Page 1

PayPal Certified
Developer Program
Study Guide
For Professional Use Only
Currently only available in English.
A usage Professional Uniquement
Disponible en Anglais uniquement pour l’instant.
Last updated: March 2008
Page 2

PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Document Number: 100018.en_US-200803
© 2008 PayPal, Inc. All rights reserved. PayPal is a registered trademark of PayPal, Inc. The PayPal logo is a trademark of PayPal, Inc. Other
trademarks and brands are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document belongs to PayPal, Inc. It may not be used, reproduced or disclosed without the written approval of PayPal, Inc.
PayPal (Europe) Ltd. is authorised and regulated by the Financial Services Authority in the United Kingdom as an electronic money institution.
PayPal FSA Register Number: 226056.
Notice of non-liability:
PayPal, Inc. is providing the information in this document to you “AS-IS” with all faults. PayPal, Inc. makes no warranties of any kind (whether express,
implied or statutory) with respect to the information contained herein. PayPal, Inc. assumes no liability for damages (whether direct or indirect), caused
by errors or omissions, or resulting from the use of this document or the information contained in this document or resulting from the application or use
of the product or service described herein. PayPal, Inc. reserves the right to make changes to any information herein without further notice.
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Online Payment Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Online Selling Basics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
The Payment Processing Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Individuals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Institutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Processes and Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
How Online Payment Processing Works. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Payment Processing Authorization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Payment Processing Settlement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
What to Look for in an Online Payment Processing Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
PayPal’s Payment Processing Solutions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Review Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Chapter 2 Internet Security and Fraud Prevention . . . . . . . . . . .23
Why Every Business Should Be Concerned About Internet Fraud . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Liability for Internet Fraud . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Internet Fraud: What It Is and How It Happens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Who Is at Risk for Online Fraud . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Reducing Exposure to Fraud. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
What Banks and Card Associations Are Doing to Prevent Online Credit Card Fraud . . . . 28
What PayPal Is Doing to Protect Your Business Against Fraud . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
How to Reduce Chargebacks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Disclosure and Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Disclosure Policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
PCI Data Security Standard Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Additional Resources About Disclosure and Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
PayPal Fraud Protection Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Detailed Service Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
PayPal Fraud Protection Services Upgrade Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Review Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 3
Page 4

Contents
Chapter 3 Getting Started With Account Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Basic Steps for Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
PayPal Sandbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Review Question . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Chapter 4 API Credentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
What API Credentials Are . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Choosing an Authentication Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Establishing API Credentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
API Signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
API Certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Using API Credentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Review Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Chapter 5 Name-Value Pair (NVP) API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Integrating with the PayPal API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Basic Steps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Create a Web Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Get API Credentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Create and Post the Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Interpret the Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Technical Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Request-Response Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Request Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Response Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Posting Using HTTPS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Review Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Chapter 6 Express Checkout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
How Express Checkout Works. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Express Checkout API Reference Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
SetExpressCheckout Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
SetExpressCheckout Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
GetExpressCheckoutDetails Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
GetExpressCheckoutDetails Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
DoExpressCheckoutPayment Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
DoExpressCheckoutPayment Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
4 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 5

Contents
Button and Logo Placement and Use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
PayPal Button as a Checkout Choice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
PayPal Button as a Payment Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Using PayPal-Hosted Images . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Redirecting to PayPal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Recommendation for Browser Redirection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Order Review Page Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Authorization & Capture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Review Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Chapter 7 Direct Payment API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
How Direct Payment Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Direct Payment API Reference Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
DoDirectPayment Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
DoDirectPayment Response. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Authorization & Capture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Review Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Chapter 8 Transactions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Authorization & Capture APIs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Authorization Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Honor Period and Authorization Period . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Authorization & Capture API Reference Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Authorization & Capture Best Practices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
For More Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Refunds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
RefundTransaction Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
RefundTransaction Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Transaction Searches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
TransactionSearch Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
TransactionSearch Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Retrieving Transaction Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
GetTransactionDetails Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
GetTransactionDetails Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Payment Notification Integration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 5
Page 6

Contents
Instant Payment Notification (IPN). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
Dispute Notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Review Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Chapter 9 Sandbox Testing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
At a Glance: Differences between the Sandbox and Live PayPal . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Accessing the PayPal Sandbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Signing Up for Sandbox Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Welcome to the PayPal Sandbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
Test Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
Setting Up Test Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Planning the Types of Test Accounts You Need . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Managing Test Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Adding a Funding Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Signing Up for Website Payments Pro. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Testing PayPal Website Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Website Payments with the “Buy Now” Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Handling Pending Transactions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120
Instant Payment Notification (IPN). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .121
Verifying a Test Refund . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .122
Transferring Funds to a Test Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .122
Clearing or Failing Test eCheck Transactions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
Sending Funds to a Seller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
Billing A Customer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .124
Testing PayPal NVP APIs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .125
Testing Express Checkout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
Testing Error Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
API Testing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .130
Testing Using AVS Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .134
Testing Using CVV Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .138
Testing Recurring Payments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .140
Review Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .141
Appendix A Answers to Review Questions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Chapter 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .143
Chapter 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .146
Chapter 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .150
6 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 7

Contents
Chapter 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
Chapter 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
Chapter 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
Chapter 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
Chapter 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .152
Appendix B General Reference Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
ShippingAddress Parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .153
PayPal-Supported Transactional Currencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .154
AVS Response Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .155
CVV2 Response Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .156
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 7
Page 8

Contents
8 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 9

List of Tables
Table 1.1 PayPal Payment Processing Solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 2.1 High Fraud Risk Quick Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 2.2 PCI Data Security Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 2.3 Merchant Levels for PCI Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 2.4 PCI Compliance Validation Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 2.5 Fraud Protection Services Purchase Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 2.6 Comparison of Fraud Protection Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 4.1 Required Security Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 5.1 URL-Encoding Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Table 5.2 General Format of a Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Table 5.3 General Format of a Successful Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 5.4 ACK Parameter Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 5.5 Format of an Error Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 6.1 Express Checkout Flow-of-Control and Integration Points . . . . . . . . . 60
Table 6.2 SetExpressCheckout Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 6.3 SetExpressCheckout Response Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 6.4 GetExpressCheckoutDetails Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Table 6.5 GetExpressCheckoutDetails Response Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Table 6.6 DoExpressCheckoutPayment Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Table 6.7 DoExpressCheckoutPayment Response Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Table 7.1 DoDirectPayment Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Table 7.2 DoDirectPayment Response Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Table 8.1 DoCapture Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Table 8.2 DoCapture Response Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Table 8.3 DoVoid Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Table 8.4 DoVoid Response Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Table 8.5 DoReauthorization Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Table 8.6 DoReauthorization Response Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Table 8.7 RefundTransaction Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Table 8.8 RefundTransaction Response Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Table 8.9 TransactionSearch Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 9
Page 10

List of Tables
Table 8.10 TransactionSearch Response Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Table 8.11 GetTransactionDetails Request Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Table 9.1 Differences between PayPal Sandbox, and Live PayPal . . . . . . . . .105
Table 9.2 API Fields That Trigger Error Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .130
Table 9.3 AVS Error Conditions and Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .134
Table 9.4 CVV Error Conditions and Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .138
Table B.1 ShippingAddress . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .153
Table B.2 PayPal-Supported Currencies and Currency Codes for Transactions . . .154
Table B.3 AVS Response Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .155
Table B.4 CVV2 Response Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .156
10 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 11

Online Payment Processing
1
Online payment processing simplifies the operation of an online store by providing a reliable,
easy, secure, and seamless experience for merchants and customers.
In this chapter, you will learn:
z Online payment processing basics
z How the payment processing network operates
z How payment processing works
z What to look for in an online payment processing solution
z PayPal’s payment processing solutions
Online Selling Basics
With the right payment processing services, online merchants can get paid quickly and easily
while protecting themselves against fraud. The most critical step in establishing an online store
is ensuring that you can accept customer payments for single or repeated transactions. Online
payment processing tools offer customers the convenience of paying by credit card, PayPal®,
or other electronic payment sources like debit cards, purchase cards, and eChecks.
Additionally, successful online merchants must make sure their stores are secure. Online fraud
rates are climbing, but smart merchants can protect themselves with security and fraud
prevention systems from a company they trust. According to CyberSource Corp., businesses
lost nearly $2.8 billion USD to online fraud in 2005, up from $2.6 billion USD in 2004.
PayPal’s Fraud Protection Services provide secure and reliable tools that offer peace of mind.
The Payment Processing Network
The payment processing network connects sellers, buyers, and banks to enable the secure and
reliable execution of online transactions. Sellers need an internet merchant account with an
acquiring bank that allows them to accept customer credit cards electronically. Customers
need a bank that issues credit cards and verifies the customer’s credit limit and available cash
balance for proposed purchases. The elements and participants include individuals,
institutions, and processes and services.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 11
Page 12

Online Payment Processing
1
How Online Payment Processing Works
Individuals
z Merchant: Someone who sells goods or services.
z Customer: The holder of the payment instrument.
Institutions
z Customer issuing bank: The institution providing the customer’s credit card.
z Acquiring bank: Provides internet merchant accounts required to enable online card
authorization and payment processing.
z Credit card associations: Financial institutions that provide credit card services in concert
with credit card associations such as Visa and MasterCard.
z Processor: A large data center that processes credit card transactions and settles funds for
merchants. A processor can be either a bank or a company dedicated to providing these
services. Ceridian is an example of a payment processor.
Processes and Services
z Authorizations: The process of verifying that customer credit cards are active and have
sufficient available credit limits.
z Settlements: Processing authorized transactions to settle funds into a merchant’s account.
z Payment processing service: A service that connects merchants, customers, and banks
involved in online transactions. A third party, such as PayPal with its secure payment
gateway, usually offers this service.
How Online Payment Processing Works
Online payment processing consists of two principal steps: authorization and settlement.
Authorization verifies that the card is active and the customer has sufficient credit to make the
transaction. Settlement is the process of charging the customer’s card account and transferring
money from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account.
Payment Processing Authorization
During authorization, a bank verifies that holders of a payment instrument, like a credit card,
have sufficient credit or funds to make a purchase. The payment authorization process engages
multiple institutions and services to verify that sufficient credit is available to complete the
transaction as follows:
1. Customer decides to purchase online and inputs credit card information.
12 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 13

2. Merchant’s website receives customer information and sends it to payment processing
service.
3. Processing service routes information to processor.
4. Processor routes information to bank that issued customer’s credit card.
5. Issuing bank sends authorization (or declination) to processor.
6. Processor routes transaction results to payment processing service.
7. Processing service sends results to merchant.
8. Merchant decides to accept or reject purchase. (Here, the merchant should take additional
precautions to ensure the credit card is not stolen and that the customer actually owns this
card.)
Payment Processing Settlement
Once the merchant has shipped the product or authorized the download of merchandise, the
merchant may request that the payment processing service settle the transaction. During
settlement, funds are transferred from the customer’s account to the merchant’s bank account.
Online Payment Processing
What to Look for in an Online Payment Processing Solution
1
1. Merchant informs the payment processing service to settle transactions.
2. Payment processing service sends transactions to processor.
3. Processor checks the information, and forwards settled transaction information to the card
association and card-issuing bank.
4. Transactions are settled to the card issuers and funds move between the acquiring bank and
issuing bank. Funds received for these transactions are sent to the merchant’s bank account.
5. Acquiring bank credits merchant’s bank account.
6. Issuing bank includes merchant’s charge on customer’s credit card account.
What to Look for in an Online Payment Processing Solution
Finding a reliable, secure, and flexible payment processing solution is critical. A payment
processing solution should be:
Secure
z Backed by an established, trustworthy company
z Comply with the Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard
z Provide comprehensive and standard antifraud features
z Store customer financial information with state-of-the-art encryption
z Supply password-protected account management
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 13
Page 14

Online Payment Processing
1
PayPal’s Payment Processing Solutions
Reliable
z Provide reliable and cost-effective acceptance and processing of a variety of payment types
z Authorize credit cards in real time
z Scale to thousands of transactions to meet peak demand
z Based on a fault-tolerant network of redundant servers to ensure uninterrupted operations
Easy to Use
z Provide easy, flexible integration with merchant’s website
z Scale rapidly and seamlessly as transaction volume increases
z Work with leading internet merchant account providers
z Provide easy-to-use tracking and reporting system
z Store transaction records securely
z Process offline transactions through a virtual terminal
z Provide recurring billing payment for services
z Offer upgrade options to accommodate future growth
PayPal’s Payment Processing Solutions
PayPal’s payment processing solutions are designed to meet the demanding and diverse needs
of a variety of online merchants. By providing affordable payment connections among
merchants, customers, and financial networks, PayPal’s solutions take advantage of the latest
technical resources to streamline transactions, while helping to prevent fraud. Products
including Payflow Link, Payflow Pro, Website Payments Standard, and Website Payments Pro
allow everyone from mom-and-pop online retail stores to enterprise-level businesses to
process transactions easily, reliably, and securely.
PayPal’s Fraud Protection Services and Recurring Billing Service for Payflow, along with
other customer service packages, include professional integration support. Most importantly,
Payflow offers one of the industry’s few payment processing services with immediate
connectivity to all major processors and most shopping carts. Note, however, that you do not
need a PayPal account to process credit cards on your website.
Once you have your own website, ask a few simple questions to determine which product is
right for you:
1. Do you need an all-in-one solution that includes an internet merchant account and
allows you to process credit cards online?
If you don’t have your own internet merchant or business bank account, PayPal can
provide a total solution with its Website Payments Standard and Website Payments Pro
solutions:
– Website Payments Pro: Website Payments Pro is an all-in-one payment solution that
allows customers to shop and pay on your site. You can accept credit cards directly on
14 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 15
Online Payment Processing
PayPal’s Payment Processing Solutions
your site and get the features of a merchant account and gateway through a single
provider at a lower cost. Website Payments Pro allows you to control your checkout from
start to finish.
For more information on Website Payments Pro, go to: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-
bin/webscr?cmd=_wp-pro-overview-outside.
– Website Payments Standard: Website Payments Standard lets customers shop on your
website and pay on PayPal. It offers a pay-peruse model with no set-up or monthly fees.
Like Website Payments Pro, it includes shipping and tax calculators, reporting tools to
measure your business, and support for international currencies.
For more information on Website Payments Standard, go to:
https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_wp-standard-overview-outside
2. Do you have your own internet merchant account or business bank account that
allows you to process credit cards online?
If you do, consider PayPal Payflow Gateway products. A gateway provides a secure
connection between your online store and your internet merchant account.
– Payflow Pro: Scalable and fully customizable, the Payflow Pro solution is
recommended for merchants who require peak site performance and direct control over
payment functionality on their site. Merchants using this service can enhance the
customer experience by allowing shoppers to complete the checkout process without
ever leaving your site.
For more information on Payflow Pro, go to: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-
bin/webscr?cmd=_payflow-pro-overview-outside.
– Payflow Link: This service is designed for merchants who require a simple solution to
selling on the web. In order to use this service, you need to add only a small piece of
HTML code that will link your customers to order forms hosted by PayPal. This simple
package allows you to process payments by credit cards, debit cards, and checks, online
and offline. It also works with most major shopping carts.
For more information on Payflow Link, go to: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-
bin/webscr?cmd=_payflow-link-overview-outside.
.
1
3. Do you need a basic payment processing service?
Look first to a basic PayPal service for processing credit cards payments. These include:
– PayPal Email Payments: Email Payments lets you send customers email invoices that
they can pay on PayPal. This simple solution does not require you to have a shopping
cart or an internet merchant account.
For more information on PayPal Email Payments, go to: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-
bin/webscr?cmd=_email-payments-overview-outside.
– PayPal Virtual Terminal: Virtual Terminal provides your business with the same
functionality as a stand-alone credit card-processing terminal, but allows you to accept
credit card payments by phone, fax, and email. You can use Virtual Terminal on any
computer with an internet connection.
For more information on PayPal Virtual Terminal, go to: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-
bin/webscr?cmd=_vt_hub-outside.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 15
Page 16

Online Payment Processing
1
PayPal’s Payment Processing Solutions
– PayPal as an Additional Payment Option: This option allows merchants to put the
PayPal logo on their own website to accept PayPal as an alternative payment source, in
addition to credit cards such as MasterCard® or Visa®.
For more information on PayPal as an Additional Payment Option, go to:
https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_additional-payment-overview-outside
.
16 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 17
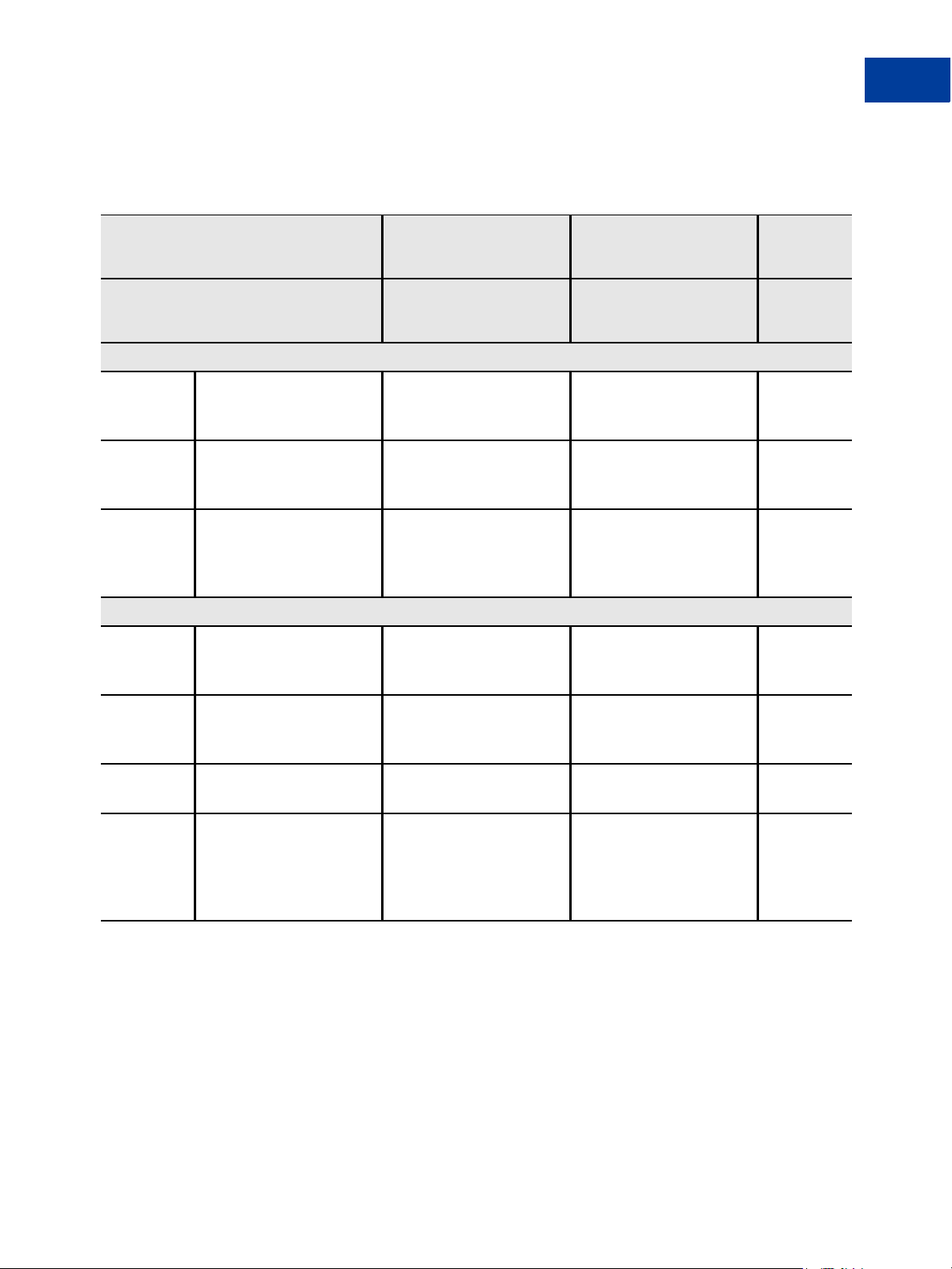
TABLE 1.1 PayPal Payment Processing Solutions
I need an all-in-one
solution
I have an internet
merchant account
Online Payment Processing
PayPal’s Payment Processing Solutions
Additional
I need basic payment
processing
payment
option
1
Website
Payments
Pro
Customer Experience
Where
customers
shop:
Where
customers
check out:
Customers
Shop on
merchant
website
Merchant
website or
on PayPal
No No No No No No No
need a
PayPal
account:
Integration
Internet
Included Not needed Required Required Not needed Included Required
merchant
account:
Shopping
Yes Yes Yes Yes Not
cart
support:
Website
Payments
Standard
Shop on
merchant
website
Payflow
Pro
Shop on
merchant
website
PayPal Merchant
website or
on PayPal
Payflow
Link
Shop on
merchant
website
Email
Payments
Varies with
merchant
business
Virtual
Terminal PayPal
Varies with
merchant
business
PayPal PayPal Phone, fax,
or mail
Not
required
required
Shop on
merchant
website
PayPal
Ye s
Technical
skills:
Ability to
APIs HTML APIs or
HTML
APIs or
HTML
Not
required
Not
required
APIs or
HTML
Included Upgrade Included Included Upgrade Included Upgrade
accept
phone, fax,
or mail
orders
N OTE: This Study Guide and the PayPal Developer Certification cover the Website Payments
Pro solution with Express Checkout.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 17
Page 18
Online Payment Processing
1
Review Questions
Review Questions
Answers to review questions are in Appendix A, “Answers to Review Questions.”
1. Indicate if each statement is True (T) or False (F).
_____ The most critical step in establishing an online store is ensuring that you can accept
_____ According to Cybersource Corp., businesses lost nearly $2.8 billion USD to online
_____ The payment processing network connects buyers, sellers, and banks to enable the
_____ By providing affordable payment connections among merchants, customers, and
2. Match each participant in the payment processing network to the role they perform.
customer payments for single or repeated transactions.
fraud in 2005, down from $3.0 billion USD in 2004.
secure and reliable execution of online transactions.
financial networks, PayPal’s solutions take advantage of the latest technical
resources to streamline transactions, while helping to prevent fraud.
Response Participant Role Performed
Merchant 1. The holder of the payment instrument.
Customer 2. A financial institution that provides credit card
services in concert with credit card associations such
as Visa and MasterCard.
Customer Issuing Bank 3. Someone who sells goods or services.
Acquiring Bank 4. A large data center that processes credit card
transactions and settles funds for merchants.
Credit Card Association 5. An institution that provides merchant accounts
required to enable online card authorization and
payment processing.
Processor 6. The institution providing the customer’s credit card.
18 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 19

Online Payment Processing
Review Questions
3. The following steps describe the payment authorization process. Indicate the correct order
of the steps by placing the step number to the left of each description.
_____ Processor routes information to bank that issued customer’s credit card.
_____ Merchant’s website receives customer information and sends it to payment
processing service.
_____ Processing service sends results to merchant.
_____ Merchant decides to accept or reject purchase.
_____ Customer decides to purchase online and inputs credit card information.
_____ Processor routes transaction results to payment processing service.
_____ Processing service routes information to processor.
_____ Issuing bank sends authorization (or declination) to processor.
4. The following steps describe the payment processing settlement process. Indicate the
correct order of the steps by placing the step number to the left of each description.
_____ Acquiring bank credits merchant’s bank account.
_____ Merchant informs the payment processing service to settle transactions.
_____ Processor checks the information, and forwards settled transaction information to
the card association and card-issuing bank.
_____ Issuing bank includes merchant’s charge on customer’s credit card account.
_____ Transactions are settled to the card issuers and funds move between the acquiring
bank and issuing bank. Funds received for these transactions are sent to the
merchant’s bank account.
_____ Payment processing service sends transactions to processor.
1
5. Finding a reliable, secure, and flexible payment processing solution is critical. What
features should a payment processing solution offer? (Select all that apply.)
_____ Backed by an established, trustworthy company
_____ Comply with Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard
_____ Store customer financial information in plain sight
_____ Authorize credit cards in real time
_____ Based on a network that provides near real-time credit card transactions
_____ Scale rapidly and seamlessly as transaction volume increases
_____ Offer upgrade options to accommodate future growth
_____ Provide recurrent billing payment for service
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 19
Page 20
Online Payment Processing
1
Review Questions
6. Match each PayPal solution to the service it offers.
Response PayPal Product Service Description
Website Payments Pro 1. Lets you send customers email invoices that they
can pay on PayPal. This simple solution does not
require you to have a shopping cart or an internet
merchant account.
Website Payments Standard 2. A gateway that provides a secure connection
between your online store and your internet
merchant account. Scalable and fully customizable,
this solution is recommended for merchants who
require peak site performance and direct control over
payment functionality on their site. Merchants using
this service can enhance the customer experience by
allowing shoppers to complete the checkout process
without ever leaving your site.
Payflow Pro 3. Allows merchants to put the PayPal logo on their
own website to accept PayPal as an alternative
payment source, in addition to credit cards such as
MasterCard® or Visa®.
Payflow Link 4. An all-in-one payment solution that allows
customers to shop and pay on your site. You can
accept credit cards directly on your site and get the
features of a merchant account and gateway through
a single provider at a lower cost.
PayPal Email Payments 5. A gateway that provides a secure connection
between your online store and your internet
merchant account. This service is designed for
merchants who require a simple solution to selling
on the web. In order to use this service, you need to
add only a small piece of HTML code that will link
your customers to order forms hosted by PayPal.
PayPal Virtual Terminal 6. Provides your business with the same functionality
as a stand-alone credit card-processing terminal, but
allows you to accept credit card payments by phone,
fax, and email.
PayPal as an Additional Payment
Option
7. Lets customers shop on your website and pay on
PayPal. It offers a pay-peruse model with no set-up
or monthly fees. It includes shipping and tax
calculators, reporting tools to measure your
business, and support for international currencies.
20 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 21

Online Payment Processing
Review Questions
7. Select the PayPal payment processing solutions that enable a customer to checkout on the
merchant’s website.
_____ Website Payments Pro
_____ Website Payments Standard
_____ Payflo Pro
_____ Payflow Link
_____ Email Payments
_____ Virtual Terminal
_____ PayPal as an Additional Payment Option
8. Select the PayPal payment processing solutions that require API or HTML technical skills
to develop payment processing applications.
_____ Website Payments Pro
_____ Website Payments Standard
_____ Payflo Pro
_____ Payflow Link
_____ Email Payments
_____ Virtual Terminal
_____ PayPal as an Additional Payment Option
1
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 21
Page 22

Online Payment Processing
1
Review Questions
22 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 23
2
Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
E-commerce has become an essential sales channel for businesses both domestically and
internationally. Unfortunately, e-commerce has also become an attractive revenue source for
criminals who perpetrate internet fraud. You need to be aware and informed so that you can
take steps to protect your business. Security for online payments is everyone’s responsibility.
In this chapter, you will learn about:
z Why every merchant should be concerned about internet fraud
z Liability for internet fraud
z Internet fraud: What it is and how it happens
z Who is at risk for online fraud
z How to reduce your exposure to fraud
z What banks and credit card associations are doing to prevent online credit card fraud
z What PayPal is doing to protect your business against fraud
z Providing disclosure to your customers and compliance with the Payment Card Industry
(PCI) standard
z PayPal® Fraud Protection Services
Why Every Business Should Be Concerned About Internet Fraud
Every merchant is at risk for fraud. When doing business online, you should be particularly
aware of fraud.
Offline merchants can see who they are doing business with, look at their customers’ credit
cards, and watch them sign the receipt. In the online world, however, customers never sign a
paper receipt, so authentication becomes a challenge. Moreover, in the online world, hackers
can break into your network without your knowledge and steal money, products, and sensitive
information. They can also steal customer identities and commit crimes against other
merchants, using your business as a launch pad for further crimes.
Internet fraud is also more difficult to detect than in the brick-and-mortar world. Criminals
who break into a physical store are much more visible than criminals who break in through the
web and erase their footprints. Additionally, in the online world, criminals have multiple
access points for break-ins, because the merchant store is networked internally and to other
businesses.
Because of these vulnerabilities, total losses from online payment fraud have steadily
increased. According to CyberSource’s 2006 Online Fraud Report, an estimated $2.8 billion
USD was lost to online fraud in the U.S. and Canada in 2005. The Nilson Report, a payment
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 23
Page 24

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
Liability for Internet Fraud
trade publication, estimates the rate of credit card fraud to be 18 cents to 24 cents per $100
USD of online sales – three to four times higher than the overall fraud rate.
The threat of online fraud is so pervasive that the U.S. government now mandates security
requirements for businesses that handle financial information online. Today these regulations
apply mainly to the banking community, but as an internet merchant you access the financial
networks for each transaction made on your site. As a result, security at the point of sale is
becoming an increasing concern for both credit card associations and the government.
Credit card associations, for their part, hold merchants liable for fraudulent transactions
because the credit card isn’t physically present during online purchases. So merchants must
take additional steps against online fraud. Credit card associations can impose stiff penalties
for fraud – expenses on top of stolen goods and related shipping costs.
Moreover, American Express, Diners Club, Discover Card, JCB, MasterCard International and
Visa U.S.A. have adopted the Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard developed
to protect account and transaction information of cardholders. The PCI standard requires
merchants to adhere to a set of information security requirements or risk substantial fines.
Security must therefore be a key concern.
Liability for Internet Fraud
In the offline world, you can take steps to safeguard your transactions by getting a signature
and authorization, thereby shifting the liability of the transaction to the card issuer. In the
online world, the liability for a fraudulent transaction always rests squarely with the merchant.
Online transactions are considered card-not-present transactions and are inherently riskier. The
financial consequences for a merchant who processes a fraudulent online transaction can be
significant:
z Inventory loss and shipping costs for physical goods that are fraudulently purchased and
then delivered
z Chargeback penalties assessed by the acquiring bank of $15-$30 USD per fraudulent
transaction
According to Gartner Group estimates, merchants reject an estimated 5% of all transactions
out of suspicion of fraud, while only 2% of transactions are actually fraudulent. The result is a
significant amount of lost sales (up to 3% of sales volume) in an attempt to reduce fraud risk.
In addition to losing product and paying chargeback penalties, your business also faces costs
due to fraud:
z Higher discount rates assessed as a result of processing fraudulent payments
z Labor cost for the merchant to investigate and resolve the chargeback
z Five- to six-figure card association fines or cancellation of a merchant’s account when card
fraud rates are consistently high
Implementing better tools and raising awareness can help you reduce lost revenue by turning
away fewer legitimate customers who seem suspicious. You can also resolve chargebacks
24 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 25

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
Internet Fraud: What It Is and How It Happens
more quickly, thus saving time and money. In some cases, online merchants have reduced their
chargeback rate from 7% to 2%.
Internet Fraud: What It Is and How It Happens
All internet payment fraud is based on stolen consumer or merchant identities. It also requires
access to payment networks to complete the fraud. The result is product theft, identity theft,
and cash theft.
z Product Theft: Occurs when a criminal uses stolen credit card information to purchase
goods and services.
z Identity Theft: Occurs when stolen credit card information is combined with readily
available social security numbers and address information to open new credit cards under
the victim’s name and address.
z Cash Theft: Occurs when criminals break into a virtual cash register by stealing merchant
account access information and impersonating you in order to issue credits or payments to
themselves.
2
Fortunately, there are ways to protect against fraud. The most important thing you can do is
choose a reliable and secure payment solution that includes basic and advanced antifraud
features. Here are some of the most common fraud-related risks facing online merchants:
Consumer Identity Theft
Criminals steal consumer credit card information through a variety of methods, including
dumpster diving for paper receipts, hacking into e-commerce networks, or using handheld
“skimmers” to digitally scan numbers from credit cards of unsuspecting people at restaurants
or cash registers. Phishers, meanwhile, will send fraudulent emails to consumers warning, for
instance, of a problem with a credit card account in an attempt to trick the person to provide
personal information. Once they’ve obtained the credit card information, these criminals can
use it to steal products outright or open other accounts by impersonating the victim.
Merchant Identity Theft
Just as offline criminals can break into a cash register, online criminals can hack into the
accounts of web merchants and funnel money to themselves. These criminals might be
employees or visitors to a building who copy unprotected login information. They then can use
the information to hack into a back-end system to hijack a merchant’s payment gateway
account, which provides the secure connection between your online store and your internet
merchant account. Through this move, they can steal cash directly from the business by
issuing themselves credit cards and payments.
Accessing Payment Networks
Once criminals have stolen an identity, they may access a payment network to complete the
fraud. Most do this through two primary channels: a web merchant’s checkout page or a
payment gateway account. Although a checkout page provides convenience for both buyer and
seller, it can raise some security concerns. For example, some criminals use the page to test
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 25
Page 26

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
Who Is at Risk for Online Fraud
stolen credit cards. For the merchant, it is crucial to use products with built-in fraud protection
to prevent this sort of digital theft.
Chargebacks
Chargebacks occur when a cardholder disputes a credit card purchase. During such disputes,
the card-issuing bank initiates a chargeback against the merchant, retrieving the funds for the
sale from the merchant’s bank account. The bank initiating the chargeback is not required to
notify the merchant or the merchant bank. Proving that the disputed transaction was legitimate
can cost merchants significant time and resources, so keeping chargebacks to a minimum is
essential. Chargebacks can hurt a merchant’s bottom line by lowering its credit rating,
diverting resources to resolve the dispute, and siphoning revenue from lost goods and shipping
costs. The most common type of chargeback occurs when the customer:
z Did not receive the item ordered
z Did not receive the item believed to be ordered
z Had his or her credit card stolen and used by the thief
z Stole merchandise or services through the fraudulent use of a chargeback
Who Is at Risk for Online Fraud
Fraud can happen to any merchant at any time, and a single fraud incident can be enough to
put a merchant out of business. That said, some merchants are at greater risk for certain types
of fraud than others. PayPal has put together the following quick reference to identify some of
the higher-than-average risk categories.
TABLE 2.1 High Fraud Risk Quick Reference
Merchant Type Potential Risk
Merchants with vulnerable security defenses Criminals take advantage of sophisticated spidering techniques to
identify merchants with network vulnerabilities, and can then
break into your network to steal account access information for
hijacking or merchant takeovers.
High-visibility merchants Fraud attempts are higher for merchants who advertise heavily or
are in the news because criminals know that merchants who
experience high transaction volumes have less time to defend
against fraud.
Products/Services Sold Potential Risk
High-ticket physical goods that are easily
resold
These items, including luxury goods, computers, and other
electronic equipment, are most attractive to criminals.
Goods that can be downloaded from the
internet
26 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
The purchase of these goods doesn’t require physical address
information, making it easier for criminals to disguise a
fraudulent transaction.
Page 27

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
Reducing Exposure to Fraud
T
ABLE 2.1 High Fraud Risk Quick Reference
Customer Base Potential Risk
International It is difficult to validate the address or identity of foreign buyers,
and it is more difficult to investigate and prosecute fraudulent
activity from an overseas source.
Sales Season Potential Risk
Heavy proportion of fourth quarter sales Criminals know that you have limited time for fraud protection
when sales volumes are high. That’s why internet fraud triples in
the fourth quarter.
Special promotions Criminals watch for special offers. They know that you have
limited time for fraud protection measures when sales volumes
are high.
Reducing Exposure to Fraud
2
It is possible to significantly reduce your exposure to fraud. There are essentially three levels
of exposure to fraud on the internet: the individual transactions, the payment gateway account,
and the merchant network. Protecting your business from fraud requires that you address each
of these levels in an integrated manner.
Transaction Level
Ensure that each transaction you accept and process is valid. You should also be careful not to
deny suspicious transactions that are actually valid.
Authenticate buyers when possible. This includes understanding who your repeat
customers are and keeping lists of repeat customers who have legitimately transacted on your
site. Make sure all customer information is encrypted and stored safely. Also, take advantage
of MasterCard® and Visa® buyer authentication programs to authenticate customers and
reduce your liability.
Screen orders for fraud patterns. There is a wealth of information associated with each
transaction that can help you understand the risk level. To effectively manage all the risk
information associated with a transaction, it is important to use a rules engine. A rules engine
automates the process of transaction screening so that you quickly fulfill orders for good
customers and proactively block risky orders. PayPal Fraud Protection Services allows you to
cost-effectively deploy a rules engine as well as benefit from PayPal’s continuously updated
lists of high-risk indicators.
Review suspicious transactions. Finally, review each transaction that is suspicious to make
sure you are doing business with a legitimate customer. Online merchants today reject 5% of
all transactions because they do not have the time or information to determine whether a
suspicious transaction is actually a good one. PayPal Fraud Protection Services allows you to
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 27
Page 28

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
What Banks and Card Associations Are Doing to Prevent Online Credit Card Fraud
automatically and continuously review only the suspicious orders, before you process them,
allowing time to make an informed decision.
Account Level
Make sure that only authorized users have access to your payment gateway account, and be
alert for suspicious account access patterns.
Lock down administrative access. With PayPal Fraud Protection Services, you can limit
access to high-risk administrative transactions, such as issuing credits. You should also change
your account password on a regular basis.
Monitor account level activity for suspicious patterns. Watch your account for signs of
unauthorized access, which could indicate merchant account takeover. Account Monitoring
from PayPal offers affordable, customized, live account monitoring staffed by experienced
fraud professionals. The service can help you catch account takeover before it does any
damage, whether the takeover is due to a hacker or fraudulent employee usage of your service.
Network Level
Ensure your network or “perimeter” is defended against unauthorized access.
Lock down network access. With PayPal Manager, you can ensure that only IP addresses
you select have access to your network.
Update all patches on servers and operating systems. Invest in regularly scheduled
security audits or port scans to identify network vulnerabilities. PayPal Fraud Protection
Services offers a free network scan from Qualys, included with every Basic or Advanced
PayPal Fraud Protection Service.
Monitor firewall activity. Enterprise e-commerce companies should also monitor their
network’s perimeter security on a 24-hour basis.
What Banks and Card Associations Are Doing to Prevent Online
Credit Card Fraud
Consumers shop online for convenience and speed, but historical authentication requirements
have often proved to be cumbersome, time-consuming, and ineffective.
New buyer authentication programs, such as MasterCard® SecureCode, and Verified by
Visa®, provide more streamlined and customer-friendly authentication through passwords.
These programs enable you to gain liability protection by prompting consumers to provide a
password with their card issuers at checkout, similar to providing a PIN number for ATM
transactions. Transactions in which consumers authenticate themselves to issuers effectively
shift liability from the merchant to the issuer. Merchants are not held liable for fraudulent
transactions processed using buyer authentication.
PayPal’s suite of Fraud Protection Services makes it easy for you to take advantage of this
powerful system. (Check with your internet merchant account provider directly to determine if
28 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 29

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
What PayPal Is Doing to Protect Your Business Against Fraud
they have deployed buyer authentication.) Through Fraud Protection Services, one seamless
integration gives you access to both Verified by Visa and MasterCard SecureCode with your
PayPal gateway service.
What PayPal Is Doing to Protect Your Business Against Fraud
The security of your information, transactions, and money is the core of our business and our
top priority at PayPal. We help you protect against fraud, so you can grow your business and
minimize losses.
PayPal leverages the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol, which provides crucial online
identity and security to help establish trust between parties involved in e-commerce
transactions. Customers can be assured that the website they’re communicating with is
genuine and that the information they send through web browsers stays private and
confidential.
Moreover, using SSL with an encryption key length of 128 bits (the highest level
commercially available), PayPal automatically encrypts your confidential information in
transit from your computer to ours. Once your information reaches us, it resides on a server
that is heavily guarded both physically and electronically. Our servers sit behind a monitored
electronic firewall and are not connected directly to the internet, so your private information is
available only to authorized computers.
2
How to Reduce Chargebacks
Dealing effectively with customer issues is a great way to minimize risk and reduce
chargebacks. By communicating clearly and keeping good records, you can avoid many
potential problems today, which are much easier than trying to resolve them with a credit card
company tomorrow. PayPal has developed these helpful tips for avoiding customer complaints
that can lead to chargebacks:
z Provide realistic delivery time estimates and use tracking that shows proof that the items
were received
z Describe the sale item in as much detail as possible. Include clear images and
measurements so that customers have a good understanding of what they’re getting.
z Make sure you clearly disclose the total cost to customers up front: the price, taxes,
shipping costs, etc.
z Provide customers with a way to contact you should they have a problem. Often a simple
email exchange or phone call clears up a misunderstanding instantly.
z Respond promptly and courteously to customer inquiries.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 29
Page 30

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
Disclosure and Compliance
Disclosure and Compliance
Disclosure Policy
Your disclosure policy tells your customers that you’re honest and dependable and that you
care about them and protecting their information. It shows your customers that you believe in
transparency and accountability. It provides a framework and standards for your business
policies, how you deal with your customer information, and how you communicate with your
customers.
Your disclosure policy typically includes five things: a business description, privacy policy,
shipping policy, return policy, and contact information. The more your customers know about
you, the more comfortable they’ll be giving you their business. So be honest, open, direct, and
precise. Here are more details about the five areas you should cover:
1. Business description. Write a clear description of what your company does, including
what products and services it provides. Post it in a prominent place on your website, often
the “About Us” section.
2. Privacy policy. Your privacy policy should clearly state how you treat and protect your
customers’ information. It’s essential that your policy is easy to find on your website,
usually linked from your homepage. Typical elements of a privacy policy include:
– What personally identifiable customer information you collect
– How the information is used
– With whom you share and do not share this information
– What choices are available to your customers regarding collection, use, and distribution
of the information
– What choices are available to your customers regarding communications from you –
email, direct mail, etc.
– The kind of security procedures in place to protect the loss, misuse, or alteration of
information under your control
– How your customers can correct any inaccuracies in the information
3. Shipping policy. You’ve made the sale. Your customers are anxious to get their purchases.
So keep that excitement and positive momentum going with a shipping policy that’s simple
and straightforward:
– Spell out your shipping terms in detail, disclosing if costs are determined by weight or
the amount of the purchase
– Indicate the classes of shipping you offer - ground, express, overnight, etc.
– Indicate if you ship to APO, FPO, and international addresses
– Tell your customers in what timeframe they can expect their purchase
– Show your customers how they can track their shipment. (Your shippers should be able
to provide most of this information for you.)
30 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 31

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
Disclosure and Compliance
4. Return policy. Your customers love simplicity and forgiveness. They sometimes make
mistakes and order the wrong products. They may be unfamiliar with what they are
ordering, and it’s not what they had in mind. By allowing your customers to return an item
in a timely fashion, and making it easy to do so, you are gaining their loyalty. A clear return
policy also comes in handy if the order arrives damaged. So make it easy for them to
initiate returns:
– Spell out exactly what your return policy is, for example that you accept returns only as
exchanges or you accept returns and will credit their payment card
– Be specific about how many days after purchase the item can be returned in order to get
a credit or exchange
– Let them know if you charge a restocking fee on returns
– Include a return shipping label with every order
– Provide clear return instructions, such as asking for a reason for the return and a
telephone number in case you have questions
– Provide guidance on how to pack the return and where they should bring it to ship it back
to you
– Include your customer service number or email address in case customers have questions
or comments.
2
5. Contact information. Keep the channels of communication open. Make it easy for your
customers to get in touch with you:
– Give examples of reasons they may want to contact you, for example questions about
privacy policy, return policy, availability of goods, etc.
– Provide a phone number, and give the days and hours the phone lines are answered
– Provide an email address, and give a timeframe when an answer can be expected
– Provide a mailing address, and suggest to whose attention it should be addressed
PCI Data Security Standard Compliance
Just as a disclosure policy describes your business and states your business practices, your
compliance with the PCI Data Security Standard communicates how much you care about
your customers and reinforces an atmosphere of safety for all online merchants.
Consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the dangers of identity theft due to
compromised data and stolen credit card information. PCI compliance assures your customers
that you’re looking out for their safety and well-being. Approach it with that in mind, and you
transform compliance into a competitive edge and asset instead of a dreaded “must do.”
Today, virtually all major credit card companies, including American Express®, Diners
Club®, Discover® Card, JCB®, MasterCard International®, and Visa® U.S.A., require
merchants and service providers to comply with the PCI standard. When you process credit
card transactions through a merchant account, you also need to meet PCI validation
requirements, including quarterly and annual audits, security self-assessments, and security
scans. Your exact validation requirements are determined by your volume of credit card
transactions.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 31
Page 32

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
Disclosure and Compliance
While validating that you’re in compliance with the PCI standard is a requirement, it’s also an
opportunity. Finding and fixing compliance gaps before your audit keeps your company
running smoothly and your reputation intact. It provides you with tangible proof that you can
communicate to your customers on how well you’re protecting them.
The quickest and easiest way to meet PCI compliance standards is to outsource the job. A
number of PayPal payment solutions are hosted, relieving the online merchant of the
compliance responsibility. The PayPal Gateway payment solution, which allows the merchant
to handle credit data, does require compliance and validation by the merchants themselves.
TABLE 2.2 PCI Data Security Standard
Standards Requirements
Build and Maintain a Secure Network 1. Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect data.
2. Do not use vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords
and other security parameters.
Protect Cardholder Data 3. Protect stored data.
4. Encrypt transmission of cardholder data and sensitive
information across public networks.
Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program 5. Use and regularly update antivirus software.
6. Develop and maintain secure systems and applications.
Implement Strong-Access Control Measures 7. Restrict access to data by business need-to-know.
8. Assign a unique ID to each person with computer access.
9. Restrict physical access to cardholder data.
Regularly Monitor and Test Networks 10. Track and monitor all access to network resources and
cardholder data.
11. Regularly test security systems and processes.
Maintain an Information Security Policy 12. Maintain a policy that addresses information security.
The compliance level of each merchant is the responsibility of the merchant’s acquiring bank
(a bank that provides credit card merchant accounts and is responsible for submitting credit
card purchase information to the credit card associations). The four merchant levels are based
on annual credit card transaction volume.
T
ABLE 2.3 Merchant Levels for PCI Compliance
Level Description
Level 1 Any merchant – regardless of acceptance channel – processing over 6 million credit card
transactions per year.
Any merchant that has suffered a hack or an attack that resulted in an account data compromise.
Any merchant identified by any card association as Level 1.
Level 2 Any merchant processing 150,000 to 6 million e-commerce transactions per year.
Level 3 Any merchant processing 20,000 to 150,000 e-commerce transactions per year.
32 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 33

T
ABLE 2.3 Merchant Levels for PCI Compliance
Level Description
Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
Disclosure and Compliance
2
Level 4
Any merchant processing fewer than 20,000 e-commerce transactions per year, and all other
merchants processing up to 6,000,000 credit card transactions per year.
In addition to adhering to the PCI Data Security Standard, compliance validation is required
for Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 merchants, and may be required for Level 4 merchants.
ABLE 2.4 PCI Compliance Validation Requirements
T
Level Validation Action Validated By
Level 1 Annual Onsite PCI Data Security Assessment
and
Quarterly Network Scan
Level 2 and 3 Annual PCI Self-Assessment Questionnaire
and
Quarterly Network Scan
Level 4
Annual PCI Self-Assessment Questionnaire
and
Quarterly Network Scan
N OTE: Level 4 merchants must comply with the PCI Data Security Standard. However,
Qualified Data Security Company or Internal
Audit if signed by Officer of the company
Qualified Independent Scan Vendor
Merchant
Qualified Independent Scan Vendor
Merchant
Qualified Independent Scan Vendor
compliance validation for merchants in this category is determined by the merchant’s
acquirer.
Additional Resources About Disclosure and Compliance
There are other online resources that can help you in developing your own disclosure policy
and meeting PCI compliance requirements. They include:
z The Privacy Planner from BBBOnLine helps you create a simple, solid, online privacy
policy for your e-commerce business: http://www.privacyplanner.com.
z The Direct Marketing Association (DMA) offers a small businessfriendly online privacy
policy generator: http://www.the-dma.org/privacy/privacypolicygenerator.shtml.
z The Federal Trade Commission offers valuable information on preventing identity theft at
http://www.consumer.gov/idtheft/. Also be sure to visit the central FTC site at
http://www.ftc.gov/ for additional information and advice.
z Both the Visa and MasterCard websites have extensive information about meeting PCI
Payment Data Security Standards: http://www.visa.com and http://www.mastercard.com.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 33
Page 34

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
PayPal Fraud Protection Services
PayPal Fraud Protection Services
Protecting your business against the consequences of even a single fraud attempt requires a
significant time commitment and ties up valuable resources. PayPal has designed its suite of
Fraud Protection Services based on merchant feedback and the needs of the online business
community. Our solution not only gives you added protection against credit card fraud, cash
fraud, and hacking attempts, but it also allows you to manage all these features quickly and
easily with a single, intuitive interface.
Each PayPal Payflow Gateway solution includes standard antifraud features:
z Card security code. A three- or four-digit number printed on the physical card, which a
customer provides to you at checkout.
z Address verification system (AVS). A system that verifies the credit card holder’s
personal address and billing information.
Each Fraud Protection service also offers a Buyer Authentication upgrade option that
seamlessly integrates an advanced antifraud feature that allows credit card holders to submit a
special password directly to their card-issuing bank during a transaction. Buyer Authentication
provides essential merchant liability protection against fraudulent credit card transactions.
TABLE 2.5 Fraud Protection Services Purchase Options
Service Merchant Type Key Benefits
Package Options
Basic Designed for merchants with low
transaction volume
Advanced Designed for merchants with mid- to
high-level transaction volumes
Upgrade Options
Account Monitoring All merchants Account activity monitoring seven days a
Buyer Authentication All merchants Card association liability protection for
Maximum ease and convenience
Maximum customization and protection
week
authenticated shoppers
Detailed Service Descriptions
Basic Fraud Protection Service
Basic Fraud Protection Service is the ideal solution for merchants who process low transaction
volumes through a Payflow payment gateway. It offers industry-leading security technology at
an affordable price and lets your business:
z Maximize liability protection. Meet credit card company standards for address
verification and card security codes.
34 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 35

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
PayPal Fraud Protection Services
z Reduce chargeback costs. Automatically reject or flag transactions that you deem
suspicious.
z Get started fast. Quickly set up and manage your security system with easy-to-use tools.
Basic Fraud Protection Service works by using:
z Filters. Quickly set up filters that you can customize to fit your business needs.
z Online reports. Easily review and then accept or reject online orders.
z Monitoring. Standard reports let you check on filter and their effects.
Advanced Fraud Protection Service
Advanced Fraud Protection Service is essential for businesses processing medium-to-high
transaction volumes, handling international customers, or selling high-risk merchandise
through a Payflow payment gateway. It is a flexible security solution that helps your business:
z Avoid losses. Special tools flag unusual orders, questionable addresses, high-risk
payments, and international orders.
z Lower costs. Spend less money on fraud management by automating order reviews and
tailoring the system to meet your needs.
2
Advanced Fraud Protection Service works by using:
z Enhanced filters. Supplement the basic filters with ones specially suited for your high-risk
needs.
z Online reports. Easily accept or reject online orders with the added security benefit of
audit reports.
z Watch lists. Create custom lists based on products or other criteria.
z Trusted transaction lists. Establish lists that accept or deny transactions based on bad
emails or credit cards.
z Full testing. Test your system before going live to determine its effect on your business
and customers.
TABLE 2.6 Comparison of Fraud Protection Services
Features
PayPal Fraud Manager
Take control: find suspicious transactions with transaction review module,
resolve chargebacks using audit trails, and tune filters to your business needs.
Unusual Order Filters
Catch common fraud warnings like high dollar amounts, high quantities, and
shipping/billing address mismatch.
Basic
Protection
Advanced
Protection
XX
XX
High-Risk Payment Filters
XX
Catch suspicious transactions like rapid repeat buying from an internet address.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 35
Page 36

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
PayPal Fraud Protection Services
ABLE 2.6 Comparison of Fraud Protection Services
T
Features
High-Risk Address Filters
Check for suspect zip codes and freight forwarders plus IP address.
Automatic Rejection Lists
Help protect you business from known offenders.
Automatic Acceptance Lists
Keep good customers buying by automatically accepting their payments.
High-Risk International Filters
Identify risky international payments.
Additional Risk Filters
Get more tools to catch warning signs like rapid card use, risky banks, and
tighter address validations.
Custom Filter Wizard
Customize new rules that match your specific business needs.
Operations Security
Identify vulnerabilities and list fixes with a security audit from Qualys.
Basic
Protection
XX
XX
Advanced
Protection
X
X
X
X
X
PayPal Fraud Protection Services Upgrade Options
Account Monitoring
The Account Monitoring service uses trained security professionals who constantly monitor
your business for suspicious activities and take action to protect it. Account Monitoring
provides:
z Security. Our full-time protection keeps an eye on suspicious activity related to credits and
refunds.
z Assistance. Our security professionals help prevent fraud by blocking settlements of
suspicious transactions. If loss occurs, we work with law enforcement and your bank to
assist in recovery.
z Prevention. We give customized recommendations to avoid future fraud.
z Ease of use. No lengthy set-up or configuration process.
Buyer Authentication
Buyer Authentication provides the Verified by Visa and MasterCard SecureCode. By adding
Buyer Authentication to your Basic or Advanced Fraud Protection Service, your business
receives merchant liability protection on qualified credit card transactions. Buyer
Authentication gives you:
z Single pre-integrated solution. Add Buyer Authentication and take full advantage of both
services without wasting staff and infrastructure resources integrating them yourself.
36 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 37

z Extra security measure. At checkout, customers are required to enter a password to verify
their identity with their credit card company.
z Maximum protection. Once the cardholder’s password is authenticated, Visa and
MasterCard cover the merchant’s liability for that transaction.
Review Questions
Answers to review questions are in Appendix A, “Answers to Review Questions.”
1. Indicate if each statement is True (T) or False (F).
_____ Every merchant is at risk for fraud.
_____ Internet fraud is as easy to detect as in the brick-and-mortar world.
_____ Credit card associations hold merchants liable for fraudulent transactions because
the credit card is not physically present during online purchases.
_____ American Express, Diners Club, Discover Card, JCB, MasterCard International, and
Visa U.S.A. have adopted the Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard
developed to protect account and transaction information of cardholders.
_____ According to Gartner Group estimates, merchants reject an estimated 2% of all
transactions out of suspicion of fraud, while in reality, 5% of transactions are
actually fraudulent.
Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
Review Questions
2
2. List the four most common fraud-related risks facing online merchants.
– ______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 37
Page 38

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
Review Questions
3. Match each participant in the payment processing network to the role they perform.
Response Risk Category Potential Risk Description
Merchants with vulnerable security
defenses
High-visibility merchants 2. It is difficult to validate the address or identity of
High-ticket goods that are easily
resold
Goods that can be downloaded from
the internet
International customer base 5. Criminals watch for special offers. They know that
Heavy proportion of fourth quarter
sales
1. Fraud attempts are higher for merchants who
advertise heavily or are in the news because
criminals know that merchants who experience high
transaction volumes have less time to defend against
fraud.
foreign buyers, and it is more difficult to investigate
and prosecute fraudulent activity from an overseas
source.
3. These items, including luxury goods, computers, and
other electronic equipment, are most attractive to
criminals.
4. Criminals know that you have limited time for fraud
protection when sales volumes are high. That’s why
internet fraud triples in the fourth quarter.
you have limited time for fraud protection measures
when sales volumes are high.
6. The purchase of these goods doesn’t require physical
address information, making it easier for criminals
to disguise a fraudulent transaction.
Special promotions 7. Criminals take advantage of sophisticated spidering
techniques to identify merchants with network
vulnerabilities, and can then break into your network
to steal account access information for hijacking or
merchant takeovers.
4. List two actions you can take to ensure that each transaction your website accepts and
processes is valid.
– ______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
38 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 39

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
Review Questions
5. Fill in the blanks to complete the following statements.
PayPal leverages the ____________________, which provides crucial online identity and
security to help establish trust between parties involved in e-commerce transactions.
Using SSL with an encryption key length of ____________________ (the highest level
commercially available), PayPal automatically encrypts your confidential information in
transit from your computer to ours.
PayPal’s servers sit behind a monitored ____________________ and are not connected
directly to the internet, so your private information is available only to authorized
computers.
6. List three ways to reduce chargebacks.
– ______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
2
______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
7. List the five areas you should cover in your website disclosure policy.
– ______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
– ______________________________________________________________________
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 39
Page 40

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
Review Questions
8. The left column in the table lists the PCI data security standards. The right column contains
a list of requirements. Indicate which requirements meet each standard. (Note: Each
standard has one or more requirements.)
Response Standards Requirements
Build and Maintain a Secure Network 1. Restrict physical access to cardholder data.
2. Regularly test security systems and processes.
Protect Cardholder Data
Maintain a Vulnerability
Management Program
Implement Strong-Access Control
Measures
Regularly Monitor and Test Networks
Maintain an Information Security
Policy
3. Develop and maintain secure systems and
4. Encrypt transmission of cardholder data and
5. Protect stored data.
6. Assign a unique ID to each person with computer
7. Use and regularly update antivirus software.
8. Do not use vendor-supplied defaults for system
9. Track and monitor all access to network resources
10. Maintain a policy that addresses information
11. Install and maintain a firewall configuration to
12. Restrict access to data by business need-to-know.
applications.
sensitive information across public networks.
access.
passwords and other security parameters.
and cardholder data.
security.
protect data.
9. Define the following standard antifraud features included with each PayPal Payflow
Gateway solution.
– Card security code
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
– Address verification system (AVS).
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
40 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 41

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
Review Questions
10.Indicate if each statement is True (T) or False (F).
_____ PayPal’s Basic Fraud Protection Service is the ideal solution for merchants who
process low transaction volumes through a Payflow payment gateway, while the
Advanced Fraud Protection Service is essential for businesses processing mediumto-high transaction volumes.
_____ Both the Basic Fraud Protection Service and the Advanced Fraud Protection Service
catch common fraud warnings like high dollar amounts, high quantities, and
shipping/billing address mismatch.
_____ To support automatic rejection lists and automatic acceptance lists, you need to
upgrade to PayPal’s Advanced Fraud Protection Service.
_____ The PayPal Basic Fraud Protection Service provides full-time protection to keep an
eye on suspicious activity related to credits and refunds.
2
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 41
Page 42

Internet Security and Fraud Prevention
2
Review Questions
42 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 43

Getting Started With Account
3
Setup
In this chapter, you will learn about:
z Steps for getting started with PayPal payment processing solutions
z Enrolling with PayPal services
z The PayPal Sandbox including how to get access to the Sandbox
Basic Steps for Getting Started
In three steps, you can acquire everything you need to begin accepting online purchases.
1. Choose payment processing services.
– Website Payments Pro
– Website Payments Standard
–Payflow Pro
–Payflow Link
– Email Payments
– Virtual Terminal
2. Set up an internet merchant account, if you don’t already have one.
All online businesses need to operate with an internet merchant account, primarily for
depositing and refunding online payments. Website Payments Pro and Standard feature an
integrated internet merchant account and gateway to make it quick and easy for you to
begin doing business online.
If you register for either Payflow Pro or Payflow Link and already have an internet
merchant account, PayPal will provide you the option to apply for an internet merchant
account with PayPal’s preferred merchant account provider.
To set up an internet merchant account, go to:
bin/webscr?cmd=_registration-run. Have the following information available:
– Account/business owner's name, address, and email
– Business name and address
– Customer service information
Allow up to three to five business days to complete the setup and approval.
https://www.paypal.com/cgi-
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 43
Page 44

Getting Started With Account Setup
3
PayPal Sandbox
3. Enroll in the selected PayPal services.
A merchant must enroll for each service they plan to use. Once you have a merchant
internet account, you can sign up for each service individually. To apply for Website
Payments Pro, follow these steps:
– Go to: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_wp-pro-overview-outside
– At the bottom of the page, click Apply for Website Payments Pro.
– When prompted, sign in using your Email Address and PayPal Password.
– Complete the steps to enroll with Website Payments Pro. You will submit an application
that includes business information and your social security number or employer
identification number and accept the billing agreement.
4. Use the PayPal APIs to implement payment processing on the merchant website.
You should carefully design and plan each merchant website implementation and feature.
Work with the website owner to define the application requirements and ensure that your
application complies with PayPal standards. This guide describes PayPal standards as they
apply to each component of a merchant application.
5. Customize your payment processing service with additional services.
.
Protect the business and customers from fraud:
– Fraud Protection Services. From simple automated credit card fraud screening to
enterprise-grade perimeter security services, PayPal can save you time and money while
protecting your business.
– Express Checkout. Provides your customers with a secure and convenient payment
flow because they don’t have to re-enter information already stored in their PayPal
account.
Accept repeat payments from customers:
– Recurring Billing Service. A fast, cost-effective way to accept repeat payments for
installment plans, monthly fees, or subscription-based services.
Offer customers an alternative to credit card payments. Providing customers with a variety
of payment choices, including credit cards and PayPal, has been shown in several industry
studies to contribute to an increase in revenue.
For More Information. For additional PayPal product and pricing information, call 1-888-
847-2747, send an email to paymentsales@paypal.com
section of the PayPal website at www.paypal.com
PayPal Sandbox
, or visit the PayPal Merchant Services
.
The PayPal Sandbox is a self-contained environment in which developers can prototype and
test PayPal applications. Before moving any PayPal-based application into production, test the
application in the Sandbox to ensure that it functions properly.
For details about the Sandbox, see Chapter 9, “Sandbox Testing”.
44 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 45

Review Question
Answers to review questions are in Appendix A, “Answers to Review Questions”.
1. The following steps describe the getting started with account setup process. Indicate the
correct order of the steps by placing the step number to the left of each description.
_____ Set up an internet merchant account, if you don’t already have one.
_____ Customize your payment processing service with additional services.
_____ Choose payment processing services.
_____ Use the PayPal APIs to implement payment processing on the merchant website.
_____ Enroll in the selected PayPal services.
2. What information do you need to set up an internet merchant account?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
Getting Started With Account Setup
Review Question
3
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
3. How many days should you allow to set up an internet merchant account?
______________________________________________________________________
4. Match each PayPal service that provides fraud protection to its description.
Response PayPal Product Service Description
Fraud Protection Services 1. Provides your customers with a secure and
convenient payment flow because they don’t have to
re-enter information already stored in their PayPal
account.
Express Checkout 2. A fast, cost-effective way to accept repeat payments
for installment plans, monthly fees, or subscriptionbased services.
Recurring Billing Service 3. Provides simple automated credit card fraud
screening to enterprise-grade perimeter security
services to save you time and money while
protecting your business.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 45
Page 46

Getting Started With Account Setup
3
Review Question
5. What is the purpose of the PayPal Sandbox?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
46 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 47

API Credentials
4
In this chapter, you will learn:
z What API credentials are
z How to establish API credentials
z How to use API credentials
What API Credentials Are
Before using the PayPal API to communicate with the API server, a developer must establish a
set of API credentials, which is data that uniquely identifies a developer to the PayPal API
server. The credentials are included with each API call. Credentials are needed per merchant
account for processing.
API credentials comprise the following:
z API username — This is assigned by PayPal. Although the API username is based on the
email address used to set up the credentials, it is not the same as the email address used to
log in to the PayPal website.
z API password — This is automatically generated and assigned by PayPal. It is a randomly
generated string of 16 characters.
z API certificate or API signature — An API signature is an encrypted string value
included with each API call. An API certificate is a file (downloaded from PayPal) that
includes a key and certificate that identify a developer. An API certificate must be installed
on a web server; therefore, it is an option only if the developer has full control of the web
server.
Choosing an Authentication Method
Each authentication method (API signature and API certificate) has pros and cons. An API
signature is easier and quicker to implement. An API certificate offers greater security.
PayPal recommends the use of an API signature, because of its greater simplicity; however,
the PayPal API performs equally well with API signatures or API certificates.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 47
Page 48

API Credentials
4
Establishing API Credentials
Establishing API Credentials
The two authentication methods have separate processes for establishing API credentials.
API Signature
To establish credentials using an API signature as the authentication method, follow these
steps:
1. Log in to a PayPal Premier or Business account.
2. In the top navigation area, click the Profile subtab.
3. Under the Account Information header, click the API Access link.
4. Click Request API Credentials.
5. Under Credential Type, click the API Signature radio button.
6. Click the agreement checkbox, and click Submit.
7. Record the API username and API password values.
8. The API signature is the Signature Hash value. Record this value, and store it in a
document in a secure location.
The developer must take the appropriate steps to protect the API signature values; these values
should be stored in a secure location on the web server.
To use the Sandbox to test an application, register a separate set of API credentials and use a
second API signature. The same API signature cannot be used for both the Sandbox and live
servers.
API Certificate
To establish credentials using an API certificate, follow these steps:
1. Generate the API certificate.
2. Encrypt the API certificate.
3. Install the API certificate in the Windows Certificate Store.
These steps are required regardless of whether the API certificate will be used with the PayPal
Sandbox or with live PayPal. Each step is detailed below.
48 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 49

API Credentials
Establishing API Credentials
Generate the API Certificate
1. Log in to a PayPal Premier or Business account.
2. In the top navigation area, click the Profile subtab.
3. Under the Account Information header, click the API Access link.
4. Click the Request API Credentials link.
5. Complete the request form by clicking the agreement checkbox and clicking Submit.
6. Save the values for API Username and API Password.
7. Click the Download Certificate button. A file named cert_key_pem.txt is
downloaded; this is the live API certificate.
8. Rename the file to something more meaningful, such as paypal_live_cert.pem (it is
not necessary to keep the .txt suffix). This will differentiate a live API certificate from
one used in the PayPal Sandbox.
Encrypt the API Certificate
4
N OTE: This step is required only with the PayPal SDK for Java, .NET, or Classic ASP.
1. Install the OpenSSL encryption tool on the system where the encryption will be performed.
Make sure to include OpenSSL in the system’s PATH variable.
2. Open a command prompt.
3. Go to the directory that contains the certificate to be encrypted.
4. Execute the following command:
openssl pkcs12 -export -in cert_key_pem.txt -inkey certificateName
-out paypal_cert.p1
where certificateName is the name of the API certificate to be encrypted.
5. When prompted, enter an encryption password. This is the Private Key Password.
6. The encryption creates a file named paypal_cert.p12. Rename this file to something
more meaningful, and note the file location. This is the encrypted API certificate.
Install the API Certificate
N OTE: This step is required only with the PayPal SDK for .NET or Classic ASP.
To use the API certificate with the .NET platform, the certificate must be imported into the
Windows Certificate Store. This is a Windows requirement, not a PayPal requirement.
To import the API certificate into the Windows Certificate Store, use the Windows HTTP
Services Certificate Configuration Tool, or WinHttpCertCfg.exe. This tool is freely
available as part of the Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 49
Page 50

API Credentials
4
Using API Credentials
To import the API certificate, execute the following command at a command prompt:
WinHttpCertCfg -i encryptedCertificateName -p privateKeyPassword
-c LOCAL_MACHINE\my -a username
where:
z encryptedCertificateName is the name of the encrypted API certificate that was generated
with OpenSSL.
z privateKeyPassword is the private key password of the encrypted API certificate.
z username is the name of the user executing the application.
If the API certificate will be used with the PayPal Sandbox, set
Do not use Everyone with a live API certificate, because granting private-key access to all
users on the server is not secure.
For an ASP.NET application, this value is ASPNET.
Under Windows IIS 5 (default configuration), this value is IWAM_
machineName is the appropriate computer name.
Under Windows IIS 6 (default configuration), this value is "NETWORK SERVICE"
(including the quotation marks).
Using API Credentials
Each request to the PayPal server must include a set of required security parameters, shown in
Table 4. 1.
TABLE 4.1 Required Security Parameters
Parameter Required/Optional Value
USER Required The API username.
PWD Required The API password.
username to Everyone.
machineName, where
VERSION Required The version number of the NVP API service.
As of this printing, this value must be 3.3. Future
versions of the NVP API service will require different
values.
SIGNATURE Optional (only if using
API signature
authentication)
SUBJECT Optional (only if
making a third-party
API call)
50 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
The API signature string.
Do not include this parameter if an API certificate is
being used.
The email address of the PayPal account that has
granted permission to make the API call.
Do not use this parameter for requests that are not thirdparty API calls.
Page 51

IMPORTANT: In the final implementation, protect the values for USER, PWD, and
N OTE: To find the latest version number, go to www.paypal.com/IntegrationCenter.
Review Questions
Answers to review questions are in Appendix A, “Answers to Review Questions.”
1. True or false: API credentials must be included with only the first request sent to the
PayPal server during each session.
2. True or false: The API username is separate from the email address used to access PayPal.
API Credentials
Review Questions
SIGNATURE. The values should be stored in a secure location, with file
permissions set so that only the system user who executes the web
application can access it.
4
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 51
Page 52

API Credentials
4
Review Questions
52 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 53

Name-Value Pair (NVP) API
5
In this chapter, you will learn:
z The basic steps for using the PayPal Name-Value Pair (NVP) API to integrate an
application with PayPal
z How to communicate with the PayPal server using the request/response model and secure
HTTP
Integrating with the PayPal API
The NVP API is a simple, programmatic interface that allows merchants to access the PayPal
API.
The NVP API makes it easy to integrate PayPal with a web. Simply construct an NVP string
and post it to the PayPal server using HTTPS. PayPal posts back a response in NVP format.
To get started with the PayPal NVP API, see the samples at
https://www.paypal.com/IntegrationCenter/ic_nvp.html
send API calls to the PayPal Sandbox test environment. The web samples are documented in
PayPal Name-Value Pair API Developer Guide and Reference.
. An application can use the samples to
Basic Steps
This section describes the basic steps for programming with the NVP API.
Create a Web Application
The NVP API implementation usually runs in a web application. You can write a new
application from scratch or use one of the samples as a starting point.
Get API Credentials
To access the API, API credentials are needed for identification (either an API signature or
API certificate).
For more information on API credentials, see “API Credentials” on page 47.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 53
Page 54

Name-Value Pair (NVP) API
5
Technical Details
Create and Post the Request
Create an NVP request string, and post it to the PayPal server. Add code to the web application
to do the following tasks:
1. Encode the name and value parameters in the request, to ensure the correct transmission of
all characters. This is described in “URL Encoding” on page 55.
2. Construct the NVP API request string, as described in “NVP Format” on page 54 and
“Request Format” on page 56.
3. Post the NVP request to the PayPal server, as described in “Posting Using HTTPS” on
page 58.
Interpret the Response
PayPal processes the request and posts back a response in NVP format. Add code to the web
application to do the following tasks:
1. Decode the name and value parameters in the response.
2. Parse the NVP API response string, as described in “NVP Format” on page 54 and
“Response Format” on page 57.
3. Take appropriate actions based on successful and failed responses.
Technical Details
This section describes details of the technologies used by the NVP API.
Request-Response Model
When using the NVP API, the application posts a request to PayPal, and PayPal returns a
response.
URL Format
The request and response are in URL-encoded format, which is defined by the Worldwide
Web Consortium (W3C). URL is defined as part of the URI specification.
NVP Format
NVP is a way of specifying name-value pairs in a string.
An NVP string conforms to the following guidelines:
54 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 55

Name-Value Pair (NVP) API
Technical Details
z The name is separated from the value by an equals sign (=); for example:
FIRSTNAME=Robert
z Name-value pairs are separated by an ampersand (&); for example:
FIRSTNAME=Robert&MIDDLENAME=Herbert&LASTNAME=Moore
z The NVP string is URL-encoded.
URL Encoding
You must URL encode the values included in each API request. The values in all API
responses are also URL encoded. URL encoding ensures the proper transmission of special
characters, characters that are not allowed in a URL, and characters that have special meaning
in a URL, such as the equal sign and ampersand. For example, notice the following NVP
string:
NAME=Robert Moore&COMPANY=R. H. Moore & Associates
The NVP string is URL-encoded as follows:
NAME=Robert+Moore&COMPANY=R%2E+H%2E+Moore+%26+Associates
Use the methods listed in Tab le 5 .1 to URL-encode or URL-decode NVP strings.
5
TABLE 5.1 URL-Encoding Methods
Encode/
Language
ASP.NET Encode System.Web.HttpUtility.UrlEncode(buffer,
Classic ASP Encode Server.URLEncode
ColdFusion Encode URLEncodedFormatstring [, charset]
Java Encode java.net.URLEncoder.encode
PHP Encode urlencode()
Decode Method
Encoding.Default)
Decode System.Web.HttpUtility.UrlDecode(buffer,
Encoding.Default)
Decode No built-in function
Decode URLDecodeurlEncodedString[, charset]
Decode java.net.URLEncoder.decode
Decode urldecode()
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 55
Page 56

Name-Value Pair (NVP) API
5
Technical Details
Request Format
Each NVP request consists of required and optional parameters and their values. Parameter
names are not case-sensitive. As shown in Tab l e 5. 2 , this document uses UPPERCASE for
parameter names and divides the parameters into required security parameters and body
parameters.
TABLE 5.2 General Format of a Request
Required security
parameters
USER=apiUsername&PWD=apiPassword&SIGNATURE=apiSignature&
SUBJECT=optionalThirdPartyEmailAddress&VERSION=3.3
The following parameters are always required:
z USER
z PWD
z VERSION=3.3
z SIGNATURE
N OTE: In the examples in this and other PayPal documents, the required security parameters
sometimes appear like this:
[requiredSecurityParameters]
Body parameters &METHOD=methodName&otherRequiredAndOptionalParameters
In practice, concatenate all parameter names and URL-encoded values in a single string. After
the METHOD parameter, the parameters can be specified in any order.
Required Security Parameters
The required security parameters are the same as the developer’s PayPal API credentials,
which are described in “API Credentials” on page 47.
API Parameters
The request body must contain the name of the API method in the METHOD parameter. In
addition, each method has required and optional parameters:
METHOD=methodName&requiredAndOptionalParameters
All API methods and their parameters are detailed in PayPal Name-Value Pair API Developer
Guide and Reference.
56 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 57

Response Format
A response from the PayPal servers is a URL-encoded name-value pair string, just like the
request. The general format of the response is described in Table 5 .3.
TABLE 5.3 General Format of a Successful Response
Name-Value Pair (NVP) API
Technical Details
5
Success response
fields
ACK=Success&TIMESTAMP=date/timeOfResponse&CORRELATIONID=
debuggingTokens&VERSION=3.3&BUILD=buildNumber
N OTE: In the examples in this and other PayPal documents, the successful response
header fields sometimes appear like this:
[successResponseFields]
API response fields &NAME1=value1&NAME2=value2...
Each response includes the ACK field. If the ACK field’s value is Success or
SuccessWithWarning, the application should process the API response fields. In a
successful response, the application can ignore all fields up to and including BUILD; the
important fields begin after BUILD.
The possible successful response fields for each method are detailed in the reference
information for the API. How the application handles the fields depends on the particular API
method called (such as filling in a form, updating a database, and so on).
ACK Parameter Values
Table 5. 4 lists the possible values for the ACK parameter.
ABLE 5.4 ACK Parameter Values
T
Type of Response Value
Successful response Success
SuccessWithWarning
Error response Error
Error Responses
If the ACK value is Error, the API response fields are not returned. The general format of an
error response is described in Table 5 . 5.
T
ABLE 5.5 Format of an Error Response
Response
fields on
error
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 57
ACK=Error&TIMESTAMP=date/timeOfResponse&CORRELATIONID=
debuggingToken&VERSION=3.3&BUILD=buildNumber&
L_ERRORCODE0=errorCode&L_SHORTMESSAGE0=shortMessage&
L_LONGMESSAGE0=longMessage&L_SEVERITYCODE0=severityCode
Page 58

Name-Value Pair (NVP) API
5
Review Questions
Multiple errors can be returned. Each set of errors has a different numeric suffix, starting with
0 and incrementing by 1 for each error.
For possible causes of errors and how to correct them, see the error-message reference
information in PayPal Name-Value Pair API Developer Guide and Reference.
Posting Using HTTPS
The web application posts the URL-encoded NVP string over an HTTPS connection to one of
the PayPal API servers. PayPal provides a live server. It also provides a Sandbox server that
allows applications to process transactions in a test environment.
API Servers for API Signature Security
If the application uses an API signature, post requests to one of the following servers:
z Sandbox — https://api-3t.sandbox.paypal.com/nvp
z Live — https://api-3t.paypal.com/nvp
API Servers for API Certificate Security
If the application uses an API certificate, post requests to one of the following servers:
z Sandbox — https://api.sandbox.paypal.com/nvp
z Live — https://api.paypal.com/nvp
Review Questions
Answers to review questions are in Appendix A, “Answers to Review Questions.”
1. What character is used to separate name/value pairs in an NVP string?
2. True or false: In an NVP request, parameter names are not case-sensitive.
3. In an NVP request, what parameter gives the name of the API call?
4. True or false: More than one error can be returned in a single error response.
58 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 59

Express Checkout
6
In this chapter you will learn:
z How Express Checkout works
z How to use the Express Checkout APIs
z How to use the PayPal Express Checkout buttons and logos
How Express Checkout Works
PayPal Express Checkout is a combination of the website checkout process, PayPal login and
review pages on https://www.paypal.com
Checkout gives developers the flexibility to put PayPal either first in the checkout process or
on the billing page along with other payment options. The customer always starts and
completes an order on the merchant’s website.
The following figure summarizes the Express Checkout work flow:
, and PayPal API requests and responses. Express
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 59
Page 60

Express Checkout
6
How Express Checkout Works
The PayPal Express Checkout API calls work as follows:
1. After selecting products to purchase, the customer clicks the Checkout with PayPal
button on the merchant’s website. This allows the customer to quickly skip entering
shipping and billing information on the merchant’s website.
2. The application passes PayPal the transaction details (SetExpressCheckout), receives
the response from PayPal, and redirects the customer’s browser to PayPal.
3. The customer logs in to PayPal.
4. The customer selects a shipping address and payment method stored on PayPal, and clicks
Continue Checkout to approve the use of PayPal. PayPal redirects the customer to the
merchant’s website.
5. The application makes an API call to retrieve transaction details
(GetExpressCheckoutDetails), and receives the response from PayPal.
6. The customer finishes the checkout process on the merchant’s website, reviews the order,
and completes the order. See “Order Review Page Setup” on page 76 for recommendations
on setting up an order-review page.
N OTE: The customer always reviews transaction details and makes the final payment on
the merchant’s website. PayPal handles the payment verification and passes the
application the customer’s shipping information. PayPal never shares the
customer’s financial information with anyone.
7. When the customer places the order, the application requests payment from PayPal
(DoExpressCheckoutPayment). PayPal sends a response and sends the customer an
email receipt for the payment.
8. The application transfers the customer to the order-confirmation page, showing the details
of the transaction.
The PayPal Express Checkout program flow-of-control and integration points are summarized
in Table 6 .1.
TABLE 6.1 Express Checkout Flow-of-Control and Integration Points
Customer... Merchant... PayPal...
Clicks
Checkout with
PayPal button.
Sends a SetExpressCheckout request with the
required information–estimated OrderTotal,
ReturnURL, and CancelURL–and optional fields,
such as MaxAmount.
Returns a SetExpressCheckout
response with Token.
Adds value of Token from response as a name-value
pair, and redirects the user’s browser to:
https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/
webscr?cmd=_express-checkout&token=
60 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
value
Page 61

Express Checkout API Reference Information
T
ABLE 6.1 Express Checkout Flow-of-Control and Integration Points (Continued)
Customer... Merchant... PayPal...
Express Checkout
6
Logs in to
PayPal,
approves
PayPal use, and
clicks
Continue or
Pay.
Clicks
Confirm
Order button
Optionally sends a
GetExpressCheckoutDetails request
with Token to retrieve customer’s
information.
Renders page in customer’s browser for the next step
in checkout process, such as the “Order Review” page.
Calls DoExpressCheckoutPayment API with the
required elements Token, OrderTotal,
PaymentAction, and PayerID returned by
GetExpressCheckoutDetails response.
Displays final page.
Redirects user’s browser to merchant’s
ReturnURL, with Token value
appended.
Returns a GetExpressCheckout-
Details response
with PayerID, email address,
shipping address, confirmed or
unconfirmed status or that shipping
address, and other details.
Returns payment info with important
TransactionID value and other
details about the payment.
Express Checkout API Reference Information
The following sections provide reference information about the parameters and fields used in
the various requests and responses involved in PayPal Express Checkout.
Further reference information is available in PayPal Name-Value Pair API Developer Guide
and Reference.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 61
Page 62

Express Checkout
6
Express Checkout API Reference Information
SetExpressCheckout Request
The SetExpressCheckout notifies PayPal that the application is using Express Checkout to
obtain payment from the customer.
TABLE 6.2 SetExpressCheckout Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of the API: SetExpressCheckout Ye s
RETURNURL A secure URL to which the customer’s browser is returned after the
customer chooses to pay with PayPal.
N OTE: PayPal recommends that the value be the final review page on
which the customer confirms the order and payment.
Character length and limitations: no limit.
CANCELURL The URL to which the customer is returned if the customer does not
approve the use of PayPal to pay the merchant.
N OTE: PayPal recommends that the value be the final review page on
which the customer confirms the order and payment.
Character length and limitations: no limit.
AMT The total cost of the order to the customer. If shipping cost and tax
charges are known, include them in this value; otherwise, this value
should be the current subtotal of the order.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator
must be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a
comma (,).
CURRENCYCODE A three-character currency code for one of the PayPal-supported
transactional currencies.
Default value: USD
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
No
MAXAMT The expected maximum total amount of the complete order, including
shipping cost and tax charges.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator
must be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a
comma (,).
62 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
No
Page 63

Express Checkout
Express Checkout API Reference Information
T
ABLE 6.2 SetExpressCheckout Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
6
PAYMENTACTION How the merchant wants to obtain payment:
z Authorization indicates this payment is a basic authorization
subject to settlement with PayPal Authorization & Capture.
z Order indicates this payment is an order authorization subject to
settlement with PayPal Authorization & Capture.
z Sale indicates this is a final sale for which the merchant is
requesting payment.
N OTE: If this value is set to Sale on
SetExpressCheckoutRequest, it cannot change to
Authorization on the final
DoExpressCheckoutPaymentRequest.
Character length and limit: Up to 13 single-byte alphabetic characters.
Default: Sale
EMAIL Email address of the customer as entered during checkout. PayPal uses
this value to prefill the PayPal membership sign-up portion of the
PayPal login page.
Character length and limit: 127 single-byte alphanumeric characters
DESC Description of items the customer is purchasing.
Character length and limit: 127 single-byte alphanumeric characters
CUSTOM A free-form field for the developer’s own use, such as a tracking
number or other value for PayPal to return in the
GetExpressCheckoutDetails response and
DoExpressCheckoutPayment response.
Character length and limitations: 256 single-byte alphanumeric
characters
No
No
No
No
INVNUM The merchant’s own unique invoice or tracking number. PayPal returns
No
this value in the DoExpressCheckoutPayment response.
Character length and limit: 127 single-byte alphanumeric characters
REQCONFIRMSHIPPING The value
1 indicates that the merchant requires that the customer’s
No
shipping address on file with PayPal be a confirmed address.
N OTE: Setting this field overrides the setting specified in the Merchant
Account Profile.
Character length and limitations: 1 single-byte numeric character.
Allowable values: 0, 1
Default value: 0
NOSHIPPING The value 1 indicates that on the PayPal pages, no shipping address
No
fields should be displayed whatsoever.
Character length and limitations: 4 single-byte numeric characters.
Allowable values: 0, 1
Default value: 0
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 63
Page 64

Express Checkout
6
Express Checkout API Reference Information
T
ABLE 6.2 SetExpressCheckout Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
ADDROVERRIDE The value 1 indicates that the PayPal pages should display the shipping
address set in this SetExpressCheckout request, not the shipping
address on file with PayPal for this customer.
N OTE: Displaying the PayPal street address on file does not allow the
customer to edit that address.
Allowable values: 0, 1
Default value: 0
TOKEN A timestamped token that tells PayPal that the payment is being
processed with Express Checkout.
N OTE: The token expires after three hours.
If the token is set here, the value of TOKEN in the response will be
identical to the value in the request.
Character length and limitations: 20 single-byte characters
LOCALECODE Locale of pages displayed by PayPal during Express Checkout.
Character length and limitations: Any two-character country code.
The following codes are supported by PayPal:
z AU
z DE
z ES
z FR
z GB
z IT
z US
All other values default to US.
A complete list of country codes is in PayPal Name-Value Pair API
Developer Guide and Reference.
No
No
No
PAGESTYLE Sets the Custom Payment Page Style for payment pages associated with
No
this button/link. This value corresponds to the HTML variable
page_style for customizing payment pages. The value is the same as
the Page Style Name chosen when adding or editing the page style from
the Profile subtab of the My Account tab of the PayPal account.
Character length and limitations: 30 single-byte alphabetic characters.
HDRIMG A URL for the image to appear at the top left of the payment page. The
No
image has a maximum size of 750 pixels wide by 90 pixels high. PayPal
recommends that the image be stored on a secure (HTTPS) server.
Character length and limit: 127 single-byte alphanumeric characters
64 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 65

Express Checkout
Express Checkout API Reference Information
T
ABLE 6.2 SetExpressCheckout Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
6
HDRBORDERCOLOR Sets the border color around the header of the payment page. The border
is a 2-pixel perimeter around the header space, which is 750 pixels wide
by 90 pixels high.
Character length and limitations: 6-character HTML hexadecimal color
code in ASCII.
HDRBACKCOLOR Sets the background color for the header of the payment page.
Character length and limitations: 6-character HTML hexadecimal color
code in ASCII.
PAYFLOWCOLOR Sets the background color for the payment page.
Character length and limitations: 6-character HTML hexadecimal color
code in ASCII.
CHANNELTYPE Type of channel:
z Merchant — Non-auction seller
z eBayItem — eBay auction
SOLUTIONTYPE Type of checkout flow:
z Sole — Express Checkout for auctions
z Mark — Normal Express Checkout
Shipping Address An optional shipping address, as described in “ShippingAddress
Parameter” on page 153. ShippingAddress is optional, but if it is
included, certain fields are required.
No
No
No
No
No
No
SetExpressCheckout Response
The SetExpressCheckout response is returned by the PayPal server after a
SetExpressCheckout request is posted.
ABLE 6.3 SetExpressCheckout Response Fields
T
Parameter Description
TOKEN A timestamped token that tells PayPal that the payment is being processed with Express Checkout.
N OTE: The token expires after three hours.
If the token was set in the SetExpressCheckout request, the value of TOKEN in the response
will be identical to the value in the request.
Character length and limitations: 20 single-byte characters
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 65
Page 66

Express Checkout
6
Express Checkout API Reference Information
GetExpressCheckoutDetails Request
A GetExpressCheckoutDetails request asks PayPal to respond with the customer’s
checkout information, such as shipping address.
TABLE 6.4 GetExpressCheckoutDetails Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of the API: GetExpressCheckoutDetails Yes
TOKEN A timestamped token, the value of which was returned by the
SetExpressCheckout response.
Character length and limitations: 20 single-byte characters.
Allowable values: An unexpired token.
Ye s
GetExpressCheckoutDetails Response
The GetExpressCheckoutDetails response provides the customer’s checkout details,
which were stored in the PayPal system.
T
ABLE 6.5 GetExpressCheckoutDetails Response Fields
Parameter Description
TOKEN The timestamped token value that was returned by the SetExpressCheckout
response and passed in the GetExpressCheckoutDetails request.
Character length and limitations: 20 single-byte characters.
EMAIL Email address of payee.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte characters.
PAYERID Unique PayPal customer account identification number.
Character length and limitations: 13 single-byte alphanumeric characters.
PAYERSTATUS Status of payer.
Character length and limitations: 10 single-byte alphabetic characters.
Possible values: verified, unverified
SALUTATION Payer’s salutation.
Character length and limitations: 20 single-byte characters.
FIRSTNAME Payer’s first name.
Character length and limitations: 25 single-byte characters.
MIDDLENAME Payer’s middle name.
Character length and limitations: 25 single-byte characters.
LASTNAME Payer’s last name.
Character length and limitations: 25 single-byte characters.
66 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 67

Express Checkout
Express Checkout API Reference Information
T
ABLE 6.5 GetExpressCheckoutDetails Response Fields (Continued)
Parameter Description
SUFFIX Payer’s suffix.
Character length and limitations: 12 single-byte characters.
COUNTRYCODE Payer’s country of residence, in the form of ISO standard 3166 two-character country
codes.
Character length and limitations: 2 single-byte characters.
BUSINESS Payer’s business name.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte characters.
SHIPTONAME Person’s name associated with this address.
Character length and limitations: 32 single-byte characters.
SHIPTOSTREET First street address.
Character length and limitations: 100 single-byte characters.
SHIPTOSTREET2 Second street address.
Character length and limitations: 100 single-byte characters.
6
SHIPTOCITY Name of city.
Character length and limitations: 40 single-byte characters.
SHIPTOSTATE State or province.
Character length and limitations: 40 single-byte characters.
SHIPTOCOUNTRYCODE Country code.
Character length and limitations: 2 single-byte characters.
SHIPTOZIP US ZIP code or other country-specific postal code.
Character length and limitations: 20 single-byte characters.
ADDRESSSTATUS Status of street address on file with PayPal.
CUSTOM A free-form field for the developer’s own use, as set in the CUSTOM parameter of the
SetExpressCheckout request.
Character length and limitations: 256 single-byte characters.
INVNUM The merchant’s own invoice or tracking number, as set in the INVNUM parameter of
the SetExpressCheckout request.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte characters.
PHONENUM Payer’s contact telephone number.
PayPal returns a contact telephone number only if the Merchant account profile
settings require that the customer enter one.
Character length and limitations: Field mask is XXX-XXX-XXXX (for U.S. numbers)
or +XXX XXXXXXXX (for international numbers)
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 67
Page 68

Express Checkout
6
Express Checkout API Reference Information
DoExpressCheckoutPayment Request
The DoExpressCheckoutPayment request performs the actual request to obtain payment
with PayPal Express Checkout.
N OTE: PayPal requires that a merchant using Express Checkout display to the customer the
same amount that the merchant sends to PayPal in the AMT parameter of the
DoExpressCheckoutPayment request.
TABLE 6.6 DoExpressCheckoutPayment Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of the API: DoExpressCheckoutPayment Ye s
TOKEN The timestamped token value that was returned by the
SetExpressCheckout response and passed by the
GetExpressCheckoutDetails request.
Character length and limitation: 20 single-byte characters.
PAYMENTACTION How the merchant wants to obtain payment:
z Authorization indicates that this payment is a basic
authorization subject to settlement with PayPal
Authorization & Capture.
z Order indicates that this payment is an order
authorization subject to settlement with PayPal
Authorization & Capture.
z Sale indicates that this is a final sale for which the
merchant is requesting payment.
N OTE: If this value was set to Sale on
SetExpressCheckoutRequest, then it cannot
change to
Authorization on the final
DoExpressCheckoutPaymentRequest.
Character length and limit: Up to 13 single-byte alphabetic
characters.
Default:
PAYERID Unique PayPal customer account identification number, as
returned by the
response.
Character length and limit: 13 single-byte alphabetic
characters.
Sale
GetExpressCheckoutDetails
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
AMT Total of order, including shipping, handling, and tax.
N OTE: Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any
currency. No currency symbol. Must have two decimal
places, decimal separator must be a period (.), and the
optional thousands separator must be a comma (,).
68 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Ye s
Page 69

Express Checkout
Express Checkout API Reference Information
T
ABLE 6.6 DoExpressCheckoutPayment Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
6
DESC Description of items the customer is purchasing.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte alphanumeric
characters.
CUSTOM A free-form field for the developer’s own use.
Character length and limitations: 256 single-byte alphanumeric
characters.
INVNUM The merchant’s own invoice or tracking number.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte alphanumeric
characters.
BUTTONSOURCE An identification code for use by third-party applications to
identify transactions.
Character length and limitations: 32 single-byte alphanumeric
characters.
NOTIFYURL The URL for receiving Instant Payment Notification (IPN)
about this transaction.
N OTE: If this value is not specified, the notification URL from
the Merchant Profile is used, if one is available.
Character length and limitations: 2,048 single-byte
alphanumeric characters.
ITEMAMT Sum of cost of all items in this order.
N OTE: Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any
currency. No currency symbol. Must have two decimal
places, decimal separator must be a period (.), and the
optional thousands separator must be a comma (,).
No
No
No
No
No
No
N OTE: ITEMAMT is required if a value is specified for
L_AMTn.
SHIPPINGAMT Total shipping costs for this order.
N OTE: Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any
currency. No currency symbol. Must have two decimal
places, decimal separator must be a period (.), and the
optional thousands separator must be a comma (,).
HANDLINGAMT Total handling costs for this order.
N OTE: Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any
currency. No currency symbol. Must have two decimal
places, decimal separator must be a period (.), and the
optional thousands separator must be a comma (,).
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 69
No
No
Page 70

Express Checkout
6
Express Checkout API Reference Information
ABLE 6.6 DoExpressCheckoutPayment Request Parameters (Continued)
T
Parameter Description Required?
TAXAMT Sum of tax for all items in this order.
N OTE: Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any
currency. No currency symbol. Must have two decimal
places, decimal separator must be a period (.), and the
optional thousands separator must be a comma (,).
N OTE: TAXAMT is required if a value is specified for
L_TAXAMTn.
CURRENCYCODE A three-character currency code for one of the PayPal-
supported transactional currencies.
Default value: USD
L_NAME
L_NUMBER
L_QTY
n Item name.
These parameters should be ordered sequentially, beginning
with 0 (for example,
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte characters.
n Item number.
These parameters should be ordered sequentially, beginning
with 0 (for example,
forth).
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte characters.
n Item quantity.
These parameters should be ordered sequentially, beginning
with 0 (for example,
Character length and limitations: any positive integer.
L_NAME0, L_NAME1, and so forth).
L_NUMBER0, L_NUMBER1, and so
L_QTY0, L_QTY1, and so forth).
No
No
No
No
No
L_TAXAMT
L_AMT
L_EBAYITEMNUMBER
70 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
n Item sales tax.
These parameters should be ordered sequentially, beginning
with 0 (for example, L_TAXAMT0, L_TAXAMT1, and so forth).
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency.
No currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal
separator must be a period (.), and the optional thousands
separator must be a comma (,).
n Cost of item.
These parameters should be ordered sequentially, beginning
with 0 (for example, L_AMT0, L_AMT1, and so on).
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency.
No currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal
separator must be a period (.), and the optional thousands
separator must be a comma (,).
n
Auction item number.
Character length: 765 single-byte characters.
No
No
No
Page 71

Express Checkout
Express Checkout API Reference Information
T
ABLE 6.6 DoExpressCheckoutPayment Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
6
L_EBAYITEMAUCTIONTXNIDn
Auction transaction identification number.
No
Character length: 255 single-byte characters.
L_EBAYITEMORDERID
n
Auction order identification number.
No
Character length: 64 single-byte characters.
ShippingAddress An optional shipping address, as described in
No
“ShippingAddress Parameter” on page 153.
ShippingAddress is optional, but if it is included, certain
fields are required.
DoExpressCheckoutPayment Response
A DoExpressCheckoutPayment response is sent by the PayPal server after an Express
Checkout transaction.
T
ABLE 6.7 DoExpressCheckoutPayment Response Fields
Field Description
TOKEN The timestamped token value that was returned by the SetExpressCheckout
response and passed by the GetExpressCheckoutDetails request.
Character length and limitation: 20 single-byte characters.
TRANSACTIONID Unique transaction ID of the payment.
N OTE: If the PaymentAction of the request was Authorization or Order, this
value is the AuthorizationID for use with the Authorization & Capture APIs.
Character length and limitations: 19 single-byte characters.
Possible values: Transaction-specific
TRANSACTIONTYPE The type of transaction.
Character length and limitations: 15 single-byte characters
Possible values:
z cart
z express-checkout
PAYMENTTYPE Indicates whether the payment is instant or delayed.
Character length and limitations: 7 single-byte characters
Possible values:
z none
z echeck
z instant
ORDERTIME Time/date stamp of payment.
Possible values: Transaction-specific
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 71
Page 72

Express Checkout
6
Express Checkout API Reference Information
T
ABLE 6.7 DoExpressCheckoutPayment Response Fields (Continued)
Field Description
AMT The final amount charged, including any shipping and taxes from the Merchant Profile.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No currency symbol.
Regardless of currency, decimal separator is a period (.), and the optional thousands
separator is a comma (,). Equivalent to 9 characters maximum for USD.
Possible values: Transaction specific
CURRENCYCODE A three-character currency code for one of the PayPal-supported transactional
currencies.
Default value: USD
FEEAMT PayPal fee amount charged for the transaction.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No currency symbol.
Regardless of currency, decimal separator is a period (.), and the optional thousands
separator is a comma (,). Equivalent to 9 characters maximum for USD.
Possible values: Transaction-specific
SETTLEAMT Amount deposited in the merchant’s PayPal account after a currency conversion.
Possible values: Transaction-specific
TAXAMT Tax charged on the transaction.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No currency symbol.
Regardless of currency, decimal separator is a period (.), and the optional thousands
separator is a comma (,). Equivalent to 9 characters maximum for USD.
Possible values: Transaction-specific
EXCHANGERATE Exchange rate if a currency conversion occurred. Relevant only if the merchant is
billing in a currency other than the primary currency. If a conversion must occur, it
occurs in the customer’s account.
Character length and limitations: A decimal that does not exceed 17 characters,
including the decimal point
Possible values: Transaction-specific
PAYMENTSTATUS Status of the payment:
z Completed — The payment has been completed, and the funds have been added
successfully to the merchant’s account balance.
z Pending — The payment is pending. See the PENDINGREASON element for more
information.
72 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 73

T
ABLE 6.7 DoExpressCheckoutPayment Response Fields (Continued)
Field Description
PENDINGREASON The reason the payment is pending:
z none — No pending reason.
z address — The payment is pending because the customer did not include a
confirmed shipping address, and the merchant’s Payment Receiving Preferences are
set such that the payments must be manually accepted or denied. To change these
preferences, the merchant must go to the Preferences section of the Profile.
z echeck — The payment is pending because it was made by an eCheck that did not
yet clear.
z intl — The payment is pending because the merchant holds a non-US account and
does not have a withdrawal mechanism. The merchant must manually accept or
deny this payment from the Account Overview.
z multi-currency — The merchant does not have a balance in the currency sent,
and the merchant does not have the Payment Receiving Preferences set to
automatically convert and accept this payment. The merchant must manually accept
or deny this payment.
z verify — The payment is pending because the merchant is not yet verified. The
merchant must verify his account before accepting this payment.
z other — The payment is pending for a reason other than those listed here. For
more information, contact PayPal customer service.
Express Checkout
Button and Logo Placement and Use
6
REASONCODE The reason for a reversal, if the transaction type is reversal:
z none — No reason code.
z chargeback — A reversal has occurred on this transaction due to a chargeback by
the customer.
z guarantee — A reversal has occurred on this transaction due to the customer
triggering a money-back guarantee.
z buyer-complaint — A reversal has occurred on this transaction due to a
complaint about the transaction from the customer.
z refund — A reversal has occurred on this transaction because the merchant gave
the customer a refund.
z other — A reversal has occurred on this transaction due to a reason not listed here.
Button and Logo Placement and Use
When you offer PayPal Express Checkout to customers, you are required to display the option
in two places on your website:
1. As a checkout choice on the shopping-cart page, display the Express Checkout button as
follows:
2. As a Payment Method on the billing page, display the PayPal acceptance mark as a
payment option.
If your site requires customers to sign in or create a store account before checkout, the Express
Checkout button should be visible before users are required to sign in.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 73
Page 74

Express Checkout
6
Button and Logo Placement and Use
If your site has a Checkout button on pages other than the Shopping Cart page (such as on
product pages), PayPal requires that you put a PayPal Express Checkout button next to these
Checkout buttons as well—if the Checkout button initiates the checkout flow. If the Checkout
button links to the Shopping Cart page, you are not required to place a PayPal button.
The HTML for the Express Checkout button and PayPal Acceptance Mark are available at
https://www.paypal.com/express-checkout-buttons
PayPal Button as a Checkout Choice
The following figure shows PayPal as a checkout-choice button:
Place the Express Checkout button on the shopping-cart page, arranged as follows:
z Always clickable
z Right below or next to each of your own cart’s checkout buttons (with the word “or”
between them)
.
z Before your website collects any shipping or billing details or displays any other payment
methods
z Aligned vertically or horizontally with your own buttons
PayPal Button as a Payment Method
The following figure shows PayPal as a payment method:
Display PayPal as the default payment option, selected next to the other payment options at the
end of checkout.
When displaying PayPal with other payment options, PayPal highly recommends that you use
radio buttons. If your website cannot accommodate radio buttons, you may use horizontal
fields or an entry in a drop-down list.
74 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 75

Using PayPal-Hosted Images
PayPal requires that you use Express Checkout button images hosted on PayPal's secure
servers, rather than hosting copies of these images on your own servers. Also, using the
buttons on the PayPal servers eliminates the need for you to maintain them yourself. If the
buttons are updated, the new buttons appear automatically in your application. Using out-ofdate PayPal buttons could reduce customer confidence in your PayPal deployment.
Express Checkout
Redirecting to PayPal
6
When you get the HTML code at https://www.paypal.com/express-checkout-buttons
work only with PayPal-hosted buttons.
Tips
z Create checkout pages that are uncluttered and free from visual distractions.
z Keep the checkout flow to as few a number of pages as possible.
z Be sure that the PayPal Express Checkout button is clickable, and all PayPal buttons are
used for the use they were intended.
z Do not use the Preview button when the next page is actually a purchase.
z Avoid using warning or legal text as part of the primary checkout experience.
z Do not alter, recolor, or resize the PayPal Express Checkout button, or adding text around
the PayPal checkout button.
Redirecting to PayPal
After the response from SetExpressCheckout, the application must redirect the customer’s
browser to PayPal. The SetExpressCheckout response includes an Express Checkout
session token. Add the value of the Token from the SetExpressCheckout response as a
name-value pair where noted, and redirect the customer’s browser to the following URL:
, it will
https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_expresscheckout&token=
N OTE: Express Checkout has a variation on this redirect URL (called “user action”) that
value_from_SetExpressCheckoutResponse
allows the application to bypass the second request-response pair
(GetExpressCheckoutDetails and GetExpressCheckoutDetailsResponse)
and change the text of the final button displayed on PayPal. For more information on
this variation, see PayPal Website Payments Pro Integration Guide.
Recommendation for Browser Redirection
To redirect the customer’s browser to the PayPal URL, PayPal recommends the HTTPS
response 302 “Object Moved”, with the PayPal URL as the value of the Location header in
the HTTPS response. Ensure that the application uses an SSL-enabled server to prevent
browser warnings about a mix of secure and nonsecure graphics.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 75
Page 76

Express Checkout
6
Order Review Page Setup
Order Review Page Setup
PayPal recommends that order review pages be set up as follows:
1. Shipping Information Section:
– Display the shipping address supplied by PayPal.
– On first use of the SetExpressCheckout API call, if the customer selected a shipping
address stored in the PayPal account, redirect the customer’s browser back to PayPal to
edit the shipping address. To redirect the browser a second time, use the
SetExpressCheckout API again, and include the Token that was received in the first
SetExpressCheckout response. (On the second SetExpressCheckout API call,
include ReturnURL, CancelURL, and other required elements only if their values are
different from the values included in the first SetExpressCheckout API call. These
values most likely will be different on the second request.)
2. Billing Information Section:
– Display the customer’s PayPal email address provided in Express Checkout.
3. Order Total:
– The application must display the same exact OrderTotal value that was sent to PayPal
in the DoExpressCheckoutPayment request.
Authorization & Capture
PayPal assumes that at the end of the checkout process, the merchant makes a final sale and
payment transaction through PayPal. If, at the point of sale, the merchant does not know the
complete cost of the order—for example, if the shipping, handling, and tax are not precisely
known or there is an upsell—a transaction can be authorized that can be captured later, with
Authorization & Capture.
PayPal uses Authorization & Capture in both Express Checkout and Direct Payment.
For information on Authorization & Capture, see “Authorization & Capture APIs” on page 87.
76 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 77

Review Questions
Answers to review questions are in Appendix A, “Answers to Review Questions.”
1. On the Order Review page, from where should the application get the value of the total
order?
2. In the SetExpressCheckout request, what is the maximum allowed value for AMT?
3. How much time elapses before a TOKEN expires?
4. Where should the PayPal checkout button appear?
5. In the DoExpressCheckoutPayment request, when is a value required for the parameter
TAXAMT?
Express Checkout
Review Questions
6
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 77
Page 78

Express Checkout
6
Review Questions
78 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 79

Direct Payment API
7
In this chapter, you will learn:
z How Direct Payment works
z How to use the Direct Payment API
How Direct Payment Works
The Direct Payment API allows a merchant to accept credit-card transactions directly on the
merchant’s website. Even though the website uses PayPal to process the credit-card
transaction, this process is invisible to customers. This means customers are not taken away
from the website; the website provides a single, unified look and feel.
IMPORTANT: Payments made through the Direct Payment API are not covered by the
PayPal Seller Protection Policy.
The Direct Payments API is part of the Website Payments Pro solution.
The PayPal Direct Payment API calls work as follows:
1. On the website, the customer chooses to pay with a credit card and enters the credit-card
number and other details.
2. The customer reviews the order.
3. When the customer clicks Pay to place the order, the application sends a
DoDirectPayment request to the PayPal server, and the payment transaction is initiated.
The DoDirectPayment request includes required information that was collected from the
customer, such as the amount of the transaction and the customer’s credit-card number and
expiration date, as well as the browser IP address and an element that specifies whether this
transaction is a final sale (complete transaction amount including shipping, handling, and
tax) or an authorization for a final amount that must be captured later with Authorization &
Capture. The DoDirectPayment response includes a transaction identification number
and other information.
N OTE: The customer does not see this step; PayPal is completely invisible to customers
before, during, and after the purchase. PayPal does not send an email receipt to the
customer, nor will the customer’s credit-card statement indicate that PayPal
processed the payment.
4. The application transfers the customer to the order-confirmation page.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 79
Page 80

Direct Payment API
7
Direct Payment API Reference Information
Direct Payment API Reference Information
The following sections contain reference information about the parameters and fields used in
the various requests and responses involved in PayPal Direct Payment.
Further reference information is available in PayPal Name-Value Pair API Developer Guide
and Reference.
DoDirectPayment Request
Use a DoDirectPayment request to charge a credit card or to authorize a credit card for later
capture.
TABLE 7.1 DoDirectPayment Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of the API: DoDirectPayment Ye s
PAYMENTACTION How the merchant wants to obtain payment:
z Authorization indicates this payment is a basic authorization
subject to settlement with PayPal Authorization & Capture.
z Sale indicates this is a final sale for which the merchant is
requesting payment.
Character length and limit: Up to 13 single-byte alphabetic characters
IPADDRESS IP address of the payer’s browser.
PayPal records this IP address as a means of detecting possible fraud.
Character length and limitations: 15 single-byte characters, including
periods (for example, 255.255.255.25).
Allowable values: Any valid Internet Protocol address.
AMT Total of the order, including shipping, handling, and tax.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator must
be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a comma
(,).
CREDITCARDTYPE Type of credit card.
Character length and limitations: Up to 10 single-byte alphabetic
characters.
Allowable values:
z Visa
z MasterCard
z Discover
z Amex
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
80 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 81

Direct Payment API
Direct Payment API Reference Information
T
ABLE 7.1 DoDirectPayment Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
7
ACCT Credit-card number.
Character length and limitations: Numeric characters only. No spaces or
punctuation. Must conform with the length required by each credit-card
type.
EXPDATE Credit-card expiration date.
Format: MMYYYY
Character length and limitations: 6 single-byte numeric characters,
including leading 0.
FIRSTNAME Payer’s first name.
Character length and limitations: 25 single-byte characters
LASTNAME Payer’s last name.
Character length and limitations: 25 single-byte characters
STREET First street address.
Character length and limitations: 100 single-byte characters
CITY City.
Character length and limitations: 40 single-byte characters
STATE State or province.
Character length and limitations: 40 single-byte characters
For state or province abbreviations, see PayPal Name-Value Pair API
Developer Guide and Reference.
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
No
No
No
COUNTRYCODE Country code.
Character length and limitations: Two single-byte characters.
For a list of country codes, see PayPal Name-Value Pair API Developer
Guide and Reference.
ZIP U.S. ZIP code or other country-specific postal code.
Character length and limitations: 20 single-byte characters
NOTIFYURL The URL for receiving Instant Payment Notification (IPN) about this
transaction.
If a URL is not specified in the request, the notification URL from the
Merchant Profile is used, if one exists.
Character length and limitations: 2,048 single-byte alphanumeric
characters.
No
No
No
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 81
Page 82

Direct Payment API
7
Direct Payment API Reference Information
T
ABLE 7.1 DoDirectPayment Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
CURRENCYCODE A three-character currency code.
Default: USD.
This parameter accepts only the following currencies:
z AUD — Australian Dollar
z CAD — Canadian DOllar
z EUR — Euro
z GBP — Pound Sterling
z JPY — Japanese Yen
z USD — US Dollar
ITEMAMT Sum of the cost of all items in this order.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator must
be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a comma
(,).
ITEMAMT is required if L_AMTn is specified.
SHIPPINGAMT Total shipping costs for this order.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator must
be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a comma
(,).
If a value for SHIPPINGAMT is specified, there also must be a value for
ITEMAMT.
No
No
No
HANDLINGAMT Total handling costs for this order.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator must
be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a comma
(,).
If a value for HANDLINGAMT is specified, there also must be a value for
ITEMAMT.
TAXAMT Sum of the tax for all items in this order.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator must
be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a comma
(,).
TAXAMT is required if L_TAXAMTn is specified.
DESC Description of items the customer is purchasing.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte alphanumeric
characters
CUSTOM A free-form field for the developer’s own use.
Character length and limitations: 256 single-byte alphanumeric
characters
No
No
No
No
82 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 83

Direct Payment API
Direct Payment API Reference Information
T
ABLE 7.1 DoDirectPayment Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
7
INVNUM The merchant’s own invoice or tracking number.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte alphanumeric
characters
BUTTONSOURCE An identification code for use by third-party applications to identify
transactions.
Character length and limitations: 32 single-byte alphanumeric
characters
NOTIFYURL The URL for receiving Instant Payment Notification (IPN) about this
transaction.
If this URL is not specified in the request, the notification URL from the
Merchant Profile is used, if one exists.
Character length and limitations: 2,048 single-byte alphanumeric
characters
L_NAME
n Item name.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte characters
These parameters should be ordered sequentially beginning with 0 (for
example, L_NAME0, L_NAME1, and so on).
L_NUMBER
n Item number.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte characters
These parameters should be ordered sequentially beginning with 0 (for
example, L_NUMBER0, L_NUMBER1, and so on).
No
No
No
No
No
L_QTY
n Item quantity.
Character length and limitations: Any positive integer
These parameters should be ordered sequentially beginning with 0 (for
example, L_QTY0, L_QTY1, and so on).
L_TAXAMT
n Item sales tax.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator must
be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a comma
(,).
These parameters should be ordered sequentially beginning with 0 (for
example, L_TAXAMT0, L_TAXAMT1, and so on).
L_AMT
n Cost of the item.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator must
be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a comma
(,).
These parameters should be ordered sequentially beginning with 0 (for
example, L_AMT0, L_AMT1, and so on).
If a value for L_AMTn is specified, there must be a value for ITEMAMT.
No
No
No
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 83
Page 84

Direct Payment API
7
Direct Payment API Reference Information
T
ABLE 7.1 DoDirectPayment Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
CVV2 Card Verification Value, version 2.
The Merchant Account settings determine whether this field is required.
Contact a PayPal Account Manager for more information.
Character length for Visa, MasterCard, and Discover: Three digits.
Character length for American Express: Four digits.
I MPORTANT: To comply with credit-card-processing regulations,
once a transaction has been completed, the application
must not store the value of CVV2.
EMAIL Email address of payer.
Character length and limit: 127 single-byte characters
STREET2 Second street address.
Character length and limit: 127 single-byte characters
PHONENUM Phone number
Character length and limit: 20 single-byte characters
ShippingAddress An optional shipping address, as described in “ShippingAddress
Parameter” on page 153. ShippingAddress is optional, but if it is
included, certain fields are required.
DoDirectPayment Response
See
description
No
No
No
No
A DoDirectPayment response comes from the PayPal server after a request to charge a
credit card or authorize a credit card for later capture.
ABLE 7.2 DoDirectPayment Response Fields
T
Field Description Possible Values
AMT The amount of the payment as specified in the
DoDirectPayment request.
AVSCODE Address Verification System response code.
Character limit: One single-byte alphanumeric character.
CVV2MATCH Result of the CVV2 check by PayPal. See “CVV2 Response
TRANSACTIONID Unique transaction ID of the payment.
NOTE: If the PAYMENTACTION of the request was
Authorization, the value of TRANSACTIONID is
the AuthorizationID for use with the
Authorization & Capture APIs.
Character length and limitation: 19 single-byte characters.
See description.
See “AVS Response Codes”
on page 155.
Codes” on page 156.
See description.
84 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 85

Authorization & Capture
PayPal assumes that at the end of the checkout process, the merchant makes a final sale and
payment transaction through PayPal. If, at the point of sale, the merchant does not know the
complete cost of the order—for example, if the shipping, handling, and tax are not precisely
known or there is an upsell—a transaction can be authorized that can be captured later, with
Authorization & Capture.
PayPal uses Authorization & Capture in both Direct Payment and Express Checkout.
For more information about Authorization & Capture, see “Authorization & Capture APIs” on
page 87.
Review Questions
Answers to review questions are in Appendix A, “Answers to Review Questions.”
1. True or false: If the merchant’s application uses Direct Payment, the name “PayPal” does
not appear on the customer’s credit-card statement.
Direct Payment API
Authorization & Capture
7
2. How does PayPal determine if the CVV2 parameter is required in the DoDirectPayment
request?
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 85
Page 86

Direct Payment API
7
Review Questions
86 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 87

Transactions
8
In this chapter, you will learn:
z How to use the Authorize & Capture APIs to authorize payments without actually
receiving them, and how to get authorized payments
z How to refund a customer’s payment
z How to search for transactions and find details of a specific transaction
z How to use PayPal’s automated payment-notification capabilities
Authorization & Capture APIs
PayPal uses Authorization & Capture in both Express Checkout and Direct Payment.
Authorization & Capture APIs provide merchants with increased flexibility in obtaining
payments from their customers. Authorization & Capture separates the authorization of
payment from the capture of the authorized payment.
Authorization & Capture is for merchants who have a delayed order-fulfillment process. It
enables merchants to modify the original authorization amount, due to order changes
occurring after the initial order is placed (such as taxes, shipping, or item availability).
Authorization & Capture allows merchants to authorize, capture, reauthorize, and void funds.
Authorization Process
1. Authorization & Capture starts when the customer authorizes a payment amount during
checkout (for example, by using the PayPal Express Checkout API with the
PAYMENTACTION element set to Authorization).
2. After the customer completes checkout, use the payment’s transaction ID with
Authorization & Capture APIs to:
– Capture a partial amount or the full authorization amount.
– Capture or reauthorize a higher amount, up to 115% of the originally authorized amount
(not to exceed an increase of $75 USD).
– Void a previous authorization.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 87
Page 88

Transactions
8
Authorization & Capture APIs
Honor Period and Authorization Period
When the customer approves an authorization, the customer’s balance can be placed on hold
for a 29-day period to ensure the availability of the authorization amount for capture.
The merchant can reauthorize a transaction only once, up to 115% of the originally authorized
amount (not to exceed an increase of $75 USD). After a successful reauthorization, PayPal
honors 100% of the authorized funds for the first 3 days of the 29-day period. A day is defined
as the start of the calendar day on which the authorization or reauthorization was made (from
12 AM PST to 11:59 PM PST).
A merchant can settle without a reauthorization from day 4 to day 29 of the authorization
period, but PayPal cannot ensure that 100% of the funds will be available after the 3-day honor
period. PayPal will not allow the merchant to capture funds if the customer’s account is
restricted or locked, a fraudulent case occurs, or the merchant’s account has a high restriction
level. PayPal makes its best effort to capture funds outside the honor period; however, there is
a possibility that funds will not be available at that time.
Buyer and seller accounts cannot be closed if there is a pending unsettled authorization.
Authorization & Capture API Reference Information
There are three APIs related to Authorization & Capture:
z DoCapture
z DoVoid
z DoReauthorization
The following sections display reference information about the parameters and fields used in
the various requests and responses involved in Authorization & Capture.
DoCapture Request
Use a DoCapture request to capture a complete or partial authorized amount.
TABLE 8.1 DoCapture Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of API: DoCapture Ye s
AUTHORIZATIONID The authorization identification number of the payment to capture. This is
the transaction ID returned from DoExpressCheckoutPayment or
DoDirectPayment.
Character length and limits: 19 single-byte characters maximum.
AMT Amount to capture.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No currency
symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator must be a
period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a comma (,).
Ye s
Ye s
88 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 89

Transactions
Authorization & Capture APIs
T
ABLE 8.1 DoCapture Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
8
CURRENCYCODE A three-character currency code for one of the PayPal-supported
transactional currencies.
Default value: USD
COMPLETETYPE The value Complete indicates this is the last capture to make.
The value NotComplete indicates there will be additional captures.
NOTE: If Complete, any remaining amount of the original authorized
transaction is automatically voided, and all remaining open
authorizations are voided.
Character length and limits: 12 single-byte alphanumeric characters.
INVNUM The invoice number or other identification number that is displayed to the
merchant and customer in the customer’s transaction history.
NOTE: This value in DoCaptureRequest will overwrite a value
previously set on DoAuthorizationRequest.
NOTE: The value is recorded only if the authorization being captured is
an order authorization, not a basic authorization.
Character length and limits: 127 single-byte alphanumeric characters.
NOTE An informational note about this settlement that is displayed to the
customer in email and in the customer’s transactional history.
Character length and limits: 255 single-byte characters.
No
Ye s
No
No
DoCapture Response
A DoCapture response contains the results of a capture of authorized funds.
ABLE 8.2 DoCapture Response Fields
T
Field Description
AUTHORIZATIONID The authorization identification number specified in the request.
Character length and limits: 19 single-byte characters maximum.
TRANSACTIONID Unique transaction ID of the payment.
Character length and limitations: 17 single-byte characteristics
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 89
Page 90

Transactions
8
Authorization & Capture APIs
T
ABLE 8.2 DoCapture Response Fields (Continued)
Field Description
PARENTTRANSACTIONID Parent or related transaction identification number. This field is populated for the
following transaction types:
z Reversal — Capture of an authorized transaction.
z Reversal — Reauthorization of a transaction.
z Capture of an order — The value of PARENTTRANSACTIONID is the original
OrderID.
z Authorization of an order — The value of PARENTTRANSACTIONID is the
original OrderID.
z Capture of an order authorization.
z Void of an order — The value of PARENTTRANSACTIONID is the original
OrderID.
Character length and limits: 16 digits in xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx format
RECEIPTID Receipt identification number.
Character length and limits: 16 digits in xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx format
TRANSACTIONTYPE The type of transaction:
z cart
z express-checkout
Character length and limits: 15 single-byte characters
PAYMENTTYPE Indicates whether the payment is instant or delayed.
Character length and limits: 7 single-byte characters
ORDERTIME Time/date stamp of payment.
For example: 2006-08-15T17:23:15Z
AMT The final amount charged, including any shipping and taxes from the Merchant
Profile.
FEEAMT PayPal fee amount charged for the transaction.
SETTLEAMT Amount deposited in the merchant’s PayPal account if there is a currency
conversion.
TAXAMT Tax charged on the transaction, if any.
EXCHANGERATE Exchange rate if a currency conversion occurred. Relevant only if the merchant is
billing a currency other than the customer’s primary currency. If this is the case, the
conversion occurs in the customer’s account.
Character length and limitations: a decimal multiplier
90 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 91

T
ABLE 8.2 DoCapture Response Fields (Continued)
Field Description
PAYMENTSTATUS The status of the payment:
z None — No status.
z Canceled-Reversal — A reversal was canceled. For example, the merchant
won a dispute with the customer, and the funds for the transaction that was
reversed were returned.
z Completed — The payment was completed, and the funds were added
successfully to the merchant’s account balance.
z Denied — The merchant denied the payment. This happens only if the
payment was previously pending because of possible reasons described in the
PENDINGREASON element.
z Expired — The authorization period for this payment was reached.
z Failed — The payment failed. This happens only if the payment was made
from the customer’s bank account.
z Pending — The payment is pending. For more information, see the
PENDINGREASON field.
z Refunded — The merchant refunded the payment.
z Reversed — A payment was reversed due to a chargeback or other type of
reversal. The funds were removed from the merchant’s account balance and
returned to the customer. The reason for the reversal is specified in the
REASONCODE element.
z Processed — A payment was accepted.
z Voided — An authorization for this transaction was voided.
Transactions
Authorization & Capture APIs
8
DoVoid Request
Use a DoVoid request to request a void for an authorization.
T
ABLE 8.3 DoVoid Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of API: DoVoid Ye s
AUTHORIZATIONID The value of the original authorization identification number returned by
PayPal.
I MPORTANT: If the merchant is voiding a transaction that was
reauthorized, use the ID from the original authorization,
not the reauthorization.
Character length and limits: 19 single-byte characters
NOTE An informational note about this void that is displayed to the customer
in email and in the transaction history.
Character length and limits: 255 single-byte characters
Ye s
No
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 91
Page 92

Transactions
8
Authorization & Capture APIs
DoVoid Response
A DoVoid response contains the results of an authorization void.
TABLE 8.4 DoVoid Response Fields
Field Description
AUTHORIZATIONID The authorization identification number specified in the request.
Character length and limits: 19 single-byte characters
DoReauthorization Request
Use a DoReauthorization request to request a reauthorization for a given amount of
money.
T
ABLE 8.5 DoReauthorization Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of API: DoReauthorization Ye s
AUTHORIZATIONID The value of a previously authorized transaction identification number
returned by PayPal.
Character length and limits: 19 single-byte characters maximum
AMT Amount to authorize.
Limitations: Must not exceed $10,000 USD in any currency. No
currency symbol. Must have two decimal places, decimal separator
must be a period (.), and the optional thousands separator must be a
comma (,).
CURRENCYCODE A three-character currency code for one of the PayPal-supported
transactional currencies.
Default value: USD
DoReauthorization Response
A DoReauthorization response contains the results of the reauthorization.
T
ABLE 8.6 DoReauthorization Response Fields
Field Description
AUTHORIZATIONID A new authorization identification number.
Character length and limits: 19 single-byte characters
Ye s
Ye s
No
92 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 93

Authorization & Capture Best Practices
The following sections describe the best practices to follow in using Authorization & Capture,
to ensure the best buying experience for customers and get the most benefit from
Authorization & Capture.
Capturing Funds on Basic Authorizations
PayPal recommends that a merchant capture funds within the honor period of three days,
because PayPal will honor the funds for a three-day period after the basic authorization. If the
merchant tries to capture funds after the three-day period and the authorization fails, the
request to capture funds may be denied.
After day 4 of the authorization period, a merchant can initiate a reauthorization, which starts a
new three-day honor period; however, the reauthorization does not extend the original
authorization period past 29 days.
The merchant should capture funds within 24 hours after shipping the customer’s order.
Customer Approval for Basic Authorizations
A customer-initiated authorization allows the merchant to capture funds from the customer’s
account of up to 115% of the originally authorized amount (not to exceed an increase of $75
USD) and up to $10,000 USD (the limit for a single purchase through PayPal).
Transactions
Refunds
8
IMPORTANT: If the merchant wants to update any details of the purchase that change the
Voiding Basic Authorizations
The merchant should void an authorization if the authorization or reauthorization will not be
used. Voiding the authorization unlocks the temporary hold placed on the customer’s funding
sources.
For More Information
For more information on all capabilities of Authorization & Capture, including order
authorization, see the PayPal documentation available through the Integration Center.
Refunds
A merchant can refund the full amount or a partial amount of a transaction with the
RefundTransaction API.
original authorization amount, PayPal requires that the merchant obtain
consent from the customer at the time of purchase or at the time of capture.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 93
Page 94

Transactions
8
Refunds
RefundTransaction Request
Use a RefundTransaction request to initiate a full or partial refund of a transaction.
TABLE 8.7 RefundTransaction Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of API call: RefundTransaction Ye s
TRANSACTIONID Unique identifier of a transaction.
Character length and limitations: 17 single-byte alphanumeric characters
REFUNDTYPE Type of refund to make:
z Full
z Partial
z Other
AMT Refund amount.
AMT is required if REFUNDTYPE is Partial.
NOTE: If REFUNDTYPE is Full, do not set AMT.
NOTE Custom memo about the refund.
Character length and limitations: 255 single-byte alphanumeric characters
RefundTransaction Response
A RefundTransaction response contains the results of the refund.
ABLE 8.8 RefundTransaction Response Fields
T
Field Description
REFUNDTRANSACTIONID Unique transaction ID of the refund.
Character length and limitations: 17 single-byte characters
Ye s
Ye s
No
No
NETREFUNDAMT Amount subtracted from PayPal balance of original recipient of payment to make
this refund.
FEEREFUNDAMT Transaction fee refunded to original recipient of payment.
GROSSREFUNDAMT Amount of money refunded to original payer.
94 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 95

Transaction Searches
To find all transactions that occurred on a particular date, use the TransactionSearch API.
The date must be in UTC/GMT format.
With TransactionSearch, always set the StartDate field. Also note the following:
z Setting TransactionID overrides all other fields (including StartDate).
z The effect of setting other elements is additive or can alter the search criteria.
TransactionSearch returns up to 100 matches. Partial matches are displayed. For example,
setting the FirstName parameter of the TransactionSearch request to “Jess” returns
results including “Jessica” and “Jesse.”
The most important element returned in the TransactionSearch response is
TransactionID, which can be passed to GetTransactionDetails to retrieve all
available information about a specific transaction. For more information on the
GetTransactionDetails API, see “Retrieving Transaction Details” on page 98.
Transactions
Transaction Searches
8
TransactionSearch Request
Use a TransactionSearch request to search for transactions that occurred on a given date.
TABLE 8.9 TransactionSearch Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of API call: TransactionSearch Ye s
STARTDATE The earliest transaction date at which to start the search.
No wildcards are allowed. The value must be in UTC/GMT format.
ENDDATE The latest transaction date to be included in the search. No
EMAIL Search by the customer’s email address.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte alphanumeric
characters.
RECEIVER Search by the receiver’s email address. If the merchant account has
only one email, this is the primary email. This also can be a
nonprimary email.
RECEIPTID Search by the PayPal Account Optional receipt ID. No
TRANSACTIONID Search by the Transaction ID.
The returned results are from the merchant’s transaction records.
Character length and limitations: 19 single-byte characters maximum.
Ye s
No
No
No
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 95
Page 96

Transactions
8
Transaction Searches
T
ABLE 8.9 TransactionSearch Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
INVNUM Search by the invoice identification key, as set for the original
transaction. This field searches the records for items sold by the
merchant, not for items purchased.
No wildcards are allowed.
Character length and limitations: 127 single-byte characters
maximum.
ACCT Search by credit-card number, as set for the original transaction. This
field searches the records for items sold by the merchant, not for items
purchased.
No wildcards are allowed.
Character length and limitations: Must be at least 11 and no more than
25 single-byte numeric characters maximum. Special punctuation,
such as dashes or spaces, is ignored.
SALUTATION Customer’s salutation.
Character length and limitations: 20 single-byte characters
FIRSTNAME Customer’s first name.
Character length and limitations: 25 single-byte characters
MIDDLENAME Customer’s middle name.
Character length and limitations: 25 single-byte characters
LASTNAME Customer’s last name.
Character length and limitations: 2025 single-byte characters
No
No
No
No
No
No
SUFFIX Customer’s suffix.
Character length and limitations: 12 single-byte characters
AUCTIONITEMNUMBER Search by auction item number of the purchased goods. No
96 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
No
Page 97

Transactions
Transaction Searches
T
ABLE 8.9 TransactionSearch Request Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description Required?
8
TRANSACTIONCLASS Search by classification of transaction.
Some possible classes of transactions are not searchable with this field
(for example, bank-transfer withdrawals).
The following classes of transaction can be searched for:
z All — All transaction classifications
z Sent — Only payments sent
z Received — Only payments received
z MassPay — Only mass payments
z MoneyRequest — Only money requests
z FundsAdded — Only funds added to balance
z FundsWithdrawn — Only funds withdrawn from balance
z Referral — Only transactions involving referrals
z Fee — Only transactions involving fees
z Subscription — Only transactions involving subscriptions
z Dividend — Only transactions involving dividends
z Billpay — Only transactions involving BillPay Transactions
z Refund — Only transactions involving refunds
z CurrencyConversions — Only transactions involving currency
conversions
z BalanceTransfer — Only transactions involving balance
transfers
z Reversal — Only transactions involving BillPay Reversals
z Shipping — Only transactions involving UPS shipping fees
z BalanceAffecting — Only transactions that affect the account
balance
z ECheck — Only transactions involving eCheck
No
AMT Search by transaction amount. No
STATUS Search by transaction status:
z Pending — The payment is pending. The specific reason the
No
payment is pending is returned by the GetTransactionDetails
API.
z Processing — The payment is being processed.
z Success — The payment was completed, and the funds were
added successfully to the merchant’s account balance.
z Denied — The merchant denied the payment. This happens only
if the payment was previously pending.
z Reversed — A payment was reversed due to a chargeback or
other type of reversal. The funds were removed from the
merchant’s account balance and returned to the customer.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 97
Page 98

Transactions
8
Retrieving Transaction Details
TransactionSearch Response
A TransactionSearch response contains the results of the transaction search.
N OTE: Each of these parameters should be numbered sequentially beginning with 0 (for
example, L_TIMESTAMP0, L_TIMESTAMP1, L_TIMESTAMP2, and so on).
TABLE 8.10 TransactionSearch Response Fields
Field Description
L_TIMESTAMP
L_TIMEZONE
L_TYPE
L_EMAIL
L_NAME
L_TRANSACTIONID
L_STATUS
L_AMT
n Total gross amount charged, including any profile shipping cost and taxes.
L_FREEAMT
L_NETAMT
n Date and time (in UTC/GMT format) the transaction occurred.
n Time zone of the transaction.
n Type of the transaction.
n Email address of the payer or the payment recipient (the “payee”). If the payment
amount is positive, this field is the recipient of the funds. If the payment is negative,
this field is the paying customer.
n Display name of the payer.
n Seller’s transaction ID.
n Status of the transaction.
n Fee that PayPal charged for the transaction.
n Net amount of the transaction.
Retrieving Transaction Details
If the merchant has the Transaction ID of a transaction, the merchant can retrieve all of the
details about that transaction from the PayPal server.
N OTE: The details for some kinds of transactions cannot be retrieved with
GetTransactionDetails (for example, bank transfer withdrawals).
98 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
Page 99

Transactions
Payment Notification Integration
GetTransactionDetails Request
Use a GetTransactionDetails request to search for a specific transaction.
TABLE 8.11 GetTransactionDetails Request Parameters
Parameter Description Required?
METHOD Name of the method: GetTransactionDetails Ye s
8
TRANSACTIONID Unique identifier of a transaction.
Character length and limitations: 17 single-byte alphanumeric characters.
GetTransactionDetails Response
A GetTransactionDetails response contains all the details and information on the
specified transaction.
The complete list of parameters returned by the GetTransactionDetails response is
documented in PayPal Name-Value Pair API Developer Guide and Reference.
Payment Notification Integration
Website Payments Pro offers multiple payment notification methods, including:
z Email
z Reporting Tools
z Instant Payment Notification (IPN)
Ye s
Merchants automatically receive an email notification in the following cases:
z Successful payment
z Pending payment
z Canceled payment
To turn off payment notifications through email, follow these steps:
1. In the My Account tab, click the Profile subtab.
2. In the Account Information column, click the Notifications link.
3. Find the Payment Notifications heading, and clear the I receive PayPal Website
Payments and Instant Purchase checkbox.
4. Click Save.
PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide March 2008 99
Page 100

Transactions
8
Payment Notification Integration
Reporting
Paypal Reporting Tools provide the information necessary to effectively measure and manage
a business. With PayPal Reporting Tools, merchants can:
z Analyze revenue sources to better understand customers’ buying behaviors.
z Automate time-consuming bookkeeping tasks.
z Accurately settle and reconcile transactions.
The following reports are available:
z Monthly Account Statements — Every month, view a summary of all credits and debits
that affect the account balance.
z Merchant Sales Reports — Every week, receive a valuable analysis of revenue by sales
channel and currency.
z History Log — View an online record of received and sent payments.
z Downloadable Logs — Keep track of transaction history by downloading it into various
file formats (suitable for financial settlements).
For more information about PayPal reports, see the PayPal Reporting Tools website
(http://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=p/xcl/rec/reports-intro-outside
).
Instant Payment Notification (IPN)
IPN provides immediate notification and confirmation of PayPal payments received. IPN
consists of three parts:
1. A customer issues payment from one of a number of processes (Website Payments
Standard FORMs, the Express Checkout APIs, MassPay, or a refund).
2. PayPal posts FORM variables to a URL specified by the merchant (either globally in the
Profile or on a per-transaction basis with the NOTIFYURL variable) that runs a program to
process the variables. The customer’s payment information (such as customer name and
payment amount) is included in the notification.
3. The server validates the notification to ensure it is legitimate.
Because credit-card and bank information are not transmitted in IPN, PayPal does not require
SSL to encrypt IPN transmissions.
Activating IPN
There are two ways to activate IPN:
z Include the NOTIFYURL variable in the DoDirectPayment or
DoExpressCheckoutPayment API call. Doing this activates IPN on a per-transaction
basis.
z In the merchant’s PayPal profile, under Selling Preferences, click Instant Payment
Notification Preferences, click Edit, click the checkbox and enter the URL of the program
100 March 2008 PayPal Certified Developer Program Study Guide
 Loading...
Loading...