Pentair 9302C-HM2C, 9302C-HMIC, 9303C-HMIC, 9302CT-GM1, 9302C-HM4C Installation, Operation, Repair And Parts Manual
...Page 1

Series 9300 Hydraulically-Driven
Centrifugal Pumps
Installation, Operation, Repair and Parts Manual
Description
Form L-1526
(12/12, Rev. B)
Hypro centrifugal pumps are designed for agricultural and
industrial spraying and transfer of a variety of fluids: water,
insecticides, herbicides, wettable powders, emulsives, liquid
fertilizers, etc. Polypropylene centrifugal pumps may also be
used to pump acid fertilizer, calcium chloride and other highly
corrosive liquids such as sulfuric and phosphoric acids.
SERIES 9302C & 9302S
Cast Iron & Stainless Steel
Centrifugal Pumps
Max. Flow Rate: .............. 100 gpm
Max. Pressure: ...................120 psi
Ports: ....................1-1/4” NPT Inlet
.................................. 1” NPT Outlet
Hydraulic Ports: ...... 1/2” NPT Inlet
.................................3/4” NPT Tank
SERIES 9303C & 9303S
Cast Iron & Stainless Steel
Centrifugal Pumps
Max. Flow Rate: .............. 147 gpm
Max. Pressure: ...................145 psi
Ports: ....................1-1/2” NPT Inlet
............................ 1-1/4” NPT Outlet
Hydraulic Ports: ...... 1/2” NPT Inlet
.................................3/4” NPT Tank
Hypro Series 9300 hydraulic motor-driven centrifugal pumps
provide smooth performance. They can be conveniently
mounted on the tractor or sprayer, becoming part of the vehicle’s hydraulic system and freeing the PTO for other uses.
The Hypro “close-coupled” design reduces the mounting
space required, eliminating long shafts and couplers between the pump and motor.
SERIES 9303P
Polypropylene
Centrifugal Pumps
Max. Flow Rate: .............. 113 gpm
Max. Pressure: ...................125 psi
Ports: ....................1-1/2” NPT Inlet
............................ 1-1/4” NPT Outlet
Hydraulic Ports: ..... 1/2” NPT Inlet
.................................3/4” NPT Tank
SERIES 9303C-SP
Cast Iron Centrifugal Pumps
Max. Flow Rate: .............. 122 gpm
Max. Pressure: ...................140 psi
Ports: ....................1-1/2” NPT Inlet
............................ 1-1/4” NPT Outlet
Hydraulic Ports: ...... 1/2” NPT Inlet
.................................3/4” NPT Tank
SERIES 9305C-HM3C
Cast Iron Centrifugal Pumps
Max. Flow Rate: .............. 190 gpm
Max. Pressure: ...................180 psi
Ports: .......................... 2” NPT Inlet
............................ 1-1/2” NPT Outlet
Hydraulic Ports: ...... 1/2” NPT Inlet
.................................3/4” NPT Tank
SERIES 9305C-
HM3C-SP, -BSP
Cast Iron Centrifugal Pumps
Max. Flow Rate: .............. 178 gpm
Max. Pressure: ...................154 psi
Ports: ..............2” NPT or BSP Inlet
......................2” NPT or BSP Outlet
Hydraulic Ports: ...... 1/2” NPT Inlet
.................................3/4” NPT Tank
SERIES 9306C & 9306S
Cast Iron & Stainless Steel
Centrifugal Pumps
Max. Flow Rate: .............. 214 gpm
Max. Pressure: ...................150 psi
Ports: .......................... 2” NPT Inlet
............................ 1-1/2” NPT Outlet
Hydraulic Ports: ..... 1/2” NPT Inlet
.................................3/4” NPT Tank
Page 2

General Safety Information
California Proposition 65 Warning -- This product
and related accessories contain chemicals known to the
State of California to cause cancer, birth defects or other
reproductive harm.
Notes are used to notify of installation, operation, or
maintenance information that is important but not safety
related.
Caution is used to indicate the presence of a hazard,
which will or may cause minor injury or property damage
if the notice is ignored.
Warning denotes that a potential hazard exists and
indicates procedures that must be followed exactly to
either eliminate or reduce the hazard, and to avoid serious
personal injury, or prevent future safety problems with
the product.
Danger is used to indicate the presence of a hazard
that will result in severe personal injury, death, or
property damage if the notice is ignored.
Do not pump flammable or explosive fluids such as
gasoline, fuel oil, kerosene, etc. Do not use in explosive
atmospheres. Components not rated for use with
Anhydrous Ammonia. The pump should be used only
with liquids compatible with the pump component
materials. Failure to follow this notice may result in
severe personal injury and/or property damage and will
void the product warranty.
1. Do not pump at pressures higher than the maximum
recommended pressure.
o
2. Maximum liquid temperature is 140
centrifugal pumps.
3. Disconnect power before servicing.
4. Release all pressure within the system before
servicing any component.
5. Drain all liquids from the system before servicing
any component. Flush with water.
6. Secure the outlet lines before starting the pump. An
unsecured line may whip, causing personal injury
and/or property damage.
7. Check hose for weak or worn condition before each
use. Make certain that all connections are tightly
secured.
8. Periodically inspect the pump and the system
components. Perform routine maintenance as
required (See Repair Instructions).
9. Use only pipe, hose and fittings rated for the
maximum psi rating of the pump.
10. Do not use these pumps for pumping water or other
liquids for human or animal consumption.
F for Series 9300
Hazardous Substance Alert
1. Always drain and flush pump before servicing or disassembling for any reason.
2. Always drain and flush pumps prior to returning unit
for repair.
3. Never store pumps containing hazardous chemicals.
4. Before returning pump for service/repair, drain out
all liquids and flush unit with neutralizing liquid.
Then, drain the pump. Attach tag or include written
notice certifying that this has been done. It is illegal
to ship or transport any hazardous chemicals without United States Environmental Protection Agency
Licensing.
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Never use your hand to check the condition of hydraulic
lines or hoses. If hydraulic fluid penetrates the skin, get
medical help immediately. Failure to get proper medical
help may result in loss of limb or life. The safest way to
check hydraulic lines or hoses is by holding a piece of
cardboard next to the hydraulic line or hose.
The sound pressure level of the pump is 80dBA. Observe
all safety precautions when operating the pump within
close proximity for extended periods of time by wearing hearing protectors. Extended exposure to elevated
sound levels will result in permanent loss of hearing
acuteness, tinnitus, tiredness, stress, and other effects
such as loss of balance and awareness.
-2-
Page 3
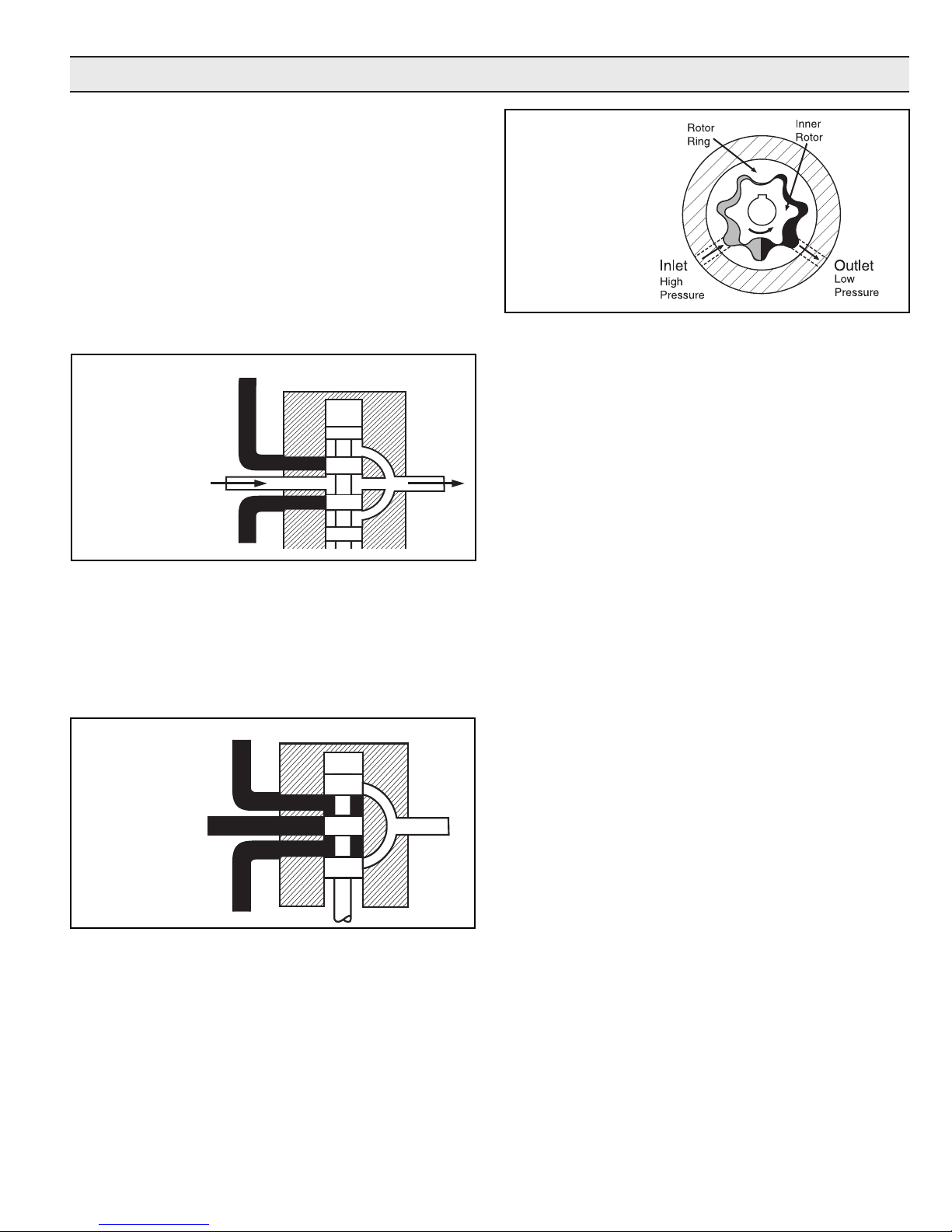
Hydraulic Pumps
General Information—Hydraulic Systems
Hydraulic pumps come in two basic types:
• Constant displacement - which will continue to put
out its rated flow regardless of pressure, until the relief valve bypasses the flow.
• Variable displacement - which will produce only the
flow needed by the implement until the total pump
output is reached. If less than the full pump output
is required, an automatic stroke control mechanism
decreases the pump output to maintain a constant
pressure and flow. The output varies according to
demand.
Open Center
Spool Valve
In Neutral
Position
Figure 1
Spool Valves
There are two basic types of spool valves used in conjunction
with these pumps — Open and Closed Center. In the Open
Center Valve (See Figure 1), the flow goes straight through
the valve when in the neutral position. This type is used for
constant displacement pumps where the flow should never
be shut off.
Closed Center
Spool Valve
In Neutral
Position
Gerotor-Type
Hydraulic Motor
Figure 3
Three Systems
Fitting these components together and installing a motor,
we have one of the three types of systems: Open Center,
Closed Center (pressure compensated) and Closed Center
Load Sensing (flow and pressure compensated).
Open Center Systems
In an Open Center System, the hydraulic pump puts out a
constant flow. If the pump puts out more oil than the motor can use, a portion of the oil must be bypassed around
the motor. When the oil is bypassed around a loop and does
no work, the energy put into it by the pump turns into heat.
Therefore, the amount of oil bypassed should be kept to a
minimum. Use the largest motor possible.
Closed Center (Pressure-Compensated) Systems
The Closed Center Pressure-Compensated system has a
variable displacement pump which will deliver flow at the
necessary rate to maintain a specified pressure. It is desirable to equip implements with a motor of a low flow range
that will cause the pump to operate between 1800 and 2100
psi [124 and 145 BAR]. A motor that requires a large volume to obtain the correct implement speed usually causes
the hydraulic pump in a closed center system to operate at
a lower pressure than desirable. This low pressure results in
unnecessary flow and the generation of heat that lowers the
lubricating quality of the oil and may damage transmission
parts. Use the smallest motor possible.
Figure 2
The Closed Center Valve (See Figure 2) is used with variable
displacement pumps. The flow is completely shut off in the
neutral position, causing the pump stroke to adjust to zero
flow. The flow stops, but the pump maintains a static pressure up to the valve.
Hydraulic Motors
Figure 3 shows an internal gear motor (Gerotor) where pressure causes the cavities between the gears to expand on one
side, developing torque. The Gerotor type of hydraulic motor
is used on Hypro pumps for its superior performance characteristics, including cooler running and higher rpm capabilities.
Closed Center Load Sensing Systems
(Flow and Pressure-Compensating)
The Closed Center Flow-Compensated System is a variation
of the pressure-compensated system, designed primarily for
more efficient operation and the generation of less heat. It
works on the principle of maintaining a constant pressure
drop from the pump to the work port of the selector valve. Any
variation in demand at the motor will cause a change in flow.
The system senses this change in flow due to the change
in pressure drop across the valve and causes the pump to
compensate by varying the pump flow. No restrictor is used
in the pressure line and no oil is bypassed.
-3-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 4
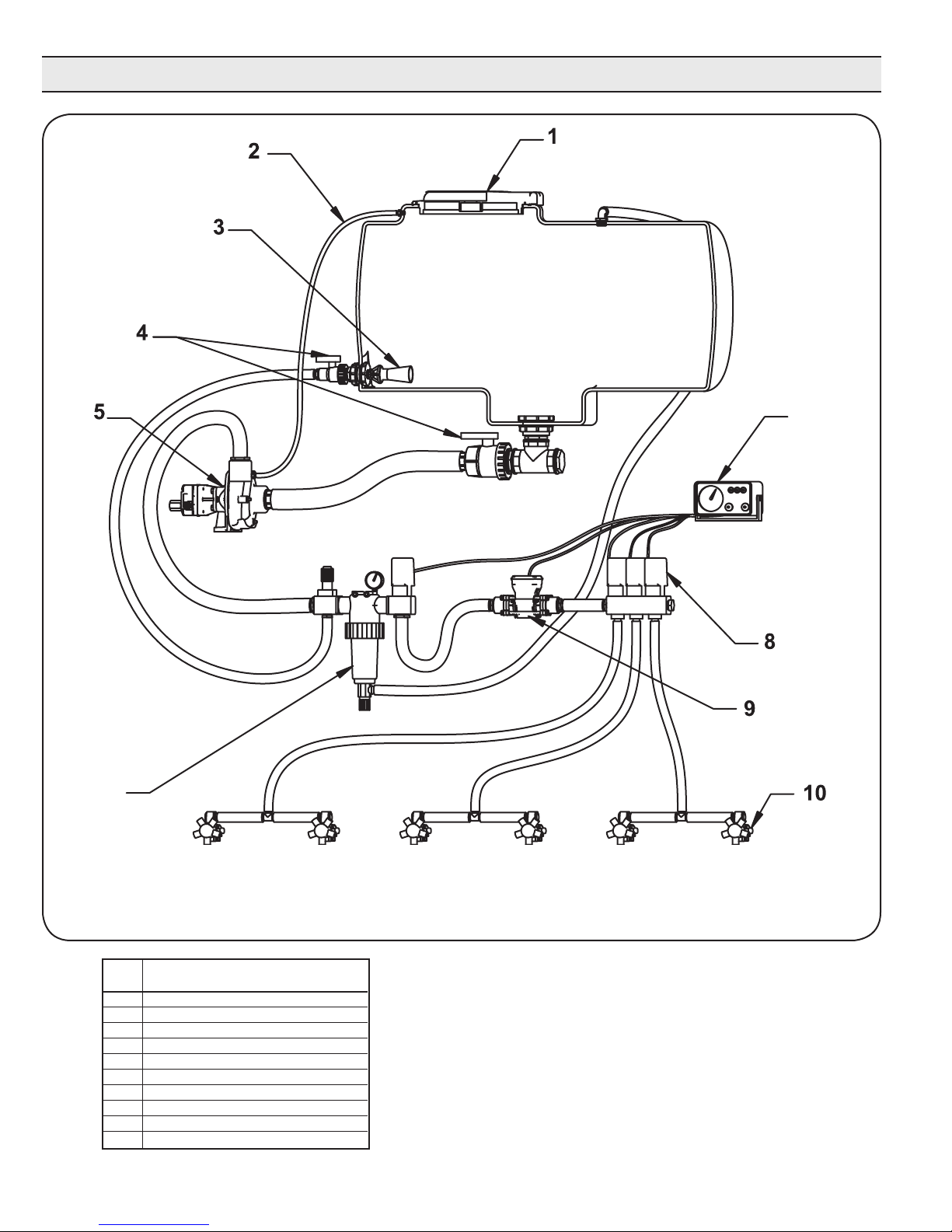
Plumbing Installation
7
6
Centrifugal Plumbing Hook-up
REF. DESCRIPTION
NO.
1 Tank Lid
2 Vent Line #3430-0456
3 Jet Agitator
4 Shut-off Ball Valves
5 Centrifugal Pump
6 Spray Control Console
7 Centrifugal Pump Control
8 Manifold Boom Valve
9 Electromagnetic Flowmeter
10 Compact Jet Turret Nozzle Body
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
-4-
Page 5

Installation Instructions
All Models — Open Center Systems
Models include Tank Port Adapter with built-in Check Valve
Assembly and Pressure Port Adapter.
HM2C and HM4C Models Only — Closed Center and
Small Open Center Systems.
Models include Tank Port Adapter with built-in Check Valve
Assembly and Pressure Port Adapter with three different
size metering orifices for HM4C models. The orifices are not
required for use with closed center systems with flow control,
such as John Deere closed center systems. Also, do not
use for small open center systems with a maximum flow of
8 gpm [30.28 lpm] for HM2C model; 10 gpm [37.85 lpm] for
HM4C model. If necessary, the pressure port adapter may be
used without a metering orifice installed in any closed center
system. For best results, the pressure differential across the
motor should be less than 2500 psi (170 bar).
Preliminary to Mounting
Consult the owners manual to determine the type and
capacity of the hydraulic system. Make sure the hydraulic
system is recommended to operate with a continuous load.
Refer to the Pump Selection Guide to confirm you have the
proper pump for your hydraulic system.
Check to see that the pump impeller can be turned by hand.
(Turn the shaft clockwise using a deep socket wrench on the
impeller nut.) If it cannot be turned, open the pump casing to
look for obstructions. Clean out any corrosion build up where
the casing fits over the eye of the impeller.
Pump Inlet Line
To achieve full capacity from the pump, the inlet line should
be at least the same size as the inlet port on the pump.
Reducing this line size will restrict the capabilities of the
pump. The line must also be free of air leaks. Check all
fittings and connections in the suction line for tightness.
The introduction of air may affect the priming and pumping
capabilities of the pump. Use good quality suction hose that
will not be collapsed by suction.
For non self-priming models, the centrifugal pump should
be mounted below the liquid level and as near to the liquid
source as possible to allow for the shortest suction line
practical. To achieve optimal performance, the suction line
should slope down into the pump. Avoid rises and humps
that could trap air in the line to the pump. The suction line
and pump should be filled with liquid prior to starting the
pump, and all discharge lines should be open.
Pump Outlet Line
The recommended orientation for the outlet port is pointing
straight up. This allows liquid to stay in the pump while it
is priming. The outlet line should be the same size as the
pressure port on the pump to give the optimal flow. The line
should have as few restrictions and elbows as possible to
optimize the pump performance and reduce pressure drop
from the pump to the spray tips.
Priming the Pump
The pump must not be run dry.
Before starting the pump, the inlet line and pump must be
filled with liquid and all discharge lines must be open. On selfpriming models, only the pump chamber needs to be filled
with liquid. The pump must not be run unless it is completely
filled with liquid because there is a danger of damaging
the mechanical seal, which depends on the liquid for its
lubrication.
Non-self-priming models should be mounted below the level
of the liquid. The suction line should slope down to the pump
and be free of dips and bends. If this cannot be done, a foot
valve should be installed in the end of the inlet line so that
the line can be completely filled with liquid before starting the
pump.
For best priming results, the top vent plug should be
removed from the pump casing. A vent line (1/4” [6.35
mm] tubing is sufficient) should be installed running
back to the top of the tank. This line prevents air lock and
allows the pump to prime itself by bleeding off trapped air. The
small stream of liquid that returns to the tank during operation
is negligible. The discharge from this line should be positioned
in the tank above the high liquid level. Self-priming models
can be primed by removing the top vent plug and filling the
priming chamber. The priming chamber will fill to the level
of the inlet port. After use, the priming chamber should be
flushed and drained to avoid chemical corrosion and damage
from freezing. Drain by removing the lower drain plug.
Controlling the Pump Flow
The best way to control the flow is by incorporating two
control valves in a pipe tee immediately after the strainer
in the discharge line. This permits controlling agitation flow
independently of nozzle flow.
In any centrifugal pump, it is the large volume of liquid which
puts load on the drive. Use only the flow needed to develop
the pressure required at the boom and to maintain adequate
agitation. Hydraulic motor-driven centrifugal pumps are
easily adjusted to the exact flow required, as explained in the
Operating Instructions of this manual.
Centrifugal Pump Control
Hypro now offers many different components for spraying
systems. The Hypro centrifugal pump control incorporates
the electric flow control valve, a self-cleaning line strainer, a
visual pressure gauge and a manual agitation control valve.
Flow Control Valve
A high-flow electric proportional valve allows for maximum
flow control to the boom valves. It provides smooth, rapid
control that can be controlled from either an electronic rate
controller or switch box.
Strainers
The recommended placement of the strainer for a centrifugal
pump is in the pump outlet line. This will eliminate any
possible restriction that the strainer could create if it were
installed in the inlet line. Ensure that the proper strainer
size and screen mesh are used to limit the pressure drop
-5-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 6
Plumbing Installation
and achieve the best filtration. Line strainers can also be
installed in the tank fill line to filter liquid as it is loaded into
the tank as well as in the boom lines to further filter the
solution prior to the spray tips. Tank baskets can also be
used to filter material added through the tank lid.
Agitation
The centrifugal pump control contains a manual agitation
control valve that can be adjusted to provide the right
amount of flow to the jet agitators in the tank to ensure
proper mixing within the tank.
Flowmeter
To eliminate the mechanical problems of a turbine flowmeter,
we recommend that an electromagnetic flowmeter be used.
These flowmeters have no moving parts to wear out and will
provide a more consistent and accurate flow reading. They
can be input into just about any electronic rate controller or
switch box.
Boom Section Valves
For rapid response and reliability, we recommend electric
plunger valves be used for boom control. The valves should
be sized accordingly to minimize the pressure drop and
maximize the flow rate. The boom tubing or hose should
be sized accordingly to ensure that a pressure drop in the
lines does not occur, causing inconsistent pressures at the
nozzles.
Nozzle Bodies
Nozzle bodies with shut-off check valves are recommended
to eliminate dripping from the spray tips when the boom
valves are shut down.
Hooking Up the Hydraulic Motor to the
Tractor Hydraulic System
Hypro Series 9300HMC hydraulic motor-driven pumps can
be mounted on either the tractor or sprayer. When hooking
up, make sure that no dirt or liquid gets into the hydraulic
motor. Keep all hydraulic connections clean. Be sure
to connect the hydraulic motor into the system correctly by
putting the pressure line to the Pressure Port Adapter and
return line to the Tank Port Adapter. The adapters on the
hydraulic motor are sized to accommodate 1/2” NPT fittings
on the pressure port and 3/4” NPT on the tank port. For
maximum performance, the hydraulic lines should also be at
least 1/2” [12.7 mm] in size for the pressure line and 3/4”
[19.05 mm] for the tank line.
The tank (OUT) port adapter with a built-in check valve
assembly will guard against reverse operation — allowing you
to reverse oil flow to operate other equipment. This adapter
must not be removed. On HM2C and HM4C model pumps,
the pressure (IN) port adapter is a two-piece assembly
consisting of an open (unrestricted) adapter with three orifices
packed loose with the pump. (See the Operations Section.)
When using the HM2C or HM4C unit on any flow- compensated
(load sensing) closed center system, or any small open center
system with a maximum flow of 8 gpm [30.28 lpm] for HM2C
or 10 gpm [37.85 lpm] for HM4C, the metering orifice should
be removed from the pressure port adapter. When using these
units on flow-compensated systems, connect to the motor
priority circuit if your tractor has one.
Standard spool valves, which are found on all tractor
hydraulic systems, may cause potentially damaging high
peak pressures in the hydraulic system when closed because
of abrupt shut-off of oil flow in both the supply and return
lines. When shutting off the pump, move the selector to the
FLOAT position to allow the centrifugal pump to come to a
stop gradually.
For further information
regarding Hypro products,
contact your local dealer or
Hypro directly at
www.hypropumps.com or by
calling 1-800-424-9776.
Open Center Systems— All Models
Adjusting Centrifugal Pump Output
HM1C, HM3C & HM5C motors have bypass screw fully
closed from the factory. HM2C & HM4C motors have bypass
screw set at 1-1/2 turns from fully closed from the factory.
1. Open the bypass adjustment screw 2-1/2 turns from fully
closed. Turn the bypass screw in to achieve the flow for
the desired gpm and psi.
2. Start the tractor. Leave the directional valve in the
neutral position and allow hydraulic oil to circulate for
approximately 10 to 15 minutes or until adequately
warmed.
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Operation
3. Prime the centrifugal pump with all valves open (See
the Installation Instructions and System Configuration
Diagram).
4. Close the agitation line valve and keep the control
valve and the boom shut-off valve open. Note the spray
pressure.
5. Open the agitation line valve until you have desired
circulation in the tank. Recheck the spray pressure. If it
is too low, close down the agitation line valve until the
desired spray pressure is reached. If the spray pressure
is too high, throttle the centrifugal pump by closing down
the control valve.
-6-
Page 7

Closed Center (Pressure-Compensated) —
HM2C and HM4C Models Only
On a pressure-compensated system, the amount of oil that
is allowed to flow through the hydraulic motor is regulated
by a metering orifice in the pressure port adapter. Three
different sizes of orifices are supplied with the HM2C and
HM4C model pumps to allow flexibility in the flow required for
individual sprayer needs.
The smaller the orifice, the less hydraulic oil goes through
the motor, so the pump will run slower and the flow of liquid
pumped and the spray pressure will also be less. As the
hydraulic oil flow is increased (by installing a larger orifice),
the amount of liquid being pumped and the spray pressure is
also increased.
Installing and Removing Metering Orifice
1. Shut off the hydraulic system.
2. Disconnect the line to the pressure port of the hydraulic
motor.
3. Remove the adapter from the motor using a 1-1/16’’
wrench. Make sure the o-ring is on the metering orifice
before installing into port adapter.
4. The orifice is removed or installed in the port adapter by
tapping either in or out of the adapter.
A. To remove — tap the orifice out from the small end
of the adapter.
B. To install — tap the orifice in from the large end of
the adapter. The orifice is seated when a snap sound
is heard.
Adjusting Centrifugal Pump Output
1. Open the bypass adjusting screw in the hydraulic motor
three (3) turns.
2. Start the tractor and allow the hydraulic oil to circulate
for approximately 10 to 15 minutes or until adequately
warmed.
3. Close and lock down the bypass adjusting screw in the
hydraulic motor.
4. Prime the centrifugal pump with all valves open (See
Installation Instructions and System Configuration
Diagram).
5. Close the agitation line valve and the control valve; open
the boom shut-off valve.
6. With the pump running, open the control valve until the
pressure gauge indicates the desired spraying pressure.
7. Open the agitation line valve until sufficient agitation is
observed. Then, if spray pressure drops, readjust the
control valve to restore to the desired pressure.
8. If a sufficient boom pressure cannot be attained, install
the #2 size orifice and repeat Steps 5 through 7.
9. If a sufficient boom pressure still cannot be attained with
the #2 size orifice, install the #3 size orifice and repeat
Steps 5 through 7.
10. If a sufficient boom pressure still cannot be attained
with the #3 size orifice, remove the orifice and repeat
Steps 5 through 7.
Closed Center (Load Sensing) — All Models
Many tractors are being introduced with load sensing
systems (also referred to as flow and pressure- compensated
systems) which simplify system setup and eliminate many
of the problems associated with using the wrong size pump
motors on a given hydraulic system. Usually, any of Hypro’s
9300HMC models may be used on this type of system,
provided the hydraulic system produces sufficient oil flow for
the hydraulic motor being used (Refer to the Pump Selection
Guide).
This system maintains a constant flow of hydraulic oil for a
given pressure drop. The flow is adjustable with a flow control
valve installed in the hydraulic system (such as the Tortoise/
Hare control on John Deere tractors). Because this system
has adjustable flow, there is no need to bypass hydraulic oil
as in an open center system, or to restrict the flow with orifices
as in a closed center pressure- compensated system.
Adjusting Centrifugal Pump Output
1. Make sure the orifice from the pressure port adapter
of the hydraulic motor has been removed (HM2C and
HM4C models only).
2. Close and lock down the bypass adjusting screw in the
hydraulic motor.
3. Set the tractor hydraulic flow control valve for minimum
hydraulic oil flow to the remote outlet (Tortoise position).
4. Start the tractor and allow the hydraulic oil to circulate
for approximately 10 to 15 minutes or until adequately
warmed.
5. Prime the centrifugal pump with all valves open (See
the Installation Instructions and System Configuration
Diagram).
6. Close the agitation line valve and open the control valve
and the boom shut-off valve.
7. Slowly adjust the tractor hydraulic flow control valve until
the desired boom pressure is attained.
8. Open the agitation line valve until sufficient agitation is
observed. If spray pressure drops, readjust the tractor
hydraulic flow control valve to restore it to the desired
pressure.
Flush Pump After Use
One of the most common causes for faulty pump performance
is gumming or corrosion inside the pump. Flush the pump
and entire system with a solution that will chemically
neutralize the liquid pumped. Mix this solution according to
the manufacturer’s directions. This will dissolve most residue
remaining in the pump, leaving the inside of the pump clean
for the next use.
To Prevent Corrosion
After cleaning the pump as directed above, flush it with a
permanent-type automobile antifreeze (Prestone®, Zerex®,
etc.) containing a rust inhibitor. Use a 50% solution, half
antifreeze and half water. A protective coating will remain on
the inner pump surfaces. Save the excess antifreeze for the
next application. Plug the ports to keep out air during storage.
For short periods of idleness, noncorrosive liquids may be left
in the pump, but air must be kept out. Plug the ports or the
seal port connections.
-7-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 8
Repair Instructions
Hypro Repair Tools:
ToolBoxNo.3010-0168•1/4”AllenWrenchNo.3020-0008
SupportBars(2)No.3010-0064•PortBrushNo.3010-0066
1/16”AllenWrenchNo.3020-0009•BrushHolderNo.3010-0067•
LargeRetainingRingPliersNo. 3010-0084 • Small RetainingRing
Pliers No. 3010-0167
NOTE:
Shop Tools Needed:
BenchVice•ArborPress•AirorHandDrill•SmallKnife
Metal Pipe - 1” dia. x 4” high (Bearing Seating Tool)
PVC Pipe - 3/4” dia. x 4” - 6” high (Seal Seating Tool)
12”CrescentWrench•TwoFlatScrewdrivers(approx.10”long)
1/2’’,9/16”,5/8”and7/8”sockets•HammerorRubberMallet
SmallScrewdriver(recommended)•LargeFile(optional)
1/2”and9/16”BoxEndWrench•LubricatingSpray(WD-40orLPS)
SmallamountHydraulicOil•CleaningSolventTank(recommended)
Pump Housing Disassembly
Instructions in italics describe procedures for the Series
9300P Polypropylene Centrifugal Pumps, when different
than the cast iron pumps.
1. Using a 9/16” box end wrench, remove the four Hex
Head Bolts holding the Pump Casing to the Mounting
Flange. (If necessary, tap Pump Casing Outlet Port with
rubber mallet or hammer to separate.) [Using a 1/2”
wrench, remove the six bolts from the front. For the two
bottom bolts securing the base, you will need to hold the
two nuts with another 1/2” wrench. Also remove the 5/16”
screw from the rear, near the outlet port.]
Visit our website at
www.hypropumps.com
for video repair procedures,
under the Tools section.
3. Once nut [and washer] is removed, place a screwdriver
on each side behind the Impeller and pry away from
the Mounting Flange (See Figure 7). Remove Woodruff
KeyfromtheShaft.RemoveO-ringfromthe Mounting
Flange.
Pump Seal Removal
1. Lightly lubricate the Shaft for easier removal of the Seal.
Using two screwdrivers positioned opposite each other,
pry the rotary portion of the Seal from the Shaft (See
Figure 8).
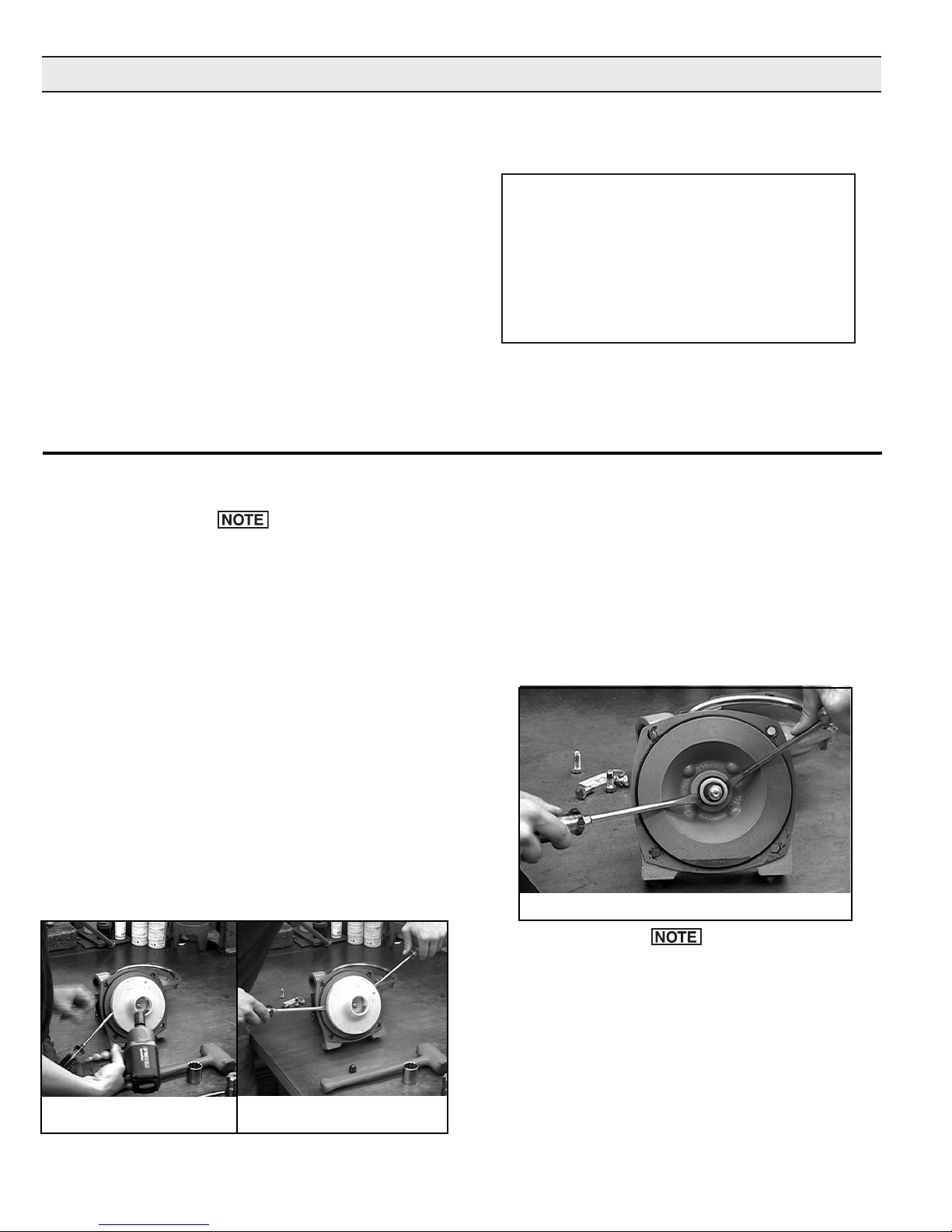
2. To remove the Impeller Nut, insert a large screwdriver
or file (at least 10” [254 mm] long) into Impeller Vanes to
prevent Impeller from turning when loosening nut. Use a
5/8” socket wrench to remove the Impeller Nut by turning
it counterclockwise (See Figure 6). [Use 7/8” deep
socket wrench to remove Plastic Seal Nut, then 9/16”
deep socket to remove Metal Jam Nut and Washer.]
Figure 6
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Figure 7
Figure 8
In the case of a severe pump seal leak, inspect the
Shaft/Bearing Assembly in the hydraulic motor for
possible contamination.
2. Using a 1/2’’ box end wrench, remove the four bolts
holding the Motor to the Mounting Flange. Remove
Motor. [Remove the Plastic Back Cover flange. Knock
the Seal out from back with a hammer and screwdriver.
Use a 1/2’’ socket wrench and 1/2’’ box end wrench to
remove the Mounting Flange from the Hydraulic Motor.]
-8-
Page 9

3. Using a screwdriver and hammer, tap out the stationary
portion of the Mechanical Seal from the motor side of the
Mounting Flange. (If the motor is not removed, the seal
can be pried out with a small screwdriver.)
The seal will be damaged by removal in this manner. A
new seal must be used when pump is reassembled.
Clean-Up Of Pump Housing
1. Using a circular bottle-type wire brush with air or hand
drill, clean the Outlet Port, Inlet Port and the sealing
areas of the o-ring on the Pump Casing and Mounting
Flange. Using the port brush, clean the seal cavity in the
Mounting Flange. [The last step should not be performed
on the 9300P.]
2. After wire brush cleaning, it is recommended that the
Pump Casing and Mounting Flange be further cleaned in
a solvent tank to remove rust and corrosion particles.
The threads of the Plastic Seal Nut are fine and can
be easily cross threaded. To prevent cross threading,
turn the Plastic Seal Nut counterclockwise until area
of thread engagement is detected; then turn the Plastic
Seal Nut clockwise until it is secure. Do not over tighten
the Plastic Seal Nut.
6. InsertaWoodruffKeyintotheShaftkeyslot;thenplace
theImpellerontheShaftandalignitwiththeKey and
press against the Mechanical Seal Assembly. Apply a
blue thread locking compound to the Impeller Nut, and
using a 5/8’’ socket wrench and using a screwdriver to hold
the Impeller, install the Impeller Nut. [On polypropylene
models, insert the Woodruff Key into the Shaft key slot.
Place the Impeller on the Shaft and align it with the Key;
then press against the Mechanical Seal Assembly. Place
the Metal Seal Washer on the Shaft. Apply a drop of blue
thread locking compound on the Impeller Nut and secure
the Impeller to the Shaft as described previously.]
Seal Replacement/Pump Housing Reassembly
If the hydraulic motor requires repair, proceed to
Disassembly and Repair of the Hydraulic Motor in the
next column.
1. Lubricate the seal cavity in the Mounting Flange with
®
WD-40
, LPS or equivalent. Do not lubricate the shaft.
2. Install the stationary portion of the Mechanical Seal by
sliding over the Shaft with the ceramic side out.
Make sure both the seal cavity and seal are clean and
lubricated.
3. To seat the seal in the seal cavity, use a piece of 3/4”
PVC pipe 4” to 6” [101.6 to 152.4 mm] in length. Lubricate
sealing surface on seal after it is seated. Do not lubricate
the shaft.
4. To install the rotary portion of the mechanical seal, place
it over the shaft with the carbon side facing in, and press
against the stationary portion (See Figure 9).
5. Install rubber gasket 1700-0100 over shaft against rotary
portion of seal.
7. Install the o-ring on the mounting flange. Replace the
o-ring if worn or damaged.
8. Place the pump casing on the mounting flange, insert
and tighten the bolts.
Disassembly and Repair of the Hydraulic Motor
The work area and motor should be as clean as
possible to prevent contamination of parts.
Figure 10
Figure 10a
1. Remove the Mounting Flange from the motor body and
place Hydraulic Motor in vise.
2. Remove Tank Port Adapter and Pressure Port Adapter
with large crescent wrench or 1-1/16” and 1-3/8” box end
wrench (See Figure 10).
Figure 9
On Models 9305C-HM3C-SP, 9505C-HM3C-BS and
9305C-HM3C, install the washer on the shaft prior to
installing the impeller nut.
3. Using a 9/16” box end wrench, loosen the nut on the Bypass Adjusting Screw (See Figure 10a).
4. Using a small screwdriver, remove the Bypass Adjusting
Screw from the Motor. (This will remove the Screw, Nut,
Washer and Thread-Seal Gasket.)
5. Using a 1/4” Allen wrench, remove the Socket Head Cap
Screws from the Motor End Plate (See Figure 10).
6. If Motor End Plate will not lift off easily, use a small screwdriver to carefully pry apart the boss portion of the End
Plate and Gerotor Housing until free (See Figure 11). If
Gerotor Housing will not lift off easily, carefully pry apart
-9-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 10

the boss area between the Gerotor Housing and the Motor Body. (It may be necessary to alternate sides when
prying apart Motor sections.)
Figure 11
7. Remove both parts of the Gerotor.
8. OnHM3C models, remove theWoodruffKey from the
Shaft. On HM1C, HM2C and HM4C models, remove the
Roll Pin from the Shaft.
9. Remove the o-ring from the Motor End Plate and Body
with a flat instrument such as a knife blade.
10. Inspect Motor End Plate, Body and Gerotor Housing for
wear and/or gouging. If gouging has occurred in both the
Motor End Plate and Body, the motor is not repairable.
If gouging has occurred in the Motor End Plate, Body or
Gerotor Housing, the part that is worn must be replaced.
If Gerotor Housing is damaged, Gerotor parts must also
be replaced.
Hydraulic Motor Shaft Disassembly and Repair
1. Remove Large Retaining Ring from Shaft with a screwdriver. Remove Thrust Bearing Assembly from Shaft (includes the Thrust Bearing and two Thrust Bearing Races) and the Seal Spacer.
2. Remove the Small Retaining Ring next to the Shaft Ball
Bearing.
3. To remove the Bearing from the shaft, place the shaft
(threaded end up) in the arbor press fixture. Place the two
support bars provided in the repair kit opposite each other and between the seal on the shaft and the arbor press
fixture. Using an arbor press, press the shaft through the
Bearing, Seal Spacer and Seal (See Figure 13).
4. Inspect the sealing area of the shaft for wear. Inspect
other Shaft Assembly Components for wear and replace
if necessary.
Figure 13
5. While motor is completely disassembled, clean all parts
in a solvent bath.
Build Shaft Sub-Assembly
To Remove the Shaft Assembly from the Motor Body
1. Remove the Slinger Ring from the Motor Shaft.
Special attention should be exercised when working with
retaining rings. Always wear safety goggles when working with spring or tension loaded fasteners or devices.
2. Using the large retaining ring pliers, remove the Retaining
Ring next to the Ball Bearing in the Motor Body.
If bearing is binding against the retaining ring so that it
cannot easily be removed, place the motor body (threaded portion of the shaft up) on arbor press. Using a piece
of un-threaded metal pipe (1” dia. x 4” high [254. mm x
101.6 mm high]), slide over the shaft and gently press
down with the arbor press just enough to relieve the
pressure on the retaining ring.
1. To assemble the seal cartridge, remove the old
seal from the cartridge by pressing it out. The cartridge is reused by assembling the new seal into cartridge, ensuring the new seal is pressed in with the lip
seal on the opposite side as shown in Fig.A.
Press
Seal Spacer
Seal
Cartridge
Fig. A
Important: To prevent damage to the seal lip extending out,
use seal spacer as shown to guard lip during assembly.
2. Install the large retaining ring onto large diameter end of
shaft.
3. From the small, threaded end of the shaft, install the
following parts in this order: thrust bearing race, thrust
bearing, 2nd thrust bearing race.
Note: The thrust bearing and races should not be reused if
they are showing any signs of wear.
Figure 12
3. Place body in position on arbor press. Threaded portion
of the Shaft should be inside the fixture. Press out shaft
assembly with arbor press (See Figure 12).
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
4. Install new type seal spacer (looks like a thick washer,
approx .130 inch thick).
5. Before installing the new seal, its lip must be expanded to
fit on the shaft. With the seal lip facing out, slide the seal
over the threaded end of the shaft and gently push the seal
onto the raised area of the shaft. Do not push the seal past
the large retaining ring groove on the shaft.
-10-
Page 11

6. Once the seal has been expanded, remove the seal from
the shaft.
7. Install seal cartridge assembly: With seal lip facing the
large end of the shaft, slide the seal cartridge assembly
over the threaded end of the shaft and gently push into the
raised area of the shaft. Align the seal lip to enter
the center diameter of the seal spacer and push until seal
body touches seal spacer.
Important: If the seal lip is longer than the seal spacer’s
width, please stop the assembly and review parts being used.
8. Assemble two o-rings on the outside body of the new seal
cartridge assembly as shown in Fig B. Install o-rings one at
a time and do not roll over each other.
(2) O-rings
Fig. B
Shaft
9. Finished shaft sub-assembly should look like this:
Figure 15
3. Turn the motor body assembly over (threaded shaft end
down) on the arbor press. Press the shaft down into
its “final position” until the small retaining ring can be
installed in the shaft next to the ball bearing.
4. Install small retaining ring on shaft.
5. Check shaft rotation at this point. It should rotate
smoothly with only slight resistance from the seal lip
pressure on the shaft. If you feel any gritty or sticking movement, return assembly to the arbor press
and lightly press on the threaded end of the shaft to
relieve press fit compression on the thrust bearing. Note: Don’t over do this press. The objective is
to move the small outer retaining ring installed in the
previous step back to ”touching only” the ball bearing
inner race.
10. Do not press, but place the shaft sub-assembly into the
motor body with threaded end of shaft up. Lubricate the
two o-rings with hydraulic or mineral oil before assembling.
Figure 14
Install Shaft Sub-Assembly Into Motor Body
Important: Make sure the surface edge of the arbor press
fixture is smooth and clean. An unthreaded piece of
pipe (1” x 4” high) is needed to support the outer race of
the seal cartridge sub-assembly and outer race of the
ball bearing during assembly. Place this pipe over the
shaft threaded end for assembly of the following steps.
1. Place the body on a support fixture in the arbor press.
Using an unthreaded piece of pipe (1” dia. x 4” high),
press the shaft subassembly down into the body until it
bottoms out. This is a light press fit and should be done
slow and easy.
2. Install the new ball bearing onto the threaded end of
the shaft. Press down using the 1” x 4” pipe until the
retaining ring can be installed in its groove in the bearing core of the motor body. Install the retaining
ring.
Important:
If gritty or sticky movement persists, it’s likely
due to re-used parts or the body needle bearing is in
need of replacement.
Reassembly of Remaining Hydraulic Motor Parts
1. Place Motor Body in a vise with large end of shaft facing
up.
2. Install the o-ring in the body.
3. Install the Roll Pin on the shaft. Place the Inner Gear of
the Gerotor onto the shaft making sure Gerotor slot lines
up with the key in the shaft.
The Roll Pin can slide up behind the inner gear of the
gerotor when the gear is installed. Make sure the key is
visible in the slot after the gear is in place.
4. Install the outer portion of the Gerotor, making sure the
Gerotor is centered within the o-ring groove on the body.
5. Install the Gerotor Housing, making sure the pins in the
Gerotor Housing line up with their respective holes in the
body.
6. Lightly lubricate the area between the Inner and Outer
Gerotor, the Outer Gerotor, and Gerotor Housing with
hydraulic oil or mineral oil.
Special attention should be exercised when working with
retaining rings. Always wear safety goggles when working with spring or tension-loaded fasteners or devices.
7. Install o-ring on the motor end plate.
8. Place end plate on gerotor housing, making sure holes in
end plate line up with pins in the gerotor housing.
-11-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 12

9. Install four Socket Head Cap Screws in Motor End Plate,
and using a 1/4” Allen wrench, tighten Cap Screws alternately and evenly in a crisscross pattern to approximately 15 foot pounds [ 20 Nm] of torque.
10. Install the Thread Seal Gasket on the Bypass Adjusting
Screw. Put the Gasket on from the slotted end and turn
until four threads on the screw are showing. Install the
Washer and the Nut. Install Bypass Adjusting Screw in
the motor end plate.
A. For closed center hydraulic systems, turn the By-
pass Adjusting Screw in until it bottoms out in the
End Plate. Tighten nut down with 9/16” box end
wrench.
B. For open center hydraulic systems, turn the Bypass
Adjusting Screw in until it bottoms out in the End
Plate; then turn back out 1
1
⁄2 full turns. Holding the
Bypass Adjusting Screw with a screwdriver, tighten
Nut. (Motor will then have to be readjusted to tractor
system.)
Troubleshooting
11. Replace o-ring on both port adapters.
12. Install Pressure Port Adapter and Tank Port Adapter
back onto the motor. (For ease of installation, tighten the
Pressure Port Adapter first, then the Tank Port Adapter.)
13. Remove Hydraulic Motor from the vise. Turn shaft by
hand to check for binding.
14. Install Slinger Ring over Motor Shaft.
15. Install Motor into Pump Mounting Flange. Insert four Hex
Head Bolts; then alternately and evenly tighten them.
[For polypropylene models, secure the Hydraulic Motor
to the Mounting Flange with four Hex Head Cap Screws
and Nuts. The nuts should be visible when the assembly
is complete.]
If the proper Hydraulic Pump Unit has been selected according
to Hypro recommendations, and the unit has been correctly
draulic system heat is excessive etc., check the following trou-
bleshooting guide for possible problems and solutions.
plumbed into the hydraulic system, operation should be quite
satisfactory. If spraying performance is unsatisfactoryor hy-
Troubleshooting Guide
Symptom Probable Cause(s) Corrective Action(s)
Low discharge Pump not primed. — Remove top most vent plug from face of pump and run
pump to expel trapped air (see Installation Instructions).
Air leaks in inlet line. — Check and reseal inlet fittings.
Blocked or clogged line strainer. — Inspect strainer and clear any debris from screen.
Impeller plugged. — Inspect and clear obstruction.
Undersize inlet line or — Suction line should be the same diameter as inlet port of pump or larger.
collapsed hose.
Improperly sized hydraulic motor. — Refer to Pump Selection Guide to determine proper size
hydraulic motor for your hydraulic system.
Bypass Adjustment Screw not — Adjust bypass screw on side of hydraulic motor
set properly. in until the desired output is attained.
Eye of impeller rubbing on volute. — Remove volute (front cover) and inspect the impeller.
If wear detected, sand the impeller eye O.D. with emery cloth.
Hydraulic system Improper hydraulic motor size. — Refer to Pump Selection Guide on our website to determine proper size
overheating for your hydraulic system.
Bypass Adjustment Screw — Close adjustment screw on side of hydraulic motor
set to bypass too much oil. to lessen the amount of oil being bypassed.
Improper metering orifice — Install proper size orifice. Refer to Installation section for proper sizing.
installed in pressure port.
Insufficient hydraulic hose size. — Check hydraulic hose size. Hose should be at least 1/2” [12.7 mm]
on the pressure port and 3/4” [19.05mm] on the tank port.
NOTE: See Hydraulic Test Kit 3430-0650 and our Operation Manual No. L-1503
for further guidance and troubleshooting.
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
-12-
Page 13

Performance Graphs
GPM
9303C-HM1C-SP Performance at 11 GPM
GRAPHS FOR HYDRAULICALLY-DRIVEN CENTRIFUGALS
9302
9302
9303
9302CT-GM1 & 9302ST-GM1
-13-
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
100
90
80
70
P
60
S
50
I
40
30
20
10
0
020406080 100 120
L/min
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
Feet of lift = 15 10
50
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
6
5
B
4
A
R
3
2
1
0
Page 14

Performance Graphs
P
S
9303C-HM1C-SP Performance at 13 GPM
05
P
S
9303C-HM2C-SP Performance at 4 GPM
P
S
9303C-HM2C-SP Performance at 6 GPM
9303C-HM1C-SP Performance at 12 GPM
9303 9303
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
120
100
80
P
S
60
I
L/min
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
050 100 150 200 250 300
8
7
6
B
5
A
4
R
40
30
20
I
L/min
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
2.5
2
1.5
B
A
R
40
20
0
020406080 100 120
Feet of lift = 15 10
50
GPM
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
140
120
100
80
L/min
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
I
60
40
20
0
020406080 100 120
Feet of lift = 15 10
50
GPM
3
2
1
0
10
0
01
Feet of Lift = 15
5
10
060708030 4020
1
0.5
0
0
GPM
9
8
7
6
B
A
5
R
4
3
2
1
0
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
-14-
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
80
70
60
50
40
I
30
20
10
0
06080 100 1204020
Feet of Lift = 15
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
10
0
5
GPM
L/min
5
4
B
3
A
R
2
1
0
Page 15

Performance Graphs
08
9303C-HM3C-SP Performance at 15 GPM
08
9303C-HM3C-SP Performance at 18 GPM
08
9303C-HM3C-SP Performance at 20 GPM
9303 9303
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 450 450
90
80
70
L/min
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
6
5
050 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
40
P
30
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
S
I
L/min
20
10
0
02
Feet of Lift = 15
10
GPM
60
P
50
S
I
40
30
20
10
0
02
Feet of Lift = 15
10
5
0
0 100 1206040
4
B
A
R
3
2
1
0
GPM
3
2.5
B
2
A
R
1.5
1
0.5
5
0
0 1006040
0
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 450 450
80
70
60
50
P
S
40
I
30
20
10
0
02
Feet of Lift = 15
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
10
GPM
L/min
5
4
B
A
3
R
2
1
5
0
0 100 1206040
0
-15-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 16

Performance Graphs
08
P
S
08
9303C-HM5C-SP Performance at 15 GPM
P
S
9303P-HM2C
GPM
9303P-HM1C
9303P-HM3C
08
9303C-HM5C-SP Performance at 13 GPM
9303 9303
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
90
80
70
60
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
P
L/min
50
S
I
40
30
20
10
0
02
Feet of Lift = 15 10 50
060 10040 120
GPM
9303C-HM5C-SP Performance at 14 GPM
L/min
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
120
100
80
60
I
40
20
0
02
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
Feet of Lift = 15 10 50
060 10040 120
GPM
6
5
4
B
A
3
R
2
1
0
8
7
6
B
5
A
4
R
3
2
1
0
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
140
13GPM
120
12GPM
100
11GPM
P
80
S
I
60
40
20
0
020406080 100 120
050 100 150 200 250 300
100
90
7GPM
80
6GPM
70
60
5GPM
50
I
40
30
20
10
0
02010 4030 50 60 70 80 90
L/min
L/min
GPM
9
8
7
6
B
A
5
R
4
3
2
1
0
6
5
B
4
A
R
3
2
1
0
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
L/min
120
100
80
P
S
60
I
40
20
0
02
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
1-1/2˝ Inlet Hose
Feet of Lift = 15 10 50
GPM
060 10040 120
050 100 150 200 250 300 350
L/min
-16-
100
90
20 GPM
80
18 GPM
70
P
60
S
15 GPM
50
I
40
30
20
10
0
0204060 10060 120
GPM
6
5
B
4
A
R
3
2
1
0
8
7
6
B
5
A
4
R
3
2
1
0
Page 17

Performance Graphs
08
P
S
9303P-HM4C
9303P-HM5C
9305C-HM3C-SP, BSP Performance at 18 GPM
9305C-HM3C-SP, BSP Performance at 19 GPM
B
A
R
9303
050 100 150 200 250 300
90
80
7GPM
70
60
6GPM
50
I
40
5GPM
30
20
10
0
020406
050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
120
15 GPM
14 GPM
100
13 GPM
80
12 GPM
P
S
60
I
40
20
0
020406080 100 120
L/min
GPM
L/min
GPM
070503010 90
9305
9305C-HM3C-SP, BSP Performance at 17 GPM
L/min
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
6
5
4
B
A
R
3
2
1
0
120
100
80
P
S
60
I
40
20
0
020 100 120 140 16060 8040
2˝ Inlet Hose
Feet of Lift = 15
10
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
5
0
0
GPM
L/min
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
8
7
6
5
B
A
4
R
3
2
1
0
140
120
100
P
80
S
I
60
40
20
0
020 100 120 140 16060 8040
2˝ Inlet Hose
Feet of Lift = 15
9
8
7
6
B
A
5
R
4
3
2
10
1
5
0
0
GPM
9305
0 100 200
160
140
120
P
100
18 GPM
17 GPM
9305C-HM3C
L/min
300 400 500 600 700
19 GPM
S
80
I
60
40
20
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
GPM
11
10
9
8
7
B
6
A
R
5
4
3
2
1
0
-17-
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
160
140
120
100
P
2˝ Inlet Hose
S
80
I
60
40
20
0
020 100 120 140 16060 8040
Feet of Lift = 15
GPM
10
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
10
8
B
A
6
R
4
2
5
0
0
L/min
Page 18

Performance Graphs
9306
9306C-HM1C-3U & 9306S-HM1C-3U
9306C-HM3C-3U & 9306S-HM3C-3U
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
9306C-HM5C-3U & 9306S-HM5C-3U
-18-
Page 19

Repair Parts Kit No. 3430-0332
Contains: One o-ring (Ref. 5),
one rubber gasket (Ref. 6), and
one mechanical seal (Ref. 7).
9302C and 9302S Series Pumps
Silicon Seal Kit No. 3430-0589
Contains one each:
1720-0083 o-ring (Ref. 5)
and mechanical seal (silicon carbide) (Ref.7).
Adapter Kit No. 3430-0187
(HM2 and HM4 Models Only):
Contains one each:
No. 3360-0021 Pressure Port Adapter
No. 3373-0020 (Size #1)
No. 3373-0021 (Size #2)
No. 3373-0022 (Size #3)
No. 1720-0108 Adapter O-ring and
No. 1720-0105 Orifice O-ring (Qty. 3)
NOTE: When ordering parts, give
QUANTITY, PART NUMBER,
DESCRIPTION, and COMPLETE
MODEL NUMBER. Reference
numbers are used ONLY to identify parts in the drawing and are
NOT to be used as order numbers.
Parts Kit No. 3430-0748
Contains: One each ball bearing
(Ref. 13), motor shaft seal (Ref.
16), thread seal gasket (Ref. 35),
two cartridge o-rings (Ref. 15) and
washer (Ref. 36); two each motor
housing o-rings (Ref. 22), and port
adapter o-rings (Ref. 30 & 32).
Hydraulic Motor Part Nos.
2500-0081C (HM1C Models)
2500-0082C (HM2C Models)
2500-0084C (HM4C Models)
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
1 4 2406-0007 Drain/Vent Plug (9302C)
1 4 2406-0016 Drain/Vent Plug (9302S)
2 1 0150-9200C Pump Casing (Model 9302C)
2A 1 0156-9200S Pump Casing (Model 9302S)
3 1 2253-0002 Impeller Nut (9302C)
3 1 2253-0006 Impeller Nut (9302S)
4 1 0401-9100P Impeller (Nylon Std. 9302C)
4 1 0402-9100P Impeller (Polypropylene Optional) (Std 9302S)
5 1 1720-0083 O-ring
6 1 1700-0100 Gasket
7 1 2120-0009 Mechanical Seal (Viton/Ceramic) (Std 9302C)
7 1 3430-0589 Mechanical Seal (Silicon Carbide) (Std 9302S)
8 1 0750-9300C Mounting Flange (9302C)
8 1 0756-9300S Mounting Flange (9302S)
9 4 2210-0020 Hex Head Cap Screw (9302C)
9 4 2210-0125 Hex Head Cap Screw (9302S)
10 1 1410-0056 Slinger Ring
11 1 1810-0014 Snap Ring
12 1 1820-0013 Retaining Ring
13 1 2000-0010 Ball Bearing
14 1 1410-0131 Cartridge, Front
15 2 1720-0268 O-ring
16 1 2104-0010 Lip Seal
17 1 1410-0130 Seal Spacer
18 1 2029-0014 Thrust Bearing Assembly
19 1 0531-2500 Shaft (HM2C/HM4C)
19 1 0533-2500 Shaft (HM1C)
20 1 0150-2500C Motor Body (includes needle bearing)
21 4 2210-0005 Hex Head Cap Screw
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
22 2 1720-0110 O-ring
23 1 1600-0045 Dowel Pin (HM2C / HM4C)
23 1 1600-0044 Dowel Pin (HM1C)
24 1 1600-0042 Dowel Pin (HM2C / HM4C)
24 1 1600-0037 Dowel Pin (HM1C)
25 1 3900-0022 Gerotor (HM1C)
25 1 3900-0023 Gerotor (HM2C)
25 1 3900-0025 Gerotor (HM4C)
26 1 0701-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM2C Models) 1/4” wide
26 1 0700-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM1C Models) 1/2” wide
26 1 0703-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM4C Models) 5/16” wide
27 1 0254-2500C2 Motor End Plate (includes needle bearing)
28 4 2270-0039 Washer
29 4 2220-0045 Cap Screw (HM2C / HM4C Models)
29 4 2220-0021 Cap Screw (HM1C Models)
30 1 1720-0108 O-ring
31 1 3360-0021A Pressure Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
32 1 1720-0262 O-ring
33 1 3320-0051A Tank Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
34 1 3220-0029 Bypass Adjusting Screw
35 1 1700-0047 Gasket
36 1 2270-0027 Washer
37 1 2250-0038 Lock Nut
38 1 1610-0032 Roll Pin (HM2C / HM4C)
38 1 1610-0031 Roll Pin (HM1C)
39 1 1810-0026 Snap Ring
40 1 1610-0012 Woodruff Key (9302C)
40 1 04432 Woodruff Key (9302S)
-19-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 20

13
12
Models 9302CT-GM1 & 9302ST-GM1
8
11
9
16
19
17
14
15
10
Note 1: Mechanical Seal Ref. 9 is not avail-
able outside of the kit form. For replacement
seal,orderKit#3430-0332orKit#3430-0589
forModel9302CT-GM1andKit#3430-0589for
Model 9302ST-GM1.
7
4
2
2
5
6
3
7
1
Note: When ordering parts, give
QUANTITY, PART NUMBER,
DESCRIPTION and COMPLETE
MODEL NUMBER. Reference
numbers are used ONLY to identify
parts in the drawing and are NOT
to be used as order numbers.
18
HydraulicMotorSealKitNo.3430-0649
Ref.
No. Qty. Part No. Description
1 1 0701-9300C Bearing Housing
2 2 2008-0001 Bearing
3 1 1410-0108 Bearing Spacer
4 1 1410-0110 Motor Pilot Ring
5 1 0517-2500 Shaft Assembly
6 2 1810-0013 Retainer Ring
7 1 2500-0033 Hydraulic Gear Motor
8 1 0750-9300C2 Mounting Flange
8* 1 0756-9300S Mounting Flange
9 1 See Note 1 Mechanical Seal
9* 1 See Note 1 Mechanical Seal
10 1 1610-0012 Key
10* 1 04432 Key
* Denotes part for 9302ST-GM1.
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Ref.
No. Qty. Part No. Description
11 1 1720-0083 O-Ring
12 1 0401-9100P Impeller (Nylaglass)
12* 1 0402-9100P Impeller (Polypropylene)
13 1 2253-0006 Acorn Nut
14 1 0150-9200C2 Pump Casing
14* 1 0156-9200S1 Pump Casing
15 4 2406-0007 Pipe Plug
15* 4 2406-0016 Pipe Plug
16 4 2210-0020 Hex Head Cap Screw
16* 4 2210-0125 Hex Head Cap Screw
17 4 2210-0130 Threaded Stud
18 4 2260-0002 Lockwasher
19 4 2250-0008 Nut
-20-
Page 21

All 9303C and 9303S Series Pumps
Repair Parts Kit No. 3430-0332
Contains: One o-ring (Ref. 5),
one rubber gasket (Ref. 6),
and one mechanical seal (Ref. 7).
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
1 4 2406-0007 Drain/Vent Plug (9303C)
1 4 2406-0016 Drain/Vent Plug (9303S)
2 1 0150-9000C Pump Casing (Model 9303C)
2 1 0150-9000S Pump Casing (Model 9303S)
2A 1 0153-9000C Pump Casing (Universal Flange Model C-U)
2A 1 0153-9000S Pump Casing (Universal Flange Model S-U)
3 1 2253-0002 Impeller Nut (9303C)
3 1 2253-0006 Impeller Nut (9303S)
4 1 0401-9100P Impeller (Nylon Std. 9303C)
4 1 0402-9100P Impeller (Polypropylene Optional) (Std 9303S)
5 1 1720-0083 O-ring
6 1 1700-0100 Gasket
7 1 2120-0009 Mechanical Seal (Viton/Ceramic) (Std 9303C)
7 1 3430-0589 Mechanical Seal (Silicon Carbide) (Std 9303S)
8 1 0750-9300C Mounting Flange (9303C)
8 1 0756-9300S Mounting Flange (9303S)
9 4 2210-0020 Hex Head Cap Screw (9303C)
9 4 2210-0125 Hex Head Cap Screw (9303S)
10 1 1410-0056 Slinger Ring
11 1 1810-0014 Snap Ring
12 1 1820-0013 Retaining Ring
13 1 2000-0010 Ball Bearing
14 1 1410-0131 Cartridge, Front
15 2 1720-0268 O-ring
16 1 2104-0010 Lip Seal
17 1 1410-0130 Seal Spacer
18 1 2029-0014 Thrust Bearing Assembly
19 1 0531-2500 Shaft (HM2C/HM4C)
19 1 0533-2500 Shaft (HM1C/HM5C)
19 1 0536-2500 Shaft (HM3C)
20 1 0150-2500C Motor Body (includes needle bearing)
21 4 2210-0005 Hex Head Cap Screw
22 2 1720-0110 O-ring
23 1 1600-0045 Dowel Pin (HM2C / HM4C)
23 1 1600-0044 Dowel Pin (HM1C/HM5C)
Silicon Seal Kit No. 3430-0589
Contains one each:
1720-0083 o-ring (Ref. 5)
and one mechanical seal (silicon
carbide) (Ref.7).
NOTE: When ordering parts, give
QUANTITY, PART NUMBER,
DESCRIPTION, and COMPLETE
MODEL NUMBER. Reference
numbers are used ONLY to identify parts in the drawing and are
NOT to be used as order numbers.
Parts Kit No. 3430-0748
Contains: One each ball bearing
(Ref. 13), motor shaft seal (Ref. 16),
thread seal gasket (Ref. 35), two
Adapter Kit No. 3430-0187
(HM2 and HM4 Models Only):
Contains one each:
No. 3360-0021 Pressure Port Adapter
No. 3373-0020 (Size #1)
No. 3373-0021 (Size #2)
No. 3373-0022 (Size #3).
No. 1720-0108 Adapter O-ring and
No. 1720-0105 Orifice O-ring (Qty 3).
cartridge o-rings (Ref. 15) and washer
(Ref. 36); two each motor housing
o-rings (Ref. 22), and port adapter
o-rings (Ref. 30 & 32).
Hydraulic Motor Part Nos.
2500-0081C (HM1C Models)
2500-0082C (HM2C Models)
2500-0083C (HM3C Models)
2500-0084C (HM4C Models)
2500-0085C (HM5C Models)
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
23 1 1600-0052 Dowel Pin (HM3C)
24 1 1600-0042 Dowel Pin (HM2C / HM4C)
24 1 1600-0037 Dowel Pin (HM1C/HM5C)
24 1 1600-0068 Dowel Pin (HM3C)
25 1 3900-0022 Gerotor (HM1C)
25 1 3900-0023 Gerotor (HM2C)
25 1 3900-0024 Gerotor (HM3C)
25 1 3900-0025 Gerotor (HM4C)
25 1 3900-0048 Gerotor (HM5C)
26 1 0701-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM2C Models) 1/4” wide
26 1 0700-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM1C Models) 1/2” wide
26 1 0703-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM4C Models) 5/16” wide
26 1 0702-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM3C Models) 1” wide
26 1 0704-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM5C Models) 5/8” wide
27 1 0254-2500C2 Motor End Plate (includes needle bearing)
28 4 2270-0039 Washer
29 4 2220-0045 Cap Screw (HM2C / HM4C Models)
29 4 2220-0021 Cap Screw (HM1C Models)
29 4 2220-0044 Cap Screw (HM3C Models)
29 4 2220-0032 Cap Screw (HM5C Models)
30 1 1720-0108 O-ring
31 1 3360-0021A Pressure Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
32 1 1720-0262 O-ring
33 1 3320-0051A Tank Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
34 1 3220-0029 Bypass Adjusting Screw
35 1 1700-0047 Gasket
36 1 2270-0027 Washer
37 1 2250-0038 Lock Nut
38 1 1610-0032 Roll Pin (HM2C / HM4C)
38 1 1610-0031 Roll Pin (HM1C / HM5C)
38 1 1610-0055 Roll Pin (HM3C)
39 1 1810-0026 Snap Ring
40 1 1610-0012 Woodruff Key (9303C)
40 1 04432 Woodruff Key (9303S)
-21-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 22

Repair Parts Kit No. 3430-0332
Contains: One o-ring (Ref. 5),
one rubber gasket (Ref. 6),
and one mechanical seal (Ref 7).
All 9303 Self-Priming Series Pumps
Silicon Seal Kit No. 3430-0589
Contains one each:
1720-0083 o-ring (Ref. 5)
and mechanical seal (silicon
carbide) (Ref. 7).
SP Chamber Kit No. 3430-0480SP
Contains: One chamber with wear
ring, (Ref. 2), one o-ring (Ref. 5),
one drain/vent plug (Ref. 1) and one
vent plug (Ref.1A).
Hydraulic Motor Part Nos.
2500-0081C (HM1C Models)
2500-0082C (HM2C Models)
2500-0083C (HM3C Models)
2500-0084C (HM4C Models)
2500-0085C (HM5C Models)
NOTE: When ordering parts, give
QUANTITY, PART NUMBER,
DESCRIPTION, and COMPLETE
MODEL NUMBER. Reference
numbers are used ONLY to identify parts in the drawing and are
NOT to be used as order numbers.
Parts Kit No. 3430-0748
Contains: One each ball bearing
(Ref. 13), motor shaft seal (Ref. 16),
thread seal gasket (Ref. 35), two
cartridge o-rings (Ref. 15) and washer (Ref. 36 ); two each motor housing
o-rings (Ref. 22), and port adapter
o-rings (Ref. 30 & 32).
Adapter Kit No. 3430-0187
(HM2 and HM4 Models Only):
Contains one each:
No. 3360-0021 Pressure Port Adapter
No. 3373-0020 (Size #1)
No. 3373-0021 (Size #2)
No. 3373-0022 (Size #3)
No. 1720-0108 Adapter O-ring and
No. 1720-0105 Orifice O-ring (Qty. 3).
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
1 1 2406-0007 Drain/Vent Plug (9303C-SP)
1 1 2406-0016 Drain/Vent Plug (9303S-SP)
1A 1 2406-0001 Vent Plug (9303C-SP)
1A 1 7SP34 Vent Plug (9303S-SP)
2 1 3430-0480SP Pump Casing (9303C-SP)
2 1 0150-9070S Pump Casing (9303S-SP)
3 1 2253-0002 Impeller Nut (9303C-SP)
3 1 2253-0006 Impeller Nut (9303S-SP)
4 1 0401-9100P Impeller (Nylon Std. 9303C-SP)
4 1 0402-9100P Impeller (Polypropylene Optional) (Std 9303S-SP)
5 1 1720-0083 O-ring
6 1 1700-0100 Gasket
7 1 2120-0009 Mechanical Seal (Viton/Ceramic) (Std 9303C-SP)
7 1 3430-0589 Mechanical Seal (Silicon Carbide) (Std 9303S-SP)
8 1 0750-9300C Mounting Flange (9303C-SP)
8 1 0756-9300S Mounting Flange (9303S-SP)
9 4 2210-0020 Hex Head Cap Screw (9303C-SP)
9 4 2210-0125 Hex Head Cap Screw (9303S-SP)
10 1 1410-0056 Slinger Ring
11 1 1810-0014 Snap Ring
12 1 1820-0013 Retaining Ring
13 1 2000-0010 Ball Bearing
14 1 1410-0131 Cartridge, Front
15 2 1720-0268 O-ring
16 1 2104-0010 Lip Seal
17 1 1410-0130 Seal Spacer
18 1 2029-0014 Thrust Bearing Assembly
19 1 0531-2500 Shaft (HM2C/HM4C)
19 1 0533-2500 Shaft (HM1C/HM5C)
19 1 0536-2500 Shaft (HM3C)
20 1 0150-2500C Motor Body (includes needle bearing)
21 4 2210-0005 Hex Head Cap Screw
22 2 1720-0110 O-ring
23 1 1600-0045 Dowel Pin (HM2C/HM4C)
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
23 1 1600-0044 Dowel Pin (HM1C/HM5C)
23 1 1600-0052 Dowel Pin (HM3C)
24 1 1600-0042 Dowel Pin (HM2C/HM4C)
24 1 1600-0037 Dowel Pin (HM1C/HM5C)
24 1 1600-0068 Dowel Pin (HM3C)
25 1 3900-0022 Gerotor (HM1C)
25 1 3900-0023 Gerotor (HM2C)
25 1 3900-0024 Gerotor (HM3C)
25 1 3900-0025 Gerotor (HM4C)
25 1 3900-0048 Gerotor (HM5C)
26 1 0701-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM2C Models) 1/4” wide
26 1 0700-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM1C Models) 1/2” wide
26 1 0703-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM4C Models) 5/16” wide
26 1 0702-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM3C Models) 1” wide
26 1 0704-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM5C Models) 5/8” wide
27 1 0254-2500C2 Motor End Plate (includes needle bearing)
28 4 2270-0039 Washer
29 4 2220-0045 Cap Screw (HM2C/HM4C Models)
29 4 2220-0021 Cap Screw (HM1C Models)
29 4 2220-0044 Cap Screw (HM3C Models)
29 4 2220-0032 Cap Screw (HM5C Models)
30 1 1720-0108 O-ring
31 1 3360-0021A Pressure Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
32 1 1720-0262 O-ring
33 1 3320-0051A Tank Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
34 1 3220-0029 Bypass Adjusting Screw
35 1 1700-0047 Gasket
36 1 2270-0027 Washer
37 1 2250-0038 Lock Nut
38 1 1610-0032 Roll Pin (HM2C/HM4C)
38 1 1610-0031 Roll Pin (HM1C/HM5C)
38 1 1610-0055 Roll Pin (HM3C)
39 1 1810-0026 Snap Ring
40 1 1610-0012 Woodruff Key (9303C-SP)
40 1 04432 Woodruff Key (9303S-SP)
-22-
Page 23

All 9300 Polypropylene Series Pumps
Repair Parts Kit No. 3430-0445
Contains: One o-ring (Ref. 13),
one rubber gasket (Ref. 11), one mechanical
seal (Ref. 12), one gasket (Ref. 8) and one
washer (Ref. 9).
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
1 4 2210-0087 Hex Head Cap Screw
2 2 2210-0016 Hex Head Cap Screw (Base Only)
3 6 2270-0041 Washer
4 4 2406-0020 Pipe Plug
5 1 0700-9000P Pump Casing
6 1 2250-0052 Impeller Nut
7 1 2250-0051 Jam Nut
8 1 1700-0097 Gasket (Viton)
9 1 2270-0057 Washer
10 1 0402-9100P Impeller
11 1 1700-0100 Rubber Gasket
12 1 2120-0009 Mechanical Seal (Viton/Ceramic) (Std 9303P)
12 1 3430-0593 Mechanical Seal (Silicon Carbide) (Optional)
13 1 1721-0083 O-ring
14 1 0750-9300P Cover
15 1 2210-0088 Screw
16 1 0750-9006C Intermediate Flange
17 1 1510-0063 Base Plate
18 2 2250-0008 Hex Nut
19 1 1410-0056 Slinger Ring
20 1 1810-0014 Snap Ring
21 1 1820-0013 Retaining Ring
22 1 2000-0010 Ball Bearing
23 1 1410-0131 Cartridge, Front
24 2 1720-0268 O-ring
25 1 2104-0010 Lip Seal
26 1 1410-0130 Seal Spacer
27 1 2029-0014 Thrust Bearing Assembly
28 1 1610-0042 Woodruff Key (9303P all except HM3C)
28A 1 1610-0053 Square Key (9303P-HM3C Only)
29 1 0534-2500 Shaft (HM2C/HM4C)
29 1 0535-2500 Shaft (HM1C/HM5C)
29 1 0537-2500 Shaft (HM3C)
30 1 1810-0026 Snap Ring
Silicon Seal Parts Kit # 3430-0593
Contains one each:
mechanical seal (Ref. 12) and o-ring (Ref. 13).
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
31 1 1610-0055 Roll Pin (HM3C)
32 1 0150-2500C Motor Body (includes needle bearing)
33 4 2210-0021 Hex Head Cap Screw
34 2 1720-0110 O-ring
35 1 1600-0045 Dowel Pin (HM2C / HM4C)
35 1 1600-0044 Dowel Pin (HM1C/HM5C)
35 1 1600-0052 Dowel Pin (HM3C)
36 1 1600-0042 Dowel Pin (HM2C/ HM4C)
36 1 1600-0037 Dowel Pin (HM1C/HM5C)
36 1 1600-0068 Dowel Pin (HM3C)
37 1 3900-0022 Gerotor (HM1C)
37 1 3900-0023 Gerotor (HM2C)
37 1 3900-0024 Gerotor (HM3C)
37 1 3900-0025 Gerotor (HM4C)
37 1 3900-0048 Gerotor (HM5C)
38 1 0701-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM2C Models) 1/4” wide
38 1 0700-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM1C Models) 1/2” wide
38 1 0703-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM4C Models) 5/16” wide
38 1 0702-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM3C Models) 1” wide
38 1 0704-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM5C Models) 5/8” wide
39 1 0254-2500C2 Motor End Plate (includes needle bearing)
40 4 2270-0039 Washer
41 4 2220-0045 Cap Screw (HM2C / HM4C Models)
41 4 2220-0021 Cap Screw (HM1C Models)
41 4 2220-0044 Cap Screw (HM3C Models)
41 4 2220-0032 Cap Screw (HM5C Models)
42 1 1720-0108 O-ring
43 1 3360-0021A Pressure Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
44 1 3320-0051A Tank Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
45 1 1720-0262 O-ring
46 1 3220-0029 Bypass Adjusting Screw
47 1 1700-0047 Gasket
48 1 2270-0027 Washer
49 1 2250-0038 Lock Nut
31 1 1610-0032 Roll Pin (HM2C / HM4C)
31 1 1610-0031 Roll Pin (HM1C / HM5C)
-23-
Adapter Kit No. 3430-0187
(HM2 and HM4 Models Only):
Contains one each:
No. 3360-0021 Pressure Port Adapter
No. 3373-0020 (Size #1)
No. 3373-0021 (Size #2)
No. 3373-0022 (Size #3)
No. 1720-0108 Adapter O-ring and
No. 1720-0105 Orifice O-ring (Qty. 3).
NOTE: When ordering parts, give
QUANTITY, PART NUMBER,
DESCRIPTION, and COMPLETE
MODEL NUMBER. Reference
numbers are used ONLY to identify
parts in the drawing and are NOT to
be used as order numbers.
Parts Kit No. 3430-0748
Contains: One each ball bearing
(Ref. 22), motor shaft seal (Ref.
25), thread seal gasket (Ref.
47), two cartridge o-rings (Ref.
24) and washer (Ref. 48); two
each motor housing o-rings (Ref.
34), and port adapter o-rings
(Ref. 42 & 45).
Hydraulic Motor Part Nos.
2500-0181C (HM1C Models)
2500-0182C (HM2C Models)
2500-0183C (HM3C Models)
2500-0184C (HM4C Models)
2500-0185C (HM5C Models)
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 24

Models 9305C-HM3C-SP and 9305C-HM3C-BSP
NOTE: When ordering parts, give
QUANTITY, PART NUMBER,
DESCRIPTION, and COMPLETE
MODEL NUMBER. Reference
numbers are used ONLY to identify parts in the drawing and are
NOT to be used as order numbers.
Silicon Seal Kit No 3430-0601
Contains one each: mechanical
seal (Ref. 8) and o-ring (Ref. 9).
Repair Parts Kit No. 3430-0500
Contains one each: mechanical seal
Hydraulic Motor Part No.
2500-0083C
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
1 1 2406-0002 1/2” NPT Drain Plug
2 1 3430-0481SP Self Priming Chamber (SP model only)
Includes a stainless wear ring, plugs, & o-ring
2 1 3430-0481BSP Self Priming Chamber (BSP model only)
Includes a stainless wear ring, plugs, & o-ring
3 1 2406-0034 1” NPT Prime Port Plug (SP model only)
3 1 2406-0036 1” BSP Prime Port Plug (BSP model only)
4 1 2253-0002 Impeller Nut
5 1 2270-0071 Washer
6 1 0403-9200P1 Impeller
7 1 1700-0100 Rubber Gasket
8 1 2120-0009 Mechanical Seal (Viton/Ceramic) (Std 9305C)
8 1 3430-0601 Mechanical Seal (Silicon Carbide) (Optional)
9 1 1720-0180 O-ring
10 1 0752-9200C Mounting Flange
11 6 2210-0086 Hex Head Cap Screw
12 1 1410-0056 Slinger Ring
13 1 1810-0014 Snap Ring
14 1 1820-0013 Retaining Ring
15 1 2000-0010 Ball Bearing
16 1 1410-0131 Cartridge, Front
17 2 1720-0268 O-ring
18 1 2104-0010 Lip Seal
(Ref. 8), o-ring (Ref. 9), and rubber
gasket (Ref. 7).
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
20 1 2029-0014 Thrust Bearing Assembly
21 1 1610-0053 Square Key
22 1 0537-2500 Shaft
23 1 1810-0026 Snap Ring
24 1 1610-0055 Roll Pin
25 1 0150-2500C Motor Body (includes needle bearing)
26 4 2210-0005 Hex Head Cap Screw
27 2 1720-0110 O-ring
28 1 1600-0052 Dowel Pin
29 1 1600-0068 Dowel Pin
30 1 3900-0024 Gerotor
31 1 0702-2500C1 Gerotor Housing 1” wide
32 1 0254-2500C2 Motor End Plate (includes needle bearing)
33 4 2270-0039 Washer
34 4 2220-0044 Cap Screw
35 1 1720-0108 O-ring
36 1 3360-0021A Pressure Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
37 1 3320-0051A Tank Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
38 1 1720-0262 O-ring
39 1 3220-0029 Bypass Adjusting Screw
40 1 1700-0047 Gasket
41 1 2270-0027 Washer
42 1 2250-0038 Lock Nut
19 1 1410-0130 Seal Spacer
Parts Kit No. 3430-0748
Contains: One each ball bearing
(Ref. 15), motor shaft seal (Ref.
18), thread seal gasket (Ref. 40),
two cartridge o-rings (Ref. 17) and
washer (Ref. 41); two each motor
housing o-rings (Ref. 27), and port
adapter o-rings (Ref. 35 & 38).
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
-24-
Page 25

Models 9305C-HM3C
Repair Parts Kit No. 3430-0500
Contains one each: mechanical seal
(Ref. 7), o-ring (Ref. 8), and rubber
Silicon Seal Kit No 3430-0601
Contains one each: mechanical
seal (Ref. 7) and O-ring (Ref. 8).
gasket (Ref. 6).
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
1 4 2406-0007 Drain / Vent Plug
2 1 0152-9200C Pump Casing
3 1 2253-0002 Impeller Nut
4 1 2270-0071 Washer
5 1 0403-9200P1 Impeller
6 1 1700-0100 Rubber Gasket
7 1 2120-0009 Mechanical Seal (Viton/Ceramic) (Std 9305C)
7 1 3430-0601 Mechanical Seal (Silicon Carbide) (Optional)
8 1 1720-0180 O-ring
9 1 0752-9200C Mounting Flange
10 6 2210-0086 Hex Head Cap Screw
11 1 1410-0056 Slinger Ring
12 1 1810-0014 Snap Ring
13 1 1820-0013 Retaining Ring
14 1 2000-0010 Ball Bearing
15 1 1410-0131 Cartridge, Front
16 2 1720-0268 O-ring
17 1 2104-0010 Lip Seal
18 1 1410-0130 Seal Spacer
19 1 2029-0014 Thrust Bearing Assembly
20 1 1610-0053 Square Key
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
21 1 0537-2500 Shaft
22 1 1810-0026 Snap Ring
23 1 1610-0055 Roll Pin
24 1 0150-2500C Motor Body (includes needle bearing)
25 4 2210-0005 Hex Head Cap Screw
26 2 1720-0110 O-ring
27 1 1600-0052 Dowel Pin
28 1 1600-0068 Dowel Pin
29 1 3900-0024 Gerotor
30 1 0702-2500C1 Gerotor Housing 1” wide
31 1 0254-2500C2 Motor End Plate (includes needle bearing)
32 4 2270-0039 Washer
33 4 2220-0044 Cap Screw
34 1 1720-0108 O-ring
35 1 3360-0021A Pressure Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
36 1 3320-0051A Tank Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
37 1 1720-0262 O-ring
38 1 3220-0029 Bypass Adjusting Screw
39 1 1700-0047 Gasket
40 1 2270-0027 Washer
41 1 2250-0038 Lock Nut
Hydraulic Motor Part No.
2500-0083C
NOTE: When ordering parts, give
QUANTITY, PART NUMBER,
DESCRIPTION, and COMPLETE
MODEL NUMBER. Reference
numbers are used ONLY to identify parts in the drawing and are
NOT to be used as order numbers.
Parts Kit No. 3430-0748
Contains: One each ball bearing
(Ref. 14), motor shaft seal (Ref.
17), thread seal gasket (Ref. 39),
two cartridge o-rings (Ref. 16) and
washer (Ref. 40); two each motor
housing o-rings (Ref. 26), and port
adapter o-rings (Ref. 34 & 37).
-25-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 26

All 9306 Series
Silicon Carbide Seal Kit No. 3430-0589
Contains one each:
mechanical seal (Ref. 7) and o-ring (Ref. 5).
Repair Parts Kit No. 3430-0332
Contains: One mechanical seal (Ref.
7), one o-ring (Ref. 5) and one rubber
gasket (Ref. 6).
NOTE: When ordering parts,
give QUANTITY, PART
NUMBER, DESCRIPTION, and
COMPLETE MODEL NUMBER.
Reference numbers are used
ONLY to identify parts in the
drawing and are NOT to be
used as order numbers.
Parts Kit No. 3430-0748
Contains: One each ball bearing
(Ref. 13),
motor shaft seal (Ref.
16), thread seal gasket (Ref. 35),
two cartridge o-rings (Ref. 15) and
washer (Ref. 36); two each motor
housing o-rings (Ref. 22), and port
adapter o-rings (Ref. 30 & 32).
Hydraulic Motor Part Nos.
2500-0081C (HM1C Models)
2500-0083C (HM3C Models)
2500-0085C (HM5C Models)
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
1 4 2406-0007 Drain/Vent Plug (9306C)
1 4 2406-0016 Drain/Vent Plug (9306S)
2 1 0154-9200C1 Pump Casing (9306C)
2 1 0154-9200S1 Pump Casing (9306S)
2A 1 0157-9200C Pump Casing (Universal Flange 220x200)
2B 1 0158-9200C Pump Casing (Universal Flange 300x220 Cast)
2B 1 0158-9200S Pump Casing (Universal Flange 300x220 S.S.)
3 1 2253-0002 Impeller Nut (9306C)
3 1 2253-0006 Impeller Nut (9306S)
4 1 0401-9200P2 Impeller (Nylon Std. 9306C)
4 1 0405-9100P2 Impeller (Polypropylene Optional) (Std. 9306S)
4 1 0407-9306P Impeller (GTX Optional)
5 1 1720-0083 O-ring
6 1 1700-0100 Gasket
7 1 2120-0009 Mechanical Seal (Viton/Ceramic) (Std. 9306C)
7 1 3430-0589 Mechanical Seal (Silicon Carbide) (Std. 9306S)
8 1 0750-9300C2 Mounting Flange (9306C)
8 1 0756-9300S Mounting Flange (9306S)
9 4 2210-0020 Hex Head Cap Screw (9306C)
9 4 2210-0125 Hex Head Cap Screw (9306S)
10 1 1410-0056 Slinger Ring
11 1 1810-0014 Snap Ring
12 1 1820-0013 Retaining Ring
13 1 2000-0010 Ball Bearing
14 1 1410-0131 Cartridge, Front
15 2 1720-0268 O-ring
16 1 2104-0010 Lip Seal
17 1 1410-0130 Seal Spacer
18 1 2029-0014 Thrust Bearing Assembly
19 1 0533-2500 Shaft (HM1C/HM5C)
19 1 0536-2500 Shaft (HM3C)
20 1 0150-2500C Motor Body (includes needle bearing)
Ref. Qty.
No. Req’d. Part No. Description
21 4 2210-0005 Hex Head Cap Screw
22 2 1720-0110 O-ring
23 1 1600-0044 Dowel Pin (HM1C/HM5C)
23 1 1600-0052 Dowel Pin (HM3C)
24 1 1600-0037 Dowel Pin (HM1C/HM5C)
24 1 1600-0068 Dowel Pin (HM3C)
25 1 3900-0022 Gerotor (HM1C)
25 1 3900-0024 Gerotor (HM3C)
25 1 3900-0048 Gerotor (HM5C)
26 1 0700-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM1C Models) 1/2” wide
26 1 0702-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM3C Models) 1” wide
26 1 0704-2500C1 Gerotor Housing (HM5C Models) 5/8” wide
27 1 0254-2500C2 Motor End Plate (includes needle bearing)
28 4 2270-0039 Washer
29 4 2220-0021 Cap Screw (HM1C Models)
29 4 2220-0044 Cap Screw (HM3C Models)
29 4 2220-0032 Cap Screw (HM5C Models)
30 1 1720-0108 O-ring
31 1 3360-0021A Pressure Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
32 1 1720-0262 O-ring
33 1 3320-0051A Tank Port Adapter (includes o-ring)
34 1 3220-0029 Bypass Adjusting Screw
35 1 1700-0047 Gasket
36 1 2270-0027 Washer
37 1 2250-0038 Lock Nut
38 1 1610-0031 Roll Pin (HM1C / HM5C)
38 1 1610-0055 Roll Pin (HM3C)
39 1 1810-0026 Snap Ring
40 1 1610-0012 Woodruff Key (9306C)
40 1 04432 Woodruff Key (9306S)
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
-26-
Page 27

Notes
-27-
L-1526 (12/12, Rev. B)
Page 28

Limited Warranty on Hypro/SHURflo Agricultural Pumps & Accessories
Hypro/SHURflo (hereafter, “Hypro”) agricultural products are warranted to be free of defects in material and workmanship under
normal use for the time periods listed below, with proof of purchase.
- Pumps: one (1) year from the date of manufacture, or one (1) year of use. This limited warranty will not
exceed two (2) years, in any event.
- Accessories: ninety (90) days of use.
This limited warranty will not apply to products that were improperly installed, misapplied, damaged, altered, or incompatible with
fluids or components not manufactured by Hypro. All warranty considerations are governed by Hypro’s written return policy.
Hypro’s obligation under this limited warranty policy is limited to the repair or replacement of the product. All returns will be tested
per Hypro’s factory criteria. Products found not defective (under the terms of this limited warranty) are subject to charges paid by the returnee for the testing and packaging of “tested good” non-warranty returns.
No credit or labor allowances will be given for products returned as defective. Warranty replacement will be shipped on a freight allowed
basis. Hypro reserves the right to choose the method of transportation.
This limited warranty is in lieu of all other warranties, expressed or implied, and no other person is authorized to give any other
warranty or assume obligation or liability on Hypro’s behalf. Hypro shall not be liable for any labor, damage or other expense, nor
shall Hypro be liable for any indirect, incidental or consequential damages of any kind incurred by the reason of the use or sale of
any defective product. This limited warranty covers agricultural products distributed within the United States of America. Other world market
areas should consult with the actual distributor for any deviation from this document.
Return Procedures
All products must be flushed of any chemical (ref. OSHA section 1910.1200 (d) (e) (f) (g) (h)) and hazardous chemicals must be labeled/
tagged before being shipped* to Hypro for service or warranty consideration. Hypro reserves the right to request a Material Safety Data
Sheet from the returnee for any pump/product it deems necessary. Hypro reserves the right to “disposition as scrap” products returned
which contain unknown fluids. Hypro reserves the right to charge the returnee for any and all costs incurred for chemical testing, and proper disposal of components containing unknown fluids. Hypro requests this in order to protect the environment and personnel from the hazards of handling unknown fluids.
Be prepared to give Hypro full details of the problem, including the model number, date of purchase, and from whom you purchased your
product. Hypro may request additional information, and may require a sketch to illustrate the problem.
Contact Hypro Service Department at 800-468-3428 to receive a Return Merchandise Authorization number (RMA#).
Returns are to be shipped with the RMA number clearly marked on the outside of the package. Hypro shall not be liable for freight damage
incurred during shipping. Please package all returns carefully. All products returned for warranty work should be sent shipping charges
prepaid to:
HYPRO/PENTAIR
Attention: Service Department
375 Fifth Avenue NW
New Brighton, MN 55112
For technical or application assistance, call the Hypro Technical/Application number: 800-445-8360, or send an email to:
technical@hypropumps.com. To obtain service or warranty assistance, call the Hypro Service and Warranty number: 800-468-3428;
or send a fax to the Hypro Service and Warranty FAX: 651-766-6618.
*Carriers, including U.S.P.S., airlines, UPS, ground freight, etc., require specific identification of any hazardous material being shipped. Failure to do so may
result in a substantial fine and/or prison term. Check with your shipping company for specific instructions.
Note:ThiswarrantydoesnotapplytoHyproPumpKitModel1538,
1551, 1538-SP and 1551-SP. This is because the user could incorrectly
assemble the parts and cause the pump to work improperly.
Hypro 2012
Printed in USA
375 Fifth Avenue NW • New Brighton, MN 55112
Phone: (651) 766-6300
www.hypropumps.com
•
800-424-9776 • Fax: 800-323-6496
 Loading...
Loading...