Partec CyFlow Cube Series, CyFlow Cube 6, CyFlow Cube 8, CyFlow Cube 8 Sorter Instrument Operating Manual

CyFlow® Cube
Instrument Operating Manual
CyFlow® Cube 6 │ CyFlow® Cube 8 │ CyFlow® Cube 8 Sorter

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
© 201
2 Partec GmbH
For in vitro diagnostic use with Partec recommended IVD reagents.
The Partec CyFlow® Cube Flow Cytometer complies with the European IVD Directive 98/79/EC and is therefore CE marked.
For in vitro diagnostic use with Partec recommended IVD reagents.
Rev018_2012-01-27
Partec GmbH • Am Flugplatz 13 • D-02828 Görlitz • Germany
Tel +49 3581 8746 0 • Fax +49 3581 8746 70
Contact Information:
E-mail: service@partec.com
2/36
IVD

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Table of Content
FOREWORD ................................................................................................................... 5
PRESENTATION ............................................................................................................. 6
B
ASICS
........................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
What is the Partec CyFlow® Cube? ....................................................................................................................................... 6
What are the applications for which the CyFlow® Cube can be used? ................................................................. 6
What are topics covered by this manual? ......................................................................................................................... 6
What other manuals are available? ..................................................................................................................................... 6
What should I know before operating the CyFlow® Cube? ....................................................................................... 6
I
N FLOW CYTOMETRY, WHAT IS
… a parameter? .............................................................................................................................................................................. 7
… a one-parameter histogram? ............................................................................................................................................. 7
… a histogram channel? ............................................................................................................................................................. 7
… the count in a histogram? .................................................................................................................................................... 7
… a peak? .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
… background in a histogram? ............................................................................................................................................... 8
The lower level (L-L) or threshold? ..........................................................................................................................................................................8
Example of a histogram ............................................................................................................................................................. 9
Example of a dotplot ................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Histogram and dotplot in immunology ............................................................................................................................ 10
... ............................................................................................................................................. 7
GETTING STARTED ..................................................................................................... 10
I
NSTRUMENT STARTING PROCEDURE
..................................................................................................................................... 11
Sheath fluid level control and/or refill ............................................................................................................................. 11
Switching on the CyFlow® Cube .............................................................................................................................................................................. 11
M
AIN CYVIEW™ LOGIN WINDOW
U
SER LEVELS
CYV
IEW™ MAIN PAGE
............................................................................................................................................................................... 12
.............................................................................................................................................................. 14
............................................................................................................................................. 12
Presentation .................................................................................................................................................................................. 14
CyView™ Controls ....................................................................................................................................................................... 15
CHANNELS – parameter definition ....................................................................................................................................................................... 15
PLOTS – display options ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 15
PROCCESS – instrument control .............................................................................................................................................................................. 17
TYPICAL SAMPLE ANALYSIS .................................................................................... 19
S
TARTING A MEASURE
M
EASURE MODES
Continous (default selection) ................................................................................................................................................ 20
Volumetric Counting with Electrodes ............................................................................................................................... 20
Volumetric Counting with Volume ..................................................................................................................................... 20
Events in Region .......................................................................................................................................................................... 20
C
LEANING PROCEDURES
Cleaning procedure during Cube running ....................................................................................................................... 21
Cleaning procedure for switching off ................................................................................................................................ 21
No cross contamination between samples ...................................................................................................................... 21
............................................................................................................................................................... 19
....................................................................................................................................................................... 20
........................................................................................................................................................... 21
3/36
Rev018_2012-01-27

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
I
NSTRUMENT SETTINGS
............................................................................................................................................................ 22
Measurement parameters ...................................................................................................................................................... 22
Gains settings .................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 22
Threshold settings (T) .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 22
Light source (L) ............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 22
Trigger properties (P) .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 22
Flow speed (S) .................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 22
Plot name ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 23
Plot properties.............................................................................................................................................................................. 23
X Log On/Y Log On ......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
Erosion levels ................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
X/Y Channel ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
Mode ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
BitRange .............................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 23
CR-Mode .............................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 23
Region name ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Home Plot name .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 24
Colour RGB ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Max count ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Sorter region ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Colour Gating On ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 24
Moving of regions within a histogram .................................................................................................................................................................. 24
Create a polygonal region ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Region properties ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Create a vertical histogram splitter ....................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Create a vertical dotplot splitter ............................................................................................................................................................................. 25
Create a horizontal dotplot splitter ....................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Create a quadrant assembly ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Change layout for regions ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Applying regions to other plots Gating Function ...................................................................................................................................... 26
Keyboard/Mouse combinations ........................................................................................................................................... 26
APPENDIX .................................................................................................................... 28
B
IOHAZARDS
M
AINTENANCE
............................................................................................................................................................................... 28
........................................................................................................................................................................... 29
Service .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 29
Transport and Storage ............................................................................................................................................................. 30
Disposal ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 30
L
ASER SAFETY
T
ECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
............................................................................................................................................................................ 31
................................................................................................................................................... 32
Optical Standard Setup ............................................................................................................................................................ 32
The Parameters ............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 32
NOTES .......................................................................................................................... 35
Rev018_2012-01-27
4/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Foreword
The CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual is aimed for a large spectrum of users, from beginner up
to the most skilled flower. The beginner or casual user will find the key functions and concepts to use the
Cube and its software. The confirmed flower will find an in-depth detail of the inner working and parameters
of the Cube to customize its use and obtain optimal performances.
CyView™ for Cube 8 is the instrument operation software for the CyFlow® Cube 8 (CY-S-3068). New
software versions and you profit from your requests: new features and software improvements. Partec is
continuously working on CyView™ to better fulfil your demands. If you have questions concerning this
manual or the software, find problems associated with CyView™ or you have a good suggestion to be
included in a new version, please let us know by sending an email or a note to Partec GmbH.
For more details about the reagent kits, suitable for use with the CyFlow® Cube, please refer to the
respective product data sheets. There are also several Application Notes available.
If you have questions, please contact your local distributor, one of the Partec subsidiaries, or Partec in
Germany (service@partec.com).
Further details and addresses can be found on our website at:
• www.partec.com/distributors
Please do not forget to add in your request the following information:
• Serial number (serial No.) of the CyFlow® Cube
• Your complete contact address
This This manual contains references to names and products from Partec and other companies
which are registered trademarks or protected by copyright.
Partec GmbH, CyFlow® Cube8, CyView™ for Cube8, Robby®.
®
Microsoft
Hewlett Packard®: Deskjet Laserjet.
Corp.: Windows, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Paint.
Rev018_2012-01-27
5/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Presentation
Basics
What is the Partec CyFlow® Cube?
The Partec CyFlow® Cube is a fully equipped desktop Flow Cytometer (FCM). CyFlow® Cube features a
modular optical concept. This allows using different lasers as light sources and the detection of up to 8
optical channels (parameters). The CyFlow® Cube allows easy optimization of the optics for any application
by simple exchange of optical filters and mirrors. The CyFlow® Cube runs with an internal PC. Data
acquisition, instrument control, and data analysis are controlled and performed by the CyView™ software.
What are the applications for which the CyFlow® Cube can be used?
Together with the software, the CyFlow® Cube offers automation for routine use and flexibility for research
use for practically any flow cytometric application. The applications cover:
Routine multi-colour immuno-phenotyping
Blood Cell Analysis/HIV monitoring (e.g. CD4 cell count)
Leukocyte Counting/Rare Event Analysis
Microorganism Analysis
Fermentation Control
Particle Concentration Analysis
True Volumetric Absolute Counting
Particle Size and Fluorescence Distribution Analysis
What are topics covered by this manual?
The CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual covers the basic operation and maintenance of the
CyFlow® Cube instrument. This manual also covers details related to the software.
What other manuals are available?
Application Notes and Service Manuals are available to get started. They contain hints to achieve the
best results.
What should I know before operating the CyFlow® Cube?
This manual assumes that you have basic knowledge on flow cytometry. In the best case a well
experienced "flower" is around - so let her/him help you. Basic books are available about flow cytometry
which may help you as well (e.g. Howard M. Shapiro, Practical Flow Cytometry. Wiley 2002).
Rev018_2012-01-27
6/36
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
In flow cytometry, what is ...
… a parameter?
In flow cytometry, parameter denotes a measured
property of the particles. Frequently, a parameter
is synonymous to an optical channel. E.g. an
instrument with 6 parameters is equipped with 6
optical detectors.
… a one-parameter histogram?
A one- parameter histogram displays the
distribution of cells among a specific property, e.g.
how many cells contain a given quantity of DNA
or bind a given number of antibody molecules.
… a histogram channel?
The measured signal intensity is assigned to one of 65536 quantity classes or channels. In a oneparameter histogram the channels are represented on the x-axis.
… the count in a histogram?
The number of cells being assigned to a given channel is referred to as channel content or simply count. In
a one-parameter histogram, the count is shown on the y-axis.
… a peak?
All cells having about equal characteristics among the analysed cell property (e.g. content of a specific
constituent like DNA), form a peak. In the case a of typical DNA histogram one peak represents the G1 and
another peak (with twice the channel value) represents the G2/M phase of the cell cycle.
In case of immunolabelled cells often one peak for unlabelled (negative) and one peak for labelled
(positive) cells can be detected. Peaks can be analysed by identifying them with region markers.
Rev018_2012-01-27
7/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
… background in a histogram?
Histograms sometimes show undesired signals in the lower channels, frequently called ´noise´ or
´background´. These signals may originate from cell fragments or other particles resulting from sample
preparation. In case of high signal amplification, background can also be caused by particle contaminated
sheath fluid.
The lower level (L-L) or threshold?
The lower level (L-L) threshold is a mean to suppress background signals. Signals below the lower level are
rejected from the signal acquisition. To exclude noise from a histogram already acquired, a region-gate can
be used.
Rev018_2012-01-27
8/36
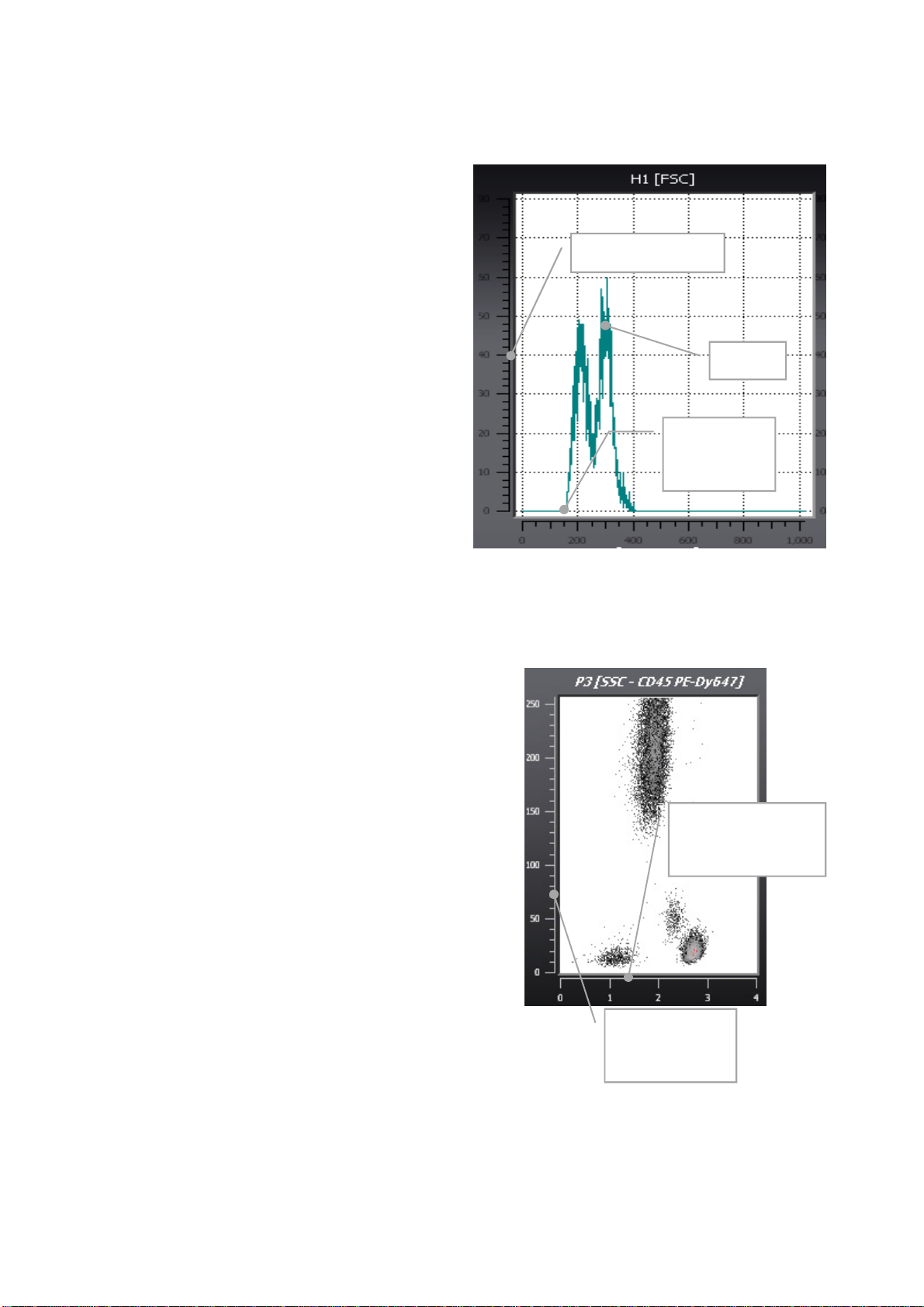
Example of a histogram
A histogram represents a distribution of measured
signals (events) over 1 dimension. Data can be
presented on the dimensions of relative particle
size or optical particle structure (Forward Scatter
(FCS) or Side Scatter (SSC)), resp. or on their
relative fluorescence intensities in different light
colours (fluorescence parameters FL1 to FL6).
In this example, the dimension represented is the
relative size (FSC) on a logarithmic scale in X,
and the number of events on a linear scale in Y.
Two peaks are visible.
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Number of events
Peaks
Example of a dotplot
A 2D dotplot presents correlated data over 2
dimensions. In the image on the right a sample of
leukocytes (after lyse of the red blood cells) is
plotted with their relative light scattering (SSC)
property against the intensity of the CD45 antigen.
The Z value represents the number of events that
have the same coordinates. 1 event will be
represented by a black point; if 10 events have
the same coordinates, the point representing
them will be grey. It will be red if more than 20
points are overlaying one another. The Z scale is
dynamic and will adapt during the measurement
to a scale of 1 (black) to the maximum overlaying
event coordinate colour coded in red.
Threshold of
lower limit
(L-L)
Log representation
for fluorescence
9/36
Linear
representation
of channels
Rev018_2012-01-27
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
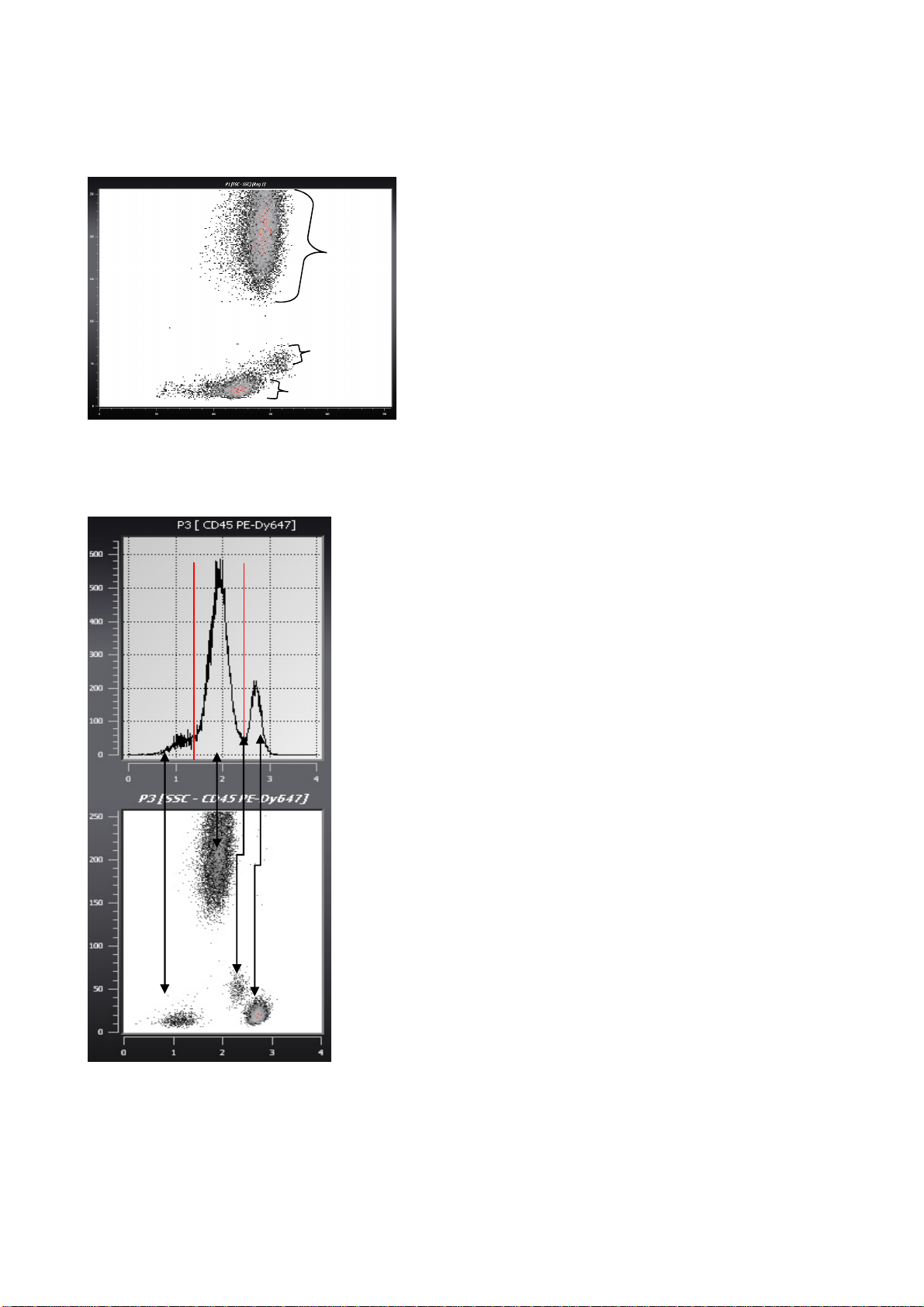
Histogram and dotplot in immunology
Lysed blood 2D dotplot
G
M
L
Histogram and dotplot of immunological staining
Neg.
Background
Slightly pos.
Pos.
Getting Started
Lysed blood is represented in a dot plot
presenting the FSC in X axis and SSC in Y axis.
Both axes are in a linear scale.
Three distinct groups are visible; they represent
the granulocytes (G), monocytes (M) and
lymphocytes (L).
This histogram represents the spectrum of the
cells presented in the previous dot plot stained
with antibodies anti-CD16 conjugated to
PhycoErytrin (PE). The X axis displays the
fluorescence in a 4-dec logarithmic scale and the
Y axis displays the number of events in a linear
scale.
This dot plot presents the cells fluorescence in X
on a logarithmic scale (CD45 FITC) versus SSC
in Y on a linear scale.
Rev018_2012-01-27
G
M
L
This data display allows an easier interpretation of
2 parametric data compared to the histogram.
Concluded from this example, the lymphocytes
are strongly stained with the anti-CD45 antibody,
the monocytes are slightly stained and the
population of granulocytes is negative.
This example is a simplification of an immunestaining analysis by flow cytometry. It is
directed to new users, and aims to link the
histogram to the dotplot representation. To
complete the analysis, gating and statistics
are required.
10/36
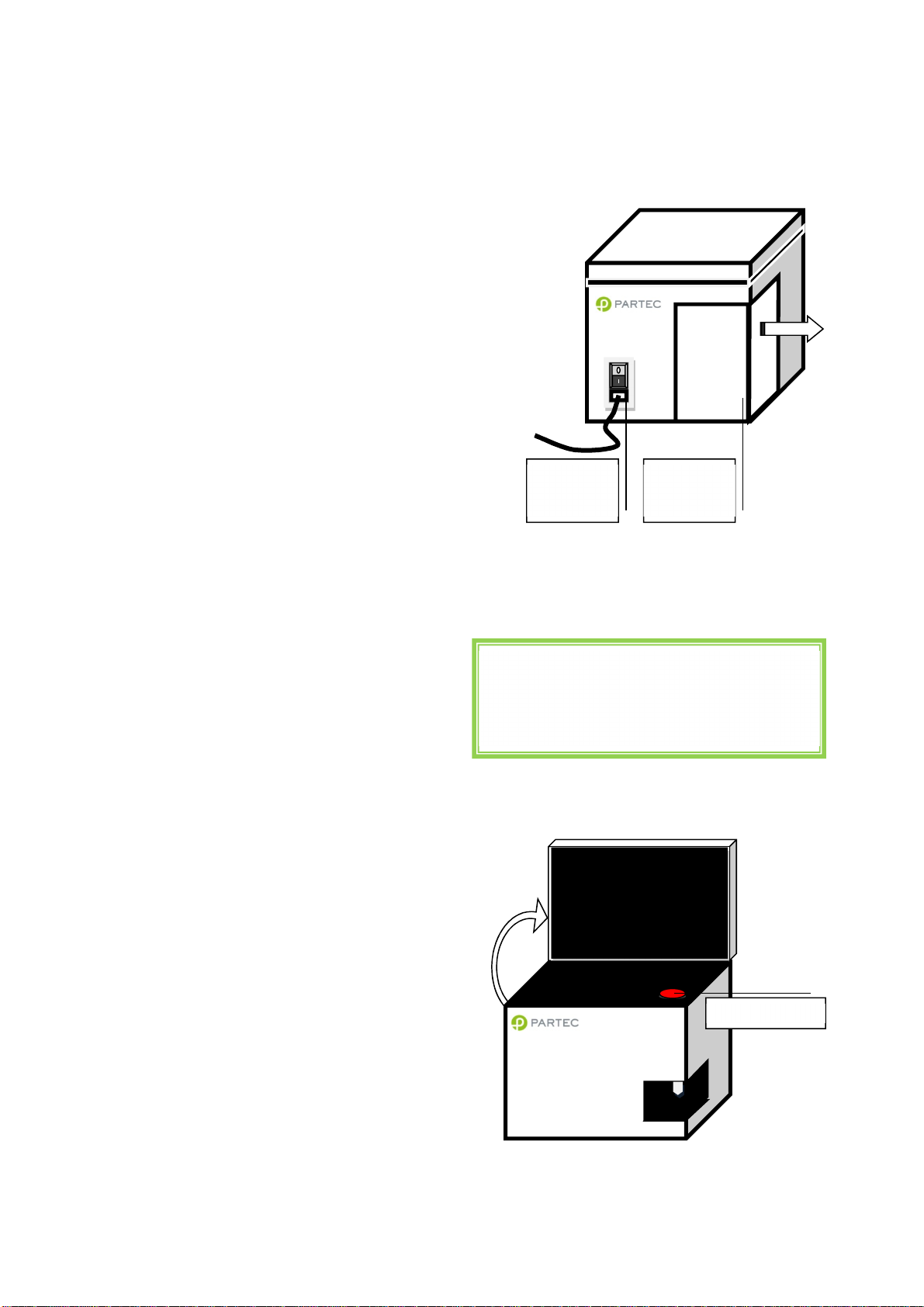
Instrument starting procedure
switch
fluid
On/Standby
measurements!
Sheath fluid level control and/or refill
Before switching on the machine, it is
recommended to check the levels of the sheath
fluid and waste bottles. They can be found at the
back-left of the apparatus in a sliding
compartment.
Make sure SHEATH bottle is filled with 800 ml of
clean, filtered, and degassed sheath fluid and is
closed with the screw top. In order to guarantee
highest quality of the measurements we highly
recommend use Partec Sheath Fluid (order no.
04-4007).
It is recommended to replace the sheath fluid at
least once a week or before any daily use.
When filling up the sheath fluid bottle make sure
no air bubbles are trapped in the yellow filter unit
inside the bottle!
Make sure WASTE bottle is empty and the screw
top is tightly closed.
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Main
power
Rear side of CyFlow® Cube showing the main
power switch and the sheath fluid and waste
bottle compartment.
Waste and
sheath
The waste bottle must be emptied after and
before each user session. When using biohazardeous samples, a volume of 50 ml of
hypochlorite 0.5% (Order No 04-4012) should be
introduce into the empty waste bottle for initial
disinfection.
Switching on the CyFlow® Cube
The power supply switch is found at the back of
the Cube next to the main supply cable. The Cube
is, in default, set in a stand-by mode. The full
activation of the Cube requires pressing lightly the
on/off tactile button on the top of the machine.
The display screen must be first lift up to access
it.
This will start the embedded computer,
automatically start the CyView™ software and load
the last employed configuration.
Casual/medium expertise user:
Once the Cube started no further steps are
necessary. You can directly start your
Rev018_2012-01-27
11/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Main CyView™ login window
User name
The log in window allows to start the software at the USER, MAIN USER or SERVICE level.
During start of the instrument the automated selftesting procedures are processed:
XML-configuration: displays the correct loading
of the setting files
Searching Device: display of the correct
recognition of the connection between the
computer and the embedded electronics
Password
Lost your login details?
Important: On each new instrument a Main User
login is already established
Login: USER (case sensitive)
Password: Cube1 (case sensitive)
Rev018_2012-01-27
Please verify that both operations are confirmed
by a green tick.
Login as a standard USER:
The code will be given to you by the main user(s)
of the instrument. The main user has the rights to
define or delete users.
12/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
User levels
Three different user levels exist:
SERVICE: Restricted to authorized Partec trained persons and for service purposes only
MAIN USER: Complete functionality of the instrument, method development
Main users can create new accounts of the Main User and User level
User: Applying standardized methods only
Users cannot create new accounts.
As a main user in order to create new accounts type in your Login name and password and select “User
Administration”.
To create a new MAIN USER account type in Name and Password and activate “Main user” followed by
“Build new account”.
To create a new USER account type in Name and Password followed by “Build new account”. (Main user
should be deactivated).
As User the own password can be changed by selecting the Name and placing a new Password followed
by “Change my password”.
As Main User the own password can be changed by selecting the Name and placing a new Password
followed by “Change my password”. As Main User any User account can be deleted by selecting the Name
followed by “Delete this account”. The Main User does not require the respective password to delete any
User account.
The default user account (Name: USER; Password: Cube1) can be deleted when logged in as Main User.
Please make sure at least one Main User remains in the user list in order to guarantee complete
functionality of the software.
To enter the CyView™ software from the user administration level select “Back to login”, login with your
personal Login name followed by “Work with CyView™.
Rev018_2012-01-27
13/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
board link
work load
L
M
and
V D
CyView™ Main Page
Presentation
Region statistics Results table
Console
PC/control
File operations
Real time
instrument
Instrument settings
Measuremen
t interface
The main window will be your interface to acquire, save, re-load and analyse your data.
Instrument real time display of workload (L), on-board memory status (M), analysis volume (V) and
analysis duration (D).
Buttons allowing to load and save data files
(.fcs data files).
Buttons dedicated to saving and retrieving
instrument settings (.xml data files or
configuration scripts).
Status of sample (high, counting phase, empty)
and of waste and sheath fluid bottles levels.
Start and Stop measure buttons.
Compensation button and random bias button.
Button for the generation of a PDF report of the
acquired data.
Console displaying the control board status.
Rev018_2012-01-27
Clear button – deletes all data during a
measurement
14/36

CyView™ Controls
CHANNELS – parameter definition
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
The CHANNELS register defines properties of PMT
channels (the parameters) present in the systems
(PMT0 – PMT7). It names the parameters (FSC, SSC,
FL1 …FLx) and defines the Color Crosstalk
Compensation.
Confirm all modifications by pressing Accept
PLOTS – display options
The PLOTS register defines properties of the
graphical plots. The basic layout in terms of number of
plots, type of plots (histograms, dot plots) and position
of the plots is defined in the used Configuration
Script.
Plots are named H1 – Hx for histograms and P1 – Px
for dotplots. As specific plot is selected with the arrow
keys.
Define a Comment characterizing the plot e.g. FSC
Switch between Lin and Log scale for X and Y Axis
Define an Erosion level for dot to be displayed (z-axis
level), e.g. an Erosion level of 2 shows only dots
representing 3 and more signals
Select X-axis channel and Y-axis channel in dot plots
or X-axis channel only for histograms
Mode (function inactive)
Select histogram resolution as Bitrange, (values 6 bit
to 12 bit)
Select CR – Mode
Confirm all modifications by pressing Accept
15/36
Rev018_2012-01-27

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
RESULTS
The RESULTS register defines properties of calculated results displayed in the RESULTS table.
Properties of result calculations
It is possible to set up calculations with the COUNT of
individual regions according to the specified formula:
NumReg1 (+ - x / ) NumReg2
--------------------------------------------------x Scale
DenomReg1 (+ - x / ) DenomReg2
NumOperator defines operator between 2
numerators „+“, „-“, „x“ or „/“
DenomOperator defines operator between 2
denominators „+“, „-“, „x“ or „/“
Unit allows to add text to the result table
Scale introduces a factor to the formula
Counter results on refers to the result of a
volumetric counting
Confirm all modifications by pressing Accept
Rev018_2012-01-27
Home Plot Name defines the plot the region
refers to
Color RGB defines the region´s color and its
color in color gating
Max Count defines a maximum count for an
“Events in Region” particle limit
Sorter Region On activates region as sorter
region (only in CyFlow® Cube Sorter)
Color Gating On activates color gating for this
region
Use Delete and New to delete and create new
regions
Use arrow keys to switch between regions
16/36

SYSTEM - properties of the instrument
The active Configuration Script
The instruments Serial Number
Total Operating Time of the instrument
Version of the instrument
Modification of the instrument
Activate Autostart function
Activates Sorter function
Defines a factor for sample Dilution
Clinic/Customer defines specific User
information
Defines sample port electrode Volume in µl
µlPerSec/mBar defines a sheath fluid flow
parameter
SW-Version specifies current software version
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
PROCCESS – instrument control
Mask or Positive selects the trigger parameters,
multiple trigger parameters are logical “or”
connections
Voltage of the individual optical parameters (0
volt - 999 volts) defines PMT signal amplification
Threshold defines the trigger signals cut-off level
(on 4 dec log scale)
Flow defines the speed of sample injection in µl/s
Lights on switches light sources on / off
17/36
Rev018_2012-01-27

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
SCRIPT – definition of measure modes
Measmode allows selection of:
- Continuous analysis
- Volumetric Counting with Electrodes
- Volumetric Counting with Volume
- Events in Region
Speed values and Volume values can be
edited and stored in FCS file and Config script
Confirm all modifications by pressing Accept
Schematic overwiew of the measure modes with. A flash indicates clearing of the data. User
selectable criteria in green, software-defined values in red.
Rev018_2012-01-27
18/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Typical Sample Analysis
A step by step procedure and what are the important steps in the data acquisition.
Starting a measure
Load a sample demo file (data files can be
selected from the folder
(C:/CyView_85\data\xxxxx.fcs). The respective
instrument settings are automatically loaded.
Fill a sample tube with 1.2 ml of calibration beads.
Check the tube for eventual imperfection or
contaminants (cracks, aggregates, hair) and
replace or remove, resp. if necessary.
Insert the tube into the sample port, push it up
until a distinct click is heard
During the data acquisition the total particle count
and the analysis rate is indicated as a sliding bar.
During the acquisition phase it is possible to
manipulate the instruments set-up e.g. by
changing samples speed, PMT voltage and
threshold levels. Use CLEAR button
to erase data after manipulations of the
instruments set-up.
By default, the continuous measure mode is preselected. In this case the measurement will only
stop automatically when the sample is consumed.
An earlier stop can be realized by pressing the
STOP button . Data can be saved with
Press the start button. In the console window,
information on the status of the measurement is
displayed. The script work is proceeding step by
step.
CyView™ StartPrerun
Console displaying control board status
Prerun and stabilization of sample flow
Start Measure
Data acquisition
The configuration file can be saved with
Besides the Continous measure mode other
measure modes can be selected:
Volumetric counting with volume
A volume can be pre-selected
Volumetric counting with electrodes
The volumetric counting is based on the
electrode status
Events in region
A particle number can be pre-selected
19/36
Rev018_2012-01-27

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Working principle of t
he
Measure modes
The following measure modes can be selected prior to start of an analysis:
Continuous
Volumetric counting with electrodes
Volumetric counting with volume
Events in region
Continous (default selection)
This default mode will allow you to run your sample until its levels reached the stop electrode.
Volumetric Counting with Electrodes
This measuring mode uses the START and STOP electrodes of the sample port to define a fixed sample
volume. In a standard sample port this “counting volume” is 200 µl. In a pre-counting phase the sample is
acquired normally as in continuous acquisition mode. Reaching the START electrode the data are
cleared and the volumetric counting phase starts. Reaching the STOP electrode the counting procedure will
be terminated and a system cleaning cycle will be initiated automatically
Absolute Volumetric
Counting with Electrode
Volumetric Counting with Volume
In the measure mode volumetric counting with volume the counting volume is flexible and can be preselected by the user. In a first analysis phase the sample is acquired normally as in continuous acquisition
mode. Reaching the pre-selected volume the data are cleared and the volumetric counting phase starts and
the pre-selected volume will be analyzed. The volume can be used as the basis for concentration
determination.
Events in Region
The Events in Region measure mode allows to define a number of particles within a specified region to
operate as STOP condition (select the respective MaxCount function in the REGIONS register).
Advice: for the measure modes Volumetric counting with volume and Events in Region there will be a
remaining sample volume left-over within the sample tube. In this case the cleaning cycle will only be
triggered when the START button is pressed. Subsequently the data can be saved.
Be aware: for all measure modes the sample analysis automatically stops when the sample is finished (the
stop electrode is reached) even if the selected end criteria is not yet realized.
Rev018_2012-01-27
20/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Cleaning Procedures
Cleaning procedure during Cube running
The Cube can be cleaned between sets of samples using the cleaning and rinsing solution (green solution,
Order No 04-4009). This procedures will allow you to reduce significantly the cross contamination and
reduce the background.
The cleaning procedure should be set as follows: connect a sample tube with distilled water to the sample
port of the cube and press START three times. The cleaning tube will be entirely aspired by the instrument
and used for cleaning.
Cleaning procedure for switching off
Before switching off the Cube, it is necessary to run the decontamination solution (violet solution, Order No
04-4010) using the clean function (Menu -> stack -> clean). Then, the same operation must be repeated
with distilled water. The Cube can be put in standby by closing CyView™ (Menu -> Exit) and closing
WindowsXP (start-> Exit-> Switch Computer Off). To power off completely the Cube, use the main power
switch at the back panel.
The waste bottle content must be discarded accordingly to the relevant biohazard regulations.
A regular thorough cleaning of the sheath fluid bottle and exchange of the yellow filter will keep the
background in the measurements to a minimum level.
No cross contamination between samples
To minimize the carry-over of one sample to the next, a cleaning cycle between sample can be done.
Start your measurement.
Click Pause, remove you sample from the sample port, introduce a sample tube filled with distilled water
Click twice on play, the sample port will be cleaned and the distilled water removed from the tube. Your
Cube is now ready for your next measurement with no cross contamination from the previous sample.
+
Rev018_2012-01-27
21/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
1
2
Instrument settings
Measurement parameters
The PROCESS register can be opened by clicking on the button Meas ( )
Flow speed (S)
This slider allows you to change the sample
.
injection speed into the flow cuvette. Low speed
values results in a better precision and accuracy.
A higher speed can be used when the particle
concentration is measured and accuracy is of
lower relevance.
Gains settings
The GAIN (G) and THRESHOLD (T) sliders must
be adjusted to obtain the optimal gain (maximum
signal and minimum background). Typically, the
Forward Scatter (FSC) will be the first gain tuned
to adjust the size of the studied particles.
To move a slider, click mouse left on the slider,
keep mouse button down and move mouse left –
right or use the scroll wheel to adjust the value.
Threshold settings (T)
The threshold allows cutting off background by
setting a lower limit of the acquired data in the
trigger parameter. This tool allows to increase the
accuracy and precision of the acquired data.
Light source (L)
This option allows to switch on/off the light
sources.
Trigger properties (P)
Single trigger:
The trigger is the parameter defining if a
signal gets recorded. Only if the trigger
parameter detects a signal, other parameters
of the system will record signals. In other
words, if a trigger is set in FSC to record only
bigger particles (e.g. threshold set at 0.3871V
with a gain value of 170V), e.g. only intact
mammalian cells will be acquired. Cell debris
and smaller particles will be excluded as long
as their FSC signal remains below the trigger
threshold.
Multiple trigger:
The option allows to use multiple trigger
parameters for signal acquisition.
Example of single (1) and multiple trigger (2)
in FSC, and FSC+SSC.
Rev018_2012-01-27
22/36

Plot properties
Plot name
A default plot name (Hx, Px) is defined in the
script. Default names of the Parameters will be
displayed. The user can modify the parameter
name (line comment) enter a parameter name
better matching the experiment.
X Log On/Y Log On
This option will allow the user to change the plot’s
scaling. Note that changing the scale will require
you to adapt the gains of the PMTs!
Erosion levels
The erosion level will set a threshold on the data
displayed (not the acquired data). Some of the
low frequency points will not be displayed allowing
a better visual discrimination of the higher
frequency data (signal against background).
X/Y Channel
The displayed parameters can be chosen from
the drop down menu; giving the user the list of the
activated parameters.
Mode
Graphical model for the data (line histogram, filled
area histogram, overlay,..)
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
To obtain the properties of a plot area, press the
Ctrl + right click on the plot.
BitRange
The values are ranging from 6 to 12. It sets the
channel resolution from 6 (64channels) up to 12
(4096channels).
CR-Mode
This option allows you to select the part of the
data you want to be displayed:
All events
Region only
Colour gating
Once the parameters set, the change must be
validated, the back and forth arrows will allow
you to navigate from one plot to the next.
Rev018_2012-01-27
23/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Region/ROI properties
Create a polygonal region
Double left click on the plot where the gate/region
is required, a first point will be set; a second click
will set a further point, and so on. Label as many
points as required with the left mouse button. To
close the gate surface, click mouse right.
Region properties
To access the region property, Ctrl+right-click on
the gate to edited. On the PLOTS register on the
right of the screen a selection of region options
are displayed.
Region name
As default, the gate will be named: region nx,
successive region: region nx+1
The user can also define a name. Remember to
validate by Accept before to move on another
region.
Home Plot name
This defines the physical plot where the region is
located.
Colour RGB
Allows to choose the colour of the region. This
colour will be reported to each plot selected as
colour gating only, illustrated in the graph on the
left hand side with an overlay of the staining of
lymphocytes in red overlaying the blue histogram
presenting all events.
Max count
This option allows to fix the maximum number of
events from a particular ROI (Region Of Interest)
to be analysed (see CyView™ 8 SCRIPT
register).
Sorter region
To set the ROI/region as a sorting gate, just by
selecting the box.
(This option is only available on the Cube
equipped with Sorter flow cuvette).
Colour Gating On
Selecting this option willallow the user to apply
this particular gate to another plot.
Moving of regions within a histogram
Move the cursor into the region and keep the left
mouse button pressed while moving the position.
Individual points of a region can be changed by
approaching with the cursor to the point and keep
the left mouse button pressed during movement.
Regions within a dotplot can be changed in size
by selecting the region with the cursor and
pressing the “Shift” button during cursor
movement
Rev018_2012-01-27
Each region can be selected with the right mouse
button for deletion.
24/36

Create a vertical histogram splitter
To create a vertical histogram splitters please
move the cursor into the histogram and press the
right mouse button. Select “Built vertical splitter
region” to divide the histogram into two sections
(VS1-1 and VS1-2). The intersection can be
modified by moving the cursor into the plot and
keeping the left mouse button pressed.
Create a vertical dotplot splitter
To create a vertical dotplot splitters move the
cursor into the dotplot and press the right mouse
button. Select “Built vertical splitter region” to
divide the dotplot into two sections (VS1-1 and
VS1-2). The intersection can be modified by
moving the cursor into the dotplot and keeping the
left mouse button pressed.
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Create a horizontal dotplot splitter
To create a horizontal dotplot splitters move the
cursor into the dotplot and press the right mouse
button. Select “Built horizontal splitter region”
to divide the dotplot into two sections (HS1-1 and
HS1-2). The intersection can be modified by
moving the cursor into the dotplot and keeping the
left mouse button pressed.
Create a quadrant assembly
To create a quadrant assembly within a dotplot
move the cursor into the dotplot and press the
right mouse button. Select “Built cross region”
to divide the dotplot into four sections (CR1-1,
CR1-2, CR1-3 and CR1-4). To change the
quadrants move the cursor into the dotplot and
keep the left mouse button pressed. To create
asymmetric quadrants please approach individual
points (at the border of the dotplot or at the
intersection point of the quadrants) with the left
mouse button and keep the left mouse button
pressed.
Change layout for regions
In the register chart file select “Regions”.
Individual regions can be selected with the <>
arrows. Regions can be transferred to other plots
by the function “Home plot name” or modified in
their color with “Color RGB”. To activate changes
press “Accept”.
Rev018_2012-01-27
25/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Applying regions to other plots
Function
To select an existing region for gating select the
respective region with the right mouse button and
select “Color gating on”.
Gating
Clicking into any histogram or plot with the right
mouse button (outside a region area) allows to
select any existing region which is labeled with
“Color gating on”. Display options are:
Show all events shows all events in
pseudo 3D color
Show color regions only shows the events
in the selected region(s) in pseudo 3D color
Show colors only shows the events in the
selected region(s) in the region color
All + Region colors shows the events in the
selected region(s) together with all events
Multi color display options are possible by
selecting multiple gates.
Rev018_2012-01-27
26/36

Keyboard/Mouse combinations
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Context Action Effect
Graphic Plot Mouse double-click Opens edit function for regions
Create Region
Right Mouse-click Ends creation of a region
Left Mouse-click Sets dot of a region
Region
click and hold left mouse Moves a region in standard steps
click and hold left mouse
+Ctrl
click and hold left mouse
+Shift
click and hold left mouse
+Shift+Ctrl
click and hold left mouse
+M
Right mouse +Alt Opens mouse menu
Moves a region in small steps
Moves a region to the original position
Moves the region by addition of an
interval to the original position in very
small steps
Move the regions name over 5 positions
(N,E,S,W,central)
Axis of a plot Right mouse +Alt Opens the Channel register
Plot Right mouse +Alt Opens Plot register
Region Central mouse
Access to contest menus and keyboard short cuts
Marks the region and moves it in all
regionplots in the visual area
Rev018_2012-01-27
27/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Appendix
Biohazards
Please note: Strict guidelines, international, as well as national regulatory standards such as
GLP (good laboratory practice) must be met for all users. Therefore, the system is
marked with the following biohazard label:
Warning: The Waste may contain biohazardous and carcinogenic
material from the samples (infectious material, dyes).
Warning: biohazards
Rev018_2012-01-27
28/36

Maintenance
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Clean the CyFlow® Cube casing on a regular base carefully with soft cloth. Water must not enter the
CyFlow® Cube or peripheral devices or come into contact with electric connections and switches. For
cleaning the screen, always use special screen cleaner and soft cloth.
Do not use any organic solvents, nitro thinner, benzol, alcohol, highly concentrated bleach etc!
For cleaning of flow cuvette, refer to the described cleaning procedure. Do not use tools to clean the flow
cuvette. In case the flow cuvette is blocked, enquire Partec for rapid exchange.
Regularly empty the waste bottle and clean with warm detergent solution and a brush.
Clean sheath reservoir with distilled water and a clean brush and flush with clean distilled water several
times.
Remember: a clean sheath fluid reservoir is critical for proper operation.
If the CyFlow® Cube will not be used for longer periods, clean flow system by using distilled water. Put a
sample tube half-ways filled with distilled water at the sample port. Clean waste and sheath reservoir, wipe
top dry.
Warning: The Waste may contain biohazardous and carcinogenic
material from the samples (infectious material, dyes).
Service
All service is to be made from an authorized service engineer. Please contact your local supplier or Partec
(service@partec.com).
For further information, please consult our web site:
Products
Application tips
Instrument and software support
News and events
And much more ...
www.partec.com
Rev018_2012-01-27
29/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Transport and Storage
For the transport of the system to a different location it will be necessary to disconnect all external data and
supply connections. In case of use with potentially bio-hazardous material, please see Partec standard
operating procedure (SOP) for decontamination. The system should be carried in upright position. During
transport or storage please take care that the system will be stored under the following conditions:
Temperature 5-50°C
Humidity 20-85% relative (non-condensing)
Room Clean environment, no direct sun light
Disposal
In case of product disposal, please proceed according to the Partec standard operating procedure (SOP)
for decontamination.
After decontamination, the system has to be disposed according to the local regulations and laws.
For further information, please contact your local distributor or Partec.
Warning: The Waste may contain biohazardous and carcinogenic
material from the samples (infectious material, dyes).
Rev018_2012-01-27
30/36

Laser Safety
CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Warning: It is prohibited to open the instrument as it is equipped
with a class 3b laser unit.
The CyFlow® Cube is a class I laser product according to the EN 60825-1:2007.
Please note: Laser light can be emitted if the housing of the device is damaged and the
protection cover for the laser beam is removed. Therefore, the system is marked
with the following laser safety labels:
Warning: laser radiation
Attention
Laser radiation Class IIIb, if cover is
removed and shutter is opened
Additional explanation
Rev018_2012-01-27
31/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Technical Specifications
Note: Due to fast technological improvements, specifications herein are subject to change. For details,
please inquire information from your local supplier.
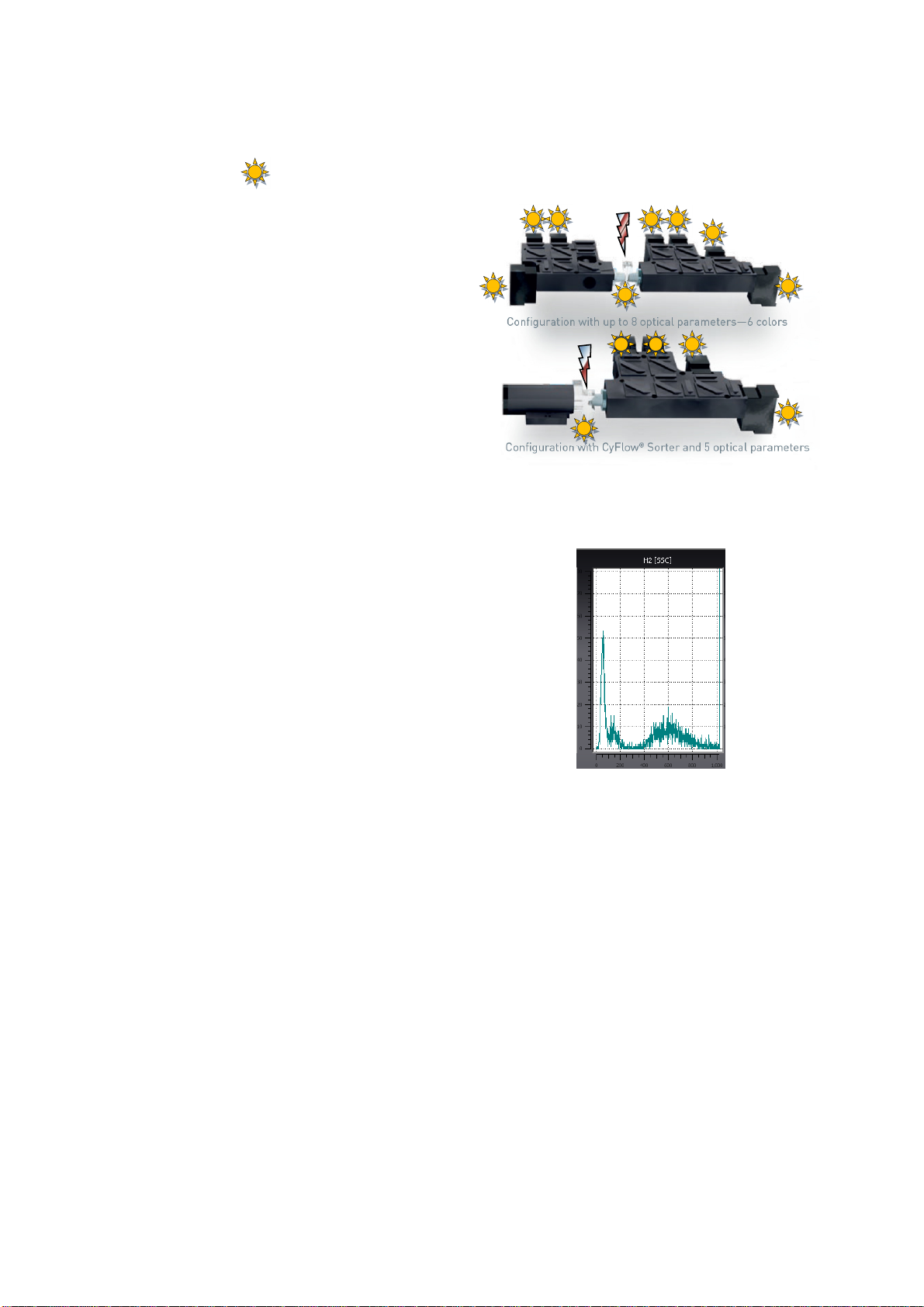
Optical Standard Setup
The Parameters
FSC: forward scatter
SSC: side scatter
FL1: green fluorescence
fluorescence origin: 488 nm laser (GFP)
FL2: orange fluorescence
fluorescence origin: 488 nm laser (PE)
FL3: blue fluorescence
fluorescence origin: UV-LED (DAPI)
FL4: red fluorescence
fluorescence origin: 638 nm laser (APC)
Example: This instrument is equipped with a blue
diode pumped solid-state Laser (20 mW) at 488
nm, a red laser diode (25mW) at 638 nm and a
365 nm UV-LED.
If required by a specific application, the optical
standard setup can be optimized by exchanging
preassembled removable mirror/filter blocks. This
is a matter of seconds and does not require any
re-adjustment.
The CyFlow® Cube flow cytometer can be
equipped with various light sources and up to
eight optical parameters. Depending on the
number of light sources and optical parameters
different optical benches are available.
Due to its modular concept the optical
configuration can be adopted to many different
clinical and scientific purposes. Standard
configurations are presented below:
Optical bench of a CyFlow® Cube with 2 lasers, UV-LED and 6 parameters.
Rev018_2012-01-27
32/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
1. CyFlow® Cube System
Size Dimensions: 500 mm L x 470 mm D x 355 mm H ( 670 mm with
open display )
Weight appr.40 kg
Maximum sound < 70 dBA
Power level
Installation/overvoltage category 2/II
Degree of protection IP 20
Operating Environment Temperature:15-30°C
Humidity: 20-85% relative (non-condensing)
Room: Clean environment. Direct sun light should be avoided.
Applications Immunophenotyping, DNA Analysis, Ploidy Analysis, Apoptosis,
Microbiology, Industrial applications, 3 to 6 Colour Analysis. True
volumetric absolute counts = counting per volume
True Volumetric Based on precise counting and mechanical fluid volume measurement
Absolute Counting No need for reference sample or beads
Instrument Check Partec Count Check Beads
Partec Calibration Beads 1 µm and 3 µm
Partec DNA Control PI
Set-up Time Max. 5 minutes
Parameters Up to 8 optical parameters: FSC, SSC, FL1, FL2, FL3, FL4, FL5, FL6
Particle Size Range 0.1 µm - 50 µm (standard cuvette)
Maximum Acquisition Speed 25,000 events/sec
Acquisition Stop Time Event- or volume-based
Trigger On all parameters, on multiple parameters or on single trigger
parameter, selectable in software
Data Resolution 65,536 channels (16 bit)
Service 1 - 3 years service contracts
Warranty 12 months on all parts except filters, mirrors, other quartz or glass
parts, disposables and cuvettes
Rev018_2012-01-27
33/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
2. CyFlow® Cube Optics
Laser / Output Red Diode Laser: 25 mW at 635 nm / 40 mW at 640 nm
Green NdYAG: 30 mW to 100 mW at 532 nm
Blue solid-state Laser: 20 mW at 488 nm
Blue laser diode: 50 mW at 488 nm
Violet Diode Laser: 100 mW at 405 nm
Ultra-Violet Diode Laser: 16 mW at 375 nm
Yellow Diode Laser: 100 mW at 561 nm
Orange Diode Laser: 50 mW at 594 nm
Detectors 1 to 8 (FSC, SSC, FL1, FL2, FL3, FL4, FL5, FL6)
Filters Standard setup and filters for all parameters according to laser configuration
Optical Coupling Standard objective mount with high numerical aperture objective, high numerical
aperture immersion gel coupling, e.g. for detection of weak cytokines (option)
Excitation Optics Elliptical 15 µm x 100 µm at 488 nm
Other beam geometries upon request
3. CyFlow® Cube Fluidics
Flow Cuvette Synthetic quartz flow cuvette (350x 200 µm) for laminar sample transport with
sheath fluid fluorescence, forward and side scatter light detection
Sample Delivery Computer controlled precision syringe pump for contamination-free sample
transport.
Built-in vacuum pump for waste container. Vacuum pressure is adjustable
(Computer controlled).
Sampling Volume Continuous up to 1500ml.
200 µl for electrode based precision absolute counting, Other counting volumes
upon request
50 – 1000 µl for syringe based precision absolute counting
Flow Rates 1) Sample volume speed adjustable continuously between 0.1 and 20 µl/s
2) Sheath fluid flow continuously adjustable in expert mode
Fluidics Volume 2 x 1-litre integrated reservoirs for sheath fluid and waste
BioSafety System Avoids sample droplets and sample cross contamination (computer controlled)
Rev018_2012-01-27
34/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Notes
Rev018_2012-01-27
35/36

CyFlow® Cube Instrument Operating Manual
Rev018_2012-01-27
Excellence in Flow Cytometry and Cell Analysis
36/36
 Loading...
Loading...