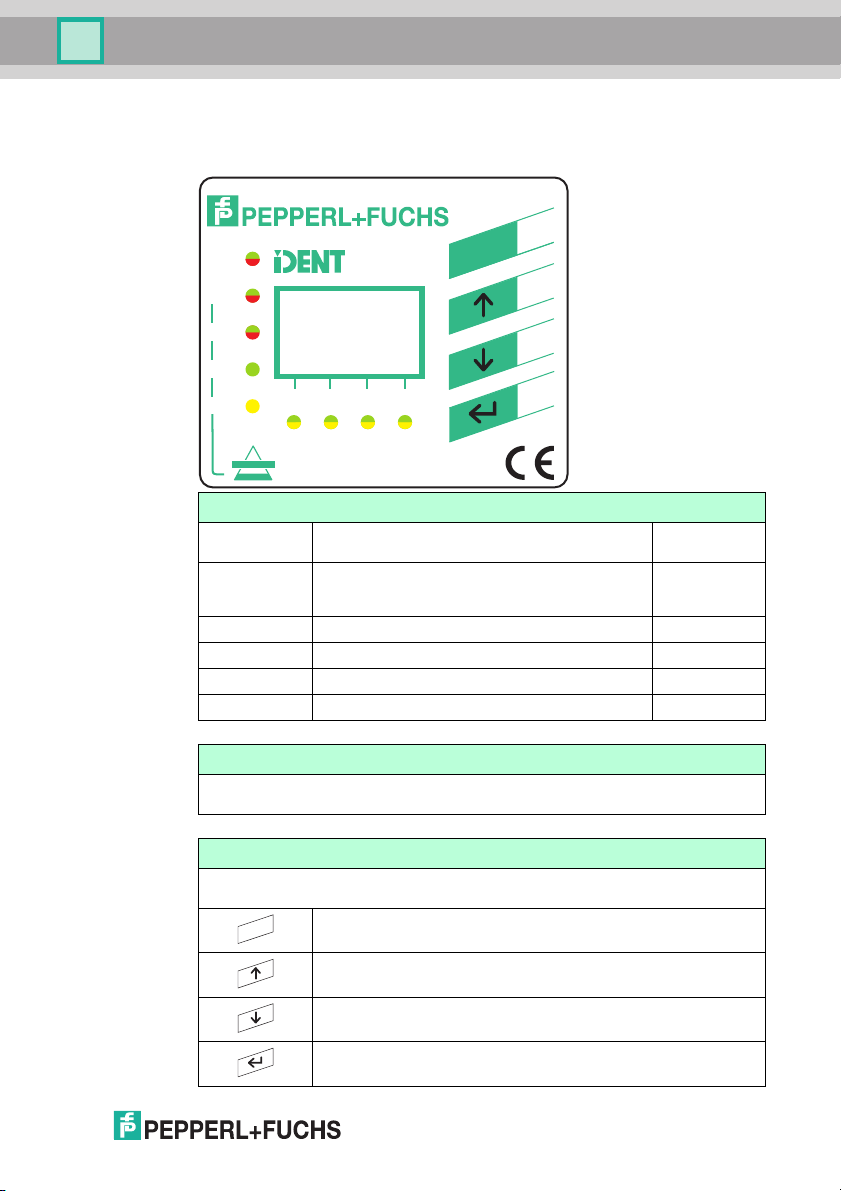
4.4 Displays and controls
The following displays and controls are located on the control interface.
LED indicators
PWR/ERR Power on
1, 2, 3, 4 Status display for R/W heads
UL Interface ready for operation green
RC Incoming remote bus connected correctly. green
BA Telegrams are transmitted. green
RD Intermediate remote bus is deactivated. Yellow
Hardware error
Command on R/W head is active
Command executed successfully (approx. 1 second)
green
red
green
yellow
2011-05
Display
Two-line multifunction display with 12 characters per line for displaying different status and
operating information and four pictograms for displaying connected reading heads.
Push buttons
Push buttons are used for controlling the display and selecting commands when
programming the control interface.
Return to higher level
Up menu item
Down menu item
RETURN (confirm input)
11
Page 12
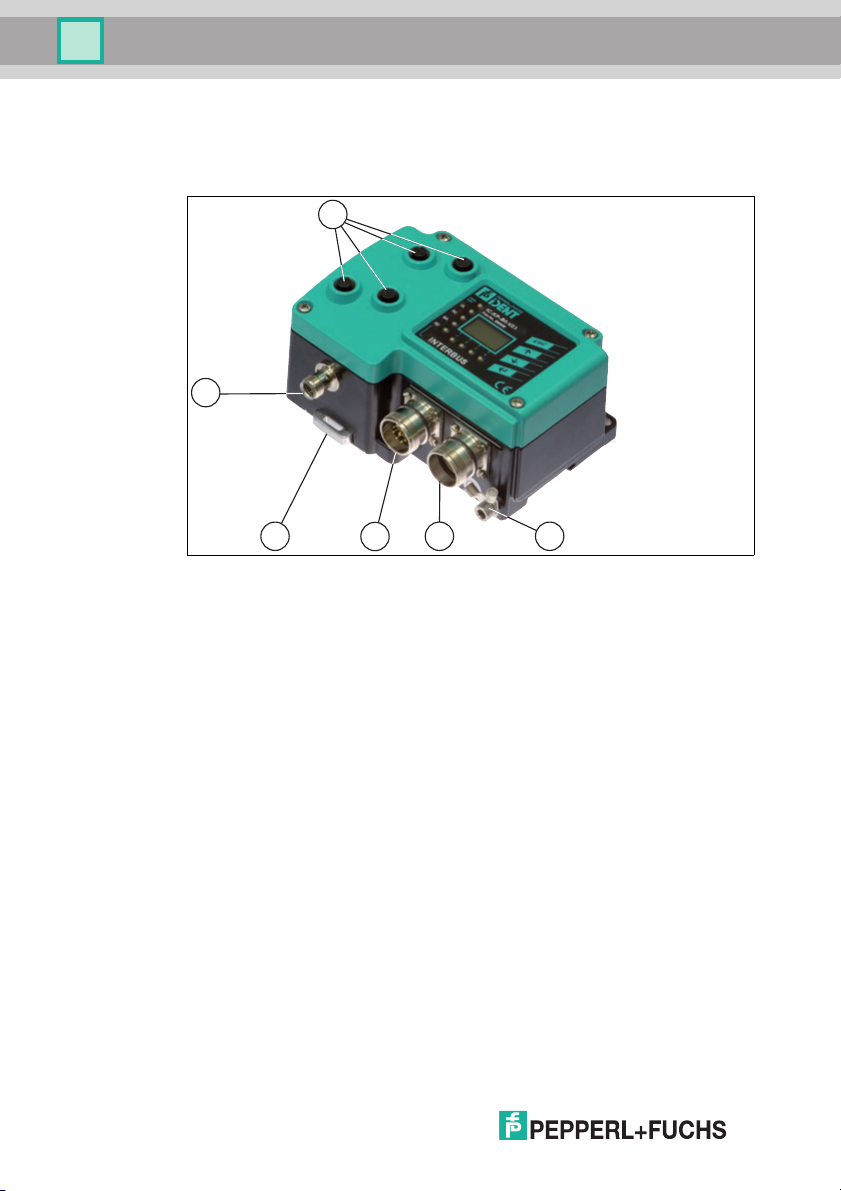
IC-KP-B5-V23
B A
1
2
3
4
Product Description
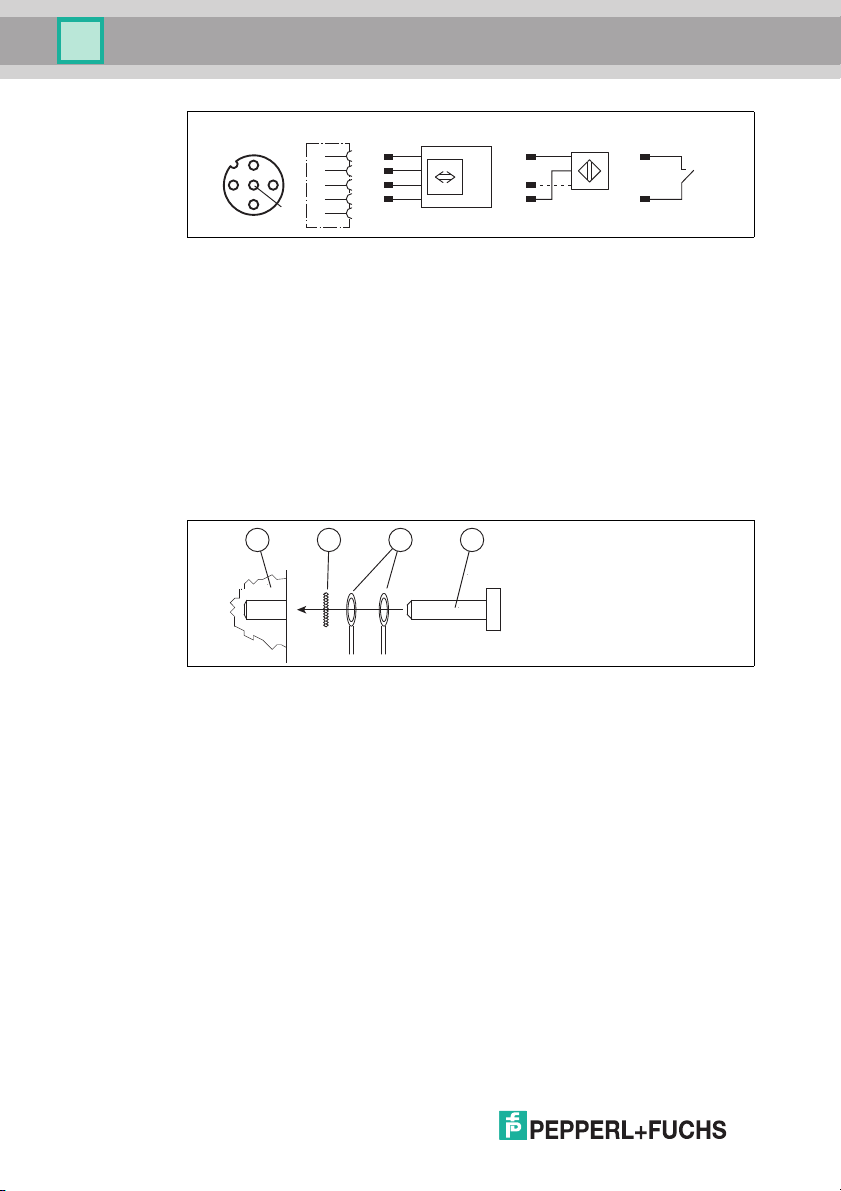
4.5 Interfaces and connections
The following interfaces and connections are located on the control interface ICKP-B5-V23.
Connections
12 connector for R/W heads (sockets) - V1
1 M
2 9-pin M23 round plug connector, outgoing bus interface - M23
3 9-pin M23 round plug connector, incoming bus interface - M23
4 M12 connector for power supply (plug) - V1
Other accessories
A Screw for ground
B Metal latches for mounting the DIN rail
Accessories
Accessories see chapter 4.7.
4.6 Delivery package
The delivery package contains:
■ 1 IDENTControl control interface
■ 1 quick start guide
■ 1 grounding screw (already fitted)
■ 1 serrated lock washer (already fitted)
■ 2 crimp connectors (already fitted)
2011-05
12
Page 13
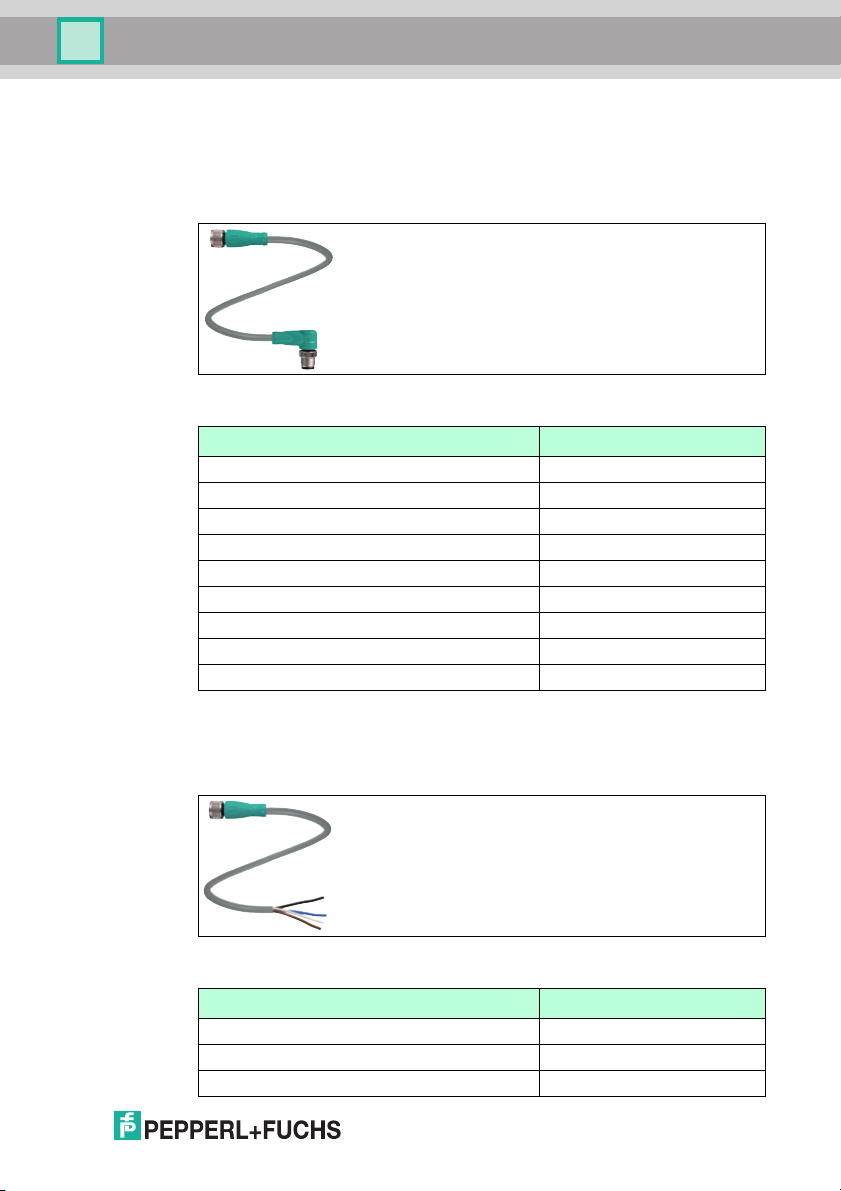
IC-KP-B5-V23
Product Description
4.7 Connection accessories
4.7.1 Connection cable for R/W heads and trigger sensors
Compatible connection cables with shielding are available for connecting the R/W
heads and trigger sensors.
Figure 4.2
Accessories Description
2 m long (straight female, angled male) V1-G-2M-PUR-ABG-V1-W
5 m long (straight female, angled male) V1-G-5M-PUR-ABG-V1-W
10 m long (straight female, angled male) V1-G-10M-PUR-ABG-V1-W
20 m long (straight female, angled male) V1-G-20M-PUR-ABG-V1-W
Field attachable female connector, straight, shielded V1-G-ABG-PG9
Field attachable male connector, straight, shielded V1S-G-ABG-PG9
Field attachable female connector, angled, shielded V1-W-ABG-PG9
Field attachable male connector, angled, shielded V1S-W-ABG-PG9
Dummy plug M12x1 VAZ-V1-B
4.7.2 Cable connectors for the power supply
Compatible M12 sockets with an open cable end for con
IDENTControl to a power supply are available in different lengths.
Figure 4.3
Accessories Designation
Length 2 m (straight socket) V1-G-2M-PUR
Length 5 m (straight socket) V1-G-5M-PUR
2011-05
Length 10 m (straight socket) V1-G-10M-PUR
necting the
13
Page 14
IC-KP-B5-V23
write head ControlIDENT Control
INTERBUS
Installation
5 Installation
5.1 Storage and transport
For storage and transport purposes, package the unit using shockproof
packaging material and protect it against moisture. The best method of protection
is to package the unit using the original packaging. Furthermore, ensure that the
ambient conditions are within allowable range.
5.2 Unpacking
Check the product for damage while unpacking. In the event of damage to the
product, inform the post office or parcel service and notify the supplier.
Check the package contents with your purchase order and the shipping
documents for:
■ Delivery quantity
■ Device type and version in accordance with the type plate
■ Accessories
■ Quick start guide
Retain the original packaging in case you have to store or ship the device again at
a later date.
Should you have any questions, please contact Pepperl+Fuchs.
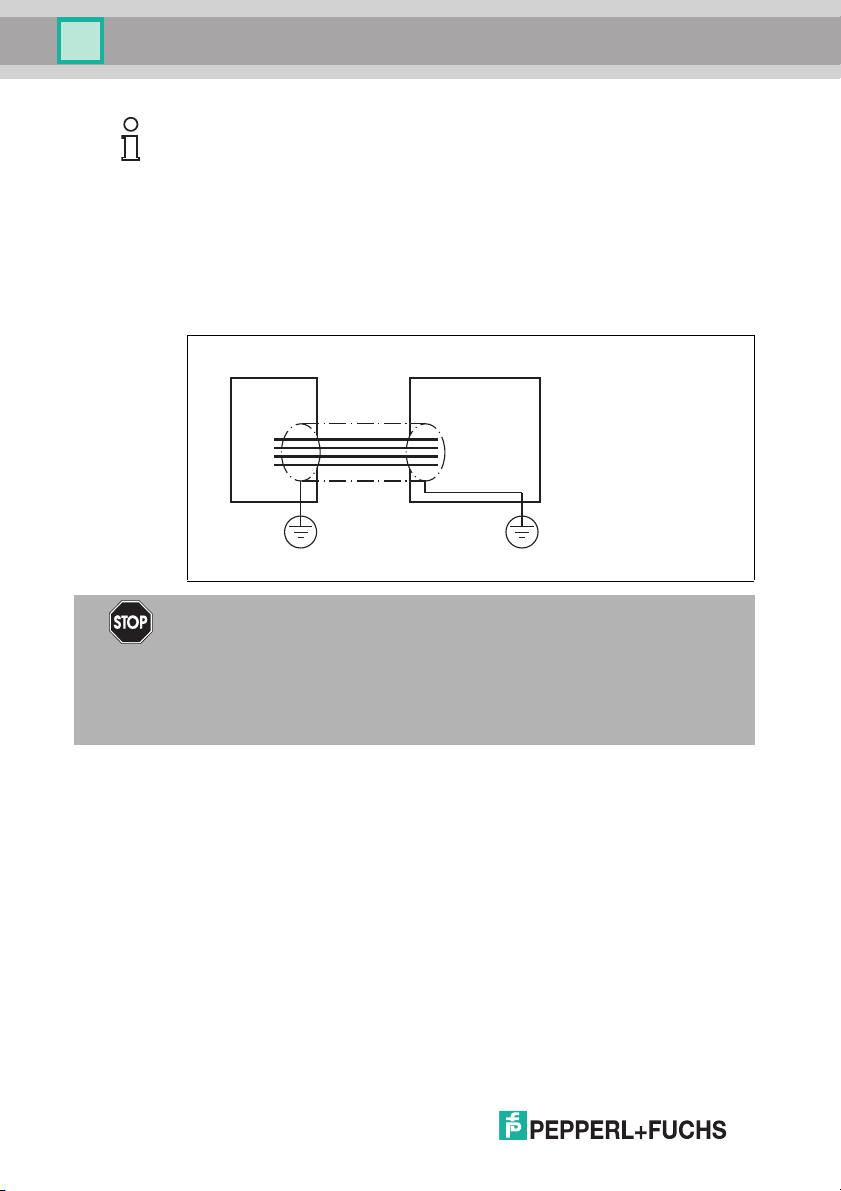
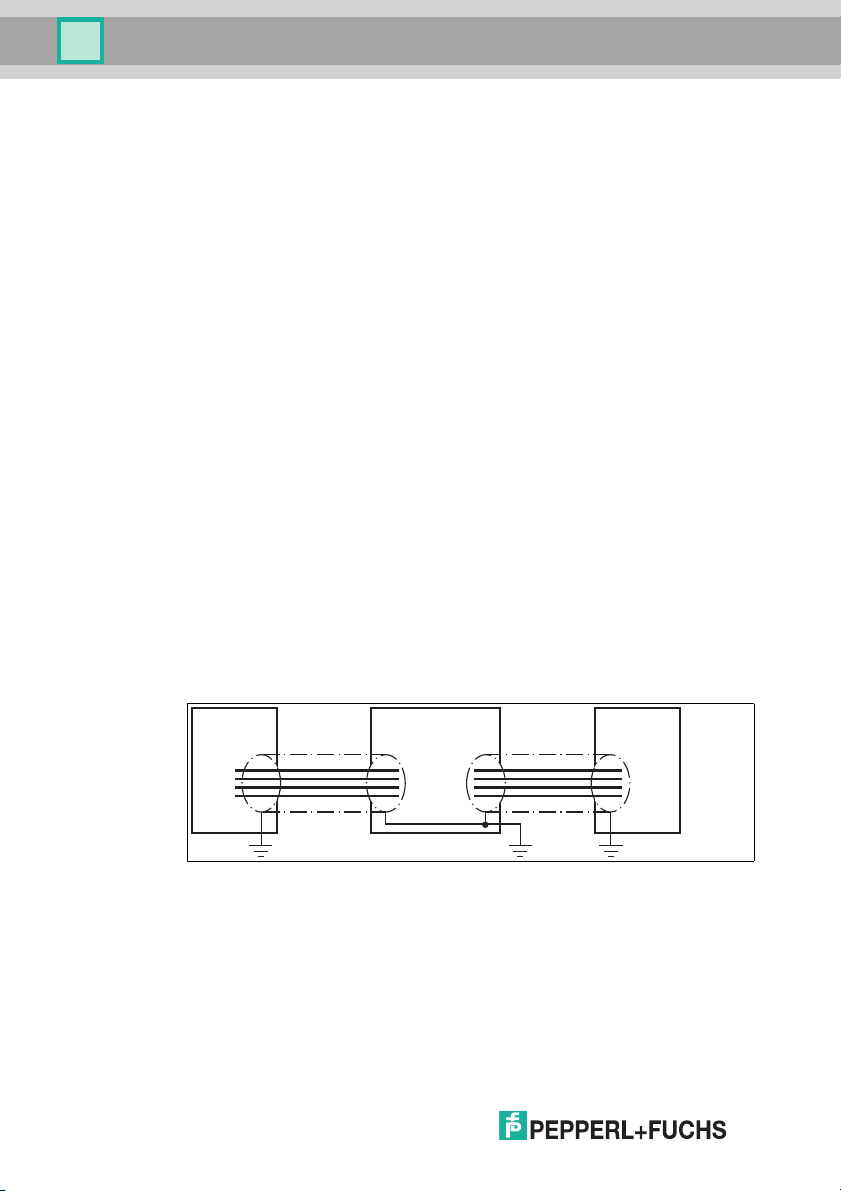
5.3 EMC concept
The outstanding noise immunity of the IDENTControl against emission and
immission is based on its consistent shielding design, which uses the principle of
the Faraday cage. Interference is caught in the shield and safely diverted via the
ground connections.
The screening of cables provides for the discharge of electromagnetic
interference. When screening a cable, both sides of the screen must be
connected to the earth with low resistance and low inductance.
14
2011-05
Page 15
IC-KP-B5-V23
4
1 3
2
Installation
Note!
If cables with double shields are used, e.g. wire mesh and metalized foil, the both
shields must be connected together, with low resistance, at the ends when
making up the cable.
Power supply cables are the source of much interference, e.g. from the supply
lines of 3-phase electric motors. For this reason, the parallel laying of power
supply cables with data and signal cables should be avoided, particularly in the
same cable duct.
The metal enclosure of the IDENTControl and the metal enclosure of the R/W
heads complete the consistent shielding concept.
The most important issue here is that the shields are connected to ground with
low resistance and low inductance. The metal enclosure ensures that the
shielding is not interrupted, i.e. the complete electronics system and all routed
cables are located within a Faraday cage.
5.4 Device connection
Electrical connection using plug connectors makes in
5.4.1 Power supply
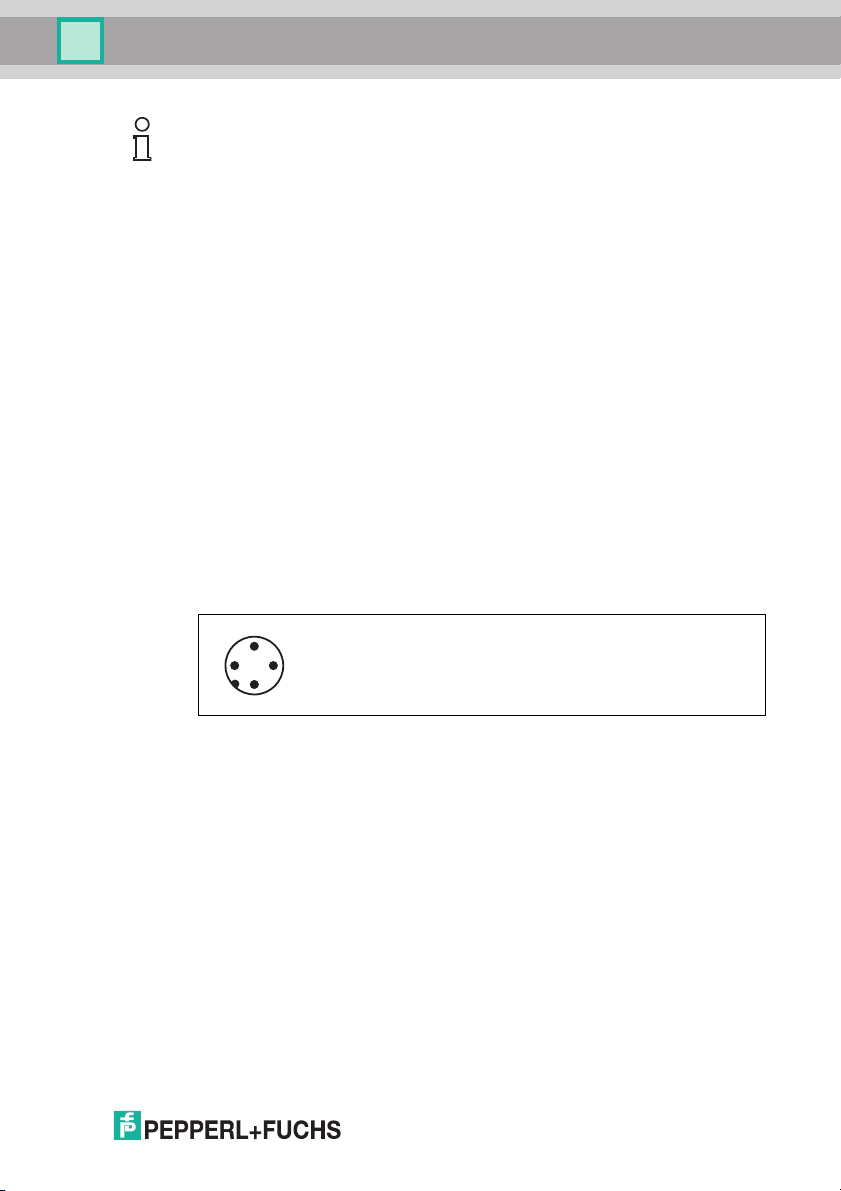
Connect the power supply via an M12 connector with integrated voltage and
reverse polarity protection indicator (green: correct polarity, red: reverse polarity).
A plug with the following pin assignment is located on the housing:
stallation simple.
2011-05
1 + 24 V
2 NC
3 GND
4 NC
Compatible connecting cable see chapter 4.7.2.
5.4.2 R/W head and trigger sensors
You can connect a maximum of four R/W heads to the IDENTControl.
You can connect a maximum of two trigger sensors to sockets 3 and 4 instead of
the R/W heads. A trigger sensor can only be assigned to a R/W head. The trigger
sensors must be PNP.
The R/W heads and trigger sensors are connected to the top of the enclosure via
M12 connectors with sockets.
15
Page 16
IC-KP-B5-V23
trigger switch
trigger sensor
read/write head
signal
socket at housing
2
1 3
4
5
+
A
-
+
-
B
1
2
3
4
5
1 2 43
Installation
Compatible R/W heads see chapter 4.3.1 and compatible connecting cables see
chapter 4.7.1.
5.4.3 Cable length between control interface and R/W heads
The maximum cable length between the control interface and a connected R/W
head is 1000 meters. If you wish to attain the maximum possible cable length,
select a suitably large cable cross-section. see chapter 4.7.1
5.4.4 Ground connection
The ground connection of the IDENTControl is located at the lower right of the
connector array. The ground conductor is screwed to the housing with a crimp
connector. In order to guarantee safe grounding, the serrated washer must be
mounted between the crimp connector and the housing.
16
1 Housing
2 Serrated lock washer
3 Crimp connector
4 Lock screw
A cross-section of at least 4 mm
2
is recommended for the ground conductor lead.
2011-05
Page 17
IC-KP-B5-V23
1
2
3
4
8
5
7
6
9
8
7
6
5
1
4
2
3
9
Installation
5.4.5 INTERBUS connection guide
Round connector: Connector - incoming interface
1 DO1
2 /DO1
3 DI1
4 /DI1
5 GND
6 NC
7 NC
8 NC
9 NC
Round connector: Socket - outgoing interface
O2
1 D
2 /DO2
3 DI2
4 /DI2
5 GND
6 NC
7 NC
8 NC
9 /RBST
2011-05
17
Page 18
IC-KP-B5-V23
Installation
5.4.6 Cables
The following INTERBUS remote bus cables should be used:
Parameter Standard Highly flexible
Cable construction Twisted pairs/i.e. 2-core, common screening
Conductor crosssection
Operating capacity 60pF/m
Impedance 120 W at 64 KHz/100 W at 1 MHz
3 x 2 x 0.22 mm
Use only screened cables constructed as twisted pairs. The best possible EMC
interference immunity can only be achieved by using screened cables.
5.4.7 Cable lengths
Depending on the type of cable used and the magnitud
interference, the distance between two devices can be up to 400 meters. The total
expansion of an INTERBUS system can be up to 12.8 kilometers. The number of
devices connected to the bus is limited to 512.
5.4.8 INTERBUS ring termination
A characteristic of the INTERBUS system is its physical ring structure. Each
connected device lies in the bus between two other stations. If this is not the case,
for example, at the end of a branch with a bus terminal, then the ring line must be
closed.
The ring line on the IDENTControl is automatically closed. If the network of the
remote bus is extended at the outgoing socket using a suitable cable, the ring line
is opened automatically for the following devices.
2
3 x 2 x 0.25 mm
Suitable for laying
underground
2
3 x 2 x 0.22 mm
e of the external
2
18
2011-05
Page 19

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commissioning
6 Commissioning
6.1 Connection
Warning!
Before commissioning, check once again that the connections are correct.
Before commissioning, familiarize yourself with the system of communication
between your interface module and the read/write station (see chapter 7).
Commissioning requires accurate knowledge of INTERBUS and the programming
of your master device.
After the supply voltage is connected, the green LED in the voltage connector and
the PWR and UL LEDs on the display panel must light up. If the LED in the
connector lights up red, the polarity of the power supply is reversed.
6.2 Preliminary considerations
Due to the complexity of field bus programming with the INTERBUS it is
unfortunately very difficult to make generally valid statements about
commissioning.
One very important aspect of the operation of an extended identification system
on the INTERBUS is the time response of the overall system. The question "How
long after the positioning of a data carrier in front of a R/W head will the read data
be available in my computer?" is answered with the aid of knowledge of the
INTERBUS protocol structure and the following formula:
= [13 * (6 + n) + 1.5 * m] * t
t
t
tt = transfer time
n = number of usable data bytes (per node, only apply input or output data byte),
here: 10 bytes
m = number of remote bus stations installed
t
= bit duration, where t
bit
tsw = software run time, where t
tPH = runtime on the transmitting medium, on copper tPH = 0.016 ms*l/km where l
is the length of the remote bus cable in km.
On large projects, or if you have little experience of programming an INTERBUS
system, you should always construct a laboratory set up of your application and
test the data transfer to the INTERBUS master before installing the system in the
plant.
+ tsw + t
bit
= 2 µs at 500 kBit/s or t
bit
sw
PH
= 200 µs
= 0.5 µs at 2 MBit/s
bit
2011-05
19
Page 20
IC-KP-B5-V23
Commissioning
Note!
The "CMD" manufacturer-independent program is available for planning,
commissioning and diagnosing INTERBUS networks.
Details of this program and information on the general theme of INTERBUS are
available from:
INTERBUS-S-Club
Postfach 1108
D-32817 Blomberg, Germany
http://www.interbusclub.com/de
Tel. +49 52 35 / 34 21 00
Fax +49 52 35 / 34 12 34
6.3 Device settings
Caution!
Device not configured or configured incorrectly
System failure caused by incorrectly configured device
Configure the device prior to commissioning.
20
You must set the various parameters prior to commiss
ioning.
The parameters are volatile and non-volatile parameters. Volatile parameters are
reset to their default setting when the system is switched off and on again.
Non-volatile parameters
Parameter Default setting Value range
General
LCD contrast 50 36 ... 71
LCD light On On / off
Language English English / German
Multiplex mode off On / off
R/W head
Trigger mode off On / off
Tag type 99 00 ... FF
INTERBUS interface
Baud rate 500 kBits/s 500k / 2M
Data hold time 0d x 10 ms 0d ... 255d x 10 ms
Volatile parameters
Parameter Default setting Value range
R/W head
Password mode Off on / off
Password 00000000 00000000 ... FFFFFFFF
2011-05
Page 21
IC-KP-B5-V23
Version
information
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
IDENTControl...
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Config
IdentControl
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Show Config
IdentControl
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
MultiplexM.
X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
TagType
XX XX XX XX
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
TriggerMode
XXX
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Triggerstate
H3:X H4:X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
IdentGateway
IC-KP-B6-..
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Reset
Config
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Config
Channels
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Aktivate
Command
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Set Tag
(ChannelNo)
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Version
ChannelNo:
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
EnhancedRead
Fixcode
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
ChannelNo: X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Enhanced
Read 1 Word
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
ChannelNo: X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Triggermode
...
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Sensor Ch.
-> X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Quit
Command
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
ChannelNo: X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Reset
Identcontrol
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Word-Address
XXXX
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
ChannelNo: X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
ChannelNo: X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Tag Type
XX
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
IXH-XXXX
XX.XX.XX
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Display
config
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Select
language
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
LCD-Light
on/off
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Adjust
LCD-Contrast
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Reset
Config
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Language
english
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
LCD-Contrast
XX
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
IDENT
Gateway...
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Set
BUS Address
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Multiplexed
XXX
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Multiplexed
Mode...
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Set
Defaults?
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Ident Ch.
-> X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Triggermode
XXX
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Restart?
X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
BUS Address
XX
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
Restart
X
IPH1 IPH2 IPH3 IPH4
stands for pressing
ESC
stands for pressing
stands for pressing
stands for pressing
Direction
Direction
Direction
Direction
֠
Commissioning
Configure the read/write station with the described system commands (see
chapter 7.4). “99” is preset as the tag type.
6.3.1 Operating the device
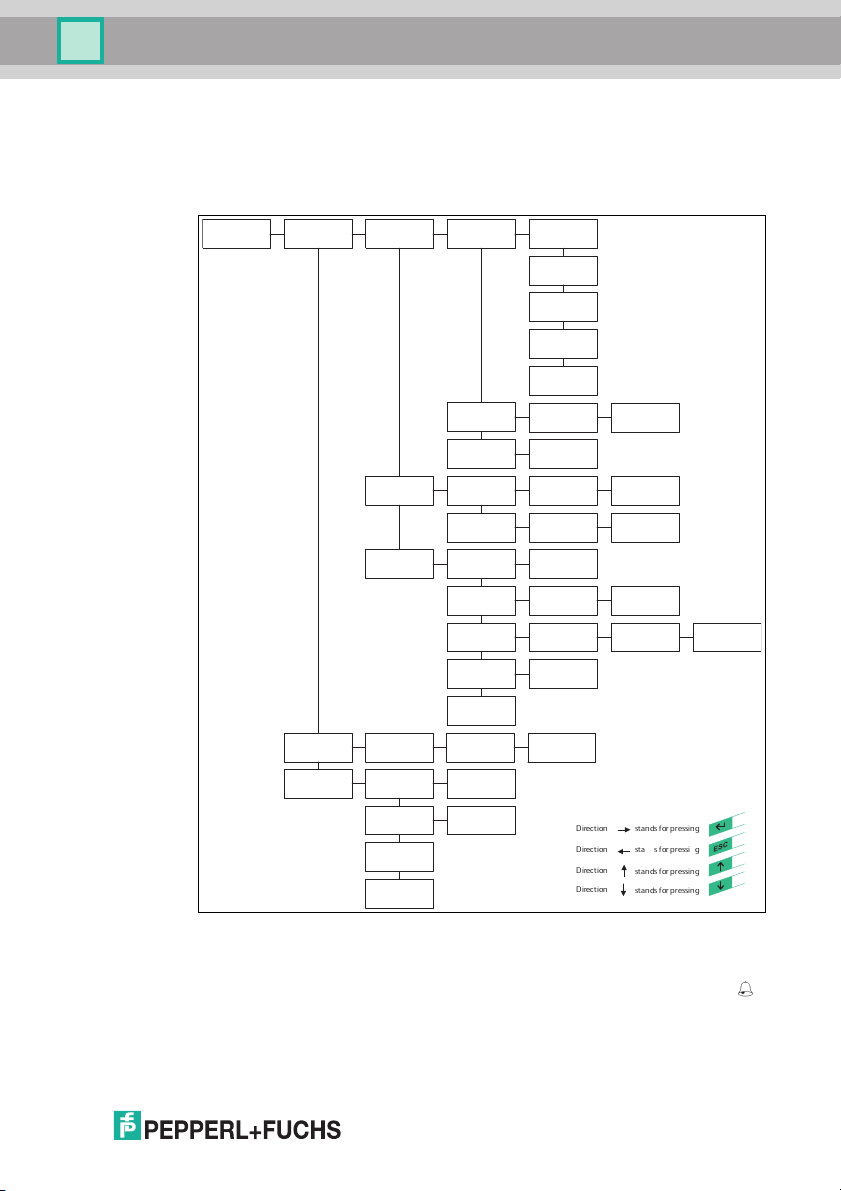
The following illustration shows how the device is operated directly:
6.4 Output of the contents of read data carriers on the
2011-05
In the first menu level, the IDENTControl shows the
on the display. Information messages of this kind are marked with a bell icon ( )
in the top right corner of the display to distinguish them from menu items.
A maximum of the first 12 characters of the read data set can be displayed. The
following characters may be excluded.
contents of read data carriers
display
21
Page 22

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commissioning
The view on the display can be toggled by pressing the arrow buttons. The
following display variants are available:
■ HEX (hexadecimal with decimal delimiter)
■ HEX2 (hexadecimal without decimal delimiter)
■ ASCII (ASC)
Note!
Data carrier content from commands that are activated manually on the
IDENTControl are always displayed, irrespective of the menu level that was just
displayed.
6.4.1 Setting the transfer rate
Setting the transfer rate
Select the transfer rate for your plant and configure via the display using the
function buttons as follows:
1. Select the Gateway/INTERBUS settings.
2. Select the baud rate.
3. Select the baud rate 500K / 2M.
4. Press return to adopt the settings and complete the
The device must be switched off and back on again or restarted using the function
buttons on the display for the INTERBUS component to adopt the new transfer
rate setting.
6.4.2 Setting the data hold time
process.
22
Setting the data hold time
The data hold time value defines the minimum duration that data is retained on the
bus before it is overwritten with new data. Preset this time via the display using
the function buttons as follows:
1. Select the Gateway/INTERBUS settings.
2. Select the data hold time.
3. Select the data hold time xxx x 10 ms.
4. Press return to adopt the settings and complete the process.
The time is adjusted in increments of 10 ms. A setting of 20, for example, means
20 x 10 ms = 200 ms.
The default setting for the data hold time is 0, i.e. new data that becomes available
is sent immediately to the bus, where it overwrites the old data.
The device must be switched off and back on again or restarted using the function
buttons on the display for the INTERBUS component to adopt the new data hold
time setting.
2011-05
Page 23
IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
7 Commands
7.1 General information on INTERBUS
The INTERBUS is a standardized field bus, which enables data exchange
between PLCs, PCs, operating and observation devices and also sensors and
actuators.
An extensive introduction to INTERBUS would go well beyond the limits of these
operating instructions. For detailed information, refer to the INTERBUS standard
DIN 19258 and to the current literature on the subject.
Note!
The INTERBUS Club publishes information brochures and an INTERBUS product
catalog.
7.1.1 Outline of the commands and data on the INTERBUS
The IDENTControl IC-KP-B5-V23 assigns 5 words to eac
in the framework protocol of the INTERBUS in both communication directions.
It is restricted in this to the cyclic transfer of the process data channel. This
means:
■ Even the instructions for the adjustment of the device are updated on every
cycle.
■ The parameter channel of the INTERBUS is not used.
■ The IDENTControl is designed as a remote bus station. The ID code is 03.
7.2 General command information
7.2.1 Software information
A command consists of the command code, a specified number of parameters,
the toggle flag and the data relating to the command. The command is entered in
the output data field.
A response is read from the input data field and consists of the echo of the
command code, a parameter, the toggle flag, the status, a reply counter and the
read data.
Some commands do not use all parameter and data fields. The device ignores the
not used data fields. The input and output data fields are structured as follows:
Output data field (command):
Byte 0 Command code
Byte 1 Parameter/Toggle flag
Byte 2 Parameter
Byte 3 Parameter
Byte 4 Write data
... ...
2011-05
Byte N (N is defined by module selection) Write data
h set of 16 bits (10 bytes)
23
Page 24
IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Input data field (response):
Byte 0 Command code (Echo)
Byte 1 Parameter/Toggle flag
Byte 2 Status
Byte 3 Reply counter
Byte 4 Read data
... ...
Byte N (N is defined by module selection) Read data
In order to send a new command to the device, the INTERBUS master must write
a command in the output data field. The new command is executed when the data
has changed relative to the last read-in. If the same command is to be executed a
number of times, the toggle flag must be inverted so that the device recognizes
that a new command has to be processed.
Upon detection of a new command "Status" is set to FFh.
After the identification system processes commands, the "Status" is output in
accordance with the status/fault message table (see chapter 7.9).
The first byte of the response corresponds to the first byte of the command call-up
(command code).
The toggle bit of the response is the same as the toggle bit of the command.
If the status is FFh (command detected), the second byte of the response also
corresponds to the second byte of the command call-up. In the actual response
(status not FFh), the second byte contains the parameters for the response, i.e.
the number of words in the response and the channel used to transmit the
response. After a read command is issued, a response with the status 00 in the
"Word count" response parameter then contains the number of words in the
response telegram (which is also the command call-up). The number of words in
a response to a write command is 0000b because the response only contains the
status and not (useful) data. Here, the second byte of the response is not the
same as the second byte of the command call-up. With read only code
commands, the word count in the response is always 0000b. 3 responses are
issued for commands to all connected R/W heads (channel = 111b): The first
response (status = FFh) is followed up by 2 other responses that contain the
status of the individual channels. The "Channel" parameter in the response
telegram contains the number of the relevant channel (001, 010).
If new response data is available, the previous data is overwritten. The
configurable data hold time value defines the minimum duration that old data is
retained before it may be overwritten with new data. The default setting for the
timer value is 0.
New commands may only be issued to the device once the answer was retrieved
from the previously issued command.
24
2011-05
Page 25

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Enhancedcommands are executed repeatedly as long as the commands remain
in the output data field. Execution stops only when a new command for the
channel on which the Enhancedcommand was executed is written to the output
data field.
When the system is switched on, the value on the reply counter is 00h. This value
increases every time the response data field is modified. This also applies if the
status changes to FFh or from 00h to 05h (with enhancedcommands: tag leaves
the detection range).
In the event of an overrun, the counter skips from FFh to 01h.
7.3 Command types
When using commands, a distinction is always made between the two command
types single mode and enhanced mode.
Single mode
The command is executed once. A response is issued immediately.
Enhanced mode
The command remains permanently active until it is interrupted by the user or by
an error message. A response is issued immediately.
The command remains active after the response is issued. Data is only
transferred if read/write tags change. Read/write tags are not read twice. If a
read/write tag leaves the read range, the status '5' is output.
7.4 Command overview
The commands in the list are described in detail on
System commands
Command code Command description
4d 04h See "Change tag (CT)" on page 28 CT
2d 02h See "Quit (QU)" on page 31 QU
3d 03h See "Version (VE):" on page 32 VE
23d 17h See "Configuration store (CS)" on page 34 CS
22d 16h See "Reset (RS)" on page 35 RS
155d 9Bh See "Set multiplexed mode (MM):" on page 36 MM
156d 9Ch See "Set trigger mode (TM):" on page 37 TM
the following pages.
Abbreviation
2011-05
25
Page 26

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Standard read/write commands
Fixcode
Command code Command description
1d 01h See "single read fixcode (SF)" on page 39 SF
29d 1Dh See "Enhanced buffered fixcode (EF)" on page 40 EF
Read data
Command code Command description
16d 10h See "single read words (SR)" on page 41 SR
25d 19h See "enhanced buffered read words (ER)" on page 42 ER
Write data
Command code Command description
64d 40h See "single write words (SW)" on page 43 SW
26d 1Ah See "enhanced buffered write words (EW)" on page 44 EW
Special command modes
Password mode with IPC03
Command code Command description
24d 18h See "Set password mode (PM)" on page 47 PM
65d 41h See "Change password (PC)" on page 48 PC
66d 42h See "Set password (PS)" on page 49 PS
Abbreviation
Abbreviation
Abbreviation
Abbreviation
26
Configuration IPC03
Command code Command description
97d 61h See "Single get configuration (SG)" on page 51 SG
104d 68h See "Enhanced buffered get configuration (EG)" on page 52 EG
18d 12h See "Single write configuration (SC)" on page 53 SC
102d 66h See "Enhanced buffered write configuration (EC)" on page 55 EC
Abbreviation
2011-05
Page 27

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Writing fixcode IPC11 and IDC-...-1K
Command code Command description
31d 1Fh See "Single write fixcode (SX)" on page 56 SX
36d 24h See "Enhanced buffered write fixcode (EX)" on page 58 EX
188d BCh See "Set tag ID code (TI)" on page 60 TI
170d AAh See "Fill data carrier (S#)" on page 61 S#
Extended commands for type IDC-...-1K read/write tags
Command code Command description
10d 0Ah See "Single read special fixcode (SS)" on page 62 SS
113d 71h See "Enhanced read special fixcode (ES)" on page 63 ES
13d 0Dh See "Single program special fixcode (SP)" on page 64 SP
117d 75h See "Enhanced program special fixcode (EP)" on page 65 EP
107d 6Bh See "Initialize data carrier (SI)" on page 66 SI
Extended commands for type IDC-...-1K and IQC... read/write tags
Command code Command description
71d 47h See "single write words with lock (SL)" on page 67 SL
72d 48h See "Enhanced write words with lock (EL)" on page 68 EL
Abbreviation
Abbreviation
Abbreviation
2011-05
Extended commands for IQH2-... read/write heads
Command code Command description
190d BEh See "read param (RP)" on page 69 RP
191d BFh See "write param (WP)" on page 70 WP
Abbreviation
27
Page 28

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
7.5 System commands
Change tag (CT)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (04h) 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Data carrier type in ASCII <TagType> (high byte)
Byte 3 Data carrier type in ASCII <TagType> (low byte)
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (04h) 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
This command tells the read/write head on the relevant channel which tag type to
communicate with. This setting is stored in the non-volatile memory on the unit.
Supported tag types
Tag type P+F
High
byte
'0' '2' IPC02 Unique, EM4102 (EM
'0' '3' IPC03 EM4450 (EM
'1' '1' IPC11 Q5 (Sokymat) R/W 5 - 125 kHz
Low
byte
designation
Chip type Access Writable
Microelectronic)
Microelectronic), Titan
fixcode 5 5 125 kHz
R/W fixcode 116 4 125 kHz
memory
[bytes]
Read only
code length
[byte]
28
Frequency
range
2011-05
Page 29

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Tag type P+F
High
byte
Low
byte
designation
Chip type Access Writable
memory
[bytes]
Read only
code length
[byte]
Frequency
range
'1' '2' IPC12 P+F FRAM R/W fixcode 8k 4 125 kHz
'2' '0'
IQC20
1)
All tags conforming to ISO
15693
R/W fixcode 8 8 13.56 MHz
'2' '1' IQC21 I-Code SLI (NXP) R/W fixcode 112 8 13.56 MHz
'2' '2' IQC22 Tag-it HF-I Plus (Texas
Instruments)
R/W fixcode 250 8 13.56 MHz
'2' '3' IQC23 my-D (Infinion) SRF55V02P R/W fixcode 224 8 13.56 MHz
'2' '4' IQC24 my-D (Infinion) SRF55V10P R/W fixcode 928 8 13.56 MHz
'3' '1' IQC31 Tag-it HF-I Standard (Texas
'3' '3'
IQC33
2)
Instruments)
Fujitsu FRAM MB89R118 R/W fixcode 2k 8 13.56 MHz
R/W fixcode 32 8 13.56 MHz
'3' '4' IQC34 Fujitsu FRAM MB89R119 R/W fixcode 29 8 13.56 MHz
'3' '5' IQC35 I-Code SLI-S (NXP) R/W fixcode 160 8 13.56 MHz
'4' '0' IQC40 All tags conforming to ISO
14443A
fixcode - 4/7 13.56 MHz
'4' '1' IQC41 Mifare UltraLight MF0 IC U1 R/W fixcode 48 7 13.56 MHz
'4' '2'
'4' '3'
IQC42
IQC43
3)
Mifare Classic MF1 IC S50 R/W fixcode 752 4 13.56 MHz
3)
Mifare Classic MF1 IC S70 R/W fixcode 3440 4 13.56 MHz
'5' '0' IDC-...-1K P+F R/W fixcode 125 4 250 kHz
'5' '2' ICC-... P+F fixcode 28 7 250 kHz
'7' '0' All tags conforming to ISO 18000-6B and
'7' '2'
'7' '3'
'7' '4'
'7' '5'
'7' '6'
'9' '9'
EPC Class 1 Gen 2
4)
IUC72
IUC73
IUC74
IUC75
IUC76
NXP UCode-EPC-G2XM R/W fixcode 64 8 868 MHz
4)
4)
4)
4)
Depends on read head
Alien Higgs-2 fixcode - 96 868 MHz
NXP UCode-EPC-G2 R/W fixcode 28 96 868 MHz
Impinj Monza 2.0 fixcode - 96 868 MHz
Alien Higgs-3 R/W fixcode 56 240 868 MHz
5)
- - - 868 MHz
- - - -
1)
IQC20 is not an actual tag type, but is used to read the UID (read only code) of all ISO 15693 compliant
tags.
2)
You can only use the tag IQC33 in combination with a read/write head IQH1-... The memory is divided
into 8-byte blocks (instead of 4-byte blocks). You must therefore enter an integral initial address for write
commands SR, ER, SW, and EW. <WordNum> specifies the number of 8-byte blocks (max. 7 here) and
must be even-numbered.
2011-05
29
Page 30

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
3)
The memory can be encrypted per sector (1 sector = 4 blocks of 16 bytes).
The default key in the transponder and the read head is FF FF FF FF FF FF
can be read with the command Read param and written with the command Write param (see System
commands) . Thus, only the key in the read head is changed, not in the transponder!
The key in the read head is stored in permanent memory.
4)
You can only use the IUC7* type tags with the read/write head IUH-F117-V1 in combination with certain
evaluation units.
5)
The tag type configured in the read/write head as the default is selected.
Note!
In a plant where only one tag type is used, it is advantageous to permanently
configure that tag type so that the read/write head detects the tag quicker.
Default tag type:
In the factory default condition, the tag type 99 is preset in the IDENTControl
(depending on the reading head type), thus the tag type preset on the reading
head is used.
. The key in the read head
ASCII
30
2011-05
Page 31

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Quit (QU)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (02h) 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (02h) 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The command running on this channel is interrupted.
31
Page 32

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Version (VE):
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Toggle bit - - - - - - - <T>
Byte 2 Parameter <Parameter>
Byte 3 Not relevant - - - - - - - -
... ... - - - - - - - -
Byte 9 Not relevant - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Toggle bit - - - - - - - <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Version data> part 1
... Data 00h ... FFh <Version data> part ...
Byte 9 Data 00h ... FFh <Version data> part 6
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
32
This command transfers the software version. The complete software version
message cannot be transferred with one command due to its length. The
individual parts of the software version message are transferred by repeated
execution of the command with the appropriate parameters.
<Parameter> Meaning <Version data> Example
0; >22 Incorrect parameter, Status '04h' Data = 0 000000
1 IDENTControl - type KPB5-V
2 IDENTControl - part number 200639
3 Identification system - software number 30373_
4 Identification system - software date 240806
5 Bus system - software number 31072_
6 Bus system - software date 160107
7 Head 1 - type ISH-18
8 Head 1 - part number 181881
9 Head 1 - software number 30597_
10 Head 1 - software date 300606
2011-05
Page 33

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
<Parameter> Meaning <Version data> Example
11 Head 2 - type __no__
12 Head 2 - part number head 2
13 Head 2 - software number 000000
14 Head 2 - software date 000000
15 Head 3 - type IPH-L2
16 Head 3 - part number 119321
17 Head 3 - software number 30420_
18 Head 3 - software date 040706
19 Head 4 - type __no__
20 Head 4 - part number head 4
21 Head 4 - software number 000000
22 Head 4 - software date 000000
2011-05
33
Page 34

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Configuration store (CS)
Command:
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 2 Command code (17h) 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1
Byte 3 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 4 Mode 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 <Mode>
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 8 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 9 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 2 Command code (17h) 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1
Byte 3 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 4 Status <Status>
Byte 5 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 8 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 9 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
34
The configuration store (CS) command allows you to store the last command sent
to the R/W head in the non-volatile memory of the IDENTControl Compact. The
R/W head executes the command automatically again if the power supply is
interrupted or the IDENTControl Compact is reset.
<Mode>='1' activates the mode.
<Mode>='0' deactivates the mode.
Configuration store is deactivated by default.
2011-05
Page 35

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Reset (RS)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (16h) 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Channel/Toggle bit - - - - - - - <T>
Byte 2 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
This command terminates all active commands. The device settings are reloaded
from the non-volatile memory.
This confirmation is issued for this command (status FFh) instead of a response.
The device resets the hardware and then restarts.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
35
Page 36

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Set multiplexed mode (MM):
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (9Bh) 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Toggle bit - - - - - - - <T>
Byte 2 Multiplex mode 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 <F>
Byte 3 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 4 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 unused - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (9Bh) 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Toggle bit - - - - - - - <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 unused - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
36
This command switches multiplex mode on and off. In multiplex mode, the R/W
heads are controlled according to the time multiplex process, i.e. only one R/W
head is active. The procedure minimizes mutual interference between R/W
heads, allowing two R/W heads to be mounted side by side.
Each IDENT channel sends a response in reply to an MM command.
Multiplex mode <F>='0': Mode off
<F>='1': Mode on
If a R/W head is not connected to a channel, the response telegram receives the
status "06h" (hardware fault) from this channel.
2011-05
Page 37

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Set trigger mode (TM):
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (9Ch) 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
Byte 1 Ident channel/sensor channel/toggle bit 0 <Ident channel> <Sensor channel> <T>
Byte 2 Trigger mode <Trigger mode>
Byte 3 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (9Ch) 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
Byte 1 Reserved/sensor channel/toggle bit 0 <Ident channel> <Sensor channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
Permitted parameters:
<Sensor channel> 3 (011b), 4 (100b)
<Ident channel> 1 (0001b), 2 (0010b), 3 (0011b), 4 (0100b)
<Trigger mode> 0 (00000000b): Trigger mode off
(but not <Sensor channel>)
1 (00000001b): Trigger mode on
2 (00000010b): Trigger mode inverted
Activating trigger mode interrupts a command running on the <Ident channel>.
If trigger mode is activated with <Trigger mode>=1 (=2), dampening the trigger
sensor generates the status 0 (5) and after changing to undamped state,
generates the status 5 (0) as a response to the <Sensor channel>. Activating
trigger mode generates a response that includes the current status of the sensor
on the <Sensor channel>.
37
Page 38

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
If a read/write command is sent to the triggered channel <Ident channel> when
trigger mode is active, this command is always activated if the <Sensor channel>
transmits status 0. <Ident channel> transmits status 0 to confirm receipt of this
command.
If you set <Ident channel> 0, the signal is transferred without influencing a reading
head.
The command activated by the <Sensor channel> initiates execution as if it had
just been restarted by the host.
The command is deactivated again if the status of the <Sensor channel> changes
to 5 or trigger mode is deactivated.
If the <Sensor channel> requests a version message, the response contains the
status 0 and no other information.
<Ident channel>=0 allows you to assign the trigger signal to channel '0' so that the
trigger signal is transmitted to the controller and not to a read head.
This function can be used to monitor functions via the PLC if trigger signals and
reading of data cannot occur simultaneously for application related reasons.
Correlation must take place in the PLC.
If a trigger command has assigned channel '0' (000b) for <Identchannel>, this
change in the status of the trigger sensor (status 0x00 and 0x05) is transmitted to
the controller via the sensor channel
This function can be used to monitor functions via the controller if trigger signals
and reading of data cannot occur simultaneously for application related reasons.
Correlation must take place in the controller.
38
2011-05
Page 39

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
7.6 Standard read/write commands
single read fixcode (SF)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (01h) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (01h) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID-Code>
Byte 5 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID-Code>
... ID code 00h ... FFh <ID-Code>
1)
Byte N
ID code 00h ... FFh <ID-Code>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
Table 7.1: 1) N = <FixLen> + 3
The R/W head makes only one attempt to read a read only code.
The length of the read only code that is output depends on the tag type. See table
"Supported tag types" on page 28.
39
Page 40

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Enhanced buffered fixcode (EF)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (1Dh) 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (1Dh) 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 5 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
... ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte N
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
40
Table 7.2: 1) N = <FixLen> + 3
The R/W head makes attempts until successful to read a read only code. Only
data that changes is transferred via the interface, i.e. the R/W head transfers data
whenever it reads a new read/write tag or whenever it reads a read/write tag
where there was previously no read/write head within the detection range.
The status '05h' (read command) is output whenever a read/write tag leaves the
detection range.
The length of the read only code that is output depends on the tag type. See table
"Supported tag types" on page 28.
2011-05
Page 41

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
single read words (SR)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (10h) 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Word address <WordAddr> (high byte)
Byte 3 Word address <WordAddr> (low byte)
Byte 4 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 unused - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (10h) 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 5 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 6 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 7 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
2011-05
Table 7.3: 1) N = 4 x <WordNum> + 3
The R/W head makes one attempt to read <WordNum> 32-bit words from the
address<WordAddr>.
41
Page 42

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
enhanced buffered read words (ER)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (19h) 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Word address <WordAddr> (high byte)
Byte 3 Word address <WordAddr> (low byte)
Byte 4 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 unused - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (19h) 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 5 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 6 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 7 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
42
Table 7.4: 1) N = 4 x <WordNum> + 3
The R/W head makes attempts until successful, to read <WordNum> 32-bit words
from the address <WordAddr>. Only modified data is transferred via the interface.
When a read/write tag leaves the detection range, the status '05h' (read
command) is output.
2011-05
Page 43

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
single write words (SW)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (40h) 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Word address <WordAddr> (high byte)
Byte 3 Word address <WordAddr> (low byte)
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
Table 7.5: 1) N = 4 x <WordNum> + 3
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (40h) 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 unused - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The R/W head makes one attempt to write <WordNum> 32-bit words from the
address<WordAddr>.
43
Page 44

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
enhanced buffered write words (EW)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (1Ah) 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Word address <WordAddr> (high byte)
Byte 3 Word address <WordAddr> (low byte)
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
Table 7.6: 1) N = 4 x <WordNum> + 3
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (1Ah) 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 unused - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
44
The read/write head repeatedly attempts to write <WordNum> 32-bit words from
the address <WordAddr> until successful. After each successful write, the head
sends the response and then switches to continuous read. The read/write head
then reads the same tag until the tag has left the detection range or a new tag
appears within the detection range. At this point, the read/write head again starts
write attempts.
The status '05h' is only output when a tag leaves the detection range or is not yet
within the detection range.
If two tags enter the read range one immediately after the other, the status '05h' is
not issued between the two readings.
2011-05
Page 45

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
7.7 Special commands
Note!
You can only use the commands in this section for the data carrier type '03'
(IPC03).
IPC03 Configuration
The storage of a data carrier IPC03 is organized by word. A data word is defined
with a length of 32 bits. For the normal data range, 29 words from addresses 3
through 31 (<WordAddr> = 00h ... 1Ch) are available.
Address Meaning <WordAddr> <ConfAddr> Note
Word 0 Password - - Write only
Word 1 Protection word - 1 Read/write
Word 2 Control word - 2 Read/write
Word 3 ...31 Data range 00h ... 1Ch - Read/write
Word 32 Device Serial Number 1Dh - Read only
Word 33 Device identification 1Eh - Read only
Word 0 contains the password. The password can only be written.
With word 1, the "Protection Word", you can define a read-protected and a writeprotected range. The "Protection Word" can only be read and written with the
correct password.
With word 2, the "Control Word", you can set various operating modes and the
read range for the operating mode "Default Read". The "Control Word" can only
be read and written with the correct password.
If you would like to use the "Protection Word" and the "Control Word", you must
first activate the password mode.
The individual bits have the following meanings:
Protection word
Bit Meaning Byte
0 ... 7 First read-protected word 0
8 ... 15 Last read-protected word 1
16 ... 23 First write-protected word 2
24 ... 31 Last write-protected word 3
2011-05
45
Page 46

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Control word
Bit Meaning Byte
0 ... 7 Read range start 0
8 ... 15 Read range end 1
16 Password mode on/off 2
17 "Read after write" operating mode on/off
18 ... 23 Open
24 ... 31 Open 3
IPC03 password mode
If the password mode in the data carrier is activated, the data range of the data
carrier is read and write-protected and can only be read or written if the R/W head
sends the correct password to the data carrier.
If the password mode in the data carrier is deactivated, every data word on the
data carrier can be read or written.
The default password of the R/W heads and the data carrier is 00000000h. In the
R/W head, the password is stored in the volatile memory and in the data carrier,
the password is stored in the non-volatile memory.
To read or write the "Protection Word" and the "Control Word", you must first enter
the password in the password mode (see the commands SC or EC).
You can also limit access to the data carriers by defining the start and end of a
read-protected and a write-protected range in the Protection Word.
Setting the password
1. Enter the correct password once with the command P
2. Activate the password mode with the command PM (set password mode).
Changing the password
To change the password in the R/W head and on the read/write tag, use the
command PC.
S (set password).
46
2011-05
Page 47

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Set password mode (PM)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (18h) 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Password mode 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 <P>
Byte 3 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (18h) 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The command PM activates and deactivates the password mode of the relevant
channel. In the password mode, the password is transferred to the data carrier
before each read/write access. If a data carrier is addressed with the wrong
password, then even the other data areas on the data carrier can no longer be
accessed.
Password mode "off": <P>=0 (0b) (deactivated)
Password mode "on": <P>=1 (1b) (activated)
47
Page 48

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Change password (PC)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (41h) 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Old password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 3)
Byte 3 Old password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 2)
Byte 4 Old password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 1)
Byte 5 Old password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 0)
Byte 6 New password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 3)
Byte 7 New password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 2)
Byte 8 New password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 1)
Byte 9 New password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 0)
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (41h) 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
48
The command PC changes the password in a tag. Enter the old and then the new
password <PSW> here. If the password has been successfully written, the
password in the read/write head also changes and the set password command
is no longer required. The password of the IPC03 can also be changed if the
password mode is deactivated.
2011-05
Page 49

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Set password (PS)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (42h) 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Reserved - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 Reserved - - - - - - - -
Byte 4 Password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 3)
Byte 5 Password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 2)
Byte 6 Password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 1)
Byte 7 Password 00h ... FFh <PSW> (byte 0)
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (42h) 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The command PSsets the password, which the R/W head communicates to the
data carrier in password mode.
Operating mode “Default Read”
In "default read" operating mode, 1 or 2 words are r
ead extremely quickly. The
area of memory earmarked for reading is already specified on the tag. The R/W
head does not have to identify the memory area for the tag.
The start and end of the read range are stored in the bytes 0 and 1 of the control
word. As soon as power is supplied to the tag, it sends data from the data range
defined by the start and end of the read range. The data range between read
range start and end is read with the read commands SR (Single read words) and
ER (enhanced buffered read words) when <WordAddr> is set to 0000h and
<WordNum> to 00h.
49
Page 50

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
The advantage of "default read" operating mode is the readout speed. The
readout of one data word (4 bytes) is twice as fast in this mode as the other
modes. The readout of two words takes approx. 1/3 less time. No more time
advantages can be gained after three data words because "default read" mode is
designed to read a maximum of two words (= 8 bytes). Reading larger data
ranges can lead to error messages if the reading head does not respond within
the planned reaction time.
Note!
The addresses for the start and end of the read range are based on the absolute
word address of the read/write tag, not on <WordAddr>.
Example: With the setting read range start 03h and read range end 03h, the R/W
head only reads the first data word in the read/write tag.
Setting "Default Read"
1. Activate the password mode.
2. Write the read range start and end into the "Control
3. Deactivate the password mode.
4. Read the data range with address designation 0000h and word count 0h.
Word".
50
2011-05
Page 51

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
IPC03 configuration
Single get configuration (SG)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (61h) 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Reserved - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 Address in the configuration range <ConfAddr>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (61h) 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 5 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 6 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 7 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The R/W head makes exactly one attempt to read a word in the configuration
range ("Protection Word" or "Control Word") from the address <ConfAddr>.
51
Page 52

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Enhanced buffered get configuration (EG)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (68h) 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Reserved - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 Address in the configuration range <ConfAddr>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (68h) 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 5 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 6 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 7 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
52
The R/W head attempts to read a word in the configuration range from the
address <ConfAddr> until successful. Only data that changes is transferred via
the interface, i.e. the R/W head transfers data whenever it reads a new data carrier
or whenever it reads a data carrier where there was previously no R/W head
within the detection range.
The status '05h' (read/write command) is output when the data carrier leaves the
detection range or if the data carrier is not yet within the detection range when the
command is executed.
If two data carriers enter the read range one immediately after the other, the status
'05h' is not issued between the two readings.
2011-05
Page 53

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Single write configuration (SC)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (12h) 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Reserved - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 Address in the configuration range <ConfAddr>
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data byte 3>
Byte 5 Data 00h ... FFh <Data byte 2>
Byte 6 Data 00h ... FFh <Data byte 1>
Byte 7 Data 00h ... FFh <Data byte 0>
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (12h) 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit 0 0 0 0 <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The R/W head makes exactly one attempt to write a word to the configuration
range ("Protection Word" or "Control Word") from the address <ConfAddr>.
The password mode must be active so that the R/W head can write to the
configuration range.
If the password mode is deactivated, every data word outside of the writeprotected range can be written to. If you would like to modify the write-protected
range, you must modify the "Protection Word" accordingly.
For example:
With the R/W head on channel 1, one data word (4 bytes) that does not contain
details of the address and data length should be transferred during each read
command (accessed with 00 byte and address 0000). Password mode must be
activated beforehand by transmitting the command Set password mode.
53
Page 54

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Byte Bit no.
Byte 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 Single write configuration 12h
Byte 1 - - - - 0 0 1 <T> Channel (=1) 02h/03h
Byte 2 - - - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 Word address in the
Byte 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Bits 16 to 31 of the control
Byte 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 00h
Byte 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 Address of the last data word
Byte 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 Address of the first data word
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
configuration range
(=control word)
word
to write
to write
02h
00h
03h
03h
The address of the first and last data word to be wr
itten is based on the absolute
address of the read/write tag (not the <WordAddr>). The address 03h is therefore
the first available word in the data range.
54
2011-05
Page 55

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Enhanced buffered write configuration (EC)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (66h) 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Reserved - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 Address in the configuration range <ConfAddr>
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data byte 3>
Byte 5 Data 00h ... FFh <Data byte 2>
Byte 6 Data 00h ... FFh <Data byte 1>
Byte 7 Data 00h ... FFh <Data byte 0>
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (66h) 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The R/W head attempts to write a word in the configuration range to the address
<ConfAddr> until successful. After each write, the status is evaluated and the
system waits until a new data carrier is within the detection range. The command
then starts again from the beginning. In order to write in the configuration range,
the password mode must be active.
The status '05h' (read/write command) is only output when a data carrier leaves
the detection range or is not yet within the detection range when the command is
executed.
If two data carriers enter the read range one immediately after the other, the status
'05h' is not issued between the two readings.
55
Page 56

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Write read only code IPC11 and IDC-..-1K
"Read-after-write" operating mode is not used.
Tags IPC11 can be programmed to behave like the IPC02 read only tag. To do
this, use the commands SX and EX. The code is read when tag type '02' or '11' is
set with the commands SF and EF.
Tags IDC-...- 1K can be programmed to behave like the ICC read only tag. This
programming occupies the first 8 bytes in the tag and occurs when the tag type
'50' is set with the commands SX or EX.
This code is read when tag type '52' is set with the commands SF or EF. If you use
the command SF or EF when tag type '50' is selected, the 4-byte read only code
of the tag is issued.
Single write fixcode (SX)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (1Fh) 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1
Byte 1 FixLen/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 FixType <FixType> (high byte)
Byte 3 FixType <FixType> (low byte)
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
56
Table 7.7: 1) N = <FixLen> + 3
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Byte 0 Command code (1Fh) 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1
Byte 1 FixLen/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
The R/W head makes only one attempt to write a read only code.
2011-05
Page 57

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
IPC11: <F
IDC-...-1K: <FixLen> = 7
ixLen> = 5
<FixType> = '02' ASCII (30h 32h), the read only code cannot be
<FixType> = '52' ASCII (35h 32h), the read only code can be
<Data> = (Byte 1 to 3): 0x30 ... 0x39; 0x41...0x46
changed
'11' ASCII (31h 31h), the read only code can be
overwritten
The first 3 bytes are hexadecimal (0h ... Fh), the last
4 bytes are decimal (0d ... 9d).
overwritten
(Byte 4 to 7): 0x30...0x39
Type IDC-...-1K tags can be programmed in such a way that they are compatible
with the type ICC-... read only carriers. This programming occupies the first 8
bytes in the tag. The read/write commands can be used to access the remaining
memory.
You must set the tag type '50' in order to program type IDC-...-1K tags. To do this,
transmit the command SX or EX.
The value range contains 7 characters:
■ the first 3 characters contain the values 0 ... F (hexadecimal code)
■ the last 4 characters contain the values 0 ... 9 (decimal code)
You must select the tag type '50' (ICC-...) beforehand in order to read out this
code. If a "read only code" command is executed when the tag type '50' (IDC-...1K) is set, the 4-byte read only code for this tag is issued.
2011-05
57
Page 58

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Enhanced buffered write fixcode (EX)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (24h) 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
Byte 1 FixLen/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 FixType <FixType> (high byte)
Byte 3 FixType <FixType> (low byte)
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
Table 7.8: 1) N = <FixLen> + 3
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (24h) 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
Byte 1 FixLen/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
58
The R/W head constantly attempts to write a read only code. After each
successful write, the response is sent and the system waits until a new tag is
within the detection range. The command then starts again from the beginning.
IPC11: <FixLen> = 5
<FixType> = '02' ASCII (30h 32h), the read only code cannot be changed
IDC-...-1K: <FixLen> = 7
<FixType> = '52' ASCII (35h 32h), the read only code can be overwritten
<Data> = (Byte 1 to 3): 0x30 ... 0x39; 0x41...0x46
'11' ASCII (31h 31h), the read only code can be overwritten
The first 3 bytes are hexadecimal (0h ... Fh), the last 4 bytes
are decimal (0d ... 9d).
(Byte 4 to 7): 0x30...0x39
2011-05
Page 59

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Type IDC-...-1K tags can be programmed in such a way that they are compatible
with the type ICC-... read only carriers. This programming occupies the first 8
bytes in the tag. The read/write commands can be used to access the remaining
memory.
You must set the tag type '50' in order to program type IDC-...-1K tags. To do this,
transmit the command SX or EX.
The value range contains 7 characters:
■ the first 3 characters contain the values 0 ... F (hexadecimal code)
■ the last 4 characters contain the values 0 ... 9 (decimal code)
You must select the tag type '50' (ICC-...) beforehand in order to read out this
code. If a "read only code" command is executed when the tag type '50' (IDC-...1K) is set, the 4-byte read only code for this tag is issued.
2011-05
59
Page 60

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Set tag ID code (TI)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (BCh) 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
Byte 1 ID length/Channel/Toggle bit <ByteNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Data <ID code>
Byte 3 Data <ID code>
Byte 4 Data <ID code>
Byte 5 Data <ID code>
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (BCh) 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Channel/Toggle bit <ByteNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
60
This command restricts the execution of all other read/write commands to the
read/write tag with the specified ID code. This also applies if another read/write
tag is located within the detection range. A targeted response is achieved from the
read/write tag as a result.
<ByteNum> = 0h: Do not make a selection. An ID code is not specified in the
telegram.
<ByteNum> = 8h (System IQ): Make a selection. An ID code must be specified in
the telegram.
<ByteNum> = 0h deletes this filter.
Note!
The TI command only adjusts a setting in the reading head. There is no HF
communication with the read/write tags.
2011-05
Page 61

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Fill data carrier (S#)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (AAh) 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit <Reserved> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Start address <WordAddr> (high byte)
Byte 3 Start address <WordAddr> (low byte)
Byte 4 Word count <WordNum> (high byte)
Byte 5 Word count <WordNum> (low byte)
Byte 6 Character <Fill sign>
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (AAh) 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit <Reserved> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The word number <WordNum> of fill signs <Fill Sign> is written to the read/write
tag from the specified start address <WordAddr>.
Extended commands for type IDC-... and IUC… tags
ype IDC-...-1K tags can be programmed to read 24-bit information (so-called
T
special read only code) very quickly. This is useful for detecting containers in
automated warehouses.
Length of the special read only code:
■ Tag of the type IDC-...-1K: 48 bit
■ Tag of the type IUC: 96 ... 240 bit
To write the special read only code use the commands SP and EP; to read it
out, use the commands SS and ES.
If SP or EP is used to write to an IDC-...-1K tag, the tag is then locked. If you wish
to write to the tag again using standard commands, unlock it using the command
SI.
61
Page 62

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Single read special fixcode (SS)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (0Ah) 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0
Byte 1 FixLen/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (0Ah) 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 5 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 6 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 7 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 8 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 9 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
62
The R/W head makes only one attempt to read a special read only code.
Note!
The <FixLen> of IDC-...-1K read/write tags is always 6 bytes.
2011-05
Page 63

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Enhanced read special fixcode (ES)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (71h) 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 3 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (71h) 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 5 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 6 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 7 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 8 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 9 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The R/W head attempts to read a special read only code until successful. Only
data that changes is transferred via the interface, i.e. the R/W head transfers data
whenever it reads a new data carrier or whenever it reads a data carrier where
there was previously no R/W head within the detection range.
The status '05h' (read command) is output whenever a data carrier leaves the
detection range.
Note!
The <FixLen> of IDC-...-1K read/write tags is always 6 bytes.
63
Page 64

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Single program special fixcode (SP)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (0Dh) 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Byte 3 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Byte 4 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 5 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 6 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 7 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 8 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 9 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (0Dh) 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1
Byte 1 FixLen/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
64
The R/W head makes only one attempt to write a special read only code.
Note!
The <FixLen> of IDC-...-1K read/write tags is always 6 bytes.
2011-05
Page 65

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Enhanced program special fixcode (EP)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (75h) 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1
Byte 1 FixLen/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Byte 3 Reserved 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Byte 4 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 5 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 6 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 7 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 8 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Byte 9 ID code 00h ... FFh <ID code>
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (75h) 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1
Byte 1 FixLen/Ident channel/Toggle bit <FixLen> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
The R/W head attempts to write a special read only code until successful. After
each successful write, the head sends the response and then switches to
continuous reading. Then the R/W head reads the same data carrier until it has
left the detection range or a new data carrier appears within the detection range.
The command then starts again with write attempts.
The status '05h' (read/write command) is output when the data carrier leaves the
detection range or if the data carrier is not yet within the detection range when the
command is executed.
If two data carriers enter the read range one immediately after the other, the status
'05h' is not issued between the two readings.
65
Page 66

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Note!
The <FixLen> of IDC-...-1K read/write tags is always 6 bytes.
Initialize data carrier (SI)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (6Bh) 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (6Bh) 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1
Byte 1 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - - - - <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 8 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
66
This command allows conventional reading and writing of IDC-...-1K read/write
tags that were configured using the EP or SP commands.
2011-05
Page 67

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Extended commands for type IQC-... read/write tags.
single write words with lock (SL)
Command:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (47h) 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Word address <WordAddr> (high byte)
Byte 3 Word address <WordAddr> (low byte)
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 5 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
Table 7.9: 1) N = 4 x <WordNum> + 3
Response:
Byte Content Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (47h) 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 unused - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 unused - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
2011-05
This command is the same as a normal write command. The data is writeprotected at the end of the write process, provided the read/write tags offer this
function.
This applies for 13.56 MHz read/write tags of the type 21, 22, 24, 33 and 35 as
well as for LF read/write tags IDC-…-1K. Write protection is only activated for
emory blocks involved in the write process. Data can continue to be written to all
m
other memory blocks.
The R/W head makes one attempt to write <WordNum> 32-bit words from the
address<WordAddr>.
67
Page 68

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Enhanced write words with lock (EL)
Command:
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (48h) 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Word address <WordAddr>(high byte)
Byte 3 Word address <WordAddr> (low byte)
Byte 4 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte 5 Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
Table 7.10: 1) 4 x <WordNum> + 6
Response:
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 0 Command code (48h) 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
Byte 1 Word number/Ident channel/Toggle bit <WordNum> <Channel> <T>
Byte 2 Status <Status>
Byte 3 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 4 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 5 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 6 not used - - - - - - - -
Byte 7 not used - - - - - - - -
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Data 00h ... FFh <Data>
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
68
This command is the same as a normal write command. The data is writeprotected at the end of the write process, provided the tags offer this function.
This applies for 13.56 MHz tags of the type 21, 22, 24, and 33 as well as for LF
tags IDC-…-1K. Write protection is only activated for memory b
locks involved in
the write process. Data can continue to be written to all other memory blocks.
The R/W head repeatedly attempts to write <WordNum> 32-bit words from the
address <WordAddr> until successful. After each successful write, the head
sends the response and then switches to continuous reading. Then the R/W head
reads the same tag until it has left the detection range or a new tag appears within
the detection range. The command then starts again with write attempts.
2011-05
Page 69

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
The status '05h' is only output when a tag leaves the detection range or is not yet
within the detection range. If two tags enter the read range one immediately after
the other, the status '05' is not issued between the two readings.
Extended commands for IQH2-... read/write heads
read param (RP)
Command:
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 0
Byte 1
Byte 2 Command code (BEh) 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0
Byte 3 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - <Channel> <T>
Byte 4 System code <SystemCode> (high byte)
Byte 5 System code <SystemCode> (low byte)
Byte 6 Parameter type <ParamTyp> (high byte)
Byte 7 Parameter type <ParamTyp> (low byte)
1)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Telegram length, high byte 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1)
Telegram length, low byte 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
This byte is only used with the TCP/IP and MODBUS TCP/IP protocol.
2011-05
Response:
Byte Contents Bit no.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Byte 0
Byte 1
Byte 2 Command code (BEh) 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0
Byte 3 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit 0 <Channel> <T>
Byte 4 Status <Status>
Byte 5 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
Byte 6 Data 00 ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00 ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
1)
2)
Telegram length, high byte 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1)
Telegram length, low byte 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1
2)
Data 00 ... FFh <Data>
This byte is only used with the TCP/IP and MODBUS TCP/IP protocol.
N = <DataLength> + 6
69
Page 70

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
write param (WP)
Command:
Byte Contents Bit no.
Byte 0
Byte 1
Byte 2 Command code (BFh) 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
Byte 3 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit - <Channel> <T>
Byte 4 System code <SystemCode> (high byte)
Byte 5 System code <SystemCode> (low byte)
Byte 6 Parameter type <ParamTyp> (high byte)
Byte 7 Parameter type <ParamTyp> (low byte)
Byte 8 Length 00 … FFh <DataLength (Byte)>
Byte 9 Data 00 ... FFh <Data>
... Data 00 ... FFh <Data>
Byte N
1)
2)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Telegram length, high byte 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1)
Telegram length, low byte 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
2)
Data 00 ... FFh <Data>
This byte is only used with the TCP/IP and MODBUS TCP/IP protocol.
N = <DataLength> + 6
70
Response:
Byte Contents Bit no.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1)
Byte 0
Byte 1
Byte 2 Command code (BFh) 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
Byte 3 Reserved/Ident channel/Toggle bit 0 <Channel> <T>
Byte 4 Status <Status>
Byte 5 Reply counter <ReplyCounter>
1)
Telegram length, high byte 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1)
Telegram length, low byte 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1
This byte is only used with the TCP/IP and MODBUS TCP/IP protocol.
2011-05
Page 71

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
IQH2-...: <SystemCode> = 'Q2' ASCII (51h 32h)
IUH-...: See handbook of the read / write head
Note!
Toggle bit
If you send two commands with the same SystemCode and same ParamTyp in
succession on the bus interface, you must change the toggle bit in the second
command in order for the node to detect the command.
7.8 Legend
<ParamTyp> = 'K1' ASCII (4Bh 31h)
RP: reads the key (12 characters ASCII from 0 ... F)
from the transponder and the read head
WP: writes the key (12 characters ASCII from 0 ... F)
into the read head
Default key = 'FF FF FF FF FF FF' ASCII
(46h46h46h46h46h46h46h46h46h46h46h46h)
2011-05
<Battery condition 1> : 1 byte, first digit of battery status (percentage, decimal,
<Battery condition 2> : 1 byte, second digit of battery status (percentage, decimal,
<Battery condition 3> : 1 byte, third digit of battery status (percentage, decimal,
<ByteNum> : 4 bits, length of <ID code>;
<Channel> : 3 bits, channel
<ConfAddr> : 1 ASCII character, word starting address in configuration area of data
<Data> : <WordNum> times 4 bytes. When communicating a word,
<F> : 1 bit, multiplex mode, 0 (0b): Mode off, 1 (1b): Mode on
<Fill Sign> : 1 ASCII character
<FixLen> : 4 bits, length of the read only code in bytes, see "This command tells
<FixType> : 2 ASCII characters, for example: '02' for IPC02
<IDCode> : 4 bytes, 6 bytes or 8 bytes (depending on the tag type)
<Ident channel> : 3 bits, channel
ASCII encoded). 30h, 31h
ASCII encoded). 30h, 39h
ASCII encoded). 30h, 39h
System MV: 4 characters (04h)
System IQ: 8 characters (08h)
Channel 1 (001b), channel 2 (010b),
channel 3 (011b), channel 4 (100b), all channels (111b)
carrier. The following applies for IPC03:
01h = Protection Word
02h = Control Word
the highest value byte is transferred first and the lowest
value byte last.
the read/write head on the relevant channel which tag type to
communicate with. This setting is stored in the non-volatile memory
on the unit." on page 28
1 (001b), 2 (010b), 3 (011b), 4 (100b), all channels (111b)
(but not <Sensor channel> in trigger mode)
71
Page 72

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
<Month> : 2 bytes ASCII, hexadecimal encoding, 01 ... 0C (01=Ja
<P> : 1 bit, password mode, 0 (0b): Mode off, 1 (1b): Mode on
<PSW> : 4 bytes HEX, password
<ReplyCounter> : 1 byte, increases by 1 after each response and confirmation. The
<Sensor channel> : 3 bits, channel
<Status> : 1 byte (see chapter 7.9)
<T> : 1 bit, toggle bit
<TagType> : 2 ASCII characters, for example: '02' for IPC02
<Trigger mode> : 8 bits
<WordAddr> : 2 bytes, word start address in the data carrier, range from 0000h to
<WordNum> : 4 bits, number of words to be read or written, range from 0h to Fh,
<Year> : 2 bytes ASCII, hexadecimal encoding, 00h ... 63h
0C=December)
reply counter starts from 0 after the system is switched on.
When the maximum value is reached, the counter skips the value 0
(from 255 to 1).
3 (011b) or 4 (100b)
0 (00000000b): Trigger mode off
1 (00000001b): Trigger mode on
2 (00000010b): Trigger mode inverted
FFFFh, depending on tag type.
depending on tag type.
The following applies for IPC03: The word count 0h is used with the
word address 0000h to read the preset data range on the read/write
tag ("Default Read").
7.9 Fault/Status messages
Status Meaning
00h The command has been executed without error.
FFh The command is processing.
nuary,
72
Error messages which triggered the identification sys
Status Meaning
01h The battery of the read/write tag is weak.
02h Reserved
03h Reserved
04h Incorrect or incomplete command or parameter not in the valid range.
05h No data carrier in the detection range.
06h Hardware error, e.g. error during self-test or R/W head defect.
07h Internal device error.
08h Reserved
09h The parameterized tag type is not compatible with the connected reading head.
0Ah Several tags in the detection range (UHF).
tem
2011-05
Page 73

IC-KP-B5-V23
Commands
Status Meaning
0Bh Reserved
0Ch Reserved
0Dh Reserved
0Eh Internal buffer overflow.
0Fh Reserved
Error messages sent by the bus connection
Status Meaning
10h Reserved
20h Reserved
40h Incorrect or incomplete command or parameter not in the valid range.
TCP/IP: The specified length of the message does not match the actual length.
2011-05
73
Page 74

IC-KP-B5-V23
148
666 67
107
22.5
494210
73
6.5
1
2
3
4
2
1
Technical specifications
8 Technical specifications
8.1 Dimensions
1 Ground
2 Connector array
8.2 General data
General data
Number of R/W heads max. 4
isplay/controls
D
74
LEDs 1, 2, 3, 4 Status display for R/W heads
LED PWR/ERR green: Power on
LED UL green: Voltage logic. Interface power ON/OK
LED RC green: Remote bus check. Incoming remote bus connected
LED BA green: Bus active. Telegrams are transmitted.
LED RD Yellow: Remote bus disable. Intermediate remote bus is
alternatively 2 R/W heads and 2 trigger sensors
green: Command to R/W head active
yellow: Approx. 1 second if command executed successfully
red: Hardware error
correctly; interface module not in reset.
deactivated.
2011-05
Page 75

IC-KP-B5-V23
Technical specifications
LC Display Two-line multifunction display with 12 characters per line
Buttons 4 buttons: ESC, up, down and return
Configuration of the control interface and display of
connected R/W heads as additional pictograms
Simple, direct command input and addressing possible
Electrical data
Rated operational
voltage U
e
Ripple ≤ 10 % at 30 V DC
Current consumption ≤ 2 A incl. R/W heads
Power consumption P03.5 W without R/W heads
Galvanic isolation Basic insulation in accordance with DIN EN 50178, rated
20 ... 30 V DC , PELV
insulation voltage 50 V
eff
Interface
Physical RS 485
Protocol INTERBUS remote bus
ID code 03
Transfer rate 500 kBit/s or 2 MBit/s can be switched internally
Conformity
Electromagnetic
compatibility
Degree of protection EN60529
EN 61000-6-2, EN 61000-6-4,
2011-05
Ambient conditions
Ambient temperature -25 ... 70 °C (248 ... 343 K)
Storage temperature -30 ... 80 °C (243 ... 353 K)
Climatic conditions Max. relative humidity 96%
Shock and impact
resistance
Oscillation (sine): 5 g, 10 ... 1000 Hz to EN 60068-2-6
Shock (half-sine): 30 g, 11 ms to EN 60068-2-27
Mechanical data
Degree of protection IP65 in accordance with EN 60529
Connection R/W heads: Shielded, 4-pin, M12 connector
Housing material Aluminum, powder-coated
Mounting Snap on to 35 mm DIN mounting rail or screw mounting
Weight Approx. 1000 g
Power supply: M12 connector
Ground: M6 grounding screw
INTERBUS: Connector, male: Incoming interface
Socket: Outgoing interface
75
Page 76

IC-KP-B5-V23
Troubleshooting
9 Troubleshooting
9.1 Fault location
Fault source Possible cause Remedy
The operating voltage LED
(PWR/ERR) does not light up.
The LED on the M12 plug lights
up red.
The icon in the display (e.g. IPH1)
does not appear even though the
R/W head is connected to port 1.
A read command (e.g. SR ...)
gives the status 4 even though the
syntax is correct.
The LEDs in the reading head
and the IPHx icon on the IDENT
Control display are flashing.
The SG or EG command (Get
configuration) gives the status 4
even though the syntax is correct.
The "RC" LED does not light up.
The station cannot be accessed.
The following stations cannot be
accessed.
The message "Access denied"
appears when the settings are
adjusted on the display.
This table will be updated and extended if necessary. Visit www.pepperl-fuchs.de to download the latest
version of the manual
Power supply is interrupted. Ensure that the power supply is
The polarity of the screw
terminal type M12 socket is
reversed.
The cable is defective or not
connected correctly.
The R/W head is defective. Check the R/W head and repair
An incorrect tag type is selected
for the relevant channel (e.g.
IPC02). The read commands
only function with data carriers
and not with code carriers.
The connected reading head
does not support the preset tag
type.
IPC03 is not selected for the
relevant channel. The
configuration commands only
function if the data carrier IPC03
is selected and not in autodetect
mode.
No connection to the interface
module or the status of the
interface module is RESET.
An unsuitable cable has been
used. Pins 5 + 9 in the connector
on the intermediate cable must
be linked together.
The master has already started
to communicate and access via
the display is disabled.
connected to a 24 V DC source.
Ensure that the connection
layout is correct.
Check the cable and repair if
necessary.
if necessary.
Preset the correct tag type (e.g.
IPC03) or "Autodetect" using the
CT... command or via the
display (IDENT Control .../
Config Channels).
Select a tag type that the reading
head supports.
Preset the tag type IPC03 using
the CT... command or via the
display (IDENT Control.../ Config
Channels).
Check the cable and
connections and repair if
necessary.
Start the interface module.
Use a suitable cable or install a
bridge between pins 5 + 9 in the
intermediate cable connector.
Interrupt or prevent the master
from communicating.
Switch the device off and back
on again.
Configure the device via the
display.
Activate communication again.
76
2011-05
Page 77

IC-KP-B5-V23
ASCII table
10 ASCII table
hex dec ASCII hex dec ASCII hex dec ASCII hex dec ASCII
00 0 NUL 20 32 Space 40 64 @ 60 96 '
01 1 SOH 21 33 ! 41 65 A 61 97 a
02 2 STX 22 34 " 42 66 B 62 98 b
03 3 ETX 23 35 # 43 67 C 63 99 c
04 4 EOT 24 36 $ 44 68 D 64 100 d
05 5 ENQ 25 37 % 45 69 E 65 101 e
06 6 ACK 26 38 & 46 70 F 66 102 f
07 7 BEL 27 39 ' 47 71 G 67 103 g
08 8 BS 28 40 ( 48 72 H 68 104 h
09 9 HT 29 41 ) 49 73 I 69 105 I
0A 10 LF 2A 42 * 4A 74 J 6A 106 j
0B 11 VT 2B 43 + 4B 75 K 6B 107 k
0C 12 FF 2C 44 , 4C 76 L 6C 108 l
0D 13 CR 2D 45 - 4D 77 M 6D 109 m
0E 14 SO 2E 46 . 4E 78 N 6E 110 n
0F 15 SI 2F 47 / 4F 79 O 6F 111 o
10 16 DLE 30 48 0 50 80 P 70 112 p
11 17 DC1 31 49 1 51 81 Q 71 113 q
12 18 DC2 32 50 2 52 82 R 72 114 r
13 19 DC3 33 51 3 53 83 S 73 115 s
14 20 DC4 34 52 4 54 84 T 74 116 t
15 21 NAK 35 53 5 55 85 U 75 117 u
16 22 SYN 36 54 6 56 86 V 76 118 v
17 23 ETB 37 55 7 57 87 W 77 119 w
18 24 CAN 38 56 8 58 88 X 78 120 x
19 25 EM 39 57 9 59 89 Y 79 121 y
1A 26 SUB 3A 58 : 5A 90 Z 7A 122 z
1B 27 ESC 3B 59 ; 5B 91 [ 7B 123 {
1C 28 FS 3C 60 < 5C 92 \ 7C 124 |
1D 29 GS 3D 61 = 5D 93 ] 7D 125 }
1E 30 RS 3E 62 > 5E 94 ^ 7E 126 ~
1F 31 US 3F 63 ? 5F 95 _ 7F 127 DEL
2011-05
77
Page 78

Subject to modifications
Copyright PEPPERL+FUCHS • Printed in Germany
www.pepperl-fuchs.com
Worldwide Headquarters
Pepperl+Fuchs GmbH
68307 Mannheim · Germany
Tel. +49 621 776-0
E-mail: info@de.pepperl-fuchs.com
USA Headquarters
Pepperl+Fuchs Inc.
Twinsburg, Ohio 44087 · USA
Tel. +1 330 4253555
E-mail: sales@us.pepperl-fuchs.com
Asia Pacific Headquarters
Pepperl+Fuchs Pte Ltd.
Company Registration No. 199003130E
Singapore 139942
Tel. +65 67799091
E-mail: sales@sg.pepperl-fuchs.com
FACTORY AUTOMATION –
SENSING YOUR NEEDS
TDOCT1274B_ENG
05/2011
 Loading...
Loading...