Page 1
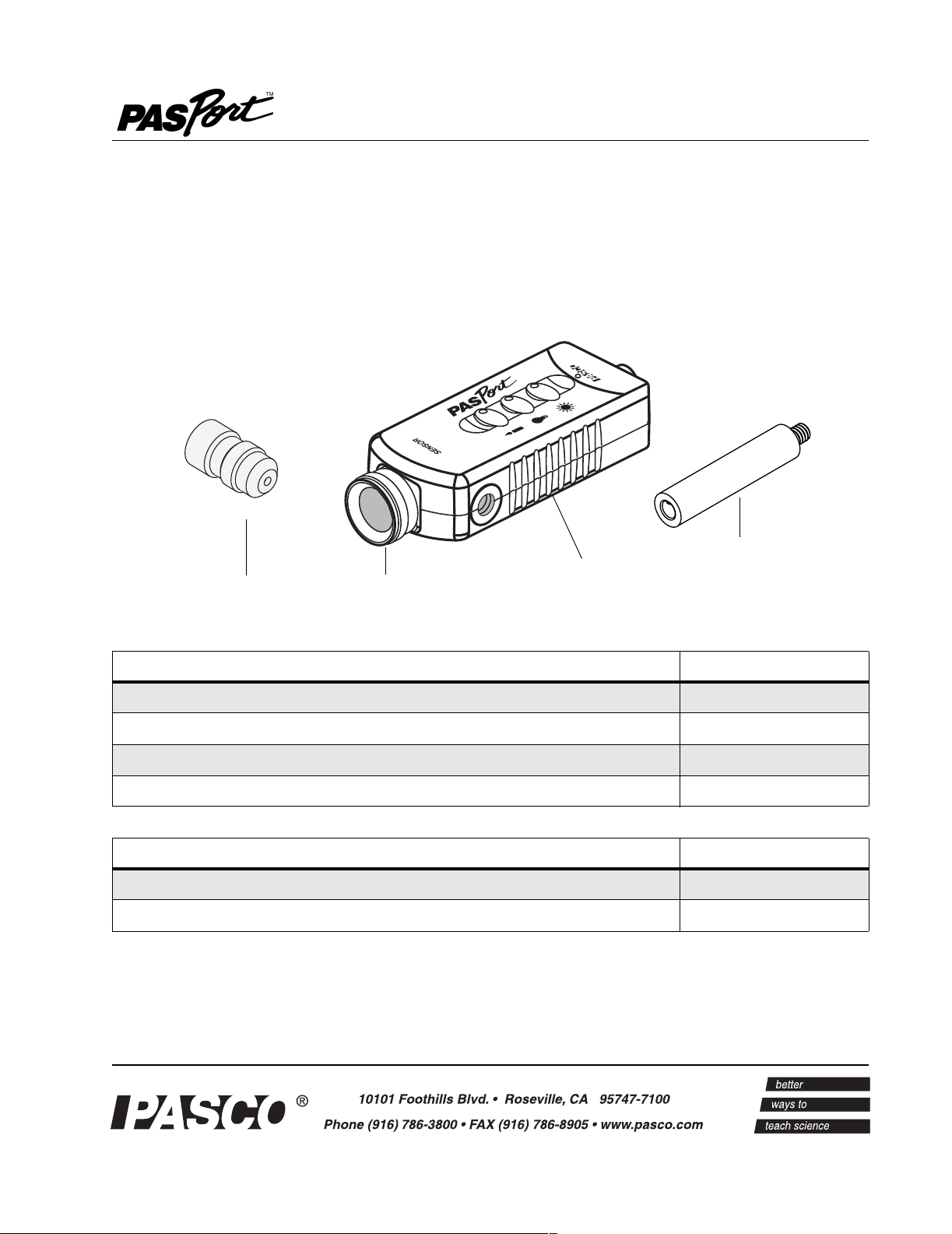
collimator
Instruction Manual
UVA Light Sensor
Model PS-2149
PS-2149
T
H
G
I
L
A
V
U
UVA Light
UVA filter and
retaining cap
Sensor
No. 012-08773A
sensor
handle
Equipment Included Replacement Part
UVA Light Sensor
UVA Filter and retaining cap
Collimator
Sensor Handle
(Contact Tech Support)
(Contact Tech Support)
(Contact Tech Support)
CI-9874 (4-pack)
Additional Equipment Required Model Number
PASPORT interface
DataStudio version 1.9 or higher
(See PASCO catalog)
(See PASCO catalog)
Page 2
UVA Light Sensor Model No. PS-2149
®
Optional Accessories Model Number
UVA Light Sensor Accessory Kit
365nm Filter Accessory
PASPORT Extension Cable
Introduction
The PASCO PS-2149 UVA Light Sensor is
designed for use with a PASCO PASPORT
interface to make measurements of relative
electromagnetic radiation intensity in the UVA
band.
The sensing element of the UVA Light Sensor is
a fairly broad-band Si photodiode. It is sensitive
to electromagnetic energy ranging from visible
light to above the UVA band. Since the radiation
typically measured by the sensor is in the UVA
band, the sensor is furnished with a UVA filter
(UG-1 glass) that blocks light in the visible
spectrum. You can remove the filter to make
broader band measurements.
The Ultraviolet (UV) radiation band extends
from very short wavelengths of 100 nm, just
below the x-ray band, to 400 nm, which is just
above visible violet light. This can be observed
in the table below.
CI-9792
CI-9841
PS-2500
The UVC band ranges from 200–280 nm.
Essentially all UVC radiation from the sun is
absorbed or scattered by ozone in the earth’s
upper atmosphere and does not reach the
surface.
UVB radiation (λ = 280–315 nm) from the sun is
also absorbed or scattered by the upper
atmosphere but under some conditions it can
reach the surface of the earth.
Vacuum UV, UVC and UVB radiation have
harmful, high-energy photons and can initiate
chemical processes including changes in
biological tissue called photo-biological
reactions. Reaction-causing UV is also called
actinic ultraviolet. It is characterized by photon
energies above about 4 electron volts (eV). To
compute the photon energy in eV from the
wavelength in nanometers (nm), use this
formula:
1240 eV nm⋅
-------------------------------
E
λ
.=
Ultraviolet Band (λ = 100–400 nm)
vacuum UV UVC UVB UVA
100–200 nm 200–280 nm 280–315 nm 315–400 nm
far UV near UV
The UV band is divided into four smaller bands
according to the nature of the radiation. The
shortest wavelengths are designated as the
vacuum UV band (λ = 100–200 nm), so called
because energy in this band can only be studied
in a vacuum. Oxygen and other gas molecules in
air absorb radiation in the vacuum UV band.
2
For example radiation with a wavelength of 315
nm has a photon energy of
1240 eV nm⋅
-------------------------------
E
315 nm
3.9 eV.≈=
UVA is the least hazardous ultraviolet radiation.
Its band extends from 315–400 nm.
It is worth noting that ordinary glass cuts off UV
radiation with wavelengths of less than about
300 nm. Thus UVA and some UVB can pass
through glass.
Page 3

Model No. PS-2149 UVA Light Sensor
®
A UV light source is required to perform certain
experiments and demonstrations with the UVA
Light Sensor. The use of a source that radiates
only in the UVA band is recommended because
it is the least hazardous UV radiation. A small
fluorescent “black” light makes a suitable UVA
source.
Other sources of UVA radiation are:
• the sun (best on clear days - but some UV
when overcast)
• sun lamps for tanning
• halogen lamps which are not “UV-protected”
• fluorescent lamps
Operation
Setting up the Sensor
Connect the UVA Light Sensor to the PASPORT
interface. If you will use a computer, connect the
PASPORT interface to the computer and launch
DataStudio.
the range that will cover the expected
measurements without topping out.
Using the Filter With Retaining Cap
The UVA Light Sensor is shipped with the filter
installed in the retaining cap. When the filter is
removed from the retaining cap, the sensor can
detect light in a wider range of wavelengths. To
remove the filter, unscrew the retaining cap from
the photodiode assembly. Be careful not to
damage the filter.
PS-2149
photodiode
assembly
T
H
G
I
L
A
V
U
1⁄4-20 threaded hole
UVA filter
retaining cap
Selecting the Gain Setting
The sensor has three gain settings depicted by
Candle, Lamp and Sun symbols. These symbols
correspond to three ranges, which cover over 7
orders of relative magnitude. The ranges, in
relative units, and the approximate maximum
(without filter) for each range are:
Range Approx. Max.
7 W/m
2
2
2
Candle 0–1
Lamp 0–100
Sun 0–10 000
70 mW/m
700 W/m
The ranges are scaled so that a reading of 50 in
the Lamp range will also be read as 50 in the Sun
range. To ensure the maximum resolution, select
Using the Filter With the Collimator
With the collimator installed, the sensor detects
light only from sources in a narrow angle.
Remove the retaining cap and replace it with the
collimator.
The filter is designed for use under conditions
where there is not a significant amount of
infrared radiation present; for instance, as part of
a spectrometer. If it is necessary to filter out IR
radiation, use the 365nm Filter Accessory
(CI-9841).
Mounting on an Experimental Apparatus
The sensor handle screws into the 1⁄4-20
threaded hole on the bottom of the sensor
enclosure. You can use the sensor handle or any
1⁄4-20 screw to secure the sensor to an
experimental apparatus.
3
Page 4

UVA Light Sensor Model No. PS-2149
®
Specifications Technical Support
sensing element Si photodiode
filter Schott UG-1 glass
spectral response 315–400 nm with
UVA filter
gain levels 1x, 100x, 10 000x
0.3
0.2
0.1
PHOTO SENSITIVITY (A/W)
0
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
WAVELENGTH (nm)
Spectral Response of Sensor (without filter)
(Typ. Ta=25 °C)
For assistance with any PASCO product, contact
PAS CO at:
Address: PASCO scientific
10101 Foothills Blvd.
Roseville, CA 95747-7100
Phone: (916) 786-3800
(800) 772-8700
Fax: (916) 786-3292
Web: www.pasco.com
Email: techsupp@pasco.com
Copyright and Warranty Information
Copyright Notice
The PASCO scientific 012-08773A UVA Light
Sensor Instruction Manual is copyrighted and all
rights reserved. However, permission is granted
to non-profit educational institutions for
reproduction of any part of this manual,
providing the reproductions are used only for
their laboratories and are not sold for profit.
Reproduction under any other circumstances,
without the written consent of PASCO scientific,
is prohibited.
Limited Warranty
For a description of the product warranty, see the
PASCO catalog.
UG-1 Filter Transmittance
4
 Loading...
Loading...