Page 1

Instant Payment
Notification Guide
For Professional Use Only
Currently only available in English.
A usage Professional Uniquement
Disponible en Anglais uniquement pour l’instant.
Last updated: June 26, 2009
Page 2

IPN Guide
Document Number: 10087.en_US-20090626
© 2009 PayPal, Inc. All rights reserved. PayPal is a registered trademark of PayPal, Inc. The PayPal logo is a trademark of PayPal, Inc. Other
trademarks and brands are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document belongs to PayPal, Inc. It may not be used, reproduced or disclosed without the written approval of PayPal, Inc.
PayPal (Europe) Ltd. is authorised and regulated by the Financial Services Authority in the United Kingdom as an electronic money institution.
PayPal FSA Register Number: 226056.
Notice of non-liability:
PayPal, Inc. is providing the information in this document to you “AS-IS” with all faults. PayPal, Inc. makes no warranties of any kind (whether express,
implied or statutory) with respect to the information contained herein. PayPal, Inc. assumes no liability for damages (whether direct or indirect), caused
by errors or omissions, or resulting from the use of this document or the information contained in this document or resulting from the application or use
of the product or service described herein. PayPal, Inc. reserves the right to make changes to any information herein without further notice.
Page 3

Contents
Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Chapter 1 Introducing IPN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
What is IPN? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
IPN Protocol and Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
IPN Messages Generated by Website Payments Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
IPN Messages Generated by PayPal APIs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
IPN Messages Generated by a Back-Office Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
IPN Messages Generated by PayPal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
A Sample IPN Message and Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Non-IPN Notification Mechanisms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Chapter 2 Implementing an IPN Listener . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Chapter 3 Identifying Your IPN Listener to PayPal . . . . . . . . . . .23
Setting Up IPN Notifications on PayPal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Dynamically Setting the Notification URL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Chapter 4 IPN Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Testing Your Listener. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
IPN Troubleshooting Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Chapter 5 IPN Operations on PayPal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Using the IPN History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Resending IPN Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Chapter 6 Using Fraud Management Filters With IPN . . . . . . . . . 37
Chapter 7 IPN Variable Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
IPN Transaction Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
IPN Guide June, 2009 3
Page 4

Contents
Transaction and Notification-Related Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Buyer Information Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Payment Information Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Auction Variables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Mass Pay Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Recurring Payments Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Subscription Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Dispute Resolution Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Payment Review Using Notifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
4 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 5

Preface
This document describes the Instant Payment Notification (IPN) message service.
Intended Audience
This document is intended for merchants implementing IPN.
Revision History
Revision history for Instant Payment Notification Guide.
TABLE P.1 Revision History
Date Description
06/26/09 Added information about IPN messages related to payment review. Updated the
section about setting up IPN notifications on PayPal and added a note about the
delivery of IPN messages to the notify URL.
06/10/09 Added IPN history and resend information and added information to the
troubleshooting section.
03/16/09 Made additions to sample code.
02/16/09 First draft.
IPN Guide June, 2009 5
Page 6

Revision History
6 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 7

1
Instant Payment Notification (IPN) is a message service that notifies you of events related to
PayPal transactions. You can use it to automate back-office and administrative functions, such
as fulfilling orders, tracking customers, and providing status and other information related to a
transaction.
z What is IPN?
z IPN Protocol and Architecture
z A Sample IPN Message and Response
z Non-IPN Notification Mechanisms
What is IPN?
IPN notifies you when an event occurs that affects a transaction. Typically, these events
represent various kinds of payments; however, the events may also represent authorizations,
Fraud Management Filter actions and other actions, such as refunds, disputes, and
chargebacks.
Introducing IPN
IPN is a message service that PayPal uses to notify you about events. These events include the
following:
z Instant payments, including Express Checkout and direct credit card payments
z eCheck payments and associated status, such as pending, completed, or denied
z Payments that may be pending for other reasons, such as those being reviewed for potential
fraud
z Events related to recurring payments and subscriptions
z Authorizations, which indicate a sale whose payment has not yet been collected
z Chargebacks, which are initiated by a credit card processor; for example, when a customer
disputes a charge
z Disputes, which are initiated by a buyer using the PayPal resolution process
z Reversals, which occur when you win a dispute or a chargeback is canceled
z Refunds, which you may choose to give
In many cases, the action that causes the event, such as a payment, occurs on your website;
however, your website is not the only source of events. In many cases, events can be generated
by Website Payment Standard buttons, the PayPal API, or by PayPal itself.
You detect and process IPN messages with a listener, sometimes called a handler, which is a
script or program that you write. It waits for messages and passes them to various back-end or
IPN Guide June, 2009 7
Page 8
Introducing IPN
What is IPN?
administrative processes that respond the messages. PayPal provides sample code that you can
modify to implement a listener that detects IPN messages.
The actions to take when your listener is notified of an event are specific to your needs.
Examples of the kinds of actions you might take when your listener receives an IPN message
include the following:
z Trigger order fulfillment or enable media downloads when a check clears or a payment is
made
z Update your list of customers
z Update accounting records
z Create specialized “to do” lists based on the kind of event
You are typically notified of events by email as well, but the IPN message service enables you
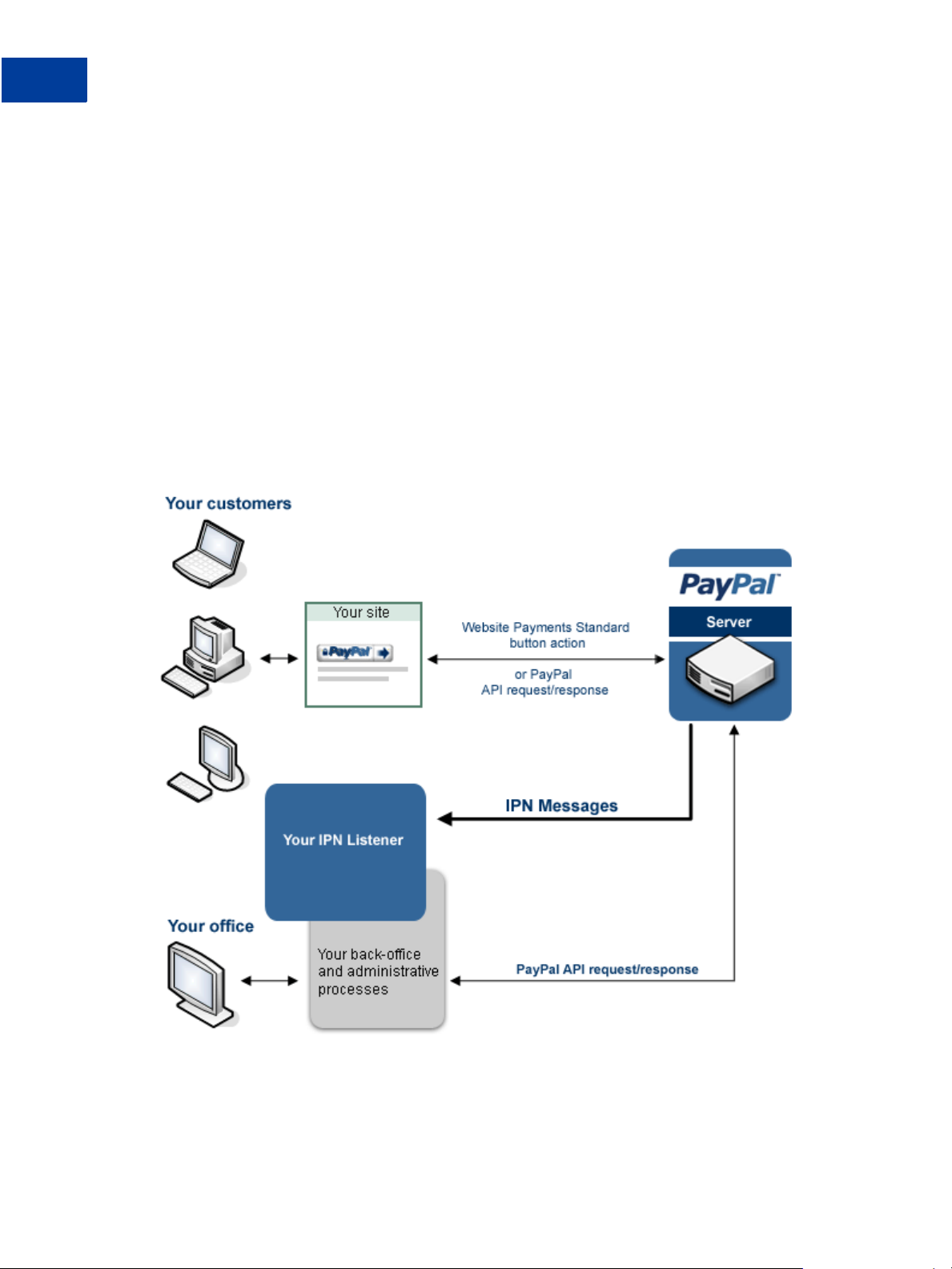
to automate your response to events. The following diagram shows how events can occur and
how PayPal responds with IPN messages that it sends to your listener:
The diagram shows requests and responses, which are the result of processing button clicks or
API operations on PayPal. PayPal sends an IPN message when it sends a response to a request.
8 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 9

Introducing IPN
IPN Protocol and Architecture
The IPN message is not actually part of the response sent to your website. Rather, the IPN
message is sent to the your listener, which allows you to take actions that are not directly tied
to the operation of your website.
NOTE: The diagram does not show the IPN authentication protocol messages that validate the
IPN message.
IPN is an asynchronous message service, meaning that messages are not synchronized with
actions on your website. Thus, listening for an IPN message does not increase the time it takes
to complete a transaction on your website.
The IPN message service does not assume that all messages will be received by your listener
in a timely manner. Because the internet is not 100% reliable, messages can become lost or
delayed. To handle the possibility of transmission and receipt delays or failures, the IPN
message service implements a retry mechanism that resends messages at various intervals
until you acknowledge that the message has successfully been received. Messages may be
resent for up to four days after the original message.
NOTE: Unless you are certain that a failure occurred on the the Internet, the most likely cause
of lost, delayed, or duplicate IPN messages is faulty logic in the listener itself.
Because messages can be delivered at any time, your listener must always be available to
receive and process messages; however, the retry mechanism also handles the possibility that
your listener could become swamped or stop responding.
The IPN message service should not be considered a real-time service. Your checkout flow
should not wait on an IPN message before it is allowed to complete. If your website waits for
an IPN message, checkout processing may be delayed due to system load and become more
complicated because of the possibility of retries.
IPN Protocol and Architecture
IPN is designed to be secure, reliable, and asynchronous. To meet these requirements, the
protocol requires you to acknowledge receipt of IPN messages. The IPN service provides a
retry mechanism to handle cases in which a message is not acknowledged; for example, when
a transmission or receipt failure occurs.
When you enable IPN, PayPal sends messages to the IPN listener at the URL you specify in
your account’s profile. You can override the URL to associate other IPN listeners with specific
transactions. In this case, you specify the listener’s URL when you set up a Website Payment
Standard button or a PayPal API operation.
The IPN protocol consists of three steps:
1. PayPal sends your IPN listener a message that notifies you of the event
2. Your listener sends the complete unaltered message back to PayPal; the message must
contain the same fields in the same order and be encoded in the same way as the original
message
IPN Guide June, 2009 9
Page 10

Introducing IPN
IPN Protocol and Architecture
3. PayPal sends a single word back, which is either VERIFIED if the message originated with
PayPal or INVALID if there is any discrepancy with what was originally sent
Your listener must respond to each message, whether or not you intend to do anything with it.
If you do not respond, PayPal assumes that the message was not received and resends the
message. PayPal continues to resend the message periodically until your listener sends the
correct message back, although the interval between resent messages increases each time. The
message can be resent for up to four days.
This resend algorithm can lead to situations in which PayPal resends the IPN message while
you are sending back the original message. In this case, you should send your response again,
to cover the possibility that PayPal did not actually receive your response the first time. You
should also ensure that you do not process the transaction associated with the message twice.
IMPORTANT: PayPal expects to receive a response to an IPN message within 30 seconds.
After PayPal verifies the message, there are additional checks that your listener or back-end or
administrative software must take:
Your listener should not perform time-consuming operations, such as creating
a process, before responding to the IPN message.
z Verify that you are the intended recipient of the IPN message by checking the email address
in the message; this handles a situation where another merchant could accidentally or
intentionally attempt to use your listener.
z Avoid duplicate IPN messages. Check that you have not already processed the transaction
identified by the transaction ID returned in the IPN message. You may need to store
transaction IDs returned by IPN messages in a file or database so that you can check for
duplicates. If the transaction ID sent by PayPal is a duplicate, you should not process it
again.
z Because IPN messages can be sent at various stages in a transaction’s progress, make sure
that the transaction’s payment status is “completed” before enabling shipment of
merchandise or allowing the download of digital media.
z Verify that the payment amount actually matches what you intend to charge. Although not
technically an IPN issue, if you do not encrypt buttons, it is possible for someone to capture
the original transmission and change the price. Without this check, you could accept a
lesser payment than what you expected.
IPN Messages Generated by Website Payments Standard
PayPal generates an IPN message when your customer clicks a Website Payments Standard
payment button, such as a Buy Now button, and completes the transaction on PayPal. You can
use this notification to kick-off order fulfillment, enable digital media downloads, store
information in a customer relationship management (CRM) or accounting system, and so on.
The following diagram shows both the web flow and the IPN message authentication protocol:
10 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 11
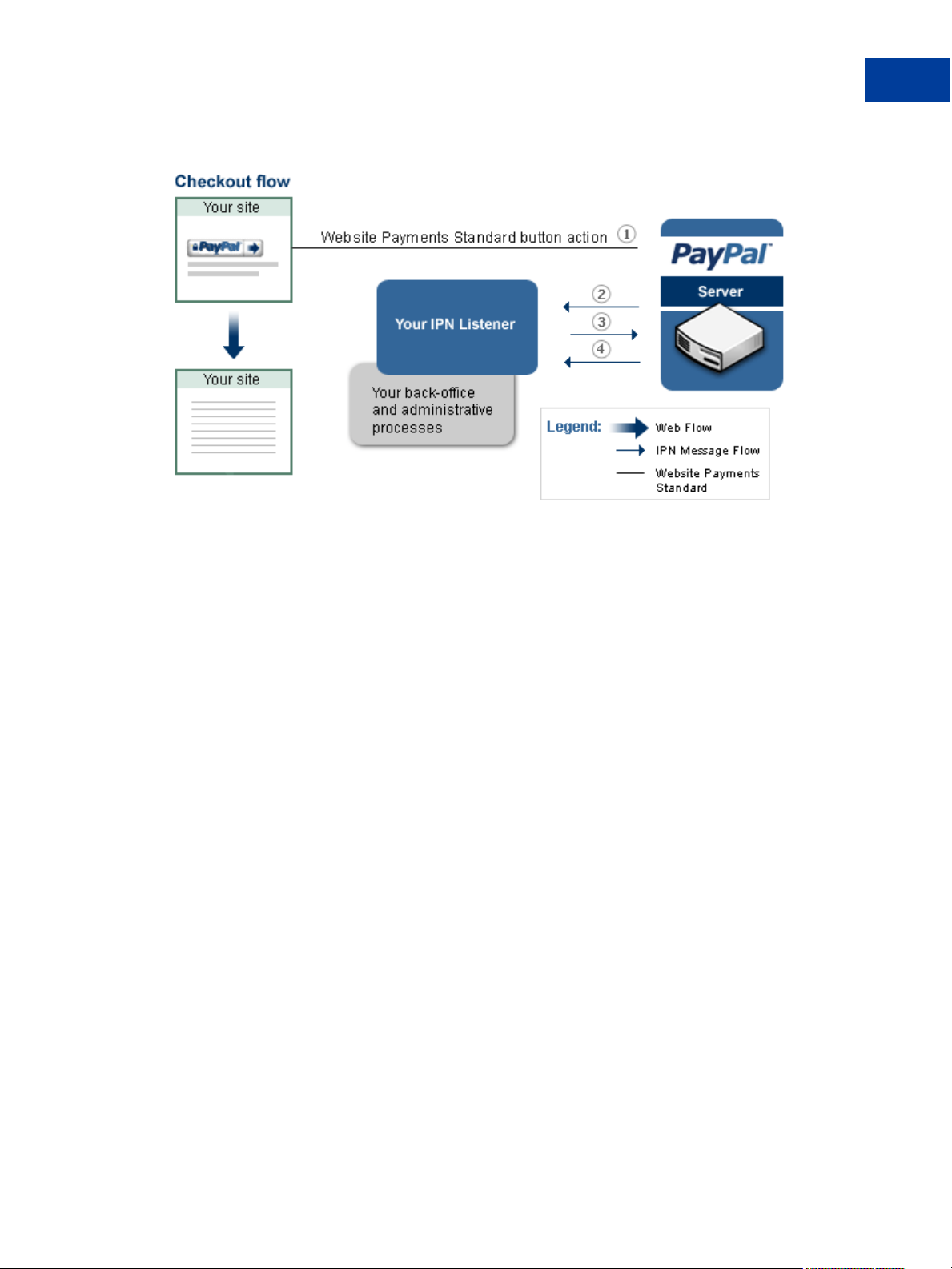
The numbers in diagram correspond to the following steps:
Introducing IPN
IPN Protocol and Architecture
1. The button action initiates a payment that completes on PayPal
2. PayPal sends your IPN listener a message that notifies you of the event
3. Your listener sends the complete unaltered message back to PayPal; the message must
contain the same fields in the same order and be encoded in the same way as the original
message
4. PayPal sends a single word back, which is either VERIFIED if the message originated with
PayPal or INVALID if there is any discrepancy with what was originally sent
Your IPN listener must implement the IPN authentication protocol (steps 2, 3, and 4 in this
diagram). After successfully completing the protocol, your back-office or administrative
process vets the contents of the message and responds appropriately. For example, if the
payment status for the transaction is “Completed,” your system can print a packing list or
email a password to your customer for downloading digital media.
IPN Messages Generated by PayPal APIs
PayPal generates an IPN message when you invoke an API operation, such as
DoExpressCheckoutPayment of DoDirectPayment during checkout. You can use this
notification to kick-off order fulfillment, enable digital media downloads, store information in
a customer relationship management (CRM) or accounting system, and so on.
The following diagram shows both the web flow and the IPN message authentication protocol:
IPN Guide June, 2009 11
Page 12

Introducing IPN
IPN Protocol and Architecture
The numbers in diagram correspond to the following steps:
1. The API operation initiates a payment on PayPal.
2. PayPal sends your IPN listener a message that notifies you of the event
3. Your listener sends the complete unaltered message back to PayPal; the message must
contain the same fields in the same order and be encoded in the same way as the original
message
4. PayPal sends a single word back, which is either VERIFIED if the message originated with
PayPal or INVALID if there is any discrepancy with what was originally sent
Your IPN listener must implement the IPN authentication protocol (steps 2, 3, and 4 in this
diagram). After successfully completing the protocol, your back-office or administrative
process vets the contents of the message and responds appropriately. For example, if the
payment status for the transaction is “Completed,” your system can print a packing list or
email a password to your customer for downloading digital media.
IPN Messages Generated by a Back-Office Procedure
PayPal generates an IPN message when you perform actions that invoke the PayPal API,
regardless of whether it is from your website or from a back-office or administrative
procedure. You can use this notification to trigger an email to your customer, store information
in a CRM or accounting system, and so on.
The following diagram shows both an administrative web flow and the IPN message
authentication protocol:
12 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 13

The numbers in diagram correspond to the following steps:
Introducing IPN
IPN Protocol and Architecture
1. Your back-office or administrative process invokes a PayPal API operation; for example, it
could invoke the RefundTransaction API operation when your employee issues a
refund.
2. PayPal sends your IPN listener a message that notifies you of the event
3. Your listener sends the complete unaltered message back to PayPal; the message must
contain the same fields in the same order and be encoded in the same way as the original
message
4. PayPal sends a single word back, which is either VERIFIED if the message originated with
PayPal or INVALID if there is any discrepancy with what was originally sent
Your IPN listener implements the IPN authentication protocol (steps 2, 3, and 4 in this
diagram). After successfully completing the protocol, your listener or back-office or
administrative process vets the contents of the message and responds appropriately. For
example, your system can notify the customer of the refund by email.
IPN Messages Generated by PayPal
Some IPN messages generated by PayPal are not directly associated with a web flow. PayPal
generates an IPN message when external events arise that might affect a transaction, such as
disputes, chargebacks, echeck clearing, and various recurring payment and subscription
events.
In this case, events that trigger IPN messages are not directly related to actions on your
website. The following diagram shows the steps your listener must take:
IPN Guide June, 2009 13
Page 14
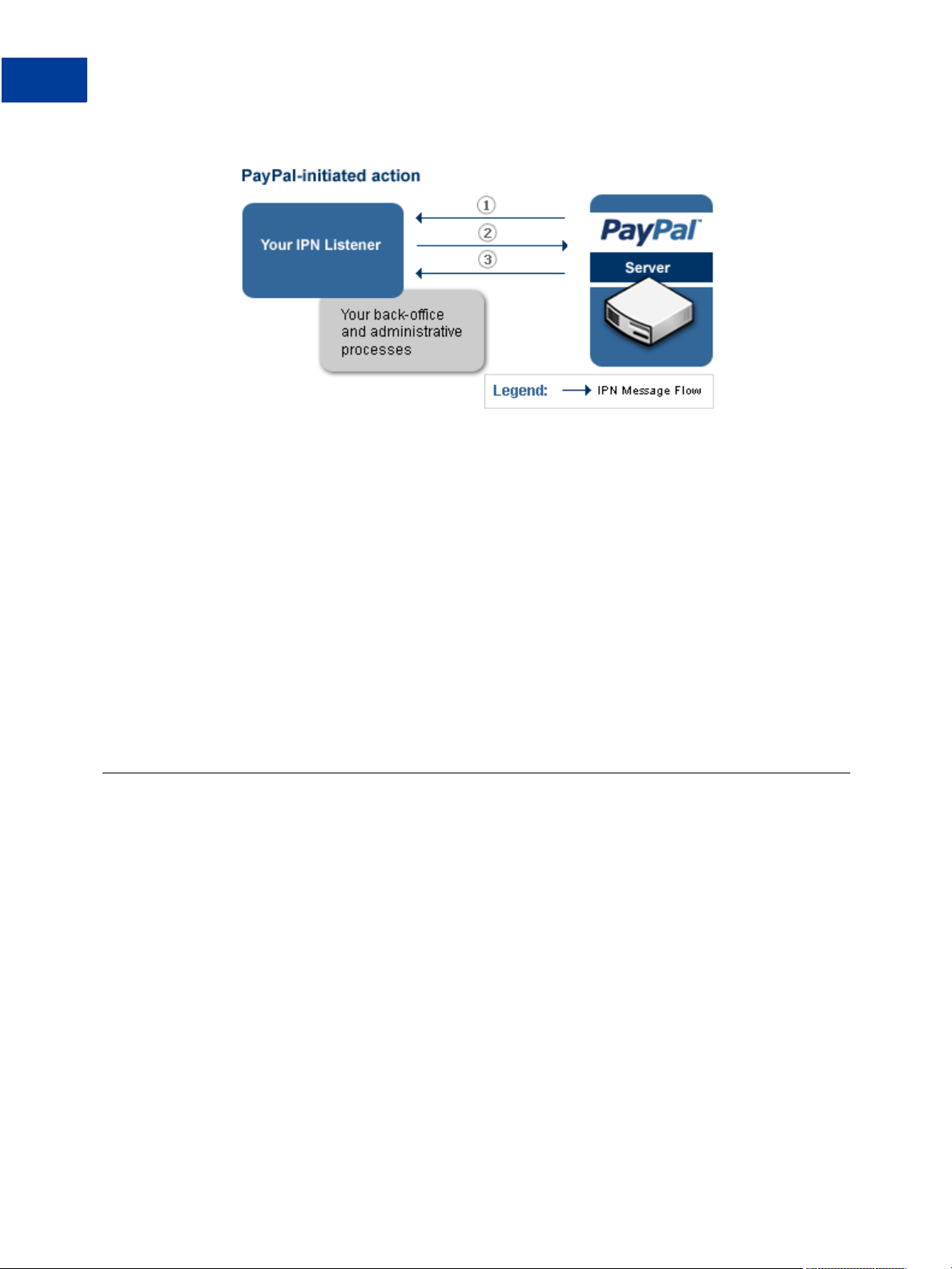
Introducing IPN
A Sample IPN Message and Response
The numbers in diagram correspond to the following steps, which implement the IPN message
authentication protocol:
1. PayPal sends your IPN listener a message that notifies you of the event
2. Your listener sends the complete unaltered message back to PayPal; the message must
contain the same fields in the same order and be encoded in the same way as the original
message
3. PayPal sends a single word back, which is either VERIFIED if the message originated with
PayPal or INVALID if there is any discrepancy with what was originally sent
After successfully completing the protocol, your back-office or administrative process vets the
contents of the message and responds appropriately. For example, the IPN messages may
trigger you to print shipping labels for items whose payments have cleared, investigate
disputes and chargebacks, store information in an accounting system, and so on.
A Sample IPN Message and Response
An IPN message consists of variables that describe the transaction. These variables contain
information about you, your customer, and the details of the transaction itself.
PayPal sends a message, similar to the following one, for a $19.95 purchase made by Express
Checkout:
14 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 15

Introducing IPN
A Sample IPN Message and Response
mc_gross=19.95&protection_eligibility=Eligible&address_status=confirmed&pay
er_id=LPLWNMTBWMFAY&tax=0.00&address_street=1+Main+St&payment_date=20%3A12%
3A59+Jan+13%2C+2009+PST&payment_status=Completed&charset=windows1252&address_zip=95131&first_name=Test&mc_fee=0.88&address_country_code=US&
address_name=Test+User¬ify_version=2.6&custom=&payer_status=verified&add
ress_country=United+States&address_city=San+Jose&quantity=1&verify_sign=Atk
OfCXbDm2hu0ZELryHFjY-Vb7PAUvS6nMXgysbElEn9v1XcmSoGtf&payer_email=gpmac_1231902590_per%40paypal.com&txn_id=61E67681CH32
38416&payment_type=instant&last_name=User&address_state=CA&receiver_email=g
pmac_1231902686_biz%40paypal.com&payment_fee=0.88&receiver_id=S8XGHLYDW9T3S
&txn_type=express_checkout&item_name=&mc_currency=USD&item_number=&residenc
e_country=US&test_ipn=1&handling_amount=0.00&transaction_subject=&payment_g
ross=19.95&shipping=0.00
Variabl e Notes
Information about you:
receiver_email = gm_1231902686_biz@paypal.com Check email address to make sure that this is not a spoof
receiver_id = S8XGHLYDW9T3S
residence_country = US
Information about the transaction:
test_ipn = 1 Testing with the Sandbox
transaction_subject =
txn_id = 61E67681CH3238416 Keep this ID to avoid processing the transaction twice
txn_type = express_checkout Type of transaction
Information about your buyer:
payer_email = gm_1231902590_per@paypal.com
payer_id = LPLWNMTBWMFAY
payer_status = verified
first_name = Test
last_name = User
address_city = San Jose
address_country = United States
address_country_code = US
address_name = Test User
address_state = CA
address_status = confirmed
IPN Guide June, 2009 15
Page 16

Introducing IPN
A Sample IPN Message and Response
Variabl e Notes
address_street = 1 Main St
address_zip = 95131
Information about the payment:
custom = Your custom field
handling_amount = 0.00
item_name =
item_number =
mc_currency = USD
mc_fee = 0.88
mc_gross = 19.95
payment_date = 20:12:59 Jan 13, 2009 PST
payment_fee = 0.88
payment_gross = 19.95
payment_status = Completed Status, which determines whether the transaction is
complete
payment_type = instant Kind of payment
protection_eligibility = Eligible
quantity = 1
shipping = 0.00
tax = 0.00
Other information about the transaction:
notify_version = 2.6 IPN version; can be ignored
charset = windows-1252
verify_sign = AtkOfCXbDm2hu0ZELryHFjYVb7PAUvS6nMXgysbElEn9v-1XcmSoGtf
Before you can trust the contents of the message, you must first verify that the message came
from PayPal. To verify the message, you must send back the contents in the exact order they
were received and precede it with the command _notify-validate, as follows:
https://www.sandbox.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_notifyvalidate&mc_gross=19.95&protection_eligibility=Eligible&address_status=conf
irmed&payer_id=LPLWNMTBWMFAY&tax=0.00&...&payment_gross=19.95&shipping=0.00
16 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 17

PayPal will then send one single-word message, VERIFIED, if the message is valid; otherwise,
it will send another single-word message, INVALID.
IMPORTANT: After you receive the VERIFIED message, there are several important checks
you must perform before you can assume that the message is legitimate and
not already processed:
Confirm that the payment status is Completed.
Use the transaction ID to verify that the transaction has not already been
processed, which prevents duplicate transactions from being processed.
Validate that the receiver’s email address is registered to you.
Verify that the price, item description, and so on, match the transaction on
your website.
Non-IPN Notification Mechanisms
You can use IPN with other notification mechanisms. For example, you can use PDT or the
API to determine real-time information about a transaction and let IPN notify you of any
changes after the transaction occurs.
Introducing IPN
Non-IPN Notification Mechanisms
If you are using Website Payments Standard, you can use PDT to obtain information about the
transaction. If you are using Express Checkout or Direct Payment, the PayPal API notifies you
of the status and details of the transaction immediately and automatically. In either case, you
can immediately display to your customer the information being returned from PayPal. You
should not use IPN for this purpose.
IPN Guide June, 2009 17
Page 18

Introducing IPN
Non-IPN Notification Mechanisms
18 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 19

2
Implementing an IPN Listener
You write your IPN listener in the scripting or programming language of your choice and host
it on your web server. You can use sample code provided by PayPal as a starting point.
The PayPal SDKs for Website Payments Standard contain sample code in various
programming languages that you can modify to create your own listener. As a good
programming practice, as well as to keep things simple, your IPN listener should listen for a
post from PayPal and dispatch it immediately to another routine or process that handles the
business logic associated with the message. If your listener is structured in this way, it will be
a simple and tight loop that listens for a message and dispatches it for processing by your
application logic.
Your listener software must
1. Wait for an HTTP post from PayPal.
2. Create a request that contains exactly the same IPN variables and values in the same order,
preceded with cmd=_notify-validate.
3. Post the request to paypal.com or sandbox.paypal.com, depending on whether you
are going live or testing your listener in the Sandbox.
4. Wait for a response from PayPal, which is either VERIFIED or INVALID.
5. If the response is VERIFIED, perform the following checks:
– Confirm that the payment status is Completed.
PayPal sends IPN messages for pending and denied payments as well; do not ship until
the payment has cleared.
– Use the transaction ID to verify that the transaction has not already been processed,
which prevents duplicate transactions from being processed.
Typically, you store transaction IDs in a database so that you know you are only
processing unique transactions.
– Validate that the receiver’s email address is registered to you.
This check provides additional protection against fraud.
– Verify that the price, item description, and so on, match the transaction on your website.
This check provides additional protection against fraud.
IPN Guide June, 2009 19
Page 20

Implementing an IPN Listener
6. If the verified response passes the checks, take action based on the value of the txn_type
variable if it exists; otherwise, take action based on the value of the reason_code
variable.
7. If the response is INVALID, save the message for further investigation.
A sample test listener using PHP
The following listener sends email to the address specified in the ipn_email variable, as in
https://
listener as a starting point for your own listener; rather than send email, your listener could
take action based on the type of transaction.
your_host/live_ipn_mail.php?ipn_email=email_address. You can use this
20 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 21

Implementing an IPN Listener
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL ^ E_NOTICE);
$email = $_GET['ipn_email'];
$header = "";
$emailtext = "";
// Read the post from PayPal and add 'cmd'
$req = 'cmd=_notify-validate';
if(function_exists('get_magic_quotes_gpc'))
{ $get_magic_quotes_exits = true;}
foreach ($_POST as $key => $value)
// Handle escape characters, which depends on setting of magic quotes
{ if($get_magic_quotes_exists == true && get_magic_quotes_gpc() == 1)
{ $value = urlencode(stripslashes($value));
} else {
$value = urlencode($value);
}
$req .= "&$key=$value";
}
// Post back to PayPal to validate
$header .= "POST /cgi-bin/webscr HTTP/1.0\r\n";
$header .= "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded\r\n";
$header .= "Content-Length: " . strlen($req) . "\r\n\r\n";
$fp = fsockopen ('www.paypal.com', 80, $errno, $errstr, 30);
// Process validation from PayPal
if (!$fp) { // HTTP ERROR
} else {
// NO HTTP ERROR
fputs ($fp, $header . $req);
while (!feof($fp)) {
$res = fgets ($fp, 1024);
if (strcmp ($res, "VERIFIED") == 0) {
// TODO:
// Check the payment_status is Completed
// Check that txn_id has not been previously processed
// Check that receiver_email is your Primary PayPal email
// Check that payment_amount/payment_currency are correct
// Process payment
// If 'VERIFIED', send an email of IPN variables and values to the
// specified email address
foreach ($_POST as $key => $value){
$emailtext .= $key . " = " .$value ."\n\n";
}
mail($email, "Live-VERIFIED IPN", $emailtext . "\n\n" . $req);
} else if (strcmp ($res, "INVALID") == 0) {
// If 'INVALID', send an email. TODO: Log for manual investigation.
foreach ($_POST as $key => $value){
$emailtext .= $key . " = " .$value ."\n\n";
IPN Guide June, 2009 21
Page 22

Implementing an IPN Listener
}
mail($email, "Live-INVALID IPN", $emailtext . "\n\n" . $req);
}
}
fclose ($fp);
?>
22 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 23

Identifying Your IPN Listener to
3
PayPal
After you implement and test your IPN listener, you make your listener known to PayPal by
specifying the listener’s URL in your account’s profile. Optionally, you can override the URL
to specify another listener for specific payments.
z Setting Up IPN Notifications on PayPal
z Dynamically Setting the Notification URL
Setting Up IPN Notifications on PayPal
After you implement and test your IPN listener, you identify the listener to PayPal by selecting
Instant Payment Notification Preferences from your account’s profile. You then specify
your listener’s URL and click the box to activate it.
Your listener must be located at the URL that you specify in the profile. Before you activate
your listener on PayPal, you should test the listener using the IPN simulator in the Sandbox.
The steps to set up your listener for Sandbox testing and to set up your listener for live
operation on PayPal are the same. The only difference is that you log into the Sandbox to set
up your listener for Sandbox testing and you log into PayPal to set up your listener for live
operation.
NOTE: Sandbox testing goes beyond simply using the IPN simulator. The IPN simulator only
sends IPN messages to a listener; it does not perform the complete operation; for
example, it does not complete a transaction. Sandbox testing involves performing the
same actions in the Sandbox as you expect to be performed when the listener goes
live.
After you log in, follow these instructions to set up your listener:
1. Click Profile on the My Account tab.
2. Click Instant Payment Notification Preferences in the Selling Preferences column.
3. Click Edit IPN Settings to specify your listener’s URL and activate the listener.
The following screen appears:
IPN Guide June, 2009 23
Page 24

Identifying Your IPN Listener to PayPal
Setting Up IPN Notifications on PayPal
4. Specify the URL for your listener in the Notification URL field.
5. Click Receive IPN messages (Enabled) to enable your listener.
6. Click Save.
The following screen appears:
7. Click Back to Profile Summary to return to the Profile after activating your listener.
You also can click Edit settings to modify your notification URL or disable your listener.
You can click Turn Off IPN to reset your IPN preferences.
24 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 25

Identifying Your IPN Listener to PayPal
Dynamically Setting the Notification URL
Dynamically Setting the Notification URL
You can specify an IPN listener for a specific payment. In this case, PayPal sends the IPN
message to the listener specified in the notification URL for a specific button or API operation
instead of the listener specified in your Profile.
To specify a notification URL
For a/an ... specify your IPN Listener’s URL in the ...
Website Payments Standard button notify_url HTML form variable
NVP API operation NOTIFYURL field of the DoDirectPayment,
DoExpressCheckoutPayment, or DoReferenceTransaction request
SOAP API operation NotifyURL field of the DoDirectPayment,
DoExpressCheckoutPayment, or DoReferenceTransaction request
NOTE: The IPN message will always be sent to your notification URL unless receiving IPNs
have been disabled. Even though you have not enabled receiving IPN messages in
your Profile or you have reset your preference by turning off IPN messages, PayPal
still sends IPN messages to the notification URL you specify for a specific payment.
IPN messages not sent because you disabled the preference in your Profile will appear
in the IPN history when you enable receiving IPNs. After they appear in the history,
you can choose whether or not to resend them.
IPN Guide June, 2009 25
Page 26

Identifying Your IPN Listener to PayPal
Dynamically Setting the Notification URL
26 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 27

IPN Testing
4
After you implement your listener and start it running on your web server, you can use the IPN
simulator in the Sandbox to send IPN messages to the URL at which your listener is running.
This tool allows you to verify that you are receiving IPN messages correctly.
z Testing Your Listener
z IPN Troubleshooting Tips
Testing Your Listener
The first level of testing is to ensure that your IPN listener receives messages and handles
them appropriately. This level of testing requires you to have your IPN listener running at your
notification URL; however, it does not require you to set up the listener in the Profile.
You must be logged into the Sandbox to use the IPN simulator. To set up and send an IPN
message using the simulator:
1. Select Instant Payment Notification (IPN) simulator from Tes t Too ls .
2. Enter the URL to receive the notification and the kind of notification you want to test on
the following screen:
When you select the kind of transaction that you want to test, a form containing test data
appears:
IPN Guide June, 2009 27
Page 28

IPN Testing
Testing Your Listener
3. Keep or modify the values of fields that you want to include in the IPN.
By default, only populated fields are displayed. You can check the Show all fields box to
view all fields. The simulator does not check the validity of fields that you change.
28 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 29

4. Click Send IPN.
The IPN message is sent to the specified URL and the results of the operation are displayed
at the top of the page.
After Completing This Task:
If your IPN listener receives a message, you know that it is properly installed on your web
server. The default messages sent by the IPN simulator are valid, thus, if your listener responds
correctly to the message, it should receive a VERIFIED message. If you do not receive any
message or if you receive an INVALID message after responding to the original message from
PayPal, you will need to troubleshoot your listener.
IPN Troubleshooting Tips
IPN failures fall into three categories: not receiving any IPN messages from PayPal, receiving
some but not all IPN messages, and receiving INVALID messages from PayPal after
responding to a message.
IPN Testing
IPN Troubleshooting Tips
If you do not receive any IPN messages from PayPal
z Check the IPN History page on PayPal. It tells you whether PayPal sent the IPN message
and whether your listener responded to it. It may also provide information about the status
of the server on which your listener is running. If necessary, from this page you can also
request that PayPal resend the IPN message.
z Check that the path to your IPN listener is correct and you are using that path correctly in
your IPN notification URL; for example, the file path is often similar to, but not the same
as, the URL.
z Verify that your firewall settings are not blocking HTTP POST messages from PayPal.
z If the logs for your web server are available, check the logs to confirm that messages are
being sent to your web server and check for any errors that may have occurred.
If you receive some messages but not others
z Verify that your IPN listener is responding to all messages, even those you do not intend to
process.
z Check that the account is valid and confirmed; for example, if you send money to an
unconfimred account, PayPal does not send an IPN message.
If you receive an INVALID message
z Check that your are posting your response to the correct URL, which is
https://www.sandbox.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr or
https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr, depending on whether you are testing
in the Sandbox or you are live, respectively.
z Verify that your response contains exactly the same IPN variables and values in the same
order, preceded with cmd=_notify-validate.
IPN Guide June, 2009 29
Page 30

IPN Testing
IPN Troubleshooting Tips
z Ensure that you are encoding your response string and are using the same character
encoding as the original message.
NOTE: If you receive multiple IPN messages for the same transaction or if messages appear
to be out of order, this is not necessarily an indication that your listener is
malfunctioning. For example, if you do not respond in time, PayPal resends the
message. You should investigate these situations; however, because they could be
caused by a logic errors or performance problems as well.
30 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 31

IPN Operations on PayPal
5
The IPN History page on PayPal provides additional information to help you troubleshoot IPN
messages. You can use the IPN History page to determine the status of IPN messages and to
resend them, if necessary.
z Using the IPN History
z Resending IPN Messages
Using the IPN History
Use the IPN History page on PayPal to view IPN messages sent to you from PayPal and
request that messages be resent. You can select the IPN messages to review by date range, by
delivery status, and by PayPal transaction
The search results contain the following information:
z The date and time that PayPal created the IPN message
IPN Guide June, 2009 31
Page 32

IPN Operations on PayPal
Using the IPN History
z Whether this IPN message was the original message or whether it was resent, which is
indicated by the asterisk (*) in the Date/time created column
z The IPN message ID assigned by PayPal
z The current status, which is one of the following values:
– Sent indicates that PayPal sent the message to your IPN listener
– Failed indicates that PayPal did not receive an acknowledgement to the message
– Queued indicates that PayPal is ready to send the message
– Retrying indicates that message was resent between 1 and 15 times and PayPal
continues to be resend the message
– Disabled indicates that the message will not be resent because the merchant’s account
has been disabled
NOTE: If you have requested that PayPal resend the IPN message and the status has not
been updated for the attempt, resending is appended to the status, e.g. Failed
- resending.
z Your server’s response to the HTTP POST that delivered the IPN message to your listener.
For more information about these codes, see
HTTP/1.1.
RFC 2616: Hypertext Transfer Protocol --
z If the message is related to a PayPal transaction, the ID of the PayPal transaction associated
with the message; you can
To see more information about an IPN message, click on the message ID. The IPN details page
appears:
32 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 33

IPN Operations on PayPal
Resending IPN Messages
In addition to the information on the IPN History page, the details contain the following
information:
z Whether this IPN message was the original message or whether it was resent
z The last time the message was resent
z The URL on which your listener is running
NOTE: You cannot change the URL; if you request PayPal to resend an IPN message, it is
sent to this URL.
z The number of retries before the message was successfully acknowledged
z The type of IPN message
Resending IPN Messages
You can use the IPN History page to request that PayPal resend one or more IPN messages.
You can search the IPN message history for the messages that may need to be resent and then
select them.
IPN Guide June, 2009 33
Page 34

IPN Operations on PayPal
Resending IPN Messages
To make a request that PayPal resend IPN messages, mark one or more messages for PayPal to
resend and click the Resend selected button to make the request:
After you make the request, PayPal notifies you that the messages have been resent and
updates the status. The status indicates that PayPal is resending the message until it actually
has been resent:
34 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 35

IPN Operations on PayPal
Resending IPN Messages
When the message has been sent, your server’s response to the HTTP POST is used to update
the HTTP response code field. A value of 200 indicates that your server successfully received
the IPN message. Other values typically indicate a server configuration error for the server that
hosts your IPN listener. For more information about these codes, see
Transfer Protocol -- HTTP/1.1. If you do not see a response code, you should check that your
RFC 2616: Hypertext
sever is running.
IPN Guide June, 2009 35
Page 36

IPN Operations on PayPal
Resending IPN Messages
36 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 37

6
Using Fraud Management Filters With IPN
Fraud Management Filter actions are reported in IPN payment messages only when a filter
causes the payment to be pended awaiting your review or a when you accept or deny a filterpended payment. Filter actions are not reported when filters flag payments for review, allow
payments to be accepted, or cause them to be denied.
When a payment occurs, an IPN message shows the transaction’s payment status as
Completed, regardless of whether a Fraud Management Filter was activated or not. There is
no special notification for transactions that are flagged by a Fraud Management Filter. If a
Fraud Management Filter is set to Deny, PayPal does not send an IPN message when the filter
actually causes the payment to be denied.
When a transaction is pended, however, PayPal sends an IPN message containing one or more
fraud_management_pending_filters_
the payment to be pended, where n=1 specifies the first filter, and so on. In addition, the
payment_status variable is set to Pending. The following example shows an IPN message
in which two filters cause the transaction to be pended:
n variables, which identify the filters that caused
IPN Guide June, 2009 37
Page 38

Using Fraud Management Filters With IPN
txn_type = virtual_terminal
payment_date = 17:11:42 Jul 15, 2008 PDT
last_name =
receipt_id = 3075-7371-4622-1677
residence_country = US
pending_reason = address
item_name =
payment_gross = 3.33
mc_currency = USD
business = acqrte_1215804264_biz@gmail.com
payment_type = instant
verify_sign = APYUGJhXGkUmvFnZf4I5co6CedKKAowZjfT4T7GXWJMDnZ0uFLkcq.oH
payer_status = unverified
test_ipn = 1
fraud_management_pending_filters_1 = Maximum Transaction Amount
tax = 0.00
txn_id = 5XN64179EB804362B
fraud_management_pending_filters_2 = Unconfirmed Address
quantity = 1
first_name =
receiver_email = acqrte_1215804264_biz@gmail.com
payer_id = PUWAJRBB8NM74
receiver_id = 2RXLTRMGT3M2G
item_number =
payment_status = Pending
shipping = 0.00
mc_gross = 3.33
custom =
charset = windows-1252
notify_version = 2.4
NOTE: If the transaction is for an authorization or an order, the auth_status variable may
also be set to Pending.
If a transaction has been pended, PayPal sends an IPN message when the payment has been
accepted or denied. The following example shows an IPN message indicating that a pended
transaction has been accepted:
38 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 39

Using Fraud Management Filters With IPN
txn_type = virtual_terminal
payment_date = 17:11:42 Jul 15, 2008 PDT
last_name =
receipt_id = 3075-7371-4622-1677
residence_country = US
item_name =
payment_gross = 3.33
mc_currency = USD
business = acqrte_1215804264_biz@gmail.com
payment_type = instant
verify_sign = AFcWxV21C7fd0v3bYYYRCpSSRl31AjcbYkD.VCCBmpD4lZq.yYTxBKkr
payer_status = unverified
test_ipn = 1
fraud_management_pending_filters_1 = Maximum Transaction Amount
tax = 0.00
txn_id = 5XN64179EB804362B
fraud_management_pending_filters_2 = Unconfirmed Address
quantity = 1
receiver_email = acqrte_1215804264_biz@gmail.com
first_name =
payer_id = PUWAJRBB8NM74
receiver_id = 2RXLTRMGT3M2G
item_number =
payment_status = Completed
payment_fee = 0.45
mc_fee = 0.45
shipping = 0.00
mc_gross = 3.33
custom =
charset = windows-1252
notify_version = 2.4
The following example shows an IPN message indicating that a pended transaction has been
denied:
IPN Guide June, 2009 39
Page 40

Using Fraud Management Filters With IPN
txn_type = virtual_terminal
payment_date = 17:09:40 Jul 15, 2008 PDT
last_name =
receipt_id = 0739-3836-3393-2098
residence_country = US
item_name =
payment_gross = 2.11
mc_currency = USD
business = acqrte_1215804264_biz@gmail.com
payment_type = instant
verify_sign = AFcWxV21C7fd0v3bYYYRCpSSRl31ASrKFBPwac7aQm47p8CMLrdParSt
payer_status = unverified
test_ipn = 1
fraud_management_pending_filters_1 = Maximum Transaction Amount
tax = 0.00
txn_id = 53R82724RM1848354
fraud_management_pending_filters_2 = Unconfirmed Address
quantity = 1
first_name =
receiver_email = acqrte_1215804264_biz@gmail.com
payer_id = PUWAJRBB8NM74
receiver_id = 2RXLTRMGT3M2G
item_number =
payment_status = Denied
shipping = 0.00
mc_gross = 2.11
custom =
charset = windows-1252
notify_version = 2.4
40 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 41

7
IPN Variable Reference
PayPal returns related variables for each kind of IPN message. Not all variables are returned
for each type of transaction.
z IPN Transaction Types
z Transaction and Notification-Related Variables
z Buyer Information Variables
z Payment Information Variables
z Auction Variables
z Mass Pay Variables
z Recurring Payments Variables
z Subscription Variables
z Dispute Resolution Variables
IPN Transaction Types
Typically, your back-end or administrative processes will perform specific actions based on
the kind of IPN message received. You can use the txn_type variable in the message to
trigger the kind of processing you want to perform.
Transaction Type
(txn_type) Description
— Credit card chargeback if the case_type variable contains chargeback
adjustment A dispute has been resolved and closed
cart Payment received for multiple items; source is Express Checkout or the PayPal
Shopping Cart.
express_checkout Payment received for a single item; source is Express Checkout
masspay Payment sent using MassPay
merch_pmt Monthly subscription paid for Website Payments Pro
new_case A new dispute was filed
recurring_payment Recurring payment received
recurring_payment
_profile_created
Recurring payment profile created
IPN Guide June, 2009 41
Page 42

IPN Variable Reference
Transaction and Notification-Related Variables
Transaction Type
(txn_type) Description
send_money Payment received; source is the Send Money tab on the PayPal website
subscr_cancel Subscription canceled
subscr_eot Subscription expired
subscr_failed Subscription signup failed
subscr_modify Subscription modified
subscr_payment Subscription payment received
subscr_signup Subscription started
virtual_terminal Payment received; source is Virtual Terminal
web_accept Payment received; source is a Buy Now, Donation, or Auction Smart Logos button
Transaction and Notification-Related Variables
Transaction and notification-related variables identify the merchant that is receiving a
payment or other notification and transaction-specific information.
Variable Name Description
business Email address or account ID of the payment recipient (that is, the
merchant). Equivalent to the values of receiver_email (if payment is
sent to primary account) and business set in the Website Payment
HTML.
NOTE: The value of this variable is normalized to lowercase characters.
Length: 127 characters
charset Character set
custom Custom value as passed by you, the merchant. These are pass-through
variables that are never presented to your customer
Length: 255 characters
notify_version Message’s version number
parent_txn_id In the case of a refund, reversal, or canceled reversal, this variable
contains the txn_id of the original transaction, while txn_id contains a
new ID for the new transaction.
Length: 19 characters
42 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 43

IPN Variable Reference
Buyer Information Variables
Variable Name Description
receiver_email Primary email address of the payment recipient (that is, the merchant). If
the payment is sent to a non-primary email address on your PayPal
account, the receiver_email is still your primary email.
NOTE: The value of this variable is normalized to lowercase characters.
Length: 127 characters
receiver_id Unique account ID of the payment recipient (i.e., the merchant). This is
the same as the recipient's referral ID.
Length: 13 characters
resend Whether this IPN message was resent (equals true); otherwise, this is the
original message.
residence_country ISO 3166 country code associated with the country of residence
Length: 2 characters
test_ipn Whether the message is a test message. It is one of the following values:
z 1 – the message is directed to the Sandbox
txn_id The merchant’s original transaction identification number for the payment
from the buyer, against which the case was registered.
txn_type The kind of transaction for which the IPN message was sent.
verify_sign Encrypted string used to validate the authenticity of the transaction
Buyer Information Variables
Buyer information identifies the buyer or initiator of a transaction by payer ID or email
address. Additional contact or shipping information may be provided.
Variable Name Description
address_country Country of customer’s address
Length: 64 characters
address_city City of customer’s address
Length: 40 characters
address_country_code ISO 3166 country code associated with customer’s address
Length: 2 characters
address_name Name used with address (included when the customer provides a Gift
Address)
Length: 128 characters
address_state State of customer’s address
Length: 40 characters
IPN Guide June, 2009 43
Page 44

IPN Variable Reference
Payment Information Variables
Variable Name Description
address_status Whether the customer provided a confirmed address. It is one of the
following values:
z confirmed – Customer provided a confirmed address.
z unconfirmed – Customer provided an unconfirmed address.
address_street Customer’s street address.
Length: 200 characters
address_zip Zip code of customer’s address.
Length: 20 characters
contact_phone Customer’s telephone number.
Length: 20 characters
first_name Customer’s first name
Length: 64 characters
last_name Customer’s last name
Length: 64 characters
payer_business_name Customer’s company name, if customer is a business
Length: 127 characters
payer_email Customer’s primary email address. Use this email to provide any credits.
Length: 127 characters
payer_id Unique customer ID.
Length: 13 characters
Payment Information Variables
Payment information identifies the amount and status of a payment transaction, including fees.
Variable Name Description
auth_amount Authorization amount
auth_exp Authorization expiration date and time, in the following format:
HH:MM:SS DD Mmm YY, YYYY PST
Length: 28 characters
auth_id Authorization identification number
Length: 19 characters
auth_status Status of authorization
exchange_rate Exchange rate used if a currency conversion occurred.
44 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 45

Variable Name Description
IPN Variable Reference
Payment Information Variables
fraud_managment_pending_fil
ters_
x
One or more filters that identify a triggering action associated with one of
the following payment_status values: Pending, Completed, Denied,
where
x is a number starting with 1 that makes the IPN variable name
unique;
x is not the filter’s ID number. The filters and their ID numbers
are as follows:
z 1 = AVS No Match
z 2 = AVS Partial Match
z 3 = AVS Unavailable/Unsupported
z 4 = Card Security Code (CSC) Mismatch
z 5 = Maximum Transaction Amount
z 6 = Unconfirmed Address
z 7 = Country Monitor
z 8 = Large Order Number
z 9 = Billing/Shipping Address Mismatch
z 10 = Risky ZIP Code
z 11 = Suspected Freight Forwarder Check
z 12 = Total Purchase Price Minimum
z 13 = IP Address Velocity
z 14 = Risky Email Address Domain Check
z 15 = Risky Bank Identification Number (BIN) Check
z 16 = Risky IP Address Range
z 17 = PayPal Fraud Model
invoice Passthrough variable you can use to identify your Invoice Number for this
purchase. If omitted, no variable is passed back.
Length: 127 characters
item_name
x Item name as passed by you, the merchant. Or, if not passed by you, as
entered by your customer. If this is a shopping cart transaction, PayPal
will append the number of the item (e.g., item_name1, item_name2,
and so forth).
Length: 127 characters
item_number Pass-through variable for you to track purchases. It will get passed back to
you at the completion of the payment. If omitted, no variable will be
passed back to you.
Length: 127 characters
mc_currency
z For payment IPN notifications, this is the currency of the payment.
z For non-payment subscription IPN notifications (i.e., txn_type=
signup, cancel, failed, eot, or modify), this is the currency of the
subscription.
z For payment subscription IPN notifications, it is the currency of the
payment (i.e., txn_type = subscr_payment)
IPN Guide June, 2009 45
Page 46

IPN Variable Reference
Payment Information Variables
Variable Name Description
mc_fee Transaction fee associated with the payment. mc_gross minus mc_fee
equals the amount deposited into the receiver_email account.
Equivalent to payment_fee for USD payments. If this amount is
negative, it signifies a refund or reversal, and either of those payment
statuses can be for the full or partial amount of the original transaction fee.
mc_gross Full amount of the customer's payment, before transaction fee is
subtracted. Equivalent to payment_gross for USD payments. If this
amount is negative, it signifies a refund or reversal, and either of those
payment statuses can be for the full or partial amount of the original
transaction.
mc_gross_
x The amount is in the currency of mc_currency, where x is the shopping
cart detail item number. The sum of mc_gross_
x should total
mc_gross.
mc_handling Total handling amount associated with the transaction.
mc_shipping Total shipping amount associated with the transaction.
mc_shipping
x This is the combined total of shipping1 and shipping2 Websi t e
Payments Standard variables, where
number. The shipping
x variable is only shown when the merchant
x is the shopping cart detail item
applies a shipping amount for a specific item. Because profile shipping
might apply, the sum of shipping
x might not be equal to shipping.
memo Memo as entered by your customer in PayPal Website Payments note
field.
Length: 255 characters
num_cart_items If this is a PayPal Shopping Cart transaction, number of items in cart.
option_name1 Option 1 name as requested by you. PayPal appends the number of the
item where
x represents the number of the shopping cart detail item (e.g.,
option_name1, option_name2).
Length: 64 characters
option_name2 Option 2 name as requested by you. PayPal appends the number of the
item where
x represents the number of the shopping cart detail item (e.g.,
option_name2, option_name2).
Length: 64 characters
option_selection1 Option 1 choice as entered by your customer.
PayPal appends the number of the item where
x represents the number of
the shopping cart detail item (e.g., option_selection1,
option_selection2).
Length: 200 characters
46 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 47

IPN Variable Reference
Payment Information Variables
Variable Name Description
option_selection2 Option 2 choice as entered by your customer.
PayPal appends the number of the item where
the shopping cart detail item (e.g., option_selection1,
option_selection2).
Length: 200 characters
payer_status Whether the customer has a verified PayPal account.
z verified – Customer has a verified PayPal account.
z unverified – Customer has an unverified PayPal account.
payment_date Time/Date stamp generated by PayPal, in the following format:
HH:MM:SS DD Mmm YY, YYYY PST
Length: 28 characters
payment_fee USD transaction fee associated with the payment. payment_gross
minus payment_fee equals the amount deposited into the receiver
email account. Is empty for non-USD payments. If this amount is
negative, it signifies a refund or reversal, and either of those payment
statuses can be for the full or partial amount of the original transaction fee.
x represents the number of
NOTE: This is a deprecated field. Use mc_fee instead.
payment_fee_
x If the payment is USD, then the value is the same as that for mc_fee_x,
where
x is the record number; if the currency is not USD, then this is an
empty string.
NOTE: This is a deprecated field. Use mc_fee_x instead.
payment_gross Full USD amount of the customer’s payment, before transaction fee is
subtracted. Will be empty for non-USD payments. This is a legacy field
replaced by mc_gross. If this amount is negative, it signifies a refund or
reversal, and either of those payment statuses can be for the full or partial
amount of the original transaction.
payment_gross_
x If the payment is USD, then the value for this is the same as that for the
mc_gross_
x, where x is the record number the mass pay item. If the
currency is not USD, this is an empty string.
NOTE: This is a deprecated field. Use mc_gross_x instead.
IPN Guide June, 2009 47
Page 48

IPN Variable Reference
Payment Information Variables
Variable Name Description
payment_status The status of the payment:
Canceled_Reversal: A reversal has been canceled. For example, you
won a dispute with the customer, and the funds for the transaction that was
reversed have been returned to you.
Completed: The payment has been completed, and the funds have been
added successfully to your account balance.
Created: A German ELV payment is made using Express Checkout.
Denied: You denied the payment. This happens only if the payment was
previously pending because of possible reasons described for the
pending_reason variable or the Fraud_Management_Filters_
variable.
Expired: This authorization has expired and cannot be captured.
Failed: The payment has failed. This happens only if the payment was
made from your customer’s bank account.
Pending: The payment is pending. See pending_reason for more
information.
Refunded: You refunded the payment.
Reversed: A payment was reversed due to a chargeback or other type of
reversal. The funds have been removed from your account balance and
returned to the buyer. The reason for the reversal is specified in the
ReasonCode element.
Processed: A payment has been accepted.
Voided: This authorization has been voided.
x
payment_type echeck: This payment was funded with an eCheck.
instant: This payment was funded with PayPal balance, credit card, or
Instant Transfer.
48 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 49

IPN Variable Reference
Payment Information Variables
Variable Name Description
pending_reason This variable is set only if payment_status = Pending.
address: The payment is pending because your customer did not include
a confirmed shipping address and your Payment Receiving Preferences is
set yo allow you to manually accept or deny each of these payments. To
change your preference, go to the Preferences section of your Profile.
authorization: You set the payment action to Authorization and have
not yet captured funds.
echeck: The payment is pending because it was made by an eCheck that
has not yet cleared.
intl: The payment is pending because you hold a non-U.S. account and
do not have a withdrawal mechanism. You must manually accept or deny
this payment from your Account Overview.
multi-currency: You do not have a balance in the currency sent, and
you do not have your Payment Receiving Preferences set to
automatically convert and accept this payment. You must manually accept
or deny this payment.
order: You set the payment action to Order and have not yet captured
funds.
paymentreview: The payment is pending while it is being reviewed by
PayPal for risk.
unilateral: The payment is pending because it was made to an email
address that is not yet registered or confirmed.
upgrade: The payment is pending because it was made via credit card
and you must upgrade your account to Business or Premier status in order
to receive the funds. upgrade can also mean that you have reached the
monthly limit for transactions on your account.
verify: The payment is pending because you are not yet verified. You
must verify your account before you can accept this payment.
other: The payment is pending for a reason other than those listed above.
For more information, contact PayPal Customer Service.
protection_eligibility ExpandedSellerProtection: Seller is protected by Expanded seller
protection
SellerProtection: Seller is protected by PayPal’s Seller Protection
Policy
None: Seller is not protected under Expanded seller protection nor the
Seller Protection Policy
quantity Quantity as entered by your customer or as passed by you, the merchant.
If this is a shopping cart transaction, PayPal appends the number of the
item (e.g. quantity1, quantity2).
IPN Guide June, 2009 49
Page 50

IPN Variable Reference
Auction Variables
Variable Name Description
reason_code This variable is set if payment_status =Reversed, Refunded, or
Cancelled_Reversal.
adjustment_reversal: Reversal of an adjustment
buyer-complaint: A reversal has occurred on this transaction due to a
complaint about the transaction from your customer.
chargeback: A reversal has occurred on this transaction due to a
chargeback by your customer.
chargeback_reimbursement: Reimbursement for a chargeback
chargeback_settlement: Settlement of a chargeback
guarantee: A reversal has occurred on this transaction due to your
customer triggering a money-back guarantee.
other: Non-specified reason.
refund: A reversal has occurred on this transaction because you have
given the customer a refund.
NOTE: Additional codes may be returned.
remaining_settle Remaining amount that can be captured with Authorization and Capture
settle_amount Amount that is deposited into the account’s primary balance after a
currency conversion from automatic conversion (through your Payment
Receiving Preferences) or manual conversion (through manually
accepting a payment).
settle_currency Currency of settle_amount.
shipping Shipping charges associated with this transaction.
Format: unsigned, no currency symbol, two decimal places.
shipping_method The name of a shipping method from the Shipping Calculations section of
the merchant's account profile. The buyer selected the named shipping
method for this transaction.
tax Amount of tax charged on payment. PayPal appends the number of the
item (e.g., item_name1, item_name2). The tax
only if there was a specific tax amount applied to a particular shopping
cart item. Because total tax may apply to other items in the cart, the sum
of tax
x might not total to tax.
transaction_entity Authorization and Capture transaction entity
x variable is included
Auction Variables
Auction information identifies the auction for which a payment is made and additional
information about the auction.
50 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 51

IPN Variable Reference
Mass Pay Variables
Variable Name Description
auction_buyer_id The customer’s auction ID.
Length: 64 characters
auction_closing_date The auction’s close date, in the following format: HH:MM:SS DD Mmm
YY, YYYY PST
Length: 28 characters
auction_multi_item The number of items purchased in multi-item auction payments. It allows
you to count the mc_gross or payment_gross for the first IPN you
receive from a multi-item auction (auction_multi_item), since each
item from the auction will generate an Instant Payment Notification
showing the amount for the entire auction.
for_auction This is an auction payment—payments made using Pay for eBay Items or
Smart Logos—as well as Send Money/Money Request payments with the
type eBay items or Auction Goods (non-eBay).
Mass Pay Variables
Mass pay information identifies the amounts and status of transactions related to mass
payments, including fees.
Variable Name Description
masspay_txn_id_
mc_currency_
mc_fee_
mc_gross_
x For Mass Payments, the transaction fee associated with the payment,
x The gross amount for the amount, where x is the record number the mass
mc_handling
payment_date For Mass Payments, the first IPN is the date/time when the record set is
x For Mass Payments, a unique transaction ID generated by the PayPal
system, where
x is the record number of the mass pay item
Length: 19 characters
x For Mass Payments, the currency of the amount and fee, where x is the
record number the mass pay item
where
x is the record number the mass pay item
pay item
x The x is the shopping cart detail item number. The handling_cart cart-
wide Website Payments variable is also included in the mc_handling
variable; for this reason, the sum of mc_handling
x might not be equal to
mc_handling
processed and the second IPN is the date/time when all payments are
completed/returned. Format: HH:MM:SS DD Mmm YY, YYYY PST
Length: 28 characters
IPN Guide June, 2009 51
Page 52

IPN Variable Reference
Recurring Payments Variables
Variable Name Description
payment_status Completed: For Mass Payments, this means that all of your payments
have been claimed, or after a period of 30 days, unclaimed payments have
been returned to you.
Denied: For Mass Payments, this means that your funds were not sent
and the Mass Payment was not initiated. This may have been caused by
lack of funds.
Processed: Your Mass Payment has been processed and all payments
have been sent.
reason_code This variable is only set if status = Failed.
1001: Invalid UserID.
1003: Country of Residence check failure
1004: Country of Funding Source check failure
receiver_email_
status_
unique_id_
x For Mass Payments, the status of the payment, where x is the record
x For Mass Payments, the primary email address of the payment recipient,
where
x is the record number of the mass pay item
Length: 127 characters
number
Completed: The payment has been processed, regardless of whether this
was originally a unilateral payment
Failed: The payment failed because of insufficient PayPal balance.
Returned: Payment has been returned after 30 days.
Reversed: This is for unilateral payments that were not claimed after 30
days and have been returned to the sender. Or the funds have been
returned because the Receiver’s account was locked.
Unclaimed: This is for unilateral payments that are unclaimed.
x For Mass Payments, the unique ID from input, where x is the record
number. This allows the merchant to cross-reference the payment
Length: 13 characters
Recurring Payments Variables
Recurring payments information identifies the amounts and status associated with recurring
payments transactions.
Variable Name Description
amount Amount of recurring payment
amount_per_cycle Amount of recurring payment per cycle
initial_payment_amount Initial payment amount for recurring payments
next_payment_date Next payment date for a recurring payment
52 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 53

IPN Variable Reference
Recurring Payments Variables
Variable Name Description
outstanding_balance Outstanding balance for recurring payments
payment_cycle Payment cycle for recurring payments
period_type Kind of period for a recurring payment
product_name Product name associated with a recurring payment
product_type Product name associated with a recurring payment
profile_status Profile status for a recurring payment
recurring_payment_id Recurring payment ID
rp_invoice_id The merchant’s own unique reference or invoice number, which can be
used to uniquely identify a profile.
Length: 127 single-byte alphanumeric characters
time_created When a recurrng payment was created
IPN Guide June, 2009 53
Page 54

IPN Variable Reference
Recurring Payments Variables
Summary of recurring payment variables
Variables Profile created message Recurring payment message
Basic Information
business X
receiver_email XX
receiver_id X
Transaction Information
payment_status X
payment_type X
payment_date X
txn_id X
initial_payment_status X
initail_payment_txn_id X
txn_type recurring_payment_profile_
created
Currency and Exchange
mc_gross X
mc_fee X
mc_currency X
payment_gross X
currency_code XX
payment_fee X
Buyer Information
first_name XX
last_name XX
address_name X
address_street X
address_city X
address_state X
recurring_payment
address_zip X
address_country X
payer_email XX
54 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 55

IPN Variable Reference
Subscription Variables
Variables Profile created message Recurring payment message
payer_id XX
payer_status XX
residence_country XX
address_country_code X
address_status X
Recurring Payment
recurring_payment_id XX
rp_invoice_id XX
product_name XX
product_type XX
period_type XX
payment_cycle XX
outstanding_balance XX
amount_per_cycle XX
initial_payment_amount XX
profile_status XX
amount XX
time_created XX
next_payment_date XX
Other Information
notify_version XX
charset XX
Subscription Variables
Subscription information identifies the amounts and parameters associated with subscription
transactions.
Variable Name Description
amount1 Amount of payment for trial period 1 for USD payments; otherwise blank
(optional).
IPN Guide June, 2009 55
Page 56

IPN Variable Reference
Subscription Variables
Variable Name Description
amount2 Amount of payment for trial period 2 for USD payments; otherwise blank
(optional).
amount3 Amount of payment for regular subscription period for USD payments;
otherwise blank.
mc_amount1 Amount of payment for trial period 1, regardless of currency (optional).
mc_amount2 Amount of payment for trial period 2, regardless of currency (optional).
mc_amount3 Amount of payment for regular subscription period, regardless of
currency.
password (optional) Password generated by PayPal and given to subscriber to access
the subscription (password will be encrypted).
Length: 24 characters
period1 (optional) Trial subscription interval in days, weeks, months, years
(example: a 4 day interval is “period1: 4 D”).
period2 (optional) Trial subscription interval in days, weeks, months, or years.
period3 Regular subscription interval in days, weeks, months, or years.
reattempt Indicates whether reattempts should occur upon payment failures (1 is
yes, blank is no).
recur_times The number of payment installments that will occur at the regular rate.
recurring Indicates whether regular rate recurs (1 is yes, blank is no).
retry_at Date PayPal will retry a failed subscription payment.
subscr_date Start date or cancellation date depending on whether transaction is
subscr_signup or subscr_cancel.
Time/Date stamp generated by PayPal, in the following format:
HH:MM:SS DD Mmm YY, YYYY PST
subscr_effective Date when the subscription modification will be effective (only for
txn_type = subscr_modify).
Time/Date stamp generated by PayPal, in the following format:
HH:MM:SS DD Mmm YY, YYYY PST
subscr_id ID generated by PayPal for the subscriber.
Length: 19 characters
username (optional) Username generated by PayPal and given to subscriber to
access the subscription.
Length: 64 characters
56 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 57

IPN Variable Reference
Subscription Variables
Summary of subscription variables
Multi-
USD
Variable Signup Cancel Modify
Basic Information
business XXXX X X X
receiver_email XXXX X X X
receiver_id XX
item_name XXXX X X X
item_number XXXX X X X
Advanced and Custom Information
invoice XXX X X X X
custom XXXX X X X
option_name1 XXXX X X X
Payment
Currency
Payment
Refund Failed EOT
option_selecti
on1
option_name2 XXXX X X X
option_selecti
on2
Transaction Information
payment_status XX X
pending_reason XX
reason_code XX
payment_date XX
txn_id XX
parent_txn_id XX
txn_type subscr_
Currency and Exchange information
mc_gross XX
mc_fee XX
XXXX X X X
XXXX X X X
signup
subscr_
cancel
subscr_
modify
subscr_payment subscr_
failed
subsc
r_eot
mc_currency XXXX X X X
settle_amount XX
exchange_rate XX
IPN Guide June, 2009 57
Page 58

IPN Variable Reference
Subscription Variables
Multi-
USD
Variable Signup Cancel Modify
payment_gross XXX
payment_fee X
Buyer Information
first_name XXXX X X X
last_name XXXX X X X
Payment
Currency
Payment
Refund Failed EOT
payer_business
_name
address_name XXXX X X
address_street XXXX X X
address_city XXXX X X
address_state XXXX X X
address_zip XXXX X X
address_
country
payer_email XXXX X X X
payer_id XXXX X X X
payer_status XXXX X X X
payment_type XX
Subscription Information
subscr_date XXX
subscr_
effective
XXXX X X
XXXX X X
X
period1 XXX
period2 XXX
period3 XXX
amount1 XXX
amount2 XXX
amount3 XXX
mc_amount1 XXX
mc_amount2 XXX
recurring XXX
58 June, 2009 IPN Guide
Page 59

IPN Variable Reference
Dispute Resolution Variables
Multi-
Variable Signup Cancel Modify
USD
Payment
Currency
Payment
Refund Failed EOT
reattempt XXX
retry_at X
recur_times XXX
username XXXX X X X
password XXXX X X X
subscr_id XXXX X X X
Dispute Resolution Variables
Dispute resolution information identifies the case ID and status associated with a dispute.
Variable Name Description
case_creation_date Date and time case was registered, in the following format: HH:MM:SS
DD Mmm YY, YYYY PST
case_id Case identification number.
Format: PP-nnn-nnn-nnn where n is any numeric character.
case_type
z chargeback: A buyer has filed a chargeback with his credit card
company, which has notified PayPal of the reason for the chargeback.
z complaint: A buyer has logged a complaint through the PayPal
Resolution Center.
z dispute: A buyer and seller post communications to one another
through the Resolution Center to try to work out issues without
intervention by PayPal.
IPN Guide June, 2009 59
Page 60

IPN Variable Reference
Payment Review Using Notifications
Variable Name Description
reason_code Reason for the case.
Values for case_type set to complaint:
z non_receipt: Buyer claims that he did not receive goods or service.
z not_as_described: Buyer claims that the goods or service received
differ from merchant’s description of the goods or service.
Values for case_type set to chargeback:
z unauthorized
z adjustment_reimburse: A case that has been resolved and close
requires a reimbursement.
z non_receipt: Buyer claims that he did not receive goods or service.
z duplicate: Buyer claims that a possible duplicate payment was
made to the merchant.
z merchandise: Buyer claims that the received merchandise is
unsatisfactory, defective, or damaged.
z special: Some other reason. Usually, special indicates a credit card
processing error for which the merchant is not responsible and for
which no debit to the merchant will result. PayPal must review the
documentation from the credit card company to determine the nature
of the dispute and possibly contact the merchant to resolve it.
Payment Review Using Notifications
If PayPal places a payment under review, PayPal sends messages containing the
payment_status and pending_reason variables. In addition, it sends a
protection_eligibility variable that identifies the kind of protection in force for the
transaction.
The initial IPN or PDT message indicates that the payment is under review:
z The payment_status variable is set to Pending.
z The pending_reason variable is set to PaymentReview.
A subsequent IPN message indicates the resolution of the payment review:
z If the transaction was successful and the payment was accepted, PayPal sends a notification
whose payment_status variable is set to Completed.
z If the transaction failed and the payment was rejected, PayPal sends a notification whose
payment_status variable is set to Reversed.
NOTE: PDTs are only available for the initial status.
60 June, 2009 IPN Guide
 Loading...
Loading...