Page 1
®
Instruction Manual with
10
1
100
GAIN
LIGHT
SENSOR
C
I-
6
604A
POL
ARI
ZERMOUNT
Experiment Guide and
Teachers’ Notes
012-06575C
*012-06575*
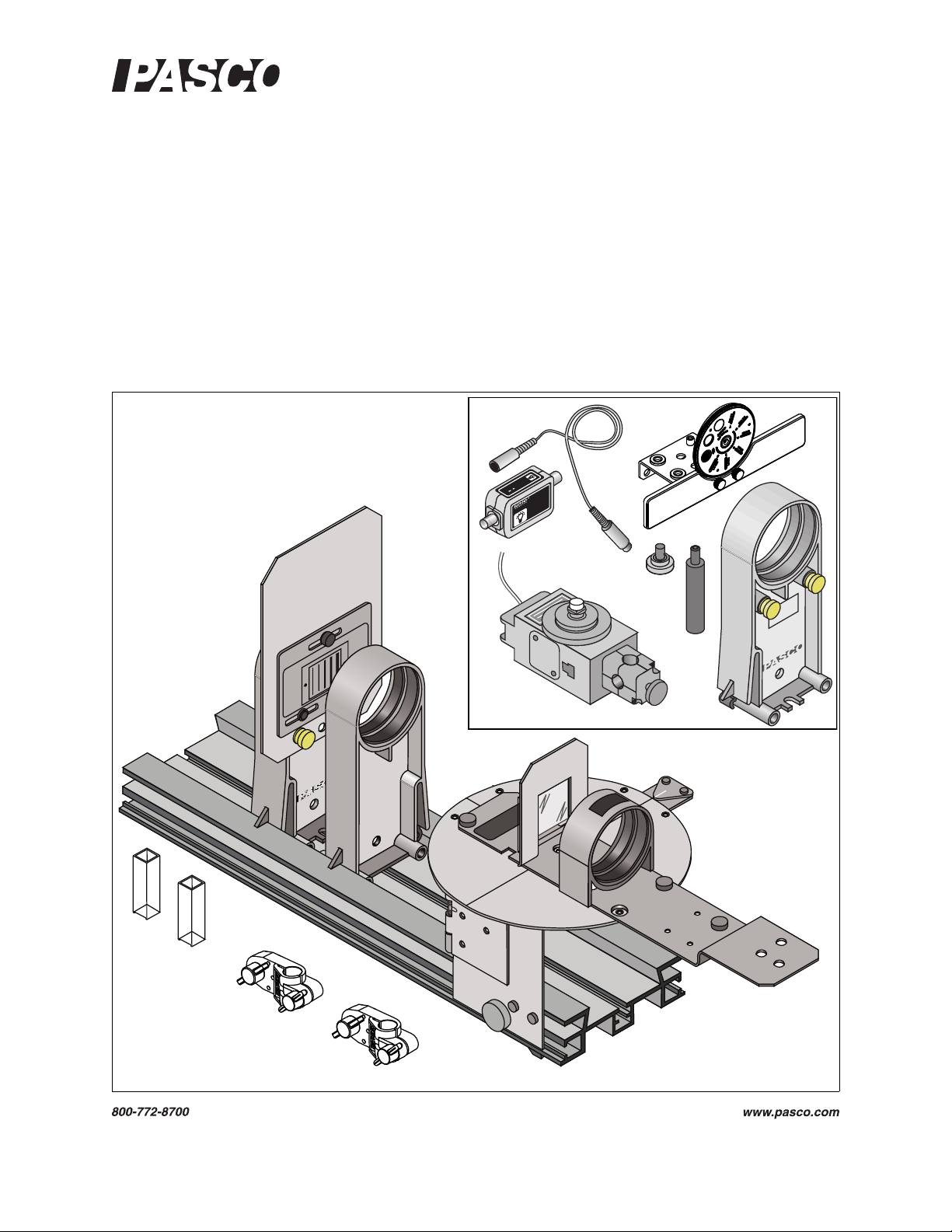
Educational Spectrophotometer
Accessory Kit and System
OS-8537 and OS-8539
Page 2

Page 3

Educational Spectrophotometer Table of Contents
Quick Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Set Up
Mounting the Rotary Motion Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Mounting the Degree Plate and Light Sensor Arm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
More Information About the Degree Plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Mounting the Aperture Bracket Light Sensor Mount and Light Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Mounting the Grating Mount. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Mounting the Spectrophotometer Base on the Optics Bench. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Rod Stand Mounting Clamps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Mounting the Collimating Slits and Lens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Positioning the Collimating Slits and Lens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Mounting the Grating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Mounting and Positioning the Focusing Lens. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Procedures
Turning the Degree Plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Masking the Light Source or the Spectrophotometer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Using the Data Acquisition Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
General Information About the Light Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
General Information About Slit Widths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Scanning a Spectrum. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Calibrating the Grating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Angular Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Cuvettes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Other Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Activity 1: Emission Spectrum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Activity 2: Absorption (Dark Line) Spectrum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Teacher’s Guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
i
Page 4

Educational Spectrophotometer Table of Contents
ii
Page 5
®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Quick Start
1
0
1
1
0
0
G
A
IN
HIGH SENSITIVITY
LIGHT SENSOR
CI-6604
Quick Start
The following pages give an overview of the Spectrophotometer equipment setup.
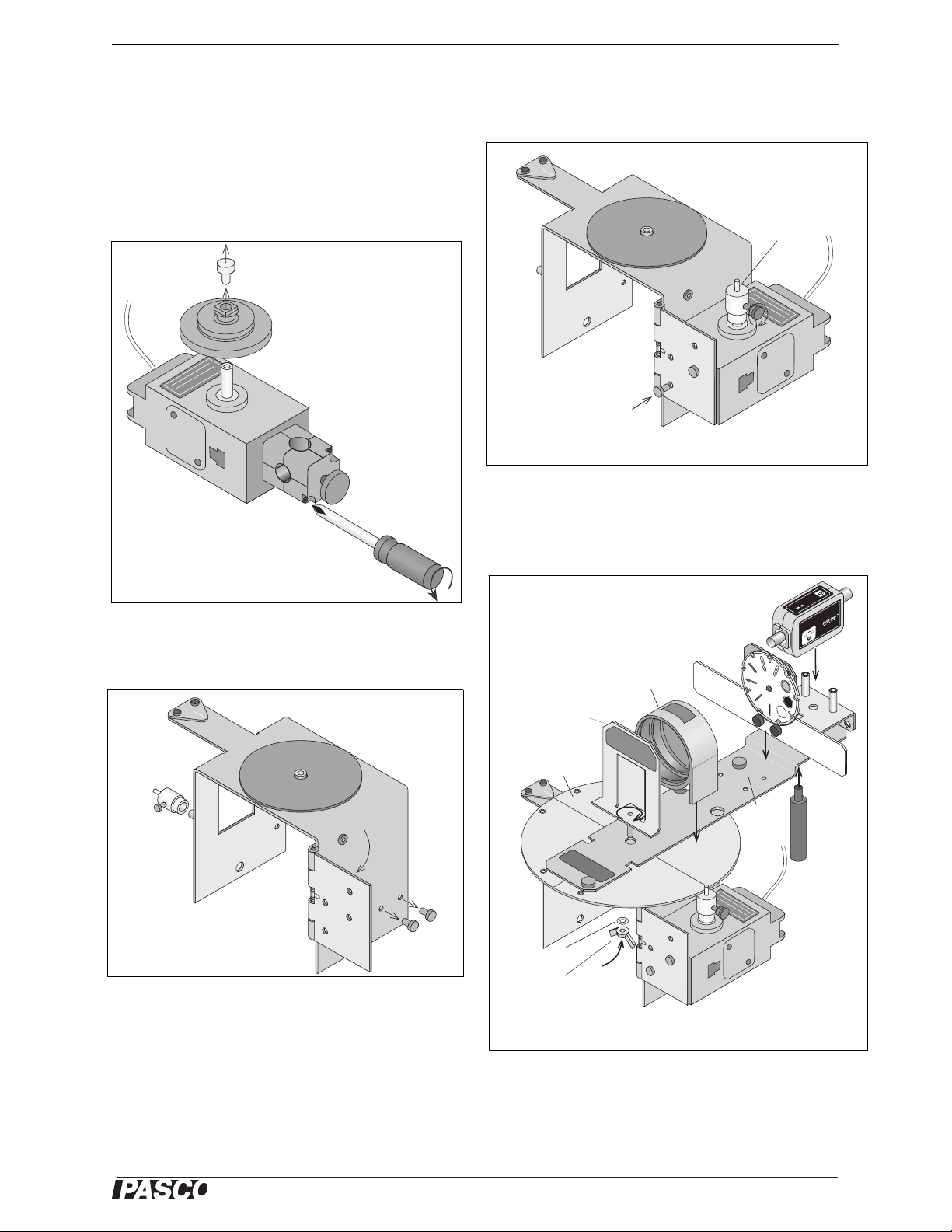
Step One: Prepare the Rotary Motion Sensor by
removing the thumbscrew, three-step pulley, and
rod clamp.
thumbscrew
three-step pulley
Rotary Motion Sensor
rod clamp
Step Three: Attach the Rotary Motion Sensor to
the Base hinge with the two small thumbscrews and
attach the Pinion to the Rotary Motion Sensor shaft.
Spectrophotometer Base
Put the Pinion
on the shaft.
hinge
Use the thumbscrews to
attach the sensor.
Rotary Motion
Quick Start 3: Attach the Sensor and Pinion
Step Four: Put the Degree Plate/Light Sensor Arm
on the Base. Attach the Grating Mount, Light Sensor Mount, and Light Sensor. Position the Focusing
Lens.
Sensor
Quick Start 1: Prepare Rotary Motion Sensor
Step Two: Prepare the Spectrophotometer Base by
removing the two small thumbscrews and Pinion
and by rotating the hinge away from the Base.
Spectrophotometer Base
Remove the
Pinion
Quick Start 2: Prepare the Hinge
Rotate the
hinge.
Remove the
thumbscrews.
Light
Sensor
Light Sensor Mount with
Aperture Disk and Screen
Focusing
Lens
Grating
Mount
Degree
Plate
Light
threaded
Sensor
Arm
lock washer
wing nut
Quick Start 4: Degree Plate & Light Sensor Arm, Grating Mount,
Focusing Lens, Light Sensor Mount, and Light Sensor
post
1
Page 6
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Quick Start
®
GRATING MOUNT
FOR USE WITH
OS-8537
SPECTROPHOTOMETER
Optics Bench
T-slot
square nut
thumbscrew
hinge
Base
GAIN
10
100
1
Collimating
Lens
Collimating
Slits
Quick Start 6: Setup for Collimation
Degree
Plate
H
IG
L
IG
H
T
Grating
glass side faces light source
Quick Start 7: Attach the Grating
GAIN
10
100
1
Scan slowly and
continuously in
one direction.
central ray
(“zeroth order”)
first order spectral lines
first order spectral lines
Grating
Step Five: Put the Spectrophotometer Base onto
one end of the Optics Bench
.
Quick Start 5: Put Base onto Optics Bench
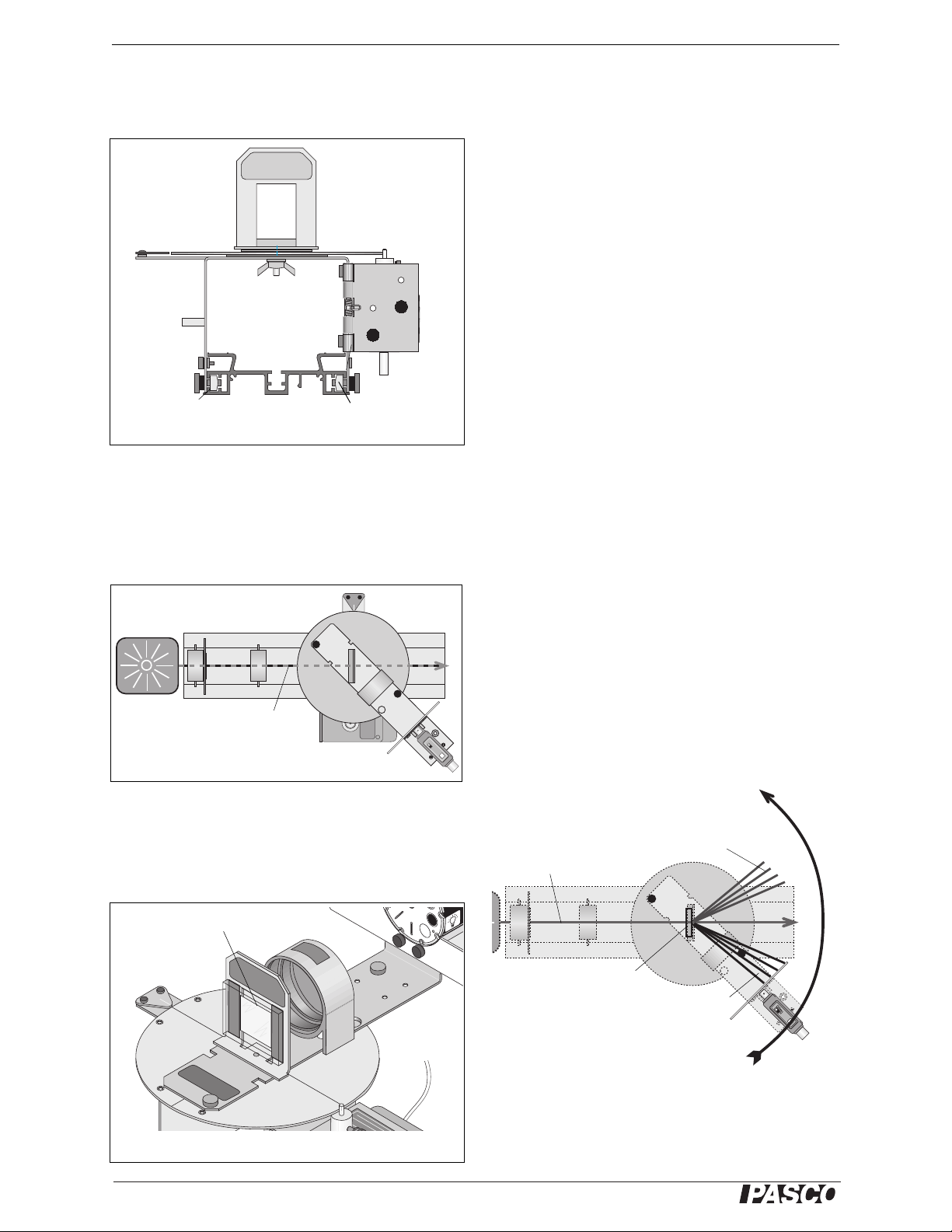
Step Six: Mount the Collimating Slits and Collimating Lens onto the Optics Bench. Set up a light
source. Adjust the Collimating Slits and Collimating Lens to collimate the light beam.
Step Eight: Set up the experiment in the data acquisition program.
1. Select the Light Sensor for Analog Channel A.
2. Select the Rotary Motion Sensor for Digital
Channels 1 and 2.
3. Set the Rotary Motion Sensor to high resolution (1440 Divisions/Rotation).
4. Create a calculation for “Actual Angular Position” based on the Angular Position data from
the Rotary Motion Sensor and the ratio of the
radius of the Degree Plate to the radius of the
small post on the Pinion (typically, a 60 to 1
ratio).
5. Select a Graph display. Set the vertical axis to
Light Intensity and the horizontal axis to your
calculation of “Actual Angular Position”.
6. Set the sampling rate to 20 Hz (20 measurements per second).
Step Nine: Scan the Spectrum
light
source
light ray
path
Step Seven: Attach the Grating to the mount so the
glass side of the Grating faces the light source.
CAUTION: Avoid touching the Grating surface.
1. Mask or hood the light source if necessary.
2. Move the Light Sensor Arm so the Light Sen-
sor is beyond the edge of the first order spectral
pattern.
3. Start recording data. Slowly and continuously
scan the spectrum. Scan the first order spectrum on one side of the central ray, through the
central ray, and through the first order spectrum on the other side.
2
Step Ten: Analyze Your Data
Page 7
®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Introduction
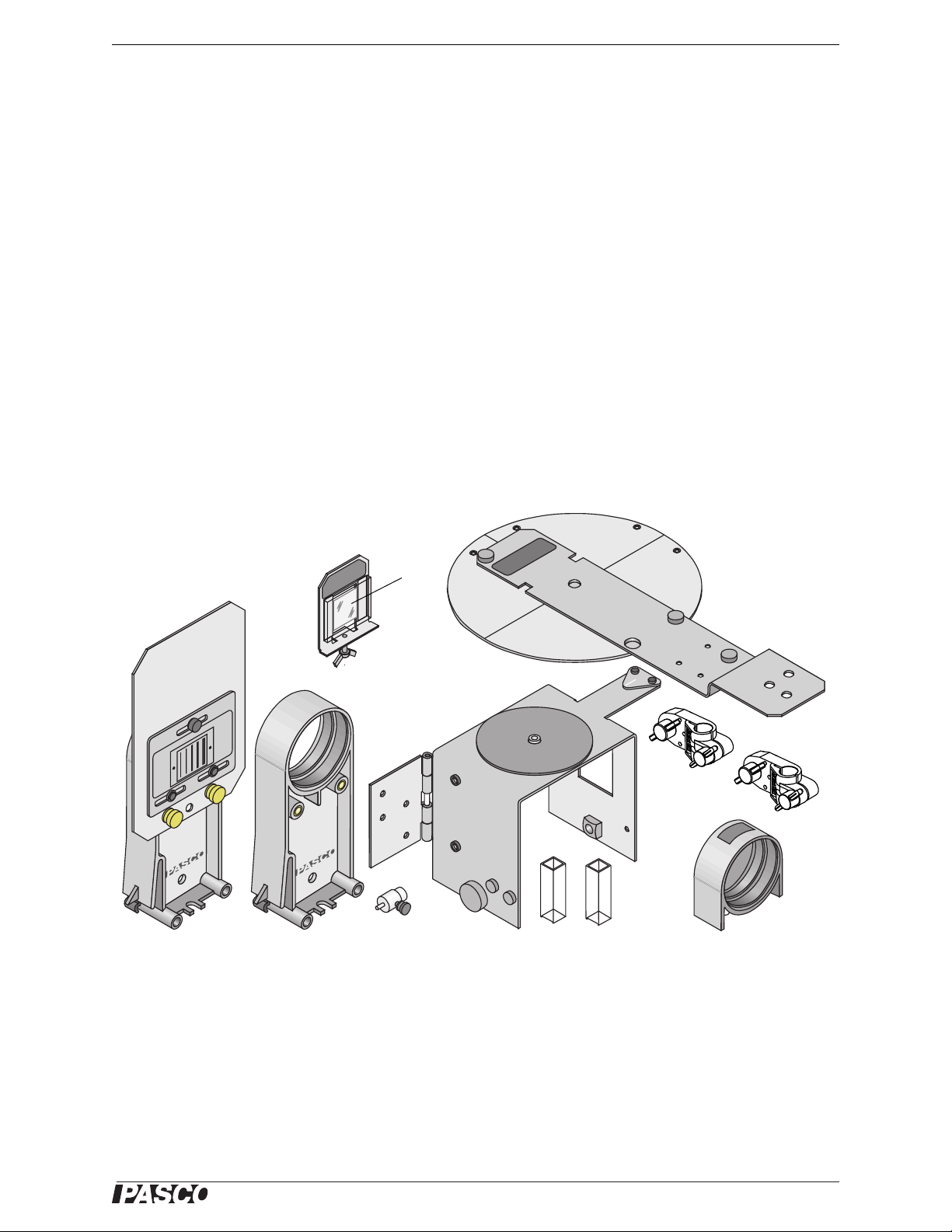
Grating Mount
Grating
Degree Plate
Light Sensor Arm
Spectrophotometer
Base
Collimating Slits
Collimating Lens
Pinion*
Cuvettes (2)
Focusing Lens
Rod Mounting
Clamps (2)
Figure 1a: Educational Spectrophometer Accessory Kit
Introduction
About This Manual
This manual describes the PASCO OS-8537 Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and the PASCO
OS-8539 Educational Spectrophotometer System. The OS-8537 Accessory Kit is designed to be mounted on the
Optics Bench of the OS-8515 Basic Optics System.
Components of the Kit
The OS-8537 Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit (see Figure 1a) includes the following items:
Spectrophotometer Base Degree Plate with Light Sensor Arm
Grating Mount Grating (~600 lines per mm)
Focusing Lens Collimating Lens
Collimating Slits Cuvettes (2)
Rod Stand Mounting Brackets (2)
(*The pinion shown in Figure 1a can be mounted on a post on the Spectrophotometer Base when not in use.)
3
Page 8
®
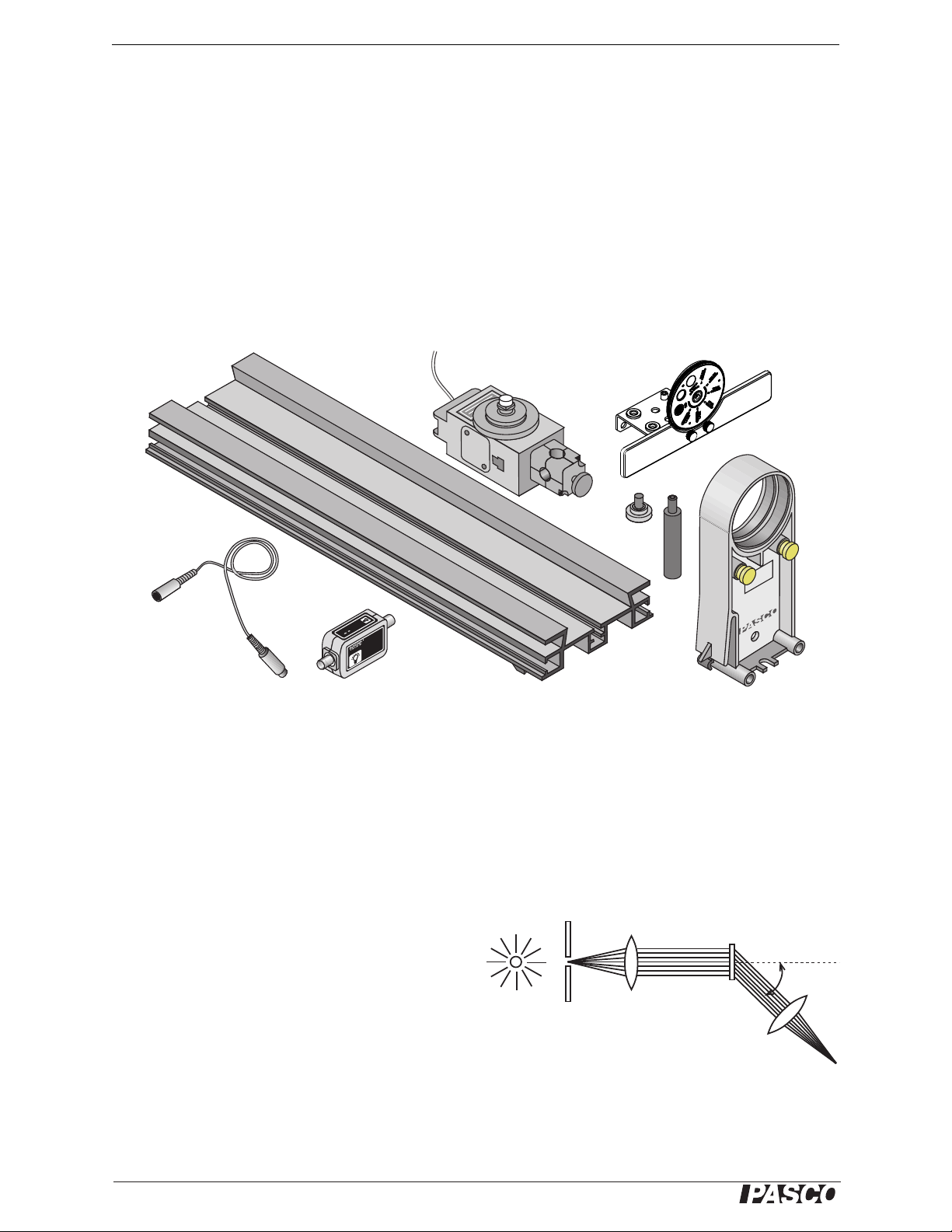
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Description
Rotary Motion Sensor
Aperture Bracket
DIN-to-DIN cable High Sensitivity Light Sensor Optics Bench (60 cm) Aperture Bracket Holder
Figure 1b: Additional Components of the Spectrophotometer System
thumbscrew
post
Light Source
Collimating Slit
Collimating Lens Diffraction Grating
Focusing Lens
spectral line
Figure 2: Grating Spectrometer
Recommended Equipment for use with the Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit:
Basic Optics System (OS-8515) High Sensitivity Light Sensor (CI-6604)
Aperture Bracket (OS-8534) Rotary Motion Sensor (CI-6538)
Components of the System
The OS-8539 Educational Spectrophotometer System includes the items in the Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit
plus the following:
Optics Bench (60 cm) Rotary Motion Sensor (CI-6538)
High Sensitivity Light Sensor (CI-6604) Aperture Bracket (OS-8534)
GAIN
1
10
100
04A
CI-66
LIGHT
SOR
SEN
Recommended Equipment for use with both the Kit and the System:
Light Source (such as SE-9466 Mercury Spectral Tube) Rod, 45 cm (ME-8736) (2)
Spectral Tube Power Supply and Mount (SE-9460) Large Rod Stand (ME-8735) (2)
Description
The Spectrophotometer allows you to view and measure the spectral pattern (spectrum) produced by a
light source. The Collimating Slits and Collimating
Lens produce a narrow beam of parallel light rays.
The Grating disperses the beam of light into a spectrum with different colors at different angles but with
all of the light of a given color in a parallel beam. The
Focusing Lens focuses these parallel beams of color
into spectral lines (see Fig. 2). The narrow slit on the
Aperture Disk (part of the Aperture Bracket) allows
light of a single color to enter the High Sensitivity Light Sensor. The High Sensitivity Light Sensor (included
with the Spectrophotometer System) measures the intensity of the light while the Rotary Motion Sensor
(included with the Spectrophotometer System) measures the angle to which the light is diffracted by the Grating.
4
MOUNT
POLARIZER
Page 9
®
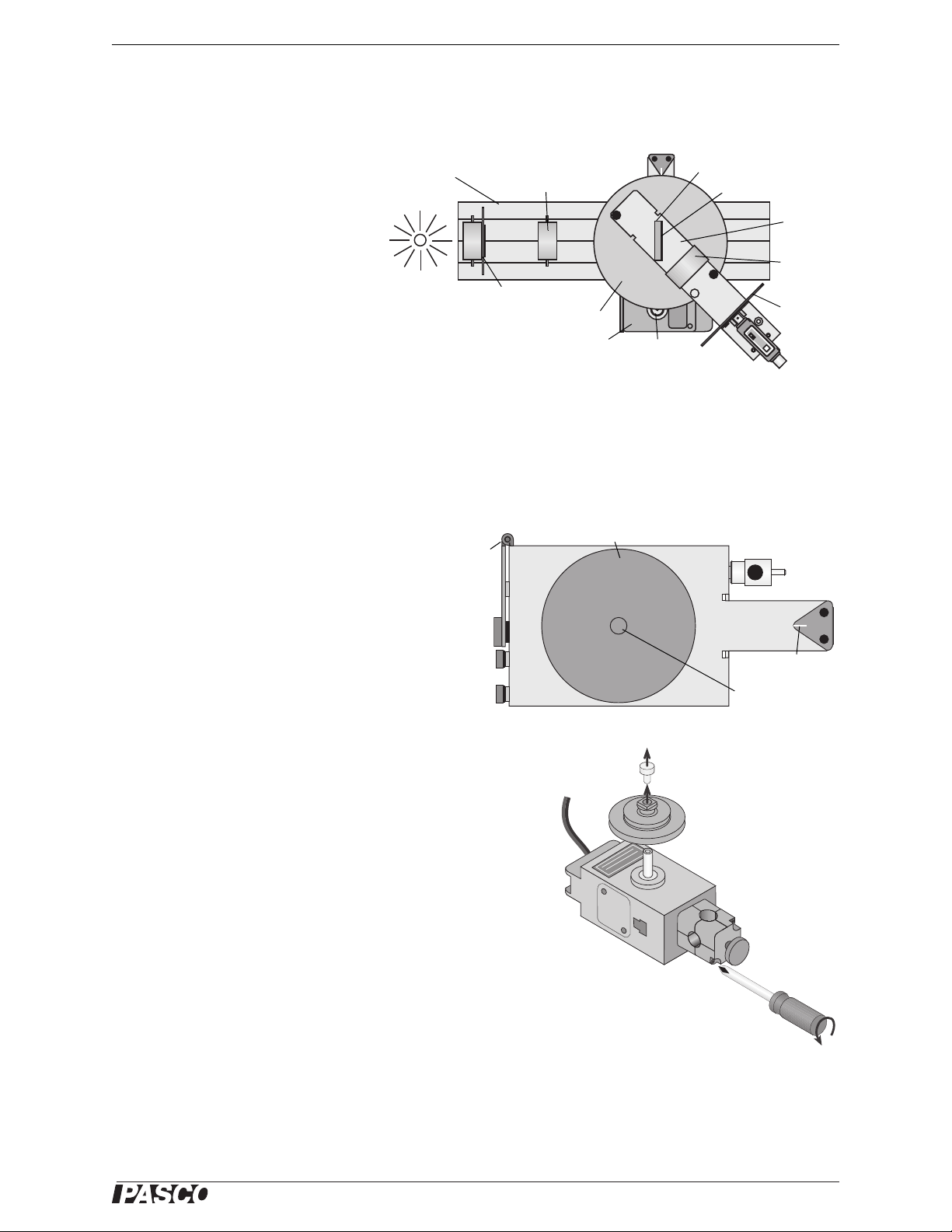
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Set Up
G
A
IN
1
0
1
0
0
1
Figure 3: Spectrophotometer System (top view)
Collimating Slit
Collimating Lens
Diffraction Grating
Grating Mount
Light Sensor
Arm
Focusing
Lens
Aperture
Disk
High Sensitivity Light Sensor
Pinion
Rotary Motion Sensor
Degree Plate
Light
Source
Optics Bench
Figure 4: Spectrophotometer Base (top view)
Hinge
Large
Thrumb
screw
Small
Thrumb
screws
Magnetic Pad
Pinion
Index
Threaded Post
Figure 5: Prepare Rotary Motion Sensor
Thumbscrew
Three-step Pulley
Rotary Motion Sensor
Rod Clamp
You can find the wavelength of each color of light using the measured angle and the Grating spacing “d”.
m = d sin m = 0, 1, 2…
where d is the distance between the
rulings on the Grating, m is the order
of the particular principal maximum,
is the angle of the diffracted light,
and is the wavelength.
The Grating disperses the beam of
light into a first order spectrum and
higher order spectra. The higher
order spectra are broader and less
bright than the first order spectra, and
may overlap.
The Grating is blazed, so one side of
the spectrum is much brighter than
the other.
Set Up
This part of the manual describes how to set
up the Spectrophotometer System (see Fig. 3).
.
Mounting the Rotary Motion Sensor
This describes how to mount the Rotary
Motion Sensor to the hinge on the Spectrophotometer Base.
The top of the Spectrophotometer Base has a
short threaded post for centering the circular Degree Plate and for
holding the Grating Mount. It also has a magnetic pad for holding
the Degree Plate, and a triangular shaped index marker. One side
of the base has a post upon which the Pinion can be stored when it
is not in use. The other side has a spring-loaded hinge and two
small thumbscrews for mounting the Rotary Motion Sensor
(included in the Spectrophotometer System). On both sides of the
base are large thumbscrews and square nuts used for mounting
the Spectrophotometer Base on the Optics Bench (see Fig. 4)
The Rotary Motion Sensor has a three step pulley attached to its
shaft with a small thumbscrew. The sensor also has a rod clamp
attached at one end.
First, remove the small thumbscrew and three step pulley from
the Rotary Motion Sensor shaft. Then, remove the rod clamp
from the Rotary Motion Sensor (see Fig. 5).
Remove the two small thumbscrews from the threaded storage holes on the side of the Spectrophotometer Base
and set them aside for the moment. Remove the Pinion from the storage post on the opposite side of the Spectrophotometer Base and set the Pinion aside for a moment (see Fig. 6).
5
Page 10
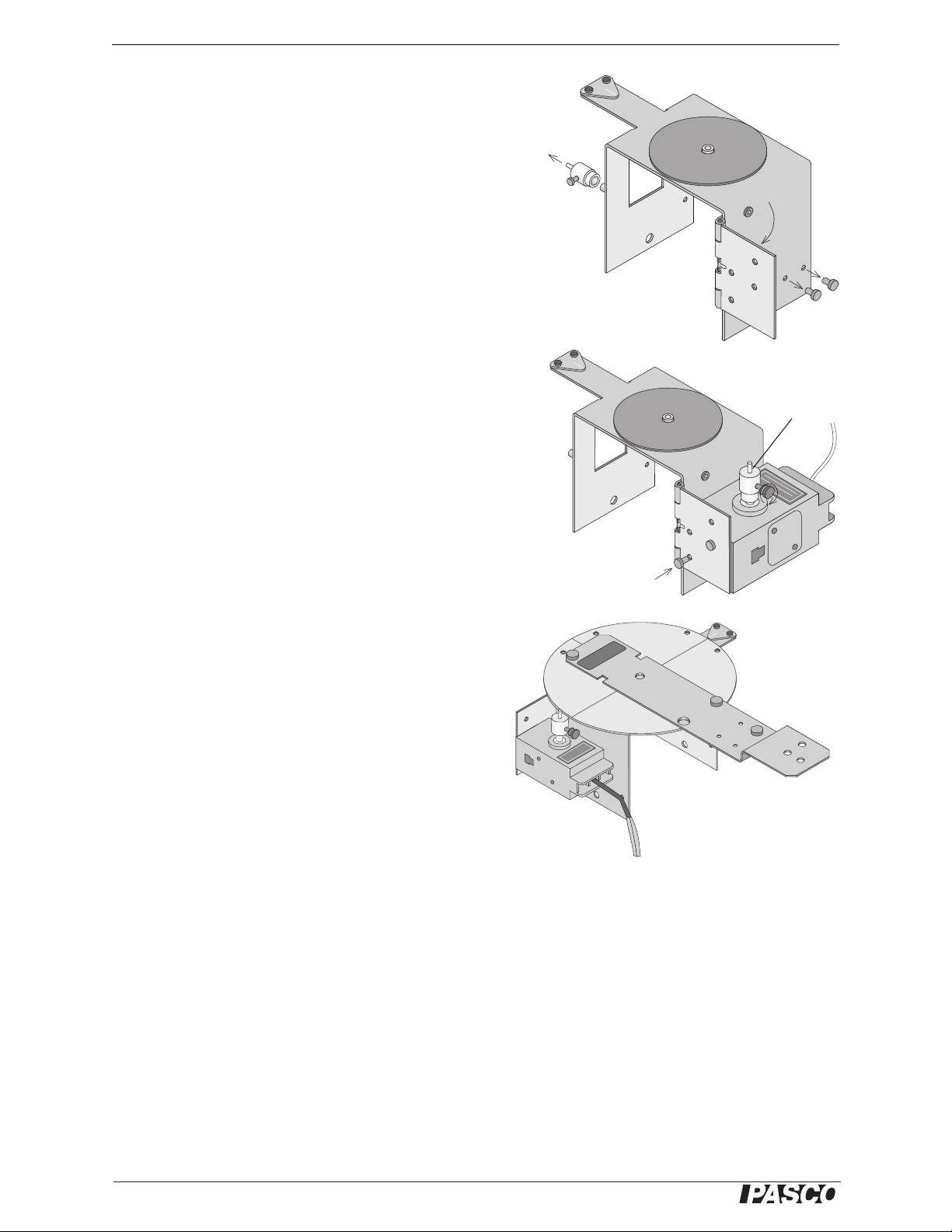
®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Set Up
Spectrophotometer Base
Remove
the pinion
Rotate
the hinge
Figure 6: Prepare the Hinge
Put the pinion
on the shaft
Use the thumb-
screws to attach
the sensor
Hinge
Figure 7: Attach the Sensor and Pinion
Figure 8: Degree Plate onto Base
Let the post on top of
the pinion rest
against the edge of
the Degree Plate.
Rotary Motion
Sensor
Light Sensor
Arm
Degree Plate
Rotate the hinge away from the side of the base until the hinge
is almost perpendicular to the base. Use the two small thumbscrews to fasten the Rotary Motion Sensor to the lower set of
holes on the inside of the hinge.
Place the Pinion all the way onto the Rotary Motion Sensor
shaft and tighten the Pinion on the shaft by turning the small
thumbscrew on the side of the Pinion (see Fig. 7).
Connect the Rotary Motion Sensor to the PASCO interface.
Mounting the Degree Plate and Light Sensor Arm
Remove the
thumbscrews
The Degree Plate and Light Sensor Arm are shipped as a unit.
The Light Sensor Arm is attached to the circular Degree Plate
with two small thumbscrews. The hole in the center of the
Degree Plate fits over the short threaded post on the top of the
Spectrophotometer Base.
Hold the Rotary Motion Sensor slightly away from the base so
the small diameter post on top of the Pinion is not in the way of
the edge of the Degree Plate. Position the hole in the plate over
the short threaded post on the top of the base. Place the Degree
Plate onto the Spectrophotometer Base. Let the small diameter
post on the top of the Pinion rest against the edge of the Degree
Plate (see Fig. 8).
Rotary Motion
Sensor
More Information About the Degree Plate
The ratio between the radius of the Degree Plate and the
radius of the small post on the top of the Pinion is
designed to be 60 to 1. In other words, the Pinion rotates
60 times for one rotation of the Degree Plate.
This assumed ratio of 60 to 1 is included in a calculation
for the actual angular displacement of the Degree Plate as
it turns during the measurement of a spectrum (see “Using
the data acquisition program” in the Procedure section).
Using the exact ratio of the Degree Plate to the small Pinion post can slightly improve the accuracy of measurement. To determine the exact ratio of the Degree Plate to
the small Pinion post, do the following to calibrate the
Degree Plate:
1. Remove the Light Sensor Arm from the Degree Plate by unscrewing the two small thumbscrews. (You can
store the thumbscrews in the empty threaded holes on the Light Sensor Arm.) Turn the Degree Plate so the
zero degree mark is exactly aligned with the index mark on the arm that extends from the Spectrophotometer
Base.
2. Start the data acquisition program. (See the software’s Help system or User’s Guide for more information.)
3. In the program, select “Rotary Motion Sensor” to be connected to the PASCO interface. If possible, set the
resolution of the Rotary Motion Sensor to 1440 Divisions/Rotation.
6
Page 11

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Set Up
Figure 9: Calculation of Ratio of Radii
NOTE: The
calculator in
your program
may differ in
appearance.
Refer to your
User’s Guide.
NOTE: The
Graph display in
your program
may differ in
appearance.
Refer to your
User’s Guide.
Figure 10: Sample Degree Plate Calibration Data
HIGH SENSITIVITY
LIGHT SENSOR
CI-6604
Figure 11: Sensor and Aperture Bracket
onto Light Sensor Arm
Aperture
Bracket Light
Sensor Mount
Light Sensor
Arm
High Sensitivity
Light Sensor
Threaded post
4. In the data acquisition program, use the
built-in Calculator to create a calculation.
Base the calculation on the “Angular Position” measurement from the Rotary Motion
Sensor. In the calculation, divide “Angular
Position” by 2where is approximately
3.1416… Label your calculation “Ratio of
Radii” (see Fig. 9).
5. In the program, select a Graph display and set
it to show the calculation “Ratio of Radii” on
its vertical axis.
6. Start recording data. Turn the Degree Plate in one direction slowly and continuously for exactly one complete rotation. Stop recording data.
7. In the Graph display, use the built-in Statistics tools
to find the maximum value of the “Ratio of Radii”
(i.e., the maximum of y - see Fig. 10). This value is
the exact ratio of the Degree Plate radius to the small
Pinion post radius. (Note: This value should be close
to 60.) Record the actual ratio.
Ratio of Radii = _______
8. Replace the Light Sensor Arm on the Degree Plate
and fasten it to the plate with the two small thumbscrews.
Mounting the Aperture Bracket Light Sensor Mount and Light Sensor
The Aperture Bracket has two main parts: the Light Sensor Mount
and the Holder. (The Holder and thumbscrew are not used and can
be put aside.) An Aperture Disk and Aperture Screen) are attached
to the front of the Light Sensor Mount.
The Light Sensor Mount has two holes: one hole in the center of the
mount and a second hole at the rear of the mount. The end of the
Light Sensor Arm has three holes: two holes along the centerline of
the arm and one hole to the side of the centerline. Line up the center
hole of the Light Sensor Mount with the centerline hole in the Light
Sensor Arm that is closest to the Degree Plate.
Line up the High Sensitivity Light Sensor so the threaded hole in its
base is above the center hole of the Light Sensor Mount. Use the
threaded post (included with the Aperture Bracket fasten the High
Sensitivity Light Sensor and Light Sensor Mount to the Light Sensor Arm (Fig. 11).
Rotate the Aperture Disk on the front of the Light Sensor Mount so
that the narrowest slit is in line with the opening to the sensor.
Connect the High Sensitivity Light Sensor to the PASCO interface.
7
Page 12

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Set Up
Align the zero line on
the Degree Plate with
the index mark.
Zero
line
Fasten the mount
with the lock washer
and wing nut
Figure 13: Base onto Optics Bench (end view)
Spectrophotometer
Base
Optics Bench
Square nut
Thumbscrew
T-Slot
Figure 14: Mounting Clamp onto Optics Bench
Top view
Put support
rod here.
Slide groove onto lip.
End view
Mounting the Grating Mount
The threaded rod on the bottom of the Grating
Mount has a lock washer and a wing nut. Remove
the lock washer and wing nut from the threaded rod,
and screw the threaded rod into the short threaded
post in the center of the Degree Plate. Do not screw
the Grating Mount all the way down onto the Light
Sensor Arm. The Grating Mount must be slightly
above the Light Sensor Arm so the Degree Plate can
move.
Line up the edge of
the Grating Mount
with the zero line.
Use the Light Sensor Arm to rotate the Degree Plate
until the zero line on the Degree Plate is aligned
with the index mark on the Spectrophotometer Base
Turn the Grating Mount so it is aligned with the
zero line on the Degree Plate and the label side of
the Grating Mount faces away from the sensor on
the Light Sensor Arm.
Figure 12: Grating Mount onto Rotating Table
Put the lock washer and wing nut back onto the threaded rod and tighten the wing nut until the Grating Mount
remains in place when the Degree Plate is rotated in either direction (Fig. 12).
Mounting the Spectrophotometer Base on the Optics Bench
You can mount the components of the Spectrophotometer on the 1.2 meter Optics Bench that is part of the
OS-8515 Basic Optics System, or the 0.6 meter (60
cm) Optics Bench that is included with the OS-8539
Spectrophotometer System. The Spectrophotometer
Base mounts into the T-slots on the sides of the Optics
Bench and the Collimating Slits and Collimating Lens
snap into the center of the Optics Bench.
To mount the Spectrophotometer Base on the Optics
Bench, loosen the thumbscrew on each side of the
Base so the square nuts can slip into the T-slots on the
sides of the Optics Bench. Insert the square nuts into
the slots and slide the Base along the bench until it is
about 20 cm from the end (Fig 13). Tighten the thumbscrews to hold the Base firmly on the bench.
Rod Stand Mounting Clamps
You can adjust the height or angle of the Optics Bench using the
Rod Stand Mounting Clamps and two rods and bases (not
included). Each clamp has a thumbscrew and a square nut at
one end, and a second thumbscrew at the other end. The thumbscrew with the square nut holds the clamp onto the bench, and
the other thumbscrew holds the clamp onto a rod. The clamp
has grooves on one side that match the lower lip of the optics
bench.
To mount the clamp on the bench, loosen the square nut and
then slide the square nut into the T-slot at the end of the optics
bench. Line up one of the grooves in the clamp with the lower
lip of the optics bench. Tighten the thumbscrew (Fig. 14).
8
Page 13

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Set Up
Figure 15: Mounting Clamp onto Rod
Optics Bench
Rod
Figure 16: Locking Clip
Collimating Slits
Optics Bench
Locking clip
Figure 17: Collimation Setup
Light
source
Collimating
Slits
Collimating Lens
Light ray
path
To mount the clamp on a support rod, loosen the other thumbscrew. Put the support rod though the hole, and then tighten the
thumbscrew (Fig 15).
Mounting and Adjusting the Collimating Slits and Lens
The Collimating Slits consist of two parts: the Collimating Slits
Plate and the Collimating Slits Holder. The slits are in a piece of
metal that is attached to a moveable slide. The slide is held on the
Collimating Slits Plate with a small thumbscrew and two permanently attached socket screws. The Collimating Slits Plate is
attached to the Collimating Slits Holder with two brass thumbscrews. Loosen the small thumbscrew in the Collimating Slits Plate in order to move the slits slide back and forth. The narrow slot in the Collimating Slits Plate
lets light through one slit at a time. The top half of the Collimating Slits Plate helps to prevent extra light from
being measured.
Snap the Collimating Slits Holder into the Optics Bench near the end of the
bench that is closest to the light source you are using. To move the holder,
grasp the holder at the base and push in on the locking clip on one side of
the holder (Fig. 16). Slide the holder along the center section of the bench
while squeezing the clip. Release the clip to lock the holder firmly in position.
Snap the Collimating Lens Holder into the Optics Bench between the Collimating Slits Holder and the Spectrophotometer Base. Position the Collimating Lens Holder about 10 cm from the Collimating Slits Holder.
Positioning the Collimating Slits and Lens
The focal length of the Collimating Lens is about 10 cm so the lens should
be positioned about 10 cm from the slits. Use the following procedure to
position the lens more precisely.
Set up a light source so that light from the source passes through one of the slits on the Collimating Slits and then
through the Collimating Lens. Rotate the Light Sensor Arm so the Aperture Bracket and Light Sensor are out of
the way and the beam of light can shine onto a distant vertical surface such as a wall (Fig. 17).
Adjust the distance between the Collimating Slits and
the Collimating Lens so that the beam of light is neither
converging nor diverging (i.e., light rays are parallel).
The beam of light should stay about the same width all
the way to the distant vertical surface. Hold a piece of
paper in the light beam’s path at various distances
along the beam’s path. Check to see that the light
beam’s width is about the same at each point along its
path. Note that the light may not be in focus during this
100
10
1
GAIN
process.
If the light beam is not perfectly vertical, loosen the small thumbscrew that holds the Collimating Slits slide and
adjust the slide, or loosen the brass thumbscrews that hold the Collimating Slits Plate onto the holder and adjust
the plate until the collimated beam is vertical. Remember to tighten the thumbscrews after you make the adjustment.
The distances between the light source and the Collimating Slits and between the Collimating Slits and the rest of
the Spectrophotometer are not critical. However, the closer the light source, the brighter the spectrum.
9
Page 14

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Set Up
Caution! Handle the Grating carefully. Avoid touching the Grating or the glass plate
to which the Grating is attached except by the edges of the glass plate.
Glass side faces light source
Grating Mount
Grating
Figure 18: Grating onto Mount
1
0
1
1
0
0
G
A
IN
HIGH SENSITIVITY
LIGHT SENSOR
C
I-6
6
0
4
Figure 19: Position Focusing Lens
Grating
Focusing Lens
Aperture Screen
Aperture Disk
Mounting the Grating
The Grating is mounted on one side of a rectangular glass plate.
There are two magnetic pads on the same side of the glass plate as
the Grating. These pads hold the Grating in place on the Grating
Mount.
Once the light from the source is collimated, attach the Grating to
the Grating Mount so that the glass side of the Grating faces the
light source (Fig. 18).
Mounting and Positioning the Focusing Lens
The Degree Plate has markings on either side of the Light Sensor
Arm that indicate the approximate position in which to place the
Focusing Lens. The Focusing Lens has two small magnets in its base that hold it in place on top of the Light Sensor Arm. Place the Focusing Lens on the Light Sensor Arm between the Grating Mount and the High Sensitivity
Light Sensor.
The Focusing Lens focal length is about 10 cm so the
lens should be positioned on the Light Sensor Arm
about 10 cm from the front of the Aperture Disk (Fig.
19).
Set up the light source, Collimating Slits, and Collimating Lens so a beam of light shines through the
Grating and Focusing Lens. Darken the room so you
can see the spectral lines more clearly. Move the
Light Sensor Arm so the central ray of light (called
the “zeroth order”) is centered on the slit at the bottom of the Aperture Disk. You should be able to see
the first order spectral lines on the Aperture Screen
on either side of the central ray of light. Adjust the
position of the Focusing Lens until the spectral lines
are sharply focused.
Note: Because the Grating is strongly blazed, the spectral lines on one side of the central ray (“zeroth order”) will
be less bright than the spectral lines on the other side.
10
Page 15

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Procedures
Figure 20: Mask the Light Source
Opaque cloth
CI-6604A
PASCO
scientific
HIGH SENSITIVITY
LIGHT SENSOR
Figure 21: Mask the Spectrophotometer
Opaque cloth
Sunlight
Binder clips
Figure 22: Create a Calculation
Procedures
Grounding
1. If you use an AC powered spectral light source, plug the power cord for the light source into a different outlet than the outlet used for your PASCO interface and computer.
2. For a very dim light source you may need to use the 100 GAIN setting on the High Sensitivity Light Sensor
and the 100x sensitivity setting in the data acquisition program. If so, connect a wire from the Spectrophotometer Base to an earth ground in order to reduce electrical “noise”. You can use one of the small thumbscrews from the Light Sensor Arm to connect a ground wire (not included) to the threaded hole on the side
of the Spectrophotometer Base opposite to the Rotary Motion Sensor.
Turning the Degree Plate
The spring in the hinge on the Spectrophotometer Base is strong enough to keep the Pinion in contact with the
edge of the Degree Plate as you move the Light Sensor Arm to turn the plate. If the small diameter post on the
Pinion slips rather than turns, make sure that the thumbscrews that hold the Rotary Motion Sensor onto the hinge
are tight. You may need to loosen the screws and then push the Rotary Motion Sensor so it is as close to the Base
as possible before re-tightening the screws.
Masking the Light Source or the Spectrophotometer
When using a bright spectral light source such as the PASCO Low Pressure Sodium Light Source, cover the source with an opaque cloth hood to
block out ambient light. Cover the light source opening with a mask that
has a 0.5 to 1.0 cm wide rectangular slot in it to reduce ghost images. Use
clothespins or binder clips to attach the edge of the cloth hood to the plate
on the Collimating Slits (Fig. 20).
When measuring solar spectra, put an opaque cloth
hood over the entire Spectrophotometer so that the
only opening to the sunlight is the Collimating Slit.
Use clothespins or binder clips to attach the edge of the
cloth hood to the plate on the Collimating Slits. Use
one hand to hold up the center of the cloth hood (Fig.
21).
Using the Data Acquisition Program
Note: See the data acquisition software’s User’s Guide
for detailed information about using the program.
1. Start the program. Select the Light Sensor to be connected to Analog Channel A and select the Rotary
Motion Sensor to be connected to Digital Channels 1 and 2.
2. In the program, set the Rotary Motion Sensor so it can record 1440 divisions per rotation.
3. In the program, select a Graph display and set it to show “Light
Intensity (% max)” on its vertical axis.
4. Use the Calculator in the program to create a calculation of the
actual angular position of the Degree Plate. If the small post on
the top of the Pinion is in contact with the edge of the Degree
Plate, the Angular Position of the Rotary Motion Sensor must
be divided by the ratio of the radius of the Degree Plate and the
radius of the small post on the Pinion*. The ratio is approxi-
11
Page 16

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Procedures
GAIN
10
100
1
Figure 23: Scan the Spectrum
First order spectral lines
Scan slowly and continuously
in one direction.
Light
Source
mately 60 to 1. If the larger diameter section at the bottom of the Pinion is used, the Angular Position of the
Rotary Motion Sensor must be divided by 15* (see Fig. 22 for an example from DataStudio).
5. Change the Graph display to show your calculation of Actual Angular Position on its horizontal axis.
(*See “Calibrating the Degree Plate” earlier in the Set Up section for more information on measuring the ratio of
the radius of the Degree Plate and the radius of the Pinion.)
General Information About the Light Sensor
The High Sensitivity Light Sensor has a GAIN (amplification) select switch on the top with three settings (1, 10
and 100). When you measure a spectrum, start with the lowest GAIN setting to measure the brightest lines. Then
switch to the next setting and re-scan the spectrum to measure the dimmer lines. Then re-scan again at the highest
GAIN setting to measure the dimmest lines.
It may also be possible to amplify the signal (increase the sensitivity) from the Light Sensor using the data acquisition program. For example, in DataStudio, the normal sensitivity setting is “Low (1x)”. The other settings are
“Medium (10x)” and “High (100x)”.
In general, you will record better data if you increase the GAIN setting on the Light Sensor before you increase
the sensitivity setting in the data acquisition program.
General Information About Slit Widths
There are five slits on the Collimating Slits slide and six slits on the Aperture Disk. You can select wider slits in
order to increase the amount of light that passes through the Grating and into the Light Sensor, but this will make
a wider spectral pattern and decrease the accuracy of your measurements.
Scanning a Spectrum
To scan a spectrum, use the threaded post under the Light
Sensor to move the Light Sensor Arm so the Light Sensor is beyond the far end of the first order spectral lines,
but not in front of any of the spectral lines in the second
order.
In the data acquisition program, begin recording data.
Then, scan the spectrum continuously but slowly in one
direction by pushing on the threaded post to rotate the
Degree Plate. Scan all the way through the first order
spectral lines on one side of the central ray (“zeroth
order”), through the central ray, and all the way through
the first order spectral lines on the other side of the central ray (Fig. 23).
The angle of a particular line in the spectral pattern is one-half of the difference of the angle between the chosen spectral line in the first order on one side of the central ray and the matching spectral line in the first order on
the other side of the central ray. Use the built-in analysis tools in the data acquisition program’s Graph display to
find the angle between the two matching spectral lines. The angle, , is one-half of the angle between the two
lines. Use m = d sin (and let the order, m, be 1) to calculate the wavelength of the chosen spectral line.
Central ray
(“zeroth order”
12
Page 17

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Procedures
Central ray
(“zeroth order”)
For example, measure
the difference in angle
between these two
lines. One half of the
difference is the angle
to use for calculating
the wavelength.
If a dim spectral line only appears on one side of the central ray (“zeroth order”), calculate where the central ray
is using a brighter spectral line that is visible on both sides of the central ray. Then determine the angle from the
central ray to the dim line to find the angle, , for that spectral line (Fig. 24).
Figure 24: Measure the Angles for both First Order Spectral Patterns
Calibrating the Grating
The number of grating lines on the Grating is approximately 600 lines per millimeter. This translates to a Grating
line spacing of d = 1666 nm (1.666…x10
-6
m).
To fi n d t he exact Grating line spacing, use a sodium lamp to calibrate the Grating. The average wavelength, , of
the yellow sodium doublet is 589.3 nm. Solving m = d sin for the line spacing, d, assuming m = 1 (for the first
order) gives
d = /sin
where is the known wavelength of the sodium doublet. To determine the angle, , find the difference in angle
between the two first order yellow lines and divide by two.
Using the calibrated Grating line spacing, d, the wavelength of any spectral line in any other spectrum can be
more accurately determined using m = d sin where the order, m, is 0,1,2,…
Angular Resolution
When the Rotary Motion Sensor is fastened to the lower set of holes on the hinge on the Spectrophotometer Base
(as described earlier), the small diameter post of the Pinion will make contact with the edge of the Degree Plate.
The shaft of the Rotary Motion Sensor will rotate approximately 60 times for every rotation of the Degree Plate
(or 360½). One rotation of the Rotary Motion Sensor shaft represents approximately 6½ of angular displacement
of the Degree Plate. The maximum resolution of the Rotary Motion Sensor is 1440 divisions per rotation. Since
one rotation is 6½, the angular resolution is 6½ divided by 1440, or one quarter of a minute (0.25’) or fifteen seconds of arc. This translates to a wavelength resolution of 2 nm, given a grating line spacing of approximately
1666 nm for the Diffraction Grating included with the Spectrophotometer.
If the Rotary Motion Sensor is fastened to the upper set of holes on the hinge, the larger diameter part of the Pinion will make contact with the edge of the Degree Plate. The shaft of the sensor will rotate 15 times for every
rotation of the Degree Plate. The maximum angular resolution is one minute or sixty seconds of arc. This translates to a wavelength resolution of 8 nm, given a grating line spacing of approximately 1666 nm.
13
Page 18

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Procedures
HIGH SENSITIVITY
LIGHT SENSOR
CI-6604
Cuvette
Aperture disk
Figure 25: Cuvette with Light Sensor
Cuvettes
The Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit includes two plastic cuvettes. These flat sided containers can
hold about five milliliters of liquid. You can use the Spectrophotometer and a cuvette to measure a substance’s
characteristic pattern of absorption and transmission.
To set up the Spectrophotometer and cuvette for measuring an absorption spectrum, do the following:
1. Unscrew the threaded post that holds the Light Sensor and Light Sensor Mount onto the Light Sensor Arm.
2. Move the Light Sensor back so its threaded hole is lined up with the rear centerline hole on the Light Sensor
Mount. Use the threaded post to reattach the Light Sensor and Light Sensor Mount to the Light Sensor Arm.
3. Place the empty cuvette in front of the opening to the
Light Sensor between the sensor and the backside of the
Aperture Disk. Make sure that the cuvette is turned so
that the smooth sides are in line with the Light Sensor
(Fig. 25).
4. Scan the spectrum from an incandescent light source
(such as a bulb powered by a regulated DC power supply).
5. Fill the cuvette with the liquid to be tested and then
rescan the spectrum of the incandescent light that is
transmitted through the liquid.
Other Information
The material on the front of the Aperture Disk may “fluoresce” under ultraviolet (UV) light. It may produce a
faint violet color when UV light shines on it. This faint violet color might be seen on the Aperture Disk when you
use a mercury light source, for example. The violet line of color appears to be a part of the spectral pattern when
the light falls on the disk, but disappears when the light falls only on the Aperture Screen. The High Sensitivity
Light Sensor cannot measure ultraviolet light.
The data acquisition program interprets the starting position of the Rotary Motion Sensor as the “zero” angular
(or linear) position. For some measurements it may be important to put a mark or stop on the edge of the Degree
Plate for reference so you can begin each trial of measurement from the same position. The Degree Plate has several threaded holes near its outer edge. You can put one of the small thumbscrews that are stored on the Light
Sensor Arm into one of these threaded holes to use as a reference point for beginning or ending a scan.
14
Page 19

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Activity 1: Emission (Bright Line) Spectrum
Grating
Figure 1.1: Ray diagram for first order diffraction pattern
Ray B
Ray A
light rays
d = grating line
spacing
path difference = = d sin
= angle of
diffraction
Activity 1: Emission (Bright Line) Spectrum
EQUIPMENT NEEDED
Spectrophotometer System (OS-8539)
or
Spectrophotometer Kit (OS-8537) High Sensitivity Light Sensor (CI-6604)
Rotary Motion Sensor (CI-6538) Basic Optics Bench (part of OS-8515)
Aperture Bracket (OS-8534) Rod, 45 cm (ME-8736) (2)
Mercury Spectral Tube and Power Supply Large Rod Stand (ME-8735) (2)
PASCO Interface Data acquisition software
Introduction
The purpose of this activity is to determine the wavelengths of the colors in the spectrum of a mercury vapor
light.
Theory
An incandescent source such as a hot solid metal
filament produces a continuous spectrum of wavelengths. Light produced by an electric discharge in
a rarefied gas of a single element contains a limited number of discrete wavelengths - an emission
or “bright line” spectrum. The pattern of colors in
an emission spectrum is characteristic of the element. The individual colors appear in the shape of
“bright lines” because the light that is separated
into the spectrum usually passes through a narrow
slit illuminated by the light source.
A grating is a piece of transparent material on
which has been ruled a large number of equally
spaced parallel lines. The distance between the
lines is called the grating line spacing, d.
Light that strikes the transparent material is diffracted by the parallel lines. The diffracted light passes through
the grating at all angles relative to the original light path. If diffracted light rays from adjacent lines on the grating
interfere and are in phase, an image of the light source can be formed. Light rays from adjacent lines will be in
phase if the rays differ in path length by an integral number of wavelengths of the light. The first place that an
image can be formed is where the path length between two adjacent light rays differs by one wavelength, .
However, the difference in path length for two adjacent light rays also depends on the grating line spacing, d, and
the angle, , at which the two light rays were diffracted by the grating.
The relationship between the wavelength of the light, , the grating line spacing, d, and diffraction angle, , is as
follows:
In the diagram (Fig. 1.1), the path length for Ray A is one wavelength longer than the path length of Ray B.
= d sin
15
Page 20

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Activity 1: Emission (Bright
CI-6604A
PASCO
scientific
HIGH SENSITIVITY
LIGHT SENSOR
Light
source
Cloth hood
Collimating
Slits
Collimating
Lens
Grating
Rotary Motion
Sensor
Focusing
Lens
Light
Sensor
Base
Rod
Bench
Figure 1.2: Equipment Setup
Figure 1.3: Create a Calculation
Procedure
In this activity, the High Sensitivity Light Sensor measures the relative intensity of colors of light in an emission
spectrum produced by light from a mercury vapor light source passing through a grating. The Rotary Motion
Sensor measures the angle, , of each band or “bright line” of color.
The data acquisition program records and displays the light intensity and the angle. You can use the program’s
built-in data analysis tools to find the angle for each color, and then you can determine the wavelength, , of each
color.
Equipment Setup
1. Set up the Spectrophotometer next to a
mercury vapor light source as shown
(Fig. 1.2). If needed, use the Rod
Stand Mounting Clamps, two rods,
and two bases to raise the Spectrophotometer to the same level as the opening to the light source. (Refer to the
Introduction for more information.)
2. If the light source has a large opening,
mask the opening so it transmits a narrow (0.5 to 1.0 cm) beam to the Collimating Slits. Put a cloth hood over the
light source and attach the edge of the
hood to the plate on the Collimating Slits.
3. Turn on the light source. Once it is warmed up, adjust the light source, Collimating Slits, Collimating Lens,
and Focusing Lens so clear images of the central ray and the first order spectral lines appear on the Aperture
Disk and Aperture Screen in front of the High Sensitivity Light Sensor. Turn the Aperture Disk so the smallest slit on the disk is in line with the central ray.
4. Connect the PASCO interface to the computer, and turn on the interface. Start the data acquisition software.
5. Connect the High Sensitivity Light Sensor cable to Analog Channel A. Connect the Rotary Motion Sensor
cable to Digital Channels 1 and 2.
Experiment Setup
Select the Sensors, Set the Sample Rate, and Create a Calculation
Refer to the User’s Guide for your version of data acquisition software for detailed information on selecting sensors, changing the
sample rate, and creating a calculation.
1. In the program, select the Rotary Motion Sensor and connect it to Digital Channels 1 and 2 and select the
Light Sensor and connect it to Analog Channel A.
2. In the program, set up the Rotary Motion Sensor for high resolution (1440 Divisions per Rotation) and set the sample rate to
20 Hz, or 20 measurements per second.
3. In the data acquisition program, use the Calculator to create a
calculation of Actual Angular Position based on the Angular
Position measurement made by the Rotary Motion Sensor and
the ratio of the radius of the Spectrophotometer’s Degree Plate
to the radius of the small post on the Pinion (Fig. 1.3). (Refer to
the Set Up section for more information.)
16
Page 21

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Activity 1: Emission (Bright Line) Spectrum
GAIN
10
100
1
Grating
First order spectral lines
Light Sensor
Scan slowly and continuously
in one direction.
Figure 1.4: Scan the Spectrum
Select the Display
Refer to the User’s Guide for your version of the PASCO data acquisition software for detailed information on displays.
1. Select a Graph display.
2. Set the axes of the Graph display so Light Intensity is on the vertical axis and Actual Angular Position is on
the horizontal axis.
Prepare to Record Data
Refer to the User’s Guide for your version of the PASCO data acquisition software for detailed information on monitoring and
recording data.
1. Darken the room. Examine the spectrum closely. Determine which of the two first order spectral patterns is
brightest. In the Data Table, list the colors you see in order starting with the color that appears farthest from
the central ray.
2. Use the Light Sensor Arm on the Spectrophotometer to turn the Degree Plate until the light sensor is beyond
the last line in the brightest first order spectral pattern.
Record Data
1. Set the GAIN select switch on top of the High Sensitivity
Light Sensor to 1.
2. Start recording data.
3. Push on the threaded post under the light sensor to slowly
and continuously scan the spectrum in one direction.
Scan all the way through the first order spectral lines on
one side of the central ray, through the central ray itself,
and all the way through the first order spectral lines on
the other side of the central ray (Fig. 1.4).
4. Stop recording data.
5. Set the GAIN select switch on top of the light sensor to
10. Put the light sensor back at its starting point. Repeat the data collection procedure.
6. Set the GAIN select switch on top of the light sensor to 100 and repeat the data collection procedure.
Analyze the Data
Refer to the User’s Guide for your version of the PASCO data acquisition software for detailed information on using the software
for data analysis.
1. Use the Graph display to examine the plot of Light Intensity versus Actual Angular Position for the first run
of data (GAIN select switch = 1).
2. Use the built-in analysis tools to determine the angle of the first line in the spectral pattern, and the angle of
the matching line in the first order spectral pattern on the other side of the central ray.
3. Determine the difference in angle between the two lines and use one-half of the difference as the angle, , to
determine the wavelength, , of that color. (If you did not calibrate the Diffraction Grating, assume d = 1666
nm.)
4. Repeat the process for the other colors in the first order spectral pattern.
17
Page 22

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Activity 1: Emission (Bright
5. Examine the plot of Light Intensity versus Actual Angular Position for your other two runs of data. Look for
other lines in the spectral pattern that may be too dim to record when the sensor was set to GAIN = 1.
Data Table
Record your data here:
Color
1
2
d sin
Conclusion
Compare your values for the wavelengths of color in the mercury vapor light spectrum to the accepted values for
wavelengths.
Extensions
Repeat the process for a different gaseous element, such as hydrogen or helium.
18
Page 23

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Activity 2: Absorption (Dark Line) Spectrum
light ray
light ray
Grating
Cuvette
Cuvette with
sample
continuous
spectrum
absorption
spectrum
Activity 2: Absorption (Dark Line) Spectrum
EQUIPMENT NEEDED
Spectrophotometer System (OS-8539)
or
Spectrophotometer Kit (OS-8537) High Sensitivity Light Sensor (CI-6604)
Rotary Motion Sensor (CI-6538) Basic Optics Bench (part of OS-8515)
Aperture Bracket (OS-8534)
and
Incandescent Light Source, DC, regulated Large Rod Stand (ME-8735) (2)
Rod, 45 cm (ME-8736) (2) Colored Liquid Sample (about 5 mL)
PASCO Interface Data acquisition software
Introduction
The purpose of this activity is to determine the wavelengths of the colors absorbed by a liquid sample.
Theory
One of the most important applications of spectrophotometers is
to identify substances by their absorption spectra. For example, it
is possible to identify tiny amounts of sodium dissolved in a complicated liquid (such as beer) because sodium has a unique
absorption spectrum.
An incandescent source such as a hot solid metal filament produces a continuous spectrum of wavelengths. A substance placed
in the path of light from a continuous spectrum source will
absorb certain colors from the continuous spectrum. The individual colors that are absorbed appear as gaps or “dark lines” in the
otherwise continuous spectrum (Fig. 2.1).
Procedure
In this activity, the High Sensitivity Light Sensor measures the relative intensity of colors of light in an continuous spectrum produced by an incandescent light. Then, the sensor measures the relative intensity of colors of
light in an absorption spectrum produced when light from the incandescent source passes through a liquid sample. The Rotary Motion Sensor measures the angle, , of each part of the continuous spectrum and then the
absorption spectrum.
The data acquisition program records and displays the light intensity and the angle. You can use the program’s
built-in data analysis tools to find the angle for each “gap” or dark line in the absorption spectrum, and then you
can determine the wavelength, .
19
Page 24

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Activity 2: Absorption (Dark
CI-6604A
PASCO
scientific
HIGH SENSITIVITY
LIGHT SENSOR
Cuvette
Light Source
binder clips
Figure 2.2: Equipment Setup for Absorption Spectrum
Equipment Setup
1. Set up the Spectrophotometer next to a DC
powered incandescent light source as
shown. Move the High Sensitivity Light
Sensor to the second position on the Light
Sensor Arm so there is room for a cuvette
between the back of the Aperture Disk and
the opening to the sensor. (Refer to the Set
Up section for more information.)
2. Put an empty cuvette in front of the High Sensitivity Light Sensor between the sensor and the back of the
Aperture Disk. Make sure that the smooth sides of the cuvette are in line with the opening to the sensor (Fig.
2.2).
3. If the light source has a large opening, mask the opening so it transmits a narrow (0.5 to 1.0 cm) beam to the
Collimating Slits. Adjust the Collimating Slits slide so the number 2 slit is in line with the light source. Put a
cloth hood over the light source and attach the edge of the hood to the plate on the Collimating Slits.
4. Turn on the light source. Once it is warmed up, adjust the light source, Collimating Slits, Collimating Lens,
and Focusing Lens so clear images of the central ray and the first order spectral pattern appear on the Aperture Disk and Aperture Screen. Turn the Aperture Disk so the second smallest slit on the disk is in line with
the central ray.
5. Connect the PASCO interface to the computer, turn on the interface. Start the data acquisition software.
6. Connect the High Sensitivity Light Sensor cable to Analog Channel A. Connect the Rotary Motion Sensor
cable to Digital Channels 1 and 2.
Experiment Setup
Select the Sensors, Set the Sample Rate, and Create a Calculation
Refer to the User’s Guide for your version of the data acquisition software for detailed information on selecting sensors, changing
the sample rate and sensitivity, and creating a calculation.
1. In the data acquisition program, select the Rotary Motion Sensor and connect it to the interface.
2. In the program, set up the Rotary Motion Sensor for high resolution (1440 Divisions per Rotation) and set
the sample rate to 20 Hz, or 20 measurements per second.
3. Set the Sensitivity for the High Sensitivity Light Sensor to 10x.
4. Use the Calculator to create a calculation of Actual Angular Position based on the Angular Position mea-
surement made by the Rotary Motion Sensor and the ratio of the radius of the Spectrophotometer’s Degree
Plate to the radius of the small post on the Pinion. (Refer to the Introduction for more information.)
Select the Display
Refer to the User’s Guide for your version of the data acquisition software for detailed information on displays.
1. Select a Graph display.
2. Set the axes of the Graph display so Light Intensity is on the vertical axis and Actual Angular Position is on
the horizontal axis.
Prepare to Record Data
Refer to the User’s Guide for your version of the data acquisition software for detailed information on displays.
20
Page 25

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Activity 2: Absorption (Dark Line) Spectrum
1. Darken the room. Examine the spectrum closely. Determine which of the two first order spectral patterns is
brightest.
2. Use the Light Sensor Arm on the Spectrophotometer to turn the Degree Plate until the light sensor is beyond
the last color in the brightest first order spectral pattern.
Record Data - Empty Cuvette
1. Set the GAIN select switch on top of the High Sensitivity Light Sensor to 10.
2. Start recording data.
3. Push on the threaded post under the light sensor to slowly and continuously scan the spectrum in one direc-
tion. Scan all the way through the first order spectral pattern on one side of the central ray, through the central ray itself, and all the way through the first order spectral pattern on the other side of the central ray.
4. Stop recording data.
Record Data - Cuvette with Liquid Sample
1. Remove the cuvette and fill it three-quarters full with the liquid sample you are testing. Cap the cuvette and
replace it in front of the sensor.
2. Start recording data.
3. Push on the threaded post under the light sensor to slowly and continuously scan the spectrum in one direc-
tion. Scan all the way through the first order spectral pattern on one side of the central ray, through the central ray itself, and all the way through the first order spectral pattern on the other side of the central ray.
4. Stop recording data.
Analyze the Data
Refer to the User’s Guide for your version of the data acquisition software for detailed information on displays.
1. Use the Graph display to compare the plot of Light Intensity versus Actual Angular Position for the first run
of data (empty cuvette) to the plot of Light Intensity versus Actual Angular Position for the second run of
data (cuvette plus liquid sample).
2. Use the built-in analysis tools of the program to find the angle of the first gap or “dark line” in the absorption
spectrum of the liquid sample. Find the angle of the corresponding gap or line in the first order on the other
side of the central ray.
3. Determine the difference between the angles and use one-half of the difference as the angle, , to determine
the wavelength, , of that gap or dark line. (If you did not calibrate the Diffraction Grating, assume d = 1666
nm.)
= d sin
4. Repeat the process for the other gaps (if any) in the first order spectral pattern.
21
Page 26

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Activity 2: Absorption (Dark
Data Table
Record your data here:
“Dark Line”
1
2
d sin
Questions
1. What color corresponds to the wavelength for each “dark line” in your absorption spectrum?
2. How does the color or colors that are absorbed out of the continuous spectrum compare to the naked eye
color of your liquid sample?
Extensions
Repeat the process for a different liquid sample, such as chlorophyll extracted from a spinach leaf.
22
Page 27

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Teacher’s Guide
Teacher’s Guide
Activity 1: Emission (Bright Line) Spectrum
Notes
1. A mercury vapor light source may take up to 20 minutes to warm up, so it is a good idea to turn it on as soon
as possible.
2. Suggestions for calibrating the Degree Plate with the small post of the Pinion and for calibrating the Grating
are given in the Set Up section of the manual.
3. Depending on which way the Degree Plate is turned, the Angular Position data from the Rotary Motion Sensor may go in the negative direction rather than the positive direction along the horizontal axis of the Graph
display. If this occurs, switch the two plugs on the end of the sensor’s cable.
Sample Data
Five of the seven lines of color for mercury vapor are shown in the example. The blue-green line is more prominent on both sides of the central ray when the GAIN select switch on the High Sensitivity Sensor is set to 100.
Data Table
Color
1
yellow 0.7808 0.0692 0.7116 0.3558 580.0 nm
green 0.7613 0.0887 0.6726 0.3363 549.0 nm
blue-green 0.3016 494.8 nm
blue 0.6908 0.1578 0.5330 0.2665 438.0 nm
violet 0.6712 0.1773 0.4939 0.2469 407.1 nm
2
d sin
Conclusion
Compare your values for the wavelengths of color in the mercury vapor light spectrum to the accepted values for
wavelengths.
Color yellow 2 yellow 1 green blue-green blue violet 2 violet 1
579.0 577.0 546.1 491.6 435.8 407.8 404.7
Extensions
Repeat the process for a different gaseous element, such as hydrogen or helium.
23
Page 28

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Teacher’s Guide
Figure TG-1: Example of Mercury Spectrum
central ray
yellow
green
blue-green
blue
violet
Figure TG-2: Example of Hydrogen Spectrum with Approximate
Wavelengths on Horizontal Axis
24
Page 29

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Teacher’s Guide (Continued)
Figure TG-3: Example of Absorption Spectrum
for Food Coloring
Figure TG-4: Example of Absorption Spectrum
for a Green Leaf
continuous
spectrum
continuous
spectrum
absorption
spectrum
absorption
spectrum
Teacher’s Guide (Continued)
Activity 2: Absorption (Dark Line) Spectrum
Notes
1. The light source from the PASCO Introductory Optics System or the light source from the PASCO Basic
Optics System can be used as the incandescent source.
2. The liquid sample should be dilute enough to see through.
3. Suggestions for calibrating the Degree Plate with the small post of the Pinion and for calibrating the Grating
are given in the Set Up section of the manual.
4. Depending on which way the Degree Plate is turned, the Angular Position data from the Rotary Motion Sensor may go in the negative direction rather than the positive direction along the horizontal axis of the Graph
display. If this occurs, switch the two plugs on the end of the sensor’s cable.
Questions
1. What color corresponds to the wavelength for each “dark line” in your absorption spectrum?
Answers will vary.
2. How does the color or colors that are absorbed out of the continuous spectrum compare to the naked eye
color of your liquid sample?
Answers will vary
Extensions
Repeat the process for a different liquid sample, such as chlorophyll extracted from a spinach leaf.
Sample Data
25
Page 30

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Teacher’s Guide (Continued)
Figure TG-5: Example of Absorption Spectrum
for a Copper Sulfate Solution
Figure TG-6: Example of Absorption Spectrum
for Cologne
continuous
spectrum
continuous
spectrum
absorption
spectrum
absorption
spectrum
26
Page 31

®
Model No. OS-8537 and OS-8539 Technical Support
Technical Support
Feedback
If you have any comments about the product or
manual, please let us know. If you have any suggestions on alternate experiments or find a problem in
the manual, please tell us. PASCO appreciates all
customer feedback. Your input helps us evaluate
and improve our product.
To Contact PASCO
For technical support, call us at 1-800-772-8700
(toll-free within the U.S.) or (916) 786-3800.
fax: (916) 786-3292
e-mail: techsupp@pasco.com
web: www.pasco.com
mail: PASCO scientific
10101 Foothills Blvd.
Roseville, CA 95747-7100 USA
Contacting Technical Support
Before you call the PASCO Technical Support staff,
it would be helpful to prepare the following information:
• If your problem is with the PASCO apparatus, note:
Name and model number (usually listed on the
label);
Approximate age of apparatus;
A detailed description of the problem/sequence of
events (in case you can’t call PASCO right away,
you won’t lose valuable data);
If possible, have the apparatus within reach when
calling to facilitate description of individual parts.
• If your problem is computer or software related,
please note:
Title and Revision Date of the software.
Type of computer (make, model, speed).
Type of external cables and peripheral devices.
• If your problem is computer or software related,
please note:
Part number and revision (listed by month and year
on the front cover);
Have the manual at hand to discuss your questions.
27
Page 32

®
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System Technical Support
28
 Loading...
Loading...