Page 1

Instruction Manual
Brewster’s Angle
Accessory
Model No. OS-8170A
012-08489B
*012-08489*
Page 2

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Table of Contents
Equipment.....................................................................................................3
Introduction...................................................................................................5
Theory...........................................................................................................5
Setup Instructions.........................................................................................6
Sensor Setup..............................................................................................10
Procedure...................................................................................................11
Analysis ......................................................................................................13
Questions....................................................................................................14
Teacher’s Guide: Discovering Brewster’s Angle.........................................15
Further Investigation...................................................................................20
I. Intensity of Reflected Light (without a polarizer)
II. Intensity of Transmitted Light
III. Snell’s Law
Acknowledgements..................................................................................... 22
Appendix A: Creating Equations in DataStudio.......................................... 23
Appendix B: Laser Safety Instructions........................................................ 24
Technical Support....................................................................................... 26
Copyright and Warranty Information........................................................... 26
2
Page 3
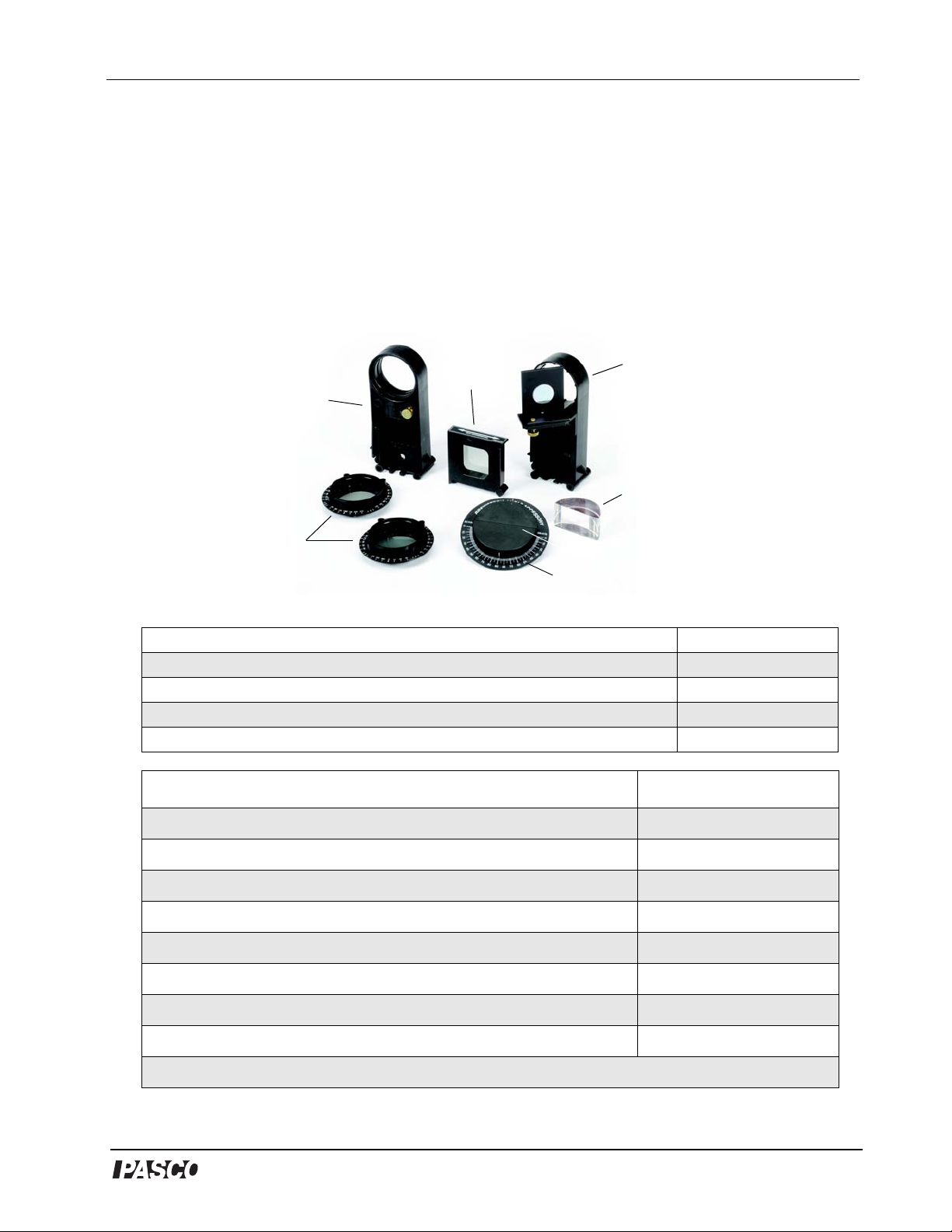
®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Beam Splitter
Semi-circular Acrylic “D” Lens
Pivot Plate Assembly
Analyzing
Polarizer
Lens Holder
Polarizers
Lens Mount
Brewster’s Angle Accessory
Model No. OS-8170A
Equipment
Included Equipment Model Number
1. Polarizer Assembly (1 lens holder and 2 round polarizers) 003-09784
2. Analyzing Polarizer (1), Lens Mount (1), and Pivot Plate Assembly (1) 003-08332
3. Beam Splitter (1) OS-8171
4. Semi-circular Acrylic Lens (1) (“D” Lens) 003-08545
Additional Equipment Required - Option 1
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory* OS-8537*
• Collimating Slits
• Spectrophotometer Base
High Sensitivity Light Sensor (2) PS-2176 or CI-6604
Rotary Motion Sensor (1) PS-2120 or CI-6538
Aperture Bracket (2) OS-8534A
Optics Bench, 60 cm (2) OS-8541
Basic Optics Diode Laser (1) OS-8525A
OR (see next page)
Model Number
*The Accessory includes unlisted items that are not used for the experiments.
3
Page 4
Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Additional Equipment Required - Option 2
Educational Spectrophotometer System OS-8539
• Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory OS-8537
• Optics Bench, 60 cm
• High Sensitivity Light Sensor
• Rotary Motion Sensor
• Aperture Bracket OS-8534A
Basic Optics Diode Laser OS-8525A
Optics Bench, 60 cm OS-8541
High Sensitivity Light Sensor CI-6604
Aperture Bracket OS-8534A
PLUS
Patch Co rd (2) See PASCO web site* or catalog
PASCO computer interface See PASCO web site* or catalog
PASCO data acquisition software See PASCO web site* or catalog
Suggested Additional Equipment
Model Number
OS-8541
CI-6604
CI-6538
Green Diode Laser OS-8458
*www.pasco.com
Complete packages of all the equipment and sensors are available from PASCO. Choose the EX9919A Brewster’s Angle Experiment (ScienceWorkshop) if you want to use ScienceWorkshop
sensors or choose the EX-9965A Brewster’s Angle Experiment (PASPORT) if you want to use
PASPORT sensors.
PASCO's Brewster's Angle Accessory is designed to be used with the Educational
Spectrophotometer System (OS-8539). In addition to the Educational Spectrophotometer
System, the experiments need the Basic Optics Diode Laser (OS-8525A), and one or more of
each of the following: Optics Bench (OS-8541), Aperture Bracket (OS-8534A), and High
Sensitivity Light Sensor. A PASCO computer interface, and PASCO data acquisition software
are also required for the experiments.
NOTE: A folder for the Brewster’s Angle experiment is available as a “.ZIP” file to download
from the PASCO web site. Go to the page that shows the EX-9919A or EX-9965A Brewster’s
Angle Experiment and click “Download”. The folder contains DataStudio setup files and sample
data files for ScienceWorkshop and PASPORT sensors, and Microsoft Word “.DOC” files for
the experiment procedure.
4
Page 5
®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
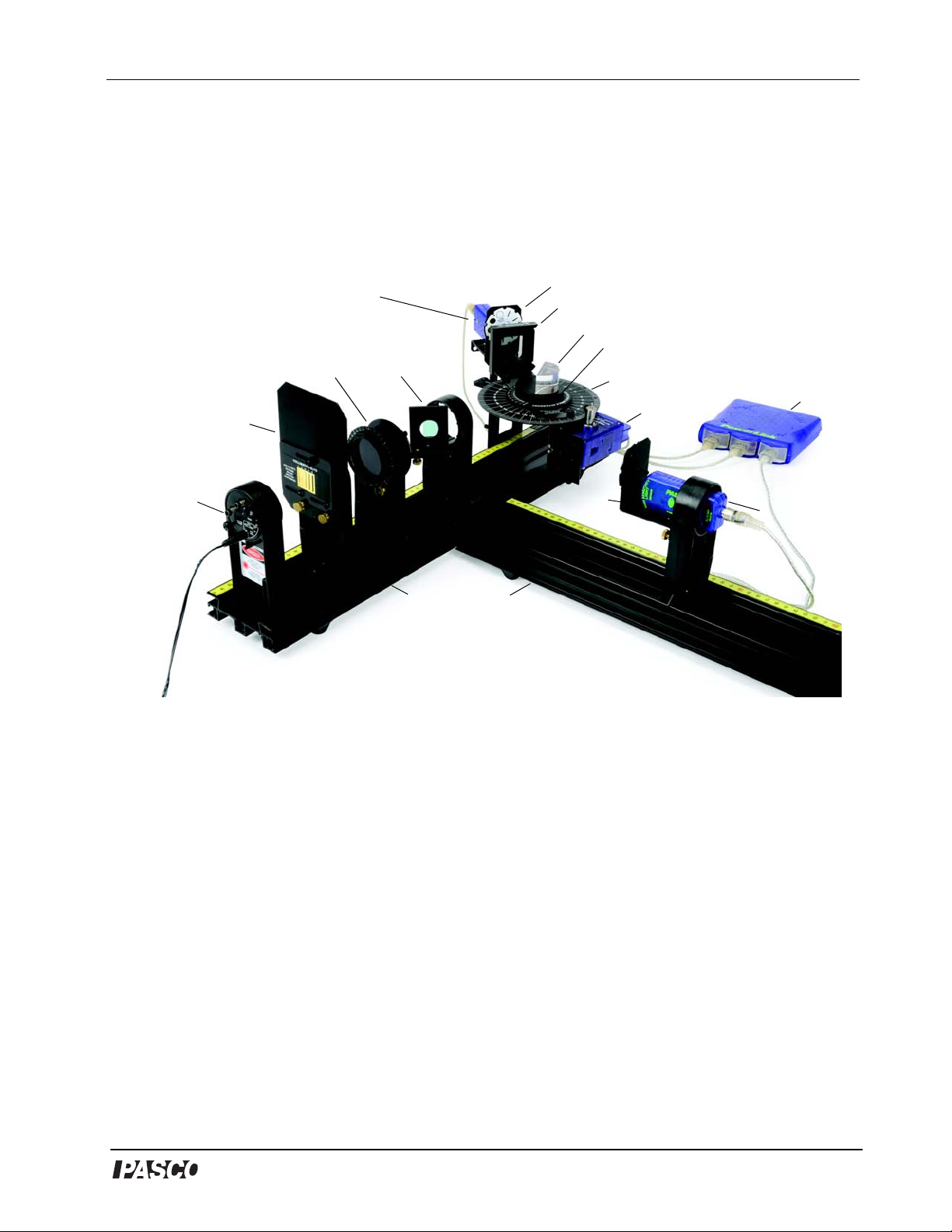
Figure 1: Brewster’s Angle Accessory Setup for Experiments
High Sensitivity Light Sensor
Aperture Bracket
Analyzing Polarizer*
“D” Lens* on Lens Mount*
Spectrophotometer Degree Plate
Rotary Motion
Sensor
Beam
Splitter*
Lens Holder* with Polarizers*
Collimating
Slits
Diode
Laser
Optics Bench
Aperture
Bracket
High
Sensitivity
Light Sensor
Interface
*Items included in the Brewster’s Angle Accessory
Pivot Plate Assembly*
Introduction
The Brewster’s Angle Accessory (OS-8170A) is used in optics for studying the polarization of
reflected light and for determining Brewster’s angle. The accessory consists of a lens holder with
two polarizers, a rotating platform (Pivot Plate Assembly) with a semi-circular “D” lens, an
analyzing polarizer, and a beam splitter.
When light reflects off a nonconducting material, the reflected light is partially polarized. The
amount of polarization depends on the incident angle and the index of refraction of the reflecting
material. The incident angle that gives the maximum polarization is called Brewster's angle.
Light from a Diode Laser is reflected off the flat side of an acrylic semi-circular (“D”) lens. The
reflected light passes through an analyzing polarizer and is detected by a Light Sensor. The angle
of incidence is measured by a Rotary Motion Sensor mounted on the Spectrophotometer Base.
The intensity of the reflected polarized light versus the incident angle is graphed to determine
the angle at which the light intensity is a minimum. This is Brewster's angle, which is used to
calculate the refraction index of acrylic.
Theory
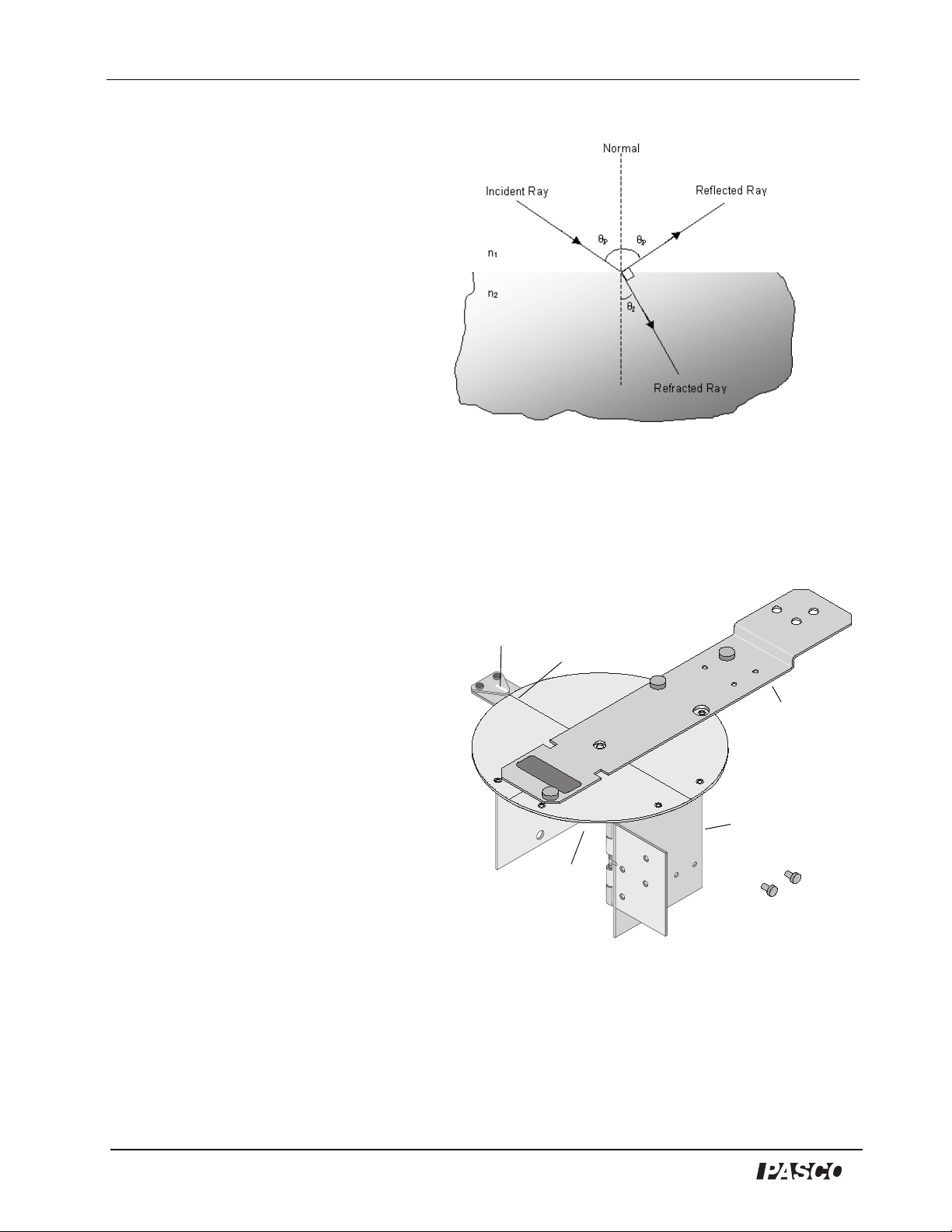
When unpolarized light reflects off a nonconducting surface, it is partially polarized parallel to
the plane of the reflective surface. There is a specific angle called Brewster's angle at which the
light is 100% polarized. This occurs when the reflected ray and the refracted ray are 90 degrees
apart.
According to Snell's Law,
n1sin
= n2sin
1
2
(1)
5
Page 6
Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Figure 2: Polarization of Unpolarized light
n
2
n
1
------
P
tan=
Spectrophotometer
Base
Spectrophotometer
Degree Plate
Spectrophotometer
Arm
Line up the 180
degree mark
Index
line
Figure 3: Assemble the Spectrophotometer Base,
Degree Plate, and Arm
where n is the index of refraction
of the medium and is the angle of
the ray from the normal.
When the angle of the incident ray
is equal to Brewster's angle, p,
n1sinP = n2sin
2
(2)
and since P + 2 = 90o,
= 90o- P, and
2
= sin(90o- P) =
sin
2
sin90ocosP - cos90osinP =
cos
P
Substituting for sin2 in Equation (2) gives n1sin
P = n2
cos
P
Therefore, (3)
Setup Instructions
Assemble the Spectrophotometer Base
1. Attach the Spectrophotometer Base at
one end of an Optics Bench.
2. Attach the Spectrophotometer Degree
Plate to the Base, but align the Degree
Plate “backwards”; that is, line up the
180 degree mark on the Degree Plate
with the index line on the Base.
3. Attach the Spectrophotometer Arm to
the Degree Plate.
(For instructions on setting up the
Spectrophotometer parts, see the
Educational Spectrophotometer
Manual. You can download a PDF file
of the manual from the PASCO web
site. Go to the page that shows the
OS-8539 and click the “Manual” tab.)
6
Page 7

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Figure 4: Mount the Rotary
Motion Sensor to the Base
Rotary Motion
Sensor
Hinge
Spindle
Degree Plate
4. Mount a High Sensitivity Light Sensor to an Aperture
Bracket and attach the Aperture Bracket/Light Sensor to
the Spectrophotometer Arm.)
5. Mount the Rotary Motion Sensor to the upper holes on the
hinge of the Spectrophotometer Base. Mount the Spindle
on the shaft of the Rotary Motion Sensor so that the bigger
diameter of the spindle is against the edge of the
Spectrophotometer Degree Plate (see Figure 4).
6. Connect a patch cord from an electrical ground to a bare
piece of metal on the Spectrophotometer Base, as
instructed by your teacher.
Attach the Pivot Plate and Lens Mount
1. Screw the Pivot Plate into the threaded hole in the center of the Spectrophotometer Degree
Plate.
2. Screw a wing nut onto the threaded post of the Pivot Plate that extends below the
Spectrophotometer Base.
3. Turn the Pivot Plate so that the index mark at the edge of the plate above the “N” in the word
ANGLE is aligned with the zero degree mark on the Spectrophotometer Degree Plate.
Note: Make sure that the Pivot Plate is not screwed down too tightly against the Degree Plate.
The Spectrophotometer Arm should be able to rotate freely and the Pivot Plate should remain
stationary as the Spectrophotometer Arm is moved. (Screw the Pivot Plate almost all the way
down and then tighten the wing nut under the Spectrophometer Base.)
4. Place the Lens Mount on the Pivot Plate so that the hole in the bottom of the lens mount
matches the post on the pivot plate.
5. The Lens Mount has two vertical index marks. For reflected light, use the mark that is on the
side with the higher step. Line up the index mark with the zero degree angle on the edge of
the Pivot Plate that is closest to the laser.
(Note: The other mark can be used for transmission studies in a Snell’s Law experiment.)
7
Page 8
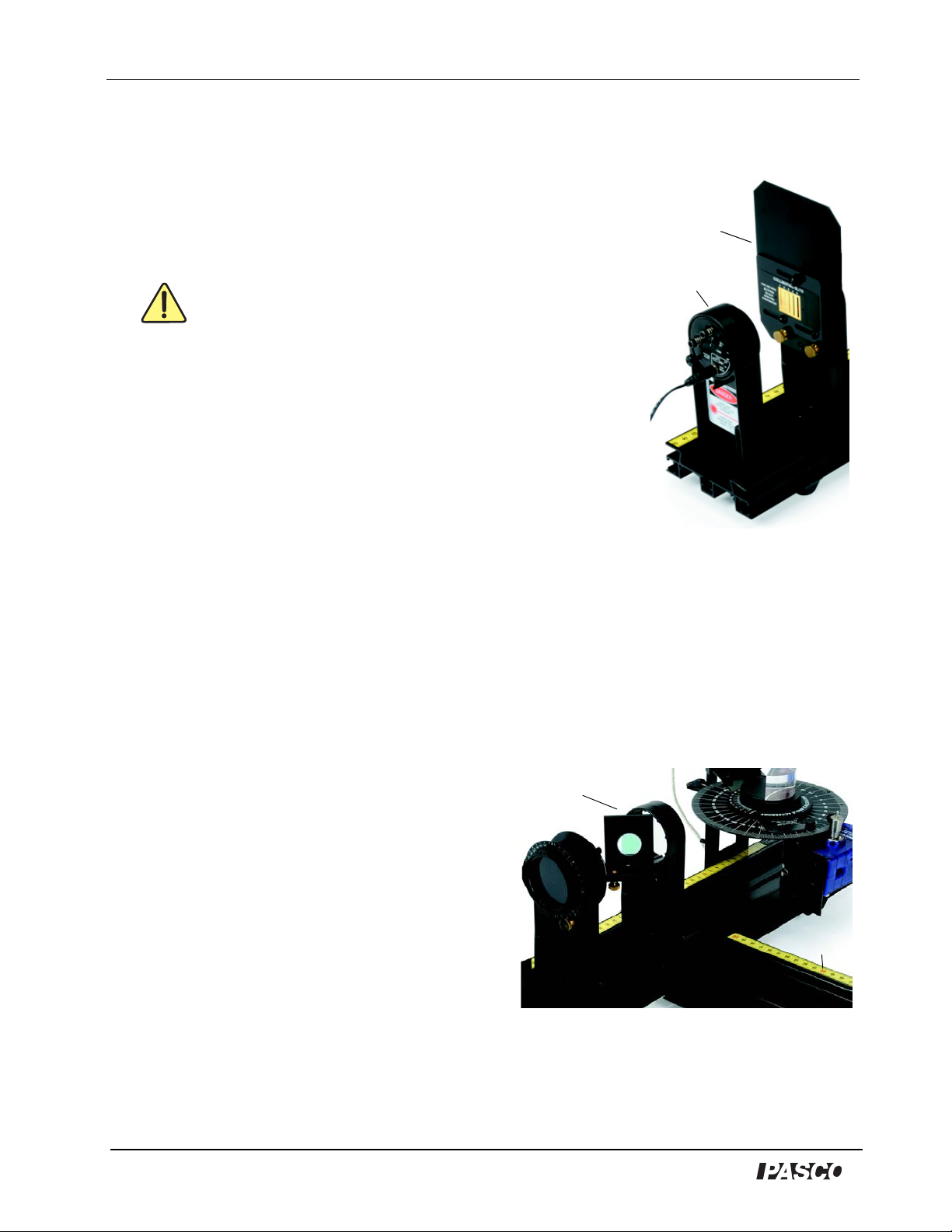
Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Figure 5: Laser and
Collimating Slits on bench
Laser
Collimating
Slits
Figure 6: Mount the Beam Splitter
Beam Splitter
2nd Optics
Bench
Align the Laser Beam
1. Put a Laser Diode on the end of the bench opposite to the
Spectrophotometer Base.. Connect the laser’s power supply to a
grounded electrical outlet and plug the power cord into the laser .
Turn on the laser (the ON-OFF switch is on the back of the
laser).
WARNING: Do not look directly into the beam of the
laser light source or reflected light from the laser light source, such
as from a mirror. Although the laser used in this experiment is of
low power, looking directly into the laser light source or its
reflected light from a mirror could cause eye damage. T o avoid eye
injury, do not look directly into the laser beam and wear laser
protective goggles. For more information about laser safety, see
Appendix B of this manual.
2. Set the Spectrophotometer Arm so that 180 degrees on the
Degree Plate is next to the index mark. Set the Aperture Bracket
disk to slit #5. Use the x-y adjustment knobs on the back of the
laser to aim the laser beam at the center of Aperture Bracket slit
#5.
3. Place the Collimating Slits on the optics bench and adjust the slit position on the Collimating
Slits so that the laser beam passes through slit #5 and also still shines on slit #5 on the
Aperture Bracket disk (see Figure 5).
4. Adjust the Brewster’s Lens Mount so that the index line on the higher step of the Lens Mount
is aligned with the zero mark on the Pivot Plate.
5. Place the “D” Lens on the lower step of the
Lens Mount with the flat side of the lens
against the edge of the higher step. If the laser
beam is not still centered on slit #5 of the
Aperture Bracket, adjust the “D” Lens side-toside until the laser beam shines on slit #5.
Make sure the “D” Lens is firmly against the
step.t
6. Mount he Beam Splitter on the bench near the
center of the bench. Check that the transmitted
laser beam still illuminates the #5 slit on the
Aperture Bracket on the Spectrophotometer
Arm. If necessary, loosen the adjustment screws on the Beam Splitter holder and move the
holder to align the laser beam with slit #5 on the Aperture Bracket disk.
8
Page 9

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Figure 7: Variability of Green Laser
Adjustment Screws
Transmitted
Beam
Reflected
Incident
Beam
Figure 8: Adjust the Beam
Splitter as needed
Controlling the Laser Intensity
1. Place the second optics bench at right angles to the first optics bench at the spot where the
Beam Splitter is mounted.
2. Mount the second High Sensitivity Light Sensor on an Aperture Bracket, and attach the
Aperture Bracket to a Lens Holder. Set the disk on the Aperture Bracket to slit #5.
3. Mount the Light Sensor/Aperture Bracket at the far end of the second optics bench (see Figure
1). Connect a patch cord between an electrical ground and a piece of bare metal on the
Aperture Bracket.
NOTE.: The second High Sensitivity Light Sensor is
used to compensate for the variability of the incident
laser beam intensity (see Figure 7). The second light
sensor on the optics bench measures the relative
incident light intensity (from the Beam Splitter)
while the light sensor on the Spectrophotometer Arm
simultaneously measures the reflected light intensity
(from the “D” Lens through the Analyzing Polarizer).
Any fluctuations in intensity can be normalized by
dividing the reflected light intensity by the relative
incident light intensity.
4. Adjust the position of the second optics bench as
needed until the reflected laser beam from the Beam
Splitter travels to slit #5 on the Aperture Bracket disk in
front of the second Light Sensor.
5. If you need to re-adjust the Beam Splitter, make sure that
the laser beam is still aligned with the first High
Sensitivity Light Sensor.
6. Snap the round Polarizers into both sides of the Lens
Holder, and mount the Lens Holder on the bench
between the Collimating Slits and the Beam Splitter . The
Polarizers help control laser intensity.
7. Rotate the second polarizer (farthest from the laser) to 45
degrees (the indicator is the bottom lip on the lens holder)
and lock it in place by tightening the brass screw. The first
polarizer (closest to the laser) is used throughout the experiment to adjust the light level.
Since the ratio of reflected light to incident light is being measured, better data will be
obtained if the incident light level is kept above 50%.
9
Page 10

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Analyzing Polarizer
“D” Lens
“D” Lens
Mount
Pivot
Plate
Spectrophotometer Degree Plate
Spectrophotometer Arm
Figure 9: Analyzing Polarizer and “D” Lens
Aperture Bracket
Light
Sensor
8. The square Analyzing Polarizer (see Figure
9) has its transmission axis marked.
Position the Analyzing Polarizer with its
label on top and with its axis horizontal.
NOTE: When the Analyzing Polarizer is
horizontal, the light passing through the
polarizer is the horizontal component
(perpendicular to the “D” lens surface) of the
light reflected from the flat surface of the “D”
lens. In this orientation, the Analyzing
Polarizer is blocking the light that is polarized
parallel to the flat surface of the “D” lens. Thus, when the incident angle is such that the
reflected light is 100% polarized parallel to the flat surface of the “D” lens (Brewster’s Angle),
the horizontal component will be zero.
During the experiment, both the horizontal and vertical components of the reflected light are
measured so the horizontal component of interest can be normalized by dividing by the sum of
the two components. This gives a percentage of the total reflected light that is horizontally
(perpendicularly) polarized.
Each measurement must also be divided by the reference light intensity to account for
momentary changes in intensity of the laser light source.
NOTE: The laser light is already polarized, but the round polarizer set at 45° solves the
problem. To make the relative intensities of the “p” (parallel) and “s” (perpendicular)
components the same, the light is polarized at 45°.
Sensor Setup
1. Connect the PASCO interface to the computer and start the data acquisition software.
2. If you are using DataStudio, open the DataStudio setup file titled “Brewsters_PASPORT.ds”
(for PASPORT) or “Brewsters.ds” (for ScienceWorkshop).
3. Plug the Rotary Motion Sensor and the two High Sensitivity Light Sensors into the interface.
Set the Light Sensor Range
1. To get full use of the Light Sensor range, set the light sensor range: for a PASPORT sensor,
press the “light bulb” button on the side of the sensor and for a ScienceWorkshop sensor, set
the “GAIN” switch on the top of the sensor to 100.
2. In the data acquisition program, click “Start” and rotate the first round polarizer (nearest to
the laser) to allow the light level to be as high as possible without exceeding 95% on the
Digits display of the Reflected Light Intensity (measured by the sensor on the
Spectrophotometer Arm) and the Reference Light Intensity (measured by the sensor on the
second optics bench). Click “Stop”.
10
Page 11

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Note: If the Reflected Light Intensity is as high as possible without exceeding 95%, but the
Reference Light Intensity is above 95%, try one of the following to reduce the Reference Light
Intensity:
• Slightly adjust the second optics bench from side-to-side so that only part of the laser beam
enters through slit #5 of the Aperture Disk.
• Rotate the Aperture Disk in front of the second light sensor so that the laser beam enters slit
#4 instead of slit #5.
Zero the Rotary Motion Sensor
1. To zero the Rotary Motion Sensor, first remove the “D” Lens. Adjust the Spectrophotometer
Arm if needed so that the laser beam is centered on slit #5 on the Aperture Bracket disk. (The
180° mark on the Spectrophotometer Degree Plate should be near the index line.)
2. Click “Start” and slowly move the arm back and forth so that the slit moves through the width
of the laser beam. Stop at the position where the Digits display shows maximum intensity.
3. Click “Stop” and do not move the arm until you use the program to take the actual data run.
(This insures that the zero for the Rotary Motion Sensor is at the center of the laser beam.)
4. Replace the “D” Lens on the lens mount against the step, centering it so the laser beam still
shines on slit #5.
Note about angle measurement: The angle of reflection from the “D” Lens is calculated by
dividing the actual angle measured by the Rotary Motion Sensor by two. The best procedure is
to set the index line on the high side of the Lens Mount to a particular angle (such as 85°) and
then move the Spectrophotometer Arm so that the angle shown on the Digits display is the same
as the angle of the Lens Mount. Note that to get the laser beam exactly on the #5 slit in front of
the Light Sensor, you must make fine adjustments while watching the Digits display for the
maximum light intensity. You can adjust either the Lens Mount or the Spectrophotometer Arm
until the intensity is maximized.
Procedure
T aking Measurement s
1. Lighting: Turn off the room lights when making a measurement. (A small light might be
useful for seeing the computer keyboard and for putting the Analyzing Polarizer on and off.)
2. Click “Start”. The “Start” button in the toolbar will change to “Keep”. Do
not click the red square (“Stop”) on the “Keep” button until all of the procedure steps are
completed.
11
Page 12

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
zero
mark
85°
Lens
Mount
Pivot
Plate
3. Remove the Analyzing Polarizer from the
Spectrophotometer Arm. Turn the Lens Mount so that the
index mark on the high step is at 85° on the Pivot Plate
(measured from the zero mark closest to the Beam
Splitter).
4. Rotate the Spectrophotometer Arm to about 85° (as
shown on the Digits display of the Angle), and, while watching the Digits display of the
Reflected Light Intensity, adjust the angle of the arm so that the laser beam reflected by the
“D” Lens shines on the #5 slit on the Aperture Bracket. (The angle does not have to be exact
- just close enough that you get enough light.)
5. If the maximum light intensity drops below 50%, adjust the round Polarizer nearest the laser
to increase the light intensity above 50%. Do not allow the reference intensity to exceed 95%.
(This will make the measurement as precise as possible. Since you are plotting the ratio of
polarized intensity over total intensity, changing the total intensity will not affect the ratio. As
you proceed it will eventually be impossible to make the maximum intensity above 50%.)
6. Place the square Analyzing Polarizer with its axis horizontal just in front of the Aperture
Bracket on the Spectrophotometer Arm. (Note: The Analyzing Polarizer must sit flat on the
arm.)
7. Press “Keep” to record the Angle, the Reflected Light Intensity, and the Reference Light
Intensity.
See “Entering the Data” (next page)
It is helpful to enter data in the table as it is collected so you can see the progression of data
towards the minimum.
When the polarizer is horizontal, the light passing through the polarizer is polarized
perpendicular to the surface of the D Lens. This is the polarized light that is a minimum at
Brewster’s Angle.
8. Rotate the square Analyzing Polarizer so its axis is vertical and set it on the
Spectrophotometer Arm just in front of the Aperture Bracket.
9. Press “Keep” to record the Angle, the Reflected Light Intensity, and the Reference Light
Intensity.
When the polarizer is vertical, the light passing through the polarizer is polarized parallel to the
surface of the D Lens. This is the polarized light that is a maximum at Brewster’s Angle. Both the
horizontal and vertical components are measured so the perpendicularly polarized light can be
normalized by dividing by the sum of the two components.
10. Remove the Analyzing Polarizer and set up for the next angle. Rotate the Lens Mount so the
index mark lines up with 80°, and move the Spectrophotometer Arm so that the angle in the
12
Page 13

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Digits display is the same (or close to it). Adjust the Spectrophotometer Arm so the Digits
display of Reflected Light Intensity is a maximum.
11. Repeat steps 6 through 9.
12. Continue to repeat the procedure, reducing the angle of the Lens Mount by five degrees until
you reach 65°. When the reflected light intensity is approaching the minimum, record data
(press “Keep”) every one degree. When you reach 50°, change the angle by five degrees each
time until you reach about 25°.
13. Click “Stop” to end data recording.
Entering the Data
It is helpful to enter data in the table as it is collected so you can see the progression of the data
towards the minimum.
There will be two sets of data for each angle. The first s et is for the perpendicular reflected light
(when the Analyzing Polarizer’s axis was horizontal), and the second set is for the parallel
reflected light (when the Analyzing Polarizer’s axis was vertical). For each angle, read the
Reflected Light Intensity and the Reference Light Intensity and enter the values into the Data
Entry Table.
1. For the first set, type the value of the Reflected Light Intensity into the “+ Polarized Light”
column. Press “Enter” and then type the Reference Light Intensity into the “+ Reference”
column. Press “Enter” after typing the value.
2. For the second set, type the value of the Reflected Light Intensity into the
“II Polarized Light” column. Press “Enter” and then type the Reference Light Intensity into
the “II Reference” column. Press “Enter” after typing the value.
Repeat the Procedure
Repeat the procedure for a different wavelength (color) laser.
Analysis
The DataStudio file that is set up for Brewster’s Angle has several built-in calculations that use
the perpendicular reflected light intensity, the parallel reflected light intensity , the re ference light
intensity, and the angle of reflection. The file also has Table displays for recorded data and
entered data and a Graph display for determining Brewster’s Angle.
13
Page 14

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Quadratic Fit
legend box
n
2
n
1
------
1. To determine Brewster’s Angle, use the Graph display (“Norm +” versus “Angle”). In the
Graph, select a group of data points on both sides of the apparent minimum.
2. Click the “Fit” menu in the toolbar of the Graph
and select “Quadratic Fit”. (Note: Double click the
Quadratic Fit legend box to open the Curve Fit
dialog box. Make sure that “Fit with first selected
data point at X = 0” is NOT selected.)
Questions
1. From the curve fit, how do you determine the minimum of the function?
2. Use Brewster’s Angle to calculate the index of refraction of the acrylic “D” Lens using
Equation (3) tanp= . What value should you use for n1?
3. Would Brewster’s Angle be larger or smaller for light in air reflecting off water?
4. Would Brewster’s Angle be larger or smaller for light in water reflecting from the “D” Lens
(that is, if the “D” Lens were submerged in water)?
5. How do polarized sunglasses reduce glare? Which direction is the axis of polarization in a pair
of polarized glasses? How would you check this?
6. Which direction is the axis of polarization of the light reflected from the “D” Lens?
7. How is the index of refraction affected by a change in the wavelength of the laser?
14
Page 15

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Teacher ’s Guide: Discovering Brewster’s Angle
Sample Data
The Table display “Green Data Collection” shows sample data of Angle, Reflected Light
Intensity, and Reference Light Intensity for a green (532 nanometer) diode laser.
15
Page 16

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Normalized reflected light
intensity (parallel)
Normalized reflected light
intensity (perpendicular)
Curve
fit
The Table display “Data Entry” shows sample data entered into the table and calculated values
for “Norm +” and “Norm ||”.
The Graph display “Green Laser” shows normalized reflected light intensity for parallel and
perpendicular polarized light versus angle.
16
Page 17

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Curve Fit dialog box for green laser
dy
dx
------
2Ax B+ 2 0.001270.142– 0== =
n
2
n
1
------
n2n
1p
tan 1.00 55.9tan 1.48 0.01== =
n2n
1p
tan 1.00 57.3tan 1.56 0.01== =
The Curve Fit dialog box for the
green laser shows the coefficients of
the quadratic formula of the curve fit.
Questions
1. From the curve fit, how do you determine the minimum of the function?
To find the minimum, set dy/dx equal to zero
for the quadratic formula
.
Solving for x gives 55.9°.
To estimate the error, use the cursor in the
Graph display to select a different set of data
points (see the Graph).
The different set of data points gives an angle
of 56.1°.
The error estimate is 55.9°±0.2°.
2. Use Brewster’s Angle to calculate the index of refraction of the acrylic “D” Lens using
Equation (3): tan
= . What value should you use for n1?
p
The value of n1 = 1.00 (for air).
for the green laser (wavelength = 532 nm)
(*See the sample data at the end of this section.)
for a blue diode laser (wavelength = 405 nm)*
17
Page 18

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
p
tan
n
2
n
1
-----
1.33
1
----------
p
53== =
p
tan
n
2
n
1
-----
1.50
1.33
----------
p
48== =
3. Would Brewster’s Angle be larger or smaller for light in air reflecting off water?
The Brewster’s Angle would be smaller for light in air reflecting off water.
4. Would Brewster’s Angle be larger or smaller for light in water reflecting from the “D” Lens
(that is, if the “D” Lens were submerged in water)?
The Brewster’s Angle would be smaller for light in water reflecting from the “D” Lens.
5. How do polarized sunglasses reduce glare? Which direction is the axis of polarization in a pair
of polarized glasses? How would you check this?
Glare is polarized reflected light. Since glare is often reflected off horizontal surfaces
(such as water), the sunglasses are polarized vertically to extinguish the horizontally
polarized reflected light. To check this, you could text the sunglasses with the Analyzing
Polarizer since it has a known axis of polarization.
6. Which direction is the axis of polarization of the light reflected from the “D” Lens?
The axis of polarization of the light reflected off the “D” Lens is parallel to the surface,
which in this case is vertical.
7. How is the index of refraction affected by a change in the wavelength of the laser?
In general, the index of refraction increases as the frequency increases (wavelength
decreases).
18
Page 19

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Curve Fit dialog box for blue laser
dy
dx
------
2Ax B+ 2 0.001640.188– 0== =
Sample Data (Blue Laser)
The following Graph display shows polarized light intensity versus angle for blue laser light
having a wavelength of 405 nm.
The Curve Fit dialog box for the blue
laser shows the coefficients of the
quadratic formula of the curve fit.
To find the minimum, set dy/dx equal
to zero for the quadratic formula
Solving for x gives 57.3°.
19
Page 20

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Further Investigation
I. Intensity of reflected light (without polarizer)
Note: This experiment uses the same setup except the Analyzing Polarizer is removed and you
do not need the second optics bench, aperture bracket, and High Sensitivity Light Sensor.
1. Reflect the laser beam off the outside plane side of the “D” lens.
2. Make a graph of Light Intensity versus Angle where Angle is a calculation:
Angle = (180-abs(x)/15)/2,
where x is the Angular Position. (For instructions on creating equations in DataStudio, see
Appendix A of this manual.)
3. Repeat Step 1 of the procedure for the Brewster's Angle experiment. Then do Step 2, except
this time, sweep the Light Sensor on the Spectrophotometer Arm through the reflected laser
beam. The result is an intensity peak. Do not stop recording data. Use a Smart Cursor to
measure the angle at maximum intensity and the magnitude of the maximum intensity. It is
useful to have the graph set on a sliding scale, but if the Smart Cursor is used, you will need
to click on “show live data” in the pull down menu to resume the sliding scale.
4. Repeat the procedure for angles in increments of 5 degrees.
5. Under the "Experiment" pull-down menu in DataStudio, click “New Empty Data Table”.
Enter the data, and make a graph of Light Intensity versus Angle.
6. Repeat the experiment with the laser beam entering the curved side of the lens and reflecting
off the inside of the plane side of the lens. This will give the critical angle for total internal
reflection.
II. Intensity of T ransmitted Light
This experiment uses the same setup as part I “Reflected Intensity,” but the slits should both be
set on #3.
1. The computer can measure the refracted angle, but not the incident angle. You must read the
markings on Brewster's base and enter them manually.
2. Arrange the curved part of the lens so it is towards the laser. Set the Pivot Plates base angle to
10 degrees. Sweep the Light Sensor through the reflected laser beam. The result is an
intensity peak. Do not stop recording data. Use a Smart Cursor to measure the angle to
maximum intensity and the magnitude of the maximum intensity
3. Repeat the procedure for angles in increments of 10 degrees.
20
Page 21

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Sample Data: Light Intensity vs. Incident Angle
4. In DataStudio, set up the displays as shown below.
5. Repeat this procedure with the lens turned around. Have the flat side of the “D” lens towards
the laser. This will show total internal reflection above angles of about 40 degrees.
21
Page 22

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Sample Data: Incident Angle vs. Refracted Angle
III. Snell’s Law
For the data from the first part of part II, graph Sin (incident angle) vs. Sin (refracted angle). The
slope of the line is the refraction index of the acrylic plastic.
In DataStudio, create the following equations:
a) refracted angle=Oi-x(deg), where Oi is the incident angle, and x is the arm angle in
degrees.
b) sin incident = sin(x), where x is the incident angle (degrees).
c) sin refracted = sin(x), where x is refracted angle (degrees).
For instructions on creating equations, see Appendix A or the DataStudio online help.
Acknowledgements
The Brewster’s Angle experiment was developed using original ideas from P.J. Ouseph,
Professor of Physics at University of Louisville, KY, from an American Journal of Physics
article titled “Polarization of Light by Reflection and the Brewster Angle”, Vol. 69, page 1166
(2001), by P.J. Ouseph, Kevin Driver, and John Conklin.
Modifications to the Brewster’s Angle experiment were suggested by Cristian Bahrim and WeiTai Hsu in an American Journal of Physics article titled “Precise measurement of the reflective
indices for dielectrics using an improved Brewster Angle method”, Vol. 77, page 337 (2009).
22
Page 23

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
Step 1: Create a new equation. On the main toolbar,
click the Calculate button to open the Calculator
dialog. In the Calculator dialog, click the New button.
Step 2: Type in and/or
build the equation.
(Use the Scientific,
Statistical, and Special
menus, and the
trigonometric functions
to build the equation.)
Click the Accept button.
Step 3: Define the
dependent variables.
Under “Variables,” use
the down arrow to select
a variable or constant,
etc. and click OK.
(Example: For “x,” select
“Data Measurement.” In
the pop-up, select
“Angular Position,” and
click OK.
Step 5: Label the
units. Click on the
Properties button to
open the Data
Properties dialog and
enter the name and
units. (Example: In
the Data Properties
dialog, type “Angle”
in the name box and
“degrees” in the units
box.)
Step 4: Enter any experiment
constants (optional). Use the (+)
button to create an experiment
constant. Click New, then enter the
name, value and units for the
constant. Click the Accept button. Go
back to the V ariables menu and select
“experiment constant.” Click OK.
Step 6: Save the
equation. Click
the Accept
button.
Note: Each time you build a new equation, click the New button. To edit a completed
equation, double click on the equation in the Data list, make your changes, and click the
Accept button to save your changes.
Appendix A: Creating Equations in DataStudio
23
Page 24

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Appendix B: Laser Safety Information
The OS-8525A Laser Diode is a low power, Class 2 laser. When Class 2 lasers are used in
accordance with Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) standards, Class 2
lasers are not harmful. However, when appropriate safety precautions are not taken, Class 2
lasers can cause permanent, irreversible damage to the eyes. As an instructor, you should always
inform your students of the hazards of lasers and the necessary preventative, safety measures.
PASCO cannot be held liable for negligent use in the classroom. As a courtesy, we are providing
you with the following laser safety instructions. These reminders are not a comprehensive list of
all possible safety measures or hazards. For more information, see the OSHA web site (http://
www.osha.gov). Also see http://www.safetymanual.com or www.laserinstitute.org
Safety Reminders:
• Never look directly into the laser or at any reflection from the laser at eye level.
•Do not point a laser at your own eye, through glass, mirrors or transparent objects in your
surroundings, or at the eyes of other individuals.
•Never remove any of the covering or components of the OS-8525A Diode Laser . If the laser
is defective, return the defective laser immediately to PASCO scientific.
•If you are uncomfortable or unsure about working around lasers, wear protective laser
goggles or spectacles.
About Laser Protective Eyewear
The eyewear must be designed for use with lasers and meet OSHA standards specific to the type
and class of laser you are using. You can tell if the type of goggle or spectacle you are using
meets laser standards by looking at the insignia on the side of the frame. Any type of plastic
chemical protective goggle will not suffice. Also, you need to select protective eyewear with the
correct filter for the wavelength range of the laser (For a Class 2 laser, you need a 400-780 nm
filter.)
Example: Laser goggles designed to protect for Class 1 lasers do not provide maximum
protection when using Class 2 lasers. For more information, see the OSHA web site
(www.osha.gov).
Laser Injuries
Severe corneal injuries or eye burns may or may not present with pain at the surface of the eye.
In retinal injuries, the individual may see red spots, or have blurred vision or altered color
perception.
Less severe injuries may not show up immediately and are more hazardous when they occur
repetitively.
24
Page 25

®
Model No. OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory
®
If you believe you have a laser injury, report the injury immediately to your instructor/
supervisor, school health department and/or safety officer. If necessary, go to an emergency
health facility or contact a medical doctor or opthalmologist.
25
Page 26

Brewster’s Angle Accessory Model No. OS-8170A
®
®
Technical Support
For assistance with the OS-8170A Brewster’s Angle Accessory or any other PASCO products,
contact PASCO as follows:
Address: PASCO scientific
10101 Foothills Blvd.
Roseville, CA 95747-7100
Phone: (916) 786-3800
FAX: (916) 786-3292
Web: www.pasco.com
Email: techsupp@pasco.com
Copyright and Warranty Information
Copyright Notice
The PASCO scientific 012-08489B Brewster’s Angle Accessory Manual is copyrighted and all
rights reserved. However, permission is granted to non-profit educational institutions for
reproduction of any part of the 012-08489B Brewster’s Angle Accessory Manual, providing the
reproductions are used only for their laboratories and are not sold for profit. Reproduction under
any other circumstances, without the written consent of PASCO scientific, is prohibited.
Limited Warranty
PASCO scientific warrants the product to be free from defects in materials and workmanship for
a period of one year from the date of shipment to the customer. PASCO will repair or replace, at
its option, any part of the product which is deemed to be defective in material or workmanship.
The warranty does not cover damage to the product caused by abuse or improper use.
Determination of whether a product failure is the result of a manufacturing defect or improper
use by the customer shall be made solely by PASCO scientific. Responsibility for the return of
equipment for warranty repair belongs to the customer. Equipment must be properly packed to
prevent damage and shipped postage or freight prepaid. (Damage caused by improper packing of
the equipment for return shipment will not be covered by the warranty.) Shipping costs for
returning the equipment after repair will be paid by PASCO scientific.
Written by:
Ann Hanks
26
 Loading...
Loading...