Page 1
Peavey Low Rider®18
00479910
Peavey Low Rider 15
00493710
INTRODUCTION
The new Low Rider driver series
represents a milestone in high-powered
sub-woofer design. An incredible 1,600
Watt program rating and extra-long cone
excursion provide maximum amounts of
amazingly clean, deep bass.
The Low Rider is a superior choice for the
bottom end of any high-powered sound
system, from DJ rigs to the largest
professional touring shows.
DESIGN
The Low Rider utilizes a variation on the
existing Kevlar
®
-impregnated cones used
on all Black Widow®speakers. The new
cone is stronger and tougher and uses an
innovative asymmetrical-M surround for
superior excursion and motion control.
High quality spring terminals accepting
large gauge wire are attached to large
diameter, high-current tinsel leads with
silver solder to withstand high currents,
high temperatures and long excursion.
The massive new voice coil uses
polyimide-insulated copper ribbon wire,
edge-wound and bonded onto an
incredibly durable and heat-resistant
polyimide composite former. The coil’s
winding length of 1.150" is an amazing
80% longer than Peavey’s standard Black
Widow coil. The long coil has much more
surface area to dissipate heat, and its
increased length drives the cone to a far
higher excursion. The coil is overcoated
with a tough thermoset epoxy for added
durability, abrasion resistance and heat
dissipation.
The coil wires are solderless diffusion
welded to high-conductivity OFHC copper
ribbon leads, which are embedded inside
the former assembly and soldered to the
tinsel leads with high temperature silver
solder. The solder joint is then coated
with a special, thermally conductive
silicone adhesive for encapsulation and
heat dissipation.
The voice coil assembly is bonded to the
Kevlar cone and new, incredibly tough
plastiseal-coated Nomex
®
progressive-roll
spider using a thermoset epoxy originally
developed for attaching nose cones onto
ICBM missiles–truly an aerospace-grade
adhesive. The spider and surround are
bonded to the frame with a strong,
toughened cyanoacrylate adhesive, which
is also used to bond the dustcap to the
cone.
The magnet structure is all-new and was
designed using extensive Finite Element
computer modeling. The back plate/pole
piece is cold-forged from a single
massive billet of ultra-low carbon steel,
includes Peavey’s patented Focused
Field Geometry and is undercut to allow
greater coil travel. The pole is extended
beyond the front plate to improve coil
cooling and make it more magnetically
linear, and the front plate is 10 mm thick
to match the long voice coil and provide a
better path for heat and magnetic energy.
The result is 50% more total magnetic
gap energy than can be found in the
standard Black Widow Super Structure
magnet assembly.
A patent-pending vent plate greatly
improves voice coil cooling. This heatconductive, ported and finned aluminum
ring delivers cool air pumped by the
spider directly to the voice coil to keep
operating temperatures under control.
The improved cooling increases power
handling and reliability and reduces
power compression.
The cast aluminum frame is tough and
rigid and has the strength needed to hold
the cone and huge magnet assembly in
perfect alignment. The deep dish design
and large spider clearance make high
excursion and high output possible.
These dynamic new drivers also utilize
the user-friendly Black Widow replaceable
basket assemblies with Rubatex
®
gaskets.
The result of these specially designed
components are truly amazing
loudspeakers. The Low Rider’s
astonishing low frequency output is due
to its high power handling capability and
its 1.4" of available cone movement.
These speakers can also be used with
small enclosures, adding a new
dimension to compact, high output sound
reinforcement systems.
SPECS
PEAVEY ELECTRONICS
ENCLOSURES Net volume Vent diameter Vent length V
b
box tuning F3, -3 dB
cubic feet/liters (qty) inches/mm inches/mm frequency in Hz point in H
Small Vented Box 5.0 / 142 (2) 6" / 152 15.25 / 387 37 40
Medium Vented Box 6.75 / 191 (2) 6" / 152 12.75 / 324 34 35
Large Vented Box 9 / 255 (2) 6" / 152 12 / 305 30 31
Single-Reflex Bandpass Sealed: 4.0 / 113
Vented: 3.5 / 85 (2) 6" / 152 5.0 / 127 65 40 ~ 104
Features and specifications subject to change without notice.
Peavey Electronics Corporation • 711 A Street • Meridian • MS • 39301
(601) 483-5365 • FAX (601) 486-1278 • www.peavey.com
©2002 Printed in the U.S.A. 9/02
80304779
ONE YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY
NOTE: For details, refer to the warranty statement. Copies of this statement may be obtained by
contacting Peavey Electronics Corporation, P.O. Box 2989, Meridian, MS 39335
Suggested enclosures
For those who want to build their own enclosures but don’t want to go through the design process using driver
parameters, Peavey provides the following optimized designs:
For Low Rider 18:
1. Small Vented Box
This enclosure is as small as many 15" cabinets but has better bass performance and handles
tons of power. This design is an excellent choice for large touring systems because it can handle
a large number of enclosures at the same load-out volume.
2. Medium Vented Box
This enclosure offers an exceptional combination of deep bass extension, high power handling
and reasonable size. It is capable of extremely high output below 40 Hz.
3. Large Vented Box
This box produces superb performance in the bottom octave for high level playback, movie
theaters, special effects and permanent installation. It reduces power handling by at least 15%
but offers usable output to 25 Hz.
4. Single-Reflex Bandpass
This special design uses the enclosure as an acoustic filter for shaped response. It’s not as
efficient as a vented system, but it doesn’t require a crossover for sub-woofer use.
1. Small vented box
This incredibly tiny enclosure has good bass performance and serious power capacity. An
excellent choice for very compact, high powered systems and bass guitar/keyboard enclosures.
2. Medium vented box
This enclosure is an exceptional compromise of deep bass extension, high power handling, and
compact size. It is capable of extremely high output to below 40 Hz for excellent performance.
3. Large vented box
The large vented box extends superb performance into the bottom octave for high level playback,
movie theater, special effects and permanent installation. The enclosure reduces power handling
by at least 15% but offers usable output to below 35 Hz.
4. Single-Reflex Bandpass
Special enclosure design that uses the enclosure as an acoustic filter for shaped response. Not
as efficient as a vented system, but it doesn’t require a crossover for subwoofer use.
ENCLOSURES Net volume Vent diameter Vent length V
b
box tuning F3, -3 dB
cubic feet/liters (qty) inches/mm inches/mm frequency in Hz point in H
Small Vented Box 2.0 / 56.6 (2) 4 / 102 12 / 305 45 48
Medium Vented Box 3.0 / 85.0 (1) 6" / 152 12-3/4 / 324 38 40
Large Vented Box 4.5 / 127.4 (3) 4" / 102 12-5/8 / 321 34 33
Single-Reflex Bandpass Sealed: 1.8 / 51.0
Vented: 1.3 / 36.8 (3) 6" / 102 9-3/4 / 248 78 45 ~ 131
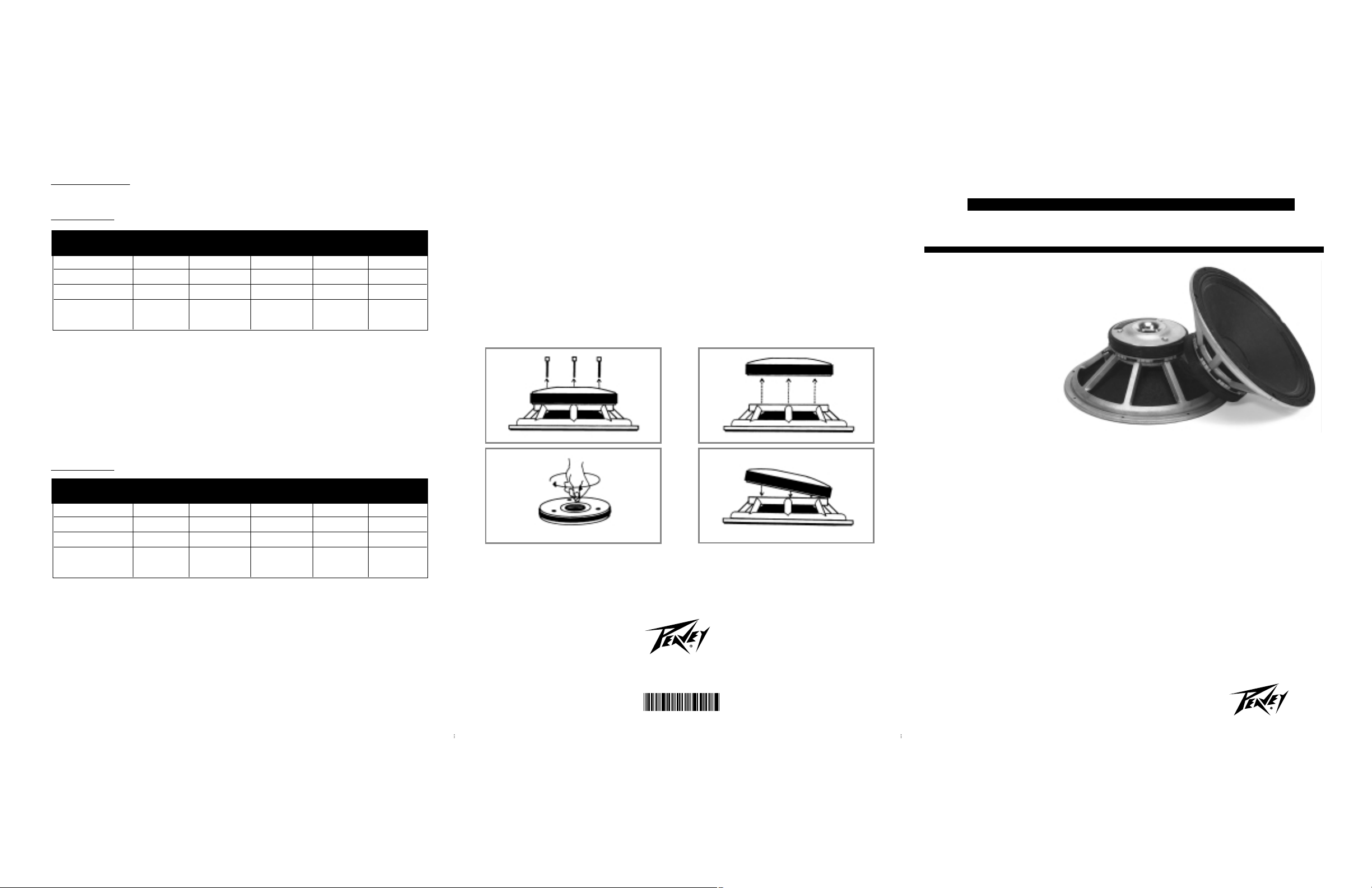
REPLACING THE SPEAKER BASKET ASSEMBLY
1. Prior to the replacement procedure, clean the work area of all metal objects and other debris.
2. With the speaker laying face-down, remove the three screws on the back of the magnet
structure with a 7/16" nut driver.
3.. After the screws are removed, lift the magnet structure off the basket frame.
4. Clean the voice coil “gap” before the magnet structure is placed on the new replacement basket
(see illustration). Fold a piece of masking tape onto itself several times, sticky side out, and insert
it into the voice coil “gap.” Run it all the way around the “gap” several times to remove all particles
and other trash before placing the magnet structure on the new replacement basket.
5. Holding the magnet structure in a slanted position, gently lower the structure down into the
basket so it rests inside the magnet structure counter bore, align the screw holes and lower the
structure into place. Insert screws and tighten.
STEP 1
STEP 2
STEP 3
STEP 4
For Low Rider 15:
Nomex is registered trademark of DuPont
Rubatex is a registered trademark of Rubatex Corporation
Page 2

APPLICATIONS
The Low Rider®is specifically designed
for sub-woofer use, with extremely high
output capabilities and massive power
handling. While most sub-woofer
applications are below 150 Hz, it is
usable to frequencies as high as 500 Hz.
The compact enclosure designs are ideal
for instrument amplification and high
portability applications such as DJ and
small touring bands. They provide solid
bass performance in extraordinarily small
enclosures. Bandpass enclosures also fit
into this range as stand-alone subwoofers.
The medium-sized enclosures are still
smaller than usual and have more bass
extension and much higher output
capabilities than conventional designs.
They are excellent choices for high
performance sound reinforcement.
These designs are the best combination
of size and bass performance.
For permanent installations and
applications requiring extremely deep
bass performance, the large vented
enclosures are ideal. The low frequency
extension and high sound pressure levels
these systems can produce is
astounding. As is typical in large, vented
systems with low vent tuning, power
handling is reduced by at least 15% due
to the increased cone excursion.
Due to the Low Rider ’s high output
capabilities, excessive levels may cause
structural damage to buildings or induce
permanent hearing loss, nausea, vertigo
or intestinal disturbances in listeners.
Please be cautious when setting
maximum sound pressure levels.
ENCLOSURES
To assist with the growing interest in
home-built enclosure designs, Peavey
includes complete parameter data on
these drivers and also provides the user
with several recommended enclosure
designs. This information and much more
can be found at www.peavey.com.
The 18" Low Rider driver performs best
with vented enclosures between 5 and 9
cubic feet (142 to 255 liters) and vent
tunings from 30 to 45 Hz. The Low Rider
18 is optimized for vented systems but
will also work with appropriate singlereflex bandpass enclosures. Sealed,
infinite baffle, horn, transmission line and
dual-reflex bandpass enclosures are not
recommended.
The Low Rider 15" driver works best in
vented enclosures between 2 and 5 cubic
feet (56.6 to 141.6 liters) and vent tunings
from 34 to 45 Hz. It can also be used in
certain single-reflex bandpass designs.
As with the Low Rider 18, sealed, infinite
baffle, horn, transmission line and dualreflex bandpass enclosures are not
recommended.
Active filtering must
be included with
amplifiers greater than 750 Watts. This
filter should be a high pass 24dB
Butterworth at a minimum of 25 Hz for
the 18" and 32 Hz for the 15". Filtering is
also recommended below 750 Watts in
order to conserve amplifier power and
reduce excessive cone motion. Failure to
use filtering with high power operation
may cause driver damage that can void
your warranty.
Enclosures should be built of quality 3/4"
to 1-1/4" (20mm to 32mm) marine, 7-ply
birch or other high-grade plywood. If you
must use construction-grade plywood,
inspect each sheet thoroughly and use
grade BC or better. Do not use plywood
thinner than 3/4" Other materials such as
particle board and MDF are not
acceptable.
Use a quality wood glue and fit joints
tightly. Dado corner joints are highly
recommended. Wood screws or a
pneumatic nailer should be used to
assemble the enclosure during gluing to
maximize joint strength.
Strength of the completed enclosure has
a great effect on the bass performance of
the finished system. Internal bracing is
required to improve the structural
strength of the cabinet. Low Riders can
generate enormous forces inside the
enclosure, and panels that aren’t stiff
enough will vibrate – reducing bass and
creating undesired sounds of their own. If
your cabinet vibrates or if the cabinet
panels are not stiff enough, add more
bracing.
Vents shown in the examples require
standard Schedule 40 PVC pipe for vent
construction. The pipe should be dadoed
tightly into the back of the baffle and
glued firmly in place with high quality
epoxy or high strength industrial-grade
hot glue. Roughen up the outside of the
pipe to improve the glue bond. Radius
the insides of the vent ends to improve
air flow and reduce vent noise.
Vents for these enclosures are much
longer than typical for a sound
reinforcement sub-woofer. This reflects
the special characteristics of the Low
Rider’s design that make it possible to
combine a large, high excursion woofer
with an unusually small enclosure. For
best performance, the inside ends of the
vents should be a distance of at least one
vent diameter from any interior wall of the
enclosure. The vent should be straight,
without elbow fittings or other methods to
bend it for greater length. Vent diameter
should not be decreased, as high air
velocity will result in noise and reduced
power handling.
Be sure to allow for the displacement of
the vent, bracing and woofer in your
enclosure design before building it.
Mistakes in net volume will mis-tune the
enclosure and can drastically reduce
performance. This requires a
considerable amount of planning before
construction, but is well worth the extra
effort.
Line the inside of the enclosure with
polyester fiber batting such as quilt
stuffing. For bandpass loosely fill the
sealed side, leave the vented side empty,
and place the Low Rider ’s magnet in the
vented side for cooling. The batting
material should conform to California
bedding fire codes. Attach the batting with
spray adhesive or staples and keep
material away from the end of the vent
tube where it can be pulled in by air flow.
Handles, protective corners, cabinet
covering, grille materials and crossovers
are available through Peavey
Accessories. Take particular care when
positioning handles, as sub-woofers tend
to be large and heavy.
Do not use 1/4" phone plugs or jacks in
the construction of your enclosures.
Power capacity of Low Rider sub-woofers
is well above safe limits for phone plugs
and jacks. Neutrik
®
Speakon®connectors
are highly recommended, and internal
cabinet wiring should be at least 16gauge stranded copper wire.
Flying of sub-woofers is not
recommended. An array of sub-woofer
enclosures at ground level will typically
outperform any other possible
arrangement.
These instructions are a general
guideline for design. Proper construction
techniques, good planning and common
sense will result in a reliable, high quality,
high performance system.
Peavey in no way accepts liability for any
damage, accidents or injury that may
result from design, construction or
operation of enclosures using this
information. Due to Peavey’s continuing
SPECIFICATIONS 1808-8HPS Low Rider 18 1508-8HPS Low Rider 15
Part # 00479910 00493710
Size: inches / mm 18 / 460 nominal 15 / 380 nominal
Frame OD inches / mm 18-1/8 / 460 15-1/4 / 387 mm
Bolt circle inches / mm 17-3/8 / 441 14-9/16 / 370mm
Cutout diameter inches/mm 16-3/4 / 425 14 / 356 mm
Depth 6-3/8 / 162 5-1/4 / 133
Impedance: 8 Ohms 8 Ohms
Power Capacity: 3200 Watts peak 3200 Watts peak
1600 Watts program 1600 Watts program
800 Watts continuous per AES 2-1984, 800 Watts continuous per AES 2-1984,
40 Hz – 400 Hz 50 Hz – 500 Hz
Usable frequency range: 25 Hz ~ 500 Hz 30 Hz ~ 500 Hz
Cone: Kevlar impregnated cellulose Kevlar impregnated cellulose
Voice coil diameter: 4"/100 mm 4"/100 mm
Voice coil material: Polyimide coated copper ribbon wire Polyimide coated copper ribbon wire
Polyimide-impregnated Polyimide-impregnated
fiberglass former fiberglass former
Nomex stiffener Nomex stiffener
Solderless diffusion welded Solderless diffusion welded
OFHC copper leads OFHC copper leads
Net weight lb. / kg: 22 / 10 21 / 9.5
Z
nom
(ohms) 8 8
R
evc
(ohms) 6.21 6.21
Sd(Square Meters) 0.1237 0..084
BL (T/M) 22.73 22.73
Fo(Hz) 28.9 33.9
Vas(liters) 403.9 155.1
Cms(uM/N) 185.9 154.8
Mms(gm) 163.2 142.3
Q
ms
8.770 10.669
Q
es
0.356 0.364
Q
ts
0.342 0.352
X
max
(mm) 9.6 9.6
Le(mH) 0.87 0.83
SPL (1 W 1m) 97.3 94.4
no(%) 2.65 1.61
Vdcubic inches / milliliters 145 / 2375 98.4 / 1613
P
max
(Watts pgm.) 1600 1600
Disp (inches
3
) / milliliters 235 / 3852 211 / 3458
efforts to improve products, features and
specifications are subject to change
without notice.
PARAMETERS
Thiele-Small parameters for Low Rider
subwoofers follow. This data is for use in
designing enclosures. Numerous software
packages are available that use this data
to simulate the response of the driver and
enclosure together for optimum
performance in any application.
PARAMETER DEFINITIONS
Z
nom
: The nominal impedance of the
driver in Ohms.
R
evc
: DC resistance of the driver in
ohms Also known as Re.
Sd: The functional radiating surface
area of the cone assembly in meters2.
BL: Efficiency of the voice coil and
magnet system in Tesla meters.
Fo: Free air resonance. Also known
as Fs.
Vas: Volume of air having the same
compliance (springiness) as the driver ’s
suspension.
Cms: Restorative force of the driver’s
suspension in micrometers/Newton.
Mms: The total mass of the moving
parts of the loudspeaker, including the air
load, in grams.
Qms: Resonance characteristics of the
mechanical factors of the loudspeaker.
Qes: Resonance characteristics of
electrical factors of the loudspeaker.
Qts: Resonance characteristics of the
electrical and mechanical factors
combined together.
X
max
: Distance the cone can move in
one direction before the coil begins to
leave the magnetic gap.
Le: Inductance of the voice coil in
millihenries.
SPL: Typical sound pressure level at 1
watt, 1 meter.
no: Electrical-to-acoustical
conversion efficiency in percent
Vd: Air displacement of the driver
from negative Xmax to positive Xmax, .
P
max
: Maximum continuous program
power in watts.
Disp: Volume displaced by the driver
inside the cabinet when mounted on its
rear flange.
Low Rider 15: Small vented 2.0cf Fb45
Low Rider 15: Medium vented 3.5cf Fb38
Low Rider 15: Large vented 5.0cf Fb34
SPL, dB
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
10 Frequency, Hz 50 100 Hz 500 1K
SPL, dB
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
10
Low Rider 15: Name:Single reflex bandpass 3.0cf
Low Rider 18: Small vented 5.0cf Fb37
Low Rider 18: Medium vented 6.75cf Fb34
Low Rider 18: Large vented 9.0cf Fb30
Low Rider 18: Single reflex bandpass 7.5cf
Frequency, Hz
50 100 Hz 500 1K
 Loading...
Loading...