Page 1
Electron Beam Energy Transfer
The transfer of energy from the electron beam into material is specified completely by
four parameters:
Absorbed dose
Depth of penetration
Uniformity
Throughput
Absorbed Dose
Absorbed Dose is defined as the amount of energy deposited into a specified mass of material.
The unit of absorbed dose is the kilogray, defined as the number of joules (J) of energy
deposited into 1 kilogram of matter. An older, but frequently used unit, is the megarad (Mrad).
1kGy = 1kJ/kg
1Mrad = 10kGy = 10kJ/kg
At a fixed electron accelerating voltage, the dose is directly proportional to the electron beam
current. Typical values of the dose needed for practical applications are:
Drying/curing of inks and coatings 15-30 kGy
Crosslinking of plastic film 25-150 kGy
Sterilization of medical products 7.5-35 kGy
© 2012 PCT Engineered Systems LLC. All Rights Reserved
Page 2
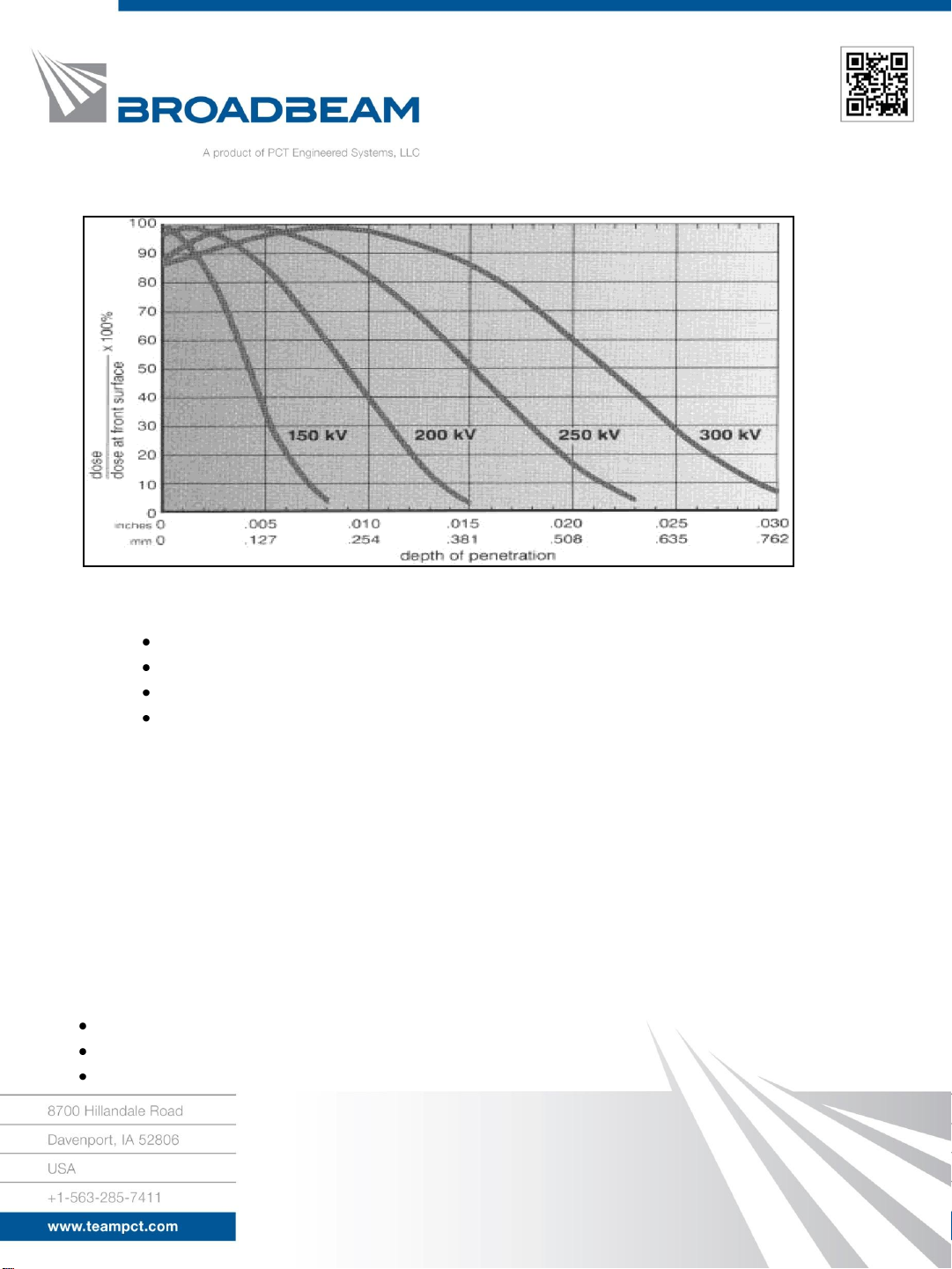
Depth of Penetration
Dose Uniformity
Dose uniformity is a direct function of the electron beam uniformity. It is specified as a
percentage deviation from the average value, e.g. 20 kGy 10%. In general, BroadBeam
processors provide uniformity between 10% and 5%; many applications can tolerate
variations of 20% or more.
Penetrating power of the electron beam is related to the accelerating voltage and the density of
the processed material. Higher voltage causes deeper penetration, and denser material reduces
the depth of penetration. The Depth Dose Curves shown in the figure are convenient aids for
estimating the penetration depth. These curves relate the dose, normalized to the dose received
by the surface of the product, to the depth of penetration in a material with mass density equal
to that of water, i.e. p = I g/CM3. Penetration into materials of different density can be
estimated by multiplying the penetration depth, found from the normalized curves, by the ratio
of the density of water to the density of the material. For example, a 200kV beam will have a
50 percent dose point at 0.009 inches (.228 mm) in water and at 0.0045 inches (0.114 mm) in a
material twice as dense (p = 2 gm/cm3).
Throughput
Throughput is a measure of the energy deposition rate and relates directly to the amount of
material that can be processed within a given time interval. It is measured in kilogray-meters
per minute, abbreviated kGyMPM, megarad-feet per minute (MRFPM) or megarad-meters per
minute (MRMPM). A BroadBeam processor rated at 3,000 MRFPM can provide a dose of 3
Mrad when the web speed is 1,000 fpm, or 5 Mrad at 600 fpm, etc. The processor automatically
adjusts the beam intensity as the web speed changes so that the dose remains constant.
© 2012 PCT Engineered Systems LLC. All Rights Reserved
 Loading...
Loading...