Page 1
Instruction Sheet
for the PASCO
Model CI-6555
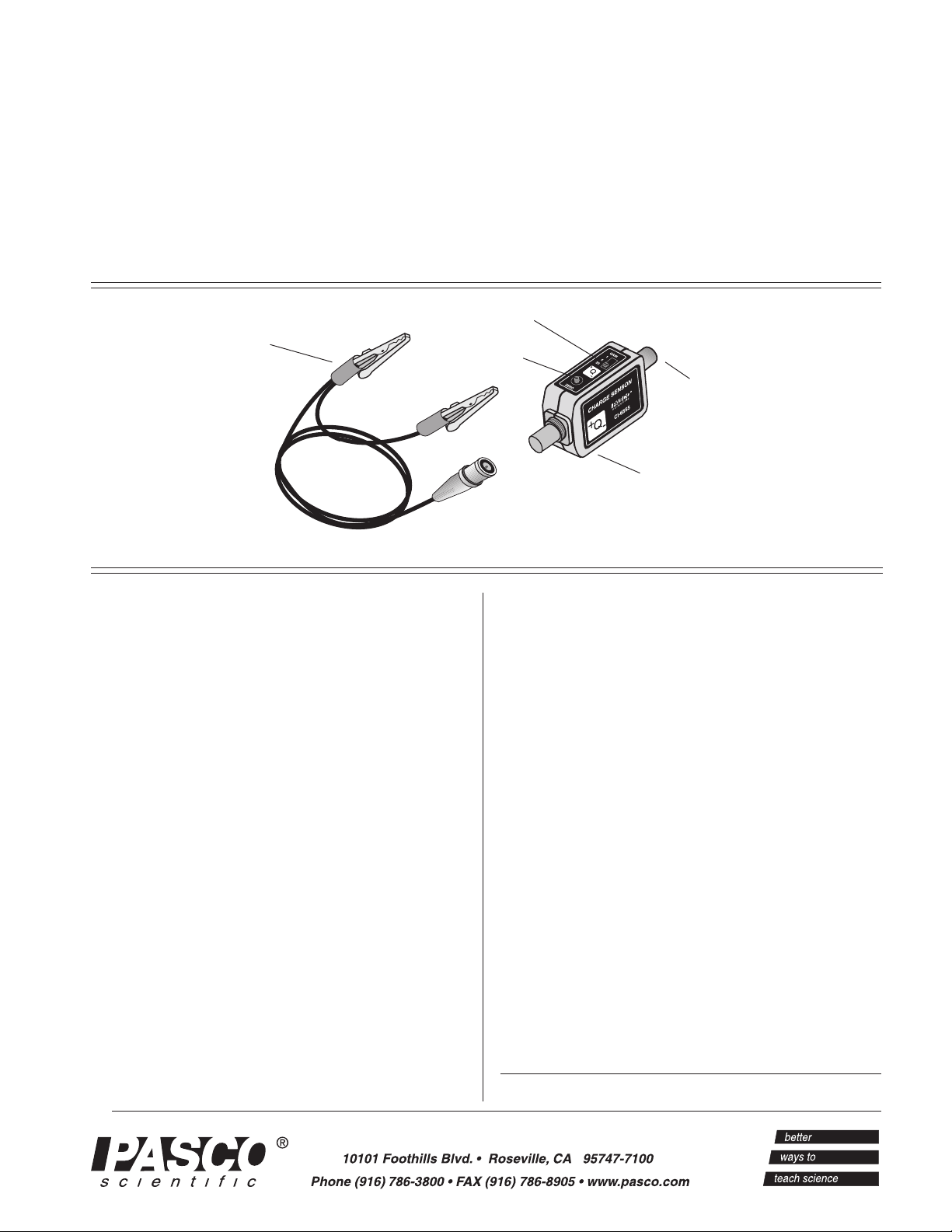
BNC/alligator cable
012-06991A
5/99
$1.00
CHARGE SENSOR
gain switch
zero switch
8-pin DIN
connector
amplifier box
Introduction
The CI-6555 Charge Sensor measures voltages
from sources where the total amount of available
charge is very small, for example, many
electrostatics experiments. It is essentially a voltage
amplifier with extremely high input resistance.
Whereas a typical digital multimeter has an input
resistance of 10 megaohms (10
Sensor has an input resistance of at least 10
ohms.
Coupled with a ScienceWorkshop
Interface, the Charge Sensor can be used as an
electronic version of the familiar laboratory
electroscope. Unlike the traditional electroscope
however, the Charge Sensor can make quantitative
measurements as well as indicate charge polarity.
7
ohms), the Charge
®
Computer
Equipment
INCLUDED
• Charge Sensor (CI-6555)
SUGGESTED ACCESSORIES:
• Faraday Ice Pail (ES-9042A)
• Charge Producers and Proof Plane (ES-9057A)
12
• Conductive Spheres (ES-9059B)
• Power Supply (ES-9077)
ADDITIONAL REQUIRED
• PASCO ScienceWorkshop Computer Interface
(300, 500, 700, or 750)
© 1999 PASCO scientific
Page 2
Charge Sensor 012-06991A
Setup Procedure
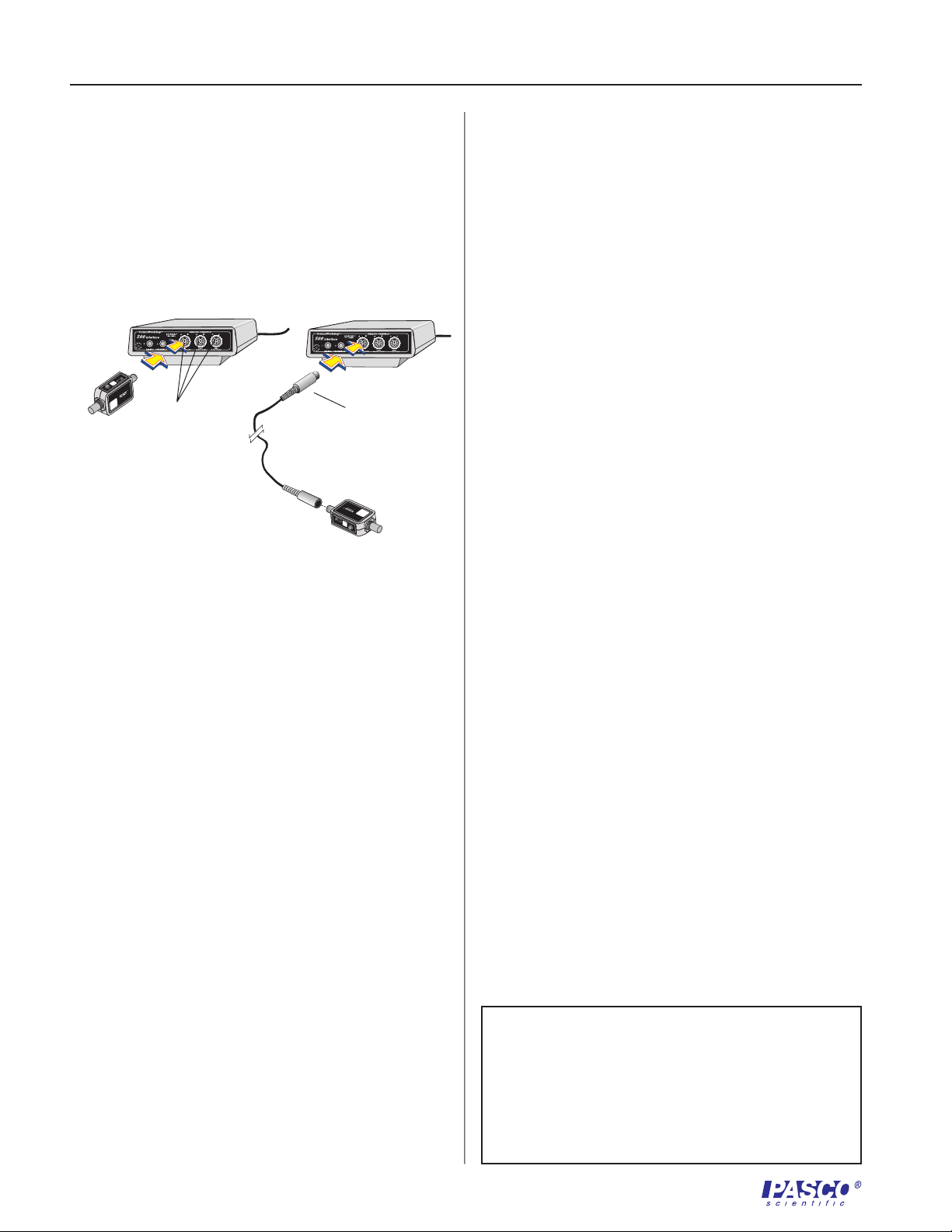
1. Insert the 8-pin DIN plug into analog input A,
B, or C of the ScienceWorkshop Interface box.
Note that the Charge Sensor will plug directly
into the interface box (Figure 1a), or an
extension cable (CI-6516, available separately)
may be used (Figure 1b).
G
A
I
N
1
5
2
0
Q
N
Z
O
E
R
O
S
N
E
S
E
G
R
A
H
55
C
5
I-6
C
+
-
Q
analog channel
a, b, c
ab
Figure 1
Two ways to connect the Charge Sensor to the
ScienceWorkshop
Interface box.
2. Attach the BNC/alligator clip probe to the BNC
connector on the amplifier box by lining up the
alignment pins. Push the BNC connector in
slightly and turn clockwise one-quarter turn to
lock.
3. Discharge the input capacitor by pressing the
ZERO switch. Set the sensitivity of the sensor
by changing the position of the GAIN switch.
The table below shows the relationship between
the position of the GAIN switch and the
measurable full-scale input voltage:
Gain Switch Position Full-Scale Input ( ±volts)
1 10.0
5 2.0
20 0.5
4. Set up the Charge Sensor in your data
acquisition software, and open a Meter display.
CI-6516 extension
cable (available
separately)
CI-6555
-
N
SO
N
Q
SE
E
+
G
R
A
CH
N
I
A
G
1
5
0
2
Q
O
ZER
Tips On Use of the Charge Sensor
1. When used on the most sensitive range (X20),
the Charge Sensor may display a small offset
voltage. That is, pressing the ZERO switch may
not cause the voltage to go exactly to zero.
Although this residual voltage is typically quite
small (less than 0.1 volts), it will be constant for
any particular GAIN setting and can be
subtracted from the final measurement to give a
more accurate reading.
2. The extremely high input resistance of the
sensor also makes it sensitive to stray
electrostatic fields in the immediate vicinity of
the case. To minimize the influence of static
fields and for the greatest accuracy, follow
these guidelines:
• Plug the Charge Sensor directly into an
interface (avoid using the extension cable, if
possible).
• Stabilize the sensor by mounting it on a rod
stand using the mounting nut on the sensor
case.
• Position the sensor and interface box as far
away from the experiment as possible.
• Wrap the sensor case in aluminum foil.
(Wrapping the sensor in aluminum foil will
not only stabilize the readings but will
demonstrate Gauss’s theorem in showing
that there can be no net field within a hollow
conductor.)
Note: Higher frequency fluctuating fields
(such as 50 or 60 Hz) will usually not be
detectable unless you are viewing the output
of the sensor on an oscilloscope.
Note: This instruction sheet was written
assuming that the user is familiar with
ScienceWorkshop or DataStudio™. Users
can gain familiarity by working through the
tutorials provided with ScienceWorkshop or
from DataStudio’s online help.
2
Page 3

012-06991A Charge Sensor
Suggested Activity
Use the Charge Sensor to demonstrate the
magnitude of charge build-up induced on PASCO
Charge Producers (ES-9057A).
In this demonstration, you connect the Charge
Sensor to a Faraday Ice Pail (ES-9042A) as shown
in Figure 2.
Charge Producer
analog channel of a
ScienceWorkshop
computer interface
to computer
Charge Sensor
Faraday Ice
Pail
Figure 2
Setup for demonstrating the magnitde of charge on the
Charge Producers.
After setting the sensor up in your data acquisition
program and opening a Meter display, briskly rub
the Charge Producers together. Next, lower one of
the Charge Producers into the inner basket of the
Faraday Ice Pail.
Result: The magnitude of the charge that was
provided when the Charge Producers were rubbed
together will be displayed on the Meter display.
The Charge Producer with the blue surface will
acquire a negative charge, and the one with the
white surface will have a positive charge. The
magnitude of the positive and negative charges will
be equivalent.
Specifications
• Input Resistance: 1012 ohms, minimum
• Input Capacitance: 0.01 uF ±5 %
• Input Voltage Range: ±10 volts
• Maximum Input Voltage: ±150 volts dc,
continuous
Limited Warranty
PASCO scientific warrants the product to be free
from defects in materials and workmanship for a
period of one year from the date of shipment to the
customer. PASCO will repair or replace, at its
option, any part of the product which is deemed to
be defective in material or workmanship. The
warranty does not cover damage to the product
caused by abuse or improper use. Determination of
whether a product failure is the result of a
manufacturing defect or improper use by the
customer shall be made solely by PASCO
scientific. Responsibility for the return of
equipment for warranty repair belongs to the
customer. Equipment must be properly packed to
prevent damage and shipped postage or freight
prepaid. (Damage caused by improper packing of
the equipment for return shipment will not be
covered by the warranty.) Shipping costs for
returning the equipment after repair will be paid by
PASCO scientific.
Address: PASCO scientific
10101 Foothills Blvd.
Roseville, CA 95747-7100
Phone: (916) 786-3800
FAX: (916) 786-8905
email: techsupp@pasco.com
web: www.pasco.com
3
Page 4

 Loading...
Loading...