Patton electronics COPPERLINK 2160 Series, COPPERLINK 2160/2W/EUI, COPPERLINK 2161/4W/EUI, COPPERLINK 2162/8W/EUI User Manual
Page 1

For Quick
Start Installation
CopperLink™ Model 2160 Series
Long Range Ethernet Extender
User Manual
Sales Office: +1 (301) 975-1000
Technical Support: +1 (301) 975-1007
E-mail: support@patton.com
WWW: www.patton.com
Part Number: 07M2160-GS, Rev. D
Revised: August 7, 2012
Page 2

Patton Electronics Company, Inc.
7622 Rickenbacker Drive
Gaithersburg, MD 20879 USA
Tel: +1 (301) 975-1000
Fax: +1 (301) 869-9293
Support: +1 (301) 975-1007
Web: www.patton.com
E-mail: support@patton.com
Trademark Statement
The term CopperLink is a trademark of Patton Electronics Company. All other trademarks presented in this document are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright © 2012, Patton Electronics Company. All rights reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Patton Electronics assumes no liability for errors that may appear in this document.
Warranty Information
Patton Electronics warrants all Model 2160 components to be free from defects, and
will—at our option—repair or replace the product should it fail within one year from
the first date of shipment.
This warranty is limited to defects in workmanship or materials, and does not cover
customer damage, abuse or unauthorized modification. If the product fails to perform
as warranted, your sole recourse shall be repair or replacement as described above.
Under no condition shall Patton Electronics be liable for any damages incurred by the
use of this product. These damages include, but are not limited to, the following: lost
profits, lost savings and incidental or consequential damages arising from the use of or
inability to use this product. Patton Electronics specifically disclaims all other warranties, expressed or implied, and the installation or use of this product shall be deemed
an acceptance of these terms by the user.
Page 3
Summary Table of Contents
1 General information...................................................................................................................................... 17
2 Applications overview.................................................................................................................................... 22
3 Hardware installation.................................................................................................................................... 27
4 Web configuration ........................................................................................................................................ 33
5 Console and Telnet configuration................................................................................................................. 69
6 Contacting Patton for assistance ................................................................................................................. 103
A Compliance information ............................................................................................................................ 106
B Specifications .............................................................................................................................................. 108
C Port pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 111
3
Page 4
Table of Contents
Summary Table of Contents ........................................................................................................................... 3
Table of Contents ........................................................................................................................................... 4
List of Figures ................................................................................................................................................. 9
List of Tables ................................................................................................................................................ 11
About this guide ........................................................................................................................................... 12
Audience............................................................................................................................................................... 12
Structure............................................................................................................................................................... 12
Precautions........................................................................................................................................................... 13
Safety when working with electricity ...............................................................................................................14
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage ....................................................................................................15
General observations .......................................................................................................................................15
Typographical conventions used in this document................................................................................................ 16
General conventions .......................................................................................................................................16
1 General information...................................................................................................................................... 17
Model 2160 overview............................................................................................................................................18
Model 2160 front panel.........................................................................................................................................19
LED descriptions ............................................................................................................................................19
Model 2160 rear panel ..........................................................................................................................................20
Port descriptions .............................................................................................................................................20
Reset button ...................................................................................................................................................21
Ground terminal .............................................................................................................................................21
2 Applications overview.................................................................................................................................... 22
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................................23
Typical application ................................................................................................................................................23
Distance charts ......................................................................................................................................................24
Distance Chart 2160 Series – Auto Mode (TCPAM-32/16) ...........................................................................24
Distance Chart 2160 Series – Optimal Mode (TCPAM-128) .........................................................................25
Distance Chart 2160 Series – TCPAM-128 ....................................................................................................26
3 Hardware installation.................................................................................................................................... 27
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................................28
Planning the installation ........................................................................................................................................28
Network diagram ............................................................................................................................................29
IP related information .....................................................................................................................................29
AC Power Mains .............................................................................................................................................29
Location and mounting requirements .............................................................................................................30
Installing the Model 2160
Unpacking the Model 2160 ............................................................................................................................30
Connecting cables ...........................................................................................................................................30
Grounding the Model 2160 and connecting power .........................................................................................31
.....................................................................................................................................30
4
Page 5

Model 2160 Series User Manual Table of Contents
Configuring the Model 2160.................................................................................................................................32
Web configuration requirements .....................................................................................................................32
Console configuration requirements ...............................................................................................................32
Telnet configuration requirements ..................................................................................................................32
4 Web configuration ........................................................................................................................................ 33
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................................35
Setting Up the WMI .............................................................................................................................................35
TCP/IP setup ..................................................................................................................................................35
System Login ..................................................................................................................................................35
Basic Configuration Options .................................................................................................................................36
Operation mode and Management port ..........................................................................................................37
DHCP server ..................................................................................................................................................37
LAN ...............................................................................................................................................................39
Review and save basic setup changes ...............................................................................................................40
Advanced Configuration Options..........................................................................................................................41
LINE ..............................................................................................................................................................41
Line Type ..................................................................................................................................................41
Annex Type ...............................................................................................................................................41
TCPAM Type ...........................................................................................................................................42
Main Rate .................................................................................................................................................42
SNR Margin .............................................................................................................................................42
Line Probe .................................................................................................................................................42
VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................43
802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN .........................................................................................................................45
Egress and Ingress Rules ......................................................................................................................45
Tag-Based VLAN Overview ................................................................................................................46
Configuring 802.1Q VLAN Tagging ..................................................................................................47
Port-Based VLAN .....................................................................................................................................48
Quality of Service (QoS) .................................................................................................................................49
Port Based Priority ....................................................................................................................................50
Scheduling Configuration. ..................................................................................................................50
WRR Configuration ...........................................................................................................................52
WFQ Configuration ...........................................................................................................................52
Port-Based Priority Table ....................................................................................................................52
VLAN Tag Priority ...................................................................................................................................53
Scheduling Configuration ...................................................................................................................54
WRR Configuration ...........................................................................................................................54
WFQ Configuration ...........................................................................................................................54
VLAN Tag Priority Table ...................................................................................................................55
Configuration Example
.......................................................................................................................55
IP DSCP Priority ......................................................................................................................................56
Scheduling Configuration ...................................................................................................................57
WRR Configuration ...........................................................................................................................57
5
Page 6

Model 2160 Series User Manual Table of Contents
WFQ Configuration ...........................................................................................................................57
IP DSCP Priority Table ......................................................................................................................58
IP DSCP Configuration Example .......................................................................................................58
Rate Limit .......................................................................................................................................................59
Flow Control ..................................................................................................................................................59
Status Options.......................................................................................................................................................60
LINE Status ....................................................................................................................................................60
Management Status .........................................................................................................................................60
LAN Status .....................................................................................................................................................61
Performance Status .........................................................................................................................................61
Administration Options ........................................................................................................................................62
Security Administration ..................................................................................................................................62
User Profiles ..............................................................................................................................................62
Remote Management Hosts ......................................................................................................................63
SNMP Administration ....................................................................................................................................63
Community Pool ......................................................................................................................................64
Trap Host Pool .........................................................................................................................................65
Remote Syslog ................................................................................................................................................65
Utility Options......................................................................................................................................................66
System Information ........................................................................................................................................66
Configuration Tool .........................................................................................................................................66
Upgrade ..........................................................................................................................................................67
Logout ............................................................................................................................................................68
Restart ............................................................................................................................................................68
5 Console and Telnet configuration................................................................................................................. 69
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................................71
Log in to the console interface ........................................................................................................................71
Log in using Telnet .........................................................................................................................................71
Interface commands ........................................................................................................................................71
Window structure ...........................................................................................................................................72
Main Menu Tree...................................................................................................................................................73
Menu tree for authorized users ........................................................................................................................73
Menu tree for unauthorized users ....................................................................................................................74
Enable Command Menu.......................................................................................................................................75
Setup Command Menu.........................................................................................................................................76
Line ................................................................................................................................................................76
Mode ........................................................................................................................................................77
Link ..........................................................................................................................................................77
Annex Type ...............................................................................................................................................77
TCPAM Type ...........................................................................................................................................77
Maximum Main Rate ................................................................................................................................77
SNR Margin .............................................................................................................................................77
Line Probe .................................................................................................................................................78
6
Page 7

Model 2160 Series User Manual Table of Contents
Clear .........................................................................................................................................................78
LAN ...............................................................................................................................................................78
VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................79
Mode ........................................................................................................................................................79
802.1Q VLAN ...................................................................................................................................80
Port-Based VLAN ...............................................................................................................................81
QoS ................................................................................................................................................................82
Mode ........................................................................................................................................................82
Queue Schedule ........................................................................................................................................82
Queue Weight ...........................................................................................................................................83
Queue Egress Rate ....................................................................................................................................84
Port-Based Priority QoS ............................................................................................................................84
VLAN Tag Priority QoS ...........................................................................................................................84
IP DSCP Priority QoS ..............................................................................................................................85
List ............................................................................................................................................................86
Rate ................................................................................................................................................................86
Management ...................................................................................................................................................87
DHCP ............................................................................................................................................................87
DHCP Server ............................................................................................................................................88
DHCP Fixed Host ....................................................................................................................................88
DNS Proxy .....................................................................................................................................................89
Host Name .....................................................................................................................................................89
Factory Default ...............................................................................................................................................89
Status Command Menu ........................................................................................................................................90
LINE Status ....................................................................................................................................................90
Interface Status ...............................................................................................................................................91
Show Command Menu.........................................................................................................................................92
Write Command...................................................................................................................................................93
Reboot Command.................................................................................................................................................93
Ping Command.....................................................................................................................................................93
Administration Command Menu ..........................................................................................................................95
User Profile .....................................................................................................................................................95
Modify/Add User ......................................................................................................................................95
Security ...........................................................................................................................................................96
Telnet TCP Port ..............................................................................................................................
.........96
Legal IP Address Pool ................................................................................................................................96
SNMP ............................................................................................................................................................97
Community ..............................................................................................................................................97
Trap host ..................................................................................................................................................98
Supervisor Password and ID ...........................................................................................................................99
Supervisor Password ..................................................................................................................................99
Supervisor ID ............................................................................................................................................99
Utility Command Menu .....................................................................................................................................100
Upgrade main software .................................................................................................................................100
7
Page 8

Model 2160 Series User Manual Table of Contents
Backup system configuration ........................................................................................................................100
Restore system configuration .........................................................................................................................100
Exit Command....................................................................................................................................................102
6 Contacting Patton for assistance ................................................................................................................. 103
Introduction........................................................................................................................................................104
Contact information............................................................................................................................................104
Warranty Service and Returned Merchandise Authorizations (RMAs).................................................................104
Warranty coverage ........................................................................................................................................104
Out-of-warranty service ...........................................................................................................................105
Returns for credit ....................................................................................................................................105
Return for credit policy ...........................................................................................................................105
RMA numbers ..............................................................................................................................................105
Shipping instructions ..............................................................................................................................105
A Compliance information ............................................................................................................................ 106
Compliance .........................................................................................................................................................107
EMC compliance: .........................................................................................................................................107
Radio and TV interference (FCC Part 15)...........................................................................................................107
CE Declaration of Conformity............................................................................................................................107
Authorized European Representative...................................................................................................................107
B Specifications .............................................................................................................................................. 108
Line Connector ...................................................................................................................................................109
Line Modulation .................................................................................................................................................109
Ethernet Connector.............................................................................................................................................109
LAN Protocols.....................................................................................................................................................109
VLAN Support....................................................................................................................................................109
QoS Support .......................................................................................................................................................109
Management Connector......................................................................................................................................109
Management Interface.........................................................................................................................................110
Front Panel Indicators.........................................................................................................................................110
Power Supply ......................................................................................................................................................110
Environment .......................................................................................................................................................110
Dimensions .........................................................................................................................................................110
Weight ................................................................................................................................................................110
C Port pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 111
Introduction........................................................................................................................................................112
Console port
........................................................................................................................................................112
Ethernet ..............................................................................................................................................................113
Line (CopperLink) ..............................................................................................................................................113
8
Page 9
List of Figures
1 Model 2160 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2 Model 2160 front panel LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3 Model 2160 rear panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4 Model 2160 application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5 Model 2160 connection diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6 Grounding stud . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
7 System login screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8 Basic setup flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
9 Operation mode and Management port setup page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
10 Basic DHCP setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
11 LAN setup page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
12 Review and save basic setup changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
13 LINE page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
14 VLAN page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
15 VLAN Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
16 802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
17 VLAN tag field . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
18 802.1Q VLAN diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
19 Port-Based VLAN page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
20 QoS page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
21 QoS - Port Based Priority page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
22 WRR Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
23 WFQ Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
24 BE Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
25 SP Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
26 QoS - Port Based Priority - WRR Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
27 QoS - Port Based Priority - WFQ Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
28 QoS - Port Based Priority Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
29 QoS - VLAN Tag Priority page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
30 IEEE 802.1Q Tagged Frame for Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
31 QoS - Tag Based Priority - WRR Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
32 QoS - Tag Based Priority - WFQ Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
33 QoS - VLAN Tag Priority Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
34 Service by WRR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
35 DSCP field . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
36 QoS - IP DSCP Priority - WRR Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
37 QoS - IP DSCP Priority - WFQ Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
38 QoS - IP DSCP Priority page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
39 DSCP Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
40 Rate Limit page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
41 Flow Control page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
42 LINE Status page (8-wire model shown) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
43 Management Status page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
44 LAN Status page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
45 Performance Status page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
46 Security Administration page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
47 Model 2160 configuration modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
9
Page 10

Model 2160 Series User Manual
48 Remote Management Host section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
49 SNMP Administration page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
50 SNMP community pool configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
51 Trap host pool configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
52 Remote Syslog configuration page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
53 System Information page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
54 Configuration Tool page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
55 Upgrade page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
56 Logout page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
57 Restart page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
58 Restart page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
59 Console/Telnet Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
60 Menu tree for authorized users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
61 Main screen for authorized users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
62 Main menu for unauthorized users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
63 Main screen for unauthorized users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
64 LINE Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
65 Interface Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
66 System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
67 Show Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
68 EIA-561 (RJ-45 8-pin) port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
10
Page 11
List of Tables
1 General conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2 Front panel LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3 Port descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4 Distance Chart 2160 Series – Auto Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5 Distance Chart Model 2160 Series – Optimal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6 Distance Chart Model 2160 Series – TCPAM-128 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
7 Line Type Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
8 Main Rate Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
9 VLAN Tag Priority Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
10 WRR Scheduling Configuration Example Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
11 Default SNMP Communities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
12 Console settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
13 Interface commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
14 Enable Command Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
15 Line Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
16 Line Type Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
17 Main Rate Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
18 LAN Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
19 VLAN Mode Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
20 802.1Q VLAN Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
21 VLAN Mode Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
22 Queue Schedule Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
23 Queue Schedule Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
24 Egress Rate (N Value) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
25 Port-Based Priority QoS Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
26 VLAN Tag Priority Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
27 VLAN Tag Priority QoS Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
28 Rate Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
29 IP DSCP Priority QoS Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
30 DHCP Command Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
31 Status Command Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
32 Interface Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
33 Show Command Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
34 RJ45 socket 10/100Base-T . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
35 RJ45 socket CopperLink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
11
Page 12
About this guide
This guide describes the CopperLink™ Model 2160 hardware, installation and basic configuration.
Audience
This guide is intended for the following users:
• Operators
• Installers
• Maintenance technicians
Structure
This guide contains the following chapters and appendices:
• Chapter 1, “General information” on page 17 provides information about Ethernet Extender features and
capabilities
• Chapter 2, “Applications overview” on page 22 describes the typical application for the Model 2160
• Chapter 3, “Hardware installation” on page 27 provides quick start hardware installation procedures
• Chapter 4, “Web configuration” on page 33 describes configuring the Model 2160 via the web interface
• Chapter 5, “Console and Telnet configuration” on page 69 describes configuring the Model 2160 via the
console interface
• Chapter 6, “Contacting Patton for assistance” on page 103 contains information on contacting Patton tech-
nical support for assistance
• Appendix A, “Compliance information” on page 106 contains compliance information for the Model 2160
• Appendix B, “Specifications” on page 108 contains for the specifications for the Model 2160
• Appendix C, “Port pin-outs” on page 111 contains pinouts for the Model 2160 ports
For best results, read the contents of this guide before you install the Model 2160.
12
Page 13

Model 2160 Series User Manual About this guide
Precautions
Notes, cautions, and warnings, which have the following meanings, are used throughout this guide to help you
become aware of potential problems. Warnings are intended to prevent safety hazards that could result in personal injury. Cautions are intended to prevent situations that could result in property damage or
impaired functioning.
Note
IMPORTANT
CAUTION
CAUTION
WARNING
WARNING
A note presents additional information or interesting sidelights.
The alert symbol and IMPORTANT heading calls attention to
important information.
The alert symbol and CAUTION heading indicate a potential
hazard. Strictly follow the instructions to avoid
property damage.
The shock hazard symbol and CAUTION heading indicate a
potential electric shock hazard. Strictly follow the instructions to
avoid property damage caused by electric shock.
The alert symbol and WARNING heading indicate a potential safety hazard.
Strictly follow the warning instructions to avoid personal injury.
The shock hazard symbol and WARNING heading indicate a potential electric
shock hazard. Strictly follow the warning instructions to avoid injury caused
by electric shock.
13
Page 14

Model 2160 Series User Manual About this guide
Safety when working with electricity
The Model 2160 contains no user serviceable parts. The equipment shall be
returned to Patton Electronics for repairs, or repaired by qualified service per-
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
sonnel. Opening the Model 2160 case will void the warranty.
Mains Voltage: Do not open the case the when the power cord is attached.
Line voltages are present within the power supply when the power cords are
connected. The mains outlet that is utilized to power the device shall be
within 10 feet (3 meters) of the device, shall be easily accessible, and protected by a circuit breaker.
For AC powered units, ensure that the power cable used meets all applicable
standards for the country in which it is to be installed, and that it is connected
to a wall outlet which has earth ground.
Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether
power to the Model 2160 is ON or OFF. To avoid electric shock, use caution
when near WAN ports. When detaching the cables, detach the end away from
the Model 2160 first.
WARNING
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of
lightning activity.
In accordance with the requirements of council directive 2002/
96/EC on Waste of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE),
ensure that at end-of-life you separate this product from other
waste and scrap and deliver to the WEEE collection system in
your country for recycling.
14
Page 15

Model 2160 Series User Manual About this guide
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
When starting to install interface cards place the interface card on its shielded plastic bag if you lay it on
your bench.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry. It occurs when electronic
printed circuit cards are improperly handled and can result in complete or intermittent failures.
Always follow ESD prevention procedures when removing and
replacing cards.
CAUTION
Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap, ensuring that it makes good
skin contact. Connect the clip to an unpainted surface of the
chassis frame to safely channel unwanted ESD voltages
to ground.
To properly guard against ESD damage and shocks, the wrist
strap and cord must operate effectively. If no wrist strap is available, ground yourself by touching the metal part of the chassis.
General observations
• C
lean the case with a soft slightly moist anti-static cloth
• Place the unit on a flat surface and ensure free air circulation
• Avoid exposing the unit to direct sunlight and other heat sources
Protect the unit from moisture, vapors, and corrosive liquid
•
s
15
Page 16
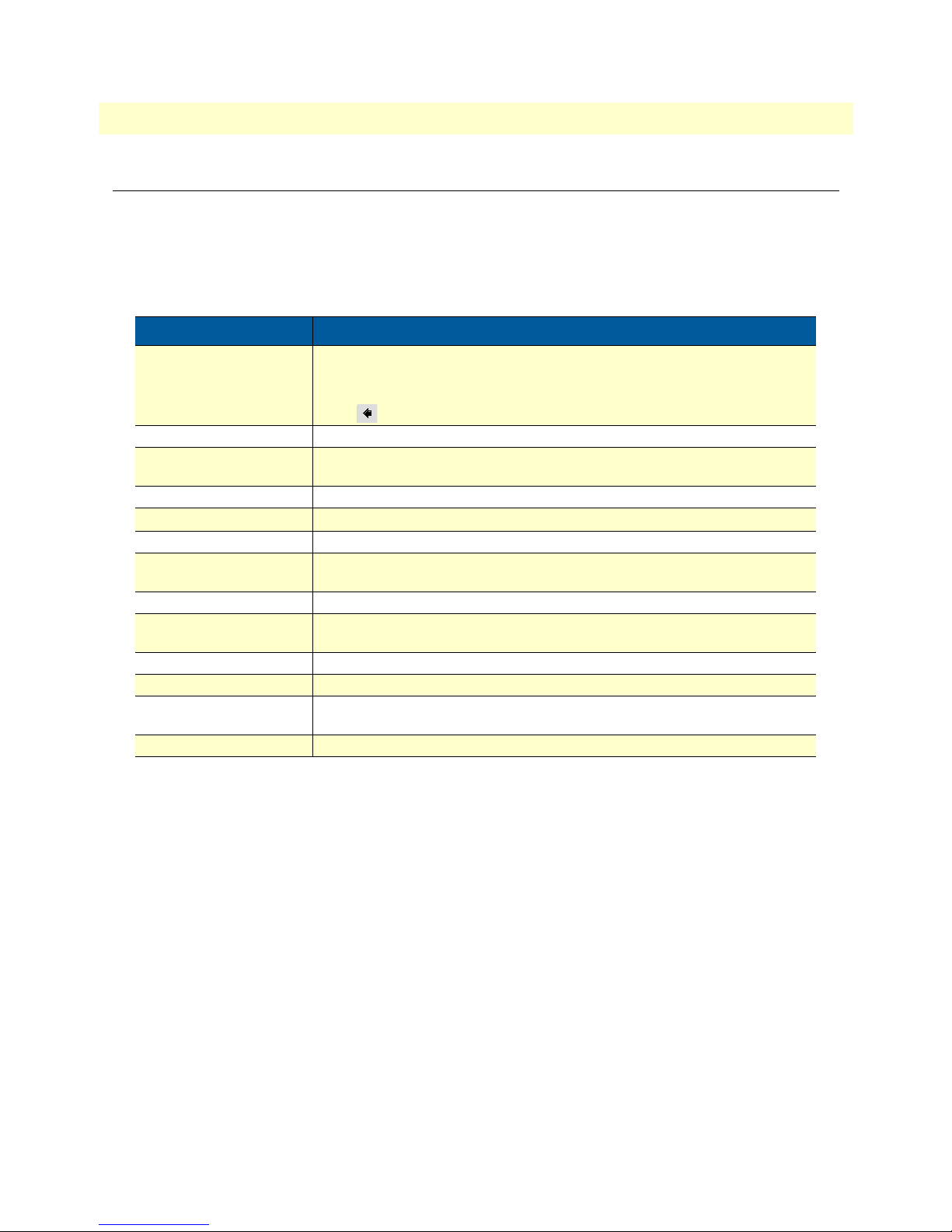
Model 2160 Series User Manual About this guide
Typographical conventions used in this document
This section describes the typographical conventions and terms used in this guide.
General conventions
The procedures described in this manual use the following text conventions:
Table 1. General conventions
Convention Meaning
Garamond blue type
Futura bold type Commands and keywords are in boldface font.
Futura bold-italic type Parts of commands, which are related to elements already named by the user, are
Italicized Futura type Variables for which you supply values are in italic font
Futura type
Garamond bold type Indicates the names of command buttons that execute an action.
< >
[ ] Elements in square brackets are optional.
{a | b | c} Alternative but required keywords are grouped in braces ({ }) and are separated
blue screen Information you enter is in blue screen font.
screen Terminal sessions and information the system displays are in screen font.
node The leading IP address or nodename of a Model 2160 is substituted with node in
# An hash sign at the beginning of a line indicates a comment line.
Indicates a cross-reference hyperlink that points to a figure, graphic, table, or section heading. Clicking on the hyperlink jumps you to the reference. When you
have finished reviewing the reference, click on the Go to Previous View
button in the Adobe® Acrobat® Reader toolbar to return to your starting point.
in boldface italic font.
Indicates the names of fields or windows.
Angle brackets indicate function and keyboard keys, such as <SHIFT>, <CTRL>,
<C>, and so on.
by vertical bars ( | )
boldface italic font.
16
Page 17
Chapter 1 General information
Chapter contents
Model 2160 overview............................................................................................................................................18
Model 2160 front panel.........................................................................................................................................19
LED descriptions ............................................................................................................................................19
Model 2160 rear panel ..........................................................................................................................................20
Port descriptions .............................................................................................................................................20
Reset button ...................................................................................................................................................21
Ground terminal .............................................................................................................................................21
17
Page 18

Model 2160 Series User Manual 1 • General information
Model 2160 overview
The Patton CopperLink™ Model 2160 simplifies and provides cost effective network extension by utilizing
pre-existing twisted pair infrastructure enables service providers to offer broadband or data backhaul services to
businesses, governments, and various institutions over existing last-mile, copper infrastructure. Today, more
than ever, operators are finding the business case for leveraging their existing copper networks to be highly
attractive from an ROI and initial investment perspective over fiber roll-outs.
Patton’s 2160 CopperLink Ethernet Extender incorporates multi-pair bonding to offer unmatched rate, reach
and reliable Ethernet connectivity, providing symmetrical 22.8 Mbps of bandwidth over 4-pair (8-wire) at distances up to 1.8 miles (2.9 km). The Model 2160 comes standard with a 4-port fast Ethernet switch with full
QoS and CoS features. VLAN (802.1q) capabilities include 4 levels of priorities, traffic flow control, and rate
control. These traffic management and QoS features enable service providers to provision for differentiated services and/or SLAs.
The following base models are available:
• 2160/2W/EUI: CopperLink Ethernet Extender (2-wire), 5.7 Mbps
• 2161/4W/EUI: CopperLink Ethernet Extender (4-wire), 11.4 Mbps
• 2162/8W/EUI: CopperLink Ethernet Extender (8-wire), 22.8 Mbps
Refer to Appendix B, “Specifications” on page 108 for a complete feature description of the Model 2160.
Model 2160 overview 18
Figure 1. Model 2160
Page 19
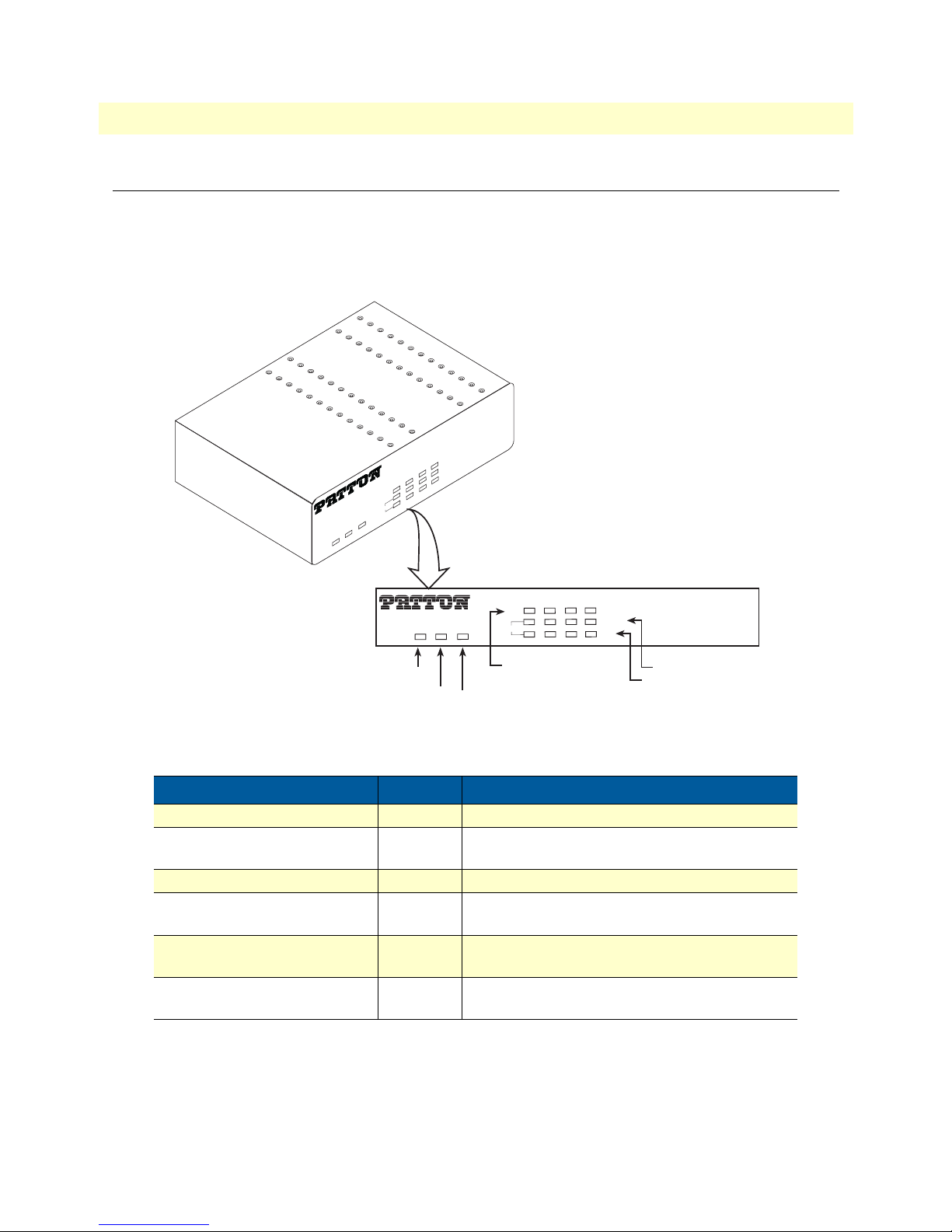
Model 2160 Series User Manual 1 • General information
Model 2160 front panel
LED descriptions
The front panel LEDs display the status of the power, system, Ethernet ports, and Line port. Figure 2 shows
the front panel LED indicators and table 2 provides a description of the LED indicators’ behavior.
2160
CopperLink™
Long Range Ethernet Extender
K
IN
T
L
C
/A
K
4
IN
L
M
0
3
0
1
2
1
N
A
W
N
A
L
Management
Alarm
Power
CopperLink™ 2160
K
IN
L
Long Range Ethernet Extender
T
C
/A
K
IN
L
M
0
0
1
LAN (1-4) Ethernet Link/Activity
LAN (1-4) Ethernet Mode
Power
Power
1
N
A
W
N
A
Alarm
Management
L
WAN(1-4) Line Connection
Alarm
Web Management Interface Connection
2
3
4
Figure 2. Model 2160 front panel LEDs
Table 2. Front panel LEDs
LED Condition Description
Power On Power is applied
Alarm On
Blink
LINE connection dropped
LINE self-test
Management On Management port is connected
WAN (1-4) LINK On
Blink
LAN (1-4) LINK/ACT On
Blink
LAN (1-4)100M On
Off
LINE is connected
LINE handshake/transmitted/received data
Ethernet is connected
Ethernet link transmitted/received data
LAN port is on 100M mode
LAN port is on 10M mode
Model 2160 front panel 19
Page 20
Model 2160 Series User Manual 1 • General information
Model 2160 rear panel
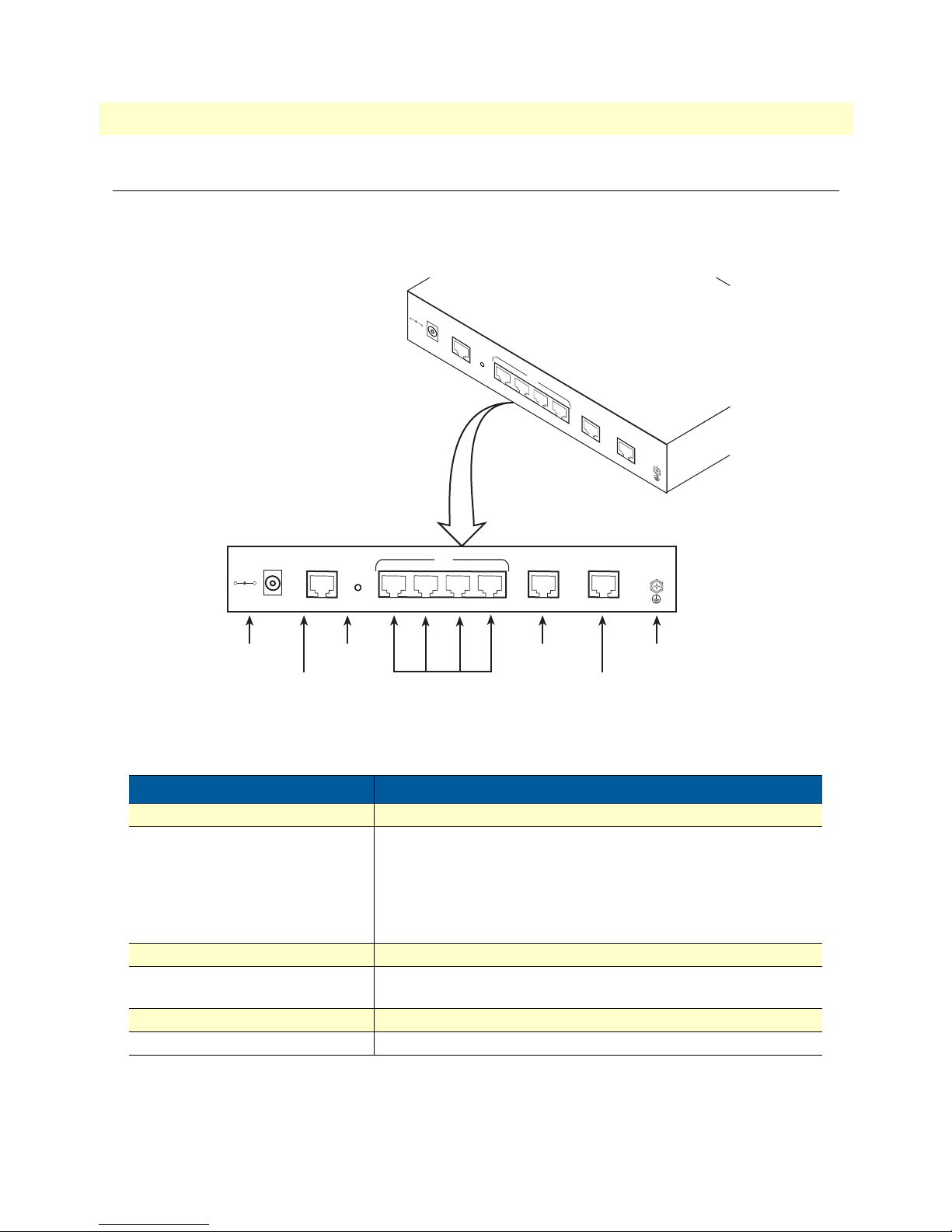
Port descriptions
The CopperLink™ Model 2160 rear panel ports are shown in figure 3 and described in table 3.
Power
+
-
Console
9
V
,
1
A
Reset
LAN
1 2 3 4
Management
Line
LAN
1 2 3 4
Management
Management
Line
Ground
+-
Power
Power Console
Reset
9V, 1A
Reset button
RJ-45 port
Console
RS-232 port
LAN (1-4)
RJ-45 port
Line
RJ-45 port
Figure 3. Model 2160 rear panel
Table 3. Port descriptions
Port Description
Power Power adaptor inlet: Input voltage 9VDC
Console (RS-232 control port) Used for service and maintenance, the Console port, an RS-232
RJ-45 connector with EIA-561 pinout, connects the router to a
serial terminal such as a PC or ASCII terminal (also called a dumb
terminal). Asynchronous default data rate 9600 bps, hardware
DSR and DTR signals for external modems are wired directly
together internally
Reset Reset button for rebooting or loading factory default settings
LAN (LAN Ethernet Ports 1-4) 10/100Base-Tx full-/half-duplex, RJ-45, auto detection and fall-
back, connects the unit to an Ethernet LAN.
Management RJ-45 for management port
Line Interface for WAN port (RJ-45)
Note
For port pinout information, see Appendix C, “Port pin-outs” on
page 111.
Model 2160 rear panel 20
Page 21

Model 2160 Series User Manual 1 • General information
Reset button
• To restart the unit with the current startup configuration—Press for less than 1 second and release the Reset
button. The Model 2160 will restart with the current startup configuration.
• To restart the unit with factory default configuration—Press the Reset button for 5 seconds until the Power
LED starts blinking. The unit will restart with factory default configuration.
• To restart the unit in bootloader mode (to be used only by trained CopperLink technicians)—Start with the
unit powered off. Press and hold the Reset button while applying power to the unit. Release the Reset button
when the Power LED starts blinking so the unit will enter bootloader mode.
Ground terminal
The marked lug or terminal should be connected to the building protective earth bus.The function of protective earth does not serve the purpose of providing protection against electrical shock,
but instead enhances surge suppression on the lines for installations where suitable bonding facilities exist.The connector type is M3 machine screw.
Model 2160 rear panel 21
Page 22
Chapter 2 Applications overview
Chapter contents
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................................23
Typical application ................................................................................................................................................23
Distance charts ......................................................................................................................................................24
Distance Chart 2160 Series – Auto Mode (TCPAM-32/16) ...........................................................................24
Distance Chart 2160 Series – Optimal Mode (TCPAM-128) .........................................................................25
Distance Chart 2160 Series – TCPAM-128 ....................................................................................................26
22
Page 23
Model 2160 Series User Manual 2 • Applications overview
Introduction
The Patton CopperLink™ Model 2160 simplifies and provides cost effective network extension by utilizing
pre-existing twisted pair infrastructure enables service providers to offer broadband or data backhaul services to
businesses, governments, and various institutions over existing last-mile, copper infrastructure. Today, more
than ever, operators are finding the business case for leveraging their existing copper networks to be highly
attractive from an ROI and initial investment perspective over fiber roll-outs.
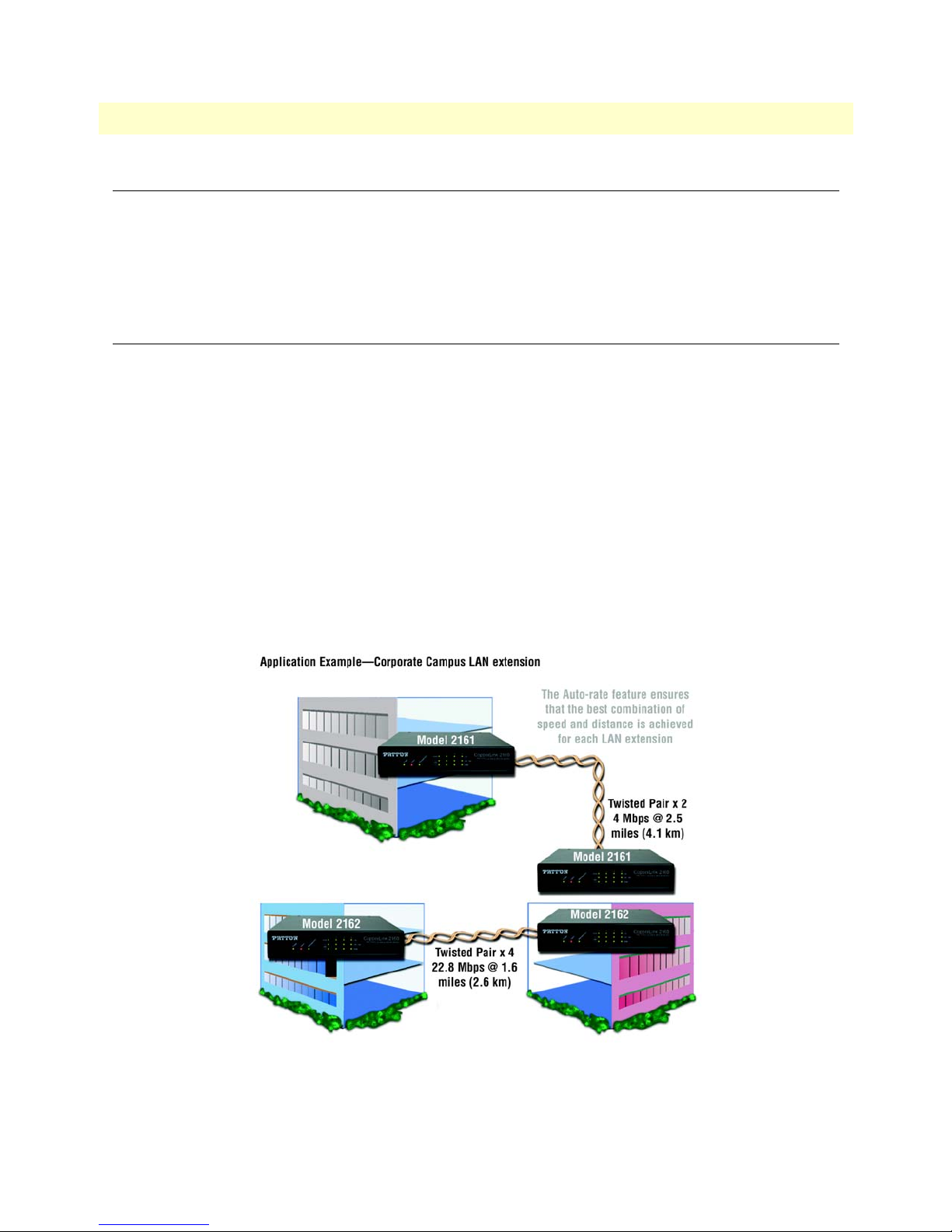
Typical application
Patton’s CopperLink Auto-Rate Ethernet Extenders are the perfect fit for simple, cost-effective high speed
Ethernet Extension. They allow customers to take advantage of the existing copper infrastructure to connect
remote LAN’s across distances and at speeds previously unthought-of. The auto-rate feature ensures the highest
speed is achieved on each connection, and the plug-n-play operation ensures they are up and running in seconds. Add in the 4 x auto-sensing full/half duplex 10/100Base-TX Ethernet ports with the integrated crossover
switch to make setup even easier. The value of these Ethernet Extenders can’t be beat!
• Auto-Rate Feature—The advanced auto-rate algorithm automatically determines the best possible rate for
each connection and sets up each extender without any need for user interface.
• Plug-and-Play—Just unpack the extenders, plug them into each end of the extension, power them up, and
they are up and running. It doesn’t get any easier!
• High Speed/Long Reach—These Ethernet Extenders provide the best combination of speed and distance
seen anywhere in the industry!
Introduction 23
Figure 4. Model 2160 application
Page 24
Model 2160 Series User Manual 2 • Applications overview
Distance charts
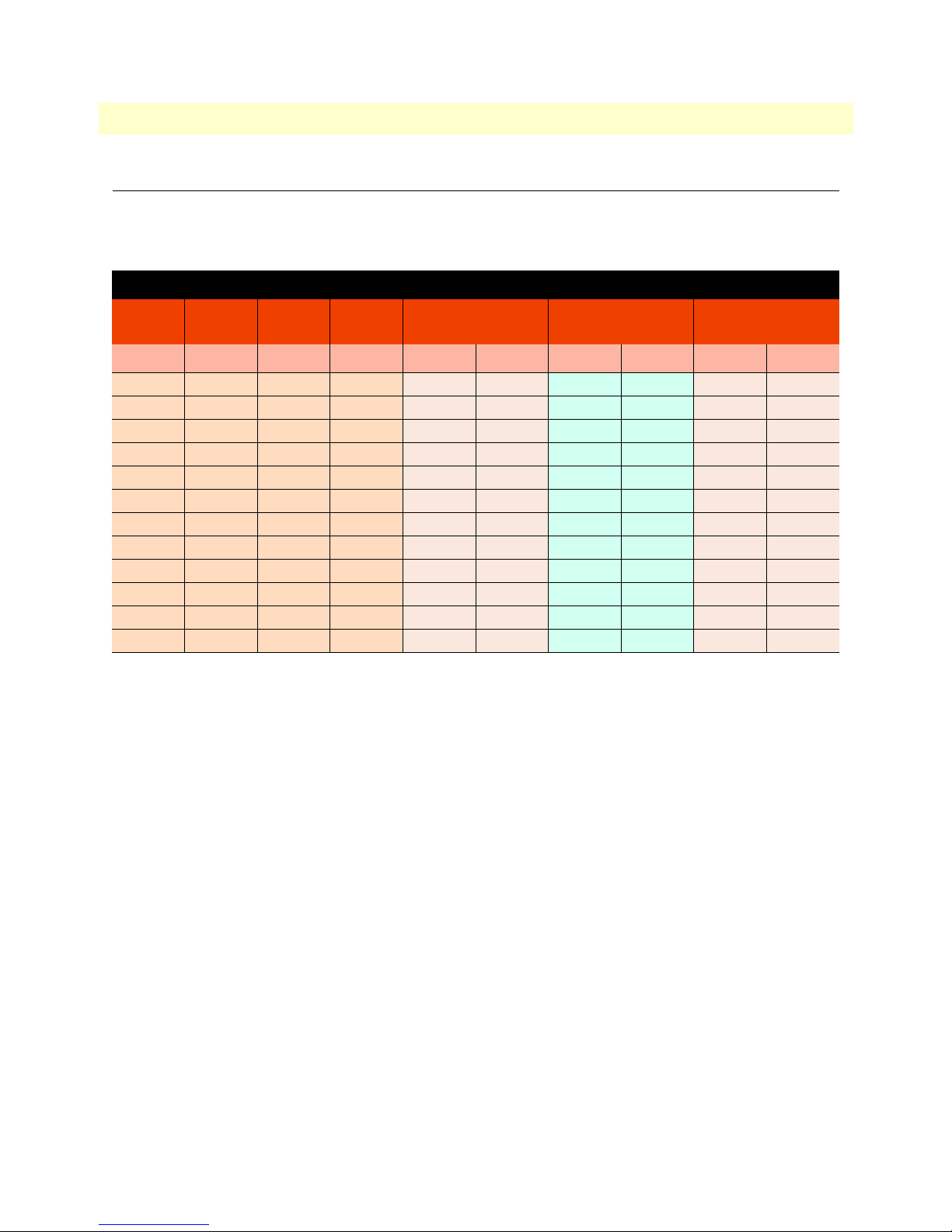
Distance Chart 2160 Series – Auto Mode (TCPAM-32/16)
Table 4. Distance Chart 2160 Series – Auto Mode
Line Rate Distance
Line
Speed
N = kbps kbps kbps kft km kft km kft km
2160
2-Wire
2161
4-Wire
2162
8-Wire
26 AWG/0.4mm 24 AWG/0.5mm 22 AWG/0.65mm
3 192 384 768 17.0 5.2 21.5 6.6 27.5 8.4
4 256 512 1024 17.0 5.2 20.5 6.2 27.0 8.2
8 512 1024 2048 14.5 4.4 17.5 5.3 23.5 7.2
12 768 1536 3072 13.5 4.1 16.0 4.9 21.5 6.6
16 1024 2048 4096 12.5 3.8 15.0 4.6 20.0 6.1
20 1280 2560 5120 12.0 3.7 14.5 4.4 19.0 5.8
24 1536 3072 6144 11.5 3.5 14.0 4.3 18.5 5.6
32 2048 4096 8192 11.0 3.4 13.5 4.1 17.5 5.3
36 2304 4608 9216 11.0 3.4 13.0 4.0 17.0 5.2
60 3840 7680 15360 9.0 2.7 11.0 3.4 14.5 4.4
72 4608 9216 18432 8.5 2.6 10.0 3.0 13.5 4.1
89 5696 11392 22784 7.5 2.3 9.0 2.7 12.0 3.7
Distance charts 24
Page 25

Model 2160 Series User Manual 2 • Applications overview
Distance Chart 2160 Series – Optimal Mode (TCPAM-128)
Table 5. Distance Chart Model 2160 Series – Optimal Mode
Line Rate Distance
Line
Speed
N = kbps kbps kbps kft km kft km kft km
2160
2-Wire
2161
4-Wire
2162
8-Wire
26 AWG/0.4mm 24 AWG/0.5mm 22 AWG/0.65mm
7 448 896 1792 20.0 6.1 24.0 7.3 31.0 9.4
8 512 1024 2048 19.0 5.8 23.0 7.0 30.0 9.1
10 640 1280 2560 18.0 5.5 20.5 6.2 28.0 8.5
11 704 1408 2816 17.0 5.2 19.0 5.8 26.5 8.1
16 1024 2048 4096 16.0 4.9 18.0 5.5 24.5 7.5
20 1280 2560 5120 15.0 4.6 17.0 5.2 23.0 7.0
22 1408 2816 5632 14.0 4.3 15.5 4.7 21.0 6.4
27 1728 3456 6912 13.0 4.0 14.5 4.4 20.0 6.1
34 2176 4352 8704 12.0 3.7 14.5 4.4 18.5 5.6
39 2496 4992 9987 11.0 3.4 13.0 4.0 17.0 5.2
44 2816 5362 11264 10.0 3.0 12.0 3.7 15.5 4.7
53 3392 6784 13568 9.0 2.7 10.5 3.2 13.5 4.1
73 4672 9344 18688 8.0 2.4 9.5 2.9 12.5 3.8
89 5696 11392 22784 7.0 2.1 8.5 2.6 10.5 3.2
110 7040 14080 28160 6.0 1.8 7.0 2.1 9.0 2.7
125 8000 16000 32000 5.0 1.5 6.0 1.8 7.5 2.3
152 9728 19456 38912 4.0 1.2 4.5 1.4 6.0 1.8
164 10496 20992 41984 3.0 0.9 3.5 1.1 4.5 1.4
198 12792 25584 51168 2.0 0.6 2.5 0.8 3.0 0.9
Distance charts 25
Page 26
Model 2160 Series User Manual 2 • Applications overview
Distance Chart 2160 Series – TCPAM-128
Table 6. Distance Chart Model 2160 Series – TCPAM-128
Line Rate Distance
Line
Speed
N = kbps kbps kbps kft km kft km kft km
2160
2-Wire
2161
4-Wire
2162
8-Wire
26 AWG/0.4mm 24 AWG/0.5mm 22 AWG/0.65mm
5 320 640 1280 22.0 6.7 26.5 8.1 34 10.4
6 384 768 1536 21.0 6.4 25.5 7.8 32.5 9.9
8 512 1024 2048 20.0 6.1 24.0 7.3 31.0 9.4
9 576 1152 2304 19.0 5.8 23.0 7.0 29.5 9.0
9 576 1152 2304 18.0 5.5 21.5 6.6 27.5 8.4
12 768 1536 3072 17.0 5.2 20.5 6.2 26.5 8.1
16 1024 2048 4096 16.0 4.9 19.5 5.9 24.5 7.5
20 1280 2560 5120 15.0 4.6 18.0 5.5 23.0 7.0
22 1408 2816 5632 14.0 4.3 16.5 5.0 21.5 6.6
27 1728 3456 6912 13.0 4.0 15.7 4.8 20.0 6.1
34 2176 4352 8704 12.0 3.7 14.5 4.4 18.5 5.6
39 2496 4992 9984 11.0 3.4 13.0 4.0 17.0 5.2
45 2880 5760 11520 10.0 3.0 12.0 3.7 15.5 4.7
53 3392 6784 13568 9.0 2.7 10.5 3.2 13.5 4.1
74 4736 9472 18944 8.0 2.4 9.5 2.9 12.5 3.8
90 5760 11520 23040 7.0 2.1 8.5 2.6 10.5 3.2
112 7168 14336 28672 6.0 1.8 7.0 2.1 9.0 2.7
126 8064 16128 32256 5.0 1.5 6.0 1.8 7.5 2.3
152 9728 19456 38912 4.0 1.2 4.5 1.4 6.0 1.8
167 10688 21376 42752 3.0 0.9 3.5 1.1 4.5 1.4
198 12672 25344 50688 2.0 0.6 2.5 0.8 3.0 0.9
220 14072 28144 56288 1.0 0.3 1.0 0.3 1.5 0.5
239 15288 30576 61152 0.5 0.2 0.5 0.2 1.0 0.3
Distance charts 26
Page 27
Chapter 3 Hardware installation
Chapter contents
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................................28
Planning the installation ........................................................................................................................................28
Network diagram ............................................................................................................................................29
IP related information .....................................................................................................................................29
AC Power Mains .............................................................................................................................................29
Location and mounting requirements .............................................................................................................30
Installing the Model 2160 .....................................................................................................................................30
Unpacking the Model 2160 ............................................................................................................................30
Connecting cables ...........................................................................................................................................30
Grounding the Model 2160 and connecting power .........................................................................................31
Configuring the Model 2160.................................................................................................................................32
Web configuration requirements .....................................................................................................................32
Console configuration requirements ...............................................................................................................32
Telnet configuration requirements ..................................................................................................................32
27
Page 28
Model 2160 Series User Manual 3 • Hardware installation
Introduction
This chapter contains information for planning the installation of the Model 2160 with the following installation procedures:
• “Unpacking the Model 2160” on page 30 lists the contents of the shipping box
• “Connecting cables” on page 30 describes how to install the port cables
• “Grounding the Model 2160 and connecting power” on page 31 describes how to ground and connect the
power source
Planning the installation
Before beginning the actual installation, we strongly recommend that you gather all the information you will
need to install and set up the device.
• Create a network diagram
• Gather IP related information
• Install the hardware and software needed to configure the Model 2160
• Verify power source reliability
When you finish preparing for your installation, go to section “Installing the Model 2160” on page 30 to
install the device.
Introduction 28
Page 29
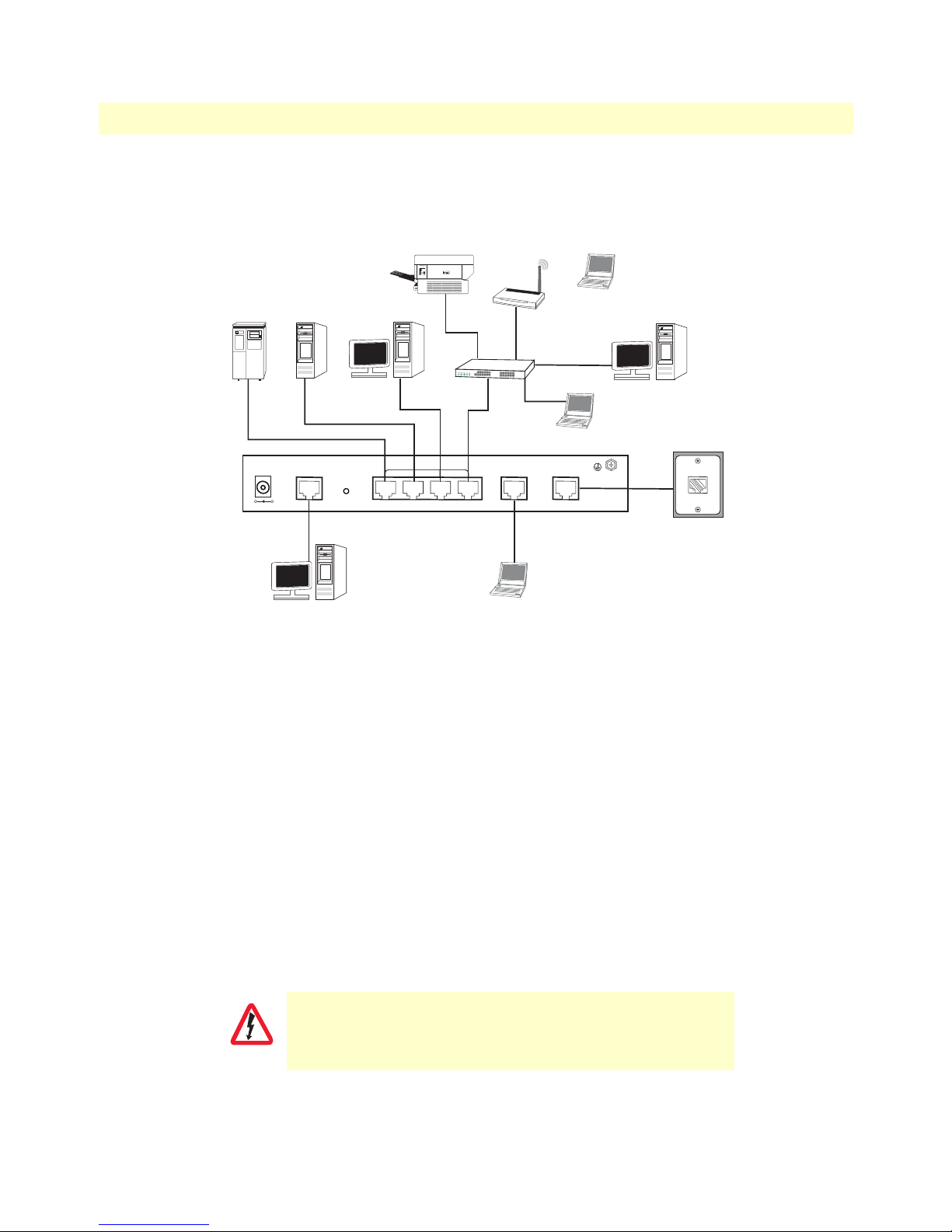
Model 2160 Series User Manual 3 • Hardware installation
Network diagram
Draw a network overview diagram that displays all neighboring IP nodes, connected elements and
telephony components. Figure 5 shows possible network connections to the Model 2160.
Printer
WAP
ServerRAID Drive
Desktop PC
Notebook
DC 9V
+-
CONSOLE
Desktop PC
Switch
Notebook
LAN
RST
LAN
MGMT
Laptop computer
LINE
Desktop PC
Figure 5. Model 2160 connection diagram
IP related information
Before you can set up the basic IP connectivity for your Model 2160 series you should have the following
information:
• IP addresses used for Ethernet LAN and WAN ports
• Subnet mask used for Ethernet LAN and WAN ports
You will need a PC (or equivalent) with a VT-100 emulation program (e.g. HyperTerminal) to configure the
software on your Model 2160.
AC Power Mains
If you suspect that your AC power is not reliable, for example if room lights flicker often or there is machinery
with large motors nearby, have a qualified professional test the power. Install a power conditioner if necessary.
Refer to “Grounding the Model 2160 and connecting power” on page 31.
The mains outlet that is utilized to power the equipment must be within
1 foot (3 meters) of the device and shall be easily accessible.
WARNING
Planning the installation 29
Page 30

Model 2160 Series User Manual 3 • Hardware installation
Note
When setting up your Model 2160 you must consider cable-length
limitations and potential electromagnetic interference (EMI) as
defined by the applicable local and international regulations. Ensure
that your site is properly prepared before beginning installation.
Location and mounting requirements
The Model 2160 is intended to be placed on a desktop or similar sturdy, flat surface that offers easy access to
the cables. Additionally, you should consider the need to access the unit for future upgrades and maintenance.
This completes the planning phase for installation. The next section begins the installation procedures.
Installing the Model 2160
Unpacking the Model 2160
Inspect the shipping carton for external damage. Note any damage before removing the container contents.
Report any equipment damage to the shipping carrier immediately for claim purposes. Save all packing material in case you need to return an item to the factory for servicing.
The Model 2160 comes with the following items:
• Model 2160 Quick Start Guide
• Model 2160
• An RJ-45-to-RJ-45 cable for use with the console and Ethernet ports
• A DB-9-to-RJ-45 (EIA-561) adapter for connecting a PC’s serial port to the Model 2160 console port
Note
Power cables are shipped separately from the Model 2160
Connecting cables
The
CAUTION
Interconnecting
and must be rated for the proper application with respect to voltage, current, anticipated temperature, flammability, and
mechanical serviceability.
cables must be acceptable for external use
1. Connect the Ethernet cable to the Management port. Model 2160 supports audi-MDIX switching so you
may use a crossover or straight-through cable.
2. Connect one end of a phone cable to the LINE port and the other end of the cable to a wall jack.
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of
lightning activity.
WARNING
Installing the Model 2160 30
Page 31

Model 2160 Series User Manual 3 • Hardware installation
Grounding the Model 2160 and connecting power
In connecting to the power source, it is important to establish a good grounding connection first, then the
power connection. Do the following:
1. Assemble a ground wire using #10 AWG wire with green-colored insulation and two ring terminals. Make
the wire long enough to reach one of the following earth ground sources:
– The building ground rod (generally located at the site’s main service entrance)
– A sprinkler system pipe
– A cold-water pipe
– Building structural steel
4
MGMT
LINE
Grounding stud
Figure 6. Grounding stud
2. Install the grounding wire between the grounding stud (see figure 6) and the grounding source.
3. Connect the power adapter to the DC 9V port on the Model 2160, and then connect to the power source.
Mains Voltage: Do not open the case the when the power cord is attached.
Line voltages are present within the power supply when the power cords are
WARNING
WARNING
connected. The mains outlet that is utilized to power the device shall be
within 10 feet (3 meters) of the device, shall be easily accessible, and protected by a circuit breaker.
The Model 2160 is not shipped with power cables. For AC powered units,
ensure that the power cable used meets all applicable standards for the country in which it is to be installed, and that it is connected to a wall outlet which
has earth ground.
The power supply automatically adjusts to accept an input voltage from 100 to 240 VAC(50/60 Hz).
IMPORTANT
Installing the Model 2160 31
Page 32

Model 2160 Series User Manual 3 • Hardware installation
Configuring the Model 2160
There are three different ways you can configure the Model 2160: the serial console, Telnet, or a web browser.
Web configuration requirements
Make sure that the PC you use for configuration has an Ethernet adapter and TCP/IP installed.
The Model 2160 provides a browser interface that allows you to configure and manage the Ethernet Extender.
After you set up the IP address for the 2160, you can access the Ethernet Extender's Web interface applications
directly in your browser by entering the IP address. You can then use your Web browser to manage and configure the unit from a PC.
Note
For detailed information on configuring the Model 2160 through the
Web interface, see Chapter 4, “Web configuration” on page 33.
Console configuration requirements
To configure the Model 2160 through the serial console, you can directly connect a terminal or a PC equipped
with a terminal-emulation program (such as Hyper Terminal) to the Ethernet Extender's console port.
Use the supplied serial cable (RJ-45 to DB9F) to connect the Model 2160 to a PC. After marking the connection, configure the terminal-emulation program to use the following parameters:
• 9600 bps
• 8 data bits
• no parity
• 1 stop bit
Note
For detailed information on configuring the Model 2160 through the
serial console, see Chapter 5, “Console and Telnet configuration” on
page 69.
Telnet configuration requirements
Make sure that the PC you use for configuration has an Ethernet adapter and TCP/IP installed. The Model
2160 supports Telnet for remote configuration. The command is “telnet 192.168.1.1” . When prompted for
the username and password for remote login, use admin for username and admin for password. All display
screens are the same as serial console configuration.
The default IP address is 192.168.1.1, but you may change the IP address for your application.
Note
For detailed information on configuring the Model 2160 through
Telnet, see Chapter 5, “Console and Telnet configuration” on
page 69.
Configuring the Model 2160 32
Page 33

Chapter 4 Web configuration
Chapter contents
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................................35
Setting Up the WMI .............................................................................................................................................35
TCP/IP setup ..................................................................................................................................................35
System Login ..................................................................................................................................................35
Basic Configuration Options .................................................................................................................................36
Operation mode and Management port ..........................................................................................................37
DHCP server ..................................................................................................................................................37
LAN ...............................................................................................................................................................39
Review and save basic setup changes ...............................................................................................................40
Advanced Configuration Options..........................................................................................................................41
LINE ..............................................................................................................................................................41
Line Type ..................................................................................................................................................41
Annex Type ...............................................................................................................................................41
TCPAM Type ...........................................................................................................................................42
Main Rate .................................................................................................................................................42
SNR Margin .............................................................................................................................................42
Line Probe .................................................................................................................................................42
VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................43
802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN .........................................................................................................................45
Egress and Ingress Rules...................................................................................................................... 45
Tag-Based VLAN Overview ................................................................................................................ 46
Configuring 802.1Q VLAN Tagging .................................................................................................. 47
Port-Based VLAN .....................................................................................................................................48
Quality of Service (QoS) .................................................................................................................................49
Port Based Priority ....................................................................................................................................50
Scheduling Configuration. .................................................................................................................. 50
WRR Configuration............................................................................................................................ 52
WFQ Configuration ........................................................................................................................... 52
Port-Based Priority Table.................................................................................................................... 52
VLAN Tag Priority ...................................................................................................................................53
Scheduling Configuration ................................................................................................................... 54
WRR Configuration............................................................................................................................ 54
WFQ Configuration ........................................................................................................................... 54
VLAN Tag Priority Table ................................................................................................................... 55
Configuration Example ....................................................................................................................... 55
IP DSCP Priority ......................................................................................................................................56
Scheduling Configuration ................................................................................................................... 57
WRR Configuration............................................................................................................................ 57
WFQ Configuration ........................................................................................................................... 57
33
Page 34

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
IP DSCP Priority Table ...................................................................................................................... 58
IP DSCP Configuration Example........................................................................................................ 58
Rate Limit .......................................................................................................................................................59
Flow Control ..................................................................................................................................................59
Status Options.......................................................................................................................................................60
LINE Status ....................................................................................................................................................60
Management Status .........................................................................................................................................60
LAN Status .....................................................................................................................................................61
Performance Status .........................................................................................................................................61
Administration Options ........................................................................................................................................62
Security Administration ..................................................................................................................................62
User Profiles ..............................................................................................................................................62
Remote Management Hosts ......................................................................................................................63
SNMP Administration ....................................................................................................................................63
Community Pool ......................................................................................................................................64
Trap Host Pool .........................................................................................................................................65
Remote Syslog ................................................................................................................................................65
Utility Options......................................................................................................................................................66
System Information ........................................................................................................................................66
Configuration Tool .........................................................................................................................................66
Upgrade ..........................................................................................................................................................67
Logout ............................................................................................................................................................68
Restart ............................................................................................................................................................68
34
Page 35

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Introduction
The Model 2160 provides a browser interface that allows you to configure and manage the Ethernet Extender.
Make sure that the PC you use for configuration has an Ethernet adapter and TCP/IP installed. After you set
up the IP address for the 2160, you can access the Ethernet Extender's Web interface applications directly in
your browser by entering the IP address. You can then use your Web browser to manage and configure the unit
from a PC.
Setting Up the WMI
This section introduces the configuration and functions of the Web Management Interface (WMI). The WMI
is an HTML-based management interface that allows you to easily set-up and manage the Model 2160.
The Model 2160 offers all monitoring and management features that allow users to manage this Model 2160
form anywhere on the network through a standard browser such as Internet Explorer.
TCP/IP setup
When DHCP is enabled, the Model 2160 acts as a DHCP server in your network. The Model 2160 will automatically assign IP address for the management port connection.
To set up TCP/IP on a Windows PC:
1. Click the Start button. Select the Control Panel.
2. Double-click on the Network icon.
3. In the Configuration window, select the TCP/IP protocol line that has been associated with your network
card and then click the property icon.
4. Click on the IP address tab and select Obtain IP address automatically. Click OK.
System Login
You may use a web browser such as Internet Explorer on your PC to connect the Model 2160. Type “http://”
and the IP address like as “http://192.168.1.1”.
The default IP address and sub net-mask of the Management port of the Model 2160 are 192.168.1.1 and
255.255.255.0. If DHCP is disabled, your PC can set the same net-mask such as 192.168.1.x where x is a
number from 2 to 254.
Introduction 35
Page 36

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Type the default User name root and default Password root and then click OK. For system security, you
should change the user name and password after initial onfiguration.
Figure 7. System login screen
Basic Configuration Options
This section contains information for setting up the operation mode and Management port IP, DHCP server,
and LAN via the WMI. Figure 8 shows a flowchart demonstrating basic setup via the WMI for the Model
2160.
Basic Configuration Options 36
Figure 8. Basic setup flowchart
Page 37

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Operation mode and Management port
To configure the operation mode and Management port in the WMI:
1. From the main menu, click Basic to display the basic installation page.
Figure 9. Operation mode and Management port setup page
2. For Operation Mode, select the radio button for CPE (Customer Premises Equipment) or CO (Central
Office). When using a “LAN to LAN” connection, one side must be set as CO and the other side must be
set as CPE.
3. Enter information for the Management port. The Model 2160 requires an IP address to be managed over
the network. The factory default IP address is 192.168.1.1. The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. The factory default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 . You can configure
another IP address and a different subnet mask for management purposes.
– IP: 192.168.1.1
– Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
– Host Name: SOHO
Some ISP providers require the Host Name as identification. You may check with your ISP to see if your
Internet service has been configured with a host name. In most cases, you can ignore this field.
4. Select an option for Trigger DHCP Service. If you don't need the DHCP service, select Disable.
5. Click Next to commit your changes and continue to the DHCP Server page (see “DHCP server” on
page 37).
DHCP server
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a communication protocol that allows network administrators to manage and automate the assignment of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses in an organization's network. Each machine that can connect to the Internet needs a unique IP address. When an organization sets up
the users with a connection to the Internet, an IP address must be assigned to each machine.
Without DHCP, the IP address must be entered manually at each computer. If computers move to another
location in another part of the network, a new IP address must be entered. DHCP lets a network administrator
Basic Configuration Options 37
Page 38

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
supervise and distribute IP addresses from a central point and automatically sends a new IP address when a
computer is plugged into a different place in the network. The embedded DHCP server assigns network configuration information to 253 users (max) accessing the Internet in the same time. For example, if the LAN IP
address is 192.168.0.1, the IP range of the LAN is 192.168.0.2 to 192.168.0.254.
To set up the DHCP Server for the Model 2160:
1. Click on Basic from the main menu, set up the Operation Mode and Management port, then click Next
to reach the DHCP Server page.
2. The DHCP server assigns the IP from the Start IP Address to the End IP Address. The legal IP address
range is from 0 to 255, but 0 is reserved as the network name and 255 is reserved for broadcast. This
implies that the legal IP address range is from 1 to 254. That means you cannot assign an IP greater than
254 or less than 1.
3. A Lease Time of 72 hours indicates that the DHCP server will reassign IP information every 72 hours.,
which is the default value for the Model 2160. You can set up the Lease Time for a range from 1 to 720
hours according to your application.
4. If you assign a fixed IP address to a device while using DHCP, you must enter the device's MAC address in
the Table of Fixed DHCP Host Entries.
5. Click Next to commit your changes and continue to the LAN page (see “LAN” on page 39).
Basic Configuration Options 38
Figure 10. Basic DHCP setup
Page 39

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
LAN
To configure LAN settings through the WMI:
1. Click on Basic from the main menu. Set up the Operation Mode and Management port, then click Next.
Set up the DHCP Server, then click Next to reach the LAN page.
Figure 11. LAN setup page
2. Choose an option for the LAN Type. If you select Disable or Dynamic IP, click Next at the bottom of the
screen to save your changes. If you select Static IP, you can enter information for IP, Subnet Mask, Gateway and DNS Server's IP.
3. If you select Static IP as the LAN Type, enter details in the Static IP section. The default values for Static
IP are:
– IP Address: 192.168.2.1
– Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
– Gateway: 0.0.0.0
– DNS Server 1: 168.95.1.1
– DNS Server 2: 168.95.192.1
4. Click Next to commit your changes and continue to the Review page (see “Review and save basic setup
changes” on page 40).
Basic Configuration Options 39
Page 40

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Review and save basic setup changes
1. Once you have entered information on the pages for Operation Mode and Management Port, DHCP
Server, and LAN, the Basic Setup Review page will display to confirm your changes.
Figure 12. Review and save basic setup changes
2. Look over the Review page to confirm the desired settings.
3. Click Restart to reboot the Model 2160 with the new settings.
4. Click Continue to configure other options.
Basic Configuration Options 40
Page 41

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Advanced Configuration Options
This section contains information for setting up advanced options for the Model 2160 via the WMI. Advanced
setup contains Model 2160 Line, VLAN, QoS and Rate Control parameters.
Note
The advanced functions are only intended for administrators to set
up. The incorrect advanced settings will affect the performance of the
Model 2160 or cause system errors and disconnection.
LINE
Click on LINE under Advanced on the main menu to reach the LINE advanced configuration page. You can
setup the Line Type (number of wires), Annex Type, TCPAM Type, Main Rate, SNR Margin, and Line Probe
settings for LINE parameters.
Figure 13. LINE page
Line Type
Select the line type for your model from the Link drop-down list. Line type means how many wires you want
to use on the line side. For example, you can select 2-wire, 4-wire or 8-wire line type for the 8-wire model.
Table 7. Line Type Chart
Line Type
2-wire 4-wire 8-wire
Model
Type
2160 2-wire model
2161 4-wire model
2162 8-wire model
•
• •
• • •
Annex Type
Select the appropriate Annex type from the drop-down list. Annex AF describes the transmission and performance requirements for North America. Annex BG describes performance and transmission requirements for
Europe.
Advanced Configuration Options 41
Page 42

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
TCPAM Type
TCPAM (Trellis Coded Pulse Amplitude Modulation) is the standard used for line coding. Select the TCPAM
type from the drop-down list. Auto is the default option for TCPAM. You can also manually set the TCPAM
type.
Main Rate
Select the line rate for your model from the Main Rate drop-down list. The main rate is the multiple of
64kbps, 128kbps, or 256kpbs- depending on your model type. Use Table 8 to determine the best main rate for
your model.
Table 8. Main Rate Chart
Model Type Multiple
2160 2-wire model 64 192–3840 768–5696 128–15296
2161 4-wire model 128 384–7680 1536–11392 256–30592
2162 8-wire model 256 768–15360 3072–22784 512–61184
TCPAM-16
= 3–60
TCPAM-32
= 12–89
TCPAM-128
= 2–239
SNR Margin
Select the desired SNR Margin value from the drop-down list. SNR margin is an index of line connection
quality. You can see the actual SNR margin in STATUS. You will experience better line connection quality for
larger SNR margin values.
For example, if you set the SNR margin is 5, the LINE connection will drop and reconnect when the SNR
margin is lower than 5. On the other hand, the device will reduce the line rate and reconnect for better line
connection quality. You may select the SNR margin from the range -10 to 21.
Line Probe
For adaptive mode applications, set the Line Probe to Enable. The Model 2160 will adapt the data rate accord-
ing to the line status. The screen will prompt the parameters that will be written in NVRAM. Check the
parameters before writing in NVRAM.
For all other applications, set the Line Probe to Disable.
Click Restart to reboot the Model 2160 with the new settings. Click Continue to configure other options.
Advanced Configuration Options 42
Page 43

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
VLAN
Click on VLAN under Advanced on the main menu to reach the VLAN advanced configuration page.
Figure 14. VLAN page
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a physical network to be partitioned into multiple logical networks. Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can belong to more than one group. With
VLAN, a device cannot directly talk to or hear from devices that are not in the same group.
With MTU (Multi-Tenant Unit) applications, VLAN is vital in providing isolation and security among the
subscribers. When properly configured, VLAN prevents one subscriber from accessing the network resources
of another on the same LAN.
VLAN also increases network performance by limiting broadcasts to a smaller and more manageable logical
broadcast domain. In traditional switched environments, all broadcast packets go to each every individual port.
With VLAN, all broadcasts are confined to a specific broadcast domain.
You can select from two types of VLAN: 802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN and Port-Based VLAN. The VLAN Setup
screen changes depending on whether you choose 802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN type or Port Based VLAN type.
The IEEE 802.1Q defines the operation of VLAN bridges that permit the definition, operation, and administration of VLAN topologies within a bridged LAN infrastructure.
Figure 15 on page 44 shows a diagram of possible VLAN connections.
Advanced Configuration Options 43
Page 44

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
VID 20
WAN2
WAN1
WAN3
WAN4
A
R
W
P
M
L
Backbone
1
N
A
W
N
A
L
G
A
I
D
WAN5
VID 30VID 10
WAN6
WAN7
WAN8
CopperLink“2160
4
3
2
K
N
I
L
Long Range Ethernet Extender
T
C
A
/
K
N
I
L
M
0
0
1
CopperLink Model 2160
Long Range Ethernet Extender
LAN2
LAN1
VID 10
LAN3
VID 20
LAN4
VID 30
Figure 15. VLAN Diagram
Advanced Configuration Options 44
Page 45

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN
Click on VLAN under Advanced on the main menu to reach the VLAN advanced configuration page. Then,
select the radio button for 802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN to display the configuration options.
Figure 16. 802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN page
• VID (Virtual LAN ID): A number to identify the VLAN segment. Select from 1 to 4094.
• PVID (Port VID): An untagged member of the default VLAN. Select from 1 to 4094.
• Link Type: Select from Access or Trunk. Access means the port can receive or send untagged packets.
Trunk means that the port can receive or send tagged packets.
In 802.1q, the VLAN information is written into the Ethernet packet itself. Each packet carries a VLAN ID
(Virtual LAN ID) called a tag. This tag allows VLANs to be configured across multiple switches.
Note
VLAN tags may be stripped by the hardware or the software.
When using 802.1q, four bytes are added to the Ethernet frame, and 12 bits are used for the VLAN ID. Theoretically, there can be up to 4096 VLANs per network.
An Ethernet packet that contains a VLAN ID is called a tagged packet. An Ethernet packet without a VLAN ID
is called an untagged packet. Typically, all packets leave untagged, unless tagged by the adapter prior to arriving
at the switch port.
Egress and Ingress Rules. Egress rules determine which frames can be transmitted out of a port, based on the
Egress List of the associated VLAN. Each VLAN has an Egress List that specifies the ports out of which frames
can be forwarded, and specifies whether the frames will be transmitted as tagged or untagged frames.
Ingress rules are a means of filtering out undesired traffic on a port. When Ingress Filtering is enabled, a port
determines if a frame can be processed based on whether the port is on the Egress List of the VLAN associated
with the frame.
When an untagged packet arrives at the switch port, the switch will write a VLAN ID into the header of the
frame according to the PVID (port VLAN) definition. Typically, most switches today have all ports set to a
default PVID of 1. When a tagged frame arrives at a switch port, the tag is respected.
A VID defines the member of a port group. A packet can only travel inside a member port when the member
port is part of a VID port group. Different VID groups are not visible to one another.
Advanced Configuration Options 45
Page 46

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Tag-Based VLAN Overview. Figure 17 shows the breakdown of the VLAN tag field.
Figure 17. VLAN tag field
The Tag Control Information (TCI) section of a VLAN tag includes information on the user Priority level,
the Canonical Format Indicator (CFI) and VLAN ID (VID).
• Tag Protocol Identifier (TPID) is a defined value of 8100 in hex. When a frame has the EtherType equal
to 8100, this frame carries the tag IEEE 802.1Q / 802.1P.
• Priority defines the priority level for different classes of traffic. There are 8 possible priority levels, with 0
being the lowest priority level and 7 being the highest level. IEEE 802.1P defines the operation for these 3
user priority bits.
• Canonical Format Indicator (CFI) is always set to zero for Ethernet switches. CFI is used for compatibility
reasons between an Ethernet-type network and Token Ring-type network. If a frame received at an Ethernet port has a CFI set to 1, then that frame should not be forwarded as it is to an untagged port.
• VLAN ID (VID) is the unique identification number of the VLAN, which is used by the standard 802.1Q.
It has 12 bits and allows the identification of 4096 (212) VLANs. Of the 4096 possible VIDs, a VID of 0 is
used to identify priority frames and the value 4095 (FFF) is reserved, so the maximum possible VLAN configurations are 4,094.
The Model 2160 initially configures one VLAN by default, VID=1. A port such as LAN1–4, line or sniffing
can have only one Port VID (PVID), but can have as many VID groups as the Model 2160 has memory in its
VLAN table to store them.
Advanced Configuration Options 46
Page 47

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Ports in the same VLAN group share the same frame broadcast domin thus increase network performance
through reduced boardcast traffic. You can modify VLAN groups at any time by adding, moving or changing
ports without any re-cabling.
SERVER
802.1Q VLAN
LAN1
LAN2
STU-C STU-R
CopperLink“2160
1 2 3 4
LINK
Long Range Ethernet Extender
WAN
LINK/ACT
LAN
DIAG
ALM
PWR
100M
ALM
PWR
DIAG
100M
CopperLink“2160
1 2 3 4
LINK
Long Range Ethernet Extender
WAN
LINK/ACT
LAN
LAN1
LAN2
CopperLink Model 2160
LAN3
Extender connection
LAN3
SERVER
1
2
3
4
5 6
7 8 9
#
0
*
LAN4
LAN4
1
2
3
4
5 6
7 8 9
#
0
*
VOIP VOIP
Figure 18. 802.1Q VLAN diagram
Configuring 802.1Q VLAN Tagging. Before enabling VLANs for the Model 2160, you must first assign
each port to the VLAN group(s) in which it will participate. By default all ports are assigned to VLAN1 as
untagged ports. Add a port as a tagged port if you want it to carry traffic for one or more VLANs, and any
intermediate network devices or the host at the other end of the connection supports VLANs. Then, assign
ports on the other VLAN-aware network devices along the path that will carry this traffic to the same
VLAN(s), either manually or dynamically using Generic VLAN Routing Protocol (GVRP). However, if you
want a port on this Model 2160 to participate in one or more VLANs, but none of the intermediate network
devices nor the host at the other end of the connection supports VLANs, then you should add this port to the
VLAN as an untagged port.
Note
VLAN-tagged frames can pass through VLAN-aware or VLANunaware network inter-connection devices, but the VLAN tags
should be stripped off before passing it on to any end-node host that
does not support VLAN tagging.
• VLAN Classification - When the Model 2160 receives a frame, it classifies the frame in one of two ways. If
the frame is untagged, the Model 2160 assigns the frame to an associated VLAN (based on the default
VLAN ID of the receiving port). But if the frame is tagged, the Model 2160 uses the tagged VLAN ID to
identify the port broadcast domain of the frame.
• Port Overlapping - You can use port overlapping to allow access to commonly shared network resources
among different VLAN groups, such as file servers or printers.
Advanced Configuration Options 47
Page 48

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
• Untagged VLANs - Untagged (or static) VLANs are typically used to reduce broadcast traffic and to
increase security. A group of network users assigned to a VLAN form a broadcast domain that is separate
from other VLANs configured on the Model 2160. Packets are forwarded only between ports that are designated for the same VLAN. Untagged VLANs can be used to manually isolate user groups or subnets.
• Port VID (PVID) - A PVID is a VLAN ID assigned to untagged frames received on the interface. (Default:
1). If an interface is not a member of VLAN 1 and you assign its PVID to this VLAN, the interface will
automatically be added to VLAN 1 as an untagged member. For all other VLANs, an interface must first be
configured as an untagged member before you can assign its PVID to that group.
• Link Type - The Link Type determines the types of frames the port can accept. Access means the port can
only receive or send untagged frame types. Trunk means that the port can only receive or send tagged frame
types.
Port-Based VLAN
Click on VLAN under Advanced on the main menu to reach the VLAN advanced configuration page. Then,
select the radio button for Port-Based VLAN to display the configuration options.
Figure 19. Port-Based VLAN page
Port-Based VLANs are VLANs where the packet forwarding decision is based on the destination MAC address
and its associated port. When using port-based VLAN, the port is assigned to a specific VLAN independent of
the user or system attached to the port. This means all users attached to the port should be members in the
same VLAN. The network administrator typically performs the VLAN assignment. The port configuration is
static and cannot be automatically changed to another VLAN without manual reconfiguration.
As with other VLAN approaches, the packets forwarded using this method do not leak into other VLAN
domains on the network. After a port has been assigned to a VLAN, the port cannot send to or receive from
devices in another VLAN.
Advanced Configuration Options 48
Page 49

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to both a network's ability to deliver data with minimum delay, and the networking methods used to control the use of bandwidth. Without QoS, all traffic date is equally likely to be
dropped when the network is congested. This can cause a reduction in network performance and mark the network inadequate for time-critical application such as video-on-demand.
Click on QoS under Advanced on the main menu to reach the QoS advanced configuration page.
Figure 20. QoS page
QoS (Quality of Service) is used to decide which devices can get priorities to pass though the Model 2160 once
the bandwidth is exhausted or fully saturated.
There are three types of QoS priority modes: Port Based Priority, VLAN Tag Priority and IP DSCP Priority.
You can also disable the QoS function.
Advanced Configuration Options 49
Page 50

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Port Based Priority
Click on QoS under Advanced on the main menu to reach the QoS advanced configuration page. Then, select
the radio button for Port Based Priority to display the configuration options.
Figure 21. QoS - Port Based Priority page
Select the ports that the port-based priority rule should be applied. There are six ports to choose from: LAN1,
LAN2, LAN3, LAN4, DSL and Sniffing.
The common setting tables are:
WRR configuration: Each queue type can setup the queue weight from 1 to 15.
WFQ configuration: Each ports and their queue type can set the bandwidth.
Scheduling Configuration. The 2160 provides three combinations of four commonly used techniques: Type
1, Type 2 and Type 3. Select a type in the Scheduling Configuration section, then provide details in the corresponding table.
If you select Type 1, refer to “WRR Configuration” on page 52.
If you select Type 2 or Type 3, refer to “WFQ Configuration” on page 52.
The Queue types are Weight Round Robin (WRR), Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ), Best Effort (BE) and
Strictly Priority (SP). Refer to the following page for more information on how each Queue Type operates.
Advanced Configuration Options 50
Page 51

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
• Weight Round Robin (WRR): All received packets will be stored into Queue 1, Queue 2, Queue 3, and
Queue 4. Assign a weight value for each queue. Then, WRR will re-assemble all packets from the four
queues based on the weight assignments.
Figure 22. WRR Example
For example, Figure 22 shows the weight value of each queue, ranging from 4, 2, 5, and 1. When the 2160
starts to process all of the packets in these queues with WRR, a new packet develops based on the weight
assignments. Then, the 2160 sends out the new packet.
• Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ): WFQ is a generalization of processor sharing, which allows several ses-
sions to share the same link. Refer to “WFQ Configuration” on page 52 to assign the data size of each
queue that can be accepted by each port.
• Best Effort (BE): The BE Queue Type is used for data applications that have low priority or the potential to
delay. BE does not use traffic priority or weight assignments, therefore BE is not recommended for high priority data, such as video or voice.
Advanced Configuration Options 51
Figure 23. WFQ Example
Figure 24. BE Example
Page 52

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
• Strictly Priority (SP): The SP Queue Type uses queues that are based on priority only. SP transmits the
highest priority queue first, then the next highest priority queue, and so on. However, if there is always
some content in the highest priority queue, then the other packets in the rest of queues will not be sent until
the highest priority queue is empty. The SP algorithm is preferred when the received packets contain some
high priority data, such as voice and video.
Figure 25. SP Example
WRR Configuration. If you selected Type 1 in the Scheduling Configuration section, then provide information for the WRR table. Assign a weight value (from 1 to 15) to determine the priority for each queue.
Figure 26. QoS - Port Based Priority - WRR Configuration
WFQ Configuration. If you selected Type 2 or Type 3 in the Scheduling Configuration section, then provide information for the WFQ table. Assign the bandwidth for each queue in each port.
Figure 27. QoS - Port Based Priority - WFQ Configuration
Port-Based Priority Table. For the last step, assign queues to their corresponding ports: LAN 1-4, DSL and
Sniffing.
Advanced Configuration Options 52
Figure 28. QoS - Port Based Priority Table
Page 53

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
VLAN Tag Priority
Click on QoS under Advanced on the main menu to reach the QoS advanced configuration page. Then, select
the radio button for VLAN Tag Priority to display the configuration options.
Figure 29. QoS - VLAN Tag Priority page
VLAN Tag Priority uses the tag field information which has been inserted into an Ethernet frame. If a port has
an 802.1Q-compliant device attached (such as this Ethernet Extender), these tagged frames can carry VLAN
membership information.
Figure 30. IEEE 802.1Q Tagged Frame for Ethernet
Priority defines the user priority level for different classes of traffic. There are 8 possible priority levels, with 0
being the lowest priority level and 7 being the highest level. Each Priority level can be set queue from 0 to 3.
Advanced Configuration Options 53
Page 54

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Table 9. VLAN Tag Priority Levels
Priority Level Traffic Type
0 (default) Best Effort
1 Background
2 Spare
3 Excellent Effort
4 Controlled Load
5 Video, less than 100 milliseconds latency and jitter
6 Voice, less than 10 milliseconds latency and jitter
7 Network Control
Scheduling Configuration. The 2160 provides three combinations of four commonly used techniques: Type
1, Type 2 and Type 3. Select a type in the Scheduling Configuration section, then provide details in the corresponding table.
If you select Type 1, refer to “WRR Configuration” on page 54.
If you select Type 2 or Type 3, refer to “WFQ Configuration” on page 54.
WRR Configuration. If you selected Type 1 in the Scheduling Configuration section, then provide information for the WRR table. Assign a weight value (from 1 to 15) to determine the priority for each queue.
“Weight” determines how important the queue is; therefore, 15 is the most important queue and 0 is the least
important queue.
Figure 31. QoS - Tag Based Priority - WRR Configuration
WFQ Configuration. If you selected Type 2 or Type 3 in the Scheduling Configuration section, then provide information for the WFQ table. Assign the bandwidth for each queue in each port.
Figure 32. QoS - Tag Based Priority - WFQ Configuration
Advanced Configuration Options 54
Page 55

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
VLAN Tag Priority Table. Select a packet with an assigned priority to correspond with each queue.
Figure 33. QoS - VLAN Tag Priority Table
Configuration Example. As an example, you can set the Model 2160 to use Weighted Round-Robin (WRR)
queuing that specifies a relative weight of each queue. WRR uses a predefined relative weight for each queue
that determines the percentage of service time to provide each queue before moving on to the next queue. This
prevents the head-of-line blocking that can occur with strict priority queuing.
Table 10. WRR Scheduling Configuration Example Values
Queue 0 1 2 3
Type 1
Weight
WRR WRR WRR WRR
1 2 4 8
For this example, set up the WRR (Type 1) to share bandwidth by using scheduling weights 1, 2, 4 and 8 for
queues 0 through 3 respectively.
Priority
Queue
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 0 0 1 2 2 3 3
According to the two tables above, the QoS values map to the Egress Queues as follows:
0 1 2 3
2 15 7 8
Priority
Queue
Queue
Weight
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0 0 2 2 3 3 1 1
This example displays that:
• Packets with priority 0 and priority 1 go to Queue 0.
• Packets with priority 2 and priority 3 go to Queue 2.
• Packets with priority 4 and priority 5 go to Queue 3.
• Packets with priority 6 and priority 7 go to Queue 1.
• When, data flow traffic is jammed:
- Queue 1 Packets will go first because weight is equal to 15 (the biggest value).
- Queue 3 Packets will go next because the weight is the second largest value.
- Queue 2 Packets are the next after Queue 3 Packets.
- Queue 0 Packets are the last one to send.
Advanced Configuration Options 55
Page 56

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
4,5 Queue 21,2 Queue 0
4,5 Queue 20,3 Queue 1
4,5 Queue 24,5 Queue 2
6,7 Queue 3
Figure 34. Service by WRR
IP DSCP Priority
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) is the 6-bit field in the header of IP packets, and it is for packet
classification purposes. The DSCP algorithm is based on IP DSCP fields in the IP header. There are 64 levels
of priority degrees (0 to 63). Figure 35 shows the DS field:
Advanced Configuration Options 56
Figure 35. DSCP field
Page 57

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Click on QoS under Advanced on the main menu to reach the QoS advanced configuration page. Then, select
the radio button for IP DSCP Priority to display the configuration options.
Scheduling Configuration. The 2160 provides three combinations of four commonly used techniques: Type
1, Type 2 and Type 3. Select a type in the Scheduling Configuration section, then provide details in the corresponding table.
WRR Configuration. If you selected Type 1 in the Scheduling Configuration section, then provide information for the WRR table. Assign a weight value (from 1 to 15) to determine the priority for each queue.
“Weight” determines how important the queue is; therefore, 15 is the most important queue and 0 is the least
important queue.
Figure 36. QoS - IP DSCP Priority - WRR Configuration
WFQ Configuration. If you selected Type 2 or Type 3 in the Scheduling Configuration section, then provide information for the WFQ table. Assign the bandwidth for each queue in each port.
Figure 37. QoS - IP DSCP Priority - WFQ Configuration
Advanced Configuration Options 57
Page 58

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
IP DSCP Priority Table. Select the queue for each DSCP level. Each DSCP value (from 0 to 63) is mapped
to a Queue value (from 0 to 3) from the drop-down list The number 0 represents the lowest priority and number 3 represents the highest priority and according various queuing strategies to tailor performance to requirements.
Figure 38. QoS - IP DSCP Priority page
IP DSCP Configuration Example. In this example, the selected operation
is Type 3. For the Type 3 combination,
s
et up Queue 1 and Queue 2 for
WFQ configuration.
For this example, assume the following actions:
• Assign DSCP 1 to Queue 0.
• Assign DSCP 14 to Queue 1.
• Assign DSCP 34 to Queue 2.
• Assign DSCP 55 to Queue 3.
Figure 39 shows the results of the configuration for the LAN 1 port.
Figure 39. DSCP Configuration Example
Advanced Configuration Options 58
Page 59

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Rate Limit
Click on Rate Limit under Advanced on the main menu to reach the Rate Control configuration page.
Figure 40. Rate Limit page
Limiting bandwidth to specific users and ports helps control network congestion, ensure high performance,
create efficient networks, and prevent a small number of users from monopolizing network bandwidth.
Rate limiting control can be used to intelligently manage bandwidth allocation in the networking. It can prevent one user or device from dominating the available network bandwidth, and it allows IT managers to allocate greater bandwidth to the departments and applications that need it.
You can set up the data rate limit on each port from 0 to 22. The data rates available are 00 (No limit), and the
Ingress Rate x 1024kbps. The default setting is No limit on each port.
Flow Control
Click on Flow Control under Advanced on the main menu to reach the Flow Control configuration page.
When the Flow Control option is enabled, the 2160 controls the packet size.
Figure 41. Flow Control page
Advanced Configuration Options 59
Page 60

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Status Options
This section contains information for monitoring status options for the Model 2160 via the WMI. The Status
menu contains Line, Management, LAN, Performance and Syslog parameters.
LINE Status
The LINE Status includes information for the run-time device status, mode, Bitrate and Performance infor-
mation such as SNR margin, atteunation and CRC error count.
Figure 42. LINE Status page (8-wire model shown)
If two Model 2160s have been linked together, you can view their run-time line rate status and performance
information from this screen. If you want to clear the performance data, click Clear CRC Error.
Note
The CPE line rate is determined by the CO setting.
Management Status
The Management Status page displays information about the Management port interface. You can view the
general status of the Management interface and DHCP client table.
Status Options 60
Figure 43. Management Status page
Page 61

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
LAN Status
The LAN Status page displays information about a LAN port. The system will allow you to select which LAN
port to view.
Figure 44. LAN Status page
Performance Status
The Performance Status page displays information about the uptime and errors of the system.
Status Options 61
Figure 45. Performance Status page
Page 62

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Administration Options
This section allows you to configure administration options for Security, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and Remote System Log.
Security Administration
For system security, you should change the default user name and password during initial setup. Otherwise,
unauthorized persons can access the Model 2160 and change the parameters. Click Security in the Administra-
tion menu to set up the parameters.
Figure 46. Security Administration page
User Profiles
For better security, change the Supervisor ID and Supervisor Password for the Model 2160. If you don't set
them, all users will be able to access the Model 2160 using the default Supervisor ID and Supervisor Password
,which is root.
You can authorize five legal users to access the Model 2160 via telnet or console only. There are two UI modes,
menu driven mode and command mode to configure the Model 2160. The default user name and Password
are admin. There are two UI modes, the WMI and the Telnet/Console mode to set up the Model 2160.
Telnet Console Mode
Supervisor Password
All functions are available
User Name
Password
Only available functions:
Ping, View Status, Configuration
Exit
Figure 47. Model 2160 configuration modes
Web Browser Mode
Supervisor ID
Supervisor Password
All functions are available
Logout
Administration Options 62
Page 63

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Remote Management Hosts
The Remote Management Host section of the Security Administration page enables you to set up the legal IP
addresses from which authorized persons can configure the Model 2160. This is the most secure way for the
network administrator to set up the legal address of configuration.
Figure 48. Remote Management Host section
A configuration of 0.0.0.0 will allow all hosts on Internet or LAN to access the Model 2160. If you leave the
trusted host list completely blank, you will block all PCs on the WAN from accessing the Model 2160. On the
other hand, only PCs in the LAN can access the Model 2160. If you type the exact IP address in the filed, only
that host can access the Model 2160.
Click Finish to commit your changes. The browser will prompt the configured parameters and check it before
writing into NVRAM. Press Restart to reboot the Model 2160 with the new settings. Click Continue to configure other options.
SNMP Administration
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provides for the exchange of messages between a network
management client and a network management agent for remote management of network nodes. These messages contain requests to get and set variables that exist in network nodes in order to obtain statistics, set configuration parameters, and monitor network events. SNMP communications can occur over the LAN or WAN
connection.
The Model 2160 can generate SNMP traps to indicate alarm conditions, and it relies on SNMP community
strings to implement SNMP security. This Model 2160 support both MIB I and MIB II.
Administration Options 63
Page 64

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Click SNMP in the Administration menu to set up the parameters.
Figure 49. SNMP Administration page
Community Pool
An SNMP community is a group of devices and management stations running SNMP. It helps define where
information is sent. The community name is used to identify the group. A SNMP device or agent may belong
to more than one community. It will not request information from management stations that do not belong to
one of its communities.
Table 11. Default SNMP Communities
Access Right Community
Read public
Write private
Click Modify to set up community pools.
Figure 50. SNMP community pool configuration
In the table of the current community pool, you can set up access:
• Status: Enable–Turn on the SNMP function; Disable–Turn off the SNMP function
• Access Right: Deny–Restrict all access; Read–Read-only access; Write–Read/write access
• Community: The password for write access.
Administration Options 64
Page 65

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
After configuring the community pool, click Finish. The browser will prompt the configured parameters and
check it before writing into NVRAM. Press Restart to reboot the Model 2160 with the new settings. Click
Continue to configure other options.
Trap Host Pool
In the table of current trap host pool, you can set up the trap host. SNMP trap is an informational message sent
from an SNMP agent to a manager. It is a management station (SNMP application) that receives traps. If you
don’t define a trap host pool, then no traps are issued.
Click Modify to set up the trap host pool.
Figure 51. Trap host pool configuration
• Version: Select version for trap host. (Version 1 is for SNMPv1; Version 2 for SNMPv2; Disable–Turn off)
• IP Address: Enter the trap host IP address
• Community: Enter the community password.
Click OK to finish the setup. The browser will prompt the configured parameters and check it before writing
into NVRAM. Press Restart to reboot the Model 2160 with the new settings. Click Continue to configure
other options.
Remote Syslog
Click Remote Syslog in the Administration menu to send the log information of the 2160 to a remote site.
Figure 52. Remote Syslog configuration page
• Service Setup
- Mode: Enable/Disable the remote syslog service
- Facility: Select from LOCAL_USE0 to LOCAL_USE9 and SEC_AUTH
• Protocol Setup
- Server IP: The IP address of the remote management server, where the logs will be sent
- Port: The port number of the specific IP address
Administration Options 65
Page 66

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Utility Options
This section allows you to manage utility options for the Model 2160, including system information, the configuration tool, upgrade information, log out of the system, and restart the system.
System Information
To review system information, click System Info in the Utility menu.
Figure 53. System Information page
You can check the MCSV, Software Version, Chipset, Firmware Version, Host Name and System Up Time.
The System Up Time item let you know how long the Model 2160 has been running since powering up.
Configuration Tool
The configuration tool has three options: Load Factory Default, Restore Configuration, and Backup Configuration. Click Config Tool in the Utility menu.
Figure 54. Configuration Tool page
Select the desired configuration function, then click Finish.
• Load Factory Default: The system will load the factory default parameters for the Model 2160.
Utility Options 66
Page 67

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Note
This option will change all of the settings back to factory default. You
will lose all of your current settings.
• Restore Configuration: Use this option to recover the backup configuration easily. Click Finish after select-
ing Restore Configuration. Browse to the backup file then click Finish again. The Model 2160 will auto-
matically restore the saved configuration.
• Backup Configuration: After you configure the Model 2160 with your desired settings, you can use the
Backup Configuration option to save your Model 2160 parameters in the PC. Select the Backup Configuration and then click Finish. Browse to the backup directory, and click Finish again. The Model 2160 will
automatically save the configuration.
Upgrade
You can update the firmware of Model 2160 using the Upgrade function. Click Upgrade in the Utility menu.
Figure 55. Upgrade page
Type the path and file name of the Firmware file you wish to upload to the Model 2160 in text box. Or, you
can also click Browse to locate the file. Click OK to begin the upgrade process. The system will reboot automatically after finishing. (Firmware upgrades will only take effect after the system reboots).
After the firmware upgrade process is complete, click System Info in the Utility menu to verify your current
firmware version number.
Utility Options 67
Page 68

Model 2160 Series User Manual 4 • Web configuration
Logout
To exit the Model 2160 Web Management Interface securely, click Logout in the Utility menu. You have to
log in with your password again after you log out. This is recommended after you finish a management session
for security reasons.
Figure 56. Logout page
Restart
To reboot the Model 2160, click Restart in the Utility menu, then click the Restart button.
The following screen displays:
Utility Options 68
Figure 57. Restart page
Figure 58. Restart page
Page 69

Chapter 5 Console and Telnet configuration
Chapter contents
Introduction..........................................................................................................................................................71
Log in to the console interface ........................................................................................................................71
Log in using Telnet .........................................................................................................................................71
Interface commands ........................................................................................................................................71
Window structure ...........................................................................................................................................72
Main Menu Tree...................................................................................................................................................73
Menu tree for authorized users ........................................................................................................................73
Menu tree for unauthorized users ....................................................................................................................74
Enable Command Menu.......................................................................................................................................75
Setup Command Menu.........................................................................................................................................76
Line ................................................................................................................................................................76
Mode ........................................................................................................................................................77
Link ..........................................................................................................................................................77
Annex Type ...............................................................................................................................................77
TCPAM Type ...........................................................................................................................................77
Maximum Main Rate ................................................................................................................................77
SNR Margin .............................................................................................................................................77
Line Probe .................................................................................................................................................78
Clear .........................................................................................................................................................78
LAN ...............................................................................................................................................................78
VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................79
Mode ........................................................................................................................................................79
802.1Q VLAN.................................................................................................................................... 80
Port-Based VLAN ............................................................................................................................... 81
QoS ................................................................................................................................................................82
Mode ........................................................................................................................................................82
Queue Schedule ........................................................................................................................................82
Queue Weight ...........................................................................................................................................83
Queue Egress Rate ....................................................................................................................................84
Port-Based Priority QoS ............................................................................................................................84
VLAN Tag Priority QoS ...........................................................................................................................84
IP DSCP Priority QoS ..............................................................................................................................85
List ............................................................................................................................................................86
Rate ................................................................................................................................................................86
Management ...................................................................................................................................................87
DHCP
............................................................................................................................................................87
DHCP Server ............................................................................................................................................88
DHCP Fixed Host ....................................................................................................................................88
DNS Proxy .....................................................................................................................................................89
69
Page 70

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Host Name .....................................................................................................................................................89
Factory Default ...............................................................................................................................................89
Status Command Menu ........................................................................................................................................90
LINE Status ....................................................................................................................................................90
Interface Status ...............................................................................................................................................91
Show Command Menu.........................................................................................................................................92
Write Command...................................................................................................................................................93
Reboot Command.................................................................................................................................................93
Ping Command.....................................................................................................................................................93
Administration Command Menu ..........................................................................................................................95
User Profile .....................................................................................................................................................95
Modify/Add User ......................................................................................................................................95
Security ...........................................................................................................................................................96
Telnet TCP Port .......................................................................................................................................96
Legal IP Address Pool ................................................................................................................................96
SNMP ............................................................................................................................................................97
Community ..............................................................................................................................................97
Trap host ..................................................................................................................................................98
Supervisor Password and ID ...........................................................................................................................99
Supervisor Password ..................................................................................................................................99
Supervisor ID ............................................................................................................................................99
Utility Command Menu .....................................................................................................................................100
Upgrade main software .................................................................................................................................100
Backup system configuration ........................................................................................................................100
Restore system configuration .........................................................................................................................100
Exit Command....................................................................................................................................................102
70
Page 71

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Introduction
This chapter provides information for configuring the Model 2160 by using the serial console with Telnet.
Log in to the console interface
The console port is a RJ-48C connector that provides a connection to a PC for monitoring and configuring the
Model 2160. Use the supplied serial cable with a female DB-9 connector to connect to the serial port of PC,
and connect the RJ-48C module jack connector to the Model 2160's console port. Start your terminal emulation program (such as Hyper Terminal) and configure the communication parameters. Use the settings shown
in Table 12 to log into the console:
Table 12. Console settings
Parameter Value
Baud rate 9600
Data Bits 8
Parity Check None
Stop Bits 1
Flow-control None
After you enter the settings for the console, press the spacebar until the login screen appears. When you see the
login screen, you can log on to the Model 2160. Enter admin for both the User Name and Password.
Log in using Telnet
The Model 2160 also supports Telnet for remote management. Connect the Ethernet cable to the Management port of Model 2160 to your computer. The Management LED on the front panel of the Model 2160 will
light up. Start your Telnet client with VT100 terminal emulation and connect to the management IP of the
Model 2160. Wait for the login prompt to display. Enter your user name and password. When you see the
login screen, you can log on to the Model 2160. Enter admin for both the User Name and Password.
Note
The default IP address is 192.168.1.1. The line command is “telnet
192.168.1.1” in DOS mode.
Interface commands
Before changing the configuration, familiarize yourself with the operations list in the following table:
Table 13. Interface commands
Keystroke Description
or I Move to the field above in the same level menu.
or K Move to field below in the same level menu.
or J Move back to the previous menu.
or L or [ENTER] Move forward to the submenu.
[HOME] or U Move to the first field.
[END] or O Move to the last field.
[TAB] Choose another parameter.
Ctrl + C Quit configuring the item.
Ctrl +Q Access help.
Introduction 71
Page 72

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
The Model 2160 uses a menu-driven interface for serial console and Telnet management. This interface displays all available commands for configuring the Ethernet Extender.
The following figure shows an example of the menu-driven interface. In the menu, scroll up/down by pressing
the I / K keys. Select one command by pressing the L key. Go back to a higher level of the menu by pressing
the J key. You can also scroll to the top/bottom with the U/O keys.
For example, to show the system information, log on to the Model 2160. Press the K key twice and select the
show command with the L key. Select the system command in the submenu. The system will display general
information. You may also use the Enter key to select a command.
Figure 59. Console/Telnet Menu
Window structure
From top to bottom, the window is divided into four parts:
• Product name: LINE Bridge
• Menu field: The menu tree prompts on this field. Symbol “>>” indicates the cursor place.
• Configuration field: Configure the parameters in this field. < parameter > indicates the parameters you can
choose and < more…> indicates that there are more options in the submenu.
• Footer: Operation commands for help
Introduction 72
Page 73

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Main Menu Tree
The commands available in the main menu tree depend on if you have logged in using a supervisor password
(authorized user) or not (unauthorized user). An authorized user can access all of the configuration commands
in the subdirectories using the enable command. Unauthorized users cannot change any configurations but
can view the status and information for the Model 2160. They may also use the ping command to check the
Model 2160’s connection.
Menu tree for authorized users
Authorized users may log into the Model 2160 with a supervisor password to obtain access to all of the configuration commands.
Main Menu Tree 73
Figure 60. Menu tree for authorized users
Page 74

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Figure 61. Main screen for authorized users
Menu tree for unauthorized users
Unauthorized users may access the following configuration commands for the Model 2160.
Figure 62. Main menu for unauthorized users
Figure 63. Main screen for unauthorized users
Main Menu Tree 74
Page 75

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Enable Command Menu
The enable command menu lists commands for setting up the Model 2160. Move the cursor “ >>” to enable
and press Enter. Type the supervisor password, which is root.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: enable <CR>
Message: Please input the following information.
Supervisor password: ****
----------------------------------------------------------------------
In the enable sub menu, you can set up management features and upgrade software, back up the system configuration and restore the system configuration via utility tools.
To save your changes, you must write the new configuration to NVRAM and reboot the Model 2160 to work
with the new settings.
When you first log in to the Model 2160 with the supervisor password, the main menu displays:
>>
enable Modify command privilege
setup Configure system
status Show running system status
show View system configuration
write Update flash configuration
reboot Reset and boot system
ping Packet internet groper command
admin Setup management features
utility TFTP upgrade utility
exit Quit system
Table 14 explains the commands available in the main menu:
Table 14. Enable Command Menu
Command Description
enable Change the configuration and write changes to nonvolatile RAM (NVRAM).
setup Initially configure the Model 2160.
status View the status of the Model 2160
show Show the system and configuration
write Update flash configuration. After you have completed all desired changes, make sure to
write the new configuration to NVRAM. Use the write command to save your changes
and reboot the system or all of your changes will not take effect.
reboot Reset and reboot system. After you have completed all desired changes, make sure to write
the new configuration to NVRAM. Use the reboot command to restart the system or all of
your changes will not take effect.
ping Check the connection to the Model 2160
admin Set up advanced management features
utility Upgrade software and backup/restore the current configuration
exit Log out of the system
Enable Command Menu 75
Page 76

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Setup Command Menu
The setup command menu lists commands for initially configuring the Model 2160. Move the cursor “ >>” to
setup in the main menu and press Enter.
When you enter the setup command, the following menu displays:
>>
line Configure line parameters
lan Configure LAN interface profile
vlan Configure virtual LAN parameters
qos Configure Quality of Service parameters
rate Configure Rate Control parameters
Management
dhcp Configure DHCP parameters
dns_proxy Configure DNS proxy parameters
hostname Configure local host name
default Restore factory default settings
Line
The line command menu lists commands for setting up the line port. Move the cursor “ >>” to line in the
setup menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
Configure management interface profile
>>
mode Configure line mode
link Configure line link
annex Configure line annex type
tcpam Configure line TCPAM type
maxMainRate Configure line max main data rate
snrMargin Configure line SNR margin
lineProbe Configure line line probe
clear Clear current CRC error count
Table 15 shows the options available within the line command menu:
Table 15. Line Options
Menu Options
Mode STU-C STU-R
Link Type 2-wire 4-wire 8-wire
Annex AF BG
TCPAM Auto TCPAM-16 TCPAM-32 TCPAM-64
Max Main Rate (3–89)
SNR Margin (-10–21)
Line Probe Disable Enable
Setup Command Menu 76
Page 77

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Mode
There are two types of Line mode:
• STU-C: Central Office (CO) terminal
• STU-R: Customer Premise Equipment (CPE)
Link
Select the line type for your model. Line type means how many wires you want to use on the CopperLink connection. For example, you can select 2-wire, 4-wire or 8-wire line type for the 8-wire model.
Table 16. Line Type Chart
Line Type
2-wire 4-wire 8-wire
Model
Type
2-wire model
4-wire model
8-wire model
•
• •
• • •
Annex Type
Enter the appropriate Annex type. Annex AF describes the transmission and performance requirements for
North America. Annex BG describes performance and transmission requirements for Europe.
TCPAM Type
TCPAM (Trellis Coded Pulse Amplitude Modulation) is the standard used for line coding. Select the TCPAM
type. Auto is the default option for TCPAM.
Maximum Main Rate
Select the line rate for your model. The main rate is the multiple of 64kbps, 128kbps, or 256kbps- depending
on your model type. Use Table 17 to determine the best main rate for your model.
Table 17. Main Rate Table
Model Type Multiple
2160 2-wire model 64 192–3840 768–5696 128–15296
2161 4-wire model 128 384–7680 1536–11392 256–30592
2162 8-wire model 256 768–15360 3072–22784 512–61184
TCPAM-16
= 3–60
TCPAM-32
= 12–89
TCPAM-128
= 2–239
SNR Margin
SNR margin is an index of line connection quality. Generally, you won’t need to change the SNR Margin. You
can view the actual SNR margin in status command menu.You will experience better line connection quality
for larger SNR margin values.
For example, if you set the SNR margin ias 5, the line connection will drop and reconnect when the SNR margin is lower than 5. On the other hand, the device will reduce the line rate and reconnect for better line connection quality. You may select the SNR margin from the range -10 to 21.
Setup Command Menu 77
Page 78

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Line Probe
For adaptive mode applications, set the Line Probe to Enable. The Model 2160 will adapt the data rate accord-
ing to the line status. For all other applications, set the Line Probe to Disable.
Clear
Use the clear command to reset the CRC error count.
LAN
The lan command menu lists commands for setting up the LAN ports. Move the cursor “ >>” to lan in the
setup menu and press Enter.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup lan <1~1>
Message: Please input the following information.
Interface number <1~1>: 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
The default interface number is 1.
You can configure the Link type, LAN IP address and subnet mask for the LAN interface.
>>
link_type Configure Link type
address LAN address and subnet mask
Table 18 shows the options available within the lan command menu:
Table 18. LAN Options
Menu Options
Link Type Disable Dynamic Static
IP Address
Subnet Mask
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup lan 1 link_type <Disable|Dynamic|Static>
Message: Please input the following information.
Link type (TAB Select) <Disable>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Select the lan 1 link_type as Disable, Dynamic or Static. Then, select address from the lan menu:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup lan 1 address <ip> <netmask>
Message: Please input the following information.
IP address (ENTER for default) <192.168.2.1>:
Subnet mask (ENTER for default) <255.255.255.0>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Set the LAN IP address and subnet mask. The default IP Address is 192.168.2.1 and the default subnet mask
is 255.255.255.0.
Setup Command Menu 78
Page 79

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
VLAN
Virtual LAN (VLAN) is defined as a group of devices on one or more LANs that are configured so that they
can communicate as if they were attached to the same wire, when in fact they are located on a number of different LAN segments. Because VLAN is based on logical instead of physical connections, it is extremely flexible.
You can setup the Virtual LAN (VLAN) parameters in VLAN command. The Model 2160 supports VLANto-PVC only for bridge mode operation, i.e., the VLAN spreads over both the CO and CPE sides, where there
is no layer 3 routing involved. The unit supports up to 8 active VLANs with shared VLAN learning (SVL)
bridge out of 4096 possible VLANs specified in IEEE 802.1Q.
The vlan command menu lists commands for setting up the line port. Move the cursor “ >>” to vlan in the
setup menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
>>
mode Trigger virtual LAN function
modify Modify virtual LAN table
pvid Modify port default VID
link_mode Modify port link type
list Show VLAN configuration
To activate the VLAN function, move the cursor “ >> “ to mode and press Enter. The products support two
types of VLAN: 802.1Q and Port-Based.
802.1Q defines the operation of VLAN bridges that permit the definition, operation, and administration of
VLAN topologies within a bridged LAN infrastructure. Port-Based VLANs are VLANs where the packet forwarding decision is based on the destination MAC address and its associated port.
Mode
You can choose from two types of VLANs: 802.1Q Tag-Based VLAN or Port Based VLAN. If you are not
going to use the VLAN function, set this option to Disable.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup vlan mode <Disable|8021Q|Port>
Message: Please input the following information.
Trigger VLAN function (TAB Select) <Disable>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table 19 shows the options available within the VLAN mode command menu:
Table 19. VLAN Mode Options
Menu Options
VLAN Mode Disable 802.1Q Tag VLAN Port-Based VLAN
Setup Command Menu 79
Page 80

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
802.1Q VLAN. To modify the VLAN rule, move the cursor to modify and press Enter.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup vlan modify <1~8> <0~4094> <string>
Message: Please input the following information.
VLAN table entry index <1~8>: 1
VID value (ENTER for default) <1>: 10
VLAN port membership (ENTER for default) <111111>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
The VLAN Port membership ris represented with 1 or 0. VLAN port membership is a 6-digit binary number
in which bit 0 to bits 5 represent LAN1 to LAN4, line and Sniffing ports respectively.
For example: [
setup vlan modify 1 10 111111
] means use index as 1 , VID = 10 and all six ports are the same
membership (VLAN ID=10).
Use the pvid command to change the member port to untagged members:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup vlan pvid <1~6> <1~4094>
Message: Please input the following information.
Port index <1~6>:
VID value (ENTER for default) <1>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
PVID (Port VID) is an untagged member from 1 to 4094 for the default VLAN.
For example:
[ set vlan pvid 1 100]
[ set vlan pvid 2 100]
[ set vlan pvid 3 100]
[ set vlan pvid 4 100]
[ set vlan pvid 5 100]
[ set vlan pvid 6 100]
This example shows that all untagged members of all ports all have the same membership (VLAN ID=100).
To modify the link type of the port, move the cursor to link_mode and press Enter. There are two types of
link: access and trunk. A Trunk link will send the tagged packet form the port. An Access link will send an
untagged packet from the port. The port index 1 to 4 represents LAN ports. Index 5 represents line, and index
6 represents Sniffing.
Setup Command Menu 80
Page 81

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup vlan link_mode <1~6> <Access|Trunk>
Message: Please input the following information.
Port index <1~6>: 1
Port link type (TAB Select) <Access>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table 20 shows the options available within the 802.1Q Tag VLAN command menu:
Access The port can receive or send untagged packets.
Trunk The port can receive or send tagged packets.
Table 20. 802.1Q VLAN Options
1 2 3 4 5 6
No. VID LAN1 LAN2 LAN3 LAN4 Line Sniffing
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PVID
Link Type Access
Trunk
Access
Trunk
Access
Trunk
Access
Trunk
Access
Trunk
Access
Trunk
Port-Based VLAN. With port-based VLAN, the port is assigned to a specific VLAN independent of the user
or system attached to the port. This means all users attached to the port should be members in the same
VLAN. The network administrator typically performs the VLAN assignment. The port configuration is static
and cannot be automatically changed to another VLAN without manual reconfiguration.
You can set up Port-Based VLAN using the method for 802.11Q. However, VID , PVID or link type do not
matter for Port-Based VLAN. Use the list command to check the status of the VLAN.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Virtual LAN Parameter
VLAN Mode : Port-Based VLAN
Virtual LAN Table
No LAN1 LAN2 LAN3 LAN4 Line Sniffing
-- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- --------
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 - - - - - -
3 - - - - - -
4 - - - - - -
5 - - - - - -
6 - - - - - -
7 - - - - - -
8 - - - - - -
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Setup Command Menu 81
Page 82

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to both a network's ability to deliver data with minimum delay, and the networking methods used to control the use of bandwidth. Without QoS, all traffic date is equally likely to be
dropped when the network is congested. This can cause a reduction in network performance and mark the network inadequate for a time-critical application such as video-on-demand.
The qos command menu lists commands for managing traffic. Move the cursor “ >>” to qos in the setup menu
and press Enter. The following menu displays:
>>
mode Trigger Quality of Service function
qSchdl Modify queue schedule type
qweight Modify queue weight
q0GrssRt Modify queue 0 egress rate
q1GrssRt Modify queue 1 egress rate
q2GrssRt Modify queue 2 egress rate
q3GrssRt Modify queue 3 egress rate
portPri Modify port priority
vlanTagPri Modify VLAN TAG priority
ipDscpPri Modify IP DSCP priority
list Show QoS configuration
Mode
You can choose from three types of QoS: Port-Based, VLAN Tag, and IP DSCP. If you are not going to use
the QoS function, set this option to Disable.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup qos mode <Disable|PortBased|VlanTag|IpDscp>
Message: Please input the following information.
Trigger qoS function (TAB Select) <Disable>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table 21 shows the options available within the QoS mode command menu:
Table 21. VLAN Mode Options
Menu Options
QoS Mode Disable Port-Based VLAN Tag IP DSCP
Queue Schedule
There are two types of queue schedule. Select from Type 1, Type 2 or Type 3. Table 22 explains the schedule
types:
Table 22. Queue Schedule Types
Queue 0 1 2 3
Type 1
Type 2
Type 3
WRR WRR WRR WRR
BE WFQ WFQ WFQ
BE WFQ WFQ SP
Setup Command Menu 82
Page 83

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup qos qSchdl <Type1|Type2|Type3>
Message: Please input the following information.
Operation type (TAB Select) <Type1>: Type1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
The Queue types are Weight Round Robin (WRR), Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ), Best Effort (BE), and
Strictly Priority (SP).
• Weight Round Robin (WRR): All received packets will be stored into Queue 1, Queue 2, Queue 3, and
Queue 4. Assign a weight value for each queue. Then, WRR will re-assemble all packets from the four
queues based on the weight assignments.
• Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ): WFQ is a generalization of processor sharing, which allows several ses-
sions to share the same link.
• Best Effort (BE): The BE Queue Type is used for data applications that have low priority or the potential to
delay. BE does not use traffic priority or weight assignments, therefore BE is not recommended for high priority data, such as video or voice.
• Strictly Priority (SP): The SP Queue Type uses queues that are based on priority only. SP transmits the
highest priority queue first, then the next highest priority queue, and so on. However, if there is always
some content in the highest priority queue, then the other packets in the rest of queues will not be sent until
the highest priority queue is empty. The SP algorithm is preferred when the received packets contain some
high priority data, such as voice and video.
Table 23. Queue Schedule Options
Menu Options
Queue Schedule Type 1 Type 2 Type 3
Queue Weight
This setting configures the weight value for each queue.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup qos qweight <0~3> <1~15>
Message: Please input the following information.
Queue index <0~3>: 0
Weight value (ENTER for default) <1>: 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
For example, the default values are shown below:
[ setup qos qweight 0 1]
[ setup qos qweight 1 2]
[ setup qos qweight 2 4]
[ setup qos qweight 3 8]
QoS Mode 0 1 2 3
Weight Value
Setup Command Menu 83
Page 84

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Queue Egress Rate
Queues 0-3 can set up the egress rate for WFQ configuration.
q0GrssRt Modify queue 0 egress rate
q1GrssRt Modify queue 1 egress rate
q2GrssRt Modify queue 2 egress rate
q3GrssRt Modify queue 3 egress rate
The egress rate N value can be set from 0 to 22. The N value 0 means no limits.
The egress data rate is a multiple of 1024kbps.
For example, the egress data rate = N value (1 to 22) x 1024 Kbps.
Table 24. Egress Rate (N Value)
Port
LAN 1
LAN 2
LAN 3
LAN 4
DSL
Egress Queue
0 1 2 3
Port-Based Priority QoS
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup qos portPri <1~6> <0~3>
Message: Please input the following information.
Port index <1~6>: 1
Queue index (ENTER for default) <3>: 3
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Set up the queue value (0, 1, 2 or 3) on each port.
Table 25. Port-Based Priority QoS Options
Port 1 (LAN1) 2 (LAN2) 3 (LAN3) 4 (LAN4) 5 (Line) 6 (Sniffing)
Queue Index
VLAN Tag Priority QoS
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup qos vlanTagPri <0~7> <0~3>
Message: Please input the following information.
VLAN TAG index <0~7>: 0
Queue index (ENTER for default) <1>: 1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Set up the queue index (0, 1, 2 or 3) on Priority VLAN Tag.
Setup Command Menu 84
Page 85

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
VLAN Tag Priority uses the tag field information which has been inserted into an Ethernet frame. If a port has
an 802.1Q-compliant device attached (such as this Ethernet Extender), these tagged frames can carry VLAN
membership information.
Priority defines the user priority level for different classes of traffic. There are 8 possible priority levels, with 0
being the lowest priority level and 7 being the highest level. Each Priority level can be set queue from 0 to 3.
Table 26. VLAN Tag Priority Levels
Priority Level Traffic Type
0 (default) Best Effort
1 Background
2 Spare
3 Excellent Effort
4 Controlled Load
5 Video, less than 100 milliseconds latency and jitter
6 Voice, less than 10 milliseconds latency and jitter
7 Network Control
For example, you can set the Model 2160 to use Weighted Round-Robin (WRR) queuing (Type 1) that specifies a relative weight of each queue. WRR uses a predefined relative weight for each queue that determines the
percentage of s time to services for each queue before moving on to the next queue.
Table 27. VLAN Tag Priority QoS Options
VLAN Tag Index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Queue Index
IP DSCP Priority QoS
Differentiated Services (DiffServ) is a class of service (CoS) model that enhances best-effort Internet services by
differentiating traffic by users, service requirements and other criteria. Packets are specifically marked, allowing
network nodes to provide different levels of service, as appropriate for video playback, voice calls or other
delay-sensitive applications, via priority queuing or bandwidth allocation.
The DSCP value used to identify 64 levels (26=64) of service determines the forwarding behavior that each
packet gets across the DiffServ network. Based on the marking rule different kinds of traffic can be marked for
different priorities of forwarding. Resources can then be allocated according to the DSCP values and the configured policies.
Set up queue index (0, 1, 2 or 3) on each DSCP:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup qos ipDscpPri <0~63> <0~3>
Message: Please input the following information.
IP DSCP index <0~63>: 0
Queue index (ENTER for default) <0>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Setup Command Menu 85
Page 86

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Table 28. IP DSCP Priority QoS Options
DSCP
Queue Index
DSCP
Queue Index
DSCP
Queue Index
DSCP
Queue Index
0 16 32 48
1 17 33 49
2 18 34 50
3 19 35 51
4 20 36 52
5 21 37 53
6 22 38 54
7 23 39 55
8 24 40 56
9 25 41 57
10 26 42 58
11 27 43 59
12 28 44 60
13 29 45 61
14 30 46 62
15 31 47 63
List
Use the list command to view the QoS settings.
Rate
The rate command menu lists commands for setting the port rate. Move the cursor “ >>” to rate in the setup
menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
>>
port Modify port rate
list Show Rate Control configuration
Select the port you want to modify, then set up the data rate.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup rate port <1~5> <0~22>
Message: Please input the following information.
Port index <1~5>: 1
rate (ENTER for default) <0>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
The data rate is a multiple of 1024kbps with the setup rate. Table 29 shows the options available to set up the
data rate:
Table 29. Rate Options
Port 1 LAN1 No Limit 128K 256K 512K 1M
Port 2 LAN2 No Limit 128K 256K 512K 1M
Port 3 LAN3 No Limit 128K 256K 512K 1M
Port 4 LAN4 No Limit 128K 256K 512K 1M
Port 5 Line No Limit 128K 256K 512K 1M
Port 6 Sniffing No Limit 128K 256K 512K 1M
Setup Command Menu 86
Page 87

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Management
The Management command menu lists commands for configuring the IP address and subnet mask for the
Management port. Move the cursor “ >>” to Management in the setup menu and press Enter. The following
menu displays:
>>
address Management IP address and subnet mask
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup Management <1~1> <more...>
Message: Please input the following information.
Interface number <1~1>:
----------------------------------------------------------------------
The Model 2160 only has one Management interface. The default interface number is 1. The default IP
address and subnet mask are 196.168.1.1 and 255.255.255.0 .
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup Management 1 address <ip> <netmask>
Message: Please input the following information.
IP address (ENTER for default) <192.168.1.1>:
Subnet mask (ENTER for default) <255.255.255.0>:
----------------------------------------------------------------------
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a communication protocol that allows network administrators to manage and automate the assignment of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses in an organization's network. Each machine that can connect to the Internet needs a unique IP address. When an organization sets up
the users with a connection to the Internet, an IP address must be assigned to each machine.
Without DHCP, the IP address must be entered manually at each computer. If computers move to another
location in another part of the network, a new IP address must be entered. DHCP lets a network administrator
supervise and distribute IP addresses from a central point and automatically sends a new IP address when a
computer is plugged into a different place in the network.
Setup Command Menu 87
Page 88

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
DHCP Server
The dhcp command menu lists commands for configuring DHCP settings. Move the cursor “ >>” to dhcp in
the setup menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
>>
generic DHCP server generic parameters
fixed DHCP server fixed host IP list
list Show DHCP configuration
The generic command menu lists commands for configuring general DHCP settings. Move the cursor “ >>” to
generic in the dhcp menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
>>
active Trigger DHCP server function
gateway Default gateway for DHCP client
netmask Subnet mask for DHCP client
ip_range Dynamic assigned IP address range
lease_time Configure max lease time
name_server1 Domain name server1
name_server2 Domain name server2
name_server3 Domain name server3
Table 30. DHCP Command Descriptions
Command Description
Active Trigger DHCP server function
Gateway Configure default gateway for DHCP client
Netmask Configure subnet mask for DHCP client
IP Range Configure dynamic assigned IP address range
Lease Time Set up dynamic IP maximum lease time
Name Server 1 Set up the IP address of name server #1
Name Server 2 Set up the IP address of name server #2
Name Server 3 Set up the IP address of name server #3
DHCP Fixed Host
The dhcp command menu lists commands for configuring DHCP settings. Move the cursor “ >>” to dhcp in
the setup menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
generic DHCP server generic parameters
>>
fixed DHCP server fixed host IP list
relay DHCP relay parameter
list Show DHCP configuration
The fixed command menu lists commands for configuring a Fixed Host IP Address list. Move the cursor “ >>”
to fixed in the dhcp menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
>>
add Add a fixed host entry
delete Delete a fixed host entry
Setup Command Menu 88
Page 89

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
When using the fixed host entry function, you must enter the MAC address and IP address at the same time.
You can configure up to 10 maximum fixed host IP addresses.
Use the list command to view the DHCP configuration.
DNS Proxy
The dns_proxy command allows you to set up three DNS servers for the Model 2160. Move the cursor “ >>”
to dns_proxy in the setup menu and press Enter.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup dns_proxy <IP> [IP] [IP]
Message: Please input the following information.
DNS server 1 (ENTER for default) <168.95.1.1>: 10.0.10.1
DNS server 2: 10.10.10.1
DNS server 3:
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Host Name
A Host Name is a unique name that attaches a host to a network. The hostname is used to identify a particular
host in various forms of electronic communication. Some ISP providers require the Host Name as identification. You may check with your ISP to see if your Internet service has been configured with a host name. In
most cases, you can ignore this field.
Move the cursor “ >>” to hostname in the setup menu and press Enter. The host name cannot use spaces and
cannot have more than 15 characters.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup hostname <name>
Message: Please input the following information.
Local hostname (ENTER for default) <SOHO>: test
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Factory Default
If you want to restore factory default settings for the Model 2160, move the cursor “ >>” to default in the setup
menu and press Enter.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: setup default <name>
Message: Please input the following information.
Are you sure? (Y/N): y
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Setup Command Menu 89
Page 90

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Status Command Menu
The status command menu lists commands for viewing the system status of interfaces on the Model 2160.
Move the cursor “ >>” to status in the main menu and press Enter.
When you enter the status command, the following menu displays:
>>
LINE Show LINE status
interface Show interface statistics status
Table 31. Status Command Menu
Command Description
LINE The LINE status includes mode, line rate, SNR margin, attenuation, and CRC error count of
the local side modem, and SNR margin, attenuation and CRC error count of remote side
modem. The modem can access remote side information via EOC (embedded operation
channel).
interface Use the interface command to view the statistic status of the Management interface.
LINE Status
The LINE command shows the status of the Line port. Move the cursor “ >>” to LINE in the status menu and
press Enter. The LINE status includes mode, line rate, SNR margin, attenuation, and CRC error count of the
local side Ethernet Extender, and SNR margin, attenuation and CRC error count of the remote side Ethernet
Extender.
Status Command Menu 90
Figure 64. LINE Status
Page 91

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Interface Status
To view the status of the Management interface, move the cursor “ >>” to interface in the status menu and
press Enter.
Figure 65. Interface Status
Table 32. Interface Statistics
Parameter Description
InOctets The number of received bytes on this port
InPackets The number of received packets on this port
OutOctets The number of transmitted bytes on this port
OutPackets The number of transmitted packets on this port
InDiscards The discarded number of received packets on this port
OutDiscards The discarded number of transmitted packets on this port
Status Command Menu 91
Page 92

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Show Command Menu
The show command menu lists commands for viewing system and configuration information for the Model
2160. Move the cursor “ >>” to show in the main menu and press Enter.
When you enter the show command, the following menu displays:
>>
system Show general information
script Show all configuration in command script
Table 33. Show Command Menu
Command Description
system Displays general system information
script Displays configuration information in command script
Move the cursor “ >>” to system in the show menu and press Enter.
Figure 66. System Information
Figure 67. Show Script
Show Command Menu 92
Page 93

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Write Command
The write command saves all new configuration changes to Flash on the Model 2160. You must use the write
command and reboot the Ethernet Extender for new configuration changes to tak effect. Move the cursor “
>>” to write in the main menu and press Enter.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: write <CR>
Message: Please input the following information.
Are you sure? (y/n): y
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Reboot Command
The reboot command restarts the Model 2160. Move the cursor “ >>” to reboot in the main menu and press
Enter.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: reboot <CR>
Message: Please input the following information.
Do you want to reboot? (y/n): y
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Type “y” to begin the reboot process.
Ping Command
The ping command checks the connection of the Model 2160 to the network. Move the cursor “ >>” to ping
in the main menu and press Enter.
The ping command sends an echo request packet to an address, and then waits for reply. The ping output can
help you evaluate path-to-host reliability, delays over the path, and whether the host can be reached or is functioning correctly.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: ping <ip> [1~65534|-t] [1~1999]
Message: Please input the following information.
IP address <IP> : 10.0.0.1
Number of ping request packets to send (TAB select): -t
Data size [1~1999]: 32
----------------------------------------------------------------------
There are 3 parameters for the ping command:
• IP address: Enter the IP address that you want to ping.
• Number of ping request packed to send: Use the TAB key to select the following options.
- Default: Sends 4 packets only
Write Command 93
Page 94

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
- 1~65534: Sets the number of ping request packets from 1 to 65534
- -t : Results run continuously until you press the Ctrl key to stop the process
• Data Size: Select from 1 to 1999
Ping Command 94
Page 95

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Administration Command Menu
The admin command menu lists commands for modifying user profiles, Telnet access, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), and supervisor information (username and password). Move the cursor “ >>” to
admin in the main menu and press Enter.
When you enter the admin command, the following menu displays:
>>
user Manage user profile
security Setup system security
snmp Configure SNMP parameter
passwd Change supervisor password
id Change supervisor ID
User Profile
The user command menu lists commands to clear, modify, and list user profiles. You can create up to 5 user
profiles to access the Model 2160 vis the console port. However, users with supervisor privleges have access to
changing the configuration of the Model 2160.
Move the cursor “ >>” to user in the admin menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
>>
clear Clear the user profile
modify Modify the user profile
list List the user profile
Use the clear command to delete a user. Use the list command to show information for a user profile. Use the
modify command to edit user information or add a new user to a user profile.
Modify/Add User
To modify a user profile or add a new user, move the cursor “ >>” to modify in the user menu and press Enter.
Select the profile number for the user profile you want to modify.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin user modify <1~5> <more...>
Message: Please input the following information.
Legal access user profile number <1~5> : 2
----------------------------------------------------------------------
The modify menu displays:
>>
attrib UI mode
profile User name and password
Move the cursor “ >>” to attrib in the modify menu and press Enter.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin user modify 2 attrib <Command|Menu>
Message: Please input the following information.
User interface (TAB Select) <Menu>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Administration Command Menu 95
Page 96

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
There are two UI modes for setting up the Model 2160, command and menu mode. The menu mode uses a
menu-driven interface. The command mode uses line commands. (Command mode is not covered in this
manual).
Move the cursor “ >>” to profile in the modify menu and press Enter.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin user modify 2 profile <name> <pass_conf>
Message: Please input the following information.
Legal user name (ENTER for default) <test>:
Input the old Access password: ****
Input the new Access password: ****
Re-type Access password: *****
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Enter the user name and set up the new access password. You must enter the new assess password twice for
confirmation.
Use the list command to view information for each user profile, including user name and UI mode.
Security
The security command menu lists commands to configure sixteen legal IP addresses for Telnet access and the
Telnet port number. Move the cursor “ >>” to security in the admin menu and press Enter. The following
menu displays:
>>
port Configure telnet TCP port
ip_pool Legal IP address pool
list Show security profile
Telnet TCP Port
To set up the Telnet TCP port, move the cursor “ >>” to port in the security menu and press Enter. You can
select a port number from 1 to 65534. The default number is 23.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin security port <1~65534>
Message: Please input the following information.
Telnet Listening TCP Port (ENTER for default) <23>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Legal IP Address Pool
The default legal address is 0.0.0.0. (on entry number 1). This means that there are no IP address restrictions
for accessing the MOdel 2160 via Telnet. To change the legal IP address pool, move the cursor “ >>” to
ip_pool in the security menu and press Enter. Select modify to set up the IP address pool.
Administration Command Menu 96
Page 97

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin security ip_pool modify <1~16> <ip>
Message: Please input the following information.
Client address pool entry number <1~16>: 1
Client IP address (ENTER for default) <0.0.0.0>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
You can configure up to sixteen entries for legal address pools. Use the clear command to remove a legal client
IP address from any pool entry number. Use the list command to view information for all of the security profiles, including the Telnet TCP port and the legal IP addresses.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provides the exchange of messages between a network management client and a network management agent for remote management of network nodes. These messages
contain requests to get and set variables that exist in network nodes in order to obtain statistics, set configuration parameters, and monitor network events. SNMP communications can occur over the LAN or WAN connection.
The Model 2160 can generate SNMP traps to indicate alarm conditions, and it relies on SNMP community
strings to implement SNMP security. This Model 2160 support both MIB I and MIB II.
The snmp command menu lists commands for configuring SNMP communities and traps. Move the cursor “
>>” to snmp in the admin menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
>>
community Configure community parameter
trap Configure trap host parameter
Community
To set up SNMP communities, move the cursor “ >>” to community in the snmp menu and press Enter. You
can configure five community entries.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin snmp community <1~5> <more...>
Message: Please input the following information.
Community entry number <1~5> : 2
----------------------------------------------------------------------
The following menu displays:
>>
edit Edit community entry
list Show community configuration
Select edit and press Enter.
Administration Command Menu 97
Page 98

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: ... 2 edit <Disable|Enable> <string> <Read_Only|Read_Write|Denied>
Message: Please input the following information.
Validate (TAB Select) <Enable>: Enable
Community (ENTER for default) <private>:
Access right (TAB Select) <Denied>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
You can set up the following options:
• Validate: Set to Enable or Disable.
• Community: Enter the desired password for community access.
• Access right: Set to Read only, Read Write or Denied.
Read_Only Users have read-only access to the community
Read_Write Users have read and write access to the community
Denied There is no access to the community
Use the list command to view all SNMP community pool entries. You can also confgiure five SNMP trap
entries.
Trap host
To set up SNMP traps, move the cursor “ >>” to trap in the snmp menu and press Enter. You can configure
five trap entries.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin snmp trap <1~5> <more...>
Message: Please input the following information.
Trap host entry number <1~5> : 2
----------------------------------------------------------------------
The following menu displays:
>>
edit Edit trap host parameter
list Show trap configuration
Select edit and press Enter.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin snmp trap 1 edit <Disable|1|2> <ip> <string>
Message: Please input the following information.
Version (TAB Select) <Disable>:
Trap host IP address (ENTER for default) <192.168.0.254>:
Community (ENTER for default) <private>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Administration Command Menu 98
Page 99

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
You can set up the following options:
• Version: Set to Disable, Version 1 or Version 2.
• Trap host IP address: Enter the dtrap host IP address.
• Community: Enter the community password.
Use the list command to view all SNMP trap host entries.
Supervisor Password and ID
The supervisor ID and password is the last option in the security command menu, but it is the most important
menu item. Users who access the Model 2160 via a web browser or console/Telnet must use the supervisor ID
and password to configure the Model 2160. You should change the supervisor ID and password after initial
configuration.
ID Password
Web Browser
Telnet/Console
• •
•
Supervisor Password
To change the supervisor password, move the cursor “ >>” to passwd in the security menu and press Enter.
The default password is root.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin passwd <pass_conf>
Message: Please input the following information.
Input old Supervisor password: ****
Input new Supervisor password: ********
Re-type Supervisor password: ********
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Supervisor ID
To change the supervisor ID, move the cursor “ >>” to id in the security menu and press Enter.
The default ID is root.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: admin id <name>
Message: Please input the following information.
Legal user name (ENTER for default) <root>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Figure 47 on page 62 shows a flowchart of user access functions using the web browser or console/Telnet.
Administration Command Menu 99
Page 100

Model 2160 Series User Manual 5 • Console and Telnet configuration
Utility Command Menu
Model 2160 has three utility tools embedded in the firmware: upgrade, backup and restore. You can update
the new firmware via TFTP upgrade tools, backup the configuration via the TFTP backup tool and restore the
configuration via the TFTP restore tool. To upgrade the firmware, you must have the new firmware file named
*.bin that will be supported by supplier. Also, you must have your own TFTP server. For backup and restore
operations, you must also have your own TFTP server to backup and restore the configuration files.
Move the cursor “ >>” to utility in the main menu and press Enter. The following menu displays:
>>
upgrade Upgrade main software
backup Backup system configuration
restore Restore system configuration
Upgrade main software
To upgrade the Model 2160 firmware, move the cursor “ >>” to upgrade in the utility menu and press Enter.
Type the TFTP server IP address and name of the upgraded firmware file.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: utility upgrade <ip> <file>
Message: Please input the following information.
TFTP server IP address (ENTER for default) <192.168.0.2>:
Upgrade filename (ENTER for default) <default.bin>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Backup system configuration
To backup the current system configuration, move the cursor “ >>” to backup in the utility menu and press
Enter. Type the TFTP server IP address and name for the backup file.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: utility backup <ip> <file>
Message: Please input the following information.
TFTP server IP address (ENTER for default) <192.168.0.2>:
Upgrade filename (ENTER for default) <default.bin>:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Restore system configuration
To restore a saved configuration file, move the cursor “ >>” to restore in the utility menu and press Enter.
Type the TFTP server IP address and name of the system configuration file you want to restore to the Model
2160.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Command: utility restore <ip> <file>
Message: Please input the following information.
TFTP server IP address (ENTER for default) <192.168.0.2>:
Upgrade filename (ENTER for default) <default.bin>:
Utility Command Menu 100
 Loading...
Loading...