Page 1

PSC
Boilers
Series
Gas
Installation,
Operation &
Maintenance
Manual
Page 2

i
USING THIS MANUAL 1
A. INSTALLATION SEQUENCE . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
B. SPECIAL ATTENTION BOXES . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1. PREINSTALLATION 2
A. ACCESSIBILITY CLEARANCES . . . . . . . . . . .2
B. CLEARANCE FROM COMBUSTIBLE
CONSTRUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
C. INSTALLATION SURVEY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
D. PLANNING THE LAYOUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
2. BOILER SET-UP 3
3. WATER PIPING AND CONTROLS 4
A. BOILER SUPPLY AND RETURN . . . . . . . . . . .4
B. SAFETY RELIEF VALVE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
C. PIPING FOR ZONED SYSTEMS . . . . . . . . . . .6
D. EXPANSION TANK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
E. INDIRECT-FIRED WATER HEATER . . . . . . . .7
F. FREEZE PROTECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
4. VENTING, VENTILATION AND
AIR INLET 8
A. GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
B. PSC WALL THIMBLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
C. ROOF TERMINATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
D. VENT PIPE INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
E. AIR INLET PIPE INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . .11
F. AIR FOR VENTILATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
G. BOILER REMOVAL FROM COMMON
VENTING SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
5. GAS PIPING 13
6. ELECTRICAL 15
A. WIRING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
B. ZONED SYSTEM WIRING . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
C. CONTROLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
D. SEQUENCE OF OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . .16
7. START-UP PROCEDURES 19
A. COMPLETING THE INSTALLATION . . . . . . .19
B. CONTROL DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
C. ADJUSTMENT OF GAS PRESSURE
REGULATOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
D. CHECKING BURNER INPUT . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
E. CHECK-OUT PROCEDURE . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
8. TROUBLESHOOTING 24
A. SHUT-DOWN CAUSED BY PILOT OUTAGE,
PRESSURE SWITCH OR FLAME ROLL-OUT
SAFETY SHUT-OFF SWITCH . . . . . . . . . . . .24
B. TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDES . . . . . . . . . .24
C. MEASURING SUCTION PRESSURE . . . . . .24
9. MAINTENANCE 28
A. GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
B. DAILY (WITH BOILER IN USE) . . . . . . . . . . .29
C. WEEKLY (WITH BOILER IN USE) . . . . . . . . .29
D. MONTHLY (WITH BOILER IN USE) . . . . . . .29
E. ANNUALLY (BEFORE START OF HEATING
SEASON) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
10. BOILER DIMENSIONS & RATINGS 32
11. REPAIR PARTS 33
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 3
1
USING THIS MANUAL
A. INSTALLATION SEQUENCE
Follow the installation instructions provided in this
manual in the order shown. The order of these
instructions has been set in order to provide the installer
with a logical sequence of steps that will minimize
potential interferences and maximize safety during
boiler installation.
B. SPECIAL ATTENTION BOXES
Throughout this manual you will see special attention
boxes intended to supplement the instructions and make
special notice of potential hazards. These categories
mean, in the judgment of PB Heat, LLC:
Indicates special attention is needed, but not directly
related to potential personal injury or property
damage.
NOTICE
Indicates a condition or hazard which will or can
cause minor personal injury or property damage.
CAUTION
DANGER
Indicates a condition or hazard which will cause
severe personal injury, death or major property
damage.
USING THIS MANUAL
Indicates a condition or hazard which may cause
severe personal injury, death or major property
damage.
WARNING
Page 4
2
PREINSTALLATION
A. ACCESSIBILITY CLEARANCES
Install boiler not less than 24″ (610 mm) between the left
side, top, and front of the boiler and adjacent wall or
other appliance, when access is required for servicing.
B. CLEARANCE FROM COMBUSTIBLE
CONSTRUCTION
The design of this boiler is certified for closet installation
with the following clearances:
1. 6″ (152 mm) between right side, front and
combustible construction.
2. 12″ (305 mm) between top of jacket and
combustible construction.
3. 1″ (25 mm) between left side, rear and combustible
construction.
4. 2″ (51 mm) between vent pipe and combustible
construction.
5. Zero clearance between wall thimble and
combustible construction.
6. This boiler is design certified for use on combustible
flooring.
C. INSTALLATION SURVEY
For new and existing installations, a Water Installation
Survey is available from PB Heat, LLC. The survey will
provide information on how a hot water boiler works
with your specific system and will provide an overview
of hot water system operation in general.
You can also use this survey to locate system problems
which will have to be corrected. To obtain copies of the
Water Installation Survey, contact your PB Heat
representative.
D. PLANNING THE LAYOUT
Prepare sketches and notes of the layout to minimize the
possibility of interferences with new or existing
equipment, piping, venting and wiring. Review
limitations on vent pipe, vent terminal, and air inlet pipe
locations and ventilation air requirements in Section 4.
1. PREINSTALLATION
Read carefully, study these instructions before beginning work.
This boiler must be installed by a qualified contractor.
The boiler warranty can be voided if the boiler is not installed, maintained and serviced correctly.
The equipment must be installed in accordance with those installation requirements of the authority having
jurisdiction or, in the absence of such requirements,to the current edition of the
National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI
Z223.1/NFPA 54 and/or CAN/CSA B49.1,
Natural Gas and Propane Installation Code
.
Where required by the authority having jurisdiction, the installation must conform to
American Society of Mechanical
Engineers Safety Code for Controls and Safety Devices for Automatically Fired Boilers,
ANSI/ASME CSD-1.
NOTICE
Do not install this boiler on carpeting. Boiler
installation on carpeting is a fire hazard. Install this
boiler on non-combustible flooring or use a
combustible floor pan to install this boiler on other
non-carpeted flooring.
DANGER
Liquefied Petroleum (LP) is heavier than air and may
collect or “pool” in a low area in the event of a leak
from defective equipment.This gas may then ignite,
resulting in a fire or explosion.
WARNING
Page 5

3
BOILER SET-UP
1. Provide a sound, level foundation. Locate boiler as
near to the outside wall as possible and centralized
with respect to the heating system.
2. Locate boiler in front of installation position before
removing crate.
4. Separate the wood shipping pallet from the boiler
base by removing two (2) hold-down bolts at each
end of the boiler base.
5. Move boiler into final position.
2. BOILER SET-UP
Page 6
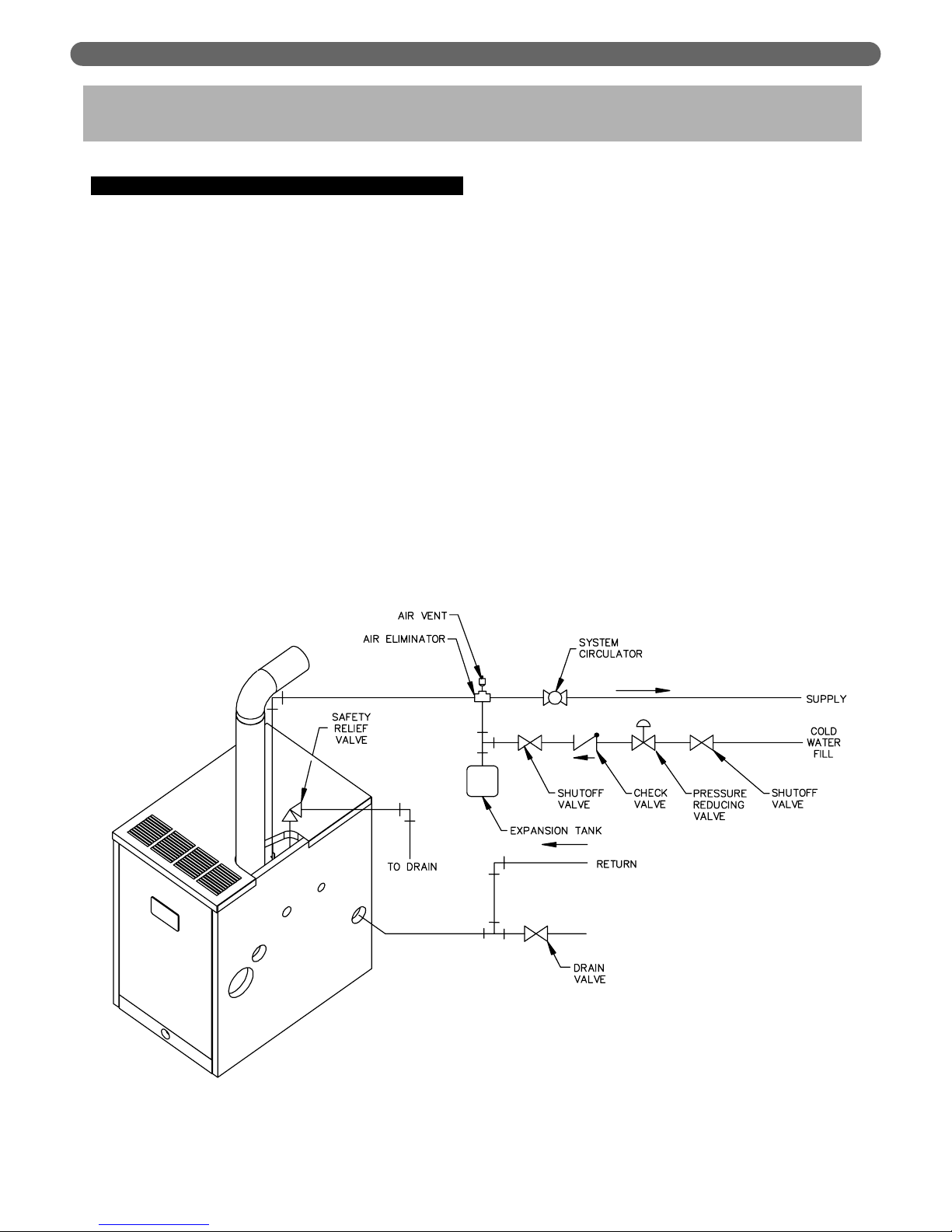
4
WATER PIPING AND CONTROLS
A. BOILER SUPPLY AND RETURN
1. Size the supply and return to suit the system. A
typical piping arrangement is shown in Figure 3.1.
Refer also to the Hydronics Institute Residential
Hydronic Heating Installation Design Guide and the
PB Heat Water Survey for additional guidance
during water piping installation.
2. Return Piping:
Pipe the outlet connection of the circulator to a tee,
provided with a drain valve, at the 1-1/4″ NPT return
tapping near the bottom of the right section. Pipe the
return to the inlet connection of the circulator.
3. Supply Piping:
a. Pipe the supply to the 1-1/2″ NPT supply tapping
at the top of the boiler.
b. Provide clearance to venting system
(see Section 4).
4. When system return water temperature will be below
130°F (54°C), pipe the boiler with a bypass
arrangement to blend the system return and hot
supply to obtain at least 130°F (54°C)entering the
boiler. For more information on bypass piping,
consult the PB Heat Water Survey.
5. If desired, install the circulator in the alternate
location shown in Figure 3.1. Consult the PB Heat
Water Survey for more information on circulator
location.
3. WATER PIPING AND CONTROLS
Figure 3.1: Supply and Return Piping
Page 7
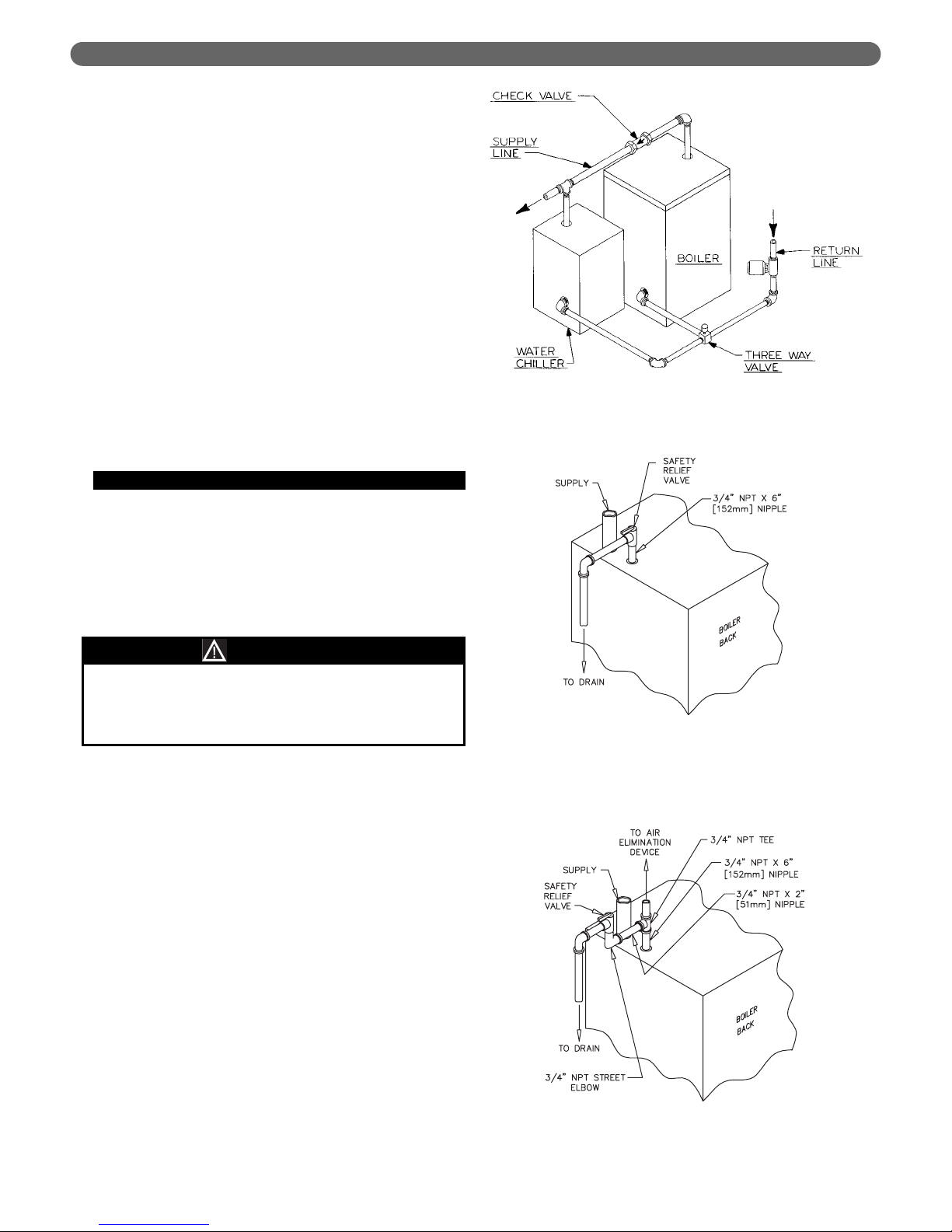
5
WATER PIPING AND CONTROLS
6. Install this boiler so that the gas ignition system
components are protected from water (dripping,
spraying, etc.) during appliance operation and
service (circulator replacement, condensate trap,
control replacements, etc.).
7. If this boiler and distribution system is used in
conjunction with a refrigeration system, pipe the
chilled medium in parallel with the boiler and install
the proper valve to prevent the chilled medium from
entering the boiler. A drawing illustrating this hookup is provided in Figure 3.2.
8. When the boiler is connected to heating coils located
in air handling units where they may be exposed to
refrigerated air circulation, install flow control valves
or other automatic means to prevent gravity
circulation of the boiler water during the cooling
cycle.
9. If this boiler is installed above radiation level,
provide a low water cutoff device, either as a part of
the boiler or at the time of boiler installation.
B. SAFETY RELIEF VALVE
1. Locate safety relief valve and fittings in bag
assembly.
2. If air elimination is not required at the safety relief
valve tapping, install valve and piping as shown in
Figure 3.3.
3. For air elimination at the safety relief valve tapping,
install valve and piping as shown in Figure 3.4.
Pipe the discharge of safety relief valve to prevent
injury in the event of pressure relief. Pipe the
discharge to a drain. Provide piping that is the same
size as the safety relief valve outlet.
CAUTION
Figure 3.4: Safety Relief Valve Hook-Up with
Air Elimination
Figure 3.3: Safety Relief Valve Hook-Up
Installation with Air Elimination in
System Piping
Figure 3.2: Parallel Hook-up with Water Chiller
Page 8
6
WATER PIPING AND CONTROLS
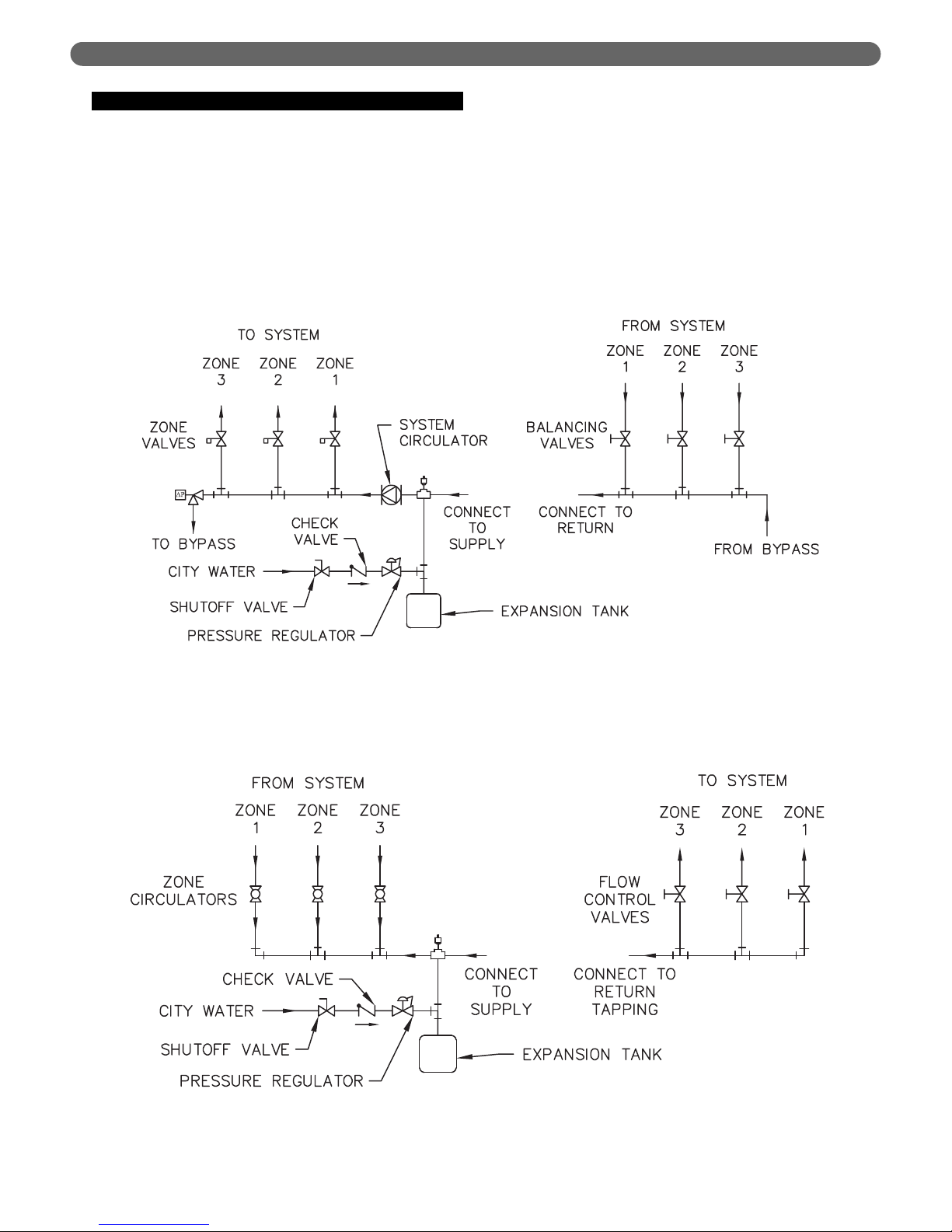
C. PIPING FOR ZONED SYSTEMS
1. See Figures 3.5 and 3.6 for basic zoned system
layouts.
2. Run each zone pipe down then up to zone to
prevent air accumulation in piping.
3. If required, provide means to isolate and drain each
zone separately.
Figure 3.5: Zone Piping with Zone Valves
Figure 3.6: Zone Piping with Circulators
Page 9
7
WATER PIPING AND CONTROLS
D. EXPANSION TANK
1. Consult the tank manufacturer’s instructions for
specific information relating to tank installation. Size
the expansion tank for the required system volume
and capacity. See Table 10.2 in Section 10 for boiler
water capacity.
2. Expansion tanks are available with built-in fill valves
and check valves for reducing supply water pressure
and maintaining minimum system pressure. Check
the design features of the tank and provide valves as
necessary.
Refer back to Figure 3.1 for typical expansion tank piping.
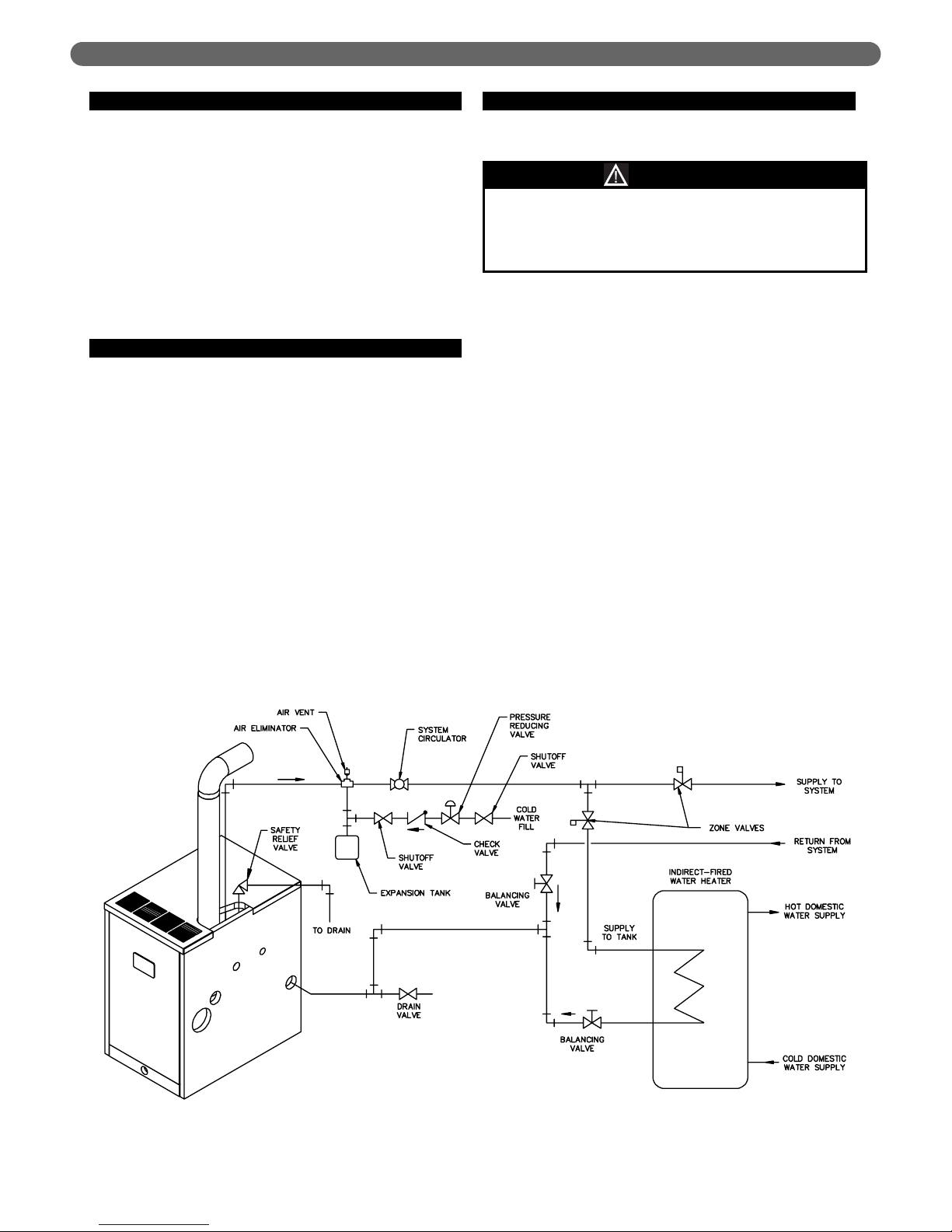
E. INDIRECT-FIRED WATER HEATER
If the boiler is to be used in conjunction with an indirectfired water heater, refer to Figure 3.7 for typical piping.
Follow the instructions provided by the water heater
manufacturer. Pipe the water heater as a separate zone.
F. FREEZE PROTECTION
For new or existing systems that must be freezeprotected:
1. Glycol in hydronic applications is specially
formulated for this purpose. It includes inhibitors
which prevent the glycol from attacking metallic
system components. Make certain that the system
fluid is checked for the correct glycol concentration
and inhibitor level.
2. The glycol solution should be tested at least once a
year and as recommended by the antifreeze
manufacturer.
3. Glycol solutions expand more than water. For
example, a 50% by volume solution expands 4.8%
in volume for a temperature increase from 32°F (0°C)
to 180°F (82°C) , while water expands 3% with the
same temperature rise. Allowance must be made for
this expansion in system design.
4. For more information, consult the PB Heat Water
Installation Survey and the antifreeze manufacturer.
Figure 3.7: Typical Piping with Indirect-Fired Water Heater
Use only inhibited propylene glycol solutions of up to
50% by volume with water. Ethylene glycol is toxic
and can attack gaskets and seals used in hydronic
systems.
WARNING
Page 10
VENTING, VENTILATION AND AIR INLET
A. GENERAL
Install vent system in accordance with Venting of
Equipment part of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
z223.1/NFPA 54 or sections 7.2, 7.3 or 7.4 of CAN/CSA
B149.1, Natural Gas and Propane Installation Code.
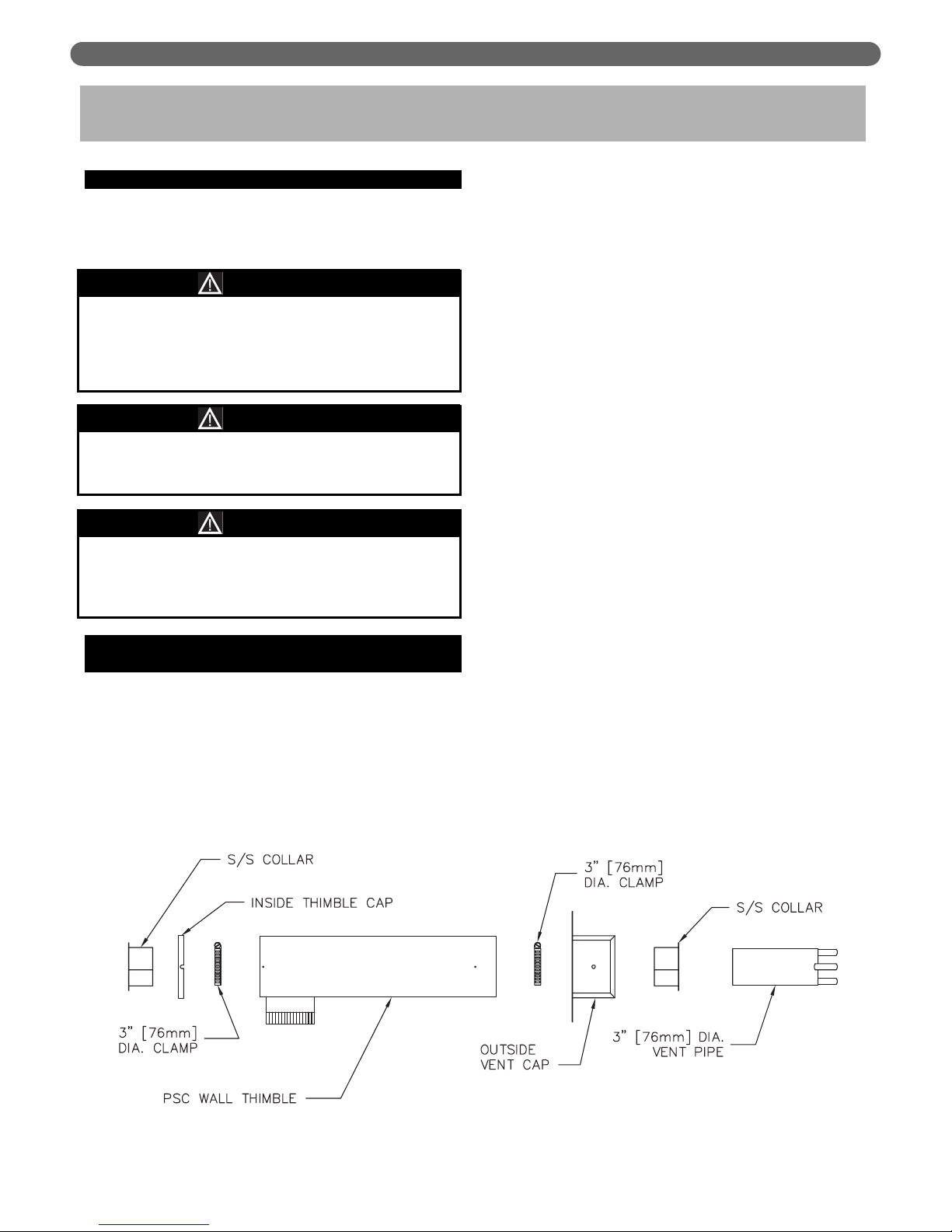
B. PSC WALL THIMBLE (SIDEWALL
VENTING ONLY)
1. Determine vent cap (terminal) location.
a. Must be within the maximum and minimum vent
and air intake lengths shown in Tables 4.1 and 4.2.
b. Maximum wall thickness for the 19-1/2″ (495 mm)
long PSC Wall Thimble (standard) is 11-1/2″ (292
mm). Maximum wall thickness for the optional
28″ (711 mm) long thimble is 20″
(508 mm).
c. Provide 2″ (51 mm) clearance between vent pipe
and combustible construction. No clearance is
required between Thimble and combustible
construction.
d. Provide 3 feet (1 meter) clearance above any
forced air inlet within 10 feet (3 meters).
e. Provide 1 foot (0.3 meters) clearance below, 1 foot
(0.3 meters) beside, or 1 foot (0.3 meters) above
any door, window, or gravity air inlet into any
building.
f. Provide 1 foot (0.3 meters) clearance between
bottom of vent terminal and ground level and
normal snow lines.
g. Provide 4 feet (1.2 meters) horizontal clearance
from from electric meters, gas meters, regulators
and relief equipment. In Canada, this dimension
must be 6 feet (2 meters).
h. Do not locate vent terminal over public walkways
where condensate could create a nuisance or
hazard.
i. When adjacent to a public walkway, locate vent
terminal at least 7 feet (2.1 meters) above grade.
j. Do not locate directly under roof overhangs to
prevent icicles from forming.
2. Cut a 5-1/8″ (130 mm) square hole in sidewall to
allow Peerless Wall Thimble to go through.
3. Insert Thimble from inside wall with 4″ (102 mm)
diameter air inlet connection facing down. Extend
Thimble 3-1/2″ (89 mm) past outside wall surface.
The cut-out opening of thimble is pointed down.
4. Use a minimum 2-1/2 foot (762 mm) piece of 3″
(76 mm) diameter AL29-4C stainless steel vent pipe
for insertion through Wall Thimble. See Vent Pipe
section below for vent pipe requirements.
4. VENTING
Figure 4.1: PSC Wall Thimble
This vent system will operate with a positive
pressure in the vent pipe. Do not connect vent
connectors serving appliances vented by natural
draft into any portion of mechanical draft systems
operating under positive pressure.
Flue gases will condense as they exit the vent
termination.This condensate can freeze on exterior
building surfaces which may cause discoloration of
these surfaces.
NOTICE
WARNING
WARNING
All joints of positive pressure vent systems must be
sealed completely to prevent leakage of flue products
into the living space.
8
Page 11
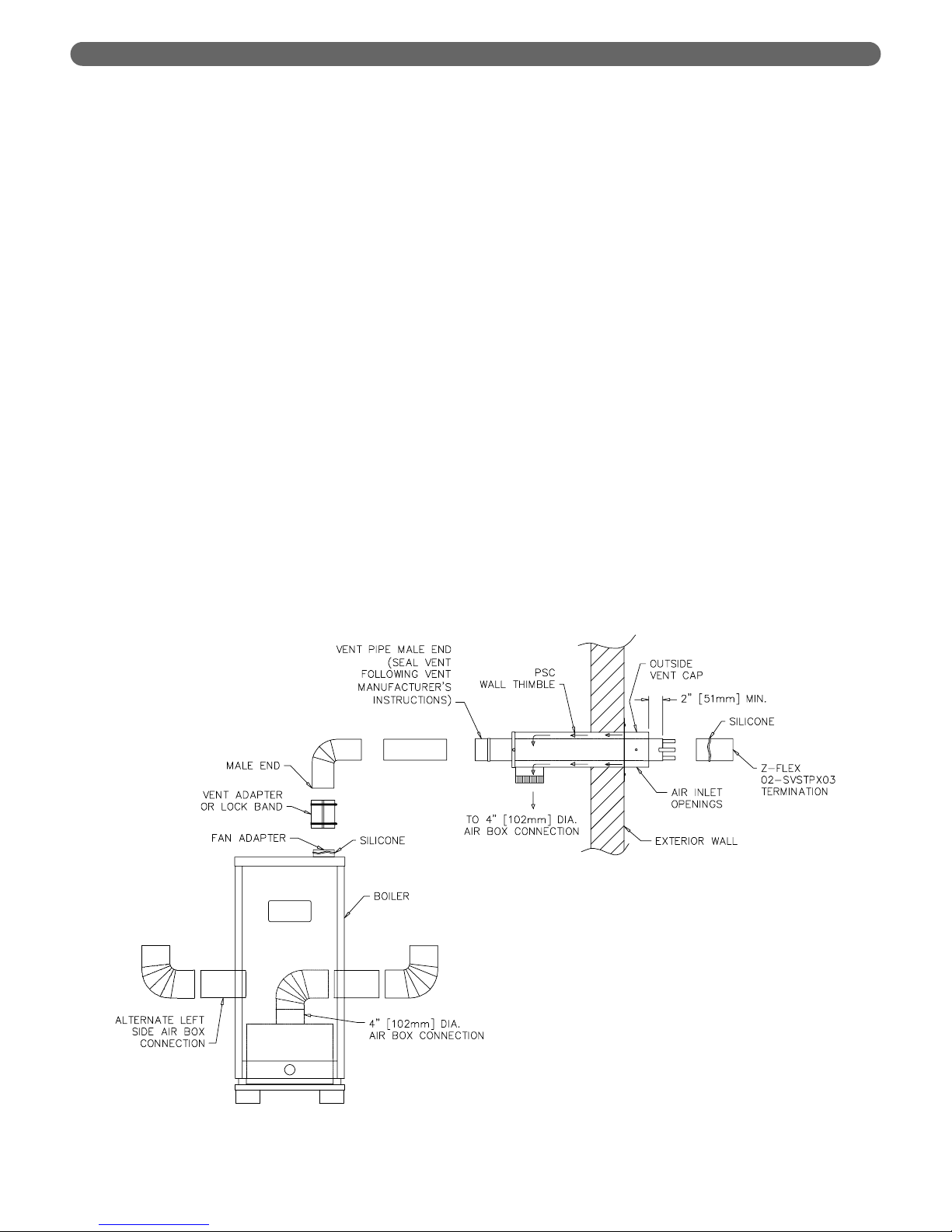
VENTING, VENTILATION AND AIR INLET
5. Slide Stainless Steel Collar over vent pipe and slide
3″ (76 mm) diameter hose clamp and collar to vent
pipe.
6. Insert pipe with collar through Outside Vent Cap and
slide 3″ (76 mm) diameter hose clamp and collar to
vent pipe.
7. Leave at least 2″ (51 mm) of vent pipe protruding
beyond face of Vent Cap and secure hose clamp and
collar to vent pipe.
8. Place Outside Vent Cap over Wall Thimble with air
openings in Vent Cap facing down. Secure Cap to
Thimble with #10 sheet metal screws.
9. Place 3″ (76 mm) diameter hose clamp over pipe
protruding through inside of Wall Thimble.
10. Place Inside Thimble Cap and Collar onto Wall
Thimble. Access hose clamp through 4″ (102 mm)
diameter collar on bottom of Thimble and secure hose
clamp over collar and vent pipe as per step 7 above.
11. Secure Inside Thimble cap to Wall Thimble with #10
screws. Seal Thimble Cap perimeter with silicone.
12. Seal all openings between Wall and Thimble and
around the 3″ (76 mm) diameter stainless steel vent
pipe that protrudes through inside and outside of
Wall Thimble.
13. Add any bracing that may be needed to support Wall
Thimble on inside of wall structure.
14. Secure Outside Vent Cap to exterior wall with four
#10 sheet metal screws provided.
15. Attach Z-Flex #2SVSTPF03 terminal to protruding
vent pipe. Refer to Figure 4.2. To attach to HEATFAB pipe, insert into pipe end and fold over tabs to
secure. Otherwise, silicone terminal to vent pipe.
Figure 4.2: Side Wall Venting System
9
Page 12
10
VENTING, VENTILATION AND AIR INLET
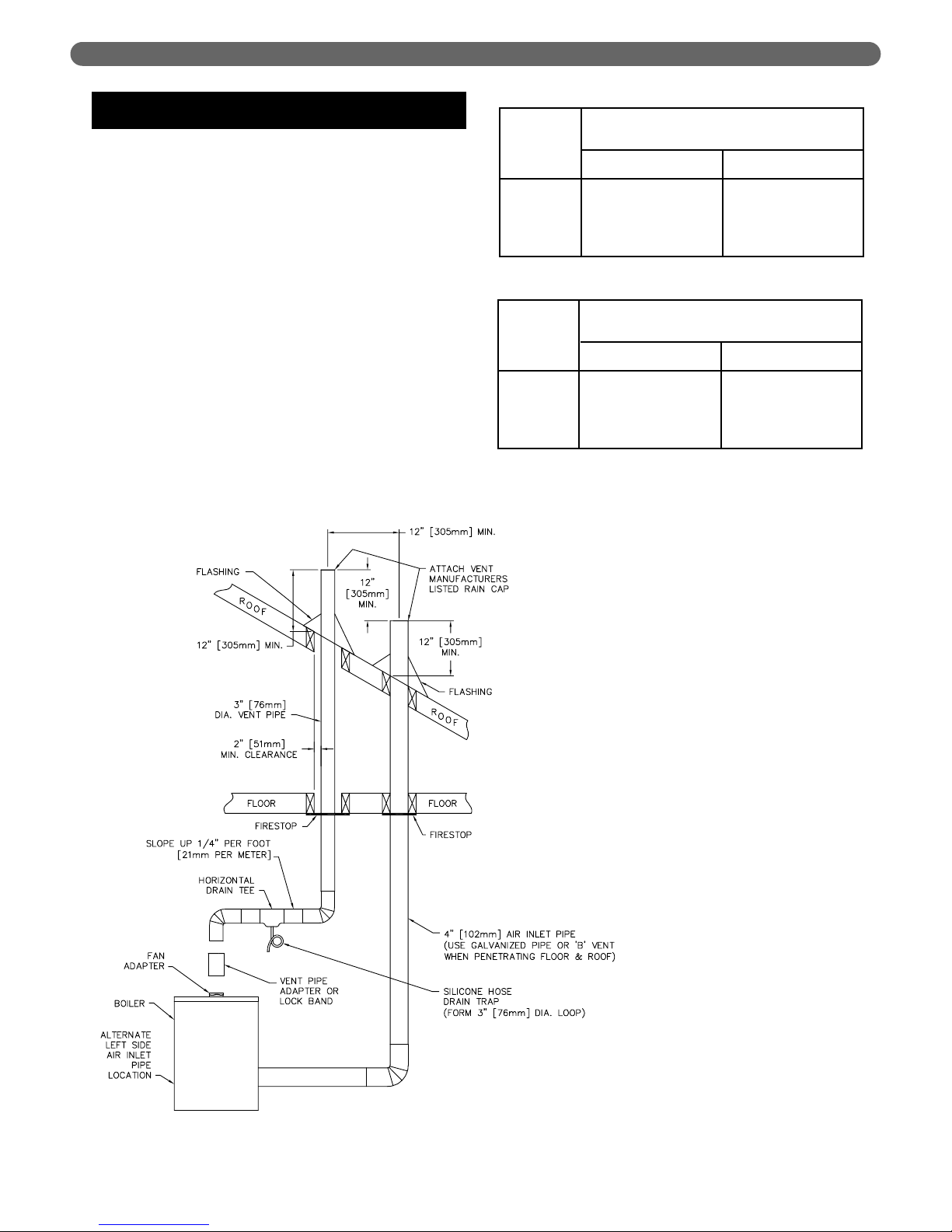
C. ROOF TERMINATIONS (VERTICAL
VENTING)
1. Vent pipe and air inlet terminations must be within
the maximum and minimum vent and air intake
lengths shown in Tables 4.1 and 4.2.
2. Vent pipe and air inlet pipe must terminate 12"
(305 mm) above expected snow lines. Vent pipe
must be a minimum 12" (305 mm) above and 12"
(305 mm) horizontally from air inlet pipe. See Figure
4.3.
3. Attach a vent manufacturer's listed rain cap to both
the vent pipe and air inlet pipe.
4. Provide 2" (51 mm) clearance between vent pipe
and combustible construction. No clearance is
required between air inlet pipe and combustible
construction.
5. See vertical venting section in vent manufacturer's
instructions for recommendations for penetration
through roof.
52 feet (15.5 m)
52 feet (15.5 m)
45 feet (13.5 m)
45 feet (13.5 m)
PSC-03
PSC-04
PSC-05
PSC-06
Boiler Model
8 feet (2.5 m)
8 feet (2.5 m)
8 feet (2.5 m)
8 feet (2.5 m)
Table 4.1:
*Equivalent Length of 3″ (76 mm) Diameter
Stainless Steel Vent Pipe
Minimum Vent Length
Maximum Vent Length
70 feet (21.0 m)
70 feet (21.0 m)
63 feet (19.0 m)
63 feet (19.0 m)
PSC-03
PSC-04
PSC-05
PSC-06
Boiler Model
12 feet (4.0 m)
12 feet (4.0 m)
12 feet (4.0 m)
12 feet (4.0 m)
Table 4.2:
*Equivalent Length of 4″ (102 mm) Diameter
Aluminum/Galvanized Air Inlet Pipe
Minimum Length
Maximum Length
*Each 90° elbow equals 5 feet (1.5 meters) of equivalent
length.
Figure 4.3: Vertical Venting System
Page 13

Figure 4.4: Vent Connection to Boiler
D . VENT PIPE INSTALLATION
1. For minimum and maximum vent pipe lengths see
Table 4.1.
2. Use only 3″ (76 mm) diameter Heat-Fab Saf-T Vent,
Z-Flex Z-Vent, ProTech FasNSeal, or Flex-L Star-34
Type AL29-4C stainless steel vent pipe and fittings for
venting of flue gases from the boiler.
3. Connect vent pipe to boiler by spreading a 1/4″
(6 mm) bead of high-temp GE-106 silicone or
Silicones Unlimited S45005 Red around the fan
adapter. Attach proper vent adapter to fan adapter
(not applicable, Z-Flex). Z-Flex vent pipe/fitting
connects directly to fan adapter, secure to fan adapter
using Z-Flex lock band. See Figure 4.4.
4. Attach remaining pipe and fittings per each
manufacturer’s vent instructions. Use only the silicone
recommended by vent pipe manufacturers. Maintain
proper clearance to combustible construction – see
Section 1, Preinstallation.
5. a. Side Wall Venting Only – Horizontal lengths of
the vent pipe shall slope down
not less than 1/4″
per lineal foot (21 mm per meter) from the boiler
to the vent terminal. If vent pipe does slope back
toward boiler, a horizontal drain is required as
described in 5B and Figure 4.3.
b. Vertical Venting Only – A horizontal drain tee is
required. Slope horizontal lengths upward
not less
than 1/4" per lineal foot (21 mm per meter) from
the boiler to the vent terminal. Install drain tee as
shown in Figure 4.3. Use silicone hose and form a
3" (76 mm) diameter loop trap with a water seal.
Pipe to drain per local code.
6. Support horizontal lengths of the vent system to
prevent sagging by use of metal strapping or
equivalent means. Locate supports at not more than
four (4) foot intervals.
7. Vertical Venting Only – If there is no solid anchor
point in the system below the roof for supporting
vertical sections of the vent pipe (i.e. Firestop
Support, etc.), a special vent support system will be
required. See vent manufacturer's instructions for
additional information.
E. AIR INLET PIPE INSTALLATION
1. For maximum air inlet pipe lengths see Table 4.2.
2. Use only 4″ (102 mm) diameter galvanized pipe or 4″
(102 mm) diameter flexible aluminum vent for
supplying combustion air to boiler inlet air box.
3. Boiler connection can be from either right or left side
of boiler jacket. Determine which jacket side air inlet
piping is to be routed and remove the 4-1/2″ (114 mm)
jacket knock-out.
4. Attach a 4″ (102 mm) diameter 90 degree elbow to
top of air box and connect air inlet piping.
5. Support air inlet piping using the same methods and
requirements as shown in the previous section for vent
pipe support.
6. Seal all connections using silicone.
7. To prevent condensation from forming on exposed
portions of Wall Thimble and 4″ (102 mm) diameter
air inlet piping, wrap exposed areas with insulation.
11
VENTING, VENTILATION AND AIR INLET
Page 14

12
VENTING, VENTILATION AND AIR INLET
F. AIR FOR VENTILATION
1. Provide air openings for adequate ventilation to
prevent ambient boiler room temperature from
exceeding 120°F (49°C) during boiler operation. This
is to maintain all the boiler controls below maximum
service temperatures. Openings should be fixed in
the open position during operation.
G. BOILER REMOVAL FROM VENTING
SYSTEM
At the time of removal of an existing boiler, follow these
steps with each appliance remaining connected to the
common venting system placed in operation, while the
other appliances remaining connected to the common
venting system are not in operation:
a. Seal any unused openings in the common venting
system.
b. Visually inspect the venting system for proper size
and horizontal pitch and determine there is no
blockage or restriction, leakage, corrosion and other
deficiencies which could cause an unsafe condition.
c. Insofar as is practical, close all building doors and
windows and all doors between the space in which
the appliances remaining connected to the common
venting system are located and other spaces of the
building. Turn on any clothes dryers and any
appliance not connected to common venting system.
Turn on any exhaust fans, such as range hoods and
bathroom exhausts, so they will operate at maximum
speed. Do not operate a summer exhaust fan. Close
fireplace dampers.
d. Place in operation the appliance being inspected.
Follow the lighting instructions. Adjust thermostat so
appliance will operate continuously.
e. Test for spillage at the draft hood relief opening after
5 minutes of main burner operation. Use the flame
of a match or candle, or smoke from a cigarette,
cigar, or pipe.
f. After it has been determined that each appliance
remaining connected to the common venting system
properly vents when tested as outlined above, return
doors, windows, exhaust fans, fireplace dampers and
any other gas-burning appliance to their previous
conditions of use.
g. Any improper operation of the common venting
system should be corrected so that the installation
conforms with the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1/NFPA 54 and/or CAN/CSA B149.1, Natural
Gas and Propane Installation Code. When resizing
any portion of the common venting system, the
common venting system should be resized to
approach minimum size as determined using the
appropriate tables in the National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54 and/or CAN/CSA B149.1,
Natural Gas and Propane Installation Code.
Page 15

1. Size and install the gas supply piping properly in
order to provide a supply of gas sufficient to meet
the maximum demand without undue loss of
pressure between the meter and the boiler.
2. Determine the volume of gas to be provided to the
boiler in cubic feet per hour. To obtain this value,
divide the Btu per hour rating (on the boiler rating
plate) by the heating value of the gas in Btu per
cubic feet. Obtain the heating value of the gas from
the gas supplier. As an alternative, use Table 5.1 on
the next page to obtain the volume of gas to be
provided to the boiler.
3. Use the value obtained above as the basis for piping
sizing. Size the gas piping in accordance with Table
5.2. Consult the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1/NFPA 54 and/or CAN/CSA B149.1, Natural
Gas and Propane Installation Code.
4. Locate the drop pipe adjacent to, but not in front of
the boiler.
5. Install a sediment trap. See Figure 5.1. Locate a tee
in the drop pipe at same elevation as the gas inlet
connection to the boiler. Extend the drop pipe to a
pipe cap.
6. Install a ground joint union ahead of the gas control
assembly to permit servicing of the control. Some
local codes require an additional service valve when
using the combination gas controls. If your code
requires such a valve, a suggested location is shown
in Figure 5.1.
7. Check piping for leaks prior to placing the boiler in
operation.
Use an approved gas detector, a non-corrosive leak
detection fluid or other leak detection method. If
leaks are found, turn off all gas flow and repair as
necessary.
8. Disconnect the boiler and its individual shut-off valve
from the gas supply piping system during any
pressure testing of that system at test pressure in
excess of 1/2 psig (3.5 kPa).
Isolate the boiler from the gas supply piping system
by closing its individual service valve during any
pressure testing of the gas supply piping system at
test pressure equal to or less than 1/2 psig (3.5 kPa).
9. Minimum permissible supply pressure for purposes of
input adjustment (Inches Water Column):
Natural Gas 5.0″ (1.2 kPa)
LP Gas 11.0″ (2.7 kPa)
Maximum permissible supply pressure to the boiler
(Inches Water Column):
Natural Gas 13.5″ (3.4 kPa)
LP Gas 13.5″ (3.4 kPa)
13
GAS PIPING
5. GAS PIPING
Figure 5.1: Gas Connection to Boiler
When checking for leaks, do not use matches,
candles, open flames or other methods that provide a
source of ignition.This can ignite a gas leak,
resulting in fire or explosion.
WARNING
Use a pipe joint sealing compound that is resistant to
the action of liquefied petroleum gas. A non-resistant
compound may lose sealing ability in the presence of
this gas, resulting in a gas leak and fire or explosion
potential.
WARNING
Do not subject the gas valve to more than 1/2 psi
(3.5 kPa) pressure. Doing so may damage the valve.
CAUTION
Page 16

14
GAS PIPING
Table 5.2: Pipe Capacity
Capacity of pipe of different diameters and lengths in cubic feet per hour (cubic meter per
hour) with pressure drop of 0.3 inches of water (75 Pa) and specific gravity of 0.60. No
allowance for an ordinary number of fittings is required.
Table 5.1: Natural Gas
Pipe
Length in
Feet (Meters)
³⁄₄
″″
Pipe
1
″″
Pipe
1¹⁄₄
″″
Pipe
1¹⁄₂
″″
Pipe
10 (3.0) 278 (7.9) 520 (14.7) 1050 (29.7) 1600 (45.3)
20 (6.1) 190 (5.4) 350 (9.9) 730 (20.7) 1100 (31.1)
30 (9.1) 152 (4.3) 285 (8.1) 590 (16.7) 890 (25.2)
40 (12.2) 130 (3.7) 245 (6.9) 500 (14.2) 760 (21.5)
50 (15.2) 115 (3.3) 215 (6.1) 440 (12.5) 670 (19.0)
60 (18.3) 105 (3.0) 195 (5.5) 400 (11.3) 610 (17.3)
Boiler
Model
Natural Gas Input LP Gas Input
Cu. Ft/hr Cu. Meter/hr Cu. Ft/hr Cu. Meter/hr
PSC-03 70 2.0 28 0.8
PSC-04 105 3.0 42 1.2
PSC-05 140 4.0 46 1.6
PSC-06 165 4.7 66 1.9
Specific Gravity 0.50 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.70 0.75
Correction Factor 1.10 1.04 1.00 0.96 0.93 0.90
Specific Gravity 0.80 0.85 0.90 1.00 1.10 1.20
Correction Factor 0.87 0.84 0.82 0.78 0.74 0.71
Specific Gravity 1.30 1.40 1.50 1.60 1.70 1.80
Correction Factor 0.68 0.66 0.63 0.61 0.59 0.58
Maximum Capacity Correction Factors for Specific Gravity
other than 0.60.
Page 17

A. WIRING
1. See Figure 6.1 for location of wiring and controls.
Use Figure 6.2 to connect the boiler to a power
supply and to connect components to the boiler.
2. Connect the boiler by a separate, permanently live
electrical supply line with a fused switch.
3. Adjust the thermostat heat anticipator to 0.2 Amp.
B. ZONED SYSTEM WIRING
See Figure 6.4 for typical wiring with zone valves. See
Figure 6.5 for typical wiring with zone circulators. When
wiring a zoned heating system, follow all applicable
codes, ordinances and regulations.
C. CONTROLS
1. For proper location of controls and accessories refer
to Figure 6.1.
2. See the attached control sheets for specific details
regarding the installation of the various controls.
3. This boiler is supplied with safety devices in addition
to the limit. For a description of these devices and
how they work to ensure the safe operation of the
boiler, see Section 7.
4. If the circulator is mounted in the supply piping,
provide longer wiring harness as required.
6. ELECTRICAL
This unit when installed must be electrically grounded in accordance with the requirements of the authority
having jurisdiction or, in the absence of such requirements, with the current edition of the
National Electrical
Code,
ANSI/NFPA 70 and/or the
Canadian Electrical Code
, Part 1, CSA C221.
NOTICE
Figure 6.1: Wiring, Controls and Safety Devices
Install all electrical wiring in accordance with the National Electrical Code and local requirements.
Do not power zone valves directly from the boiler
transformer. Doing so will greatly reduce the life of
the transformer. Use a separate transformer sized to
handle the total of all zone valve electrical loads.
NOTICE
15
ELECTRICAL
Page 18

16
ELECTRICAL
D. SEQUENCE OF OPERATION
1. Thermostat calls for heat, energizes R8285 Control
Relay (CR).
2. R8285 Control Relay (CR) energizes circulator.
3. Limit senses boiler water temperature. Prevents
boiler operation until water temperature falls
approximately 15
°
F (8°C) below the cut-out
temperature.
4. Limit energizes Fan and R4222 Isolation Relay (IR).
5. Negative pressure induced by fan switches Pressure
Switch, continuing power through closed R4222
contacts (IR-1) and flame roll-out switch.
6. Gas valve energizes.
a. Igniter on.
b. Pilot gas on, igniting pilot.
7. Pilot flame detected.
a. Igniter off.
b. Main gas on, igniting main burners.
Note: If pilot flame is not detected within 30 seconds,
the igniter is turned off for 30 seconds, and then turned
back on for another 30 seconds. If the pilot remains
undetected in this second ignition period, the igniter and
pilot are turned off for 5 minutes. The sequence then
resumes at Step 6a.
8. Call for heat ends.
a. Pilot and main gas off, extinguishing pilot and
main burners.
b. Fan and circulator off.
Figure 6.2: Wiring and Connection Diagram
Page 19

17
ELECTRICAL
Figure 6.3: Ignition System Operating Sequence
Page 20

18
ELECTRICAL
Figure 6.4: Zone Wiring with Zone Valves
Figure 6.5: Zone Wiring with Circulators
Page 21

A. COMPLETING THE INSTALLATION
1. Confirm that all water, gas and electricity are
turned off.
2. Inspect the boiler combustion chamber for foreign
objects and remove if present.
3. Check physical condition of burners and pilot. Make
certain that there are no unusual bends or
perforations in the burners or pilot. Replace
components if necessary.
4. Verify that water piping, venting, gas piping and
electrical wiring and components are installed
properly. Refer back to previous sections of these
instructions as well as equipment manufacturer’s
instructions as necessary.
5. Fill the boiler and system with water, making certain
to vent all air from all points in the system. To check
water level in the system, open and close each vent
in the system. Water should exit from each vent
when it is opened.
6. The pressure reducing valve on the fill line will
typically allow the system to be filled and pressurized
to 12 psi (83 kPa). Consult the valve and expansion
tank manufacturer for more specific information.
7. Check joints and fittings throughout the system for
leaks. If leaks are found, drain the system and repair
as required.
8. Connect a manometer to the 1/8″ NPT inlet pressure
tap on the gas valve. See Figure 7.2.
9. Confirm that the gas supply pressure to the boiler is
above the minimum and below the maximum values
for the gas being used. See the end of Section 5 for
these values. If a supply pressure check is required,
isolate the boiler and gas valve before performing
the pressure check. If the supply pressure is too high
or too low, contact the gas supplier.
10. Turn on electricity and gas to boiler.
11. Light the boiler by following the Lighting/Operating
Instructions label mounted to the jacket panel. The
initial ignition may require several tries as the piping
is purged of air.
12. Use the sequence description and Figure 6.3 in
Section 6 (Electrical) to follow light-off and shutdown
sequences and to assist in diagnosing problems. If
the boiler does not function properly, consult Section
8, Troubleshooting.
7. START-UP PROCEDURES
19
START-UP PROCEDURES
Page 22

20
START-UP PROCEDURES
Figure 7.1: Gas Valve, Manifold and Burner Assembly – Intermittent Ignition
Figure 7.2: Valve Tapping and Adjustment Screw Locations
Page 23

21
START-UP PROCEDURES
Figure 7.3: Operating Instructions
Page 24

22
START-UP PROCEDURES
B. CONTROL DESCRIPTIONS
See Figure 6.1 in Section 6 (Electrical) for locations of
these devices.
1. FLAME ROLL-OUT SAFETY SHUT-OFF SWITCH
(FLAME ROLL-OUT SWITCH) – A thermally
activated switch located between the first burner
from the left and the manifold bracket. The flame
roll-out safety shut-off switch will sense excessive
temperature caused by continued flame roll-out and
shut down main burner gas. This is a non-recycling
switch that must be replaced once it has been
activated and the cause of the roll-out eliminated.
2. DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH – This device
senses a negative or suction pressure in the blower
housing and air box when the blower is energized. If
there is not excessive blockage in the venting system
or air inlet vent the switch will close, allowing power
to energize the ignition system.
3. LIMIT – A thermally activated, manually adjustable
switch located on the right side of the boiler. The
temperature sensing element is placed in the supply
and will shut down main burner gas if the supply
water exceeds the preset temperature limit. This is a
recycling switch that will automatically reset when
the supply water falls below the preset temperature.
4. LOW WATER CUT-OFF (FOR GRAVITY SYSTEMS
OR HOT WATER BOILERS INSTALLED ABOVE
RADIATION LEVEL) – A level-sensing device (float
or probe) located in supply piping near the boiler. If
water level in the system drops below the control’s
position, it will shut down main burner gas. The
control will automatically reset once the water level
rises above its position.
C. ADJUSTMENT OF GAS PRESSURE
REGULATOR
1. Move the manometer to either the outlet pressure
tap on the gas valve or to the burner manifold test
tap. Set manifold pressure as follows for various
gases.
a. Natural Gas . . .3.5″ Water Column (0.9 kPa)
b. LP Gas . . . . . .10.0″ Water Column (2.5 kPa)
2. To adjust gas pressure, turn adjusting screw of gas
pressure regulator counterclockwise to decrease
pressure, clockwise to increase pressure. Refer to
Figure 7.2 for location of gas pressure regulator.
Replace the cap screw when adjustment is complete.
3. In no case should the final manifold pressure vary
more than ±0.3 inches water column (0.07 kPa)
from the above specified pressures. Any necessary
major changes in the flow should be made by
changing the size of the burner orifice spuds.
4. When adjustment is complete, turn off boiler, gas
flow and electricity to boiler. Remove manometer
and plug tapping with plug provided. Turn utilities
back on and resume checkout.
D. CHECKING BURNER INPUT
1. Refer to rating label mounted on the jacket top panel
to obtain the rated BTU per hour input. In no case
shall the input to the boiler exceed the value shown
on the rating label.
2. Check input by use of the following formula
(PB Heat suggests reading meter for 2 Cu.Ft.
[0.0566 cubic meter]):
U.S. Customary Units:
Input (BTU/Hr.)= 3600 x F x H
T
Where:
3600 – Seconds per hour
F – Cubic Feet of Gas Registered on Meter
H – Heat Value of Gas in BTU/Cubic Feet
T – Time in Seconds the Meter is Read
SI Metric Units
Input (kW)= 3600 x F x H
T x 3.6
Where:
3600 – Seconds per hour
3.6 – Megajoule (MJ) per kilowatt hour (kWhr)
F – Cubic Meters of Gas Registered on Meter
H – Heating Value of Gas in MJ/Cubic Meter
T – Time in Seconds the Meter is Read
3. As an alternative, use Table 7.1a and 7.1b. Use the
heating value provided by gas supplier. Use a
stopwatch to record the time it takes for 2 cubic feet
(0.0566 cubic meter) of gas to pass through the
meter. Read across and down to determine rate.
E. CHECK-OUT PROCEDURE
1. After starting the boiler, be certain all controls are
working properly. Check to be sure that the limit will
shut off the boiler in the event of excessive water
temperature. This can be done by lowering the limit
setting until the main burners shut down. When
proper limit function is confirmed, return the dial to
its previous setting.
2. To check operation of the ignition system safety
shut-off features:
a. Turn gas supply off.
b. Set thermostat or controller above room
temperature to call for heat. Watch for igniter
glow at pilot burner.
c. Igniter will continue to glow for 30 seconds, de-
energize for 30 seconds, then re-energize and
glow for another 30 seconds. It will then deenergize for 5 minutes before restarting the
sequence.
d. Turn gas supply on.
e. Reset the boiler and control by following
Operating Instructions.
f. Observe boiler operation through one complete
cycle.
Page 25

3. Low Water Cut-Off (if used) – Consult the
manufacturer’s instructions for the low water cut-off
operational check procedure.
4. Check the system to make sure there are no leaks or
overfilling problems which might cause excessive
make-up water to be added. Make-up water causes
liming in the boiler and brings in oxygen. Oxygen
can cause severe damage to the boiler though
oxygen corrosion pitting.
5. Check the expansion tank and automatic fill valve (if
used) to confirm that they are operating correctly. If
either of these components causes high pressure in
the system, the boiler relief valve will weep or open,
allowing fresh water to enter the system.
6. Do not allow the system controls to subject the boiler
to excessively low water temperatures, which would
cause condensation of flue gases and corrosion of
the boiler. Operate the boiler at a temperature above
130°F (54°C). Adjust the boiler limit as required to
maintain boiler temperature above this level.
7. Check the general condition of the system including
piping support, joints, etc. Check cleanliness of the
radiators, baseboard units and/or convectors. Clean
them to the extent possible. If radiators do not heat
evenly, vent any remaining air from them.
8. Review operation and User’s Information Manual
with end-user.
9. Complete the Warranty Card and submit it to PB
Heat, LLC.
10. Hang the Installation, Operation and Maintenance
Manual, User’s Information Manual, and Vent
Manufacturer’s Information Manual in an accessible
position near the boiler
23
START-UP PROCEDURES
Table 7.1a: Meter Conversion Natural Gas
(U.S. Customary Units)
Table 7.1b: Meter Conversion Natural Gas
(SI Metric System)
Burner inputs in kW for various meter timings and
heating values. (Tables based on 0.0566 cubic meters
of gas through the meter).
Burner inputs in Btu/hr for various meter timings and
heating values. (Tables based on 2 cubic feet of gas
through the meter).
Time that
meter is
read (sec)
Heat Value of Gas
(MJ/cubic meter)
37.26 38.19 39.12
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
105
110
115
120
125
84.36
70.30
60.25
52.72
46.86
42.18
38.34
35.15
32.44
30.13
28.12
26.36
24.81
23.43
22.20
21.09
20.08
19.17
18.34
17.57
16.87
86.46
72.05
61.76
54.04
48.03
43.23
39.30
36.03
33.25
30.88
28.82
27.02
25.43
24.02
22.75
21.62
20.59
19.65
18.80
18.01
17.29
88.57
73.81
63.26
55.35
49.20
44.28
40.26
36.90
34.06
31.63
29.52
27.68
26.05
24.60
23.31
22.14
21.09
20.13
19.25
18.45
17.71
Time that
meter is
read (sec)
Heat Value of Gas
(Btu/cubic foot)
1000 1025 1050
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
105
110
115
120
125
288000
240000
205714
180000
160000
144000
130909
120000
110769
102857
96000
90000
84706
80000
75789
72000
68571
65455
62609
60000
57600
295200
246000
210857
184500
164000
147600
134182
123000
113538
105429
98400
92250
86824
82000
77684
73800
70286
67091
64174
61500
59040
302400
252000
216000
189000
168000
151200
137455
126000
116308
108000
100800
94500
88941
84000
79579
75600
72000
68727
65739
63000
60480
Page 26

24
TROUBLESHOOTING
A. SHUT-DOWN CAUSED BY PILOT
OUTAGE, PRESSURE SWITCH OR
FLAME ROLL-OUT SAFETY
SHUT-OFF SWITCH
In the event of a shut-down caused by a pilot outage,
action of the pressure switch or flame roll-out safety
shut-off switch effecting a shut-down of the main
burners:
a. Refer to the Lighting/Operating Instructions in Figure
7.3 to properly turn off the gas to the boiler.
b. Turn off all electric power to the boiler.
c. Call a qualified heating service organization or local
gas company and have the cause of the shut-down
investigated and corrected.
d. Refer to Operating Instructions to re-start boiler.
B. TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDES
Use Table 8.1 and Figure 8.2 to assist in determining
causes and providing corrective actions to boiler
problems. These guides must be used only by qualified
service technicians. These individuals must follow all
applicable codes and regulations in repair of any boiler
problems.
C. MEASURING SUCTION PRESSURE
Pressure switch requires minimum -0.45″ W.C. (-112 Pa)
fan suction pressure to energize control circuit. Measure
when boiler has been operating at least 15 minutes. See
Figure 8.1.
8. TROUBLESHOOTING
Should overheating occur or the gas supply fail to
shut off, do not turn off or disconnect the electrical
supply to the pump.This may aggravate the problem
and increase the likelihood of boiler damage. Instead,
shut off the gas supply at a location external to the
appliance.
CAUTION
Do not use this appliance if any part has been under
water. Improper or dangerous operation may result.
Immediately call a qualified service technician to
inspect the boiler and to replace any part of the
control system and any gas control which has been
under water.
WARNING
Label all wires prior to disconnection when servicing
controls.Wiring errors can cause improper and
dangerous operation.Verify proper operation after
servicing.
CAUTION
When servicing or replacing items that communicate
with the boiler water, be certain that:
●●
There is no pressure on the boiler.
●●
The boiler is not hot.
●●
The power is off.
When servicing the gas valve or pilot, be certain that:
●●
The gas is off.
●●
The electricity is off.
DANGER
Page 27

25
Figure 8.1: Measuring Fan Suction Pressure
TROUBLESHOOTING
*
Page 28

26
TROUBLESHOOTING
Table 8.1: Boiler Troubleshooting Guide (Burners Functioning)
PROBLEM POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIVE ACTIONS
1. See Figure 8.2
Burners not functioning.
1. See Figure 8.2
1. Defective gas valve.
2. Short circuit.
Burners will not shut
down.
1. Use Figure 8.2 to troubleshoot intermittent
ignition gas valve. Replace if necessary.
2. Check and correct wiring.
1. Manifold gas pressure too low.
2. Improperly sized/drilled orifice spuds.
3. Leaking gas valve.
4. Burrs on orifice.
5. Low supply gas pressure.
Flashback or burning
at orifice spuds.
1. Adjust to proper pressure.
2. Install correct spuds.
3. Replace valve.
4. Remove burrs.
5. Contact gas supplier if natural gas. Adjust
regulator if LP gas.
1. Insufficient pilot flame.
2. Pilot burner/orifice clogged.
3. Overfiring.
4. Misaligned burners or pilot.
Delayed ignition.
1. Increase pilot gas flow.
2. Clean pilot burner and orifice.
3. Reduce rate to input on rating label.
4. Realign burners or pilot.
1. Vent pipe not sloped towards vent terminal.
Condensation at boiler
vent connector/fan.
1. Install condensate trap per vent manufacturer’s
. instructions.
2. Slope vent pipe towards vent terminal.
1. Underfiring.
2. Limit set too low.
3. Air in system.
4. Circulator malfunctioning.
5. Circulation system clogged.
6. Incorrect thermostat heat anticipator setting.
Boiler not heating
properly.
1. Increase rate to input on rating label.
2. Reset limit to higher setting.
3. Vent air from all points in system.
4. Check circulator, replace if necessary.
5. Shut down and cool boiler, drain and flush
system.
6. Adjust heat anticipator.
1. Leaks in gas piping or fittings.
2. Leaks in gas service line or meter.
3. Leaks in venting system.
4. Overfiring.
Fumes or gas odors
1. Locate and repair or replace.
2. Shut down boiler and notify gas provider.
3. Locate and repair or replace.
4. Reduce rate to input on rating label.
Page 29

27
TROUBLESHOOTING
Figure 8.2: Boiler Troubleshooting Guide (Burners Not Functioning)
ENDVIEW OF
INSET A
CONTROL
HARNESS
24VOLT
HOT
CONNECTOR
24
VOLTS
INSET B
HSI
TERMINAL
24VOLT
THERMOSTAT
24
VOLTS
24VOLT
ASSURE GASVALVE SWITCH IS
IN "ON" POSITION
DISCONNECT SYSTEM CONTROL
TURN OFF GAS SUPPLY
●●●
●
CHECK FOR DAMAGED OR MISSING
TERMINALS IN CONNECTOR
COMMON
HARNESS
SETTHERMOSTATTO CALL
FOR HEAT
●
●
●
LINEVOLTAGE POWER
LOWVOLTAGETRANSFORMER
LIMIT CONTROLLER
WIRING
THERMOSTAT
CHECK:
●●●●●
NO
YES
CHECK FOR PROPERVOLTAGE
AT CONTROL HARNESS (SEE INSET
A).VOLTAGE SHOULD BE 24V
BETWEENTHERMOSTAT AND
24V COMMON, AND 24V BETWEEN
24V COMMON AND 24V HOT.
NO
UNPLUG PILOT BURNER CABLE.
NO
PLUG HARNESS INTO GASVALVE
CONTROL.WAIT FOR INTERNAL
CHECK DELAY
REPLACE GASVALVE
RECONNECT PILOT BURNER
CABLE
YES
MEASUREVOLTAGE AT GAS VALVE
HSI ELEMENT OUTPUT (SEE INSET B)
24V NOMINAL
REPLACEIGNITER/FLAMERODASSEMBLY
RECONNECT PILOT BURNER CABLE
YES
IGNITERWARMS UP AND
GLOWS RED
NOTE:IGNITERWILL CYCLE OFF
AND BACK ON ONCE DURINGTHE
90 SECOND IGNITIONTRIAL
REPLACE GASVALVE
CHECKTHAT PILOT GAS IS FLOWING.
WAITTO ASSURE PILOT GAS TUBING
IS PURGED.
●●●
NO NO
PILOT BURNER LIGHTS
TURN ON GAS SUPPLY
●
●
CHECKTRANSFORMER AND
LINEVOLT SUPPLY
NO
YES
MEASUREVOLTAGE BETWEEN 24V
HOT AND 24V COMMON LEADSTO GAS
VALVE. MUST MEASURE AT LEAST
19.5VAC WITH IGNITER POWERED.
●●●●●●●
YES
SEE INSET ATO IDENTIFY PROPER
LEAD.THIS CHECK MUST BE DONE
WITHTHE GASVALVE CONNECTED
AND IGNITER POWERED.
REPLACEIGNITER/FLAMERODASSEMBLY
●
YES
CYCLETHERMOSTAT OFF AND BACK ON
CHECKTHAT PILOT FLAME MAKES
●
IF MAIN BURNERS DO NOT LIGHT,
REPLACE GASVALVE
CHECK FOR GOOD ELECTRICAL
IF BOTH OFTHE ABOVE ARE GOOD,
GOOD CONTACT WITH PILOT BURNER
FLAME ROD.
CONNECTIONTHROUGHTHE PILOT
TUBING
REPLACE IGNITER/FLAME ROD
●●●●●●●
NO
YES
MAINVALVE OPENS AND
MAIN BURNER LIGHTS
ASSEMBLY.
●
SYSTEM IS OKAY
SEETABLE 8.1
YES
DO BURNERS
FUNCTION?
YES
NO
DOES IGNITERWARM
UP AND GLOW RED?
(INTERMITTENTLY)
YES
NO
SWITCH "NO"TERMINALTO GROUND.
IF NOVOLTAGE,CHECK FOR:
- BLOCKED OR CRACKED SUCTION
x
1) CHECK FOR 24VAC AT PRESSURE
1)x
1)x
1)x
IS FAN RUNNING?
TUBING.
- FAN NOT GENERATING ADEQUATE
1)x-
1)x
SUCTION PRESSURE.
1)x-
CHECK FOR BROKEN/LOOSEWIRE.
CHECK FOR 120VAC BETWEEN R4222
RELAY BLACK AND WHITE WIRES. IF
2)x-
- IF NOVOLTAGE AT ONLY ONE BLWIRE,
2)x
2)x-
2)x-
SO,REPLACE RELAY.
3) CHECK FOR 24VAC AT FLAME ROLL-OUT
2)x-x3)x
SWITCH. IF SWITCH IS BLOWN,CORRECT
- DEFECTIVE PRESSURE SWITCH.
BLUEWIRESTO GROUND:
- IF NOVOLTAGE AT EITHER BL WIRES,
2) CHECK FOR 24VAC AT R4222 RELAY
1)xx2)x
2)x
CAUSE OF ROLL-OUT BEFORE
REPLACING SWITCH.
3)x
3)x
NO
NO
CHECKFOR 120VACHIGHLIMIT CONTROL.IF
POWERATONETERMINAL BUTNOTBOTH,
REPLACELIMITCONTROL.
NO
JUMPERTHERMOSTAT
AT CONNECTIONS
"G" AND "Y" ON R8285.
DOES BOILER RUN?
CHECK FOR 24VAC AT PRESSURE SWITCH
TERMINALS "C" AND "NC"TO GROUND:
IFVOLTAGE AT "NC" BUT NOT "C",
PRESSURE SWITCH IS STUCK IN
RUNNING POSITION. CHECK FOR BLOCKED
●●●●●
AIRTUBE.IF OKAY, REPLACE PRESSURE
●
●
YES
CORRECT
THERMOSTAT
PROBLEM
SWITCH.
IF NOVOLTAGE AT EITHER PRESSURE
SWITCHTERMINAL "C" OR "NC"TO
GROUND,CHECK FOR 120VAC INCOMING
POWER INSIDE JUNCTION BOX.IF PROPER
INCOMING POWER,REPLACE R8285.
●●●
●
Page 30

28
MAINTENANCE
9. MAINTENANCE
WARNING
Product Safety Information
Refractory Ceramic Fiber Product
This appliance contains materials made from refractory ceramic fibers (RCF). Airborne RCF,
when inhaled, have been classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer
(IARC), as a possible carcinogen to humans. After the RCF materials have been exposed to
temperatures above 1800°F (980°C), they can change into crystalline silica, which has been
classified by the IARC as carcinogenic to humans. If particles become airborne during service or repair, inhalation of these particles may be hazardous to your health.
Avoid Breathing Fiber Particulates and Dust
Suppliers of RCF recommend the following precautions be taken when handling these
materials:
Precautionar
y Measures:
Provide adequate ventilation.
Wear a NIOSH/MSHA approved respirator.
Wear long sleeved, loose fitting clothing and gloves to prevent skin contact.
Wear eye goggles.
Minimize airborne dust prior to handling and removal by water misting the material and
avoiding unnecessary disturbance of materials.
Wash work clothes separately from others. Rinse washer thoroughly after use.
Discard RCF materials by sealing in an airtight plastic bag.
Fir
st Aid Procedures:
Inhalation: If breathing difficulty or irritation occurs, move to a location with fresh clean air.
Seek immediate medical attention if symptoms persist.
Skin Contact:Wash affected area gently with a mild soap and warm water. Seek immediate
medical attention if irritation persists.
Eye Contact: Flush eyes with water for 15 minutes while holding eyelids apart. Do not rub
eyes. Seek immediate medical attention if irritation persists.
Ingestion: Drink 1 to 2 glasses of water. Do not induce vomiting. Seek immediate medical
attention.
Page 31

29
A. GENERAL
1. Disconnect this boiler from the gas supply piping
during any pressure testing of the gas system.
2. Check pipes adjacent to cold walls or in unheated
spaces. Insulate and tape them if necessary to be
sure they can’t freeze up. Keeping the water moving
at all times will reduce the likelihood of freezing. See
Section 3 for antifreeze instructions.
3. If there is considerable foreign matter in the boiler
water, the boiler should be shut down and allowed to
cool, then drained and thoroughly flushed out. Use
the drain valve at the bottom of the return
connection to drain the boiler. Pipe the drain cock to
a suitable drain or containment device if antifreeze is
used. Flush the system to remove remaining matter.
If there is evidence that hard scale has formed on the
internal surfaces, the boiler should be cleaned by
chemical means as prescribed by a qualified water
treatment specialist.
B. DAILY (WITH BOILER IN USE)
Daily boiler observation can be performed by the owner.
If any potential problems are found, a qualified installer
or service technician/agency must be notified.
1. Remove any combustible materials, gasoline and
other flammable liquids and substances that generate
flammable vapors from the area where the boiler is
contained. Make certain that the boiler area has
ample air for ventilation and that there are no
obstructions to the free flow of air to and from the
boiler.
2. Observe general boiler conditions (unusual noises,
vibrations, etc.)
3. Observe operating temperature and pressure on the
combination gauge located on the right side of the
boiler. Boiler pressure should never be higher than
5 psi (35 kPa) below the rating shown on the safety
relief valve (25 psig [172 kPa] maximum for a 30
psig [207 kPa] rating, 45 psig [310 kPa] maximum
for a 50 psig [345 kPa] rating). The valve rating can
be found on the top of the safety relief valve (see
Figure 3.4 for location of the safety relief valve).
Boiler temperature should never be higher than
250°F (121°C).
4. Check for water leaks in boiler and system piping.
5. Smell around the appliance area for gas. If you smell
gas, follow the procedure listed in the Operating
Instructions to shut down appliance in Figure 7.3.
C. WEEKLY (WITH BOILER IN USE)
1. Flush float-type low-water cut-off (if used) to remove
sediment from the float bowl as stated in the
manufacturer’s instructions.
D. MONTHLY (WITH BOILER IN USE)
1. Check boiler room floor drains for proper
functioning.
2. Check function of the safety relief valve (monthly
unless specified otherwise by manufacturer) by
performing the following test:
a. Check valve piping to determine that it is
properly installed and supported.
b. Check boiler operating temperature and pressure.
c. Lift the try lever on the safety relief valve to the
full open position and hold it for at least five
seconds or until clean water is discharged.
d. Release the try lever and allow the valve to close.
If the valve leaks, operate the lever two or three
times to clear the valve seat of foreign matter. It
may take some time to determine if the valve has
shut completely.
e. If the valve continues to leak, it must be replaced
before the boiler is returned to operation.
f. Check that operating pressure and temperature
have returned to normal.
g. Check again to confirm that valve has closed
completely and is not leaking.
3. Test low-water cut-off (if used) as described by the
manufacturer.
4. Test limit as described in Section 7, “Check-Out
Procedure.”
MAINTENANCE
Page 32

30
MAINTENANCE
5. Test function of gas safety shut-off features as
described by gas valve and ignition control
manufacturer.
E. ANNUALLY (BEFORE START OF HEATING
SEASON)
1. Inspect flueways, burners and vent system. See
Figure 9.2.
a. Refer to the Operating Instructions in Figure 7.3
to properly turn off the gas to the boiler. Turn off
all electrical power to the boiler.
b. Remove jacket removable door, air inlet pipe, air
box cover, and air box diffuser screen.
d. Remove burner hitch pin clips. Disconnect pilot
tubing at compression elbow.
e. Disconnect pilot harness at gas valve. Gently pull
pilot harness further inside air box to be able to
remove burner with attached pilot.
f. Remove burners and pilot.
g. Brush gas outlet ports lightly using a soft bristle
brush. If extensive corrosion in outlet ports,
replace.
h. Examine pilot hood and igniter for corrosion,
scale, ceramic cracking. Replace if necessary.
i. Remove 3″ (76 mm) diameter vent pipe from fan
adapter.
j. Remove top jacket panel, flue collector/fan
assembly, and flue baffles.
k. Examine flueways and flue collector/fan for scale,
soot, and loose rust.
l. If necessary, brush flueways with wire brush and
remove scale and loose rust from flue baffles. If
corroded, replace baffles.
m. Reinstall flue baffles.
n. Examine flue collector blanket seal.
Reposition/replace as necessary to assure air tight
seal between flue collector and heat exchanger.
o. Reinstall flue collector/fan assembly.
p. Reinstall jacket top panel.
q. Reinstall pilot, burners, hitch pin clips. Reconnect
pilot harness to gas valve, gently pulling harness
to length required to reach gas valve.
r. Reinstall air box diffuser.
s. Examine air box cover seal. Reposition/replace as
necessary to assure air tight seal.
t. Reinstall air box cover.
u. Examine entire vent system for corrosion,
support and joint integrity. Repair as necessary.
Remove any debris inside vent.
v. Reconnect vent pipe to fan adapter. Reseal using
high-temp silicones as shown in Section 4,
Venting, Ventilation and Air Inlet.
w. Refer to Operating Instructions in Figure 7.3 to
properly return the boiler to operation.
2. Check the pilot and main burner flame. See Figure
9.1. The pilot should provide a steady flame
enveloping 3/8″ to 1/2″ (1 cm to 1.2 cm) of the flame
sensor. If required, adjust the pilot as stated in the
gas valve manufacturer’s instructions. The main
burner flame inner cone should be approximately
1-1/2″ (4 cm) high and should have a very sharp,
blue color characteristic.
Figure 9.1: Intermittent Pilot and Main
Burner Flame
When servicing or replacing components, be
absolutely certain that the following conditions are
met:
●●
Water, gas and electricity are off.
●●
The boiler is at room temperature.
●●
There is no pressure in the boiler.
DANGER
Leaks in the vent system will cause products of
combustion to enter structure (vent system operates
under positive pressure).
WARNING
Soot accumulation indicates boiler malfunction.
Cause of malfunction must be determined and
corrected before returning boiler to service.
WARNING
Page 33

31
MAINTENANCE
Figure 9.2: Inspection of Flueways, Burners, and Vent System.
Page 34

32
BOILER DIMENSIONS & RATINGS
10. BOILER DIMENSIONS & RATINGS
Figure 10.1: Boiler Views
Table 10.1: Series PSC Boiler Dimensions
Table 10.2: Series PSC Boiler Ratings
1 Net I=B=R water ratings based on an allowance of 1.15.
2 Consult factory before selecting a boiler for installations having unusual piping and pickup
requirements, such as intermittent system operation, extensive piping systems, etc.
3 Heating Capacity and Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) ratings are based on U.S.
Government test.
SERIES PSC BOILER DIMENSIONS
Boiler
Model
Number
Jacket Width “A”
PSC-03
12¹⁄₂″
318 mm
PSC-04
15⁷⁄₈″
403 mm
PSC-05
19¹⁄₄″
489 mm
PSC-06
22⁵⁄₈″
575 mm
SERIES PSC BOILER RATINGS
Boiler
Model
Number
Input
DOE Heating
Capacity
3
Net I=B=R
Ratings Water
1,2
Seasonal
Efficiency
3
(AFUE)%
Water Content
MBH kW MBH kW MBH kW Gallon Liter
PSC-03 70 21 58 17 50 15 83.0 4.72 17.87
PSC-04 105 31 88 26 77 23 83.0 6.00 22.71
PSC-05 140 41 117 34 102 30 83.0 7.28 27.56
PSC-06 175 51 146 43 127 37 83.0 8.56 32.40
Page 35

33
REPAIR PARTS
REPAIR PARTS
SERIES PSC GAS BOILER
Repair parts are available from your installer or by contacting PB Heat, LLC, New
Berlinville, PA. Use the figures and tables on pages 32-36 to assist in ordering parts.
Note: Remember to include boiler model number and serial number when ordering parts.
11. REPAIR PARTS
Figure 11.1
Page 36

34
REPAIR PARTS
Table 11.1
Base Assembly
Floor Pan
Base Rear Panel Assembly
Base Observation Port Cover
Base/Air box Spacer
Air Box Right Side
Air Box Left Side
Air Box Top/Front Cover
Air Box Diffuser Screen
Rope Gasket Seal, Air Box
Flame Rollout Switch, Thermodisc G4AM00167C
Flame Rollout Switch Bracket
Burner Less Pilot Bracket
Burner with Pilot Bracket
Orifice, #48, normal altitude Natural Gas only
Orifice, #56, normal altitude LP Gas only
Gas Manifold
Item
No.
Description
7800
50100
PSC2000
51771
(2) 50152
PSC2023
PSC2024
50143
PSC2025
(56″) 50718
51587
50136
(3) 51537
51539
(4) 50894
(4) 50899
50121
7803
50103
PSC2000-3
51771
(2) 50152
PSC2023
PSC2024
50146
PSC2025-3
(76″) 50718
51587
50136
(9) 51537
51539
(10) 50894
(10) 50899
50124
7802
50102
PSC2000-2
51771
(2) 50152
PSC2023
PSC2024
50145
PSC2025-2
(69″) 50718
51587
50136
(7) 51537
51539
(8) 50894
(8) 50899
50123
7801
50101
PSC2000-1
51771
(2) 50152
PSC2023
PSC2024
50144
PSC2025-1
(63″) 50718
51587
50136
(5) 51537
51539
(6) 50894
(6) 50899
50122
(Quantity/Length) Stock Code
PSC-0 3 PSC-0 4 PSC-05 PSC-06
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Page 37

35
REPAIR PARTS
Figure 11.2
Page 38

REPAIR PARTS
36
Table 11.2
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Insulation Blanket, 1/2″ x 1.50″, block to base
Block
Flue Baffle
Insulation Blanket, 1/2″ x .75″, flue collector to block
Flue Collector
Gasket, Orifice Plate
Orifice Plate, normal altitude Natural Gas models only
Orifice Plate, normal altitude LP Gas models only
Fan
Fan Adapter
Jacket Set
Gas Valve, SV9501M2700, Natural Gas models only
Gas Valve, SV9501M2064, LP Gas models only
Pilot Assembly, Q3480B1058, w/Natural Gas Orifice
Pilot, Q3480B1058, LP Gas models only
Limit Control, L4080B1253 (less well)
Pressure Switch, Standard altitude, FS6124A2481
Transformer Relay Center, R8285D1026
Relay (mounted on jacket), R4222D1005
Safety Relief Valve, 30psi, Conbraco 10-408-05
Safety Relief Valve, 50psi, Watts #350
Temperature-Pressure Gauge
Circulator, Taco 007
Flange Set, Taco 110-Z53BP, 1 1/4″
Heat-Fab Vent Adapter 7301 AMTK
Z-Flex Locking Band SVSLBX03
ProTech Vent Adapter FSA-PSC/DE-3
Flex-L Star-34 Vent Adapter SRAPPA3
Wall Thimble Assembly, up to 11 1/2″ walls
Wall Thimble Assembly, up to 20″ walls
Heat-Fab vent pipe, elbows
Z-Flex, ProTech, Flex-L vent pipe, elbows
Item
No.
Description
(47″) 50867
90419
(2) 51584
(34″)50866
50131
(2) 50135
PSC5002
PSC5003
50775
50200
90366
51682
51691
7794
50205
50210
50080
50786
50790
50501
99950
51774
50782
51048
50199 (Also Available From Heat-Fab Distributor)
Available from Z-Flex Distributor
Available from ProTech Distributor
Available from Flex-L Distributor
90249
90350
Specify item including pipe length. Also available from Heat-Fab Distr.
Available from Vent Manufacturer Distributors
(61″) 50867
90421
(4) 51584
(47″)50866
50133
(2) 50135
PSC5002-2
PSC5003-2
50775
50200
90368
(54″) 50867
90420
(3) 51584
(41″)50866
50132
(2) 50135
PSC5002-1
PSC5003-1
50775
50200
90367
(Quantity/Length) Stock Code
PSC-0 3 PSC-0 4 PSC-05 PSC-06
(67″) 50867
90422
(5) 51584
(54″)50866
50134
(2) 50135
PSC5002-3
PSC5003-3
50775
50200
90369
Page 39

PSC
Boilers
Series
Gas
Installation,
Operation &
Maintenance
Manual
TO THE INSTALLER:
This manual is the property of the owner and must
be affixed near the boiler for future reference.
TO THE OWNER:
This boiler should be inspected annually by a
Qualified Service Agency.
HI Division
of gama
ASME
PB HEAT, LLC
PO BOX 447 • NEW BERLINVILLE, PA 19545-0447
©2005 WEB-1
PSC8030 R6 (9/05-2M)
Printed in U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...