Page 1
Chlorine ezSample™(EZ-2339)
0.50 – 6.00 ppm
Instrument Set-up
The PASPort Water Quality Colorimeter is specifically designed to support PASCO’s ezSample chemical test kits. Set
up the PASPort Water Quality Colorimeter according to the equipment instructions. The calibration procedure is listed
in the equipment instruction manual. Calibration may be appropriate, depending on the application or intended use.
Choose the appropriate test routine from the PASPort Water Quality Colorimeter menu.
Safety Information
Read the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) before performing this test procedure. Wear safety glasses and disposable
gloves.
Free Chlorine Test Procedure
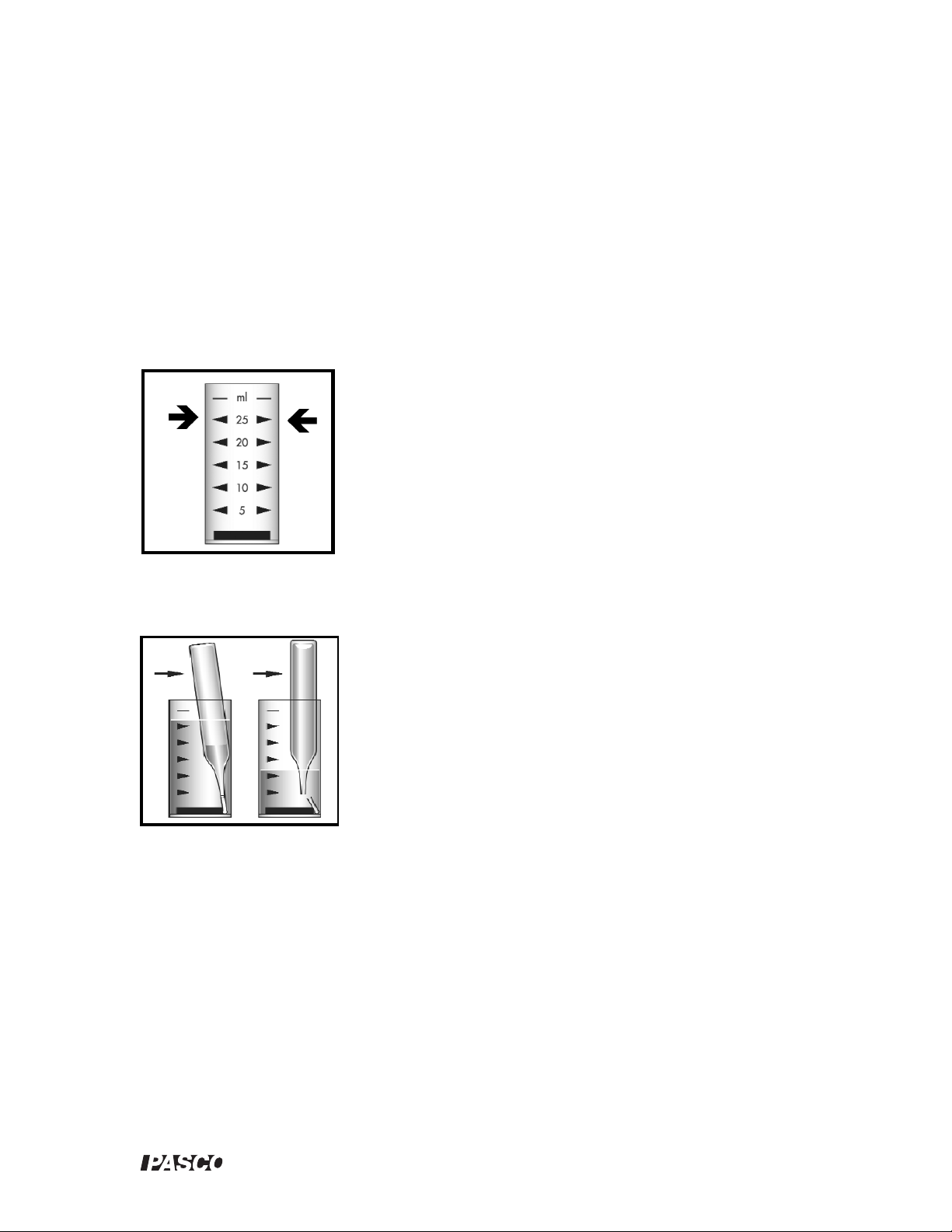
1. Fill the sample cup to the 25 mL mark with the sample (fig 1).
Figure 1.
2. Immediately snap the tip by pressing the ampoule against the side of the cup. The ampoule will fill leaving a small
bubble to facilitate mixing (fig 2).
Figure 2.
3. Mix the contents of the ampoule by inverting it several times, allowing the bubble to travel from end to end each
time. Tap the bottom of the ampoule on a hard surface to cause any tiny bubbles that have collected on the ampoule
wall to rise to the top of the liquid in the ampoule. Wipe all liquid from the exterior of the ampoule.
4. Wait 1 minute for color development.
5. Read the concentration value of the ezSample ampoule in the PASPORT Water Quality Colorimeter.
Total Chlorine Procedure
1. Fill the sample cup to the 25 mL mark with the sample
2. Add 5 drops of A-2500 Activator Solution. Stir briefly. Wait 1 minute.
3. Perform the Free Chlorine Test Procedure using this pretreated sample.
®
1 012-10113C
Page 2

Test Method Description
The ezSample test method employs the DPD chemistry.
phenylenediamine) to form a pink colored species in direct proportion to the chlorine concentration. Total chlorine, the
sum of free and combined chlorine, is determined by adding an excess of potassium iodide to the sample. Chloramines
(combined chlorine) oxidize the iodide to iodine. The iodine then oxidizes DPD to the pink colored species. Results are
expressed in ppm (mg/Liter) Cl
at >500 ppm may prevent color development
2. Halogens, ozone and halogenating agents will produce high test results. Chlorine,
.
1
Free chlorine oxidizes DPD (N,N-diethyl-p-
Accuracy and practical detection limit (PDL)
The lower limit of the stated test range is the “Practical Detection Limit (PDL).” Accuracy may be compromised if test
results are outside of the test range. Test results obtained at or below the PDL should be further confirmed for best
accuracy.
References
1. APHA Standard Methods, 20th ed., p. 4-63, method 4500-CI G (1998)
2. EPA Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes, method 330.5 (1983)
®
2 012-10113C
 Loading...
Loading...