
ISSUE 2
User Manual
DP231C

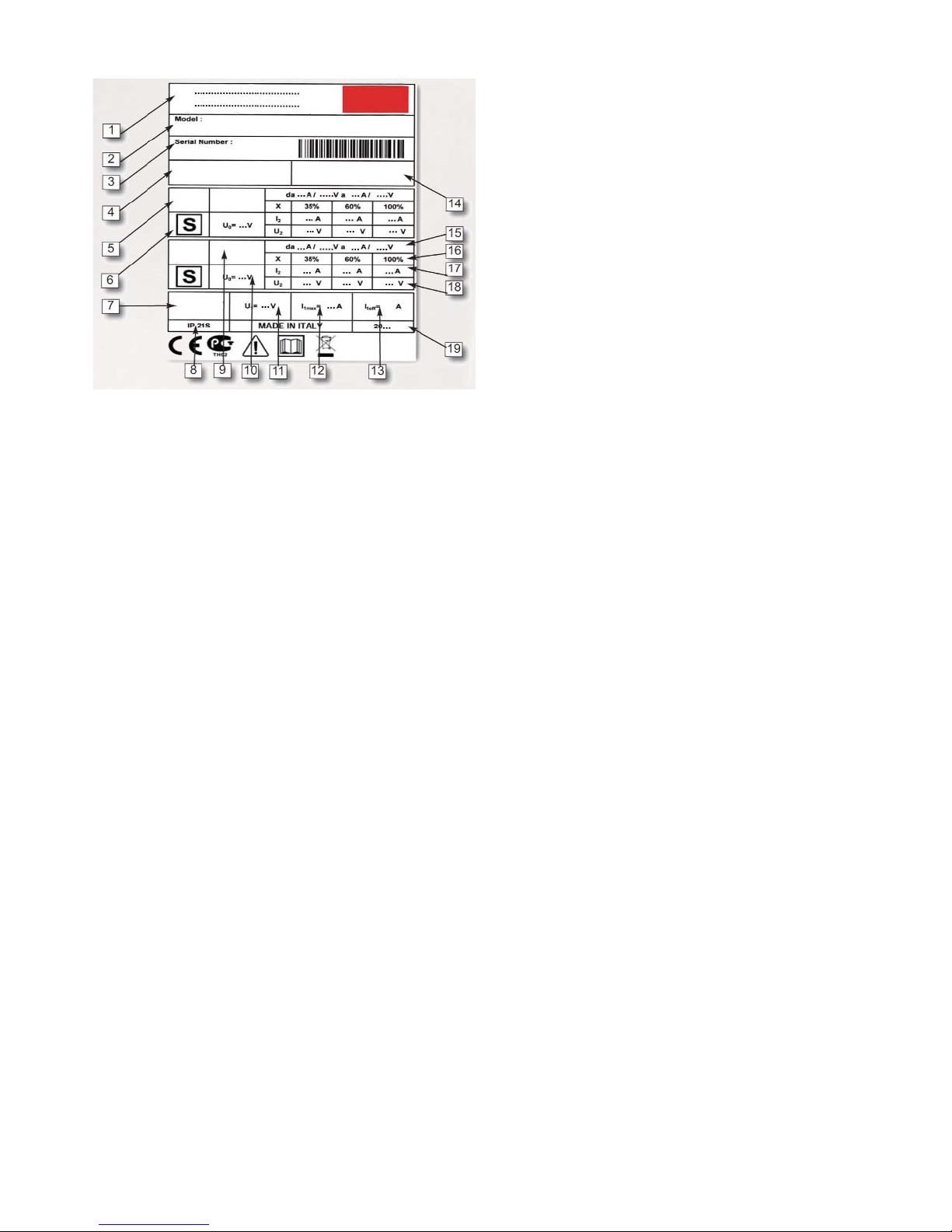
DATA PLATE
1. MANUFACTURER’S NAME, ADRESS AND COMPANY LOGO
2. MODEL
3. SERIAL NUMBER
4. BLOCK DIAGRAM
5. WELDING OUTPUT
6. SUITABLE FOR ENVIRONMENT WITH INCREASED HAZARD OF
ELECTRIC SHOCK
7. POWER SUPPLY
8. DEGREE OF PROTECTION
9. TYPE OF WELDING OUTPUT CURRENT
10. INPUT VOLTAGE
11. RATED INPUT VOLTAGE
12. MAXIMUM RATED INPUT CURRENT
13. MAXIMUM EFFECTIVE INPUT CURRENT
14. APPLICABLE STANDARDS
15. RANGE OF WELDING VOLTAGE-CURRENT
16. DUTY CYCLE
17. RATED WELDING CURRENT
18. CONVENTIONAL LOAD VOLTAGE
19. YEAR OF CONSTRUCTION
CONSTRUCTION SPECIFICATIONS:
WEIGHT [Kg]: 23
Dimensions:
Width [mm]: 220
Depth [mm]: 560
Height [mm]: 480
Protection rating: IP 21S
Height S.L.M. [m]: 1000
Usage temp. [°C]: -10/+40
Storage temp. [°C]: -20/+55 T
est temp. [°C]: 40
Applicable standards: EN.60974-1 EN.60974-10
Group/Class: Gruppo 2 Classe A
Thermal protection: Termostato Incorporato
ELECTRICAL INPUT :
Line voltage: 230
No. phases: 1
Frequency [Hz]: 50/60
Effective line current [A]: 21,6
Maximum line current [A]: 40,3
Input Power [kVA]: 5
Circuit protection: Time-delay fuses or Co K magnetothermal curve
OUT-PUT CHARACTERISTICS:
Static characteristics: Cadente
Fill Diameter: 0.6-0.8-1.0-1.2
Welding mode: MIG/MAG
Weld current range: from 15A / 14,75V to 235A / 25,75V
Open circuit voltage [V]: 55
Output current and tension: Duty [%]: 35 60 100
I2 [A]: 220 160 130
U2 [V]: 25 22 20,5
Welding mode: TIG
Weld current range: from 15A / 10,6V to 235A / 19,4V
Open circuit voltage [V]: 55
Out-put current and tension: Duty [%]: 35 60 100
I2 [A]: 220 160 130
U2 [V]: 18,8 16,4 15,2
Welding mode: MMA
Weld current range: from 15A / 10,6V to 185A / 17,4V Open circuit voltage [V]: 55
Duty [%]: 35 60 100
I2 [A]: 185 138 109
U2 [V]: 27,4 25,52 24,36 6 1.

GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS AND NOTES
FOR CONSULTING THIS MANUAL
The “DP231C” welders are made using
INVERTER technology. They are extremely
compact and versatile devices that can be used
in all those situations that require minimum
obstruction, combined with the highest
performance.
These welders use both manual and
synergic MMA, TIG and MIG/MAG (short arc,
pulse or double pulse).
The innovative operator interface system, which
uses a large 5,7” TFT colour screen, allows for
simple and intuitive use of the equipment, without
renouncing on the possibility to personalise all of
the welding settings.
All of the main parameters of the machine
are stored on a memory card (SD-Card), keeping
the equipment constantly up-dated with the
latest welding developments. If the memory card
is removed the equipment will cease to function,
providing an optimal antitheft system and
safeguard against inappropriate use. Thanks
to the advanced control techniques adopted,
the product is extremely reliable and easy to
use. This instruction manual provides detailed
information on the machine settings: reading the
entire manual will allow you to appreciate the
extreme exibility and practicality of use.
Caution: the device must only be used in the
manner and for the purpose described in this
manual. Never use inappropriately or for any
other purpose.
2. DESCRIPTION OF THE EQUIPMENT using this selector you can choose the
gas outlet dedicated for each welding
process
INTERNA L TAP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Fig.1
Fig.2
17
18
19
20
21

8. USB port: only for technical assistance.
9. Knob for setting the main welding parameter:
the main welding parameter can be set with
this knob: Welding MMA/TIG: sets the welding
current.
11. Air grills (must never be obstructed).
12. “-” dinse front connector: negative pole inlet.
Connection socket TIG torch mode. MMA Mode:
Ground clamp MIG Mode: Ground clamp
13. Connector for remote control.
14. “+” dinse front connector: positive pole inlet.
MMA Mode:Electrode holder TIG Mode:Ground
clamp MIG Mode with gas: Not used
15. Gas Outlet: MMA Mode: inactive TIG Mode:
Gas connection to the welding torch (Internal
tap positioned on TIG GAS) MIG Mode with gas:
inactive (internal tap positioned on MIG GAS) 16.
EUROCONNECTOR (SEPARATED TROLLEY):
quick connector for welding torch. This connector
is used to supply welding gas to the torch, the
electrical contacts of the torch button and the
welding current.
FIGURE 2:
17. ON-OFF switch: turns the machine on and
off.
18. Input cable: connection cable to the mains
power equipped.
19. Welding gas inlet MMA Mode: Not used TIG
Mode: GAS connection to the cylinder MIG Mode
with gas: GAS connection to the cylinder
20. Fuse
21.Connector for supplying power to the
Graphic display: The display 5.7 inch color’’
shows different screens depending on whether
the machine is in welding mode or setting mode.
In welding mode, the display is divided into ve
main parts:
Part 1: State of the machine
Part 2: Meaning of the active buttons (buttons 2,
3, 4, 5 of g. 1)
Part 3: Value of the measurements set
Part 4: Type of process selection
Part 5: Indicates the values set for the various
welding parameters (to change the set value,
highlight the value with knob 10 and press to
conrm; the value is highlighted as a contrast.
Change the value by turning the knob and conrm
the new value by pressing knob 10 again).
Highlighted value: Indicates the welding
parameter that is being changed with knob 10.
VIEWS: - At start-up, the Parweld logo and the
Firmware revision are displayed.
CONTROL BUTTONS: (2, 3, 4, 5,6 in g.1)
Each control button is associated with a specic
function shown on the display.
7.SD slot: This slot, covered by a special plastic
cover, must contain the SD-Card supplied with
the machine; without this card, the machine
remains inactive and a special signal is reported
on the display.
liquid cooling system (Optional): Warning the
connector contains dangerous voltages: NEVER
use it for purposes other than those for which it
was specically designed.
Part 1
Part 2
Part 3
Part 4
Part 5

FIGURE 3: 22. WIRE SPOOL SUPPORT The
300mm MIG welding spool requires an external
support
23. WIRE FEEDER SYSTEM: see gure 3A for
a more detailed image.
24. WIRE-FEEDER MOTOR
25. WIRE TENSION REGULATOR: Adjusts the
tension of the welding wire.
26. INLET OF THE WIRE FEEDER MOTOR
27. WIREFEEDER SPOOLS
28. GAS VALVE: The Gas Valve can be rotated
in three positions.
GAS MIG Position: The tap feeds the
Euroconnector with the gas from the cylinder
connection (19) (For MIG with GAS welding).
GAS TIG Position: The tap feeds the front
connection (14) with the gas from the cylinder
connection (19) (For TIG welding).
22 23
24
25
26
27
28
Fig.3A
Fig.3

WELDING WIRE
To load the welding wire, follow these instructions
carefully, in the order described below. Warning:
before inserting the wire, always remove the gas
nozzle and the wire feeder tip from the welding
torch.
1. Disconnect the cable from the power supply
(18 of Fig. 2).
Caution: before proceeding with the next
step, make sure the torch cable (Fig. 4) is well
extended and that the welding wire does not
have any bends or burrs. Failure to follow these
precautions could damage the wire-feeding tube
inside the torch. Once the wire has been threaded
through the torch, attach the wire-feeder tip and
the gas nozzle.
N.B. When changing the diameter of the wire,
make sure that the correct cable of the wirefeeder spool is facing towards the inside of the
machine. To do so, ensure that the diameter and
type of wire is legible (facing towards the outside
of the machine) Remember that the spools with
2. Unscrew the
ball-grip knob in
the centre of the
spool support of the
welding wire (22 of
Fig. 3).
3. If necessary,
depending on the
size of the spool
used, remove the
bearing spool.
4. Remove the
plastic wrap from the
new spool and place
the spool on the
appropriate support
(22 of Fig. 3).
4. Replace the ballgrip knob.
5. Please note that
the hex socket (M8)
situated in the centre
of the spool support
is part of the wire
tension system.
6. Lower the roll
feeder (25 of Fig.
3A)
7. Insert the wire
into the inlet tube
(26 of Fig. 3A) of
the wire feeder
motor. .
8. Run the wire
under the wire
feeder spools all the
way to the out-let of
the Euroconnector.
9. Lower the
upper spools
10. Lift the knob of
plastic (25 of Fig
3A) of the pressure
regulator of the
wire.

a ‘V’ cable are suitable for feeding iron and
steel wire. The spools with a ‘U’ are suitable for
aluminium wire.
4. MIG/MAG WELDING To choose this welding
mode use switch 10, select MIG and press
conrm.
Switch 9 adjusts the machine power.
There are three principal MIG-MAG welding
modes:
1.Manual short arc
2.Synergic short arc
3.Pulsed arc synergic
4.1 Manual Short Arc MIG Welding
By turning switch 10 it is possible to choose from
the different MIG-MAG welding modes; press
the switch to select the desired option.
MIG/MAG welding (Metal Inert Gas and Metal
Active Gas) is continuous wire feed welding that
provides a higher current density compared to
welding with a uxcovered electrode; this allows
increased penetration and speed and the joint
can be lled with less strokes. Welding is carried
out by melting a metallic electrode, consisting of
a continuous wire, in a welding pool at a constant
speed, controlled by the welding torch. When
the wire starts to feed, it touches the area that
requires welding, creating an electric arc; the arc
melts the wire, which is then deposited on the
workpiece.
This welder can be used with the following types
of wire:
1. Solid wire: must always be used with a gas
shield.
2. Flux cored for gas welding: the centre of the
wire contains a mineral product that improves
the quality of the weld (this must always be used
with gas).
The correct method for connecting the torch and
the earth cable can be seen in the table below:
WELDING
PROCESS
Euroconnettor
16 of Fig.1
‘+’ Front
socket 14
of Fig.1
‘-’ Front
socket 12
of Fig.1
MIG/MAG
TORCH
CABLE
NOT
USED
EARTH
CABLE
Once selected the follow screen will appear: Wire
speed: This sets the speed of the welding wire.
The welding current and the wire speed must be
adjusted, taking into consideration the thickness
of the workpiece. Larger pieces will require a
higher wire speed.
For best results, the wire speed must be adjusted
during welding.

soft-start: This adjusts the contact speed of the
wire, creating a softer weld spark; the higher the
level the lower the contact speed.
Inductance: This adjusts the variation speed of
the welding current for a sharper (low levels) or
softer arc (high levels).
2t-4t-4Bi-level: This allows the user to set the 2
step or 4 step functions
2t: : In 2 step mode, the machine will weld for as
long as the torch trigger is held down.
4t: In 4 step mode, one press of the torch trigger
will start the welding process; press the button
again and the welder will stop.
4Bi: NIn 4 step bi-level mode, one press of
the torch trigger will start the welding process;
successively, brief pressure on the trigger (for
a duration of less than 1s) will make the welder
pass from the welding current to the second
level and vice versa. Pressing the torch trigger
for lengthy periods of time will halt the welding
process.
Spot welding: This allows the user to set (when
different to 0) the maximum welding duration in
seconds.
Pause: This allows the user to set (when different
to 0) the duration of the pause between two
successive tacks.
Pre gas time: This allows the user to set the time
of the gas supply, before feeding the welding
current.
Post gas time: This allows the user to set the
time of the gas supply, when the welding current
stops.
Burnback: This allows the use to adjust the
length of the wire at the end of the torch when
the welding process ends.
Hot start : This allows the user to set the welding
ignition current to create a soft weld spark; this is
generally used with the softstart setting.
Water pump: This turns the water system ON or
OFF, if present.
4.2 Synergic Short Arc MIG WELDING Synergic
MIG welding allows the user to easily adjust
the weld settings, according to the different
materials that require welding. During synergic
welding, switch 9 of Fig 1 simultaneously adjusts
the tension or the speed of the wire. The other
parameters are automatically adjusted to the
set power, according to the diameter and type
of wire selected. The percentage of the length of
the arc can be varied using the ‘welding tension’
setting. Welding quality can be further improved
by adjusting the ‘electronic inductance’ and
‘deposit’ settings.
Turn switch 10 to choose from the different MIG-
MAG welding options; press the switch again to
conrm the chosen option.
Once selected, the screen with the welding wire
material options will appear:
Settings that do not appear on the screen are
accessible by turning switch 10.

Once the type of wire has been selected (using
switch 10), the settings page for the welding wire
diameter will appear.
L2 span: When the two level mode is active the
duration of the second power level can be set.
L2 amplitude: When the two level mode is active
the second power level (L2) can be set with
respect to the set power (level L1).
2t-4t-4bilevel: This function adjusts the 2 step or
4 step settings.
2t: In 2 step mode, the machine will weld for as
long as the torch trigger is pressed down.
4t: : In 4 step mode, press the trigger once to
start the torch, press again to stop the torch.
4Bi: In 4 step Bi- Level mode, press the trigger
once to start the torch, successively, briey
pressing the trigger (for less than 1s) will cause
the set welding current to pass to second level
and vice versa. Prolonged pressure on the torch
trigger will halt the welding process.
2nd level: This option is for setting the values the
wire speed, corresponding to the second power
level, which is active when the values of the
2t-4t-4bi-level is set to 4bi.
Initial/nal current: it allows to switch up (ON) or
down (OFF) mode with starting/nal current.
Initial current: allows setting the value at which
the welding current is brought to immediately
after the striking of the electric arc
Initial time: allows setting the time of the current
established by the Initial Current parameter. In
4t/4bi mode this time is irrelevant and the initial
current is kept for as long as the torch button is
held down.
Ramp ls- > l1: allows setting the duration of the
upslope of the welding current.
Ramp l1- > lf: allows setting the duration of the
downslope of the welding current
Final current: allows setting the value at which
the welding current is brought to on completion
of the downslope
Final time: allows setting the time of the current
established by the Final Current parameter. In
4t/4bi mode, this time is irrelevant and the nal
current is kept for as long as the torch button is
held down.
Spot welding: This sets the maximum welding
duration (when different to 0), in seconds.
Pause: This sets the duration of the pauses
(when different to 0), between two successive
tacks.
Pre gas time: This sets the gas supply time
before the welding current is supplied.
Post gas time: This sets the gas supply time after
the welding current supply ends. 13
Burnback: This adjusts the length of the wire in
Selecting this option will take you to the welding
screen:
Arc length: This changes the length of the electric
weld arc with respect to the pre-set synergic
values.
Deposit: This modies the deposit of the ller
material (velocity of the wire) with respect to the
pre-set synergic values. I
nductance: This changes the variation speed of
the welding current to achieve a sharper (low
values) or softer arc (high values).
Double short: This activates (ON) or deactivates
(OFF) the two level option, i.e. the continuous
switching between two different welding tension
levels.
L1 span: When the two level mode is active the
duration of the rst power level can be set.

the tip of the torch, when the welding process
comes to an end. Soft-start: this adjusts the
contact speed of the wire, to obtain a soft weld
spark; the higher the values the lower the contact
speed. Hot-start: This sets the weld ignition
current, in order to achieve a softer weld spark;
this is generally used with the soft-start option.
Water pump: When present, this turns the water
system ON or OFF.
4.3 Pulse synergic MIG WELDING
Pulse synergic MIG welding allows obtaining
a relatively cold welding bead and good
penetration.
The low energy input makes this welding process
particularly suitable for thin layers and for
materials such as stainless steel and aluminium.
During welding with synergic adjustment, the
wire speed (i.e. welding power) can be adjusted
with knob 9 shown in Fig.1.
The other parameters are automatically adjusted
to the set power depending on the type and
diameter of the wire selected. By turning switch
10 it is possible to choose from the different MIG-
MAG welding modes;press the switch to select
the desired option. Once selected, the screen
with the welding wire material options will appear
Once the type of wire has been selected(using
switch 10), the settings page for the welding wire
diameter will appear. The wire’s diameters could
not be available for all models.
Selecting this option will take you to the welding
screen:
Arc length: This changes the length of the electric
weld arc with respect to the pre-set msynergic
values.
Deposit: This modies the deposit of the
ller material (velocity of the wire) with respect to
the pre-set synergic values.
Double pulse: This activates (ON) or
deactivates(OFF) the two level option, i.e. the
continuous switching between two different
welding tension levels.
Settings that do not appear on the screen are
accessible by turning switch 10.

L1 span: When the two level mode is active the
duration of the rst power level can be set.
L2 span: When the two level mode is active the
duration of the second power level can be set.
L2 amplitude: When the two level mode is active
the second power level (L2) can be set with
respect to the set power (level L1).
2t-4t-4bilevel: This function adjusts the 2 step or
4 step settings.
2t: In 2 step mode, the machine will weld for as
long as the torch trigger is pressed down.
4t: : In 4 step mode, press the trigger once to
start the torch, press again to stop the torch.
4Bi: In 4 step Bi- Level mode, press the trigger
once to start the torch, successively, briey
pressing the trigger (for less than 1s) will cause
the set welding current to pass to second level
and vice versa. Prolonged pressure on the torch
trigger will halt the welding process.
2nd level: This option is for setting the values the
wire speed, corresponding to the second power
level, which is active when the values of the
2t-4t-4bi-level is set to 4bi.
Initial/nal current: it allows to switch up (ON) or
down (OFF) mode with starting/nal current.
Initial current: allows setting the value at which
the welding current is brought to immediately
after the striking of the electric arc
Initial time: allows setting the time of the current
established by the Initial Current parameter. In
4t/4bi mode this time is irrelevant and the initial
current is kept for as long as the torch button is
held down.
Ramp ls- > l1: allows setting the duration of the
upslope of the welding current.
Ramp l1- > lf: allows setting the duration of the
downslope of the welding current
Final current: allows setting the value at which
the welding current is brought to on completion
of the downslope
Final time: allows setting the time of the current
established by the Final Current parameter. In
4t/4bi mode, this time is irrelevant and the nal
current is kept for as long as the torch button is
held down.
Spot welding: This sets the maximum welding
duration (when different to 0), in seconds.
Pause: This sets the duration of the pauses
(when different to 0), between two successive
tacks.
Pre gas time: This sets the gas supply time
before the welding current is supplied.
Post gas time: This sets the gas supply time after
the welding current supply ends. 13
Burnback: This adjusts the length of the wire in
the tip of the torch, when the welding process
comes to an end. Soft-start: this adjusts the
contact speed of the wire, to obtain a soft weld
spark; the higher the values the lower the contact
speed. Hot-start: This sets the weld ignition
current, in order to achieve a softer weld spark;
this is generally used with the soft-start option.
Water pump: When present, this turns the water
system ON or OFF.
WORK-
PIECE
THICK-
NESS
WIRE
DIAMETER
WELDING
CURRENT
ARC
mm mm A
0.8 - 1.0 0.6 - 0.8 60-100 Short-Arc
1.5 - 2.0 0.8 - 1.0 80-120 Short-Arc
2.0 - 3.0 1.0 - 1.2 100-130 Short-Arc
3.0 - 4.0 1.2 120-200 Short-Arc
> 4.0 1 150÷200 Spray-Arc
> 4.0 1.2 200÷300 Spray-Arc
5. MIG WELDING CONECTOR
The connector for the welding cables comes with
a quick connect system that uses appropriate
connectors.
5.1. MIG TORCH We would advise you to carry
out regular controls on the condition of the
welding torch;in particular, always check the
nozzle the wire feeder tip and the internal liner of
the torch. These parts must be kept well-cleaned
and intact. If the wire stops threading correctly.
replace the liner. N.B. Each wire and diameter
corresponds to an appropriate wire feeder tip
and liner. Always make sure you are using the
correct type.
5.2 CONNECTOR FOR MIG WELDING with a
traditional torch
1) Connect the earth cable to the appropriate
‘-‘ socket on the front of the device (12 of Fig
1).Insert the connector by lining up the key with
the groove and turn in a clockwise direction until
it stops. Do not fasten too tightly!
2) Connect the torch to the appropriate socket
in the front of the device (16 di Fig 1),turning the
connector in a clockwise direction until it stops.
Do not fasten too tightly!
Warning: the machine is provided with sockets

for the MIG welding torch (Fig 4) This accessory
has a long life-time if periodical controls of the
gas nozzle and the wire feeder tip are carried out
(Fig 4A) (Fig 4B).These parts must be kept wellcleaned and intact. Replace the wire liner when
the wire no longer threads correctly.
5.3 CONNECTOR FOR MIG WELDING with a
Spool or Push-Pull torch
1) Connect the earth cable to the appropriate ‘-‘
socket. (12 of gure 1). Insert by lining up the key
with the groove and turn in a clockwise direction
until it stops. Do not fasten too tightly!
2) Connect the torch to the appropriate socket
on the front of the device (16 of Fig 1),turning in
a clockwise direction until it stops. Do not fasten
too tightly!
3) Insert the connector of the torch into the
appropriate female socket.
MIG WELDING: Connect the pressure regulator
to the cylinder, after which attach the gas tube
of the torch to the latter. MIG welding is usually
carried out with a constant current, with a positive
pole (“+ “see g.5).
SHORT ARC (short-circuit transfer):this brings
the electrode into direct contact with the
weld pool, which creates a short-circuit that
extinguishes the arc, after which the arc reignites
and the cycle is repeated.
. - the tension directly inuences the appearance
of the welding seam, but the dimensions of
the welding surface can be varied, according
to requirements, by manual movement of the
torch to obtain variable deposits with a constant
tension.
- the speed of the movement of the wire is in
relation to the welding current.
7. ADJUSTING THE WELDER
Once the welding tension has been set, maintain
the length of the electric arc between 5 and 10
mm and adjust the wire speed to achieve the best
welding results. Initially, carry out a welding test
on a well-cleaned sample, free of any coating,
rust or paint.
NOTE The torch trigger controls the following
functions:
- gas ow
- wire movement
- welding current
Fig.5
SPRAY ARC (spray transfer):
this allows the droplets to detach from the
tip of the electrode, which successively reach
the weld pool.
The fact the arc is visible, reduces the need
for the operator to strictly observe the adjustment
tables, allowing for direct control of
the welding pool.
The MIG torch cable
is connected to the
Euroconnector(16
ofg.1), whilst
the earth cable of
the work piece is
connected to the
‘-‘socket on the
front(12 di g.1).
At this stage adjust the welding current using
the potentiometer (9 of Fig.1), situated on the
front panel. The diameter of the electrode and
the welding current settings must be selected
according to the thickness of the workpiece.
6. STRIKING AN ARC IN MIG WELDING The
MIG-MAG welding process is when an electric arc
is created between a consumable wire and the
workpiece, protected within a gas atmosphere.
This atmosphere can be either inert (Argon) or
active (CO2 or a mixture of Argon and CO2).The
wire is continuously fed through a torch by a wire
feeder to the weld pool. A solid wire or ux-cored
wire can be used. The transfer methods of the
ller material dene different arc types:

8. HOW TO ACHIEVE THE BEST
WELDING RESULTS
Hold the torch at an angle of 45° from the
workpiece. Keep the gas nozzle (Fig. 4A) at
a distance of approximately 6 mm from the
workpiece.
2. Move the torch with a continuous movement,
using a push, not pull, motion. This will guarantee
the gaseous shield of the arc.
3. Avoid welding in high winds. If the wind is
too strong it could carry the gas away from the
welding pool, creating a porous (weak) weld.
4. Keep the wire clean: never use rusty wire.
5. Make sure the torch cable is free of dents
or coils, which could compromise the correct
movement of the wire.
6. When changing the wire spool, always clean
the wire feed tube with compressed air.
9. MMA WELDING To select this welding mode,
use switch 10, select MMA and press conrm.
Always make sure that the earth and the
electrode clamp holder are kept far apart.
9.1 MMA WELDING Manual This mode can be
accessed using switch 10.
Electric arc welding with a covered MMA (Metal
Manual Arc) electrode or SMAW (Shielded Metal
Arc Welding) is a manual welding procedure that
takes advantage of the heat generated by the
electric arc, which strikes between a covered
earthed electrode and the workpiece. This
procedure allows for the creation of joints in any
position, in the workshop, outdoors, in conned
areas or places that are difcult to access.
With the DP231C it is possible to weld any
type of electrode and diameter. The spark of
the arc occurs by placing the electrode close
to the workpiece. The correct connection of the
electrode clamp holder and the earth cable can
be seen in the table below:
WELDING
PROCESS
Front Socket
+
14 di Fig.1
Front Socket
-
12 di Fig.1
MMA
ELECTRODE
CLAMP
HOLDER
EARTH CA-
BLE
Selecting this option will take you to the welding
screen: Switch 9 in g. 1 adjusts the welding
current (very thick workpieces require a higher
current).
Furthermore, switch 10 adjusts the parameters
shown in the gure below:

Arc Force: This sets the current increase ratio in
relation to the welding current, that the welder
can force, in order to keep the arc appropriately
ignited in any position.
Hot Start: This sets the current increase ratio in
relation to the welding current, that the welder
can force when the arc is ignited, to improve the
quality of the same.
Hot start span: This sets the time period when
the jot start current is forced.
Remote: This switches the remote control (which
connects to socket 13 of g.1) of the current
intensity ON or OFF.
10 WELDING TABLE Use the table below to
calculate the welding current, according to the
type of electrode used:
ELECTRODE
DIAMETER
WELDING
CURRENT
ELECTRODE
LENGTH
mm A mm
2.0 45-60 300
2.5 60-100 300
3.25 90-140 450
4.0 140-170 450
5.0 190-230 450
11. CONNECTION FOR MMA WELDING
The Dinse connector is inserted by lining-up the
key with the groove and turning the connector in
a clockwise direction until it stops. The electrode
clamp holder and earth must be connected
to the ‘+’ and ‘-‘ terminals, according to the
specications of the electrodes used.
. IGNITING THE MMA ARC
This is carried out by stopping a while over the
last crater (i.e. the end of the welding seam),
returning slowly on the previously deposited
seam for approximately two centimetres and,
only at this point, moving the electrode away
from the workpiece to turn off the arc.
Create the contact
for igniting the arc
at a distance of
approximately 5
cm from the initial
welding point.
Immediately move
the electrode
towards the
workpiece, without
touching it, in order
to keep the arc
ignited.
Quickly bring the
electrode, without
turning off the arc,
towards the point
where the welding
seam will begin.
Begin welding,
advancing slowly.
The distance
between the tip of
the electrode and the
workpiece must be as
identical as possible
to the diameter of
the electrode in use.
process; press the
button again to stop
welding. 4Bi:

WELDING
PROCESS
Front socket +
14 di Fig.1
Front socket -
12 di Fig.1
TIG CAVO MASSA
CAVO
TORCIA
13. TIG WELDING To select this welding mode :
turn switch 10, select TIG and press conrm.
Inert gas (Argon) welding with an infusible
Tungsten electrode and arc (often call TIG
(Tungsten Inert Gas) for short, is a welding
procedure whereby the heat is produced by an
arc that strikes between a tungsten electrode
(which is not consumable) and the workpiece.
The welding is carried out by fusing the edges
of the workpiece or by adding other ller material
using specic types of rod to create a joint. The
torch is ignited by touching the workpiece with
the electrode and then lifting. The TIG procedure
can be adapted to any work position and can
also be applied to very thin sheets of metal (0,20,3 mm). The TIG procedure is distinguished by
the ease with which the arc can be controlled, a
powerful and concentrated thermal source and
the simple manner in which the ller material can
be controlled. This makes the TIG procedure
particularly suitable for precision welding on a
wide variety of thicknesses, in difcult positions
and on pipes which require full penetration. The
TIG procedure can be used on various types of
metals, such as, ferrous materials, alloys, nickel,
copper, titanium, magnesium. During welding,
potentiometer 9 in g. 1, for example, regulates
the welding current. The correct connection of the
torch and earth cable is shown in the following
table:
13.1 TIG WELDING (Lift-Arc) Button 9 controls
the current and the machine power.
Select this option and the welding screen will
appear:
Make sure that the pulse setting is switched off.
If not, use the menu and set the option PULSE
to OFF, as shown in the above gure. During
welding it is possible to adjust the current using
button 9 in g. 1. Both the welding current values
and the relative arc tension used will be displayed
continually on the screen.
ADJUSTMENTS AND SETTINGS:
Button 10 adjusts the welding settings on the
screen: prolonged pressure on the torch trigger
will stop the welding process.
2t-4t-4bilevel: This function sets the 2 tempi or 4
tempi mode.
2t: In 2 tempi mode, the machine welds for the
entire time the torch trigger is pressed down.
4t: In 4 step mode, pressing the torch trigger
once starts the welding process; press the button
again to stop welding.
4Bi: In 4 step Bi-Level mode, press the torch
trigger once to start welding. Successively, brief
pressure on the trigger (less than 1s) makes the

initial current settings.
slope up: This sets the upslope of the welding
current.
slope down: This sets the duration of the downslope time of the welding current.
end current: this sets the values of the welding
current on completion of the downslope.
end time: This sets the time period when the
current established in the end current settings is
applied.
post gas time: This sets the gas supply time at
the end of the supply of the welding current.
pulse mode: This allows for the activation (ON)
or deactivation (OFF) of the pulse welding mode;
when the pulse welding mode is active, for a
certain period of time, the machine will supply
the welding current and for another period of time
the current dened in the I background settings
will be supplied. The number of current pulses
for a set period of time are based on the values
of the frequency settings.
background current: This sets the base current
used during pulse mode.
pulse frequency: This sets the pulse frequency
when pulse welding mode is active.
pulse balance: When pulse welding mode is
active, this sets the ratio between the time the
welding current and the base current is applied.
water pump: Where present, this turns the water
system ON or OFF.
remote: This turns the remote control of the
current intensity supplied ON or OFF.
spot welding: This sets the maximum welding
duration (if different to 0), in seconds.
14. CONNECTOR FOR TIG WELDING
1) Connect the earth cable to the appropriate ‘+’
socket on the front of the device (18 of g 1).
Insert by lining-up the key with the groove and
turn in a clockwise direction until it stops. Do not
fasten too tightly!
2) Connect the torch to the appropriate ‘-‘ socket
on the front of the device (17 of g 1).
3) Insert by lining-up the key with the groove and
turn in a clockwise direction until it stops. Do not
fasten too tightly!
4) Insert the torch pulse signal connector into the
socket (part 2 of the display);
TIG WELDING: Before connecting the gas make
sure the cylinder contains pure Argon gas. Never
use any other type of gas. Connect the pressure
regulator to the cylinder, after which, connect the
latter to the gas tube of the torch. TIG welding is
usually carried out with a constant current, with a
negative pole (‘-‘ see g.6).
The diameter of the electrode and the welding
current settings must be selected according to
the thickness of the workpiece.
15. IGNITION OF THE TIG ARC Rest the ceramic
of the TIG torch on the workpiece (step 1 of g.7);
bring the tungsten electrode into contact with the
workpiece, then press the torch trigger, whilst
moving in a circular motion where the ceramic is
positioned (see step 2 of g.7).
The cable
of the TIG
torch is then
inserted into
the negative
socket (12 of
g.1), whilst
the earth
cable of the
workpiece is
connected to
the positive
socket. (14
of g.1). At
this stage it
is possible
to adjust
the welding
current
using the
potentiometer
(9 of g. 1)
on the front
panel.

Where: Sw is the torch trigger
P is the potentiometer for controlling the current.
17.1 REMOTE CONTROL OF THE WELDING
CURRENT With remote connector 13 in Fig. 1, it
is possible to adjust the current near to the point
where the welding is being carried out. To do
so, it is necessary to create a connection with
potentiometer P, shown in gure 8. The value of
the potentiometer is not a critical factor: between
2.2kOhm and 10kOhm 1/2W can be used.
Turn the potentiometer and select the welding
current in a range between zero and the set
value.
18. CONNECTING THE OUTPUTS
Connection of the welding cables occurs via a
Dinse quick-connect system with appropriate
connectors.
19. CONNECTING THE GAS CYLINDER
AND THE GAS REGULATOR For TIG and
MIG welding only. For MMA welding, skip this
paragraph entirely.
Fig.9
1
2
3
4
5
6
At this stage, ignite the arc by moving the electrode
away from the workpiece a few millimetres (step
3 of g.7). While maintaining the same distance
from the weld pool, whilst keeping the torch
trigger held down. Release the button to interrupt
the welding process.
16.POWER CONNECTOR
Before connecting the machine check the
tension, number of phases and the power
supply frequency. The admissible power supply
is indicated in the ‘Specic Techniques’ section
on page 5 of this manual and on the information
plate on the machine. Check that the earth
of the welder has been connected correctly.
Furthermore, make sure that the plug provided
with the equipment is compatible with the local
grid sockets. Make sure that the power supply
provides sufcient power for the machine to
function (tension ranges) The power supply
grid protection devices to be used are listed in
the ‘Specic techniques’ section of the present
manual. The machine is provided with a specic
power cable that does not usually require an
extension lead; in the event an extension lead is
required, use one of the same capacity [length?
sezione?] or higher than the machine in use,
according to the length of the cable. A 2.5 mm²
three-pole cable + earth, of the same size or
larger.
17. REMOTE CONNECTION Figure 8 shows
the connections of the remote connector (13 of
g 1).
1. Connect the pressure regulator (2) to the
cylinder (3). Make sure the regulator is suitable
for the cylinder pressure. Attach the connector
nut (6) of the regulator (2) to the cylinder (3).
(Do not screw too tightly; excessive force could
damage the valve (1) of the cylinder (3).)
2. Connect the gas tube (4) to the regulator (2)
and secure with a cable tie (5).
3. Make sure that the gas tube is connected to
the welder correctly.

Inappropriate handling and use could cause
serious accidents. Never stack the cylinders or
expose to excessive heat, ames or sparks. Do
not bash the cylinders together. Contact your
supplier for further information on the use and
maintenance of the cylinders.
Warning: Never use damaged cylinders: in this
case, advise your supplier immediately.
20. ORDINARY MACHINE MAINTENANCE
Every three months periodically remove dust from
the suction nozzle using compressed air. Always
direct the air from the inside towards the outside
of the machine to avoid blowing dirt inside the
welder. When carrying out this operation, always
make sure the machine is not connected to the
power supply.
22. MEMORISING THE WORK POINT As
illustrated in the previous paragraphs, the
welder allows for a notable personalisation of
the work point (when used both manually and
synergically). The work point for a workpiece
can be saved in the memory and rapidly recalled
at a later date. To save a work point follow the
instructions below:
1. Select ready to weld on the display.
2. Set the appropriate parameters for the welding
mode required.
5- Press switch 10 to conrm the selected letter.
6- Repeat steps 2 and 3 to complete the name.
7- Conrm the name by pressing the TICK button
again . From this moment onwards the work
point will be memorised with its own name and
displayed with the other welding procedures.
Meaning of the back :
sp button: cancels the previous letter
inserted.
Cancel: cancels the operation.
OK: conrms the name of the work point
. 23. LOCKING A WORK POINT
The welder can lock the functions of switch
9 and 10, so that once a work point has been
saved it cannot be changed, unless modied by
a member of staff with a password, which can be
dened at the discretion of the user. To proceed
with locking a work point, it is necessary to rst
enter the necessary parameters for the required
welding settings. Once this has been done,
proceed as follows:
1. Press switch 9 of g. 1 for approximately 5
seconds; the message in Fig. A will appear.
3- Press the MEM+ button (4 of g 1).
4- Turn switch 10 (g 1), chose the rst letter of
the name with which you want to save the work
point.

After which, select button 1 of g. A, with the
name ‘Lock’ on the black and white display and
the symbol for the colour display.
2. You will then be asked to enter the password,
which must be kept safe to make future
modications of the work point, should the need
arise.
To enter the password, proceed as follows:
1- Turn switch 10 (g 1) and select the rst letter
of the password.
2- To conrm the selection press switch 10.
3- Repeat steps 2 and 3 to complete the
password.
4- Conrm by pressing the switch again. Fig.A
Fig.B 24
3. Once the password has been conrmed
the display will show the message in Fig. C, a
lock symbol in the area 1 of the display and the
functions Unlock and Reset pw (reset password)
which correspond to buttons 2 and 3 (g. 1)
respectively, in area 2 of the display;
4. To exit the lock option of the work stage, briey
press switch 9 in g. 1;
5. Should the need to modify the work stage
arise, activate the ‘Unlock’ option by pressing the
function button. The unlock function will require
the user to enter the password that was set and
activated as described above.
6. The reset password option can be activated
by pressing the (Reset pw) button.
WARNING: The Reset Password option
should only be used when there is no way of
tracing the work stage and when the Lock/
Unlock password has been lost. To use this
function contact the constructor technical
support department directly.

1. Control panel
2. Power control board
3. Motor control board
4. Welding process control panel
5. Power Inverter
6. Auxiliary transformer

EC declaration of conformity
Hereby we declare that the machines as stated below
Type: DP231C
Conform to the EC Directives: 73/23/EEC and 89/336/EEC
European standard: EN/IEC 60974-1
This is to certify that the tested sample is in conformity with all provisions of the above detailed EU directives and product standards.
RoHS Compliance Declaration
Directive 2002/95/ec of the European Parliament
Restriction of use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment
Type: DP231C
The above listed products are certied to be compliant with the rohs directive with all homogeneous component parts being controlled to ensure
material contents as per the list below.
Cadmium 0.01% by weight
Lead 0.1% by weight
Mercury 0.1% by weight
Hexavalent chromium 0.1% by weight
Polybrominated biphenyl’s (pbbs) 0.1% by weight
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (pbdes) 0.1% by weight
It should be noted that under specic exempted applications, where lead is used as an alloying element the following limits are applied in
accordance with the regulations.
Copper and copper alloy parts use less than 4% by weight of each homogeneous component.
Steel and steel alloy parts use less than 4% by weight of each homogeneous component.
Aluminium and aluminium alloy parts use less than 4% by weight of each homogeneous component.
Only dispose off in authorised sites for electrical and electronic waste do not dispose of with general refuse or landll waste.

WEEE Statement
WEEE (Waste Electrical & Electronic Equipment) 2002/96/EC
In relation to implementing the legislation, Parweld has established relevant recycling and recovery methods. We have been fully compliant
against the marking requirements since August 2005. Parweld is registered in the UK with the Environment agency as detailed below. For
WEE compliance outside the UK please contact your supplier/Importer
Parweld is registered with a compliance scheme Ofcial registration number is WEE/FD0255QV
When your equipment reaches the end of its service life you should return it to Parweld where it will be reconditioned or processed for
recycling.
Statement of warranty
Limited Warranty:
Parweld Ltd, hereafter, “Parweld” warrants its customers that its products will be free of defects in workmanship or material. Should any failure
to conform to this warranty appear within the time period applicable to the Parweld products as stated below, Parweld shall, upon notication
thereof and substantiation that the product has been stored, installed, operated, and maintained in accordance with Parweld’s specications,
instructions, recommendations and recognized standard industry practice, and not subject to misuse, repair, neglect, alteration, or accident,
correct such defects by suitable repair or replacement, at Parweld’s sole option, of any components or parts of the product determined by
Parweld to be defective.
Parweld makes no other warranty, express or implied. This warranty is exclusive and in lieu of all others, including, but not limited to any
warranty of merchantability or tness for any particular purpose.
Limitation of Liability:
Parweld shall not under any circumstances be liable for special, indirect or consequential damages, such as, but not limited to, lost prots and
business interruption. The remedies of the purchaser set forth herein are exclusive and the liability of Parweld with respect to any contract, or
anything done in connection therewith such as the performance or breach thereof, or from the manufacture, sale, delivery, resale, or use of any
goods covered by or furnished by Parweld whether arising out of contract, negligence, strict tort, or under any warranty, or otherwise, shall not,
except as expressly provided herein, exceed the price of the goods upon which such liability is based. No employee, agent, or representative
of Parweld is authorized to change this warranty in any way or grant any other warranty.
Purchaser’s rights under this warranty are void if replacement parts or accessories are used which in Parweld’s sole judgement may impair the
safety or performance of any Parweld product.
Purchaser’s rights under this warranty are void if the product is sold to purchaser by non-authorized persons.

Parweld Limited
Bewdley Business Park
Long Bank
Bewdley
Worcestershire
England
DY12 2TZ
tel. +44 1299 266800
fax. +44 1299 266900
www.parweld.com
info@parweld.co.uk
Parweld Limited
Bewdley Business Park
Long Bank
Bewdley
Worcestershire
England
DY12 2TZ
tel. +44 1299 266800
fax. +44 1299 266900
web: www.parweld.com
email: info@parweld.co.uk
Contact Your Local Distributor:
 Loading...
Loading...